Page 1

F-Secure Anti-Virus for
Microsoft Exchange
Deployment Guide
Page 2

"F-Secure" and the triangle symbol are registered trademarks of F-Secure Corporation and F-Secure
product names and symbols/logos are either trademarks or registered trademarks of F-Secure
Corporation. All product names referenced herein are trademarks or registered trademarks of their
respective companies. F-Secure Corporation disclaims proprietary interest in the marks and names of
others. Although F-Secure Corporation makes every effort to ensure that this information is accurate,
F-Secure Corporation will not be liable for any errors or omission of facts contained herein. F-Secure
Corporation reserves the right to modify specifications cited in this document without prior notice.
Companies, names and data used in examples herein are fictitious unless otherwise noted. No part of
this document may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic or
mechanical, for any purpose, without the express written permission of F-Secure Corporation.
Copyright © 1993-2010 F-Secure Corporation. All rights reserved.
Portions Copyright © 2003 Commtouch ® Software Ltd.
Copyright © 1997-2009 BitDefender.
This product includes software developed by the Apache Software Foundation (http://
www.apache.org/). Copyright © 2000-2007 The Apache Software Foundation. All rights reserved.
This product includes PHP, freely available from http://www .php.net/. Copyright © 1999-2007 The PHP
Group. All rights reserved.
This product includes code from SpamAssassin. The code in the files of the SpamAssassin distribution
are Copyright © 2000-2002 Justin Mason and others, unless specified otherwise in that particular file.
All files in the SpamAssassin distribution fall under the same terms as Perl itself, as described in the
“Artistic License”.
This product may be covered by one or more F-Secure patents, including the following:
GB2353372 GB2366691 GB2366692 GB2366693 GB2367933 GB2368233
GB2374260
Page 3

Contents
About This Guide 4
How This Guide Is Organized .............................................................................................. 5
Conventions Used in F-Secure Guides................................................................................ 6
Symbols ...................................................................................................................... 6
Chapter 1 Introduction 8
1.1 Overview......................................................................................................................9
1.2 How F-Secure Anti-Virus for Microsoft Exchange Works........................... ... ... .... ... ...10
1.3 Key Features..............................................................................................................13
1.4 Scanning Methods .............................. ... ....................................... ... .... ... ... ... .............15
1.5 F-Secure Anti-Virus Mail Server and Gateway Products ...........................................16
Chapter 2 Deployment 17
2.1 Installation Modes......................................................................................................18
2.2 Network Requirements...............................................................................................19
2.3 Deployment Scenarios...............................................................................................20
2.3.1 Single Exchange Server (2003/2007/2010)....................................................21
2.3.2 Multiple Exchange 2003 Servers....................................................................22
2.3.3 Multiple Exchange Server 2007/2010 Roles ..................................................23
2.3.4 Large organization using Exchange 2007/2010.............................................25
2.3.5 Centralized Quarantine Management.............................................................27
1
Page 4

Chapter 3 Installation 30
3.1 System Requirements................... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... .... ... ... ....................................... ... ...31
3.1.1 Installation on Microsoft Exchange Server 2003............................................31
3.1.2 Installation on Microsoft Exchange Server 2007............................................33
3.1.3 Installation on Microsoft Exchange Server 2010............................................35
3.2 Centralized Management Requirements............. .... ... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... ... .... ... ...36
3.3 Other System Component Requirements..................................................................36
3.3.1 SQL Server Requirements ................................... ... .... ... ... ... ..........................37
3.3.2 Additional Windows Components............................ .... ... ... ... ..........................39
3.3.3 Web Browser Software Requirements ...........................................................39
3.4 Improving Reliability and Performance ......................................................................39
3.5 Centrally Administered or Stand-alone Installation? ..................................................40
3.6 Installation Overview..................................................................................................41
3.7 Installing F-Secure Anti-Virus for Microsoft Exchange.................. ... .... ... ... ... ... .... ... ...42
3.8 After the Installation ...................................................................................................55
3.8.1 Importing Product MIB files to F-Secure Policy Manager Console.................55
3.8.2 Configuring the Product..................................................................................56
3.9 Upgrading from Previous Product Versions...............................................................58
3.10 Upgrading the Evaluation Version..............................................................................60
3.11 Uninstalling F-Secure Anti-Virus for Microsoft Exchange ..........................................61
Chapter 4 Configuring F-Secure Spam Control 62
4.1 Overview....................................................................................................................63
4.2 Realtime Blackhole List Configuration .......................................................................64
4.2.1 Configuring Realtime Blackhole Lists.............................................................64
4.2.2 Optimizing F-Secure Spam Control Performance..........................................66
AppendixA Deploying the Product on a Cluster 68
A.1 Installation Overview................................................................................................. 69
A.2 Creating Quarantine Storage.... .... ... ... ... .... ... .............................................................71
A.2.1 Quarantine Storage in Active-Passive Cluster ...............................................71
A.2.2 Quarantine Storage in Active-Active Cluster..................................................76
A.2.3 Creating the Quarantine Storage for a Single Copy Cluster Environment.....79
2
Page 5

A.2.4 Creating the Quarantine Storage for a Continuous
Cluster Replication Environment............. .... ... ... ... ..........................................86
A.2.5 Creating the Quarantine Storage for a Database
Availability Group Environment ......................................................................90
A.3 Installing the Product........................... ... .... ...................................... .... ... ... ... ... .... ... ...94
A.3.1 Installing on Clusters with Quarantine as Cluster Resource ..........................94
A.3.2 Installing on Clusters with Quarantine on a Dedicated Computer..................97
A.4 Administering the Cluster Installation with F-Secure Policy Manager........................99
A.5 Using the Quarantine in the Cluster Installation.......................................................100
A.6 Using the Product with High Availability
Architecture in Microsoft Exchange Server 2010................................. ... ... ... ... .... ... .102
A.7 Uninstallation............................................................................................................103
A.8 Troubleshooting .......................................................................................................103
AppendixB Services and Processes 104
B.1 List of Services and Processes..................................... ... ... .... ... ............................. 105
Technical Support 108
F-Secure Online Support Resources ............................................................................... 109
Web Club ....................... ... .... ...................................... .... ... ...................................... .... ....111
Virus Descriptions on the Web .........................................................................................111
About F-Secure Corporation
3
Page 6

ABOUT THIS GUIDE
How This Guide Is Organized...................................................... 5
Conventions Used in F-Secure Guides....................................... 6
4
Page 7

How This Guide Is Organized
F-Secure Anti-Virus for Microsoft Exchange Deployment Guide is divided
into the following chapters:
Chapter 1. Introduction. General information about F-Secure Anti-V irus
for Microsoft Exchange and other F-Secure Anti-Virus Mail Server and
Gateway products.
Chapter 2. Deployment. Instructions and examples how to set up your
network environment before you can install F-Secure Anti-Virus for
Microsoft Exchange.
Chapter 3. Installation. Instructions how to install and set up F-Secure
Anti-Virus for Microsoft Exchange.
Chapter 4. Configuring F-Secure Spam Control. instructions on how to
configure F-Secure Spam Control.
Appendix A. Deploying the Product on a Cluster. Instructions how to
deploy and use F-Secure Anti-Virus for Microsoft Exchange on a cluster.
Appendix B. Services and Processes. Describes services, devices and
processes of F-Secure Anti-Virus for Microsoft Exchange.
About This Guide 5
Technical Support. Contains the contact information for assistance.
About F-Secure Corporation. Describes the company background and
products.
See the F-Secure Policy Manager Administrator's Guide for detailed
information about installing and using the F-Secure Policy Manager
components:
F-Secure Policy Manager Console, the tool for remote
administration of F-Secure Anti-Virus for Microsoft Exchange.
F-Secure Policy Manager Server, which enables communication
between F-Secure Policy Manager Console and the managed
systems.
Page 8
6
Conventions Used in F-Secure Guides
This section describes the symbols, fonts, and terminology used in this
manual.
Symbols
WARNING: The warning symbol indicates a situation with a
risk of irreversible destruction to data.
IMPORTANT: An exclam ation mark provides important informa tion
that you need to consider.
REFERENCE - A book refers you to related information on the
topic available in another document.
NOTE - A note provides additional information that you should
consider.
l
TIP - A tip provides information that can help you perf or m a task
more quickly or easily.
Fonts
An arrow indicates a one-step procedure.
Arial bold (blue) is used to refer to menu names and commands, to
buttons and other items in a dialog box.
Arial Italics (blue) is used to refer to other chapters in the manual, book
titles, and titles of other manuals.
Arial Italics (black) is used for file and folder names, for figure and table
captions, and for directory tree names.
Courier New is used for messages on your compute r screen.
Courier New bold is used for information that you must type.
Page 9

SMALL CAPS (BLACK) is used for a key or key combination on your
keyboard.
CHAPTER 2 7
PDF Document
For More Information
Arial underlined (blue)
Arial italics is used for window and dialog box names.
This manual is provided in PDF (Portable Document Format). The PDF
document can be used for online viewing and printing using Adobe®
Acrobat® Reader. When pr inting the manual, please print the entire
manual, including the copyright and disclaimer statements.
Visit F-Secure at http://www.f-secure.com for documentation, training
courses, downloads, and service and supp o rt contacts.
In our constant attempts to improve our documentation, we would
welcome your feedback. If you have any questions, comments, or
suggestions about this or any other F-Secure document, please conta ct
us at documentation@f-secure.com
is used for user interface links.
.
Page 10

1
INTRODUCTION
Overview....................................................................................... 9
How F-Secure Anti-Virus for Microsoft Exchange Works........... 10
Key Features.............................................................................. 13
Scanning Methods...................................................................... 15
F-Secure Anti-Virus Mail Server and Gateway Products............ 16
8
Page 11

1.1 Overview
CHAPTER 1 9
Introduction
Malicious code, such as computer viruses, is one of the main threats for
companies today. In the past, malicious code spread mainly via disks and
the most common viruses were the ones that infected disk boot sectors.
When users began to use office applications with macro capabilities such as Microsoft Office - to write documen t s and distribu te them via mail
and groupware servers, macro viruses started spreading rapidly.
After the millennium, the most common spreading mechanism has been
the e-mail. Today about 90% of viruses arrive via e-mail. E-mails provide
a very fast and efficient way for viruses to spread themselves without any
user intervention and that is why e-mail worm outbreaks, like Sober,
Netsky and Bagle, have caused a lot of damage around the world.
F-Secure Anti-Virus Mail Server and Gateway products are designed to
protect your company's mail and groupware servers and to shield the
company network from any malicious code that travels in HTTP or SMTP
traffic. In addition, they protect your company network against spam. The
protection can be implemented on the gateway level to screen all
incoming and outgoing e-mail (SMTP), web surfing (HTTP and
FTP-over-HTTP) and file transfer (FTP) traffic. Furthermore, it can be
implemented on the mail server level so that it does not only protect
inbound and outbound traffic but also internal mail traffic and public
sources, such as public folders on Microsoft Exchange servers.
Providing the protection already on the gateway level has plenty of
advantages. The protection is easy and fast to set up and install,
compared to rolling out antivirus protection on hundreds or thousands of
workstations. The protection is also invisible to the end users which
ensures that the system cannot be by-passed and makes it easy to
maintain. Of course, protecting the gateway level alone is not enough to
provide a complete antivirus solution; file server and workstation level
protection is needed, also.
Why clean 1000 workstations when you can clean one attachment at the
gateway level?
Page 12

10
1.2 How F-Secure Anti-Virus for Microsoft Exchange Works
F-Secure Anti-Virus for Microsoft Exchange is designed to detect and
disinfect viruses and other malicious code from e-mail transmissions
through Microsoft Exchange Server. Scanning is done in real time as the
mail passes through Microsoft Exchange Server. On-demand scanning of
user mailboxes and public folders is also available.
Scanning
Attachments and
Message Bodies
Flexible and Scalable
Anti-Virus Protection
Alerting F-Secure Anti-Virus for Microsoft Exchange has extensive alerting
Powerful and Always
Up-to-date
F-Secure Anti-Virus for Microsoft Exchange scans attachments and
message bodies for malicious code. It can also be instructed to remove
particular attachments according to the file name or the file extension.
If the intercepted mail contains malicious code, F-Secure Anti-Virus for
Microsoft Exchange can be configured to disinfect or drop the content.
Any malicious code found during the scan process can be placed in the
Quarantine, where it can be further examined. Stripped attachments can
also be placed in the Quarantine for further examination.
F-Secure Anti-Virus for Microsoft Exchange is installed on Microsoft
Exchange Server and it intercepts mail traveling to and from mailboxes
and public folders. The messages and documents are scanned with the
scanning component, F-Secure Content Scanner Server, which also
disinfects the infected messages.
functions, which means that the system administrator can specify a
recipient, such as the network administrator, to be notified about the
infection found in the data content.
F-Secure Anti-Virus for Microsoft Exchange uses the award-winning
F-Secure Anti-Virus techniques and scanning engines to ensure the
highest possible detection rate and disinfection capability. The F-Secure
Anti-Virus definition databases are upda ted typically multiple times a day
and they provide F-Secure Anti-Virus for Microsoft Exchange an always
up-to-date protection capability.
Page 13

