Page 1

DSP56364 24-Bit Digital Signal
Processor
Users Manual
Document Number: DSP56364UM
Rev. 2
08/2006
Page 2

How to Reach Us:
Home Page:
www.freescale.com
E-mail:
support@freescale.com
USA/Europe or Locations Not Listed:
Freescale Semiconductor
Technical Information Center, CH370
1300 N. Alma School Road
Chandler, Arizona 85224
+1-800-521-6274 or +1-480-768-2130
support@freescale.com
Europe, Middle East, and Africa:
Freescale Halbleiter Deutschland GmbH
Technical Information Center
Schatzbogen 7
81829 Muenchen, Germany
+44 1296 380 456 (English)
+46 8 52200080 (English)
+49 89 92103 559 (German)
+33 1 69 35 48 48 (French)
support@freescale.com
Japan:
Freescale Semiconductor Japan Ltd.
Headquarters
ARCO Tower 15F
1-8-1, Shimo-Meguro, Meguro-ku,
Tokyo 153-0064, Japan
0120 191014 or +81 3 5437 9125
support.japan@freescale.com
Asia/Pacific:
Freescale Semiconductor Hong Kong Ltd.
Technical Information Center
2 Dai King Street
Tai Po Industrial Estate
Tai Po, N.T., Hong Kong
+800 2666 8080
support.asia@freescale.com
For Literature Requests Only:
Freescale Semiconductor Literature Distribution Center
P.O. Box 5405
Denver, Colorado 80217
1-800-521-6274 or 303-675-2140
Fax: 303-675-2150
LDCForFreescaleSemiconductor@hibbertgroup.com
Information in this document is provided solely to enable system and software implementers to use
Freescale Semiconductor products. There are no express or implied copyright licenses granted
hereunder to design or fabricate any integrated circuits or integrated circuits based on the information
in this document.
Freescale Semiconductor reserves the right to make changes without further notice to any products
herein. Freescale Semiconductor makes no warranty, representation or guarantee regarding the
suitability of its products for any particular purpose, nor does Freescale Semiconductor assume any
liability arising out of the application or use of any product or circuit, and specifically disclaims any
and all liability, including without limitation consequential or incidental damages. “Typical” parameters
that may be provided in Freescale Semiconductor data sheets and/or specifications can and do vary
in different applications and actual performance may vary over time. All operating parameters,
including “Typicals”, must be validated for each customer application by customer’s technical experts.
Freescale Semiconductor does not convey any license under its patent rights nor the rights of others.
Freescale Semiconductor products are not designed, intended, or authorized for use as components
in systems intended for surgical implant into the body, or other applications intended to support or
sustain life, or for any other application in which the failure of the Freescale Semiconductor product
could create a situation where personal injury or death may occur. Should Buyer purchase or use
Freescale Semiconductor products for any such unintended or unauthorized application, Buyer shall
indemnify and hold Freescale Semiconductor and its officers, employees, subsidiaries, affiliates, and
distributors harmless against all claims, costs, damages, and expenses, and reasonable attorney
fees arising out of, directly or indirectly, any claim of personal injury or death associated with such
unintended or unauthorized use, even if such claim alleges that Freescale Semiconductor was
negligent regarding the design or manufacture of the part.
Freescale™ and the Freescale logo are trademarks of Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. All other
product or service names are the property of their respective owners.
© Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. 2006. All rights reserved.
Page 3

Contents
Manual Conventions
1 Overview
1.1 Introduction. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-1
1.2 Features. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-2
1.3 Audio Processor Architecture. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-3
1.4 Core Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-4
1.5 DSP56300 Core Functional Blocks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-4
1.5.1 Data ALU . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-4
1.5.1.1 Data ALU Registers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-5
1.5.1.2 Multiplier-Accumulator (MAC) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-5
1.5.2 Address Generation Unit (AGU) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-5
1.5.3 Program Control Unit (PCU) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-6
1.5.4 Internal Buses . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-6
1.5.5 Direct Memory Access (DMA) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-7
1.5.6 PLL-based Clock Oscillator . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-7
1.5.7 JTAG TAP and OnCE Module. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-8
1.6 Data and Program memory . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-8
1.6.1 Reserved Memory Spaces. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-8
1.6.2 Program ROM Area Reserved for Freescale Use. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-8
1.6.3 Bootstrap ROM. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-8
1.6.4 Dynamic Memory Configuration Switching . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-8
1.6.5 External Memory Support . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-9
1.7 Internal I/O Memory Map. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-9
1.8 Status Register (SR) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-10
2 Signal/Connection Descriptions
2.1 Signal Groupings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-1
2.2 Power . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-3
2.3 Ground . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-3
2.4 Clock and PLL . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-4
2.5 External Memory Expansion Port (Port A) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-4
2.5.1 External Address Bus . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-4
2.5.2 External Data Bus . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-5
2.5.3 External Bus Control . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-5
2.6 Interrupt and Mode Control . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-6
2.7 Serial Host Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-7
2.8 Enhanced Serial Audio Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-10
2.9 JTAG/OnCE Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-13
2.10 GPIO Signals . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-14
BookTitle, Rev. #
Freescale Semiconductor iii
Page 4

3 Memory Configuration
3.1 Memory Spaces. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-1
3.1.1 Program Memory Space . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-1
3.1.1.1 Program RAM. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-1
3.1.1.2 Program ROM. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-1
3.1.1.3 Bootstrap ROM. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-2
3.1.1.4 Reserved Program Memory Locations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-2
3.1.2 Data Memory Spaces . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-2
3.1.2.1 X Data Memory Space . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-2
3.1.2.2 X Data RAM. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-3
3.1.2.3 Y Data Memory Space . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-3
3.1.2.4 Y Data RAM. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-3
3.2 Memory Space Configuration. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-3
3.3 Internal Memory Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-3
3.3.1 RAM Locations. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-4
3.3.2 ROM Locations. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-4
3.3.3 Dynamic Memory Configuration Switching . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-5
3.4 Memory Maps. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-6
3.5 External Memory Support . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-8
3.6 Internal I/O Memory Map. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-8
4 Core Configuration
4.1 Introduction. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-1
4.2 Operating Mode Register (OMR) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-1
4.2.1 Mode C (MC) - Bit 2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-2
4.2.2 Address Attribute Priority Disable (APD) - Bit 14. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-2
4.2.3 Address Tracing Enable (ATE) - Bit 15 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-2
4.3 Operating Modes. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-3
4.4 Bootstrap Program . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-4
4.5 Interrupt Priority Registers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-4
4.6 DMA Request Sources . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-7
4.7 PLL and Clock Generator . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-7
4.7.1 PLL Multiplication Factor (MF0-MF11) - Bits 0-11 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-7
4.7.2 Crystal Range Bit (XTLR) - Bit 15 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-8
4.7.3 XTAL Disable Bit (XTLD) - Bit 16 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-8
4.7.4 Clock Output Disable Bit (COD) - Bit 19 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-8
4.7.5 PLL Pre-Divider Factor (PD0-PD3) - Bits 20-23. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-8
4.8 Device Identification (ID) Register . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-8
4.9 JTAG Identification (ID) Register . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-8
4.10 JTAG Boundary Scan Register (BSR) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-9
BookTitle, Rev. #
iv Freescale Semiconductor
Page 5

5 General Purpose Input/Output Port (GPIO)
5.1 Introduction. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-1
5.2 GPIO Programming Model. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-1
5.2.1 Port B Control Register (PCRB). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-2
5.2.1.1 PCRB Control Bits (PC[3:0]) - Bits 3-0 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-2
5.2.1.2 PCRB Reserved Bits - Bits 23-4. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-2
5.2.1.3 PRRB Direction Bits (PDC[3:0]) - Bits 3-0 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-3
5.2.1.4 PRRB Reserved Bits - Bits 23-4. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-3
5.2.2 Port B GPIO Data Register (PDRB). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-3
5.2.2.1 PDRB Data Bits (PD[3:0]) - Bits 3-0 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-3
5.2.2.2 PDRB Reserved Bits - Bits 23-4. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-3
6 Enhanced Serial AUDIO Interface (ESAI)
6.1 Introduction. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-1
6.2 ESAI Data and Control Pins . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-3
6.2.1 Serial Transmit 0 Data Pin (SDO0) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-3
6.2.2 Serial Transmit 1 Data Pin (SDO1) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-3
6.2.3 Serial Transmit 2/Receive 3 Data Pin (SDO2/SDI3) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-3
6.2.4 Serial Transmit 3/Receive 2 Data Pin (SDO3/SDI2) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-4
6.2.5 Serial Transmit 4/Receive 1 Data Pin (SDO4/SDI1) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-4
6.2.6 Serial Transmit 5/Receive 0 Data Pin (SDO5/SDI0) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-4
6.2.7 Receiver Serial Clock (SCKR) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-4
6.2.8 Transmitter Serial Clock (SCKT) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-5
6.2.9 Frame Sync for Receiver (FSR) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-6
6.2.10 Frame Sync for Transmitter (FST) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-7
6.2.11 High Frequency Clock for Transmitter (HCKT) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-7
6.2.12 High Frequency Clock for Receiver (HCKR) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-7
6.3 ESAI Programming Model . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-7
6.3.1 ESAI Transmitter Clock Control Register (TCCR) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-8
6.3.1.1 TCCR Transmit Prescale Modulus Select (TPM7–TPM0) - Bits 0–7 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-8
6.3.1.2 TCCR Transmit Prescaler Range (TPSR) - Bit 8 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-9
6.3.1.3 TCCR Tx Frame Rate Divider Control (TDC4–TDC0) - Bits 9–13 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-10
6.3.1.4 TCCR Tx High Frequency Clock Divider (TFP3-TFP0) - Bits 14–17 . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-11
6.3.1.5 TCCR Transmit Clock Polarity (TCKP) - Bit 18 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-12
6.3.1.6 TCCR Transmit Frame Sync Polarity (TFSP) - Bit 19. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-12
6.3.1.7 TCCR Transmit High Frequency Clock Polarity (THCKP) - Bit 20 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-12
6.3.1.8 TCCR Transmit Clock Source Direction (TCKD) - Bit 21 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-12
6.3.1.9 TCCR Transmit Frame Sync Signal Direction (TFSD) - Bit 22 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-12
6.3.1.10 TCCR Transmit High Frequency Clock Direction (THCKD) - Bit 23 . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-12
6.3.2 ESAI Transmit Control Register (TCR) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-13
6.3.2.1 TCR ESAI Transmit 0 Enable (TE0) - Bit 0 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-13
6.3.2.2 TCR ESAI Transmit 1 Enable (TE1) - Bit 1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-13
6.3.2.3 TCR ESAI Transmit 2 Enable (TE2) - Bit 2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-14
BookTitle, Rev. #
Freescale Semiconductor v
Page 6

6.3.2.4 TCR ESAI Transmit 3 Enable (TE3) - Bit 3 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-14
6.3.2.5 TCR ESAI Transmit 4 Enable (TE4) - Bit 4 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-14
6.3.2.6 TCR ESAI Transmit 5 Enable (TE5) - Bit 5 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-15
6.3.2.7 TCR Transmit Shift Direction (TSHFD) - Bit 6. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-15
6.3.2.8 TCR Transmit Word Alignment Control (TWA) - Bit 7 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-15
6.3.2.9 TCR Transmit Network Mode Control (TMOD1-TMOD0) - Bits 8-9 . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-16
6.3.2.10 TCR Tx Slot and Word Length Select (TSWS4-TSWS0) - Bits 10-14 . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-18
6.3.2.11 TCR Transmit Frame Sync Length (TFSL) - Bit 15 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-19
6.3.2.12 TCR Transmit Frame Sync Relative Timing (TFSR) - Bit 16 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-21
6.3.2.13 TCR Transmit Zero Padding Control (PADC) - Bit 17 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-21
6.3.2.14 TCR Reserved Bit - Bits 18 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-21
6.3.2.15 TCR Transmit Section Personal Reset (TPR) - Bit 19 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-21
6.3.2.16 TCR Transmit Exception Interrupt Enable (TEIE) - Bit 20 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-21
6.3.2.17 TCR Transmit Even Slot Data Interrupt Enable (TEDIE) - Bit 21 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-22
6.3.2.18 TCR Transmit Interrupt Enable (TIE) - Bit 22 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-22
6.3.2.19 TCR Transmit Last Slot Interrupt Enable (TLIE) - Bit 23 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-22
6.3.3 ESAI Receive Clock Control Register (RCCR) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-22
6.3.3.1 RCCR Receiver Prescale Modulus Select (RPM7–RPM0) - Bits 7–0. . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-23
6.3.3.2 RCCR Receiver Prescaler Range (RPSR) - Bit 8 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-23
6.3.3.3 RCCR Rx Frame Rate Divider Control (RDC4–RDC0) - Bits 9–13 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-23
6.3.3.4 RCCR Rx High Frequency Clock Divider (RFP3-RFP0) - Bits 14-17 . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-24
6.3.3.5 RCCR Receiver Clock Polarity (RCKP) - Bit 18 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-24
6.3.3.6 RCCR Receiver Frame Sync Polarity (RFSP) - Bit 19 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-24
6.3.3.7 RCCR Receiver High Frequency Clock Polarity (RHCKP) - Bit 20 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-24
6.3.3.8 RCCR Receiver Clock Source Direction (RCKD) - Bit 21 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-25
6.3.3.9 RCCR Receiver Frame Sync Signal Direction (RFSD) - Bit 22 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-25
6.3.3.10 RCCR Receiver High Frequency Clock Direction (RHCKD) - Bit 23 . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-26
6.3.4 ESAI Receive Control Register (RCR) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-26
6.3.4.1 RCR ESAI Receiver 0 Enable (RE0) - Bit 0 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-27
6.3.4.2 RCR ESAI Receiver 1 Enable (RE1) - Bit 1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-27
6.3.4.3 RCR ESAI Receiver 2 Enable (RE2) - Bit 2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-27
6.3.4.4 RCR ESAI Receiver 3 Enable (RE3) - Bit 3 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-28
6.3.4.5 RCR Reserved Bits - Bits 4-5, 17-18 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-28
6.3.4.6 RCR Receiver Shift Direction (RSHFD) - Bit 6. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-28
6.3.4.7 RCR Receiver Word Alignment Control (RWA) - Bit 7 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-28
6.3.4.8 RCR Receiver Network Mode Control (RMOD1-RMOD0) - Bits 8-9 . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-28
6.3.4.9 RCR Receiver Slot and Word Select (RSWS4-RSWS0) - Bits 10-14 . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-29
6.3.4.10 RCR Receiver Frame Sync Length (RFSL) - Bit 15 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-30
6.3.4.11 RCR Receiver Frame Sync Relative Timing (RFSR) - Bit 16 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-30
6.3.4.12 RCR Receiver Section Personal Reset (RPR) - Bit 19 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-31
6.3.4.13 RCR Receive Exception Interrupt Enable (REIE) - Bit 20 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-31
6.3.4.14 RCR Receive Even Slot Data Interrupt Enable (REDIE) - Bit 21 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-31
6.3.4.15 RCR Receive Interrupt Enable (RIE) - Bit 22 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-31
6.3.4.16 RCR Receive Last Slot Interrupt Enable (RLIE) - Bit 23 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-31
6.3.5 ESAI Common Control Register (SAICR). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-32
BookTitle, Rev. #
vi Freescale Semiconductor
Page 7

6.3.5.1 SAICR Serial Output Flag 0 (OF0) - Bit 0 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-32
6.3.5.2 SAICR Serial Output Flag 1 (OF1) - Bit 1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-32
6.3.5.3 SAICR Serial Output Flag 2 (OF2) - Bit 2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-32
6.3.5.4 SAICR Reserved Bits - Bits 3-5, 9-23 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-32
6.3.5.5 SAICR Synchronous Mode Selection (SYN) - Bit 6 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-33
6.3.5.6 SAICR Transmit External Buffer Enable (TEBE) - Bit 7 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-33
6.3.5.7 SAICR Alignment Control (ALC) - Bit 8 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-33
6.3.6 ESAI Status Register (SAISR) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-34
6.3.6.1 SAISR Serial Input Flag 0 (IF0) - Bit 0 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-35
6.3.6.2 SAISR Serial Input Flag 1 (IF1) - Bit 1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-35
6.3.6.3 SAISR Serial Input Flag 2 (IF2) - Bit 2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-35
6.3.6.4 SAISR Reserved Bits - Bits 3-5, 11-12, 18-23 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-35
6.3.6.5 SAISR Receive Frame Sync Flag (RFS) - Bit 6. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-36
6.3.6.6 SAISR Receiver Overrun Error Flag (ROE) - Bit 7 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-36
6.3.6.7 SAISR Receive Data Register Full (RDF) - Bit 8 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-36
6.3.6.8 SAISR Receive Even-Data Register Full (REDF) - Bit 9 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-36
6.3.6.9 SAISR Receive Odd-Data Register Full (RODF) - Bit 10 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-36
6.3.6.10 SAISR Transmit Frame Sync Flag (TFS) - Bit 13 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-37
6.3.6.11 SAISR Transmit Underrun Error Flag (TUE) - Bit 14 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-37
6.3.6.12 SAISR Transmit Data Register Empty (TDE) - Bit 15 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-37
6.3.6.13 SAISR Transmit Even-Data Register Empty (TEDE) - Bit 16 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-37
6.3.6.14 SAISR Transmit Odd-Data Register Empty (TODE) - Bit 17 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-38
6.3.7 ESAI Receive Shift Registers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-41
6.3.8 ESAI Receive Data Registers (RX3, RX2, RX1, RX0) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-41
6.3.9 ESAI Transmit Shift Registers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-41
6.3.10 ESAI Transmit Data Registers (TX5, TX4, TX3, TX2,TX1,TX0) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-41
6.3.11 ESAI Time Slot Register (TSR) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-41
6.3.12 Transmit Slot Mask Registers (TSMA, TSMB) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-41
6.3.13 Receive Slot Mask Registers (RSMA, RSMB) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-43
6.4 Operating Modes. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-44
6.4.1 ESAI After Reset . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-44
6.4.2 ESAI Initialization . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-44
6.4.3 ESAI Interrupt Requests . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-45
6.4.4 Operating Modes – Normal, Network, and On-Demand . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-46
6.4.4.1 Normal/Network/On-Demand Mode Selection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-46
6.4.4.2 Synchronous/Asynchronous Operating Modes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-46
6.4.4.3 Frame Sync Selection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-47
6.4.4.4 Shift Direction Selection. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-47
6.4.5 Serial I/O Flags . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-48
6.5 GPIO - Pins and Registers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-48
6.5.1 Port C Control Register (PCRC). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-48
6.5.2 Port C Direction Register (PRRC) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-49
6.5.3 Port C Data register (PDRC) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-49
6.6 ESAI Initialization Examples . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-50
6.6.1 Initializing the ESAI Using Individual Reset . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-50
BookTitle, Rev. #
Freescale Semiconductor vii
Page 8

6.6.2 Initializing Just the ESAI Transmitter Section . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-51
6.6.3 Initializing Just the ESAI Receiver Section . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-51
7 Serial Host Interface
7.1 Introduction. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-1
7.2 Serial Host Interface Internal Architecture. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-2
7.3 SHI Clock Generator . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-3
7.4 Serial Host Interface Programming Model. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-3
7.4.1 SHI Input/Output Shift Register (IOSR)—Host Side. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-5
7.4.2 SHI Host Transmit Data Register (HTX)—DSP Side . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-6
7.4.3 SHI Host Receive Data FIFO (HRX)—DSP Side . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-6
7.4.4 SHI Slave Address Register (HSAR)—DSP Side . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-6
7.4.4.1 HSAR Reserved Bits—Bits 17–0,19 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-7
7.4.4.2 HSAR I2C Slave Address (HA[6:3], HA1)—Bits 23–20,18 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-7
7.4.5 SHI Clock Control Register (HCKR)—DSP Side . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-7
7.4.5.1 Clock Phase and Polarity (CPHA and CPOL)—Bits 1–0 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-7
7.4.5.2 HCKR Prescaler Rate Select (HRS)—Bit 2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-9
7.4.5.3 HCKR Divider Modulus Select (HDM[7:0])—Bits 10–3 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-9
7.4.5.4 HCKR Reserved Bits—Bits 23–14, 11. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-9
7.4.5.5 HCKR Filter Mode (HFM[1:0]) — Bits 13–12 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-9
7.4.6 SHI Control/Status Register (HCSR)—DSP Side . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-10
7.4.6.1 HCSR Host Enable (HEN)—Bit 0 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-10
7.4.6.1.1 SHI Individual Reset. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-11
7.4.6.2 HCSR I2C/SPI Selection (HI2C)—Bit 1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-11
7.4.6.3 HCSR Serial Host Interface Mode (HM[1:0])—Bits 3–2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-11
7.4.6.4 HCSR I2C Clock Freeze (HCKFR) - Bit 4. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-11
7.4.6.5 HCSR Reserved Bits—Bits 23, 18 and 16 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-12
7.4.6.6 HCSR FIFO-Enable Control (HFIFO)—Bit 5 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-12
7.4.6.7 HCSR Master Mode (HMST)—Bit 6. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-12
7.4.6.8 HCSR Host-Request Enable (HRQE[1:0])—Bits 8–7 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-12
7.4.6.9 HCSR Idle (HIDLE)—Bit 9 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-13
7.4.6.10 HCSR Bus-Error Interrupt Enable (HBIE)—Bit 10 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-13
7.4.6.11 HCSR Transmit-Interrupt Enable (HTIE)—Bit 11 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-14
7.4.6.12 HCSR Receive Interrupt Enable (HRIE[1:0])—Bits 13–12. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-14
7.4.6.13 HCSR Host Transmit Underrun Error (HTUE)—Bit 14 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-15
7.4.6.14 HCSR Host Transmit Data Empty (HTDE)—Bit 15 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-15
7.4.6.15 Host Receive FIFO Not Empty (HRNE)—Bit 17 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-15
7.4.6.16 Host Receive FIFO Full (HRFF)—Bit 19 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-16
7.4.6.17 Host Receive Overrun Error (HROE)—Bit 20. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-16
7.4.6.18 Host Bus Error (HBER)—Bit 21 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-16
7.4.6.19 HCSR Host Busy (HBUSY)—Bit 22 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-16
7.5 SPI Bus Characteristics. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-16
7.6 I
7.6.1 Overview. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-17
2
C Bus Characteristics. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-17
BookTitle, Rev. #
viii Freescale Semiconductor
Page 9

7.6.2 I2C Data Transfer Formats . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-19
7.7 SHI Programming Considerations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-20
7.7.1 SPI Slave Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-20
7.7.2 SPI Master Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-21
2
7.7.3 I
7.7.3.1 Receive Data in I
C Slave Mode. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-21
2
C Slave Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-22
7.7.3.2 Transmit Data In I2C Slave Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-23
7.7.4 I2C Master Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-23
7.7.4.1 Receive Data in I2C Master Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-24
7.7.4.2 Transmit Data In I2C Master Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-25
7.7.5 SHI Operation During DSP Stop . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-25
Appendix A Bootstrap ROM
A.1 DSP56364 Bootstrap Program . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .A-1
Appendix B BDSL File
B.1 BSDL FILE. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . B-1
Appendix C Programmer’s Reference
C.1 Introduction. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C-1
C.1.1 Peripheral Addresses. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C-1
C.1.2 Interrupt Addresses . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C-1
C.1.3 Interrupt Priorities. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C-1
C.2 Programming Sheets . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C-8
BookTitle, Rev. #
Freescale Semiconductor ix
Page 10

