Page 1

F-Secure Policy
Manager Proxy
Administrator’s Guide
Page 2

"F-Secure" and the triangle symbol are registered trademarks of F-Secure Corporation and F-Secure
product names and symbols/logos are either trademarks or registered trademarks of F-Secure
Corporation. All product names referenced herein are trademarks or registered trademarks of their
respective companies. F-Secure Corporation disclaims proprietary interest in the marks and names of
others. Although F-Secure Corporation makes every effort to ensure that this information is accurate,
F-Secure Corporation will not be liable for any errors or omission of facts contained herein. F-Secure
Corporation reserves the right to modify specifications cited in this document without prior notice.
Companies, names and data used in examples herein are fictitious unless otherwise noted. No part of
this document may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic or
mechanical, for any purpose, without the express written permission of F-Secure Corporation.
This product may be covered by one or more F-Secure patents, including the following:
GB2353372 GB2366691 GB2366692 GB2366693 GB2367933 GB2368233
GB2374260
Copyright © 2007 F-Secure Corporation. All rights reserved. 12000076-7A11
Page 3

Contents
About This Guide 5
How This Guide Is Organized .............................................................................................. 6
Who Should Use This Guide................................................................................................ 7
Conventions Used in F-Secure Guides................................................................................ 8
Symbols .......... ...... ....... ............................................. .................................................. 8
Chapter 1 Introduction 10
1.1 An Up-To-Date System is a Secure System..............................................................11
1.2 When Should You Use F-Secure Policy Manager Proxy? .........................................12
1.3 How are F-Secure Policy Manager Proxy and F-Secure Anti-Virus Proxy Different?14
Chapter 2 Installation 15
2.1 System Requirements........ ....... ...... ....... ...... ............................................. .................16
2.2 Installing F-Secure Policy Manager Proxy ...................... ....... ...... ....... ...... .................16
2.2.1 Local Installation.............................................................................................16
Chapter 3 Configuration 22
3.1 Overview ....................................................................................................................23
3.2 Remote Configuration ............................ ...... ...... ....... ...... ....... ....................................23
3.2.1 Chained Proxy Configuration..........................................................................24
Chapter 4 F-Secure Policy Manager Proxy on Linux 26
4.1 Introduction ................................................................................................................27
iii
Page 4

4.2 System Requirements........ ....... ...... ....... ...... ............................................. .................27
4.3 Installation..................................................................................................................27
4.4 Configuration..............................................................................................................28
4.4.1 Chained Proxy Configuration..........................................................................28
4.5 Upgrading...................................................................................................................29
4.6 Uninstallation..............................................................................................................30
4.7 Frequently Asked Questions ......................................................................................30
Chapter 5 Troubleshooting 32
5.1 Overview ....................................................................................................................33
5.2 The Error Log.............................................................................................................33
5.3 Reading the Error Log................................................................................................33
5.3.1 Message Structure .........................................................................................33
5.3.2 Message Levels..............................................................................................35
5.4 Error Numbers............................................................................................................36
5.4.1 Internal Error Numbers...................................................................................36
5.4.2 External Error Numbers..................................................................................36
5.5 Troubleshooting with the Error Log............................................................................36
5.5.1 Some Example Error Messages.....................................................................37
5.6 The Status Report Log...............................................................................................37
Technical Support 39
Overview ............................................................................................................................ 40
Web Club ...........................................................................................................................40
Virus Descriptions on the Web.................................................................................. 40
Advanced Technical Support .............................................................................................40
F-Secure Technical Product Training .................................................................................41
Training Program ...................................................................................................... 41
Contact Information................................................................................................... 42
About F-Secure Corporation
iv
Page 5

ABOUT THIS GUIDE
How This Guide Is Organized...................................................... 6
Who Should Use This Guide....................................................... 7
Conventions Used in F-Secure Guides....................................... 8
5
Page 6

How This Guide Is Organized
The F-Secure Policy Manager Proxy Administrator’s Guide provides an
overview of F-Secure Policy Manager Proxy concepts, a step-by-step
guide to installation and all the information you need to set up and
manage your F-Secure Policy Manager Proxy.
F-Secure Policy Manager Proxy Administrator’s Guide is divided into the
following chapters:
Chapter 1. Introduction provides general information about F-Secure
Policy Manager Proxy
Chapter 2. Installation contains a step-by-step guide to installing
F-Secure Policy Manager Proxy.
Chapter 3. Configuration describes how F-Secure Policy Manager Proxy
is configured.
Chapter 4. F-Secure Policy Manager Proxy on Linux describes how to
install, configure and troubleshoot F-Secure Policy Manager Proxy for
Linux.
Chapter 5. Troubleshooting describes how the diagnostic log files are
read.
and how it works.
About This Guide 6
Technica l S u ppo rt provides contact information for assistance and details
about the Web Club.
About F-Secure Corporation describes the company background and
products
Page 7

7
Who Should Use This Guide
This guide is intended for system administrators. It is assumed that the
reader has:
Working knowledge of Microsoft Windows Server operating
systems.
A basic understanding of the Internet and TCP/IP protocols.
Page 8
Conventions Used in F-Secure Guides
This section describes the symbols, fonts, and terminology used in this
manual.
Symbols
WARNING: The warning symbol indicates a situation with a
risk of irreversible destruction to data.
IMPORTANT: An exclamation mark provides important
information that you need to consider.
REFERENCE - A book refers you to related information on the
topic available in another document.
NOTE - A note provides additional information that you should
consider.
l
8
Fonts
TIP - A tip provides information that can help you perform a task
more quickly or easily.
⇒ An arrow indicates a one-step procedure.
Arial bold (blue) is used to refer to menu names and commands, to
buttons and other items in a dialog box.
Arial Italics (blue) is used to refer to other chapters in the manual, book
titles, and titles of other manuals.
Arial Italics (black) is used for file and folder names, for figure and table
captions, and for directory tree names.
Courier New is used for messages on your computer screen.
Page 9

9
Courier New bold is used for information that you must type.
SMALL CAPS (BLACK) is used for a key or key combination on your
keyboard.
PDF Document
For More Information
Arial underlined (blue )
Arial italics is used for window and dialog box names.
This manual is provided in PDF (Portable Document Format). The PDF
document can be used for online viewing and printing using Adobe®
Acrobat® Reader. When printing the manual, please print the entire
manual, including the copyright and disclaimer statements.
Visit F-Secure at http://www.f-secure.com for documentation, training
courses, downloads, and service and support contacts.
In our constant attempts to improve our documentation, we would
welcome your feedback. If you have any questions, comments, or
suggestions about this or any other F-Secure document, please contact
us at documentation@f-secure.com
is used for user interface links.
.
Page 10

