Page 1

Fr
ees
cale S
em
iconduct
or
, I
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
nc...
M5407C3 User's Manual
M5407C3UM/D
Rev. 1.1, 8/2000
Page 2

Fr
ees
cale S
em
iconduct
or
, I
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
nc...
Information in this document is provided solely to enable system and software
implementers to use Freescale Semiconductor products. There are no express or
implied copyright licenses granted hereunder to design or fabricate any integrated
circuits or integrated circuits based on the information in this document.
Freescale Semiconductor reserves the right to make changes without further notice to
any products herein. Freescale Semiconductor makes no warranty, representation or
guarantee regarding the suitability of its products for any particular purpose, nor does
Freescale Semiconductor assume any liability arising out of the application or use of
any product or circuit, and specifically disclaims any and all liability, including without
limitation consequential or incidental damages. “Typical” parameters which may be
provided in Freescale Semiconductor data sheets and/or specifications can and do
vary in different applications and actual performance may vary over time. All operating
parameters, including “Typicals” must be validated for each customer application by
customer’s technical experts. Freescale Semiconductor does not convey any license
under its patent rights nor the rights of others. Freescale Semiconductor pro ducts are
not designed, intended, or authorized for use as components in systems intended for
surgical implant into the body, or other applications intended to support or sustain life,
or for any other application in which the failure of the Freescale Semiconductor product
could create a situation where personal injury or death may occur. Should Buyer
purchase or use Freescale Semiconductor products for any such unintended or
unauthorized application, Buyer shall indemnify and hold Freescale Semiconductor
and its officers, employees, subsidiaries, affiliates, and distributors harmless against all
claims, costs, damages, and expenses, and reasonable attorney fees arising out of,
directly or indirectly, any claim of personal injury or death associated with such
unintended or unauthorized use, even if such claim alleges that Freescale
Semiconductor was negligent regarding the design or manufacture of the part.
How to Reach Us:
Home Page:
www.freescale.com
E-mail:
support@freescale.com
USA/Europe or Locations Not Listed:
Freescale Semiconductor
Technical Information Center, CH370
1300 N. Alma School Road
Chandler, Arizona 85224
+1-800-521-6274 or +1-480-768-2130
support@freescale.com
Europe, Middle East, and Africa:
Freescale Halbleiter Deutschland GmbH
Technical Information Center
Schatzbogen 7
81829 Muenchen, Germany
+44 1296 380 456 (English)
+46 8 52200080 (English)
+49 89 92103 559 (German)
+33 1 69 35 48 48 (French)
support@freescale.com
Japan:
Freescale Semiconductor Japan Ltd.
Headquarters
ARCO Tower 15F
1-8-1, Shimo-Meguro, Meguro-ku,
Tokyo 153-0064
Japan
0120 191014 or +81 3 5437 9125
support.japan@freescale.com
Asia/Pacific:
Freescale Semiconductor Hong Kong Ltd.
Technical Information Center
2 Dai King Street
Tai Po Industrial Estate
Tai Po, N.T., Hong Kong
+800 2666 8080
support.asia@freescale.com
For Literature Requests Only:
Freescale Semiconductor Literature Distribution Center
P.O. Box 5405
Denver, Colorado 80217
1-800-441-2447 or 303-675-2140
Fax: 303-675-2150
LDCForFreescaleSemiconductor@hibbertgroup.com
© Motorola Inc., 2000. All rights reserved.
Page 3

Fr
ees
cale S
em
iconduct
or
, I
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
nc...
Matrix Design warrants this product against defects in material and workmanship for
a period of sixty (60) days from the original date of purchase.
to the original customer only and is in lieu of all other warrants, including
implied warranties of merchantability and fitness.
liable for any incidental or consequential damages. During the warranty period,
Matrix Design will replace, at no charge, components that fail, provided the product
is returned (properly packed and shipped prepaid) to Matrix Design at address below.
Dated proof of purchase (such as a copy of the invoice) must be enclosed with the
shipment. We will return the shipment prepaid via UPS.
This warranty does not apply if, in the opinion of Matrix Design, the product has been
damaged by accident, misuse, neglect, misapplication, or as a result of service or
modification (other than specified in the manual) by others.
Please send the board and cables with a complete description of the problem to:
LIMITED W ARRANTY
This warranty extends
In no event will the seller be
Matrix Design & Manufacturing, Inc.
2914 Montopolis Drive #290
Austin, TX 78741
Phone: (512) 385-9210
Fax: (512) 385-9224
http://www.cadreiii.com
Page 4

Fr
ees
cale S
em
iconduct
or
, I
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
nc...
This board generates, uses, and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed
properly , may cause interference to radio communications. As temporarily permitted
by regulation, it has not been tested for compliance with the limits for class a
computing devices pursuant to Subpart J of Part 15 of FCC rules, which are designed
to provide reasonable protection against such interference. Operation of this product
in a residential area is likely to cause interference, in which case the user, at his/her
own expense, will be required to correct the interference.
WARNING
Page 5

Fr
ees
cale S
em
iconduct
or
, I
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
nc...
apps docs:ColdFire:5407:Eval Board UM NEW:5407C3UMTOC.fm 8/14/00
CONTENTS
Paragraph
Number
Title
Chapter 1
M5407C3 Board
1.1 General Hardware Description ........................................................................... 1-1
1.2 System Memory.................................................................................................. 1-4
1.3 Serial Communication Channels......................................................................... 1-4
1.4 Parallel I/O Ports................................................................................................. 1-4
1.5 Programmable Timer/Counter............................................................................ 1-5
1.6 PCI Controller..................................................................................................... 1-5
1.7 On Board Ethernet .............................................................................................. 1-5
1.8 System Configuration ......................................................................................... 1-5
1.9 Installation And Setup......................................................................................... 1-7
1.9.1 Unpacking....................................................................................................... 1-7
1.9.2 Preparing the Board for Use ........................................................................... 1-7
1.9.3 Providing Power to the Board......................................................................... 1-8
1.9.4 Selecting Terminal Baud Rate........................................................................ 1-8
1.9.5 The Terminal Character Format ..................................................................... 1-8
1.9.6 Connecting the Terminal ................................................................................ 1-8
1.9.7 Using a Personal Computer as a Terminal...................................................... 1-8
1.10 System Power-up and Initial Operation............................................................ 1-11
1.11 M5407C3 Jumper Setup ................................................................................... 1-11
1.12 Using The BDM Port........................................................................................ 1-13
Chapter 2
Using the Monitor/Debug Firmware
Page
Number
2.1 What Is dBUG?................................................................................................... 2-1
2.2 Operational Procedure ........................................................................................ 2-3
2.2.1 System Power-up............................................................................................ 2-3
2.2.2 System Initialization....................................................................................... 2-4
2.2.2.1 Hard RESET Button. .................................................................................. 2-5
2.2.2.2 ABORT Button........................................................................................... 2-5
Contents v
PRELIMINAR WITHOUT NOTICE
Page 6

vi
Fr
ees
cale S
em
iconduct
or
, I
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
nc...
Paragraph
Number
2.5 TRAP #15 Functions ........................................................................................ 2-39
2.5.1 OUT_CHAR................................................................................................. 2-39
2.5.2 IN_CHAR..................................................................................................... 2-39
2.5.3 CHAR_PRESENT........................................................................................ 2-40
2.5.4 EXIT_TO_dBUG.......................................................................................... 2-40
CONTENTS
Title
Page
Number
Chapter 3
Hardware Description and Reconfiguration
3.1 The Processor and Support Logic....................................................................... 3-1
3.1.1 Processor......................................................................................................... 3-1
3.1.2 Reset Logic..................................................................................................... 3-1
3.1.3 HIZ Signal....................................................................................................... 3-2
3.1.4 Clock Circuitry ............................................................................................... 3-2
3.1.5 Watchdog Timer............................................................................................. 3-2
3.1.6 Interrupt Sources............................................................................................. 3-2
3.1.7 Internal SRAM................................................................................................ 3-3
3.1.8 The MCF5407 Registers and Memory Map................................................... 3-4
3.1.9 Reset Vector Mapping.................................................................................... 3-5
3.1.10 TA Generation ................................................................................................ 3-5
3.1.11 Wait State Generator....................................................................................... 3-6
3.1.12 SDRAM DIMM.............................................................................................. 3-6
3.1.13 Flash ROM...................................................................................................... 3-7
3.1.14 JP15 Jumper and User’s Program................................................................... 3-7
3.2 Serial Communication Channels......................................................................... 3-7
3.2.1 MCF5407 UARTs........................................................................................... 3-7
3.2.2 I2C Module..................................................................................................... 3-8
3.3 Real-Time Clock................................................................................................. 3-8
3.4 Parallel I/O Port .................................................................................................. 3-8
3.5 On-Board Ethernet Logic.................................................................................... 3-8
3.6 Connectors and Expansion Bus ........................................................................ 3-11
3.6.1 Expansion Connectors - J1 and J2................................................................ 3-11
3.6.2 The Debug Connector J5 .............................................................................. 3-13
Appendix A
Configuring dBUG for Network Downloads
Appendix B
ColdFire to ISA, IRQ7 and Reset Logic Abel Code
Appendix C
M5407C3 User’s Manual
Page 7

Fr
ees
cale S
em
iconduct
or
, I
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
nc...
Paragraph
Number
CONTENTS
Title
Page
Number
SDRAM MUX PAL Equation
Appendix D
Evaluation Board BOM
Appendix E Schematics
Appendix F
Errata
Contents vii
PRELIMINAR WITHOUT NOTICE
Page 8

Fr
ees
cale S
em
iconduct
or
, I
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
nc...
Paragraph
Number
CONTENTS
Title
Page
Number
viii
M5407C3 User’s Manual
PRELIMINAR WITHOUT NOTICE
Page 9

Fr
ees
cale S
em
iconduct
or
, I
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
nc...
apps docs:ColdFire:5407:Eval Board UM NEW:5407C3UMLOF.fm 8/14/00
ILLUSTRATIONS
Figure
Number
1-1 5407 Block Diagram..................................................................................................... 1-3
1-2 Minimum System Configuration .................................................................................. 1-6
1-3 Pin assignment for female P4 (Terminal) connector. ................................................... 1-9
1-4 Jumper Locations........................................................................................................ 1-10
2-1 Flow Diagram of dBUG Operational Mode. ................................................................ 2-4
3-1 The J5 Connector pin assignment............................................................................... 3-14
Title
Page
Number
Illustrations ix
PRELIMINAR WITHOUT NOTICE
Page 10

x
Fr
ees
cale S
em
iconduct
or
, I
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
nc...
Figure
Number
ILLUSTRATIONS
Title
Page
Number
BookTitle
PRELIMINAR WITHOUT NOTICE
Page 11

Fr
ees
cale S
em
iconduct
or
, I
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
nc...
apps docs:ColdFire:5407:Eval Board UM NEW:5407C3UMLOT.fm 8/14/00
TABLES
Table
Number
1-1 Power Supply Connections........................................................................................... 1-8
1-2 Jumper Settings........................................................................................................... 1-11
1-3 Jumper Settings........................................................................................................... 1-13
1-4 Jumper Settings........................................................................................................... 1-13
2-1 dBUG Command Summary.......................................................................................... 2-7
3-1 The M5407C3 Memory Map........................................................................................ 3-5
3-2 J1 Connector Pin Assignment..................................................................................... 3-11
3-3 J2 Connector pin assignment......................................................................................3-12
D-1 MCF5407EVM_BOM.................................................................................................D-1
Title
Page
Number
Tables xi
PRELIMINAR WITHOUT NOTICE
Page 12

Fr
ees
cale S
em
iconduct
or
, I
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
nc...
Table
Number
TABLES
Title
Page
Number
xii
M5407C3 User’s Manual
PRELIMINAR WITHOUT NOTICE
Page 13

Fr
ees
cale S
em
iconduct
or
, I
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
nc...
Chapter 1
M5407C3 Board
The M5407C3 is a versatile single board computer based on MCF5407 ColdFire®
Processor. It may be used as a powerful microprocessor based controller in a variety of
applications. With the addition of a terminal, it serves as a complete microcomputer for
reference, development/evaluation, training and educational use. The user need only
connect an RS-232 compatible terminal (or a personal computer with terminal emulation
software) and power supply to have a fully functional system.
Provisions have been made to connect this board to additional user supplied peripherals, via
the Microprocessor Expansion Bus connectors, to expand memory and I/O capabilities.
Additional peripherals may require bus buffers to minimize additional bus loading.
Furthermore, provisions have been made in the PC-board to permit configuration of the
board in a way, which best suits, an application. Options available are: upgrade to
512MBytes SDRAM, 512K SRAM, and commercially available slave PCI devices.
1.1 General Hardware Description
The M5407C3 board provides the RAM, Flash ROM, on board NE2000 compatible
Ethernet interface (10M bit/sec), RS232, and all the built-in I/O functions of the MCF5407
for learning and evaluating the attrib utes of the microprocessor . The MCF5407 is a member
of the ColdFire® family of processors. It is a 32-bit processor with 32-bit of address bus
and 32 lines of data. The processor has eight 32-bit data registers, eight 32-bit address
registers, a 32-bit program counter, and a 16-bit status register.
The MCF5407 has a System Integration Module referred to as the SIM. The module
incorporates many of the functions needed for system design. These include programmable
chip-select logic, System Protection logic, General purpose I/O, and Interrupt controller
logic. The chip-select logic can select up to eight memory banks and peripherals in addition
to two banks of DRAM’s. The chip-select logic also allows programmable number of
wait-states to allow the use of slower memory (refer to
Freescale for detailed information about the SIM.). The M5407C3 uses four (CS[3:0]) of
the eight chip selects to access the Flash ROM’s (CS0), PCI bridge chip (CS1), SRAM
MCF5407 User's Manual by
Chapter 1. M5407C3 Board 1-1
Page 14

Fr
ees
cale S
em
iconduct
or
, I
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
nc...
General Hardware Description
to the user.
The M5407C3 will work with most PC100 SDRAM DIMMs with a few exceptions. The
MCF5407 supports up to two banks of SDRAM, but double-sided DIMMs require 4 bank
selects to access all of the chips. Therefore when using double-sided DIMMs only half of
the available memory will be accessible. Since DIMMs are manuf actured primarily for use
in PCs the DQM signals on some DIMMS are routed so that the SDRAM can only be
accessed correctly as a 64-bit port so the M5407C3 will not be able to access the SDRAM
correctly.
1-2
M5407C3 User’s Manual
Page 15
Fr
ees
cale S
em
iconduct
or
, I
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
nc...
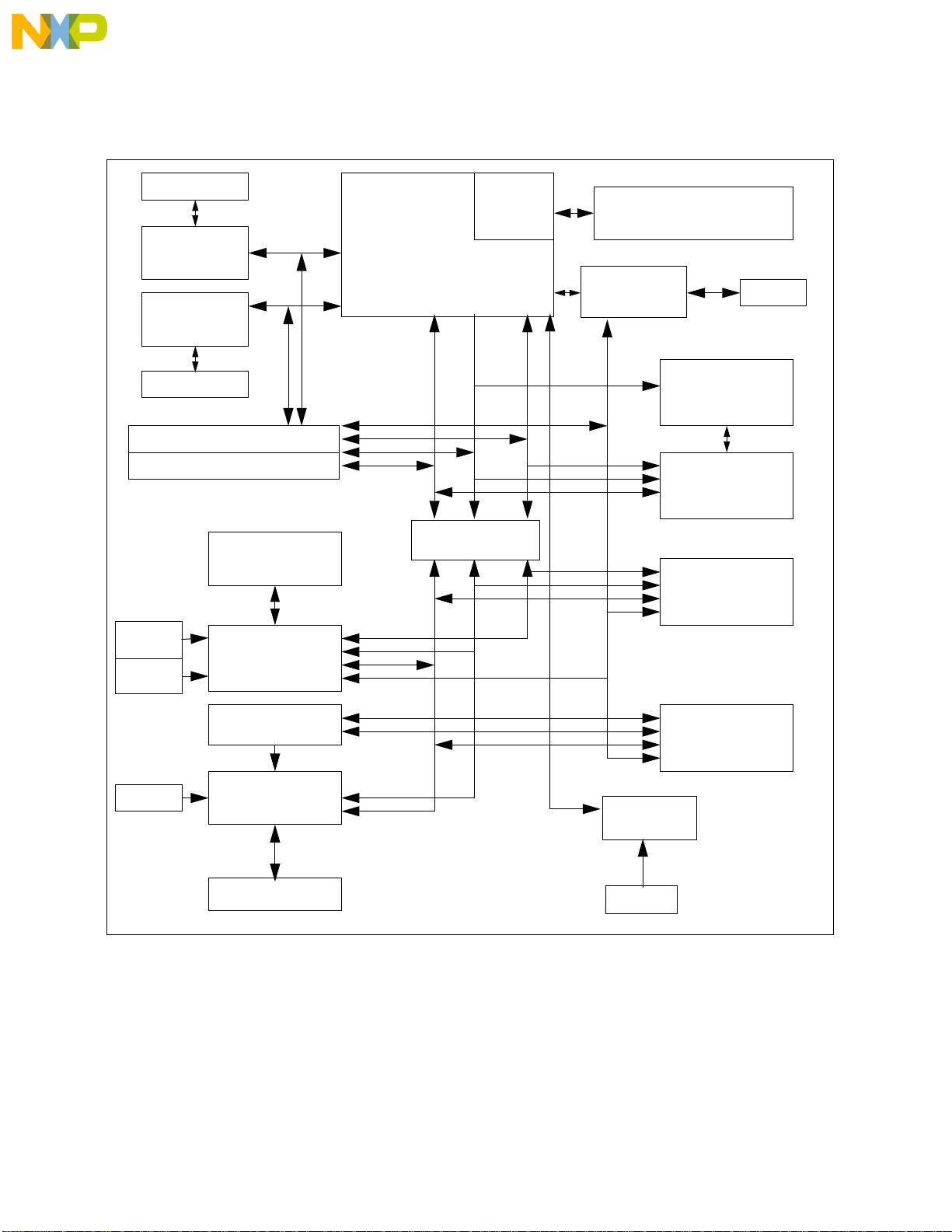
Figure 1-1 shows the 5407 block diagram.
General Hardware Description
(1) DB-9
(1) RS232
drivers
(1) RS232
drivers
(1) DB-9
Expansion Connector#1
Expansion Connector#2
Osc.
EEPROM
Osc.
PCI slot
PCI Interface
PAL
Davicom
10 Mb/sec
RJ45 Connector
ColdFire® MCF5407
data[31:0]
External
Data
Bus
addr[31:0]
Buffers
External
Address
Bus
Debug
Module
Control Signals
Control Signals
26-pin debug connector
Bus Clk Drv
512KB Sync
FSRAM
32 bit 3.3V
(not populated)
Flash
16 bit
1MB minimum
Real TIme
Clock
Osc.
SDRAM
External
Mux (PAL)
SDRAM
32bit 3.3V
Osc.
Figure 1-1. 5407 Block Diagram
Chapter 1. M5407C3 Board 1-3
Page 16

