Page 1

FCR230
Modbus-BACnet
EN
Modbus signal types 2
Modbus signals 4
Coil status register 5
Input register 6
Holding register 7
BACnet signal types 12
BACnet signals 13
1
Page 2

Modbus signal types
EXOL types EXOL signal types:
R = Floating point number (Real) (-3.3E38 - 3.3E38)
I = Whole number (Integer) (-32768 - 32767)
X = Index (0 - 255)
L = Logic (Logic) (0/1)
Modbus types Modbus signal types (types listed below):
1 = Coil Status Register (Modbus function = 1, 5 and 15)
2 = Discrete Input (Modbus function = 2)
3 = Coil Status Register (Modbus function = 3, 6 and 16)
4 = Input Register (Modbus function = 4)
Supports the following Modbus functions:
1 = Read Coils
2 = Read Discrete Input
3 = Read Holding Register
4 = Read Input Register
5 = Write Single Coil
6 = Write Single Register
15 = Write Multiple Coils
16 = Write Multiple Registers
Scaling factor Modbus All floating point numbers have a scaling factor of 10. Integers, Index and Logic signals always
have a scaling factor of 1.
EXOline/Modbus The RCF controller will automatically switch between EXOline and Modbus, depending on
what type of communication is used. This switch-over will take place without any errors in
communication resulting. The exception is when communicating via Modbus with a
configuration of 8 bits, no parity and 1 stop bit, in which case the switch must be made
manually.
Wiring, Modbus A Modbus type protocol consists of multiple layers (OSI model). The bottom layer is always
the physical layer, the number of connection wires and signal levels. The next layer describes
the communication digits (number of bits, stop bits, parity bits etc). After these come the layers
describing Modbus-specific functions (number of digits per message, the meaning of different
messages, etc). For Modbus, the bottom layer can be either RS485, RS422 or RS232.
RS485 and RS422 RS485 and RS422 constitute the purely electrical part of the protocol, ie. the physical layer.
RS485 has two connections, A and B. Often, there is also a Protective earth (N on EXO
controllers). RS485 units are connected A A and B B. It may prove necessary to shift A
and B in order to make Modbus work properly. RS485 is a so called half duplex
communication: The communication can only go in one direction, eg. the main unit will
initially send a request, and thereafter listen to the reply. A and B are used both for sending
and receiving.
2
Page 3

RS422 is a full duplex communication, meaning that 4 connecting wires are required; 2 for
sending (Tx+ and Tx-) and 2 for receiving (Rx+ and Rx-). Tx is used for sending and Rx for
receiving, meaning the Tx in a unit must be connected to the Rx in another and vice versa.
Pertaining to signal levels, etc., RS422 and RS485 are identical.
In order to connect RS485 and RS422: Connect Tx+ to Rx+ and Tx- to Rx- on the RS422 unit.
We have now changed a 4-wire system to a 2-wire system and can connect them to A and B
on the RS485 unit. It is usually easiest to find out what fits where simply by experimenting.
Wrong polarity makes the system not function but is incapable of harming any unit.
Tx+ -----|---------------------------------------- A (or B)
|
Rx+ -----|
Tx- -----|---------------------------------------- B (or A)
|
Rx- -----|
Bit rate, two stop bits, parity is next layer.
These settings must correspond to the settings in the main unit. Find out what the settings for
the main unit are, and then enter the same settings into the controller.
Parity can be set to odd, even (FS) or none. If no parity is set, two stop bits will automatically
be used. If odd or even parity is set only one stop bit will be used, or the total amount of bits
will be too great. 1 start bit, 8 data bits, 1 parity bit and 1 stop bit gives a total of 11 bits, which
is the maximum.
