Page 1

T.I.M.E. SYNERGIC
Primärgetakteter MIG/MAGSchweißgleichrichter
BEDIENUNGSANLEITUNG
ERSATZTEILLISTE
Primary transistor-switched
MIG/MAG welding rectifier
OPERATING
INSTRUCTIONS
SPARE PARTS
LIST
Redresseur de soudage
à hacheur primaire MIG/MAG
MODE
D´EMPLOI
LISTE DE PIÈCES
DE RECHANGE
42,0410,0409 012001
Page 2

2
Page 3

SEHR GEEHRTER FRONIUS-KUNDE
Die vorliegende Bedienungsanleitung soll Sie mit Bedienung und Wartung der T.I.M.E. Synergic vertraut machen. Es liegt in Ihrem Interesse,
die Bedienungsanleitung aufmerksam zu lesen, und die hier angegebenen Weisungen gewissenhaft zu befolgen. Sie vermeiden dadurch Störungen durch Bedienungsfehler. Das Gerät wird Ihnen dies durch stete
Einsatzbereitschaft und lange Lebensdauer lohnen.
INHALTSVERZEICHNIS
Sehr geehrter Fronius-Kunde .................................................................. 3
Sicherheitsvorschriften............................................................................. 4
Allgemeines ........................................................................................... 4
Bestimmungsgemässe Verwendung................................................... 4
Verpflichtungen des Betreibers........................................................... 4
Verpflichtungen des Personals ........................................................... 4
Persönliche Schutzausrüstung............................................................ 4
Gefahr durch schädliche Gase und Dämpfe ..................................... 4
Gefahr durch Funkenflug ..................................................................... 4
Gefahren durch Netz- und Schweiss-Strom ...................................... 4
Besondere Gefahrenstellen ................................................................. 4
Informelle Sicherheitsmassnahmen ................................................... 5
Sicherheitsmassnahmen am Aufstellort............................................. 5
Vagabundierende Schweisströme ...................................................... 5
Sicherheitsmassnahmen im Normalbetrieb ....................................... 5
Sicherheitstechnische Inspektion ....................................................... 5
Veränderungen am Schweissgerät..................................................... 5
Ersatz- und Verschleissteile ................................................................ 5
Kalibrieren von Schweissgeräten ....................................................... 5
Die CE-Kennzeichnung ........................................................................ 5
Urheberrecht ......................................................................................... 5
Allgemeines ............................................................................................... 6
Prinzip der T.I.M.E. Synergic ............................................................... 6
Verfahrensprüfung nach EN 288 / 7 ................................................... 6
Gerätekonzept....................................................................................... 6
Bedienelemente und Anschlüsse............................................................ 7
Stromquelle T.I.M.E. Synergic ............................................................. 7
Drahtvorschub T.I.M.E. 30 ................................................................... 9
Kühlgerät FK 71 .................................................................................. 10
Fernbedienung TR 34 T.I.M.E........................................................... 10
Fernbedienung TP 4 SP..................................................................... 11
Stromquelle in Betrieb nehmen ............................................................. 11
Bestimmungsgemässe Verwendung................................................. 11
Aufstellbestimmungen ........................................................................ 11
Netzstecker anschliessen .................................................................. 11
Netzanschluss ..................................................................................... 11
Stromquelle zusammenbauen........................................................... 12
Verbindungsschlauchpaket mit Stromquelle/Kühlgerät verbinden 12
Verbindungsschlauchpaket mit Drahtvorschub verbinden............. 13
Gasflasche montieren / anschliessen .............................................. 13
FRONIUS INTERNATIONAL GMBH & COKG
Achtung! Die Inbetriebnahme des Gerätes darf nur durch geschultes Personal und nur im Rahmen der technischen Bestimmungen erfolgen. Vor Inbetriebnahme unbedingt das Kapitel
"Sicherheitsvorschriften" lesen.
Schweissbrenner montieren .............................................................. 13
Kühlgerät in Betrieb nehmen............................................................. 13
Drahtspule einsetzen ......................................................................... 13
Drahtelektrode einlaufen lassen ....................................................... 13
Vorschubrollen wechseln ................................................................... 14
MIG/MAG-Schweissen ........................................................................... 14
Einstellrichtlinien für den T.I.M.E.-Process ...................................... 14
Einstellwerte für Nahtart, Schweissposition und Nahtdicke .......... 15
WIG-Schweissen..................................................................................... 15
Variante I.............................................................................................. 15
Variante II ............................................................................................ 15
Inbetriebnahme ................................................................................... 16
E-Handschweissen ................................................................................. 16
Roboterschweissen ................................................................................ 16
Das Setup-Menü ..................................................................................... 17
In das Setup-Menü einsteigen .......................................................... 17
Das Setup-Menü verlassen ............................................................... 17
Parameterbeschreibung..................................................................... 17
Pflege und Wartung ................................................................................ 17
Fehlerdiagnose und -behebung ............................................................ 18
Fehlermeldungen an den Anzeigen.................................................. 18
Fehler an der Schweissanlage .......................................................... 18
Technische Daten ................................................................................... 22
Stromquelle T.I.M.E. Synergic ........................................................... 22
Drahtvorschub T.I.M.E. 30 ................................................................. 22
Kühlgerät FK 71 .................................................................................. 22
LED-Checkliste, Einstellregler und Sicherungen ................................ 23
Operating Instructions
Mode d´emploi
Ersatzteilliste
Fronius - Vertriebs- und Service-Niederlassungen
DEUTSCH
3
Page 4

SICHERHEITSVORSCHRIFTEN
ALLGEMEINES
Das Schweißgerät ist nach dem Stand der Technik und den anerkannten
sicherheitstechnischen Regeln gefertigt. Dennoch drohen bei Fehlbedienung oder Mißbrauch Gefahr für
- Leib und Leben des Bedieners oder Dritten,
- das Schweißgerät und andere Sachwerte des Betreibers,
- die effiziente Arbeit mit dem Schweißgerät.
Alle Personen, die mit der Inbetriebnahme, Bedienung, Wartung und
Instandhaltung des Schweißgerätes zu tun haben, müssen
- entsprechend qualifiziert sein,
- Kenntnisse vom Schweißen haben und
- diese Bedienungsanleitung genau beachten.
Störungen, die die Sicherheit beeinträchtigen können, sind umgehend
zu beseitigen.
Es geht um Ihre Sicherheit!
BESTIMMUNGSGEMÄSSE VERWENDUNG
Das Schweißgerät ist ausschließlich für Arbeiten im Sinne der bestimmungsgemäßen Verwendung (siehe Kapitel "Schweißgerät in Betrieb
nehmen") zu benutzen.
Zur bestimmungsgemäßen Verwendung gehört auch
- das Beachten aller Hinweise aus der Bedienungsanleitung
- die Einhaltung der Inspektions- und Wartungsarbeiten
VERPFLICHTUNGEN DES BETREIBERS
Der Betreiber verpflichtet sich, nur Personen am Schweißgerät arbeiten
zu lassen, die
- mit den grundlegenden Vorschriften über Arbeitssicherheit und Unfallverhütung vertraut und in die Handhabung des Schweißgerätes
eingewiesen sind
- das Sicherheitskapitel und die Warnhinweise in dieser Bedienungsanleitung gelesen, verstanden und durch ihre Unterschrift bestätigt
haben
Das sicherheitsbewußte Arbeiten des Personals ist in regelmäßigen
Abständen zu überprüfen.
Befinden sich Personen in der Nähe so müssen
- diese über die Gefahren unterrichtet,
- Schutzmittel zur Verfügung gestellt bzw.
- Schutzwände bzw. -Vorhänge aufgebaut werden.
GEFAHR DURCH SCHÄDLICHE GASE UND DÄMPFE
- Entstehenden Rauch sowie schädliche Gase durch geeignete Mittel
aus dem Arbeitsbereich absaugen.
- Für ausreichende Frischluftzufuhr sorgen.
- Lösungsmitteldämpfe vom Strahlungsbereich des Lichtbogens fernhalten.
GEFAHR DURCH FUNKENFLUG
- Brennbare Gegenstände aus dem Arbeitsbereich entfernen.
- An Behältern in denen Gase, Treibstoffe, Mineralöle und dgl. gelagert
sind/waren, darf nicht geschweißt werden. Durch Rückstände besteht Explosionsgefahr.
- In feuer- u. explosionsgefährdeten Räumen gelten besondere Vorschriften - entsprechende nationale und internationale Bestimmungen beachten.
GEFAHREN DURCH NETZ- UND SCHWEISS-STROM
- Ein Elektroschock kann tödlich sein. Jeder Elektroschock ist grundsätzlich lebensgefährlich.
- Durch hohe Stromstärke erzeugte magnetische Felder können die
Funktion lebenswichtiger elektronischer Geräte (z.B. Herzschrittmacher) beeinträchtigen. Träger solcher Geräte, sollten sich durch ihren
Arzt beraten lassen, bevor sie sich in unmittelbarer Nähe des Schweißarbeitsplatzes aufhalten.
- Sämtliche Schweißkabel müssen fest, unbeschädigt und isoliert sein.
Lose Verbindungen und angeschmorte Kabel sofort erneuern.
- Netz- u. Gerätezuleitung regelmäßig von einer Elektro-Fachkraft auf
Funktionstüchtigkeit des Schutzleiters überprüfen lassen.
- Vor Öffnen des Schweißgerätes sicherstellen, daß dieses stromlos
ist. Bauteile die elektrische Ladung speichern entladen.
- Sind Arbeiten an spannungsführenden Teilen notwendig, ist eine
zweite Person hinzuzuziehen, die notfalls den Hauptschalter ausschaltet.
VERPFLICHTUNGEN DES PERSONALS
Alle Personen, die mit Arbeiten am Schweißgerät beauftragt sind, verpflichten sich, vor Arbeitsbeginn
- die grundlegenden Vorschriften über Arbeitssicherheit und Unfallverhütung zu beachten
- das Sicherheitskapitel und die Warnhinweise in dieser Bedienungsanleitung zu lesen und durch ihre Unterschrift zu bestätigen, daß sie
diese verstanden haben
PERSÖNLICHE SCHUTZAUSRÜSTUNG
Treffen Sie für Ihre persönliche Sicherheit folgende Vorkehrungen:
- Festes, auch bei Nässe, isolierendes Schuhwerk tragen
- Hände durch isolierende Handschuhe schützen
- Augen durch Schutzschild mit vorschriftsmäßigem Filtereinsatz vor
UV-Strahlen schützen
- Nur geeignete (schwer entflammbare) Kleidungsstücke verwenden
- Bei erhöhter Lärmbelastung Gehörschutz verwenden
BESONDERE GEFAHRENSTELLEN
- Nicht in die rotierenden Zahnräder des Drahtantriebes greifen.
- In feuer- und explosionsgefährdeten Räumen gelten besondere Vorschriften - entsprechende nationale und internationale Bestimmungen beachten.
- Schweißgeräte für Arbeiten in Räumen mit erhöhter elektrischer
Gefährdung (z.B. Kessel) müssen mit dem Zeichen S (Safety) gekennzeichnet sein.
- Schweißverbindungen mit besonderen Sicherheitsanforderungen sind
nur von speziell ausgebildeten Schweißern durchzuführen.
- Bei Krantransport der Stromquelle Ketten bzw. Seile in einem möglichst kleinen Winkel zur Senkrechten in allen Kranösen einhängen Gasflasche und Drahtvorschubgerät entfernen.
- Bei Krantransport des Drahtvorschubes immer eine isolierende Drahtvorschubaufhängung verwenden
4
Page 5

INFORMELLE SICHERHEITSMASSNAHMEN
- Die Bedienungsanleitung ist ständig am Einsatzort des Schweißgerätes aufzubewahren.
- Ergänzend zur Bedienungsanleitung sind die allgemein gültigen
sowie die örtlichen Regeln zu Unfallverhütung und Umweltschutz
bereitzustellen und zu beachten.
- Alle Sicherheits- und Gefahrenhinweise am Schweißgerät sind in
lesbarem Zustand zu halten.
SICHERHEITSMASSNAHMEN AM AUFSTELLORT
- Das Schweißgerät muß auf ebenem und festen Untergrund standsicher aufgestellt werden. Ein umstürzendes Schweißgerät kann Lebensgefahr bedeuten!
- In feuer- und explosionsgefährdeten Räumen gelten besondere Vorschriften - entsprechende nationale und internationale Bestimmungen beachten.
- Durch innerbetriebliche Anweisungen und Kontrollen sicherstellen,
daß die Umgebung des Arbeitsplatzes stets sauber und übersichtlich
ist.
VERÄNDERUNGEN AM SCHWEISSGERÄT
- Ohne Genehmigung des Herstellers keine Veränderungen, Ein- oder
Umbauten am Schweißgerät vornehmen.
- Bauteile in nicht einwandfreiem Zustand sofort austauschen.
ERSATZ- UND VERSCHLEISSTEILE
- Nur Original-Ersatz- und Verschleißteile verwenden. Bei fremdbezogenen Teilen ist nicht gewährleistet, daß sie beanspruchungs- und
sicherheitsgerecht konstruiert und gefertigt sind.
- Bei Bestellung genaue Benennung und Sach-Nummer laut Ersatzteilliste, sowie Seriennummer Ihres Gerätes angeben.
KALIBRIEREN VON SCHWEISSGERÄTEN
Aufgrund internationaler Normen ist eine regelmäßige Kalibrierung von
Schweißgeräten empfohlen. Fronius empfiehlt ein Kalibrierintervall von
12 Monaten. Setzen Sie sich für nähere Informationen mit Ihrem FroniusPartner in Verbindung!
DEUTSCH
VAGABUNDIERENDE SCHWEISSTRÖME
- Für eine feste Verbindung der Werkstückklemme mit dem Werkstück
sorgen
- Bei elektrisch leitfähigem Boden das Schweißgerät, wenn möglich,
isoliert aufstellen
Bei Nichtbeachtung kommt es zu vagabundierenden Schweißströmen,
die zur Zerstörung von Schutzleitern, des Schweißgerätes und anderen
elektrischen Einrichtungen führen können.
SICHERHEITSMASSNAHMEN IM NORMALBETRIEB
- Schweißgerät nur betreiben, wenn alle Schutzeinrichtungen voll
funktionstüchtig sind.
- Vor Einschalten des Schweißgerätes sicherstellen, daß niemand
gefährdet werden kann.
- Mindestens einmal pro Woche das Schweißgerät auf äußerlich erkennbare Schäden und Funktionsfähigkeit der Sicherheitseinrichtungen überprüfen.
SICHERHEITSTECHNISCHE INSPEKTION
Der Betreiber ist verpflichtet, das Schweißgerät nach Veränderung, Einoder Umbauten, Reparatur, Pflege und Wartung sowie mindestens alle
zwölf Monate durch eine Elektro-Fachkraft auf ordnungsgemäßen Zustand überprüfen zu lassen.
DIE CE-KENNZEICHNUNG
Das Schweißgerät erfüllt die grundlegenden Anforderungen der Niederspannungs- und Elektromagnetischen Verträglichkeits-Richtlinie und ist
daher CE-gekennzeichnet.
URHEBERRECHT
Das Urheberrecht an dieser Bedienungsanleitung verbleibt bei der Firma
Fronius International GmbH&Co.KG
Text und Abbildungen entsprechen dem technischen Stand bei Drucklegung. Änderungen vorbehalten. Der Inhalt der Bedienungsanleitung
begründet keinerlei Ansprüche seitens des Käufers. Für Verbesserungsvorschläge und Hinweise auf Fehler in der Bedienungsanleitung sind wir
dankbar.
Bei der Überprüfung sind zumindest folgende Vorschriften zu beachten:
- IEC (EN) 60 974-1 - Einrichtungen zum Lichtbogenschweißen, Teil 1:
Schweißstromquellen
- VBG 4, §5 - Elektrische Anlagen und Betriebmittel
- VBG 15, §33 / §49 - Schweißen, Schneiden und verwandte Arbeitsverfahren
- VDE 0701-1 - Instandsetzung, Änderung und Prüfung elektrischer
Geräte; allgemeine Anforderungen
- VDE 0702-1 - Wiederholungsprüfungen an elektrischen Geräten
Nähere Informationen für die Instandsetzung, Änderung und anschließende Prüfung von Schweißgeräten erhalten Sie bei Ihrer Fronius
Servicestelle, die Ihnen auf Wunsch die Arbeitanweisung „Sicherheitstechnische Überprüfung von Schweißgeräten“ (AA-PMÜ-01) zur Verfügung stellt.
ud_fr_st_sv_00145 0120015
Page 6

ALLGEMEINES
PRINZIP DER T.I.M.E. SYNERGIC
Der T.I.M.E. Process ist ein Hochleistungs- MAG Schweißverfahren,
welches höchste Wirtschaftlichkeit mit ausgezeichneter Schweißnahtqualität verbindet. Durch die Verarbeitung von Massivdrähten unter
höheren Drahtgeschwindigkeiten ergibt sich die höhere Abschmelzleistung, wobei durch spezielle Schutzgasgemische eine hochwertige
Schweißverbindung entsteht.
Aspekte wie Nahtaussehen, mechanisch-technologische Gütewerte,
Nahtübergänge, Bindefehlersicherheit und geringe Spritzerneigung sind
wesentliche Vorteile des Verfahrens. Durch die Einführung eines zweiten Gasgemisches „T.I.M.E.-II“ ist es nunmehr möglich, falls nötig,
porenfreie Schweißnähte zu erzielen. Im wesentlichen besteht der T.I.M.E.
Process aus der Verknüpfung fortschrittlichster Stromquellentechnologie, leistungsfähigen Drahtvorschubgeräten und Schweißbrennern, der
entsprechenden Gasephysik und dem Knowhow der richtigen Anwendung dieser Elemente.
VERFAHRENSPRÜFUNG NACH EN 288 / 7
Zukünftig wird es auf dem Gebiet der Schweißtechnik in Europa mehrere
Möglichkeiten der Anerkennung von Schweißanweisungen WPS geben.
Eine davon ist entsprechend der ÖNORM EN 288/1 die Normverfahrensprüfung nach EN 288 / 7. Durch eine derartige Normverfahrensprüfung
werden alle wesentlichen Einflußgrößen untersucht und somit ein genormtes Schweißverfahren festgelegt.
GERÄTEKONZEPT
Das Baukastenprinzip stand Pate für die T.I.M.E. Synergic. Die einzelnen Steuerkomponenten sind verschraubt und lassen sich einfach und
problemlos auf ein robustes Fahrwerk montieren.
Die Gasflasche ist im Fahrwagen integriert und vertieft angebracht.
Dadurch läßt sich die Gasflasche rasch und einfach wechseln bzw.
manipulieren. Die Anlage hat zwar kleine Abmessungen, ist aber so
gebaut, daß sie auch unter härtesten Bedingungen zuverlässig arbeitet.
Pulverbeschichtete Blechgehäuse, geschützt angebrachte Bedienungselemente und Strombuchsen mit Bajonettverriegelung erlauben höchste
Anforderungen.
Das tragbare Drahtvorschubgerät kann über den Aufnahmebolzen der
Stromquelle nach beiden Seiten drehbar aufgesetzt bzw. zur Erweiterung des Arbeitsbereiches abgenommen werden. Verschließbare Abdeckungen schützen Drahtrolle und Antriebssystem vor anfallendem
Schleifstaub.
Der isolierte Transportgriff und ein Fahrwerk mit groß dimensionierten
Rädern sowie optimal angebrachte Kranösen machen den Transport
sowohl innerbetrieblich als auch im Baustelleneinsatz mobiler und leichter.
Diese Art der Anerkennung ist attraktiv, weil sie die Möglichkeit bietet,
die Kosten, die mit der Anerkennung für den einzelnen Hersteller verbunden sind, zu senken. Eine einmal durchgeführte WPS ist anerkannt,
wenn die Bereiche für alle Einflußgrößen in dem zulässigen Bereich für
das Normschweißverfahren bleiben. Dies wird unter anderem auch
durch ein programmiertes Parameterfeld in der Stromquelle gewährleistet. Für weitere Informationen verweisen wir auf die Normverfahrensprüfung.
Abb.1 Schweißanlage T.I.M.E. Synergic
6
Page 7

