Page 1

Freescale Semiconductor
Technical Data
MPC862/857T/857DSL
PowerQUICC™ Family
Hardware Specifications
Document Number: MPC862EC
Rev. 3, 2/2006
This document contains detailed information on power
considerations, DC/AC electrical characteristics, and AC
timing specifications for the M PC862/857T/857DSL family
(refer to Table 1 for a list of devices). The MPC862P, which
contains a PowerPC™ core processor, is the superset device
of the MPC862/857T/857DSL family. For functional
characteristics of the processor, refer to the MPC862
PowerQUICC™ Family Users Manual (MPC862UM/D).
Contents
1. Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
2. Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
3. Maximum Tolerated Ratings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
4. Thermal Characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
5. Power Dissipation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
6. DC Characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
7. Thermal Calculation and Measurement . . . . . . . . . . 12
8. Layout Practices . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
9. Bus Signal Timing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
10. IEEE 1149.1 Electrical Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . 44
11. CPM Electrical Characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
12. UTOPIA AC Electrical Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . 68
13. FEC Electrical Characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 69
14. Mechanical Data and Ordering Info r m ation . . . . . . . 72
15. Document Revision History . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 86
© Freescale Semiconductor, Inc., 2006. All rights reserved.
Page 2
Overview
1Overview
The MPC862/857T/857DSL is a derivative of Freescale’s MPC860 PowerQUICC™ family of devices. It
is a versatile single-chip integrated microprocess or and peripheral combination that can be used in a
variety of controller applications and communications and networking systems. The
MPC862/857T/857DSL provides enhanced A T M functionality over that of other A TM-enabled members
of the MPC860 family.
Table 1 shows the functionality supported by the members of the MPC862/857T/857DSL family.
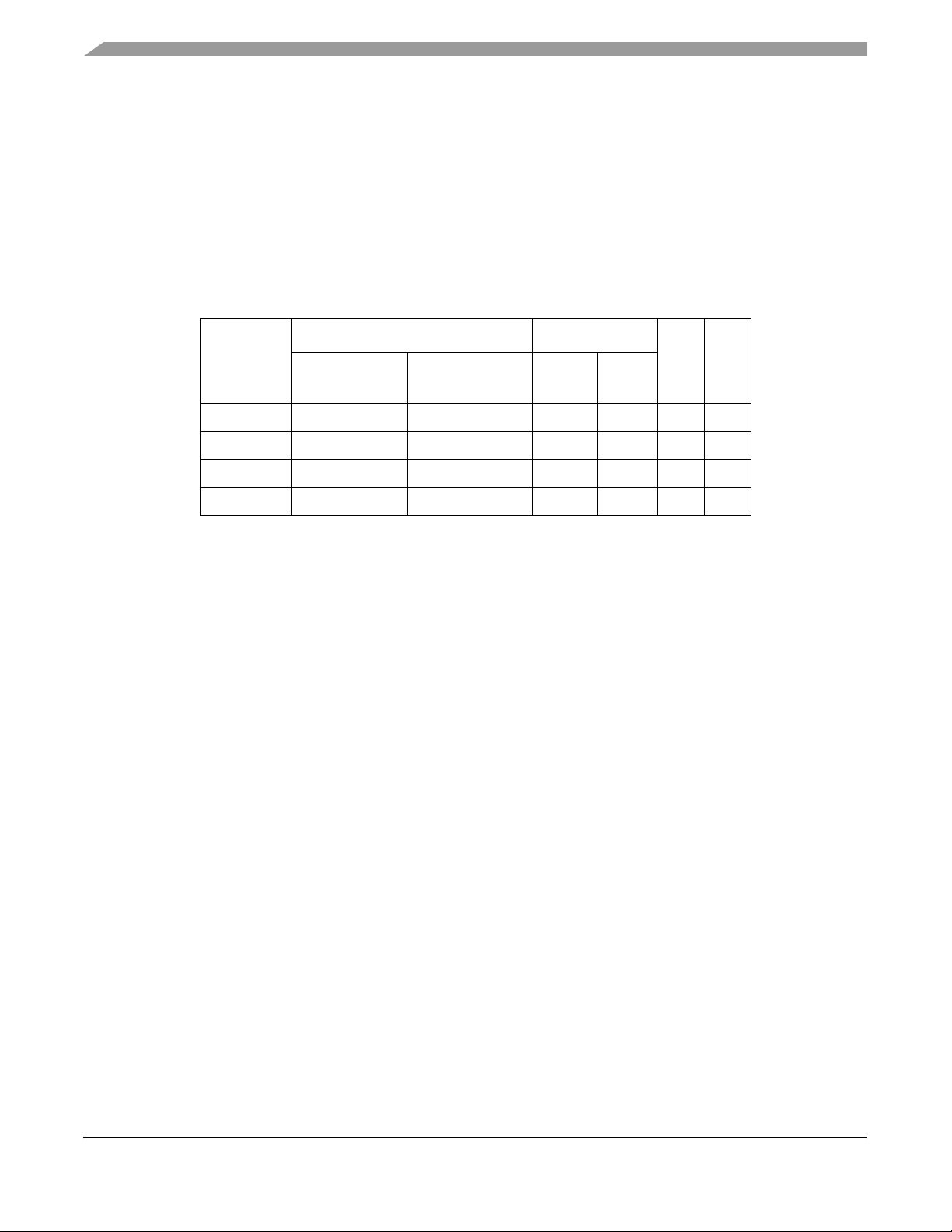
Table 1. MPC862 Family Functionality
Cache Ethernet
Part
MPC862P 16 Kbyte 8 Kbyte Up to 4 1 4 2
MPC862T 4 Kbyte 4 Kbyte Up to 4 1 4 2
MPC857T 4 Kbyte 4 Kbyte 1 1 1 2
MPC857DSL 4 Kbyte 4 Kbyte 1 1 1
1
On the MPC857DSL, the SCC (SCC1) is for ethernet only. Also, the MPC857DSL does
not support the Time Slot Assigner (TSA).
2
On the MPC857DSL, the SMC (SMC1) is for UART only.
Instruction
Cache
Data Cache 10T 10/100
SCC SMC
1
2
1
2Features
The following list summarizes the key MPC862/857T/857DSL features:
• Embedded single-issue, 32-bit MPC8xx core (implementing the PowerPC architecture) with
thirty-two 32-bit general-purpose registers (GPRs)
— The core performs branch prediction with conditional prefetch, without conditional execution
— 4- or 8-Kbyte data cache and 4- or 16-Kbyte instruction cache (see Table 1).
– 16-Kbyte instruction cache (MPC862P) is four-way, set-associative with 256 sets; 4-Kbyte
instruction cache (MPC862T , MPC857T, and MPC857DSL) is two-way, set-associative
with 128 sets.
– 8-Kbyte data cache (MPC862P) is two-way , set-associative with 256 sets; 4-Kbyte data
cache (MPC862T , MP C857T, and MPC857DSL) is two-way, set-associative with 128 sets.
– Cache coherency for both instruction and data caches is maintained on 128-bit (4-word)
cache blocks.
– Caches are physically addressed, implement a least recently used (LRU) replacement
algorithm, and are lockable on a cache block basis.
— MMUs with 32-entry TLB, fully associative instruction and data TLBs
— MMUs support multiple page sizes of 4, 16, and 512 Kbytes, and 8 Mbytes; 16 virtual address
spaces and 16 protection groups
— Advanced on-chip-emulation debug mode
MPC862/857T/857DSL PowerQUICC™ Family Hardware Specifications, Rev. 3
2 Freescale Semiconductor
Page 3

Features
• The MPC862/857T/857DSL pr ovides enhanced ATM functionality over that of the MPC860SAR.
The MPC862/857T/857DSL adds major new features available in “enhanced SAR” (ESAR) mode,
including the following:
— Improved operation, administration and maintenance (OAM) support
— OAM performance monitoring (PM) support
— Multiple APC priority levels available to support a range of traffic pace requirements
— ATM port-to-port switching capability without the need for RAM-based microcode
— Simultaneous MII (10/100Base-T) and UTOPIA (half-duplex) capability
— Optional statistical cell counters per PHY
— UTOPIA level 2 compliant interface with added FIFO buffering to reduce the total cell
transmission time. (The earlier UTOPIA level 1 specification is also supported.)
— Multi-PHY support on the MPC857T
— Four PHY support on the MPC857DSL
— Parameter RAM for both SPI and I2C can be relocated without RAM-based microcode
— Supports full-duplex UTOPIA both master (ATM side) and slave (PHY side) operation using
a “split” bus
— AAL2/VBR functionality is ROM-resident
• Up to 32-bit data bus (dynamic bus sizing for 8, 16, and 32 bits)
• 32 address lines
• Memory controller (eight banks)
— Contains complete dynamic RAM (DRAM) controller
— Eac h bank can be a chip select or RAS to support a DRAM bank
— Up to 30 wait states programmable per memory bank
— Glueless interface to Page mode/EDO/SDRAM, SRAM, EPROMs, flash EPROMs, and other
memory devices.
— DRAM controller programmable to support most size and speed memory interfaces
— Four CAS lines, four WE lines, one OE line
— Boot chip-select available at reset (options for 8-, 16-, or 32-bit memory)
— Variable block sizes (32 Kbyte–256 Mbyte)
— Selectable write protection
— On-chip bus arbitration logic
• General-purpose timers
— Four 16-bit timers cascadable to be two 32-bit timers
— Gate mode can enable/disable counting
— Interrupt can be masked on reference match and event capture
• Fast Ethernet controller (FEC)
— Simultaneous MII (10/100Base-T) and UTOPIA operation when using the UTOPIA
multiplexed bus.