3
Page 4
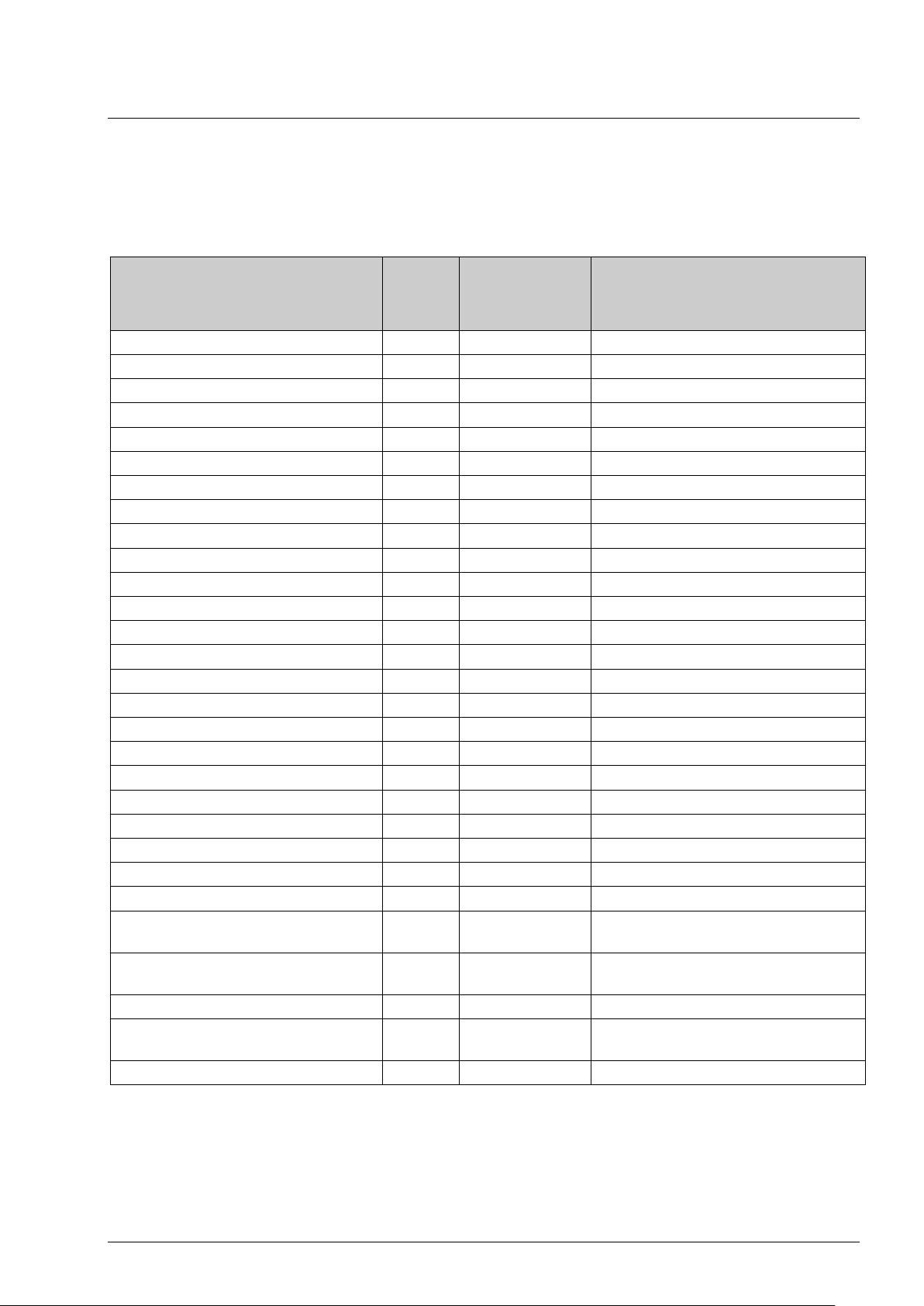
Modbus signals
RC_Actual_L.RegioDigOut(0)
L,2 5 Not used
RC_Actual_L.RegioUDigOut1
L,2
11
Heating (Value on digital output 4)
RC_Actual_L.RegioDIChangeOver
L,2
16
Indicates change-over from digital input
RC_Actual_L.RegioCVHeatPulsProp
L,2
21
Indicates pulse prop. heating
Discrete inputs
Name of signal Type
RC_Actual_L.RegioDigIn(0) L,2 1 Not used
RC_Actual_L.RegioDigIn1 L,2 2 Value on digital input 1
Not used in this model L,2 3
RC_Actual_L.RegioUDigIn1 L,2 4 Value on universal digital input 1
RC_Actual_L.RegioDigOut1 L,2 6 Value on digital output 1
RC_Actual_L.RegioDigOut2 L,2 7 Value on digital output 2
RC_Actual_L.RegioDigOut3 L,2 8 Value on digital output 3
Not used in this model L,2 9-10
RC_Actual_L.RegioUDigOut2 L,2 12 Cooling (Value on digital output 5)
RC_Actual_L.RegioDIOpenWindow L,2 13 Indicates open window
Not used in this model L,2 14
RC_Actual_L.RegioDIPresences L,2 15 Indicates presence from digital input
RC_Actual_L.RegioFanSpeed1 L,2 17 Indicates fan speed 1
RC_Actual_L.RegioFanSpeed2 L,2 18 Indicates fan speed 2
RC_Actual_L.RegioFanSpeed3 L,2 19 Indicates fan speed 3
Not used in this model L,2 20
Modbus
address
Description
RC_Actual_L.RegioCVCoolPulsProp L,2 22 Indicates pulse prop. cooling
RC_Actual_L.RegioCVHeatInc L,2 23 Indicates increase heating/cooling DO4
RC_Actual_L.RegioCVHeatDec L,2 24 Indicates decrease heating/cooling DO5
Not used in this model L,2 25-26
RC_Actual_L.RegioAIChangeOverState L,2 27 Indicates change-over status from
analogue input
RC_Actual_L.RegioChangeOverState L,2 28 Indicates change-over status from both
digital and analogue input
Not used in this model L,2 29-30