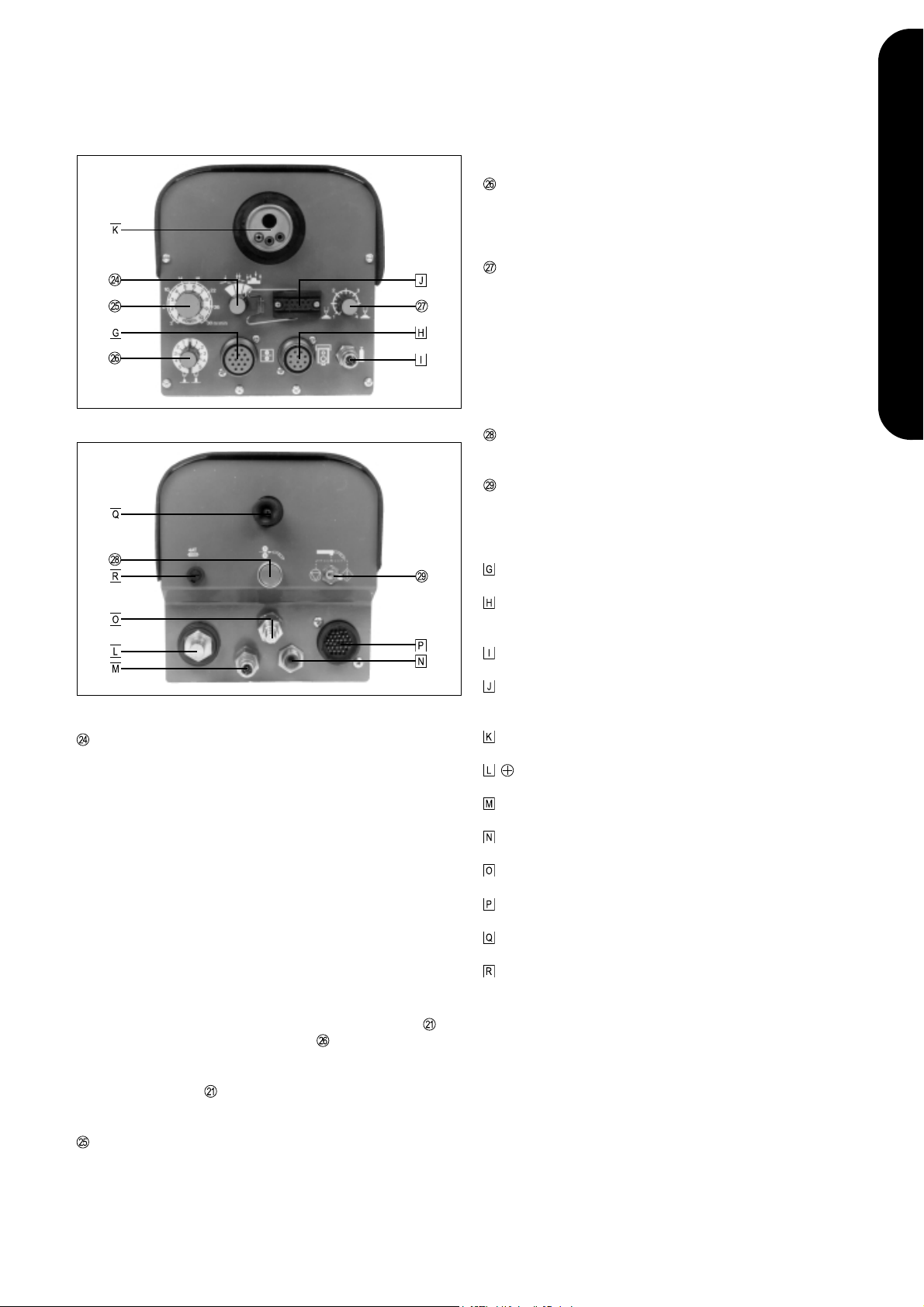
BEDIENELEMENTE UND ANSCHLÜSSE
STROMQUELLE T.I.M.E. SYNERGIC
Abb.2 Vorderseite Stromquelle T.I.M.E. Synergic
Anzeige Manuell / No Program
- leuchtet, im MIG/MAG-Manuellbetrieb (mit Fernbedienung TR 34
T.I.M.E.) ständig, wenn am Programm-Wahlschalter eine programmierte Position ausgewählt ist
- leuchtet im E-Handschweißbetrieb ständig
- blinkt, wenn am Programm-Wahlschalter eine nicht programmierte
Position ausgewählt ist
Anzeige Übergangslichtbogen ... zwischen Kurz- und Sprühlichtbogen entsteht ein spritzerbehafteter Übergangslichtbogen. Um diesen zu Vermeiden leuchtet die Anzeige Übergangslichtbogen.
Anzeige T.I.M.E. leuchtet, wenn ein T.I.M.E. Programm angewählt
ist - es gilt die Skalierung für Drahtgeschwindigkeit 0-30 m/min
Anzeige Hold ... bei jedem Schweißende werden die aktuellen IstWerte von Schweißstrom und -spannung gespeichert - die Anzeige
Hold leuchtet
Bereichsschalter m/min - mm - V ... zur Anwahl der gewünschten
Funktion
m/min.......Drahtvorschubgeschwindigkeit
mm...........Blechdicke
V...............Leerlauf- oder Schweißspannung (Volt)
Anzeige m/min - mm - V
- Drahtgeschwindigkeit (m/min) ... Sollwert im MIG/MAG-Programm-
und Manuell-Betrieb
- Blechdicke (mm) im MIG/MAG-Programmbetrieb
- Schweißspannung (V) ... Sollwert im MIG/MAG-Programmbetrieb
- Schweißspannung (V) ... Istwert im MIG/MAG-Programm- und
Manuell- sowie E-Handschweißbetrieb
- Schweißspannung (V) ... Hold-Wert im MIG/MAG-Programm- und
Manuellbetrieb
DEUTSCH
Abb.3 Rückseite Stromquelle T.I.M.E. Synergic
Netzschalter
Anzeige Betriebsbereit ... leuchtet wenn der Netzschalter auf „I“
geschaltet ist
Anzeige Übertemperatur leuchtet ...
- wenn Gerät thermisch überlastet ist
- Stecker für Kühlgerätversorgung nicht eingesteckt ist
- Kühlgerät defekt ist
- Wasserdurchfluß zu gering ist (nur mit Option Strömungswächter)
Anzeige Über- bzw. Unterspannung leuchtet ...
- wenn die Netzspannung außerhalb des Toleranzbereiches liegt
(Stromquelle schaltet ab)
- für 10 s., wenn Netzeinbrüche oder Überspannungsspitzen vorliegen (Stromquelle schaltet ab und sofort wieder ein)
Programm-Wahlschalter (0-99) dient zur Anwahl des gewünschten
Puls-, Standard- bzw. T.I.M.E. Schweißprogrammes in Abhängigkeit
von Schutzgas und Zusatzwerkstoff
Hinweis! Erscheint zusätzlich zur angezeigten Blechdicke der Buchstabe H (z. B. H12), so bedeutet dies, daß sich der angezeigte Wert trotz
Erhöhung der Schweißleistung nicht mehr nach oben verändert.
Anzeige Schweißstrom
- Sollwert im MIG/MAG-Manuell- bzw. E-Handschweißbetrieb
- Istwert im MIG/MAG-Programm- und Manuellbetrieb
- Hold-Wert im MIG/MAG-Programmbetrieb
Hinweis! Begriffsdefinition von Soll-, Ist- und Hold-Wert:
- Sollwert ist der je nach Schweißverfahren vorwählbare, und im
Leerlauf angezeigte „gewünschte“ Wert
- Istwert ist jener während der Schweißung angezeigte „tatsächliche“
Wert
- Hold-Wert ist jener nach Ende der Schweißung angezeigte „gespeicherte“ Wert.
Einstellregler P-Start ... 0 - 30 m/min (T.I.M.E.) bzw. 1 - 10 (Power)
empfohlene Einstellung T.I.M.E.: 9 m/min
- Abhängig von der Anzeige T.I.M.E. gilt die Skalierung für Drahtge-
schwindigkeit (0 - 30 m/min) bzw. Schweißleistung (1-10)
- P-Start beeinflußt die Stabilität des Lichtbogens in der Zündphase
(sichere Zündung des Lichtbogens) bzw. das Abbinden von
Schweißnähten
- In Betriebsart T.I.M.E. 4-Takt kann mittels P-Start die Start-
Drahtgeschwindigkeit eingestellt werden; der eingestellte Wert ist
absolut, d.h. der Wert ist unabhängig von der eingestellten
Schweißleistung
7
Page 8
Einstellregler P-End ... 0 - 30 m/min (T.I.M.E.) bzw. 1 - 10 (Power)
empfohlene Einstellung T.I.M.E.: 5 bzw. 9 m/min
- Abhängig von der Anzeige T.I.M.E. gilt die Skalierung für Drahtgeschwindigkeit (0 - 30 m/min) bzw. Schweißleistung (1-10)
- In Betriebsart T.I.M.E. 4-Takt kann mittels P-End die End-Drahtgeschwindigkeit eingestellt werden; der eingestellte Wert ist absolut, d.h. der Wert ist unabhängig von der eingestellten
Schweißleistung
Einstellregler Slope T.I.M.E. 4-Takt ... 0,2 - 7,0 s.
empfohlene Einstellung: 1 s.
Einstellregler Endstrom T.I.M.E. 4-Takt ... Einstellrad nicht verstellen; Einstellrad muß in Mittelstellung stehen
Taste Drahteinfädeln ... zum gas- und stromlosen Einfädeln der
Drahtelektrode in das Brennerschlauchpaket
Option Push/Pull-Abgleich ... zum Drehzahlabgleich bei Verwendung eines Push-Pull Brenners.
Programmübersichtstabelle ... gibt Aufschluß über die programmierten Puls-, Standard- und T.I.M.E.-Programme.
- [S] ... nur Standardprogramm gespeichert
- [P] ... nur Pulsprogramm gespeichert
Hinweis! Das Programm mit der Kennzeichnung „EN 288/7“ wurde im
Rahmen einer Verfahrensprüfung geschweißt und läßt nur Schweißparameter zu, welche in der Prüfung abgedeckt wurden.
MATERIAL GAS %
EN 440 G2
EN 70 S-6
EN 288/7
Fe1 (SG 2/3) CO
Fe2 (SG 2/3)
CrNi 19 9
CrNi 18 8
AlSi 5
AlMg 5
Al 99,5
Rutil
Basic
Metal
CrNi
FüllDraht/
Flux
C. Wire
T.I.M.E.
T.I.M.E. II
T.I.M.E.
2
Ar 82 CO
Ar 97,5 CO
Ar 97,5 CO
Ar 100
Ar 100
Ar 100
Ar 82 CO
Ar 82 CO2 18
Ar 82 CO
Ar 82 CO
100 S13
18
2
2,5
2
2,5
2
18
2
18
2
18
2
PROG. CODE
1,0
0,8 1,2
2 3
7
S11
S16
17
S14 S15
18 19
21 22 23 24
25 26 27
29 30 31
33 34 35
37 38 39 40
S44
S43
47
51
55 56
1,6
20
28
32
36
48
52
- Strombuchse mit Bajonettverschluß ... dient zum
- Anschluß des Verbindungsschlauchpaketes beim MIG/MAG
Schweißen
- Anschluß für das Massekabel beim WIG-Schweißen
- Anschluß für Elektroden- bzw. Massekabel bei der Elektrodenhandschweißung (je nach Elektrodentype)
- Strombuchse mit Bajonettverschluß ... dient zum
- Anschluß für das Massekabel beim MIG/MAG-Schweißen
- Stromanschluß des WIG-Schweißbrenners
- Anschluß für Elektroden- bzw. Massekabel bei der Elektrodenhandschweißung (je nach Elektrodentype)
Anschlußbuchse Steuerstecker ... Verbindungsschlauchpaket
- Buchse mit Bajonettverschluß ... Verbindungsschlauchpaket
Anschlußbuchse Kühlgerät FK71 ... zum Anschluß des Steuerstek-
kers Kühlgerät
Hinweis! Ist das Kühlgerät nicht eingesteckt, leuchtet die Anzeige
Übertemperatur an der Stromquelle. Es ist keine Schweißung möglich.
Option Gasvorwärm-Steckdose 230V / 80W ... zur elektrischen
Versorgung des Gasvorwärmers bei Verwendung von CO2 als Schutzgas
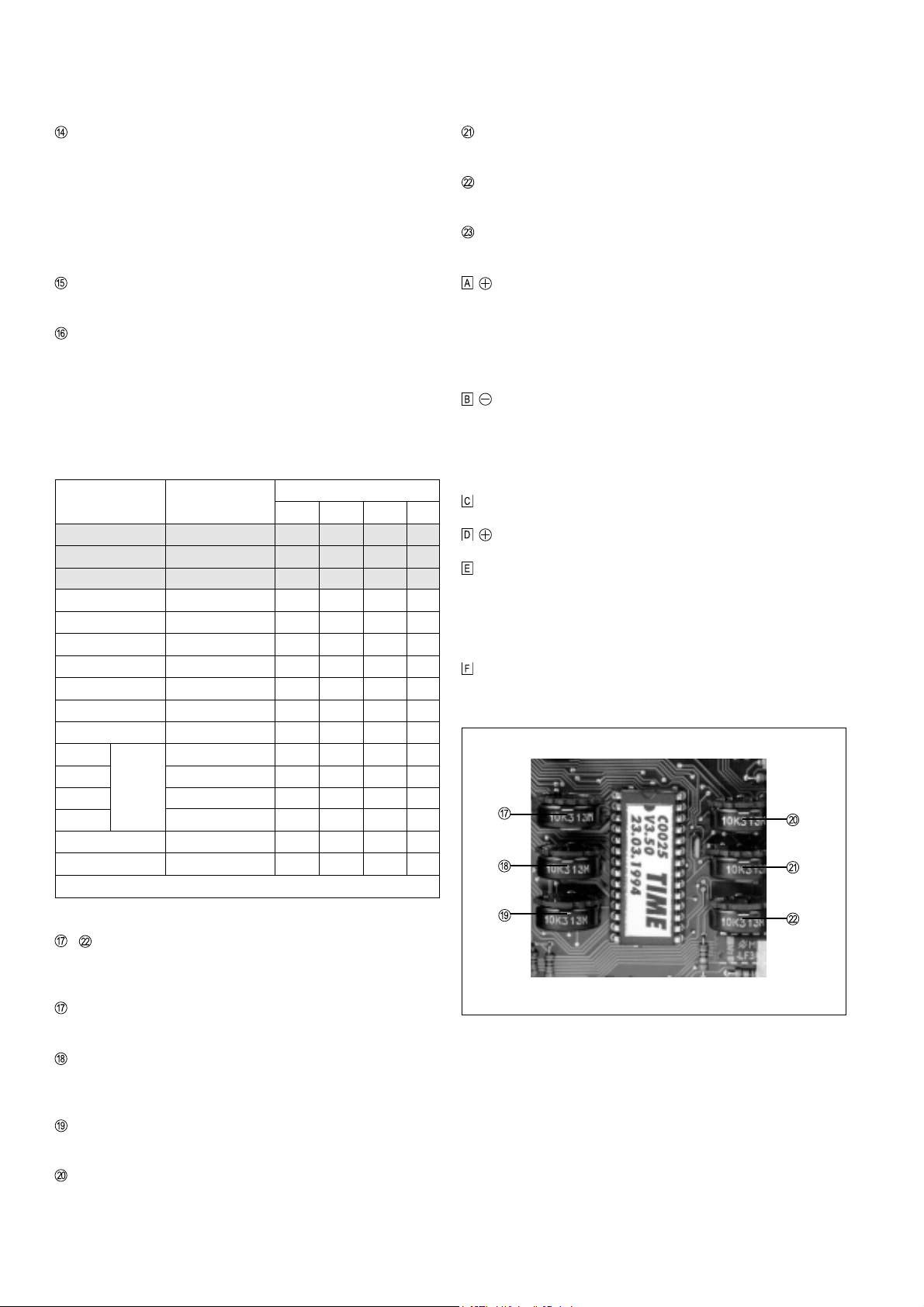
EPROM Nr.: C0027
Abb.4 Programmübersichtstabelle
- Hintergrundparameter ... entfernen Sie die Programmüber-
sichtstabelle um weitere für den Schweißprozeß maßgebliche Parameter einzustellen.
Einstellregler Gasvorströmzeit ... 0,1 - 3,0 s.
empfohlene Einstellung: 0,1 s. (Minimum)
Einstellregler Anschleichgeschwindigkeit ... Minimum bis 100%
der eingestellten Drahtgeschwindigkeit
empfohlene Einstellung: 50% (Mittel)
Einstellregler Gasnachströmzeit ... 0,5 - 4,0 s.
empfohlene Einstellung: 2 s. (Mittel)
Einstellregler Startstrom T.I.M.E. 4-Takt ... Einstellrad nicht verstellen; Einstellrad muß in Mittelstellung stehen
Abb.5 Detailansicht "Interne 4-Takt-Parameter"
8
Page 9
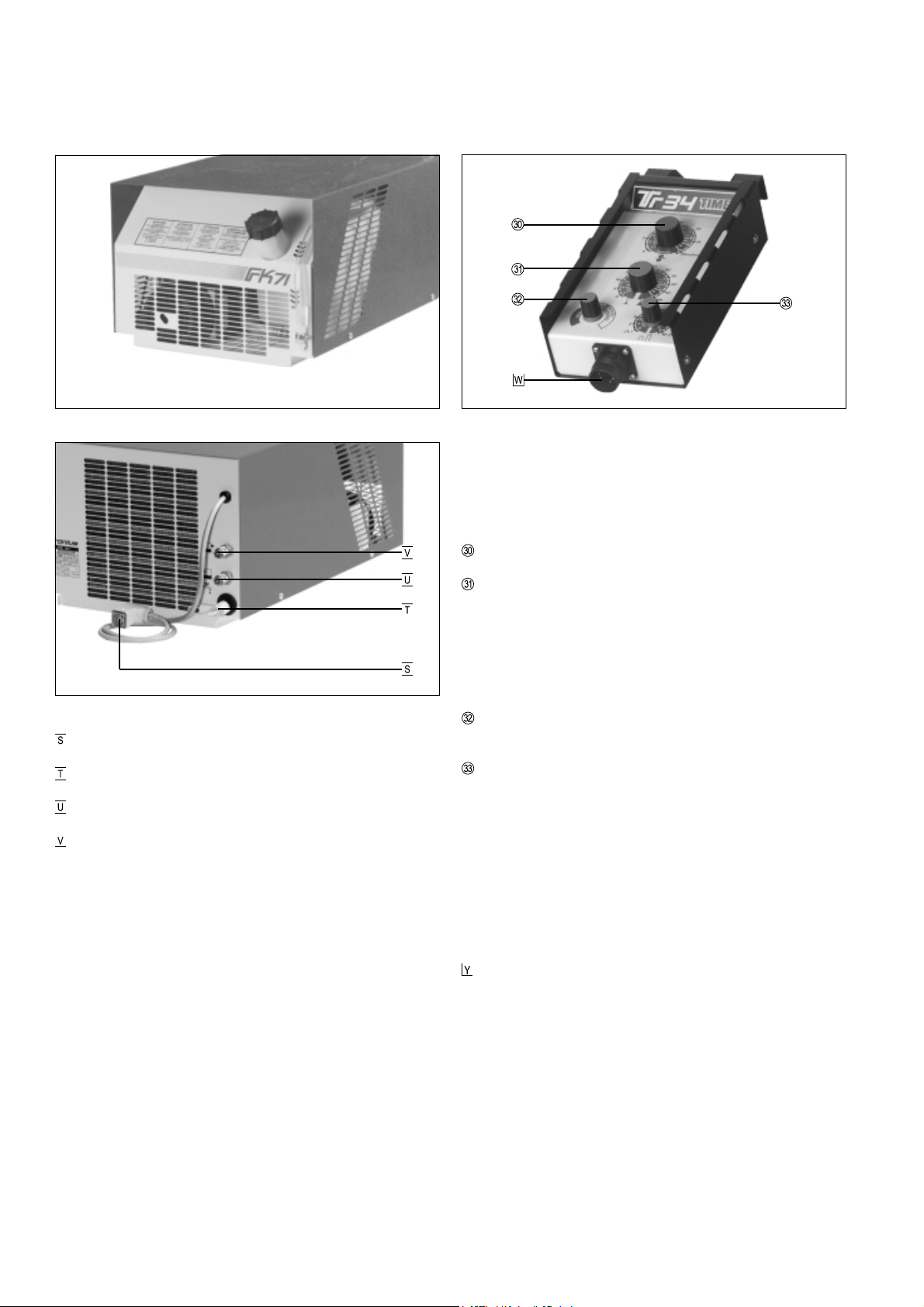
DRAHTVORSCHUB T.I.M.E. 30
Hinweis! Bei Verwenden einer nicht schweißbaren Drahtgeschwindigkeit bleibt der unterste schweißbare Wert eingestellt.
Einstellregler Lichtbogenlängenkorrektur ... zur stufenlosen Korrektur der eingestellten Lichtbogenlänge im Bereich von +/- 20%
(Anzeige des Spannungssollwertes nur im Standard/Programmbetrieb)
Abb.6 Vorderseite Drahtvorschub T.I.M.E. 30
Abb.7 Rückseite Drahtvorschub T.I.M.E. 30
Einstellregler Nachbrennzeitkorrektur
- Standard/Manuellbetrieb ... Nachbrennzeit lt. Skala im Bereich
von 1-4 (0 - 0,4 s.) stufenlos einstellbar
- Puls- und Standard/Programmbetrieb ... vor Beginn der Schweißung ist der Einstellregler auf den Skalen-Mittelwert einzustellen;
die Parameter für die Nachbrennzeit sind im jeweiligen Schweißprogramm integriert
- Einstellregler links ... minimale Tropfenbildung am Drahtende
- Einstellregler rechts ... größere Tropfenbildung am Drahtende
Taste Drahteinfädeln ... zum gas- und stromlosen Einfädeln der
Drahtelektrode in das Brennerschlauchpaket
Schalter Brenner Ein-Aus ... zum Deaktivieren der Brennertaste
(z.B. bei Krantransport)
- linke Schalterstellung ... Brennertaste deaktiviert
- rechte Schalterstellung ... Brennertaste aktiviert
Anschlußbuchse Option Zwischentrieb
Anschlußbuchse Fernbedienung ... zum Anschluß der gewünsch-
ten Fernbedienung
Anschlußbuchse Schutzgas
Anschlußbuchse Brennersteuerung ... zum Anschluß des Steuer-
steckers des Schweißbrenners
DEUTSCH
Schalter Betriebsart ... zur Anwahl der Betriebsart
- 2-Takt Betrieb
- 4-Takt Betrieb
- T.I.M.E. 4-Takt Betrieb
2-Takt Betrieb
- Drücken und Halten der Brennertaste: Schweißbeginn
- Loslassen der Brennertaste: Schweißende
4-Takt Betrieb
- Drücken und Loslassen der Brennertaste: Schweißbeginn
- Erneutes Drücken und Loslassen der Brennertaste: Schweißende
T.I.M.E. 4-Takt Betrieb ... zum Abrufen der Start-, Schweiß- und
Endstromparameter über die Brennertaste
- Drücken und Halten der Brennertaste: Schweißbeginn mit eingestelltem Startstrom (P-Start)
- Loslassen der Brennertaste: Startstrom sinkt über Slope
auf den am Schweißleistungsregler eingestellten Schweißstrom ab
- Erneutes Drücken und Halten der Brennertaste: Schweißstrom
sinkt über Slope auf den eingestellten Endstrom (P-End) ab
- Loslassen der Brennertaste: Schweißende
Einstellregler Schweißleistung (Power)
- Skala 1-10 ... zum stufenlosen Einstellen der Schweißleistung
(nur wenn Anzeige T.I.M.E. nicht leuchtet)
- Skala Drahtgeschwindigkeit 0-30m/min ... zum stufenlosen Einstellen der Drahtgeschwindigkeit (nur wenn Anzeige T.I.M.E.
leuchtet)
Brenner-Zentralanschluß ... zur Aufnahme des Schweißbrenners
- Buchse mit Bajonettverschluß ... Verbindungsschlauchpaket
Steckanschluß Wasserrücklauf ... Verbindungsschlauchpaket
Anschlußbuchse Schutzgas ... Verbindungsschlauchpaket
Steckanschluß Wasservorlauf ... Verbindungsschlauchpaket
Anschlußbuchse Steuerstecker ... Verbindungsschlauchpaket
Drahteinlauf
Sicherung Drahtvorschubmotor (4A träge)
Hinweis! Der Motor des Drahtvorschubes ist wassergekühlt. Um den
Motor zu kühlen muß der Drahtvorschub immer mit dem Kühlwasser des
Brenners verbunden sein.
9
Page 10
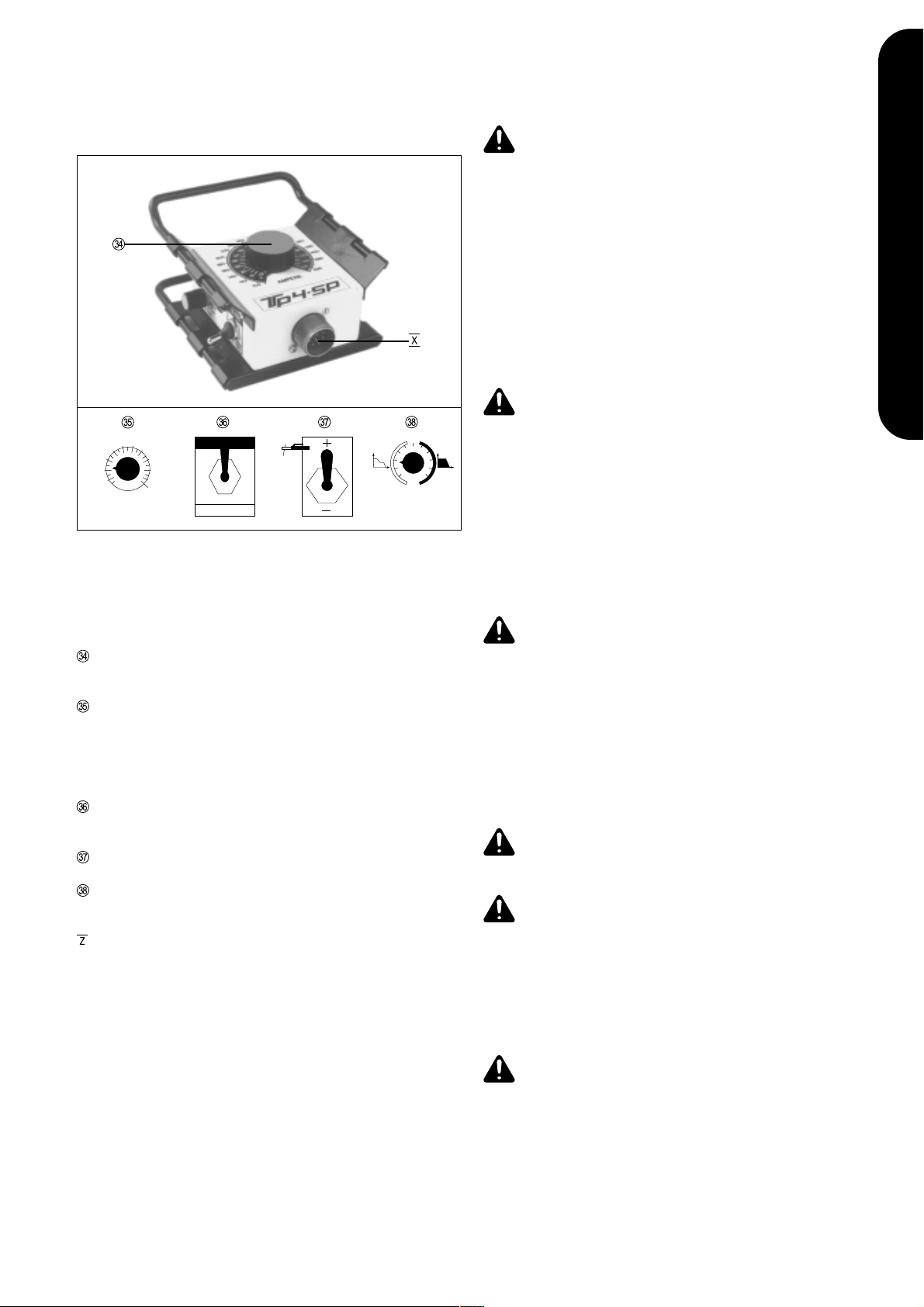
KÜHLGERÄT FK 71
FERNBEDIENUNG TR 34 T.I.M.E.
Abb.8 Kühlgerät FK 71
Abb.9 Rückseite Kühlgerät FK 71
Stecker Kühlgerätversorgung
Vorrichtung Wasserablauf
Steckanschluß Wasservorlauf (blau)
Steckanschluß Wasserrücklauf (rot)
Abb.10 Fernbedienung TR 34 T.I.M.E.
Für die Standard/Programm-, Puls/Programm- und die Standard/Manuell -Schweißung wird die Fernbedienung TR 34 T.I.M.E. benötigt.
Hinweis! Bedienelemente an der Fernbedienung haben immer Priorität;
sie bestimmen die Funktion der Anlage.
Einstellregler Schweißleistung (Power)
Einstellregler Lichtbogenlängenkorrektur
- rote Skala ... zur stufenlosen Korrektur der eingestellten Lichtbogenlänge im Bereich von +/- 20% im Puls- und Standard/Programmbetrieb
- schwarze Skala ... zur stufenlosen Einstellung der Schweißspannung im Bereich von 0 - 50 V im Standard-/Manuellbetrieb (Anzeige No Program leuchtet)
Schalter Betriebsart ... zur Vorwahl der gewünschten Betriebsart
bei der MIG/MAG-Schweißung
Einstellregler Tropfenablöse- bzw. Dynamikkorrektur
- rote Skala ... stufenlose Korrekturmöglichkeit der Tropfenablöseenergie
links ... geringere Tropfenablösekraft
neutral ... neutrale Tropfenablösekraft
rechts ... erhöhte Tropfenablösekraft
- schwarze Skala ... zur Beeinflussung der Kurzschlußdynamik im
Moment des Tropfenüberganges
links ... härterer und stabilerer Lichtbogen
neutral ... neutraler Lichtbogen
rechts ... weicher und spritzerarmer Lichtbogen
Anschlußbuchse Fernbedienkabel
10
Page 11
STROMQUELLE IN BETRIEB NEHMEN
FERNBEDIENUNG TP 4 SP
50
60
40
30
20
10
0
Abb.11 Fernbedienung TP 4 SP
Hot Start
70
80
90
100
T
3-150
100-450
Hinweis! Bedingt durch die Kennlinie können mit der T.I.M.E. Synergic
keine CEL-Elektroden verschweißt werden.
Einstellregler Schweißstrom ... zum stufenlosen Einstellen des
Schweißstromes in den Bereichen 3-150A bzw. 100-450A
Einstellregler Hot-Start ... 0 - 100% des eingestellten Schweißstrom; nur wirksam in der Zündphase der Elektrode
Hinweis! Der maximale Hot-Start Gesamtstrom wird automatisch durch
den Kurzschlußstrom begrenzt.
0
1
1
2
2
3
B
3
4
CEL
4
5
5
Achtung! Vor Erstinbetriebnahme das Kapitel „Sicherheitsvorschriften“ lesen.
BESTIMMUNGSGEMÄSSE VERWENDUNG
Das Schweißgerät ist ausschließlich zum MIG/MAG-, Elektroden- und
WIG-Schweißen bestimmt.
Eine andere oder darüber hinausgehende Benutzung gilt als nicht
bestimmungsgemäß. Für hieraus entstehende Schäden haftet der Hersteller nicht.
Zur bestimmungsgemäßen Verwendung gehört auch
- das Beachten aller Hinweise aus der Bedienungsanleitung
- die Einhaltung der Inspektions- und Wartungsarbeiten
Achtung! Das Schweißgerät nie zum Auftauen von Rohren
verwenden.
AUFSTELLBESTIMMUNGEN
Das Schweißgerät ist nach Schutzart IP21 geprüft, das bedeutet:
- Schutz gegen Eindringen fester Fremdkörper größer Ø 12mm
- Schutz gegen senkrecht fallende Wassertropfen
Die Schweißanlage kann, gemäß Schutzart IP21, im Freien aufgestellt
und betrieben werden. Die eingebauten elektrischen Teile sind jedoch
vor unmittelbarer Nässeeinwirkung zu schützen.
Achtung! Schweißanlage auf ebenem und festen Untergrund
standsicher aufstellen. Eine umstürzende Schweißanlage kann
Lebensgefahr bedeuten.
Der Lüftungskanal stellt eine wesentliche Sicherheitseinrichtung dar.
Bei der Wahl des Aufstellort ist zu beachten, daß die Kühlluft ungehindert
durch die Luftschlitze an Vorder- und Rückseite ein- bzw. austreten
kann. Anfallender metallischer Staub (z.B. bei Schmirgelarbeiten) darf
nicht direkt in die Anlage gesaugt werden.
DEUTSCH
Bereichsschalter ... unterteilt den Gesamtschweißbereich der Anlage in zwei sich überschneidende Einzelbereiche
Polumschalter ... keine Funktion
Einstellregler Dynamik ... zur Beeinflussung der Kurzschlußdyna-
mik im Moment des Tropfenüberganges
Anschlußbuchse Fernbedienkabel
NETZSTECKER ANSCHLIESSEN
Achtung! Netzstecker müssen der Netzspannung und der Stromaufnahme des Schweißgerätes entsprechen (siehe Technische
Daten)
Achtung! Die Absicherung der Netzzuleitung ist den Technischen Daten zu entnehmen.
NETZANSCHLUSS
Die Schweißanlage ist für die am Leistungsschild angegebene Netzspannung ausgelegt. Die Absicherung der Netzzuleitung ist den Technischen Daten zu entnehmen.
Achtung! Die Stromquelle ist ab Werk auf 400V geschaltet!
Bedingt durch den Toleranzbereich von +/- 10% kann die Stromquelle auch am 3x380V~ Netz betrieben werden. Bei Störungen
Unter- bzw. Überspannung muß der Spannungsbereich durch
Umstecken der Steckverbindung angepaßt werden.
Bei einer Netzspannung von 3x230V~, 3x440V~ oder 3x500V~ ist ein
FRONIUS-Vorschalttrafo zu verwenden. Dieser ist jederzeit nachrüstbar
und kann zwischen Fahrwagen und Stromquelle montiert werden. Auf
Sonderwunsch kann die Stromquelle auch für 3x440V~ oder 3x500V~
ausgelegt werden.
11
Page 12
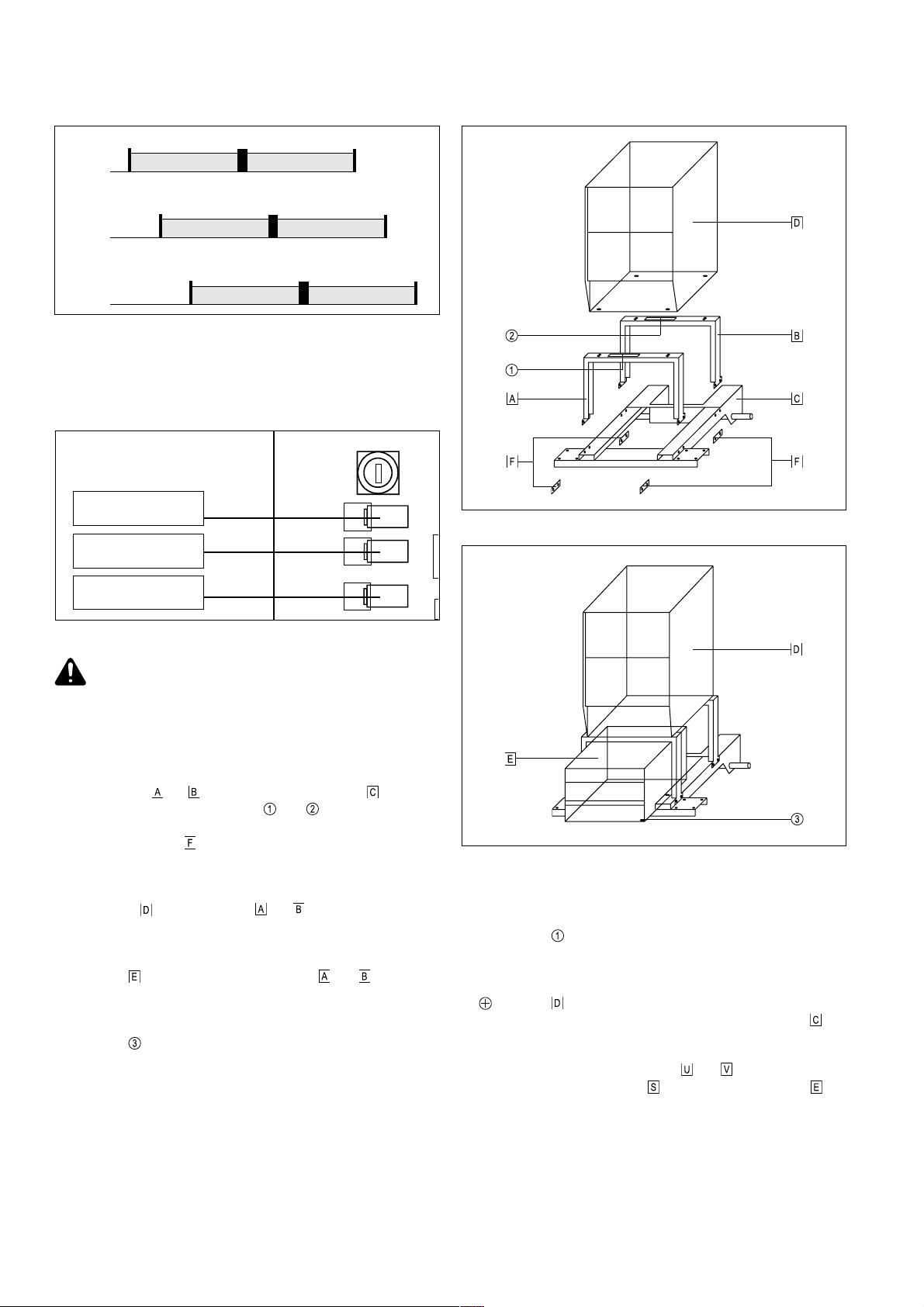
380V
342V
-10%
380V
418V
+10%
360V
400V
415V
Abb.12 Toleranzbereiche der Netzspannungen 3x380V / 400V / 415V~
-10%
373V
400V
+10%
415V
-10%
440V
456V
+10%
Das Schweißgerät kann serienmäßig mit einer Netzspannung von 3x380
V~, 3x400 V~ oder 3x415 V~ betrieben werden, sofern der Steuertrafo
auf den, für die anliegende Betriebsspannung richtigen Wert geschaltet
ist.
Steckverbindung X7 für
Netz-Umschaltung 400V~
Steckverbindung X6 für
Netz-Umschaltung 415V~
Steckverbindung X8 für
Netz-Umschaltung 380V~
Abb.13 Netzumschaltung 3x380V / 400V / 415V~ am Steuertrafoprint VM 34.
Abb.14 Montage der Stromquelle
Achtung! Ist das Gerät für eine Sonderspannung ausgelegt,
gelten die Technischen Daten am Leistungsschild. Netzstecker,
Netzzuleitung sowie deren Absicherung sind entsprechend auszulegen.
STROMQUELLE ZUSAMMENBAUEN
- Montagebügel und von oben auf Fahrwerkrahmen so aufstekken, daß sich die Ausnehmungen und beider Montagebügel
links oben befinden
- Befestigungsbleche (komplett mit montierten Käfigmuttern) wie
aus nachfolgender Abbildung ersichtlich, von rückwärts einlegen und
mittels Stahlschrauben M8 x 20, versehen mit Beilagen und Sprengringen vorerst locker verschrauben.
- Stromquelle auf Montagebügel und aufsetzen und von unten
mit 4 Stk. Stahlschrauben M8 x 16, kompl. mit Beilagen und Sprengringen festschrauben.
- Beide Montagebügel am Fahrwerkrahmen festschrauben
- Kühlgerät von vorne durch Montagebügel und einschieben
und positionieren (rückwärtige Führungslasche unterhalb einschieben).
- Die Fixierung wird, wie aus nachfolgender Abbildung ersichtlich, nur
am Punkt vorgenommen (Stahlschraube M8 x 16 von unten, mit
Beilage und Sprengring).
Abb.15 Montage der Stromquelle
VERBINDUNGSSCHLAUCHPAKET MIT
STROMQUELLE / KÜHLGERÄT VERBINDEN
- Netzschalter in Stellung „O“
- Zugentlastung des Verbindungsschlauchpaketes mittels vorhandener Schraube fixieren
- Bajonettstecker Schweißpotential des Verbindungsschlauchpaket an
- Buchse anstecken und durch Drehen verriegeln
- 37-poligen Steuerstecker in Anschlußbuchse Steuerstecker einstecken und Überwurfmutter festschrauben
- Schlauch Wasservor- und rücklauf des Verbindungsschlauchpaket
farbrichtig an den Steckanschlüssen und anstecken
- Stecker Kühlgerätversorgung mit der Anschlußbuchse der
Stromquelle verbinden.
Hinweis! Ist das Kühlgerät nicht eingesteckt, leuchtet die Anzeige
Übertemperatur an der Stromquelle. Es ist keine Schweißung möglich.
12
Page 13

VERBINDUNGSSCHLAUCHPAKET MIT
DRAHTVORSCHUB VERBINDEN
- Netzschalter in Stellung „O“
- Drahtvorschub (mit eingepreßter Isolierhülse) auf den Aufnahmezapfen der Stromquelle aufsetzen
- Schelle der Zugentlastung lockern und Verbindungsschlauchpaket
seitenrichtig bis zum Metallklemmrohr des Schutzschlauches durchziehen
Hinweis! Leitungen nicht kreuzen oder knicken
- Bajonettbuchse Schweißpotential des Verbindungsschlauchpaket an
Buchse anstecken und durch Drehen verriegeln
- 37-poligen Steuerbuchse in Anschlußbuchse Steuerstecker einstecken und Überwurfmutter festschrauben
- Gasschlauch des Verbindungsschlauchpaket an Anschlußbuchse
Schutzgas anstecken und mit Überwurfmutter festziehen
Hinweis! Zuvor kontrollieren ob Dichtungs-O-Ringe eingelegt sind
Hinweis! Nur sauberes Leitungswasser verwenden. Andere Frostschutz-
mittel sind wegen ihrer elektrischen Leitfähigkeit nicht zu empfehlen.
Achtung! Da Fronius auf Faktoren wie Qualität, Reinheit und
Füllstand der Kühlflüssigkeit keinen Einfluß hat, wird für die
Kühlmittelpumpe keine Garantie übernommen.
Außentemperatur Mischverhältnis Wasser : Spiritus
DEUTSCH
+ °C bis -5°C 4 l : 1 l
-5°C bis -10°C 3,75 l : 1,25 l
-10°C bis -15°C 3,5 l : 1,5 l
-15°C bis -20°C 3,25 l : 1,75 l
Achtung! Der Wasserdurchfluß muß im Betrieb in regelmäßigen
Abständen kontrolliert werden - ein einwandfreier Rückfluß muß
ersichtlich sein.
- Schlauch Wasservor- und rücklauf des Verbindungsschlauchpaket
farbrichtig an den Steckanschlüssen und anstecken und mit
Überwurfmutter festziehen
- Schelle der Zugentlastung festschrauben
GASFLASCHE MONTIEREN / ANSCHLIESSEN
- Gasflasche auf Fahrwagenboden des Fahrwagens aufsetzen
- Gasflasche mit Sicherungskette fixieren
Hinweis! Optimale Fixierung nur im oberen Teil der Gasflasche (nicht
am Flaschenhals)
- Schutzkappe der Gasflasche entfernen
- Gasflaschenventil kurz nach links drehen um umliegenden Schmutz
zu entfernen
- Dichtung am Druckminderer überprüfen
- Druckminderer auf Gasflasche aufschrauben und festziehen
- Anschluß Schutzgas des Verbindungsschlauchpakets mittels Gasschlauch mit dem Druckminderer verbinden
SCHWEISSBRENNER MONTIEREN
- Netzschalter in Stellung „O“
- Richtig ausgerüsteten Schweißbrenner mit dem Einlaufrohr voran in
den Brenner-Zentralanschluß einschieben
- Überwurfmutter zur Fixierung von Hand festziehen
- Steuerstecker des Schweißbrenners am Anschluß Brennersteuerung einstecken und verriegeln
- Gasschlauch des Schweißbrenners in das Gasanschlußstück einstecken und verriegeln
KÜHLGERÄT IN BETRIEB NEHMEN
Hinweis! Vor jeder Inbetriebnahme des Kühlgerätes Kühlflüssigkeitsstand sowie Reinheit der Kühlflüssigkeit kontrollieren. Werkseitig ist das
Kühlgerät mit ca. 2l Kühlflüssigkeit (Mischverhältnis von 1:1) gefüllt.
- Netzschalter in Stellung „O“
- Schraubkappe entfernen
- Kühlflüssigkeit einfüllen (Mischverhältnis lt. nachfolgender Tabelle)
- Schraubkappe wieder anbringen
Bei erschwerten Bedingungen (große Schlauchpaketlängen, große Höhenunterschiede, etc.) sollten Sie das Kühlgerät FK 71 R mit einer
Kühlleistung von 2,6 kW und einem Pumpendruck von 4,4 bar verwenden.
DRAHTSPULE EINSETZEN
Achtung! Die Drahtspulenaufnahme dient nur zur Aufnahme
und Sicherung von genormten Schweißdrahtrollen bis max. 20
kg.
- Netzschalter
- Drahtspulenabdeckung öffnen
- Drahtspule auf Drahtspulenaufnahme seitenrichtig aufsetzen
- Arretierbolzen in vorgesehene Öffnung am Spulenkörper einrasten
- Bremswirkung mittels Spannschraube einstellen
- Drahtspulenabdeckung wieder schließen
Hinweis! Bremse so einstellen, daß die Drahtspule nach Schweißende
nicht nachläuft - Spannschraube jedoch wegen möglicher Überlastung
des Motors nicht übermäßig festziehen.
in Stellung „O“
DRAHTELEKTRODE EINLAUFEN LASSEN
- Netzschalter in Stellung „O“
- Drahtspulenabdeckung öffnen
- Spannvorrichtungen und nach vorne schwenken
- Druckhebel und nach oben klappen
- Drahtelektrode über das Einlaufrohr des 4-Rollenantriebes etwa 5
cm in das Einlaufrohr des Schweißbrenners schieben
- Druckhebel und nach unten klappen
- Spannvorrichtungen und in senkrechte Position schwenken
- Mittels Spannmuttern und Anpreßdruck einstellen
Hinweis! Anpreßdruck so einstellen, daß die Drahtelektrode nicht deformiert wird, jedoch ein einwandfreier Drahttransport gewährleistet ist.
- Brennerschlauchpaket möglichst geradlinig auslegen
- Gasdüse am Schweißbrenner abziehen
- Kontaktrohr abschrauben
- Netzstecker einstecken
- Netzschalter in Stellung "I" schalten
- Netzkontrolleuchte leuchtet
- Programm-Wahlschalter in gewünschte Position schalten (Anzeige No Program darf nicht leuchten)
13
Page 14
MIG/MAG-SCHWEISSEN
- Bereichsschalter für Digitalanzeigen in Stellung m/min schalten
- Mit Einstellregler Schweißleistung eine Wert von ~ 5 m/min
einstellen
Achtung! Während des Drahteinfädelns Schweißbrenner vom
Körper weg halten.
- Taste Drahteinfädeln drücken bis die Drahtelektrode aus dem
Brenner herausragt
- Einfädel-Vorgang durch Loslassen der Taste Drahteinfädeln beenden
Hinweis! Nach Loslassen der Brennertaste soll die Drahtspule nicht
nachlaufen. Gegebenenfalls Bremse nachjustieren.
- Kontaktrohr einschrauben
- Gasdüse aufsetzen
- Drahtspulenabdeckung schließen
- Netzschalter in Stellung „O“ schalten
Achtung! Vor Erstinbetriebnahme das Kapitel „Sicherheitsvorschriften“ sowie „Stromquelle in Betrieb nehmen“ lesen.
- Massekabel in Strombuchse einstecken und verriegeln
- Mit anderem Ende des Massekabels Verbindung zum Werkstück
herstellen
- Netzstecker einstecken
- Netzschalter einschalten
- Netzkontrolleuchte leuchtet
Achtung! Wassergekühlte Anlagen: Der Wasserdurchfluß muß
im Betrieb in regelmäßigen Abständen kontrolliert werden - ein
einwandfreier Rückfluß muß ersichtlich sein.
- Schweißprogramm mit Programm-Wahlschalter vorwählen (Anzeige No Program darf nicht aufleuchten oder blinken)
Hinweis! Sämtliche Programme wurden mit einem Standardbrenner
geschweißt (außer T.I.M.E.-Programme). Bei der Schweißung von Standardprogrammen mit T.I.M.E.-Brenner kann dies daher zu Veränderung
der Schweißeigenschaften führen.
- Schalter Betriebsart am Drahtvorschub in gewünschte Position
schalten
- Fernbedienung an Anschlußbuchse Fernbedienung anschließen
(für die Pulsschweißung die Fernbedienung TR 34 T.I.M.E. anschließen. Schalter Betriebsart an der Fernbedienung TR 34 T.I.M.E. auf
Pulsschweißung stellen)
- Einstellregler Lichtbogenlängenkorrektur auf „0“ stellen
- Einstellregler Tropfenablösekorrektur auf „0“ stellen
- gewünschte Stromstärke mittels Einstellregler Schweißleistung
einstellen (Sollwertanzeige an der Anzeige Stromstärke)
- Gasflaschenventil öffnen
- Gasmenge einstellen
- Brennertaste drücken und Schweißvorgang einleiten
Abb.16 4-Rollenantrieb
VORSCHUBROLLEN WECHSELN
Um eine optimale Förderung der Drahtelektrode zu gewährleisten müssen die Vorschubrollen dem zu verschweißendem Drahtdurchmesser
sowie der Drahtlegierung angepaßt sein.
- Netzschalter in Stellung „O“
- Drahtspulenabdeckung öffnen
- Spannvorrichtungen und nach vorne schwenken
- Druckhebel und nach oben klappen
- Steckachsen - herausziehen
- Vorschubrollen - entfernen
- Neue Vorschubrollen einlegen
Hinweis! Vorschubrollen so einlegen, daß die Bezeichnung für den
Drahtdurchmesser lesbar ist.
- Steckachsen - wieder einschieben - Verdrehsicherung der
Steckachse muß einrasten
- Druckhebel und nach unten klappen
- Spannvorrichtungen und in senkrechte Position schwenken
- Mittels Spannmuttern und Anpreßdruck einstellen
- Drahtspulenabdeckung schließen
Hinweis! In manchen Fällen ist es notwendig die Gasvor- bzw.
Gasnachströmzeit und/oder Anschleichgeschwindigkeit zu korrigieren.
EINSTELLRICHTLINIEN FÜR DEN T.I.M.E.-PROCESS
Durch die Einknopf-Bedienung der T.I.M.E. Synergic ist nur die entsprechende Drahtgeschwindigkeit einzustellen; die Schweißspannung stellt
sich automatisch ein. Lediglich die Lichtbogenlänge ist entsprechend zu
korrigieren.
Berechnung der Abschmelzleistung
Diese Formel gilt nur für einen Drahtdurchmesser von 1,2 mm und unund niedriglegierte Stahldrähte. Spritzerverluste sind nicht berücksichtigt (typisch 1 - 2 %).
Abschmelzleistung [kg/h] =
z.B. Drahtgeschwindigkeit = 20m/min
Abschmelzleistung [kg/h] =
Drahtgeschwindigkeit [m/min] x 60 x 8,9
1000
20 m/min x 60 x 8,9
1000
= 10,68 kg/h
14
Page 15
WIG-SCHWEISSEN
Berechnung der Schweißgeschwindigkeit
Diese Formel gilt nur für einen Drahtdurchmesser von 1,2 mm und unund niedriglegierte Stahldrähte. Spritzerverluste (typisch 1 - 2 %) sowie
Geometrieabweichungen wie Wurzelspalte und Nahtüberhöhungen (typisch 10 - 20 % niedrigere Geschwindigkeit) sind nicht berücksichtigt.
Schweißgeschwindigkeit [cm/min] =
Drahtgeschwindigkeit [m/min] x 1,13 x 100
Nahtquerschnittsfläche [mm
2
]
z.B. Kehlnaht a 6 (Kehlnaht a 6 hat eine Nahtquerschnittsfläche von 36
mm2) und Drahtgeschwindigkeit von 20m/min
Schweißgeschwindigkeit [cm/min] =
20 m/min x 1,13 x 100
36 mm
2
= 62,8 cm/min
Da bei Mehrlagenschweißung die Raupenquerschnitte schwierig zu
bestimmen sind, wird die Berechnung der Schweißgeschwindigkeit sehr
aufwendig. Ein Planimeter oder Millimeterpapier leistet hier wertvolle
Dienste. Einstellwerte für Nahtart, Schweißposition und Nahtdicke siehe
nachfolgend.
EINSTELLWERTE FÜR NAHTART,
SCHWEISSPOSITION UND NAHTDICKE
Stumpfnähte
Kehlnähte
VARIANTE I
Benötigt werden die Fernbedienung TP 4-SP und das WIG-Set (HandSchweißbrenner AL 22-S / AL 16-S mit Gasschlauch, Gasdruckminderer
und Ersatzteilbox).
Hinweis! Bei dieser Variante des WIG-Schweißens verursacht die Werkstückberührung einen Kurzschlußstrom, dessen Höhe dem eingestellten
Schweißstrom entspricht. Zündvorgänge ab 10 A haben durchwegs eine
Beschädigung von Werkstückoberfläche und Wolframelektrodenspitze
zur Folge und beeinträchtigen die Schweißnahtqualität durch Wolframeinschlüsse.
- Die Zündung des Schweißlichtbogens erfolgt durch Werkstückberührung der Wolframelektrode.
- Um den Schweißvorgang zu unterbrechen einfach den Schweißbrenner vom Werkstück abheben, bis der Lichtbogen erlischt. Endkraterfüllung durch Stromabsenkung bzw. Gasschutz des Endkraters sind
nicht gegeben.
DEUTSCH
Wannenlage
- Wurzelschweißung
unregelmäßige Spalten und
Spaltbreiten über 2mm: 2,5 4,5m/min
gleichmäßige Spalten von 2mm:
9m/min
- Füllagen
unterer Bereich: 12-15m/min
oberer Bereich: 15-23m/min
- Decklagen: 15-18m/min
Querposition
- Wurzelschweißung
unregelmäßige Spalten und
Spaltbreiten über 2mm: 2,5 4,5m/min
gleichmäßige Spalten von 2mm:
9m/min
- Füllagen: 12 - 18m/min
- Decklagen: 9 - 12m/min
Überkopfnaht
- Wurzelschweißung: 3 - 4m/min
- Füllagen: 9 - 11m/min
- Decklagen: 9 - 11m/min
Steignaht: 3 - 6m/min
Fallnaht: 9 - 11m/min
Horizontalposition
- a3: 12 - 14m/min
- a4: 12 - 16m/min
- a5: 15 - 18m/min
- a6: 18 - 23m/min
- a7: 20 - 23m/min
- ab a8 nur mehrlagig 20 - 23m/min
- Kerbraupe mit 10 - 12m/min
Überkopfposition
- 9 - 11m/min für alle Nahtdicken
und ein- oder mehrlagige
Schweißnähte
Fallnaht
- 9 - 11m/min; maximal a3,5 in
einer Lage schweißen,
- dickere Nähte mehrlagig
Steignaht
- 4 - 6m/min; minimale Nahtdicke
a6
Wannenlage
- a3: 12 - 14m/min.
- a4: 12 - 14m/min.
- a5: 17 - 23m/min.
- a6: 17 - 23m/min.
- ab a7: 22 - 30m/min.
Abb.17 WIG-Set
VARIANTE II
Benötigt werden die Fernbedienung TP 4-SP, die Fußfernbedienung TR
52-1 ein Signalverteiler sowie das WIG-Set (Handschweißbrenner AL
22-S / AL 16-S mit Gasschlauch, Gasdruckminderer und Ersatzteilbox).
Bei Verwenden dieser Kombination bieten sich folgende Vorteile:
- Reduktion des Schweißstromes im Moment der Werkstückberührung
mittels Fußfernbedienung
- Endkraterfüllung durch Stromabsenkung mittels Fußfernbedienung
(langsames Entlasten des Fußpedals bewirkt ein Absenken des
Schweißstromes auf ca. 10 A) möglich - optimaler Gasschutz gewährleistet
- Schweißstrombegrenzung mittels Schweißstromregler am Fernbedienung TP 4-SP - einerseits steht immer der gesamte Pedalweg für
den gewählten Bereich zur Verfügung, andererseits kann z.B. eine
dünne Wolframelektrode bei Durchtreten des Pedals bis zum Anschlag nicht überlastet werden bzw. abschmelzen.
Abb.18 Signalverteiler
15
Page 16