BookTitle, Rev. #
x Freescale Semiconductor
Page 11

List of Figures
Figure 1-1 DSP56364 Block Diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-2
Figure 2-1 Signals Identified by Functional Group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-2
Figure 3-1 Memory Maps for MS=0, SC=0 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-6
Figure 3-2 Memory Maps for MS=1, SC=0 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-6
Figure 3-3 Memory Maps for MS=0, SC=1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-7
Figure 3-4 Memory Maps for MS=1, SC=1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-7
Figure 4-1 Operating Mode Register (OMR) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-2
Figure 4-2 Interrupt Priority Register P . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-6
Figure 4-3 Interrupt Priority Register C . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-6
Figure 5-1 GPIO Port B Control Register (PCRB) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-1
Figure 5-2 GPIO Port B Direction Register (PRRB) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-2
Figure 5-3 GPIO Port B Data Register (PDRB) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-2
Figure 6-1 ESAI Block Diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-2
Figure 6-2 TCCR Register . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-8
Figure 6-3 ESAI Clock Generator Functional Block Diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-9
Figure 6-4 ESAI Frame Sync Generator Functional Block Diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-11
Figure 6-5 TCR Register . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-13
Figure 6-6 Normal and Network Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-17
Figure 6-7 Frame Length Selection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-20
Figure 6-8 RCCR Register . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-23
Figure 6-9 RCR Register . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-27
Figure 6-10 SAICR Register . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-32
Figure 6-11 SAICR SYN Bit Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-34
Figure 6-12 SAISR Register . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-35
Figure 6-13 ESAI Data Path Programming Model ([R/T]SHFD=0) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-39
Figure 6-14 ESAI Data Path Programming Model ([R/T]SHFD=1) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-40
Figure 6-15 TSMA Register . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-42
Figure 6-16 TSMB Register . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-42
Figure 6-17 RSMA Register . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-43
Figure 6-18 RSMB Register . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-43
Figure 6-19 PCRC Register . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-49
Figure 6-20 PRRC Register . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-49
Figure 6-21 PDRC Register . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-50
Figure 7-1 Serial Host Interface Block Diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-2
Figure 7-2 SHI Clock Generator . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-3
Figure 7-3 SHI Programming Model—Host Side . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-3
Figure 7-4 SHI Programming Model—DSP Side . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-4
Figure 7-5 SHI I/O Shift Register (IOSR) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-6
Figure 7-6 SPI Data-To-Clock Timing Diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-8
Figure 7-7 I2C Bit Transfer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-17
Figure 7-8 I2C Start and Stop Events . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-18
Figure 7-9 Acknowledgment on the I
Figure 7-10 I
2
C Bus Protocol For Host Write Cycle . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-19
Figure 7-11 I2C Bus Protocol For Host Read Cycle . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-19
Figure C-1 Status Register (SR). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C-9
2
C Bus . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-18
DSP56364 24-Bit Digital Signal Processor Users Manual, Rev. 2
Freescale Semiconductor xi
Page 12

Figure C-2 Operating Mode Register (OMR) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C-10
Figure C-3 Interrupt Priority Register-Core (IPR-C). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C-11
Figure C-4 Interrupt Priority Register- Peripherals (IPR-P) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C-12
Figure C-5 Phase Lock Loop Control Register (PCTL) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C-13
Figure C-6 SHI Slave Address (HSAR) and Clock Control Register (HCKR) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C-14
Figure C-7 SHI Host Transmit Data Register (HTX) and Host Receive Data Register (HRX) (FIFO)
C-15
Figure C-8 SHI Host Control/Status Register (HCSR) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C-16
Figure C-9 ESAI Transmit Clock Control Register (TCCR). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C-17
Figure C-10 ESAI Transmit Clock Control Register (TCR) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C-18
Figure C-11 ESAI Receive Clock Control Register (RCCR) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C-19
Figure C-12 ESAI Receive Clock Control Register (RCR). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C-20
Figure C-13 ESAI Common Control Register (SAICR) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C-21
Figure C-14 ESAI Status Register (SAISR) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C-22
Figure C-15 Port B Registers (PCRB, PRRB, PDRB). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C-23
Figure C-16 Port C Registers (PCRC, PRRC, PDRC). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C-24
DSP56364 24-Bit Digital Signal Processor Users Manual, Rev. 2
xii Freescale Semiconductor
Page 13

List of Tables
Table 2-1 DSP56364 Functional Signal Groupings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-1
Table 2-2 Power Inputs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-3
Table 2-3 Grounds . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-3
Table 2-4 Clock and PLL Signals . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-4
Table 2-5 External Address Bus Signals . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-4
Table 2-6 External Data Bus Signals . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-5
Table 2-7 External Bus Control Signals . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-5
Table 2-8 Interrupt and Mode Control . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-7
Table 2-9 Serial Host Interface Signals . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-8
Table 2-10 Enhanced Serial Audio Interface Signals . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-10
Table 2-11 JTAG/OnCE Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-13
Table 2-12 GPIO Signals . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-14
Table 3-1 Memory Space Configuration Bit Settings for the DSP56364 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-3
Table 3-2 Internal Memory Configurations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-4
Table 3-3 On-chip RAM Memory Locations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-4
Table 3-4 On-chip ROM Memory Locations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-4
Table 4-1 DSP56364 Operating Modes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-3
Table 4-2 Interrupt Priority Level Bits . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-5
Table 4-3 DMA Request Sources . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-7
Table 4-4 Identification Register Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-8
Table 4-5 JTAG Identification Register Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-8
Table 4-6 DSP56364 BSR Bit Definition . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-9
Table 5-1 GPIO Pin Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-3
Table 6-1 Receiver Clock Sources (asynchronous mode only) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-5
Table 6-2 Transmitter Clock Sources . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-6
Table 6-3 Transmitter High Frequency Clock Divider . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-11
Table 6-4 Transmit Network Mode Selection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-16
Table 6-5 ESAI Transmit Slot and Word Length Selection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-18
Table 6-6 Receiver High Frequency Clock Divider . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-24
Table 6-7 SCKR Pin Definition Table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-25
Table 6-8 FSR Pin Definition Table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-26
Table 6-9 HCKR Pin Definition Table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-26
Table 6-10 ESAI Receive Network Mode Selection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-29
Table 6-11 ESAI Receive Slot and Word Length Selection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-29
Table 6-12 PCRC and PRRC Bits Functionality . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-49
Table 7-1 SHI Interrupt Vectors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-5
Table 7-2 SHI Internal Interrupt Priorities . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-5
Table 7-3 SHI Noise Reduction Filter Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-10
Table 7-4 SHI Data Size . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-11
Table 7-5 HREQ Function In SHI Slave Modes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-12
Table 7-6 HCSR Receive Interrupt Enable Bits . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-14
Table C-1 Internal I/O Memory Map . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C-1
Table C-2 DSP56364 Interrupt Vectors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C-5
Table C-3 Interrupt Sources Priorities Within an IP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C-6
DSP56364 24-Bit Digital Signal Processor Users Manual, Rev. 2
Freescale Semiconductor xiii
Page 14

DSP56364 24-Bit Digital Signal Processor Users Manual, Rev. 2
xiv Freescale Semiconductor
Page 15

Preface
This manual contains the following sections and appendices.
SECTION 1—DSP56364 OVERVIEW
• Provides a brief description of the DSP56364, including a features list and block diagram. Lists
related documentation needed to use this chip and describes the organization of this manual.
SECTION 2—SIGNAL/CONNECTION DESCRIPTIONS
• Describes the signals on the DSP56364 pins and how these signals are grouped into interfaces.
SECTION 3—MEMORY CONFIGURATION
• Describes the DSP56364 memory spaces, RAM and ROM configuration, memory configurations
and their bit settings, and memory maps.
SECTION 4—CORE CONFIGURATION
• Describes the registers used to configure the DSP56300 core when programming the DSP56364,
in particular the interrupt vector locations and the operation of the interrupt priority registers.
Explains the operating modes and how they affect the processor’s program and data memories.
SECTION 5—GENERAL PURPOSE INPUT/OUTPUT (GPIO)
• Describes the DSP56364 GPIO capability and the programming model for the GPIO signals
(operation, registers, and control).
SECTION 6—ENHANCED SERIAL AUDIO INTERFACE (ESAI)
• Describes the full-duplex serial port for serial communication with a variety of serial devices.
SECTION 7—SERIAL HOST INTERFACE (SHI)
• Describes the serial input/output interface providing a path for communication and
program/coefficient data transfers between the DSP and an external host processor. The SHI can
also communicate with other serial peripheral devices.
APPENDIX A—BOOTSTRAP PROGRAM
• Lists the bootstrap code used for the DSP56364.
APPENDIX B—BSDL LISTING
• Provides the BSDL listing for the DSP56364.
APPENDIX C—PROGRAMMING REFERENCE
• Lists peripheral addresses, interrupt addresses, and interrupt priorities for the DSP56364. Contains
programming sheets listing the contents of the major DSP56364 registers for programmer
reference.
DSP56364 24-Bit Digital Signal Processor Users Manual, Rev. 2
Freescale Semiconductor xv
Page 16
Manual Conventions
The following conventions are used in this manual:
• Bits within registers are always listed from most significant bit (MSB) to least significant bit
(LSB).
• When several related bits are discussed, they are referenced as AA[n:m], where n>m. For purposes
of description, the bits are presented as if they are contiguous within a register. However, this is not
always the case. Refer to the programming model diagrams or to the programmer’s sheets to see
the exact location of bits within a register.
• When a bit is described as “set”, its value is 1. When a bit is described as “cleared”, its value is 0.
• The word “assert” means that a high true (active high) signal is pulled high to VCC or that a low
true (active low) signal is pulled low to ground. The word “deassert” means that a high true signal
is pulled low to ground or that a low true signal is pulled high to VCC.
Signal/Symbol Logic State Signal State Voltage
1
PIN
PIN False Deasserted V
PIN True Asserted V
PIN False Deasserted Ground
1
PIN is a generic term for any pin on the chip.
2
Ground is an acceptable low voltage level. See the appropriate data sheet for the range of
acceptable low voltage levels (typically a TTL logic low).
3
VCC is an acceptable high voltage level. See the appropriate data sheet for the range of acceptable
high voltage levels (typically a TTL logic high).
High True/Low True Signal Conventions
True Asserted Ground
CC
CC
2
3
• Pins or signals that are asserted low (made active when pulled to ground)
— In text, have an overbar (e.g., RESET is asserted low).
— In code examples, have a tilde in front of their names. In example below, line 3 refers to the
SS0 pin (shown as ~SS0).
• Sets of pins or signals are indicated by the first and last pins or signals in the set (e.g., HA1–HA8).
• Code examples are displayed in a monospaced font, as shown below:
.
BFSET #$0007,X:PCC; Configure: line 1
; MISO0, MOSI0, SCK0 for SPI master line 2
; ~SS0 as PC3 for GPIO line 3
Example Sample Code Listing
• Hex values are indicated with a dollar sign ($) preceding the hex value, as follows: $FFFFFF is the
X memory address for the core interrupt priority register (IPR-C).
• The word “reset” is used in four different contexts in this manual:
— the reset signal, written as “RESET,”
DSP56364 24-Bit Digital Signal Processor Users Manual, Rev. 2
xvi Freescale Semiconductor
Page 17

— the reset instruction, written as “RESET,”
— the reset operating state, written as “Reset,” and
— the reset function, written as “reset.”
DSP56364 24-Bit Digital Signal Processor Users Manual, Rev. 2
Freescale Semiconductor xvii
Page 18

DSP56364 24-Bit Digital Signal Processor Users Manual, Rev. 2
xviii Freescale Semiconductor
Page 19

1 Overview
1.1 Introduction
The DSP56364 24-Bit Digital Signal Processor, a new audio digital signal processor based on the 24-bit
DSP56300 architecture, is targeted to applications that require digital audio signal processing such as
sound field processing, acoustic equalization and other digital audio algorithms.
The DSP56364 supports digital audio applications requiring sound field processing, acoustic equalization,
and other digital audio algorithms. The DSP56364 uses the high performance, single-clock-per-cycle
DSP56300 core family of programmable CMOS digital signal processors (DSPs) combined with the audio
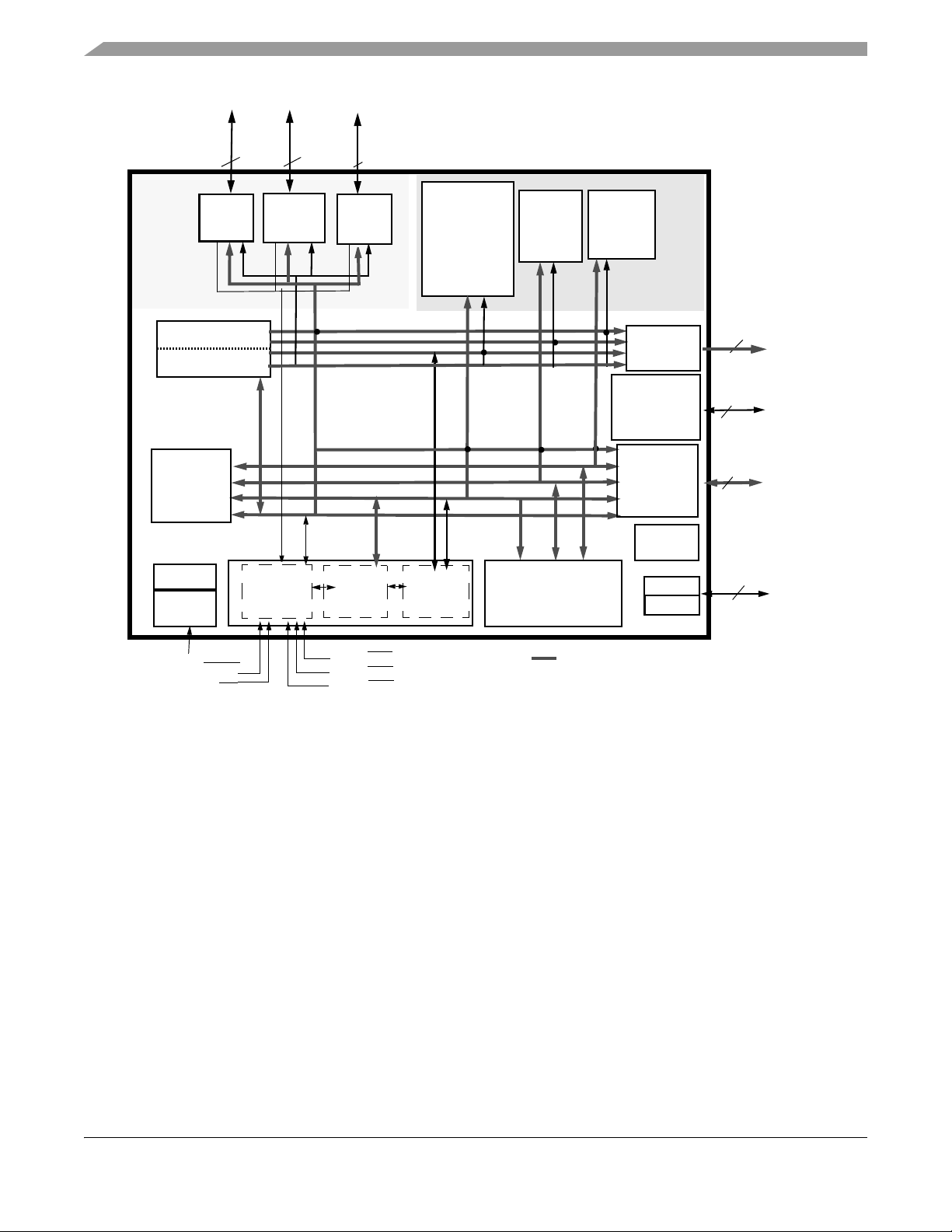
signal processing capability of the Freescale Symphony™ DSP family, as shown in Figure 1-1. This
design provides a two-fold performance increase over Freescale’s popular Symphony family of DSPs
while retaining code compatibility. Significant architectural enhancements include a barrel shifter, 24-bit
addressing, instruction cache, and direct memory access (DMA).
This document is intended to be used with the following Freescale publications:
• DSP56300 24-Bit Digital Signal Processor Family Manual, Freescale publication DSP56300FM.
• DSP56364 24-Bit Digital Signal Processor Technical Data Sheet, Freescale publication
DSP56364.
The DSP56300 24-Bit Digital Signal Processor Family Manual, Freescale publication DSP56300FM
provides a description of the components of the DSP56300 modular chassis which is common to all
DSP56300 family processors and includes a detailed description of the instruction set. This document
provides a detailed description of the core configuration, memory, and peripherals that are specific to the
DSP56364. The electrical specifications, timings and packaging information can be found in the
DSP56364 Technical Data Sheet.
DSP56364 24-Bit Digital Signal Processor Users Manual, Rev. 2
Freescale Semiconductor 1-1
Page 20
Features
PERIPHERAL
EXPANSION
AREA
GENERATION UNIT
INTERNAL
DATA BU S
SWITCH
CLOCK
GEN
GPIO
ADDRESS
SIX CHANNELS
DMA UNIT
PLL
4
PROGRAM
INTERRUPT
CONT
ESAI
12
PIO_EB
5
SHI
24-BIT
DSP56300
CORE
PROGRAM
DECODE
CONT
PROGRAM
RAM
0.5K x 24
PR O GR A M R O M
8K x 24
Bootstrap ROM
192 x 24
PROGRAM
ADDRESS
GEN
X
MEMORY
RAM
1K X 24
XM_EB
YA B
PM_EB
XAB
PA B
DAB
DDB
YDB
XDB
PDB
GDB
DATA A L U
24 X 24+56
TWO 56-BIT ACCUMULATORS
56-BIT MAC
→
BARREL SHIFTER
Y MEMORY
RAM
1.5K X 24
MEMORY
EXPANSION
AREA
YM_EB
ADDRESS BUS
DRAM & SRAM
INTERFACE
EXTERNAL
EXTERNAL
SWITCH
BUS
DATA BUS
SWITCH
POWER
MGMT
JTAG
OnCE™
ADDRESS
18
CONTROL
6
8
4
DATA
EXTAL
RESET
PINIT/NMI
1.2 Features
• DSP56300 modular chassis
— 100 Million Instructions Per Second (MIPS) with an 100 MHz clock at 3.3V.
— Object Code Compatible with the 56K core.
— Data ALU with a 24 × 24 bit multiplier-accumulator and a 56-bit barrel shifter. 16-bit
arithmetic support.
— Program Control with position independent code support and instruction cache support.
— Six-channel DMA controller.
— PLL based clocking with a wide range of frequency multiplications (1 to 4096), predivider
factors (1 to 16) and power saving clock divider (2i: i = 0 to 7). Reduces clock noise.
— Internal address tracing support and OnCE‰ for Hardware/Software debugging.
— JTAG port.
MODA/IRQA
MODB/IRQB
MODD/IRQD
24 BITS BUS
Figure 1-1 DSP56364 Block Diagram
DSP56364 24-Bit Digital Signal Processor Users Manual, Rev. 2
1-2 Freescale Semiconductor
Page 21

Audio Processor Architecture
— Very low-power CMOS design, fully static design with operating frequencies down to DC.
— STOP and WAIT low-power standby modes.
• On-chip Memory Configuration
— 1.5K × 24 Bit Y-Data RAM.
—1K × 24 Bit X-Data RAM.
—8K × 24 Bit Program ROM.
— 0.5K × 24 Bit Program RAM and 192 × 24 Bit Bootstrap ROM.
— 0.75K × 24 Bit from Y Data RAM can be switched to Program RAM resulting in up to
1.25K × 24 Bit of Program RAM.
• Off-chip memory expansion
— External Memory Expansion Port with 8-bit data bus.
— Off-chip expansion up to 2 × 16M x 8-bit word of Data memory when using DRAM.
— Off-chip expansion up to 2 × 256K x 8-bit word of Data memory when using SRAM.
— Simultaneous glueless interface to SRAM and DRAM.
• Peripheral modules
— Serial Audio Interface (ESAI): up to 4 receivers and up to 6 transmitters, master or slave. I2S,
Sony, AC97, network and other programmable protocols. Unused pins of ESAI may be used
as GPIO lines.
— Serial Host Interface (SHI): SPI and I2C protocols, multi master capability, 10-word receive
FIFO, support for 8, 16 and 24-bit words.
— Four dedicated GPIO lines.
• 100-pin plastic TQFP package.
1.3 Audio Processor Architecture
This section defines the DSP56364 audio processor architecture. The audio processor is composed of the
following units:
• The DSP56300 core is composed of the Data ALU, Address Generation Unit, Program Controller,
Instruction-Cache Controller, DMA Controller, PLL-based clock oscillator, Memory Module
Interface, Peripheral Module Interface and the On-Chip Emulator (OnCE). The DSP56300 core is
described in the document DSP56300 24-Bit Digital Signal Processor Family Manual, Motorola
publication DSP56300FM.
• Memory modules.
• Peripheral modules. The SHI, ESAI and GPIO peripheral are described in this document.
See Figure 1-1 for the block diagram of the DSP56364.
DSP56364 24-Bit Digital Signal Processor Users Manual, Rev. 2
Freescale Semiconductor 1-3
Page 22

Core Description
1.4 Core Description
The DSP56364 uses the DSP56300 core, a high-performance, single clock cycle per instruction engine that
provides up to twice the performance of Freescale's popular DSP56000 core family while retaining code
compatibility with it.
The DSP56300 core provides the following functional blocks:
• Data arithmetic logic unit (Data ALU)
• Address generation unit (AGU)
• Program control unit (PCU)
• Bus interface unit (BIU)
• DMA controller (with six channels)
• Instruction cache controller
• PLL-based clock oscillator
• OnCE module
• JTAG TAP
• Memory
The DSP56300 core family offers a new level of performance in speed and power, provided by its rich
instruction set and low power dissipation, thus enabling a new generation of wireless, telecommunications,
and multimedia products. Significant architectural enhancements to the DSP56300 core family include a
barrel shifter, 24-bit addressing, an instruction cache, and direct memory access (DMA).
Core features are described fully in the DSP56300 Family Manual. Pinout, memory, and peripheral
features are described in this manual.
1.5 DSP56300 Core Functional Blocks
1.5.1 Data ALU
The Data ALU performs all the arithmetic and logical operations on data operands in the DSP56300 core.
The components of the Data ALU are as follows:
• Fully pipelined 24-bit × 24-bit parallel multiplier-accumulator (MAC)
• Bit field unit, comprising a 56-bit parallel barrel shifter (fast shift and normalization; bit stream
generation and parsing)
• Conditional ALU instructions
• 24-bit or 16-bit arithmetic support under software control
• Four 24-bit input general purpose registers: X1, X0, Y1, and Y0
• Six Data ALU registers (A2, A1, A0, B2, B1, and B0) that are concatenated into two general
purpose, 56-bit accumulators (A and B), accumulator shifters
• Two data bus shifter/limiter circuits
DSP56364 24-Bit Digital Signal Processor Users Manual, Rev. 2
1-4 Freescale Semiconductor
Page 23

DSP56300 Core Functional Blocks
1.5.1.1 Data ALU Registers
The Data ALU registers can be read or written over the X memory data bus (XDB) and the Y memory data
bus (YDB) as 24- or 48-bit operands (or as 16- or 32-bit operands in 16-bit arithmetic mode). The source
operands for the Data ALU, which can be 24, 48, or 56 bits (16, 32, or 40 bits in 16-bit arithmetic mode),
always originate from Data ALU registers. The results of all Data ALU operations are stored in an
accumulator.
All the Data ALU operations are performed in two clock cycles in pipeline fashion so that a new
instruction can be initiated in every clock, yielding an effective execution rate of one instruction per clock
cycle. The destination of every arithmetic operation can be used as a source operand for the immediately
following arithmetic operation without a time penalty (in other words, without a pipeline stall).
1.5.1.2 Multiplier-Accumulator (MAC)
The MAC unit comprises the main arithmetic processing unit of the DSP56300 core and performs all of
the calculations on data operands. In the case of arithmetic instructions, the unit accepts as many as three
input operands and outputs one 56-bit result of the following form- Extension:Most Significant
Product:Least Significant Product (EXT:MSP:LSP).
The multiplier executes 24-bit × 24-bit, parallel, fractional multiplies, between two’s-complement signed,
unsigned, or mixed operands. The 48-bit product is right-justified and added to the 56-bit contents of either
the A or B accumulator. A 56-bit result can be stored as a 24-bit operand. The LSP can either be truncated
or rounded into the MSP. Rounding is performed if specified.
1.5.2 Address Generation Unit (AGU)
The AGU performs the effective address calculations using integer arithmetic necessary to address data
operands in memory and contains the registers used to generate the addresses. It implements four types of
arithmetic: linear, modulo, multiple wrap-around modulo, and reverse-carry. The AGU operates in parallel
with other chip resources to minimize address-generation overhead.
The AGU is divided into two halves, each with its own Address ALU. Each Address ALU has four sets of
register triplets, and each register triplet is composed of an address register, an offset register, and a
modifier register. The two Address ALUs are identical. Each contains a 24-bit full adder (called an offset
adder).
A second full adder (called a modulo adder) adds the summed result of the first full adder to a modulo
value that is stored in its respective modifier register. A third full adder (called a reverse-carry adder) is
also provided.
The offset adder and the reverse-carry adder are in parallel and share common inputs. The only difference
between them is that the carry propagates in opposite directions. Test logic determines which of the three
summed results of the full adders is output.
Each Address ALU can update one address register from its respective address register file during one
instruction cycle. The contents of the associated modifier register specifies the type of arithmetic to be used
in the address register update calculation. The modifier value is decoded in the Address ALU.
DSP56364 24-Bit Digital Signal Processor Users Manual, Rev. 2
Freescale Semiconductor 1-5
Page 24