RC_Actual_L. RegioPresence L,2 31 Occupancy indication (with on- and
switch-off delay)
Not used in this model L,2 32-33
4
Page 5
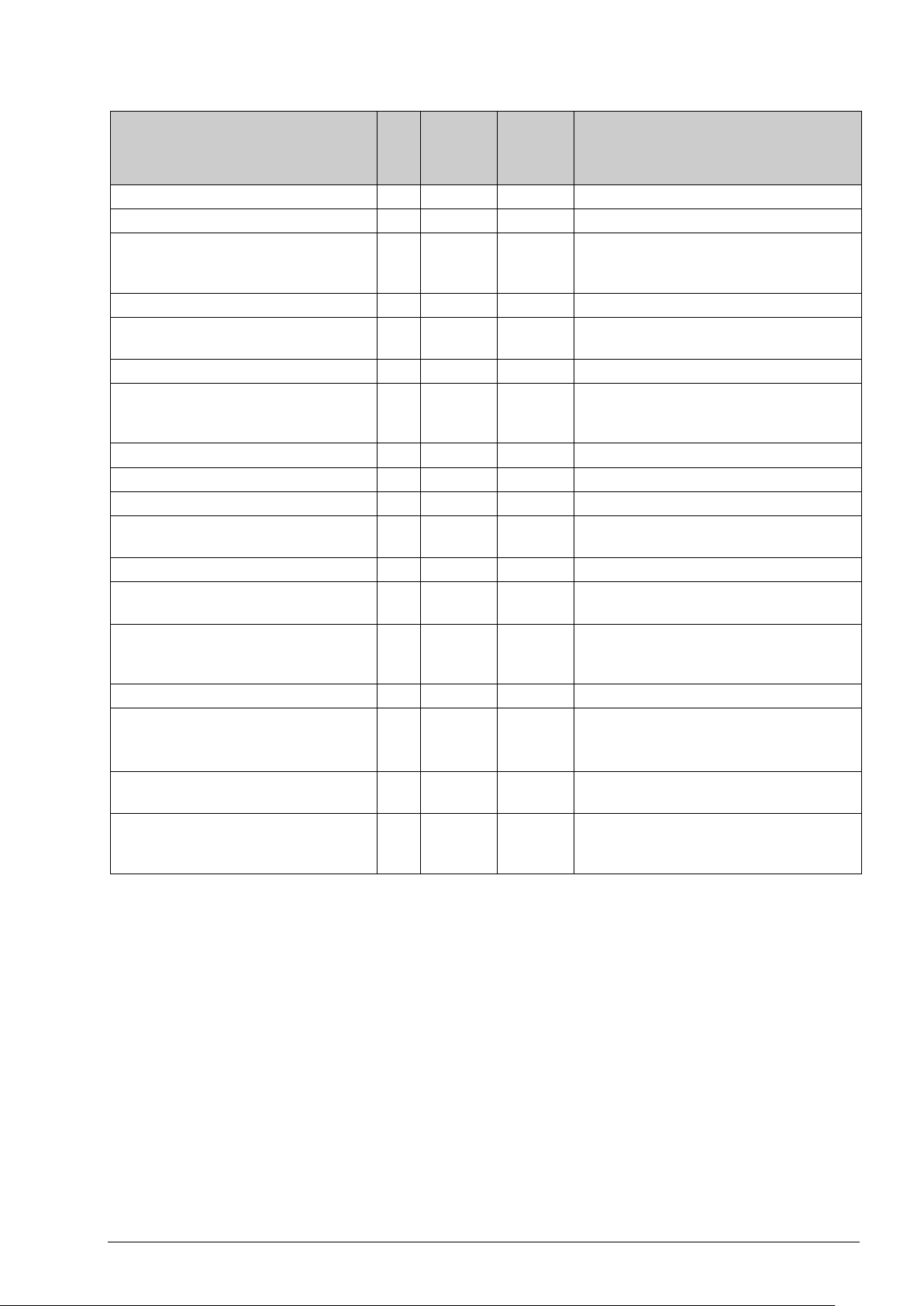
Coil status register
unless this value is first set to “0”.
the fan can be switched off.
Name of signal Type
Not used in this model L,1 1 0
RC_Setp_L.RegioShutDown L,1 2 0 Puts the unit in Shutdown mode.
RC_Setp_L.RegioFireAlarmStop L,1 3 0 Places the unit in Shutdown mode and
RC_Setp_L.RegioDiNC(0) L,1 4 0 Not used
RC_Setp_L.RegioDi1NC L,1 5 0 Normally open (NO) or normally closed
Not used in this model L,1 6 .
RC_Setp_L.RegioUDi1NC L,1 7 0
Not used in this model L,1 8 -
RC_Setp_L. RegioDO4NC L,1 9 1 DO4 NO/NC
RC_Setp_L.RegioDO5NC L,1 10 1 DO5 NO/NC
RC_Setp_L.RegioDilAct L,1 11 0 DI1-activation (presence/window)
RC_Setp_L.RegioMPAct L,1 12 0 Activation of Mould protection.
RC_Setp_L.RegioTermoModel L,1 13 0 EEPROM storage of Thermo model
RC_Setp_L.RegioMinFanSpeed L,1 14 1 The fan is run at its minimum speed setting
Modbus
address
Default
value
Description
prevents it from being activated again,
(NC) on digital input. 0=NO, 1=NC.
Normally open (NO) or normally closed
(NC) on universal digital input. 0=NO,
1=NC.
Economy/Off
variable (3-point actuator)
if the automatic fan control calculates that
Not used in this model
RC_Setp_L.RegioComFactoryDefaults
RC_Setp_L.RegioBlockConfig
RC_Setp_L.RegioPreventManualFanSp
eed
- 15
L,1 16 0
L,1 21 0 Blocks the option to enter the parameter
L,1 22 0 Prevents the fan speed from being changed
-
Set communication parameters to factory
settings (does not apply to addresses):
1 = Factory settings (resets to 0)
list using the buttons on RCF.
manually if the fan is not set to auto
(parameter 25).