- Schweißbrenner anheben und in Normallage schwenken - Lichtbogen zündet (siehe Abbildung c)
- Schweißung durchführen
Abb.19 Fußfernbedienung TR 52-1
INBETRIEBNAHME
- Netzstecker ausstecken
- Netzschalter in Stellung "0" schalten
- MIG/MAG-Schweißbrenner abmontieren
- Stromstecker des WIG-Schweißbrenners in - Strombuchse einstecken und durch Drehen nach rechts verriegeln
- Stromstecker des Massekabels in - Strombuchse einstecken und
durch Drehen nach rechts verriegeln
- Schweißbrenner bestücken (siehe Bedienungsanleitung Schweißbrenner)
- Masseverbindung mit Werkstück herstellen
- Druckregler an der Schutzgasflasche befestigen
- Gasschlauch mit Druckregler verbinden
- Gasflaschenventil öffnen
- Variante I: Fernbedienung TP 4-SP an Buchse des Drahtvorschub
T.I.M.E. 30 anschließen
- Variante II: Fernbedienkombination TP 4-SP, Signalverteiler und TR
52-1 an Buchse des Drahtvorschub T.I.M.E. 30 anschließen
Achtung! Sobald der Netzschalter in Stellung "I" geschaltet ist,
ist die Wolframelektrode spannungsführend. Beachten Sie, daß
die Wolframelektrode zu diesem Zeitpunkt keine elektrisch leitenden oder geerdeten Teile wie z.B. Werkstück, Gehäuse, etc.
berührt.
a) Gasdüse aufsetzen b) Zünden durch
Werkstückberührung
Abb.20 Brenneranstellung
c) Lichtbogen gezündet
E-HANDSCHWEISSEN
- Netzstecker ausstecken
- Netzschalter in Stellung "O" schalten
- MIG/MAG Schweißbrenner abmontieren
- Schweißkabel je nach Elektrodentype in Strombuchse einstecken
und durch Drehen nach rechts verriegeln
- Fernbedienung TP 4-SP an Buchse des Vorschubgerätes T.I.M.E.
30 anschließen
- Netzstecker einstecken
Achtung! Sobald der Netzschalter in Stellung "I" geschaltet
ist, ist die Stabelektrode spannungsführend. Beachten Sie, daß
die Stabelektrode zu diesem Zeitpunkt keine elektrisch leitenden
oder geerdeten Teile wie z.B. Werkstück, Gehäuse, etc. berührt.
- Netzschalter in Stellung "I" schalten
- Anzeige Betriebsbereit leuchtet
- Schweißbereich mit Bereichsschalter am TP 4-SP auswählen
- Schweißstrom mit Einstellregler Schweißstrom am TP 4-SP auswählen
- Dynamik mit Einstellregler Dynamik am Fernbedienung TP 4-SP
auswählen
- Hot-Start mit Einstellregler Hot-Start am Fernbedienung TP 4-SP
auswählen
- Schweißung durchführen
- Netzstecker einstecken
- Netzschalter in Stellung "I" schalten
- Anzeige Betriebsbereit leuchtet
- Gasabsperrventil am Schweißbrenner öffnen bzw. Brennertaste drükken und am Druckregler die gewünschte Gasmenge einstellen
- Einstellregler Dynamik am Fernbedienung TP 4-SP auf Skalenwert "0" stellen
- Einstellregler Hot-Start am Fernbedienung TP 4-SP auf Skalenwert "0" stellen
- Schweißbereich mit Bereichsschalter am TP 4-SP auswählen
- Schweißstrom mit Einstellregler Schweißstrom am Fernbedienung TP 4-SP einstellen oder wie in Variante II beschrieben begrenzen
- Gasdüse an der Zündstelle aufsetzen, sodaß zwischen Wolframspitze und Werkstück 2-3 mm Abstand bestehen (siehe Abbildung a)
- Schweißbrenner langsam aufrichten bis die Wolframnadel das Werkstück berührt (siehe Abbildung b)
ROBOTERSCHWEISSEN
Die Stromquelle T.I.M.E. Synergic ist in Verbindung mit den Komponenten Roboterinterface TSST 153, Zwischenschlauchpaket, Kühlgerät FK71
und Robotervorschub VR 153 für die Roboterschweißung geeignet
Drahtvorschubgerät VR 153
- spezial drehzahlgeregelter Vorschubmotor gewährleistet eine exakte Drahtvorschubgeschwindigkeit
- Option Push-Pull-Brenner
- Drahteinschleich- und Gasprüftaste direkt am Drahtvorschubgerät
16
Page 17
Roboterinterface TS ST 153
- Einstellschraube der Ansprechgasmenge für die Gasmangelerkennung
- Einstellpotentiometer für Abbrandkorrektur
- Einstellpotentiometer für Tropfenablösekorrektur
- Anzeige des Zustandes der „Ein- und Ausgangssignale“ sowie der
Spannungsversorgungen und Sollwerte mittels Leuchtdioden.
Verbindungsschlauchpaket
- in den Längen 4m bzw. 8m erhältlich
Kühlgerät FK71
- Schweißbetrieb ist nur bei angestecktem Kühlgerät FK71 möglich
Detailierte Hinweise entnehmen Sie bitte den entsprechenden Bedienungsanleitungen.
Stromquelle T.I.M.E. Synergic
Kühlgerät FK 71 mit Wasserwächter
Roboterinterface
Robotersteuerung
Roboter
VR 153 T.I.M.E. mit einstellbarem Gaswächter
T.I.M.E.-Maschinenbrenner
Verbindungsschlauchpaket VR153, 4/8m
Verbindungskabel Stromquelle / Roboter, 8m
Programmierfernbedienung TR 23P
PARAMETERBESCHREIBUNG
00 ...SMS-Software-Versionsanzeige
01 ...SMS-Print-Versionsanzeige
02 ...NMI-Print-Versionsanzeige
03 ... Anzeige der DIP-Schalterstellung, TPS 330 / 450
04 ... Anzeige der DIP-Schalterstellung, TPS / TS
05 ... Anzeige der DIP-Schalterstellung, DYN - KORR.
06 ... Anzeige der DIP-Schalterstellung, VR 22m / 30m
07 ... Anzeige der DIP-Schalterstellung, Kühlgerätautomatik
08 ...Eingangs-Leitspannungstest
09 ... VR - Auto-Test
12 ...Schweißkreis-Induktivitäts-/Widerstandsmessung
16 ... VR - MIN.-Justierhilfe
17 ... VR - MAX.-Justierhilfe
18 ... VR - Linearitätskontrolle bei 15m/min bzw. 11 m/min
19 ... VR - Schlupftest
20 ... VR - Motorstrom-Anzeige
21 ...Hallshunt-Test
22 ... Test der Spannungsmessung
24 ... RTC - Jahres - Einstellung
25 ... RTC - Monats - Einstellung
26 ... RTC - Datums - Einstellung
27 ... RTC - Wochentag - Einstellung
28 ... RTC - Stunden - Einstellung
29 ... RTC - Minuten - Einstellung
30 ... RTC - Sekunden - Einstellung
32 ... Auswahl der Landessprache (D/E)
33 ... Auswahl der Druckoption
34 ... Einstellung der Bauteilintervalle für Ausdruck
35 ... Einstellung der Intervallzeit: Minuten
36 ... Einstellung der Intervallzeit: Sekunden
40 ... Einstellung für Grenzwertabschaltung (Ein/Aus)
41 ... Einstellung der Zündüberwachung
42 ... Einstellung der Zünd-Timeout-Drahtlänge
43 ... Einstellung der Zündüberwach-Ausblendzeit
44 ... Einstellung der Lichtbogen-Abrißzeit
45 ... Einstellung der TR 23P - Doppelkopf-Funktionen
DEUTSCH
Abb.21 Darstellung der Standardausführung bei Roboterbetrieb
DAS SETUP-MENÜ
Hinweis! Das Setup-Menü kann nur in Stromquellen mit dem Aufdruck
"PRO" aktiviert werden.
IN DAS SETUP-MENÜ EINSTEIGEN
- Schweißdraht auskoppeln
- Schweißstromkabel von den Strombuchsen trennen
- Netzschalter in Stellung "I" schalten und innerhalb der ersten drei
Sekunden den Bereichsschalter der Digitalanzeigen mehrmals
umschalten
- Testprogramm durch Anwahl der Programmnummer aufrufen
DAS SETUP-MENÜ VERLASSEN
- Netzschalter der Stromquelle in Stellung "O" schalten (eingestellten
Parameter werden gespeichert)
PFLEGE UND WARTUNG
Achtung! Vor Öffnen des Schweißgerätes, Gerät abschalten,
Netzstecker ziehen und ein Warnschild gegen Wiedereinschalten anbringen - gegebenenfalls Elkos entladen.
Um das Schweißgerät über Jahre hinweg einsatzbereit zu halten sind
folgende Punkte zu beachten:
- Sicherheitstechnische Inspektion laut vorgegebenen Intervallen durchführen (siehe Kapitel „Sicherheitsvorschriften“)
- Je nach Aufstellort, aber mindestens zweimal jährlich, Geräteseitenteile entfernen und das Schweißgerät mit trockener, reduzierter
Druckluft sauberblasen. Elektronische Bauteile nicht aus kurzer Entfernung anblasen.
- Bei starkem Staubanfall die Kühlluftkanäle reinigen.
Bei wassergekühlten Schweißbrennern
- Brenneranschlüsse auf Dichtheit prüfen
- Wasserstand und Wasserqualität kontrollieren (stets nur saubere
Kühlflüssigkeit einfüllen)
- Wasserrückflußmenge im Kühlmittelbehälter überwachen
17
Page 18

FEHLERDIAGNOSE UND -BEHEBUNG
Achtung! Gerät darf nur von geschultem Fachpersonal geöffnet werden. Vor Öffnen des Schweißgerätes, Gerät abschalten, Netzstecker
ziehen und ein Warnschild gegen Wiedereinschalten anbringen - gegebenenfalls Elkos entladen. Müssen Sicherungen ausgetauscht werden,
sind diese durch gleiche Werte zu ersetzen. Bei Verwendung zu starker Sicherungen erlischt der Garantieanspruch nach eventuellen
Folgeschäden.
FEHLERMELDUNGEN AN DEN ANZEIGEN
Die Stromquelle ist mit einem Selbstdiagnosesystem ausgestattet! Auftretende Störungen werden erkannt und an den Anzeigen in Form eines ErrorCodes (E00 - E99) angezeigt.
Fehlermeldung Beschreibung
E01 Interner Fehler in der T.I.M.E. Synergic Steuerung! (Fehler beim Hauptspeichertest)
E02 Interner Fehler in der T.I.M.E. Synergic Steuerung! (Fehler beim AD-/DA-Wandlerabgleich)
E03 Funktion ist nicht implementiert!
E04 VR-Autotest: Es wurde keine Motordrehbewegung festgestellt!
E05 VR-Autotest: Minimum- und Maximumdrehzahl sind fehlerhaft!
E06 VR-Autotest: Maximumdrehzahl ist fehlerhaft!
E07 VR-Autotest: Maximum konnte nicht erreicht werden! (Bis zur halben Motoraussteuerung stimmt die Motoreinstellung)
E08 VR-Autotest: Minimum und Maximum sind richtig eingestellt; Problem ist bei Drehzahl-Mitte aufgetreten! (Linearitätsfehler)
E09 VR-Autotest: Hochlaufzeit überschritten!
E19 HALLSHUNT-Verstärkungsjustierung: HALLSHUNT-Offset zu groß, um Verstärkung einzustellen!
E30 Autotest: Kein Kurzschluß im Schweißkreis
E33 Vorgang vom Benutzer abgebrochen!
E34 Falsches Eprom: Stromquelle wurde mit einem Eprom „Drehschalter“ anstatt „Programm-Wahlschalter“ ausgestattet!
E35 Falsches Eprom für Printversion: Sie haben eine alte Eprom-Version in den Steuerprint gesteckt
FEHLER AN DER SCHWEISSANLAGE
Fehler Ursache Behebung
Gerät hat keine Funktion
Anzeige Betriebsbereit leuchtet nicht,
Anzeige m/min - mm - V leuchtet, Anzeige
Schweißstrom leuchtet
Anzeige m/min - mm - V und Anzeige
Schweißstrom leuchten nicht
Netzzuleitung unterbrochen
Netzsicherung defekt
Versorgung der Leistungsteilsteuerung
nicht vorhanden
Steuer-Versorgungsspannung nicht vorhanden Sicherung 2F1 und 2F12 kontrollieren und
Netzzuleitung kontrollieren
Netzsicherung wechseln
Sicherung 1F10 kontrollieren bzw. erneuern
defekte erneuern
Anzeige Betriebsbereit leuchtet, Anzeige m/
min - mm - V und Anzeige Schweißstrom
leuchten nicht
kein Schweißstrom
Anzeige Betriebsbereit leuchtet, Anzeige
Über- bzw. Unterspannung leuchtet
Anzeige Betriebsbereit leuchtet, Anzeige
Übertemperatur leuchtet
Regler-Versorgung fehlt Sicherung 2F6 kontrollieren bzw. auswech-
seln
Phasenausfall Netzabsicherung, Netzstecker und Netzzu-
leitung kontrollieren
Netzspannung kontrollierenNetzspannung zu hoch oder zu niedrig- ÜberUnterspannungsüberwachung hat abgeschaltet
Thermo-Sicherheitsautomatik hat abgeschaltet (Ventilator läuft)
18
Abkühlphase abwarten. Gerät schaltet nach
kurzer Zeit selbständig wieder ein; ansonst:
Gerät zum Service
Einschaltdauer berücksichtigenGerät überlastet, Einschaltdauer überschritten
Page 19

Fehler Ursache Behebung
Kühlluftzufuhr unzureichend für ausreichende Luftzufuhr sorgen
Leistungsteil stark verschmutzt Gerät öffnen und mit trockener Preßluft aus-
blasen
Anzeige Betriebsbereit leuchtet, Vorschubmotor läuft
Lichtbogen setzt fallweise aus
Anzeige Betriebsbereit leuchtet, Anzeige
Über- bzw. Unterspannung leuchtet ca. 10 s.
Kühlgerät FK71 läuft nicht, 5pol. Kühlgerätstecker nicht eingesteckt
Kühlgerät FK71 läuft nicht - Sicherung 2F3
defekt
FK71 läuft nicht
Sicherung 2F5 für Gerätelüfter defekt Sicherung am Steuertrafo VM34 wechseln
Über- Unterspannungsüberwachung hat abgeschaltet
keine Leerlaufspannung
Schweißbrenner defekt Brenner wechseln
+ Pol des Verbindungsschlauchpaketes nicht
angeschlossen
Netzseitig fehlt eine Phase
Kurzzeitige Netzspannungsschwankungen
Über- Unterspannungsüberwachung schaltet
fallweise ab
Kühlgerätstecker seitenrichtig einstecken und
verriegeln
Sicherung am Steuertrafo VM34. wechseln
Sicherung am Steuertrafo VM34. wechselnSicherung 2F4 defekt - Lüfter im Kühlgerät
Lüfter wechselnLüfter in der Stromquelle defekt
Netzspannung kontrollieren
Leerlaufspannung an Anzeige m/min - mm - V
überprüfen (ca. 51V)
Sicherung 2F8 am Steuertrafo VM34. kontrollieren bzw. wechseln
Verbindung zum Werkstück herstellenMassekabel nicht angeschlossen
Kabel einstecken und verriegeln
Netzzuleitung überprüfen
Netzspannung kontrollieren
DEUTSCH
keine Funktion bei Betätigen der Brennertaste
Anzeige Betriebsbereit leuchtet, kein
Schweißstrom - Vorschubmotor läuft nicht kein Schutzgas
Anzeige Betriebsbereit leuchtet, Anzeige
Manuell / NoProgram blinkt
unruhiger Lichtbogen - starke Spritzerverluste
Brenner-Steuerstecker nicht eingesteckt oder
Steckverbindung defekt
Brennertaste oder Brenner-Steuerleitung defekt
Programmwahlschalter in falscher Position Programmwahl korrigieren
falsche Fernbedienung in Verwendung Fernbedienung TR34 T.I.M.E. od. TP4-SP
Schalter Brenner Ein-Aus in Stellung „Brennertaste deaktiviert“
Verbindungsschlauchpaket defekt oder nicht
angeschlossen
Programm-Wahlschalter in falscher Positionschlechte Schweißeigenschaft
Standardprogramm wurde mit einem
T.I.M.E.-Brenner geschweißt
Bei Programmbetrieb:Lichtbogen zu kurz oder
zu lang
Bei Manuellbetrieb: Arbeitspunkt nicht optimal
eingestellt
Steuerstecker einstecken und verriegeln,
Steckverbindung prüfen, notfalls wechseln
Brenner reparieren bzw. austauschen
Sicherung 2F7 kontrollieren bzw. austauschenNegative Versorgung fehlt
verwenden bzw. ohne Fernbedienung arbeiten
Schalter Brenner Ein-Aus in Stellung „Brennertaste aktiviert“ schalten
Schlauchpaket überprüfen
Programmwahl korrigieren
Standardbrenner verwenden bzw. auf kurzes
Stick-Out achten
Lichtbogenlänge mittels Einstellregler Lichtbogenlängenkorrektur optimieren
Parameter für Schweißspannung, Drahtgeschwindigkeit und Dynamik abstimmen (siehe aufgedruckte Richtwerttabellen)
Lichtbogendynamik zu hart
19
Dynamik mit Fernbedienung TR34 T.I.M.E.
im Standard-Manuellbetrieb korrigieren
Page 20

Fehler Ursache Behebung
Kontaktrohr erneuernKontaktrohr zu groß oder Bohrung ausgeschliffen
Masseverbindung schlecht für guten Kontakt zwischen Masseklemme
und Werkstück sorgen
verschmorte Teile austauschen, - notfalls
neues Massekabel verwenden
falsche Drahtlegierung -falscher Drahtdurchmesser
Verbindungsschlauchpaket oder Massekabel
zu lange, Kabelquerschnitt zu gering
Verbindungsschlauchpaket oder Massekabel
verlegt oder falsch aufgewickelt
Ungleichmäßige Drahtgeschwindigkeit Bremse zu stark angezogen Bremse lockern
Bohrung des Kontaktrohres zu klein
Drahtführungsseele im Brenner zu kurz, verstopft oder zu eng
Anpreßdruck der Vorschubrollen zu gering
eingelegte Drahtrolle kontrollieren bzw. wech-
seln
Schweißbarkeit des Grundwerkstoffes über-
prüfen
Schweißparameter korrigieren - Kabelquer-
schnitt vergrößern, ansonst neue Schweiß-
programme erstellen
Schlauchpaket bzw. Kabel möglichst gerade
auslegen oder bifilar aufwickeln
Richtiges Kontaktrohr für entsprechenden
Durchmesser einschrauben
je nach Brennertype Düsenstock oder Draht-
düse abschrauben und Länge der Seele prü-
fen
Seele mit richtigem Innendurchmesser wäh-
len
Geknickte oder verschmutzte Seele unbe-
dingt wechseln
Rändelmutter der Druckeinstellschraube so
einstellen, daß die Drahtelektrode nicht de-
formiert, jedoch einwandfrei gefördert wird
Schweißdraht bildet zwischen Vorschubrollen und Drahteinlaufdüse eine Schleife
Anzeige Betriebsbereit leuchtet, Leerlaufspannung ist vorhanden, Schutzgas strömt
nicht
Anzeige Betriebsbereit leuchtet, Leerlaufspannung ist vorhanden, Schutzgas strömt
falsche Drahtdüse auf eingesetzten Wert achten
Kontaktrohr zu eng Kontaktrohr wechseln
Innendurchmesser der Drahtführungsseele zu
klein
Drahtführungsseele verstopft, rostig, abgeknickt oder zu kurz
Anpreßdruck der Vorschubrollen zu stark
ser)
Motorsicherung defektDrahtvorschubmotor läuft nicht
Schalter Brenner Ein-Aus am Drahtvorschub
auf "AUS"
Steuerversorgung zum Drahtvorschub unterbrochen
Kohlebürsten abgenützt, Motor defekt
Richtige Seele für jeweiligen Drahtdurchmes-
ser einsetzen
Seele austauschen
Anpreßdruck mittels Rändelmutter verringern
Motorplatte richtig ausrüstenfalsche Antriebrollen (Nutform, Nutdurchmes-
Schweißbrenner umrüstenSchweißbrenner falsch ausgerüstet
Motorsicherung 2F9 am Steuertrafo VM34.
austauschen
Schalter Brenner Ein-Aus am Drahtvorschub
auf "EIN" stellen
37-poligen Steuerstecker- und Verbindungs-
schlauchpaket von Stromquelle zum Vor-
schubgerät prüfen
Spannung am Motor messen; liegt die Motor-
spannung an, Motor austauschen
20
Page 21

Fehler Ursache Behebung
Drahtvorschubmotor hat immer volle
Drehzahl
Drahtgeschwindigkeit weicht von den
programmierten Tabellenwerten ab
Nach Drücken der Brennertaste im
Leerlauf zu wenig Drahtgeschwindigkeit
Nach Drücken der Brennertaste erreicht
die Drahtgeschwindigkeit max. 22m/min.
Gas strömt auch nach Loslassen der
Brennertaste
Fernbedienung hat keine Funktion falsche Fernbedienung
Sollwert immer max. Verbindungsschlauchpaket kontrollieren
Motorregler bekommt keinen Drehzahlistwert
V-Nut-Rollen montiert programmierten Werte beziehen sich auf Tra-
Drahtvorschubmotor läuft mit eingestellter Anschleichdrehzahl
falsches Eprom in der Stromquelle Eprom kontrollieren
Dip-Schalter S6 bzw. S7 falsch eingestellt Dip-Schalter S6 bzw. S7 kontrollieren
Gasmagnetventil defekt oder verunreinigt Magnetventil reinigen oder austauschen
Fernbedienung oder Fernbedienkabel defekt
37-poligen Steuerstecker- und Verbindungsschlauchpaket von Stromquelle zum Vorschubgerät überprüfen
pez- oder Halbrundnut-Vorschubrollen. Bei
Verwendung von V-Nut-Rollen muß die Lichtbogenlänge korrigiert werden
Drahtgeschwindigkeit erhöht sich erst nach
Auftreffen des Schweißdrahtes am Werkstück.
Zur Ermittlung der tatsächlichen Vorschubgeschwindigkeit muß die Einschleichtaste gedrückt werden
Motorreglerprint NMI4. austauschenMotorreglerprint NMI4. schadhaft
nur Fernbedienung TR34 T.I.M.E. bzw. TP4SP verwenden
Fernbedienkabel vom Drahtvorschub trennen und Sollwerte (m/min.) prüfen
DEUTSCH
Draht brennt nach Schweißende am
Schweißbad fest
Draht brennt nach Schweißende am
Kontaktrohr fest
Schweißstrom an der Gasdüse Spritzeranhäufung in der Gasdüse (speziell bei
Schweißbrenner wird zu heiß - Einschaltdauer ist nicht überschritten (nur wassergekühlte Anlagen)
Vorschubmotor wird nicht gebremst - Kohlebürsten abgenützt
Nachbrennzeit zu lange eingestellt Nachbrennzeit mit Einstellregler Nachbrenn-
Zwangslagenschweißung)
bzw. defekt
zu wenig Kühlflüßigkeit im Kühlgerät FK71 Kühlflüßigkeit nachfüllen
Wasservor- und Wasserrücklauf vertauscht
Wasserkreislauf verstopft bzw. Wasserschläuche geknickt
Motorspannung messen; liegt die Motorspannung an, Motor austauschen
Motorreglerprint NMI4. austauschenMotorreglerprint NMI4. defekt
zeitkorrektur verkürzen
Gasdüse abziehen, Kontaktrohr, Düsenstock
und Gasdüse reinigen - gegebenenfalls mit
Fronius-Trennmittel einsprühen
wenn nötig, neuen Isolierteil einsetzenIsolierteil oder Spritzerschutz nicht montiert
Wasserschläuche richtig anschließen
Schraubkappe des Wasserbehälters öffnen
und Rücklauf kontrollieren.
21
Page 22

TECHNISCHE DATEN
Achtung! Ist das Gerät für eine Sonderspannung ausgelegt,
gelten die Technischen Daten am Leistungsschild. Netzstecker,
Netzzuleitung sowie deren Absicherung sind entsprechend auszulegen.
STROMQUELLE T.I.M.E. SYNERGIC
Netzspannung (+/-10%) 3 x 380 / 400 / 415 V~, 50 - 60 Hz
Netzabsicherung 40 A träge
Cos phi 150 A 0,98
450 A 0,99
Scheinleistung bei 60% ED 27 kVA
100% ED 21 kVA
Wirkungsgrad 90 %
Schweißstrombereich stufenlos 3 - 450 A
Schweißstrom bei 60% ED 450 A
100% ED 360 A
Leerlaufspannung 50 V
Arbeitsspannung MIG/MAG 0 - 50 V
Elektrode 0 -55 V
WIG 0 - 55 V
KÜHLGERÄT FK 71
Netzspannung 2 x 380 - 415 V, 50 - 60 Hz
Stromaufnahme 0,6 A
Drehzahl 2800 U/min (50 Hz), 3200 U/min (60 Hz)
Kühlleistung 2420 W
Max. Fördermenge 3,64 l/min.
Max. Pumpendruck 3,3 bar
Kühlmittelinhalt ca. 5,5 l
Schutzart IP 23
Maße l/b/h mm 575/365/265
Gewicht (ohne Kühlmittel) 21 kg
Schutzart IP 21
Kühlart AF
Isolationsklasse F
Prüfzeichen S, CE
DRAHTVORSCHUB T.I.M.E. 30
Netzspannung 42 V
Motor Nennstrom 4,2 A
Nennleistung 180 W
Drehmoment 21 Ncm
Drahtgeschwindigkeit 0 - 30 m/min
Untersetzung 17,6 : 1
Schutzart IP 23
Schutzklasse III
Gewicht 12,5 kg
22
Page 23
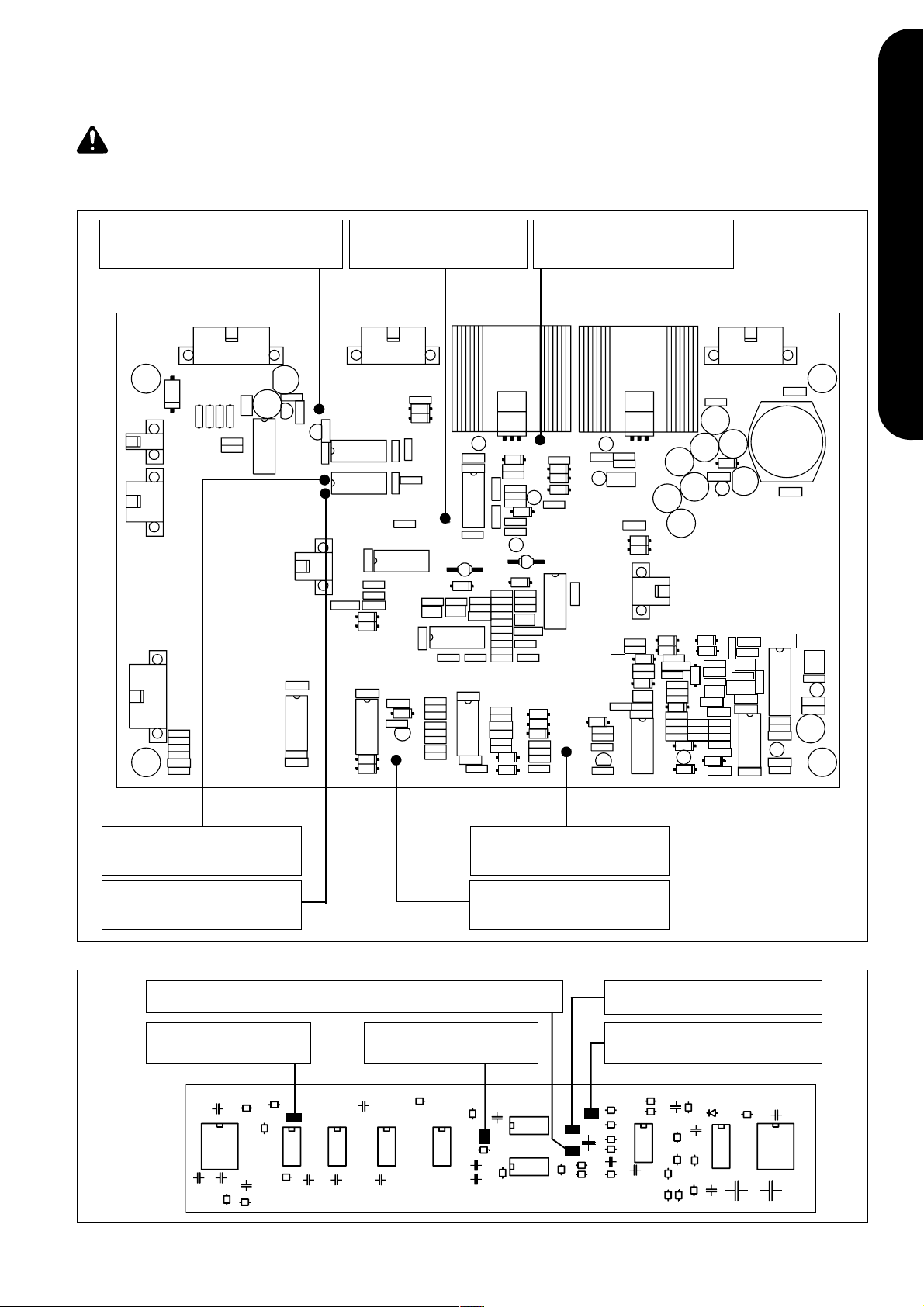
LED-CHECKLISTE, EINSTELLREGLER UND SICHERUNGEN
Achtung! Gerät darf nur von geschultem Fachpersonal geöffnet werden. Vor Öffnen des Schweißgerätes, Gerät abschalten, Netzstecker
ziehen und ein Warnschild gegen Wiedereinschalten anbringen - gegebenenfalls Elkos entladen. Müssen Sicherungen ausgetauscht werden,
sind diese durch gleiche Werte zu ersetzen. Bei Verwendung zu starker Sicherungen erlischt der Garantieanspruch nach eventuellen
Folgeschäden. Nicht bezeichnete Einstellregler dürfen nicht verstellt werden!
Transientenschutz
LED-Anzeige leuchtet nur bei aktivem
Überspannungsschutz
LED-Anzeige für PWM-Start
LED +5V / +15V
Muß bei eingeschaltetem Gerät immer
leuchten
DEUTSCH
LED-Anzeige leuchtet bei
Netzspannungsüberschreitungen von
mehr als 15%
LED-Anzeige leuchtet bei
Netzüberspannung von mehr als 44% oder
bei Ausfall einer Phase
Abb.22 Anzeigen auf Print PWM 3
Stromquelle Start
LED-Anzeige leuchtet nur bei MIG/MAG-Startsignal
Stromflußsignal
LED-Anzeige leuchtet, wenn
Schweißstrom fließt
Abb.23 Anzeigen auf Print WM 34A
Sollwert-Schweißstrom
Helligkeit der LED-Anzeige nimmt mit
steigendem Sollwert zu
LED-Anzeige leuchtet ca. 10 Sek.
bei einer Netzüber- bzw. Netzunterspannung
von +/- 10%
Keine Funktion
LED-Anzeige bleibt immer dunkel
23
Keine Funktion
LED-Anzeige bleibt immer dunkel
LED-Anzeige leuchtet bei einprogrammiertem
Abbrandimpuls
Page 24
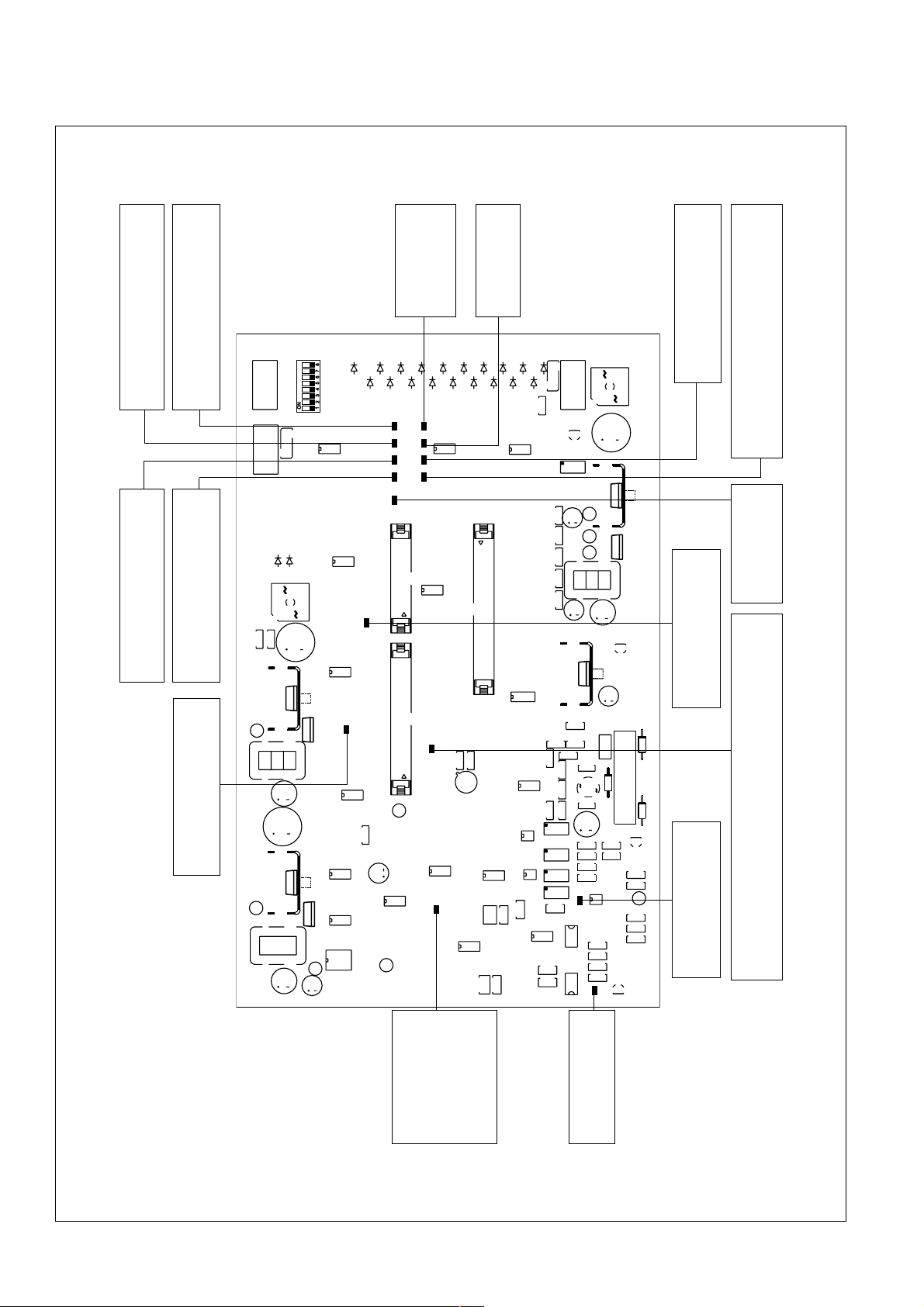
LED-Anzeige +15V muß bei eingeschaltetem
LED-Anzeige +10V muß bei eingeschaltetem
Gerät immer leuchten
LED-Anzeige +5V muß bei eingeschaltetem
Gerät immer leuchten ansonst F6 defekt
Gerät immer leuchten ansonst F6 defekt
LED-Anzeige -15V muß bei eingeschaltetem
Gerät immer leuchten ansonst F7 defekt
LED-Anzeige BRT 2
leuchtet bei gedrückter
Brennertaste 2 (zur Zeit
nicht verwendet.)
LED-Anzeige BRT
leuchtet bei gedrückter
Brennertaste
LED-Anzeige Einschleichen leuchtet bei
gedrückter Einschleichtaste
LED-Anzeige Vorschub A leuchtet bei verwendeter
Doppel-vorschubsteuerung, wenn auf Vorschub A
geschaltet ist
LED-Anzeige Gasprüfen
leuchtet bei gedrückter
Gasprüftaste
Motorbremse
LED-Anzeige leuchtet wenn
Vorschubmotor gebremst wird
Sollwert-Drahtvorschub
Helligkeit der LED-Anzeige nimmt mit
steigendem Sollwert zu
Abb.24 Anzeigen und Einstellregler auf Print NMI 4.
Anlage für die Zeitdauer
Motor-Reset
von 1 sec.
LED-Anzeige leuchtet:
- nach Einschalten der
- nach Überstrom an den
24
Drahtvorschubmotoren
Stromflußsignal
LED-Anzeige leuchtet wenn
Schweißstrom fließt
LED-Anzeige leuchtet wenn
Leerlaufspannung anliegt
LED-Anzeige leuchtet ca. 10 Sek.:
a) bei Auftreten einer Netzüber - bzw. Netzunterspannung von +/- 10 %
b) bei einem Übertemperaturfehler des Gerätes.
Page 25