CHAPTER 1 11
Introduction
F-Secure Anti-Virus scanner consistently r anks at the top when compar ed
to competing products. Our team of dedicated virus resea rchers is on call
24-hours a day responding to new and emerging threats. In fact,
F-Secure is one of the only companies to release tested virus definition
updates continuously, to make sure our customers are receiving the
highest quality service and protection.
Virus and Spam
Outbreak Detection
Stand-alone and
Centralized
Administration Modes
Scalability and
Reliability
Easy to
Administer
Massive spam and virus outbreaks consist of millions of messages which
share at least one identifiable pattern that can be used to distinguish the
outbreak. Any message that contains one or more of these patterns can
be assumed to be a part of the same spam or virus outbreak.
F-Secure Anti-Virus for Microsoft Exchange can identify these patterns
from the message envelope, headers and body, in any language,
message format and encoding type. It can detect spam messages and
new viruses during the first minutes of the outbreak.
F-Secure Anti-Virus for Microsoft Exchange can be installed either in
stand-alone or centrally administered mode. Depending on how it has
been installed, F-Secure Anti-Virus for Microsoft Exchange is managed
either with the F-Secure Anti-Virus for Microsoft Exchange Web Console
or F-Secure Policy Manager.
F-Secure Policy Manager provides a scalable way to manage the security
of multiple applications on multiple operating systems, from one central
location. F-Secure Policy Manager is comprised of two components,
F-Secure Policy Manager Console and F-Secure Policy Manager Server,
which are used to administer applications. They are seamlessly
integrated with the F-Secure Management Agents that handle all
management functions on local hosts.
If F-Secure Anti-Virus for Microsoft Exchange is installed in stand-alone
mode it can be managed with the web-based user interface.
If F-Secure Anti-Virus for Microsoft Exchange has been installed in
centrally administered configuration, it is managed with F-Secure Policy
Manager. With its graphical user interface, F-Secure Policy Manager
Console provides a centralized view of the domains and hosts in your
network, lets you configure the security policies for all F-Secure
Page 14

12
components and set up scheduled scans and run manual scanning
operations. F-Secure Policy Manager receives status information from
F-Secure Anti-Virus for Microsoft Exchange.
F-Secure Policy Manager Server is the server side component that
handles communication between F-Secure Anti-Virus for Microsoft
Exchange and F-Secure Policy Manager Console. It exchanges security
policies, software updates, status information, statistics, alerts, and other
information between F-Secure Policy Manager Console and all managed
systems.
Figure 1-1 (1) E-mail arrives from the Internet to F-Secure Anti-Virus for Microsoft
Exchange, which (2) filters malicious content from mails and attachments, and (3)
delivers cleaned files forward.
Page 15

1.3 Key Features
F-Secure Anti-Virus for Microsoft Exchange provides the following
features and capabilities.
Superior Protection Superior detection rate with multiple scanning engines.
Scanning engines updated automatically with the latest versions.
Automatic malicious code detection and disinfection.
The grayware scan detects spyware, adware, dialers, joke
programs, remote access tools, and any other unwelcome files
and programs.
Heuristic scanning detects also unknown Windows and macro
viruses.
Recursive scanning of ARJ, BZ2, CAB, GZ, JAR, LZH, MSI,
RAR, TAR, TGZ, Z and ZIP archive files.
Automatic and consistent virus definition database updates.
Suspicious and unsafe attachments can be stripped away from
e-mails.
Password protected archives can be treated as unsafe.
Intelligent file type recognition.
Message filtering based on keywords in message subjects and
text.
CHAPTER 1 13
Introduction
Virus Outbreak
Detection
The virus outbreak detection is an additional active layer of
protection that automatically detects virus outbreaks and
quarantines suspicious messages.
Virus outbreaks are transparen tly detected and infected
messages are quarantined before the outbreak becomes
widespread.
Quarantined unsafe messages can be reprocessed
automatically.
Page 16

14
Transparen cy and
Scalability
Viruses are intercepted before they can enter the network and
spread out on workstations and servers.
Real-time scanning of internal, inbound and outbound mail
messages and public folder notes.
Automatic protection of new mailboxes and public folders.
Total transparency to end-users. Users cannot bypass the
system, which means that messages and documents cannot be
exchanged without scanning.
Management Controlling and monitoring the behavior of the products remotely.
Starting predefined operations remotely.
Monitoring statistics provided by the products remotely with
F-Secure Policy Manager or F-Secure Anti-Virus for Microsoft
Exchange Web Console.
Possibility to configure and manage stand-alone installations with
the convenient F-Secure Anti-Virus for Microsoft Exchange Web
Console.
You can manage and search quarantined content with the
F-Secure Anti-Virus for Microsoft Exchange Web Console.
When F-Secure Anti-Virus for Windows Servers is installed on
the same computer, both products can be administered with the
common web-based user interface.
Protection against
Spam
Possible spam messages are transparently detected before they
become widespread.
Efficient spam detection based on different analyses on the
e-mail content.
Multiple filtering mechanisms guarantee the high accuracy of
spam detection.
Spam m essages can be separated from legitimate messages and
processed using the Spam Confidence Levels.
Spam detection works in every language and message format.
Page 17

1.4 Scanning Methods
Virus Scanning
The virus scan uses virus definition databases to detect and disinfect
viruses. Virus definition databases are updated typically multiple times a
day and they provide an always up-to-date protection capability.
Heuristic Scanning
The heuristic scan analyzes files for suspicious code behavior so that the
product can detect unknown malware.
Proactive Virus Threat Detection
The proactive virus threat detection analyzes e-mail messages for
possible virus patterns and security threats. All possibly harmful
messages are quarantined as unsafe. The proactive virus thr eat detection
can detect new viruses during the first minutes of the outbr ea k.
Grayware Scanning
The grayware scan detects applications that have annoying or
undesirable behavior that can reduce the performance of computers on
the network and introduce significant security risks to your organization.
Grayware includes spyware, adware, dialers, joke programs, remote
access tools, and any other unwelcome files and programs that can
perform a variety of undesired and threatening actions, such as irritating
users with pop-up windows, logging user key strokes, and exposing the
computer to vulnerabilities.
CHAPTER 1 15
Introduction
Page 18

16
1.5 F-Secure Anti-Virus Mail Server and Gateway Products
The F-Secure Anti-Virus product line consists of workstation, file server,
mail server, gateway and mobile products.
F-Secure Anti-Virus for Microsoft Exchange™ protects your
Microsoft Exchange users from malicious code contained within
files they receive in mail messages and documents they open
from shared databases. Malicious code is also stopped in
outbound messages and in notes being posted on public folders.
The product operates transparently and scans files in the
Exchange Server Information Store in real-time. Manual and
scheduled scans of user mailboxes and public folders are also
supported.
F-Secure Internet Gatekeeper for Linux™ provides a
high-performance solution at the Internet gateway level, stopping
viruses and other malicious code before they spread to end use rs
desktops or corporate servers. The product scans SMTP, HTTP,
FTP and POP3 traffic for viruses, worms and trojans, and blocks
and filters out specified file types. ActiveX and Java code can
also be scanned or blocked. The product receives updates
automatically from F-Secure, keeping the virus protection always
up to date. A powerful and easy-to-use management console
simplifies the installation and configuration of the product.
F-Secure Messaging Security Gateway™ delivers the
industry’s most complete and effective security for e-mail. It
combines a robust enterprise-class messaging platform with
perimeter security, antispam, antivirus, secure messaging and
outbound content security capabilities in an easy-to-deploy,
hardened appliance.
Page 19

2
DEPLOYMENT
Installation Modes....................................................................... 18
Network Requirements............................................................... 19
Deployment Scenarios............................................................... 20
17
Page 20

18
2.1 Installation Modes
F-Secure Anti-Virus for Microsoft Exchange can be installed either in
stand-alone or centrally administered mode. In stand-alone installation,
F-Secure Anti-Virus for Microsoft Exchange is managed with Web
Console. In centrally administered mode, it is managed centrally with
F-Secure Policy Manager components: F-Secure Policy Manager Server
and F-Secure Policy Manager Console.
To administer F-Secure Anti-Virus for Microsoft Exchange in the centrally
administered mode, you have to install the following components:
F-Secure Policy Manager Server (on a dedicated machine)
F-Secure Policy Manager Console (on the administ ra to r's
machine or on the same machine with F-Secure Policy Manager
Server).
For up-to-date information on supported platforms, see
F-Secure Policy Manager Release Notes.
Page 21
2.2 Network Requirements
This network configuration is valid for all scenarios described in this
chapter. Make sure that the following network traffic can pass through:
Service Process Inbound ports Outbound ports
CHAPTER 2 19
Deployment
F-Secure Content Scanner
Server
F-Secure Anti-Virus for
Microsoft Exchange Web
Console
F-Secure
Update Agent
F-Secure Network Request
Broker
F-Secure Management
Agent
F-Secure Quarantine
Manager
Automatic
%ProgramFiles%\F-Secure\Cont
ent Scanner Server\fsavsd.exe
%ProgramFiles%\F-Secure\Web
User Interface\bin\fswebuid.exe
%ProgramFiles%\F-Secure\FSA
UA\program\fsaua.exe
%ProgramFiles%\F-Secure\Com
mon\fnrb32.exe
%ProgramFiles%\F-Secure\Com
mon\fameh32.exe
%ProgramFiles%\F-Secure\Quar
antine Manager\fqm.exe
18971 (TCP) (on
localhost only)
25023 DNS (53, UDP and TCP),
- DNS (53, UDP and TCP),
- DNS (53, UDP/TCP),
- DNS (53, UDP/TCP),
- DNS (53, UDP/TCP),
DNS (53, UDP/TCP),
HTTP (80) or another
known port used for
HTTP proxy
1433 (TCP), only with the
dedicated SQL server
HTTP (80) and/or another
port used to connect to
F-Secure
Server
HTTP (80) or another port
used to connect to
F-Secure Policy Manager
Server
SMTP (25)
1433 (TCP), only with the
dedicated SQL server
Policy Manager
F-Secure World Map
Reporting Service
%ProgramFiles%\F-Secure\Cont
ent Scanner
Server\fswmrsvc.exe
- DNS (53, UDP/TCP),
SMTP (25)
Page 22

