Page 1

F-Secure Policy Manager Proxy
Administrator's Guide
Page 2

Page 3

Contents
Chapter 1: Introduction.......................................................................5
Chapter 2: Installation.........................................................................9
Chapter 3: Configuration...................................................................11
F-Secure Policy Manager Proxy | TOC | 3
System requirements................................................................................................................6
An up-to-date system is a secure system.................................................................................7
When should you use F-Secure Policy Manager Proxy?.........................................................8
Installing the product locally....................................................................................................10
Configuring the product remotely............................................................................................12
Chapter 4: Using the product on Linux...........................................13
Installing the product...............................................................................................................14
Configuring the product..........................................................................................................15
Upgrading the product............................................................................................................16
Uninstalling the product..........................................................................................................17
Frequently asked questions....................................................................................................18
Chapter 5: Troubleshooting..............................................................19
The error log...........................................................................................................................20
Message structure in the error log...............................................................................20
Message levels............................................................................................................21
Error numbers.........................................................................................................................22
Troubleshooting with the error log..........................................................................................23
The status report log...............................................................................................................24
Page 4

4 | F-Secure Policy Manager Proxy | TOC
Page 5
Introduction
Chapter
1
Topics:
•
System requirements
•
An up-to-date system is a secure
system
•
When should you use F-Secure
Policy Manager Proxy?
This guide provides an overview of the product concepts, a step-by-step
guide to installation as well as other information you need to manage the
product.
Page 6