Einstellregler für HotStart-Zeit von 0,5 - 2,0 Sek.
abhängig vom eingestelltem Schweißstrom-Sollwert
DEUTSCH
Abb.25 Anzeigen und Einstellregler auf Print MIG 45.
Abb.26 Codiermöglichkeiten am Print NMI4.
Regler Out (PWM Sollwert)
Helligkeit der LED-Anzeige nimmt mit
steigendem Sollwert zu
S1 Aus / Off Ein / ON
S1/1 450 A 330 A
S1/2 Sonderfunktion Aus Sonderfunktion Ein
S1/3 Puls & Standard Standard
S1/4 ohne Dynamik-Korrektur mit Dynamik-Korrektur
(nur bei Standardbetrieb)
S1/5 ohne Doppelkopf mit Doppelkopf
S1/6 VR A nmax = 30 m/min VR A nmax = 22 m/min
S1/7 VR B nmax = 30 m/min VR B nmax = 22 m/min
S1/8 Kühlgerätabschaltung Automatik Kühlgerätabschaltung Dauerbetrieb
Leerlaufspannung Ein
LED-Anzeige leuchtet, solange der Befehl zum
Einschalten der Leerlaufspannung anliegt
25
Page 26
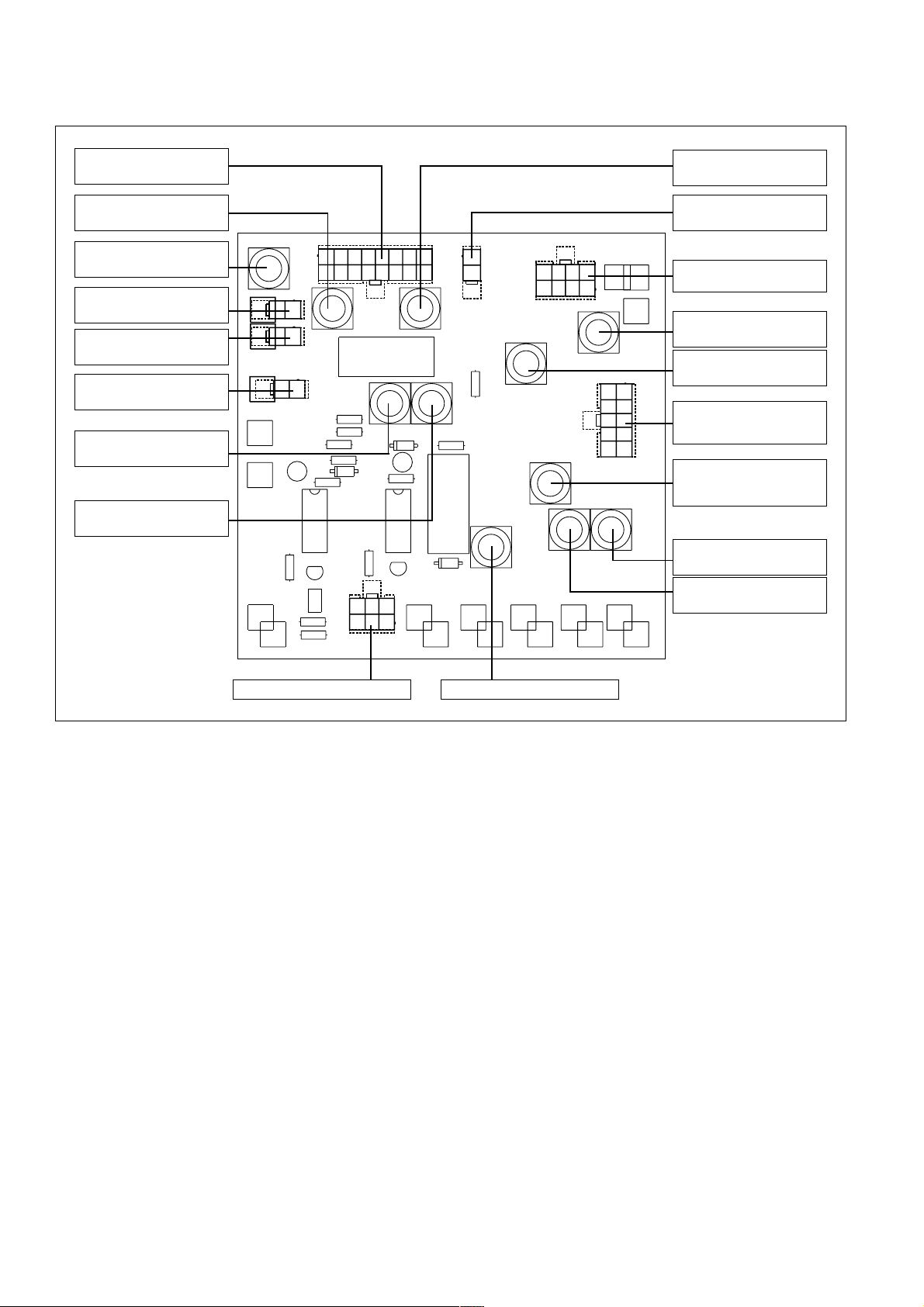
Steckverbindung X5
Spannungsversorgung primär
Primär 0V~
F1 6,3 A träge
Kühlgerätpumpe 380V~
F3 0,63 A träge
Primär 380V~
F12 6,3 A träge
Steckverbindung X6 für
Netz-Umschaltung 415V
Steckverbindung X7 für
Netz-Umschaltung 400V
Steckverbindung X8 für
Netz-Umschaltung 380V
Lüfter für Kühlgerät 230V~
F4 0,315 A träge
Lüfter 230V~
F5 0,315 A träge
Steckverbindung X1
für Gerätelüfter
Steckverbindung X4
Spannungsversorgung für BM 45.
Vorschubmotor (VR152) 42V~
F9 10 A träge
Pull-Mig Motor 42V~
F10 2 A träge
Steckverbindung X3
Versorgung für Steuerelektronik
NMI 4.
Versorgung NMI 4.
20V~ (+15V / +10V / +5V)
F6 2 A träge
Leerlaufspannung 36V~
F8 0,315 A träge
Versorgung NMI 4.
20V~(-15V), F7 1 A träge
Abb.27 Sicherungen auf Print VM34B
Steckverbindung X2 PWM
Nicht belegt
26
Page 27

OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS
ENGLISH
1
Page 28

2
Page 29

CONTENTS
DEAR FRONIUS CUSTOMER
This brochure is intended to familiarise you with how to operate and
maintain your T.I.M.E. Synergic. You will find it well worthwhile to read
through the manual carefully and to follow all the instructions it contains.
This will help you to avoid operating errors - and the resultant malfunctions. Your machine will repay you by giving you constant operational readiness for many years to come.
FRONIUS INTERNATIONAL GMBH & CO KG
Warning! The machine may only be put into service by trained
personnel, and only in accordance with the technical directions.
Before you start using the machine, you must read the section
headed "Safety rules".
Dear Fronius Customer ............................................................................ 3
Safety rules................................................................................................ 4
General remarks ................................................................................... 4
Utilisation for intended purpose only .................................................. 4
Obligations of owner/operator ............................................................. 4
Obligations of personnel ...................................................................... 4
Personal protective equipment ........................................................... 4
Hazards from noxious gases and vapours ........................................ 4
Hazards from flying sparks .................................................................. 4
Hazards from mains and welding current .......................................... 4
Particular danger spots ........................................................................ 4
Informal safety precautions ................................................................. 4
Safety precautions at the installation location .................................. 5
Vagrant welding currents ..................................................................... 5
Safety precautions in normal operation ............................................. 5
Safety inspection .................................................................................. 5
Alterations to the welding machine..................................................... 5
Spares and wearing parts.................................................................... 5
Calibration of welding machines ......................................................... 5
CE-marking............................................................................................ 5
Copyright ............................................................................................... 5
General remarks ....................................................................................... 6
Principle of the T.I.M.E. Synergic........................................................ 6
Welding procedure approval test to EN 288-7 .................................. 6
Machine concept................................................................................... 6
Controls and connections ........................................................................ 7
T.I.M.E. Synergic power source .......................................................... 7
T.I.M.E. 30 wirefeeder .......................................................................... 9
FK 71 cooling unit............................................................................... 10
TR 34 T.I.M.E. remote-control unit.................................................... 10
TP 4 SP remote-control unit .............................................................. 11
Starting to use the power source .......................................................... 11
Utilisation for intended purpose only ................................................ 11
Machine set-up regulations ............................................................... 11
Plug the machine into the mains....................................................... 11
Mains connection ................................................................................ 11
Assembling the power source ........................................................... 12
Fixing the interconnecting cable to the power source and
cooling unit .......................................................................................... 12
Mounting the Interconnecting cable to the wirefeeder ................... 13
Mounting / connecting the gas cylinder ........................................... 13
Mounting the welding torch ............................................................... 13
Starting up the cooling unit................................................................ 13
Mounting the wire spool ..................................................................... 13
Feeding in the wire electrode ............................................................ 13
Changing the feed rollers .................................................................. 14
MIG/MAG welding ................................................................................... 14
Adjustment guidelines for the T.I.M.E. Process .............................. 14
Setting-values for seam-type, welding position and seam
thickness .............................................................................................. 15
TIG welding ............................................................................................. 15
Variant I................................................................................................ 15
Variant II............................................................................................... 15
Start-up ................................................................................................ 16
Manual electrode welding ...................................................................... 16
Robot welding.......................................................................................... 16
The Set-up Menu .................................................................................... 17
To access the Set-up Menu ............................................................... 17
To exit the Set-up Menu ..................................................................... 17
Description of Parameters ................................................................. 17
Care and maintenance ........................................................................... 17
Troubleshooting ...................................................................................... 18
Error messages on the displays........................................................ 18
Faults on the welding machine ......................................................... 18
Technical Data ......................................................................................... 22
T.I.M.E. Synergic power source ........................................................ 22
T.I.M.E. 30 wirefeeder ........................................................................ 22
FK 71 cooling unit............................................................................... 22
LED Checklist, dials and fuses.............................................................. 23
Mode d´emploi
Spare parts list
Fronius - Sales and service offices
ENGLISH
3
Page 30

SAFETY RULES
GENERAL REMARKS
This welding machine has been made in accordance with the state of the
art and all recognised safety rules. Nevertheless, incorrect operation or
misuse may still lead to danger for
- the life and well-being of the welder or of third parties,
- the welding machine and other tangible assets belonging to the
owner/operator,
- efficient working with the welding machine.
All persons involved in any way with starting up, operating, servicing and
maintaining the welding machine must
- be suitably qualified
- know about welding and
- follow exactly the instructions given in this manual.
Any malfunctions which might impair machine safety must be eliminated
immediately.
It’s your safety that’s at stake!
UTILISATION FOR INTENDED PURPOSE ONLY
The welding machine may only be used for jobs as defined by the
“Intended purpose” (see the section headed "Starting to use the welding
machine").
Utilisation in accordance with the “Intended purpose” also comprises
- following all the instructions given in this manual
- performing all stipulated inspection and servicing work
OBLIGATIONS OF OWNER/OPERATOR
The owner/operator undertakes to ensure that the only persons allowed
to work with the welding machine are persons who
- are familiar with the basic regulations on workplace safety and
accident prevention and who have been instructed in how to operate
the welding machine
- have read and understood the sections on safety and the warnings
contained in this manual, and have confirmed as much with their
signatures
Regular checks must be performed to ensure that personnel are still
working in a safety-conscious manner.
OBLIGATIONS OF PERSONNEL
Before starting work, all persons entrusted with carrying out work on the
welding machine shall undertake
- to observe the basic regulations on workplace safety and accident
prevention
- to read the sections on safety and the warnings contained in this
manual, and to sign to confirm that they have understood these
PERSONAL PROTECTIVE EQUIPMENT
For your personal safety, take the following precautions:
- Wear stout footwear that will also insulate even in wet conditions
- Protect your hands by wearing insulating gloves
- Protect your eyes from UV rays with a safety shield containing
regulation filter glass
- Only use suitable (i.e. flame-retardant) clothing
- Where high noise levels are encountered, use ear-protectors
Where other persons are nearby during welding, you must
- instruct them regarding the dangers,
- provide them with protective equipment and/or
- erect protective partitions or curtains.
HAZARDS FROM NOXIOUS GASES AND VAPOURS
- Extract all fumes and gases away from the workplace, using suitable
means.
- Ensure a sufficient supply of fresh air.
- Keep all solvent vapours well away from the arc radiation.
HAZARDS FROM FLYING SPARKS
- Move all combustible objects well away from the welding location.
- Welding must NEVER be performed on containers that have had
gases, fuels, mineral oils etc. stored in them. Even small traces of
these substances left in the containers are a major explosion hazard.
- Special regulations apply to rooms at risk from fire and/or explosion.
Observe all relevant national and international regulations.
HAZARDS FROM MAINS AND WELDING CURRENT
- An electric shock can be fatal. Every electric shock is hazardous to
life.
- Magnetic fields generated by high amperages may impair the functioning of vital electronic devices (e.g. heart pacemakers). Users of
such devices should consult their doctors before going anywhere
near the welding workplace.
- All welding cables must be firmly attached, undamaged and properly
insulated. Replace any loose connections and scorched cables immediately.
- Have the mains and the appliance supply leads checked regularly by
a qualified electrician to ensure that the PE conductor is functioning
correctly.
- Before opening up the welding machine, make absolutely sure that
this is "dead". Discharge any components that may store an electrical
charge.
- If work needs to be performed on any live parts, there must be a
second person on hand to switch of the machine at the main switch
in an emergency.
PARTICULAR DANGER SPOTS
- Do not put your fingers anywhere near the rotating toothed wheels of
the wirefeed drive.
- Special regulations apply to rooms at risk from fire and/or explosion.
Observe all relevant national and international regulations.
- Welding machines for use in spaces with increased electrical danger
(e.g. boilers) must be identified by the “S” (for safety) mark.
- Welding-joins to which special safety requirements apply must only
be carried out by specially trained welders.
- When hoisting the power source by crane, always attach the chains
or ropes to the hoisting lugs at as close an angle to the vertical as
possible. Before hoisting, remove the gas cylinder and the wirefeed
unit.
- When hoisting the wirefeed unit by crane, always use an insulating
suspension arrangement.
INFORMAL SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
- The instruction manual must be kept at the welding-machine location
at all times.
4
Page 31

- In addition to the instruction manual, copies of both the generally
applicable and the local accident prevention and environmental
protection rules must be kept on hand, and of course observed in
practice.
- All the safety instructions and danger warnings on the welding
machine itself must be kept in a legible condition.
ALTERATIONS TO THE WELDING MACHINE
- Do not make any alterations, installations or modifications to the
welding machine without getting permission from the manufacturer
first.
- Replace immediately any components that are not in perfect condition.
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS AT THE INSTALLATION
LOCATION
- The welding machine must be placed on an even, firm floor in such a
way that it stands firmly. A welding machine that topples over can
easily kill someone!
- Special regulations apply to rooms at risk from fire and/or explosion.
Observe all relevant national and international regulations.
- By means of internal instructions and checks, ensure that the workplace and the area around it are always kept clean and tidy.
VAGRANT WELDING CURRENTS
- Ensure the workpiece clamp is connected tightly to the workpiece
- Set the welding machine up insulated where the floor conducts
electricity
If these instructions are not followed vagrant welding currents occur,
these can destroy earthed conductor terminals and other electrical
equipment.
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS IN NORMAL OPERATION
- Only operate the welding machine if all its protective features are fully
functional.
- Before switching on the welding machine, ensures that nobody can
be endangered by your turning on the machine.
- At least once a week, check the machine for any damage that may be
visible from the outside, and check that the safety features all function
correctly.
SAFETY INSPECTION
The owner/operator is obliged to have the machine checked for proper
condition by a trained electrician after any alterations, installations of
additional components, modifications, repairs, care and maintenance,
and in any case at least every twelve months.
SPARES AND WEARING PARTS
- Use only original spares and wearing parts. With parts sourced from
other suppliers, there is no certainty that these parts will have been
designed and manufactured to cope with the stressing and safety
requirements that will be made of them.
- When ordering spare parts, please state the exact designation and
the relevant part number, as given in the spare parts list. Please also
quote the serial number of your machine.
CALIBRATION OF WELDING MACHINES
In view of international standards, regular calibration of welding machinery is advisable. Fronius recommends a 12-month calibration interval.
For more information, please contact your Fronius partner!
CE-MARKING
The welding machine fulfils the fundamental requirements of the LowVoltage and Electromagnetic Compatibility Directive and is thus CEmarked.
COPYRIGHT
Copyright to this instruction manual remains the property of Fronius
International GmbH&Co.KG.
Text and illustrations are all technically correct at the time of going to
print. Right to effect modifications is reserved. The contents of the
instruction manual shall not provide the basis for any claims whatever on
the part of the purchaser. If you have any suggestions for improvement,
or can point out to us any mistakes which you may have found in the
manual, we should be most grateful.
ENGLISH
In the course of such inspection, the following regulations must be
observed (as a minimum):
- IEC (EN) 60 974-1 - Arc welding equipment - Part 1: Welding power
sources
- VBG 4, §5 - Electrical plant and apparatus
- VBG 15, §33 / §49 - Welding, cutting and allied processes
- VDE 0701-1 - Repair, modification and inspection of electrical
appliances; general requirements
- VDE 0702-1 - Repeat tests on electrical appliances
Further information on corrective maintenance, modification and
inspection of welding machines is available from your regional or national
Fronius service centre,who will be pleased to provide you with a copy of
the Work Instruction “Safety Inspection of Welding Machinery” (AAPMÜ-01) upon request.
ud_fr_st_sv_00146 0120015
Page 32

GENERAL REMARKS
PRINCIPLE OF THE T.I.M.E. SYNERGIC
The T.I.M.E. Process is a high-performance MAG welding process that
unites the very highest economic efficiency with outstanding weld seam
quality. Its higher deposition rate results from the use of solid wires at
higher wirefeed speeds, with special shielding gas mixtures being used
to ensure a high-grade welded join.
Among the key advantages of this process are aspects such as the weldseam appearance, mechanical-technological property values, weld
interfaces, freedom from inadequate fusion, and low tendency to spatter.
With the introduction of a second gas mixture, known as “T.I.M.E.-II”, it
is now possible to achieve pore-free weld seams where necessary.
Essentially, the T.I.M.E. Process is the interaction of state-of-the-art
power-source technology, powerful wirefeeders and welding torches,
the relevant gas physics, and the know-how needed to make the best
possible use of these factors.
WELDING PROCEDURE APPROVAL TEST TO EN 288-7
In the field of welding engineering in Europe, there will in future be
several possible ways in which recognition can be obtained for welding
procedure specifications (WPS). One of these is the standard welding
procedure approval test to EN 288 -7, as stipulated in ÖNORM EN 288-
1. In a welding procedure approval test of this type, all key influential
variables are investigated, resulting in the definition of a standardised
welding process.
MACHINE CONCEPT
The modular system was the inspiration behind T.I.M.E. Synergic. The
individual control components are joined by screw-type connections and
are easy to mount on the sturdy trolley.
The gas cylinder is integrated in the trolley in a recessed, low-level
location which makes the cylinder quick and easy to change and
manipulate. The machine may have compact dimensions, but it is built to
function dependably under even the toughest operating conditions. The
machine’s powder-coated sheet-steel housing, protected controls and
bayonet-latching current sockets satisfy the most exacting user
requirements.
The portable wirefeeder can be mounted on the location pivot on the
power source, enabling it to be swivelled to either side, or it can be
dismounted so as to extend the work zone. The wire spool and drive
system are protected from swarf by closeable covers.
The insulated transport handle and a trolley with extra-large wheels and
optimally placed crane-hoisting lugs make the machines easier to move
around, both in the factory and out in the field.
The attraction of this type of approval is that it offers a way of reducing
the costs that each individual manufacturer would incur in connection
with the approval. A WPS that has been carried out once is approved if
the ranges of all influencing variables remain within the permissible
range for the standard weld process in question. This is ensured by a
programmed parameter field in the power source, among other things.
For more information on this topic, please refer to the weld-procedure
approval test itself.
Fig.1 T.I.M.E. Synergic welding machine
6
Page 33

CONTROLS AND CONNECTIONS
T.I.M.E. SYNERGIC POWER SOURCE
Fig.2 Front of T.I.M.E. Synergic power source
Manual / No Program indicator
- is lit up all the time in MIG/MAG manual mode (with TR 34 T.I.M.E.
remote control unit) if a programmed position is selected on the
program selector switch
- is lit up all the time in manual electrode welding
- flashes if a non-programmed position is selected on the program
selector switch
Intermediate arc indicator ... Between the dip-transfer arc and the
spray arc, a spatter-prone intermediate arc occurs. To help the welder
avoid this, the ‘Intermediate arc’ indicator lights up when such an arc
occurs.
T.I.M.E. indicator ... glows when a T.I.M.E. program is selected - the
scale for wirefeed speed 0-30 m/min applies.
Hold indicator ... every time you finish a welding operation, the
actual values for welding current and voltage are stored, and the
“Hold” indicator lights up
m/min - mm - V selector switch ... for selecting the desired function:
m/min.......Wirefeed speed
mm..........Sheet thickness
V.............Open-circuit voltage or welding voltage
m/min - mm - V indicator
- Wirefeed speed (m/min) ... Command value in MIG/MAG program
and manual modes
- Sheet thickness (mm) in MIG/MAG program mode
- Welding voltage (V) ... Command value in MIG/MAG program
mode
- Welding voltage (V) ... Actual value in MIG/MAG program and
manual modes, and in manual-electrode mode
- Welding voltage (V) ... Hold-value in MIG/MAG program and
manual modes
ENGLISH
Fig.3 Back of T.I.M.E. Synergic power source
Mains switch
“Ready” indicator ... glows when the mains switch is on “I”
Overtemperature indicator glows when ...
- the machine is thermally overloaded
- the mains plug of the cooling unit is not plugged in
- the cooling unit is out of order
- the water throughflow is insufficient (only with optional rate-of-flow
watchdog)
Over / undervoltage indicator glows ...
- when the mains voltage is outside the tolerance range (power
source cuts out)
- for 10 sec in the event of supply voltage dips or overvoltage peaks
(power source switches itself off and straight back on again)
Program selector switch (0-99) for selecting the required pulsedarc, standard or T.I.M.E. welding program, depending on the shielding
gas and filler metal
N.B.! If the letter H appears in front of the sheet thickness in the display
(e.g. H12), this means that the value displayed cannot be increased any
further, even if the welding power is increased.
Welding current indicator
- Command value in MIG/MAG manual or manual-electrode mode
- Actual value in MIG/MAG program and manual modes
- Hold-value in MIG/MAG program mode
N.B.! Definition of the terms ‘command value’, ‘actual value’ and ‘hold
value’:
- The command value is the “desired” value which can be pre-selected
(depending on the welding process in question), and which is shown
when the machine is in open circuit
- The actual value is the “real” value displayed during the welding
operation
- The “hold” value is the “stored” value which is displayed at the end of
the welding operation.
P-Start dial ... 0 - 30 m/min (T.I.M.E.) or 1 - 10 (Power)
Recommended setting for T.I.M.E.: 9 m/min
- Depending on the contents of the T.I.M.E. display, the scale refers
to wirefeed speed (0 - 30 m/min) or welding power (1-10)
- P-Start influences the stability of the arc in the ignition phase
(reliable arc ignition) and for the boxing of weld-seams
- In the T.I.M.E. 4-step mode, P-Start can be used to set the start-
up wirefeed speed; this set value is an absolute value, i.e. it is
independent of whatever value has been set for the welding power
7
Page 34

P-End dial ... 0 - 30 m/min (T.I.M.E.) or 1 - 10 (Power)
Recommended setting for T.I.M.E.: 5 and 9 m/min respectively
- Depending on the contents of the T.I.M.E. display, the scale refers
to wirefeed speed (0 - 30 m/min) or welding power (1-10)
- In the T.I.M.E. 4-step mode, P-End can be used to set the final
wirefeed speed; this set value is an absolute value, i.e. it is
independent of whatever value has been set for the welding power
Optional push/pull adjustment ... for adjusting the speed when
using a push-pull torch.
Program overview table ... gives information on the programmed
pulsed-arc, standard and T.I.M.E. programs.
- [S] ... only standard program is stored
- [P] ... only pulsed-arc program is stored
N.B.! The program named “EN 288/7” was welded in the context of a
weld-procedure approval test and only allows welding parameters that
have been covered in this test.
MATERIAL GAS %
EN 440 G2
EN 70 S-6
EN 288/7
T.I.M.E.
T.I.M.E. II
T.I.M.E.
Fe1 (SG 2/3) CO2 100
Fe2 (SG 2/3)
CrNi 19 9
CrNi 18 8
AlSi 5
AlMg 5
Al 99,5
Rutile
Basic
Metal
Fluxcored
wire
CrNi
Ar 82 CO
Ar 97.5 CO
Ar 97.5 CO
Ar 100
Ar 100
Ar 100
Ar 82 CO
Ar 82 CO2 18
Ar 82 CO
Ar 82 CO
2
2
2
2
18
2
2
18
18
18
2.5
2.5
PROG. CODE
1.0
0.8 1.2
2 3
7
S11
S13
S14 S15
17
18 19
21 22 23 24
26 27
25
30 31 32
29
34 35 36
33
38 39 40
37
S43
47
51 52
55 56
1.6
S16
20
28
S44
48
T.I.M.E. 4-step slope dial ... 0.2 - 7.0 s.
Recommended setting: 1 s.
T.I.M.E. 4-step final-current dial ... Do not adjust this dial; dial must
be in the middle position
Wire-inch button ... for feeding the wire electrode into the torch
hosepack with no flow of gas or current
- Current socket with bayonet latch ... for
- connecting the interconnecting cable in MIG/MAG welding
- connecting the earth cable in TIG welding
- connecting electrodes or the earth cable in manual electrode
welding (depending on the type of electrode being used)
- Current socket with bayonet latch ... for
- connecting the earth cable in MIG/MAG welding
- current connection for TIG welding torch
- connecting electrodes or the earth cable in manual electrode
welding (depending on the type of electrode being used)
Torch control connection socket ... interconnecting cable
- Socket with bayonet latch ... interconnecting cable
Connection socket for FK71 cooling unit ... for connecting the
control plug for the cooling unit
N.B.! If the cooling unit is not plugged in, the overtemperature indicator
lights up on the power source. Welding is not possible.
Optional gas pre-heating socket 230V / 80W ... for electrical supply
to gas pre-heater when CO2 shielding gas is being used
EPROM n°: C0027
Fig.4 Program overview table
- Background parameters ...remove the program overview table
in order to uncover further key parameters which can be set for the
welding process.
Gas pre-flow time dial ... 0.1 - 3.0 s.
Recommended setting: 0.1 s. (minimum)
Soft-start speed dial ... Minimum up to 100% of the pre-set wirefeed
speed
Recommended setting: 50% (medium)
Gas post-flow time dial ... 0.5 - 4.0 s.
Recommended setting: 2 s. (medium)
T.I.M.E. 4-step starting-current dial ... Do not adjust this dial; dial
must be in the middle position
Fig.5 Close up of "Internal 4-step parameters"
8
Page 35

T.I.M.E. 30 WIREFEEDER
Fig.6 Front view of T.I.M.E. 30 wirefeeder
N.B.! If you attempt to use a non-weldable wirefeed speed, the lowest
weldable value will be set.
Arc-length correction dial ... For continuous correction of the preset arc-length within a +/- 20% range (voltage command value is only
indicated in Standard Program mode)
Burn-back time correction dial
- Standard Manual mode ... Burn-back time is continuously
adjustable from 1-4 on scale (0 - 0.4 s.)
- Pulsed-Arc and Standard Program mode ... Before the start of
welding, the dial must be set to the middle value on the scale; the
parameters for the burn-back time are integrated within the welding
program in question
- Dial turned all the way to left ... minimal droplet formation on wireend
- Dial turned all the way to right ... more droplet formation on wireend
Wire-inching button ... for feeding the wire electrode into the torch
hosepack with no flow of gas or current
Torch On/Off switch ... for deactivating the torch trigger (e.g. when
the machine is to be hoisted by crane)
- left-hand switch position ... torch trigger deactivated
- right-hand switch position ... torch trigger activated
Fig.7 Rear view of T.I.M.E. 30 wirefeeder
Mode switch ... for selecting the operating mode
- 2-step mode
- 4-step mode
- T.I.M.E. 4-step mode
2-step mode
- Press and hold the torch trigger: Start of welding
- Release the torch trigger: End of welding
4-step mode
- Press and release the torch trigger: Start of welding
- Press and release the torch trigger again: End of welding
T.I.M.E. 4-step mode ... For retrieving the start-up, welding and finalcurrent parameters via the torch trigger
- Press and hold the torch trigger: Start of welding, with the pre-set
starting current (P-Start)
- Release the torch trigger: Starting current drops via slope to the
welding current set on the welding power dial
- Press and hold the torch trigger again: Welding current drops via
slope to the pre-set final current (P-End)
- Release the torch trigger: End of welding
Connection socket for optional intermediate feeder
Remote-control connection socket ... for connecting up the required
remote-control unit
Shielding gas connection socket
ENGLISH
Torch-control connection socket ... for connecting up the control
plug from the welding torch
Torch central connector ... for attaching the welding torch
- Socket with bayonet latch ... Interconnecting cable
Plug-type connection for water return flow ... Interconnecting
cable
Shielding gas connection socket ... Interconnecting cable
Plug-type connection for water forward flow ... Interconnecting
cable
Connection socket for control plug ... Interconnecting cable
Wire inlet
Fuse for wirefeeder motor (4A slow)
N.B.! The wirefeeder motor is water-cooled. The motor will only be
cooled if the wirefeeder is always connected up to the coolant circuit of
the torch.
Welding-power dial
- 1-10 scale ... For continuous setting of the welding power (only if
T.I.M.E. indicator is not lit up)
- Wirefeed speed 0-30m/min scale ... For continuous setting of the
wirefeed speed (only if T.I.M.E. indicator is lit up)
9
Page 36

FK 71 COOLING UNIT
TR 34 T.I.M.E. REMOTE-CONTROL UNIT
Fig.8 FK 71 cooling unit
Fig.9 Rear of FK 71 cooling unit
Cooling-unit supply-lead plug
Coolant draining device
Plug-type connection for water forward flow (blue)
Plug-type connection for water return flow (red)
Fig.10 TR 34 T.I.M.E. remote-control unit
For the Standard/Program, Pulsed-Arc/Program and Standard/Manual
welding modes, a TR 34 T.I.M.E. remote-control unit is needed.
N.B.! Controls on the remote-control unit always take priority over the
power source, i.e. they dictate how the machine is to function.
Welding power dial
Arc-length correction dial
- red scale ... for continuous correction of the pre-set arc-length
within a +/- 20% range, in Pulsed-Arc and Standard/Program
modes
- black scale ... for continuous adjustment of the welding voltage
within a 0 - 50 V range in Standard/Manual mode (‘No Program’
indicator lights up)
Operating mode switch ... for pre-selecting the required operating
mode in MIG/MAG welding
Droplet detachment / arc-force correction dial
- red scale ... stepless correction facility for droplet-detachment
energy
left ... decreased droplet-detachment force
neutral ... neutral droplet-detachment force
right ... increased droplet-detachment force
- black scale ... for influencing the short-circuit force at the instant
of droplet transfer
left ... harder and more stable arc
neutral ... neutral arc
right ... soft, low-spatter arc
Connection socket for remote-control cable
10
Page 37

STARTING TO USE THE POWER
SOURCE
TP 4 SP REMOTE-CONTROL UNIT
50
60
40
30
20
10
0
Fig.11 TP 4 SP remote-control unit
Hot Start
70
80
90
100
T
3-150
100-450
N.B.! Owing to the characteristic, it is not possible to weld CEL electrodes
with the T.I.M.E. Synergic.
Welding current dial... for continuous setting of the welding current
in the 3-150A and 100-450A ranges
Hot-Start dial ... 0 - 100% of the pre-set welding current; only
effective in the electrode ignition phase
N.B.! The maximum Hot-Start total current is automatically limited by the
short-circuit current.
0
1
1
2
2
3
B
3
4
CEL
4
5
5
Warning! Before starting to use for the first time, read the section
headed “Safety rules”.
UTILISATION FOR INTENDED PURPOSE ONLY
The welding machine is intended to be used SOLELY for MIG/MAG, rod
electrode and TIG welding.
Any other use, or any use going beyond the above, is deemed to be “not
for the intended purpose” and the manufacturer shall not be liable for any
damage resulting therefrom.
“Utilisation for the intended purpose” shall also be deemed to encompass:
- the observance of all instructions in the operating manual
- the carrying out of all prescribed inspection and maintenance work
Warning! Never use the welding machine for thawing frozen
pipes!
MACHINE SET-UP REGULATIONS
The welding machine is tested to “Degree of protection IP21”, meaning:
- Protection against penetration by solid foreign bodies with diameters
larger than 12 mm
- Protection against dripping water falling vertically
The welding machine can be set up and operated outdoors in accordance
with IP21. However, the built-in electrical components must be protected
against direct wetting.
Warning! Place the welding machine on an even, firm floor in
such a way that it stands firmly. A welding machine that topples
over can easily kill someone.
The venting duct is a very important safety feature. When choosing the
machine location, make sure that it is possible for the cooling air to enter
and exit unhindered through the louvers on the front and back of the
machine. Any metallic dust from e.g. grinding-work must not be allowed
to get sucked into the machine.
ENGLISH
Range switch ... subdivides the overall welding range of the machine
into two separate but overlapping ranges
Polarity reverser ... no function
Arc-force dial ... for influencing the short-circuit force at the instant
of droplet transfer
Connection socket for remote-control cable
PLUG THE MACHINE INTO THE MAINS
Warning! Mains plugs must be suitable for the mains voltage and
the current input of the welding machine (see Technical Data)
Warning! For details of fuse protection of the mains supply lead,
please see the Technical Data.
MAINS CONNECTION
The welding machine is designed to run on the mains voltage given on
the rating plate. For details of fuse protection of the mains supply lead,
please see the Technical Data.
Warning! The power source is factory-connected for 400 V. This
means that thanks to its +/-10% tolerance range, the power
source can also be run on the 3x380 V~ mains. In the event of
undervoltage or overvoltage errors, the voltage range must be
corrected by reconnecting the plug-type connectors (on the VM
34 auxiliary transformer board) for the correct supply voltage.
For mains voltages of 3x230V~, 3x440V~ or 3x500V~, a FRONIUS
series transformer must be used. This can be readily retrofitted, and can
be mounted between the trolley and the power source. On request, the
power source can also be designed for 3x440V~ or 3x500V~.
11
Page 38

380V
342V
-10%
380V
418V
+10%
360V
400V
415V
Fig.12 Tolerance ranges of 3x380V / 400V / 415V~ mains voltages
-10%
373V
400V
+10%
415V
-10%
440V
456V
+10%
The welding machine can be run as standard on a mains voltage of 3x380
V~, 3x400 V~ or 3x415 V~, provided that the auxiliary transformer is
switched to the correct value for the operating -voltage supply.
Plug connector X7 for
400V~ mains reconnection
Plug connector X6 for
415V~ mains reconnection
Plug connector X8 for
380V~ mains reconnection
Fig.13 3x380V / 400V / 415V~ mains reconnection on VM 34 auxiliary transformer
board.
Fig.14 Assembling the power source
Warning! If the machine is designed to run on a special voltage,
the Technical Data shown on the rating plate apply. The mains
plug and mains supply lead, and their fuse protection, must be
dimensioned accordingly.
ASSEMBLING THE POWER SOURCE
- Fit mounting brackets and down onto the trolley frame so that
the openings and in both mounting brackets are at the top left
- Insert the fastening plates (complete with pre-mounted nuts) from
the rear, as shown in Fig.14, and screw on loosely using M8 x 20 steel
screws with washers and retaining rings.
- Place the power source onto mounting brackets and and
screw on from below using four M8x16 steel screws complete with
washers and retaining rings.
- Now screw both mounting brackets firmly to the trolley frame
- Working from the front, insert the cooling unit through mounting
brackets and and position it. (The guide tongue at the rear must
slot in underneath).
- As you can see in Fig. 15, the unit only needs to be fastened at Point
, using an M8x16 steel screw (inserted from below), with washer
and retaining ring.
Fig.15 Assembling the power source
FIXING THE INTERCONNECTING CABLE TO THE
POWER SOURCE AND COOLING UNIT
- Shift the mains switch into the “O” position
- Fix the strain-relief device of the interconnecting cable using the
screw provided
- Plug the “Welding potential” bayonet plug of the interconnecting
cable to the - socket and turn it to latch it
- Plug the 37-pole control plug into the control-plug socket and
fasten it tightly with the swivel nut
- Plug the water forward-flow and return-flow hoses of the interconnecting cable to the plug-on connectors and , red-to-red and
black-to-black
- Connect the cooling-unit supply plug to socket on the power
source
N.B.! If the cooling unit is not plugged in, the overtemperature indicator
lights up on the power source. Welding is not possible.
12
Page 39

MOUNTING THE INTERCONNECTING CABLE TO
THE WIREFEEDER
- Shift the mains switch to the “O” position
- Place the wirefeeder (with press-fit insulating sleeve) onto the location
pivot on the power source
- Loosen the cable grip and pull the interconnecting cable through, the
right way round, as far as the metal clamping sleeve on the protective
hose
N.B. ! Do not cross over or kink any of the lines
- Plug the “Welding potential” bayonet socket of the interconnecting
cable to socket and turn it to latch it
- Plug the 37-pole control socket into the control-plug socket and
fasten it tightly with the swivel nut
- Plug the gas hose of the interconnecting cable onto the shielding gas
socket and tighten with the swivel nut
N.B. ! First check whether O-ring seals have been inserted
N.B.! Use clean tap water only. The electrical conductivity of all other
antifreeze agents makes them unsuitable for use here.
Warning! As Fronius has no influence on factors such as the
quality, purity and filling-level of the coolant, no warranty is given
for the coolant pump.
Outside temperature Water-to-spirit mixing ratio
+ °C to -5°C 4 l : 1 l
-5°C to -10°C 3.75 l : 1.25 l
-10°C to -15°C 3.5 l : 1.5 l
-15°C to -20°C 3.25 l : 1.75 l
Warning! The coolant circulation must be checked at regular
intervals while the machine is in operation - it must be possible to
see that the return-flow to the reservoir is working correctly.
- Plug the water forward-flow and return-flow hoses of the interconnecting cable to the plug-on connectors and , red-to-red and
black-to-black, and tighten with the swivel nut
- Screw down the tension-relieving cable-grip
MOUNTING / CONNECTING THE GAS CYLINDER
- Stand the cylinder on the platform of the power-source trolley
- Fix the gas cylinder in place with both safety chains
N.B.! The cylinder is only fixed properly if the chains are placed around
the top part of the cylinder (but not around the neck of the cylinder)
- Take off the protective cap from the cylinder
- Give the cylinder valve a quick turn to the left so as to blow off any dirt
that may have accumulated
- Check the seal on the pressure regulator
- Screw the pressure regulator onto the gas cylinder and tighten it
- Link up the shielding-gas connector on the interconnecting cable to
the pressure regulator, by means of the gas hose
MOUNTING THE WELDING TORCH
- Shift the mains switch to the “O” position
- Check that the torch is correctly tooled up. Insert it - infeed tube first
- into the central torch connector
- Tighten the swivel nut by hand to fix the torch in place
- Plug the control plug of the welding torch onto the torch control
connection and latch it
- Plug the gas-hose of the welding torch into the gas connector and
latch it
Under more difficult conditions (extra-long hosepacks, big height
differences etc.), use the FK 71 R cooling unit, with a cooling power of
2.6 kW and a pump pressure of 4.4 bar.
MOUNTING THE WIRE SPOOL
Warning! The wire-reel fixture is only for holding and securing
standard welding-wire reels of max. 20 kg.
- Shift the mains switch
- Open the wire-spool cover
- Mount the wire spool onto the spool holder - the right way round
- Slot the locking bolt into the opening provided on the body of the spool
- Adjust the braking force with the clamping screw
- Replace the wire-spool cover or side panel
N.B.! The brake should always be adjusted so that the wire does not
continue unreeling after the end of welding - but without overtightening
the clamping screw, as this would cause motor overload.
to the “O” position
FEEDING IN THE WIRE ELECTRODE
- Shift the mains switch to the “O” position
- Open the wire-spool cover
- Pivot the clamping devices and forwards
- Pull the pressure levers and upwards
- Insert the wire electrode though the infeed tube of the 4-roller drive
and around 5 cm into the infeed tube of the welding torch
- Push the pressure levers and downwards
- Pivot the clamping devices and into the vertical position
- Set the contact pressure by means of the clamping nuts and
ENGLISH
STARTING UP THE COOLING UNIT
N.B.! Always check the volume and cleanliness of the coolant water
before starting to use the unit. The cooling unit is factory-filled with
approx. 2l of coolant (mixing ratio 1:1) before dispatch.
- Shift the mains switch to the “O” position
- Remove the screw cap
- Top up with coolant (mixing ratio as per following table)
- Screw the cap back on again
N.B.! Set a contact pressure that is high enough to ensure smooth wire
feed, but not so high that the wire electrode is deformed.
- Arrange the hosepack in as straight a line as possible
- Detach the gas nozzle from the torch
- Unscrew the contact tube
- Plug in the mains plug
- Shift the mains switch to the “I” position
- Mains control lamp lights up
- Shift the program selector switch to the required position (‘No
Program’ indicator must not light up)
13
Page 40