20
2.3 Deployment Scenarios
Depending on how the Microsoft Exchange Server roles are deployed in
your environment, you might consider various scenarios of deploying
F-Secure Anti-Virus for Microsoft Exchange. There are various ways to
deploy F-Secure Anti-Virus for Microsoft Exch ange that are suitable to
different environments:
If you have just a single Microsoft Exchange Server, see “Single
Exchange Server (2003/2007/2010)”, 21.
If you have multiple Microsoft Exchange Servers, see “Multiple
Exchange 2003 Servers”, 22.
If you have multiple Microsoft Exchange Servers with Exchange
Edge and Mailbox Server roles, see “Multiple Exchange Server
2007/2010 Roles”, 23.
If you have multiple Microsoft Exchange Servers deployed on
dedicated servers with server roles and possibly clustered
mailbox servers, see “Large organization using Exchange 2007/
2010”, 25.
If you have multiple Microsoft Exchange Server installations and
you want to configure the product to use one SQL server and
database for the quarantine management, see “Centralized
Quarantine Management”, 27.
Page 23
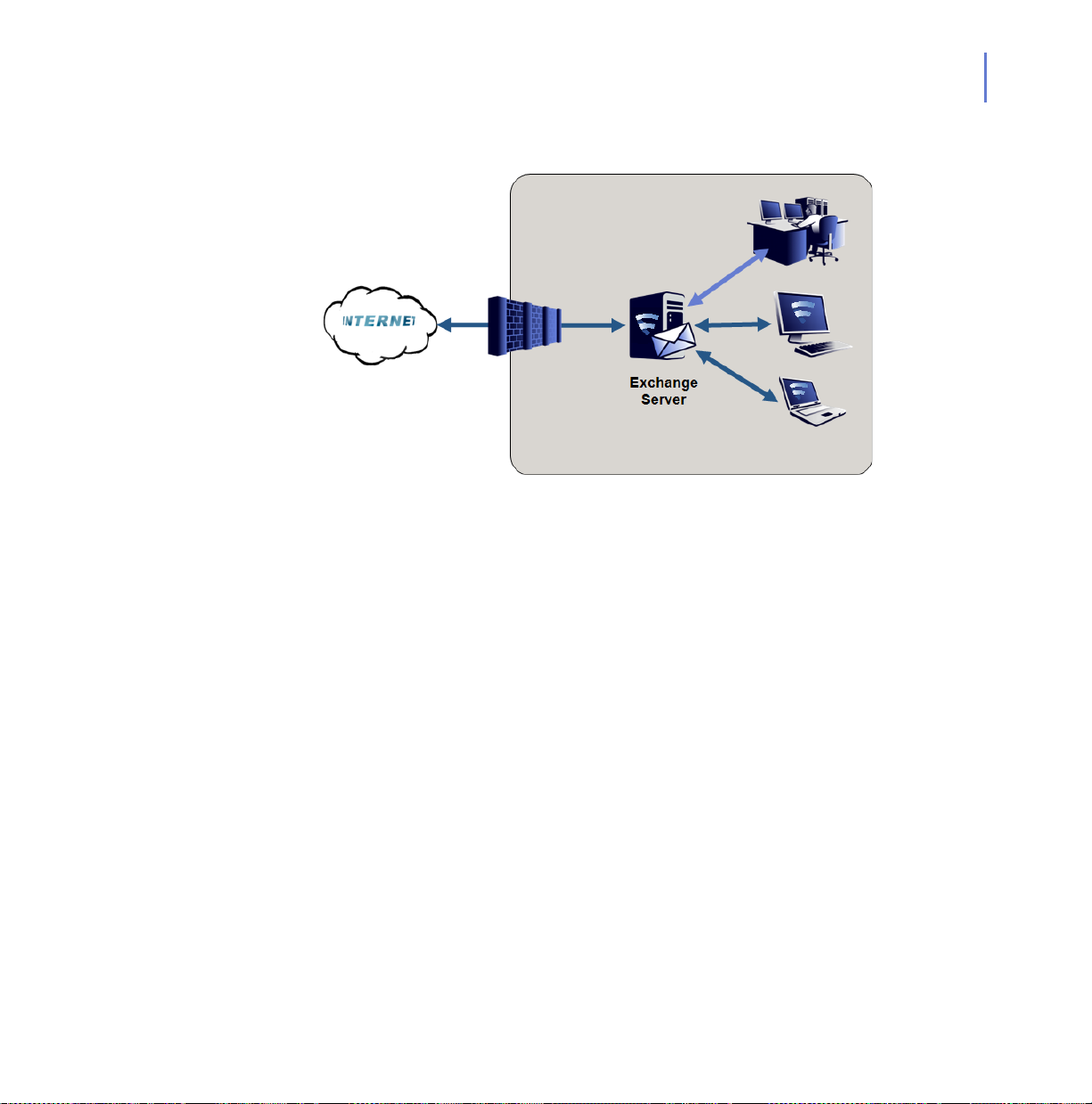
2.3.1 Single Exchange Server (2003/2007/2010)
Your organization has a single server (Microsoft Exchange Server 2003/
2007/2010 or Microsoft Small Business Server 2003/2008) that holds all
mailboxes, public folders and sends and receives all inbound and
outbound messages over SMTP. Usually , the server is loca ted behind the
firewall or router.
CHAPTER 2 21
Deployment
Installing F-Secure Anti-Virus for Microsoft Exchange
Install F-Secure Anti-Virus for Microsoft Exchange to the server running
Microsoft Exchange Server or Microsoft Small Business Server.
Administration Modes
You can install the product in st and -alone mo de and a dminister it with the
Web Console.
The product receives anti-virus and spam database updates from
F-Secure Update Server.
Page 24
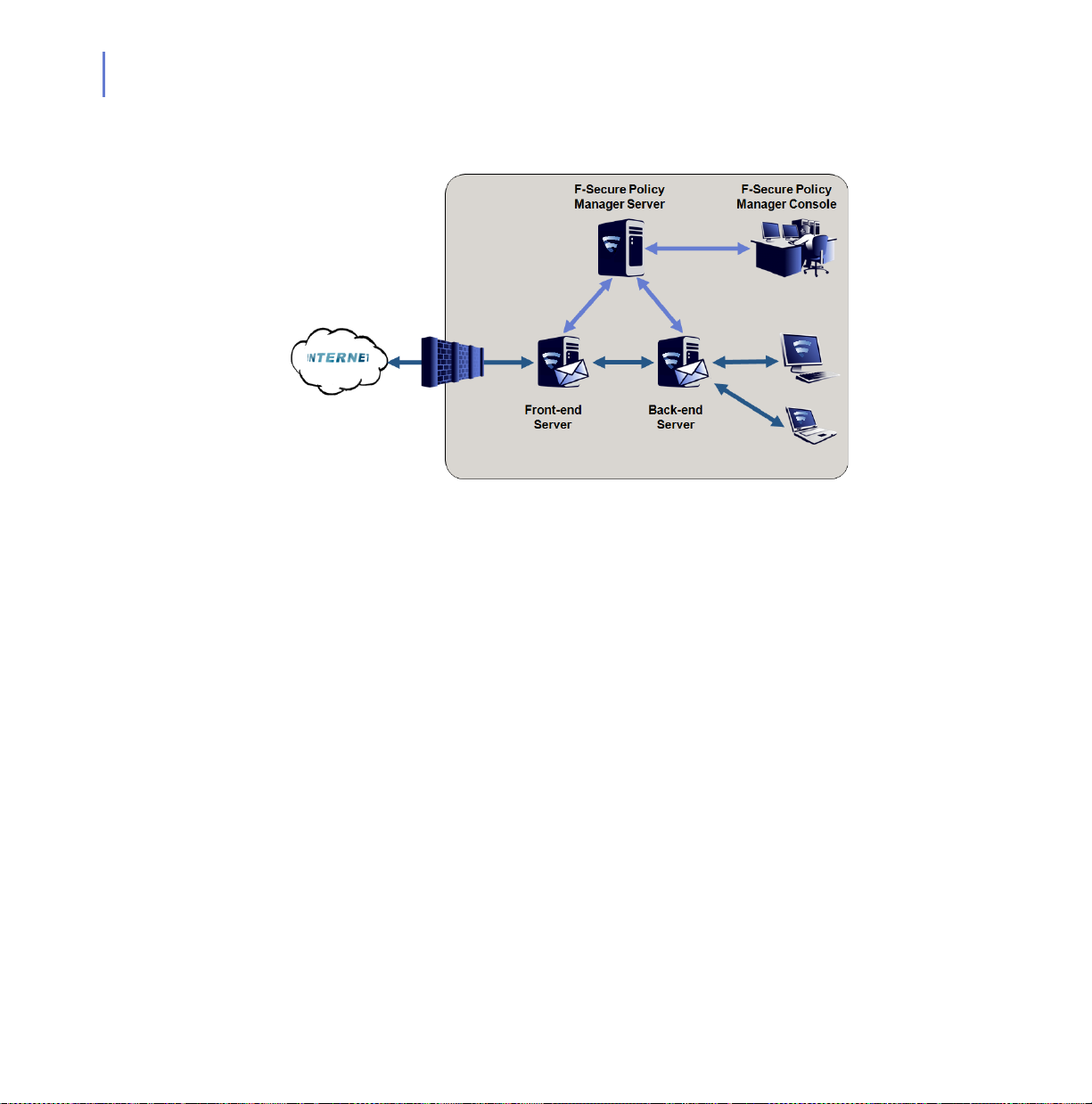
22
2.3.2 Multiple Exchange 2003 Servers
Your organization has multiple Microsoft Exchange Server 2003
installations. Usually, the front-end server is located in the perimeter
network and receives inbound mail using SMTP and forwards all
messages to the back-end server. The back-end Exchange server holds
all mailboxes and public folders. In a larger organization, back-end
servers may be clustered.
Installing F-Secure Anti-Virus for Microsoft Exchange
Install F-Secure Anti-Virus for Microsoft Exchange to both front-end and
back-end Exchange servers. In addition, the front-end server can be
protected with F-Secure Spam Control.
Administration Modes
Install F-Secure Policy Manager Server on a dedicated server or on the
same server with one of Exchange servers. You can administer the
product with F-Secure Policy Manager Console.
When you install the product, configure each insta llation to conn ect to the
same F-Secure Policy Manager Server.
Page 25
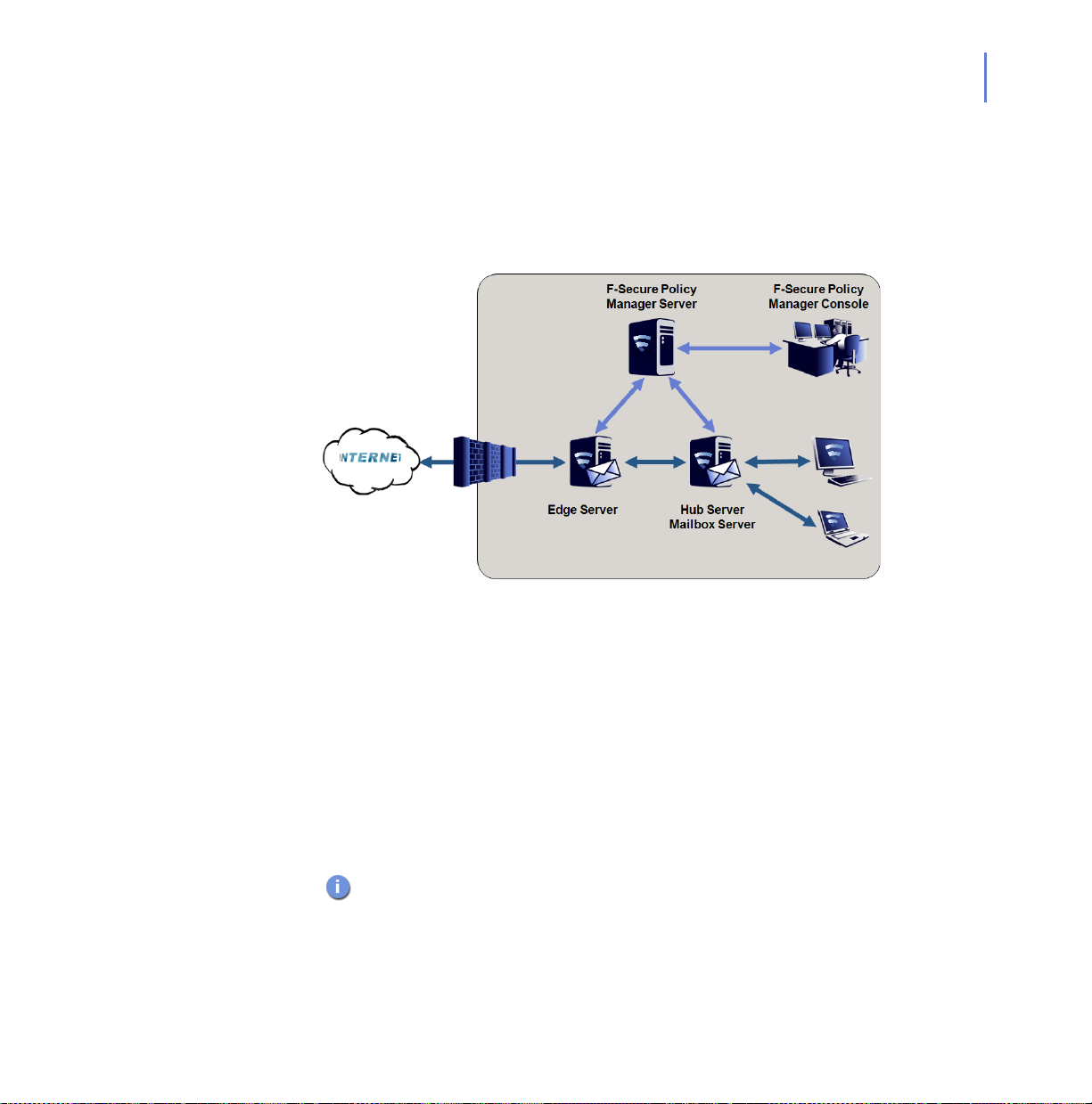
The product installations receive anti-virus and sp am database updates
from F-Secure Policy Manager Server, which receives updates from
F-Secure Update Server.
2.3.3 Multiple Exchange Server 2007/2010 Roles
CHAPTER 2 23
Deployment
Your organization has multiple Microsoft Exchange Server 2007/2010
installations. Exchange Edge and Mailbox Server roles are deployed to
separate servers and the Hub Server is deployed either on a separate
server or on the same server with the Mailbox Server. The Edge Server
handles incoming and outgoing messages using SMTP and Mailbox
Server holds all mailboxes and public folders and Hub Server routes mail
traffic between Exchange servers.
Installing F-Secure Anti-Virus for Microsoft Exchange
Install F-Secure Anti-Virus for Microsoft Exchange to all servers where
Exchange Edge, Hub and Mailbox Server roles are deployed. In add ition,
the Edge server can be protected with F-Secure Spam Control.
If the Exchange role is changed later, the product has to be
reinstalled.
Page 26