Fr
ees
cale S
em
iconduct
or
, I
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
nc...
System Memory
1.2 System Memory
One on board Flash ROM (U12) is used to store the M5407C3 dBUG debugger/monitor
firmware in the lower 128 KBytes. The AM29PL160C-XX device is 16Mbits (16 bit by 1
MByte) giving a total of 2MBytes of Flash memory.
The PCI bridge chip provides the interface to the Universal 32-bit PCI on board connector
allowing the user to experiment and develop new applications to commercially available
slave PCI based peripherals products.
The MCF5407 has 4KBytes of internal SRAM organized as two independently
configurable 2 Kbyte blocks. each block can be configured for either data or instruction
space.
There is one 168-pin DIMM socket for SDRAM. System ships with 1M x 8 Bank x 16-Bits
SDRAM totaling 16M of volatile memory. Various SDRAM configurations are supported.
The internal caches of the MCF5407 are non-blocking. The data cache is 8 KByte, 4-way
set-associative with a 16-byte line size. The instruction cache is 16 KBytes, 4-way
set-associative with a 16-byte line size. The ROM Monitor currently does not utilize the
caches, but programs downloaded with the ROM Monitor can use the cache.
The M5407C3 evaluation board has a foot print for 512 KByte SRAM but is unpopulated.
1.3 Serial Communication Channels
The MCF5407 has 2 built-in UART’s (UART0 and UART1) with independent baud rate
generators. The signals of both channels are passed through external Driver/Receivers to
make the channel compatible with RS-232. An RS232 serial cable with DB9 connectors is
included. UART0 (P4) is used by the debugger for the user to access with a terminal. In
addition, the signals of both channels are available on the 120 pin expansion connector J2.
UART0 channel is the “TERMINAL” channel used by the debugger for communication
with external terminal/PC. The “TERMINAL’ baud rate defaults to 19200.
1.4 Parallel I/O Ports
MCF5407 offers one 16-bit general-purpose parallel I/O port. Each pin can be individually
programmed as input or output. The parallel port bits PP[7:0] are multiplexed with
TT[1:0], TM[2:0], DREQ[1:0], and XTIP. The second set of parallel port bits PP[15:8] is
multiplexed with address bus bits A[31:24]. Both bytes of the parallel port are controlled
by the Pin Assignment Register (PAR). The pins are programmable on a pin by pin basis.
The setting of the multiplexed pins is determined by the configuration byte during reset.
After reset, PP[7:0] are configured as parallel port output pins and the PP[15:8] are
configured as A[31:24]. PP[7:4] are general purpose outputs and PP[3:0] are used by the
ROM Monitor to automatically configure the SDRAM address lines via the U27 mux.
1-4
M5407C3 User’s Manual
Page 17

Fr
ees
cale S
em
iconduct
or
, I
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
nc...
Programmable Timer/Counter
1.5 Programmable Timer/Counter
The MCF5407 has two built in general purpose timer/counters. These timers are available
to the user . The signals for each timer are a v ailable on the 120 pin e xpansion connector J2.
1.6 PCI Controller
The MCF5407 connects to the PCI controller (U17) via the PCI host interface. The PCI
controller is configured for master mode. U18 contains the arbitration logic for the PCI bus.
This logic is such that the PCI controller (U17) defaults to allowing the 5407 bus
mastership. A PCI card wishing to arbitrate the bus away from the controller must use
signal REQ# to request the bus. U18 will then arbitrate the bus away from U17 and assert
GNT# to the PCI card to show that the card has been granted the bus. Similarly the
controller can arbitrate the bus back using signals /REQ and /GNT . By default the controller
currently has priority over the card in the equations in U18, if the user wanted to alter this
priority they could do so by editing file "ISA5407.abl" available on the ColdFire website
(www.mot.com/coldfire).
1.7 On Board Ethernet
The M5407C3 has an on board Ethernet (NE2000 compatible controller) operating at 10M
bits/sec. The on board dBUG ROM monitor is programmed to allow a user to download
files from a network to memory in different formats. The current compiler formats
supported are S-Record, COFF, ELF, or Image. Refer to Appenix A for details on how to
configure.
1.8 System Configuration
The M5407C3 board requires only the following items for minimum system configuration:
• The M5407C3 board (provided).
• Power supply, 7V to 14V DC with minimum of 1.0 Amp.
• RS-232C compatible terminal or a PC with terminal emulation software.
• RS-232 Communication cable (provided).
Refer to Section 2.2.2, “System Initialization” for initial setup.
Chapter 1. M5407C3 Board 1-5
Page 18
System Configuration
Fr
ees
cale S
em
iconduct
or
, I
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
nc...
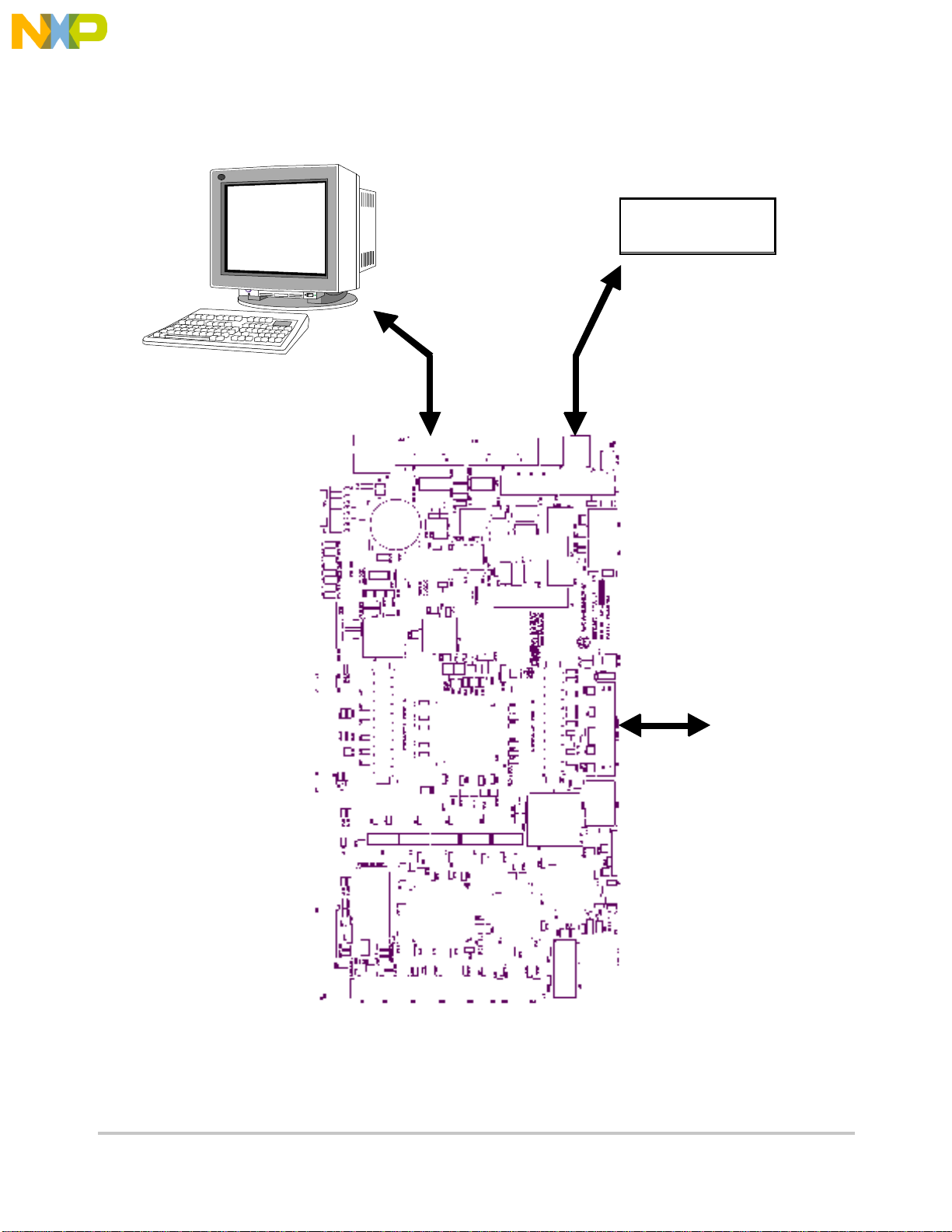
Figure 1-2 displays minimum system configuration.
dBUG>
RS-232 Terminal
Or PC
+7.0 to +14VDC
Input Power
BDM
Conne ctor
1-6
Figure 1-2. Minimum System Configuration
M5407C3 User’s Manual
Page 19

Fr
ees
cale S
em
iconduct
or
, I
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
nc...
Installation And Setup
1.9 Installation And Setup
The following sections describe all the steps needed to prepare the board for operation.
Please read the following sections carefully before using the board. When you are
preparing the board for the first time, be sure to check that all jumpers are in the default
locations. Default marking are on the board next to the individual jumpers and a master
jumper table is on the underside of the board. After the board is functional in its default
mode, you may use the Ethernet by following the instructions provided in Appendix A.
1.9.1 Unpacking
Unpack the computer board from its shipping box. Save the box for storing or reshipping.
Refer to the following list and verify that all the items are present. You should have
received:
• M5407C3 Single Board Computer
• M5407C3 User's Manual, this documentation
• One RS-232 communication cable
• One debug wiggler cable
• Programmers Reference Manual
• A selection of Third Party Developer Tools and Literature
NOTE:
Avoid touching the mos devices. Static discharge can and will
damage these devices.
Once you verified that all the items are present, remove the board from its protecti ve jack et.
Check the board for any visible damage. Ensure that there are no broken, damaged, or
missing parts. If you have not received all the items listed above or they are damaged,
please contact Matrix Design immediately.
1.9.2 Preparing the Board for Use
The board as shipped is ready to be connected to a terminal and the power supply without
any need for modification. Howe ver , follow the steps below to insure proper operation from
the first time you apply the power. Figure 3 Jumper Table and Locations shows the
placement of the jumpers and the connectors, which you need to refer to in the following
sections. The steps to be taken are:
a) Connecting the power supply.
b) Connecting the terminal.
Chapter 1. M5407C3 Board 1-7
Page 20

Fr
ees
cale S
em
iconduct
or
, I
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
nc...
Installation And Setup
1.9.3 Providing Power to the Board
The board accepts two means of power supply connections. Connector P6 is a 2.1mm
power jack and P3 lever actuated connector. The board accepts 7V to 14V DC at 1.5 Amp
via either one of the connectors.
Table 1-1. Power Supply Connections
Contact Number Voltage
1 +7–14V DC
2 Ground
1.9.4 Selecting Terminal Baud Rate
The serial channel of MCF5407 which is used for serial communication has a built in timer
used by the dBUG ROM monitor to generate the baud rate used to communicate with a
terminal.. It can be programmed to a number of baud rates. After the power -up or a manual
RESET, the dBUG ROM monitor firmware configures the channel for 19200 baud. After
the dBUG ROM monitor is running, you may issue the SET command to choose any baud
rate supported by the dBUG ROM monitor. Refer to Chapter 2 for the discussion of this
command.
1.9.5 The Terminal Character Format
The character format of the communication channel is fixed at the power-up or RESET.
The character format is 8 bits per character, no parity, and one stop bit. You need to insure
that your terminal or PC is set to this format.
1.9.6 Connecting the Terminal
The board is now ready to be connected to a terminal. Use the RS-232 male/female DB-9
serial cable to connect the PC to the M5407C3. The cable has a 9-pin female D-sub
terminal connector at one end and a 9-pin male D-sub connector at the other end. Connect
the 9-pin male connector to P4 connector on M5407C3. Connect the 9-pin female
connector to one of the available serial communication channels normally referred to as
COM1 (COM2, etc.) on the IBM PC’s or compatible. Depending on the kind of serial
connector on the back of your PC, the connector on your PC may be a male 25-pin or 9-pin.
You may need to obtain a 9-pin-to-25-pin adapter to make the connection. If you need to
build an adapter , refer to Figure 2 which shows the pin assignment for the 9-pin connector
on the board.
1.9.7 Using a Personal Computer as a Terminal
You may use your personal computer as a terminal provided you also have a terminal
emulation software such as PROCOMM, KERMIT, QMODEM, Windows 95/98/2000
1-8
M5407C3 User’s Manual
Page 21

Fr
ees
cale S
em
iconduct
or
, I
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
nc...
Installation And Setup
Hyper Terminal or similar packages. Then connect as described in 1.9.6, “Connecting the
Terminal.”
Once the connection to the PC is made, you are ready to power-up the PC and run the
terminal emulation software. When you are in the terminal mode, you need to select the
baud rate and the character format for the channel. Most terminal emulation software
packages provide a command known as "Alt-p" (press the p ke y while pressing the Alt k ey)
to choose the baud rate and character format. Make sure you select 8 bits, no parity, one
stop bit, see section The Terminal Character Format. Then, select the baud rate as 19200.
Now you are ready to apply power to the board.
Figur 1-3 shows pin assignments for female terminal connector.
5
Figure 1-3. Pin assignment for female P4 (Terminal) connector.
1
69
Pin assignments are as follows.
1. Data Carrier Detect, Output (shorted to pins 4 and 6).
2. Receive Data, Output from board (receive refers to terminal side).
3. Transmit Data, Input to board (transmit refers to terminal side).
4. Data Terminal Ready, input (shorted to pin 1 and 6).
5. Signal Ground.
6. Data Set Ready, Output (shorted to pins 1 and 4).
7. Request to Send, input.
8. Clear to send, output.
9. Not connected.
Figure 1-4 shows jumper locations.
Chapter 1. M5407C3 Board 1-9
Page 22
Installation And Setup
Fr
ees
cale S
em
iconduct
or
, I
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
nc...
1-10
Figure 1-4. Jumper Locations
M5407C3 User’s Manual
Page 23