MIG/MAG WELDING
- Shift the selector switch for digital indications into the m/min
position
- Set a value of ~ 5 m/min on the welding power dial
Warning! During the wire-infeed operation, hold the welding
torch facing away from your body.
- Press the wire-inch button until the wire electrode protrudes out of
the end of the torch
- To end the wire-infeed operation, release the wire-inch button
N.B.! The wire spool must not continue to unreel after you release the
torch trigger. Re-adjust the brake if necessary.
- Screw in the contact tube
- Fit the gas nozzle
- Close the wire-spool cover
- Shift the mains switch to the “O” position
Warning! Before starting up for the first time, read the sections
headed “Safety rules” and “Starting to use the power source”.
- Plug the earth cable into the current socket and latch it in firmly.
- Connect the other end of the earth cable to the workpiece
- Plug the machine into the mains
- Switch the machine on at the mains switch
- Mains control lamp lights up
Warning! On water-cooled machines, the water-flow must be
checked at regular intervals while the machine is in operation you must be able to see that the coolant is flowing back properly.
- Pre-select the welding program with the program selector switch
(‘No Program’ indicator must not light up or start flashing)
N.B.! All the programs were welded with a standard torch (apart from
T.I.M.E. programs). When standard programs are welded with a T.I.M.E.
torch, this may lead to changes in the welding properties.
- Shift the operating-mode switch on the wirefeeder into the desired
position
- Connect the remote-control unit to the remote-control socket (for
pulsed-arc welding, connect up the TR 34 T.I.M.E. remote-control
unit and set the operating-mode switch on the TR 34 T.I.M.E. to
‘Pulsed-arc welding’)
- Set the arc-length correction dial to “0”
- Set the droplet-detachment correction dial to “0”
- Set the required amperage on the welding power dial (command
value is shown on the amperage indicator)
- Open the gas-cylinder valve
- Set the gas-flow rate
- Press the torch trigger and start welding
Fig.16 4-roller drive
CHANGING THE FEED ROLLERS
In order to achieve satisfactory wire travel, the feed rollers must be
suitable for the diameter and alloy of the wire to be welded.
- Shift the mains switch to the “O” position
- Open the wire-spool cover
- Pivot the clamping devices and forwards
- Pull the pressure levers and upwards
- Pull out axles -
- Remove feed rollers -
- Insert new feed rollers
N.B.! Insert the feed rollers in such a way that you can still see and read
the designation for the wire diameter.
- Push axles - back in again - the anti-twist lock of each axle must
latch into place
- Push the pressure levers and downwards
- Pivot the clamping devices and into the vertical position
- Set the contact pressure by means of the clamping nuts and
- Close the wire-spool cover
N.B.! In some cases, it may be necessary to correct the gas pre-flow time
or gas post-flow time and/or the soft-start speed .
ADJUSTMENT GUIDELINES FOR THE T.I.M.E.
PROCESS
Thanks to the single-dial operation of the T.I.M.E. Synergic, it is only
necessary to set the appropriate wirefeed speed ; the correct welding
voltage is then set automatically. Corrections are only then needed to the
arc length.
Calculating the deposition rate
This formula only holds good for a wire diameter of 1.2 mm and for
unalloyed and low-alloy steel wires. It takes no account of spattering
losses (typically 1 - 2 %).
Deposition rate [kg/h] =
e.g. wirefeed speed = 20m/min
Deposition rate [kg/h] =
Wirefeed speed [m/min] x 60 x 8.9
1000
20 m/min x 60 x 8.9
1000
= 10.68 kg/h
14
Page 41

TIG WELDING
Calculating the welding speed
This formula only holds good for a wire diameter of 1.2 mm and for
unalloyed and low-alloy steel wires. It takes no account of spattering
losses (typically 1 - 2 %) or of geometrical deviations such as root gaps
and weld overfill (typically 10 - 20 % lower speed).
Welding speed [cm/min] =
Wirefeed speed [m/min] x 1.13 x 100
Weld sectional area [mm
2
]
e.g. ‘a 6’ fillet weld (‘a 6’ fillet weld has a weld sectional area of 36 mm2)
and a wirefeed speed of 20m/min
Welding speed [cm/min] =
20 m/min x 1.13 x 100
36 mm
2
= 62.8 cm/min
As the bead cross-sections in multi-pass welding are difficult to determine,
this makes the computation of the welding speed a rather complicated
affair. A planimeter or squared graph paper will be found very helpful
here. See below for setting-values for different types of seam, welding
positions and seam thicknesses.
SETTING-VALUES FOR SEAM-TYPE, WELDING
POSITION AND SEAM THICKNESS
Butt welds
Fillet welds
VARIANT I
Variant I requires the TP 4-SP remote-control unit and the TIG Set
(consisting of AL 22-S / AL 16-S hand-held welding torch with gas hose,
gas pressure regulator and spare-parts box).
N.B.! In this variant of TIG welding, the electrode touch-down on the
workpiece causes a short-circuit current of the same size as the pre-set
welding current. Ignition cycles from 10 A upwards invariably result in
damage to the surface of the workpiece and the tip of the tungsten
electrode, and impair the weld-seam quality by leaving tungsten inclusions.
- Ignition of the welding arc is effected by touching down the tungsten
electrode onto the workpiece.
- To interrupt the welding operation, simply lift the torch away from the
workpiece until the arc goes out. In this case, there will be no filling
of the end-crater at reduced current, and thus no gas-shielding of the
end-crater.
Gravity position
- Root welding,
irregular gaps and root
widths of over 2mm:
2.5 - 4.5m/min
Regular 2mm gaps: 9m/min
- Filler passes
lower region: 12-15m/min
upper region: 15-23m/min
- Top passes: 15-18m/min
Horizontal-vertical position
- Root welding,
irregular gaps and root
widths of over 2mm:
2.5 - 4.5m/min
Regular 2mm gaps: 9m/min
- Filler passes: 12 - 18m/min
- Top passes: 9 - 12m/min
Overhead weld
- Root welding: 3 - 4m/min
- Filler passes: 9 - 11m/min
- Top passes: 9 - 11m/min
Vertical-up welds: 3 - 6m/min
Vertical-down welds: 9 - 11m/min
Horizontal position
- a3: 12 - 14m/min
- a4: 12 - 16m/min
- a5: 15 - 18m/min
- a6: 18 - 23m/min
- a7: 20 - 23m/min
- >a8 only multi-pass 20 - 23m/min
- Notch beads at 10 - 12m/min
Overhead position
- 9 - 11m/min for all seam
thicknesses and single or multipass weld seams
Vertical-down welds
- 9 - 11m/min; max. a3.5: weldable
in one pass,
- thicker seams: multi-pass
Vertical-up welds
- 4 - 6m/min; min. seam
thickness a6
Gravity position
- a3: 12 - 14m/min.
- a4: 12 - 14m/min.
- a5: 17 - 23m/min.
- a6: 17 - 23m/min.
- ab a7: 22 - 30m/min.
ENGLISH
Fig.17 TIG Set
VARIANT II
Variant II requires the TP 4-SP remote-control unit, the TR 52-1 pedal
remote-control unit, a signal distributor and the TIG Set (AL 22-S / AL 16S hand-held welding torch with gas hose, gas pressure regulator and
spare-parts box).
Using this combination offers the following advantages:
- Reduction of the welding current at the instant of electrode touchdown, using the pedal-operated remote-control unit
- Crater-filling is possible, by lowering the current using the pedal
remote-control unit (gradually taking the pressure off the pedal
causes the welding current to drop to approx. 10 A) - optimum gas
shielding is assured
- Welding-current limitation by means of welding -current regulator on
the TP 4-SP remote-control unit: On the one hand, the entire pedal
travel is always available for the selected range, yet on the other hand
it is not possible for e.g. a thin tungsten electrode to be overloaded
and/or to melt if the pedal is pushed all the way down to the floor.
Fig.18 Signal distributor
15
Page 42

- Raise the torch and pivot it into the normal position - the arc ignites
(see Fig. 20c)
- Start welding
Fig.19 TR 52-1 pedal-operated remote-control unit
START-UP
- Unplug the machine from the mains
- Shift the mains switch to the “O” position
- Dismount the MIG/MAG welding torch
- Plug the current plug of the TIG welding torch into the current
socket and turn it clockwise to latch it
- Plug the current plug of the earthing cable into the current socket
and turn it clockwise to latch it
- Tool up the welding torch (see welding-torch instruction manual)
- Make an earthing connection to the workpiece
- Attach a pressure regulator to the shielding-gas cylinder
- Connect the gas-hose to the pressure regulator
- Open the valve on the gas cylinder
- Variant I: Connect the TP 4-SP remote-control unit to socket on the
T.I.M.E. 30 wirefeeder
- Variant II: Connect the remote-control combination TP 4-SP, signal
distributor and TR 52-1 to the socket on the T.I.M.E. 30 wirefeeder
Warning! As soon as you shift the mains switch into the "I"
position, the tungsten electrode becomes LIVE. Make sure that
when this happens, the tungsten electrode does not touch any
electrically conducting or earthed parts such as e.g. the workpiece,
machine housing etc.
- Plug the machine into the mains
- Shift the mains switch to the “I” position
- ‘Ready’ indicator lights up
- Open the gas cut-off valve on the torch and/or press the torch trigger
and set the desired gas flow rate on the pressure regulator
- Set the arc-force dial on the TP 4-SP remote-control unit to a scale
value of "0"
- Set the Hot-Start dial on the TP 4-SP remote-control unit to a scale
value of "0"
- Select the welding range with range-switch on the TP 4-SP
- Set the welding current with the welding-current dial on the TP 4SP remote-control unit or set a current-limitation as described in
Variant II
- Place the gas nozzle on the ignition location so that there is a gap of
2 - 3 mm between the tungsten tip and the workpiece (see Fig. 20a)
- Gradually tilt up the welding torch until the tungsten tip touches the
workpiece (see Fig. 20b)
a) Fit gas nozzle b) Touch workpiece to
ignite arc
Fig.20 Torch tilt angle
c) Arc is ignited
MANUAL ELECTRODE WELDING
- Unplug the machine from the mains
- Shift the mains switch to the “O” position
- Dismount the MIG/MAG welding torch
- Depending on the type of electrode, plug the welding cable into the
current socket and turn it clockwise to latch it
- Connect the TP 4-SP remote-control unit to socket on the T.I.M.E.
30 wirefeeder
- Plug the machine into the mains
Warning! As soon as you shift the mains switch into the "I"
position, the rod electrode becomes LIVE. Make sure that when
this happens, the rod electrode does not touch any electrically
conducting or earthed parts such as e.g. the workpiece, machine
housing etc.
- Shift the mains switch to the “I” position
- ‘Ready’ indicator lights up
- Select the welding range with range-switch on the TP 4-SP
- Set the welding current with the welding-current dial on the TP 4SP
- Set the arc force with the arc-force dial on the TP 4-SP remotecontrol unit
- Set the Hot-Start with the Hot-Start dial on the TP 4-SP remotecontrol unit
- Start welding
ROBOT WELDING
In conjunction with the TSST 153 robot interface, an interconnecting
cable, the FK71 cooling unit and the VR 153 robot wirefeeder, the
T.I.M.E. Synergic power source is suitable for use in robot welding.
VR 153 wirefeeder
- Special speed-controlled feed motor ensures exact wirefeed speeds
- Optional push-pull torch
- Wire-inch and gas-test button directly on the wirefeeder
16
Page 43

TS ST 153 robot interface
- Adjustment screw for setting the threshold gas-flow rate that will
trigger the ‘insufficient gas’ detection feature
- Adjustment potentiometer for burn-back correction
- Adjustment potentiometer for droplet-detachment correction
- LED status indication of “input and output signals” and of voltage
supply lines and command values
Interconnecting cable
- available in lengths of 4m or 8m
FK71 cooling unit
- welding is only possible when the FK71 cooling unit is connected up
For more detailed information, please see the respective instruction
manuals.
T.I.M.E. Synergic power source
FK 71 cooling unit with coolant watchdog
Robot interface
Robot control unit
Robot
VR 153 T.I.M.E. with adjustable gas watchdog
T.I.M.E. machine torch
Interconnecting cable for VR153, 4m/8m
Power source / robot cable, 8m
TR 23P programming remote-control unit
DESCRIPTION OF PARAMETERS
00 ... Displays SMS software version
01 ... Displays SMS board version
02 ... Displays NMI board version
03 ... Displays position of TPS330 / 450 DIP-switch
04 ... Displays position of TPS/TS DIP-switch
05 ... Displays position of ARCF-CORR DIP-switch
06 ... Displays position of WF 22m / 30m DIP-switch
07 ... Displays pos. of DIP-switch for cooling-unit auto control
08 ... Input command-voltage test
09 ... Automatic wirefeed test
12 ... Welding circuit inductivity and resistance measurement
16 ... MIN. wirefeed adjustment aid
17 ... MAX. wirefeed adjustment aid
18 ... Wirefeed linearity check (at 15m/min or 11 m/min)
19 ... Wirefeed slippage test
20 ... Displays wirefeeder motor current
21 ... Hall-shunt test
22 ... Voltage measurement test
24 ... RTC year setting
25 ... RTC month setting
26 ... RTC date (day) setting
27 ... RTC day-of-week setting
28 ... RTC hours setting
29 ... RTC minutes setting
30 ... RTC seconds setting
32 ... Language selection (En/Gn)
33 ... Print-out options
34 ... Weldment print-out intervals
35 ... Interval time: Minutes
36 ... Interval time: Seconds
40 ... Limit-value cut-out ON/OFF
41 ... Ignition-monitoring options
42 ... Wire stickout for ignition time-out
43 ... Setting the ignition-monitoring time-lag
44 ... Arc-break time
45 ... TR 23P twin-head functions
ENGLISH
Fig.21 Schematic representation of standard configuration for robot welding
THE SET-UP MENU
N.B.! The set-up menu can only be activated in power sources bearing
the legend "PRO".
TO ACCESS THE SET-UP MENU
- Uncouple the welding wire
- Unplug the welding -current cable from the current sockets
- Shift the mains switch to the “I” position and - within the first three
seconds - switch the digital-indicator range-switch back and
forward several times
- Call up the test program by selecting the program number
TO EXIT THE SET-UP MENU
- Shift the mains switch of the power source to the “O” position (the
parameters you have just set will be stored)
CARE AND MAINTENANCE
Warning! Before opening up the welding machine, switch it off,
unplug it from the mains and put up a warning sign to stop
anybody inadvertently switching it back on again. If necessary,
discharge the electrolytic capacitors.
In order to keep your welding machine operational for years to come, you
should observe the following points:
- Carry out safety inspections at the stipulated intervals (see the
section headed “Safety rules”)
- Depending on the machine location, but no less often than twice a
year, remove the side panels from the machine and blow the inside
of the machine clean with dry, reduced-blow compressed air. Do not
aim air-jets at electronic components from too close a range.
- If a lot of dust has accumulated, clean the cooling-air ducts.
On water-cooled welding torches:
- Check that the torch connections are watertight
- Check the volume and quality of the coolant water (only top up with
clean coolant water)
- Keep an eye on the volume of coolant returning to the coolant
reservoir
17
Page 44

TROUBLESHOOTING
Warning! Machine may only be opened up by suitably trained and skilled personnel! Before opening up the welding machine, switch it off,
unplug it from the mains and put up a warning sign to stop anybody inadvertently switching it back on again. If necessary, discharge the
electrolytic capacitors. If fuses need replacing, they must be replaced by fuses of the same rating. No warranty claims will be accepted in
respect of damage caused by the use of too high a rating of fuse.
ERROR MESSAGES ON THE DISPLAYS
The power source is equipped with a self-diagnosis system! Any errors that occur will be recognised and indicated on the displays in the form of an
error code (E00 - E99).
Error message Description
E01 Internal error in the T.I.M.E. Synergic control system! (Error in main-memory test)
E02 Internal error in the T.I.M.E. Synergic control system! (Error in AD/DA converter adjustment!)
E03 Function not implemented!
E04 Automatic wirefeed test: No motor rotation detected!
E05 Automatic wirefeed test: Min. and max. speeds are faulty!
E06 Automatic wirefeed test: Max. speed is faulty!
E07 Automatic wirefeed test: Max. could not be reached (motor adjustment only OK up to half-way up the motor control range)
E08 Automatic wirefeed test: Min. and max. are correctly adjusted, but problem has occurred in middle of speed range (linearity
fault)
E09 Automatic wirefeed test: Acceleration time exceeded (too slow!)
E19 HALL-SHUNT gain adjustment: HALL-SHUNT offset is too big for gain to be adjusted!
E30 Autotest: No shorting in welding circuit!
E33 Procedure aborted by user!
E34 Incorrect EPROM: Power source has been fitted with a “rotary switch” Eprom instead of a “program selector switch” one!
E35 Incorrect EPROM for this board version: You have plugged an out-of-date EPROM version into the control board
FAULTS ON THE WELDING MACHINE
Fault Cause Remedy
Machine does not function
‘Ready’ indicator is not lit up, ‘m/min - mm V’ indicator is lit up, welding-current indicator
is lit up
‘m/min - mm - V’ indicator and weldingcurrent indicator are not lit up
‘Ready’ indicator is lit up, m/min - mm - V
indicator and welding- current indicator are
not lit up
Break in mains supply lead
Mains fuse is defective
No voltage supply to power-section control
No control-system supply voltage Check fuses 2F1 and 2F12 and replace if
No voltage supply to controller Check / change fuse 2F6
Check mains supply lead
Change mains fuse
Check / replace fuse 1F10
faulty
No welding current
‘Ready’ indicator is lit up, over/undervoltage
indicator is lit up
‘Ready’ indicator is lit up, overtemperature
indicator is lit up
Phase failure Check mains fuse, mains plug and mains
supply lead
Check mains voltageMains voltage too high or too low - over/
undervoltage watchdog has cut out
Thermostatic cut-out system has been tripped
(fan is running)
ed
18
Wait until machine automatically comes back
on after end of cooling phase - if it does not,
call After-Sales Service
Do not exceed duty cycleMachine overloaded, duty c. has been exceed-
Page 45

Fault Cause Remedy
Insufficient flow of cooling air Ensure an adequate flow of cooling air
Power section badly soiled Open up the unit and blow clean with dry
compressed air
‘Ready’ indicator is lit up, feeder motor is
running
Arc-outs occur from time to time
‘Ready’ indicator is lit up, over/undervoltage
indicator lights up for approx. 10 s.
FK71 cooling unit is not running, 5-pole coolingunit plug is not plugged in
FK71 cooling unit is not running - fuse 2F3 is
faulty
not running
Fuse 2F5 for machine fan is faulty Change fuse on VM34 auxiliary transformer
Over/undervoltage watchdog has cut out Check mains voltage
No open-circuit voltage
Welding torch is faulty Change torch
+ pole of interconnecting cable is not connected Plug in the cable and latch it
A mains phase is missing
Transient mains voltage fluctuations cause
over/ undervoltage watchdog to cut out
occasionally
Plug in the cooling-unit plug, the right way
around, and latch it into place
Change fuse on VM34 auxiliary transformer.
Change fuse on VM34 auxiliary transformer.Fuse 2F4 is faulty - fan in FK71 cooling unit is
Change fanFan in the power source is faulty
Check open-circuit voltage on ‘m/min - mm V’ indicator (approx. 51V)
Check / change fuse 2F8 on VM34 auxiliary
transformer.
Ensure good contact to workpieceEarthing cable not connected
Check mains supply lead
Check mains voltage
ENGLISH
No function when torch trigger is pressed
‘Ready’ indicator is lit up, no welding current
- feeder motor is not running - no shielding
gas
‘Ready’ indicator is lit up, Manual /
NoProgram indicator is flashing
Unsteady arc - heavy spatter losses
Torch control plug not plugged in or plug-in
connector is faulty
Torch trigger or torch control lead is faulty
Program selector switch is in wrong position Correct the program selection
Wrong remote-control unit is being used Use a TR34 T.I.M.E. or TP4-SP remote-control
Torch On/Off switch is in the “torch trigger
deactivated” position
Interconnecting cable is faulty or not connected Check the interconnecting cable
Program selector switch is in wrong positionPoor welding properties
Standard program was welded using a T.I.M.E.
torch
In Program mode: Arc is too short or too long
In Manual mode: Operating point is not set to
optimum values
Arc force is too hard
Plug in and latch the control plug, check plugin connections and change where necessary
Repair or replace torch
Check or replace fuse 2F7No negative supply
unit, or work without a remote-control unit
Shift the Torch On/Off switch to the “torch
trigger activated” position
Correct the program selection
Use a standard torch and keep the stick-out
short
Use the arc-length correction dial to optimise
the length of the arc
Co-ordinate the parameters for welding
voltage, wirefeed speed and arc force (see
tables of guideline values printed on machine)
Correct the arc force with the TR34 T.I.M.E.
remote-control unit in Standard-Manual mode
19
Page 46

Fault Cause Remedy
Change the contact tubeContact tube is too large, or its bore is worn
Poor earth connection Ensure good contact between earthing clamp
and workpiece
Replace any burnt/charred parts - use a new
earthing cable if necessary
Incorrect alloy and/or diameter of wire
Interconnecting cable or earthing cable is too
long, cross-sectional area of cable is too small
Interconnecting cable or earthing cable is badly
laid out or incorrectly reeled in
Uneven wirefeed speed Braking force is set too high Loosen the brake
Contact-tube bore is too narrow
Wire inner liner in torch is too short, blocked or
too narrow
Wirefeed rollers have insufficient contact
pressure
Welding wire forms a loop between the
feed rollers and the wire inlet nozzle
Wrong wire nozzle Check value stamped onto nozzle
Contact tube is too narrow Change the contact tube
Check / change the wire spool
Check the weldability of the base metal
Correct the welding parameters - use a cable
with a larger cross-sectional area, otherwise
create new welding programs
Arrange the hosepack or cable as straight as
possible, or reel in in a “bifilar” pattern
Screw in the right contact tube for the diameter
of wire being welded
Remove contact tip or wire nozzle, depending
on the type of torch, and check the length of
the liner
Fit an inner liner with the correct internal
diameter
Change any kinked or blocked liners (this is
essential!)
Set the knurled nut on the pressure set-screw
so that the wire electrode is fed smoothly, yet
without being deformed
‘Ready’ indicator is lit up, open-circuit
voltage is present, no flow of shielding gas
‘Ready’ indicator is lit up, open-circuit
voltage is present, shielding gas is flowing
Inner diameter of wire inner liner is too narrow
Wire inner liner blocked, rusty, kinked or too
short
Contact pressure of feed rollers is too high
groove)
Motor fuse is defectiveWirefeeder motor is not running
Torch On/Off switch on wirefeeder is on "OFF"
Break in control-voltage supply to wirefeeder Check 37-pole control plug and interconnec-
Carbon brushes worn out; motor defective
Insert liner of the correct size for the diameter
of wire being used
Replace the inner liner
Reduce contact pressure by turning knurled
nut
Set up motor base-plate correctlyIncorrect drive rollers (shape and diameter of
Tool-up the welding torch correctlyWelding torch not tooled up correctly
Change motor fuse 2F9 on the VM34 auxiliary
transformer
Shift the torch On/Off switch on the wirefeeder
to the "ON" position
ting cable from power source to wirefeeder
Measure voltage on motor. If motor voltage is
present, the motor must be changed.
20
Page 47

Fault Cause Remedy
Wirefeeder motor always runs at full
speed
Wirefeed speed deviates from the programmed values shown in the Table
After the torch trigger is pressed in open
circuit, the wirefeed speed is too slow
After the torch trigger is pressed, the
wirefeed speed reaches max. 22m/min.
Gas continues to flow even after the torch
trigger is released
Remote control does not function Wrong remote-control unit
Wire burns onto weld pool after end of
welding
Command value is always ‘max.’ Check interconnecting cable
Motor controller receives no actual speed value
V-groove rollers have been mounted The programmed values are for trapezoidal
Wirefeeder motor is running at the pre-set softstart speed
Wrong EPROM in the power source Check EPROM
DIP switch S6 or S7 is not on correct setting Check DIP switch S6 or S7
Gas solenoid valve is defective or dirty Clean or change the solenoid valve
Remote-control unit or r.-c. cable are faulty
Wirefeeder motor is not being braked; carbon
brushes are worn out
Check 37-pole control plug and interconnecting cable from power source to wirefeeder
or semicircular-grooved feed rollers. If you
use V-groove rollers, you must correct the
arc-length
Wirefeed speed only increases once the welding wire has hit the workpiece. To determine
the actual wirefeed speed, you must press
the wire-inch button.
Change motor controller board NMI4Motor controller board NMI4 is defective
Only use TR34 T.I.M.E. or TP4-SP remotecontrol units
Disconnect remote-control cable from wirefeeder and check command values (m/min.)
Measure motor voltage. If motor voltage is
present, the motor must be changed
Wire burns onto contact tube after end of
welding
Welding current on the gas nozzle Accumulations of spatter in the gas nozzle
Welding torch overheats - even though
duty cycle has not been exceeded (only
applies to water-cooled machines)
Burn-back time set too long Use the burn-back time correction dial to
(especially in out-of-position welding)
or else defective
Not enough coolant in FK71 cooling unit Top up with coolant
Forward and return-flow hoses wrong way round
Coolant circuit blocked or hoses kinked
Change motor controller board NMI4Motor controller board NMI4 is defective
shorten the burn-back time
Detach the gas nozzle and clean the contact
tube, contact tip and gas nozzle - spray with
Fronius anti-stick agent if necessary
Fit a new insulation piece if necessaryInsulation piece or spatter guard not mounted,
Connect the coolant hoses the right way round
Undo the screw cap of the water reservoir and
check the return flow
ENGLISH
21
Page 48

TECHNICAL DATA
Warning! If the machine is designed to run on a special voltage,
the Technical Data shown on the rating plate apply. The mains
plug and mains supply lead, and their fuse protection, must be
dimensioned accordingly.
T.I.M.E. SYNERGIC POWER SOURCE
Mains voltage (+/-10%) 3 x 380 / 400 / 415 V~, 50 - 60 Hz
Mains fuse protection 40 A slow-blow
Cos phi 150 A 0.98
450 A 0.99
Apparent power at 60% duty cycle 27 kVA
100% duty cycle 21 kVA
Efficiency 90 %
Welding current range (continuous) 3 - 450 A
Welding current at 60% duty cycle 450 A
100% duty cycle 360 A
Open-circuit voltage 50 V
Working voltage MIG/MAG 0 - 50 V
Electrode 0 - 55 V
TIG 0 - 55 V
FK 71 COOLING UNIT
Mains voltage 2 x 380 - 415 V, 50 - 60 Hz
Power consumption 0.6 A
Speed 2800 rpm (50 Hz), 3200 rpm (60 Hz)
Cooling capacity 2420 W
Max. delivery capacity 3.64 l/min.
Max. pump pressure 3.3 bar
Coolant volume approx. 5.5 l
Degree of protection IP 23
Dimensions L x W x H mm 575/365/265
Weight (without coolant) 21 kg
Degree of protection IP 21
Type of cooling AF
Insulation class F
Approval marks S, CE
T.I.M.E. 30 WIREFEEDER
Mains voltage 42 V
Motor, rated current 4.2 A
Rated power 180 W
Torque 21 Ncm
Wirefeed speed 0 - 30 m/min
Reduction ratio 17.6 : 1
Degree of protection IP 23
Safety class III
Weight 12.5 kg
22
Page 49

LED CHECKLIST, DIALS AND FUSES
Warning! Machine may only be opened up by suitably trained and skilled personnel! Before opening up the welding machine, switch it off,
unplug it from the mains and put up a warning sign to stop anybody inadvertently switching it back on again. If necessary, discharge the
electrolytic capacitors. If fuses need replacing, they must be replaced by fuses of the same rating. No warranty claims will be accepted in
respect of damage caused by the use of too high a rating of fuse. Dials not shown here must not be adjusted!
Transient protection
LED indicator is only lit up if the overvoltage protector
is activated
LED indicator for start of PWM
LED +5V / +15V
Must always be lit up for as long as the
machine is switched on
LED indicator lights up if a mains
overvoltage of more than 15%
occurs
LED indicator lights up if a mains
overvoltage of more than 44% occurs, or if
there is a phase failure
Fig.22 LED indicators on board PWM 3
Power-source start-up
LED indicator only lights up on MIG/MAG start-up signal
Current-flow signal
LED indicator is lit up when welding
current is flowing
Welding-current command value
The higher the command value, the more
brightly the LED indicator glows
LED indicator lights up for approx. 10 sec.
if there is a mains overvoltage or
undervoltage of +/- 10%
No function
LED indicator always stays dark
ENGLISH
No function
LED indicator always stays dark
LED indicator lights up to show a programmed
burn-back impulse
Fig.23 LED indicators on board WM 34A
23
Page 50

LED indicator +15V must always be lit up as
LED indicator +10V must always be lit up for
as long as the machine is ON
LED indicator +5V must always be lit up as
long as machine is ON, otherwise F6 faulty
long as machine is ON, otherwise F6 faulty
LED indicator -15V must always be lit up as
long as machine is ON, otherwise F7 faulty
LED indicator BRT 2
lights up when torch
trigger 2 is pressed (not
used at present)
LED indicator BRT
lights up when torch
trigger is pressed
‘Wire-inch’ LED indicator lights up when
the wire-inch button is pressed
‘Wirefeeder A’ LED indicator is lit up when a twin-
wirefeed control is being used and this is switched to
Wirefeeder A
‘Gas-test’ LED indicator
lights up when the gas-test
button is pressed
Motor brake
LED indicator lights up when the
wirefeeder motor is braked
Wirefeed command value
The higher the command value, the
more brightly the LED indicator glows
Fig.24 LED indicators and dials on board NMI 4.
switched on, for a period
Motor reset
of 1 sec.
LED indicator lights up:
- after the machine is
- after an overcurrent on
24
the wirefeeder motors
Current-flow signal
LED indicator is lit up when
welding current is flowing
LED indicator lights up when
open-circuit voltage is present
LED indicator lights up for approx. 10 sec.:
a) if a mains overvoltage or undervoltage of +/- 10 % occurs
b) if there is a machine overheating error.
Page 51

Setting-dial for HotStart time, from 0.5 to 2.0 sec.
depending upon pre-set welding-current command value
Fig.25 LED indicators and dials on board MIG 45.
Fig.26 Coding possibilities on board NMI4.
Controller Out (PWM command value)
The higher the command value, the more
brightly the LED indicator glows
S1 OFF ON
S1/1 450 A 330 A
S1/2 Special function OFF Special function ON
S1/3 Pulsed-Arc & Standard Standard
S1/4 Without arc-force correction With arc-force correction
(only in Standard mode)
S1/5 Without twin-head With twin-head
S1/6 WF A nmax = 30 m/min WF A nmax = 22 m/min
S1/7 WF B nmax = 30 m/min WF B nmax = 22 m/min
S1/8 Cooling-unit cut-out (automatic) Cooling-unit cut-out (continuous operation)
Open-circuit voltage ON
LED indicator is lit up for as long as the command to
switch on the open-circuit voltage is given
ENGLISH
25
Page 52

Plug connector X5
primary voltage supply
Primary 0V~
F1 6.3 A slow-blow
Cooling-unit pump 380V~
F3 0.63 A slow-blow
Primary 380V~
F12 6.3 A slow-blow
Plug connector X6 for
415V mains reconnection
Plug connector X7 for
400V mains reconnection
Plug connector X8 for
380V mains reconnection
Fan for cooling unit 230V~
F4 0.315 A slow-blow
Fan 230V~
F5 0.315 A slow-blow
Plug connector X1
for machine fan
Plug connector X4
voltage supply to BM 45.
Wirefeeder motor (VR152) 42V~
F9 10 A slow-blow
Pull-Mig motor 42V~
F10 2 A slow-blow
Plug connector X3
Supply to NMI 4 control
electronics
Supply to NMI 4
20V~ (+15V / +10V / +5V)
F6 2 A slow-blow
Open-circuit voltage 36V~
F8 0.315 A slow-blow
Supply to NMI 4
20V~(-15V), F7 1 A slow-blow
Fig.27 Fuses on board VM34B
Plug connector X2 PWM
Vacant
26
Page 53

MODE D´EMPLOI
FRANÇAIS
1
Page 54

2
Page 55

SOMMAIRE
CHER CLIENT DE FRONIUS,
La présente brochure est destinée à vous familiariser avec la commande
et l‘entretien de la T.I.M.E. Synergic. Lisez attentivement le mode
d‘emploi et observez scrupuleusement les instructions. Vous éviterez
ainsi des pannes dues à de fausses manoeuvres. Vous en serez
récompensé par la fiabilité de fonctionnement et la longue durée de vie
de votre appareil.
FRONIUS SCHWEISSMASCHINEN
VERTRIEB GMBH & COKG
Attention ! Seules des personnes qualifiées sont autorisées à
effectuer la mise en service de l‘appareil et ceci uniquement dans
le cadre de la réglementation technique. Lisez attentivement le
chapitre „Consignes de sécurité“ avant de procéder à la mise en
service.
Cher client de Fronius, ............................................................................. 3
Consignes de sécurité.............................................................................. 4
Généralités ............................................................................................ 4
Uilisation conforme ............................................................................... 4
Obligations de l‘exploitant ................................................................... 4
Obligations du personnel ..................................................................... 4
Equipement de protection individuel .................................................. 4
Risque provenant du dégagement de vapeurs et gaz de nocifs ..... 4
Risques provenant de la projection d‘étincelles ............................... 4
Risques provenant du courant secteur et du courant de soudage . 4
Zones particulièrement dangereuses ................................................. 4
Mesures de sécurité relatives à l‘information .................................... 5
Mesures de sécurité sur le lieu d‘installation de la soudeuse......... 5
Courants de soudage vagabonds ....................................................... 5
Mesures de sécurité en fonctionnement normal ............................... 5
Contrôle de sécurité ............................................................................. 5
Modifications apportées à la soudeuse.............................................. 5
Pièces de rechange et pièces d‘usure ............................................... 5
Etalonnage de postes à souder .......................................................... 5
Label CE ................................................................................................ 5
Droits d‘auteur....................................................................................... 5
Généralités ................................................................................................ 6
Principe de la T.I.M.E. Synergic .......................................................... 6
Vérification de procédé suivant EN 288 / 7 ....................................... 6
Conception de l'appareil ...................................................................... 6
Éléments de commande et connexions ................................................. 7
Source de courant T.I.M.E. Synergic .................................................. 7
Avance de fil T.I.M.E. 30 ..................................................................... 9
Appareil de refroidissement FK 71 .................................................. 10
Télécommande TR 34 T.I.M.E........................................................... 10
Télécommande TP 4 SP .................................................................... 11
Mise en service de la source de courant ............................................. 11
Utilisation selon les prescriptions ..................................................... 11
Instructions d’installation ................................................................... 11
Brancher la fiche de réseau .............................................................. 11
Branchement sur secteur................................................................... 11
Assemblage de la source de courant ............................................... 12
Connecter le Faisceau de câbles de connexion avec la source
de courant / l'appareil de refroidissement ....................................... 12
Raccorder le faisceau de câbles de connexion à l'avance de fil .. 13
Monter et raccorder la bouteille à gaz ............................................. 13
Monter la torche de soudage ............................................................ 13
Mise en service de l'appareil de refroidissement............................ 13
Montage de la bobine de fil ............................................................... 13
Introduction du fil-Électrode .............................................................. 13
Changer les galets d'avance de fil ................................................... 14
Soudage MIG/MAG................................................................................. 14
Instructions de réglage du procédé T.I.M.E. .................................... 14
Valeurs de réglage de type de courant, Type de cordon, position
de soudage et épaisseur de cordon ................................................. 15
Soudage TIG ........................................................................................... 15
Variante I.............................................................................................. 15
Variante II ............................................................................................ 15
Mise en service ................................................................................... 16
Soudage manuel à l'électrode enrobée ............................................... 16
Soudage robot......................................................................................... 16
Le menu setup......................................................................................... 17
Entrer dans le menu setup ................................................................ 17
Quitter le menu setup ......................................................................... 17
Description des paramètres .............................................................. 17
Soins et entretien.................................................................................... 17
Diagnostic de défauts et réparation...................................................... 18
Messages de défaut sur les indications ........................................... 18
Défauts de l'installation de soudage ................................................ 18
Caractéristiques techniques .................................................................. 22
Source de courant T.I.M.E. Synergic ................................................ 22
Avance de fil T.I.M.E. 30 .................................................................... 22
Appareil de refroidissement FK 71 ................................................... 22
DEL-Check-list, Régulateurs et coupe-circuits.................................... 23
Liste de pièces de rechange
Fronius - Bureaux de vente et bureaux de service
FRANÇAIS
3
Page 56