5
Page 6
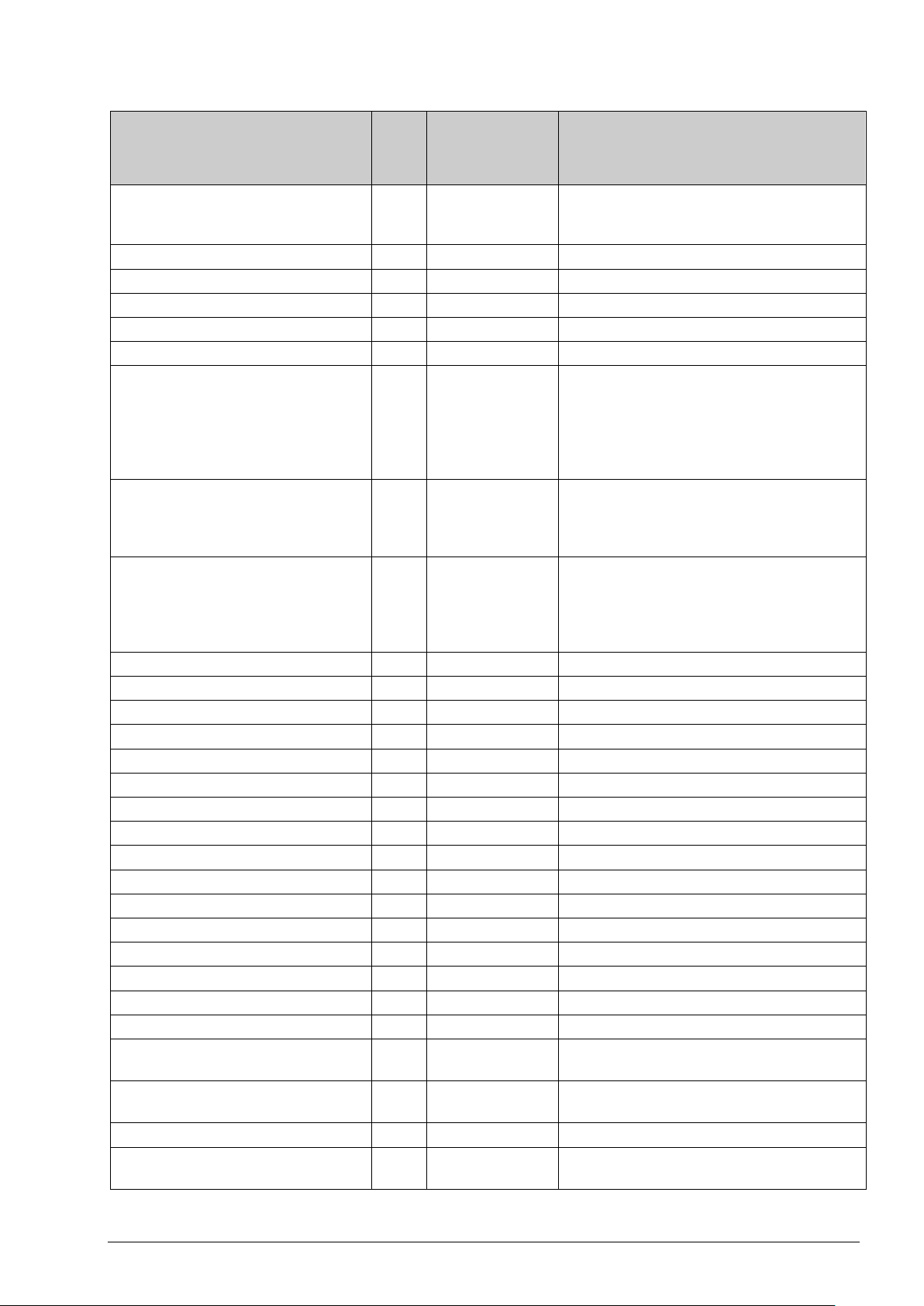
Input register
RC_Actual_X.RegioVerMinor
X,4 3 Minor version
2 = Cooling
RC_Actual_R.RegioRoomTempInt
R,4
13
Room temperature from internal sensor
RC_Actual_R.RegioUAnaOut2
R,4
18
Value on universal analogue output 2
RC_Actual_R.RegioCoolOutput
R,4
23
Cooling output signal (0…100 %)
RC_Actual_R.RegioSupplyAirPIDout
R, 4
48
Supply air controller output
Name of signal Type
RC_Actual_X.RegioSoftware X,4 1 Type of Regio software:
RC_Actual_X.RegioVerMajor X,4 2 Major version
RC_Actual_X.RegioVerBranch X,4 4 Branch version
RC_Actual_X.RegioRevision X,4 5 Revision
Not used in this model X,4 6
RC_Actual_X.RegioUnitState X,4 7 Current running mode:
RC_Actual_X.RegioControllerState X,4 8 Current control:
RC_Actual_X.RegioFanSpeed X,4 9 Current fan speed:
Not used in this model X,4 10
RC_Actual_R.RegioRoomTemp R,4 11 Room temperature
RC_Actual_R.RegioRoomTempExt R,4 12 Room temperature from external sensor
Modbus
address
Description
0 = RCP
1 = RC
0 = Off
1 = Economy/Standby
2 = Not used
3 = Not used
4 = Comfort
0 = Off
1 = Heating
0 = Off
1 = Fan speed 1 active
2 = Fan speed 2 active
3 = Fan speed 3 active
RC_Actual_R.RegioAIChangeOver R,4 14 Change-over temperature
RC_Actual_R.RegioAnaIn1 R,4 15 Value on analogue input 1
RC_Actual_R.RegioUAnaIn1 R,4 16 Value on universal analogue input 1
RC_Actual_R.RegioUAnaOut1 R,4 17 Value on universal analogue output 1
Not used in this model 19
RC_Actual_R.RegioPIDSetP R,4 20 Controller setpoint
RC_Actual_R.RegioPIDOutput R,4 21 Controller output signal (0…100 %)
RC_Actual_R.RegioHeatOutput R,4 22 Heating output signal (0…100 %)
RC_Actual_R.RegioAI1Raw R,4 24 Raw value for analogue input 1
RC_Actual_R.RegioUI1Raw R,4 25 Raw value for universal input 1
RC_Actual_R.RoomTemp_NTC2 R,4 26
RC_Actual_R.RegioSupplyAirTemp R, 4 47 Supply air temperature from sensor connected
RC_Actual_R.RegioPID2Setp R, 4 49 Room controller output (scaled) and supply air
Room temperature input value from secondary
internal sensor
to AI1
controller setpoint
6
Page 7

RC_Setp_X.RegioCoolOutputSelect
X,3 4 2
Manual/Auto cooling output
hysteresis start/stop fan speed