System Power-up and Initial Operation
Fr
ees
cale S
em
iconduct
or
, I
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
nc...
1.10 System Power-up and Initial Operation
Now that you hav e connected all the cables, you may apply power to the board. After power
is applied, the dBUG initializes the board then displays the power-up message on the
terminal, which includes the amount of memory present.
Hard Reset
DRAM Size: 32M
Copyright 1995-2000 Motorola, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
ColdFire MCF5407 EVS Firmware v2e.1a.1a (Build XXX on XXX XX 20XX
17:27:52)
Enter 'help' for help.
dBUG>
The board is now ready for operation under the control of the debugger as described in
Chapter 2. If you do not get the above response, perform the following checks:
1. Make sure that the power supply is properly configured for polarity, voltage level,
and current capability (~1A) and is connected to the board.
2. Check that the terminal and board are set for the same character format and baud.
3. Press the RESET button to insure that the board has been initialized properly.
If dBUG does not come up try removing power from the board and then powering up the
board with the SDRAM DIMM removed. The LEDs (D1-D8) should flash indicating that
there is a problem with the serial cable, terminal, or SDRAM jumpers.
If you still are not receiving the proper response, your board may have been damaged in
shipping. Contact Matrix Design for further instructions.
1.11 M5407C3 Jumper Setup
Jumper settings are as follows:
Note ‘*’ is used to indicate that default setting.
‘**’ is used to indicate mandatory setting for proper operation.
Table 1-2. Jumper Settings
Jumper Function
JP1 * ON LED D10 driven by TOUT0
OFF LED D10 NOT driven by TOUT0
JP2 * ON LED D9 driven by TOUT1
Chapter 1. M5407C3 Board 1-11
Page 24
M5407C3 Jumper Setup
Fr
ees
cale S
em
iconduct
or
, I
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
nc...
Jumper Function
On/On/x Reserved --On/Off/On Reserved --On/Off/Off *1/3 40.0–54.0/120.0–162 MHz
Off/On/On 1/4 25.0–40.5/100.0–162 MHz
Off/On/Off 1/5 25.0–32.4/125.0–162 MHz
Off/Off/On 1/6 25.0–27.0/150.0–162 MHz
Off/Off/Off Reserved ---
Table 1-2. Jumper Settings (Continued)
JP6/D[3]/
BE[3:0] CONF
JP7/D[4]/
ADDR_CONF
JP9/D[6]/PS1 JP8/D[5]/PS0 Boot CS0 Port Size at Reset
ON / 0 ON / 0 32-bit Port
ON / 0 OFF / 1 8-bit Port
OFF / 1 ON / 0 16-bit Port
* OFF / 1 * OFF / 1 16-bit Port
JP10/D[7]/AA ON / 0 Boot CS0 Auto Acknowledge (AA) DISABLED
JP11 * ON EVCC (+3.3V) Power to ColdFire MCF5407 I/O
JP12 ** ON IVCC (+1.8V) Power to ColdFire MCF5407 core
JP13 * ON Pull up enabled on !DREQ1 / PP[5]
JP14 * ON Pull up enabled on !DREQ0 / PP[6]
JP15 * 1-2 Boot ROM Monitor from Flash
JP16 * 1-2 Enable writes to PCI EEPROM
JP17 * 1-2 +3.3 V to J5 Debug Header Pin 9
ON / 0 BE[3:0] is enabled as byte write enables only
* OFF / 1 BE[3:0] is enabled as byte enables for reads & write
ON / 0 PP[15:0], defaulted to inputs upon reset
* OFF / 1 ADDR[31:24]/TIP/DREQ[1:0]/TM[2:1]
* OFF / 1 Boot CS AA Enabled with 15 wait states
2-3 Boot User Code from user Flash Space
1
2-3 Disable writes to PCI EEPROM
2-3 +1.8 V to J5 Debug Header Pin 9
1
JP18 ** 1-2 Default Clocking
2-3 Alternate Clocking
JP19 ** OFF Default Clocking
ON Alternate Clocking
JP20 ** 1-2 Default Core Power (+1.8V)
2-3 Alternate Core Power (+3.3V)
1
JP16 functionality is opposite that of the silkscreen. The table is correct.
1-12 M5407C3 User’s Manual
Page 25
Using The BDM Port
Fr
ees
cale S
em
iconduct
or
, I
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
nc...
Table 1-3. Jumper Settings
JP21 JP22 JP23 JP24 Function
* 1-2 * 1-2 * 1-2 * 1-2 Driven by PP[3:0]
2-3 2-3 2-3 2-3 8 col, 11 row
OFF 2-3 2-3 2-3 9 col, 11 row
2-3 OFF 2-3 2-3 10 col, 11 row
OFF OFF 2-3 2-3 8 col, 12 row
2-3 2-3 OFF 2-3 9 col, 12 row
OFF 2-3 OFF 2-3 10 col, 12 row
2-3 OFF OFF 2-3 11 col, 12 row
OFF OFF OFF 2-3 8 col, 13 row
2-3 2-3 2-3 OFF 9 col, 13 row
OFF 2-3 2-3 OFF 10 col, 13 row
2-3 OFF 2-3 OFF 11 col, 13 row
Table 1-4. Jumper Settings
Jumper Function
1
JP25
JP26 * 1-2 +3.3 V to J5 Debug Header Pin 25
JP27 * 1-2 ColdFire CS1 used on PCI !SELECT
JP28 * 1-2 ColdFire Normal/BDM Mode
1
JP29
JP30 * 1-2 STROBE signal on PCI controller tied to GND
1
The settings for JP25 and JP29 differ from those given on the back of the silkscreen. The settings
listed in this table are correct.
*ON Enable serial clock SCL to PCI EEPROM
2-3 +1.8 V to J5 Debug Header Pin 25
2-3 ColdFire !A31 used on PCI !SELECT
2-3 ColdFire Normal/JTAG Mode
*ON Enable serial data SDA to PCI EEPROM
2-3 STROBE signal on PCI controller tied to !TS
1.12 Using The BDM Port
The MCF5407 has a built in debug mechanism referred to as BDM (background debug
module). The M5407C3 has the Freescale defined debug module connector , J5, to facilitate
this connection.
Chapter 1. M5407C3 Board 1-13
Page 26

Using The BDM Port
Fr
ees
cale S
em
iconduct
or
, I
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
nc...
In order to use the BDM, simply connect the 26-pin connector at the end of the BDM
wiggler cable provided Freescale from P&E Microcomputer Systems to the J5 connector.
No special setting is needed. Refer to the ColdFire® User's Manual BDM Section for
additional instructions.
NOTE:
BDM functionality and use is supported via third party
developer software and hardware tools.
1-14 M5407C3 User’s Manual
Page 27

Fr
ees
cale S
em
iconduct
or
, I
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
nc...
Chapter 2
Using the Monitor/Debug Firmware
The M5407C3 single board computer has a resident firmware package that provides a
self-contained programming and operating environment. The firmware, named dBUG,
provides the user with monitor/debug interface, inline assembler and disassembly, program
download, register and memory manipulation, and I/O control functions. This Chapter is a
how-to-use description of the dBUG package, including the user interface and command
structure.
2.1 What Is dBUG?
dBUG is a traditional ROM monitor/debugger that offers a comfortable and intuitive
command line interface that can be used to download and execute code. It contains all the
primary features needed in a debugger to create a useful debugging environment.
dBUG is a resident firmware package for the ColdFire® family single board computers.
The firmware (stored in one 1Mx16 Flash ROM device) provides a self-contained
programming and operating environment. dBUG interacts with the user through
pre-defined commands that are entered via the terminal. These commands are defined in
Section 2.4, “Commands.”
The user interface to dBUG is the command line. A number of features have been
implemented to achieve an easy and intuitive command line interface.
dBUG assumes that an 80x24 character dumb-terminal is utilized to connect to the
debugger. For serial communications, dBUG requires eight data bits, no parity, and one
stop bit, 8N1. The default baud rate is 19200 but can be changed after the power-up.
The command line prompt is “dBUG> “. Any dBUG command may be entered from this
prompt. dBUG does not allow command lines to exceed 80 characters. Where ver possible,
dBUG displays data in 80 columns or less. dBUG echoes each character as it is typed,
eliminating the need for any “local echo” on the terminal side.
In general, dBUG is not case sensitive. Commands may be entered either in upper or lo wer
case, depending upon the user’s equipment and preference. Only symbol names require
Chapter 2. Using the Monitor/Debug Firmware 2-1
Page 28

What Is dBUG?
Fr
ees
cale S
em
iconduct
or
, I
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
nc...
Most commands can be recognized by using an abbreviated name. For instance, entering
“h” is the same as entering “help”. Thus, it is not necessary to type the entire command
name.
The commands DI, GO, MD, STEP and TRACE are used repeatedly when debugging.
dBUG recognizes this and allows for repeated execution of these commands with minimal
typing. After a command is entered, simply press <RETURN> or <ENTER> to in v oke the
command again. The command is executed as if no command line parameters were
provided.
An additional function called the "TRAP 15 handler" allows the user program to utilize
various routines within dBUG. The TRAP 15 handler is discussed at the end of this chapter .
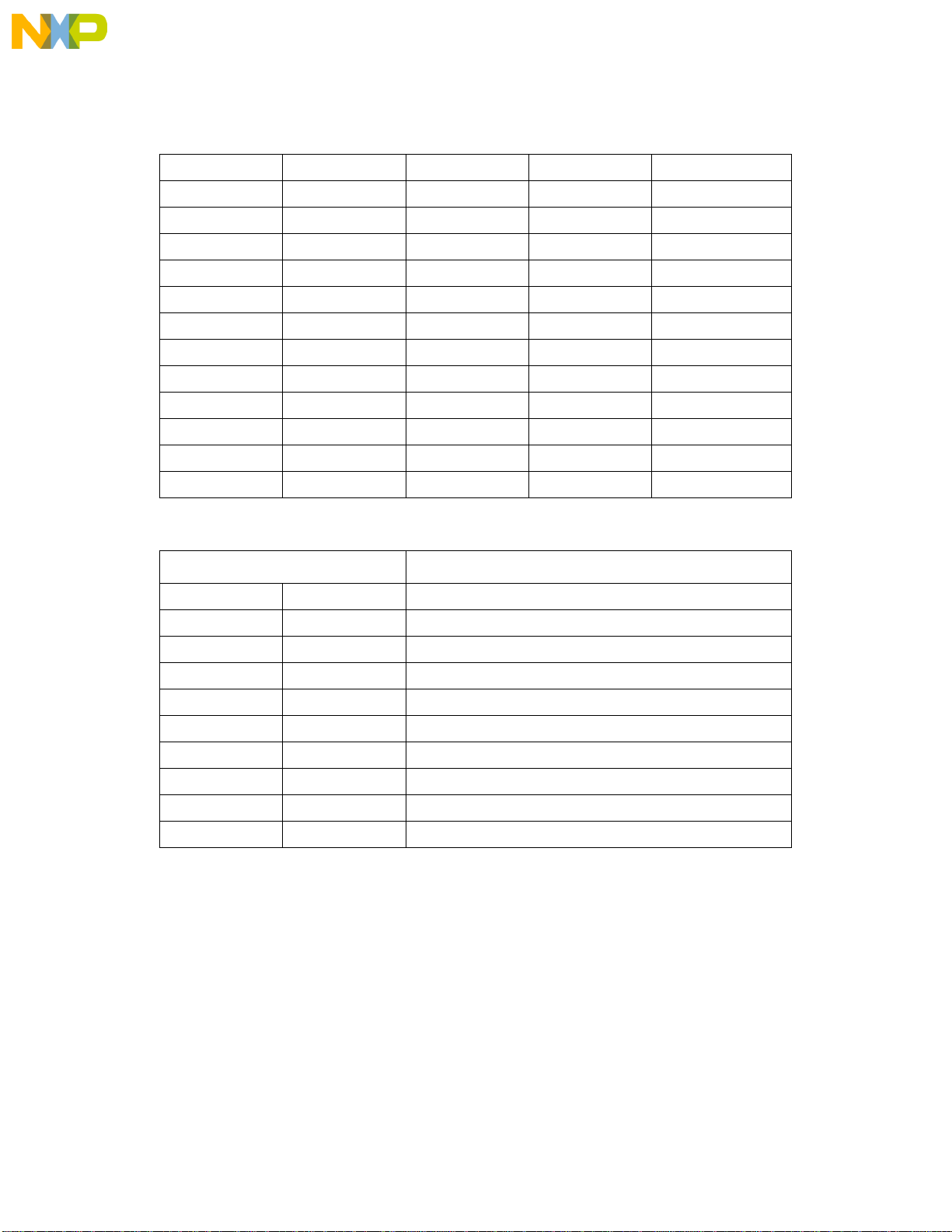
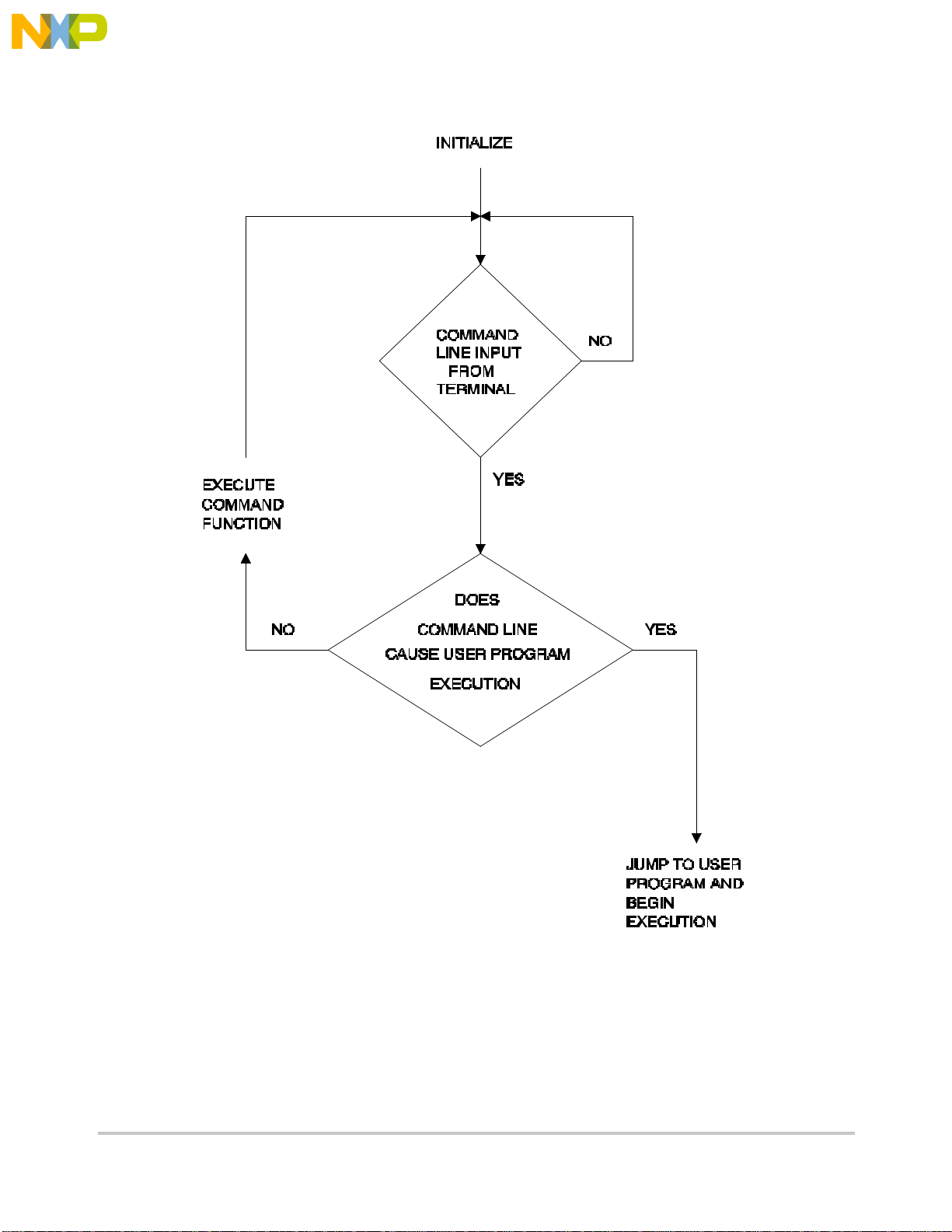
The operational mode of dBUG is demonstrated in Figure 2-1. After the system
initialization, the board waits for a command-line input from the user terminal. When a
proper command is entered, the operation continues in one of the two basic modes. If the
command causes execution of the user program, the dBUG firmware may or may not be
re-entered, depending on the discretion of the user. For the alternate case, the command
will be executed under control of the dBUG firmw are, and after command completion, the
system returns to command entry mode.
During command execution, additional user input may be required depending on the command function.
For commands that accept an optional <width> to modify the memory access size, the valid values are:
• B8-bit (byte) access
• W16-bit (word) access
• L32-bit (long) access
When no <width> option is provided, the default width is .W, 16-bit.
The core ColdFire® register set is maintained by dBUG. These are listed below:
• A0-A7
• D0-D7
•PC
•SR
All control registers on ColdFire® are not readable by the supervisor-programming model,
and thus not accessible via dBUG. User code may change these registers, but caution must
be exercised as changes may render dBUG inoperable.
A reference to “SP” (stack pointer) actually refers to general purpose address register seven, “A7."
2-2 M5407C3 User’s Manual
Page 29

Operational Procedure
Fr
ees
cale S
em
iconduct
or
, I
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
nc...
2.2 Operational Procedure
System power-up and initial operation are described in detail in Chapter 1. This information
is repeated here for convenience and to prevent possible damage.
2.2.1 System Power-up
• Be sure the power supply is connected properly prior to power-up.
• Make sure the terminal is connected to TERMINAL (P4) connector.
• Turn power on to the board.
Chapter 2. Using the Monitor/Debug Firmware 2-3
Page 30
Operational Procedure
Fr
ees
cale S
em
iconduct
or
, I
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
nc...
Figur 2-1shows the dUBG operational mode.
Figure 2-1. Flow Diagram of dBUG Operational Mode.
2.2.2 System Initialization
The act of powering up the board will initialize the system. The processor is reset and
dBUG is invoked.
dBUG performs the following configurations of internal resources during the initialization.
2-4 M5407C3 User’s Manual
Page 31

Operational Procedure
Fr
ees
cale S
em
iconduct
or
, I
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
nc...
The instruction cache is invalidated and disabled. The Vector Base Register, VBR, points
to the Flash. However, a copy of the exception table is made at address $00000000 in
SDRAM. To take over an exception vector, the user places the address of the exception
handler in the appropriate vector in the vector table located at 0x00000000, and then points
the VBR to 0x00000000.
The Software Watchdog T imer is disabled and internal timers are placed in a stop condition.
Interrupt controller registers initialized with unique interrupt level/priority pairs. Please
refer to the dBUG source files on theColdFire website (www .freescale.com/coldfire) for the
complete initialization code sequence.
After initialization, the terminal will display:
Hard Reset
DRAM Size: 32M
Copyright 1995-2000 Motorola, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
ColdFire MCF5407 EVS Firmware v2e.1a.1a (Build XXX on XXX XX 20XX
17:27:52)
Enter 'help' for help.
dBUG>
If you did not get this response check the setup. Refer to Section 1.10 System Power-Up
and Initial Operation. Note the date ‘xxx 199x xx:xx:xx’ may vary in different revisions.
Other means can be used to re-initialize the M5407C3 Computer Board firmware. These
means are discussed in the following paragraphs.
2.2.2.1 Hard RESET Button.
Hard RESET (S1) is the button. Depressing this button causes all processes to terminate,
resets the MCF5407 processor and board logic and restarts the dBUG firmware. Pressing
the RESET button would be the appropriate action if all else fails.
2.2.2.2 ABORT Button.
ABORT (S2) is the button located next to RESET button. The abort function causes an
interrupt of the present processing (a level 7 interrupt on MCF5407) and gives control to
the dBUG firmware. This action differs from RESET in that no processor register or
memory contents are changed, the processor and peripherals are not reset, and dBUG is not
restarted. Also, in response to depressing the ABOR T b utton, the contents of the MCF5407
core internal registers are displayed.
The abort function is most appropriate when software is being debugged. The user can
interrupt the processor without destroying the present state of the system. This is
Chapter 2. Using the Monitor/Debug Firmware 2-5
Page 32