CONSIGNES DE SÉCURITÉ
GÉNÉRALITÉS
La soudeuse répond aux derniers développements techniques et satisfait à la réglementation généralement reconnue en matière de sécurité.
En cas de fausse manoeuvre ou de mauvaise utilisation, elle présente
toutefois certains risques
- pour la santé et la vie de l‘utilisateur ou d‘un tiers,
- pour l‘appareil et pour d‘autres biens matériels de l‘exploitant,
- liés à la qualité du travail effectué avec la soudeuse.
Toutes les personnes intervenant dans la mise en service, la manipulation et l‘entretien de la soudeuse doivent
- avoir la qualification requise,
- avoir des connaissances suffisantes en soudure et
- observer scrupuleusement les instructions de service.
Tout dérangement susceptible d‘affecter la sécurité doit être réparé sans
délai.
Votre sécurité est en jeu !
UILISATION CONFORME
La soudeuse a été conçue exclusivement pour une utilisation de le cadre
des travaux prévus (voir chapitre „Mise en service de l’appareil de
soudage“).
L‘utilisation conforme implique également l‘observation
- de toutes les consignes figurant dans les instructions de service
- des travaux d‘inspection et d‘entretien prescrits.
OBLIGATIONS DE L‘EXPLOITANT
L‘exploitant s‘engage à n‘autoriser l‘utilisation de la soudeuse qu‘à des
personnes
- connaissant les prescriptions fondamentales concernant la sécurité
du travail et la prévention d‘accidents et familiarisées avec la manipulation de la soudeuse
- ayant lu et compris les avertissements figurant dans ces instructions
de service, et l‘ayant confirmé en apposant leur signature.
L‘exploitant est tenu de contrôler régulièrement si le personnel travaille
en respectant les prescriptions en matière de sécurité.
OBLIGATIONS DU PERSONNEL
Toutes les personnes chargées de travailler avec la soudeuse s‘engagent à
- respecter les prescriptions fondamentales en matière de sécurité du
travail et de prévention des accidents,
- à lire le chapitre concernant la sécurité ainsi que les avertissements
figurant dans les présentes instructions de service et à attester par
leur signature qu‘ils les ont compris, ceci avant d‘entamer le travail.
EQUIPEMENT DE PROTECTION INDIVIDUEL
Prenez les dispositions suivantes pour préserver votre sécurité :
- portez des chaussures solides, isolantes. Ces chaussures doivent
rester isolantes même dans un environnement humide
- protégez les mains par des gants isolants
- protégez les yeux des rayons ultraviolets en utilisant un écran de
soudeur doté de verres filtrants réglementaires
- portez uniquement des vêtements appropriés (difficilement inflammables)
- en cas de production importante de bruit, portez un casque antibruit
Toutes les personnes se trouvant dans le voisinage de l‘arc électrique
doivent
- être informées des dangers
- équipées des moyens de protection adéquats ;
- si nécessaire, prévoir des cloisons ou tentures de protection.
RISQUE PROVENANT DU DÉGAGEMENT DE
VAPEURS ET GAZ DE NOCIFS
- Prévoir un système d‘aspiration adéquat pour évacuer les fumées et
gaz nocifs de la zone de travail.
- Veiller à une ventilation suffisante.
- Eviter que les vapeurs dégagées par des solvants pénétrent dans la
zone de rayonnement de l‘arc électrique.
RISQUES PROVENANT DE LA PROJECTION
D‘ÉTINCELLES
- Eloigner tout objet inflammable de la zone de travail.
- Il est interdit de souder sur des réservoirs contenant ou ayant contenu
des gaz, des carburants, des huiles minérales et substances analogues. Même des résidus de ces substances présentent un risque
d‘explosion.
- Dans les locaux exposés au risque d‘incendie ou d‘explosion, une
réglementation particulière est applicable. Respecter la réglementation nationale et internationale qui s‘y rapporte.
RISQUES PROVENANT DU COURANT SECTEUR ET
DU COURANT DE SOUDAGE
- Une décharge électrique peut avoir des conséquences graves. En
principe, toute décharge peut être mortelle.
- Les champs magnétiques générés par de fortes intensités de courant
peuvent affecter le fonctionnement d‘appareils électroniques vitaux
(par exemple, stimulateurs cardiaques). Les personnes porteuses
d‘appareils de ce genre devraient consulter leur médecin avant de se
tenir à proximité immédiate d‘une zone de soudage.
- Tous les câbles de soudage doivent être bien fixés, intacts et isolés.
Remplacer immédiatement tout raccord lâche ou câble brûlé.
- Faire vérifier régulièrement par un électricien professionnel le conducteur de terre de la ligne d‘alimentation secteur et la ligne
d‘alimentation de l‘appareil.
- Avant d‘ouvrir l‘appareil à souder, s‘assurer qu‘il ne puisse pas être
accidentellement rebranché. Décharger les composants susceptibles d‘être électriquement chargés.
- Au cas où des interventions sur des éléments sous tension seraient
nécessaires, il est indispensable de faire appel à une seconde
personne qui puisse, le cas échéant, couper l‘alimentation électrique.
ZONES PARTICULIÈREMENT DANGEREUSES
- Ne jamais approcher les doigts des roues dentées du système
d‘entraînement du fil lorsqu‘il est en fonctionnement.
- Dans les locaux exposés au risque d‘incendie ou d‘explosion, une
réglementation particulière est applicable. Respecter la réglementation nationale et internationale qui s‘y rapporte.
- Les soudeuses destinées aux travaux dans des locaux à risques
électriques accrus (p. ex. chaudières) doivent être pourvus du label
S (Safety).
- Les soudures exigeant des mesures de sécurité particulières doivent
obligatoirement être réalisées par des soudeurs ayant reçu la formation adéquate.
4
Page 57

- Lors du transport par grue de la source de courant, toujours accrocher
les chaînes ou les câbles dans les anneaux de levage en gardant un
angle le plus perpendiculaire possible. Retirer la bouteille de gaz et
l‘unité d‘entraînement du fil.
- Lors du transport par grue de l‘unité d‘entraînement du fil, toujours
utiliser une suspension isolante.
MESURES DE SÉCURITÉ RELATIVES À
L‘INFORMATION
- Les instructions de service doivent être conservées en permanence
sur le lieu d‘utilisation de la soudeuse.
- En complément aux instructions de service, la réglementation généralement valable et la réglementation locale concernant la prévention d‘accidents et la protection de l‘environnement doivent à tout
moment être disponibles et respectés.
- Toutes les consignes de sécurité et les avertissements de danger
apposés sur la soudeuse doivent rester lisibles.
MESURES DE SÉCURITÉ SUR LE LIEU
D‘INSTALLATION DE LA SOUDEUSE
- Le poste à souder doit être installé sur un sol ferme et plat offrant
suffisamment de stabilité. Le renversement de la soudeuse présente
un grave danger !
- Dans les locaux exposés au risque d‘incendie ou d‘explosion, une
réglementation particulière est applicable. Respecter la réglementation nationale et internationale qui s‘y rapporte.
- Assurer par des directives et des contrôles internes que l‘environnement du lieu de travail soit toujours propre et ordonné.
COURANTS DE SOUDAGE VAGABONDS
- Veiller à une liaison solide de la pince à pièces usinées avec la pièce
usinée
- Lorsque le fond est conducteur électriquement, mise en place, si
possible, de l’appareil de soudage de sorte à l’isoler
En cas d’inobservation, des courants de soudage vagabonds surviennent pouvant conduire à la destruction de conducteurs de protection, de
l’appareil de soudage et d’autres installations électriques.
MESURES DE SÉCURITÉ EN FONCTIONNEMENT
NORMAL
- N‘utiliser la soudeuse que si tous les dispositifs de sécurité fonctionnent.
- Avant la mise en circuit de l‘appareil, s‘assurer que personne ne peut
être mis en danger.
- Au moins une fois par semaine, vérifier si la soudeuse ne présente
aucune détérioration détectable de l‘extérieur et contrôler le
fonctionnement des dispositifs de sécurité.
- VBG 4, §5 - Installations électriques et matériel électrique
- VBG 15, §33 / §49 - Soudure, découpage et opérations analogues
- VDE 0701-1 - Réparation, modification et contrôle d‘appareils électriques; exigences générales
- VDE 0702-1 - Essais de répétition sur les appareils électriques
Pour des renseignements plus précis concernant la mise en service, la
modification et l‘essai de postes de soudage, veuillez demander
l‘instruction de travail „Inspection de sécurité d‘appareils de soudage“
(AA-PMÜ-01) à votre poste de service Fronius.
MODIFICATIONS APPORTÉES À LA SOUDEUSE
- Aucune modification, transformation ou montage ne peuvent être
effectués sur la soudeuse sans l‘autorisation du constructeur.
- Remplacer immédiatement tout composant présentant un défaut
quelconque.
PIÈCES DE RECHANGE ET PIÈCES D‘USURE
- N‘utiliser que des pièces de rechange ou des pièces d‘usure d‘origine.
Les pièces d‘autres fabricants n‘offrent pas les garanties de sécurité
et de fonctionnement suffisantes.
- Pour toute commande, prière d‘indiquer la dénomination et le numéro
de référence exacts, comme indiqués sur la liste des pièces de
rechange, ainsi que le numéro de série de l‘appareil.
ETALONNAGE DE POSTES À SOUDER
Les normes internationales préconisent l‘étalonnage à intervalle régulier
des postes à souder. Fronius recommande d‘effectuer cet étalonnage
tous les 12 mois. Si vous désirez de plus amples informations à ce sujet,
n‘hésitez pas à contacter votre concessionnaire Fronius !
LABEL CE
La soudeuse satisfait aux exigences fondamentales de la directive en
matière de basse tension et de compatibilité électromagnétique et a
obtenu le label CE.
DROITS D‘AUTEUR
La société Fronius International GmbH&Co.KG est propriétaire des
droits d‘auteurs sur ces instructions de service.
Le texte et les figures correspondent à l‘état de la technique au moment
de la mise sous presse. Sous réserve de modification. Le contenu des
présentes instructions de service ne fondent aucun recours de la part de
l‘acheteur. Nous sommes reconnaissants pour toute proposition
d‘amélioration ou indication d‘erreurs figurant dans les instructions de
service.
CONTRÔLE DE SÉCURITÉ
Après toute modification, réparation, ou entretien de la soudeuse et au
moins une fois tous les douze mois, l‘exploitant est tenu de faire effectuer
un contrôle de état par un électricien professionnel.
Pour la vérification, tenir compte des prescriptions suivantes :
- IEC (EN) 60 974-1 - Matériel de soudage électrique - Partie 1:
Sources de courant pour soudage
FRANÇAIS
5
ud_fr_st_sv_00147 012001
Page 58

GÉNÉRALITÉS
PRINCIPE DE LA T.I.M.E. SYNERGIC
Le procédé T.I.M.E. est un procédé de soudage MAG de haute capacité
combinant une efficience maximale et une qualité excellente du cordon
de soudure. Le travail avec fils massifs à vitesses de fil plus élevées
donne une capacité de fusion plus élevée et une soudure de haute
qualité grâce aux mélanges spéciaux de gaz de protection.
Des facteurs comme l’aspect extérieur du cordon, les valeurs de qualité
mécanique-technologique, les transitions de cordons, sécurité contre
manques de fusion et peu de projections comptent parmi les avantages
essentiels de ce procédé. Grâce à l’introduction d’un deuxième mélange
de gaz "T.I.M.E.-II" on peut maintenant, si nécessaire, produire des
soudures sans soufflures ou piqûres. Le procédé T.I.M.E. principalement combine la technologie de sources de courant la plus avancée, des
torches et appareils d'avance de fil performants, la physique des gaz
correspondante et le savoir-faire de l'application appropriée de ces
éléments.
VÉRIFICATION DE PROCÉDÉ SUIVANT EN 288 / 7
Désormais il y aura dans le domaine de technique de soudure plusieurs
possibilités de reconnaissance d'instructions de soudage WPS. Suivant
la norme ÖNORM EN 288 / 1 une possibilité est la vérification de procédé
standard suivant EN 288 / 7. Une telle vérification de procédé standard
examine toutes les valeurs importantes d'influence et ainsi définit un
procédé de soudage standardisé.
CONCEPTION DE L'APPAREIL
La conception de la T.I.M.E est basée sur le principe modulaire. Les
composants individuels de commande sont vissés et peuvent être montés
facilement et sans problèmes sur un chariot robuste.
La bouteille à gaz est intégrée dans le chariot et montée en position
abaissée. Ceci permet le remplacement et la manipulation rapides et
faciles. Malgré les dimensions réduites de l'installation elle est construite
de telle manière qu'elle fonctionne de manière fiable aussi sous les
conditions les plus sévères. Le boîtier en tôle à recouvrement par
poudre, les éléments de commande installés de manière protégée et les
douilles de courant à verrouillage à baïonnette répondent aux demandes
les plus exigeantes.
L'appareil d'avance de fil portatif peut être monté sur le boulon de fixation
de la source de courant et peut tourner des deux côtés et peut être enlevé
pour élargir le champ de travail. Des recouvrements qui peuvent être
fermés protègent la bobine de fil et le système d'entraînement contre la
poussière de meulage produite.
La poignée de transport isolée et un chariot à grandes roues ainsi que
les oreilles de levage par grue localisées de manière optimale facilitent
le transport à l'intérieur de l'usine et lors de l'utilisation au chantier.
Ce type de reconnaissance est attractif, parce qu'il offre la possibilité de
réduire les frais de reconnaissance de chaque fabricant individuel. Une
fois exécutée une WPS est reconnue, si toute les valeurs d'influence
restent dans la gamme admissible du procédé de soudage standard.
Ceci est garanti entre autres aussi par les paramètres programmés dans
la source de courant. Pour plus d'informations nous vous renvoyons à
la vérification de procédé standard.
Fig.1 Installation de soudage T.I.M.E. Synergic
6
Page 59

ÉLÉMENTS DE COMMANDE ET CONNEXIONS
SOURCE DE COURANT T.I.M.E. SYNERGIC
Fig.2 Face source de courant T.I.M.E. Synergic
Indication Manuel / No Program
- illuminée en permanence en service manuel MIG/MAG (avec télécommande TR 34 T.I.M.E.), si le sélecteur de programme est mis sur
une position programmée
- illuminée en permanence en service de soudage manuel à l'électrode
enrobée
- clignote, si le sélecteur de programme n'est pas mis sur une position
programmée
Indication arc de transition ... entre arc court et arc avec fusion en
pluie se produit un arc de transition avec projections. Afin de l'éviter
l'indication "arc de transition" est illuminée.
Indication T.I.M.E. est illuminée, quand un programme T.I.M.E. est
sélectionné - l'échelle graduéee de vitesse de fil 0-30 m/min est
applicable.
Indication Hold ... à chaque fin de soudage les valeurs effectifs
actuelles de courant et tension de soudage sont mémorisées l'indication Hold est illuminée.
Sélecteur de gamme m/min - mm - V ... pour sélectionner la fonction
désirée m/min.......vitesse d'avance de fil
mm...........épaisseur de tôle
V...............tension de marche à vide ou de soudage (volt)
Indication m/min - mm - V
- Vitesse de fil (m/min) ... valeur théorique en programme MIG/MAG
et en service manuel
- Épaisseur de tôle (mm) en service de programme MIG/MAG
- Tension de soudage (V) ... valeur théorique n service de program-
me MIG/MAG
- Tension de soudage (V) ... valeur effective en programme MIG/
MAG, manuel et manuel à l'électrode enrobée
- Tension de soudage (V) ... valeur Hold en service de programme
MIG/MAG er service manuel
Fig.3 Dos source de courant T.I.M.E. Synergic
Interrupteur de réseau
Indication "prêt á être mis en service"... illuminée quand
l'interrupteur de réseau est mis sur "I"
Indication température trop élevée illuminée ...
- quand l'appareil est thermiquement surchargée
- la fiche de l'alimentation d'appareils de refroidissement n'est pas
branchée
- l'appareil de refroidissement est défectueux
- le débit d'eau est insuffisant (seulement avec l'option de contrôleur de débit)
Indication tension trop élevée ou trop basse illuminé ...
- quand la tension de réseau se trouve en dehors de la gamme de
tolérance (source de courant déconnecte)
- pendant 10 s. en cas d'interruptions de réseau ou pointes de
surtension (source de courant déconnecte et reconnecte immédiatement)
Sélecteur de programme (0-99) sert à sélectionner le programme
désiré de soudage par impulsion, standard ou T.I.M.E. suivant le gaz
de protection et le matériau d'apport.
Note! Si une lettre (p. ex. H 12) est indiquée en plus de l'épaisseur de
tôle, ceci signifie que la valeur indiquée malgré l'augmentation de la
puissance de soudage n'est plus augmentée.
Indication courant de soudage
- Valeur théorique en service manuel MIG/MAG ou manuel à
l'électrode enrobée
- Valeur effective en programme MIG/MAG ou en service manuel
- Valeur Hold en service de programme MIG/MAG
Note! Définition des notions de valeur théorique, valeur effective et
valeur Hold:
- La valeur théorique est la valeur "désirée" qui peut être sélectionnée
préalablement suivant le procédé de soudage et qui est indiquée en
marche à vide.
- La valeur effective est la valeur "effective" indiquée pendant le
soudage.
- La valeur Hold est la valeur "mémorisée" qui est indiquée après la fin
du soudage.
Régulateur démarrage P ... 0 - 30 m/min (T.I.M.E.) ou 1 - 10 (Power)
réglage recommandé T.I.M.E.: 9 m/min
- Suivant l'indication T.I.M.E. l'échelle graduée pour vitesse de fil (0
- 30 m/min) ou pour puissance de soudage (1-10) est applicable
- Démarrage P influence la stabilité de l'arc dans la phase
d'amorçage (amorçage sûr de l'arc) ou la termination des cordons
de soudure.
- En mode de fonctionnement T.I.M.E. 4 temps on peut régler la
vitesse de fil moyennant démarrage P, la valeur réglée est absolue, à savoir la valeur est indépendante de la puissance de
soudage réglée.
FRANÇAIS
7
Page 60

Régulateur P-End ... 0 - 30 m/min (T.I.M.E.) ou 1 - 10 (Power)
réglage recommandé T.I.M.E.: 5 ou 9 m/min
- Suivant l'indication T.I.M.E. l'échelle graduée de vitesse de fil (0
- 30 m/min) ou de puissance de soudage (1-10) est applicable.
- En mode de service T.I.M.E. 4 temps on peut régler la vitesse
finale du fil moyennant P-fin; la valeur réglée est absolue, à savoir
la valeur est indépendante de la puissance de soudage réglée.
Option égalisation Push/Pull ... pour égaliser le nombre de tours
avec utilisation d'une torche Push-Pull
Tableau synoptique de programme ... informe des programmes
programmés de soudage à impulsion, standard et T.I.M.E.
- [S] ... seulement programme standard mémorisé
- [P] ... seulement programme de soudage par impulsion mémorisée
Note! Le programme avec la désignation "EN 288/7" fut soudé dans le
cadre d'une vérification de procédé et n'admet que les paramètres de
soudage utilisés dans la vérification.
Régulateur Slope T.I.M.E. 4 temps ... 0,2 - 7,0 s.
réglage recommandé: 1 s.
Régulateur courant final T.I.M.E. 4 temps ... ne pas modifier la roue
de réglage; la roue de réglage doit être en position médiane
Touche d'introduction de fil... pour l'introduction du fil-électrode
dans le faisceau de câbles sans gaz et courant
- Douille de courant à fermeture baïonnette... sert de
- raccord du faisceau de câbles lors du soudage MIG/MAG
- raccord du câble de mise à la masse lors du soudage TIG
- raccord du câble d'électrode ou du câble de mise à la masse lors
du soudage manuel à l'électrode enrobée (suivant type d'électrode)
- Douille de courant à fermeture baïonnette... sert de
- raccord du faisceau de câbles lors du soudage MIG/MAG
- raccord de courant de la torche TIG
- raccord du câble d'électrode ou du câble de mise à la masse lors
du soudage manuel à l'électrode enrobée (suivant type d'électrode)
MATÉRIAU GAZ %
EN 440 G2
EN 70 S-6
EN 288/7
Fe1 (SG 2/3) CO
Fe2 (SG 2/3)
CrNi 19 9
CrNi 18 8
AlSi 5
AlMg 5
Al 99,5
Rutil
Basic
Metal
CrNi
Fig.4 Tableau synoptique de programme
Filfourré/
Flux
C. Wire
T.I.M.E.
T.I.M.E. II
T.I.M.E.
100 S13
2
Ar 82 CO
Ar 97,5 CO
Ar 97,5 CO
2
18
2
2
2,5
2,5
Ar 100
Ar 100
Ar 100
Ar 82 CO
2
18
Ar 82 CO2 18
Ar 82 CO
Ar 82 CO
2
2
18
18
CODE PROGRAMMÉ
1,0
0,8 1,2
2 3
7
S11
S16
17
S14 S15
18 19
21 22 23 24
25 26 27
29 30 31
33 34 35
37 38 39 40
S44
S43
47
51
55 56
EPROM no.: C0027
1,6
20
28
32
36
48
52
Douille de raccord ... faisceau de câbles de connexion
- Douille à fermeture baïonnette ... faisceau de câbles de
connexion
Douille de raccord appareil de refroidissement FK71 ... pour
brancher la fiche de commande de l'appareil de refroidissement
Note! Quand l'appareil de refroidissement n'est pas branché, l'indication
de température trop élevée de la source de courant est illuminée. Le
soudage n'est pas possible.
Option prise de préchauffage de gaz 230 V / 80 W... pour
l'alimentation électrique du préchauffeur de gaz avec utilisation de
comme gaz de protection
CO
2
- Paramètres de fond ... enlevez le tableau synoptique de pro-
gramme pour régler d'autres paramètes importants pour le procédé
de soudage.
Régulateur prédébit de gaz ... 0,1 - 3,0 s.
réglage recommandé: 0,1 s. (minimum)
Régulateur vitesse d'approche ... minimum jusqu'à 100% de la
vitesse de fil réglée
réglage recommandé: 50% (moyen)
Régulateur postdébit de gaz ... 0,5 - 4,0 s.
réglage recommandé: 2 s. (moyen)
Régulateur courant de démarrage T.I.M.E. 4 temps... ne pas
changer la roue de réglage; la roue de réglage doit être en position
moyenne
Fig.5 Détail "Paramètres internes 4-temps"
8
Page 61

AVANCE DE FIL T.I.M.E. 30
Fig.6 Face avance de filT.I.M.E. 30
Régulateur de puissance de soudage (Power)
- Échelle graduée 1-10 ... pour le réglage continu de puissance de
soudage (seulement quand l'indication T.I.M.E. n'est pas illuminée)
- Échelle graduée vitesse de fil 0-30m/min ... pour le réglage
continu de la vitesse de fil (seulement quand l'indication T.I.M.E.
est illuminée)
Remarque! En cas d'utilisation d'une vitesse de fil non soudable la
valeur la plus basse soudable reste réglée.
Régulateur correction de longueur d'arc ... pour la correction
continue de la longueur réglée d'arc dans la gamme de +/-20%
(indication de la valeur théorique de tension seulement en mode de
fonctionnement standard/programme)
Régulateur correction de la période de post-combustion
- Mode de fonctionnement standard/manuel ... réglage continu de
la période de post-combustion suivant l'échelle graduée dans la
gamme de 1-4 (0 - 0,4 s.)
- Mode de fonctionnement d'impulsion et standard ... avant le début
du soudage il faut régler le régulateur sur la valeur moyenne de
l'échelle graduée; les paramètres de la période de post-combustion sont intégrés dans le programme de soudage correspondant
- Régulat. à gauche ... formation de gouttes minimale au bout de fil
- Régulat. à droite... formation de gouttes plus élevée au bout de fil
Fig.7 Dos avance de fil T.I.M.E. 30
Sélécteur de mode de fonctionnement ... pour sélectionner le
mode de fonctionnement
- mode de fonctionnement à 2 temps
- mode de fonctionnement à 4 temps
- mode de fonctionnement T.I.M.E. à 4 temps
Mode de fonctionnement à 2 temps
- Appuyer sur la gâchette du pistolet et la maintenir appuyée: début
de soudage
- Lâcher la gâchette du pistolet: fin de soudage
Mode de fonctionnement à 4 temps
- Appuyer sur la gâchette du pistolet et la lâcher: début de soudage
- Appuyer de nouveau sur la gâchette du pistolet et la lâcher: fin de
soudage
Mode de fonctionnement T.I.M.E. à 4 temps ... pour appeler les
paramètres de démarrage, soudage et courant final moyennant la
gâchette du pistolet
- Appuyer sur la gâchette du pistolet et la maintenir appuyée: début
de soudage à courant de démarrage (démarrage P)
- Lâcher la gâchette du pistolet: Le courant de démarrage est réduit
suivant Slope
jusqu'au courant de soudage réglé sur le régu-
lateur de puissance de soudage
- Appuyer de nouveau sur la gâchette du pistolet et la maintenir
appuyée: le courant de soudage est réduit suivant Slope
jusqu'au courant final réglé (fin P)
- Lâcher la gâchette du pistolet: fin de soudage
Touche d'introduction de fil ... pour l'introduction du fil-électrode
sans gaz et courant dans le faisceau de câbles
Interrupteur torche On-OFF ... pour désactiver la gâchette du
pistolet (p. ex. lors du transport par grue)
- Position gauche de l'interrupt. ... gâchette du pistolet désactivée
- Position droite de l'interrupteur ... gâchette du pistolet activée
Douille de connexion option entraînement intermédiaire
Douille de connexion télécommande ... pour raccorder la télécom-
mande désirée
Douille de connexion gaz de protection
Douille de connexion commande de la torche... pour raccorder la
fiche de commande de la torche de soudage
Raccord central de la torche ... pour raccorder la torche de soudage
- Douille à fermeture à baïonnette ... faisceau de câbles de
connexion
Connexion à fiches retour d'eau ... faisceau de câbles de connex.
Douille de connexion gaz de protection ... faisceau de câbles de
connexion
Connexion à fiches aller d'eau ... faisceau de câbles de connexion
Connexion à fiches fiche de commande ... faisceau de câbles de
connexion
Introduction de fil
Coupe-circuit moteur d'avance de fil (4A à action retardée)
Note! Le moteur de l'avance de fil est refroidi par l'eau. Afin de refroidir
le moteur, l'avance de fil doit toujours être connectée avec l'eau de
refroidissement de la torche.
FRANÇAIS
9
Page 62

APPAREIL DE REFROIDISSEMENT FK 71
TÉLÉCOMMANDE TR 34 T.I.M.E.
Fig.8 Appareil de refroidissement FK 71
Fig.9 Dos de l'appareil de refroidissement FK 71
Fiche d'alimentation de l'appareil de refroidissement
Dispositif d'écoulement d'eau
Connexion à fiches d'aller d'eau (bleu)
Connexion à fiches de retour d'eau (rouge)
Fig.10 Télécommande TR 34 T.I.M.E.
Pour le soudage standard/programme, impulsion/programme et standard/manuel on a besoin de la télécommande TR 34 T.I.M.E..
Note! Les éléments de commande sur la télécommande ont toujours la
priorité; ils déterminent la fonction de l'installation.
Régulateur puissance de soudage (Power)
Régulateur correction de longueur d'arc
- échelle graduée rouge ... pour la correction continue de la longueur d'arc réglée dans la gamme de +/- 20% en mode de
fonctionnement à impulsion et standard/programme
- échelle graduée noire ... pour la correction continue de la tension
de soudage dans la gamme de 0 - 50 V en mode de fonctionnement standard/manuel (indication No Program illuminée)
Interrupteur mode de fonctionnement ... pour la présélection du
mode de fonctionnement lors du soudage MIG/MAG
Régulateur détachement de gouttes ou correction de dynamique
- échelle graduée rouge... correction continue de l'énergie de détachement de gouttes
à gauche ... force de détachement de gouttes plus réduite
neutre ... force de détachement de gouttes neutre
à droite... force de détachement de gouttes augmentée
- échelle graduée noire ... influence sur la dynamique de courtcircuit au moment de transfert de gouttes
à gauche... arc plus dur et plus stable
neutre ... arc neutre
à droite ... arc souple avec peu de projections
Douille de connexion câble de télécommande
10
Page 63

MISE EN SERVICE DE LA SOURCE
DE COURANT
TÉLÉCOMMANDE TP 4 SP
50
60
40
30
20
10
0
Fig.11 Télécommande TP 4 SP
Hot Start
70
80
90
100
T
3-150
100-450
Note! Dû à la caractéristique on ne peut pas souder des électrodes CEL
avec la T.I.M.E. Synergic.
Régulateur courant de soudage ... réglage continu du courant de
soudage dans les gammes de 3 - 150 A et 100 - 450 A
Régulateur Hot-Start ... 0 - 100% du courant de soudage réglé;
seulement actif dans la phase d'amorçage de l'électrode
Note! Le courant maximal total Hot-Start est automatiquement limité par
le courant de court-circuit.
Sélecteur de gamme... divise la gamme totale de soudage de
l'installation en deux gammes individuelles chevauchantes
Commutateur de polarité... sans fonction
Régulateur de dynamique ... influence sur la dynamique de court-
circuit au moment de transfert de gouttes
Douille de connexion câble de télécommande
0
1
1
2
2
3
B
3
4
CEL
4
5
5
Attention! Avant la première mise en service il faut lire le
chapitre "Instructions de sécurité".
UTILISATION SELON LES PRESCRIPTIONS
L’appareil de soudage est destiné uniquement au soudage MIG/MAG,
soudage d'électrodes et soudage TIG.
Toute utilisation différente ou plus générale n’est pas conforme. Le
fabricant décline toute responsabilité en cas de dommages résultant
d’une telle utilisation non conforme.
L’utilisation conforme comprend également
- l’observation de toutes les remarques des instructions de service
- l’exécution des travaux d’inspection et d’entretien
Attention! Il ne faut jamais utiliser l’appareil de soudage pour
dégeler des tuyaux.
INSTRUCTIONS D’INSTALLATION
L’appareil de soudage est vérifié suivant le type de protection IP21 ce qui
signifie:
- protection contre la pénétration de corps étrangers solides d’un
diamètre de plus de 12 mm
- protection contre des gouttes d’eau qui tombent verticalement
Suivant type de protection IP21 l’appareil de soudage peut être installé
et opéré en plein air. Les éléments électriques installés doivent toutefois
être protégés contre l’effet immédiat de l’humidité.
Attention! Installer l’appareil de soudage de manière stable sur
une base plane et solide. Une installation de soudage renversée
peut signifier un danger mortel.
La canalisation d’air est un dispositif de sécurité essentiel. Lors du choix
du lieu d’installation il faut veiller à ce que l’air de refroidissement passe
librement à travers les fentes d’aération sur la face et sur le dos. La
poussière métallique produite (p. ex. lors du travail d’émerisage ne doit
pas être aspirée directement dans l’installation.
BRANCHER LA FICHE DE RÉSEAU
Attention! Les fiches de réseau doivent correspondre à la tension de réseau et à la consommation de courant de l'appareil de
soudage (voir les caractéristiques techniques)
Attention! La protection par coupe-circuits de l'alimentation du
réseau est indiquée dans les caractéristiques techniques.
BRANCHEMENT SUR SECTEUR
L’appareil de soudage est désigné pour la tension de réseau spécifiée
sur la plaque indicatrice. La protection par coupe-circuits de l’alimentation
par le réseau est indiquée dans les caractéristiques techniques.
Attention! À l'usine la source de courant est réglée sur 400 V! En
raison de la gamme de tolérance de +/- 10% la source de courant
peut aussi être opérée par le réseau de 3x380V~. En cas de
défauts de surtension ou sous-tension la gamme de tension doit
être adaptée en branchant la connexion à fiches sur un autre
raccord.
Avec une tension de réseau de 3x230V~, 3x440V~ ou 3x500V~ il faut
utiliser un transfo FRONIUS intercalé en amont. Ce transfo peut être
installé à tout moment et peut être monté entre le chariot et la source de
courant. Sur demande spéc. la source de cour. peut être désignée aussi
pour 3x440V~ ou 3x500V~.
11
FRANÇAIS
Page 64

380V
342V
-10%
380V
418V
+10%
360V
400V
415V
Fig.12 Gammes de tolérance des tensions de réseau 3x380V / 400V / 415V~
-10%
373V
400V
+10%
415V
-10%
440V
456V
+10%
L'appareil de soudage peut être opéré en série par une tension de réseau
de 3x380 V~, 3x400 V~ ou 3x415 V~ pourvu que le transfo de commande
soit réglé sur la valeur correcte qui correspond à la tension de service
active.
Connexion à fiches X7 pour
commutation de réseau 400V~
Connexion à fiches X6 pour
commutation de réseau 415V~
Connexion à fiches X8 pour
commutation de réseau 380V~
Fig.13 Commutation de réseau 3x380V / 400V / 415V~ sur la plaquette à circuits
imprimés du transfo de commande VM 34.
Fig.14 Montage de la source de courant
Attention! Si l’appareil est réglé sur une tensions spéciale, les
caractéristiques techniques sont comme indiquées sur la plaque
indicatrice . La fiche de réseau, et l’alimentation par réseau ainsi
que sa protection par coupe-circuits doivent être désignées de
manière correspondante.
ASSEMBLAGE DE LA SOURCE DE COURANT
- Monter les étriers de montage et d'en haut sur le cadre du chariot
de telle manière que les trous et des deux étriers de montage
se trouvent en haut à gauche
- Insérer les tôles de fixation (complètes avec écrous à cage
montés) de derrière comme on peut voir dans la figure suivante et les
fixer d'abord légèrement serré par les vis d'acier M8 x 20 avec
rondelles et joncs.
- Monter la source de courant sur les étriers de montage et et
les fixer d'en bas par 4 vis d'acier M8 x 16, complètes avec rondelles
et joncs.
- Serrer par vis les deux étriers de montage sur le cadre du chariot.
- Insérer l'appareil de refroidissement d'avant à travers les barres de
montage et et le positionner (insérer en dessous la barre de
guidage inférieure).
- Comme on peut voir dans la figure suivante la fixation est assurée
seulement au point (vis d'acier M8 x 16 d'en bas, avec rondelle et
jonc).
Fig.15 Montage de la source de courant
CONNECTER LE FAISCEAU DE CÂBLES DE
CONNEXION AVEC LA SOURCE DE COURANT /
L'APPAREIL DE REFROIDISSEMENT
- Interrupteur de réseau en position "O"
- Fixer la décharge de traction du faisceau de câbles de connexion par
la vis existante
- Brancher la fiche à baïonnette potentiel de soudage sur la douille
et la tourner pour la verrouiller
- Brancher la fiche de commande à 37 broches sur la douille de
connexion du raccord de commande et fixer la collerette de fixation
- Brancher le tuyau flexible d'aller et de retour d'eau du faisceau de
câbles de connexion sur les couleurs correctes des connexions à
fiches et .
- Raccorder la fiche d'alimentation de l'appareil de refroidissement
dans la douille de connexion de la source de courant.
Note! Quand l'appareil de refroidissement n'est pas branché, l'indication
de température trop élevée de la source de courant est illuminée. Le
soudage n'est pas possible.
12
Page 65

RACCORDER LE FAISCEAU DE CÂBLES DE
CONNEXION À L'AVANCE DE FIL
Note! Utiliser seulement de l'eau de conduite propre. D'autres produits
antigel ne peuvent pas être recommandés en raison de leur conductivité.
- Interrupteur de réseau en position "O"
- Monter l'avance de fil (avec cosse isolante encastrée) sur le boulon
de fixation de la source de courant
- Desserrer l'agrafe de serrage de la décharge de traction et faire
passer du bon côté le faisceau de câbles de connexion jusqu'au tuyau
métallique de serrage de la gaine protectrice.
Note! Ne pas croiser ou plier les lignes
- Raccorder la douille à baïonnette potentiel de soudage du faisceau
de câbles de connexion à la douille
- Brancher la douille de commande à 37 broches sur la douille de
connexion de raccord de commande et la fixer par la collerette de
fixation
- Brancher le tuyau flexible de gaz du faisceau de câbles de connexion
sur la douille de connexion de gaz de protection et le serrer par la
collerette de fixation
Note! Vérifier d'abord que les joints toriques d'étanchéité sont bien mis
- Brancher les tuyaux flexibles d'aller et de retour d'eau du faisceau de
câbles de connexion sur les couleurs correctes des connexions à
fiches
- Serrer par vis l'agrafe de serrage de la décharge de traction.
et et les serrer par la collerette de fixation
et la tourner pour verrouiller
MONTER ET RACCORDER LA BOUTEILLE À GAZ
- Mettre la bouteille à gaz sur la base du chariot de la source de courant
- Fixer la bouteille à gaz moyennant la chaîne de sécurité
Note! La fixation optimale n’est assurée que sur la partie supérieure de
la bouteille à gaz (non sur le col de la bouteille)
- Enlever le capot protecteur de la bouteille à gaz
- Tourner la vanne de la bouteille à gaz brièvement à gauche pour
enlever les boues autour de la place de travail
- Vérifier le joint du détendeur de gaz
- Visser le détendeur de gaz sur la bouteille à gaz moyennant et le
serrer
- Connecter le raccord de gaz de protection au détendeur de gaz
moyennant le tuyau flexible de gaz
MONTER LA TORCHE DE SOUDAGE
- Interrupteur de réseau en position "O"
- Raccorder la torche de soudage correctement équipée avec le tube
d’entrée d’abord au raccord central de torche
- Serrer à main la collerette de fixation
- Brancher la fiche de commande de la torche sur le raccord de
commande de la torche et la verrouiller
- Brancher le tuyau flexible de gaz de la torche sur la pièce de raccord
de gaz et le verrouiller
MISE EN SERVICE DE L'APPAREIL DE
REFROIDISSEMENT
Note! Avant chaque mise en service de l'appareil de refroidissement il
faut contrôler le niveau du liquide de refroidissement ainsi que la pureté
du liquide de refroidissement. À l'usine l'appareil de refroidissement est
rempli d'environ 2l de liquide de refroidissem. (rapport de mélange 1:1).
- Interrupteur de réseau en position "O"
- Enlever le bouchon fileté
- Remplir le liquide de refroidissement (rapport de mélange voir la table
suivante)
- Monter de nouveau le bouchon fileté
Attention! Étant donné que Fronius n'a pas d'influence sur la
qualité, pureté et le niveau du liquide de refroidissement, aucune
garantie ne peut être assumée en ce qui concerne la pompe à
réfrigérant.
Température extérieure Rapport de mélange eau : esprit de vin
+ °C à -5°C 4 l : 1 l
-5°C à -10°C 3,75 l : 1,25 l
-10°C à -15°C 3,5 l : 1,5 l
-15°C à -20°C 3,25 l : 1,75 l
Attention! Il faut contrôler régulièrement le débit d'eau - le retour
sans perturbations doit être visible.
En cas de conditions plus sévères (grandes longueurs de faisceau de
câbles, grandes différences de niveau, etc.) vous devriez utiliser l'appareil
de refroidissement FK 71 R d' une puissance frigorifique de 2,6 kW et
une pression de refoulement de 4,4 bar.
MONTAGE DE LA BOBINE DE FIL
Attention! Le porte-bobine sert de support et fixation de bobines
standardisées de fil de soudage jusqu'à 20 kg au maximum.
- Interrupteur de réseau
- Ouvrir la couverture de la bobine de fil
- Monter la bobine de fil du bon côté sur le porte-bobine
- Faire encliqueter le boulon d’arrêt dans l’ouverture prévue sur le
corps de la bobine.
- Régler l’effet de freinage moyennant vis de tension
- Refermer la couverture de la bobine de fil
Note! Régler le frein de telle manière que la bobine de fil ne continue pas
à tourner après la fin du soudage - il faut toutefois éviter tout serrage
excessif de la vis de tension pour ne pas surcharger le moteur.
en position "O"
INTRODUCTION DU FIL-ÉLECTRODE
- Interrupteur de réseau en position "O"
- Ouvrir la couverture de la bobine de fil
- Faire pivoter vers avant les dispositifs tendeurs et
- Plier vers le haut les leviers d'appui et
- Pousser le fil-électrode à travers le tube d’entrée de l'entraînement
à 4 galets environ 5 cm dans le tuyau d'entrée de la torche de soudage
- Rabattre les leviers d'appui et
- Faire pivoter les dispositifs tendeurs et dans une position
verticale
- Régler la pression d'appui moyennant les écrous tendeurs et .
Note! Régler la pression d’appui de telle manière que le fil-électrode ne
soit pas déformé, mais le transport de fil soit assuré sans problèmes.
- Étendre le faisceau de câbles de la torche en ligne droite
- Enlever la buse de gaz de la torche
- Dévisser le tube-contact
- Enficher la fiche de réseau
-- Mettre l’interrupteur de réseau
- Témoin lumineux de réseau illuminé
- Régler le sélecteur de programme sur la position désirée (indication "No Program" ne doit pas être illuminée)
13
dans la position "I"
FRANÇAIS
Page 66