6 | F-Secure Policy Manager Proxy | Introduction
System requirements
The system requirements for the product are listed here.
To install F-Secure Policy Manager Proxy, your system must meet the following minimum requirements:
Windows:Operating system:
• Windows Server 2003 SP1 or higher (32-bit);
Standard, Enterprise, Small Business Server or
Web Server editions
• Windows Server 2003 SP1 or higher (64-bit);
Standard or Enterprise editions
• Windows Server 2008 SP1 (32-bit); Standard,
Enterprise, Web Server or Server Core editions
• Windows Server 2008 SP1 (64-bit); Standard,
Enterprise, Web Server, Small Business Server or
Server Core editions
• Windows Server 2008 R2; Standard, Enterprise,
Web Server, Server Core or Foundation editions
Network:
Supported F-Secure software:
Linux:
• Red Hat Linux Enterprise 3 or 4
• Suse Linux 9.x or 10.0
• Suse Linux Enterprise Server 9
• Debian GNU Linux Sarge 3.1
Pentium III 450MHz, 1GHz or faster is recommended.Processor:
256 MB of RAM, 512 MB is recommended.Memory:
500 MB of free hard disk space.Disk space:
10-Mbit connection, 100-Mbit connection
recommended.
• F-Secure Policy Manager
• F-Secure Client Security
• F-Secure Anti-Virus for Workstations
• F-Secure Anti-Virus for Windows/Citrix Servers
• F-Secure Anti-Virus for MS Exchange
• F-Secure Linux Security
Page 7
F-Secure Policy Manager Proxy | Introduction | 7
An up-to-date system is a secure system
To be protected, a workstation must have the latest defence against viruses and other malware that exist on
the Internet.
This guide provides an overview of the product concepts, a step-by-step guide to installation as well as other
information you need to manage the product.
What is the virus definition database?
Information against known viruses, worms and other malware are compiled into the virus definition database.
This virus definition database is regularly made available to all the workstations with F-Secure products
installed. It is this virus definition database that enables F-Secure products to protect a workstation from
viruses and malware.
How do the virus definitions get to F-Secure products?