1
INTRODUCTION
An Up-To-Date System is a Secure System............................... 11
When Should You Use F-Secure Policy Manager Proxy?.......... 12
How are F-Secure Policy Mana ger Pr oxy an d F-S ecu re Anti -Virus
Proxy Different?.......................................................................... 14
10
Page 11
11
\
1.1 An Up-To-Date System is a Secure System
To be protected, a workstation must have the latest defence against
viruses and other malware that exist in the internet.
What Is The Virus Definition Database?
Information against known viruses, worms and other malware are
compiled into the virus definition database.
This virus definition database is regularly made available to all the
workstations with F-Secure Client Security installed. It is this virus
definition database that enables F-Secure Client Security to protect a
workstation from viruses and malware.
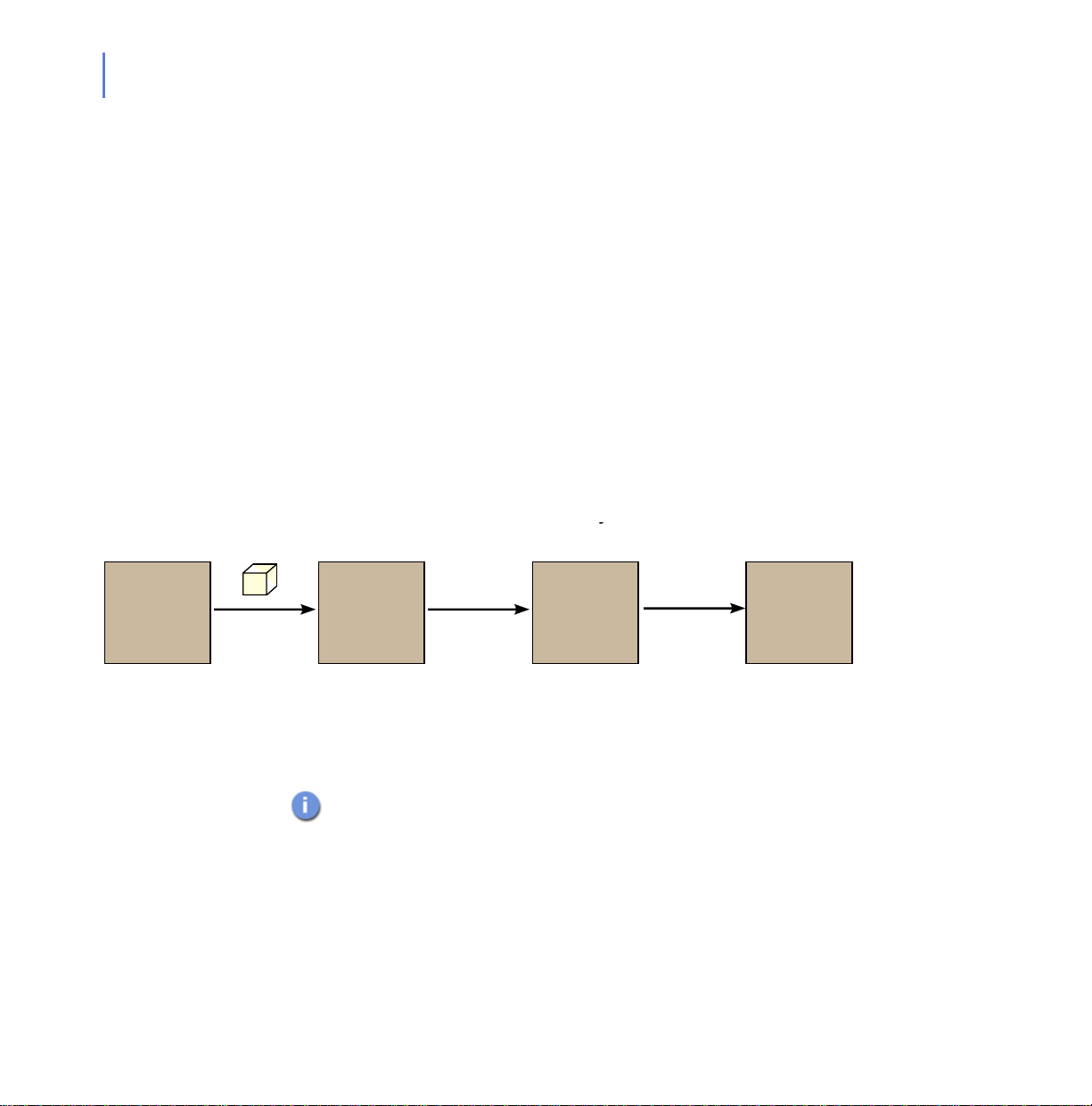
How Do the Virus Definition Databases Get To F-Secure Client
Security?
)6HFXUH9LUXV
'HILQLWLRQ'DWDEDVH
)6HFXUH
8SGDWH
6HUYHU
)6HFXUH
3ROLF\
0DQDJHU
Figure 1-1 A typical virus definition database delivery chain.
)6HFXUH
3ROLF\
0DQDJHU
)6HFXUH
&OLHQW
6HFXULW\
The virus definition database travels through the steps shown in Figure
1-1.
Figure 1-1 is the primary path; there are fallback paths if one or
more of the links is unavailable (for example if the machine running
F-Secure Policy Manager has a power cut).
Page 12