SOUDAGE MIG/MAG
- Régler le sélecteur de gamme pour indications numériques sur la
position m/min
- Régler sur le régulateur de la puissance de soudage une valeur de
~ 5 m/min
Attention! Pendant l’introduction de fil il faut que la torche ne soit
pas dirigée vers le corps.
- Appuyer sur la touche d'introduction de fil jusqu'à ce que le filélectrode dépasse de la torche
- Terminer l'introduction en lâchant la touche d'introduction de fil .
Note!Après avoir lâché la gâchette du pistolet la bobine de fil ne devrait
plus tourner. Si nécessaire, il faut rajuster le frein.
- Visser le tube-contact
- Monter la buse de gaz
- Fermer la couverture de la bobine de fil
- Mettre l'interrupteur de réseau en position "O"
Fig.16 Entraînement à 4 galets
CHANGER LES GALETS D'AVANCE DE FIL
Afin d’assurer une avance optimale du fil-électrode les galets d’avance
de fil doivent être adaptés au diamètre et à l’alliage du fil à souder.
- Interrupteur de réseau en position "O"
- Ouvrir la couverture de la bobine de fil
- Faire pivoter les dispositifs tendeurs et vers l'avant
- Plier les leviers d'appui et vers le haut
- Retirer les essieux embrochables -
- Enlever les galets d'avance -
- Monter les nouveaux galets d'avance
Note! Monter les galets d’avance de telle manière que la désignation du
diamètre de fil soit lisible.
- Insérer de nouveaux les essieux embrochables - - l’arrêt de
fixation de l’essieu embrochable doit encliqueter
- Rabattre les leviers d'appui et
- Faire pivoter les dispositifs tendeurs et dans la position verticale
- Régler la pression d'appui moyennant les écrous tendeurs et
- Fermer la couverture de la bobine de fil.
Attention! Avant la première mise en service il faut lire le
chapitre “Instructions de sécurité“ et “Mise en service de la
source de courant“.
- Brancher le câble de mise à la masse sur la douille de courant et le
verrouiller
- L'autre bout du câble de mise à la masse doit être connecté avec la
pièce à usiner
- Brancher la fiche de réseau
- Connecter la fiche de réseau
- Témoin de réseau illuminé
Attention! Installations refroidies par l'eau: Le débit d'eau doit
être contrôlé régulièrement pendant l'opération - le retour sans
perturbations doit être visible.
- Présélectionner le programme de soudage par le sélecteur de programme (indication "No Program" ne doit pas être illuminée ou
clignoter)
Note! Toutes les programmes ont été soudées par une torche standard
(sauf programmes T.I.M.E.). Lors du soudage de programmes standard
par une torche T.I.M.E. ceci risque de modifier les caractéristiques de
soudage.
- Mettre le sélecteur de mode de fonctionnement sur la position
désirée
- Brancher la télécommande sur la douille de raccord de télécommande (pour le soudage par impulsion il faut raccorder la télécommande TR 34 T.I.M.E. Régler le sélecteur de mode de fonctionnement sur
la télécommande TR 34 T.I.M.E. sur soudage par impulsion)
- Mettre le régulateur de correction de longueur de l'arc sur "0"
- Mettre le régulateur de correction de détachement de gouttes sur
"0"
- Régler l'intensité de courant désirée moyennant le régulateur de
puissance de soudage (indication de valeur théorique sur l'indication d'intensité de courant)
- Ouvrir la vanne de la bouteille à gaz
- Régler la quantité de gaz
- Appuyer sur la gâchette du pistolet et commencer le soudage
Note! Quelquefois il faut corriger le prédébit ou le postdébit de gaz
et/ou la vitesse d'approche .
INSTRUCTIONS DE RÉGLAGE DU PROCÉDÉ T.I.M.E.
Par la commande à un seul bouton de la T.I.M.E. Synergic il faut régler
seulement la vitesse de fil correspondante; la tension de soudage se
règle automatiquement. Seulement la longueur d'arc doit être corrigée
de manière correspondante.
Calcul de la puissance de fusion
Cette formule ne vaut que pour un diamètre de fil de 1,2 mm et des fils
d'acier non ou faiblement alliés. Des pertes par projection n'ont pas été
prises en considération. (typiquement 1 - 2%).
Puissance de fusion[kg/h] =
p.ex. vitesse de fil = 20m/min
Puissance de fusion[kg/h] =
Vitesse de fil[m/min] x 60 x 8,9
1000
20 m/min x 60 x 8,9
1000
= 10,68 kg/h
14
Page 67

SOUDAGE TIG
Calcul de la vitesse de soudage
Cette formule ne vaut que pour un diamètre de fil de 1,2 mm et des fils
d'acier non ou faiblement alliés. Des pertes par projection ainsi que
déviations de géométrie telles que fente à la racine et surhaussements
de soudure (typiquement 10-20% vitesse basse) n'ont pas été prises en
considération.
Vitesse de soudage[cm/min] =
Vitesse de fil[m/min] x 1,13 x 100
Surface de la section transversale de la
soudure[mm
2
]
p.ex.soudure d'angle a 6 (la soudure d'angle a 6 a une surface de section
transversale de 36 mm2) et vitesse de fil de 20m/min
Vitesse de soudage[cm/min] =
20 m/min x 1,13 x 100
36 mm
2
= 62,8 cm/min
Étant donné qu'en cas de soudage en plusieurs passes il est difficile de
déterminer les sections transversales des passes de soudure, il résulte
très laborieux de calculer la vitesse de soudage. Un planimètre ou du
papier millimétré est très utile. Les valeurs de réglage de type de cordon,
position de soudage et épaisseur de soudure sont les suivantes:
VALEURS DE RÉGLAGE DE TYPE DE COURANT,
TYPE DE CORDON, POSITION DE SOUDAGE ET
ÉPAISSEUR DE CORDON
VARIANTE I
On a besoin de la télécommande TP 4-SP et du set TIG (torche de
soudage à la main AL 22-S / AL 16-S avec tuyau flexible à gaz, détendeur
de gaz et boîte de pièces de rechange).
Note! Dans cette variante du soudage TIG le contact avec la pièce à
usiner provoque un courant de court-circuit dont l'intensité dépend du
courant de soudage réglé. Les amorçage à partir de 10 A causent
toujours un endommagement de la surface de la pièce à usiner et de la
pointe de l'électrode en tungstène et réduisent la qualité du cordon de
soudage par des inclusions de tungstène.
- L'amorçage de l'arc se fait par le contact de l'électrode en tungstène
avec la pièce à usiner.
- Afin d'interrompre le soudage il suffit d'interrompre le contact de la
torche avec la pièce à usiner jusqu'à ce que l'arc s'éteigne. Remplissage de cratère final par réduction de courant et protection du cratère
final par gaz ne sont pas pourvus.
Soudures bout à bout
Position en gouttière
- soudage de la passe de fond
fentes irrégulières et largeurs de
fente de plus de 2mm: 2,5 4,5m/min
fentes régulières de 2mm: 9m/min
- passes de remplissage
gamme inférieure: 12-15m/min
gamme supérieure: 15-23m/min
- passes de couverture: 15-18m/min
Position transversale
- soudage de la passe de fond
fentes irrégulières et largeurs de
fente de plus de 2mm: 2,5 4,5m/min
fentes régulières de 2mm: 9m/min
- passes de remplissage: 12 - 18m/
min
- passes de couverture: 9 - 12m/min
Soudage au plafond
- soudage de la passe de fond: 3 4m/min
- passes de remplissage: 9-11m/min
- passes de couverture: 9 - 11m/min
Cordon montant: 3 - 6m/min
Cordon descendant : 9 - 11m/min
Soudure d'angle
Position horizontale
- a3: 12 - 14m/min
- a4: 12 - 16m/min
- a5: 15 - 18m/min
- a6: 18 - 23m/min
- a7: 20 - 23m/min
- à partir de a8 seulement en
plusieurs passes 20 - 23m/min
- cordon de balayage de 10-12m/min
Soudage au plafond
- 9 - 11m/min pour toutes les
épaisseurs de cordon et cordons
en une ou plusieurs passes
Cordon descendant
- 9 - 11m/min; maximum a3,5
soudage en une passe,
- cordons plus épais en plusieurs
passes
Cordon montant
- 4 - 6m/min; épaisseur minimale
de cordon a6
Position en gouttière
- a3: 12 - 14m/min.
- a4: 12 - 14m/min.
- a5: 17 - 23m/min.
- a6: 17 - 23m/min.
- ab a7: 22 - 30m/min.
Fig.17 Set TIG
VARIANTE II
On a besoin de la télécommande TP 4-SP, la télécommande à pédale TR
52-1, un distributeur de signaux ainsi que du set TIG (torche de soudage
à la main AL 22-S / 16-S avec tuyau flexible à gaz, détendeur de gaz et
boîte de pièces de rechange).
L'utilisation de cette combinaison offre les avantages suivants:
- Réduction du courant de soudage au moment du contact avec la
pièce à usiner par la télécommande à pédale.
- Remplissage du cratère final par réduction de courant moyennant la
télécommande à pédale (décharge lente de la pédale provoque une
réduction du courant de soudage à environ 10 A) est possible - ce qui
garantit une protection optimale par gaz
- Limitation de courant de soudage sur la télécommande TP 4-SP d'un côté toute la course de la pédale est disponible pour la gamme
sélectionnée, de l'autre côté une mince électrode en tungstène par
exemple ne peut pas être surchargée ou fondre quand la pédale est
appuyée à fond.
Fig.18 Distributeur de signaux
15
FRANÇAIS
Page 68

- Dresser la torche de soudage davantage et la mettre en position
normale - l'arc s'amorce (voir fig. c)
- Exécuter le soudage
Fig.19 Télécommande à pédaleTR 52-1
MISE EN SERVICE
- Débrancher la fiche de réseau
- Mettre l'interrupteur de réseau en position "0"
- Démonter la torche MIG/MAG
- Brancher la fiche de courant de la torche TIG sur la douille de courant
et la tourner à droite pour la verrouiller
- Brancher la fiche de courant du câble de mise à la masse sur la douille
de courant et la tourner à droite pour la verrouiller
- Équiper la torche de soudage (voir instructions de service de la torche
de soudage)
- Établir la connexion de la masse avec la pièce à usiner
- Monter le détendeur de pression sur la bouteille à gaz
- Connecter le tuyau flexible à gaz avec le détendeur de pression
- Ouvrir la vanne de la bouteille à gaz
- Variante I: Raccorder la télécommande TP 4-SP sur la douille de
l'avance de fil T.I.M.E. 30
- Variante II: Combinaison de télécommande TP 4-SP, distributeur de
signaux et TR 52-1 sur la douille de l'avance de fil T.I.M.E. 30
Attention! Quand l'interrupteur de réseau se trouve dans la
position "I", l'électrode en tungstène est sous tension. Veillez à
ce que l'électrode en tungstène en ce moment ne soit pas en
contact avec des éléments conducteurs ou mis à la terre tels
qu'outils, boîtiers, etc.
- Brancher la fiche de réseau
- Mettre l'interrupteur de réseau en position "I"
- Indication "prêt à être mis en service" illuminée
- Ouvrir la vanne d'arrêt de gaz sur la torche de soudage, appuyer sur
la gâchette et régler la quantité de gaz désirée sur le détendeur de
pression
- Mettre le régulateur de dynamique sur la télécommande TP 4-SP
sur la valeur "0" de l'échelle graduée
- Mettre le régulateur de Hot-Start sur la télécommande TP 4-SP sur
la valeur "0" de l'échelle graduée
- Sélectionner la gamme de soudage par le sélecteur de gamme de
la TP 4-SP
- Régler le courant de soudage par le régulateur de courant de sou-
dage de la télécomm.TP 4-SP ou le limiter comme décrit pour la
variante II
- Mettre la buse de gaz sur le point d'amorçage, de manière qu'entre
la pointe en tungstène et la pièce à usiner reste une dist. de 2-3 mm
(voir fig. a)
- Dresser la torche de soudage lentement jusqu'à ce que la pointe en
tungstène touche la pièce à usiner (voir fig. b)
a) Mettre la buse de gaz
sur la pièce à usiner
Fig.20 Inclinaison de la torche
b) Amorçage par contact
avec la pièce à usiner
c) Arc amorcé
SOUDAGE MANUEL À
L'ÉLECTRODE ENROBÉE
- Débrancher la fiche de réseau
- Mettre l'interrupteur de réseau en position "O"
- Démonter la torche de soudage MIG/MAG
- Brancher le câble de soudage suivant le type d'électrode sur la douille
de courant et tourner à droite pour le verrouiller
- Raccorder la télécommande TP 4-SP sur la douille de l'appareil
d'avance T.I.M.E. 30
- Brancher la fiche de réseau
Attention! Quand l'interrupteur de réseau
tion "I", l'électrode en barre est sous tension. Veillez à ce que
l'électrode en baguette en ce moment ne soit pas en contact avec
des éléments conducteurs ou mis à la terre tels qu'outils, boîtiers,
etc.
- Mettre l'interrupteur de réseau en position "I"
- Indication "prêt à être mis en service" illuminée
- Sélectionner la gamme par le sélecteur de gamme de la TP 4-SP
- Sélectionner le courant de soudage par le régulateur de courant de
soudage de la TP 4-SP
- Sélectionner la dynamique par le régulateur de dynamique de la
télécommande TP 4-SP
- Sélectionner Hot-Start par le régulateur de Hot-Start de la télécommande TP 4-SP
- Exécuter le soudage
se trouve en posi-
SOUDAGE ROBOT
En combinaison avec les composants d'interface robot TSST 153,
faisceau de câbles intermédiaire, appareil de refroidissement FK71 et
avance robot VR 153 la source de courant T.I.M.E. Synergic est appropriée pour le soudage robot.
Appareil d'avance de fil VR 153
- Le moteur d'avance de fil spécial à réglage de vitesse garantit une
vitesse d'avance de fil exacte.
- Option torche push-pull
- Bouton d'introduction de fil et de contrôle de gaz directement sur
l'appareil d'avance de fil
16
Page 69

Interface robot TS ST 153
- Vis de réglage de la quantité de seuil de gaz pour la reconnaissance
de manque de gaz.
- Potentiomètre de réglage de la correction de la période de postcombustion
- Potentiomètre de réglage de la correction de détachement de gouttes
- Indication de l'état des "signaux d'entrée et de sortie" ainsi que des
alimentation en courant et valeurs théoriques par diodes électroluminescentes.
Faisceau de câbles de connexion
- disponible dans les longueurs de 4met . m
Appareil de refroidissementFK71
- Le soudage est possible seulement avec appareil de refroidissement
FK71 branché
Des indications plus détaillées se trouvent dans les instructions de
service correspondantes.
Source de courant T.I.M.E. Synergic
Appareil de refroidissement FK 71 avec contrôleur d'eau
Interface robot
Commande robot
Robot
VR 153 T.I.M.E. avec contrôleur d'eau réglable
Torche-machine T.I.M.E.
Faisceau de câbles de connexion VR153, 4/8m
Câble de connexion source de courant / Robot, 8m
Télécommande programmable TR 23P
Fig.21 Représentation de la version standard avec service robot
DESCRIPTION DES PARAMÈTRES
00 ... Indication de la version du logiciel SMS
01 ... Indication de la version de la plaquette à circuits imprimés SMS
02 ... Indication de la version de la plaquette à circuits imprimés NMI
03 ... Indication de la position du commutateur DIP, TPS 330 / 450
04 ... Indication de la position du commutateur DIP, TPS / TS
05 ... Indication de la position du commutateur DIP, DYN - KORR.
06 ... Indication de la position du commutateur DIP, VR 22m / 30m
07 Indication de la position du commutateur DIP, commande automa-
tique de l'appareil de refroidissement
08 ... Essai de la tension pilote d'entrée
09 ... Essai VR - Auto
12 ... Mesure de résistance / inductance du circuit de soudage
16 ... Aide à l'ajustage VR - MIN.
17 ... Aide à l'ajustage VR - MAX.
18 ... VR - contrôle de linéarité à 15m/min et 11 m/min
19 ... VR - essai de glissement
20 ... VR - indication du courant du moteur
21 ... Essai Hallshunt
22 ... Essai de la mesure de tension
24 ... RTC - réglage de l'année
25 ... RTC - réglage du moi
26 ... RTC - réglage de la date
27 ... RTC - réglage du jour
28 ... RTC - réglage de l'heure
29 ... RTC - réglage des minutes
30 ... RTC - réglage des secondes
32 ... Sélection de la langue de pays (D/E)
33 ... Sélection de l'option d'imprimante
34 ... Réglage des intervalles des éléments pour l'impression
35 ... Réglage du temps d'intervalle: minutes
36 ... Réglage du temps d'intervalle: secondes
40 Réglage pour la déconnexion en cause du dépassement des valeur
limites (on/off)
41 ... Réglage du contrôle d'amorçage
42 ... Réglage der de la longueur de fil du timeout d'amorçage
43 ... Réglage du temps d'interruption de surveillance d'amorçage
44 ... Réglage du temps de rupture de l'arc
45 ... Réglage des fonctions de tête double de la TR 23P
SOINS ET ENTRETIEN
LE MENU SETUP
Note! Le menu setup peut être activé seulement dans des sources de
courant avec l'impression "PRO".
ENTRER DANS LE MENU SETUP
- Découpler le fil de soudage
- Séparer le câble de courant de soudage des douilles de courant
- Mettre l'interrupteur de réseau dans la position "I" et commuter le
sélecteur de gamme des indications numériques plusieurs fois
pendant les premières trois secondes
- Appeler le programme d'essai moyennant sélection du numéro de
programme.
QUITTER LE MENU SETUP
- Mettre l'interrupteur de réseau de la source de courant dans la
position "O" (les paramètres réglés sont mémorisés)
Attention! Avant d'ouvrir l'appareil de soudage il faut déconnecter l'appareil, retirer la fiche de réseau et attacher un panneau
d'avertissement pour éviter la reconnexion - si nécessaire, il faut
décharger les condensateurs électrolytiques.
Pour tenir l'appareil de soudage en bon état prêt à être mis en service il
faut observer les points suivants:
- Inspection technique des aspects de sécurité suivant les intervalles
prescrits (voir chapitre "Instructions de sécurité")
- Au moins deux fois par an (ou plus souvent suivant le lieu d'installation)
il faut enlever les parties latérales de l'appareil et purger l'appareil de
soudage par de l'air comprimé à pression réduite sec. Il ne faut pas
souffler de courte distance sur les éléments électroniques.
- En cas d'une forte production de poussière il faut nettoyer les
conduits d'air de refroidissement
Avec torches de soudage refroidies par l'eau:
- Vérifier l'étanchéité des connexions de la torche
- Contrôler le débit d'eau et la qualité de l'eau (remplir seulement du
liquide de refroidissement propre)
- Surveiller la quantité de retour d'eau dans le récipient de réfrigérant
17
FRANÇAIS
Page 70

DIAGNOSTIC DE DÉFAUTS ET RÉPARATION
Attention! L'appareil ne doit être ouvert que par du personnel expert formé. Avant d'ouvrir l'appareil de soudage il faut déconnecter l'appareil,
retirer la fiche de réseau et attacher un panneau d'avertissement pour éviter toute reconnexion - si nécessaire, il faut décharger les
condensateurs électrolytiques. S'il faut remplacer des coupe-circuits il faut les remplacer par coupe-circuits de même valeur. En cas
d'utilisation de coupe-circuits trop forts nous n'assumons aucune garantie en cas d'éventuels dommages consécutifs.
MESSAGES DE DÉFAUT SUR LES INDICATIONS
La source de courant est équipée d'un système d'auto- diagnostic! Les défauts qui se produisent sont reconnus et indiqués sur les indications sous
forme d'un code d'erreur (E00 - E99).
Message de défaut Description
E01 Défaut interne dans la commande de la T.I.M.E. Synergic! (défaut lors de l'essai de la mémoire principale)
E02 Défaut interne dans la commande de la T.I.M.E. Synergic! (défaut lors de l'égalisation AD/DA)
E03 La fonction n'est pas installée!
E04 Essai automatique d'avance: aucun mouvement de marche du moteur n'était détecté!
E05 Essai automatique d'avance: défaut de vitesse minimale et maximale!
E06 Essai automatique d'avance: défaut de vitesse maximale!
E07 Essai automatique d'avance: le maximum n'a pas pu être atteint! (réglage de moteur correct jusqu' à la mi-vitesse de moteur)
E08 Essai automatique d'avance: minimum et maximum correctement réglés; le problème est apparu à mi-vitesse! (faute de linéarité)
E09 Essai automatique d'avance: dépassement du temps d'accélération!
E19 Ajustement de l'amplification de HALLSHUNT: décalage HALLSHUNT trop élevé pour régler l'amplification!
E30 Essai automatique: pas de court-circuit dans le circuit de soudage
E33 Processus interrompu par l'utilisateur!
E34 Eprom erroné: la source de courant fut équipée d'un Eprom "commutateur rotatif" au lieu de "sélecteur de programme"!
E35 Eprom erroné pour la version de la plaquette à circuits imprimés: vous avez enfiché une ancienne version d'Eprom dans la
plaquette à circuits imprimés de commande
DÉFAUTS DE L'INSTALLATION DE SOUDAGE
Défaut Diagnostic Réparation
Appareil sans fonction
L'indication "prêt à être mis en service" n'est
pas illuminée, l'indication "m/min - mm - V"
est illuminée, l' indication de courant de
soudage est illuminée.
L'indication "m/min - mm - V" et l'indication de
courant de soudage ne sont pas illuminées.
L'indication"prêt à être mis en service" est
illuminée, l'indic. "m/min - mm - V" et l'indic. de
courant de soudage ne sont pas illuminées.
Interruption de l'alimentation du résau
Défaut des coupe-circuits du réseau
Pas d'alimentation de la commande du bloc de
puissance
Pas de tension d'alimentation de commande Contrôler les coupe-circuits 2F1 et 2F12 et
Pas d'alimentation du régulateur Contrôler le coupe-circuits 2F6 et remplacer
Contrôler l'alimentation de réseau
Remplacer le coupe-circuit de réseau
Contrôler et remplacer le coupe-circuit 1F10,
si nécessaire
remplacerles coupe-circuits défectueux
si nécessaire
Pas de source de courant
L'indication "prêt à être mis en service" est
illuminée, l'indication de tension trop élevée
ou trop basse est illuminée
L'indication "prêt à être mis en service" est
illuminée, l'indication de température trop
élevée est illuminée
Défaillance de phase Contrôler les coupe-circuits de réseau, les
fiches de réseau et l'alimentation de réseau
Tension de réseau trop élevée ou trop basse.
Le contrôle de tension trop élevée ou trop
basse a déconnecté
Le détecteur thermique de sécurité a déconnecté (le ventilateur marche)
durée de mise en circuit.
18
Contrôler la tension de réseau
Attendre la phase de refroidiss. L'appareil
reconnecte automatiquement après peu de
temps; sinon il faut porter l'appareil au serv.
après-vente
Observer le facteur de serviceSurcharge de l'appareil,dépassement de la
Page 71

Défaut Diagnostic Réparation
Amenée insuffisante d'air de refroidissement Établir une amenée suffisante d'air
Bloc de puissance fortement encrassé Ouvrir l'appareil et le purger par de l'air com-
primé sec
L'indication "prêt à être mis en service" est
illuminée, le moteur d'avance de fil marche
Appareil de refroidiss. FK71 ne marche pas,
fiche de l'appar. de refroidiss. à 5 borches non
branchée
Appareil de refroidissement FK71 ne marche
pas - défaut du coupe-circuit 2F3
Défaut du coupe-circuit 2F4 - le ventilateur dans
l'appareil de refroidissem. FK71 ne marche pas
Défaut du coupe-circuit 2F5 pour le ventilateur de l'appareil
Le contrôle de tension trop élevée ou trop
basse a déconnecté
Manque de tension de marche à vide
Défaut de l'appareil de soudage Remplacer l'appareil de soudage
Pôle positif du faisceau de câbles de connexion n'est pas connecté
Brancher la fiche de l'appareil de refroidissement du bon côté et la verrouiller
Remplacer le coupe-circuit sur le transformateur de commande VM34.
Remplacer le coupe-circuit sur le transformateur de commande VM34.
Remplacer le ventilateurDéfaut du ventilateur dans la source de courant
Remplacer le coupe-circuit sur le transformateur de commande VM34
Contrôler la tension de réseau
Contrôler la tension de marche à vide sur
l'indication m/min - mm - V (approx. 51V)
Contrôler et remplacer le coupe-circuit 2F8
sur le transformateur de commande VM34.
Établir la connexion avec la pièce de travailLe câble de mise à la masse n'est pas connecté
Brancher le câble et le verrouiller
Arc intermittent
L'indication "prêt à être mis en service" est
illuminée, l'indication de tension trop élevée
ou trop basse est illuminée pendant approx.
10 s.
Pas de fonction lors de l'activation de la
gâchette du pistolet
L'indication "prêt à être mis en service" est
illuminée, manque de courant de soudage le moteur d'avance ne marche pas - pas de
gaz de protection
L'indication "prêt à être mis en service" est
illuminée,l'indication "Manuell / NoProgram"
clignote
arc instable - fortes pertes par projections
Manque d'une phase du côté du réseau
Fluctuations de courte durée de la tension de
réseau, contrôle de tension trop élevée ou trop
basse déconnecte de temps en temps
La fiche de commande de la torche n'est pas
branchée ou la connexion à fiches est défectueuse
Défaut de la gâchette du pistolet ou du câble de
commande de la torche
Manque d'alimentation negative
Position erronée du sélecteur de programme Corriger la sélection de programme
Utilisation d'une télécommande erronée Utiliser la télécommande TR34 T.I.M.E. ou
Interrupteur de connexion/déconnexion de torche en pos. „gâchette du pistolet désactivée“
Faisceau de câbles de connexion défectueux
ou non branché
Position erronée du sélecteur de programmeMauvaises caractéristiques de soudage
Le programme standard était soudé avec une
torche T.I.M.E.
Vérifier l'alimentation par le réseau
Contrôler la tension de réseau
Brancher et verrouiller la fiche de commande,
contrôler la connexion à fiches et, si nécess.,
remplacer
Réparer ou remplacer la torche
Vérifier et remplacer, si nécess., le coupecircuit 2F7
TP4-SP ou travailler sans télécommande
Mettre l´interrupteur de connexion/déconn. de
torche en pos. "gâchette du pistolet activée"
Vérifier le faisceau de câbles de connexion
Corriger la sélection de programme
Utiliser une torche standard ou veiller à un
stick-out court
FRANÇAIS
En cas de fonctionnement à programme: arc
trop court ou trop long
En cas de fonctionnement manuel: mauvais
réglage du point de travail
19
Optimiser la longueur d'arc moyennant le
régulateur de correction de longueur d'arc
Ajuster les paramètres de tension de soudage, de vitesse de fil et de dynamique (voir les
tables de valeurs de référence imprimées)
Page 72

Défaut Diagnostic Réparation
Dynamique d'arc trop dure
Mauvaise connexion de mise à la masse Assurer un bon contact entre la pince de mise
Mauvais alliage de fil - mauvais diamètre de fil
Faisceau de câbles de connexion ou câble de
mise à la masse trop long, section de câble
insuffisante
Faisceau de câbles de connexion ou câble de
mise à la masse embrouillé ou mal enroulé
Vitesse de fil irrégulière Frein trop fortement serré Desserrer le frein
Forure trop petite du tube-contact
Âme de guidage dans la torche trop courte,
obstruée ou trop étroite.
Corriger la dynamique par la télécomm.TR34
T.I.M.E. en fonctionnement manuel standard
Remplacer le tube-contactTube-contact trop grand ou forure usée
à la masse et la pièce à usiner
Rempl. les parties carbonisées - si nécessaire,
utiliser un nouveau câble de mise à la masse
Contrôler et, si nécessaire, remplacer la bobine de fil montée
Contrôler la soudabilité du matériau de base
Corriger les paramètres de soudage - augmenter la section du câble, sinon établir de
nouveaux programmes de soudage
Mettre le faisc. de câbles et câbles en pos. aussi.
rectil. que poss. ou enrouler de manière bifilaire
Visser le tube-contact correct pour le diamètre correspondant
Suivant le type de torche dévisser le portebuse ou la buse de fil et vérifier la longueur
d'âme
Le fil de soudage forme une boucle entre
les galets d'avance et la buse d'entrée du
fil
Le moteur d'avance de fil ne marche pas
L'indication "prêt à être mis en service" est
illuminée, la tension de marche à vide est
active, le gaz de protection ne passe pas
L'indication "prêt à être mis en service" est
illuminée, la tension de marche à vide est
active, le gaz de protection passe
Choisir une âme à diamètre intérieur correct
Remplacer absolument toute âme pliée ou
encrassée
Pression d'appui insuffisante des galets
d'avance
Mauvaise buse de fil Veiller à la valeur utilisée
Tube-contact trop étroit Remplacer le tube-contact
Diamètre intérieur trop petite de l'âme de guidage de fil
Âme de guidage de fil obstruée, enrouillée,
pliée ou trop courte
Pression d'appui trop forte des galets d'avance
gorge, diamètre de la gorge)
Défaut du coupe-circuit du moteur
L'interrupteur de conn. / déconn. de la torche
sur l'avance de fil est réglé sur "AUS" (déconnecté)
Interruption de l'alimentation en courant sur
l'avance de fil
Régler l'écrou moleté de la vis de réglage
d'appui de telle manière que le fil-électrode
ne soit pas déformé mais transporté sans
problèmes
Utiliser la bonne âme pour le diamètre de fil
utilisé
Remplacer l'âme
Réduire la pression d'appui moy. l'écrou moleté
Équiper correctement la plaque de moteurGalets d'actionnement erronés (forme de la
Changer l'équipem. de la torche de soudageMauvais équipement de la torche de soudage
Remplacer le coupe-circuit de moteur 2F9
sur le transformateur de commande VM34.
Régler l´interrupteur de connex. / déconnex.
de la torche sur l´avance de fil sur "EIN"
(connecté)
Vérifier la fiche de commande à 37 broches et
le faisceau de câbles de connexion de la
source de courant à l'appareil d'avance de fil
Usure des balais de charbon, défaut du moteur
20
Mesurer la tension au moteur; s'il y a de la
tension au moteur, il faut remplacer le moteur
Page 73

Défaut Diagnostic Réparation
Le moteur d'avance de fil fonctionne
toujours à pleine vitesse
La vitesse de fil diffère des valeurs
programmées sur la table
Après avoir appuyé sur la gâchette du
pistolet en marche à vide la vitesse de fil
est insuffisante
Après avoir appuyé sur la gâchette du
pistolet la vitesse maximale de fil est de
22m/min.
Gaz passe aussi après avoir lâché la
gâchette du pistolet
La télécommande est sans fonction Télécommande erronée
Toujours valeur de consigne max. Contrôler le faisceau de câbles de connexion
Le régulateur de moteur de reçoit pas de valeur
effective de vitesse
Montage de galets à gorge en V Le valeurs programmées valent pour des
Le moteur d'avance de fil marche à la vitesse
d'approche réglée
Éprom erroné dans la source de courant Contrôler l'Éprom
Mauvais réglage du commutateur S6 ou S7 Contrôler les commutateurs DIP S6 et S7
Vanne magnét. à gaz défectueuse ou encrassée
Défaut du régulateur de moteur NMI4.
Contrôler la fiche de commande à 37 broches
et le faisceau de câbles de connexion de la
source de courant à l'appareil d'avance de fil
galets d'avance à gorge trapézoïdale ou
gorge demi-ronde. En cas d'utilisation de
galets à gorge en V il faut corriger la longueur
d'arc.
La vitesse de fil augmente seulement après
le contact du fil de soudage avec la pièce à
usiner. Il faut appuyer sur la touche
d'introduction pour déterminer la vitesse
d'avance effective.
Nettoyer ou remplacer la vanne magnét. à
gaz
Remplacer la plaquette à circuits imprimés
régulatrice de moteur NMI4 .
Utiliser uniquement la télécommande TR34
T.I.M.E. ou TP4-SP
Défaut de la télécommande ou du câble de
télécommande
Après la fin du soudage le fil colle dans le
bain de soudage
Après la fin du soudage le fil colle sur le
tube-contact
Courant de soudage sur la buse de gaz Accumulation de projections dans la buse de
L'installation de soudage s'échauffe trop la durée de mise en circuit n'est pas
dépassée (seulement installations
refroidies par l'eau)
Le moteur d'avance de fil n'est pas freiné - les
balais de charbon sont usés
Défaut de la plaquette à circuits imprimés régulatrice de moteur NMI4.
Période de post-combustion trop longue réglée Réduire la période de post-combustion par le
gaz (particulièrement lors du soudage en position)
Élément isolant ou protection contre projections non installé ou défectueux
Pas assez de réfrigérant dans l'appareil de
refroidissement FK71
Aller et retour d'eau échangés
Circuit d'eau obstrué ou tuyaux flexibles d'eau
pliés
Séparer le câble de télécommande de
l'avance de fil et contrôler les valeurs
théoriques (m/min)
Mesurer la tension du moteur; s'il y a une
tension du moteur, il faut remplacer le moteur
Remplacer la plaquette à circuits imprimés
régulatrice de moteur NMI4.
régulateur de correction de la période de
post-combustion
Retirer la buse de gaz, nettoyer le tube-contact, le porte-buse et la buse de gaz - si
nécessaire arroser par agent séparateur de
Fronius
Si nécessaire, installer un nouvel élément
isolant
Remplir du réfrigérant
Connecter correctement les tuyaux flexibles
d'eau
Ouvrir le bouchon fileté du réservoir d'eau et
contrôler le retour.
21
FRANÇAIS
Page 74

CARACTÉRISTIQUES TECHNIQUES
Attention! Si l’appareil est réglé sur une tensions spéciale, les
caractéristiques techniques sont comme indiquées sur la plaque
indicatrice . La fiche de réseau, et l’alimentation par réseau ainsi
que sa protection par coupe-circuits doivent être désignées de
manière correspondante.
SOURCE DE COURANT T.I.M.E. SYNERGIC
Tension de réseau (+/-10%) 3 x 380 / 400 / 415 V~, 50 - 60 Hz
Coupe-circuits de réseau 40 A à action retardée
Cos phi 150 A 0,98
450 A 0,99
Puissance apparente à 60% ED/facteur de service 27 kVA
100% ED/facteur de service 21 kVA
Rendement 90 %
Gamme de courant de soudage continue 3 - 450 A
Courant de soudage à 60% ED/facteur de service 450 A
100% ED/facteur de service 360 A
Tension de marche à vide 50 V
Tension de travail MIG/MAG 0 - 50 V
Électrode 0 -55 V
TIG 0 - 55 V
APPAREIL DE REFROIDISSEMENT FK 71
Tension de réseau 2 x 380 - 415 V, 50 - 60 Hz
Consommation de courant 0,6 A
Couple de rotation 2800 tr/min (50 Hz), 3200 tr/min (60 Hz)
Puissance frigorifique 2420 W
Débit max. 3,64 l/min.
Refoulement max. de la pompe 3,3 bar
Contenu de refrigérant approx. 5,5 l
Type de protection IP 23
Dimensions longueur/largeur/hauteur mm 575/365/265
Poids (sans réfrigérant) 21 kg
Type de protection IP 21
Type de refroidissement AF
Classe d'isolation F
Signe d'homologation S, CE
AVANCE DE FIL T.I.M.E. 30
Tension de réseau 42 V
Courant nominal du moteur 4,2 A
Puissance nominale 180 W
Couple de rotation 21 Ncm
Vitesse de fil 0 - 30 m/min
Réduction 17,6 : 1
Type de protection IP 23
Classe de protection III
Poids 12,5 kg
22
Page 75

DEL-CHECK-LIST, RÉGULATEURS ET COUPE-CIRCUITS
Attention! L'appareil ne doit être ouvert que par du personnel expert. Avant d'ouvrir l'appareil de soudage il faut déconnecter l'appareil, retirer
la fiche de réseaau et applique un panneau d'avertissement afinnd d'éviter une reconnexion - si nécessaire décharger les condensateurs
électrolytiques. S'il faut remplacer des coupe-circuits il faut utiliser des coupe-circuits de la même valeur. En cas d'utilisation de coupe-circuits
trop forts nous n'assumons aucune garantie en cas d'éventuels dommages consécutifs! Il ne faut pas utiliser des régulateurs non désignés.
Protection contre surtensions dans le circuit intermediare
L'indication DEL est illuminée seulement avec protection
active contre surtension
Indication DEL pour démarrage PWM
DEL +5V / +15V
Doit être toujours illuminée quand l'appareil
est connecté
L'indication DEL est illuminée lors de
dépassements de réseau
de plus de 15%
L'indication DEL est illuminée lors de
dépassements de réseau de plus de 44%
ou lors de défaillance d'une phase
Fig.22 Indications sur la plaquette à circuits imprimés PWM 3
Source de courant démarrage
L'indicatiion DEL est illuminée seulement lors d'un signal de démarrage MIG/MAG
Signal de conduction de courant
L'indication DEL est illuminée quand le
courant de soudage circule
Fig.23 Indications sur la plaquette à circuits imprimés WM 34A
Valeur de consigne du courant de soudage
La clarté de l'indication DEL augmente avec
l'augmentation de la valeur de consigne
L'indication de la DEL est illuminée pendant
approx. 10 secondes lors de tensions plus
élevée ou plus basses de réseau de +/- 10%
Pas de fonction
L'indication DEL reste toujours sombre
23
Pas de fonction
L'indication DEL reste toujours sombre
L'indication DEL est illuminée avec impulsion de
post-combustion programmée
FRANÇAIS
Page 76