MPC862/857T/857DSL PowerQUICC™ Family Hardware Specifications, Rev. 3
Freescale Semiconductor 3
Page 4

Features
• System integration unit (SIU)
— Bus monitor
— S oftware watchdog
— Periodic interrupt timer (PIT)
— Low-power stop mode
— Clock synthesizer
— Decrementer, time base, and real-time clock (RTC) from the PowerPC architecture
— Reset controller
— IEEE 1149.1 test access port (JTAG)
• Interrupts
— Seven external interrupt request (IRQ) lines
— 12 port pins with interrupt capability
— The MPC862P and MPC862T have 23 internal interrupt sources; the MPC857T and
MPC857DSL have 20 internal interrupt sources
— Programmable priority between SCCs (MPC862P and MPC862T)
— Programmable highest priority request
• Communications processor module (CPM)
— RISC controller
— Communication-specific commands (for example, GRACEFUL STOP TRANSMIT, ENTER HUNT
MODE, and RESTART TRANSMIT)
— Supports continuous mode transmission and reception on all serial channels
— Up to 8-Kbytes of dual-port RAM
— The MPC862P and MPC862T have 16 serial DMA (SDMA) channels; the MPC857T and
MPC857DSL have 10 serial DMA (SDMA) channels
— Three parallel I/O registers with open-drain capability
• Four baud rate generators
— Independent (can be connected to any SCC or SMC)
— Allow changes during operation
— Autobaud support option
• The MPC862P and MPC862T have four SCCs (serial communication controller) The MPC857T
and MPC857DSL have one SCC, SCC1; the MPC857DSL supports ethernet only
— Serial ATM capability on all SCCs
— Optional UTOPIA port on SCC4
— Ethernet/IEEE 802.3 optional on SCC1–4, supporting full 10-Mbps operation
— HDLC/SDLC
— HDLC bus (implements an HDLC-based local area network (LAN))
— Asynchronous HDLC to support PPP (point-to-point protocol)
— AppleTalk
4 Freescale Semiconductor
MPC862/857T/857DSL PowerQUICC™ Family Hardware Specifications, Rev. 3
Page 5

Features
— Univer sal asynchronous receiver transmitter (UART)
— Synchronous UART
— Serial infrared (IrDA)
— Binary synchronous communication (BISYNC)
— Totally transparent (bit streams)
— Totally transparent (frame based with optional cyclic redundancy check (CRC))
• Two SMCs (serial management channels) (The MPC857DSL has one SMC, SMC1 for UART)
— UART
— Transparent
— Gener al circuit i nte rface ( GCI ) controller
— Can be connected to the time-division multiplexed (TDM) channels
• One serial peripheral interface (SPI)
— Supports master and slave modes
— Supports multiple-master operation on the same bus
• One inter-integrat ed circuit (I2C) port
— Supports master and slave modes
— Multiple-master environment support
• Time-slot assigner (TSA) (The MPC857DSL does not have the TSA)
— Allows SCCs and SMCs to run in multiplexed and/or non-multiplexed operation
— Supports T1, CEPT, PCM highway, ISDN basic rate, ISDN primary rate, user defined
— 1- or 8-bit resolution
— Allows independent transmit and receive routing, frame synchronization, clocking
— Allows dynamic changes
— On the MPC862P and MPC862T, can be internal ly connected to six serial channels (four SCCs
and two SMCs); on the MPC857T , can be connected to three serial channels (one SCC and two
SMCs)
• Parallel interface port (PI P)
— Centronics interface support
— Supports fast connection between compatible ports on MPC862/857T/857DSL or MC68360
• PCMCIA interface
— Master (socket) interface, release 2.1 compliant
— Supports one or two PCMCIA sockets dependent upon whether ESAR functionality is enabled
— 8 memory or I/O windows supported
• Low power support
— Full on—All units fully powered
— Doze—Core functional units disabled except tim e base dec rementer , PL L, memory controller,
RTC, and CPM in low-power standby
MPC862/857T/857DSL PowerQUICC™ Family Hardware Specifications, Rev. 3
Freescale Semiconductor 5
Page 6

Features
— Sleep—All units disabled except RTC, PIT, time base, and decrementer with PLL active for
fast wake up
— Deep sleep—All units disabled including PLL except RTC, PIT, time base, and decrementer.
— Power down mode— All units powered down except PLL, RTC, PIT, time base and
decrementer
• Debug interface
— Eight comparators: four operate on instruction address, two operate on data address, and two
operate on data
— Supports conditions: = ≠ < >
— Eac h watchpoint can generate a break point internally
• 3.3 V operation with 5-V TTL compatibility except EXTAL and EXTCLK
• 357-pin plastic ball grid array (PBGA) package
• Operation up to 100MHz
The MPC862/857T/857DSL is comprised of three modules that each use the 32-bit internal bus: the
MPC8xx core, the system integration unit (SIU), and the communication processor module (CPM). The
MPC862P/862T block diagram is shown in Figure 1. The MPC857T /857DSL block diagram is s hown in
Figure 2.
MPC862/857T/857DSL PowerQUICC™ Family Hardware Specifications, Rev. 3
6 Freescale Semiconductor
Page 7
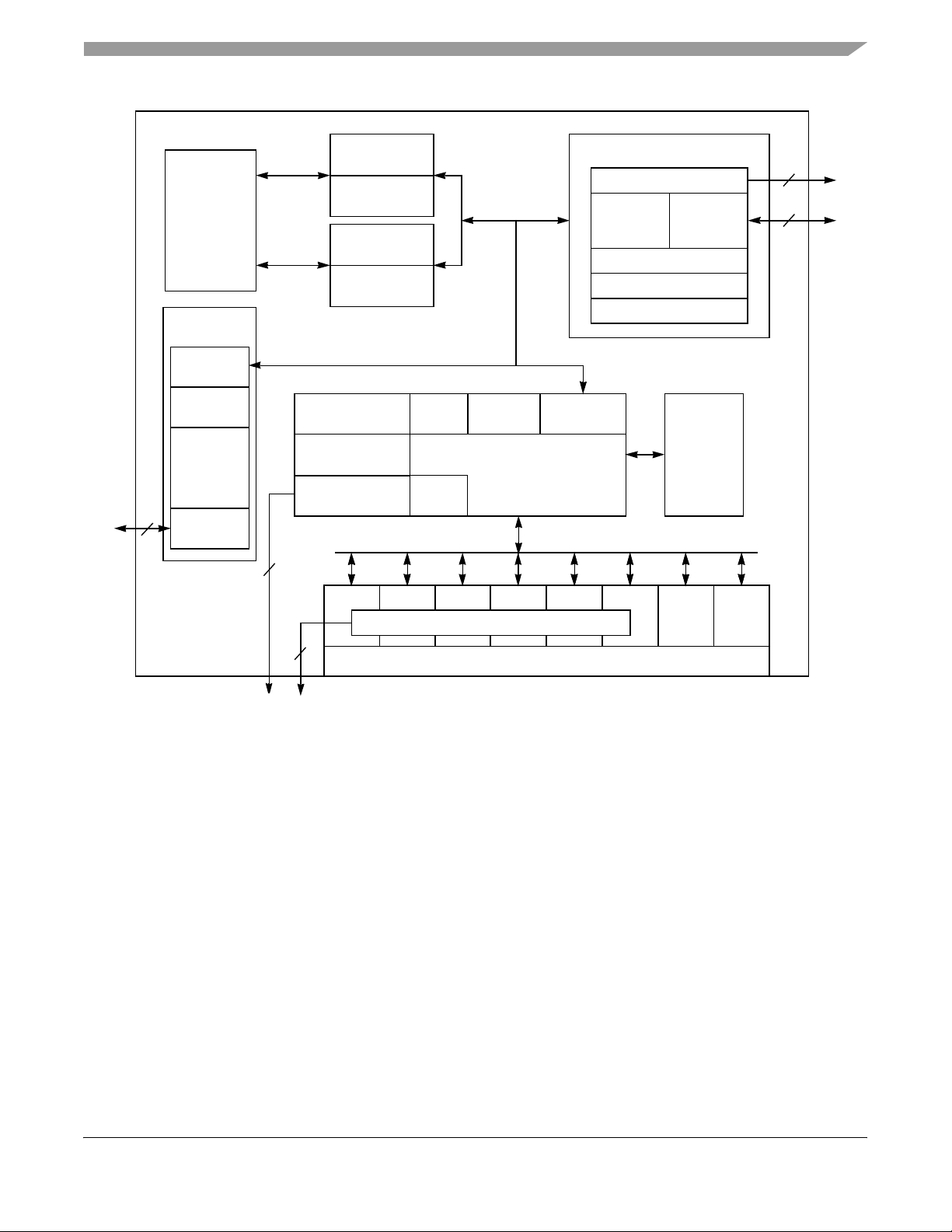
Features
Embedded
MPC8xx
Processor
Core
Fast Ethernet
Controller
DMAs
FIFOs
10/100
Base-T
Media Access
Control
MII
Instruction
Bus
Load/Store
Bus
Parallel I/O
4 Baud Rate
Generators
Parallel Interface Port
and UTOPIA
16-Kbyte*
Instruction Cache
Instruction MMU
32-Entry ITLB
8-Kbyte*
Data Cache
Data MMU
32-Entry DTLB
SCC1
Unified
Bus
4
Interrupt
Timers
Timers
Controllers
32-Bit RISC Controller
and Program
ROM
SCC3 SCC4
Time Slot Assigner
Time Slot Assigner
System Interface Unit (SIU)
Bus Interface
8-Kbyte
Dual-Port RAM
Memory Controller
Internal
Unit
System Functions
Real-Time Clock
PCMCIA/ATA Interface
External
Bus Interface
Unit
16
Serial
and
2
Independent
DMA
Channels
I2CSPISMC2SMC1SCC2
Serial Interface
*The MPC862T contains 4-Kbyte instruction cache and 4-Kbyte data cache.