CHAPTER 1 12
Introduction
What Does F-Secure Policy Manager Do?
F-Secure Policy Manager allows you to centrally manage all the F-Secure
products in your network. It is the central monitoring and configuration
point for your network.
See F-Secure Policy Manager Administrator’s Guide for more
information.
What Does F-Secure Policy Manager Proxy Do?
F-Secure Policy Manager Proxy helps deliver the virus definition
databases quickly and efficiently.
1.2 When Should You Use F-Secure Policy Manager Proxy?
The effects of F-Secure Policy Manager Proxy are most obvious in large,
vastly spread networks; for example a large corporation with remote
offices in different parts of the globe. An example of one situation where
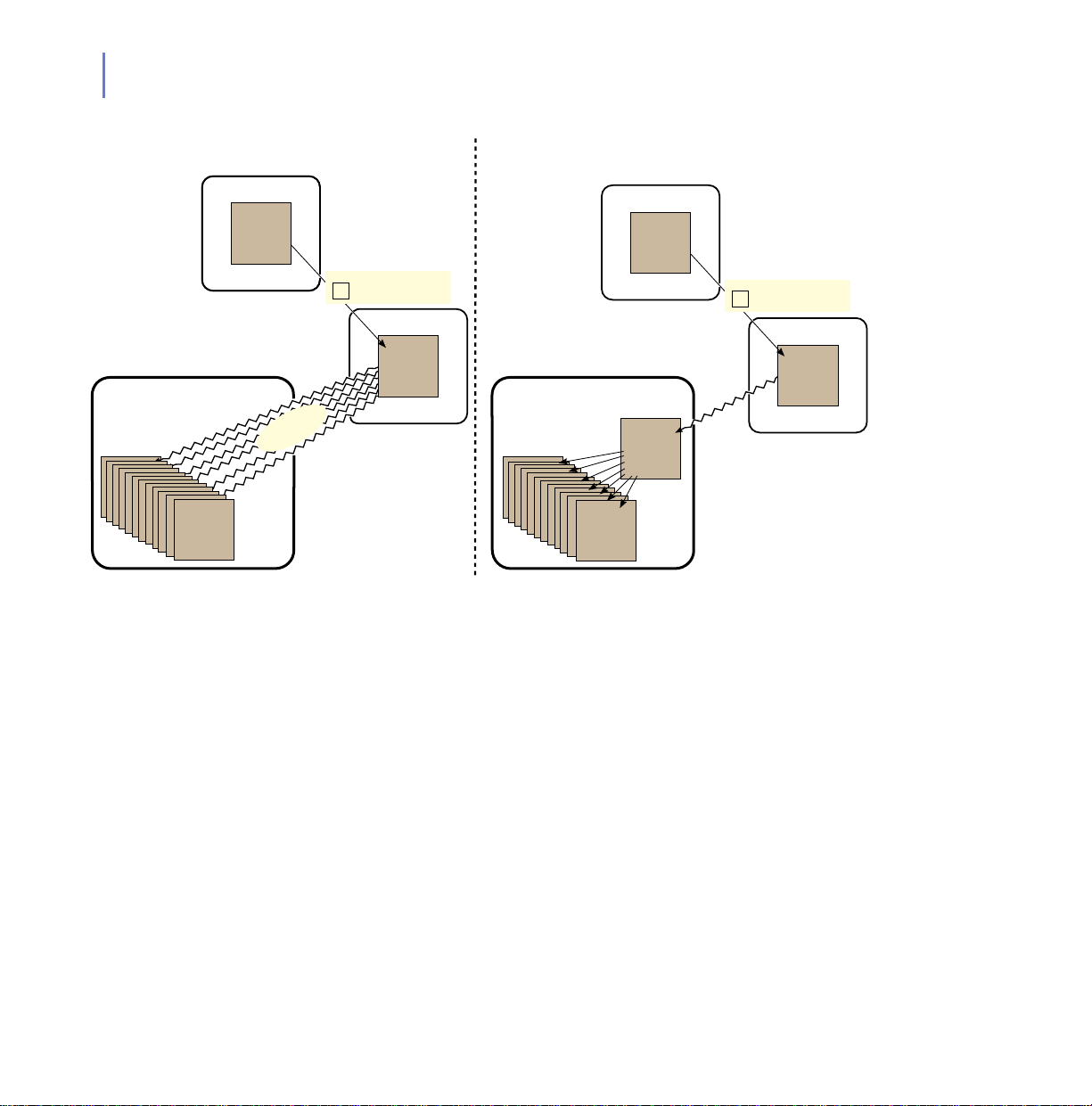
F-Secure Policy Manager Proxy is useful is shown in Figure 1-2.
Page 13
13
)6HFXUH3ROLF\0DQDJHU3UR[\
5HJLRQDO2IILFH
)6HFXUH
$QWL9LUXV
&OLHQW
6HFXULW\
)6HFXUH
&OLHQW
6HFXULW\
:LWKRXW
)6HFXUH
)6HFXUH
8SGDWH
6HUYHU
:LWK
)6HFXUH
)6HFXUH
8SGDWH
6HUYHU
)6HFXUH
3ROLF\
0DQDJHU
3UR[\
6ORZ
&RQQHFWLRQ
)6HFXUH9LUXV
'HILQLWLRQ'DWDEDVH
&RUSRUDWH
+HDGTXDUWHUV
)6HFXUH
3ROLF\
0DQDJHU
0DQ\6ORZ
&RQQHFWLRQV
)6HFXUH9LUXV
'HILQLWLRQ'DWDEDVH
&RUSRUDWH
+HDGTXDUWHUV
)6HFXUH
3ROLF\
0DQDJHU
)6HFXUH3ROLF\0DQDJHU3UR[\
5HJLRQDO2IILFH
)6HFXUH
$QWL9LUXV
&OLHQW
6HFXULW\
)6HFXUH
&OLHQW
6HFXULW\
Figure 1-2 On the right, with F-Secure Policy Manager Proxy, the numbe r of slow
connections is dramatically reduced.
There are three reasons to use F-Secure Policy Manager Proxy:
To Decrease Network Bandwidth Usage
You should use F-Secure Policy Manager Proxy when you have a group
of workstations far away from you F-Secure Policy Manager Server; for
example a “remote office” scenario like in Figure 1-2.
To Decrease Virus Definition Database Delivery Time
You should use F-Secure Policy Manager Proxy when you have a group
of workstations separated from the F-Secure Policy Manager Server by a
slow connection (for example a dialup connection), for example in a
situation like in Figure 1-2
Page 14

To Decrease F-Secure Policy Manager Hardware Load
You should use F-Secure Policy Manager Proxy, if the server hardware
running the F-Secure Policy Manager is unable to cope with the number
of virus definition database requests it receives.
1.3 How are F-Secure Policy Manager Proxy and F-Secure Anti-Virus Proxy Different?
They are designed to work with different F-Secure products.
CHAPTER 1 14
Introduction
Works with F-Secure Client Security
versions
Works with F-Secure Policy Manager
versions
Can deliver virus definition databases
without an upstream connection?
Both can function in the same network.
F-Secure Policy
Manager Proxy
6.0 and later Earlier than 6.0
6.0 and later Earlier than 6.0
no yes
F-Secure
Anti-Virus Proxy
Page 15

2
INSTALLATION
System Requirements................................................................ 16
Installing F-Secure Policy Manager Proxy.................................. 16
15
Page 16

2.1 System Requirements
To install F-Secure Policy Manager Proxy, your system must meet the
following minimum requirements:
Processor: Intel Pentium III 450MHz processor or faster
Memory: 256 MB RAM
Disk Space: 300 MB; 500 MB or more is recommended. The disk space
required depends on the size of the installation.
Network: 10 Mbit; 100Mbit is recommended.
CHAPTER 2 16
Installation
Operating
System:
F-Secure
Software:
Windows Server 2000
Windows Server 2003
F-Secure Client Security 6 or later
F-Secure Policy Manager 6 or later
2.2 Installing F-Secure Policy Manager Proxy
There are two possible methods of installing F-Secure Policy Manager
Proxy:
Locally; see further instructions in the “Local Installation”
Remotely; see further instructions in the F-Secure Policy
Manager Administrator’s Guide.
2.2.1 Local Installation
Installing F-Secure Policy Manager Proxy is a two-step process:
1. Install F-Secure Policy Manager Proxy
2. Configure F-Secure Client Security to use F-Secure Policy Manager
Proxy.
Page 17

17
Step 1. 1. Run the setup.exe file.
2. Click the Next button on the first screen of the installer.
3. Read through the license agreement and click the I ac cept this
agreement option. Click Next.
4. Select the Custom option and click Next to continue.
Figure 2-1 Custom installation
Page 18