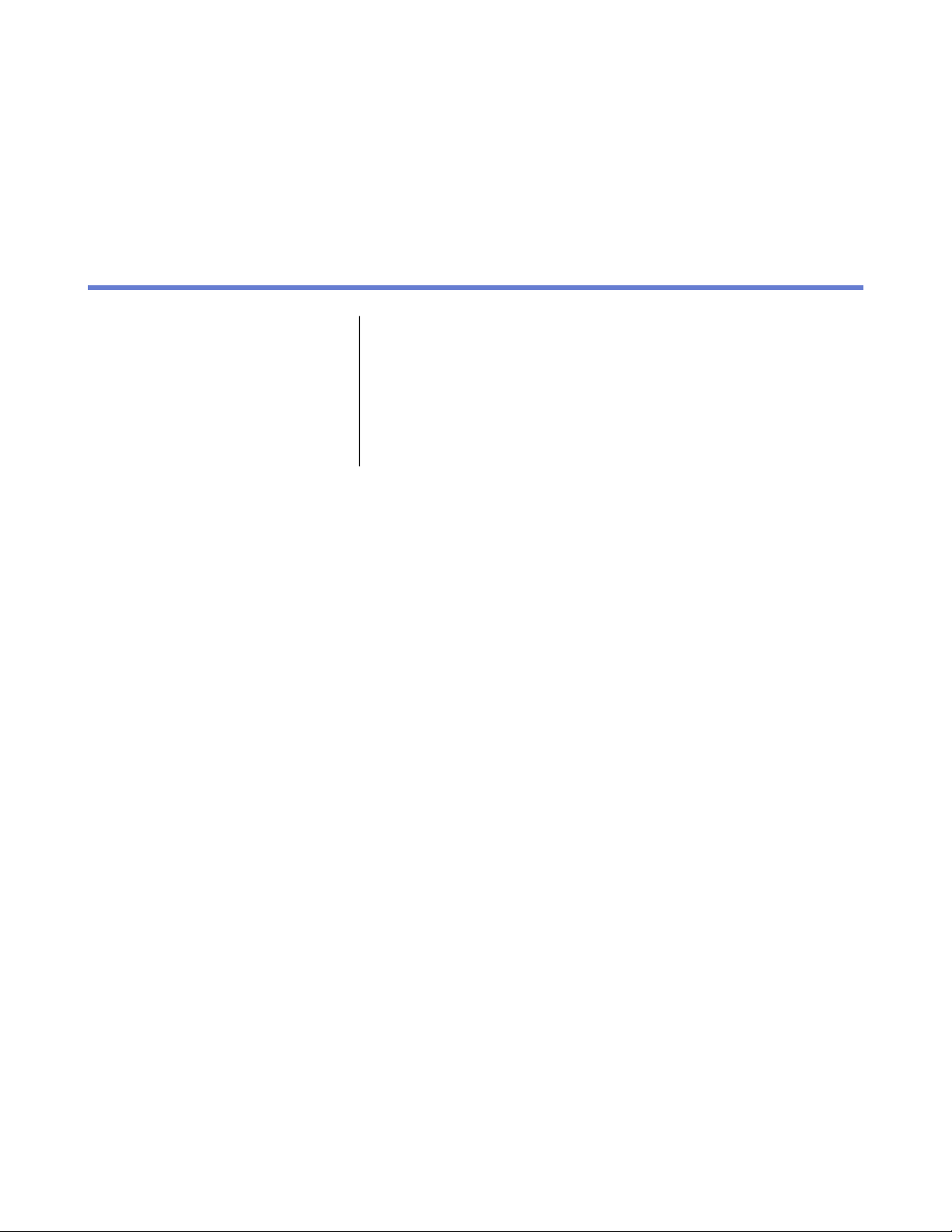
The figure above is an example of the steps the virus definition database takes to get to F-Secure products,
in this case to F-Secure Client Security. This is the primary path; there are also fallback paths if one or more
of the links is unavailable (for example if the machine running F-Secure Policy Manager has a power cut).
What does F-Secure Policy Manager do?
F-Secure Policy Manager allows you to centrally manage all the F-Secure products in your network. It is the
central monitoring and configuration point for your network. See the F-Secure Policy Manager Administrator's
Guide, available on the F-Secure web site at http://www.f-secure.com for more details.
What does F-Secure Policy Manager Proxy do?
F-Secure Policy Manager Proxy helps deliver the virus definition databases quickly and efficiently.
Page 8
8 | F-Secure Policy Manager Proxy | Introduction
When should you use F-Secure Policy Manager Proxy?
You do not have to use F-Secure Policy Manager Proxy to update the virus definitions database, but it does
provide certain advantages.
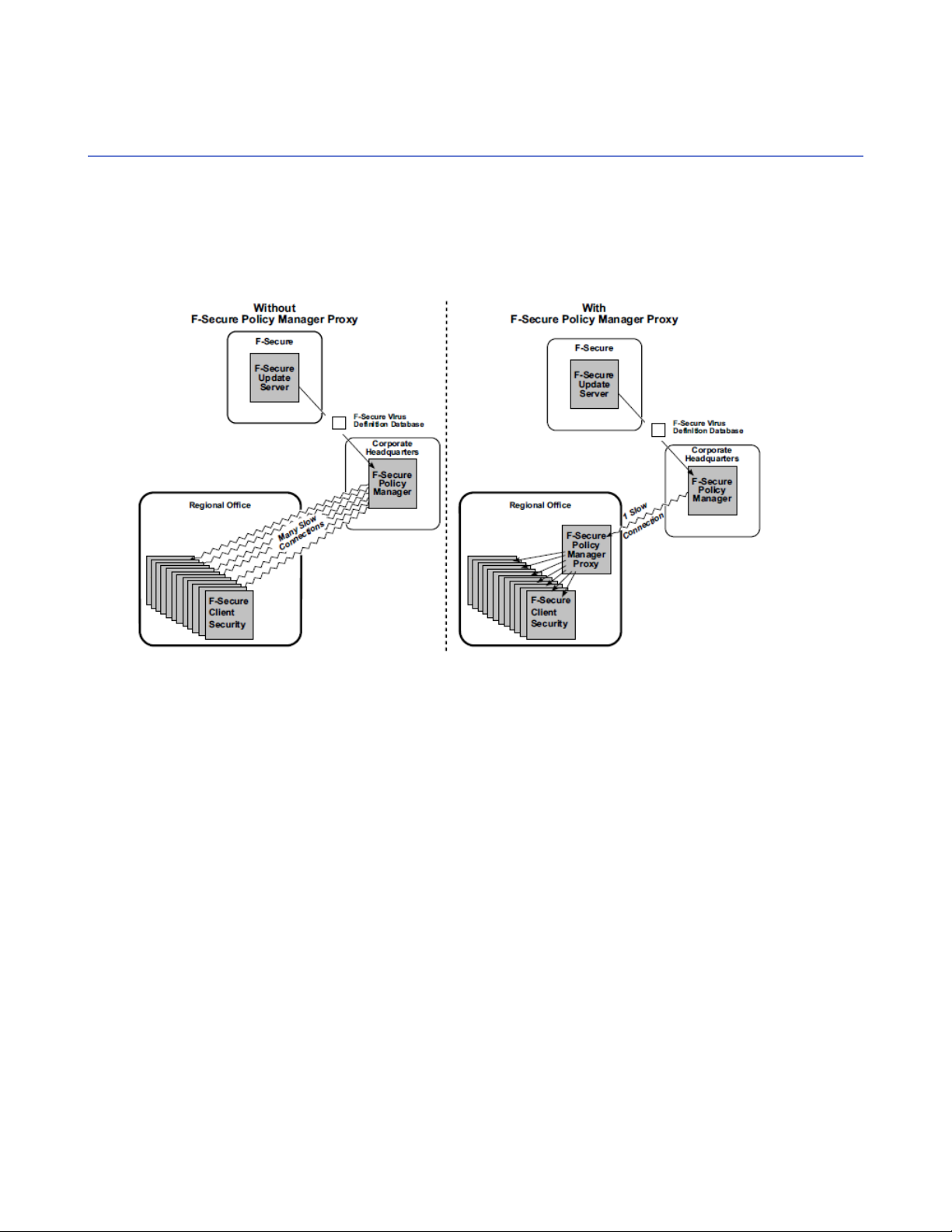
The effects of F-Secure Policy Manager Proxy are most obvious in large, vastly spread networks; for example,
a large corporation with remote offices in different parts of the globe. The following figure is an example of a
situation where F-Secure Policy Manager Proxy is useful:
There are three reasons to use F-Secure Policy Manager Proxy:
• To decrease the use of network bandwidth.
You should use F-Secure Policy Manager Proxy when you have a group of workstations far away from
your Policy Manager Server.
• To decrease the delivery time for virus definition updates.
You should use F-Secure Policy Manager Proxy when you have a group of workstations separated from
your Policy Manager Server by a slow connection, for example a dialup connection.
• To decrease the hardware load on Policy Manager.
You should use F-Secure Policy Manager Proxy if the server hardware running Policy Manager is unable
to cope with the number of requests it receives for virus definition updates.
Page 9