24
Administration Modes
Install F-Secure Policy Manager Server on a dedicated server or on the
same server with one of Exchange servers. You can administer the
product with F-Secure Policy Manager Console.
When you install the product, configure each insta llation to conn ect to the
same F-Secure Policy Manager Server.
The product installations receive anti-virus and sp am database updates
from F-Secure Policy Manager Server, which receives updates from
F-Secure Update Server.
Page 27
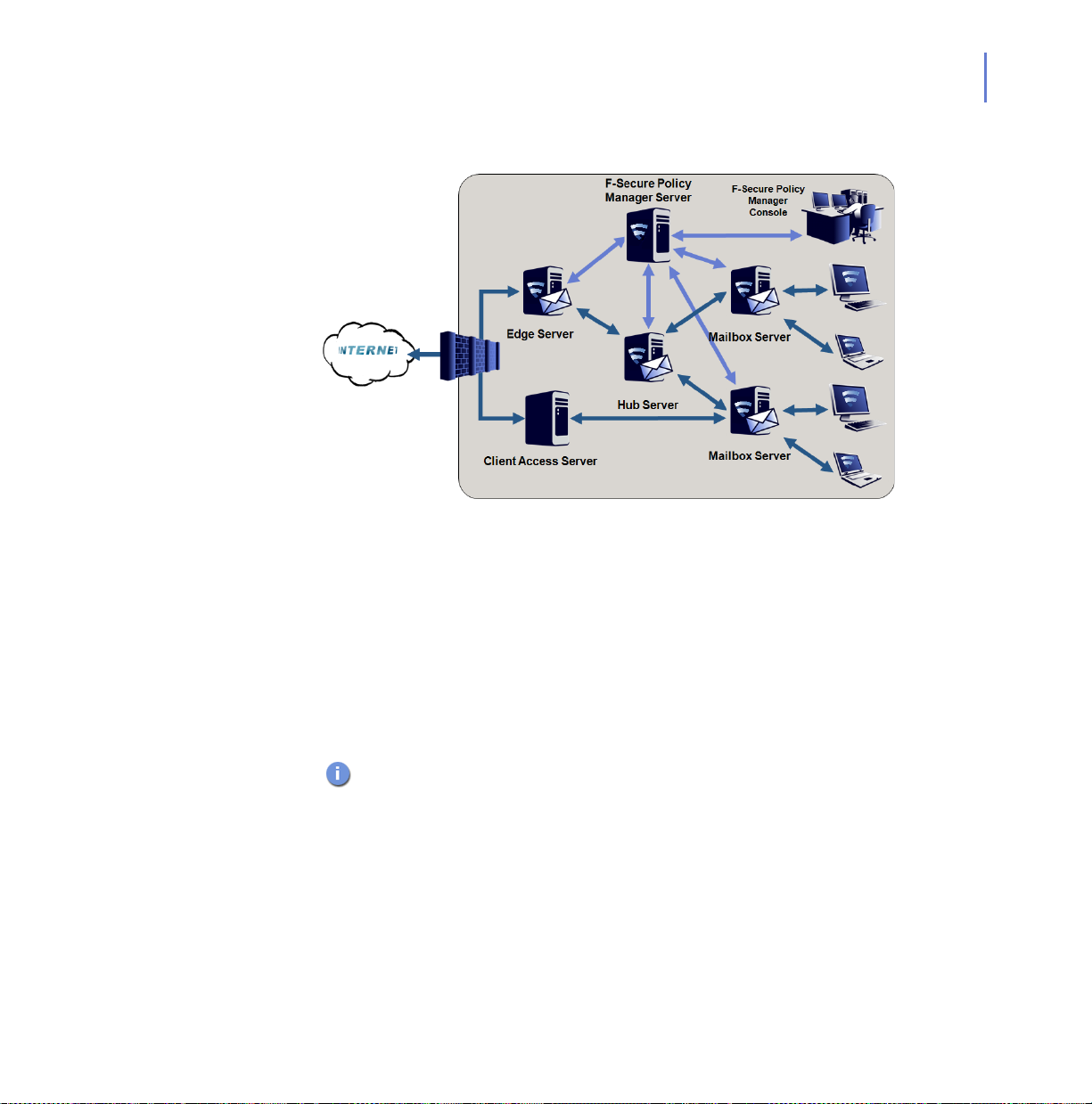
2.3.4 Large organization using Exchange 2007/2010
Your organization has multiple Microsoft Exchange Server 2007/2010
installations. All Exchange roles are deployed on dedicated servers.
Mailbox servers are possibly clustered.
CHAPTER 2 25
Deployment
Installing F-Secure Anti-Virus for Microsoft Exchange
Install F-Secure Anti-Virus for Microsoft Exchange to the server where
Exchange Edge, Hub and Mailbox Server roles are deployed. In add ition,
the Edge server can be protected with F-Secure Spam Control.
Do not install the product to Client Access or Unified Messaging Server
roles.
This version of the product does not support cluster installations of
Microsoft Exchange Server 2010 yet.
Installing F-Secure Spam Control
If you have a license for F-Secure Spam Control, you can install it on the
Edge server.
Page 28

26
Administration Modes
Install F-Secure Policy Manager Server on a dedicated server. You can
administer the product with F-Secure Policy Manager Console.
When you install the product, configure each insta llation to conn ect to the
same F-Secure Policy Manager Server.
The product installations receive anti-virus and sp am database updates
from F-Secure Policy Manager Server, which receives updates from
F-Secure Update Server.
Page 29
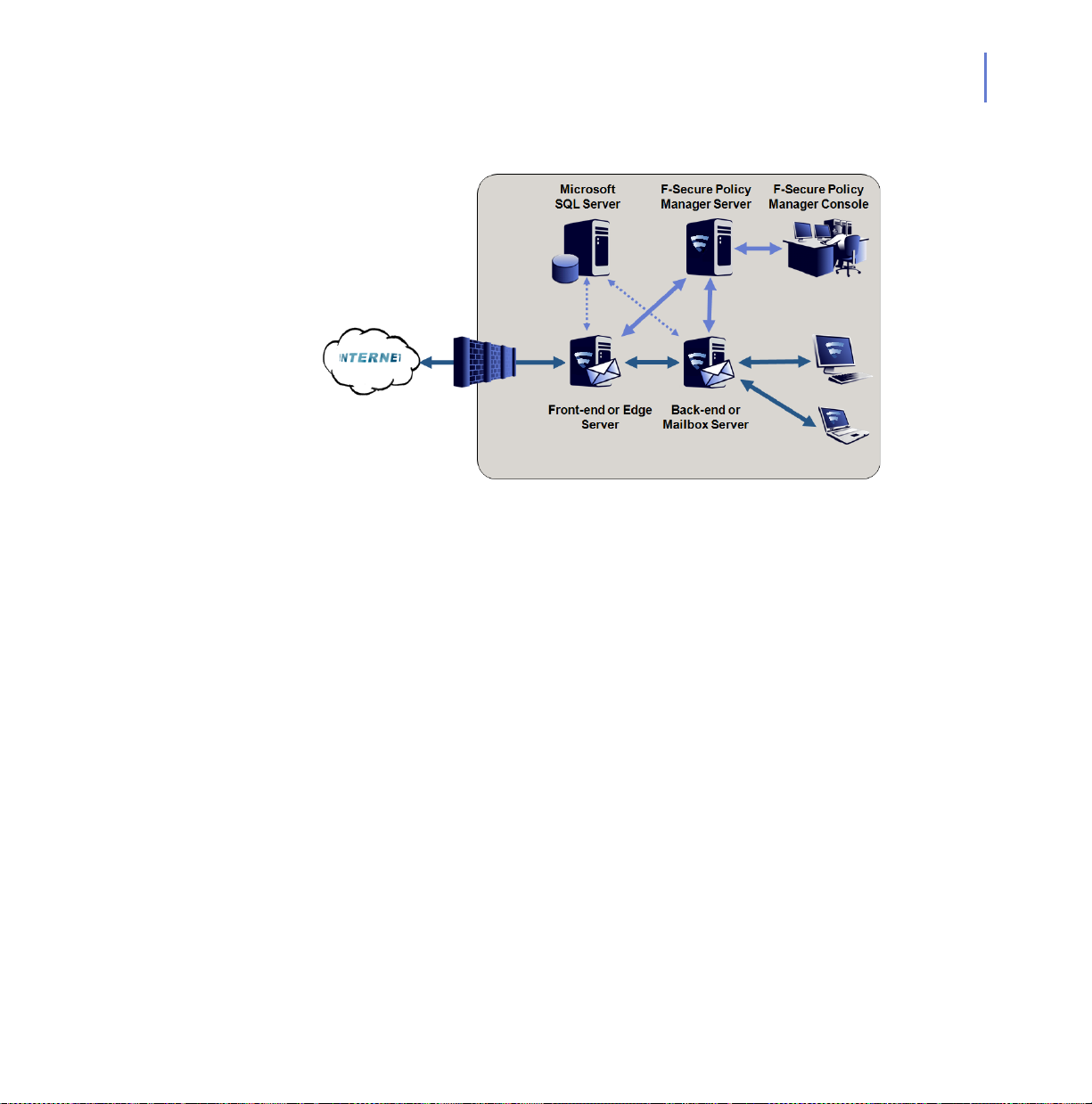
2.3.5 Centralized Quarantine Management
Your organization has multiple Microsoft Exchange Server installations.
For example, you have front-end and back-end servers running
Exchange Server 2003, or a network configuration with Edge and Mailbox
roles running Exchange Server 2007/2010.
CHAPTER 2 27
Deployment
Microsoft SQL Server is installed on a dedicated server or on the server
running F-Secure Policy Manager Server.
Page 30

28
Installing F-Secure Anti-Virus for Microsoft Exchange
When you install the product, configure each installation to use the same
SQL server and database.
Make sure that the SQL server, the database name, user name
and password are identical in the quarantine configuration for all
F-Secure Anti-Virus for Microsoft Exchange installations.
Make sure that all the servers are allowed to communicate with
the SQL server using mixed mode authentication. For more
information, see “Enabling the mixed mode authentication in the
Microsoft SQL Server”, 28.
In environments with heavy e-mail traffic, it is recommended to
use a Microsoft SQL server installed on a separate server. When
using the free Microsoft SQL Server 2005 Express Edition
included in F-Secure Anti-Virus for Microsoft Exchange, the
Quarantine database size is limited to 4 GB.
You can use F-Secure Anti-Virus for Microsoft Exchange Web
Console to manage and search quarantined content. For more
information, consulft F-Secure Anti-Virus for Microsoft Exchange
Administrator’s Guide.
Enabling the mixed mode authentication in the Microsoft SQL
Server
If you install Microsoft SQL Server 2005/2008 separately, it supports
Windows Authentication only by default. You have to change the
authentication to mixed mode during the setup or configure it later with
Microsoft SQL Server user interface.
The mixed mode authentication allows you to log into the SQL server with
either your Windows or SQL username and password.
Make sure that the sa password is strong when you change the
authentication mode from the Windows authentication to the mixed
authentication mode.
Follow these steps to change the authentication mode:
Page 31

CHAPTER 2 29
Deployment
1. Open Microsoft SQL Server Management Studio or Microsoft SQL
Server Management Studio Express.
If you do not have Microsoft SQL Server Management Studio
installed, you can freely download Management Studio Express from
the Microsoft web site
.
2. Connect to the SQL server.
3. In Object Explorer, go to Security > Logins.
4. Right-click on sa and select Properties.
5. Open the General page and change the password. Confirm the new
password that you entered.
6. Open the Status page and select Enabled in the Login section.
7. Click OK.
8. In Object Explorer, right-click on the server name and select
Properties.
9. On the Security page, select SQL Server and Windows
Authentication mode under Server authentication.
10. Click OK.
11. Right-click on the server name and select Restart.
Wait for a moment for the service to restart before you continue.
12. Use Management Studio to test the connection to the SQL server with
the sa account and the new password you set.
Page 32

3
INSTALLATION
System Requirements................................................................ 31
Centralized Management Requirements.................................... 36
Other System Component Requirements................................... 36
Improving Reliability and Performance....................................... 39
Installation Overview.................................................................. 41
Installing F-Secure Anti-Virus for Microsoft Exchange............... 42
After the Installation.................................................................... 55
Upgrading from Previous Product Versions................................ 58
Upgrading the Evaluation Version.............................................. 60
Uninstalling F-Secure Anti-Virus for Microsoft Exchange........... 61
30
Page 33