CHAPTER 2 18
Installation
5. Make sure the box next to F-Secure Policy Manager Proxy is checked
and click Next.
Figure 2-2 Components
Page 19
19
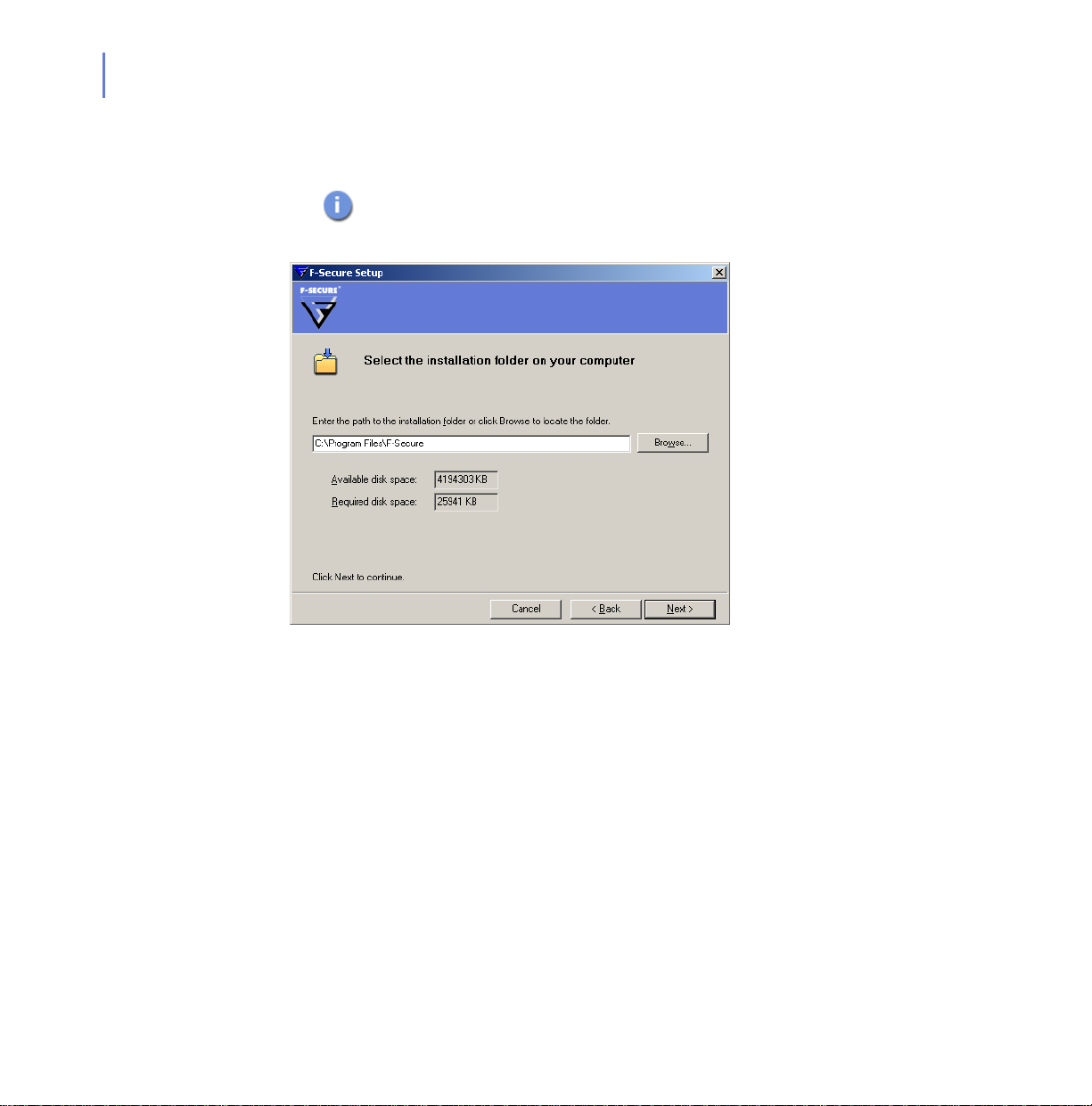
6. Select where to install F-Secure Policy Manager Proxy in the dialog
by clicking the Browse button. Click Next.
If a previous installation of an F-Secure product was detected
on the computer, this dialog is not displayed and the previous
installation directory is used.
Figure 2-3 Installation folder
7. If a previous installation of an F-Secure product is detected, you will
be asked if you would like to use the same settings as the previous
installed product. If you select Yes the dialogs in steps 8–10 will be
skipped. If you select No, you can continue through steps 8–10 and
select new setting s.
Page 20

CHAPTER 2 20
Installation
8. Select the Central management with F-Secure Policy Manager option
and click Next.
Figure 2-4 Central management
9. Copy the public key file, admin.pub from the F-Secure Policy
Manager Server to the local file system. Click Browse and select this
key file. Click Next
Figure 2-5 Public key installation
Page 21

21
10. Enter the IP address of the F-Secure Policy Manager Server you wish
the F-Secure Policy Manager Proxy to communicate with. Click Next
Figure 2-6 F-Secure Policy Manager Server IP address
11. Click Start to begin.
12. When the progress bar is full, click Next.
13. F-Secure Policy Manager Proxy is now running. Click Finish to close
the final dialog.
Step 2. In a centrally managed network you should configure F-Secure Client
Security to use F-Secure Policy Manager Proxy by distributing a new
policy with this configuration.
For more information about policies and remote configuration,
please consult the F-Secure Policy Manager Administrator’s
Guide
Page 22

3
CONFIGURATION
Overview..................................................................................... 23
Remote Configuration................................................................. 23
22
Page 23