Fr
ees
cale S
em
iconduct
or
, I
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
nc...
Command Line Usage
2.2.2.3 Software Reset Command.
dBUG does have a command that causes the dBUG to restart as if a hardware reset was
invoked. The command is "RESET".
2.3 Command Line Usage
The user interface to dBUG is the command line. A number of features have been
implemented to achieve an easy and intuitive command line interface.
dBUG assumes that an 80x24 ASCII character dumb terminal is used to connect to the
debugger . For serial communications, dBUG requires eight data bits, no parity , and one stop
bit (8N1). The baud rate default is19200 bps — a speed commonly available from
workstations, personal computers and dedicated terminals.
The command line prompt is: dBUG>
Any dBUG command may be entered from this prompt. dBUG does not allow command
lines to exceed 80 characters. Wherever possible, dBUG displays data in 80 columns or
less. dBUG echoes each character as it is typed, eliminating the need for any local echo on
the terminal side.
The <Backspace> and <Delete> keys are recognized as rub-out keys for correcting
typographical mistakes.
Command lines may be recalled using the <Control> U, <Control> D and <Control> R key
sequences. <Control> U and <Control> D cycle up and down through previous command
lines. <Control> R recalls and executes the last command line.
In general, dBUG is not case-sensitive. Commands may be entered either in uppercase or
lowercase, depending upon the user’s equipment and preference. Only symbol names
require that the exact case be used.
Most commands can be recognized by using an abbreviated name. For instance, entering h
is the same as entering help. Thus it is not necessary to type the entire command name.
The commands DI, GO, MD, STEP and TRACE are used repeatedly when debugging.
dBUG recognizes this and allows for repeated execution of these commands with minimal
typing. After a command is entered, press the <Return> or <Enter> key to invoke the
command again. The command is executed as if no command line parameters were
provided.
2.4 Commands
This section lists the commands that are available with all versions of dBUG. Some board
or CPU combinations may use additional commands not listed below.
2-6 M5407C3 User’s Manual
Page 33

Fr
ees
cale S
em
iconduct
or
, I
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
nc...
Table 2-1. dBUG Command Summary
MNEMONIC
ASM asm <<addr> stmt> Assemble
BC bc addr1 addr2 length Block Compare
BF bf <width> begin end data <inc> Block Fill
BM bm begin end dest Block Move
BR br addr <-r> <-c count> <-t trigger> Breakpoint
BS bs <width> begin end data Block Search
DC dc value Data Convert
DI di<addr> Disassemble
DL dl <offset> Download Serial
DN dn <-c> <-e> <-i> <-s <-o offset>> <filename> Download Network
GO go <addr> Execute
GT gt addr Execute To
HELP help <command> Help
IRD ird <module.register> Internal Register Display
IRM irm module.register data Internal Register Modify
LR lr<width> addr Loop Read
LW lw<width> addr data Loop Write
MD md<width> <begin> <end> Memory Display
MM mm<width> addr <data> Memory Modify
MMAP mmap Memory Map Display
RD rd <reg> Register Display
RM rm reg data Register Modify
RESET reset Reset
SD sd Stack Dump
SET set <option value> Set Configurations
SHOW show <option> Show Configurations
STEP step Step (Over)
SYMBOL symbol <symb> <-a symb value> <-r symb> <-C|l|s>Symbol Management
TRACE trace <num> Trace (Into)
UPDBUG updbug Update dBUG
UPUSER upuser <bytes> Update User Flash
VERSION version Show V ersion
SYNTAX
DESCRIPTION
Commands
Chapter 2. Using the Monitor/Debug Firmware 2-7
Page 34

Commands
Fr
ees
cale S
em
iconduct
or
, I
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
nc...
ASM Assembler
Usage: ASM <<addr> stmt>
The ASM command is a primitive assembler. The <stmt> is assembled and the resulting
code placed at <addr>. This command has an interactive and non-interactive mode of
operation.
The value for address <addr> may be an absolute address specified as a hexadecimal v alue,
or a symbol name. The value for stmt must be valid assembler mnemonics for the CPU.
For the interactive mode, the user enters the command and the optional <addr>. If the
address is not specified, then the last address is used. The memory contents at the address
are disassembled, and the user prompted for the new assembly. If valid, the new assembly
is placed into memory, and the address incremented accordingly. If the assembly is not
valid, then memory is not modified, and an error message produced. In either case, memory
is disassembled and the process repeats.
The user may press the <Enter> or <Return> key to accept the current memory contents
and skip to the next instruction, or a enter period to quit the interactive mode.
In the non-interactive mode, the user specifies the address and the assembly statement on
the command line. The statement is the assembled, and if valid, placed into memory,
otherwise an error message is produced.
Examples:
To place a NOP instruction at address 0x00010000, the command is:
asm 10000 nop
To interactively assembly memory at address 0x00400000, the command is:
asm 400000
2-8 M5407C3 User’s Manual
Page 35

Commands
Fr
ees
cale S
em
iconduct
or
, I
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
nc...
BC Block Compare
Usage: BC addr1 addr2 length
The BC command compares two contiguous blocks of memory on a byte by byte basis. The
first block starts at address addr1 and the second starts at address addr2, both of length
bytes.
If the blocks are not identical, the address of the first mismatch is displayed. The value for
addresses addr1 and addr2 may be an absolute address specified as a hexadecimal value or
a symbol name. The value for length may be a symbol name or a number converted
according to the user defined radix (hexadecimal by default).
Example:
To verify that the data starting at 0x20000 and ending at 0x30000 is identical to the data
starting at 0x80000, the command is:
bc 20000 80000 10000
Chapter 2. Using the Monitor/Debug Firmware 2-9
Page 36

Commands
Fr
ees
cale S
em
iconduct
or
, I
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
nc...
BF Block Fill
Usage: BF<width> begin end data <inc>
The BF command fills a contiguous block of memory starting at address begin, stopping at
address end, with the value data. <W idth> modifies the size of the data that is written. If no
<width> is specified, the default of word sized data is used.
The value for addresses begin and end may be an absolute address specified as a
hexadecimal value, or a symbol name. The value for data may be a symbol name, or a
number converted according to the user-defined radix, normally hexadecimal.
The optional value <inc> can be used to increment (or decrement) the data value during the
fill.
This command first aligns the starting address for the data access size, and then increments
the address accordingly during the operation. Thus, for the duration of the operation, this
command performs properly-aligned memory accesses.
Examples:
To fill a memory block starting at 0x00020000 and ending at 0x00040000 with the value
0x1234, the command is:
bf 20000 40000 1234
To fill a block of memory starting at 0x00020000 and ending at 0x0004000 with a byte
value of 0xAB, the command is:
bf.b 20000 40000 AB
To zero out the BSS section of the target code (defined by the symbols bss_start and
bss_end), the command is:
bf bss_start bss_end 0
To fill a block of memory starting at 0x00020000 and ending at 0x00040000 with data that
increments by 2 for each <width>, the command is:
bf 20000 40000 0 2
2-10 M5407C3 User’s Manual
Page 37

Commands
Fr
ees
cale S
em
iconduct
or
, I
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
nc...
BM Block Move
Usage: BM begin end dest
The BM command moves a contiguous block of memory starting at address begin and
stopping at address end to the new address dest. The BM command copies memory as a
series of bytes, and does not alter the original block.
The values for addresses begin, end, and dest may be absolute addresses specified as
hexadecimal values, or symbol names. If the destination address o verlaps the block defined
by begin and end, an error message is produced and the command exits.
Examples:
To copy a block of memory starting at 0x00040000 and ending at 0x00080000 to the
location 0x00200000, the command is:
bm 40000 80000 200000
To copy the target code’s data section (defined by the symbols data_start and data_end) to
0x00200000, the command is:
bm data_start data_end 200000
NOTE:
Refer to “upuser” command for copying code/data into Flash
memory.
Chapter 2. Using the Monitor/Debug Firmware 2-11
Page 38

Fr
ees
cale S
em
iconduct
or
, I
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
nc...
Commands
BR Breakpoints
Usage: BR addr <-r> <-c count> <-t trigger>
The BR command inserts or removes breakpoints at address addr. The value for addr may
be an absolute address specified as a hexadecimal value, or a symbol name. Count and
trigger are numbers converted according to the user-defined radix, normally hexadecimal.
If no argument is provided to the BR command, a listing of all defined breakpoints is
displayed.
The -r option to the BR command removes a breakpoint defined at address addr. If no
address is specified in conjunction with the -r option, then all breakpoints are removed.
Each time a breakpoint is encountered during the execution of target code, its count value
is incremented by one. By default, the initial count value for a breakpoint is zero, b ut the -c
option allows setting the initial count for the breakpoint.
Each time a breakpoint is encountered during the execution of target code, the count value
is compared against the trigger value. If the count v alue is equal to or greater than the trigger
value, a breakpoint is encountered and control returned to dBUG. By default, the initial
trigger value for a breakpoint is one, but the -t option allows setting the initial trigger for
the breakpoint.
If no address is specified in conjunction with the -c or -t options, then all breakpoints are
initialized to the values specified by the -c or -t option.
Examples:
To set a breakpoint at the C function main() (symbol _main; see “symbol” command), the
command is:
br _main
When the target code is executed and the processor reaches main(), control will be returned to dBUG.
To set a breakpoint at the C function bench() and set its trigger value to 3, the command is:
br _bench -t 3
When the target code is executed, the processor must attempt to execute the function
bench() a third time before returning control back to dBUG.
To remove all breakpoints, the command is:
br -r
2-12 M5407C3 User’s Manual
Page 39

Commands
Fr
ees
cale S
em
iconduct
or
, I
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
nc...
BS Block Search
Usage: BS<width> begin end data
The BS command searches a contiguous block of memory starting at address begin,
stopping at address end, for the value data. <Width> modifies the size of the data that is
compared during the search. If no <width> is specified, the default of word sized data is
used.
The values for addresses begin and end may be absolute addresses specified as he xadecimal
values, or symbol names. The v alue for data may be a symbol name or a number converted
according to the user-defined radix, normally hexadecimal.
This command first aligns the starting address for the data access size, and then increments
the address accordingly during the operation. Thus, for the duration of the operation, this
command performs properly-aligned memory accesses.
Examples:
To search for the 16-bit value 0x1234 in the memory block starting at 0x00040000 and
ending at 0x00080000:
bs40000 80000 1234
This reads the 16-bit word located at 0x00040000 and compares it against the 16-bit value
0x1234. If no match is found, then the address is incremented to 0x00040002 and the next
16-bit value is read and compared.
To search for the 32-bit value 0xABCD in the memory block starting at 0x00040000 and
ending at 0x00080000:
bs.l40000 80000 ABCD
This reads the 32-bit word located at 0x00040000 and compares it against the 32-bit value
0x0000ABCD. If no match is found, then the address is incremented to 0x00040004 and
the next 32-bit value is read and compared.
Chapter 2. Using the Monitor/Debug Firmware 2-13
Page 40

Commands
Fr
ees
cale S
em
iconduct
or
, I
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
nc...
DC Data Conversion
Usage: DC data
The DC command displays the hexadecimal or decimal value data in hexadecimal, binary,
and decimal notation.
The value for data may be a symbol name or an absolute value. If an absolute value passed
into the DC command is prefixed by ‘0x’, then data is interpreted as a hexadecimal value.
Otherwise data is interpreted as a decimal value.
All values are treated as 32-bit quantities.
Examples:
To display the decimal and binary equivalent of 0x1234, the command is:
dc 0x1234
To display the hexadecimal and binary equivalent of 1234, the command is:
dc 1234
2-14 M5407C3 User’s Manual
Page 41

Commands
Fr
ees
cale S
em
iconduct
or
, I
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
nc...
DI Disassemble
Usage: DI <addr>
The DI command disassembles target code pointed to by addr. The value for addr may be
an absolute address specified as a hexadecimal value, or a symbol name.
Wherever possible, the disassembler will use information from the symbol table to produce
a more meaningful disassembly. This is especially useful for branch target addresses and
subroutine calls.
The DI command attempts to track the address of the last disassembled opcode. If no
address is provided to the DI command, then the DI command uses the address of the last
opcode that was disassembled.
The DI command is repeatable.
Examples:
To disassemble code that starts at 0x00040000, the command is:
di 40000
To disassemble code of the C function main(), the command is:
di _main
Chapter 2. Using the Monitor/Debug Firmware 2-15
Page 42

Fr
ees
cale S
em
iconduct
or
, I
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
nc...
Commands
DL Download Console
Usage: DL <offset>
The DL command performs an S-record download of data obtained from the console,
typically a serial port. The value for of fset is converted according to the user-defined radix,
normally hexadecimal. Please reference the ColdFire Microprocessor Family
Programmer’s Reference Manual for details on the S-Record format.
If offset is provided, then the destination address of each S-record is adjusted by offset.
The DL command checks the destination download address for validity. If the destination
is an address outside the defined user space, then an error message is displayed and
downloading aborted.
If the S-record file contains the entry point address, then the program counter is set to reflect
this address.
Examples:
To download an S-record file through the serial port, the command is:
dl
To download an S-record file through the serial port, and add an offset to the destination
address of 0x40, the command is:
dl 0x40
2-16 M5407C3 User’s Manual
Page 43

Commands
Fr
ees
cale S
em
iconduct
or
, I
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
nc...
DN Download Network
Usage: DN <-c> <-e> <-i> <-s> <-o offset> <filename>
The DN command downloads code from the network. The DN command handle files which
are either S-record, COFF, ELF or Image formats. The DN command uses Trivial File
Transfer Protocol (TFTP) to transfer files from a network host.
In general, the type of file to be downloaded and the name of the file must be specified to
the DN command. The -c option indicates a COFF download, the -e option indicates an
ELF download, the -i option indicates an Image download, and the -s indicates an S-record
download. The -o option works only in conjunction with the -s option to indicate an
optional offset for S-record download. The filename is passed directly to the TFTP server
and therefore must be a valid filename on the server.
If neither of the -c, -e, -i, -s or filename options are specified, then a default filename and
filetype will be used. Default filename and filetype parameters are manipulated using the
SET and SHOW commands.
The DN command checks the destination download address for validity. If the destination
is an address outside the defined user space, then an error message is displayed and
downloading aborted.
For ELF and COFF files which contain symbolic debug information, the symbol tables are
extracted from the file during download and used by dBUG. Only global symbols are kept
in dBUG. The dBUG symbol table is not cleared prior to downloading, so it is the user’s
responsibility to clear the symbol table as necessary prior to downloading.
If an entry point address is specified in the S-record, COFF or ELF file, the program counter
is set accordingly.
Examples:
To download an S-record file with the name “srec.out”, the command is:
dn -s srec.out
To download a COFF file with the name “coff.out”, the command is:
dn -c coff.out
To download a file using the default filetype with the name “bench.out”, the command is:
dn bench.out
To download a file using the default filename and filetype, the command is:
dn
Chapter 2. Using the Monitor/Debug Firmware 2-17
Page 44

Commands
Fr
ees
cale S
em
iconduct
or
, I
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
nc...
GO Execute
Usage: GO <addr>
The GO command executes target code starting at address addr. The value for addr may be
an absolute address specified as a hexadecimal value, or a symbol name.
If no argument is provided, the GO command begins executing instructions at the current
program counter.
When the GO command is executed, all user-de fined breakpoints are inserted into the target
code, and the context is switched to the target program. Control is only regained when the
target code encounters a breakpoint, illegal instruction, trap #15 exception, or other
exception which causes control to be handed back to dBUG.
The GO command is repeatable.
Examples:
To execute code at the current program counter, the command is:
go
To execute code at the C function main(), the command is:
go _main
To execute code at the address 0x00040000, the command is:
go 40000
2-18 M5407C3 User’s Manual
Page 45

Commands
Fr
ees
cale S
em
iconduct
or
, I
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
nc...
GT Execute To
Usage: GT addr
The GT command inserts a temporary breakpoint at addr and then executes target code
starting at the current program counter. The value for addr may be an absolute address
specified as a hexadecimal value, or a symbol name.
When the GT command is executed, all breakpoints are inserted into the target code, and
the context is switched to the target program. Control is only reg ained when the target code
encounters a breakpoint, illegal instruction, or other exception which causes control to be
handed back to dBUG.
Examples:
To execute code up to the C function bench(), the command is:
gt _bench
Chapter 2. Using the Monitor/Debug Firmware 2-19
Page 46

Commands
Fr
ees
cale S
em
iconduct
or
, I
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
nc...
IRD Internal Register Display
Usage: IRD <module.register>
This command displays the internal registers of different modules inside the MCF5407. In
the command line, module refers to the module name where the register is located and
register refers to the specific register to display.
The registers are organized according to the module to which they belong. The available
modules on the MCF5407 are CS, DMA0, DMA1, DMA2, DMA3, DRAMC, PP, MBUS,
SIM, TIMER1, TIMER2, UART0 and UART1. Refer to the MCF5407 user’s manual for
more information on these modules and the registers they contain.
Example:
ird sim.rsr
2-20 M5407C3 User’s Manual
Page 47