Figure 1. MPC862P/862T Block Diagram
MPC862/857T/857DSL PowerQUICC™ Family Hardware Specifications, Rev. 3
Freescale Semiconductor 7
Page 8
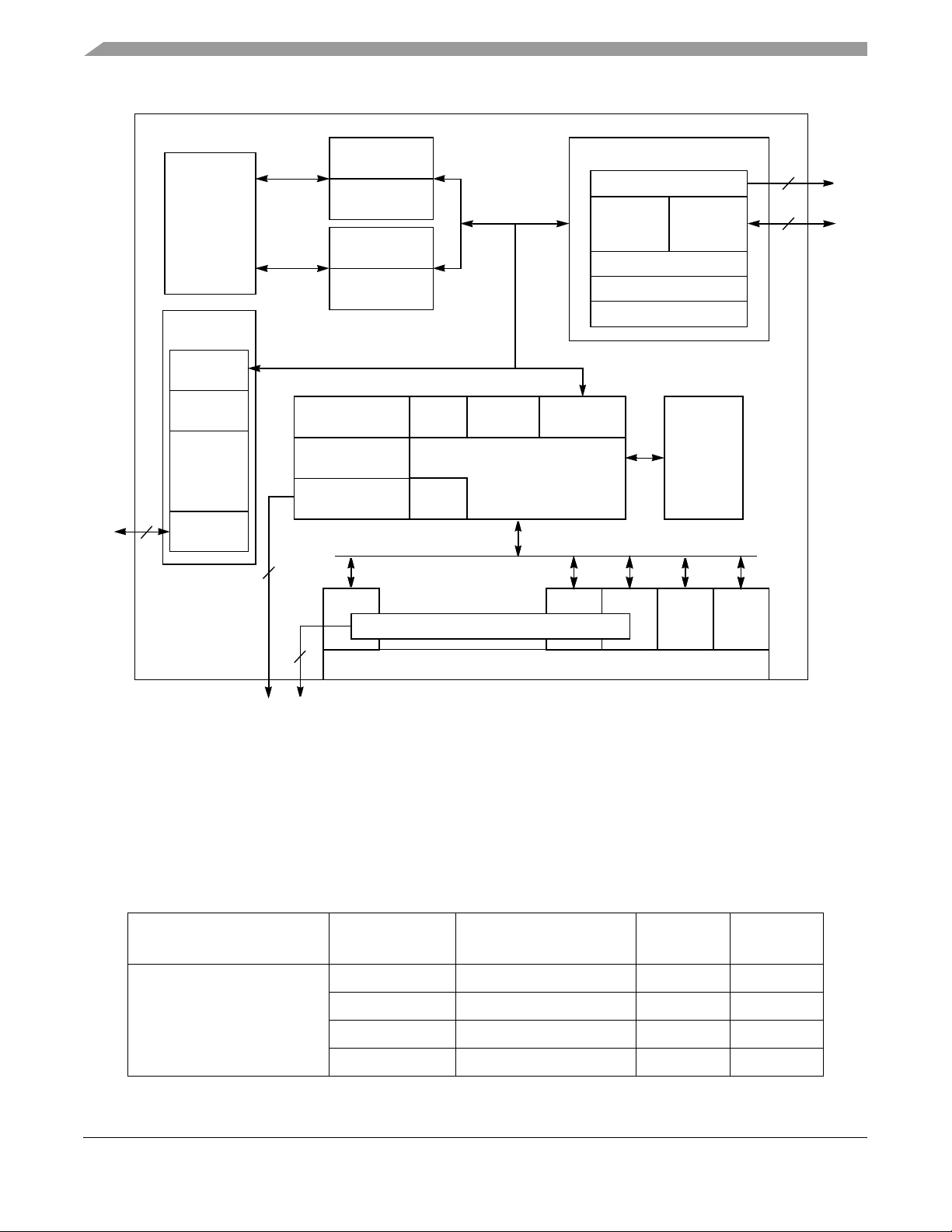
Maximum Tolerated Ratings
Embedded
MPC8xx
Processor
Core
Fast Ethernet
Controller
DMAs
FIFOs
10/100
Base-T
Media Access
Control
MII
Instruction
Bus
Load/Store
Bus
Parallel I/O
4 Baud Rate
Generators
Parallel Interface Port
and UTOPIA
4-Kbyte
Instruction Cache
Instruction MMU
32-Entry ITLB
4-Kbyte
Data Cache
Data MMU
32-Entry DTLB
SCC1
Unified
Bus
4
Interrupt
Timers
Timers
Controllers
32-Bit RISC Controller
and Program
ROM
Time Slot Assigner
Time Slot Assigner
System Interface Unit (SIU)
Bus Interface
8-Kbyte
Dual-Port RAM
Memory Controller
Internal
Unit
System Functions
Real-Time Clock
PCMCIA/ATA Interface
External
Bus Interface
Unit
10
Serial
and
2
Independent
DMA
Channels
I2CSPISMC2*SMC1
Serial Interface
*The MPC857DSL does not contain SMC2 nor the Time Slot Assigner, and provides eight SDMA controllers.
Figure 2. MPC857T/MPC857DSL Block Diagram
3 Maximum Tolerated Ratings
This section provides the maximum tolerated voltage and temperature ranges for the
MPC862/857T/857DSL. Table 2 provides the maximum ratings.
Table 2. Maximum Tolerated Ratings
(GND = 0 V)
Rating Symbol Value Unit
Supply voltage
1
VDDH -0.3 to 4.0 V -
VDDL -0.3 to 4.0 V -
KAPWR -0.3 to 4.0 V -
VDDSYN -0.3 to 4.0 V -
Max Freq
(MHz)
MPC862/857T/857DSL PowerQUICC™ Family Hardware Specifications, Rev. 3
8 Freescale Semiconductor
Page 9
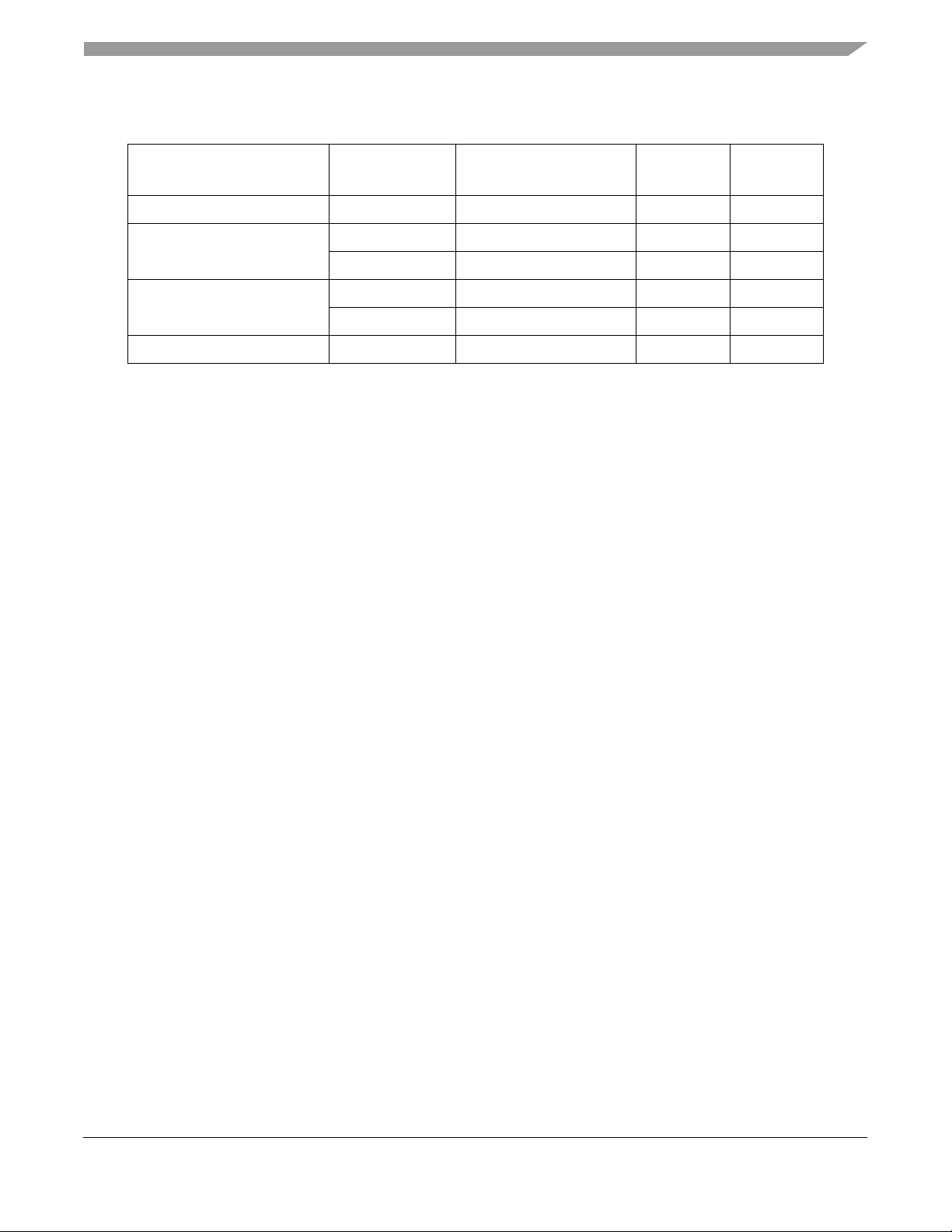
Table 2. Maximum Tolerated Ratings (continued)
(GND = 0 V)
Maximum Tolerated Ratings
Rating Symbol Value Unit
Input voltage
Temperature
Temperature
Storage temperature range T
1
The power supply of the device must start its ramp from 0.0 V.
2
Functional operating conditions are provided with the DC electrical specifications in Ta b le 5 . Absolute maximum
2
3
(standard)
3
(extended) T
4
V
in
T
A(min)
T
j(max)
A(min)
T
j(max)
stg
GND-0.3 to VDDH V -
0 °C 100
105 °C 100
-40 °C 80
115 °C 80
-55 to +150 °C -
Max Freq
(MHz)
ratings are stress ratings only; functional operation at the maxima is not guaranteed. Stress beyond those listed
may affect device reliability or cause permanent damage to the device.
Caution: All inputs that tolerate 5 V cannot be more than 2.5 V greater than the supply voltage. This restriction
applies to power-up and normal operation (that is, if the MPC862/857T/857DSL is unpowered, voltage greater
than 2.5 V must not be applied to its inputs).
3
Minimum temperatures are guaranteed as ambient temperature, TA. Maximum temperatures are guaranteed as
junction temperature, T
4
JTAG is tested only at ambient, not at standard maximum or extended maximum.
.
j
This device contains circuitry protecting against damage due to high-static voltage or electrical fields;
however, it is advised that normal precautions be taken to avoid application of any voltages higher than
maximum-rated voltages to this high-impedance circuit. Reliability of operation is enhanced if unused
inputs are tied to an appropriate logic voltage level (for example, either GND or VCC).
MPC862/857T/857DSL PowerQUICC™ Family Hardware Specifications, Rev. 3
Freescale Semiconductor 9
Page 10
Thermal Characteristics
4 Thermal Characteristics
Table 3 shows the thermal characteristics for the MPC862/857T/857DSL.
Table 3. MPC862/857T/857DSL Thermal Resistance Data
Rating Environment Symbol Value Unit
Junction to ambient
Junction to board
Junction to case
Junction to package top
1
Junction temperature is a function of on-chip power dissipation, package thermal resistance, mounting site
(board) temperature, ambient temperature, air flow, power dissipation of other components on the board,
and board thermal resistance.
2
Per SEMI G38-87 and JEDEC JESD51-2 with the single layer board horizontal.
3
Per JEDEC JESD51-6 with the board horizontal.
4
Thermal resistance between the die and the printed circuit board per JEDEC JESD51-8. Board temperature
is measured on the top surface of the board near the package.
5
Indicates the average thermal resistance between the die and the case top surface as measured by the cold
plate method (MIL SPEC-883 Method 1012.1) with the cold plate temperature used for the case
temperature. For exposed pad packages where the pad would be expected to be soldered, junction to case
thermal resistance is a simulated value from the junction to the exposed pad without contact resistance.
6
Thermal characterization parameter indicating the temperature difference between package top and the
junction temperature per JEDEC JESD51-2.