23
3.1 Overview
F-Secure Policy Manager Proxy is configured remotely through the
F-Secure Policy Manager Console.
For more information about the F-Secure Policy Manager, see the
F-Secure Policy Manager Administrator’s Guide.
3.2 Remote Configuration
Configuring F-Secure Policy Manager Proxy remotely is done in the
F-Secure Policy Manager Console through the advanced editing mode.
To enter this mode:
1. Go to the View drop-down menu.
2. Click Advanced Mode.
Page 24
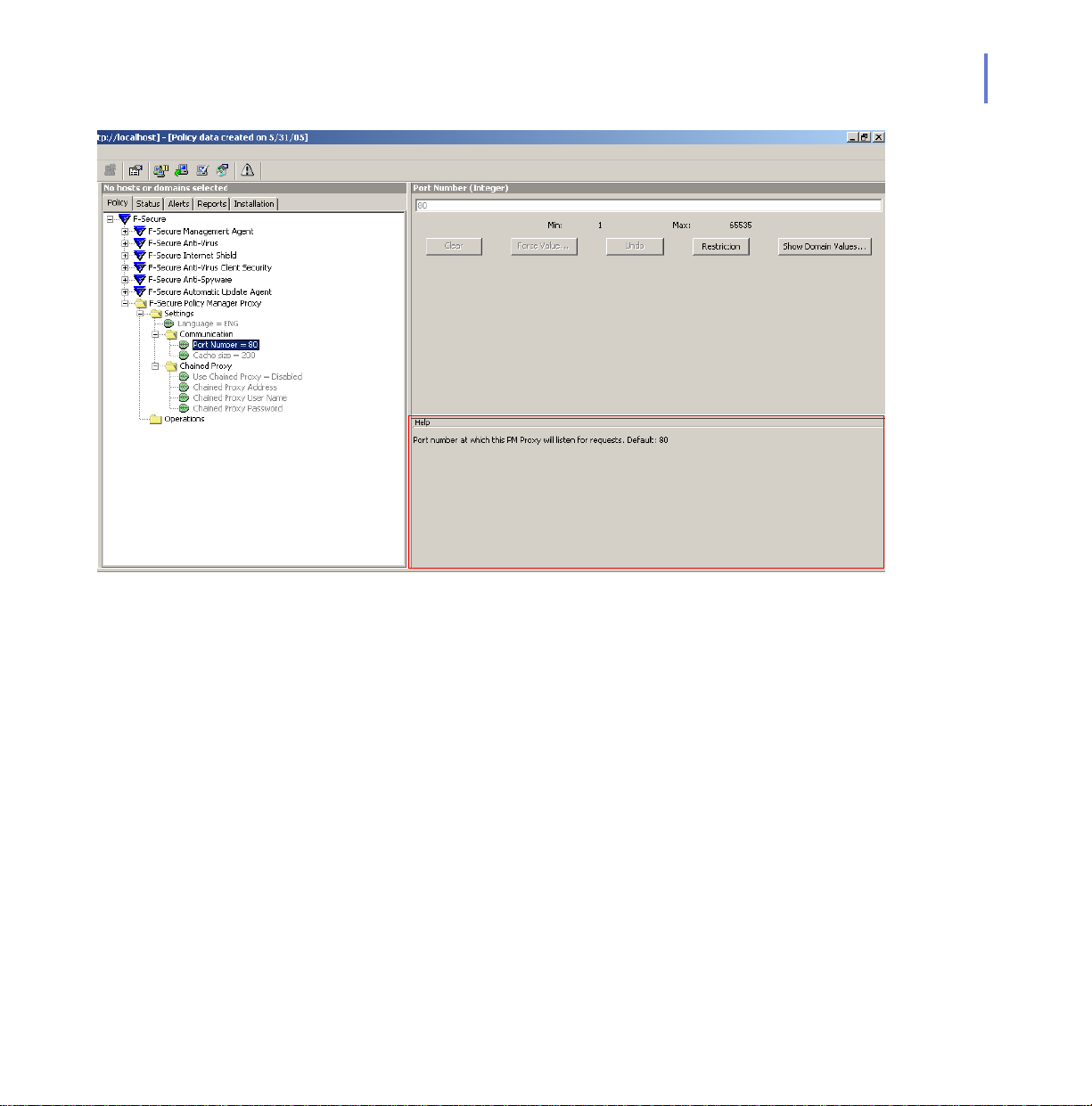
CHAPTER 3 24
Configuration
Figure 3-1 The F-Secure Policy Manager Console showing the settings available
for the F-Secure Policy Manager Proxy.
You can find explanations of each of the configuration options in the help
area (see Figure 3-1).
3.2.1 Chained Proxy Configuration
F-Secure Policy Manager Proxy can connect through another F-Secure
Policy Manager Proxy or HTTP proxy; this is a ‘chained proxy
configuration.’
Page 25
25
)6HFXUH9LUXV
'HILQLWLRQ'DWDEDVH
)6HFXUH
3ROLF\
0DQDJHU
([WUD3UR[\
)6HFXUH
3ROLF\0DQDJHU
3UR[\RU+773
3UR[\
)6HFXUH
3ROLF\
0DQDJHU
3UR[\
Figure 3-2 An example chained proxy configuration.
A chained proxy configuration may be necessary to:
traverse network boundaries or,
reduce load from F-Secure Policy Manager Server.
)6HFXUH
&OLHQW
6HFXULW\
Page 26

4
F-SECURE POLICY
ANAGER PROXY ON
M
INUX
L
Introduction................................................................................. 27
System Requirements................................................................ 27
Installation.................................................................................. 27
Configuration.............................................................................. 28
Upgrading................................................................................... 29
Uninstallation.............................................................................. 30
Frequently Asked Questions...................................................... 30
26
Page 27

27
4.1 Introduction
This chapter describes how to install, configure and troubleshoot
F-Secure Policy Manager Proxy for Linux.
4.2 System Requirements
To install F-Secure Policy Manager Proxy for Linux, your system must
meet the following minimum requirements:
Processor: Intel Pentium III 1GHz processor or faster
Memory: 512 MB of RAM or more is recommended
Disk space to install: 90 MB
Free disk space: 100 MB of free hard disk space; 500 MB or
Operating System: Red Hat Enterprise Linux 4
more is recommended.
Red Hat Enterprise Linux 3
SUSE Linux 10.0
SUSE Linux 9.x
SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 9
Debian GNU Linux Sarge 3.1
4.3 Installation
1. Log in as root.
2. Open a terminal.
F-Secure Software: F-Secure Client Security 6 or later
F-Secure Policy Manager 6 or later
Page 28

F-Secure Policy Manager Proxy on Linux
3. To install type:
Debian Based Distributions RPM Based Distributions
CHAPTER 4 28
dpkg -i
f-secure-policy-manager-proxy_1.0.<buil
d>_i386.deb
F-Secure Policy Manager Proxy is started automatically after the
installation.
rpm -i
f-secure-policy-manager-proxy-1.0.<bu
ild>-1.i386.rpm
4.4 Configuration
1. Configure F-Secure Policy Manager Proxy by editing the following
configuration file:
/opt/etc/f-secure/fspmp/conf/proxy.cfg
2. Restart F-Secure Policy Manager Proxy to apply configuration
changes by typing:
# /etc/init.d/fspmp restart
4.4.1 Chained Proxy Configuration
F-Secure Policy Manager Proxy can connect through another F-Secure
Policy Manager Proxy or HTTP proxy; this is a ‘chained proxy
configuration.’ For more information, see “Chained Proxy Configuration”,
24.
To configure chained proxies:
1. Open the F-Secure Policy Manager Proxy configuration file:
/opt/etc/f-secure/fspmp/conf/proxy.cfg
2. Add the host name or IP address of the F-Secure Policy Manager
Proxy or HTTP Proxy with which this proxy communicates in
chained_proxy_ip_addr=
Page 29