3.1 System Requirements
F-Secure Anti-Virus for Microsoft Exchange is installed on the computer
running Microsoft Exchange Server.
The release notes document contains the latest information about
the product and might have changes to system requirements and
the installation procedure. It is highly recommended to read the
release notes before you proceed with the installation.
3.1.1 Installation on Microsoft Exchange Server 2003
The product can be installed on a computer runnin g Microsoft® Exchange
Server 2003 with the latest service pack
CHAPTER 3 31
Installation
Operating system:
Microsoft® Windows Server 2003,
Standard Edition with the latest
service pack
Microsoft® Windows Server 2003,
Enterprise Edition with the latest
service pack
Microsoft® Windows Server 2003 R2,
Standard Edition
Microsoft® Windows Server 2003 R2,
Enterprise Edition
Microsoft® Small Business Server
2003
Microsoft® Small Business Server
2003 R2
Processor: 32-bit processor: Intel Pentium 4 or
compatible, 2GHz or faster
Memory: 1 GB minimum
Disk space to install: 300 MB.
Page 34

32
For performance and security reasons, it is
not possible to install the product on any other
than an NTFS partition.
Disk space for
processing:
Other: A CD-ROM drive is required if you are
Cluster Environment
The product supports the following cluster models of Microsoft Exchange
Server 2003:
Active - Active Cluster
Active - Passive Cluster
For detailed instructions how to deploy and install the product on a
cluster, see “Deploying the Product on a Cluster”, 68.
10 GB or more. The required disk space
depends on the number of mailboxes, amount
of data traffic and the size of the Information
Store.
installing the product from CD-ROM.
Page 35

3.1.2 Installation on Microsoft Exchange Server 2007
The product can be installed on a computer running one of the following
Microsoft Exchange Server versions:
Microsoft® Exchange Server 2007 (64-bit version) with the latest
service pack
Microsoft® Small Business Server 2008
The 32-bit evaluation version of Microsof t Exchange Server 2007 is
not supported.
CHAPTER 3 33
Installation
Operating system:
Microsoft® Windows Server 2003,
Standard x64 Edition with the latest
service pack
Microsoft® Windows Server 2003,
Enterprise x64 Edition with the latest
service pack
Microsoft® Windows Server 2003 R2,
Standard x64 Edition
Microsoft® Windows Server 2003 R2,
Enterprise x64 Edition
Microsoft® Windows Server 2008,
Standard Edition
Microsoft® Windows Server 2008,
Enterprise Edition
Microsoft® Small Business Server
2008
Processor:
Intel x64 processor with Extended
Memory 64 Technology (EM64T)
AMD processor that supports the
AMD64 platform
Memory: 2 GB minimum
Disk space to install: 300 MB.
Page 36

34
For performance and security reasons, it is
not possible to install the product on any other
than an NTFS partition.
Disk space for
processing:
10 GB or more. The required disk space
depends on the number of mailboxes, amount
of data traffic and the size of the Information
Store.
Other: A CD-ROM drive is required if you are
installing the product from CD-ROM.
Microsoft Exchange Server Roles
The product supports the following roles of Microsoft Exchange Server
2007:
Edge Server role
Hub Server role
Mailbox Server role
Combo Server (Mailbox Server and Hub Server roles)
Cluster Environment
The product supports the following cluster models of Microsoft Exchange
Server 2007:
Cluster Continuous Replication (CCR)
Single Copy Cluster (SCC)
For detailed instructions how to deploy and install the product on a
cluster, see “Deploying the Product on a Cluster”, 68.
Page 37

3.1.3 Installation on Microsoft Exchange Server 2010
The product can be installed on a computer running the fo llowing
Microsoft Exchange Server version:
Microsoft® Exchange Server 2010
CHAPTER 3 35
Installation
Operating system:
Microsoft® Windows Server 2008,
Standard Edition
Microsoft® Windows Server 2008,
Enterprise Edition
Microsoft® Windows Server 2008 R2,
Standard Edition
Microsoft® Windows Server 2008 R2,
Enterprise Edition
Processor:
Intel x64 processor with Extended
Memory 64 Technology (EM64T)
AMD processor that supports the
AMD64 platform
Memory: 4 GB minimum
Disk space to install: 300 MB.
For performance and security reasons, it is
not possible to install the product on any other
than an NTFS partition.
Disk space for
processing:
10 GB or more. The required disk space
depends on the number of mailboxes, amount
of data traffic and the size of the Information
Store.
Other: A CD-ROM drive is required if you are
installing the product from CD-ROM.
Page 38

36
Microsoft Exchange Server Roles
The product supports the following roles of Microsoft Exchange Server
2010:
Edge Server role
Hub Server role
Mailbox Server role
Combo Server (Mailbox Server and Hub Server roles)
Cluster Environment
The current version of the product supports Microsoft Exchange Server
2010 high-availability solutions based on Database Availability Groups
(DAG).
3.2 Centralized Management Requirements
F-Secure Policy Manager 9.00 or later is required if you plan to install the
product in the centralized administration mode and manage it with
F-Secure Policy Manager Console.
IMPORTANT: If you are using a previous version of F-Secure
Policy Manager, upgrade it to the late st version before you install
F-Secure Anti-Virus for Microsoft Exchange 9.0.
3.3 Other System Component Requirements
The product requires Microsoft® SQL Server for the quarantine
management. Depending on the selected deployment and administration
method, you may need have some additional software as well.
Page 39

3.3.1 SQL Server Requirements
The product requires Microsoft® SQL Server for the quarantine
management. The following versions of Microsoft SQL Server are
recommended to use:
Microsoft SQL Server 2005 (Enterprise, Standard, Workgroup or
Express edition) with the latest service pack
Microsoft SQL Server 2008 (Enterprize, Standard, Workgroup or
Express edition)
Microsoft SQL Server 2005 Express Edition Service Pack 3 is distributed
with the product and can be installed during F-Secure Anti-Virus for
Microsoft Exchange Setup.
When centralized quarantine management is used, the SQL server
must be reachable from the network and file sharing must be
enabled.
The product supports also Microsoft SQL Server 2000 with Service Pack
4 and Microsoft SQL Server 2000 Desktop Engine (MSDE) with Service
Pack 4.
CHAPTER 3 37
Installation
Which SQL Server to Use for the Quarantine Database?
As a minimum requirement, the Quarantine database should have the
capacity to store information about all inbound and outbound mail to and
from your organization that would normally be sent during 2-3 days.
The upgrade installation does not upgrade the SQL server if you
choose to use the existing database.
If you want to upgrade MSDE 2000 to SQL Server 2005 Express,
follow the instructions on the Microsoft web page:
http://www.microsoft.com/technet/prodtechnol/sql/2005/
msde2sqlexpress.mspx.
Page 40

38
Take the following SQL server specific considerations into account when
deciding which SQL server to use:
Microsoft SQL Server
2005 Express Edition
Microsoft SQL
Server 2000, 2005
and 2008
When using Microsoft SQL Server 2005/2008 Express Ed ition,
the Quarantine database size is limited to 4 GB.
Microsoft SQL Server 2005/2008 Express Edition supports
Microsoft Windows Server 2008.
It is not recommended to use Microsoft SQL Server 2005
Express Edition if you are planning to use centralized quarantine
management with multiple F-Secure Anti-Virus for Microsoft
Exchange installations.
Microsoft SQL Server 2005 Expre ss Edition is delivered
together with F-Secure Anti-Virus for Microsoft Exchange, and
you can install it during the F-Secure Anti-Virus for Microsoft
Exchange Setup.
If your organization sends a large amount of e-mails, it is
recommended to use Microsoft SQL Server 2000, 2005 or 2008.
It is recommended to use Microsoft SQL Server if you are
planning to use centralized quarantine management with multiple
F-Secure Anti-Virus for Microsoft Exchange installations.
Note that the product does not support Windows Authentication
when connecting to Microsoft SQL Server. The Microsoft SQL
Server that the product will use for the Quarantine database
should be configured to use Mixed Mode authentication.
If you plan to use Microsoft SQL Server 2000, 2005 or 2008,
you must purchase it and obtain your own license before you
start to deploy F-Secure Anti-Virus for Microsoft Exchange. To
purchase Microsoft SQL Server 2005 or 2008, contact your
Microsoft reseller.
Page 41

3.3.2 Additional Windows Components
Depending on how you deploy the product to your network system, the
following Windows components may be required:
Microsoft .NET Framework version 2.0 is required to install
Microsoft SQL Server 2005 Express Edition, and Microsoft .NET
Framework version 3.5 is required with Microsoft SQL Server
2008 Express Edition.
If you plan to have Microsoft SQL Server on the same server,
Microsoft .NET Framework must be installed before installing
F-Secure Anti-Virus for Microsoft Exchange. Microsoft .NET
Framework can be downloaded from the Microsoft Download
Center.
3.3.3 Web Browser Software Requirements
In order to administer the product with F-Secure Anti-Virus for Microsoft
Exchange Web Console, one of the following web browsers is required:
Microsoft Internet Explorer 6.0 or later
Mozilla Firefox 2.0 or later
Opera 9.00 or later
Any other web browser supporting HTTP 1.0, SSL, javascripts and
cookies may be used as well. Microsoft Internet Explorer 5.5 or earlier
cannot be used to administer the product.
CHAPTER 3 39
Installation
3.4 Improving Reliability and Performance
You can improve the system reliability and overall performance by
upgrading the following components.
Page 42

40
Processor If the system load is high, a fast processor on the Microsoft Exchange
Server speeds up the e-mail message processing. As Microsoft
Exchange Server handles a large amount of data, a fast processor alone
is not enough to guarantee a fast operation of F-Secure Anti-Virus for
Microsoft Exchange.
Memory Memory consumption is directly proportional to the size of processed
mails - scanning a single mail may use memory in amounts up to three
times the size of the mail concerned. If the average size of mail messages
is big, or Microsoft Exchange Server has to process large messages
regularly , increasing the amo unt of physical memory increa ses the overall
performance.
If large messages are processed only now and then, it might be enough
to increase the size of the virtual memory. In this case, large messages
will slow the system down.
Hard Drive Hard drive size is an important reliability factor. Hard drive performance is
crucial for Microsoft Exchange Server to perform well. For best
performance, a RAID system is recommended; for servers with only
moderate load, SCSI hard disks are adequate. If your server has an IDE
hard disk, DMA access support is recommended.
Operating
System
It is highly recommended to have the latest service packs for the
operating system being used. These fixes make the platform more stable
and thus increase the reliability of the system.
3.5 Centrally Administered or Stand-alone Installation?
F-Secure Anti-Virus for Microsoft Exchange can be managed either with
F-Secure Anti-Virus for Microsoft Exchange Web Console or F-Secure
Policy Manager Console. You can select the management method when
you install the product.
Page 43

If you already use F-Secure Policy Manager to administer other F-Secure
products, it is recommended to install F-Secure An ti-Virus for Microsoft
Exchange in centralized administration mode.
The quarantined mails are managed using the F-Secure Anti-Virus for
Microsoft Exchange Web Console in both centrally administered and
stand-alone installations. In centrally managed environments all other
features are managed with F-Secure Policy Manager.
3.6 Installation Overview
F-Secure Anti-Virus for Microsoft Exchange can be installed to the same
computer that runs F-Secure Anti-Virus for Servers 9.0. When both
products are installed on the same computer, they can be managed with
the common Web Console.
You should uninstall any potentially conflicting products, such as other
anti-virus, file encryption, and disk encryption software, which employ
low-level device drivers, before you install F-Secure Anti-Virus for
Microsoft Exchange.
CHAPTER 3 41
Installation
To administer F-Secure Anti-Virus for Microsoft Exchange in centralized
administration mode, you need to install F-Secure Policy Manager
Console and F-Secure Policy Manager Server. Detailed information on
F-Secure Policy Manager Console and F-Secure Policy Manager Server
is provided in the F-Secure Policy Manager Administrator's Guide.
You need to log in with administrator-level privileges to install F-Secure
Anti-Virus for Microsoft Exchange.
Follow these steps to set up F-Secure Anti-Virus for Microsoft Exchange:
Centralized Administration mode:
1. Run F-Secure Policy Manager setup to set up F-Secure Policy
Manager Server. See F-Secure Policy Manager Administrator’s
Guide for instructions.
2. Install F-Secure Anti-Virus for Microsoft Exchange. For more
information, see “Installing F-Secure Anti-Virus for Microsoft
Exchange”, 42.
Page 44