L'indication DEL +10V doit être toujours
illuminée quand l'appareil est connecté
L'indication DEL +15V doit être toujours
illuminée quand l'appareil est connecté, sinon
F6 est défectueux
L'indication DEL + 5V doit être toujours
illuminée quand l'appareil est connecté,
sinon F6 est défectueux
L'indication DEL -15V doit être toujours
illuminée quand l'appareil est connecté,
sinon F7 est défectueux
L'indication DEL BRT2
est illuminée quand la
gâchette du pistolet 2 est
appuyée (actuellement
non utilisée.)
L'indication DEL BRT
est illuminée quand la
gâchette du pistolet est
appuyée
L'indication DEL d'introduction est
illuminée quand la touche d'introduction
est appuyée.
L'indication DEL d'avance A est illuminée quand la
commande d'avance double est utilisée et quand on a
réglé l'installation sur avance A.
Indication DEL vérification
de gaz est illuminée quand
la touche de vérification de
gaz est appuyée
Frein moteur
L'indication DEL est illuminée, quand
le moteur d'avance est freiné
Valeur de cons. de l'avance de fil La
clarté de l'indication DEL augmente avec
l'augmentation de la valeur de consigne
Abb.24 Anzeigen und Einstellregler auf Print NMI 4.
connexion de
l'installation.
courant aux moteurs
Remise à la valeur initiale du
moteur L'indication DEL est
illuminée:
- pendant 1 sec. après la
d'avance de fil
- après surintensité de
24
Signal de conduction de
courant
L'indication DEL est illuminée
quand le courant de soudage
circule
L'indicatal DEL est illuminée quand
une tension de marche à vide est
active.
L'indicatio DEL est illuminée pendant environ 10 sec.:
a) en cas d'une tension trop élevée ou trop basse du réseau de +/- 10 %
b) en cas d'un défaut de température trop élevée de l'appareil.
Page 77

Régulateur de la période HotStart de 0,5 - 2,0 séc. suivant la
valeur de consigne du courant de soudage réglée
Régulateur Out (valeur de consigne PWM)
La clarté de l'indication DEL augmente avec
l'augmentation de la valeur de consigne
Fig.25 Indications et régulateurs sur la plaquette à circuits imprimés MIG 45.
S1 déconnecté/ off connecté/ on
S1/1 450 A 330 A
S1/2 fonction speciale off fonction spéciale on
S1/3 impulsion & standard standard
S1/4 sans correction de dynamique avec correcion de dynamique
(seulement en service standard)
S1/5 sans tête double avec tête double
S1/6 VR A nmax = 30 m/min VR A nmax = 22 m/min
S1/7 VR B nmax = 30 m/min VR B nmax = 22 m/min
S1/8 Déconnexion automatique Service permanent de déconnexion
de l'appareil de refroidissement de l'appareil de refroidissement
Fig.26 Possibilités de codage sur la plaquette à circuits imprimés NMI4.
Tension de marche à vide connectée
L'indication DEL est illuminée tant que la commande de
connexion de la tension de marche à vide est donnée
25
FRANÇAIS
Page 78

Connexion à fiches X5
Alimentation en courant primaire
Primaire 0V~
F1 6,3 A à action retardée
Pompe de l'appareil de refroidiss.
380V~F3 0,63 A à action retardée
Primaire 380V~
F12 6,3 A à action retardée
Connexion à fiches X6 pour
la commutation du réseau 415V
Connexion à fichesX7 pour
la commutation du réseau 400V
Connexion à fichesX8 pour
la commutation du réseau 380V
Ventilateur pour l'appareil de
refroidissement 230V~F4 0,315
A à action retardée
Ventilateur 230V~
F5 0,315 A à action retardée
Steckverbindung X1
für Gerätelüfter
Connexion à fiches X4
Alimentation en cour. pour BM 45.
Moteur d'avance(VR152) 42V~
F9 10 A à action retardée
Moteur Pull-Mig 42V~
F10 2 A à action retardée
Connexion à fiches X3
Alimentation pour l'électronique
de commande NMI 4.
Alimentation NMI 4.
20V~ (+15V / +10V / +5V)
F6 2 A à action retardée
Tension de marche à vide 36V~
F8 0,315 A à action retardée
AlimentationNMI 4.
20V~(-15V), F7 1 A à action
retardée
Connexion à fichesX2 PWM
Fig.27 Coupe-circuits sur la plaquette à circuits imprimés VM34B
Non occupé
26
Page 79

ErsatzteillisteD
GB
Spare Parts List
Liste de pièces de rechange
F
Lista parti di ricambio
I
Lista de repuestos
E
Lista de peças sobresselentes
P
NL
Onderdelenlijst
N
Reservdelsliste
CZ
Seznam náhradních dílů
RUS
Список запасных частей
SK Zoznam náhradných dielov
ud_fr_st_tb_00150 012008
Page 80

20 17 19 16
20
18
12
10
11 13
49 37,38 53,54
18
51
52
4,6,8
4,5,8
21,22
41
9
7
14
15
24
23
48
29
43
31
1
42
30
47
46
32,81,
82,83
33,34
26
27
35 40 55 39 50
44,45
24
25 23
64
62,
63
60
28
61
71,72
56
59
57
65 66
84
807780
74,75
N.C.
73
78
67,68
56
36
70
58
69
76
76
79
76
7878
53,54
TIME SYNERGIC 4,075,077
Ersatzteilliste / Spare parts list / Listes de pièces de rechange / Lista de repuestos / Lista de pecas sobresselentes / Lista dei Ricambi
el_fr_st_mi_00139 012000
/3
1
Page 81

POS. BENENNUNG ARTICLE DENOMINATION
1 EINBAUBUCHSE -70 600 CURRENT SOCKET/5O-7O MM2/6OOA EMBASE FEMELLE 50/70 600A 43.0003.0031
2 NETZK. H07RNF 4G6 E5 63A 5M MAIN CABLE HO7RNF 4G6 E5 63 5M CABLE DE RESEAU 4G6 E5 63 5M 43.0004.1331
3 STECKERKRAGEN 5 380 63 PLUG 5 380 63 PRISE 5POLES 380V 63A 43.0003.0055
4 LED-HALTERUNG D=8MM/10x19.5 MOUNTING FOR LED SYSTEME FIXATION DE LED 41.0015.0024
5 LEUCHTDIODE 1.5 R P LED 1.5 V/RED/PLASTIK DIODE DE SIGNALISATION 41.0006.0025
6 LEUCHTDIODE 1.5 G 5 P LIGTH-EMITTING-DIODE 1,5 G 5 P DIODE DE SIGNALISATION 41.0006.0045
7 DRUCK FRONTPL.UNT.TIME SYN. AC FRONT PANEL TIME SYNERGIC PANNEAU FRONTAL TIME SYNERGIC 32.0409.2342
8 LED-ZUGENTLASTUNG D=9MM/12x19 TRACTION RELEASE FOR LED DECONNEXION LED 41.0015.0025
9 SCHALTKNE ROT SW 5 ZG 28 SWITCH RED SW 5 ZG 28 INTERRUPTEUR ROUGE 42.0406.0207
10 EINSCHUB TPS TIME INSERT TPS TIME PLATINE TPS TIME 43.0001.3186
11 DRUCK FRONTPL. 3 TIME SYN. AC FRONT PANEL TPS TIME SYNERGIC PANNEAU FRONTAL TIME SYNERGIC 42.0409.2364
12 BLINDSTOPFEN M6 ST3/CITOTIG 3 BLIND STOPPER BOUTON BUTOIR AVEUGLE 42.0300.0607
13 DREHKNOPF D=16 SW SW SW TURNING KNOB D=16 BOUTON TOURNANT 16 42.0406.0217
14 DRUCK SEITENT.L. TT330-02 AM SIDE PANEL L. TT330-02 PANNEAU LATERAL GAUCHE 45.0200.0658
15 DRUCK SEITENT.R. TT330-02 AM SIDE PANEL R. TT330-02 PANNEAU LATERAL DROIT 45.0200.0670
16 DECKEL RT TS330-02 COVER RED TS330-02 COUVERCLE ROUGE TS330 02 AM2.0200.6538
17 GRIFFROHR SW TS330-02 HANDLE TUBE BLACK TS330-02 TUYAU POIGNEE NOIR BE2.0200.6808
18 GRIFFAUFN. GERADE TP200 HANDLE MOUNTING STRAIGHT TP200 MONTAGE POIGNEE TP200 42.0405.0063
19 FLASCHENKETTE 30x650 BOTTLE CHAIN 3O X 65O CHAINE DE BOUTEILLE 42.0407.0017
20 KRANAUFNAHME SW TT330 LIFTING FATILITY BLACK TT330 INSTRUMENT DE LEVAGE BE2.0200.5774
21 KÜHLKREIS FK71 COOLING UNIT FK71 REFROIDISSEUR FK71 4.045.802
22 KÜHLKREIS FK71 60HZ COOLING UNIT FK71 60HZ REFRODISSEUR FK71 60HZ 4.045.803
23 FAHRWAGEN MW300/450 CARRIAGE MW300/450 CHARIOT MW300/450 4.045.740
24 KONSOLE FÜR FK7/FK71 CONSOLE MW300/450 CONSOLE REFROIDISSEUR FK7 4.045.741
25 LENKROLLE STAHL 160 RL 205 11 TUMBLER GEAR D=16O GALET PIVOTANT MSG1 44.0001.0078
26 LAUFRAD KUNST 200 GL 58 20 WHEEL D=200 MM ROUE 200 MM 44.0001.0051
27 STARLOCK 20 STAR LOCK D= 2O BLOCAGE EN ETOILE 20 44.0001.0106
28 DROSSEL PRIM. TPS450 INDUCTANCE PRIM. TPS450 INDUCTEUR PRIMAIRE TPS450 43.0010.0122
29 DRUCK GEHÄUSE TIME SYNERGIC AC CASE TIME SYNERGIC CHASSIS TIME SYNERGIC 46.0750.0496
30 ZUGENTLASTUNG PVC PG16 TRACTION RELEASE PVC PG16 ECROU FREIN PVC PG16 42.0300.1511
31 HALLGENERATOR HP4 HALL GENERATOR HP4 GENERAEUR DE HALL HP4 43.0001.0862
32 TREIBERTR. TS330,TPS450 DRIVER TRANSFORM. TS330,TPS450 TRANSFORMATEUR TS330,TPS450 33.0005.2142
33 VENTILATORT. TIME NEUTRAL FUN-PIECE TIME NEUTRAL PIECE DE VENTILATEUR TIME NEU. 44.0001.1178
34 PRINT LEISTUNGSSCHILD GR3 * PRINT RATING PLATE GR3 * PLAQUE SIGNALÉTIQUE IMPRIME G3 * 42.0409.2621
35 SCHUTZBESCHALT. EMV/+ BRENNER PROTECTION CIRCUIT EMV/+ TORCH DISJONCTEUR DE PROTECTION EMV/ 43.0001.1012
36 SCHUTZBESCHALT. EMV/- WERKST. PROTECTION CIRCUIT EMV/- DISJONCTEUR DE PROTECTION EMV/ 43.0001.1011
37 KONELK 4700 350 S 20 SCH ELECTROLYTIC CAPACITOR 47OO uF CONDENSATEUR 4700 UF 41.0005.0170
38 KONELK 3300 450 S 20 SCH ELECTROLYTIC CAPACITOR 330 450 CONDENSATEUR 3300 450 S20 SCH 41.0005.0250
39 KONFOL 22y 850 S 5 SCH FOIL CAPACITOR 22y 850 S 5 SCH CONDENSATEUR 41.0005.0193
40 WIDKOH100K 2 5 CARBON RESISTOR 100K 2 5 RESISTANCE CARBONE 41.0001.0248
41 SCHALTNOCK OS 3 20 EA 3 CAM SWITCH 0S 3 10 EA 3 COMMUTATEUR M/A 43.0002.0238
42 KLEMMLEISTE 10 12 35 3EFDS TERMINAL STRIP EKL 3E BORNIER EKL 3E 41.0009.0066
43 WIDDRA 22R 50 5 METAL RESISTOR 22R 50 5 RESISTANCE METAL 22R 50 5 41.0001.0532
44 SCHÜTZ 380 10 30 CONTACTOR 380 10 30 CONTACTEUR 380 10 30 43.0008.0104
45 EINSCHALTVERZÖG. 380V 5 SEC. TURN ON DELAY 380V 5SEC. TEMPORISATEUR 380V 5S 43.0008.0102
46 SCHUTZLEITERDROSSEL 4MM² DISCHARGE-COIL 4MM² BOBINE DE DECHARGE 4MM2 43.0004.1153
47 PRINT NF 340 PC-BOARD NF 340 CIRCUIT ELECTRONIQUE NF 340 4.070.544
48 VENTILATOR M.F. 10 80x80x38 FAN M.F. 10 80X80X38 VENTILATEUR 10 80X80X38 43.0006.0117
49 DRUCK GEHÄUSE STG TS330-02 AC HOUSING MIG-STG TS330-02 CHASSIS MIG-STG TS330-02 46.0750.0379
50 GUMMIDURCHF. 35 RUBBER PASSAGE D=35 TAPIS CAOUTCHOUC 35 42.0402.0039
51 TASTER N290/K1 GRÜN TRIGGER GREEN N 290/K1 GACHETTE VERTE N 290 K1 43.0002.0079
52 BUCHSENGEHÄUSE 23 37 EINB. SOCKET-CASE 23 37 CASE SUPPORT 23 37 43.0003.0482
53 STEUERTR. 220-415V/50H MIG-MAG AUXILIARY TRANF.220-415V/50 HZ TRANSFORMATEUR AUXILIAIRE 220- 33.0005.2158
54 STEUERTR. 380/440/500V 50-60HZ AUXILIARY TRANF.380/440/500V50 TRANSFORMATEUR AUXILIAIRE 380- 33.0020.0004
55 PRINT PWM 3 D PC-BOARD PWM 3 D CIRCUIT ELECTRONIQUE 4.070.355
56 PRINT RCP 3 PRINT CIRCUIT BOARD RCP 3 CIRCUIT ELECTRONIQUE 4.070.163
57 DIOSIL 400 60 DO5 SF SILICON DIODE 400 60 DO5 SF DIODE AU SILICIUM 41.0003.0034
58 A-DROSSEL TP450 INDUCTANCE OUTPUT TP450 INDUCTANCE DE SORTIE 33.0010.0112
59 VENTILATOR M.F. 220V42W 150x55 FAN MOTOR 220V42W 150X55 MOTEUR VENTILATEUR 220V42W 150 43.0006.0039
60 MUTTER-PLASTIK PYB 7041 NUT-PLASTIC PYB 7041 ECROU PLASTIQUE PYB 7041 42.0400.0132
61 ZÜNDHILFE-RCD TPS450 IGNITION-HELP RCD TPS450 ASSISTANCE ALLUMAGE 43.0001.0733
62 STECKDOSENGEHÄUSE 5 380 10 CASE FOR PLUG SOCKET CAPOT RECEPTACLE PRISE 43.0003.0141
63 STECKDOSENEINSATZ 5 380 10 PLUG SOCKET HA 4 B SOCLE PRISE HA4B 43.0003.0148
64 SICHERUNGSSET MIG-STG. TS330 FUSE-SET MIG-STG. TS330 FUSIBLE-SET MIG-STG. TS330 43.0012.0004
65 PRINT NMI 4 D PC-BOARD NMI 4D CIRCUIT ELECTRONIQUE 4.070.379
TIME SYNERGIC 4,075,077
Ersatzteilliste / Spare parts list / Listes de pièces de rechange / Lista de repuestos / Lista de pecas sobresselentes / Lista dei Ricambi
el_fr_st_mi_00139 012000
/3
2
Page 82

POS. BENENNUNG ARTICLE DENOMINATION
66 PRINT KI 34 A PC-BOARD KI34 A CIRCUIT ELECTRONIQUE 4.070.242
67 PRINT NVZ 42 PC-BOARD NVZ 42 CIRCUIT ELECTRONIQUE NVZ 42 4.070.376
68 PRINT NVZ 50 PC-BOARD NVZ 50 CIRCUIT ELECTRONIQUE NVZ 42 4.070.497
69 PRINT PV 45 S PC-BOARD PV 45 S CIRCUIT ELECTRONIQUE PV 45 S 4.070.362
70 THERMOELEMENT TP 592S/1 TP 592S/1 CPL. TP 330 TP 592S/1 TP 330 43.0001.0600
71 GLESIL 1K2 60 G35 F 3 SILICON RECTIFIER 1K2 60 G35 REDRESSEUR AU SILICIUM 41.0002.0037
72 GLESIL 1K6 60 G35 F 3 GLESIL 1K6 60 G35 F 3 REDRESSEUR AU SILICIUM 1K6 60 41.0002.0045
73 SLT 450A TT/TP450/GLE451 POWER MODULE SEC.450A TT/TP450 MODULE DE PUISSANCE SEC 43.0001.0519
74 SCHWEISSTR. 380/400/415V TP450 WELDING TRANSF. TP450-02 TRANSFORMATEUR DE SOUDAGE 33.0005.4069
75 SCHWEIßTR. 440V TP/TT/MW450 WELDING TRANSF.440V TP/TT/MW45 TRANSFORMATEUR DE SOUDAGE 33.0005.0422
76 SICHERUNG 0.315 250 T 5x20 FUSE ,315 250 T 5X20 FUSIBLE 0,315 250 T 5X20 41.0007.0095
77 SICHERUNG 0.63 250 T 5x20 FUSE O.63A/25OV/SLOW BLOW/5X2O FUSIBLE 0,63A/250V 5X20 41.0007.0046
78 SICHERUNG 1 250 T 5x20 FUSE 1A/25O V/SLOW BLOW/5X2O FUSIBLE 1A/250 5X20 41.0007.0014
79 SICHERUNG 2 250 T 5x20 FUSE 2A/25OV/SLOW BLOW/5X2O FUSIBLE 2A/250V 5X20 41.0007.0037
80 SICHERUNG 6.3 250 T 5x20 FUSE 6.3 A/25OV/SLOW BLOW/5X2O FUSIBLE 6,3A/250V 5X20 41.0007.0065
81 SICHKLEIN 0.125 T 19372 FUSE SMALL 0.125 T 19372 FUSIBLE PETIT 0.125 T 19372 41.0007.0043
82 SICHKLEIN 1 T 19372 FUSE SMALL 1 T 19372 FUSIBLE PETIT 1 T 19372 41.0007.0087
83 SICHKLEIN 2 T 19372 FUSE SMALL 2 T 19372 FUSIBLE PETIT 2 T 19372 41.0007.0112
84 PLT GEPRÜFT 450A TT/TP450/GLE/ POWER MODULE PRIM. CHECK 450A MODULE DE PUISSANCE PRIM 43.0001.0521
* BITTE SERIENNUMMER ANGEBEN PLEASE INDICATE SERIAL NUMBER INDIQUER NUMERO DE SERIE *
TIME SYNERGIC 4,075,077
Ersatzteilliste / Spare parts list / Listes de pièces de rechange / Lista de repuestos / Lista de pecas sobresselentes / Lista dei Ricambi
el_fr_st_mi_00139 012000
/3
3
Page 83

27,38
28
26
10
11
12
13
30 31
33 34 36
25
4
2,3
5-9
35
15
1
16 17
29
20
37
19
22
24
32
18
21
14
23
POS. BENENNUNG ARTICLE DENOMINATION
1 DRUCK GEHÄUSE VR153 TIME CASE VR153 TIME CHASSIS VR153 TIME 45.0200.0890
2 DRUCK FRONTPL.U. VR153 FRONT PANEL BELOW VR153 PANNEAU AVANT INFERIEUR 32.0409.1729
3 DRUCK FRONTPL.U. VR153-4R W RO FRONT PANEL BELOW VR153-4R W PANNEAU AVANT INFERIEUR 32.0409.1880
4 DRUCK RÜCKFR. VR153 TIME REAR PANEL VR153 TIME PANNEAU ARRIERE VR153 TIME 45.0200.0891
5 MOTORPL. 42V 4R EC. O.RÄ. M.T. MOTOR PLATE 42V 4R EC. W.WH. PLAQUE DE MOTEUR 42V 4R EC 44.0001.1093
6 MOTORPL. 42V 4R D-ZA O.RÄ.M.T MOTOR PLATE 42V 4R D-ZA PLAQUE DE MOTEUR 42V 4R D-ZA 44.0001.1095
7 MOTORPL. 42V 4R F-ZA O.RÄ.M.T. MOTOR PLATE 24V 4R F-ZA PLAQUE DE MOTEUR 24V 4R F-ZA 44.0001.1096
8 MOTORPL. 42V 4R F-ZA 1.2TI 30M MOTOR PLATE 42V 4R F-ZA 1.2TI PLAQUE DE MOTEUR 42V 4R F-ZA 44.0001.1058
9 MOTORPL.42V 4R EC.1.2TI 30M MT MOTOR PLATE 42V 4R EC.1.2TI PLAQUE DE MOTEUR 42V 4R EC 44.0001.1065
10 STECKDOSENGEHÄUSE EB 20 PLUG-HOUSING EB 20 LOGEMENT PRISE EB 20 43.0003.0256
11 STECKDOSENEINSATZ 20 14 PLUG-SOCKET-INSERT 20 14 SUPPORT PRISE INTERNE 43.0003.0248
12 STECKDOSENGEHÄUSE EB 18 PLUG-HOUSING EB 18 LOGEMENT PRISE EB 18 43.0003.0255
13 STECKDOSENEINSATZ 18 4 PLUG-SOCKET-INSERT 18 4 SUPPORT PRISE INTERNE 43.0003.0245
14 TASTER N290/K1 GRÜN TRIGGER GREEN N 290/K1 GACHETTE VERTE N 290 K1 43.0002.0079
15 MAGNETVENTIL-KL.42 0-10 G1/8" MAGNETIC VALVE SMAL 42 0-10 ELECTROVANNE 42 0/10 43.0013.0004
16 MUTTER-LOCKNUT R3/8" SW21x4.5 LOCKNUT R 3/8" SW 21X6.5 CONTRE ECROU 42.0001.0133
17 ANSCHLUSSCHR. R3/8" SW21X45 PICK-UP TUBE R3/8" SW21X45 TUBE PICK UP SW 21X45 42.0001.2666
18 MAGNETVENTILA. R1/8"R3/8" SOLENOID VALVE CONNECTION RACORD VALVE SOLENOID 42.0401.0085
19 SCHLAUCHTÜLLE M.O-RG. R1/8"x31 HOSE CONNECTION R1/8"/D=7.5 RACCORD R1/8 7,5 42.0001.0090
20 STROMSTECKER EB 50-70 600 CURRENT PLUG 5O-7OMM2/6OO A PRISE COURANT 50/70 600A 43.0003.0146
21 DREHKNOPF D=16 GR GR GR TURN KNOB D=16 GREY/GREY/GREY BOUTON A 3 POSITIONS 16 42.0406.0081
22 DRUCKWÄCHTERAUFN. VR153 MOUNTING PRESSURE CONTR.VR153 CONTROLE DE MONTEE DE 44.0001.0709
23 DRUCKWÄCHT EPDM M10X1 S 0,1-1B WATER FLOW SWITCH INTERRUPTEUR DEBIT EAU 43.0002.0005
24 SCHNELLKUPPL.WASSER 21KATS06 QUICK CONNECTION W RACCORD RAPIDE 44.0001.0348
25 DECKEL SW VR153 TIME COVER PLATE BLACK VR153 TIME COUVERCLE NOIR VR153 TIME BE2.0200.8525
26 SCHLP.HALT.SW PR4-O/M HOSE PACK MOUNT. BLACK PR4-0/M MONTAGE FAISCEAU NOIR PR4 BE2.0200.2677
27 ZUGENTLASTUNG SW VR152-MP TRACTION RELEASE BLACK ECROU FREIN VR153-MP BE2.0200.7817
28 RÄNDELSCHRAUBE M8x25 KNURLED SCREW ECROU MOLETE 42.0401.0004
29 KISTENVERSCHLUSS 95X30X15 BOX-FASTENER 95x30x15 FIXATIONS BOITE 95X30X15 42.0407.0055
30 VERSCHLUSSHAKEN FORM3 25MM VZ LOCK-CLAMP FORM3 25MM VZ FERMETURE CROCHET 42.0200.2474
31 SCHARNIER S053B120 S6 HINGE SO53B120 S6 CHARNIERE SO53B120 S6 42.0200.6480
32 ABDECKKAPPE 32.0/34.8/11.5/3.2 HEYCO-COVERING D=32MM COUVERCLE 32.0/34.8/11.5/3.2 42.0300.1770
33 FRONTPL.O.SW VR123-R FRONT PANEL ABOVE BLACK VR123- PANNEAU AVANT INFERIEUR BE2.0200.4755
34 RÜCKFRONT(DECKEL)SW VR153 TIME REAR PANEL VR153 TIME PANNEAU ARRIERE VR153 TIME BE2.0200.8527
35 FRONTPL.U. SW VR153 TIME FRONT PANEL VR153 TIME PANNEAU FRONTAL VR153 TIME BE2.0200.8849
36 DRAHTEINLAUFBLOCK VR149/153/- WIRE-INFEED-BLOCK VR149/153/- BOBINE FIL DEVIDOIR 44.0450.0893
37 BUCHSENGEHÄUSE 23 37 EINB. SOCKET-CASE 23 37 CASE SUPPORT 23 37 43.0003.0482
38 ZUGENTLASTUNG SW VR123-2R/4R TRACTION RELEASE BLACK ECROU FREIN VR123-3R/4R BE2.0200.7817
VR153-K / TIME 4.045.777 / 000 / 001 / 002 / 4.045.773.000 / 000
Ersatzteilliste / Spare parts list / Listes de pièces de rechange / Lista de repuestos / Lista de pecas sobresselentes / Lista dei Ricambi
el_fr_st_dv_00032 012000
1/1
Page 84

Page 85

Page 86

Page 87

Page 88

Page 89

Page 90

Page 91

2
19
12
1
5
18
3
11
1516
13
4
17
67-10
14
POS. BENENNUNG ARTICLE DENOMINATION
KÜHLKREIS FK71 50/60HZ FK 71 50/60HZ COOLING UNIT REFROIDISSEUR FK 71 50/60HZ 4,045,802
1 DRUCK GEHÄUSE FK71 CASE FK71 COUVERCLE FK71 46,0450,0208
2 MANTEL RT FK71 SHEATH FK71 CHEMISE FK71 AM2,0200,8776
3 VENTILATOR M.F. 220V42W 150x55 FAN MOTOR 220V42W 150X55 MOTEUR VENTILATEUR 220V42W 150 43,0006,0039
4 NETZK. PVC ÖY 5X0,75 1,45M MAIN CABLE PVC 5X0.75 1.45M FK CABLE DE DISTRIBOUTION 5X0.75 43,0004,1509
5 WASSERKÜHLER WATER COOLER REFRIGERATEUR A L.EAU 24,0450,0972
6 KLEMMLEISTE 2,5 12 16 1EFDS TERMINAL STRIP 2.5MM2/EKL 1 BORNIER BK 2,5MM2/EKL 1 41,0009,0060
7 SCHNELLKUPPLUNG AG R1/8" NW5 QUICK CONNECT AG R1/8" NW5 RACCORD RAPIDE AG R1/8" NW5 44,0001,1145
8 WASSERANSCHL. SW VST357/457 WATER-CONNECT BLUE VST357/457 CONNECTION EAU BLEU VST357/457 42,0405,0189
9 MUTTER KST ROT VST357/457 NUT KST RED VST357/457 ECROU ROUGE VST357/457 42,0405,0186
10 MUTTER KST SW VST 357/457 NUT KST BLUE VST 357/457 ECROU BLEU VST357/457 42,0405,0187
11 ABDECKKAPPE 11.0/13.5/10.3/3.2 COVER-DISC 11.0/13.5/10.3/3.2 COUVERCLE 11.0/13.5/10.3/3.2 42,0300,1724
12 KLEMME 1OHR 16.6 STUFENLOS CLAMPING 1 CLIP 16.6 PINCE 1OREILLE 16.6 42,0407,0442
13 ZUGENTLASTUNG PVC 7.1-9 3 TRACTION RELEASE D=7.1-9/3MM ECROU DE FREIN 7,1/9 3 MM 42,0407,0011
14 PUMPE Y2841.0023 M.YDS3-MOTOR PUMP Y2841.0023 M.YDS3-M POMPE Y2841.0023 M.YDS3-M 43,0006,0172
15 TANKDECKEL FK2600 COVER FK2600 TANK CAP FK2600 42,0401,0865
16 WASSERBEHÄLTER FK 71 WATERTANK FK71 RESERVOIR D.EAU FK71 32,0300,2312
17 SCHLAUCH RAUFI MG 8x3 TR RAUFILAM HOSE MG 8X3 TR TUYAU RAUFILAM MG 8X3 TR 40,0001,0008
18 WINKELSTÜCK KST. D=10,0/7,0x31 ANGLE ADAPTER KST D=10.0/70X31 RACCORD ANGULAIRE D=10,0/7x31 42,0300,2019
19 SCHLAUCH PVC OG 10X2 TR PVC HOSE 10x2 TR TUYAU PVC 10x2 TR 40,0001,0393
FK 71
Ersatzteilliste / Spare parts list / Listes de pièces de rechange / Lista de repuestos / Lista de pecas sobresselentes / Lista dei Ricambi
el_fr_st_kg_00045 012001
1/1
Page 92

TR 34 4,046,003
TR 34 TIME 4,046,056
42,0406,0083
32,0405,0160
43,0003,0486
42,0406,0080
42,0409,1594
42,0409,2377 - TIME
43,0002,0153
41,0001,0509
42,0406,0084
42,0409,1593
BE4,0750,0058
42,0409,2376 - TIME
TR 34
TR 34
BE2,0200,5381
TIME
42,0300,0501
Remote Control
Ersatzteilliste / Spare parts list / Listes de pièces de rechange / Lista de repuestos / Lista de pecas sobresselentes / Lista dei Ricambi
el_fr_st_fb_00006 012003
1/1
Page 93

2
4,5,6,12
13
3
7,8,9,12
10
14
1
11
7,8,9,12 14
15
POS. BENENNUNG ARTICLE DENOMINATION
1 BODEN SW TP4-SP BOTTON BLACK TP4-SP BOUTON NOIR TP4-SP BE4.0460.0009
2 SCHUTZBÜGEL SW TP4-SP PROTECTION BOW BLACK TP4-SP PROTECTION ARC NOIRE BE4.0460.0010
3 DRUCK FRONTPL. TP4-SP FRONT PANEL TP4-SP PANNEAU FRONTAL TP4/SP 46.0460.0001
4 DECKEL 40 rot P COVER 40 RED P CACHE BOUTON ROUGE 40 P 42.0406.0250
5 DREHKNOPF 40 schw 6mm ACHSE P TURNING KNOB 40BLACK AXLE6MM P BOUTON A TOURNER NOIR 40 42.0406.0247
6 PFEILSCH 40 rot P ARROW-DISK 40 RED P BOUTON CRANTE ROUGE 40 P 42.0406.0249
7 DECKEL 16 grau P COVER D=16 GREY P CACHE BOUTON GRIS 16 P 42.0406.0107
8 DREHKNOPF 16 schw 6mm ACHSE P TURNING KNOB D=16 BLACK 6MM P BOUTON TOURNANT NOIR 42.0406.0099
9 MUTTERABD 16 rot P NUT-COVER 16 RED CAPOT ECROU ROUGE 16 42.0406.0213
10 ANBAUGEHÄUSE STIFT STROMQU FR MOUNTING CASE PIN FR ELEMENT RAPPORT BROCHE 32.0405.0160
11 STIFTKONTAKT C 1 CPC PIN CONTACT C 1 CPC CONTACT AIGUILLE C1 CPC 43.0003.0486
12 WIDPOT 2K2 10 ABW 1 RESISTOR 2K2 10 ABW 1 RESISTANCE 2K2 10 ABW 1 41.0001.0509
13 PRINT YTP 6 A PC-BOARD YTP 6 A CIRCUIT ELECTRONIQUE YTP 6 A 4.070.293
14 SCHALTKIPP 12146AK SWITCH TOGGLE 12146AK INTER A BASCULE 12146AK 43.0002.0284
15 HAFTMAGNET 63 24 6.5 CLAMPING MAGNET 63 24 6.5 ECROU MAGNETIQUE 63 24 44.0001.0739
TP4-SP 4.046.024
Ersatzteilliste / Spare parts list / Listes de pièces de rechange / Lista de repuestos / Lista de pecas sobresselentes / Lista dei Ricambi
el_fr_st_fb_00017 001999
1/1
Page 94

TR 52-1 4,045,316
42,0300,1145
42,0001,1492
42,0404,0033
BE4,0750,0082
44,0750,0086
43,0002,0004
4,070,034 - TR52
TR 52
BE2,0200,3845
44,0750,0085
42,0404,0152
42,0403,0083
42,0408,0035
41,0001,0015
32,0405,0160
43,0003,0486
BE4,0750,0081
TR 52-1
42,0409,0875
BE4,0750,0083
Remote Control
Ersatzteilliste / Spare parts list / Listes de pièces de rechange / Lista de repuestos / Lista de pecas sobresselentes / Lista dei Ricambi
1/1
el_fr_st_fb_00003 012003
Page 95

Motorplate 42V 4R
Ersatzteilliste / Spare parts list / Listes de pièces de rechange / Lista de repuestos / Lista de pecas sobresselentes / Lista dei Ricambi
el_fr_st_mp_01220 012008
1/4
Page 96

Motorplate 42V 4R
Ersatzteilliste / Spare parts list / Listes de pièces de rechange / Lista de repuestos / Lista de pecas sobresselentes / Lista dei Ricambi
el_fr_st_mp_01220 012008
2/4
Page 97

Motorplate 42V 4R
Ersatzteilliste / Spare parts list / Listes de pièces de rechange / Lista de repuestos / Lista de pecas sobresselentes / Lista dei Ricambi
el_fr_st_mp_01220 012008
3/4
Page 98

Motorplate 42V 4R
Ersatzteilliste / Spare parts list / Listes de pièces de rechange / Lista de repuestos / Lista de pecas sobresselentes / Lista dei Ricambi
el_fr_st_mp_01220 012008
4/4
Page 99

b r ake me chanis m.
Ersatzteilliste / Spare parts list / Listes de pièces de rechange / Lista de repuestos / Lista de pecas sobresselentes / Lista dei Ricambi
el_fr_st_so_00182 012004
1/1
Page 100

POS. BENENNUNG ARTICLE DENOMINATION
1 SCHLAUCH SCHUTZ MG 45x1,5 SW HOSE PROTECTION WF 45X1,5 BLA TUYAU DE PROTECTION MG 40.0001.0095
2 ZUGENTLASTUNG TA500 TRACTION RELEASE TA500 ECROU FREIN TA500 44.0750.0009
3 KLEMME SCHRAUB 32-50 CLAMP SCREW 32-50 VIS DE CONNEXION 32/50 42.0407.0072
4 ZUGENTL.ROHR SPL.TRABANT/HUMAN CORD FASTENER PIPE D=44X50 ATTACHE TUYAU 44X50 42.0001.1337
5 KÜHLERSCHL. D=48X4.5X50 COOLER-HOSE D=48x4.5x50 TUYAU DE REFROIDISSEUR 42.0300.1449
6 SCHWEISSKABEL H01N2-D 95MM2 WELD. BABLE 955MM2 GSFFUö CABLE DE SOUDAGE H01N2-D 95MM² 40.0003.0015
7 KABELSTECKER -95 800 CABLE-PLUG -95 800 CABLE-PRISE -95 800 43.0003.0301
8 KABELKUPPLUNG -95 800 CABLE-COUPLING -95 800 RACCORD DE CABLE -95 800 43.0003.0385
9 KABEL PVC ÖY 12x0.75 PVC-CABLE öY 12X0,75 CABLE PVC OY 12X0,75 40.0003.0117
10 SCHUTZKAPPE 23 PROTECTION CAP 23 CAPOT PROTECTION 43.0003.0484
11 STIFTGEHÄUSE 23 37 PIN HOUSING 23 37 PROTECTION AIGUILLE 23 37 43.0003.0483
12 STIFTKONTAKT C 1 CPC PIN CONTACT C 1 CPC CONTACT AIGUILLE C1 CPC 43.0003.0486
13 BUCHSENGEHÄUSE 23 37 KUPP. SOCKET CASE 23 37 CAPOT SUPPORT 23 27 KUPP. 43.0003.0566
14 BUCHSENKONTAKT C 1 CPC SOCKET-CONTACT C 1 CPC SUPPORT CONTACT C 1 CPC 43.0003.0485
15 KABEL PVC YSLYJZ 18x0.5 PVC-CABLE YSLYJZ 18x0.5 CABLE PVC YSLYJZ 18X0,5 40.0003.0284
16 SCHLAUCH SILI MG 20x1.0 WS INSULATION HOSE GL-SI/S15 20X1 TUYAU ISOLANT GL SI/S15 40.0001.0106
17 SCHLAUCH PVC MG 5x3 SW HOSE PVC THREADED D=5X3 BLACK TUYAU PVC FILETE NOIR 40.0001.0012
18 KLEMME 1OHR M. EINLAGE 11,3 HOSE CLAMP 11,3 COLLIER DE SERRAGE 11,3 42.0407.0062
19 ANSCHLUSS GASARMATUR 1/4" CONNECTION FOR GAS ARMATURE RACCORD GAZ 44.0450.0281
20 KLEMME 1OHR M. EINLAGE 13,3 CLAMP 1 EAR W.INSERT 13.3 COLLIER DE SERRAGE 13,3 42.0407.0063
21 ÜBERWURFMUTTER R3/8"/D=20x13 CAP NUT R 3/8 „ D=20X13 CHAPEAU ECROU R 3/8 20X13 42.0001.0943
22 SCHLAUCHANSCHL. D=13x32 ST1/2/ HOSE CONNECTION D=13.OX32 RACCORD TUYAU 13X32 42.0001.0942
23 DICHTUNG RUND ID= 7x2.0 NBR 70 SEALING ROUND 7x2.0 NBR70 RONDELLE DE JOINT 7x2.0 NBR70 42.0402.0053
24 SCHLAUCH RAUFI MG 8x3 TR RAUFILAM HOSE MG 8X3 TR TUYAU RAUFILAM MG 8X3 TR 40.0001.0008
25 SCHLAUCHANSCHL.NIPPEL 21SBTF08 HOSE CONNECTION NIPP. 21SBTF08 RACCORD DE TUYAU 21 SBTF08 44.0001.1004
26 SCHNELLKUPPLUNG 21KBTF08 QUICK CONNECT 21KBTF08 RACCORD RAPIDE 21KBTF08 44.0001.1139
27 STECKNIPPEL 21SFTF08MXX PLUG NIPPLE 21SFTF08MXX MANCHON PRISE 21SFTFO8MXX 44.0001.0971
30M W. MEYER PAPENBURG 4,047,112
Ersatzteilliste / Spare parts list / Listes de pièces de rechange / Lista de repuestos / Lista de pecas sobresselentes / Lista dei Ricambi
el_fr_st_vp_00099 011999
1/1
 Loading...
Loading...