29
3. Specify the TCP port of the F-Secure Policy Manager Proxy or HTTP
4. If the HTTP Proxy with which this proxy communicates requires a
5. If the HTTP Proxy with which this proxy communicates requires a
6. Restart F-Secure Policy Manager Proxy to apply configuration
4.5 Upgrading
1. Log in as root.
2. Open a terminal.
3. Type:
Proxy with which this proxy communicates in:
chained_proxy_port=
user name for authentication, enter it in:
http_proxy_user=
password for authentication, enter it in:
http_proxy_password=
changes by typing:
# /etc/init.d/fspmp restart
Debian Based Distributions RPM Based Distributions
dpkg -i
f-secure-policy-manager-proxy_1.0.<buil
d>_i386.deb
Upgrading does not change the previous configuration.
rpm -U
f-secure-policy-manager-proxy-1.0.<bu
ild>-1.i386.rpm
Page 30

CHAPTER 4 30
F-Secure Policy Manager Proxy on Linux
4.6 Uninstallation
1. Log in as root.
1. Open a terminal.
2. Type:
Debian Based Distributions RPM Based Distributions
dpkg -r f-secure-policy-manager-proxy rpm -e f-secure-policy-manager-console
Log files and configuration files are not removed as these are
irreplaceable and contain valuable information. To remove these,
type:
rm -rf /opt/f-secure/fspmp
4.7 Frequently Asked Questions
Q. How can I check that F-Secure Policy Manager Proxy is running?
A. You can check this by typing:
/etc/init.d/fspmp status
Q. How can I start F-Secure Policy Manager Proxy manually?
A. T ype:
/etc/init.d/fspmp start
Q. Why does F-Secure Policy Manager Proxy not start?
A. Check the runtime errors, warnings and other information that are
logged in
/var/opt/f-secure/fspmp/log/log
Page 31

31
Q. Where are the F-Secure Policy Manager Proxy files located in the
Linux version?
A. To list all files and their places type:
Debian Based Distributions RPM Based Distributions
dpkg -L f-secure-policy-manager-proxy rpm -ql f-secure-policy-manager-proxy
Q. Can I configure F-Secure Policy Manager Proxy not to start on
system start up?
A. Yes, type:
Debian Based Distributions RPM Based Distributions
update-rc.d -f fspmp remove chkconfig --del fspmp
To configure F-Secure Policy Manager Proxy to start on system start
up again, type:
Debian Based Distributions RPM Based Distributions
update-rc.d fspmp defaults chkconfig --add fspmp
Page 32

5
TROUBLESHOOTING
Overview..................................................................................... 33
The Error Log............................................................................. 33
Reading the Error Log................................................................ 33
Error Numbers............................................................................ 36
Troubleshooting with the Error Log ............................................ 36
The Status Report Log............................................................... 37
32
Page 33

33
5.1 Overview
The F-Secure Policy Manager Proxy keeps detailed logs of activity and
any errors that have occurred. Two time-annotated log files kept:
the “The Error Log”, 33; a record of any errors that occurred,
the “The Status Report Log”, 37; a running summary of the
5.2 The Error Log
The Error Log file is used to store messages generated by F-Secure
Policy Manager Proxy. Some of the messages provide information about
normal operations (for example, startup, shutdown, daily maintenance).
Other messages indicate errors.
In addition to the current Error Log file, three previous Error Log files are
kept. By default these are located at:
c:\program files\f-secure\fspmp\log\log (current)
c:\program files\f-secure\fspmp\log\log.o (previous)
c:\program files\f-secure\fspmp\log\log.oo (older)
c:\program files\f-secure\fspmp\log\log.ooo (oldest)
F-Secure Policy Manager Proxy’s activity.
If you changed the install directory during installation then these
paths will be relative to the path that you selected, for example,
[install_directory]\fspmp\log\log.o
5.3 Reading the Error Log
5.3.1 Message Structure
Every message in the log contains the following information:
The date and time the message was generated.
Page 34

CHAPTER 5 34
Troubleshooting
May-28-12:20:28.461 2-ERR 00017999 379 iad_open(): A
library/system-call open() failed for file
c:\program
files\f-secure\FSPMP\data\misc\license.dat, see
errno (reason: 2)
The message level, as explained in the section “Message
Levels”. The level is written both as a number, as well as a
3-letter category (ERR/WRN/INF/DBG).
May-28-12:20:28.461 2-ERR 00017999 379 iad_open(): A
library/system-call open() failed for file
c:\program
files\f-secure\FSPMP\data\misc\license.dat, see
errno (reason: 2)
The F-Secure Policy Manager Proxy error number (in case of an
error).
May-28-12:20:28.461 2-ERR 00017999 379 iad_open(): A
library/system-call open() failed for file
c:\program
files\f-secure\FSPMP\data\misc\license.dat, see
errno (reason: 2)
The thread-ID of the thread that issued the message.
May-28-12:20:28.461 2-ERR 00017999 379 iad_open(): A
library/system-call open() failed for file
c:\program
files\f-secure\FSPMP\data\misc\license.dat, see
errno (reason: 2)
A brief explanation of what happened.
May-28-12:20:28.461 2-ERR 00017999 379 iad_open(): A
library/system-call open() failed for file
c:\program
files\f-secure\FSPMP\data\misc\license.dat, see
errno (reason: 2)
Page 35

35
The message may also include the following if it was due to an error:
The reason for the error, which may include one or both of the
5.3.2 Message Levels
Messages in the log have various levels of importance:
following:
If the message reports an error that was a consequence of a
previous message (issued by the same thread), the reason
usually specifies the original message that the current
message is associated with.
If the message reports an external error (as explained in
“External Error Numbers”), the external error code is usually
specified as the reason.
May-28-12:20:28.461 2-ERR 00017999 379
iad_open(): A library/system-call open() failed
for file c:\program
files\f-secure\FSPMP\data\misc\license.dat, see
errno (reason: 2)
Level Meaning
1 critical error
2 error
3 warning
4 information
0 unassigned
Page 36