42
3. Import the product MIB files to F-Secure Policy Manager, if th ey
cannot be uploaded there during the installation. For more
information, see “Importing Product MIB files to F-Secure Policy
Manager Console”, 55.
4. Check that F-Secure Automatic Update Agent can retrieve the latest
virus and spam definition databases. For more information, consult
F-Secure Anti-Virus for Microsoft Exchange Administrator’s Guide.
Stand-alone mode:
1. Install F-Secure Anti-Virus for Microsoft Exchange. For more
information, see “Installing F-Secure Anti-Virus for Microsoft
Exchange”, 42.
2. Check that F-Secure Automatic Update Agent can retrieve the latest
virus and spam definition databases. For more information, consult
F-Secure Anti-Virus for Microsoft Exchange Administrator’s Guide.
After the installation is complete, check and configure the product
settings.
3.7 Installing F-Secure Anti-Virus for Microsoft Exchange
Follow these instructions to install F-Secure Anti-Virus for Microsoft
Exchange and F-Secure Spam Control.
Step 1. 1. Insert the F-Secure CD in your CD-ROM drive.
2. Select F-Secure Anti-Virus for Microsoft Exchange from the Install
Software menu.
Page 45

Step 2. Read the information in the Welcome screen.
Click Next to continue.
Step 3. Read the license agreement.
CHAPTER 3 43
Installation
If you accept the agreement, check the I accept this agreement
checkbox and click Next to continue.
Page 46

44
Step 4. Enter the product keycode.
Click Next to continue.
Step 5. Choose the components to install.
For more information about F-Secure Spam Control, consult F-Secure
Anti-Virus for Microsoft Exchange Administrator’s Guide. Click Next.
Page 47

Step 6. Choose the destination folder for the installation.
Click Next to continue.
Step 7. Choose the administration method.
CHAPTER 3 45
Installation
If you install F-Secure Anti-Virus for Microsoft Exchange in stand-alone
mode, you cannot configure settings and receive alerts and status
information in F-Secure Policy Manager Console. Click Next to continue.
Page 48

46
If you selected the stand-alone installation, continue to Step 10., 47.
If you select the stand-alone mode, use the F-Secure An ti-V irus for
Microsoft Exchange Web Console to change product settings and
to view statistics. For more information, consult F-Secure Anti-V irus
for Microsoft Exchange Administrator’s Guide.
Step 8. The centrally managed administration mode requires the public
management key. Enter the path to the public management key file
admin.pub that was created during F-Secure Policy Manager Console
setup.
You can transfer the public key in various ways (use a shared folder on
the file server, a USB device, or send the key as an attachment in an
e-mail message). Click Next to continue.
Page 49

CHAPTER 3 47
Step 9. In the centrally managed administration mode, enter the IP address or
URL of the F-Secure Policy Manager Server you installed earlier.
Click Next to continue.
Step 10. Enter an SMTP address that will be used by F-Secure Anti-Virus for
Microsoft Exchange to send warning and informational messages to
end-users.
Installation
The SMTP address should be a valid, existing address that is allowed to
send messages. Click Next to continue.
Page 50

48
Step 11. Specify the Quarantine management method.
If you want to manage the Quarantine database locally, select Local
quarantine management. Select Centralized quarantine management if
you install the product on multiple servers. Click Next to continue.
Step 12. Specify the location of the Quaran tine database.
If you want to install Microsoft SQL Server 2005 Express Edition and the
Quarantine database on the same server as the product installation,
select (a) Install and use Microsoft SQL Server 2005 Express Edition.
If you are using Microsoft SQL Server already, select (b) Use the existing
installation of MIcrosoft SQL Server.
Page 51

Click Next to continue to either (a) or (b) based on your selection.
a Specify the installation and the database directory for Microsoft
SQL Server 2005 Express Edition.
Enter the password for the database server administra tor account
that will be used to create the new database. Click Next to
continue.
b Specify the computer name of the SQL Server wh ere you wan t to
create the Quarantine database.
CHAPTER 3 49
Installation
Enter the password for the sa account that you use to log on to
the server. Click Next to continue.
Page 52

50
Step 13. Specify the name for the SQL database that stores information
about the quarantined content.
Enter the user name and the password that you want to use to
connect to the quarantine database.
• Use a different account than the server administrator
account. If the new account does not exist, the product
creates it during the installation.
• The password should be strong enough to comply with your
current Windows password security policy.
Click Next to continue.
Page 53

CHAPTER 3 51
Installation
If the server has a database with the same name, you can either
use the existing database, remove the existin g da tabase and
create a new one or keep the existing database and cre ate a new
one with a new name.
Click Next to continue.
Step 14. Select whether you want to install the product with F-Secure World Map
Support.
The product can collect and send statistics about viruses and other
malware to the F-Secure World Map service. If you agree to send
statistics to F-Secure World Map, select Yes and click Next to continue.
If you enable F-Secure World Map support, make sure that the server can
relay messages properly. For more information, consult F-Secure
Anti-Virus for Microsoft Exchange Administrator’s Guide.
Page 54

52
Step 15. If you selected the centralized administration mode, specify the DNS
name or IP address of the F-Secure Policy Manager Server and the
administration port.
Click Next to continue.
Step 16. If you selected the centralized administration mode, the installation
program connects to specified F-Secure Policy Manager Se rver
automatically to install F-Secure Anti-Virus for Microsoft Exchang e MIB
files. If the installation program cannot connect to F-Secure Policy
Manager Server, the following dialog opens.
Make sure that the computer where you are inst alling F-Secure Anti-V irus
for Microsoft Exchange is allowed to connect to the administratio n port (by
default, 8080) on F-Secure Policy Manager Server, or if you use proxy,
make sure that the connection is allowed from the proxy to the server.
Check that any firewall does not block the connection. For more
information, see F-Secure Policy Manager Administrator’s Guide.
Page 55

If you want to skip installing MIB files, click Cancel. You can install MIB
files later either manually or by running the Setup again.
If the product MIB files cannot be uploaded to F-Secure Policy
Manager during installation, you can import them manually.
For more information, see “Importing Product MIB files to F-Secure
Policy Manager Console”, 55.
Step 17. The list of components that will be installed is displayed.
CHAPTER 3 53
Installation
Click Start to install listed components.
Page 56

54
Step 18. The installation status of the components is displayed.
Click Next to continue.
Step 19. The installation is complete.
Click Finish to close the Setup wizard.
Page 57

CHAPTER 3 55
Installation
3.8 After the Installation
After the installation is complete, importing product MIBs to F-Secure
Policy Manager (if that is required), and perform the initial configuration of
the product.
3.8.1 Importing Product MIB files to F-Secure Policy Manager Console
If you are using the product in centrally managed mode, there are cases
when the F-Secure Anti-Virus for Microsof t Exchange MIB JAR file cannot
be uploaded to F-Secure Policy Manager Server during the in stallation. In
these cases you will have to import the MIB files to F-Secure Policy
Manager. You will have to import the MIB files if:
F-Secure Anti-Virus for Microsoft Exchange is located in a
different network segment than F-Secure Policy Manager, and
there is a firewall between them blocking access to Policy
Manager’s administrative port (8080).
F-Secure Policy Manager Server has been configured so that
administrative connections from anywhere else than the localhost
are blocked.
To import the MIBs with F-Secure Policy Manager Console, follow these
instructions:
1. Open the Tools menu and select the Installation packages option.
2. Click Import.
3. When the Import Installation Packages dialog opens, browse to the
Jars directory to locate the jar file.
4. Click Open to import the installation package.
5. After importing the new MIB files, restart F-Secure Policy Manager
Console.
Page 58

56
3.8.2 Configuring the Product
After the installation, F-Secure Anti-Virus for Microsoft Exchange is
functional, but it is using mostly default values. It is highly recommended
to go through all the settings of all installed components.
Configure F-Secure Anti-Virus for Microsoft Exchange.
If F-Secure Anti-Virus for Microsoft Exchange has been installed
in the centralized administration mode, use F-Secure Policy
Manager Console to configure the settings for F-Secure Content
Scanner Server and F-Secure Anti-Virus for Microsoft Exchange
and distribute the policy.
If F-Secure Anti-Virus for Microsoft Exchange has been installed
in stand-alone mode, use the F-Secure Anti-Virus for Microsoft
Exchange Web Console to configure the settings of F-Secure
Anti-Virus for Microsoft Exchange.
Specify the IP addresse s of ho sts that belong to your
organization. For more information, see “Network Configuration”,
57.
Verify that the product is able to retrieve the virus and spam
definition database updates.
If necessary, reconfigure your firewalls or other devices that may
block the database downloads. For more information, see
“Network Requirements”, 19.
If F-Secure Anti-Virus for Microsoft Exchange is installed on the
same computer with Microsoft Exchange Se rver 2010, which is in
the Mailbox server role, specify the primary SMTP address for the
account which is used to scan items in public folders. The user
account must have permissions to access and modify items in the
public folders.
If the organization has multiple Microsoft Exchange Server
installations and Mailbox servers are deployed on dedicated
servers, you have to configure the Hub Transport Role and
Mailbox Role Servers so that quarantined messages can be
delivered: For more information, see “Configuring Mailbox Role
Servers”, 100.
Page 59

For more information, consult F-Secure Anti-Vir us for Microsoft Exchange
Administrator’s Guide.
Network Configuration
The mail direction is based on the Internal Domains and Internal SMTP
senders settings and it is determined as follows:
1. E-mail messages are considered internal if they come from internal
SMTP sender hosts and mail recipients belong to one o f the specified
internal domains (internal recipients).
2. E-mail messages are considered outbound if they come from
internal SMTP sender hosts and mail recipients do not belong to the
specified internal domains (external recipients).
3. E-mail messages that come from hosts that are not defined as
internal SMTP sender hosts are conside red inbound.
4. E-mail messages submitted via MAPI or Pickup Folder are treated as
if they are sent from the internal SMTP sender host.
If e-mail messages come from internal SMTP sender hosts and
contain both internal and external recipients, message s are split
and processed as internal and outbound respectively.
CHAPTER 3 57
Installation
If F-Secure Anti-Virus for Microsoft Exchange has been installed in the
centralized administration mode, configure the mail direction with
F-Secure Policy Manager Console.
If F-Secure Anti-Virus for Microsoft Exchange has been installed in
stand-alone mode, configure the mail direction with F-Secure Anti-Virus
for Microsoft Exchange Web Console.
For more information, consult F-Secure Anti-Virus for Microsoft
Exchange Administrator’s Guide.
Page 60

58
3.9 Upgrading from Previous Product Versions
To upgrade from the product version 7.10 or 8.0, follow the standard
installation instructions.
To upgrade from the product version 6.62, follow instructions described in
this section.
IMPORTANT: F-Secure Anti-Virus for Microsoft Exchange 9.0
does not support Microsoft Exchange Server 2000 nor Microsoft
Windows Server 2000. You cannot upgrade the product that is
running on those platforms.
Backup your current configuration before starting the upgrade.
We recommend that you upgrade you r Microsoft SQL Se rver to the
latest version. If you are using MSDE, upgrade it to Microsoft SQL
Server 2005 Express Edition.
Standalone
Mode
Centralized
Administration
Mode
1. Install F-Secure Anti-Virus for Microsoft Exchange. For more
information, see “Installing F-Secure Anti-Virus for Microsoft
Exchange”, 42.
• Your previous settings are migrated to the new version du ring the
installation.
• You may need to reboot the system to complete the installation.
2. After the installation, open F-Secure Anti-Virus for Microsoft
Exchange Web Console and check the policy migration report. The
link to the report is in the Getting Started page.
The report file is located on the local disk in:
%Program Files%\F-Secure\Anti-Virus Agent for Microsoft
Exchange\msemigrpt.htm.
3. Check the product configuration to finish the upgrade.
Before you install the latest version of the product, upgrade F-Secure
Policy Manager to version 9.0 or later.
We recommend that you back up your policy data (select Save
Policy As in the Policy Manager Console) before the upgrade.
Page 61

CHAPTER 3 59
Installation
1. Install F-Secure Anti-Virus for Microsoft Exchange. For more
information, see “Installing F-Secure Anti-Virus for Microsoft
Exchange”, 42.
2. The setup program imports the JAR package that contains the
product MIB files and the migration tool to F-Secure Policy Manager
automatically. If the JAR package could not be imported, import it
manually after the installation.
Close F-Secure Policy Manager Console after the JAR package has
been imported.
3. After the F-Secure Anti-Virus for Microsoft Exchange installation is
complete, open F-Secure Policy Manager Console.
4. F-Secure Policy Manager Console prompts you to migrate the
previous policy settings to the new version.
Policy settings are migrated for all hosts and domains that you
manage with F-Secure Policy Manager. If you administer
multiple installations of F-Secure Anti-Virus for Microsoft
Exchange, migrate policy settings after you have upgraded all
installations of the product.
5. To migrate policy settings, click Yes.
If you want to migrate policy settings later, follow these instructions:
a Open F-Secure Policy Manager Console.
bGo to F-Secure > F-Secure Anti-Virus for Microsoft Exchange >
Operations > Policy Migration.
c Click Migrate.
6. After the policy migration is complete, check the migration report and
change the product settings if needed.
7. Distribute po licie s to fin ish th e up gr ade .
Page 62