1
Natural Convection Single layer board (1s) R
Four layer board (2s2p) R
Air flow (200 ft/min) Single layer board (1s) R
Four layer board (2s2p) R
4
5
6
Natural Convection Ψ
Air flow (200 ft/min) Ψ
θJA
θJMA
θJMA
θJMA
R
θJB
R
θJC
JT
JT
2
3
3
3
37 °C/W
23
30
19
13
6
2
2
5 Power Dissipation
Table 4 provides power dissipation information. The modes are 1:1, where CPU and bus speeds are equal,
and 2:1 mode, where CPU frequency is twice bus speed.
Table 4. Power Dissipation (PD)
Die Revision Frequency Typical
0
(1:1 Mode)
A.1, B.0
(1:1 Mode)
50 MHz 656 735 mW
66 MHz TBD TBD mW
50 MHz 630 760 mW
66 MHz 890 1000 mW
1
Maximum
MPC862/857T/857DSL PowerQUICC™ Family Hardware Specifications, Rev. 3
10 Freescale Semiconductor
2
Unit
Page 11
Table 4. Power Dissipation (PD) (continued)
DC Characteristics
Die Revision Frequency Typical
A.1, B.0
(2:1 Mode)
B.0
(2:1 Mode)
1
Typical power dissipation is measured at 3.3 V.
2
Maximum power dissipation is measured at 3.5 V.
66 MHz 910 1060 mW
80 MHz 1.06 1.20 W
100 MHz 1.35 1.54 W
1
Maximum
2
NOTE
Values in Table 4 represent VDDL based power dissipation and d o not include I/O
power dissipation over VDDH. I/O power dissipation varies widely by application
due to buffer current, depending on external circuitry.
6 DC Characteristics
Table 5 provides the DC electrical characteristics for the MPC862/857T/857DSL.
Table 5. DC Electrical Specifications
Characteristic Symbol Min Max Unit
Operating voltage VDDH, VDDL,
KAPWR,
VDDSYN
3.135 3.465 V
Unit
KAPWR
(power-down
mode)
KAPWR
(all other
operating
modes)
Input High Voltage (all inputs except EXTAL and EXTCLK) VIH 2.0 5.5 V
Input Low Voltage
EXTAL, EXTCLK Input High Voltage VIHC 0.7*(VCC) VCC+0.3 V
Input Leakage Current, Vin = 5.5 V (Except TMS, TRST
DSCK and DSDI pins)
Input Leakage Current, Vin = 3.6 V (Except TMS, TRST
DSCK, and DSDI)
Input Leakage Current, Vin = 0 V (Except TMS, TRST
DSCK, and DSDI pins)
Input Capacitance
Output High Voltage, IOH = -2.0 mA, VDDH = 3.0 V
(Except XTAL, XFC, and Open drain pins)
1
,
,
,
2
VIL GND 0.8 V
I
in
I
In
I
In
C
in
VOH 2.4 — V
2.0 3.6 V
VDDH – 0.4 VDDH V
— 100 µA
—10µA
—10µA
—20pF
MPC862/857T/857DSL PowerQUICC™ Family Hardware Specifications, Rev. 3
Freescale Semiconductor 11
Page 12
Thermal Calculation and Measurement
Table 5. DC Electrical Specifications (continued)
Characteristic Symbol Min Max Unit
Output Low Voltage
IOL = 2.0 mA (CLKOUT)
IOL = 3.2 mA
IOL = 5.3 mA
IOL = 7.0 mA (TXD1/PA14, TXD2/PA12)
IOL = 8.9 mA (TS
1
VIL(max) for the I2C interface is 0.8 V rather than the 1.5 V as specified in the I2C standard.
2
Input capacitance is periodically sampled.
3
A(0:31), TSIZ0/REG, TSIZ1, D(0:31), DP(0:3)/IRQ(3:6), RD/WR, BURST, RSV/IRQ2,
IP_B(0:1)/IWP(0:1)/VFLS(0:1), IP_B2/IOIS16_B/AT2, IP_B3/IWP2/VF2, IP_B4/LWP0/VF0, IP_B5/LWP1/VF1,
IP_B6/DSDI/AT0, IP_B7/PTR/AT3, RXD1 /PA15, RXD2/PA13, L1TXDB/PA11, L1RXDB/PA10, L1TXDA/PA9,
L1RXDA/PA8, TIN1/L1RCLKA/BRGO1/CLK1/PA7, BRGCLK1/TOUT1
TIN2/L1TCLKA/BRGO2/CLK3/PA5, TOUT2
BRGCLK2/L1RCLKB/TOUT3
REJCT1
BRGO2/I2CSCL/PB26, SMTXD1/PB25, SMRXD1/PB24, SMSYN1
SMTXD2/L1CLKOB/PB21, SMRXD2/L1CLKOA/PB20, L1ST1/RTS1
L1ST3/L1RQB
L1ST2/RTS2
CTS2
CTS4
PD12/L1RSYNCB, PD11/RXD3, PD10/TXD3, PD9/RXD4, PD8/TXD4, PD5/REJECT2, PD6/RTS4
PD4/REJECT3, PD3, MII_MDC, MII_TX_ER, MII_EN, MII_MDIO, MII_TXD[0:3].
4
BDIP/GPL_B(5), BR, BG, FRZ/IRQ6, CS(0:5), CS(6)/CE(1)_B, CS(7)/CE(2)_B, WE0/BS_B0/IORD,
WE1
GPL_A
ALE_B/DSCK/AT1, OP(0:1), OP2/MODCK1/STS
3
4
, TA, TEA, BI, BB, HRESET, SRESET)
/CLK4/PA4, TIN3/BRGO3/CLK5/PA3,
/CLK6/PA2, TIN4/BRGO4/CLK7/PA1, L1TCLKB/TOUT4/CLK8/PA0,
/SPISEL/PB31, SPICLK/PB30, SPIMOSI/PB29, BRGO4/SPIMISO/PB28, BRGO1/I2CSDA/PB27,
/PB17, L1ST4/L1RQA/PB16, BRGO3/PB15, RSTRT1/PB14, L1ST1/RTS1/DREQ0/PC15,
/DREQ1/PC14, L1ST3/L1RQB/PC13, L1ST4/L1RQA/PC12, CTS1/PC11, TGATE1/CD1/PC10,
/PC9, TGATE2/CD2/PC8, CTS3/SDACK2/L1TSYNCB/PC7, CD3/L1RSYNCB/PC6,
/SDACK1/L1TSYNCA/PC5, CD4/L1RSYNCA/PC4, PD15/L1TSYNCA, PD14/L1RSYNCA, PD13/L1TSYNCB,
/BS_B1/IOWR, WE2/BS_B2/PCOE, WE3/BS_B3/PCWE, BS_A(0:3), GPL_A0/GPL_B0, OE/GPL_A1/GPL_B1,
(2:3)/GPL_B(2:3)/CS(2:3), UPWAITA/GPL_A4, UPWAITB/GPL_B4, GPL_A5, ALE_A, CE1_A, CE2_A,
, OP3/MODCK2/DSDO, BADDR(28:30).
VOL — 0.5 V
/CLK2/PA6,
/SDACK1/PB23, SMSYN2/SDACK2/PB22,
/PB19, L1ST2/RTS2/PB18,
, PD7/RTS3,
7 Thermal Calculation and Measurement
For the following discussions, PD= (VDD x IDD) + PI/O, where PI/O is the power dissipation of the I/O
drivers.
7.1 Estimation with Junction-to-Ambient Thermal Resistance
An estimation of the chip junction temperature, TJ, in °C can be obtained from the equation:
TJ = TA +(R
where:
TA = ambient temperature (ºC)
R
= package junction-to-ambient thermal resistance (ºC/W)
θJA
= power dissipation in package
P
D
The junction-to-ambient thermal resistance is an industry standard value which provides a quick and easy
estimation of thermal perf ormance. However , the answer is only an es timate; test cases have demons trated
that errors of a factor of two (in the quantity T
MPC862/857T/857DSL PowerQUICC™ Family Hardware Specifications, Rev. 3
θJA
x PD)
) are possible.
J-TA
12 Freescale Semiconductor
Page 13
Thermal Calculation and Measurement
7.2 Estimation with Junction-to-Case Thermal Resistance
Historically , the thermal resist ance has frequently been expressed as the sum of a junction-to-case thermal
resistance and a case-to-ambient thermal resistance:
R
θJA
= R
θJC
+ R
θCA
where:
R
= junction-to-ambient thermal resistance (ºC/W)
θJA
R
= junction-to-case thermal resistance (º C/W)
θJC
= case-to-ambient thermal resistance (ºC/W)
R
θCA
R
is device related and cannot be influenced by the user. The user adjusts the thermal environment to
θJC
affect the case-to-ambient thermal resistance, R
. For instance, the user can change the air flow around
θCA
the device, add a heat sink, change the mounting arrangement on the printed circuit board, or change the
thermal dissipation on the printed circuit board surrounding the device. This thermal model is most useful
for ceramic packages with heat sinks where some 90% of the heat flows through the case and the heat sink
to the ambient environment. For most packages, a better model is required.