Not used in this model
X,3
17 -
Holding register
Name of signal Type
Not used in this model X,3 1-2 -
RC_Setp_X.RegioHeatOutputSelect X,3 3 2 Manual/Auto heating output
RC_Setp_X.RegioFanSelect X,3 5 4 Select fan mode:
RC_Setp_X. RegioFanControlMode X,3 6 3 Select fan control:
RC_Setp_X.RegioFanSpeed1Start X,3 7 20
RC_Setp_X.RegioFanSpeed2Start X,3 8 60 Controller output signal in %
RC_Setp_X.RegioFanSpeed3Start X,3 9 RCFx-230CD =
RC_Setp_X.RegioFanSpeedHyst X,3 10 5 Controller output signal
Modbus
address
Default
setting
90
All others = 100
Description
0 = Off
1 = Manual speed 1
2 = Manual speed 2
3 = Manual speed 3
4 = Auto
0 = No control
1 = The fan is controlled by
heating requirement
2 = The fan is controlled by
cooling requirement
3 = The fan is controlled by
both heating and cooling
requirement
Controller output signal in %
for fan speed 1
for fan speed 2
Controller output signal in %
for fan speed 3
RC_Setp_X.RegioFanSpeedMax X,3 11 3 Number of fan speeds (1-3)
Not used in this model X,3 12 -
RC_Setp_X.RegioChangeOverSelect X,3 13
RC_Setp_X.RegioRemoteState X,3 14 5 Used for remote control:
RC_Setp_X.RegioUnitReturnState X,3 15 - Pre-set running mode:
Not used in this model X,3 16
7
RCFM-230Cxx
= 0
RCF-230Cxx =
2
Manual/Auto Change-over
(0=Heating, 1=Cooling,
2=Auto)
0 = Off
1 = Economy/Standby
2 = Not used
3 = Not used
4 = Comfort
5 = No remote control
0 = Off
1 = Standby
Page 8

Name of signal Type
RC_Setp_X.RegioCVCoolType
X,3
20 0 Type of actuator, cooling
Not used in this model
X,3
25-27
-
2 = Condensation alarm)
EC)
Modbus
address
Default
setting
Description
RC_Setp_X.RegioControllerMode X,3 18
RC_Setp_X.RegioCVHeatType X,3 19 0 Type of actuator, heating:
RC_Setp_X.RegioCVHeatExerciseInterval X,3 21 23 Time (in hours) between
RC_Setp_X.RegioCVCoolExerciseInterval X,3 22 23 Time (in hours) between
Not used in this model X,3 23 -
RC_Setp_X.RegioAi1 X,3 24 0 Signal connected on AI1:
RCFM-230Cxx
= 2
RCF-230Cxx =
3
Control mode selection:
2= Heating or Cooling via
change-over
3 = Heating/Cooling
4 = Electric heating
0 = 0…10 V
1 = 2…10 V
2 = 10…2 V
3 = 10…0 V
exercise of heating actuator.
exercise of cooling actuator.