60
3.10 Upgrading the Evaluation Version
If you want to use F-Secure Anti-Virus for Microsoft Exchange af ter your
evaluation period expires, you need a new keycode. Contact your
software vendor or renew your license online.
After you have received the new keycode, you can either reinstall
F-Secure Anti-Virus for Microsoft Exchange with your new keycode (see
“Installing F-Secure Anti-Virus for Microsoft Exchange”, 42) or register the
new keycode from F-Secure Settings and Statistics.
To register the new keycode:
8. Log in to the F-Secure Anti-Virus for Microsoft Exchange Web
Console. The evaluation screen is opened.
9. Eenter the new keycode you have received and click Register
Keycode.
If you do not want to continue to use F-Secure Anti-Virus for Microsoft
Exchange after your evaluation license expires, you should uninstall the
software.
When the license expires, F-Secure Anti-Virus for Microsoft Exchange
stops processing e-mails and messages posted to public folders.
However, the messages are still delivered to the recipients.
Page 63

3.11 Uninstalling F-Secure Anti-Virus for Microsoft Exchange
To uninstall F-Secure Anti-Virus for Microsoft Exchange, select Add/
Remove Programs from the Windows Control Panel. To uninstall
F-Secure Anti-Virus for Microsoft Exchange completely, uninstall the
components in the following order:
1. F-Secure Spam Control (if it was installed)
2. F-Secure Anti-Virus for Microsoft Exchange
Some files and directories may remain after the uninstallation and
can be removed manually.
CHAPTER 3 61
Installation
Page 64

CONFIGURING
4
F-S
C
Overview..................................................................................... 63
Realtime Blackhole List Configuration........................................ 64
ECURE SPAM
ONTROL
62
Page 65

4.1 Overview
CHAPTER 4 63
Configuring F-Secure Spam Control
When F-Secure Spam Control is enabled, incoming messages that are
considered as spam can be marked as spam automatically. The product
can add an X-header with the spam flag or predefined text in the
message header and end users can then create filtering rules that direct
the messages marked with the spam flag header into a junk mail folder.
F-Secure Spam Control databases can be updated with F-Secure
Automatic Update Agent. Database updates are digitally signed for
maximum security, and you can use only these updates for updating the
F-Secure Sp am Control spam definition databases.
F-Secure Spam Control databases are need ed for the heuristic
spam scanning only.
In Microsoft Exchange 2007 and 2010 environments, the Microsoft
Exchange server can move messages to the Junk mail folder based on
the spam confidence level value. This feature is available immediately
after the product has been installed, if the end user has activated this
functionality . For more information on how to con figure this functionality at
the end-user’s workstations, consult the documentation of the used e-mail
client.
Page 66

64
4.2 Realtime Blackhole List Configuration
This section describes how to enable and disable Realtime Blackhole
Lists, how to optimize F-Secure Spam Control performance, and how to
specify blocked and safe recipients and senders by using black- and
whitelisting.
4.2.1 Configuring Realtime Blackhole Lists
The product supports DNS Blackhole List (DNSBL), also known as
Realtime Blackhole List (RBL), functionality in spam filtering. The
functionality is enabled by default.
To test DNSBL/RBL:
1. Make sure you have a working DNS server configured in Windows
Server networking. The primary DNS server should be configured to
allow recursive DNS queries. DNS protocol is used to make the
DNSBL/RBL queries.
2. Make sure you do not have a firewall preventing DNS access from
the host where F-Secure Spam Control is running.
3. Test the DNS functionality by running the nslookup command at
Microsoft Windows command prompt on the host running F-Se cure
Spam Control.
An example:
C:\>nslookup 2.0.0.127.sbl-xbl.spamhaus.org.
Server: <your primary DNS server's name should appear
here>
Address: <your primary DNS server's IP address should
appear here>
Non-authoritative answer:
Name: 2.0.0.127.sbl-xbl.spamhaus.org
Addresses: 127.0.0.2, 127.0.0.4, 127.0.0.6
4. If the test is successful, continue with these instructions. If the test is
not successful, you should double-check your DNS and firewall
configuration.
Page 67

CHAPTER 4 65
Configuring F-Secure Spam Control
5. Find the sample configuration file fssc_example.cfg in F-Secure
Spam Control installation directory:
<Product installation directory>\Spam Control\fssc_example.cfg
6. Copy the file to the same directory with the name fssc.cfg
7. Open fssc.cfg in a text editor (like Windows Notepad).
8. The configuration file has instructions inside. For typical use, you can
leave the settings like they are. However, it is recommended to
configure at least the trusted_networks setting to identify the public
IP address(es) of your network. For more information, see the
instructions in fssc_example.cfg.
9. When the configuration file is ready, restart F-Secure Content
Scanner Server through F-Secure Anti-Virus for Microsoft Exchange
Web Console.
To verify that DNSBL/RBL is working correctly:
1. If DNSBL/RBL is operating correctly, you should see this kind of
headers in messages classified as spam:
X-Spam-Status: YES, database-version=2005-04-06_1 hits=9
required=5 tests=RCVD_IN_DSBL, RCVD_IN_NJABL_PROXY,
RCVD_IN_SORBS_DUL
Tests like RCVD_IN_DSBL, RCVD_IN_NJABL, RCVD_IN_SORBS,
RCVD_IN_BL_SPAMCOP_NET , RCVD_IN_DSBL, RCVD_IN_XBL indicate that
DNSBL/RBL was successfully used to classify the mail.
2. If DNS functionality is not operating correctly, you may see a
significant decrease in the product throughput. In that case, disa ble
the DNSBL/RBL functionality by changing the dns_available setting
in fssc.cfg to:
dns_available no
and restarting F-Secure Content Scanner Server through F-Secure
Anti-Virus for Microsoft Exchange Web Console.
You can force F-Secure Spam Control to use a specific DNS server (not
necessarily configured in Microsoft Windows networking) b y adding a new
system environment variable as described in the instructions below.
However, this should be needed only in troubleshooting situations.
Normally it is best to use the Windows networking settings.
Page 68

66
To force F-Secure Spam Control to use a specific DNS server, do the
following:
1. Right-click the My Computer icon and select Properties.
2. Select Advanced and click the Environment Variables.. button.
3. In the System variables panel click New.
4. In the New System Variable dialog specify the new variable as
follows:
Variable Name: RES_NAMESERVERS
Variable Value: <the IP address of the desired DNS server>
5. Click OK.
6. Restart the computer to take the new system environment variable
into use.
4.2.2 Optimizing F-Secure Spam Control Performance
Due to the nature of DNSBL/RBL, processing time for each mail
increases when DNS queries are made. If needed, the performance can
be improved by increasing the number of mails being processed
concurrently by F-Secure Spam Control.
By default, the product processes a maximum of three e-mails at the
same time, because there can be three Spam Scanner engine instances
running simultaneously. The number of Spam Scanner instances can be
controlled by using a command-line switch for F-Secu re Content Scanner
Server.
To change the value to 5, so that a maximum five mails can be processed
at the same time, type: fsavsd.exe --spam-scanner-instances=x (x is the
value you want to take into use), for example:
C:\Program Files\F-Secure\Content Scanner Server>
fsavsd.exe --spam-scanner-instances=5
F-Secure Content Scanner Server Daemon, 7.20.134
Copyright (c) 1998-2009 F-Secure Corporation
Page 69

Configuring F-Secure Spam Control
'spam-scanner-instances' (oid=1.3.6.1.4.1.2213.18.1.35.500)
has been set to 5.
To take the new setting into use, restart F-Secure Content Scanner
Server.
IMPORTANT: Each additional instance of the Sp am Scanner takes
approximately 25Mb of memory (process fsavsd.exe). Typically
you should not need more than 5 instances.
CHAPTER 4 67
Page 70

APPENDIX:
A
Deploying the Product
on a Cluster
Installation Overview.................................................................. 69
Creating Quarantine Storage...................................................... 71
Administering the Cluster Installation with F-Secure Policy
Manager..................................................................................... 99
Using the Quarantine in the Cluster Installation....................... 100
Using the Product with High Availability Architecture in Microsoft
Exchange Server 2010............................................................. 102
Uninstallation............................................................................ 103
Troubleshooting........................................................................ 103
68
Page 71

A.1 Installation Overview
Follow these steps to deploy and use F-Secure Anti-Virus for Microsoft
Exchange on a cluster.
1. Install F-Secure Policy Manager on a dedicated server. If you already
have F-Secure Policy Manager installed in the network, you can use it
to administer F-Secure Anti-Virus for Microsoft Exchange. For more
information, see F-Secure Policy Manager Administrator’s Guide.
2. Install Microsoft SQL Server 2000, 2005 or 2008 on a dedicated
server. Microsoft SQL Server must be installed with the mixed
authentication mode (Windows Authentica tio n an d SQ L S erve r
Authentication). After the installation, make sure that Named Pipes
and TCP/IP protocols are enabled in SQL Server network
configuration.
3. Create the quarantine storage where the product will place
quarantined e-mail messages and attachments.
In the active-passive cluster environment, continue to “Quarantine
Storage in Active-Passive Cluster
In the active-active cluster environment, continue to “Quarantine
Storage in Active-Active Cluster
In the Single Copy Cluster (SCC) environment, continue to
“
Creating the Quarantine Storage for a Single Copy Cluster
Environment
In the Continuous Cluster Replication (CCR) environment,
continue to “
Replication Environment
In the Database Availability Group (DAG) environment continue
to “
Creating the Quarantine Storage for a Database Availability Group
Environment
APPENDIX A 69
Deploying the Product on a Cluster
”, 71.
”, 76.
”, 79.
Creating the Quarantine Storage for a Continuous Cluster
”, 86.
”, 90.
Page 72

70
4. Install the product on one node at the time, starting from the active
node. Make sure the product is fully up and running before starting
the installation on the passive node.
Do not move cluster resources to the passive node before you
install all passive nodes first.
In the environment with Quarantine as cluster resource, see more
information on “
Resource
In the environment with Quarantine on dedicated computer, see
”, 94.
more information on “
Dedicated Computer
Installing on Clusters with Quarantine as Cluster
Installing on Clusters with Quarantine on a
”, 97.
5. Create a policy domain for the cluster in F-Secure Policy Manager
and import cluster nodes there. See “
Installation with F-Secure Policy Manager
Administering the Cluster
”, 99.
6. Log on each node and configure the Web Console to accept
connections from authorized hosts.
Page 73

Deploying the Product on a Cluster
A.2 Creating Quarantine Storage
Follow instructions in this section to create the Quarantine Storage in the
cluster environment.
A.2.1 Quarantine Storage in Active-Passive Cluster
For active-passive cluster, the Quarantine Storage can be created on a
dedicated computer or as a cluster resource. For more information on
how to to install the Quarantine Storage on a dedicated computer, see
“
Quarantine Storage in Active-Active Cluster”, 76.
To install Quarantine as a cluster resource, follow these instructions:
1. Log on to the active node of the cluster with the domain administrator
account.
2. Create a directory for the quarantine storage on the physical disk
shared by the cluster nodes. You can create it on the same disk with
Microsoft Exchange Server storage and log file s. For example, crea te
Quarantine directory on disk D:.
3. Go to Windows Start menu > All Progra ms > Administrative Tools and
select Cluster Administrator.
4. Under Groups, right-click Exchange Virtual Server and select New >
Resource.
APPENDIX A 71
Page 74

72
Enter the following information:
Name: F-Secure Quarantine Storage
Resource Type: File Share
Group: make sure that your Exchange Virtual Server is selected.
Click Next.
5. Possible Owners dialog opens.
Page 75

Deploying the Product on a Cluster
6. Verify that all nodes that are running Exchange Server are listed
under Possible owners and click Next.
7. Dependencies dialog opens.
APPENDIX A 73
Page 76

74
In Available resources, select the Exchange Server Network Name
and the disk with the quarantine storage directory and click Add to
add them to Resource dependencies. Click Next.
8. File Share Parameters dialog opens.
Type FSAVMSEQS$ as Share name. (Note: the dollar ($)
character at the end of the share name make s th e sha re hid de n
when you view network resources of the cluster with Windows
Explorer.)
Enter the directory name you created on step 2 as Path (for
example, D:\Quarantine).
In the Comment box, type F-Secure Quarantine Storage.
Make sure that User limit is set to Maximum allowed.
Click Permissions
9. Permissions dialog opens.
Page 77