5.4 Error Numbers
Every error message written to the log contains an error number. This
number uniquely specifies what went wrong.There are two types of
errors:
Internal errors; those generated by F-Secure Policy Manager
Proxy.
External errors; those generated by the operating system or other
external products.
5.4.1 Internal Error Numbers
A complete list of all the error numbers is loca ted, by default at:
c:\program files\f-secure\fspmp\doc\log_error_codes.txt.
If you changed the install directory during installation these paths
will be relative to the path that you selected, for example,
[install_directory]\fspmp\doc\log_error_codes.txt
CHAPTER 5 36
Troubleshooting
5.4.2 External Error Numbers
If an error message in the log was caused by an external error, the
external error code is appended to the message in the Error Log. Usually,
the description of F-Secure Policy Manager Proxy error number describes
the kind of external error that occurred, and suggests places to look it up.
5.5 Troubleshooting with the Error Log
Errors in the Error Log can come from multiple threads; each message in
the Error Log is marked with the number of the thread that generated it.
Page 37
37
5.5.1 Some Example Error Messages
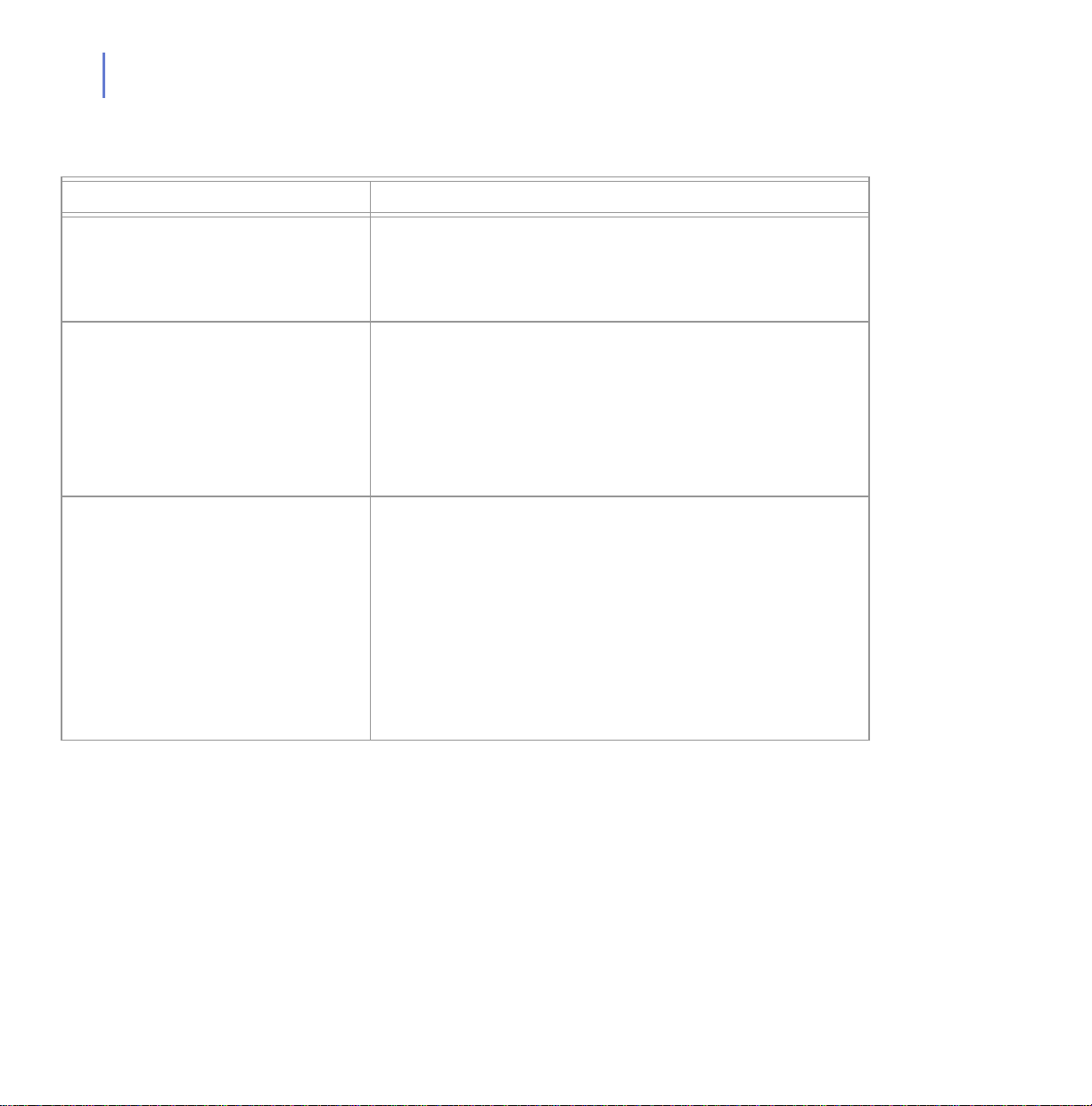
Error Message Meaning
Not enough disk space for a full
cache : 50 required, 0 already
occupied, only 8 more available
Removed 74381 bytes for free
disk space smaller than cache
margins
socket 93 (92998ce:80)
main_mux(): connection broken
This warning indicates that the available disk space is less
than the amount F-Secure Policy Manager Proxy is set to
use. F-Secure Policy Manager Proxy will operate more
efficiently if you free up some disk space.
This message displays when the disk is almost full. If the
disk does completely fill, this may cause unpredictable
system behavior.
The proxy server restricts itself to never use the last 3
Mbytes of disk space, but some other application or user
may completely fill the disk. When you see this message you
should make some more space on the disk.
When this line appears in the Error Log, look for previous
lines containing information about the same socket (in this
case, 93) and the same address (in this case: 92998ce:80).
A previous entry such as:
socket 103 (502fcbc7:8080)::RecvMore():
(m_http_value != m_length_value + 4)
notifies you that the server with which F-Secure Policy
Manager Proxy is trying to communicate is not valid. In this
case F-Secure Client Security has probably set the wrong IP
address for F-Secure Policy Manager.
5.6 The Status Report Log
The Status Report Log contains regular summaries of F-Secure Policy
Manager Proxy’s status.
Page 38
CHAPTER 5 38
Troubleshooting
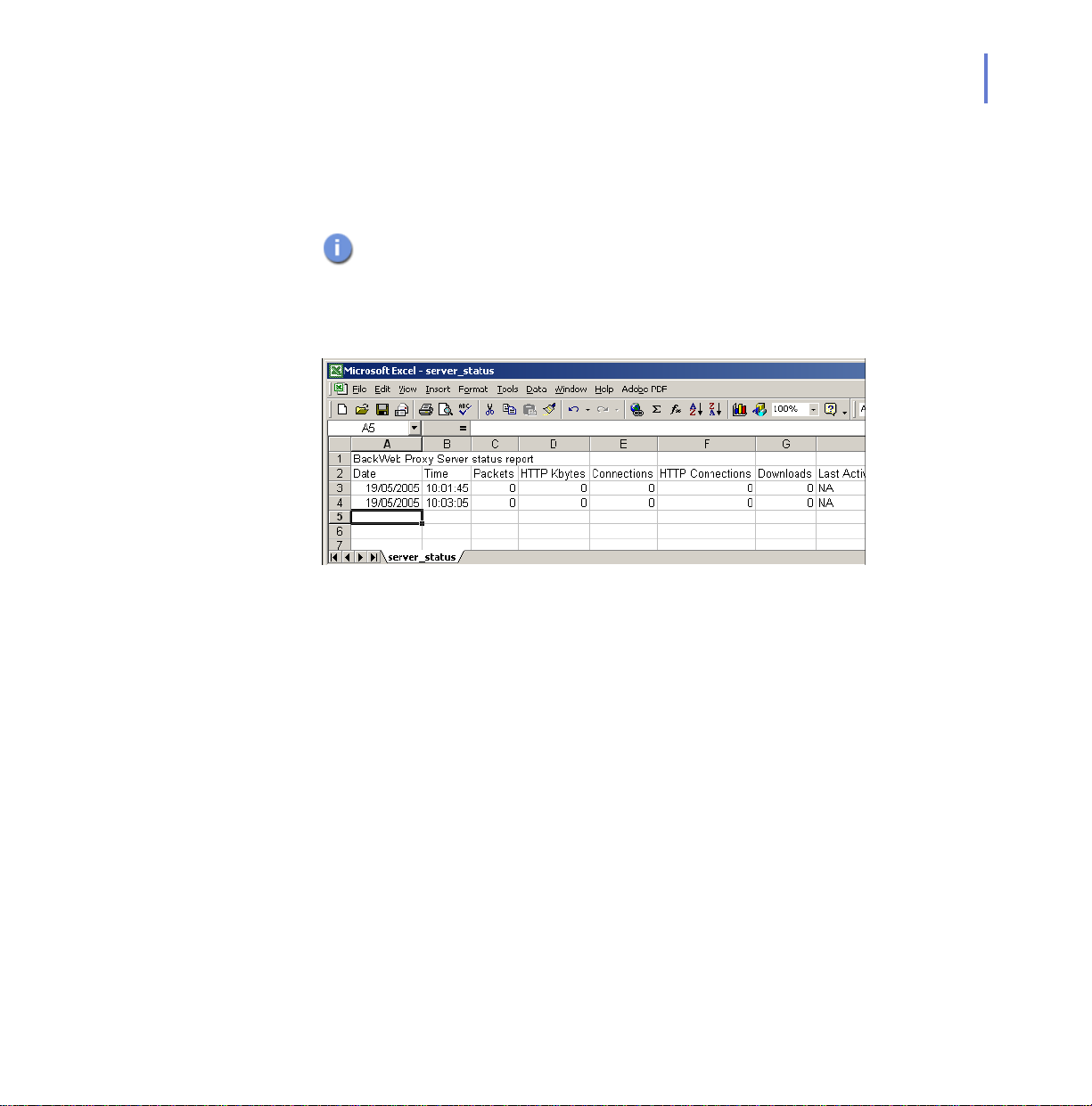
Every 10 minutes, F-Secure Policy Manager Proxy creates a record in the
Status Report Log which contains the date, time and various counters
(packets count, connected client count, etc.). The Status Report Log is
located, by default at: c:\program files\f-secure\fspmp\log\server_status.
If you changed the install directory during installation then these
paths will be relative to the path that you selected, for example,
[install_directory]\fspmp\report\server_status
Although the Status Report Log is a text file and can be viewed in any text
editor, it is easier read in a spreadsheet program.
Figure 5-1 An example Status Report Log viewed in Microsoft Excel™
Page 39