Commands
Fr
ees
cale S
em
iconduct
or
, I
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
nc...
IRM Internal Register Modify
Usage: IRM module.register data
This command modifies the contents of the internal registers of different modules inside the
MCF5407. In the command line, module refers to the module name where the register is
located and register refers to the specific register to modify. The data parameter specifies
the new value to be written into the register.
The registers are organized according to the module to which they belong. The available
modules on the MCF5407 are CS, DMA0, DMA1, DMA2, DMA3, DRAMC, PP, MBUS,
SIM, TIMER1, TIMER2, UART0 and UART1. Refer to the MCF5407 user’s manual for
more information on these modules and the registers they contain.
Example:
T o modify the TMR re gister of the first T imer module to the value 0x0021, the command is:
irm timer1.tmr 0021
Chapter 2. Using the Monitor/Debug Firmware 2-21
Page 48

Commands
Fr
ees
cale S
em
iconduct
or
, I
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
nc...
HELP Help
Usage: HELP <command>
The HELP command displays a brief syntax of the commands available within dBUG. In
addition, the address of where user code may start is given. If command is provided, then
a brief listing of the syntax of the specified command is displayed.
Examples:
To obtain a listing of all the commands available within dBUG, the command is:
help
To obtain help on the breakpoint command, the command is:
help br
2-22 M5407C3 User’s Manual
Page 49

Commands
Fr
ees
cale S
em
iconduct
or
, I
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
nc...
LR Loop Read
Usage: LR<width> addr
The LR command continually reads the data at addr until a key is pressed. The optional
<width> specifies the size of the data to be read. If no <width> is specified, the command
defaults to reading word sized data.
Example:
To continually read the longword data from address 0x20000, the command is:
lr.l 20000
Chapter 2. Using the Monitor/Debug Firmware 2-23
Page 50

Commands
Fr
ees
cale S
em
iconduct
or
, I
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
nc...
LW Loop Write
Usage: LW<width> addr data
The LW command continually writes data to addr. The optional width specifies the size of
the access to memory. The default access size is a word.
Examples:
To continually write the longword data 0x12345678 to address 0x20000, the command is:
lw.l 20000 12345678
Note that the following command writes 0x78 into memory:
lw.b 20000 12345678
2-24 M5407C3 User’s Manual
Page 51

Commands
Fr
ees
cale S
em
iconduct
or
, I
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
nc...
MD Memory Display
Usage: MD<width> <begin> <end>
The MD command displays a contiguous block of memory starting at address begin and
stopping at address end. The values for addresses be gin and end may be absolute addresses
specified as hexadecimal values, or symbol names. Width modifies the size of the data that
is displayed. If no <width> is specified, the default of word sized data is used.
Memory display starts at the address begin. If no beginning address is provided, the MD
command uses the last address that was displayed. If no ending address is provided, then
MD will display memory up to an address that is 128 beyond the starting address.
This command first aligns the starting address for the data access size, and then increments
the address accordingly during the operation. Thus, for the duration of the operation, this
command performs properly-aligned memory accesses.
Examples:
To display memory at address 0x00400000, the command is:
md 400000
To display memory in the data section (defined by the symbols data_start and data_end),
the command is:
md data_start
To display a range of bytes from 0x00040000 to 0x00050000, the command is:
md.b 40000 50000
To display a range of 32-bit values starting at 0x00040000 and ending at 0x00050000:
md.l 40000 50000
Chapter 2. Using the Monitor/Debug Firmware 2-25
Page 52

Commands
Fr
ees
cale S
em
iconduct
or
, I
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
nc...
MM Memory Modify
Usage: MM<width> addr <data>
The MM command modifies memory at the address addr. The value for addr may be an
absolute address specified as a hexadecimal value, or a symbol name. Width specifies the
size of the data that is modified. If no <width> is specified, the default of word sized data
is used. The value for data may be a symbol name, or a number converted according to the
user-defined radix, normally hexadecimal.
If a value for data is provided, then the MM command immediately sets the contents of addr
to data. If no value for data is provided, then the MM command enters into a loop. The loop
obtains a value for data, sets the contents of the current address to data, increments the
address according to the data size, and repeats. The loop terminates when an invalid entry
for the data value is entered, i.e., a period.
This command first aligns the starting address for the data access size, and then increments
the address accordingly during the operation. Thus, for the duration of the operation, this
command performs properly-aligned memory accesses.
Examples:
To set the byte at location 0x00010000 to be 0xFF, the command is:
mm.b 10000 FF
To interactively modify memory beginning at 0x00010000, the command is:
mm 10000
2-26 M5407C3 User’s Manual
Page 53

Commands
Fr
ees
cale S
em
iconduct
or
, I
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
nc...
MMAP Memory Map Display
Usage: mmap
This command displays the memory map information for the M5407C3 evaluation board.
The information displayed includes the type of memory, the start and end address of the
memory , and the port size of the memory . The display also includes information on how the
Chip-selects are used on the board.
Here is an example of the output from this command:
Type Start End Port Size
-------------------------------------------------- SDRAM 0x00000000 0x00FFFFFF 32-bit
Vector Table 0x00000000 0x000003FF 32-bit
USER SPACE 0x00020000 0x00FFFFFF 32-bit
MBAR 0x10000000 0x100003FF 32-bit
Internal SRAM0 0x20000000 0x200007FF 32-bit
Internal SRAM1 0x20000800 0x20000FFF 32-bit
External SRAM 0x30000000 0x3007FFFF 32-bit
Ethernet IO 0x40000300 0x400FFFFF 16-bit
Flash 0x7FE00000 0x7FFFFFFF 16-bit
PCI 0xFFFF0000 0xFFFF3FFF 32-bit
Chip Selects
--------------- CS0 Flash
CS1 PCI
CS2 Ext SRAM
CS3 Ethernet
CS4 not in use
CS5 not in use
CS6 not in use
CS7 not in use
Chapter 2. Using the Monitor/Debug Firmware 2-27
Page 54

Commands
Fr
ees
cale S
em
iconduct
or
, I
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
nc...
RD Register Display
Usage: RD <reg>
The RD command displays the register set of the target. If no argument for re g is pro vided,
then all registers are displayed. Otherwise, the value for reg is displayed.
dBUG preserves the registers by storing a copy of the register set in a buffer. The RD
command displays register values from the register buffer.
Examples:
To display all the registers and their values, the command is:
rd
To display only the program counter:
rd pc
Here is an example of the output from this command:
PC: 00000000 SR: 2000 [t.Sm.000...xnzvc]
An: 00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000 01000000
Dn: 00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000
2-28 M5407C3 User’s Manual
Page 55

Commands
Fr
ees
cale S
em
iconduct
or
, I
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
nc...
RM Register Modify
Usage: RM reg data
The RM command modifies the contents of the register reg to data. The value for reg is
the name of the register, and the value for data may be a symbol name, or it is converted
according to the user-defined radix, normally hexadecimal.
dBUG preserves the registers by storing a copy of the register set in a buffer. The RM
command updates the copy of the register in the buf fer. The actual value will not be written
to the register until target code is executed.
Examples:
To change register D0 on MC68000 and ColdFire to contain the value 0x1234, the
command is:
rm D0 1234
Chapter 2. Using the Monitor/Debug Firmware 2-29
Page 56

Commands
Fr
ees
cale S
em
iconduct
or
, I
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
nc...
RESET Reset the Board and dBUG
Usage: RESET
The RESET command resets the board and dBUG to their initial power-on states.
The RESET command executes the same sequence of code that occurs at power-on. If the
RESET command fails to reset the board adequately, cycle the power or press the reset
button.
Examples:
To reset the board and clear the dBUG data structures, the command is:
reset
2-30 M5407C3 User’s Manual
Page 57

Fr
ees
cale S
em
iconduct
or
, I
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
nc...
Commands
SET Set Configurations
Usage: SET <option value>
The SET command allows the setting of user-configurable options within dBUG. With no
arguments, SET displays the options and values available. The SHOW command displays
the settings in the appropriate format. The standard set of options is listed below.
• baud - This is the baud rate for the first serial port on the board. All communications
between dBUG and the user occur using either 9600 or 19200 bps, eight data bits,
no parity, and one stop bit, 8N1.
• base - This is the default radix for use in converting a number from its ASCII text
representation to the internal quantity used by dBUG. The default is hexadecimal
(base 16), and other choices are binary (base 2), octal (base 8), and decimal (base
10).
• client - This is the network Internet Protocol (IP) address of the board. For netw ork
communications, the client IP is required to be set to a unique value, usually
assigned by your local network administrator.
• server - This is the network IP address of the machine which contains files accessible
via TFTP. Your local network administrator will ha ve this information and can assist
in properly configuring a TFTP server if one does not exist.
• gateway - This is the netw ork IP address of the g ateway for your local subnetwork.
If the client IP address and server IP address are not on the same subnetwork, then
this option must be properly set. Your local network administrator will have this
information.
• netmask - This is the network address mask to determine if use of a gateway is
required. This field must be properly set. Your local network administrator will ha ve
this information.
• filename - This is the default filename to be used for network download if no name
is provided to the DN command.
• filetype - This is the default file type to be used for network download if no type is
provided to the DN command. Valid values are: “srecord”, “coff”, and “elf”.
• mac - This is the ethernet Media Access Control (MAC) address (a.k.a hardware
address) for the evaluation board. This should be set to a unique v alue, and the most
significant nibble should always be even.
Examples:
To set the baud rate of the board to be 19200, the command is:
set baud 19200
Chapter 2. Using the Monitor/Debug Firmware 2-31
Page 58

Commands
Fr
ees
cale S
em
iconduct
or
, I
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
nc...
SHOW Show Configurations
Usage: SHOW <option>
The SHOW command displays the settings of the user -configurable options within dB UG.
When no option is provided, SHOW displays all options and values.
Examples:
To display all options and settings, the command is:
show
To display the current baud rate of the board, the command is:
show baud
Here is an example of the output from a show command:
dBUG> show
base: 16
baud: 19200
server: 192.0.0.1
client: 192.0.0.2
gateway: 0.0.0.0
netmask: 255.255.255.0
filename: test.srec
filetype: S-Record
mac: 00:CF:54:07:C3:01
2-32 M5407C3 User’s Manual
Page 59

Commands
Fr
ees
cale S
em
iconduct
or
, I
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
nc...
STEP Step Over
Usage: STEP
The STEP command can be used to “step over” a subroutine call, rather than tracing e very
instruction in the subroutine. The ST command sets a temporary breakpoint one instruction
beyond the current program counter and then executes the target code.
The STEP command can be used to “step over” BSR and JSR instructions.
The STEP command will work for other instructions as well, but note that if the STEP
command is used with an instruction that will not return, i.e. BRA, then the temporary
breakpoint may never be encountered and dBUG may never regain control.
Examples:
To pass over a subroutine call, the command is:
step
Chapter 2. Using the Monitor/Debug Firmware 2-33
Page 60

Commands
Fr
ees
cale S
em
iconduct
or
, I
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
nc...
SYMBOL Symbol Name Management
Usage: SYMBOL <symb> <-a symb value> <-r symb> <-c|l|s>
The SYMBOL command adds or removes symbol names from the symbol table. If only a
symbol name is provided to the SYMBOL command, then the symbol table is searched for
a match on the symbol name and its information displayed.
The -a option adds a symbol name and its value into the symbol table. The -r option
removes a symbol name from the table.
The -c option clears the entire symbol table, the -l option lists the contents of the symbol
table, and the -s option displays usage information for the symbol table.
Symbol names contained in the symbol table are truncated to 31 characters. Any symbol
table lookups, either by the SYMBOL command or by the disassembler, will only use the
first 31 characters. Symbol names are case-sensitive.
Symbols can also be added to the symbol table via in-line assembly labels and ethernet
downloads of ELF formatted files.
Examples:
To define the symbol “main” to have the value 0x00040000, the command is:
symbol -a main 40000
To remove the symbol “junk” from the table, the command is:
symbol -r junk
To see how full the symbol table is, the command is:
symbol -s
To display the symbol table, the command is:
symbol -l
2-34 M5407C3 User’s Manual
Page 61

Commands
Fr
ees
cale S
em
iconduct
or
, I
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
nc...
TRACE Trace Into
Usage: TRACE <num>
The TRACE command allows single-instruction execution. If num is provided, then num
instructions are executed before control is handed back to dBUG. The value for num is a
decimal number.
The TRACE command sets bits in the processors’ supervisor registers to achieve
single-instruction execution, and the target code e x ecuted. Control returns to dB UG after a
single-instruction execution of the target code.
This command is repeatable.
Examples:
To trace one instruction at the program counter, the command is:
tr
To trace 20 instructions from the program counter, the command is:
tr 20
Chapter 2. Using the Monitor/Debug Firmware 2-35
Page 62

Commands
Fr
ees
cale S
em
iconduct
or
, I
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
nc...
UPDBUG Update dBUG
Usage: updbug
The updbug command is used to update the dBUG image in Flash. When updates to the
M5407C3 dBUG are available, the updated image is downloaded to address 0x00020000.
The new image is placed into Flash using the UPDBUG command. The user is prompted
for verification before performing the operation. Use this command with extreme caution,
as any error can render dBUG useless!
2-36 M5407C3 User’s Manual
Page 63

Commands
Fr
ees
cale S
em
iconduct
or
, I
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
nc...
UPUSER Update User Flash
Usage: UPUSER <bytes>
The UPUSER command places user code and data into space allocated for the user in Flash.
The optional parameter bytes specifies the number of bytes to copy into the user portion of
Flash.If the bytes parameter is omitted, then this command writes to the entire user space.
There are seven sectors of 256K each available as user space. Users access this memory
starting at address 0xFFE40000.
Examples:
To program all 7 sectors of user Flash, the command is:
upuser
To program only 1000 bytes into user Flash, the command is:
upuser 1000
Chapter 2. Using the Monitor/Debug Firmware 2-37
Page 64

Commands
Fr
ees
cale S
em
iconduct
or
, I
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
nc...
VERSION Display dBUG Version
Usage: VERSION
The VERSION command displays the version information for dBUG. The dBUG version,
build number and build date are all given.
The version number is separated by a decimal, for example, “v 2b.1c.1a”.
In this example, v 2b . 1c . 1a
dBUG common
major and minor
revision
CPU major
and minor
revision
{
{
{
board major
and minor
revision
The version date is the day and time at which the entire dBUG monitor was compiled and built.
Examples:
To display the version of the dBUG monitor, the command is:
version
2-38 M5407C3 User’s Manual
Page 65

TRAP #15 Functions
Fr
ees
cale S
em
iconduct
or
, I
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
nc...
2.5 TRAP #15 Functions
An additional utility within the dBUG firmware is a function called the TRAP 15 handler.
This function can be called by the user program to utilize various routines within the dBUG,
to perform a special task, and to return control to the dBUG. This section describes the
TRAP 15 handler and how it is used.
There are four TRAP #15 functions. These are: OUT_CHAR, IN_CHAR, CHAR_PRESENT, and EXIT_TO_dBUG.
2.5.1 OUT_CHAR
This function ( function code 0x0013) sends a character, which is in lower 8 bits of D1, to
terminal.
Assembly example:
/* assume d1 contains the character */
move.l #$0013,d0 Selects the function
TRAP #15 The character in d1 is sent to terminal
C example:
void board_out_char (int ch)
{
/* If your C compiler produces a LINK/UNLK pair for this routine,
* then use the following code which takes this into account
*/
#if l
/* LINK a6,#0 -- produced by C compiler */
asm (“ move.l8(a6),d1”); /* put ‘ch’into d1 */
asm (“ move.l#0x0013,d0”); /* select the function */
asm (“ trap#15”); /* make the call */
/* UNLK a6 -- produced by C compiler */
#else
/* If C compiler does not produce a LINK/UNLK pair, the use
* the following code.
*/
asm (“ move.l4(sp),d1”); /* put ‘ch’into d1 */
asm (“ move.l#0x0013,d0”); /* select the function */
asm (“ trap#15”); /* make the call */
#endif
}
2.5.2 IN_CHAR
Chapter 2. Using the Monitor/Debug Firmware 2-39
Page 66

Fr
ees
cale S
em
iconduct
or
, I
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
nc...
TRAP #15 Functions
Assembly example:
move.l #$0010,d0 Select the function
trap #15 Make the call, the input character is in d1.
C example:
int board_in_char (void)
{
asm (“ move.l#0x0010,d0”); /* select the function */
asm (“ trap#15”); /* make the call */
asm (“ move.ld1,d0”); /* put the character in d0 */
}
2.5.3 CHAR_PRESENT
This function (function code 0x0014) checks if an input character is present to receive. A
value of zero is returned in D0 when no character is present. A non-zero v alue in D0 means
a character is present.
Assembly example:
move.l #$0014,d0 Select the function
trap #15 Make the call, d0 contains the response (yes/no).
C example:
int board_char_present (void)
{
asm (“ move.l#0x0014,d0”); /* select the function */
asm (“ trap#15”); /* make the call */
}
2.5.4 EXIT_TO_dBUG
This function (function code 0x0000) transfers the control back to the dBUG, by
terminating the user code. The register context are preserved.
Assembly example:
move.l #$0000,d0 Select the function
trap #15 Make the call, exit to dBUG.
C example:
void board_exit_to_dbug (void)
{
asm (“ move.l#0x0000,d0”); /* select the function */
2-40 M5407C3 User’s Manual
Page 67