0 = Not used (Internal Room
sensor used)
1 = External Room sensor
3-10 = No function
11 = Supply air temperature
limitation sensor
RC_Setp_X.RegioDi2 X,3 28 N/A Not used (Signal connected on
DI2:
1 = Open window
RC_Setp_X.RegioDi3 X,3 29 N/A Not used
RC_Setp_X.RegioUi1 X,3 30 0 Signal connected on UI1:
0 = Not used
1 = Change-over sensor,
digital
2 = Change-over sensor,
analogue
3=Off mode (open window)
Not used in this model X,3 31 - 41 -
RC_Setp_X.RegioUo1 X,3 42 RCF-230CAD
= 3
RCF-230CTDEC = 17
All others = 1
Signal connected on UO1:
0 = Not used
1 = Thermo valve,
Heating/Cooling (not (C)AD)
2 = Not used
3 = Analogue valve
Heating/Cooling (only (C)AD)
4-16 = Not used
17 = EC fan analogue out
AO1, Thermo valve heating
DO4 (only RCF-230-CTD-
8
Page 9

Name of signal Type
character, ie. at least 5 ms.
heating (sec)
cooling (sec)
Modbus
address
Default
setting
Description
RC_Setp_X.RegioUo2 X,3 43
RC_Setp_X.RegioModbusSlaveAddr X,3 44 Factory set Address Modbus slave
RC_Setp_X.RegioModbusParity X,3 45 2 Parity and stop bits for
RC_Setp_X.RegioModbusCharTimeout X,3 46 3 Modbus timeout for characters
RC_Setp_X.RegioModbusAnswerDelay X,3 47 5 Response lag Modbus (t3.5), in
RC_Setp_X.RegioDispBacklightLO X,3 48 10 Display backlight low (0...100)
RC_Setp_X.RegioDispBacklightHi X,3 49 30
RC_Setp_X.RegioDispContrast X,3 50 15 Contrast (0…15)
RC_Setp_X.RegioDisplayViewMode X,3 51 2 Viewing options for the
Not used in this model X,3 52-55 -
Not used in this model I,3 56 -
RC_Setp_I.RegioPresenceOffTime I,3 57 0 Switch-off delay when
RC_Setp_I.RegioPresenceOnTime I,3 58 0 Switch-on delay when
RC_Setp_I.RegioCVHeatPeriodTime I,3 59 60 Period time for pulse prop.
RC_Setp_I.RegioCVCoolPeriodTime I,3 60 60
RC_Setp_I.RegioCVHeatRunTime I,3 61 120 Run time closed valve to open,
RCF-230CAD
= 4
All others = 2
Signal connected on UO2:
0 = Not used
1 = Not used
2 = Thermo valve, Cooling
(not (C)AD)
3 = Not used
4 = Analogue valve Cooling
(only (C)AD)
Modbus communication:
0 = 8N2
1 = 8O1
2 = 8E1
3 = 8N1
(t1.5), in ms. Should be 1.5
times a character, ie. at least 2
ms.
ms. Should be 3.5 times a
Display backlight high
(0...100)
display:
0 = Room temperature and
setpoint when adjusting
1 = Room temperature and
setpoint when adjusting
2 = Setpoint
3 = Setpoint displacement
changing to no presence (min)
changing to presence (min)
control valve, heating (sec)
Period time for pulse prop.
control valve, cooling (sec)
RC_Setp_I.RegioCVCoolRunTime I,3 62 120 Run time closed valve to open,
Not used in this model X,3 63-67 -
Not used in this model R,3 68-69 -
RC_Setp_R.RegioStandbySetPDeadBand R,3 70 8°C Deadband for Economy mode
9
Page 10

Name of signal Type
RC_Setp_R.RegioFrostSetP
R,3
73
N/A
Not used
RC_Setp_R.RegioPIDITime
R,3
78
300 sec
Room controller I time
band)
R,3
92 - Not used
230CTD-EC).
Modbus
address
Default
setting
Description
RC_Setp_R.RegioUnOccSetPHeat R,3 71 15°C
RC_Setp_R.RegioUnOccSetPCool R,3 72 30°C Cooling setpoint when in
RC_Setp_R.RegioSetpointOffsetPos R,3 74 13°C Max. upward setpoint
RC_Setp_R.RegioSetpointOffsetNeg R,3 75 17°C Max. downward setpoint
RC_Setp_R.RegioSetPOffset R,3 76 0 Setpoint displacement
RC_Setp_R.RegioPIDPGain R,3 77 10°C Room controller P-band
RC_Setp_R.RegioCVDeadband R,3 79 N/A Not used (Control valve dead
RC_Setp_R.RegioAIChangeOverLimitLo
w
RC_Setp_R.RegioAIChangeOverLimitHigh R,3 81 28°C Controller switches over to
RC_Setp_R.RegioAi1Comp R,3 82 0°C Compensation for analogue
RC_Setp_R. RegioUi1Comp R,3 83 0°C Compensation for universal
RC_Setp_R.RegioInternalTempComp R,3 84 0°C
RC_Setp_R.RegioTempFilterFactor R,3 85 0.2°C Filter factor for temperature on
Not used in this model R,3 86-89 -
RC_Setp_R.RegioThermostatHyst R,3 90 10 Room hysteresis
RC_Setp_R.RegioComfortSetPDeadBand R,3 91 RCFM-230Cxx
R,3 80 18°C
= 0
RCF-230Cxx =
2
Heating setpoint when in
Unoccupied mode
Unoccupied mode
displacement
displacement
Controller switches over to
control of cooling if changeover temperature is lower
control of heating if changeover temperature is higher
input 1
input 1
Compensation for internal
room sensor
analogue input
0 = No filter
1 = Max filter
Deadband for Comfort mode
(DB)
R,3 93 - Not used
RC_Setp_R.RegioHeatOutputManual R,3 94 0 % Manual output heating output
RC_Setp_R.RegioCoolOutputManual R,3 95 0 % Manual output cooling output
RC_Setp_R.RegioRoomTempRemote R,3 96 -255 Used for remote control of
RC_SetpExt_R.RegioMinECFanSpeed R,3 282 1 V
10
(0…100 %)
(0…100 %)
room temperature. External
Room sensor must be selected.