DSP56300 Core Functional Blocks
1.5.3 Program Control Unit (PCU)
The PCU performs instruction prefetch, instruction decoding, hardware DO loop control, and exception
processing. The PCU implements a seven-stage pipeline and controls the different processing states of the
DSP56300 core. The PCU consists of the following three hardware blocks:
• Program decode controller (PDC)
• Program address generator (PAG)
• Program interrupt controller (PIC)
The PDC decodes the 24-bit instruction loaded into the instruction latch and generates all signals necessary
for pipeline control. The PAG contains all the hardware needed for program address generation, system
stack, and loop control. The PIC arbitrates among all interrupt requests (internal interrupts, as well as the
five external requests: IRQA, IRQB, IRQD, and NMI), and generates the appropriate interrupt vector
address.
PCU features include the following:
• Position independent code support
• Addressing modes optimized for DSP applications (including immediate offsets)
• On-chip instruction cache controller
• On-chip memory-expandable hardware stack
• Nested hardware DO loops
• Fast auto-return interrupts
The PCU implements its functions using the following registers:
• PC—program counter register
• SR—Status register
• LA—loop address register
• LC—loop counter register
• VBA—vector base address register
• SZ—stack size register
• SP—stack pointer
• OMR—operating mode register
• SC—stack counter register
The PCU also includes a hardware system stack (SS).
1.5.4 Internal Buses
To provide data exchange between blocks, the following buses are implemented:
• Peripheral input/output expansion bus (PIO_EB) to peripherals
• Program memory expansion bus (PM_EB) to program memory
• X memory expansion bus (XM_EB) to X memory
DSP56364 24-Bit Digital Signal Processor Users Manual, Rev. 2
1-6 Freescale Semiconductor
Page 25

DSP56300 Core Functional Blocks
• Y memory expansion bus (YM_EB) to Y memory
• Global data bus (GDB) between registers in the DMA, AGU, OnCE, PLL, BIU, and PCU as well
as the memory-mapped registers in the peripherals
• DMA data bus (DDB) for carrying DMA data between memories and/or peripherals
• DMA address bus (DAB) for carrying DMA addresses to memories and peripherals
• Program Data Bus (PDB) for carrying program data throughout the core
• X memory Data Bus (XDB) for carrying X data throughout the core
• Y memory Data Bus (YDB) for carrying Y data throughout the core
• Program address bus (PAB) for carrying program memory addresses throughout the core
• X memory address bus (XAB) for carrying X memory addresses throughout the core
• Y memory address bus (YAB) for carrying Y memory addresses throughout the core
All internal buses on the DSP56300 family members are 24-bit buses. See Figure 1-1, DSP56364 block
diagram.
1.5.5 Direct Memory Access (DMA)
The DMA block has the following features:
• Six DMA channels supporting internal and external accesses
• One-, two-, and three-dimensional transfers (including circular buffering)
• End-of-block-transfer interrupts
• Triggering from interrupt lines and all peripherals
1.5.6 PLL-based Clock Oscillator
The clock generator in the DSP56300 core is composed of two main blocks: the PLL, which performs
clock input division, frequency multiplication, and skew elimination; and the clock generator (CLKGEN),
which performs low-power division and clock pulse generation. PLL-based clocking:
• Allows change of low-power divide factor (DF) without loss of lock
• Provides output clock with skew elimination
• Provides a wide range of frequency multiplications (1 to 4096), predivider factors (1 to 16), and a
power-saving clock divider (2
The PLL allows the processor to operate at a high internal clock frequency using a low frequency clock
input. This feature offers two immediate benefits:
• A lower frequency clock input reduces the overall electromagnetic interference generated by a
system.
• The ability to oscillate at different frequencies reduces costs by eliminating the need to add
additional oscillators to a system.
i
: i = 0 to 7) to reduce clock noise
DSP56364 24-Bit Digital Signal Processor Users Manual, Rev. 2
Freescale Semiconductor 1-7
Page 26

Data and Program memory
1.5.7 JTAG TAP and OnCE Module
The DSP56300 core provides a dedicated user-accessible TAP fully compatible with the IEEE 1149.1
Standard Test Access Port and Boundary Scan Architecture. Problems associated with testing high-density
circuit boards led to developing this standard under the sponsorship of the Test Technology Committee of
IEEE and JTAG. The DSP56300 core implementation supports circuit-board test strategies based on this
standard.
The test logic includes a TAP consisting of four dedicated signals, a 16-state controller, and three test data
registers. A boundary scan register links all device signals into a single shift register. The test logic,
implemented utilizing static logic design, is independent of the device system logic.
The OnCE module provides a nonintrusive means of interacting with the DSP56300 core and its
peripherals so a user can examine registers, memory, or on-chip peripherals. This facilitates hardware and
software development on the DSP56300 core processor. OnCE module functions are provided through the
JTAG TAP signals.
1.6 Data and Program memory
The on-chip memory configuration of the DSP56364 is affected by the state of the MS (Memory Switch)
control bit in the OMR register, and by the SC bit in the Status Register. Refer to Section 3, "Memory
Configuration".
1.6.1 Reserved Memory Spaces
The reserved memory spaces should not be accessed by the user. They are reserved for future expansion.
1.6.2 Program ROM Area Reserved for Freescale Use
The last 128 words ($FF2F80-$FF2FFF) of the Program ROM are reserved for Freescale use. This
memory area is reserved for use as expansion area for the bootstrap ROM as well as for testing purposes.
Customer code should not use this area. The contents of this Program ROM segment is defined by the
Bootstrap ROM source code in Appendix A, "Bootstrap ROM".
1.6.3 Bootstrap ROM
The 192-word Bootstrap ROM occupies locations $FF0000-$FF00BF. The bootstrap ROM is
factory-programmed to perform the bootstrap operation following hardware reset. The contents of the
Bootstrap ROM are defined by the Bootstrap ROM source code in Appendix A, "Bootstrap ROM".
1.6.4 Dynamic Memory Configuration Switching
The internal memory configuration is altered by re-mapping RAM modules from Y data memory into
program memory space and vice-versa. The contents of the switched RAM modules are preserved.
The memory can be dynamically switched from one configuration to another by changing the MS bit in
OMR. The address ranges that are directly affected by the switch operation are specified in Tab le 3-1 The
DSP56364 24-Bit Digital Signal Processor Users Manual, Rev. 2
1-8 Freescale Semiconductor
Page 27

Internal I/O Memory Map
memory switch can be accomplished provided that the affected address ranges are not being accessed
during the instruction cycle in which the switch operation takes place. Accordingly, the following
condition must be observed for trouble-free dynamic switching:
NOTE
No accesses (including instruction fetches) to or from the affected address
ranges in program and data memories are allowed during the switch cycle.
NOTE
The switch cycle actually occurs 3 instruction cycles after the instruction
that modifies the MS bit.
Any sequence that complies with the switch condition is valid. For example, if the program flow executes
in the address range that is not affected by the switch, the switch condition can be met very easily. In this
case a switch can be accomplished by just changing the MS bit in OMR in the regular program flow,
assuming no accesses to the affected address ranges of the data memory occur up to 3 instructions after the
instruction that changes the OMR bit. Special care should be taken in relation to the interrupt vector
routines since an interrupt could cause the DSP to fetch instructions out of sequence and might violate the
switch condition.
Special attention should be given when running a memory switch routine using the OnCE™ port. Running
the switch routine in Trace mode, for example, can cause the switch to complete after the MS bit change
while the DSP is in Debug mode. As a result, subsequent instructions might be fetched according to the
new memory configuration (after the switch), and thus might execute improperly.
1.6.5 External Memory Support
The DSP56364 does not support the SSRAM memory type. It does support SRAM and DRAM as
indicated in the DSP56300 24-Bit Digital Signal Processor Family Manual, Motorola publication
DSP56300FM. Note that the DSP56364 has only an 8-bit data bus. This means that no instruction fetches
from external memory are possible, and care should be taken to ensure that no program memory instruction
fetch access occurs in the external memory space. The DMA may be used to automatically pack and
unpack 24-bit data into the 8-bit wide external memory, during DMA data transfers.
Also, care should be taken when accessing external memory to ensure that the necessary address lines are
19
available. For example, when using glueless SRAM interfacing, it is possible to directly address 2
memory locations (512K) when using the 18 address lines and the two programmable address attribute
lines. Using DRAM access mode, the full 16M addressing range may be used.
1.7 Internal I/O Memory Map
The DSP56364 on-chip peripheral modules have their register files programmed to the addresses in the
internal X-I/O memory range (the top 128 locations of the X data memory space). See Section 3, “Memory
Configuration.”
DSP56364 24-Bit Digital Signal Processor Users Manual, Rev. 2
Freescale Semiconductor 1-9
Page 28

Status Register (SR)
1.8 Status Register (SR)
Refer to the DSP56300 24-Bit Digital Signal Processor Family Manual, Freescale publication
DSP56300FM/AD for a description of the Status Register bits.
The Cache Enable bit (Bit 19) in the Status Register must be kept cleared since the DSP56364 does not
have an on-chip instruction cache.
DSP56364 24-Bit Digital Signal Processor Users Manual, Rev. 2
1-10 Freescale Semiconductor
Page 29
2 Signal/Connection Descriptions
2.1 Signal Groupings
The input and output signals of the DSP56364 are organized into functional groups, which are listed in
Table 2-1 and illustrated in Figure 2-1.
The DSP56364 is operated from a 3.3 V supply; however, some of the inputs can tolerate 5 V. A special
notice for this feature is added to the signal descriptions of those inputs.
Table 2-1 DSP56364 Functional Signal Groupings
Functional Group
Power (V
Ground (GND) 14 Ta bl e 2 - 3
Clock and PLL 3 Tab l e 2-4
Address bus
Data bus 8 Tab l e 2-6
Bus control 6 Tab l e 2-7
Interrupt and mode control 4 Tab l e 2-8
General Purpose I/O Port B
SHI 5 Tab l e 2-9
ESAI Port C
JTAG/OnCE Port 4 Ta b le 2 - 1 1
1
Port A is the external memory interface port, including the external address bus, data bus, and control signals.
2
Port B signals are the GPIO signals.
3
Port C signals are the ESAI port signals multiplexed with the GPIO signals.
)18Ta bl e 2 - 2
CC
1
Por t A
2
3
Number of
Signals
18 Ta bl e 2 - 5
4 Ta b le 2 - 1 2
12 Ta ble 2 - 1 0
Detailed
Description
DSP56364 24-Bit Digital Signal Processor Users Manual, Rev. 2
Freescale Semiconductor 2-1
Page 30
Signal Groupings
PORT A ADDRESS BUS
A0-A17
VCCA (4)
GNDA (4)
PORT A DATA BUS
D0-D7
VCCD (1)
GNDD (1)
PORT A BUS CONTROL
AA0-AA1/RAS0-RAS1
RESERVED (4)
CAS
RD
WR
TA
VCCC (1)
GNDC (1)
INTERRUPT AND
MODE CONTROL
MODA/IRQA
MODB/IRQB
MODD/IRQD
RESET
PLL AND CLOCK
PINIT/NMI
DSP56364
Port B
Port C
OnCE ON-CHIP EMULATION/
TDI
TCK
TDO
TMS
JTAG PORT
GPIO
PB0-PB3
SERIAL AUDIO INTERFACE (ESAI)
SCKT [PC3]
FST [PC4]
HCKT [PC5]
SCKR [PC0]
FSR [PC1]
HCKR [PC2]
SDO0 [PC11]
SDO1 [PC10]
SDO2/SDI3 [PC9]
SDO3/SDI2 [PC8]
SDO4/SDI1 [PC7]
SDO5/SDI0 [PC6]
VCCSS (3)
GNDS (3)
PCAP
VCCP
GNDP
EXTAL
SERIAL HOST INTERFACE (SHI)
MOSI/HA0
SS/HA2
MISO/SDA
SCK/SCL
HREQ
QUIET POWER
VCCHQ (4)
VCCLQ (4)
GNDQ (4)
Figure 2-1 Signals Identified by Functional Group
DSP56364 24-Bit Digital Signal Processor Users Manual, Rev. 2
2-2 Freescale Semiconductor
Page 31

2.2 Power
Table 2-2 Power Inputs
Power Name Description
Power
V
CCP
PLL Power—V
CCP
should be provided with an extremely low impedance path to the V
(4) Quiet Core (Low) Power—V
V
CCQL
be tied externally to all other chip power inputs. The user must provide adequate external decoupling
capacitors. There are four V
(4) Quiet External (High) Power—V
V
CCQH
externally to all other chip power inputs. The user must provide adequate decoupling capacitors. There
are four V
V
(4) Address Bus Power—V
CCA
CCQH
inputs.
I/O drivers. This input must be tied externally to all other chip power inputs. The user must provide
adequate external decoupling capacitors. There are four V
(1) Data Bus Power—V
V
CCD
tied externally to all other chip power inputs. The user must provide adequate external decoupling
capacitors. There is one V
(1) Bus Control Power—V
V
CCC
externally to all other chip power inputs. The user must provide adequate external decoupling capacitors.
There is one V
V
(3) SHI and ESAI —V
CCS
CCC
other chip power inputs
three V
CCS
inputs.
is VCC dedicated for PLL use. The voltage should be well-regulated and the input
power rail. There is one V
CC
is an isolated power for the internal processing logic. This input must
CCQL
inputs.
CCQL
is a quiet power source for I/O lines. This input must be tied
CCQH
is an isolated power for sections of the address bus
CCA
inputs.
CCA
is an isolated power for sections of the data bus I/O drivers. This input must be
CCD
inputs.
CCD
is an isolated power for the bus control I/O drivers. This input must be tied
CCC
CCP
input.
inputs.
is an isolated power for the SHI and ESAI. This input must be tied externally to all
CCS
. The user must provide adequate external decoupling capacitors. There are
L
2.3 Ground
Table 2-3 Grounds
Ground Name Description
GND
P
GNDQ (4) Quiet Ground—GNDQ is an isolated ground for the internal processing logic. This connection must be
GND
A (4)
(1) Data Bus Ground—GNDD is an isolated ground for sections of the data bus
GND
D
Freescale Semiconductor 2-3
PLL Ground—GNDP is ground-dedicated for PLL use. The connection should be provided with an
extremely low-impedance path to ground. V
located as close as possible to the chip package. There is one GND
should be bypassed to GNDP by a 0.47 µF capacitor
CCP
connection.
P
tied externally to all other chip ground connections. The user must provide adequate external decoupling
capacitors. There are four GND
connections.
Q
Address Bus Ground—GNDA is an isolated ground for sections of the address bus I/O drivers. This
connection must be tied externally to all other chip ground connections. The user must provide adequate
external decoupling capacitors. There are four GND
connections.
A
I/O drivers. This connection must be tied externally to all other chip ground connections. The user must
provide adequate external decoupling capacitors. There is one GND
connections.
D
DSP56364 24-Bit Digital Signal Processor Users Manual, Rev. 2
Page 32

Clock and PLL
Table 2-3 Grounds (continued)
Ground Name Description
GNDC (1) Bus Control Ground—GNDC is an isolated ground for the bus control I/O drivers. This connection must
be tied externally to all other chip ground connections. The user must provide adequate external
decoupling capacitors. There is one GND
(3) SHI and ESAI —GNDS is an isolated ground for the SHI and ESAI. This connection must be tied
GND
S
externally to all other chip ground connections. The user must provide adequate external decoupling
capacitors. There are three GND
connections.
S
connections.
C
2.4 Clock and PLL
Table 2-4 Clock and PLL Signals
Signal
Name
EXTAL Input Input External Clock Input—An external clock source must be connected to EXTAL in
PCAP Input Input PLL Capacitor—PCAP is an input connecting an off-chip capacitor to the PLL
PINIT/NMI Input Input PLL Initial/Nonmaskable Interrupt—During assertion of RESET, the value of
Signal
Typ e
State during
Reset
Signal Description
order to supply the clock to the internal clock generator and PLL.
filter. Connect one capacitor terminal to PCAP and the other terminal to V
If the PLL is not used, PCAP may be tied to V
PINIT/NMI
determining whether the PLL is enabled or disabled. After RESET
and during normal instruction processing, the PINIT/NMI
a negative-edge-triggered nonmaskable interrupt (NMI) request internally
synchronized to internal system clock.
This input is 5 V tolerant.
is written into the PLL Enable (PEN) bit of the PLL control register,
, GND, or left floating.
CC
Schmitt-trigger input is
de assertion
CCP
2.5 External Memory Expansion Port (Port A)
When the DSP56364 enters a low-power standby mode (stop or wait), it tri-states the relevant port A
signals: D0–D7, AA0, AA1, RD, WR, CAS.
.
2.5.1 External Address Bus
Table 2-5 External Address Bus Signals
Signal
Name
A0–A17 Output Keeper active Address Bus—A0–A17 are active-high outputs that specify the address for
2-4 Freescale Semiconductor
Signal
Typ e
State during
Reset
external program and data memory accesses. Otherwise, the signals are kept to
their previous values by internal weak keepers. To minimize power dissipation,
A0–A17 do not change state when external memory spaces are not being
accessed.
DSP56364 24-Bit Digital Signal Processor Users Manual, Rev. 2
Signal Description
Page 33

2.5.2 External Data Bus
Table 2-6 External Data Bus Signals
External Memory Expansion Port (Port A)
Signal
Name
D0–D7 Input/Output Tri-stated Data Bus—D0–D7 are active-high, bidirectional input/outputs that provide the
Signal Type
State during
Reset
Signal Description
bidirectional data bus for external program and data memory accesses. D0–D7
are tri-stated during hardware reset and when the DSP is in the stop or wait
low-power standby mode.
2.5.3 External Bus Control
Table 2-7 External Bus Control Signals
Signal
Name
AA0–AA1/R
AS0–RAS1
CAS Output Tri-stated Column Address Strobe— CAS
Signal
Typ e
Output Tri-stated Address Attribute or Row Address Strobe—When defined as AA, these
State during
Reset
Signal Description
signals can be used as chip selects or additional address lines. When defined as
RAS
, these signals can be used as RAS for DRAM interface. These signals are
tri-statable outputs with programmable polarity. These signals are tri-stated
during hardware reset and when the DSP is in the stop or wait low-power standby
mode.
is an active-low output used by DRAM to strobe
the column address. This signal is tri-stated during hardware reset and when the
DSP is in the stop or wait low-power standby mode.
DSP56364 24-Bit Digital Signal Processor Users Manual, Rev. 2
Freescale Semiconductor 2-5
Page 34

Interrupt and Mode Control
Table 2-7 External Bus Control Signals (continued)
Signal
Name
RD Output Tri-stated Read Enable—RD is an active-low output that is asserted to read external
WR Output Tri-stated Write Enable— WR
TA Input Ignored Input Transfer Acknowledge—If there is no external bus activity, the TA
Signal
Typ e
State during
Reset
Signal Description
memory on the data bus. This signal is tri-stated during hardware reset and when
the DSP is in the stop or wait low-power standby mode.
is an active-low output that is asserted to write external
memory on the data bus. This signal is tri-stated during hardware reset and when
the DSP is in the stop or wait low-power standby mode.
input is
ignored. The TA
extend an external bus cycle indefinitely. Any number of wait states
(1, 2. . .infinity) may be added to the wait states inserted by the BCR by keeping
TA
deasserted. In typical operation, TA is deasserted at the start of a bus cycle,
is asserted to enable completion of the bus cycle, and is deasserted before the
next bus cycle. The current bus cycle completes one clock period after TA
asserted synchronous to the internal system clock. The number of wait states is
determined by the TA
longer. The BCR can be used to set the minimum number of wait states in
external bus cycles.
In order to use the TA
wait state. A zero wait state access cannot be extended by TA
otherwise improper operation may result. TA
asynchronously, depending on the setting of the TAS bit in the operating mode
register (OMR).
TA
functionality may not be used while performing DRAM type accesses,
otherwise improper operation may result.
input is a data transfer acknowledge (DTACK) function that can
input or by the bus control register (BCR), whichever is
functionality, the BCR must be programmed to at least one
deassertion,
can operate synchronously or
is
2.6 Interrupt and Mode Control
The interrupt and mode control signals select the chip’s operating mode as it comes out of hardware reset.
After RESET
2-6 Freescale Semiconductor
is deasserted, these inputs are hardware interrupt request lines.
DSP56364 24-Bit Digital Signal Processor Users Manual, Rev. 2
Page 35

Table 2-8 Interrupt and Mode Control
Serial Host Interface
Signal Name
MODA/IRQA
MODB/IRQB
Signal
Typ e
Input Input Mode Select A/External Interrupt Request A—MODA/IRQA is an active-low
Input Input Mode Select B/External Interrupt Request B—MODB/IRQB is an active-low
State
during
Reset
Signal Description
Schmitt-trigger input, internally synchronized to the internal system clock.
MODA/IRQA
becomes a level-sensitive or negative-edge-triggered, maskable interrupt request
input during normal instruction processing. MODA, MODB, and MODD select one
of 8 initial chip operating modes, latched into the OMR when the RESET
deasserted. If IRQA
multiple processors can be re synchronized using the WAIT instruction and
asserting IRQA
and IRQA
This input is 5 V tolerant.
Schmitt-trigger input, internally synchronized to the internal system clock.
MODB/IRQB
becomes a level-sensitive or negative-edge-triggered, maskable interrupt request
input during normal instruction processing. MODA, MODB, and MODD select one
of 8 initial chip operating modes, latched into OMR when the RESET
deasserted. If IRQB
multiple processors can be re-synchronized using the WAIT instruction and
asserting IRQB
This input is 5 V tolerant.
selects the initial chip operating mode during hardware reset and
signal is
is asserted synchronous to the internal system clock,
to exit the wait state. If the processor is in the stop standby state
is asserted, the processor will exit the stop state.
selects the initial chip operating mode during hardware reset and
signal is
is asserted synchronous to the internal system clock,
to exit the wait state.
MODD/IRQD
RESET Input Input Reset—RESET
Input Input Mode Select D/External Interrupt Request D—MODD/IRQD is an active-low
Schmitt-trigger input, internally synchronized to the internal system clock.
MODD/IRQD
becomes a level-sensitive or negative-edge-triggered, maskable interrupt request
input during normal instruction processing. MODA, MODB, and MODD select one
of 8 initial chip operating modes, latched into OMR when the RESET
deasserted. If IRQD
multiple processors can be re synchronized using the WAIT instruction and
asserting IRQD
This input is 5 V tolerant.
is placed in the reset state and the internal phase generator is reset. The
Schmitt-trigger input allows a slowly rising input (such as a capacitor charging) to
reset the chip reliably. When the RESET
operating mode is latched from the MODA, MODB, and MODD inputs. The
RESET
supplied before deassertion of RESET
This input is 5 V tolerant.
selects the initial chip operating mode during hardware reset and
signal is
is asserted synchronous to the internal system clock,
to exit the wait state.
is an active-low, Schmitt-trigger input. When asserted, the chip
signal is deasserted, the initial chip
signal must be asserted during power up. A stable EXTAL signal must be
.
2.7 Serial Host Interface
The SHI has five I/O signals that can be configured to allow the SHI to operate in either SPI or I2C mode
DSP56364 24-Bit Digital Signal Processor Users Manual, Rev. 2
Freescale Semiconductor 2-7
Page 36