TRAP #15 Functions
Fr
ees
cale S
em
iconduct
or
, I
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
nc...
asm (“ trap#15”); /* exit and transfer to dBUG */
}
Chapter 2. Using the Monitor/Debug Firmware 2-41
Page 68

TRAP #15 Functions
Fr
ees
cale S
em
iconduct
or
, I
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
nc...
2-42 M5407C3 User’s Manual
Page 69

Fr
ees
cale S
em
iconduct
or
, I
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
nc...
Chapter 3
Hardware Description and
Reconfiguration
This chapter provides a functional description of the M5407C3 board hardware. With the
description given here and the schematic diagram in Appendix E, the user can gain a good
understanding of the board's design. In this manual, an active low signal is indicated by a
"-" preceding the signal name in this text and a bar over the signal name in the schematics.
3.1 The Processor and Suppor t Logic
This part of the Chapter discusses the CPU and general supporting logic on the M5407C3 board.
3.1.1 Processor
The microprocessor used in the M5407C3 is the highly integrated Freescale ColdFire® MCF5407,
32-bit processor. The MCF5407 implements a ColdFire version 4 core with 16 KByte instruction
cache and 8 KByte of data cache, two UART channels, two T imers, 4 KBytes of SRAM, Freescale
M-Bus Module supporting the I2C, two-byte wide parallel I/O port, and the supporting integrated
system logic. All the re gisters of the core processor are 32 bits wide e xcept for the Status Re gister
(SR) which is 16 bits wide. This processor communicates with external de vices ov er a 32-bit wide
data bus, D0-D31 with support for 8 and 16-bit ports. This chip can address 4 GBytes of memory
space using internal chip-select logic. All the processor's signals are available through the
expansion connectors (J1 and J2). Refer to section 3.6 for pin assignment.
The MCF5407 has an IEEE JTAG-compatible port and BDM port used with third party
tools. The board is configured to boot up in the normal/BDM mode of operation. These
signals are available at port J5. The processor also has the logic to generate up to eight (8)
chip selects, -CS0 to -CS7, and support for 2 banks of ADRAM (not on evaluation board)
or 2 banks of SDRAM (on evaluation board).
3.1.2 Reset Logic
Chapter 3. Hard ware Description and Reconfiguration 3-1
Page 70

The Processor and Support Logic
Fr
ees
cale S
em
iconduct
or
, I
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
nc...
U19 is used to produce active low power-on RESET signal which feeds into the
ispLSI2032. The reset switch is fed into U19 which generates U18's input for reset. The
U18 device generates the system reset (-CF_RSTI) and Ethernet RESET (ETH_RST)
signals.
dBUG performs the following configurations of internal resources during the initialization.
The instruction cache is invalidated and disabled. The Vector Base Register, VBR, points
to the Flash. A copy of the exception table is made at address $00000000 in the SDRAM.
The Software Watchdog Timer is disabled, Bus Monitor enabled, and internal timers are
placed in a stop condition. Interrupt controller registers are initialized with unique interrupt
level/priority pairs. PP[7:0] are configured as paralell port output pins and PP[15:8] are
configured as A[31:24]. PP[7:4] are general purpose outputs and PP[3:0] are used by the
ROM monitor to automaticaly configure the SDRAM address lines via the U27 mux.
3.1.3 HIZ Signal
The assertion of the -HIZ signal forces all output drivers to a high-impedance state. The
-HIZ signal is actively driven by the ispLSI2032V-100LJ (U18). -HIZ is only driven low
(asserted) during reset. This Signal is av ailable on the 120 pin expansion connector J1. This
signal should not be driven by the user.
3.1.4 Clock Circuitry
The M5407C3 uses a 50MHZ oscillator (U21) to provide the clock to CLKIN pin of the
processor. In addition to U21, there also exist a 20MHz oscillator (U10) which feeds into
the Ethernet chip, a PCI bus master 33MHZ oscillator (U30) and a 32.768 KHZ crystal
(Y1) for the real-time clock. The CLKIN driv es the clock b uf fer chip (U24). The b uf fered
CLKIN drives the 5407 and the ispLSI2032 for Ethernet timing (1/6 bus clock), SRAM
(U13), and SDRAM (U26).
3.1.5 Watchdog Timer
The duration of the Watchdog is selected by BMT0-1 bits in System Protection Register.
The dBUG initializes this register with the value 00, which pro vides for 1024 system clock
time-out but dBUG does NOT enable it.
3.1.6 Interrupt Sources
The ColdFire® family of processors can receive interrupts for seven levels of interrupt
priorities. When the processor receives an interrupt which has higher priority than the
current interrupt mask (in status register), it will perform an interrupt acknowledge c ycle at
the end of the current instruction cycle. This interrupt acknowledge cycle indicates to the
source of the interrupt that the request is being acknowledged and the device should pro vide
the proper vector number to indicate where the service routine for this interrupt level is
3-2 M5407C3 User’s Manual
Page 71

Fr
ees
cale S
em
iconduct
or
, I
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
nc...
The Processor and Support Logic
located. If the source of interrupt is not capable of providing a vector, its interrupt should
be set up as autovector interrupt which directs the processor to a predefined entry into the
exception table (refer to the MCF5407 User's Manual).
The processor goes to an exception routine via the exception table. This table is in the Flash
and the VBR points to it. However, a copy of this table is made in the RAM starting at
$00000000. To set an exception vector , the user places the address of the exception handler
in the appropriate vector in the vector table located at $00000000, and then points the VBR
to $00000000.
The MCF5407 has four external interrupt request lines. You can program the external
interrupt request pins to level 1, 3, 5, and 7 or le vels 2, 4, 6, and 7. The M5407C3 configures
these lines as level 1, 3, 5, and 7. There are also six internal interrupt requests from T imer0,
Timer1, Software watchdog timer, UART0, UART1, and MBUS. Each interrupt source,
external and internal, can be programmed for any priority level. In case of similar priority
level, a second relative priority between 0 to 3 will be assigned.
However, the software watchdog is programmed for Level 7, priority 2 and uninitialized
vector. The UART0 is programmed for Level 3, priority 2 and autovector. The UART1 is
programmed for Level 3, priority 1 and auto vector. The M-Bus is at Lev el 3, priority 0 and
autovector. The T imers are at Le vel 5 with T imer0 with priority 3 and T imer1 with priority
2 and both for autovector.
NOTE:
No interrupt sources should have the same le v el and priority as
another. Programming two interrupt sources with the same
level and priority can result in undefined operation.
The M5407C3 uses -IRQ7 to support the ABORT function using the ABORT switch S2.
This switch is used to force a non-maskable interrupt (level 7, priority 3) if the user's
program execution should be aborted without issuing a RESET (refer to Chapter 2 for more
information on ABORT). Since the ABORT switch is not capable of generating a vector in
response to level seven interrupt acknowledge from the processor, the debugger programs
this request for autovector mode.
The -IRQ1 line of the MCF5407 is connected to the PCI connector J3 pin A6 signal INTA#.
The -IRQ5 line of the MCF5407 is connected to the PCI controller (U17) pin 12 signal
-IRQ_OUT.
Refer to MCF5407 User’s Manual for more information about the interrupt controller.
3.1.7 Internal SRAM
Chapter 3. Hard ware Description and Reconfiguration 3-3
Page 72

Fr
ees
cale S
em
iconduct
or
, I
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
nc...
The Processor and Support Logic
configured as data space but is not used by dBUG except during system initialization. After
system initialization is complete it is available to the user. The memory is relocatable to
any 2 KByte boundary.
If one or both of the internal SRAMs will be used to store instructions, then the RAMBAR
should initially be set up for data. While the SRAM is programmed as data the code can be
loaded into the SRAM. After the code has been moved reprogram the RAMB AR so that the
SRAM is defined as instruction. Now the code stored in the SRAM can execute.
3.1.8 The MCF5407 Registers and Memory Map
The memory and I/O resources of the M5407C3 are divided into three groups, MCF5407
Internal, External resources, and the ethernet controller. All the I/O registers are memory
mapped.
The MCF5407 has built in logic and up to eight chip-select pins (-CS0 to -CS7) which are
used to enable external memory and I/O devices. In addition there are two -RAS lines for
DRAM’s. There are registers to specify the address range, type of access, and the method
of -TA generation for each chip-select and -RAS pins. These registers are programmed by
dBUG to map the external memory and I/O devices.
The M5407C3 uses chip-select zero (-CS0) to enable the Flash ROM (refer to Section 3.3.)
The M5407C3 uses -RAS1, -RAS2, -CAS0, -CAS1, -CAS2, and -CAS3 to enable the
SDRAM DIMM module (refer to Section 3.2), -CS2 for SRAM (not populated), -CS3 for
Ethernet Bus I/O space, and -CS1 for the PCI bridge chip.
The chip select mechanism of the MCF5407 allows the memory mapping to be defined
based on the memory space desired (User/Supervisor, Program/Data spaces).
All the MCF5407 internal registers, configuration registers, parallel I/O port registers,
UART registers and system control registers are mapped by MB AR register at an y 1 KByte
boundary . It is mapped to 0x10000000 by dBUG. For complete map of these registers refer
to the MCF5407 User's Manual.
The M5407C3 board can have up to 512 MBytes of SDRAM installed. The first 16 MBytes
of memory space are reserved for this memory. Refer to Section 3.2 for a discussion of
RAM. The dBUG is programmed in one Am29PL160C-XX Flash ROM which occupies 2
MBytes of the address space. The first 256 KBytes are used by ROM Monitor and the
remainder is left for user use. Refer to section 3.3.
dBUG maps all the I/O space of the Ethernet bus to the MCF5407 memory at address
$40000000. Refer to section 3.6
3-4 M5407C3 User’s Manual
Page 73

Fr
ees
cale S
em
iconduct
or
, I
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
nc...
The Processor and Support Logic
Table 3-1 shows the M5407C3 memory maps.
Table 3-1. The M5407C3 Memory Map
Address Range Signal and Device Memory Access Time
$00000000-$00020000 SDRAM space for dBug ROM monitor use refer to manufacturer spec
$00020000-$00FFFFFF SDRAM space refer to manufacturer spec
$10000000-$100003FF System Integration Module (SIM) registers internal access
$20000000-$200007FF SRAM0 internal access (1 clock)
$20000800-$20000FFF SRAM1 internal access (1 clock)
$30000000-$300003FF
$40000000-$400FFFFF -CS3, 1M Ethernet Bus Area external TA from PLD (U18)
$7FE00000-$7FFFFFFF -CS0, 2M Flash ROM 8-7-7-7
$FFFF0000-$FFFFFFFF -CS1, PCI Bridge Chip external TA from PCI (U17)
1
Not installed. SRAM footprint accepts Motorola’s MCM69F737TQ chip and any other SRAM with the same
electrical specifications and package.
1
-CS2, External SRAM 2-1-1-1
All the unused area of the memory map is available to the user.
3.1.9 Reset Vector Mapping
After reset, the processor attempts to get the initial stack pointer and initial program counter
values from locations $000000-$000007 (the first eight bytes of memory space). This
requires the board to have a nonvolatile memory device in this range with proper
information. However, in some systems, it is preferred to have RAM starting at address
$00000000. In MCF5407, the -CS0 responds to any accesses after reset until the CSMR0
is written. Since -CS0 (the global chip select) is connected to Flash ROM, the Flash ROM
appears at address $00000000 which provides the initial stack pointer and program counter
(the first 8 bytes of the Flash ROM). The initialization routine programs the chip-select
logic, locates the Flash ROM to start at $7FE00000 and the configures the rest of the
internal and external peripherals.
3.1.10 TA Generation
The processor starts a bus cycle by asserting -TS with other control signals. The processor
then waits for an acknowledgment (-TA) either from within (Auto acknowledge mode) or
by the externally addressed device before it can complete the b us cycle. -T A is used not only
to indicate the completion of the bus cycle, it also allo ws devices with dif ferent access times
to communicate with the processor properly (i.e. asynchronously). The MCF5407, as part
Chapter 3. Hard ware Description and Reconfiguration 3-5
Page 74

Fr
ees
cale S
em
iconduct
or
, I
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
nc...
The Processor and Support Logic
generate -TA internally after a preprogrammed number of wait states. In order to support
future expansion of the board, the -TA input of the processor is also connected to the
Processor Expansion Bus, J2. This allows the expansion boards to assert this line to
indicate their -TA to the processor. On the expansion boards, however, this signal should
be generated through an open collector buffer with no pull-up resistor; a pull-up resistor is
included on the board. All the -TA’ s from the e xpansion boards should be connected to this
line.
3.1.11 Wait State Generator
The Flash ROM and SDRAM DIMM on the board may require some adjustments on the
cycle time of the processor to make them compatible with processor speed. To extend the
CPU bus cycles for the slower devices, the chip-select logic of the MCF5407 can be
programmed to generate an internal -TA after a given number of wait states. Refer to
Sections 3.1.12 and 3.1.13 for information about the wait state requirements of SDRAM
and Flash ROM respectively.
3.1.12 SDRAM DIMM
The M5407C3 has one 168-pin DIMM socket (U26) for a SDRAM DIMM. The M5407C3
will work with most PC100 SDRAM DIMMs with a few exceptions. The 5407 supports up
to two banks of SDRAM, but double-sided DIMMs require 4 bank selects to access all of
the chips. Therefore when using double-sided DIMMs only half of the available memory
will be accessible. Since DIMMs are manufactured primarily for use in PCs some DIMMs
have the DQM (byte enables) and RAS (bank selects) routed so that the DIMM cannot be
accessed as a 32-bit port.
In order to support SDRAM DIMMs with different configurations the M5407C3 uses a
helper mux (U27) to configure the address line connections to the DIMM socket. See the
Connecting the MCF5307 to 168-Pin Unbuffered SDRAM DIMMs application note on the
coldfire website (www.freescale.com/coldfi re) for more information. JP21-JP24 are used
to configure the inputs to the helper mux. When dBUG comes up it will read the SDRAM
configuration information from the EEPROM on the DIMM and drive the proper
configuration data for the helper mux on PP[0:3].
If you are using a third party debugger or want to use PP[0:3] then the jumpers JP21-JP24
should be moved to the correct settings for the particular DIMM you are using. There are a
couple of ways to determine which settings should be used. First, the jumper settings for
different combinations of row and column addresses are listed in the jumper table
silkscreen on the back of the board. The settings can also be determined by allowing the
board to boot up under dBUG control. Since dBUG driv es the configuration data on PP[0:3]
the data will be seen on the LEDs (D1-D4). If the LED is on then the corresponding jumper
should be OFF, and if the LED is off then the jumper should be in position 2-3.
3-6 M5407C3 User’s Manual
Page 75

Serial Communication Channels
Fr
ees
cale S
em
iconduct
or
, I
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
nc...
3.1.13 Flash ROM
There is one 2 MByte Flash ROM on the M5407C3, U12.
The board is shipped with one Am29PL160C, 2 MByte Flash ROM. The first 256K of the
Flash contains ROM Monitor firmware. The remaining memory is available to the user.
The MCF5407 chip-select logic can be programmed to generate the -TA for -CS0 signal
after a certain number of wait states (i.e. auto acknowledge mode). dBUG programs this
parameter to six wait-states.
3.1.14 JP15 Jumper and User’s Program
This jumper allows users to test code from the boot without having to overwrite the ROM Monitor.
When the jumper is set between pins 1 and 2, the behavior is normal. When the jumper is
set between pins 2 and 3, the board boots from the second half of Flash (0x7FF00000).
Procedure:
1. Compile and link as though the code was to be placed at the base of the flash, but
setup so that it will download to the SDRAM starting at address 0xE0000. The user
should refer to the compiler for this, since it will depend upon the compiler used.
2. Set up the jumper (JP15) for Normal operation, pin1 connected to pin 2.
3. Download to SDRAM (If using serial or ethernet, start ROM Monitor first. If using
BDM via wiggler, download first, then start ROM Monitor by pointing PC to
0x7fe00400 and run.)
4. In ROM Monitor, run 'upuser' command.
5. Move jumper (JP15) to pin 2 connected to pin 3 and push the reset button (S1). User
code should be running.
3.2 Serial Communication Channels
The M5407C3 offers a number of serial communications. They are discussed in this section.
3.2.1 MCF5407 UARTs
The MCF5407 has two built in U AR Ts, each with its own software programmable baud rate
generators; one channel is the ROM Monitor to Terminal output and the other is available
to the user . The ROM Monitor programs the interrupt level for U ART0 to Level 3, priority
Chapter 3. Hard ware Description and Reconfiguration 3-7
Page 76