Starting voltage for EC fan.
The fan will never receive a
signal of a lower voltage than
the set value
(only RCF-
Page 11

Name of signal Type
control
temperature limitation is active
RC_SetpExt_R.RegioMaxECFanSpeed R,3 283 10 V Maximum speed of the EC fan
RC_SetpExt_R.RegioRCFSetPoint R,3 284 22°C Basic setpoint
RC_Setp_R.SupplyAirTLim_HeatHi R, 3 289
RC_Setp_R.SupplyAirTLim_HeatLo R, 3 290 24°C Supply air min limitation for
RC_Setp_R.SupplyAirTLim_CoolHi R, 3 291 24°C Supply air max limitation for
RC_Setp_R.SupplyAirTLim_CoolLo R, 3 292 12°C Supply air min limitation for
RC_Setp_R.SupplyAirTLim_CascadeFact R, 3 293 3°C Cascade factor between room
RC_Setp_R.SupplyAirTLim_FrostProtect R, 3 294 8°C Frost protection temperature
Modbus
address
Default
setting
35°C
Description
Supply air max limitation for
cascade control and heating
cascade control and heating
control
cascade control and cooling
control
cascade control and cooling
control
controller and supply air
controller
for supply air when supply air
11
Page 12

BACnet signal types
BACnet In order to communicate via BACnet, the protocol has to be changed either via Regio
Object type The BACnet types of the signals (types in the list below):
Out_of_service The property out_of_service is not writable for all Object Types.
Commandable The value objects are not commandable (i.e. does not use a priority array).
EDE files EDE files for BACnet are included in the Regio tool
©
or via the parameter list in the display. Once the protocol has been set to BACnet,
tool
it can only be switched back to EXOline and Modbus via the display.
• Analogue inputs
• Analogue values
• Binary inputs
• Binary values
• Loop
• Multistate inputs
• Multistate values
• Device
©
installation.
12
Page 13

BACnet signals
input 1
when in “Economy” mode
when in “Economy” mode
Analogue inputs
Object name Object ID Description Unit Writeable
RC_Actual_R.RegioRoomTemp Analog input, 0
RC_Actual_R.RegioAIChangeOver
RC_Actual_R.RegioAnaIn1
RC_Actual_R.RegioUAnaIn1
RC_Actual_R.RegioSupplyAirTemp
Analog input, 1
Analog input, 2
Analog input, 3
Analog input, 4
Room temperature °C No
Change-over temperature
Value on analogue input 1
Value on universal analogue
Supply air temperature
°C No
°C No
V No
°C No
Analogue values
Object name Object ID Description Unit
RC_Actual_R.RegioUAnaOut1 Analog value, 0 Value on universal
analogue output 1
RC_Actual_R.RegioUAnaOut2 Analog value, 1 Value on universal
analogue output 2
RC_Actual_R.RegioSetPAdjustment Analog value, 2 Setpoint displacement from
internal unit
RC_Actual_R.RegioPIDSetP Analog value, 3 Controller setpoint °C No
V No
V No
°C No
Writeabl
e
RC_Actual_R.RegioPIDOutput Analog value, 4 Controller output % No
RC_Actual_R.RegioHeatOutput Analog value, 5 Heating control % No
RC_Actual_R.RegioCoolOutput Analog value, 6 Cooling control % No
Not used in this model Analog value, 7-8 Yes
RC_Setp_R.RegioUnOccSetPHeat Analog value, 9 The room heating setpoint
RC_Setp_R.RegioUnOccSetPCool Analog value, 10 The room cooling setpoint
Not used in this model Analog value, 11
RC_Setp_R.RegioSetPOffset Analog value, 12 Setpoint displacement
13
°C Yes
°C Yes
°C Yes
during presence
Page 14

Object name Object ID Description Unit
mode
the EC fan
Writeabl
e
RC_Setp_R.RegioHeatOutputManual Analog value, 13 Manual value heating
output
RC_Setp_R.RegioCoolOutputManual Analog value, 14 Manual value cooling
output
RC_Setp_R.RegioRoomTempRemote Analog value, 15 Remote control of room
temperature.