Serial Host Interface
.
Signal
Name
Signal
Typ e
SCK Input or
output
SCL Input or
output
MISO Input or
output
Table 2-9 Serial Host Interface Signals
State
during
Reset
Tri-stated SPI Serial Clock—The SCK signal is an output when the SPI is configured as a master
and a Schmitt-trigger input when the SPI is configured as a slave. When the SPI is
configured as a master, the SCK signal is derived from the internal SHI clock generator.
When the SPI is configured as a slave, the SCK signal is an input, and the clock signal
from the external master synchronizes the data transfer. The SCK signal is ignored by
the SPI if it is defined as a slave and the slave select (SS
the master and slave SPI devices, data is shifted on one edge of the SCK signal and is
sampled on the opposite edge where data is stable. Edge polarity is determined by the
SPI transfer protocol.
2
I
C Serial Clock—SCL carries the clock for I2C bus transactions in the I2C mode. SCL
is a Schmitt-trigger input when configured as a slave and an open-drain output when
configured as a master. SCL should be connected to V
This signal is tri-stated during hardware, software, and individual reset. Thus, there is
no need for an external pull-up in this state.
This input is 5 V tolerant.
Tri-stated SPI Master-In-Slave-Out—When the SPI is configured as a master, MISO is the
master data input line. The MISO signal is used in conjunction with the MOSI signal for
transmitting and receiving serial data. This signal is a Schmitt-trigger input when
configured for the SPI Master mode, an output when configured for the SPI Slave
mode, and tri-stated if configured for the SPI Slave mode when SS
external pull-up resistor is not required for SPI operation.
Signal Description
) signal is not asserted. In both
through a pull-up resistor.
CC
is deasserted. An
SDA Input or
open-drain
output
2
I
C Data and Acknowledge—In I2C mode, SDA is a Schmitt-trigger input when
receiving and an open-drain output when transmitting. SDA should be connected to
V
through a pull-up resistor. SDA carries the data for I2C transactions. The data in
CC
SDA must be stable during the high period of SCL. The data in SDA is only allowed to
change when SCL is low. When the bus is free, SDA is high. The SDA line is only
allowed to change during the time SCL is high in the case of start and stop events. A
high-to-low transition of the SDA line while SCL is high is a unique situation, and is
defined as the start event. A low-to-high transition of SDA while SCL is high is a unique
situation defined as the stop event.
This signal is tri-stated during hardware, software, and individual reset. Thus, there is
no need for an external pull-up in this state.
This input is 5 V tolerant.
DSP56364 24-Bit Digital Signal Processor Users Manual, Rev. 2
2-8 Freescale Semiconductor
Page 37

Table 2-9 Serial Host Interface Signals (continued)
Serial Host Interface
Signal
Name
Signal
Typ e
MOSI Input or
output
State
during
Signal Description
Reset
Tri-stated SPI Master-Out-Slave-In—When the SPI is configured as a master, MOSI is the
master data output line. The MOSI signal is used in conjunction with the MISO signal
for transmitting and receiving serial data. MOSI is the slave data input line when the
SPI is configured as a slave. This signal is a Schmitt-trigger input when configured for
the SPI Slave mode.
HA0 Input I
2
C Slave Address 0—This signal uses a Schmitt-trigger input when configured for the
2
I
C mode. When configured for I2C slave mode, the HA0 signal is used to form the
slave device address. HA0 is ignored when configured for the I
2
C master mode.
This signal is tri-stated during hardware, software, and individual reset. Thus, there is
no need for an external pull-up in this state.
This input is 5 V tolerant.
SS Input Input SPI Slave Select—This signal is an active low Schmitt-trigger input when configured
for the SPI mode. When configured for the SPI Slave mode, this signal is used to enable
the SPI slave for transfer. When configured for the SPI master mode, this signal should
be kept deasserted (pulled high). If it is asserted while configured as SPI master, a bus
error condition is flagged. If SS
is deasserted, the SHI ignores SCK clocks and keeps
the MISO output signal in the high-impedance state.
HA2 I
2
C Slave Address 2—This signal uses a Schmitt-trigger input when configured for the
2
I
C mode. When configured for the I2C Slave mode, the HA2 signal is used to form the
slave device address. HA2 is ignored in the I
2
C master mode.
HREQ Input or
Output
This signal is tri-stated during hardware, software, and individual reset. Thus, there is
no need for an external pull-up in this state.
This input is 5 V tolerant.
Tri-stated Host Request—This signal is an active low Schmitt-trigger input when configured for
the master mode but an active low output when configured for the slave mode.
When configured for the slave mode, HREQ
is asserted to indicate that the SHI is ready
for the next data word transfer and deasserted at the first clock pulse of the new data
word transfer. When configured for the master mode, HREQ
is an input. When asserted
by the external slave device, it will trigger the start of the data word transfer by the
master. After finishing the data word transfer, the master will await the next assertion of
HREQ
to proceed to the next transfer.
This signal is tri-stated during hardware, software, personal reset, or when the
HREQ1–HREQ0 bits in the HCSR are cleared. There is no need for external pull-up in
this state.
This input is 5 V tolerant.
DSP56364 24-Bit Digital Signal Processor Users Manual, Rev. 2
Freescale Semiconductor 2-9
Page 38

Enhanced Serial Audio Interface
2.8 Enhanced Serial Audio Interface
Table 2-10 Enhanced Serial Audio Interface Signals
Signal
Name
HCKR Input or output GPIO
PC2 Input, output, or
HCKT Input or output GPIO
PC5 Input, output, or
Signal Type
disconnected
disconnected
State during
Reset
disconnected
disconnected
Signal Description
High Frequency Clock for Receiver—When programmed as an input, this
signal provides a high frequency clock source for the ESAI receiver as an
alternate to the DSP core clock. When programmed as an output, this signal
can serve as a high-frequency sample clock (e.g., for external digital to
analog converters [DACs]) or as an additional system clock.
Port C 2—When the ESAI is configured as GPIO, this signal is individually
programmable as input, output, or internally disconnected.
The default state after reset is GPIO disconnected.
This input is 5 V tolerant.
High Frequency Clock for Transmitter—When programmed as an input,
this signal provides a high frequency clock source for the ESAI transmitter
as an alternate to the DSP core clock. When programmed as an output, this
signal can serve as a high frequency sample clock (e.g., for external DACs)
or as an additional system clock.
Port C 5—When the ESAI is configured as GPIO, this signal is individually
programmable as input, output, or internally disconnected.
The default state after reset is GPIO disconnected.
This input is 5 V tolerant.
FSR Input or output GPIO
disconnected
PC1 Input, output, or
disconnected
Frame Sync for Receiver—This is the receiver frame sync input/output
signal. In the asynchronous mode (SYN=0), the FSR pin operates as the
frame sync input or output used by all the enabled receivers. In the
synchronous mode (SYN=1), it operates as either the serial flag 1 pin
(TEBE=0), or as the transmitter external buffer enable control (TEBE=1,
RFSD=1).
When this pin is configured as serial flag pin, its direction is determined by
the RFSD bit in the RCCR register. When configured as the output flag OF1,
this pin will reflect the value of the OF1 bit in the SAICR register, and the
data in the OF1 bit will show up at the pin synchronized to the frame sync in
normal mode or the slot in network mode. When configured as the input flag
IF1, the data value at the pin will be stored in the IF1 bit in the SAISR
register, synchronized by the frame sync in normal mode or the slot in
network mode.
Port C 1—When the ESAI is configured as GPIO, this signal is individually
programmable as input, output, or internally disconnected.
The default state after reset is GPIO disconnected.
This input is 5 V tolerant.
DSP56364 24-Bit Digital Signal Processor Users Manual, Rev. 2
2-10 Freescale Semiconductor
Page 39

Enhanced Serial Audio Interface
Table 2-10 Enhanced Serial Audio Interface Signals (continued)
Signal
Name
FST Input or output GPIO
PC4 Input, output, or
SCKR Input or output GPIO
Signal Type
disconnected
State during
Reset
disconnected
disconnected
Signal Description
Frame Sync for Transmitter—This is the transmitter frame sync
input/output signal. For synchronous mode, this signal is the frame sync for
both transmitters and receivers. For asynchronous mode, FST is the frame
sync for the transmitters only. The direction is determined by the transmitter
frame sync direction (TFSD) bit in the ESAI transmit clock control register
(TCCR).
Port C 4—When the ESAI is configured as GPIO, this signal is individually
programmable as input, output, or internally disconnected.
The default state after reset is GPIO disconnected.
This input is 5 V tolerant.
Receiver Serial Clock—SCKR provides the receiver serial bit clock for the
ESAI. The SCKR operates as a clock input or output used by all the enabled
receivers in the asynchronous mode (SYN=0), or as serial flag 0 pin in the
synchronous mode (SYN=1).
When this pin is configured as serial flag pin, its direction is determined by
the RCKD bit in the RCCR register. When configured as the output flag OF0,
this pin will reflect the value of the OF0 bit in the SAICR register, and the
data in the OF0 bit will show up at the pin synchronized to the frame sync in
normal mode or the slot in network mode. When configured as the input flag
IF0, the data value at the pin will be stored in the IF0 bit in the SAISR
register, synchronized by the frame sync in normal mode or the slot in
network mode.
PC0 Input, output, or
disconnected
SCKT Input or output GPIO
disconnected
PC3 Input, output, or
disconnected
DSP56364 24-Bit Digital Signal Processor Users Manual, Rev. 2
Port C 0—When the ESAI is configured as GPIO, this signal is individually
programmable as input, output, or internally disconnected.
The default state after reset is GPIO disconnected.
This input is 5 V tolerant.
Transmitter Serial Clock—This signal provides the serial bit rate clock for
the ESAI. SCKT is a clock input or output used by all enabled transmitters
and receivers in synchronous mode, or by all enabled transmitters in
asynchronous mode.
Port C 3—When the ESAI is configured as GPIO, this signal is individually
programmable as input, output, or internally disconnected.
The default state after reset is GPIO disconnected.
This input is 5 V tolerant.
Freescale Semiconductor 2-11
Page 40

Enhanced Serial Audio Interface
Table 2-10 Enhanced Serial Audio Interface Signals (continued)
Signal
Name
SDO5 Output GPIO
SDI0 Input Serial Data Input 0—When programmed as a receiver, SDI0 is used to
PC6 Input, output, or
SDO4 Output GPIO
SDI1 Input Serial Data Input 1—When programmed as a receiver, SDI1 is used to
PC7 Input, output, or
Signal Type
disconnected
disconnected
State during
Reset
disconnected
disconnected
Signal Description
Serial Data Output 5—When programmed as a transmitter, SDO5 is used
to transmit data from the TX5 serial transmit shift register.
receive serial data into the RX0 serial receive shift register.
Port C 6—When the ESAI is configured as GPIO, this signal is individually
programmable as input, output, or internally disconnected.
The default state after reset is GPIO disconnected.
This input is 5 V tolerant.
Serial Data Output 4—When programmed as a transmitter, SDO4 is used
to transmit data from the TX4 serial transmit shift register.
receive serial data into the RX1 serial receive shift register.
Port C 7—When the ESAI is configured as GPIO, this signal is individually
programmable as input, output, or internally disconnected.
The default state after reset is GPIO disconnected.
This input is 5 V tolerant.
SDO3 Output GPIO
disconnected
SDI2 Input Serial Data Input 2—When programmed as a receiver, SDI2 is used to
PC8 Input, output, or
disconnected
SDO2 Output GPIO
disconnected
SDI3 Input Serial Data Input 3—When programmed as a receiver, SDI3 is used to
PC9 Input, output, or
disconnected
Serial Data Output 3—When programmed as a transmitter, SDO3 is used
to transmit data from the TX3 serial transmit shift register.
receive serial data into the RX2 serial receive shift register.
Port C 8—When the ESAI is configured as GPIO, this signal is individually
programmable as input, output, or internally disconnected.
The default state after reset is GPIO disconnected.
This input is 5 V tolerant.
Serial Data Output 2—When programmed as a transmitter, SDO2 is used
to transmit data from the TX2 serial transmit shift register
receive serial data into the RX3 serial receive shift register.
Port C 9—When the ESAI is configured as GPIO, this signal is individually
programmable as input, output, or internally disconnected.
The default state after reset is GPIO disconnected.
This input is 5 V tolerant.
DSP56364 24-Bit Digital Signal Processor Users Manual, Rev. 2
2-12 Freescale Semiconductor
Page 41

Table 2-10 Enhanced Serial Audio Interface Signals (continued)
JTAG/OnCE Interface
Signal
Name
SDO1 Output GPIO
PC10 Input, output, or
SDO0 Output GPIO
PC11 Input, output, or
Signal Type
disconnected
disconnected
State during
Reset
disconnected
disconnected
2.9 JTAG/OnCE Interface
Table 2-11 JTAG/OnCE Interface
Signal Description
Serial Data Output 1—SDO1 is used to transmit data from the TX1 serial
transmit shift register.
Port C 10—When the ESAI is configured as GPIO, this signal is individually
programmable as input, output, or internally disconnected.
The default state after reset is GPIO disconnected.
This input is 5 V tolerant.
Serial Data Output 0—SDO0 is used to transmit data from the TX0 serial
transmit shift register.
Port C 11—When the ESAI is configured as GPIO, this signal is individually
programmable as input, output, or internally disconnected.
The default state after reset is GPIO disconnected.
This input is 5 V tolerant.
Signal
Name
TCK Input Input Test Clock—TCK is a test clock input signal used to synchronize the JTAG test
TDI Input Input Test Data Input—TDI is a test data serial input signal used for test instructions and
TDO Output Tri-stated Test Data Output—TDO is a test data serial output signal used for test instructions
TMS Input Input Test Mode Select—TMS is an input signal used to sequence the test controller’s
Signal
Type
State
during
Reset
Signal Description
logic. It has an internal pull-up resistor.
This input is 5 V tolerant.
data. TDI is sampled on the rising edge of TCK and has an internal pull-up resistor.
This input is 5 V tolerant.
and data. TDO is tri-statable and is actively driven in the shift-IR and shift-DR
controller states. TDO changes on the falling edge of TCK.
state machine. TMS is sampled on the rising edge of TCK and has an internal
pull-up resistor.
This input is 5 V tolerant.
DSP56364 24-Bit Digital Signal Processor Users Manual, Rev. 2
Freescale Semiconductor 2-13
Page 42

GPIO Signals
2.10 GPIO Signals
Table 2-12 GPIO Signals
Signal
Name
GPIO0-
GPIO3
Signal Type
Input, output or
disconnected
State during
Reset
disconnected GPIO0-3- The General Purpose I/O pins are used for control and handshake
functions between the DSP and external circuitry. Each Port B GPIO pin may
be individually programmed as an input, output or disconnected
Signal Description
DSP56364 24-Bit Digital Signal Processor Users Manual, Rev. 2
2-14 Freescale Semiconductor
Page 43

3 Memory Configuration
3.1 Memory Spaces
The DSP56364 provides the following three independent memory spaces:
•Program
• X data
• Y data
Each memory space uses (by default) 18 external address lines for addressing, allowing access to 256K of
external memory when using the SRAM operating mode, and 16 M when using the DRAM operating
mode. Program and data word length is 24 bits, and internal memory uses 24-bit addressing.
The DSP56364 provides a 16-bit compatibility mode that effectively uses 16-bit addressing for each
memory space, allowing access to 64K of memory for each. This mode puts zeros in the most significant
byte of the usual (24-bit) program and data word and ignores the zeroed byte, thus effectively using 16-bit
program and data words. The 16-bit Compatibility mode allows the DSP56364 to use 56000 object code
without change (thus minimizing system cost for applications that use the smaller address space). See the
DSP56300 Family Manual, Section 6.4, for further information.
3.1.1 Program Memory Space
Program memory space consists of the following:
• Internal program memory, consisting of program RAM, 0.5K by default, and program ROM, 8K
x 24-bit
• Bootstrap program ROM (192 x 24-bit)
3.1.1.1 Program RAM
On-chip program RAM occupies the lowest 0.5K (default) or 1.25K locations in the program memory
space (depending on the setting of the MS bit). The program RAM default organization is 2 banks of 256
24-bit words (0.5K). The upper 3 banks of Y data RAM can be configured as program RAM by setting the
MS bit.
3.1.1.2 Program ROM
The program ROM contains customer-supplied code. For further information on supplying code for a
customized DSP56364 program ROM, please contact your Freescale regional sales office.
The last 128 words ($FF2F80-$FF2FFF) of the program ROM are reserved for Freescale use. This
memory area is reserved for use as expansion area for the bootstrap ROM as well as for testing purposes.
DSP56364 24-Bit Digital Signal Processor Users Manual, Rev. 2
Freescale Semiconductor 3-1
Page 44

Memory Spaces
Customer code should not use this area. The contents of this program ROM segment is defined by the
bootstrap ROM source code in Appendix A, "Bootstrap ROM".
3.1.1.3 Bootstrap ROM
The bootstrap code is accessed at addresses $FF0000 to $FFF0BF (192 words) in program memory space.
The bootstrap ROM is factory-programmed to perform the bootstrap operation following hardware reset.
The bootstrap ROM can not be accessed in 16-bit address compatibility mode. See Appendix A for a
complete listing of the bootstrap code.
3.1.1.4 Reserved Program Memory Locations
Program memory space at locations $FF00C0 to $FF0FFF and $FF3000 to $FFFFFF is reserved and
should not be accessed.
3.1.2 Data Memory Spaces
Data memory space is divided into X data memory and Y data memory to match the natural partitioning
of DSP algorithms. The data memory partitioning allows the DSP56364 to feed two operands to the Data
ALU simultaneously, enabling it to perform a multiply-accumulate operation in one clock cycle.
X and Y data memory space are similar in structure and functionality, but there are two differences
between them. First, part of Y data RAM may be switched over to program RAM, while X data RAM is
fixed in size. Second, the upper 128 words of each space are reserved for different uses. The upper 128
words of X data memory are reserved for internal I/O. It is suggested that the programmer reserve the
upper 128 words of Y data memory for external I/O. (For further information, see Section 3.1.2.1, "X Data
Memory Space" and Section 3.1.2.3, "Y Data Memory Space")
X and Y data memory space each consist of the following:
• Internal data RAM memory (X data RAM (1K), and Y data RAM (default size is 1.5K, but 0.75K
of Y data RAM can be switched to program RAM)
• (Optionally) Off-chip memory expansion (up to 256K in the 24-bit address mode and 64K in the
16-bit address mode).
3.1.2.1 X Data Memory Space
The on-chip peripheral registers and some of the DSP56364 core registers occupy the top 128 locations of
X data memory ($FFFF80–$FFFFFF in the 24-bit address mode or $FF80–$FFFF in the 16-bit address
mode). This area is called X-I/O space, and it can be accessed by MOVE and MOVEP instructions and by
bit oriented instructions (BCHG, BCLR, BSET, BTST, BRCLR, BRSET, BSCLR, BSSET, JCLR, JSET,
JSCLR, and JSSET). For a listing of the contents of this area, see the programming sheets in Section C.2,
"Programming Sheets".
The reserved X memory space from $FF0000 to $FFEFFF should not be accessed.
DSP56364 24-Bit Digital Signal Processor Users Manual, Rev. 2
3-2 Freescale Semiconductor
Page 45

Memory Space Configuration
3.1.2.2 X Data RAM
The on-chip X data RAM consists of 24-bit wide, high-speed, internal static RAM occupying 1K locations
in the X memory space. The X data RAM organization is 4 banks of 256 24-bit words.
3.1.2.3 Y Data Memory Space
The off-chip peripheral registers should be mapped into the top 128 locations of Y data memory
($FFFF80–$FFFFFF in the 24-bit address mode or $FF80–$FFFF in the 16-bit address mode) to take
advantage of the move peripheral data (MOVEP) instruction and the bit oriented instructions (BCHG,
BCLR, BSET, BTST, BRCLR, BRSET, BSCLR, BSSET, JCLR, JSET, JSCLR, and JSSET).
The reserved Y memory space from $FF0000 to $FFEFFF should not be accessed.
3.1.2.4 Y Data RAM
The on-chip Y data RAM consists of 24-bit wide, high-speed, internal static RAM occupying 1.5K
(default) or 0.75K locations in the Y memory space. The size of the Y data RAM is dependent on the
setting of the MS bit (default: MS is cleared). The Y data RAM default organization is 6 banks of 256
24-bit words. Three banks of RAM may be switched to program RAM by setting the MS bit.
3.2 Memory Space Configuration
Memory space addressing is for 24-bit words by default. The DSP56364 switches to 16-bit address
compatibility mode by setting the 16-bit compatibility (SC) bit in the SR.
Table 3-1 Memory Space Configuration Bit Settings for the DSP56364
Bit Abbreviation Bit Name Bit Location
SC 16-bit Compatibility SR 13 16 M word address space
Cleared = 0 Effect
(Default)
(24-bit word)
Set = 1 Effect
64 K word address space
(16-bit word)
Accessible external memory in the 24-bit mode is limited to a maximum of 512K when using the SRAM
operating mode and to 16M when using the DRAM operating mode.
Memory maps for the different configurations are shown in Figure 3-1 to Figure 3-4.
3.3 Internal Memory Configuration
The following subsections discuss the internal memory configuration of the DSP56364. The size and
location configurations for RAM and ROM for the DSP56364 are given below.
DSP56364 24-Bit Digital Signal Processor Users Manual, Rev. 2
Freescale Semiconductor 3-3
Page 46

Internal Memory Configuration
Bit Settings Memory Sizes (24-bit words)
Table 3-2 Internal Memory Configurations
MS SC
0 0 0.5K 8K 192 1K 1.5K
1 0 1.25K 8K 192 1K 0.75K
0 1 0.5K n.a. n.a. 1K 1.5K
1 1 1.25K n.a. n.a. 1K 0.75K
Prog.
RAM
Prog.
ROM
Boot
ROM
X Data
RAM
Y Data
RAM
Memory maps for the different configurations are shown in Figure 3-1 to Figure 3-4.
3.3.1 RAM Locations
The actual memory locations for program RAM and Y data RAM in their own memory space are
determined by the MS bit. The memory location of X data RAM is independent of the MS bit. The
addresses of the different RAMs are listed in Table 3-3.
Table 3-3 On-chip RAM Memory Locations
Bit Settings RAM Memory Locations
MS SC Program RAM X Data RAM Y Data RAM
0 X $000000-$0001FF $000000-$0003FF $000000-$0005FF
1 X $000000-$0004FF $000000-$0003FF $000000-$0002FF
3.3.2 ROM Locations
The actual memory locations for ROMs in their own memory space are fixed, but when the SC bit is set
(i. e. the chip is in 16-bit mode), the program ROM and the bootstrap ROM are not accessible. ROM
addresses are listed in Table 3-4.
Table 3-4 On-chip ROM Memory Locations
Bit Settings ROM Memory Locations
MS SC Program ROM Boot ROM
X 0 $FF1000-$FF2FFF $FF0000-$FF00BF
X 1 no access no access
DSP56364 24-Bit Digital Signal Processor Users Manual, Rev. 2
3-4 Freescale Semiconductor
Page 47

Internal Memory Configuration
3.3.3 Dynamic Memory Configuration Switching
The internal memory configuration is altered by remapping RAM modules from Y data memory into
program memory space and vice-versa. The contents of the switched RAM modules are preserved.
The memory can be dynamically switched from one configuration to another by changing the MS bit in
OMR. The address ranges that are directly affected by the switch operation are specified in Table 3-3. The
memory switch can be accomplished provided that the affected address ranges are not being accessed
during the instruction cycle in which the switch operation takes place. For trouble-free dynamic switching,
no accesses (including instruction fetches) to or from the affected address ranges in program and data
memories are allowed during the switch cycle.
NOTE
The switch cycle actually occurs three instruction cycles after the
instruction that modifies the MS bit.
Any sequence that complies with the switch condition is valid. For example, if the program flow executes
in the address range that is not affected by the switch, the switch condition can be met very easily. In this
case a switch can be accomplished by just changing the MS bit in OMR in the regular program flow,
assuming no accesses to the affected address ranges of the data memory occur up to three instructions after
the instruction that changes the OMR bit. Special care should be taken in relation to the interrupt vector
routines since an interrupt could cause the DSP to fetch instructions out of sequence and might violate the
switch condition.
Special attention should be given when running a memory switch routine using the OnCE port. Running
the switch routine in trace mode, for example, can cause the switch to complete after the MS bit change
while the DSP is in debug mode. As a result, subsequent instructions might be fetched according to the
new memory configuration (after the switch), and thus might execute improperly.
DSP56364 24-Bit Digital Signal Processor Users Manual, Rev. 2
Freescale Semiconductor 3-5
Page 48