Fr
ees
cale S
em
iconduct
or
, I
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
nc...
Real-Time Clock
through the RS-232 driver/recei ver and are a v ailable on DB-9 connectors P4 and P5. Refer
to the MCF5407 User’s Manual for programming and the register map.
3.2.2 I2C Module
The MCF5407 has a built in I2C module which allows interchip bus interface for a number of I/O
devices. It is compatible with industry-standard I2C Bus. The M5407C3 uses this to access the
SDRAM eeprom parameters. The two I2C signals are SDA and SCL which are a v ailable on the J2
expansion connector and J6 (this connector is unpopulated, see BOM in Appendix XXX for part
number). These signals are open-collector signals. However, they have pull-up resistors on the
M5407C3. These signals are connected to the SDRAM DIMM module I2C interface but not used
by the debugger . The interrupt control re gister for I2C is set for Level 3, priority 0 and autov ector.
Please note the MCF5407 I2C module is only 3.3V tolerant. Level shifters should be used if 5V
devices are being interfaced to the MCF5407 I2C.
3.3 Real-Time Clock
The M41T11M is a real-time clock incorporating 64 bytes of low power static RAM and a
built-in 32.768KHz oscillator , driv en from an external crystal. The first 8 bytes of RAM are
used to provide the clock/calendar storage, which are configured in BCD format. The
remaining 56 bytes of RAM is available for use as battery backed storage - if the battery
site on the M5407C3 is populated. Addresses and data are transferred via the I2C
bus to the M41T11M within which an address register is incremented after each read or
write of data. The device is year 2000 compliant and has automatic leap year compensation.
There are counters within the device for seconds, minutes, hours, day , date, month, year and
century.
3.4 Parallel I/O Port
The MCF5407 has one 16-bit parallel port. All the pins have dual functions. They can be
configured as I/O or their alternate function via the Pin Assignment register . dBug programs
the parllel port pins as follows:
P[3:0] connects to the SDRAM mux control and LEDs.
P[7:4] connects to LEDs and are available to the user during dBUG.
P[15:8] are configured as A[31:24].
3.5 On-Board Ethernet Logic
The M5407C3 includes the necessary logic, drivers, and the NE2000 compatible Ethernet
chip to allow 10M bit transfer rate on a network. The Ethernet-space addresses are located
starting at 0x40000000.
The interface base address is 0x300 and uses IRQ3. Howe v er , the Ethernet base address in
3-8 M5407C3 User’s Manual
Page 77

Fr
ees
cale S
em
iconduct
or
, I
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
nc...
On-Board Ethernet Logic
our system as mentioned earlier is 0x40000000. Which brings the address of chip to
0x40000300. Note that all registers should be addressed as W ORD accesses (even though
the registers are bytes). Note that the even address registers are addressed as they are (no
change), the read word will have the byte of the data in the lower byte of the word.
For odd addressed bytes, the address is mapped to 0x400083xx-1. Note that odd-bytes are
addressed as even addresses but increased by 0x8000. Still the read byte will be in the
lower byte of the read word
Below is an example of the data structure used to define the re gisters. For more information
on the Davicom DM9008 visit the Davicom website (www.davicom8.com).
typedef struct
{
NATURAL16CR;
union
{
struct
{
/* Even registers */
NATURAL16 CLDA1;/* CLDA1 (rd) PSTOP (wr) */
NATURAL16 TSR; /* TSR (rd) TPSR (wr) */
NATURAL16 FIFO; /* FIFO (rd) TBCR1 (wr) */
NATURAL16 CRDA0;/* CRDA0 (rd) RSAR0 (wr) */
NATURAL16 RBCR0;/* Remote Byte Count 0 (wr) */
NATURAL16 RSR; /* RSR (rd) RCR (wr) */
NATURAL16 CNTR1;/* CNTR1 (rd) DCR (wr) */
NATURAL16 DATAPORT;
NATURAL16 reserved[(0x10000-0x0012)/2];
/* Odd registers */
NATURAL16 CLDA0;/* CLDA0 (rd) PSTART (wr) */
NATURAL16 BNRY; /* Boundary pointer (rd wr) */
NATURAL16 NCR; /* NCR (rd) TBCR0 (wr) */
NATURAL16 ISR; /* Interrupt Status Register (rd wr) */
NATURAL16 CRDA1;/* CRDA1 (rd) RSAR1 (wr) */
NATURAL16 RBCR1;/* Remote Byte Count 1 (wr) */
NATURAL16 CNTR0;/* CNTR0 (rd) TCR (wr) */
NATURAL16 CNTR2;/* CNTR2 (rd) IMR (wr) */
} page0;
struct
{
/* Even registers */
NATURAL16 PAR1; /* Physical Address Byte 1 */
Chapter 3. Hard ware Description and Reconfiguration 3-9
Page 78

Fr
ees
cale S
em
iconduct
or
, I
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
nc...
On-Board Ethernet Logic
NATURAL16 MAR4; /* Multicast Address Byte 4 */
NATURAL16 MAR6; /* Multicast Address Byte 6 */
NATURAL16 reserved[(0x10000-0x0010)/2];
/* Odd registers */
NATURAL16 PAR0; /* Physical Address Byte 0 */
NATURAL16 PAR2; /* Physical Address Byte 2 */
NATURAL16 PAR4; /* Physical Address Byte 4 */
NATURAL16 CURR; /* Current Page Register (rd wr) */
NATURAL16 MAR1; /* Multicast Address Byte 1 */
NATURAL16 MAR3; /* Multicast Address Byte 3 */
NATURAL16 MAR5; /* Multicast Address Byte 5 */
NATURAL16 MAR7; /* Multicast Address Byte 7 */
} page1;
struct
{
/* Even registers */
NATURAL16 PSTOP;/* PSTOP (rd) CLDA1 (wr) */
NATURAL16 TPSR; /* Transmit Page Start Address (rd) */
NATURAL16 ACU; /* Address Counter Upper */
NATURAL16 reserved0;
NATURAL16 reserved2;
NATURAL16 RCR; /* Receive Configuration Register (rd) */
NATURAL16 DCR; /* Data Configuration Register (rd) */
NATURAL16 reserved[(0x10000-0x0010)/2];
/* Odd registers */
NATURAL16 PSTART;/* PSTART (rd) CLDA0 (wr) */
NATURAL16 RNPP; /* Remote Next Packet Pointer */
NATURAL16 LNPP; /* Local Next Packet Pointer */
NATURAL16 ACL; /* Address Counter Lower */
NATURAL16 reserved1;
NATURAL16 reserved3;
NATURAL16 TCR; /* Transmit Configuration Register (rd) */
NATURAL16 IMR; /* Interrupt Mask Register (rd) */
} page2;
} regs;
} NS8390;
The main purpose for this setup is to allow the use of Ethernet card (NE2000 compatible)
to facilitate network download, refer to chapter 2 for network download command (DN).
The dBUG driver is 100% NE2000 compatible.
The Ethernet Bus interrupt request line is connected via the 2032V PLD to IRQ3.
The on board ROM MONITOR is programmed to allow a user to download files from a
network to memory in different formats. The current compiler formats supported are
S-Record, COFF, ELF, or Image.
3-10 M5407C3 User’s Manual
Page 79

Connectors and Expansion Bus
Fr
ees
cale S
em
iconduct
or
, I
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
nc...
3.6 Connectors and Expansion Bus
There are 2 expansion connectors on the M5407C3 (J1 and J2) which are used to connect
the board to external I/O devices and/or expansion boards.
3.6.1 Expansion Connectors - J1 and J2
Table 3-2 shows pin assignments for the J1 connector.
Table 3-2. J1 Connector Pin Assignment
Pin Signal Pin Signal Pin Signal Pin Signal
1 1.8V 2 1.8V 61 D20 62 A15
3 1.8V 4 GND 63 D21 64 A16
5 D0 6 -HIZ 65 D22 66 GND
7 D1 8 -BKPT_TMS 67 GND 68 A17
9 GND 10 DSDI_TDI 69 D23 70 A18
11 D2 12 1.8V 71 D24 72 A19
13 D3 14 DSDO_TDO 73 D25 74 3.3V
15 3.3V 16 TCK 75 3.3V 76 A20
17 D4 18 DSCLK_TRST 77 D26 78 A21
19 D5 20 GND 79 D27 80 A22
21 GND 22 A0 81 D28 82 GND
23 D6 24 A1 83 GND 84 A23
25 D7 26 3.3V 85 D29 86 A24
27 3.3.V 28 A2 87 D30 88 A25
29 D8 30 A3 89 D31 90 3.3V
31 D9 32 A4 91 3.3V 92 A26
33 D10 34 GND 93 SIZ0 94 A27
35 GND 36 A5 95 SIZ1 96 A28
37 D11 38 A6 97 GND 98 GND
39 D12 40 A7 99 -OE 100 A29
41 D13 42 3.3V 101 -CS0 102 A30
43 3.3V 44 A8 103 -CS1 104 A31
45 D14 46 A9 105 3.3V 106 1.8V
Chapter 3. Hard ware Description and Reconfiguration 3-11
Page 80

Connectors and Expansion Bus
Fr
ees
cale S
em
iconduct
or
, I
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
nc...
Table 3-2. J1 Connector Pin Assignment (Continued)
Pin Signal Pin Signal Pin Signal Pin Signal
51 GND 52 A11 111 1.8V 112 1.8V
53 D17 54 A12 113 5V 114 5V
55 D18 56 A13 115 5V 116 5V
57 D19 58 3.3V 117 GND 118 GND
59 3.3V 60 A14 119 GND 120 GND
Table 3-3 shows the pin assignments of the J2 connector.
Table 3-3. J2 Connector pin assignment
Pin Signal Pin Signal Pin Signal Pin Signal
1 1.8V 2 1.8V 61 TIN1 62 GND
5 -CS2 6 PP0 63 -R_RAS0/SO0 64 GND
3 GND 4 GND 65 -R_RAS1/S02 66 MTMOD1
7 -CS3 8 PP1 67 GND 68 MTMOD0
9 -CS4 10 3.3V 69 -R_CAS0/DQM070 1.8V
11 1.8V 12 PP2 71 -R_CAS1/DQM172 CLKIN
13 -CS5 14 PP3 73 -R_CAS2/DQM274 GND
15 -CS6 16 PP4 75 3.3V 76 -RSTO
17 -CS7 18 GND 77 -R_CAS3/DQM378 1.8V
19 GND 20 PP5 79 -RDRAMW 80 BCLKO
21 -AS 22 PP6 81 -R_SRAS 82 GND
23 R/-W 24 PP7 83 GND 84 EDGESEL
25 -TA 26 1.8V 85 -R_SCAS 86 3.3V
27 3.3V 28 PSTDDATA7 87 R_SCKE 88 TXD0
29 -TS 30 PSTDDATA6 89 -BWE0 90 RXD0
31 -CF_RSTI* 32 GND 91 3.3V 92 -RTS0
33 -IRQ7 34 PSTDDATA5 93 -BWE1 94 -CTS0
35 GND 36 PSTDDATA4 95 -BWE2 96 GND
37 -IRQ5 38 3.3V 97 -BWE3 98 TXD1
39 -IRQ3 40 PSTDDATA3 99 GND 100 RXD1
3-12 M5407C3 User’s Manual
Page 81

Connectors and Expansion Bus
Fr
ees
cale S
em
iconduct
or
, I
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
nc...
Table 3-3. J2 Connector pin assignment (Continued)
Pin Signal Pin Signal Pin Signal Pin Signal
41 -IRQ1 42 PSTDDATA2 101 SCL 102 -RTS1
43 1.8V 44 GND 103 SDA 104 -CTS1
45 -BR 46 PSTDDATA1 105 GND 106 1.8V
47 -BD 48 PSTDDATA0 107 1.8V 108 1.8V
49 -BG 50 1.8V 109 3.3V 110 3.3V
51 GND 52 PSTCLK 111 -A31 112 -CS_FPCIBD*
53 TOUT1 54 GND 113 5V 114 5V
55 TOUT0 56 MTMOD3 115 5V 116 5V
57 TIN0 58 MTMOD2 117 GND 118 GND
59 3.3V 60 1.8V 119 GND 120 GND
* -CFRSTI and -CS_FPCIBD are board specific control signals, NOT processor signals.
See the schematics and PLD equations in the appendix.
3.6.2 The Debug Connector J5
The MCF5407 does have background Debug Port, Real-Time Trace Support, and
Real-Time Deb ug Support. The necessary signals are a vailable at connector J5. Figure 3-1
shows the J5 Connector pin assignment shows the pin assignment.
Chapter 3. Hard ware Description and Reconfiguration 3-13
Page 82

Connectors and Expansion Bus
Fr
ees
cale S
em
iconduct
or
, I
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
nc...
DEVELOPER RESERVED
GND
GND
-RST_IN
I/O PAD VOLTAGE
GND
PSTDDATA6
PSTDDATA4
PSTDDATA2
PSTDDATA0
FREESCALE RESERVED
GND
CORE VOLTAGE
Figure 3-1. The J5 Connector pin assignment
1
3
5
7
9
11
13
15
17
19
21
23
25
2
4
6
8
10
12
14
16
18
20
22
24
26
-BKPT
DSCLK
DEVELOPER RESERVED
DSI
DSO
PSTDDATA7
PSTDDATA5
PSTDDATA3
PSTDDATA1
GND
FREESCALE RESERVED
PST_CLK
-TA
3-14 M5407C3 User’s Manual
Page 83

Fr
ees
cale S
em
iconduct
or
, I
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
nc...
Appendix A
Configuring dBUG for Network
Downloads
The dBUG module has the ability to perform downloads over an Ethernet network using
the T rivial File Transfer Protocol, TFTP. Prior to using this feature, several parameters are
required for network downloads to occur . The information that is required and the steps for
configuring dBUG are described below.
A.1 Required Network Parameters
For performing network downloads, dB UG needs 6 parameters; 4 are network-related, and
2 are download-related. The parameters are listed below, with the dBUG designation
following in parenthesis.
All computers connected to an Ethernet network running the IP protocol need 3
network-specific parameters. These parameters are:
Internet Protocol, IP, address for the computer (client IP),
IP address of the Gateway for non-local traffic (gateway IP), and
Network netmask for flagging traffic as local or non-local (netmask).
In addition, the dBUG network download command requires the following three parameters:
IP address of the TFTP server (server IP),
Name of the file to download (filename),
Type of the file to download (filetype of S-record, COFF, ELF, or Image).
Your local system administrator can assign a unique IP address for the board, and also
provide you the IP addresses of the gateway, netmask, and TFTP server. Fill out the lines
below with this information.
Client IP:___.___.___.___(IP address of the board)
Server IP:___.___.___.___(IP address of the TFTP server)
Gateway:___.___.___.___(IP address of the gateway)
Appendix A. Configuring dBUG for Network Downloads A-1
Page 84

Configuring dBUG Network Parameters
Fr
ees
cale S
em
iconduct
or
, I
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
nc...
A.2 Configuring dBUG Network Parameters
Once the network parameters have been obtained, the Rom Monitor must be configured.
The following commands are used to configure the network parameters.
set client <client IP>
set server <server IP>
set gateway <gateway IP>
set netmask <netmask>
set mac <addr>
For example, the TFTP server is named ‘santafe’ and has IP address 123.45.67.1. The
board is assigned the IP address of 123.45.68.15. The gatew ay IP address is 123.45.68.250,
and the netmask is 255.255.255.0. The commands to dBUG are:
set client 123.45.68.15
set server 123.45.67.1
set gateway 123.45.68.250
set netmask 255.255.255.0
set mac 00:CF:54:07:03:01
The last step is to inform dBUG of the name and type of the file to download. Prior to
giving the name of the file, keep in mind the following.
Most, if not all, TFTP servers will only permit access to files starting at a particular
sub-directory. (This is a security feature which prevents reading of arbitrary files by
unknown persons.) For e xample, SunOS uses the directory /tftp_boot as the default TFTP
directory. When specifying a filename to a SunOS TFTP server, all filenames are relative
to /tftp_boot. As a result, you normally will be required to copy the file to download into
the directory used by the TFTP server.
A default filename for network downloads is maintained by dBUG. To change the default
filename, use the command:
set filename <filename>
When using the Ethernet network for download, either S-record, COFF, ELF , or Image files
may be downloaded. A default filetype for network downloads is maintained by dBUG as
well. To change the default filetype, use the command:
set filetype <srecord|coff|elf|image>
Continuing with the above example, the compiler produces an executable COFF file,
‘a.out’. This file is copied to the /tftp_boot directory on the server with the command:
rcp a.out santafe:/tftp_boot/a.out
Change the default filename and filetype with the commands:
set filename a.out
A-2 M5407C3 User’s Manual
Page 85

Fr
ees
cale S
em
iconduct
or
, I
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
nc...
Troubleshooting Network Problems
set filetype coff
Finally, perform the network download with the ‘dn’ command. The network download
process uses the configured IP addresses and the default filename and filetype for initiating
a TFTP download from the TFTP server.
A.3 Troubleshooting Network Problems
Most problems related to network downloads are a direct result of improper configuration.
Verify that all IP addresses configured into dBUG are correct. This is accomplished via the
‘show ’command.
Using an IP address already assigned to another machine will cause dBUG network
download to fail, and probably other severe network problems. Make certain the client IP
address is unique for the board.
Check for proper insertion or connection of the network cable. IS status LED lit indicating
that network traffic is present?
Check for proper configuration and operation of the TFTP server. Most Unix workstations
can execute a command named ‘tftp’ which can be used to connect to the TFTP server as
well. Is the default TFTP root directory present and readable?
If ‘ICMP_DESTINATION_UNREACHABLE’ or similar ICMP message appears, then a
serious error has occurred. Reset the board, and wait one minute for the TFTP server to
time out and terminate any open connections. Verify that the IP addresses for the server and
gateway are correct.
Appendix A. Configuring dBUG for Network Downloads A-3
Page 86

Troubleshooting Network Problems
Fr
ees
cale S
em
iconduct
or
, I
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
nc...
A-4 M5407C3 User’s Manual
Page 87