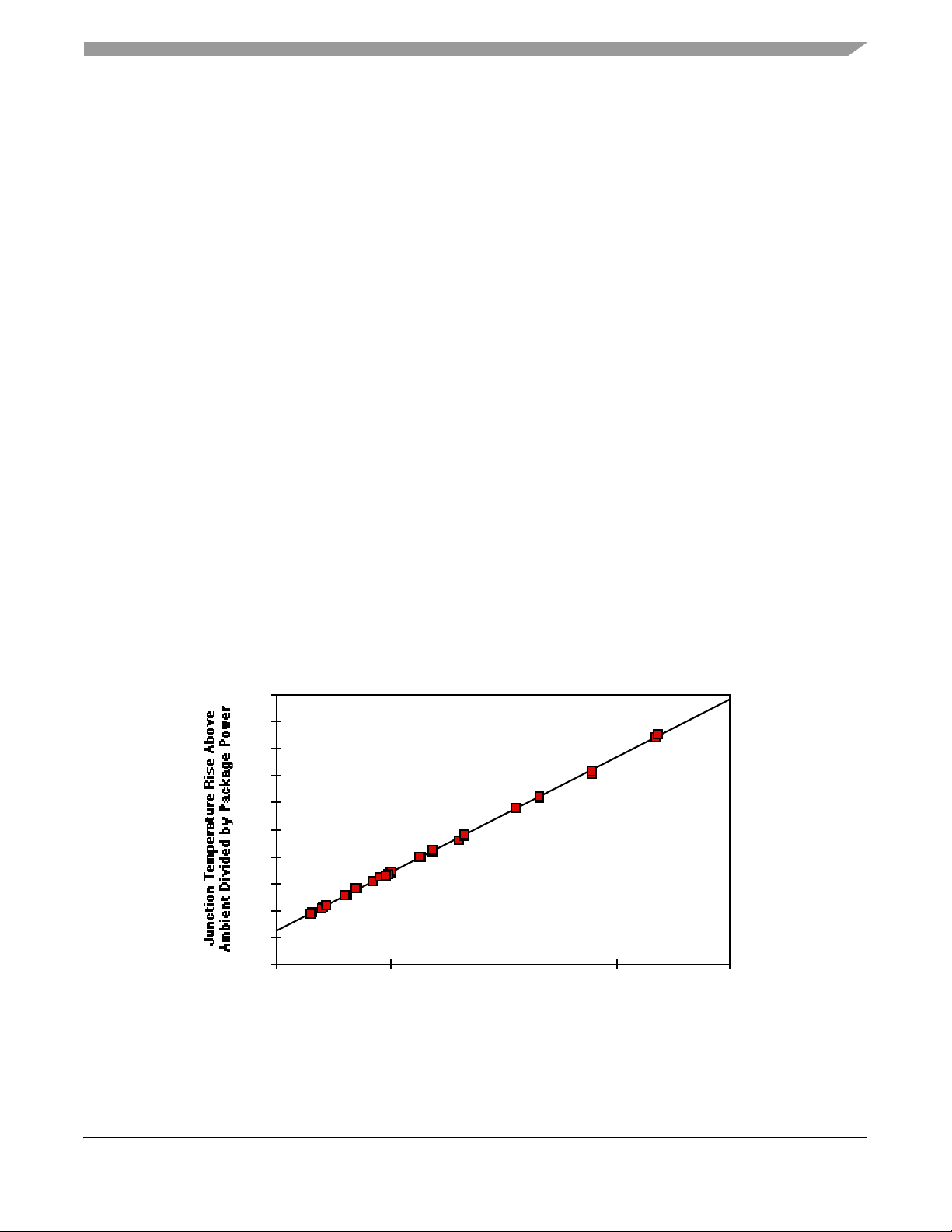
7.3 Estimation with Junction-to-Board Thermal Resistance
A simple package thermal model which has demonstrated reasonable accuracy (about 20%) is a two
resistor model consisting of a junction-to-board and a junction-to-case thermal resistance. The
junction-to-case covers the situation where a heat sink is used or where a substantial amount of heat is
dissipated from the top of the package. The junction-to-board thermal resistance describes the thermal
performance when most of the heat is conducted to the printed circuit board. It has been observed that the
thermal performance of most plastic packages and especially PBGA packages is strongly dependent on the
board temperature; see Figure 3.
100
90
80
70
60
50
40
30
20
10
0
020406080
Board Temperture Rise Above Ambient Divided by Package
Power
Figure 3. Effect of Board Temperature Rise on Thermal Behavior
MPC862/857T/857DSL PowerQUICC™ Family Hardware Specifications, Rev. 3
Freescale Semiconductor 13
Page 14

Thermal Calculation and Measurement
If the board temperature is known, an estimate of the junction temperature in the environment can be made
using the following equation:
TJ = TB +(R
θJB
x PD)
where:
R
= junction-to-board thermal resistance (ºC/W)
θJB
TB = board temperature (ºC)
PD = power dissipation in package
If the board temperature is known and the heat loss from the package case to the air can be ignored,
acceptable predictions of junction temperature can be made. For this method to work, the board and board
mounting must be similar to the test board used to determine the junction-to-board thermal resistance,
namely a 2s2p (board with a power and a ground plane) and vias attaching the thermal balls to the ground
plane.
7.4 Estimation Using Simulation
When the board temperature is not known, a thermal simulation of the application is needed. The simple
two resistor model can be used with the thermal simulation of the applic ation [2], or a more accurate and
complex model of the package can be used in the thermal simulation.
7.5 Experimental Determination
To determine the junction temperature of the device in the application after prototypes are available, the
thermal characterization parame ter (ΨJT) can be used to determine the junction temperature with a
measurement of the temperature at the top center of the package case using the following equation:
TJ = TT +(ΨJT x PD)
where:
Ψ
= thermal characterization parameter
JT
TT = thermocouple temperature on top of package
= power dissipation in package
P
D
The thermal characterization parameter is measured per JESD51-2 specification published by JEDEC
using a 40-gauge type T thermocouple epoxied to the top center of the package case. The thermocouple
should be positioned so that the thermocouple junction rests on the package. A small amount of epoxy is
placed over the thermocouple junction and over about 1 mm of wire extending from the junction. The
thermocouple wire is placed flat against the package case to avoid measurement errors caused by cooling
effects of the thermocouple wire.
MPC862/857T/857DSL PowerQUICC™ Family Hardware Specifications, Rev. 3
14 Freescale Semiconductor
Page 15
Layout Practices
7.6 References
Semiconductor Equipment and Materials International (415) 964-5111
805 East Middlefield Rd.
Mountain View, CA 94043
MIL-SPEC and EIA/JESD (JEDEC) Specificat ions 800-854-7179 or
(Available from Global Engine ering Documents) 303-397-7956
JEDEC Spec if ic ation s http://www.jedec.o rg
1. C.E. Triplett and B. Joiner, “An Experimental Characterization of a 272 PBGA Within an Automotive
Engine Controller Module,” Proceedings of SemiTherm, San Diego, 1998, pp. 47-54.
2. B. Joiner and V. Adams, “Measurement and Simulation of Junction to Board Thermal Resistance and
Its Application in Thermal Modeling,” Proceedings of SemiTherm, San Diego, 1999, pp. 212-220.
8 Layout Practices
Each VCC pin on the MPC862/857T/857DSL should be provided with a low-impedance path to the board’s
supply. Each GND pin should likewise be provided with a low-impedance path to ground. The power
supply pins drive distinct groups of logic on chip. The VCC power supply should be bypassed to ground
using at least four 0.1 µF by-pass capacitors located as close as possible to the four sides of the package.
The capacitor leads and associated printed circuit traces connecting to chip VCC and GND should be kept
to less than half an inch per capacitor lead. A four-layer board is recommended, employing two inner
layers as VCC and GND planes.
All output pins on the MPC862/857T/857DSL have fast rise and fall times. Printed circuit (PC) trace
interconnection length should be minimized in order to minimize undershoot and reflections caused by
these fast output switching times. This recommenda tion particularly applies to the address and data busses.
Maximum PC trace lengths of six inches are recommended. Capacitance calculations should consider all
device loads as well as parasitic capacitances due to the PC traces. Attention to proper PCB layout and
bypassing becomes especially critical in systems with higher capacitive loads because these loads create
higher transient currents in the VCC and GND circuits. Pull up all unused inputs or signals that will be
inputs during reset. Special care should be taken to minimize the noise levels on the PLL supply pins.
9 Bus Signal Timing
The maximum bus speed supported by the MPC862/857T/857DSL is 66 MHz. Higher-speed parts must
be operated in half-speed bus mode (for example, an MPC862/857T/857DSL used at 80MHz must be
configured for a 40 MHz bus). Table 6 shows the period ranges for standard part frequencies.
Table 6. Period Range for Standard Part Frequencies
50 MHz 66 MHz 80 MHz 100 MHz
Freq
Min Max Min Max Min Max Min Max
Period 20.00 30.30 15.15 30.30 25.00 30.30 20.00 30.30
MPC862/857T/857DSL PowerQUICC™ Family Hardware Specifications, Rev. 3
Freescale Semiconductor 15
Page 16
Bus Signal Timing
Table 7 provides the bus operation timing for the MPC862/857T/857DSL at 33 MHz, 40 Mhz, 50 MHz
and 66 Mhz.
The timing for the MPC862/857T/857DSL bus shown assumes a 50-pF load for maximum delays and a
0-pF load for minimum delays.