Memory Maps
3.4 Memory Maps
$FFFFFF
$FF3000
$FF1000
$FF00C0
$FF0000
$000200
$000000
PROGRAM
INTERNAL
RESERVED
8K INTERNAL
ROM
INTERNAL
RESERVED
BOOT ROM
EXTERNAL
0.5K INTERNAL
RAM
PROGRAM
X DATA
$FFFFFF
$FFFF80
$FFF000
$FF0000
$000400
$000000
INTERNAL I/O
(128 words)
EXTERNAL
INTERNAL
RESERVED
EXTERNAL
1K INTERNAL
RAM
Figure 3-1 Memory Maps for MS=0, SC=0
X DATA
$FFFFFF
$FFFF80
$FFF000
$FF0000
$000600
$000000
Y DATA
EXTERNAL I/O
(128 words)
EXTERNAL
INTERNAL
RESERVED
1.5K INTERNAL
Y DATA
EXTERNAL
RAM
$FFFFFF
$FF3000
$FF1000
$FF00C0
$FF0000
$000500
$000000
INTERNAL
RESERVED
8K INTERNAL
ROM
INTERNAL
RESERVED
BOOT ROM
EXTERNAL
1.25K INTERNAL
RAM
$FFFFFF
$FFFF80
$FFF000
$FF0000
$000400
$000000
INTERNAL I/O
(128 words)
EXTERNAL
INTERNAL
RESERVED
EXTERNAL
1K INTERNAL
RAM
Figure 3-2 Memory Maps for MS=1, SC=0
$FFFFFF
$FFFF80
$FFF000
$FF0000
$000300
$000000
EXTERNAL I/O
(128 words)
EXTERNAL
INTERNAL
RESERVED
EXTERNAL
0.75K INTERNAL
RAM
DSP56364 24-Bit Digital Signal Processor Users Manual, Rev. 2
3-6 Freescale Semiconductor
Page 49

Memory Maps
$FFFF
$0200
$0000
PROGRAM
EXTERNAL
0.5K INTERNAL
RAM
PROGRAM
X DATA
$FFFF
$FF80
$0400
$0000
INTERNAL I/O
(128 words)
EXTERNAL
1K INTERNAL
RAM
Figure 3-3 Memory Maps for MS=0, SC=1
X DATA
$FFFF
$FF80
$0600
$0000
Y DATA
EXTERNAL I/O
(128 words)
1.5K INTERNAL
Y DATA
EXTERNAL
RAM
$FFFF
$0500
$0000
EXTERNAL
1.25K INTERNAL
RAM
$FFFF
$FF80
$0400
$0000
INTERNAL I/O
(128 words)
EXTERNAL
1K INTERNAL
RAM
Figure 3-4 Memory Maps for MS=1, SC=1
$FFFF
$FF80
$0300
$0000
EXTERNAL I/O
(128 words)
EXTERNAL
0.75K INTERNAL
RAM
DSP56364 24-Bit Digital Signal Processor Users Manual, Rev. 2
Freescale Semiconductor 3-7
Page 50

External Memory Support
3.5 External Memory Support
The DSP56364 does not support the SSRAM memory type. It does support SRAM and DRAM as
indicated in the DSP56300 24-Bit Digital Signal Processor Family Manual, Freescale publication
DSP56300FM/AD. Note that the DSP56364 has only an 8-bit data bus. This means that no instruction
fetches from external memory are possible, and care should be taken to ensure that no program memory
instruction fetch access occurs in the external memory space. The DMA may be used to automatically pack
and unpack 24-bit data into the 8-bit wide external memory, during DMA data transfers.
Also, care should be taken when accessing external memory to ensure that the necessary address lines are
available. For example, when using glueless SRAM interfacing, it is possible to directly address 219
memory locations (512K) when using the 18 address lines and the two programmable address attribute
lines. Using DRAM access mode, the full 16M addressing range may be used.
3.6 Internal I/O Memory Map
The DSP56364 on-chip peripheral modules have their register files programmed to the addresses in the
internal X-I/O memory range (the top 128 locations of the X data memory space) as shown in Appendix
A, "Bootstrap ROM".
DSP56364 24-Bit Digital Signal Processor Users Manual, Rev. 2
3-8 Freescale Semiconductor
Page 51

4 Core Configuration
4.1 Introduction
This chapter contains DSP56300 core configuration information details specific to the DSP56364. These
include the following:
• Operating modes
• Bootstrap program
• Interrupt sources and priorities
• DMA request sources
•OMR
• PLL control register
• AA control registers
• JTAG BSR
For more information on specific registers or modules in the DSP56300 core, refer to the DSP56300
Family Manual (DSP56300FM).
4.2 Operating Mode Register (OMR)
The contents of the Operating Mode Register (OMR) are shown in Figure 4-1. Refer to the DSP56300
24-Bit Digital Signal Processor Family Manual, Freescale publication DSP56300FM for a description of
the OMR bits.
DSP56364 24-Bit Digital Signal Processor Users Manual, Rev. 2
Freescale Semiconductor 4-1
Page 52

Operating Mode Register (OMR)
SCS EOM COM
23222120191817161514131211109876543210
SD
SEN
SEN - Stack Extension Enable EBD - External Bus Disable
WRP - Extended Stack Wrap Flag TAS - TA Synchronize Select MD - Operating Mode D
WRP
EOV
EUN
XYS
APD
ATE - Address Tracing Enable MS - Memory Switch Mode
APD - Address Priority Disable SD - Stop Delay
ATE
TAS
CDP1:0
MS
EBD
MD
MC
MB
MA
EOV - Extended Stack Overflow
Flag
EUN - Extended Stack Underflow
Flag
XYS - Stack Extension Space
Select
- Reserved bit. Read as zero, should be written with zero for future compatibility
CDP1 - Core-Dma Priority 1 MB - Operating Mode B
CDP0 - Core-Dma Priority 0 MA - Operating Mode A
MC - Operating Mode C - Always
set.
Figure 4-1 Operating Mode Register (OMR)
4.2.1 Mode C (MC) - Bit 2
The Mode C (MC) bit is set during hardware reset and should be left set in the DSP56364.
4.2.2 Address Attribute Priority Disable (APD) - Bit 14
The Address Attribute Priority Disable (APD) bit is used to turn off the address attribute priority
mechanism. When this bit is set, more than one address attribute pin AA/RAS
asserted according to its AAR settings. The APD bit is cleared by hardware reset.
(1:0) may be simultaneously
4.2.3 Address Tracing Enable (ATE) - Bit 15
The Address Tracing Enable (ATE) bit is used to turn on Address Tracing (AT) Mode. When the AT Mode
is enabled, the DSP56300 Core reflects the addresses of internal fetches and program space moves
(MOVEM) to the Address Bus (A0-A17), if the Address Bus is not needed by the DSP56300 Core for
external accesses. The ATE bit is cleared on hardware reset.
DSP56364 24-Bit Digital Signal Processor Users Manual, Rev. 2
4-2 Freescale Semiconductor
Page 53

Operating Modes
4.3 Operating Modes
The operating modes are as shown in Table 4-1 The operating modes are latched from MODA, MODB
and MODD pins during reset. Each operating mode is briefly described below. The operation of all
bootstrap modes is defined by the Bootstrap ROM source code in Appendix A, "Bootstrap ROM".
Table 4-1 DSP56364 Operating Modes
Mode MOD D MOD B MOD A
$4 0 0 0 $FF0000 Jump to PROM starting address
$5 0 0 1 $FF0000 Bootstrap from byte-wide memory
$6 0 1 0 $FF0000 Reserved
$7 0 1 1 $FF0000 Reserved for Burn-in testing
$C 1 0 0 $FF0000 Reserved
$D 1 0 1 $FF0000 Bootstrap from SHI (slave SPI mode)
$E 1 1 0 $FF0000 Bootstrap from SHI (slave I
$F 1 1 1 $FF0000 Bootstrap from SHI (slave I2C mode, clock freeze
Reset
Vector
enabled)
disabled)
Description
2
C mode, clock freeze
Mode 4 The DSP starts fetching instructions from the starting address of the on-chip Program
ROM.
Mode 5 The bootstrap program loads instructions through Port A from external byte-wide memory
starting at address P:$D00000. The bootstrap code expects to read 3 bytes specifying the
number of program words, 3 bytes specifying the address to start loading the program
words and then 3 bytes for each program word to be loaded. The number of words, the
starting address and the program words are read least significant byte first followed by the
mid and then by the most significant byte. The program words will be stored in contiguous
PRAM memory locations starting at the specified starting address. After reading the
program words, program execution starts from the same address where loading started. The
SRAM memory access type is selected by the values in Address Attribute Register 1
(AAR1), with 31 wait states for each memory access. Address $D00000 is reflected as
address $00000 on Port A pins A0-A17.
Mode 6 Reserved.
Mode 7 Reserved for Burn-In testing.
Mode C Reserved.
Mode D In this mode, the internal PRAM is loaded from the Serial Host Interface (SHI). The SHI
operates in the SPI slave mode, with 24-bit word width.The bootstrap code expects to read
a 24-bit word specifying the number of program words, a 24-bit word specifying the
DSP56364 24-Bit Digital Signal Processor Users Manual, Rev. 2
Freescale Semiconductor 4-3
Page 54

Bootstrap Program
address to start loading the program words and then a 24-bit word for each program word
to be loaded. The program words will be stored in contiguous PRAM memory locations
starting at the specified starting address. After reading the program words, program
execution starts from the same address where loading started.
Mode E Same as mode 5, except the SHI interface operates in the I2C slave mode with clock freeze
enabled.
Mode F Same as mode 5, except the SHI interface operates in the I2C slave mode with clock freeze
disabled (compatible to DSP56000 family).
4.4 Bootstrap Program
The bootstrap program is factory-programmed in an internal 192 word by 24-bit bootstrap ROM located
in program memory space at locations $FF0000–$FF00BF. The bootstrap program can load any program
RAM segment from an external byte-wide EPROM or the SHI. The bootstrap program described here, and
listed in Appendix A, is a default, which may be modified or replaced by the customer.
On exiting the Reset state, the DSP56364 does the following:
1. Samples the MODA, MODB, and MODD signal lines
2. Loads their values into bits MA, MB, and MD in the OMR
The contents of the MA, MB, MC, and MD bits determine which bootstrap mode the DSP56364 enters.
See Table 4-1 for a tabular description of the mode bit settings for the operating modes.
The bootstrap program options can be invoked at any time by setting the appropriate MA, MB, and MD
bits in the OMR and jumping to the bootstrap program entry point, $FF0000. The mode selection bits in
the OMR can be set directly by software.It is recommended to keep the MC bit set to 1.
In bootstrap modes 5, D, E, and F, the bootstrap program expects the following data sequence when
downloading the user program through an external port:
1. Three bytes defining the number of (24-bit) program words to be loaded
2. Three bytes defining the (24-bit) start address to which the user program loads in the DSP56364
program memory
3. The user program (three bytes for each 24-bit program word). The program words will be stored
in contiguous PRAM memory locations starting at the specified starting address.
The three bytes for each data sequence must be loaded with the least significant byte first.
Once the bootstrap program completes loading the specified number of words, it jumps to the specified
starting address and executes the loaded program.
4.5 Interrupt Priority Registers
There are two interrupt priority registers in the DSP56364: IPR-C is dedicated for DSP56300 Core
interrupt sources and IPR-P is dedicated for DSP56364 peripheral interrupt sources. The interrupt priority
registers are shown in Figure 4-2 and Figure 4-3 The Interrupt Priority Level bits are defined in Table 4-2 .
DSP56364 24-Bit Digital Signal Processor Users Manual, Rev. 2
4-4 Freescale Semiconductor
Page 55

Interrupt Priority Registers
The interrupt vectors are shown in Table C-2 and the interrupt priorities are shown in Table C-3 in
Appendix C, "Programmer’s Reference".
Table 4-2 Interrupt Priority Level Bits
IPL bits
00 No —
01 Yes 0
10 Yes 1
11 Yes 2
Interrupts
Enabled
Interrupt
Priority
LevelxxL1 xxL0
DSP56364 24-Bit Digital Signal Processor Users Manual, Rev. 2
Freescale Semiconductor 4-5
Page 56

Interrupt Priority Registers
91011
8
22
23
Reserved bit. Read as zero, should be written with zero for future compatibility.
21 20 19 18 17 16 15 14 13 12
Figure 4-2 Interrupt Priority Register P
91011
8
IDL2 IDL1 IDL1
01234567
ESL0ESL1SHL0SHL1
ESAI IPL
SHI IPL
reserved
reserved
reserved
reserved
reserved
01234567
IAL0IAL1IAL2IBL0IBL1IBL2
22
23
Reserved bit. Read as zero, should be written with zero for future compatibility.
21 20 19 18 17 16 15 14 13 12
D2L0D2L1D3L0D3L1D4L0D4L1D5L0D5L1
Figure 4-3 Interrupt Priority Register C
IRQA IPL
IRQA mode
IRQB IPL
IRQB mode
reserved
reserved
IRQD IPL
IRQD mode
D0L0D0L1D1L0D1L1
DMA0 IPL
DMA1 IPL
DMA2 IPL
DMA3 IPL
DMA4 IPL
DMA5 IPL
DSP56364 24-Bit Digital Signal Processor Users Manual, Rev. 2
4-6 Freescale Semiconductor
Page 57

DMA Request Sources
4.6 DMA Request Sources
The DMA Request Source bits (DRS0-DRS4 bits in the DMA Control/Status registers) encode the source
of DMA requests used to trigger the DMA transfers. The DMA request sources may be the internal
peripherals or external devices requesting service through the IRQA, IRQB and IRQD pins. The DMA
Request Sources are shown in Table 4-3 .
Table 4-3 DMA Request Sources
DMA Request Source Bits
DRS4...DRS0
00000 External (IRQA
00001 External (IRQB pin)
00010 Reserved
00011 External (IRQD
00100 Transfer Done from DMA channel 0
00101 Transfer Done from DMA channel 1
00110 Transfer Done from DMA channel 2
00111 Transfer Done from DMA channel 3
01000 Transfer Done from DMA channel 4
01001 Transfer Done from DMA channel 5
01010 Reserved
01011 ESAI Receive Data (RDF=1)
Requesting Device
pin)
pin)
01100 ESAI Transmit Data (TDE=1)
01101 SHI HTX Empty
01110 SHI FIFO Not Empty
01111 SHI FIFO Full
10000-11111 RESERVED
4.7 PLL and Clock Generator
4.7.1 PLL Multiplication Factor (MF0-MF11) - Bits 0-11
The DSP56364 PLL multiplication factor is set to 6 during hardware reset, i.e. the Multiplication Factor
Bits MF0-MF11 in the PLL Control Register (PCTL) are set to $005.
DSP56364 24-Bit Digital Signal Processor Users Manual, Rev. 2
Freescale Semiconductor 4-7
Page 58

Device Identification (ID) Register
4.7.2 Crystal Range Bit (XTLR) - Bit 15
The Crystal Range (XTLR) bit controls the on-chip crystal oscillator transconductance. The on-chip
crystal oscillator is not used on the DSP56364 since no XTAL pin is available. The XTLR bit is set to zero
during hardware reset in the DSP56364.
4.7.3 XTAL Disable Bit (XTLD) - Bit 16
The XTAL Disable Bit (XTLD) is set to 1 (XTAL disabled) during hardware reset in the DSP56364.
4.7.4 Clock Output Disable Bit (COD) - Bit 19
The Clock Output Disable Bit (COD) is set to 0 during hardware reset. Since no clock output pin is
available in the DSP56364, this bit does not affect the functionality of the clock generator.
4.7.5 PLL Pre-Divider Factor (PD0-PD3) - Bits 20-23
The DSP56364 PLL Pre-Divider factor is set to 1 during hardware reset, i.e. the Pre-Divider Factor Bits
PD0-PD3 in the PLL Control Register (PCTL) are set to $0.
4.8 Device Identification (ID) Register
The Device Identification Register (IDR) is a 24 bit read only factory programmed register used to identify
the different DSP56300 core-based family members. This register specifies the derivative number and
revision number. This information may be used in testing or by software. Table 4-4 shows the ID register
configuration.
Table 4-4 Identification Register Configuration
23 16 15 12 11 0
Reserved Revision Number Derivative Number
$00 $0 $364
4.9 JTAG Identification (ID) Register
The JTAG Identification (ID) Register is a 32 bit, read only thought JTAG, factory programmed register
used to distinguish the component on a board according to the IEEE 1149.1 standard. Table 4-5 shows the
JTAG ID register configuration.
31 28 27 22 21 12 11 1 0
Table 4-5 JTAG Identification Register Configuration
Version Information
0000 000110 0001100100 00000001110 1
DSP56364 24-Bit Digital Signal Processor Users Manual, Rev. 2
4-8 Freescale Semiconductor
Customer Part
Number
Sequence
Number
Manufacturer
Identity
1
Page 59

JTAG Boundary Scan Register (BSR)
4.10 JTAG Boundary Scan Register (BSR)
The boundary scan register (BSR) in the DSP56364 JTAG implementation contains bits for all device
signal and clock pins and associated control signals. All bidirectional pins have a single register bit in the
boundary scan register for pin data, and are controlled by an associated control bit in the boundary scan
register. The boundary scan register bit definitions are described in Table 4-6 The BSDL file may be found
in Appendix B, "BDSL File".
Table 4-6 DSP56364 BSR Bit Definition
Bit
#
Pin Name Pin Type
GPIO3 - Control
GPIO3 Input/Output Data
GPIO2 - Control CAS Output3 Data
GPIO2 Input/Output Data
GPIO1 - Control
GPIO1 Input/Output Data RES Input Data
GPIO0 - Control
GPIO0 Input/Output Data
D7 Input/Output Data HREQ Input/Output Data
D6 Input/Output Data
D5 Input/Output Data
D4 Input/Output Data MISO/SDA - Control
BSR Cell
Type
Bit
#
Pin Name Pin Type
WR Output3 Data
CAS - Control
TA Input Data
EXTAL Input Data
PINIT Input Data
HREQ - Control
SCK/SCL - Control
SCK/SCL Input/Output Data
BSR Cell
Typ e
D[7:0] - Control
D3 Input/Output Data
D2 Input/Output Data MOSI/HA0 Input/Output Data
D1 Input/Output Data
D0 Input/Output Data
A17 Output3 Data
A16 Output3 Data
A15 Output3 Data
A14 Output3 Data
A13 Output3 Data
DSP56364 24-Bit Digital Signal Processor Users Manual, Rev. 2
Freescale Semiconductor 4-9
MISO/SDA Input/Output Data
MOSI/HA0 - Control
SS Input Data
SDO5/SDI0 - Control
SDO5/SDI0 Input/Output Data
SDO4/SDI1 - Control
SDO4/SDI1 Input/Output Data
SDO3/SDI2 - Control
SDO3/SDI2 Input/Output Data
Page 60

JTAG Boundary Scan Register (BSR)
Table 4-6 DSP56364 BSR Bit Definition (continued)
Bit
#
Pin Name Pin Type
A12 Output3 Data
A[17:9] - Control
A11 Output3 Data
A10 Output3 Data SDO1 Input/Output Data
A9 Output3 Data
A8 Output3 Data SDO0 Input/Output Data
A7 Output3 Data HCKR - Control
A[8:0] - Control HCKR Input/Output Data
A6 Output3 Data HCKT - Control
A5 Output3 Data HCKT Input/Output Data
A4 Output3 Data SCKR - Control
A3 Output3 Data SCKR Input/Output Data
A2 Output3 Data SCKT - Control
A1 Output3 Data SCKT Input/Output Data
BSR Cell
Type
Bit
#
Pin Name Pin Type
SDO2/SDI3 - Control
SDO2/SDI3 Input/Output Data
SDO1 - Control
SDO0 - Control
BSR Cell
Typ e
A0 Output3 Data FSR - Control
AA0 - Control FSR Input/Output Data
AA0 Output3 Data FST - Control
AA1 - Control FST Input/Output Data
AA1 Output3 Data MODA Input Data
RD,WR - Control MODB Input Data
RD Output3 Data MODD Input Data
DSP56364 24-Bit Digital Signal Processor Users Manual, Rev. 2
4-10 Freescale Semiconductor
Page 61

5 General Purpose Input/Output Port (GPIO)
5.1 Introduction
The General Purpose Input/Output (GPIO) pins are used for control and handshake functions between the
DSP and external circuitry. The GPIO port has 4 I/O pins (GPIO0-GPIO3) that are controlled through a
set of memory-mapped registers. Each GPIO pin may be individually programmed as an output or as an
input.
5.2 GPIO Programming Model
The GPIO port is controlled by three registers: Port B Control register (PCRB), Port B Direction register
(PRRB) and Port B GPIO Data register (PDRB). These registers are shown in Figure 5-1, Figure 5-2, and
Figure 5-3.
76543210
PC3 PC2 PC1 PC0 PCRB
15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 X:$FFFFCF
23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
Reserved, read as zero, should be written with zero for future
compatibility
Figure 5-1 GPIO Port B Control Register (PCRB)
DSP56364 24-Bit Digital Signal Processor Users Manual, Rev. 2
Freescale Semiconductor 5-1
Page 62

GPIO Programming Model
76543210
15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 X:$FFFFCE
23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
76543210
PDC3 PDC2 PDC1 PDC0 PRRB
Reserved, read as zero, should be written with zero for future
compatibility
Figure 5-2 GPIO Port B Direction Register (PRRB)
PD3 PD2 PD1 PD0 PDRB
15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 X:$FFFFCD
23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
Reserved, read as zero, should be written with zero for future
compatibility
Figure 5-3 GPIO Port B Data Register (PDRB)
5.2.1 Port B Control Register (PCRB)
The read/write Port B Control Register (PCRB) controls the functionality of the GPIO pins in conjunction
with the Port B Direction Register (PRRB).
5.2.1.1 PCRB Control Bits (PC[3:0]) - Bits 3-0
When a PC[i] bit is cleared, the corresponding GPIO[i] pin is three-stated if PDC[i] is cleared, or it is an
output if PDC[i] is set. When a PC[i] bit is set, the corresponding GPIO[i] pin is an input if PDC[i] is
cleared, or it is an open-drain output if PDC[i] is set. Refer to Table 5-1 for a summary of the GPIO
configuration control. Hardware and software reset clear the PC[3:0] bits.
5.2.1.2 PCRB Reserved Bits - Bits 23-4
These bits are reserved and unused. They read as 0s and should be written with 0s for future compatibility.
DSP56364 24-Bit Digital Signal Processor Users Manual, Rev. 2
5-2 Freescale Semiconductor
Page 63

GPIO Programming Model
Port B Direction Register (PRRB)
The read/write Port B Direction Register controls the direction of data transfer for each GPIO pin.
5.2.1.3 PRRB Direction Bits (PDC[3:0]) - Bits 3-0
When PDC[i] is set, the GPIO port pin[i] is configured as output. When PDC[i] is cleared the GPIO port
pin[i] is configured as input. See Table 5-1 . Hardware and software reset clear the PDC[3:0] bits.
5.2.1.4 PRRB Reserved Bits - Bits 23-4
These bits are reserved and unused. They read as 0s and should be written with 0s for future compatibility.
Table 5-1 GPIO Pin Configuration
PDC[i] PC[i] GPIO Pin[i] Function
0 0 Three-Stated (Disconnected)
01Input
1 0 Output
1 1 Open-drain output
5.2.2 Port B GPIO Data Register (PDRB)
The read/write Port B Data Register (PDRB) is used to read data from or write data to the GPIO pins.
5.2.2.1 PDRB Data Bits (PD[3:0]) - Bits 3-0
If a GPIO pin [i] is configured as a GPIO input, then the corresponding PD[i] bit will reflect the value
present on this pin. If a GPIO pin [i] is configured as a GPIO output, then the value written into the
corresponding PD[i] bit will be reflected on the pin. The PD[3:0] bits are not affected by hardware or
software reset.
5.2.2.2 PDRB Reserved Bits - Bits 23-4
These bits are reserved and unused. They read as 0s and should be written with 0s for future compatibility.
DSP56364 24-Bit Digital Signal Processor Users Manual, Rev. 2
Freescale Semiconductor 5-3
Page 64

GPIO Programming Model
NOTES
DSP56364 24-Bit Digital Signal Processor Users Manual, Rev. 2
5-4 Freescale Semiconductor
Page 65

6 Enhanced Serial AUDIO Interface (ESAI)
6.1 Introduction
The Enhanced Serial Audio Interface (ESAI) provides a full-duplex serial port for serial communication
with a variety of serial devices including one or more industry-standard codecs, other DSPs,
microprocessors, and peripherals which implement the Freescale SPI serial protocol. The ESAI consists
of independent transmitter and receiver sections, each section with its own clock generator. It is a superset
of the 56300 Family ESSI peripheral and of the 56000 Family SAI peripheral.
The ESAI block diagram is shown in Figure 6-1. The ESAI is named synchronous because all serial
transfers are synchronized to a clock. Additional synchronization signals are used to delineate the word
frames. The normal mode of operation is used to transfer data at a periodic rate, one word per period. The
network mode is similar in that it is also intended for periodic transfers; however, it supports up to 32
words (time slots) per period. This mode can be used to build time division multiplexed (TDM) networks.
In contrast, the on-demand mode is intended for non-periodic transfers of data and to transfer data serially
at high speed when the data becomes available. This mode offers a subset of the SPI protocol.
DSP56364 24-Bit Digital Signal Processor Users Manual, Rev. 2
Freescale Semiconductor 6-1
Page 66