Installation
Chapter
2
Topics:
•
Installing the product locally
There are two methods of installing F-Secure Policy Manager Proxy:
• Locally, for which you will find instructions in this section.
• Remotely, for which you will find instructions in the Policy Manager
Administrator's Guide, which is available on the F-Secure web site at
http://www.f-secure.com.
Page 10

10 | F-Secure Policy Manager Proxy | Installation
Installing the product locally
Here you will find steps for installing F-Secure Policy Manager Proxy locally.
To install the product:
1. Run the setup.exe file.
2. Click the Next button on the first page of the installation wizard.
3. Read through the license agreement and click the I accept this agreement option, then click Next.
4. Select where to install Policy Manager Proxy using the Browse button, then click Next.
Note: If a previous installation of an F-Secure product is detected on the computer, this dialog is not
displayed and the previous installation directory is used.
5. If a previous installation of the product is detected, you will be asked if you want to use the same settings
as in the previously installed product:
• If you select Yes, the dialogs in the following three steps will be skipped.
• If you select No, you can continue through the following steps and select new settings.
6. Select Central management with F-Secure Policy Manager, then click Next.
7. Copy the admin.pub public key file from Policy Manager Server to the local system by clicking Browse
and selecting the file, then click Next.
8. Enter the IP address of the Policy Manager Server installation you want Policy Manager Proxy to
communicate with, then click Next.
9. Click Start to begin the installation process.
When the progress bar is full, click Next. Policy Manager Proxy is now running.
10. Click Finish to close the installation wizard.
In a centrally managed network, you should configure F-Secure products to use Policy Manager Proxy by
distributing a new policy with this configuration. For more information about policies and remote configuration,
see the Policy Manager Administrator's guide, which is available on the F-Secure web site at
http://www.f-secure.com.
Page 11

Configuration
Chapter
3
Topics:
•
Configuring the product remotely
F-Secure Policy Manager Proxy is configured remotely through Policy
Manager Console.
Page 12

12 | F-Secure Policy Manager Proxy | Configuration
Configuring the product remotely
You can configure F-Secure Policy Manager Proxy remotely in F-Secure Policy Manager Console.
To configure F-Secure Policy Manager Proxy in Policy Manager Console:
1. Select View ➤ Advanced Mode from the menu.
The Advanced mode UI opens.
2. Select F-Secure Policy Manager Proxy from the list of F-Secure products.
You can select the necessary settings from the corresponding item in the tree view. Explanations of each
of the configuration options are shown in the help area.
You can configure F-Secure Policy Manager Proxy to connect through another F-Secure Policy Manager
Proxy or HTTP proxy. This type of configuration is called a chained proxy configuration, and it might be needed
to:
• cross network boundaries, or
• reduce the load on Policy Manager Server.
Page 13

Using the product on Linux
Chapter
4
Topics:
•
Installing the product
•
Configuring the product
•
Upgrading the product
•
Uninstalling the product
•
Frequently asked questions
This section describes how to install and configure F-Secure Policy
Manager Proxy on Linux.
Page 14

14 | F-Secure Policy Manager Proxy | Using the product on Linux
Installing the product
This topic describes how to install F-Secure Policy Manager Proxy on Linux.
1. Log in as root.
2. Open a terminal.
3. Enter the following command to start the installation:
• Debian-based distributions: dpkg -i
f-secure-policy-manager-proxy_2.0.<build>_i386.deb.
• RPM-based distributions: rpm -i
f-secure-policy-manager-proxy-2.0.<build>-1.i386.rpm.
F-Secure Policy Manager Proxy will start up automatically once the installation is complete.
Page 15

F-Secure Policy Manager Proxy | Using the product on Linux | 15
Configuring the product
This topic describes how to configure F-Secure Policy Manager Proxy on Linux.
1. Configure F-Secure Policy Manager Proxy by editing the /opt/etc/f-secure/fspmp/conf/proxy.cfg
file.
For example, f you need to configure chained proxies:
a) Add the host name or IP address of the Policy Manager Proxy or HTTP proxy with which this proxy
communicates to the line chained_proxy_ip_addr=.
b) Specify the TCP port of the Policy Manager Proxy or HTTP proxy with which this proxy communicates
on the line chained_proxy_port=.
c) If the HTTP proxy with which this proxy communicates requires a user name for authentication, add
the user name to the line http_proxy_user=.
d) If the HTTP proxy with which this proxy communicates requires a password for authentication, add the
password to the line http_proxy_password=.
2. Restart F-Secure Policy Manager Proxy to apply the configuration changes by entering the command
/etc/init.d/fspmp restart.
Page 16