Table 7. Bus Operation Timings
33 MHz 40 MHz 50 MHz 66 MHz
Num Characteristic
Min Max Min Max Min Max Min Max
B1 CLKOUT period 30.30 30.30 25.00 30.30 20.00 30.30 15.15 30.30 ns
Unit
B1a EXTCLK to CLKOUT phase skew
(EXTCLK > 15 MHz and MF <= 2)
B1b EXTCLK to CLKOUT phase skew
(EXTCLK > 10 MHz and MF < 10)
B1c CLKOUT phase jitter (EXTCLK > 15
MHz and MF <= 2)
B1d CLKOUT phase jitter
1
1
B1e CLKOUT frequency jitter (MF < 10)
B1f CLKOUT frequency jitter (10 < MF <
500)
1
B1g CLKOUT frequency jitter (MF > 500)
B1h Frequency jitter on EXTCLK
2
B2 CLKOUT pulse width low (MIN = 0.040
x B1)
B3 CLKOUT width high (MIN = 0.040 x
B1)
3
B4 CLKOUT rise time
(MAX = 0.00 x B1
+ 4.00)
33
CLKOUT fall time3 (MAX = 0.00 x B1 +
B5
4.00)
-0.90 0.90 -0.90 0.90 -0.90 0.90 -0.90 0.90 ns
-2.30 2.30 -2.30 2.30 -2.30 2.30 -2.30 2.30 ns
-0.60 0.60 -0.60 0.60 -0.60 0.60 -0.60 0.60 ns
-2.00 2.00 -2.00 2.00 -2.00 2.00 -2.00 2.00 ns
1
— 0.50 — 0.50 — 0.50 — 0.50 %
— 2.00 — 2.00 — 2.00 — 2.00 %
1
— 3.00 — 3.00 — 3.00 — 3.00 %
— 0.50 — 0.50 — 0.50 — 0.50 %
12.10 — 10.00 — 8.00 — 6.10 — ns
12.10 — 10.00 — 8.00 — 6.10 — ns
— 4.00 — 4.00 — 4.00 — 4.00 ns
— 4.00 — 4.00 — 4.00 — 4.00 ns
B7 CLKOUT to A(0:31), BADDR(28:30),
RD/WR
, BURST, D(0:31), DP(0:3)
7.60 — 6.30 — 5.00 — 3.80 — ns
invalid (MIN = 0.25 x B1)
B7a CLKOUT to TSIZ(0:1), REG
AT(0:3), BDIP
, PTR invalid (MIN = 0.25
, RSV,
7.60 — 6.30 — 5.00 — 3.80 — ns
x B1)
B7b CLKOUT to BR
VF(0:2) IWP(0:2), LWP(0:1), STS
4
invalid
, BG, FRZ, VFLS(0:1),
(MIN = 0.25 x B1)
B8 CLKOUT to A(0:31), BADDR(28:30)
RD/WR
, BURST, D(0:31), DP(0:3)
7.60 — 6.30 — 5.00 — 3.80 — ns
7.60 13.80 6.30 12.50 5.00 11.30 3.80 10.00 ns
valid (MAX = 0.25 x B1 + 6.3)
MPC862/857T/857DSL PowerQUICC™ Family Hardware Specifications, Rev. 3
16 Freescale Semiconductor
Page 17
Num Characteristic
Bus Signal Timing
Table 7. Bus Operation Timings (continued)
33 MHz 40 MHz 50 MHz 66 MHz
Unit
Min Max Min Max Min Max Min Max
B8a CLKOUT to TSIZ(0:1), REG, RSV,
AT(0 : 3 ) B D I P
, PTR valid (MAX = 0.25 x
B1 + 6.3)
B8b CLKOUT to BR
, BG, VFLS(0:1),
VF(0:2), IWP(0:2), FRZ, LWP(0:1),
STS
Valid 4 (MAX = 0.25 x B1 + 6.3)
B9 CLKOUT to A(0:31), BADDR(28:30),
RD/WR
TSIZ(0:1), REG
, BURST, D(0:31), DP(0:3),
, RSV, AT(0:3), PTR
High-Z (MAX = 0.25 x B1 + 6.3)
B11 CLKOUT to TS
, BB assertion (MAX =
0.25 x B1 + 6.0)
B11a CLKOUT to TA
, BI assertion (when
driven by the memory controller or
PCMCIA interface) (MAX = 0.00 x B1
5
+ 9.30
B12 CLKOUT to TS
)
, BB negation (MAX =
0.25 x B1 + 4.8)
B12a CLKOUT to TA
, BI negation (when
driven by the memory controller or
PCMCIA interface) (MAX = 0.00 x B1
+ 9.00)
7.60 13.80 6.30 12.50 5.00 11.30 3.80 10.00 ns
7.60 13.80 6.30 12.50 5.00 11.30 3.80 10.00 ns
7.60 13.80 6.30 12.50 5.00 11.30 3.80 10.00 ns
7.60 13.60 6.30 12.30 5.00 11.00 3.80 11.30 ns
2.50 9.30 2.50 9.30 2.50 9.30 2.50 9.80 ns
7.60 12.30 6.30 11.00 5.00 9.80 3.80 8.50 ns
2.50 9.00 2.50 9.00 2.50 9.00 2.50 9.00 ns
B13 CLKOUT to TS
, BB High-Z (MIN =
0.25 x B1)
B13a CLKOUT to TA
, BI High-Z (when
driven by the memory controller or
PCMCIA interface) (MIN = 0.00 x B1 +
2.5)
B14 CLKOUT to TEA
assertion (MAX =
0.00 x B1 + 9.00)
B15 CLKOUT to TEA
High-Z (MIN = 0.00 x
B1 + 2.50)
B16 TA
, BI valid to CLKOUT (setup time)
(MIN = 0.00 x B1 + 6.00)
B16a TEA
, KR, RETRY, CR valid to
CLKOUT (setup time) (MIN = 0.00 x
B1 + 4.5)
B16b BB
B17 CLKOUT to TA
, BG, BR, valid to CLKOUT (setup
6
time)
(4MIN = 0.00 x B1 + 0.00)
, TEA, BI, BB, BG, BR
valid (hold time) (MIN = 0.00 x B1 +
7
1.00
)
7.60 21.60 6.30 20.30 5.00 19.00 3.80 14.00 ns
2.50 15.00 2.50 15.00 2.50 15.00 2.50 15.00 ns
2.50 9.00 2.50 9.00 2.50 9.00 2.50 9.00 ns
2.50 15.00 2.50 15.00 2.50 15.00 2.50 15.00 ns
6.00 — 6.00 — 6.00 — 6.00 — ns
4.50 — 4.50 — 4.50 — 4.50 — ns
4.00 — 4.00 — 4.00 — 4.00 — ns
1.00 — 1.00 — 1.00 — 2.00 — ns
MPC862/857T/857DSL PowerQUICC™ Family Hardware Specifications, Rev. 3
Freescale Semiconductor 17
Page 18
Bus Signal Timing
Num Characteristic
Table 7. Bus Operation Timings (continued)
33 MHz 40 MHz 50 MHz 66 MHz
Unit
Min Max Min Max Min Max Min Max
B17a CLKOUT to KR, RETRY, CR valid
(hold time) (MIN = 0.00 x B1 + 2.00)
B18 D(0:31), DP(0:3) valid to CLKOUT
rising edge (setup time)
8
(MIN = 0.00
x B1 + 6.00)
B19 CLKOUT rising edge to D(0:31),
DP(0:3) valid (hold time)
x B1 + 1.00
9
)
B20 D(0:31), DP(0:3) valid to CLKOUT
falling edge (setup time)
8
(MIN = 0.00
10
(MIN = 0.00
x B1 + 4.00)
B21 CLKOUT falling edge to D(0:31),
DP(0:3) valid (hold Time)
10
(MIN =
0.00 x B1 + 2.00)
B22 CLKOUT rising edge to CS
asserted
GPCM ACS = 00 (MAX = 0.25 x B1 +
6.3)
B22a CLKOUT falling edge to CS
asserted
GPCM ACS = 10, TRLX = 0 (MAX =
0.00 x B1 + 8.00)
B22b CLKOUT falling edge to CS
asserted
GPCM ACS = 11, TRLX = 0, EBDF =
0 (MAX = 0.25 x B1 + 6.3)
2.00 — 2.00 — 2.00 — 2.00 — ns
6.00 — 6.00 — 6.00 — 6.00 — ns
1.00 — 1.00 — 1.00 — 2.00 — ns
4.00 — 4.00 — 4.00 — 4.00 — ns
2.00 — 2.00 — 2.00 — 2.00 — ns
7.60 13.80 6.30 12.50 5.00 11.30 3.80 10.00 ns
— 8.00 — 8.00 — 8.00 — 8.00 ns
7.60 13.80 6.30 12.50 5.00 11.30 3.80 10.00 ns
B22c CLKOUT falling edge to CS
asserted
GPCM ACS = 11, TRLX = 0, EBDF =
1 (MAX = 0.375 x B1 + 6.6)
B23 CLKOUT rising edge to CS
negated
GPCM read access, GPCM write
access ACS = 00, TRLX = 0 & CSNT =
0 (MAX = 0.00 x B1 + 8.00)
B24 A(0:31) and BADDR(28:30) to CS
asserted GPCM ACS = 10, TRLX = 0
(MIN = 0.25 x B1 - 2.00)
B24a A(0:31) and BADDR(28:30) to CS
asserted GPCM ACS = 11 TRLX = 0
(MIN = 0.50 x B1 - 2.00)
B25 CLKOUT rising edge to OE
, WE(0:3)
asserted (MAX = 0.00 x B1 + 9.00)
B26 CLKOUT rising edge to OE
negated
(MAX = 0.00 x B1 + 9.00)
MPC862/857T/857DSL PowerQUICC™ Family Hardware Specifications, Rev. 3
10.90 18.00 10.90 18.00 7.00 14.30 5.20 12.30 ns
2.00 8.00 2.00 8.00 2.00 8.00 2.00 8.00 ns
5.60 — 4.30 — 3.00 — 1.80 — ns
13.20 — 10.50 — 8.00 — 5.60 — ns
— 9.00 9.00 9.00 9.00 ns
2.00 9.00 2.00 9.00 2.00 9.00 2.00 9.00 ns
18 Freescale Semiconductor
Page 19
Num Characteristic
Bus Signal Timing
Table 7. Bus Operation Timings (continued)
33 MHz 40 MHz 50 MHz 66 MHz
Unit
Min Max Min Max Min Max Min Max
B27 A(0:31) and BADDR(28:30) to CS
asserted GPCM ACS = 10, TRLX = 1
(MIN = 1.25 x B1 - 2.00)
B27a A(0:31) and BADDR(28:30) to CS
asserted GPCM ACS = 11, TRLX = 1
(MIN = 1.50 x B1 - 2.00)
B28 CLKOUT rising edge to WE
negated GPCM write access CSNT
= 0 (MAX = 0.00 x B1 + 9.00)
B28a CLKOUT falling edge to WE
negated GPCM write access
TRLX = 0, 1, CSNT = 1, EBDF = 0
(MAX = 0.25 x B1 + 6.80)
B28b CLKOUT falling edge to CS
GPCM write access TRLX = 0,1,
CSNT = 1 ACS = 10 or ACS = 11,
EBDF = 0 (MAX = 0.25 x B1 + 6.80)
B28c CLKOUT falling edge to WE
negated GPCM write access
TRLX = 0, CSNT = 1 write access
TRLX = 0,1, CSNT = 1, EBDF = 1
(MAX = 0.375 x B1 + 6.6)
B28d CLKOUT falling edge to CS
GPCM write access TRLX = 0,1,
CSNT = 1, ACS = 10, or ACS = 11,
EBDF = 1 (MAX = 0.375 x B1 + 6.6)
(0:3)
(0:3)
negated
(0:3)
negated
35.90 — 29.30 — 23.00 — 16.90 — ns
43.50 — 35.50 — 28.00 — 20.70 — ns
— 9.00 — 9.00 — 9.00 — 9.00 ns
7.60 14.30 6.30 13.00 5.00 11.80 3.80 10.50 ns
— 14.30 — 13.00 — 11.80 — 10.50 ns
10.90 18.00 10.90 18.00 7.00 14.30 5.20 12.30 ns
— 18.00 — 18.00 — 14.30 — 12.30 ns
B29 WE
B29a WE
B29b CS
B29c CS
Freescale Semiconductor 19
(0:3) negated to D(0:31), DP(0:3)
High-Z GPCM write access, CSNT
= 0, EBDF = 0 (MIN = 0.25 x B1 - 2.00)
(0:3) negated to D(0:31), DP(0:3)
High-Z GPCM write access, TRLX = 0,
CSNT = 1, EBDF = 0 (MIN = 0.50 x B1
- 2.00)
negated to D(0:31), DP(0:3), High
Z GPCM write access, ACS = 00,
TRLX = 0,1 & CSNT = 0 (MIN = 0.25 x
B1 - 2.00)
negated to D(0:31), DP(0:3)
High-Z GPCM write access, TRLX = 0,
CSNT = 1, ACS = 10, or ACS = 11
EBDF = 0 (MIN = 0.50 x B1 - 2.00)
MPC862/857T/857DSL PowerQUICC™ Family Hardware Specifications, Rev. 3
5.60 — 4.30 — 3.00 — 1.80 — ns
13.20 — 10.50 — 8.00 — 5.60 — ns
5.60 — 4.30 — 3.00 — 1.80 — ns
13.20 — 10.50 — 8.00 — 5.60 — ns
Page 20
Bus Signal Timing
Num Characteristic
Table 7. Bus Operation Timings (continued)
33 MHz 40 MHz 50 MHz 66 MHz
Unit
Min Max Min Max Min Max Min Max
B29d WE(0:3) negated to D(0:31), DP(0:3)
High-Z GPCM write access, TRLX = 1,
CSNT = 1, EBDF = 0 (MIN = 1.50 x B1
- 2.00)
B29e CS
negated to D(0:31), DP(0:3)
High-Z GPCM write access, TRLX = 1,
CSNT = 1, ACS = 10, or ACS = 11
EBDF = 0 (MIN = 1.50 x B1 - 2.00)
B29f WE
(0:3) negated to D(0:31), DP(0:3)
High Z GPCM write access, TRLX = 0,
CSNT = 1, EBDF = 1 (MIN = 0.375 x
B1 - 6.30)
B29g CS
negated to D(0:31), DP(0:3)
High-Z GPCM write access, TRLX = 0,
CSNT = 1 ACS = 10 or ACS = 11,
EBDF = 1 (MIN = 0.375 x B1 - 6.30)
B29h WE
(0:3) negated to D(0:31), DP(0:3)
High Z GPCM write access, TRLX = 1,
CSNT = 1, EBDF = 1 (MIN = 0.375 x
B1 - 3.30)
B29i CS
negated to D(0:31), DP(0:3)
High-Z GPCM write access, TRLX = 1,
CSNT = 1, ACS = 10 or ACS = 11,
EBDF = 1 (MIN = 0.375 x B1 - 3.30)
43.50 — 35.50 — 28.00 — 20.70 — ns
43.50 — 35.50 — 28.00 — 20.70 — ns
5.00 — 3.00 — 1.10 — 0.00 — ns
5.00 — 3.00 — 1.10 — 0.00 — ns
38.40 — 31.10 — 24.20 — 17.50 — ns
38.40 — 31.10 — 24.20 — 17.50 — ns
B30 CS
B30a WE
, WE(0:3) negated to A(0:31),
BADDR(28:30) Invalid GPCM write
access
11
(MIN = 0.25 x B1 - 2.00)
(0:3) negated to A(0:31),
BADDR(28:30) Invalid GPCM, write
access, TRLX = 0, CSNT = 1, CS
negated to A(0:31) invalid GPCM write
access TRLX = 0, CSNT =1 ACS = 10,
or ACS == 11, EBDF = 0 (MIN = 0.50
x B1 - 2.00)
B30b WE
(0:3) negated to A(0:31) Invalid
GPCM BADDR(28:30) invalid GPCM
write access, TRLX = 1, CSNT = 1.