Introduction
RSMA
RSMB
DDBGDB
TX0
SDO0 [PC11]
Shift Register
TSMA
TSMB
RCCR
RCR
TCCR
TCR
SAICR
SAISR
TSR
TX1
SDO1 [PC10]
Shift Register
TX2
SDO2/SDI3 [PC9]
Shift Register
RX3
TX3
SDO3/SDI2 [PC8]
Shift Register
RX2
TX4
SDO4/SDI1 [PC7]
Shift Register
RX1
Clock / Frame Sync
Generators
and
Control Logic
RCLK
TX5
SDO5/SDI0 [PC6]
Shift Register
TCLK
RX0
[PC3] SCKT
[PC4] FST
[PC5] HCKT
[PC0] SCKR
[PC1] FSR
[PC2] HCKR
Figure 6-1 ESAI Block Diagram
DSP56364 24-Bit Digital Signal Processor Users Manual, Rev. 2
6-2 Freescale Semiconductor
Page 67

ESAI Data and Control Pins
6.2 ESAI Data and Control Pins
Three to twelve pins are required for operation, depending on the operating mode selected and the number
of transmitters and receivers enabled. The SDO0 and SDO1 pins are used by transmitters 0 and 1 only. The
SDO2/SDI3, SDO3/SDI2, SDO4/SDI1, and SDO5/SDI0 pins are shared by transmitters 2 to 5 with
receivers 0 to 3. The actual mode of operation is selected under software control. All transmitters operate
fully synchronized under control of the same transmitter clock signals. All receivers operate fully
synchronized under control of the same receiver clock signals.
6.2.1 Serial Transmit 0 Data Pin (SDO0)
SDO0 is used for transmitting data from the TX0 serial transmit shift register. SDO0 is an output when
data is being transmitted from the TX0 shift register. In the on-demand mode with an internally generated
bit clock, the SDO0 pin becomes high impedance for a full clock period after the last data bit has been
transmitted, assuming another data word does not follow immediately. If a data word follows immediately,
there is no high-impedance interval.
SDO0 may be programmed as a general-purpose I/O pin (PC11) when the ESAI SDO0 function is not
being used.
6.2.2 Serial Transmit 1 Data Pin (SDO1)
SDO1 is used for transmitting data from the TX1 serial transmit shift register. SDO1 is an output when
data is being transmitted from the TX1 shift register. In the on-demand mode with an internally generated
bit clock, the SDO1 pin becomes high impedance for a full clock period after the last data bit has been
transmitted, assuming another data word does not follow immediately. If a data word follows immediately,
there is no high-impedance interval.
SDO1 may be programmed as a general-purpose I/O pin (PC10) when the ESAI SDO1 function is not
being used.
6.2.3 Serial Transmit 2/Receive 3 Data Pin (SDO2/SDI3)
SDO2/SDI3 is used as the SDO2 for transmitting data from the TX2 serial transmit shift register when
programmed as a transmitter pin, or as the SDI3 signal for receiving serial data to the RX3 serial receive
shift register when programmed as a receiver pin. SDO2/SDI3 is an input when data is being received by
the RX3 shift register. SDO2/SDI3 is an output when data is being transmitted from the TX2 shift register.
In the on-demand mode with an internally generated bit clock, the SDO2/SDI3 pin becomes high
impedance for a full clock period after the last data bit has been transmitted, assuming another data word
does not follow immediately. If a data word follows immediately, there is no high-impedance interval.
SDO2/SDI3 may be programmed as a general-purpose I/O pin (PC9) when the ESAI SDO2 and SDI3
functions are not being used.
DSP56364 24-Bit Digital Signal Processor Users Manual, Rev. 2
Freescale Semiconductor 6-3
Page 68

ESAI Data and Control Pins
6.2.4 Serial Transmit 3/Receive 2 Data Pin (SDO3/SDI2)
SDO3/SDI2 is used as the SDO3 signal for transmitting data from the TX3 serial transmit shift register
when programmed as a transmitter pin, or as the SDI2 signal for receiving serial data to the RX2 serial
receive shift register when programmed as a receiver pin. SDO3/SDI2 is an input when data is being
received by the RX2 shift register. SDO3/SDI2 is an output when data is being transmitted from the TX3
shift register. In the on-demand mode with an internally generated bit clock, the SDO3/SDI2 pin becomes
high impedance for a full clock period after the last data bit has been transmitted, assuming another data
word does not follow immediately. If a data word follows immediately, there is no high-impedance
interval.
SDO3/SDI2 may be programmed as a general-purpose I/O pin (PC8) when the ESAI SDO3 and SDI2
functions are not being used.
6.2.5 Serial Transmit 4/Receive 1 Data Pin (SDO4/SDI1)
SDO4/SDI1 is used as the SDO4 signal for transmitting data from the TX4 serial transmit shift register
when programmed as transmitter pin, or as the SDI1 signal for receiving serial data to the RX1 serial
receive shift register when programmed as a receiver pin. SDO4/SDI1 is an input when data is being
received by the RX1 shift register. SDO4/SDI1 is an output when data is being transmitted from the TX4
shift register. In the on-demand mode with an internally generated bit clock, the SDO4/SDI1 pin becomes
high impedance for a full clock period after the last data bit has been transmitted, assuming another data
word does not follow immediately. If a data word follows immediately, there is no high-impedance
interval.
SDO4/SDI1 may be programmed as a general-purpose I/O pin (PC7) when the ESAI SDO4 and SDI1
functions are not being used.
6.2.6 Serial Transmit 5/Receive 0 Data Pin (SDO5/SDI0)
SDO5/SDI0 is used as the SDO5 signal for transmitting data from the TX5 serial transmit shift register
when programmed as transmitter pin, or as the SDI0 signal for receiving serial data to the RX0 serial shift
register when programmed as a receiver pin. SDO5/SDI0 is an input when data is being received by the
RX0 shift register. SDO5/SDI0 is an output when data is being transmitted from the TX5 shift register. In
the on-demand mode with an internally generated bit clock, the SDO5/SDI0 pin becomes high impedance
for a full clock period after the last data bit has been transmitted, assuming another data word does not
follow immediately. If a data word follows immediately, there is no high-impedance interval.
SDO5/SDI0 may be programmed as a general-purpose I/O pin (PC6) when the ESAI SDO5 and SDI0
functions are not being used
6.2.7 Receiver Serial Clock (SCKR)
SCKR is a bidirectional pin providing the receivers serial bit clock for the ESAI interface. The direction
of this pin is determined by the RCKD bit in the RCCR register.The SCKR operates as a clock input or
output used by all the enabled receivers in the asynchronous mode (SYN=0), or as serial flag 0 pin in the
synchronous mode (SYN=1).
DSP56364 24-Bit Digital Signal Processor Users Manual, Rev. 2
6-4 Freescale Semiconductor
Page 69

ESAI Data and Control Pins
When this pin is configured as serial flag pin, its direction is determined by the RCKD bit in the RCCR
register. When configured as the output flag OF0, this pin reflects the value of the OF0 bit in the SAICR
register, and the data in the OF0 bit shows up at the pin synchronized to the frame sync being used by the
transmitter and receiver sections. When this pin is configured as the input flag IF0, the data value at the
pin is stored in the IF0 bit in the SAISR register, synchronized by the frame sync in normal mode or the
slot in network mode.
SCKR may be programmed as a general-purpose I/O pin (PC0) when the ESAI SCKR function is not being
used.
NOTE
Although the external ESAI serial clock can be independent of and
asynchronous to the DSP system clock, the DSP clock frequency must be at
least three times the external ESAI serial clock frequency and each ESAI
serial clock phase must exceed the minimum of 1.5 DSP clock periods.
For more information on pin mode and definition, see Table 6-7 and on receiver clock signals see
Table 6-1 .
Table 6-1 Receiver Clock Sources (asynchronous mode only)
Receiver
RHCKD RFSD RCKD
Bit Clock
Source
OUTPUTS
000SCKR
001HCKR SCKR
010SCKR FSR
0 1 1 HCKR FSR SCKR
1 0 0 SCKR HCKR
1 0 1 INT HCKR SCKR
1 1 0 SCKR HCKR FSR
1 1 1 INT HCKR FSR SCKR
6.2.8 Transmitter Serial Clock (SCKT)
SCKT is a bidirectional pin providing the transmitters serial bit clock for the ESAI interface. The direction
of this pin is determined by the TCKD bit in the TCCR register. The SCKT is a clock input or output used
by all the enabled transmitters in the asynchronous mode (SYN=0) or by all the enabled transmitters and
receivers in the synchronous mode (SYN=1) (see Table 6-2 ).
DSP56364 24-Bit Digital Signal Processor Users Manual, Rev. 2
Freescale Semiconductor 6-5
Page 70

ESAI Data and Control Pins
Table 6-2 Transmitter Clock Sources
Transmitter
THCKD TFSD TCKD
000SCKT
0 0 1 HCKT SCKT
010SCKT FST
0 1 1 HCKT FST SCKT
1 0 0 SCKT HCKT
1 0 1 INT HCKT SCKT
1 1 0 SCKT HCKT FST
1 1 1 INT HCKT FST SCKT
Bit Clock
Source
OUTPUTS
SCKT may be programmed as a general-purpose I/O pin (PC3) when the ESAI SCKT function is not being
used.
NOTE
Although the external ESAI serial clock can be independent of and
asynchronous to the DSP system clock, the DSP clock frequency must be at
least three times the external ESAI serial clock frequency and each ESAI
serial clock phase must exceed the minimum of 1.5 DSP clock periods.
6.2.9 Frame Sync for Receiver (FSR)
FSR is a bidirectional pin providing the receivers frame sync signal for the ESAI interface. The direction
of this pin is determined by the RFSD bit in RCR register. In the asynchronous mode (SYN=0), the FSR
pin operates as the frame sync input or output used by all the enabled receivers. In the synchronous mode
(SYN=1), it operates as either the serial flag 1 pin (TEBE=0), or as the transmitter external buffer enable
control (TEBE=1, RFSD=1). For further information on pin mode and definition, see Table 6-8 and on
receiver clock signals see Table 6-1 .
When this pin is configured as serial flag pin, its direction is determined by the RFSD bit in the RCCR
register. When configured as the output flag OF1, this pin reflects the value of the OF1 bit in the SAICR
register, and the data in the OF1 bit shows up at the pin synchronized to the frame sync being used by the
transmitter and receiver sections. When configured as the input flag IF1, the data value at the pin is stored
in the IF1 bit in the SAISR register, synchronized by the frame sync in normal mode or the slot in network
mode.
FSR may be programmed as a general-purpose I/O pin (PC1) when the ESAI FSR function is not being
used.
DSP56364 24-Bit Digital Signal Processor Users Manual, Rev. 2
6-6 Freescale Semiconductor
Page 71

ESAI Programming Model
6.2.10 Frame Sync for Transmitter (FST)
FST is a bidirectional pin providing the frame sync for both the transmitters and receivers in the
synchronous mode (SYN=1) and for the transmitters only in asynchronous mode (SYN=0) (see Table 6-2).
The direction of this pin is determined by the TFSD bit in the TCR register. When configured as an output,
this pin is the internally generated frame sync signal. When configured as an input, this pin receives an
external frame sync signal for the transmitters (and the receivers in synchronous mode).
FST may be programmed as a general-purpose I/O pin (PC4) when the ESAI FST function is not being
used.
6.2.11 High Frequency Clock for Transmitter (HCKT)
HCKT is a bidirectional pin providing the transmitters high frequency clock for the ESAI interface. The
direction of this pin is determined by the THCKD bit in the TCCR register. In the asynchronous mode
(SYN=0), the HCKT pin operates as the high frequency clock input or output used by all enabled
transmitters. In the synchronous mode (SYN=1), it operates as the high frequency clock input or output
used by all enabled transmitters and receivers. When programmed as input this pin is used as an alternative
high frequency clock source to the ESAI transmitter rather than the DSP main clock. When programmed
as output it can serve as a high frequency sample clock (to external DACs for example) or as an additional
system clock. See Table 6-2.
HCKT may be programmed as a general-purpose I/O pin (PC5) when the ESAI HCKT function is not
being used.
6.2.12 High Frequency Clock for Receiver (HCKR)
HCKR is a bidirectional pin providing the receivers high frequency clock for the ESAI interface. The
direction of this pin is determined by the RHCKD bit in the RCCR register. In the asynchronous mode
(SYN=0), the HCKR pin operates as the high frequency clock input or output used by all the enabled
receivers. In the synchronous mode (SYN=1), it operates as the serial flag 2 pin. For further information
on pin mode and definition, see Table 6-9 and on receiver clock signals see Table 6-1.
When this pin is configured as serial flag pin, its direction is determined by the RHCKD bit in the RCCR
register. When configured as the output flag OF2, this pin reflects the value of the OF2 bit in the SAICR
register, and the data in the OF2 bit shows up at the pin synchronized to the frame sync being used by the
transmitter and receiver sections. When configured as the input flag IF2, the data value at the pin is stored
in the IF2 bit in the SAISR register, synchronized by the frame sync in normal mode or the slot in network
mode.
HCKR may be programmed as a general-purpose I/O pin (PC2) when the ESAI HCKR function is not
being used.
6.3 ESAI Programming Model
The ESAI can be viewed as five control registers, one status register, six transmit data registers, four
receive data registers, two transmit slot mask registers, two receive slot mask registers and a
DSP56364 24-Bit Digital Signal Processor Users Manual, Rev. 2
Freescale Semiconductor 6-7
Page 72

ESAI Programming Model
special-purpose time slot register. The following paragraphs give detailed descriptions and operations of
each bit in the ESAI registers.
The ESAI pins can also function as GPIO pins (Port C), described in Section 6.5, "GPIO - Pins and
Registers".
6.3.1 ESAI Transmitter Clock Control Register (TCCR)
The read/write Transmitter Clock Control Register (TCCR) controls the ESAI transmitter clock generator
bit and frame sync rates, the bit clock and high frequency clock sources and the directions of the HCKT,
FST and SCKT signals. (See Figure 6-2). In the synchronous mode (SYN=1), the bit clock defined for the
transmitter determines the receiver bit clock as well. TCCR also controls the number of words per frame
for the serial data.
11109876543210
X:$FFFFB6 TDC2 TDC1 TDC0 TPSR TPM7 TPM6 TPM5 TPM4 TPM3 TPM2 TPM1 TPM0
23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16 15 14 13 12
THCKD TFSD TCKD THCKP TFSP TCKP TFP3 TFP2 TFP1 TFP0 TDC4 TDC3
Figure 6-2 TCCR Register
Hardware and software reset clear all the bits of the TCCR register.
The TCCR control bits are described in the following paragraphs.
6.3.1.1 TCCR Transmit Prescale Modulus Select (TPM7–TPM0) - Bits 0–7
The TPM7–TPM0 bits specify the divide ratio of the prescale divider in the ESAI transmitter clock
generator. A divide ratio from 1 to 256 (TPM[7:0]=$00 to $FF) may be selected. The bit clock output is
available at the transmit serial bit clock (SCKT) pin of the DSP. The bit clock output is also available
internally for use as the bit clock to shift the transmit and receive shift registers. The ESAI transmit clock
generator functional diagram is shown in Figure 6-3.
DSP56364 24-Bit Digital Signal Processor Users Manual, Rev. 2
6-8 Freescale Semiconductor
Page 73

ESAI Programming Model
HCKR
RHCKD
SCKR
RCKD
SCKT
RHCKD=1
F
OSC
DIVIDE
BY 2
PRESCALE
DIVIDE BY 1
OR
DIVIDE BY 8
DIVIDER
DIVIDE BY 1
TO DIVIDE BY
256
DIVIDER
DIVIDE BY 1
TO DIVIDE BY
16
RHCKD=0
FLAG0 OUT
(SYNC MODE)
FLAG0 IN
(SYNC MODE)
RPSR RPM0 - RPM7
INTERNAL BIT CLOCK
RFP0 - RFP3
RSWS4-RSWS0
RX WORD
CLOCK
TX WORD
CLOCK
SYN=0
SYN=1
INTERNAL BIT CLOCK
SYN=0
SYN=1
RCLOCK
TCLOCK
RX WORD
LENGTH DIVIDER
RX SHIFT REGISTER
TSWS4-TSWS0
TX WORD
LENGTH DIVIDER
TCKD
THCKD
TX SHIFT REGISTER
HCKT
TPSR TPM0 - TPM7
TFP0 - TFP3
THCKD=0
PRESCALE
DIVIDE
F
OSC
BY 2
DIVIDE BY 1
OR
DIVIDE BY 8
DIVIDER
DIVIDE BY 1
TO DIVID E BY
256
DIVIDER
DIVIDE BY 1
TO DIVIDE BY
16
THCKD=1
Notes:
is the DSP56300 Core internal clock frequency.
1. F
OSC
Figure 6-3 ESAI Clock Generator Functional Block Diagram
6.3.1.2 TCCR Transmit Prescaler Range (TPSR) - Bit 8
The TPSR bit controls a fixed divide-by-eight prescaler in series with the variable prescaler. This bit is
used to extend the range of the prescaler for those cases where a slower bit clock is desired. When TPSR
is set, the fixed prescaler is bypassed. When TPSR is cleared, the fixed divide-by-eight prescaler is
DSP56364 24-Bit Digital Signal Processor Users Manual, Rev. 2
Freescale Semiconductor 6-9
Page 74

ESAI Programming Model
operational (see Figure 6-3). The maximum internally generated bit clock frequency is Fosc/4; the
minimum internally generated bit clock frequency is Fosc/(2 x 8 x 256)=Fosc/4096.
NOTE
Do not use the combination TPSR=1 and TPM7-TPM0=$00, which causes
synchronization problems when using the internal DSP clock as source
(TCKD=1 or THCKD=1).
6.3.1.3 TCCR Tx Frame Rate Divider Control (TDC4–TDC0) - Bits 9–13
The TDC4–TDC0 bits control the divide ratio for the programmable frame rate dividers used to generate
the transmitter frame clocks.
In network mode, this ratio may be interpreted as the number of words per frame minus one. The divide
ratio may range from 2 to 32 (TDC[4:0]=00001 to 11111) for network mode. A divide ratio of one
(TDC[4:0]=00000) in network mode is a special case (on-demand mode).
In normal mode, this ratio determines the word transfer rate. The divide ratio may range from 1 to 32
(TDC[4:0]=00000 to 11111) for normal mode. In normal mode, a divide ratio of 1 (TDC[4:0]=00000)
provides continuous periodic data word transfers. A bit-length frame sync (TFSL=1) must be used in this
case.
The ESAI frame sync generator functional diagram is shown in Figure 6-4.
DSP56364 24-Bit Digital Signal Processor Users Manual, Rev. 2
6-10 Freescale Semiconductor
Page 75

ESAI Programming Model
RX WORD
CLOCK
TX WORD
CLOCK
RDC0 - RDC4
RECEIVER
FRAME RATE
DIVIDER
RECEIVE
CONTROL
LOGIC
TDC0 - TDC4
TRANSMITTER
FRAME RATE
DIVIDER
TRANSMIT
CONTROL
LOGIC
RFSL
SYNC
TYPE
RECEIVE
FRAME SYNC
TFSL
SYNC
TYPE
TRANSMIT
FRAME SYNC
INTERNAL RX FRAME CLOCK
RFSD=1
SYN=0
RFSD=0
SYN=1
FLAG1 IN
(SYNC MODE)
INTERNAL TX FRAME CLOCK
SYN=0
RFSD
FSR
SYN=1
FLAG1OUT
(SYNC MODE)
TFSD
FST
Figure 6-4 ESAI Frame Sync Generator Functional Block Diagram
6.3.1.4 TCCR Tx High Frequency Clock Divider (TFP3-TFP0) - Bits 14–17
The TFP3–TFP0 bits control the divide ratio of the transmitter high frequency clock to the transmitter
serial bit clock when the source of the high frequency clock and the bit clock is the internal DSP clock.
When the HCKT input is being driven from an external high frequency clock, the TFP3-TFP0 bits specify
an additional division ratio in the clock divider chain. See Table 6-3 for the specification of the divide ratio.
The ESAI high frequency clock generator functional diagram is shown in Figure 6-3.
Table 6-3 Transmitter High Frequency Clock Divider
TFP3-TFP0 Divide Ratio
$0 1
$1 2
$2 3
$3 4
... ...
$F 16
DSP56364 24-Bit Digital Signal Processor Users Manual, Rev. 2
Freescale Semiconductor 6-11
Page 76

ESAI Programming Model
6.3.1.5 TCCR Transmit Clock Polarity (TCKP) - Bit 18
The Transmitter Clock Polarity (TCKP) bit controls on which bit clock edge data and frame sync are
clocked out and latched in. If TCKP is cleared the data and the frame sync are clocked out on the rising
edge of the transmit bit clock and latched in on the falling edge of the transmit bit clock. If TCKP is set
the falling edge of the transmit clock is used to clock the data out and frame sync and the rising edge of
the transmit clock is used to latch the data and frame sync in.
6.3.1.6 TCCR Transmit Frame Sync Polarity (TFSP) - Bit 19
The Transmitter Frame Sync Polarity (TFSP) bit determines the polarity of the transmit frame sync signal.
When TFSP is cleared, the frame sync signal polarity is positive (i.e the frame start is indicated by a high
level on the frame sync pin). When TFSP is set, the frame sync signal polarity is negative (i.e the frame
start is indicated by a low level on the frame sync pin).
6.3.1.7 TCCR Transmit High Frequency Clock Polarity (THCKP) - Bit 20
The Transmitter High Frequency Clock Polarity (THCKP) bit controls on which bit clock edge data and
frame sync are clocked out and latched in. If THCKP is cleared the data and the frame sync are clocked
out on the rising edge of the transmit bit clock and latched in on the falling edge of the transmit bit clock.
If THCKP is set the falling edge of the transmit clock is used to clock the data out and frame sync and the
rising edge of the transmit clock is used to latch the data and frame sync in.
6.3.1.8 TCCR Transmit Clock Source Direction (TCKD) - Bit 21
The Transmitter Clock Source Direction (TCKD) bit selects the source of the clock signal used to clock
the transmit shift registers in the asynchronous mode (SYN=0) and the transmit shift registers and the
receive shift registers in the synchronous mode (SYN=1). When TCKD is set, the internal clock source
becomes the bit clock for the transmit shift registers and word length divider and is the output on the SCKT
pin. When TCKD is cleared, the clock source is external; the internal clock generator is disconnected from
the SCKT pin, and an external clock source may drive this pin. See Table 6-2 .
6.3.1.9 TCCR Transmit Frame Sync Signal Direction (TFSD) - Bit 22
TFSD controls the direction of the FST pin. When TFSD is cleared, FST is an input; when TFSD is set,
FST is an output. See Table 6-2 .
6.3.1.10 TCCR Transmit High Frequency Clock Direction (THCKD) - Bit 23
THCKD controls the direction of the HCKT pin. When THCKD is cleared, HCKT is an input; when
THCKD is set, HCKT is an output. See Table 6-2 .
DSP56364 24-Bit Digital Signal Processor Users Manual, Rev. 2
6-12 Freescale Semiconductor
Page 77