16 | F-Secure Policy Manager Proxy | Using the product on Linux
Upgrading the product
This topic describes how to upgrade F-Secure Policy Manager Proxy on Linux.
1. Log in as root.
2. Open a terminal.
3. Enter the following command to upgrade the product:
• Debian-based distributions: dpkg -i
f-secure-policy-manager-proxy_2.0.<build>_i386.deb.
• RPM-based distributions: rpm -U
f-secure-policy-manager-proxy-2.0.<build>-1.i386.rpm.
Upgrading the product does not change the previous configuration.
Page 17

F-Secure Policy Manager Proxy | Using the product on Linux | 17
Uninstalling the product
This topic describes how to uninstall F-Secure Policy Manager Proxy from your Linux system.
1. Log in as root.
2. Open a new terminal.
3. Enter the following command to uninstall the product:
• Debian-based distributions: dpkg -i
f-secure-policy-manager-proxy_2.0.<build>_i386.deb.
• RPM-based distributions: rpm -U
f-secure-policy-manager-proxy-2.0.<build>-1.i386.rpm.
Note: Log files and configuration files are not removed as these contain valuable information and
cannot be replaced. If you want to remove these files as well, enter the command rm -rf
/opt/f-secure/fspmp.
Page 18

18 | F-Secure Policy Manager Proxy | Using the product on Linux
Frequently asked questions
Here are some answers to frequently asked questions regarding F-Secure Policy Manager Proxy on Linux.
AnswerQuestion
How can I check that F-Secure Policy Manager Proxy
is running?
manually?
Why does F-Secure Policy Manager Proxy not start
up?
located in the Linux version?
to start on system startup?
You can check this by entering the command
/etc/init.d/fspmp status.
Enter the command /etc/init.d/fspmp start.How can I start F-Secure Policy Manager Proxy
Check the runtime errors, warnings and other
information, which are logged in
/var/opt/f-secure/fspmp/log/log.
To list all files and their locations, enter:Where are the F-Secure Policy Manager Proxy files
• dpkg -L f-secure-policy-manager-proxy
for Debian-based distributions.
• rpm -ql f-secure-policy-manager-proxy
for RPM-based distributions.
Yes, enter:Can I configure F-Secure Policy Manager Proxy not
• update-rc.d -f fspmp remove for
Debian-based distributions.
• chkconfig --del fspmp for RPM-based
distributions.
To configure F-Secure Policy Manager Proxy to start
on system startup again, enter:
• update-rc.d fspmp defaults for
Debian-based distributions.
• chkconfig --add fspmp for RPM-based
distributions.
Page 19

Troubleshooting
Chapter
5
Topics:
•
The error log
•
Error numbers
•
Troubleshooting with the error log
•
The status report log
F-Secure Policy Manager Proxy keeps detailed logs of activity and any
errors that have occurred. The two time-annotated log files are:
• the error log, which records any errors that have occurred, and
• the status report log, which is a running summary of Policy Manager
Proxy activity.
Page 20

20 | F-Secure Policy Manager Proxy | Troubleshooting
The error log
Here you will find information on the error log for F-Secure Policy Manager Proxy.
The error log file is used to store messages generated by F-Secure Policy Manager Proxy. Some of the
messages provide information about normal operations (startup, shutdown and daily maintenance, for example).
Other messages indicate errors.
In addition to the current error log file, three previous error log files are kept. By default, these are located as
follows:
• c:\program files\f-secure\fspmp\log\log (current log file).
• c:\program files\f-secure\fspmp\log\log.o (previous log file).
• c:\program files\f-secure\fspmp\log\log.oo (older log file).
• c:\program files\f-secure\fspmp\log\log.ooo (oldest log file).
Note: If you changed the installation directory when installing the product, then these paths will be
relative to the path that you selected. For example, [install_directory]\fspmp\log\log.o.
Message structure in the error log
The structure of messages in the error log is described here.
Every message in the error log contains the following information:
• The date and time the message was generated:
May-28-12:20:28.461 2-ERR 00017999 379 iad_open(): A
library/system-call open() failed for file
c:\program
files\f-secure\FSPMP\data\misc\license.dat, see
errno (reason: 2)
• The message level. The level is written both as a number and a three-letter category (ERR/WRN/INF/DBG):
May-28-12:20:28.461 2-ERR 00017999 379 iad_open(): A
library/system-call open() failed for file
c:\program
files\f-secure\FSPMP\data\misc\license.dat, see
errno (reason: 2)
• The Policy Manager Proxy error number (in the event of an error):
May-28-12:20:28.461 2-ERR 00017999 379 iad_open(): A
library/system-call open() failed for file
c:\program
files\f-secure\FSPMP\data\misc\license.dat, see
errno (reason: 2)
• The ID of the thread that issued the message:
May-28-12:20:28.461 2-ERR 00017999 379 iad_open(): A
library/system-call open() failed for file
c:\program
files\f-secure\FSPMP\data\misc\license.dat, see
errno (reason: 2)
• A brief explanation of what happened:
May-28-12:20:28.461 2-ERR 00017999 379 iad_open(): A
library/system-call open() failed for file
c:\program
Page 21