Technical Support
Overview..................................................................................... 40
Web Club.................................................................................... 40
Advanced Technical Support...................................................... 40
F-Secure Technical Product Training......................................... 41
39
Page 40

Overview
F-Secure Technical Support is available by e-mail and from the F-Secure
Web site. You can access our Web site from within your F-Secure
application or from your Web browser.
Web Club
The F-Secure Web Club provides assistance to users of F-Secure
products. To enter, choose the Web Club command from the Help menu
in the F-Secure application. The first time you use this option, enter the
path and name of your Web browser and your location.
To connect to the Web Club directly from your Web browser, go to:
http://www.f-secure.com/webclub/
Virus Descriptions on the Web
F-Secure Corporation maintains a comprehensive collection of
virus-related information on its Web site. To view the Virus Information
Database, go to:
Technical Support 40
http://www.f-secure.com/virus-info/.
Advanced Technical Support
For advanced technical support, go to the F-Secure Support Center at
http://support.f-secure.com/
directly.
For basic technical assistance, please contact your F-Secure distributor.
Please include the following information with your support request:
or contact your local F-Secure distributor
Page 41

41
1. Name and version number of your F-Secure software program
(including the build number).
2. Name and version number of your operating system (including the
build number).
3. A detailed description of the problem, including any error messages
displayed by the program, and any other details, which could help us
duplicate the problem.
When contacting F-Secure support by telephone, please do the following
so that we may help you more effectively and save time:
Be at your computer so you can follow instructions given by the
support technician, or be prepared to write down instructions.
Have your computer turned on and (if possible) in the state it was
in when the problem occurred. Or you should be ready to
replicate the problem on the computer with minimum effort.
After installing the F-Secure software, you may find a Readme file
in the F-Secure folder in the Windows Start > Programs menu. The
Readme file contains late-breaking information about the product.
F-Secure Technical Product Training
F-Secure provides technical product training, material and information for
our distributors, resellers and customers to succeed with F-Secure
security products and services. Training can also be obtained through
F-Secure Certified Training Partners. With these tools and expertise, our
partners are able to differentiate their business from their competitors with
a unique and powerful solution for enterprise security, and obtain higher
levels of customer satisfaction while increasing market share and
profitability.
Training Program
For more detailed information about our course offerings, please go to our
F-Secure Technical Product Training page on the Internet at:
http://www.f-secure.com/products/training/
Page 42

The courses take place in modern and well-equipped classrooms. All of
our courses consist of theory and hands-on parts. At the end of each
course there is a certification exam. Contact your local F-Secure office or
F-Secure Certified Training Partner to get information about the courses
and schedules.
Contact Information
General issues: Training@f-secure.com
Registration: Training-Registration@f-secure.com
Feedback: Training-Feedback@f-secure.com
Technical Support 42
Page 43

About F-Secure Corporation
F-Secure Corporation is the fastest growing publicly listed company in the
antivirus and intrusion prevention industry with more than 50% revenue
growth in 2004. Founded in 1988, F-Secure has been listed on the Helsinki
Stock Exchange since 1999. We have our headquarters in Helsinki, Finland,
and offices in USA, France, Germany, Italy, Sweden, the United Kingdom and
Japan. F-Secure is supported by service partners, value added resellers and
distributors in over 50 countries. F-Secure protection is also available through
mobile handset manufacturers such as Nokia and as a service through major
Internet Service Providers, such as Deutsche Telekom, France Telecom and
Charter Communications. The latest real-time virus threat scenario news are
available at the F-Secure Antivirus Research Team weblog at
http://www.f-secure.com/weblog/
Services for Individuals and Businesses
F-Secure services and software protect individuals and businesses against
computer viruses and other threats coming through the Internet or mobile
networks. Our award-winning solutions include antivirus and desktop firewall
with intrusion prevention, antispam and antispyware solutions. Our key
strength is our proven speed of response to new threats. For businesses our
solutions feature a centr ally -m ana ged and well-in teg ra ted su ite of sol uti ons
for workstations and servers alike. Focused partners offer security as a
service for companies that do not wish to build in-house security expertise.
.
Visit our websit e at http://www.f-secure.com/products/
products and services.
to learn more about our
 Loading...
Loading...