RC_Setp_R.RegioStandbySetPDeadBand Analog value, 16 Deadband for Standby
Not used in this model Analog value, 17-26
RC_Setp_R.RegioMinECFanSpeed Analog value, 27 Lowest possible speed for
RC_Setp_R.RegioMaxFanSpeed Analog value, 28 Highest possible speed for
the EC fan
RC_Setp_R.RegioAIChangeOverLimitLow Analog value, 29 Cooling if lower change-
over temperature
RC_Setp_R.RegioAIChangeOverLimitHigh Analog value, 30 Heating if higher change-
over temperature
RC_Setp_R.RegioThermostatHyst Analog value, 31
RC_Setp_R.RegioComfortSetPDeadband Analog value, 32 Deadband for comfort
RC_SetpExt_R.RegioRCFSetPoint Analog Value, 33 Basic setpoint for the
RC_Actual_R.RegioPID2Setp Analog Value, 34 Calculated supply air
Room temperature
hysteresis
mode.
controller
setpoint
% Yes
% Yes
°C Yes
°C Yes
% Yes
% Yes
°C Yes
°C Yes
°C Yes
°C Yes
°C Yes
°C No
Binary inputs
Object name Object ID Description Values Writeable
RC_Actual_L.RegioDIOpenWindow Binary input, 0 Indicates open window
Not used in this model Binary input, 1 No
RC_Actual_L.RegioDIPresences Binary input, 2 Indicates presence from
digital input
RC_Actual_L.RegioDIChangeOver Binary input, 3 Indicates change-over
from digital input
Not used in this model Binary input, 4-6 No
All binary inputs have normal polarity.
ACTIVE/
INACTIVE
ACTIVE/
INACTIVE
ACTIVE/
INACTIVE
No
No
No
14
Page 15

Binary values
analogue input
this value is first set to “0”.
Object name Object ID Description Values Writeable
Not used in this model Binary value, 0 No
RC_Actual_L.RegioCVHeatPulsProp Binary value, 1 Indicates pulse prop. heating ACTIVE/
INACTIVE
RC_Actual_L.RegioCVCoolPulsProp Binary value, 2 Indicates pulse prop. cooling ACTIVE/
INACTIVE
RC_Actual_L.RegioCVHeatInc Binary value, 3 Indicates heating increase
RC_Actual_L.RegioCVHeatDec Binary value, 4 Indicates heating decrease ACTIVE/
Not used in this model Binary value, 5-6 No
RC_Actual_L.RegioChangeOverState Binary value, 7 Indicates change-over status
from both digital and
Not used in this model Binary value, 8 No
RC_Actual_L.RegioFireAlarmStop Binary value, 9 Places the unit in Shutdown
mode and prevents it from
being activated again, unless
RC_Setp _L.RegioShutDown Binary value, 10
RC_Setp_L.RegioBlockConfig Binary value, 12 Prevents parameter menu
All binary values have normal polarity.
Places the unit in Shutdown
mode
access via display
ACTIVE/
INACTIVE
INACTIVE
ACTIVE/
INACTIVE
ACTIVE/
INACTIVE
ACTIVE/
INACTIVE
ACTIVE/
INACTIVE
No
No
No
No
No
Yes
Yes
Yes
Loop
Object name Object ID Description
Controller Loop, 0 The Regio controller
15
Page 16

Multistate inputs
3=Automatic output
Object name Object ID Description Values Writeable
Not used in this model Multistate input, 0 No
RC_Actual_X.RegioUnitState Multistate input, 1 Current running
mode
RC_Actual_X.RegioControllerState Multistate input, 2 Current control
mode
RC_Actual_X.RegioFanSpeed Multistate input, 3 Current fan speed 1=Off
1=Off
2=Economy/Standby
3=Not used
4=Not used
5=Comfort
1=Off
2=Heating
3=Cooling
2=Fan speed 1
3=Fan speed 2
4=Fan speed 3
No
No
No
Multistate values
Object name Object ID Description Values Writeable
RC_Setp_X.RegioHeatOutputSelect Multistate value, 0 Manual/Auto
heat output
RC_Setp_X.RegioCoolOutputSelect Multistate value, 1 Manual/Auto
cool output
1=Off
2=Manual output
3=Automatic output
1=Off
2=Manual output
Yes
Yes
RC_Setp_X.RegioFanSelect Multistate value, 2 Fan mode select 1=Off
2=Manual speed 1
3=Manual speed 2
4=Manual speed 3
5=Auto
6=Auto 2
7=Auto 1
Not used in this model Multistate value, 3 Manual/Auto
forced ventilation
RC_Setp_X.RegioChangeOverSelect Multistate value, 4 Manual/Auto
change-over
RC_Setp_X.RegioRemoteState Multistate value, 5
Remote control
unit state
1=Off
2=Manual on
3=Auto
1=Heating
2=Cooling
3=Auto
1=Off
2=Economy/Standby
3=Not used
4=Not used
5=Comfort
6=No remote control
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
16
Page 17

Object name Object ID Description Values Writeable
RC_Non_Modbus.RegioButtonActiv
eConf
Device
The Device object contains to writeable properties; Description and Location. Description can be 17 characters in length and Location can be 33 characters, as long
as single byte character encoding is used.
Multistate value, 6 Buttons active
1=No buttons
2=Occupancy button
only
3=INCREASE/DECR
EASE only
4=Occupancy button
and
INCREASE/DECREA
SE
5=Fan button only
6=Occupancy button
and fan button
7=INCREASE/DECR
EASE and fan button
8=All buttons
Yes
20191111, HH
17
 Loading...
Loading...