F-Secure Policy Manager Proxy | Troubleshooting | 21
files\f-secure\FSPMP\data\misc\license.dat, see
errno (reason: 2)
If the message was due to an error, it may also include the reason for the error, which can consist of one or
both of the following:
• If the message reports an error that was a consequence of a previous message (issued by the same
thread), the reason usually specifies the original message that the current message is associated with.
• If the message reports an external error, the external error code is usually specified as the reason:
May-28-12:20:28.461 2-ERR 00017999 379 iad_open(): A
library/system-call open() failed for file
c:\program
files\f-secure\FSPMP\data\misc\license.dat, see
errno (reason: 2)
Message levels
Here you will find a description of the levels allocated to messages in the error log.
Message in the error log have different levels of importance:
MeaningLevel
Critical error1
Error2
Warning3
Information4
Unassigned0
Page 22

22 | F-Secure Policy Manager Proxy | Troubleshooting
Error numbers
Every error message written to the log contains an error number.
This error number uniquely specifies what went wrong. There are two types of errors.
Internal error numbers
A complete list of all the error numbers is located by default in c:\program
files\f-secure\fspmp\doc\log_error_codes.txt.
Note: If you changed the installation directory when installing the product, then these paths will be
relative to the path that you selected. For example,
[install_directory]\fspmp\doc\log_error_codes.txt.
External error numbers
If an error message in the log was caused by an external error, the external error number is included in the
message in the error log. The description of the Policy Manager Proxy error usually describes the kind of
external error that occurred and suggests places to look it up.
Page 23

F-Secure Policy Manager Proxy | Troubleshooting | 23
Troubleshooting with the error log
Here you will find some more information on how to use the error log for troubleshooting purposes.
Errors in the error log can come from multiple threads; each message in the error log is marked with the
number of the thread that generated it.
Here are some examples of error messages:
MeaningError message
Not enough disk space for a full
cache : 50 required, 0 already
occupied, only 8 more available
Removed 74381 bytes for free
disk space smaller than cache
margins
socket 93 (92998ce:80)
main_mux(): connection broken
This warning indicates that the amount of available
disk space is less than the amount that Policy Manager
Proxy is set to use. Policy Manager Proxy will run more
efficiently if you free up some disk space.
This message is shown when the disk is almost full.
If the does fill up completely, it may cause
unpredictable system behavior.
The proxy server restricts itself to never using the last
three megabytes of disk space, but some other
application or user may fill up the disk completely.
When you see this message, you should free up some
more space on the disk.
When this line appears in the error log, look for
previous lines containing information about the same
socket (in this case, 93) and the same address (in this
case, 92998ce:80).
A previous entry such as:
socket 103 (502fcbc7:8080)::RecvMore():
(m_http_value != m_length_value + 4)
notifies you that the server with which Policy Manager
Proxy is trying to communicate is not valid. In this
case, an F-Secure product has probably set the wrong
IP address for Policy Manager.
Page 24

24 | F-Secure Policy Manager Proxy | Troubleshooting
The status report log
The status report log contains regular summaries of the status of Policy Manager Proxy.
Every 10 minutes, Policy Manager Proxy creates a record in the status report log containing the date, time
and various counters (packets count, connected clients count, etc.). The status report log is by default located
under c:\program files\f-secure\fspmp\reports\server_status.
Note: If you changed the installation directory when installing the product, then these paths will be
relative to the path that you selected. For example,
[install_directory]\fspmp\reports\server_status.
Although the status report log is a text file and can be viewed in any text editor, it is easier to read in a
spreadsheet program.
 Loading...
Loading...