Deploying the Product on a Cluster
Add Administrator, Exch ange Domain Servers and SYSTEM to the
Group or user names. Remove Everyone account. Grant Change and
Read permissions for Exchange Domain Servers and SYSTEM, and
Full Control, Change and Read permissions for Administrator
account. Click OK.
10. In File Share Parameters dialog, click Advanced.
APPENDIX A 75
Make sure that Normal share is selected in Advanced File Share
Properties. Click OK.
11. In File Share Parameters dia l og, click Finish to create F-Secure
Quarantine Storage resource.
Page 78

76
12. Right-click the F-Secure Quarantine S torage resource and click Bring
Online.
A.2.2 Quarantine Storage in Active-Active Cluster
For an active-active cluster installation, the quarantine storage must be
set on a dedicated computer . This computer shou ld be the member of th e
same domain as your Exchange Servers.
1. Log on to the server where you plan to create the quarantine storage
(for example, APPSERVER) with a domain administrator account.
2. Create a directory (for example, C:\Quarantine) for the quarantine
storage on the local hard disk.
3. Right-click the directory in the Windows Explorer and select Sharing
and Security.
4. The Sharing tab opens.
Page 79

Deploying the Product on a Cluster
Type FSAVMSEQS$ as Share name and make sure that User limit is
set to Maximum Allowed.
Click Permissions
5. Permissions dialog opens.
APPENDIX A 77
Add Administrator, Exch ange Domain Servers and SYSTEM to the
Group or user names. Remove Everyone account. Grant Change and
Read permissions for Exchange Domain Servers and SYSTEM, and
Full Control, Change and Read permissions for Administrator
account. Click OK.
6. In the directory properties dialog, go to the Security tab.
Page 80

78
Remove all existing groups and users and add Administrator,
Exchange Domain Servers and SYSTEM to the Group or user
names. Grant all except Full Control permissions for Exchange
Domain Servers and SYSTEM. Grant all permissions for
Administrator. Click OK.
7. To verify that the quarantine storage is accessible, log on as the
domain administrator to any node in the cluster and try to open
\\<Server>\FSAVMSEQS$\ with Windows Explorer, where <Server>
is the name of the server where you created the quarantine storage
share.
Page 81

Deploying the Product on a Cluster
A.2.3 Creating the Quarantine Storage for a Single Copy
Cluster Environment
For single copy cluster, the Quarantine Storage can be created on a
dedicated computer or as a cluster resource. For more information on
how to to install the Quarantine Storage on a dedicated computer, see
“
Creating the Quarantine Storage for a Continuous Cluster Replication
Environment
To install Quarantine as a cluster resource, follow the instructions for
either “
84.
Windows 2003 Based Cluster
1. Log on to the active node of the cluster with the domain administrator
account.
2. Create a directory for the quarantine storage on the physical disk
shared by the cluster nodes.
You can create it on the same disk where the Exchange Server
storage and logs are located. For examp l e, cr ea te Qua ra n tine
directory on disk D:.
3. Go to Start menu > All Programs > Administrative Tools > Cluster
Administrator.
4. Right-click the Exchange Virtual Server under the Groups and select
New > Resource.
5. The New Resource wizard opens.
”, 86.
Windows 2003 Based Cluster”, 79, or “Windows 2008 based cluster”,
APPENDIX A 79
Page 82

80
a. Type F-Secure Quarantine Storage as the name of the new
resource.
b. In the Resource Type list, select File Share.
c. In the Group list, make sure that your Exchange Virtual Server is
selected.
Click Next to continue.
6. Make sure that all nodes that are running Exchange Ser ver ar e listed
in the Possible owners list.
Click Next to continue.
Page 83

APPENDIX A 81
Deploying the Product on a Cluster
7. Select the Exchange Server Network Name and the Physical Disk
under Available resources and click Add to move them to the
Resource dependencies list.
Click Next to continue.
8. Use the following settings as the File Share parameters.
a. Type FSAVMSEQS$ as the share name and F-Secure
Quarantine Storage as comment.
The dollar ($) character at the end of the share name
makes the share hidden when you view the network
resources of the cluster with Windows Explorer.
b. Make sure that User Limit is set to Maximum allowed.
Page 84

82
Click Permissions to change permissions.
9. Change permissions as follows:
a. Add Administrator, Exchange Domain Servers and SYSTEM to
the Group or user names list.
b. Remove the Everyone account.
c. Grant Change and Read permissions for Exchange Domain
Servers and SYSTEM.
d. Grant Full Control, Change and Read permissions for the
Administrator account.
Page 85

Deploying the Product on a Cluster
Click OK to continue.
10. Click Advanced to open Advanced File Share Properties.
APPENDIX A 83
Make sure that Normal share is selected.
Click OK to continue.
11. Click Finish to create the F-Secure Quarantine Storage resource.
Page 86

84
12. Right-click the F-Secure Quarantine Storage resource and select
Bring Online.
Windows 2008 based cluster
1. Log on to the active node of the cluster with the domain administrator
account.
2. Create a directory for the quarantine storage on the physical disk
shared by the cluster nodes.
You can create it on the same disk where the Exchange Server
storage and logs are located.
3. After the quarantine directory is created, it has to be shared. When
you share the quarantine directory, it becomes visible in the Failover
Cluster Manager. To share the directory, right-click the quarantine
folder and select Share.
Page 87

APPENDIX A 85
Deploying the Product on a Cluster
Add Administrators, Exchange Servers and SYSTEM with Contributor
permission levels. Press Share to close the window and enable the
share.
4. Check that everything is configured correctly. The Failover Cluster
Manager view should look like this:
Page 88

86
5. During the F-Secure Anti-Virus for Microsoft Exchange installation,
select the quarantine share you just created when the installation
asks for the quarantine path.
Use the UNC path in form of \\CLUSTERNAME\QUARANTINE. (In
the example above, \\LHCLUMB\Quarantine.)
A.2.4 Creating the Quarantine Storage for a Continuous
Cluster Replication Environment
For a Continuous Cluster Replication (CCR) cluster installation, the
quarantine storage must be set on a dedicated computer. This computer
has to be a member in the same domain with Exchange Servers.
1. Log on to the server where you plan to create the quarantine storage
(for example, APPSERVER) with the domain administrator account.
2. Open Windows Explorer and create a directory (for example,
C:\Quarantine) for the quarantine storage on the physical disk.
3. Right-click the directory and select Sharing and Security.
Page 89

Deploying the Product on a Cluster
4. Go to the Sharing tab.
a. Type FSAVMSEQS$ as the share name and F-Secure
Quarantine Storage as comment.
APPENDIX A 87
The dollar ($) character at the end of the share name
makes the share hidden when you view the network
resources of the cluster with Windows Explorer.
b. Make sure that User Limit is set to Maximum allowed.
Click Permissions to set permissions.
Page 90

88
5. Change permissions as follows:
a. Remove all existing groups and users.
a. Add Administrator, Exchange Domain Servers and SYSTEM to
the Group or user names list.
b. Grant Change and Read permissions for Exchange Domain
Servers and SYSTEM.
c. Grant Full Control, Change and Read permissions for the
Administrator account.
Click OK to continue.
Page 91

Deploying the Product on a Cluster
6. Go to the Security tab.
a. Remove all existing groups and users.
a. Add Administrator, Exchange Domain Servers and SYSTEM to
the Group or user names list.
b. Grant all except Full Control permissions for Exchange Domain
Servers and SYSTEM.
c. Grant all permissions for the Administrator account.
APPENDIX A 89
Click OK to finish.
To make sure that the quarantine storage is accessible, follow these
instructions:
1. Log on as the domain administrator to any node of the cluster.
2. Try to open \\<Server>\FSAVMSEQS$\ with Windows Explorer,
where <Server> is the name of the server where you just created the
quarantine storage share.
Page 92

90
A.2.5 Creating the Quarantine Storage for a Database
Availability Group Environment
For the Database Availability Group (DAG) installation, the quarantine
storage must be set on a dedicated computer. This computer has to be a
member in the same domain with Exchange Servers.
1. Log on to the server where you will create the quarantine storage (for
example, APPSERVER) with the domain administrator account.
2. Open Windows Explorer and create a directory (for example,
C:\Quarantine) for the quarantine storage.
3. Right-click the directory and select Properties from the menu.
4. Go to the Sharing tab.
5. Click Advanced Sharing to share the directory.
6. Select Share this folder.
Page 93

Deploying the Product on a Cluster
a. Type FSA VMSEQS$ as the share name and F-Secure Quarantine
Storage as a comment.
The dollar ($) character at the end of the shar e name hides
the share when you view the network resources of the
cluster with Windows Explorer.
b. Make sure that User Limit is set to Maximum that is allowed
(16777216).
7. Click Permissions to set permissions for the share.
8. Change permissions as follows:
a. Remove all existing groups and users.
b. Add Administrator , Exchange Servers a nd SYSTEM to th e Group
or user names list.
c. Grant Change and Read permissions for Exchange Servers and
SYSTEM.
d. Grant Full Control, Change and Read permissions for the
Administrator account.
APPENDIX A 91
Page 94

92
9. Click OK to continue.
10. Go to the Security tab and click Edit.
a. Remove all existing groups and users.
b. Add Administrator, Exchange Servers and SYSTEM to the Gro up
or user names list.
c. Grant all except Full Control permissions for Exch an ge Ser ver s
and SYSTEM.
d. Grant all permissions for the Administrator account.
Page 95

APPENDIX A 93
Deploying the Product on a Cluster
11. Click OK to continue.
After you have configured the quarantine storage, make sure that it is
accessible. Follow these instructions:
1. Log on as the domain administrator to any node of the cluster.
2. Open \\<Server>\FSAVMSEQS$\ with Windows Explorer, where
<Server> is the name of the server where you created the quar antine
storage share.
Page 96

94
A.3 Installing the Product
Follow the instructions in this section to install the product on the
active-passive and active-active clusters, CCR, SCC and DAG
installations.
A.3.1 Installing on Clusters with Quarantine as Cluster
Resource
This section describes how to install the product on on clusters where
Quarantine is configured as cluster resource in Exchange Virtual Server.
1. Log on to the active node of the cluster using a domain administrator
account.
2. Run F-Secure Anti-Virus for Microsoft Exchange setup wizard. Install
the product in the centralized management mode. Specify the IP
address of F-Secure Policy Manager Server and admin.pub that you
created during the F-Secure Policy Manager installation. For more
information, see “
3. The setup wizard asks for the location of the quarantine directory.
Centralized Management Requirements”, 36.
Page 97

APPENDIX A 95
Deploying the Product on a Cluster
Specify the UNC path to the Quarantine Storage share that you
created before the installation as the Quarantine Directory. For
example, \\<EVSName>\FSAVMSEQS$, where <EVSName> is the
network name of your Exchange Virtual Server.
4. The setup program asks to specify the SQL Server to use for the
quarantine database.
Select the server running Microsoft SQL Server.
5. The setup program asks to specify the database name where
quarantined items are stored.
Page 98

96
Specify the name for the database and enter user name and
password that will be used to access the database.
6. Complete the installation on the active node.
7. Log on to the passive node of the cluster using a domain
administrator account. Repeat steps 2-4.
8. After you specify the SQL Server to use, the setup wizard asks you to
specify the quarantine database.
Page 99

APPENDIX A 97
Deploying the Product on a Cluster
Select Use the existing database.
9. Complete the installation on the passive node.
A.3.2 Installing on Clusters with Quarantine on a Dedicated
Computer
This section describes how to install the product on clusters where
Quarantine is installed on a dedicated computer.
1. Log on to the first node of the cluster using a domain administrator
account.
2. Run F-Secure Anti-Virus for Microsoft Exchange setup wizard. Install
the product in the centralized management mode. Specify the IP
address of F-Secure Policy Manager Server and admin.pub that you
created during the F-Secure Policy Manager installation. For more
information, see “
3. The setup wizard asks for the location of the quarantine directory.
Centralized Management Requirements”, 36.
Specify the UNC path to the Quarantine Storage share that you
created before the installation as the Quarantine Directory. For
example, \\<Server>\FSAVMSEQS$, where <Server> is the name of
the server where you created the quarantine storage share.
Page 100

98
4. The setup program asks to specify the SQL Server to use for the
quarantine database.
Select the server running Microsoft SQL Server.
5. The setup program asks to specify the database name where
quarantined items are stored.
Specify the name for the database and enter user name and
password that will be used to access the database.
 Loading...
Loading...