CS
negated to A(0:31) Invalid GPCM
write access TRLX = 1, CSNT = 1,
ACS = 10, or ACS == 11 EBDF = 0
(MIN = 1.50 x B1 - 2.00)
MPC862/857T/857DSL PowerQUICC™ Family Hardware Specifications, Rev. 3
5.60 — 4.30 — 3.00 — 1.80 — ns
13.20 — 10.50 — 8.00 — 5.60 — ns
43.50 — 35.50 — 28.00 — 20.70 — ns
20 Freescale Semiconductor
Page 21
Num Characteristic
Bus Signal Timing
Table 7. Bus Operation Timings (continued)
33 MHz 40 MHz 50 MHz 66 MHz
Unit
Min Max Min Max Min Max Min Max
B30c WE(0:3) negated to A(0:31),
BADDR(28:30) invalid GPCM write
access, TRLX = 0, CSNT = 1.
CS
negated to A(0:31) invalid GPCM
write access, TRLX = 0, CSNT = 1
ACS = 10, ACS == 11, EBDF = 1
(MIN = 0.375 x B1 - 3.00)
B30d WE
B31 CLKOUT falling edge to CS
B31a CLKOUT falling edge to CS
B31b CLKOUT rising edge to CS
(0:3) negated to A(0:31),
BADDR(28:30) invalid GPCM write
access TRLX = 1, CSNT =1,
CS
negated to A(0:31) invalid GPCM
write access TRLX = 1, CSNT = 1,
ACS = 10 or 11, EBDF = 1
requested by control bit CST4 in the
corresponding word in the UPM
(MAX = 0.00 X B1 + 6.00)
requested by control bit CST1 in the
corresponding word in the UPM
(MAX = 0.25 x B1 + 6.80)
requested by control bit CST2 in the
corresponding word in the UPM
(MAX = 0.00 x B1 + 8.00)
valid - as
valid - as
valid - as
8.40 — 6.40 — 4.50 — 2.70 — ns
38.67 — 31.38 — 24.50 — 17.83 — ns
1.50 6.00 1.50 6.00 1.50 6.00 1.50 6.00 ns
7.60 14.30 6.30 13.00 5.00 11.80 3.80 10.50 ns
1.50 8.00 1.50 8.00 1.50 8.00 1.50 8.00 ns
B31c CLKOUT rising edge to CS
requested by control bit CST3 in the
corresponding word in the UPM
(MAX = 0.25 x B1 + 6.30)
B31d CLKOUT falling edge to CS
requested by control bit CST1 in the
corresponding word in the UPM
EBDF = 1 (MAX = 0.375 x B1 + 6.6)
B32 CLKOUT falling edge to BS
requested by control bit BST4 in the
corresponding word in the UPM
(MAX = 0.00 x B1 + 6.00)
B32a CLKOUT falling edge to BS
requested by control bit BST1 in the
corresponding word in the UPM,
EBDF = 0 (MAX = 0.25 x B1 + 6.80)
B32b CLKOUT rising edge to BS
requested by control bit BST2 in the
corresponding word in the UPM
(MAX = 0.00 x B1 + 8.00)
MPC862/857T/857DSL PowerQUICC™ Family Hardware Specifications, Rev. 3
valid- as
valid, as
valid- as
valid - as
valid - as
7.60 13.80 6.30 12.50 5.00 11.30 3.80 10.00 ns
9.40 18.00 7.60 16.00 13.30 14.10 11.30 12.30 ns
1.50 6.00 1.50 6.00 1.50 6.00 1.50 6.00 ns
7.60 14.30 6.30 13.00 5.00 11.80 3.80 10.50 ns
1.50 8.00 1.50 8.00 1.50 8.00 1.50 8.00 ns
Freescale Semiconductor 21
Page 22
Bus Signal Timing
Num Characteristic
Table 7. Bus Operation Timings (continued)
33 MHz 40 MHz 50 MHz 66 MHz
Unit
Min Max Min Max Min Max Min Max
B32c CLKOUT rising edge to BS valid - as
requested by control bit BST3 in the
corresponding word in the UPM
(MAX = 0.25 x B1 + 6.80)
B32d CLKOUT falling edge to BS
requested by control bit BST1 in the
corresponding word in the UPM,
EBDF = 1 (MAX = 0.375 x B1 + 6.60)
B33 CLKOUT falling edge to GPL
requested by control bit GxT4 in the
corresponding word in the UPM
(MAX = 0.00 x B1 + 6.00)
B33a CLKOUT rising edge to GPL
requested by control bit GxT3 in the
corresponding word in the UPM
(MAX = 0.25 x B1 + 6.80)
B34 A(0:31), BADDR(28:30), and D(0:31)
to CS
valid - as requested by control bit
CST4 in the corresponding word in the
UPM (MIN = 0.25 x B1 - 2.00)
B34a A(0:31), BADDR(28:30), and D(0:31)
to CS
valid - as requested by control bit
CST1 in the corresponding word in the
UPM (MIN = 0.50 x B1 - 2.00)
valid- as
valid - as
Vali d - as
7.60 14.30 6.30 13.00 5.00 11.80 3.80 10.50 ns
9.40 18.00 7.60 16.00 13.30 14.10 11.30 12.30 ns
1.50 6.00 1.50 6.00 1.50 6.00 1.50 6.00 ns
7.60 14.30 6.30 13.00 5.00 11.80 3.80 10.50 ns
5.60 — 4.30 — 3.00 — 1.80 — ns
13.20 — 10.50 — 8.00 — 5.60 — ns
B34b A(0:31), BADDR(28:30), and D(0:31)
to CS
valid - as requested by CST2 in
the corresponding word in UPM
(MIN = 0.75 x B1 - 2.00)
B35 A(0:31), BADDR(28:30) to CS
as requested by control bit BST4 in the
corresponding word in the UPM
(MIN = 0.25 x B1 - 2.00)
B35a A(0:31), BADDR(28:30), and D(0:31)
to BS
valid - As Requested by BST1 in
the corresponding word in the UPM
(MIN = 0.50 x B1 - 2.00)
B35b A(0:31), BADDR(28:30), and D(0:31)
to BS
valid - as requested by control bit
BST2 in the corresponding word in the
UPM (MIN = 0.75 x B1 - 2.00)
B36 A(0:31), BADDR(28:30), and D(0:31)
to GPL
valid as requested by control
bit GxT4 in the corresponding word in
the UPM (MIN = 0.25 x B1 - 2.00)
MPC862/857T/857DSL PowerQUICC™ Family Hardware Specifications, Rev. 3
valid -
20.70 — 16.70 — 13.00 — 9.40 — ns
5.60 — 4.30 — 3.00 — 1.80 — ns
13.20 — 10.50 — 8.00 — 5.60 — ns
20.70 — 16.70 — 13.00 — 9.40 — ns
5.60 — 4.30 — 3.00 — 1.80 — ns
22 Freescale Semiconductor
Page 23
Num Characteristic
Bus Signal Timing
Table 7. Bus Operation Timings (continued)
33 MHz 40 MHz 50 MHz 66 MHz
Unit
Min Max Min Max Min Max Min Max
B37 UPWAIT valid to CLKOUT falling edge
12
(MIN = 0.00 x B1 + 6.00)
B38 CLKOUT falling edge to UPWAIT valid
12
(MIN = 0.00 x B1 + 1.00)
B39 AS
valid to CLKOUT rising edge
13
6.00 — 6.00 — 6.00 — 6.00 — ns
1.00 — 1.00 — 1.00 — 1.00 — ns
7.00 — 7.00 — 7.00 — 7.00 — ns
(MIN = 0.00 x B1 + 7.00)
B40 A(0:31), TSIZ(0:1), RD/WR
, BURST,
7.00 — 7.00 — 7.00 — 7.00 — ns
valid to CLKOUT rising edge
(MIN = 0.00 x B1 + 7.00)
B41 TS
valid to CLKOUT rising edge (setup
7.00 — 7.00 — 7.00 — 7.00 — ns
time) (MIN = 0.00 x B1 + 7.00)
B42 CLKOUT rising edge to TS
valid (hold
2.00 — 2.00 — 2.00 — 2.00 — ns
time) (MIN = 0.00 x B1 + 2.00)
B43 AS
negation to memory controller
— TBD — TBD — TBD — TBD ns
signals negation (MAX = TBD)
1
Phase and frequency jitter performance results are only valid if the input jitter is less than the prescribed value.