ESAI Programming Model
6.3.2 ESAI Transmit Control Register (TCR)
The read/write Transmit Control Register (TCR) controls the ESAI transmitter section. Interrupt enable
bits for the transmitter section are provided in this control register. Operating modes are also selected in
this register. See Figure 6-5.
11109876543210
X:$FFFFB5 TSWS1 TSWS0 TMOD1 TMOD0 TWA TSHFD TE5 TE4 TE3 TE2 TE1 TE0
23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16 15 14 13 12
TLIE TIE TEDIE TEIE TPR
Reserved bit - read as zero; should be written with zero for future compatibility.
Figure 6-5 TCR Register
PADC TFSR TFSL TSWS4 TSWS3 TSWS2
Hardware and software reset clear all the bits in the TCR register.
The TCR bits are described in the following paragraphs.
6.3.2.1 TCR ESAI Transmit 0 Enable (TE0) - Bit 0
TE0 enables the transfer of data from TX0 to the transmit shift register #0. When TE0 is set and a frame
sync is detected, the transmit #0 portion of the ESAI is enabled for that frame. When TE0 is cleared, the
transmitter #0 is disabled after completing transmission of data currently in the ESAI transmit shift
register. The SDO0 output is tri-stated, and any data present in TX0 is not transmitted (i.e., data can be
written to TX0 with TE0 cleared; but data is not transferred to the transmit shift register #0).
The normal mode transmit enable sequence is to write data to one or more transmit data registers before
setting TEx. The normal transmit disable sequence is to clear TEx, TIE and TEIE after TDE equals one.
In the network mode, the operation of clearing TE0 and setting it again disables the transmitter #0 after
completing transmission of the current data word until the beginning of the next frame. During that time
period, the SDO0 pin remains in the high-impedance state.The on-demand mode transmit enable sequence
can be the same as the normal mode, or TE0 can be left enabled.
6.3.2.2 TCR ESAI Transmit 1 Enable (TE1) - Bit 1
TE1 enables the transfer of data from TX1 to the transmit shift register #1. When TE1 is set and a frame
sync is detected, the transmit #1 portion of the ESAI is enabled for that frame. When TE1 is cleared, the
transmitter #1 is disabled after completing transmission of data currently in the ESAI transmit shift
register. The SDO1 output is tri-stated, and any data present in TX1 is not transmitted (i.e., data can be
written to TX1 with TE1 cleared; but data is not transferred to the transmit shift register #1).
The normal mode transmit enable sequence is to write data to one or more transmit data registers before
setting TEx. The normal transmit disable sequence is to clear TEx, TIE and TEIE after TDE equals one.
DSP56364 24-Bit Digital Signal Processor Users Manual, Rev. 2
Freescale Semiconductor 6-13
Page 78

ESAI Programming Model
In the network mode, the operation of clearing TE1 and setting it again disables the transmitter #1 after
completing transmission of the current data word until the beginning of the next frame. During that time
period, the SDO1 pin remains in the high-impedance state. The on-demand mode transmit enable sequence
can be the same as the normal mode, or TE1 can be left enabled.
6.3.2.3 TCR ESAI Transmit 2 Enable (TE2) - Bit 2
TE2 enables the transfer of data from TX2 to the transmit shift register #2. When TE2 is set and a frame
sync is detected, the transmit #2 portion of the ESAI is enabled for that frame. When TE2 is cleared, the
transmitter #2 is disabled after completing transmission of data currently in the ESAI transmit shift
register. Data can be written to TX2 when TE2 is cleared but the data is not transferred to the transmit shift
register #2.
The SDO2/SDI3 pin is the data input pin for RX3 if TE2 is cleared and RE3 in the RCR register is set. If
both RE3 and TE2 are cleared the transmitter and receiver are disabled, and the pin is tri-stated. Both RE3
and TE2 should not be set at the same time.
The normal mode transmit enable sequence is to write data to one or more transmit data registers before
setting TEx. The normal transmit disable sequence is to clear TEx, TIE and TEIE after TDE equals one.
In the network mode, the operation of clearing TE2 and setting it again disables the transmitter #2 after
completing transmission of the current data word until the beginning of the next frame. During that time
period, the SDO2/SDI3 pin remains in the high-impedance state. The on-demand mode transmit enable
sequence can be the same as the normal mode, or TE2 can be left enabled.
6.3.2.4 TCR ESAI Transmit 3 Enable (TE3) - Bit 3
TE3 enables the transfer of data from TX3 to the transmit shift register #3. When TE3 is set and a frame
sync is detected, the transmit #3 portion of the ESAI is enabled for that frame. When TE3 is cleared, the
transmitter #3 is disabled after completing transmission of data currently in the ESAI transmit shift
register. Data can be written to TX3 when TE3 is cleared but the data is not transferred to the transmit shift
register #3.
The SDO3/SDI2 pin is the data input pin for RX2 if TE3 is cleared and RE2 in the RCR register is set. If
both RE2 and TE3 are cleared the transmitter and receiver are disabled, and the pin is tri-stated. Both RE2
and TE3 should not be set at the same time.
The normal mode transmit enable sequence is to write data to one or more transmit data registers before
setting TEx. The normal transmit disable sequence is to clear TEx, TIE and TEIE after TDE equals one.
In the network mode, the operation of clearing TE3 and setting it again disables the transmitter #3 after
completing transmission of the current data word until the beginning of the next frame. During that time
period, the SDO3/SDI2 pin remains in the high-impedance state. The on-demand mode transmit enable
sequence can be the same as the normal mode, or TE3 can be left enabled.
6.3.2.5 TCR ESAI Transmit 4 Enable (TE4) - Bit 4
TE4 enables the transfer of data from TX4 to the transmit shift register #4. When TE4 is set and a frame
sync is detected, the transmit #4 portion of the ESAI is enabled for that frame. When TE4 is cleared, the
DSP56364 24-Bit Digital Signal Processor Users Manual, Rev. 2
6-14 Freescale Semiconductor
Page 79

ESAI Programming Model
transmitter #4 is disabled after completing transmission of data currently in the ESAI transmit shift
register. Data can be written to TX4 when TE4 is cleared but the data is not transferred to the transmit shift
register #4.
The SDO4/SDI1 pin is the data input pin for RX1 if TE4 is cleared and RE1 in the RCR register is set. If
both RE1 and TE4 are cleared the transmitter and receiver are disabled, and the pin is tri-stated. Both RE1
and TE4 should not be set at the same time.
The normal mode transmit enable sequence is to write data to one or more transmit data registers before
setting TEx. The normal transmit disable sequence is to clear TEx, TIE and TEIE after TDE equals one.
In the network mode, the operation of clearing TE4 and setting it again disables the transmitter #4 after
completing transmission of the current data word until the beginning of the next frame. During that time
period, the SDO4/SDI1 pin remains in the high-impedance state. The on-demand mode transmit enable
sequence can be the same as the normal mode, or TE4 can be left enabled.
6.3.2.6 TCR ESAI Transmit 5 Enable (TE5) - Bit 5
TE5 enables the transfer of data from TX5 to the transmit shift register #5. When TE5 is set and a frame
sync is detected, the transmit #5 portion of the ESAI is enabled for that frame. When TE5 is cleared, the
transmitter #5 is disabled after completing transmission of data currently in the ESAI transmit shift
register. Data can be written to TX5 when TE5 is cleared but the data is not transferred to the transmit shift
register #5.
The SDO5/SDI0 pin is the data input pin for RX0 if TE5 is cleared and RE0 in the RCR register is set. If
both RE0 and TE5 are cleared the transmitter and receiver are disabled, and the pin is tri-stated. Both RE0
and TE5 should not be set at the same time.
The normal mode transmit enable sequence is to write data to one or more transmit data registers before
setting TEx. The normal transmit disable sequence is to clear TEx, TIE and TEIE after TDE equals one.
In the network mode, the operation of clearing TE5 and setting it again disables the transmitter #5 after
completing transmission of the current data word until the beginning of the next frame. During that time
period, the SDO5/SDI0 pin remains in the high-impedance state. The on-demand mode transmit enable
sequence can be the same as the normal mode, or TE5 can be left enabled.
6.3.2.7 TCR Transmit Shift Direction (TSHFD) - Bit 6
The TSHFD bit causes the transmit shift registers to shift data out MSB first when TSHFD equals zero or
LSB first when TSHFD equals one (see Figure 6-13 and Figure 6-14).
6.3.2.8 TCR Transmit Word Alignment Control (TWA) - Bit 7
The Transmitter Word Alignment Control (TWA) bit defines the alignment of the data word in relation to
the slot. This is relevant for the cases where the word length is shorter than the slot length. If TWA is
cleared, the data word is left-aligned in the slot frame during transmission. If TWA is set, the data word is
right-aligned in the slot frame during transmission.
DSP56364 24-Bit Digital Signal Processor Users Manual, Rev. 2
Freescale Semiconductor 6-15
Page 80

ESAI Programming Model
Since the data word is shorter than the slot length, the data word is extended until achieving the slot length,
according to the following rule:
1. If the data word is left-aligned (TWA=0), and zero padding is disabled (PADC=0), then the last data
bit is repeated after the data word has been transmitted. If zero padding is enabled (PADC=1),
zeroes are transmitted after the data word has been transmitted.
2. If the data word is right-aligned (TWA=1), and zero padding is disabled (PADC=0), then the first
data bit is repeated before the transmission of the data word. If zero padding is enabled (PADC=1),
zeroes are transmitted before the transmission of the data word.
6.3.2.9 TCR Transmit Network Mode Control (TMOD1-TMOD0) - Bits 8-9
The TMOD1 and TMOD0 bits are used to define the network mode of ESAI transmitters according to
Table 6-4 . In the normal mode, the frame rate divider determines the word transfer rate – one word is
transferred per frame sync during the frame sync time slot, as shown in Figure 6-6. In network mode, it is
possible to transfer a word for every time slot, as shown in Figure 6-6. For more details, see Section 6.4,
"Operating Modes".
In order to comply with AC-97 specifications, TSWS4-TSWS0 should be set to 00011 (20-bit slot, 20-bit
word length), TFSL and TFSR should be cleared, and TDC4-TDC0 should be set to $0C (13 words in
frame). If TMOD[1:0]=$11 and the above recommendations are followed, the first slot and word will be
16 bits long, and the next 12 slots and words will be 20 bits long, as required by the AC97 protocol.
Table 6-4 Transmit Network Mode Selection
TMOD1 TMOD0 TDC4-TDC0 Transmitter Network Mode
0 0 $0-$1F Normal Mode
0 1 $0 On-Demand Mode
0 1 $1-$1F Network Mode
1 0 X Reserved
1 1 $0C AC97
DSP56364 24-Bit Digital Signal Processor Users Manual, Rev. 2
6-16 Freescale Semiconductor
Page 81

ESAI Programming Model
Normal Mode
SERIAL
FRAME SYNC
RECEIVER INTERRUPT (OR DMA
REQUEST) AND FLAGS SET
TRANSMITTER INTERRUPT (OR DMA REQUEST)
AND FLAGS SET
DATA DATA
SERIAL DATA
NOTE: Interrupts occur and data is transferred once per frame sync.
Network Mode
SERIAL
FRAME SYNC
Figure 6-6 Normal and Network Operation
RECEIVER INTERRUPT (OR DMA REQUEST)
AND FLAGS SET
TRANSMITTER INTERRUPTS (OR DMA
REQUEST) AND FLAGS SET
SLOT 0 SLOT 1 SLOT 2 SLOT 0 SLOT 1
SERIAL DATA
NOTE: Interrupts occur and a word may be transferred at every time slot.
DSP56364 24-Bit Digital Signal Processor Users Manual, Rev. 2
Freescale Semiconductor 6-17
Page 82

ESAI Programming Model
6.3.2.10 TCR Tx Slot and Word Length Select (TSWS4-TSWS0) - Bits 10-14
The TSWS4-TSWS0 bits are used to select the length of the slot and the length of the data words being
transferred via the ESAI. The word length must be equal to or shorter than the slot length. The possible
combinations are shown in Table 6-5 . See also the ESAI data path programming model in Figure 6-13 and
Figure 6-14.
Table 6-5 ESAI Transmit Slot and Word Length Selection
TSWS4 TSWS3 TSWS2 TSWS1 TSWS0 SLOT LENGTH WORD LENGTH
00000 8 8
00100 12 8
00001 12
01000 16 8
00101 12
00010 16
01100 20 8
01001 12
00110 16
00011 20
10000 24 8
01101 12
01010 16
00111 20
11110 24
11000 32 8
10101 12
10010 16
01111 20
11111 24
DSP56364 24-Bit Digital Signal Processor Users Manual, Rev. 2
6-18 Freescale Semiconductor
Page 83

ESAI Programming Model
Table 6-5 ESAI Transmit Slot and Word Length Selection (continued)
TSWS4 TSWS3 TSWS2 TSWS1 TSWS0 SLOT LENGTH WORD LENGTH
01011 Reserved
01110
10001
10011
10100
10110
10111
11001
11010
11011
11100
11101
6.3.2.11 TCR Transmit Frame Sync Length (TFSL) - Bit 15
The TFSL bit selects the length of frame sync to be generated or recognized. If TFSL is cleared, a
word-length frame sync is selected. If TFSL is set, a 1-bit clock period frame sync is selected. See
Figure 6-7 for examples of frame length selection.
DSP56364 24-Bit Digital Signal Processor Users Manual, Rev. 2
Freescale Semiconductor 6-19
Page 84

ESAI Programming Model
SERIAL CLOCK
RX, TX FRAME SYNC
WORD LENGTH: TFSL=0, RFSL=0
RX, TX SERIAL DATA
NOTE: Frame sync occurs while data is valid.
SERIAL CLOCK
RX, TX FRAME SYNC
RX, TX SERIAL DATA
NOTE: Frame sync occurs for one bit time preceding the data.
SERIAL CLOCK
RX FRAME SYNC
RX SERIAL DATA
TX FRAME SYNC
DATA DATA
ONE BIT LENGTH: TFSL=1, RFSL=1
DATA DATA
MIXED FRAME LENGTH: TFSL=1, RFSL=0
DATA DATA
TX SERIAL DATA
SERIAL CLOCK
RX FRAME SYNC
RX SERIAL DATA
TX FRAME SYNC
TX SERIAL DATA
DATA DATA
MIXED FRAME LENGTH: TFSL=0, RFSL=1
DATA DATA
DATA DATA
Figure 6-7 Frame Length Selection
DSP56364 24-Bit Digital Signal Processor Users Manual, Rev. 2
6-20 Freescale Semiconductor
Page 85

ESAI Programming Model
6.3.2.12 TCR Transmit Frame Sync Relative Timing (TFSR) - Bit 16
TFSR determines the relative timing of the transmit frame sync signal as referred to the serial data lines,
for a word length frame sync only (TFSL=0). When TFSR is cleared the word length frame sync occurs
together with the first bit of the data word of the first slot. When TFSR is set the word length frame sync
starts one serial clock cycle earlier (i.e together with the last bit of the previous data word).
6.3.2.13 TCR Transmit Zero Padding Control (PADC) - Bit 17
When PADC is cleared, zero padding is disabled. When PADC is set, zero padding is enabled. PADC, in
conjunction with the TWA control bit, determines the way that padding is done for operating modes where
the word length is less than the slot length. See the TWA bit description in Section 6.3.2.8, "TCR Transmit
Word Alignment Control (TWA) - Bit 7" for more details.
Since the data word is shorter than the slot length, the data word is extended until achieving the slot length,
according to the following rule:
1. If the data word is left-aligned (TWA=0), and zero padding is disabled (PADC=0), then the last data
bit is repeated after the data word has been transmitted. If zero padding is enabled (PADC=1),
zeroes are transmitted after the data word has been transmitted.
2. If the data word is right-aligned (TWA=1), and zero padding is disabled (PADC=0), then the first
data bit is repeated before the transmission of the data word. If zero padding is enabled (PADC=1),
zeroes are transmitted before the transmission of the data word.
6.3.2.14 TCR Reserved Bit - Bits 18
This bit is reserved. It reads as zero, and it should be written with zero for future compatibility.
6.3.2.15 TCR Transmit Section Personal Reset (TPR) - Bit 19
The TPR control bit is used to put the transmitter section of the ESAI in the personal reset state. The
receiver section is not affected. When TPR is cleared, the transmitter section may operate normally. When
TPR is set, the transmitter section enters the personal reset state immediately. When in the personal reset
state, the status bits are reset to the same state as after hardware reset. The control bits are not affected by
the personal reset state. The transmitter data pins are tri-stated while in the personal reset state; if a stable
logic level is desired, the transmitter data pins should be defined as GPIO outputs, or external pull-up or
pull-down resistors should be used. The transmitter clock outputs drive zeroes while in the personal reset
state. Note that to leave the personal reset state by clearing TPR, the procedure described in Section 6.6,
"ESAI Initialization Examples" should be followed.
6.3.2.16 TCR Transmit Exception Interrupt Enable (TEIE) - Bit 20
When TEIE is set, the DSP is interrupted when both TDE and TUE in the SAISR status register are set.
When TEIE is cleared, this interrupt is disabled. Reading the SAISR status register followed by writing to
all the data registers of the enabled transmitters clears TUE, thus clearing the pending interrupt.
DSP56364 24-Bit Digital Signal Processor Users Manual, Rev. 2
Freescale Semiconductor 6-21
Page 86

ESAI Programming Model
6.3.2.17 TCR Transmit Even Slot Data Interrupt Enable (TEDIE) - Bit 21
The TEDIE control bit is used to enable the transmit even slot data interrupts. If TEDIE is set, the transmit
even slot data interrupts are enabled. If TEDIE is cleared, the transmit even slot data interrupts are
disabled. A transmit even slot data interrupt request is generated if TEDIE is set and the TEDE status flag
in the SAISR status register is set. Even time slots are all even-numbered time slots (0, 2, 4, etc.) when
operating in network mode. The zero time slot in the frame is marked by the frame sync signal and is
considered to be even. Writing data to all the data registers of the enabled transmitters or to TSR clears the
TEDE flag, thus servicing the interrupt.
Transmit interrupts with exception have higher priority than transmit even slot data interrupts, therefore if
exception occurs (TUE is set) and TEIE is set, the ESAI requests an ESAI transmit data with exception
interrupt from the interrupt controller.
6.3.2.18 TCR Transmit Interrupt Enable (TIE) - Bit 22
The DSP is interrupted when TIE and the TDE flag in the SAISR status register are set. When TIE is
cleared, this interrupt is disabled. Writing data to all the data registers of the enabled transmitters or to TSR
clears TDE, thus clearing the interrupt.
Transmit interrupts with exception have higher priority than normal transmit data interrupts, therefore if
exception occurs (TUE is set) and TEIE is set, the ESAI requests an ESAI transmit data with exception
interrupt from the interrupt controller.
6.3.2.19 TCR Transmit Last Slot Interrupt Enable (TLIE) - Bit 23
TLIE enables an interrupt at the beginning of last slot of a frame in network mode. When TLIE is set the
DSP is interrupted at the start of the last slot in a frame in network mode regardless of the transmit mask
register setting. When TLIE is cleared the transmit last slot interrupt is disabled. TLIE is disabled when
TDC[4:0]=$00000 (on-demand mode). The use of the transmit last slot interrupt is described in
Section 6.4.3, "ESAI Interrupt Requests".
6.3.3 ESAI Receive Clock Control Register (RCCR)
The read/write Receive Clock Control Register (RCCR) controls the ESAI receiver clock generator bit and
frame sync rates, word length, and number of words per frame for the serial data. The RCCR control bits
are described in the following paragraphs (see Figure 6-8).
DSP56364 24-Bit Digital Signal Processor Users Manual, Rev. 2
6-22 Freescale Semiconductor
Page 87

ESAI Programming Model
11109876543210
X:$FFFFB8 RDC2 RDC1 RDC0 RPSR RPM7 RPM6 RPM5 RPM4 RPM3 RPM2 RPM1 RPM0
23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16 15 14 13 12
RHCKD RFSD RCKD RHCKP RFSP RCKP RFP3 RFP2 RFP1 RFP0 RDC4 RDC3
Figure 6-8 RCCR Register
Hardware and software reset clear all the bits of the RCCR register.
6.3.3.1 RCCR Receiver Prescale Modulus Select (RPM7–RPM0) - Bits 7–0
The RPM7–RPM0 bits specify the divide ratio of the prescale divider in the ESAI receiver clock generator.
A divide ratio from 1 to 256 (RPM[7:0]=$00 to $FF) may be selected. The bit clock output is available at
the receiver serial bit clock (SCKR) pin of the DSP. The bit clock output is also available internally for use
as the bit clock to shift the receive shift registers. The ESAI receive clock generator functional diagram is
shown in Figure 6-3.
6.3.3.2 RCCR Receiver Prescaler Range (RPSR) - Bit 8
The RPSR controls a fixed divide-by-eight prescaler in series with the variable prescaler. This bit is used
to extend the range of the prescaler for those cases where a slower bit clock is desired. When RPSR is set,
the fixed prescaler is bypassed. When RPSR is cleared, the fixed divide-by-eight prescaler is operational
(see Figure 6-3). The maximum internally generated bit clock frequency is Fosc/4, the minimum internally
generated bit clock frequency is Fosc/(2 x 8 x 256)=Fosc/4096.
NOTE
Do not use the combination RPSR=1 and RPM7-RPM0=$00, which causes
synchronization problems when using the internal DSP clock as source
(RHCKD=1 or RCKD=1).
6.3.3.3 RCCR Rx Frame Rate Divider Control (RDC4–RDC0) - Bits 9–13
The RDC4–RDC0 bits control the divide ratio for the programmable frame rate dividers used to generate
the receiver frame clocks.
In network mode, this ratio may be interpreted as the number of words per frame minus one. The divide
ratio may range from 2 to 32 (RDC[4:0]=00001 to 11111) for network mode. A divide ratio of one
(RDC[4:0]=00000) in network mode is a special case (on-demand mode).
In normal mode, this ratio determines the word transfer rate. The divide ratio may range from 1 to 32
(RDC[4:0]=00000 to 11111) for normal mode. In normal mode, a divide ratio of one (RDC[4:0]=00000)
provides continuous periodic data word transfers. A bit-length frame sync (RFSL=1) must be used in this
case.
DSP56364 24-Bit Digital Signal Processor Users Manual, Rev. 2
Freescale Semiconductor 6-23
Page 88

ESAI Programming Model
The ESAI frame sync generator functional diagram is shown in Figure 6-4.
6.3.3.4 RCCR Rx High Frequency Clock Divider (RFP3-RFP0) - Bits 14-17
The RFP3–RFP0 bits control the divide ratio of the receiver high frequency clock to the receiver serial bit
clock when the source of the receiver high frequency clock and the bit clock is the internal DSP clock.
When the HCKR input is being driven from an external high frequency clock, the RFP3-RFP0 bits specify
an additional division ration in the clock divider chain. See Table 6-6 for the specification of the divide
ratio. The ESAI high frequency generator functional diagram is shown in Figure 6-3.
Table 6-6 Receiver High Frequency Clock Divider
RFP3-RFP0 Divide Ratio
$0 1
$1 2
$2 3
$3 4
... ...
$F 16
6.3.3.5 RCCR Receiver Clock Polarity (RCKP) - Bit 18
The Receiver Clock Polarity (RCKP) bit controls on which bit clock edge data and frame sync are clocked
out and latched in. If RCKP is cleared the data and the frame sync are clocked out on the rising edge of the
receive bit clock and the frame sync is latched in on the falling edge of the receive bit clock. If RCKP is
set the falling edge of the receive clock is used to clock the data and frame sync out and the rising edge of
the receive clock is used to latch the frame sync in.
6.3.3.6 RCCR Receiver Frame Sync Polarity (RFSP) - Bit 19
The Receiver Frame Sync Polarity (RFSP) determines the polarity of the receive frame sync signal. When
RFSP is cleared the frame sync signal polarity is positive (i.e the frame start is indicated by a high level
on the frame sync pin). When RFSP is set the frame sync signal polarity is negative (i.e the frame start is
indicated by a low level on the frame sync pin).
6.3.3.7 RCCR Receiver High Frequency Clock Polarity (RHCKP) - Bit 20
The Receiver High Frequency Clock Polarity (RHCKP) bit controls on which bit clock edge data and
frame sync are clocked out and latched in. If RHCKP is cleared the data and the frame sync are clocked
out on the rising edge of the receive bit clock and the frame sync is latched in on the falling edge of the
receive bit clock. If RHCKP is set the falling edge of the receive clock is used to clock the data and frame
sync out and the rising edge of the receive clock is used to latch the frame sync in.
DSP56364 24-Bit Digital Signal Processor Users Manual, Rev. 2
6-24 Freescale Semiconductor
Page 89