Fr
ees
cale S
em
iconduct
or
, I
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
nc...
Appendix B
ColdFire to ISA, IRQ7 and Reset Logic
Abel Code
module isa2
title 'isa controller'
"June 18 '00 version v4 of the 5407
"isa2 device 'ispLSI';
;"*****************************************************"
;"This abel file contains the code for a NE2000 compatible ethernet"
;"for the 5407 Coldfire processor as well as reset"
;"It was targeted to Lattice ispLSI LV 2032 PLD "
;"CS: B25D "
;"*****************************************************"
;"*****************************************************"
;"Declaration Section "
;"*****************************************************"
;" constants"
C,P,X,Z,H,L = .C.,.P.,.X.,.Z.,1,0;
;"*****************************************************"
DLYIOCHRDY0 node ISTYPE 'reg_d,buffer';
DLYIOCHRDY,ENDIT,END16,END8 node;
STARTISA node ISTYPE 'reg_d,buffer';
SBHE,IOR,IOW,ISAOE node;
DA,DLYDA node ISTYPE 'reg_d,buffer';
DAOE,CLK16MHZ node ISTYPE 'reg_d,buffer';
CLK8MHZ node ISTYPE 'reg_d,buffer';
Appendix B. ColdFire to ISA, IRQ7 and Reset Logic Abel Code B-1
Page 88

Fr
ees
cale S
em
iconduct
or
, I
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
nc...
BCLK0 node ISTYPE 'reg_d,buffer';
BCLK1 node ISTYPE 'reg_d,buffer';
BCLK2 node ISTYPE 'reg_d,buffer';
DIV6Q0 node ISTYPE 'reg_d,buffer';
DIV6Q1 node ISTYPE 'reg_d,buffer';
GNTANC_L pin 3; "Output - to Anchor 3042 to grant PCI bus
RST_L pin 4; "Output - to ColdFire reset
DB_CS_L pin 5; "Output - Data buffer enable for ethernet
A0IN pin 6; "INPUT - A0 received from CF through buffers
IOCHRDY pin 7; "Input - asserted by ethernet
CS0_L pin 8; "Input - Chip select 0 from ColdFire
IOCS16L pin 9; "Input - asserted by ethernet
SIZ1 pin 10;
XCLK0 pin 11; "Input - global clock currently 50MHz
IOWL pin 15; "Input - write signal from ethernet
RD pin 16; "INPUT - R/W* from the ColdFire
DIV6Q2 pin 17 ISTYPE 'reg_d,buffer';
BALE pin 18; "Output - address latch enable
A0 pin 19; "OUTPUT - A0 sent to the ethernet
CS1_L pin 20; "Input - Chip select 1 from ColdFire
CS2_L pin 21; "Input - Chip select 2 from ColdFire
CS3_L pin 22; "Input - From ColdFire
CS_FPCIBD_L pin 25; "Output - Chip selects 0,1 & 2 or'd for
data buffers
PORIN_L pin 26; "Input - Suppy Voltage Supervisor
GNTPCI_L pin 27; "Output - Grant signal to the PCI connector
ETHER_IRQ pin 28; "Input - Ethernet IRQ 3
IRQ3 pin 29; "Output - IRQ 3 into the ColdFire
RST_H pin 30; "Output - to the Ethernet
REQPCI_L pin 31; "Input - request from the PCI connector
HIZ_L pin 32; "Output - to ColdFire *HIZ
IORL pin 37; "Input - read signal from ethernet
A31 pin 38; "Input - A31 signal for CS to PCI controller
A16 pin 39;
TAL pin 40; "Input / Output - Transfer acknowledge
B-2 M5407C3 User’s Manual
Page 89

Fr
ees
cale S
em
iconduct
or
, I
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
nc...
REQANC_L pin 41; "Input - request from the PCI controller
NOT_A31 pin 42; "Output - Inverted A31 for CS to PCI
controller
SIZ0 pin 43;
BDM_RST_L pin 44; "Input - BDM reset input
; "********************************"
; " Lattice attributes "
; "********************************"
pLSI property 'CLK XCLK0 CLK0 ';
pLSI property 'CLK CLK8MHZ SLOWCLK ';
pLSI property 'ISP ON';
pLSI property 'PULLUP ON';
pLSI property 'Y1_AS_RESET OFF';
; "--------------------------------"
; " Output inverter macro "
; "--------------------------------"
OB21 MACRO (XO0, A0)
{
?XO0 = !?A0;
};
; "--------------------------------"
; " Tristate Output inverter macro "
; "--------------------------------"
OT21 MACRO (XO0, A0, OE)
{
?XO0.OE = ?OE;
?XO0 = !?A0;
};
Appendix B. ColdFire to ISA, IRQ7 and Reset Logic Abel Code B-3
Page 90

Fr
ees
cale S
em
iconduct
or
, I
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
nc...
{
[?Q0..?Q2].clk = ?CLK;
?Q0.D = ?Q0.Q & !?CS $ ?EN & !?CS ;
?Q1.D = ?Q1.Q & !?CS $ ( ?Q0.Q & ?EN & !?CS );
?Q2.D = ?Q2.Q & !?CS $ ( ?Q0.Q & ?Q1.Q & ?EN & !?CS );
};
equations
;"###########################################"
;"Bidirectional circuit equations"
;"###########################################"
OT21 (TAL, DA, DAOE)
OB21 (IORL, IOR)
OB21 (IOWL, IOW)
OB21 (RST_L, RST_H)
IRQ3 = !ETHER_IRQ;
!DB_CS_L = !RST_H & !CS3_L;
!CS_FPCIBD_L = !RST_H & (!CS0_L # !CS1_L # !CS2_L);
NOT_A31 = !A31;
!GNTPCI_L = !REQPCI_L & GNTANC_L; " Grant PCI bus if not in use
by the PCI
" controller.
!GNTANC_L = !REQANC_L & GNTPCI_L; " Grant PCI controller the bus
if not
" already granted to the PCI connector.
RST_H = !PORIN_L # !BDM_RST_L;
HIZ_L = 1;
B-4 M5407C3 User’s Manual
Page 91

Fr
ees
cale S
em
iconduct
or
, I
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
nc...
DAOE := !CS3_L # DA;
DAOE.clk = XCLK0 ;
A0 = !SIZ1 & SIZ0 & !A0IN #
A16 ;
SBHE = STARTISA & !SIZ1 & SIZ0 & !A0IN #
STARTISA & SIZ1 & !SIZ0 & !A0IN #
STARTISA & !SIZ1 & !SIZ0 & !A0IN ;
CLK16MHZ := !CLK16MHZ ;
CLK16MHZ.clk = XCLK0 ;
CLK8MHZ := CLK8MHZ & !CLK16MHZ #
!CLK8MHZ & CLK16MHZ ;
CLK8MHZ.clk = XCLK0 ;
CLK4MHZ := CLK4MHZ $ ( CLK16MHZ & CLK8MHZ ) ;
CLK4MHZ.clk = XCLK0 ;
" Total div. 6 to produce 8.333MHz
for Ethernet
" controller - Davicom DM9008
from 50MHz - XCLK0.
DIV6Q0 := !DIV6Q0 & !DIV6Q1 ; " First D-type in divide by 3
chain using XCLK0.
DIV6Q0.clk = XCLK0 ;
DIV6Q1 := DIV6Q0 & !DIV6Q1 ; " Second D-type in div. by 3
chain using XCLK0.
Appendix B. ColdFire to ISA, IRQ7 and Reset Logic Abel Code B-5
Page 92

Fr
ees
cale S
em
iconduct
or
, I
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
nc...
DIV6Q2.clk = DIV6Q1 ;
DA := !CS3_L & END16 & ENDIT & !IOCS16L & RD & !CLK8MHZ & SBHE #
!CS3_L & END8 & ENDIT & RD & !CLK8MHZ #
DLYDA & !CS3_L #
DA & !CS3_L;
DA.clk=XCLK0;
DLYDA :=!CS3_L & END16 & ENDIT & !IOCS16L & !RD & !CLK8MHZ & SBHE #
!CS3_L & END8 & ENDIT & IOCS16L & !RD & !CLK8MHZ #
!CS3_L & END8 & ENDIT & !SBHE & !RD & !CLK8MHZ ;
DLYDA.clk=XCLK0;
STARTISA := !CS3_L & !ENDIT ;
STARTISA.clk = CLK8MHZ ;
CBU43 (BCLK0,BCLK1,BCLK2,CLK8MHZ,STARTISA,!STARTISA)
BALE = STARTISA & !CLK8MHZ & !BCLK2 & !BCLK1 & !BCLK0 & !IOR & !IOW ;
IOR = STARTISA & !BCLK2 & !BCLK1 & BCLK0 & !CLK8MHZ & RD #
IOR & !CS3_L ;
IOW = STARTISA & !BCLK2 & !BCLK1 & BCLK0 & !CLK8MHZ & !RD #
IOW & STARTISA ;
END16 = !BCLK2 & BCLK1 & !BCLK0 & !CLK8MHZ#
END16 & STARTISA ;
END8 = BCLK2 & !BCLK1 & BCLK0 & !CLK8MHZ #
END8 & STARTISA ;
ENDIT = END16 & !IOCS16L & IOCHRDY & DLYIOCHRDY0 & DLYIOCHRDY & SBHE & STARTISA#
B-6 M5407C3 User’s Manual
Page 93

Fr
ees
cale S
em
iconduct
or
, I
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
nc...
END8 & IOCS16L & IOCHRDY & DLYIOCHRDY0 & DLYIOCHRDY & STARTISA #
END8 & !SBHE & IOCHRDY & DLYIOCHRDY0 & DLYIOCHRDY & STARTISA ;
DLYIOCHRDY0:= IOCHRDY;
DLYIOCHRDY0.clk = CLK8MHZ ;
DLYIOCHRDY = IOCHRDY & CLK8MHZ #
DLYIOCHRDY & !CLK8MHZ ;
;"****************************************************"
;" Test Vector Section"
;"****************************************************"
test_vectors 'HIZ_L Test Vector'
([XCLK0,PORIN_L,BDM_RST_L,CS3_L]->[RST_H])
[P,1,1,1,]->[X];
[C,1,1,1,]->[X];
[C,1,0,1,]->[X];
[C,1,0,1,]->[X];
[C,1,1,1,]->[X];
[C,1,1,1,]->[X];
[C,0,1,1,]->[X];
[C,0,1,1,]->[X];
[C,0,1,1,]->[X];
[C,1,1,1,]->[X];
[C,1,1,0,]->[X];
[C,1,1,1,]->[X];
[C,1,1,1,]->[X];
[C,1,1,1,]->[X];
[C,0,1,1,]->[X];
[C,0,1,1,]->[X];
[C,0,1,1,]->[X];
[C,0,1,1,]->[X];
Appendix B. ColdFire to ISA, IRQ7 and Reset Logic Abel Code B-7
Page 94

Fr
ees
cale S
em
iconduct
or
, I
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
nc...
[C,0,1,1,]->[X];
[C,0,1,1,]->[X];
[C,1,1,1,]->[X];
[C,1,1,1,]->[X];
[C,1,1,1,]->[X];
[C,1,1,1,]->[X];
[C,1,1,0,]->[X];
[C,1,1,1,]->[X];
[C,1,1,1,]->[X];
[C,1,1,1,]->[X];
end
B-8 M5407C3 User’s Manual
Page 95

Fr
ees
cale S
em
iconduct
or
, I
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
nc...
apps docs:ColdFire:5407:Eval Board UM NEW:5407_C_SDRAM_Equations.fm 8/11/00
Appendix C
SDRAM MUX PAL Equation
module SDRAMmux
title 'SDRAM Mux Controller for the MCF5407EVM'
"MAR 16 '99 First revision of the code based on Bill Benners application note"
"5307mux device 'ispLSI22LV10';
;"*****************************************************"
;"This abel file contains the code to mux the address lines"
;"allowing the MCF5407 to support all 168pin 1Bank x 64 bit PC compliant DIMMS"
;"It was targeted to Lattice ispLSI 22LV10 PAL "
;"All logic with this PAL is com
;"CS:4C86 "
;"*****************************************************"
;"*****************************************************"
;"Declaration Section "
;"*****************************************************"
;" constants"
C,P,X,Z,H,L = .C.,.P.,.X.,.Z.,1,0;
;"*****************************************************"
M0 PIN 3; "Mux Input (0)
M1 PIN 4; "Mux Input (1)
M2 PIN 5; "Mux Input (2)
M3 PIN 6; "Mux Input (3)
CA18 PIN 2; "Input - ColdFire driven address (18)
Appendix C. SDRAM MUX P AL Equation C-1
Page 96

Fr
ees
cale S
em
iconduct
or
, I
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
nc...
CA23 PIN 12; "Input - ColdFire driven address (23)
CA24 PIN 13; "Input - ColdFire driven address (24)
CA25 PIN 16; "Input - ColdFire driven address (25)
CA26 PIN 23; "Input - ColdFire driven address (26)
CA27 PIN 21; "Input - ColdFire driven address (27)
SA8 PIN 24; "Output - SDRAM input address (A8)
SA9 PIN 19; "Output - SDRAM input address (A9)
SA10 PIN 25; "Output - SDRAM input address (A10)
SA11 PIN 17; "Output - SDRAM input address (A11)
SA12 PIN 27; "Output - SDRAM input address (A12)
SA13 PIN 20; "Output - SDRAM input address (A13)
BA0 PIN 18; "Output - SDRAM input address (BA0)
BA1 PIN 26; "Output - SDRAM input address (BA1)
select = [M3,M2,M1,M0];
; "********************************"
; " Lattice attributes "
; "********************************"
"pLSI property 'CLK XCLK0 CLK0 ';
"pLSI property 'CLK CLK8MHZ SLOWCLK ';
pLSI property 'ISP ON';
pLSI property 'PULLUP ON';
pLSI property 'Y1_AS_RESET OFF';
equations
;"###########################################"
;"COMBINATORIAL Logic Only"
;"###########################################"
when (select == 0) then { SA8=CA18;
SA9=CA19;
SA10=CA20;
BA0=CA21;
C-2 BookTitle
Page 97

Fr
ees
cale S
em
iconduct
or
, I
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
nc...
BA1=CA22;
}
when (select == 1) then { SA8=CA19;
SA9=CA20;
SA10=CA21;
BA0=CA22;
BA1=CA23;
}
when (select == 2) then { SA8=CA19;
SA9=CA21;
SA10=CA22;
BA0=CA23;
BA1=CA24;
}
when (select == 3) then { SA8=CA18;
SA9=CA19;
SA10=CA20;
SA11=CA21;
BA0=CA22;
BA1=CA23;
}
when (select == 4) then {
SA8=CA19;
SA9=CA20;
SA10=CA21;
SA11=CA22;
BA0=CA23;
BA1=CA24;
}
Appendix C. SDRAM MUX P AL Equation C-3
Page 98

Fr
ees
cale S
em
iconduct
or
, I
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
nc...
SA9=CA21;
SA10=CA22;
SA11=CA23;
BA0=CA24;
BA1=CA25;
}
when (select == 6) then {
SA8=CA19;
SA9=CA21;
SA10=CA23;
SA11=CA24;
BA0=CA25;
BA1=CA26;
}
when (select == 7) then { SA8=CA18;
SA9=CA19;
SA10=CA20;
SA11=CA21;
SA12=CA22;
BA0=CA23;
BA1=CA24;
}
when (select == 8) then { SA8=CA19;
SA9=CA20;
SA10=CA21;
SA11=CA22;
SA12=CA23;
BA0=CA24;
BA1=CA25;
}
when (select == 9) then { SA8=CA19;
SA9=CA21;
C-4 BookTitle
Page 99

Fr
ees
cale S
em
iconduct
or
, I
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
nc...
SA10=CA22;
SA11=CA23;
SA12=CA24;
BA0=CA25;
BA1=CA26;
}
when (select == ^h0A) then { SA8=CA19;
SA9=CA21;
SA10=CA23;
SA11=CA24;
SA12=CA25;
BA0=CA26;
BA1=CA27;
}
"****************************************************"
" Test Vector Section"
"****************************************************"
test_vectors 'M0, M1, M2, M3 Test Vector'
([M3, M2, M1, M0, CA18, CA19, CA20, CA21, CA22, CA23, CA24, CA25, CA26,
CA27]->[SA8, SA9, SA10, SA11, SA12, BA0, BA1])
[0,0,0,0,1,0,1,0,1,0,1,0,1,0]->[X,X,X,X,X,X,X];
[0,0,0,1,1,0,1,0,1,0,1,0,1,0]->[X,X,X,X,X,X,X];
[0,0,1,0,1,0,1,0,1,0,1,0,1,0]->[X,X,X,X,X,X,X];
[0,0,1,1,1,0,1,0,1,0,1,0,1,0]->[X,X,X,X,X,X,X];
[0,1,0,0,1,0,1,0,1,0,1,0,1,0]->[X,X,X,X,X,X,X];
[0,1,0,1,1,0,1,0,1,0,1,0,1,0]->[X,X,X,X,X,X,X];
[0,1,1,0,1,0,1,0,1,0,1,0,1,0]->[X,X,X,X,X,X,X];
[0,1,1,1,1,0,1,0,1,0,1,0,1,0]->[X,X,X,X,X,X,X];
[1,0,0,0,1,0,1,0,1,0,1,0,1,0]->[X,X,X,X,X,X,X];
[1,0,0,1,1,0,1,0,1,0,1,0,1,0]->[X,X,X,X,X,X,X];
end
Appendix C. SDRAM MUX P AL Equation C-5
Page 100

Fr
ees
cale S
em
iconduct
or
, I
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
nc...
C-6 BookTitle
 Loading...
Loading...