ESAI Programming Model
6.3.3.8 RCCR Receiver Clock Source Direction (RCKD) - Bit 21
The Receiver Clock Source Direction (RCKD) bit selects the source of the clock signal used to clock the
receive shift register in the asynchronous mode (SYN=0) and the IF0/OF0 flag direction in the
synchronous mode (SYN=1).
In the asynchronous mode when RCKD is set, the internal clock source becomes the bit clock for the
receive shift registers and word length divider, and is the output on the SCKR pin. In the asynchronous
mode when RCKD is cleared, the clock source is external; the internal clock generator is disconnected
from the SCKR pin, and an external clock source may drive this pin.
In the synchronous mode when RCKD is set, the SCKR pin becomes the OF0 output flag. If RCKD is
cleared, then the SCKR pin becomes the IF0 input flag. See Table 6-1 and Table 6-7 .
Table 6-7 SCKR Pin Definition Table
Control Bits
SCKR PIN
SYN RCKD
0 0 SCKR input
0 1 SCKR output
10IF0
11OF0
6.3.3.9 RCCR Receiver Frame Sync Signal Direction (RFSD) - Bit 22
The Receiver Frame Sync Signal Direction (RFSD) bit selects the source of the receiver frame sync signal
when in the asynchronous mode (SYN=0), and the IF1/OF1/Transmitter Buffer Enable flag direction in
the synchronous mode (SYN=1).
In the asynchronous mode when RFSD is set, the internal clock generator becomes the source of the
receiver frame sync, and is the output on the FSR pin. In the asynchronous mode when RFSD is cleared,
the receiver frame sync source is external; the internal clock generator is disconnected from the FSR pin,
and an external clock source may drive this pin.
In the synchronous mode when RFSD is set, the FSR pin becomes the OF1 output flag or the Transmitter
Buffer Enable, according to the TEBE control bit. If RFSD is cleared, then the FSR pin becomes the IF1
input flag. See Table 6-1 and Table 6-8.
DSP56364 24-Bit Digital Signal Processor Users Manual, Rev. 2
Freescale Semiconductor 6-25
Page 90

ESAI Programming Model
Table 6-8 FSR Pin Definition Table
Control Bits
FSR Pin
SYN TEBE RFSD
0 X 0 FSR input
0 X 1 FSR output
100 IF1
101 OF1
110 reserved
1 1 1 Transmitter Buffer Enable
6.3.3.10 RCCR Receiver High Frequency Clock Direction (RHCKD) - Bit 23
The Receiver High Frequency Clock Direction (RHCKD) bit selects the source of the receiver high
frequency clock when in the asynchronous mode (SYN=0), and the IF2/OF2 flag direction in the
synchronous mode (SYN=1).
In the asynchronous mode when RHCKD is set, the internal clock generator becomes the source of the
receiver high frequency clock, and is the output on the HCKR pin. In the asynchronous mode when
RHCKD is cleared, the receiver high frequency clock source is external; the internal clock generator is
disconnected from the HCKR pin, and an external clock source may drive this pin.
When RHCKD is cleared, HCKR is an input; when RHCKD is set, HCKR is an output.
In the synchronous mode when RHCKD is set, the HCKR pin becomes the OF2 output flag. If RHCKD
is cleared, then the HCKR pin becomes the IF2 input flag. See Table 6-1 and Table 6-9 .
Table 6-9 HCKR Pin Definition Table
Control Bits
HCKR PIN
SYN RHCKD
0 0 HCKR input
0 1 HCKR output
10IF2
11OF2
6.3.4 ESAI Receive Control Register (RCR)
The read/write Receive Control Register (RCR) controls the ESAI receiver section. Interrupt enable bits
for the receivers are provided in this control register. The receivers are enabled in this register (0,1,2 or 3
DSP56364 24-Bit Digital Signal Processor Users Manual, Rev. 2
6-26 Freescale Semiconductor
Page 91

ESAI Programming Model
receivers can be enabled) if the input data pin is not used by a transmitter. Operating modes are also
selected in this register.
11109876543210
X:$FFFFB7 RSWS1 RSWS0 RMOD RMOD RWA RSHFD
23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16 15 14 13 12
RLIE RIE REDIE REIE RPR
Reserved bit - read as zero; should be written with zero for future compatibility.
Figure 6-9 RCR Register
RFSR RFSL RSWS4 RSWS3 RSWS2
RE3 RE2 RE1 RE0
Hardware and software reset clear all the bits in the RCR register.
The ESAI RCR bits are described in the following paragraphs.
6.3.4.1 RCR ESAI Receiver 0 Enable (RE0) - Bit 0
When RE0 is set and TE5 is cleared, the ESAI receiver 0 is enabled and samples data at the SDO5/SDI0
pin. TX5 and RX0 should not be enabled at the same time (RE0=1 and TE5=1). When RE0 is cleared,
receiver 0 is disabled by inhibiting data transfer into RX0. If this bit is cleared while receiving a data word,
the remainder of the word is shifted in and transferred to the RX0 data register.
If RE0 is set while some of the other receivers are already in operation, the first data word received in RX0
will be invalid and must be discarded.
6.3.4.2 RCR ESAI Receiver 1 Enable (RE1) - Bit 1
When RE1 is set and TE4 is cleared, the ESAI receiver 1 is enabled and samples data at the SDO4/SDI1
pin. TX4 and RX1 should not be enabled at the same time (RE1=1 and TE4=1). When RE1 is cleared,
receiver 1 is disabled by inhibiting data transfer into RX1. If this bit is cleared while receiving a data word,
the remainder of the word is shifted in and transferred to the RX1 data register.
If RE1 is set while some of the other receivers are already in operation, the first data word received in RX1
will be invalid and must be discarded.
6.3.4.3 RCR ESAI Receiver 2 Enable (RE2) - Bit 2
When RE2 is set and TE3 is cleared, the ESAI receiver 2 is enabled and samples data at the SDO3/SDI2
pin. TX3 and RX2 should not be enabled at the same time (RE2=1 and TE3=1). When RE2 is cleared,
receiver 2 is disabled by inhibiting data transfer into RX2. If this bit is cleared while receiving a data word,
the remainder of the word is shifted in and transferred to the RX2 data register.
If RE2 is set while some of the other receivers are already in operation, the first data word received in RX2
will be invalid and must be discarded.
DSP56364 24-Bit Digital Signal Processor Users Manual, Rev. 2
Freescale Semiconductor 6-27
Page 92

ESAI Programming Model
6.3.4.4 RCR ESAI Receiver 3 Enable (RE3) - Bit 3
When RE3 is set and TE2 is cleared, the ESAI receiver 3 is enabled and samples data at the SDO2/SDI3
pin. TX2 and RX3 should not be enabled at the same time (RE3=1 and TE2=1). When RE3 is cleared,
receiver 3 is disabled by inhibiting data transfer into RX3. If this bit is cleared while receiving a data word,
the remainder of the word is shifted in and transferred to the RX3 data register.
If RE3 is set while some of the other receivers are already in operation, the first data word received in RX3
will be invalid and must be discarded.
6.3.4.5 RCR Reserved Bits - Bits 4-5, 17-18
These bits are reserved. They read as zero, and they should be written with zero for future compatibility.
6.3.4.6 RCR Receiver Shift Direction (RSHFD) - Bit 6
The RSHFD bit causes the receiver shift registers to shift data in MSB first when RSHFD is cleared or
LSB first when RSHFD is set (see Figure 6-13 and Figure 6-14).
6.3.4.7 RCR Receiver Word Alignment Control (RWA) - Bit 7
The Receiver Word Alignment Control (RWA) bit defines the alignment of the data word in relation to the
slot. This is relevant for the cases where the word length is shorter than the slot length. If RWA is cleared,
the data word is assumed to be left-aligned in the slot frame. If RWA is set, the data word is assumed to be
right-aligned in the slot frame.
If the data word is shorter than the slot length, the data bits which are not in the data word field are ignored.
For data word lengths of less than 24 bits, the data word is right-extended with zeroes before being stored
in the receive data registers.
6.3.4.8 RCR Receiver Network Mode Control (RMOD1-RMOD0) - Bits 8-9
The RMOD1 and RMOD0 bits are used to define the network mode of the ESAI receivers according to
Table 6-10. In the normal mode, the frame rate divider determines the word transfer rate – one word is
transferred per frame sync during the frame sync time slot, as shown in Figure 6-6. In network mode, it is
possible to transfer a word for every time slot, as shown in Figure 6-6. For more details, see Section 6.4,
"Operating Modes".
In order to comply with AC-97 specifications, RSWS4-RSWS0 should be set to 00011 (20-bit slot, 20-bit
word), RFSL and RFSR should be cleared, and RDC4-RDC0 should be set to $0C (13 words in frame).
DSP56364 24-Bit Digital Signal Processor Users Manual, Rev. 2
6-28 Freescale Semiconductor
Page 93

ESAI Programming Model
Table 6-10 ESAI Receive Network Mode Selection
RMOD1 RMOD0 RDC4-RDC0 Receiver Network Mode
0 0 $0-$1F Normal Mode
0 1 $0 On-Demand Mode
0 1 $1-$1F Network Mode
1 0 X Reserved
1 1 $0C AC97
6.3.4.9 RCR Receiver Slot and Word Select (RSWS4-RSWS0) - Bits 10-14
The RSWS4-RSWS0 bits are used to select the length of the slot and the length of the data words being
received via the ESAI. The word length must be equal to or shorter than the slot length. The possible
combinations are shown in Table 6-11. See also the ESAI data path programming model in Figure 6-13
and Figure 6-14.
Table 6-11 ESAI Receive Slot and Word Length Selection
RSWS4 RSWS3 RSWS2 RSWS1 RSWS0 SLOT LENGTH WORD LENGTH
00000 8 8
00100 12 8
00001 12
01000 16 8
00101 12
00010 16
01100 20 8
01001 12
00110 16
00011 20
10000 24 8
01101 12
01010 16
00111 20
11110 24
DSP56364 24-Bit Digital Signal Processor Users Manual, Rev. 2
Freescale Semiconductor 6-29
Page 94

ESAI Programming Model
Table 6-11 ESAI Receive Slot and Word Length Selection (continued)
RSWS4 RSWS3 RSWS2 RSWS1 RSWS0 SLOT LENGTH WORD LENGTH
11000 32 8
10101 12
10010 16
01111 20
11111 24
01011 Reserved
01110
10001
10011
10100
10110
10111
11001
11010
11011
11100
11101
6.3.4.10 RCR Receiver Frame Sync Length (RFSL) - Bit 15
The RFSL bit selects the length of the receive frame sync to be generated or recognized. If RFSL is cleared,
a word-length frame sync is selected. If RFSL is set, a 1-bit clock period frame sync is selected. See
Figure 6-7 for examples of frame length selection.
6.3.4.11 RCR Receiver Frame Sync Relative Timing (RFSR) - Bit 16
RFSR determines the relative timing of the receive frame sync signal as referred to the serial data lines,
for a word length frame sync only. When RFSR is cleared the word length frame sync occurs together with
the first bit of the data word of the first slot. When RFSR is set the word length frame sync starts one serial
clock cycle earlier (i.e. together with the last bit of the previous data word).
DSP56364 24-Bit Digital Signal Processor Users Manual, Rev. 2
6-30 Freescale Semiconductor
Page 95

ESAI Programming Model
6.3.4.12 RCR Receiver Section Personal Reset (RPR) - Bit 19
The RPR control bit is used to put the receiver section of the ESAI in the personal reset state. The
transmitter section is not affected. When RPR is cleared, the receiver section may operate normally. When
RPR is set, the receiver section enters the personal reset state immediately. When in the personal reset
state, the status bits are reset to the same state as after hardware reset.The control bits are not affected by
the personal reset state.The receiver data pins are disconnected while in the personal reset state. Note that
to leave the personal reset state by clearing RPR, the procedure described in Section 6.6, "ESAI
Initialization Examples" should be followed.
6.3.4.13 RCR Receive Exception Interrupt Enable (REIE) - Bit 20
When REIE is set, the DSP is interrupted when both RDF and ROE in the SAISR status register are set.
When REIE is cleared, this interrupt is disabled. Reading the SAISR status register followed by reading
the enabled receivers data registers clears ROE, thus clearing the pending interrupt.
6.3.4.14 RCR Receive Even Slot Data Interrupt Enable (REDIE) - Bit 21
The REDIE control bit is used to enable the receive even slot data interrupts. If REDIE is set, the receive
even slot data interrupts are enabled. If REDIE is cleared, the receive even slot data interrupts are disabled.
A receive even slot data interrupt request is generated if REDIE is set and the REDF status flag in the
SAISR status register is set. Even time slots are all even-numbered time slots (0, 2, 4, etc.) when operating
in network mode. The zero time slot is marked by the frame sync signal and is considered to be even.
Reading all the data registers of the enabled receivers clears the REDF flag, thus servicing the interrupt.
Receive interrupts with exception have higher priority than receive even slot data interrupts, therefore if
exception occurs (ROE is set) and REIE is set, the ESAI requests an ESAI receive data with exception
interrupt from the interrupt controller.
6.3.4.15 RCR Receive Interrupt Enable (RIE) - Bit 22
The DSP is interrupted when RIE and the RDF flag in the SAISR status register are set. When RIE is
cleared, this interrupt is disabled. Reading the receive data registers of the enabled receivers clears RDF,
thus clearing the interrupt.
Receive interrupts with exception have higher priority than normal receive data interrupts, therefore if
exception occurs (ROE is set) and REIE is set, the ESAI requests an ESAI receive data with exception
interrupt from the interrupt controller.
6.3.4.16 RCR Receive Last Slot Interrupt Enable (RLIE) - Bit 23
RLIE enables an interrupt after the last slot of a frame ended in network mode only. When RLIE is set the
DSP is interrupted after the last slot in a frame ended regardless of the receive mask register setting. When
RLIE is cleared the receive last slot interrupt is disabled. Hardware and software reset clear RLIE. RLIE
is disabled when RDC[4:0]=00000 (on-demand mode). The use of the receive last slot interrupt is
described in Section 6.4.3, "ESAI Interrupt Requests".
DSP56364 24-Bit Digital Signal Processor Users Manual, Rev. 2
Freescale Semiconductor 6-31
Page 96

ESAI Programming Model
6.3.5 ESAI Common Control Register (SAICR)
The read/write Common Control Register (SAICR) contains control bits for functions that affect both the
receive and transmit sections of the ESAI.See Figure 6-10.
11109876543210
X:$FFFFB4
23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16 15 14 13 12
Reserved bit - read as zero; should be written with zero for future compatibility.
ALC TEBE SYN OF2 OF1 OF0
Figure 6-10 SAICR Register
Hardware and software reset clear all the bits in the SAICR register.
6.3.5.1 SAICR Serial Output Flag 0 (OF0) - Bit 0
The Serial Output Flag 0 (OF0) is a data bit used to hold data to be send to the OF0 pin. When the ESAI
is in the synchronous clock mode (SYN=1), the SCKR pin is configured as the ESAI flag 0. If the receiver
serial clock direction bit (RCKD) is set, the SCKR pin is the output flag OF0, and data present in the OF0
bit is written to the OF0 pin at the beginning of the frame in normal mode or at the beginning of the next
time slot in network mode.
6.3.5.2 SAICR Serial Output Flag 1 (OF1) - Bit 1
The Serial Output Flag 1 (OF1) is a data bit used to hold data to be send to the OF1 pin. When the ESAI
is in the synchronous clock mode (SYN=1), the FSR pin is configured as the ESAI flag 1. If the receiver
frame sync direction bit (RFSD) is set and the TEBE bit is cleared, the FSR pin is the output flag OF1, and
data present in the OF1 bit is written to the OF1 pin at the beginning of the frame in normal mode or at the
beginning of the next time slot in network mode.
6.3.5.3 SAICR Serial Output Flag 2 (OF2) - Bit 2
The Serial Output Flag 2 (OF2) is a data bit used to hold data to be send to the OF2 pin. When the ESAI
is in the synchronous clock mode (SYN=1), the HCKR pin is configured as the ESAI flag 2. If the receiver
high frequency clock direction bit (RHCKD) is set, the HCKR pin is the output flag OF2, and data present
in the OF2 bit is written to the OF2 pin at the beginning of the frame in normal mode or at the beginning
of the next time slot in network mode.
6.3.5.4 SAICR Reserved Bits - Bits 3-5, 9-23
These bits are reserved. They read as zero, and they should be written with zero for future compatibility.
DSP56364 24-Bit Digital Signal Processor Users Manual, Rev. 2
6-32 Freescale Semiconductor
Page 97

ESAI Programming Model
6.3.5.5 SAICR Synchronous Mode Selection (SYN) - Bit 6
The Synchronous Mode Selection (SYN) bit controls whether the receiver and transmitter sections of the
ESAI operate synchronously or asynchronously with respect to each other (see Figure 6-11). When SYN
is cleared, the asynchronous mode is chosen and independent clock and frame sync signals are used for
the transmit and receive sections. When SYN is set, the synchronous mode is chosen and the transmit and
receive sections use common clock and frame sync signals.
When in the synchronous mode (SYN=1), the transmit and receive sections use the transmitter section
clock generator as the source of the clock and frame sync for both sections. Also, the receiver clock pins
SCKR, FSR and HCKR now operate as I/O flags. See Table 6-7 , Table 6- 8 and Tabl e 6-9 for the effects of
SYN on the receiver clock pins.
6.3.5.6 SAICR Transmit External Buffer Enable (TEBE) - Bit 7
The Transmitter External Buffer Enable (TEBE) bit controls the function of the FSR pin when in the
synchronous mode. If the ESAI is configured for operation in the synchronous mode (SYN=1), and TEBE
is set while FSR pin is configured as an output (RFSD=1), the FSR pin functions as the transmitter external
buffer enable control, to enable the use of an external buffers on the transmitter outputs. If TEBE is cleared
then the FSR pin functions as the serial I/O flag 1. See Table 6-8 for a summary of the effects of TEBE on
the FSR pin.
6.3.5.7 SAICR Alignment Control (ALC) - Bit 8
The ESAI is designed for 24-bit fractional data, thus shorter data words are left aligned to the MSB (bit
23). Some applications use 16-bit fractional data. In those cases, shorter data words may be left aligned to
bit 15. The Alignment Control (ALC) bit supports these applications.
If ALC is set, transmitted and received words are left aligned to bit 15 in the transmit and receive shift
registers. If ALC is cleared, transmitted and received word are left aligned to bit 23 in the transmit and
receive shift registers.
NOTE
While ALC is set, 20-bit and 24-bit words may not be used, and word length
control should specify 8-, 12- or 16-bit words, otherwise results are
unpredictable.
DSP56364 24-Bit Digital Signal Processor Users Manual, Rev. 2
Freescale Semiconductor 6-33
Page 98

ESAI Programming Model
ASYNCHRONOUS (SYN=0)
TRANSMITTER
CLOCK
SCKT
ESAI BIT
CLOCK
SCKR
NOTE: Transmitter and receiver may have different clocks and frame syncs.
SCKT
ESAI BIT
CLOCK
EXTERNAL TRANSMIT CLOCK
INTERNAL CLOCK
EXTERNAL RECEIVE CLOCK
CLOCK FRAME
SYNCHRONOUS (SYN=1)
CLOCK
EXTERNAL CLOCK
INTERNAL CLOCK
RECEIVER
TRANSMITTER
FRAME
SYNC
SYNC
FRAME
SYNC
SDO
EXTERNAL TRANSMIT FRAME SYNC
INTERNAL FRAME SYNC
EXTERNAL RECEIVE FRAME SYNC
SDI
SDO
EXTERNAL FRAME SYNC
INTERNAL FRAME SYNC
FST
FSR
FST
CLOCK FRAME
RECEIVER
NOTE: Transmitter and receiver have the same clocks and frame syncs.
SYNC
SDI
Figure 6-11 SAICR SYN Bit Operation
6.3.6 ESAI Status Register (SAISR)
The Status Register (SAISR) is a read-only status register used by the DSP to read the status and serial
input flags of the ESAI. See Figure 6-12. The status bits are described in the following paragraphs.
DSP56364 24-Bit Digital Signal Processor Users Manual, Rev. 2
6-34 Freescale Semiconductor
Page 99

ESAI Programming Model
11109876543210
X:$FFFFB3 RODF REDF RDF ROE RFS IF2 IF1 IF0
23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16 15 14 13 12
TODE TEDE TDE TUE TFS
Reserved bit - read as zero; should be written with zero for future compatibility.
Figure 6-12 SAISR Register
6.3.6.1 SAISR Serial Input Flag 0 (IF0) - Bit 0
The IF0 bit is enabled only when the SCKR pin is defined as ESAI in the Port Control Register, SYN=1
and RCKD=0, indicating that SCKR is an input flag and the synchronous mode is selected. Data present
on the SCKR pin is latched during reception of the first received data bit after frame sync is detected. The
IF0 bit is updated with this data when the receiver shift registers are transferred into the receiver data
registers. IF0 reads as a zero when it is not enabled. Hardware, software, ESAI individual, and STOP reset
clear IF0.
6.3.6.2 SAISR Serial Input Flag 1 (IF1) - Bit 1
The IF1 bit is enabled only when the FSR pin is defined as ESAI in the Port Control Register, SYN =1,
RFSD=0 and TEBE=0, indicating that FSR is an input flag and the synchronous mode is selected. Data
present on the FSR pin is latched during reception of the first received data bit after frame sync is detected.
The IF1 bit is updated with this data when the receiver shift registers are transferred into the receiver data
registers. IF1 reads as a zero when it is not enabled. Hardware, software, ESAI individual, and STOP reset
clear IF1.
6.3.6.3 SAISR Serial Input Flag 2 (IF2) - Bit 2
The IF2 bit is enabled only when the HCKR pin is defined as ESAI in the Port Control Register, SYN=1
and RHCKD=0, indicating that HCKR is an input flag and the synchronous mode is selected. Data present
on the HCKR pin is latched during reception of the first received data bit after frame sync is detected. The
IF2 bit is updated with this data when the receive shift registers are transferred into the receiver data
registers. IF2 reads as a zero when it is not enabled. Hardware, software, ESAI individual, and STOP reset
clear IF2.
6.3.6.4 SAISR Reserved Bits - Bits 3-5, 11-12, 18-23
These bits are reserved for future use. They read as zero.
DSP56364 24-Bit Digital Signal Processor Users Manual, Rev. 2
Freescale Semiconductor 6-35
Page 100

ESAI Programming Model
6.3.6.5 SAISR Receive Frame Sync Flag (RFS) - Bit 6
When set, RFS indicates that a receive frame sync occurred during reception of the words in the receiver
data registers. This indicates that the data words are from the first slot in the frame. When RFS is clear and
a word is received, it indicates (only in the network mode) that the frame sync did not occur during
reception of that word. RFS is cleared by hardware, software, ESAI individual, or STOP reset. RFS is valid
only if at least one of the receivers is enabled (REx=1).
NOTE
In normal mode, RFS always reads as a one when reading data because there
is only one time slot per frame – the “frame sync” time slot.
6.3.6.6 SAISR Receiver Overrun Error Flag (ROE) - Bit 7
The ROE flag is set when the serial receive shift register of an enabled receiver is full and ready to transfer
to its receiver data register (RXx) and the register is already full (RDF=1). If REIE is set, an ESAI receive
data with exception (overrun error) interrupt request is issued when ROE is set. Hardware, software, ESAI
individual, and STOP reset clear ROE. ROE is also cleared by reading the SAISR with ROE set, followed
by reading all the enabled receive data registers.
6.3.6.7 SAISR Receive Data Register Full (RDF) - Bit 8
RDF is set when the contents of the receive shift register of an enabled receiver is transferred to the
respective receive data register. RDF is cleared when the DSP reads the receive data register of all enabled
receivers or cleared by hardware, software, ESAI individual, or STOP reset. If RIE is set, an ESAI receive
data interrupt request is issued when RDF is set.
6.3.6.8 SAISR Receive Even-Data Register Full (REDF) - Bit 9
When set, REDF indicates that the received data in the receive data registers of the enabled receivers have
arrived during an even time slot when operating in the network mode. Even time slots are all
even-numbered slots (0, 2, 4, 6, etc.). Time slots are numbered from zero to N-1, where N is the number
of time slots in the frame. The zero time slot is considered even. REDF is set when the contents of the
receive shift registers are transferred to the receive data registers. REDF is cleared when the DSP reads all
the enabled receive data registers or cleared by hardware, software, ESAI individual, or STOP resets. If
REDIE is set, an ESAI receive even slot data interrupt request is issued when REDF is set.
6.3.6.9 SAISR Receive Odd-Data Register Full (RODF) - Bit 10
When set, RODF indicates that the received data in the receive data registers of the enabled receivers have
arrived during an odd time slot when operating in the network mode. Odd time slots are all odd-numbered
slots (1, 3, 5, etc.). Time slots are numbered from zero to N-1, where N is the number of time slots in the
frame. RODF is set when the contents of the receive shift registers are transferred to the receive data
registers. RODF is cleared when the DSP reads all the enabled receive data registers or cleared by
hardware, software, ESAI individual, or STOP resets.
DSP56364 24-Bit Digital Signal Processor Users Manual, Rev. 2
6-36 Freescale Semiconductor
 Loading...
Loading...