2
If the rate of change of the frequency of EXTAL is slow (I.e. it does not jump between the minimum and maximum
values in one cycle) or the frequency of the jitter is fast (I.e., it does not stay at an extreme value for a long time) then
the maximum allowed jitter on EXTAL can be up to 2%.
3
The timings specified in B4 and B5 are based on full strength clock.
4
The timing for BR output is relevant when the MPC862/857T/857DSL is selected to work with external bus arbiter.
The timing for BG
5
For part speeds above 50MHz, use 9.80ns for B11a.
6
The timing required for BR input is relevant when the MPC862/857T/857DSL is selected to work with internal bus
arbiter. The timing for BG
output is relevant when the MPC862/857T/857DSL is selected to work with internal bus arbiter.
input is relevant when the MPC862/857T/857DSL is selected to work with external bus
arbiter.
7
For part speeds above 50MHz, use 2ns for B17.
8
The D(0:31) and DP(0:3) input timings B18 and B19 refer to the rising edge of the CLKOUT in which the TA input
signal is asserted.
9
For part speeds above 50MHz, use 2ns for B19.
10
The D(0:31) and DP(0:3) input timings B20 and B21 refer to the falling edge of the CLKOUT. This timing is valid only
for read accesses controlled by chip-selects under control of the UPM in the memory controller, for data beats where
DLT3 = 1 in the UPM RAM words. (This is only the case where data is latched on the falling edge of CLKOUT.)
11
The timing B30 refers to CS when ACS = 00 and to WE(0:3) when CSNT = 0.
12
The signal UPWAIT is considered asynchronous to the CLKOUT and synchronized internally. The timings specified
in B37 and B38 are specified to enable the freeze of the UPM output signals as described in Figure 19.
13
The AS signal is considered asynchronous to the CLKOUT. The timing B39 is specified in order to allow the behavior
specified in Figure 22.
MPC862/857T/857DSL PowerQUICC™ Family Hardware Specifications, Rev. 3
Freescale Semiconductor 23
Page 24
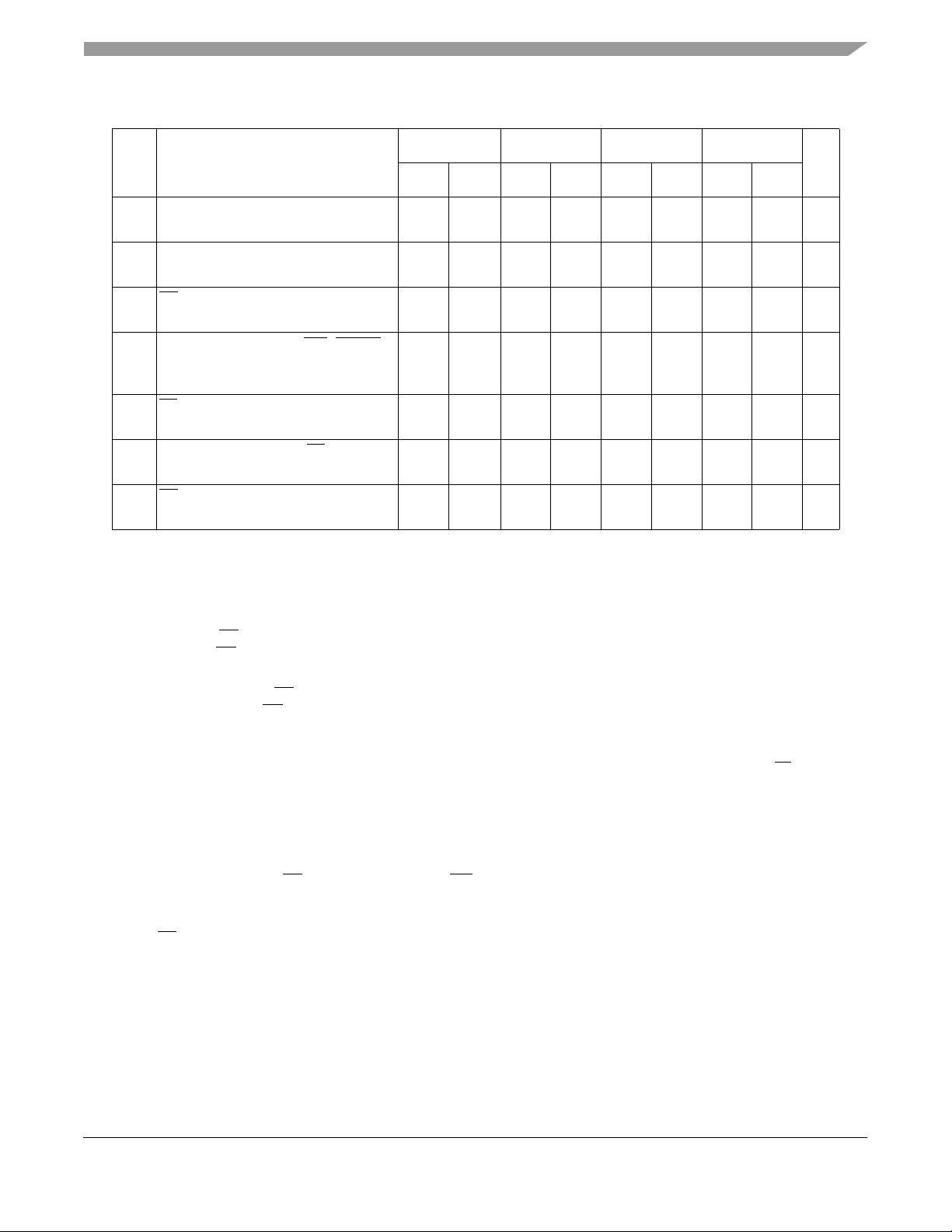
Bus Signal Timing
Figure 4 is the control timing diagram.
CLKOUT
Outputs
Outputs
Inputs
Inputs
Legend:
2.0 V
B
2.0 V
0.8 V
A
B
2.0 V
0.8 V
0.8 V
2.0 V
0.8 V
C
2.0 V
0.8 V
0.8 V
A
D
2.0 V
0.8 V
2.0 V
2.0 V
0.8 V
2.0 V
0.8 V
D
C
2.0 V
0.8 V
A Maximum output delay specification.
B Minimum output hold time.
C Minimum input setup time specification.
D Minimum input hold time specification.
Figure 4. Control Timing
Figure 5 provides the timing for the external clock.
CLKOUT
B1
B1
B4
Figure 5. External Clock Timing
B3
B2
B5
MPC862/857T/857DSL PowerQUICC™ Family Hardware Specifications, Rev. 3
24 Freescale Semiconductor
Page 25
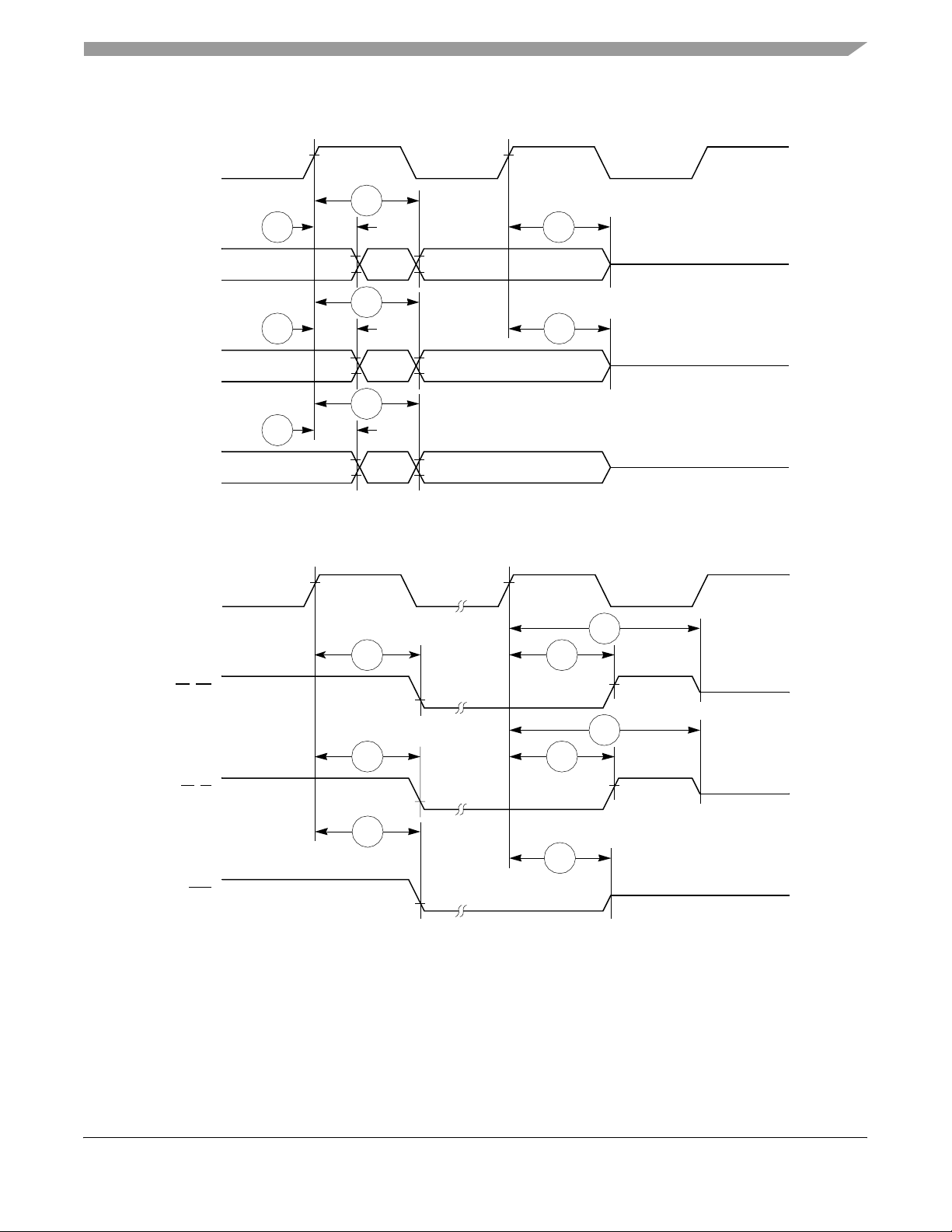
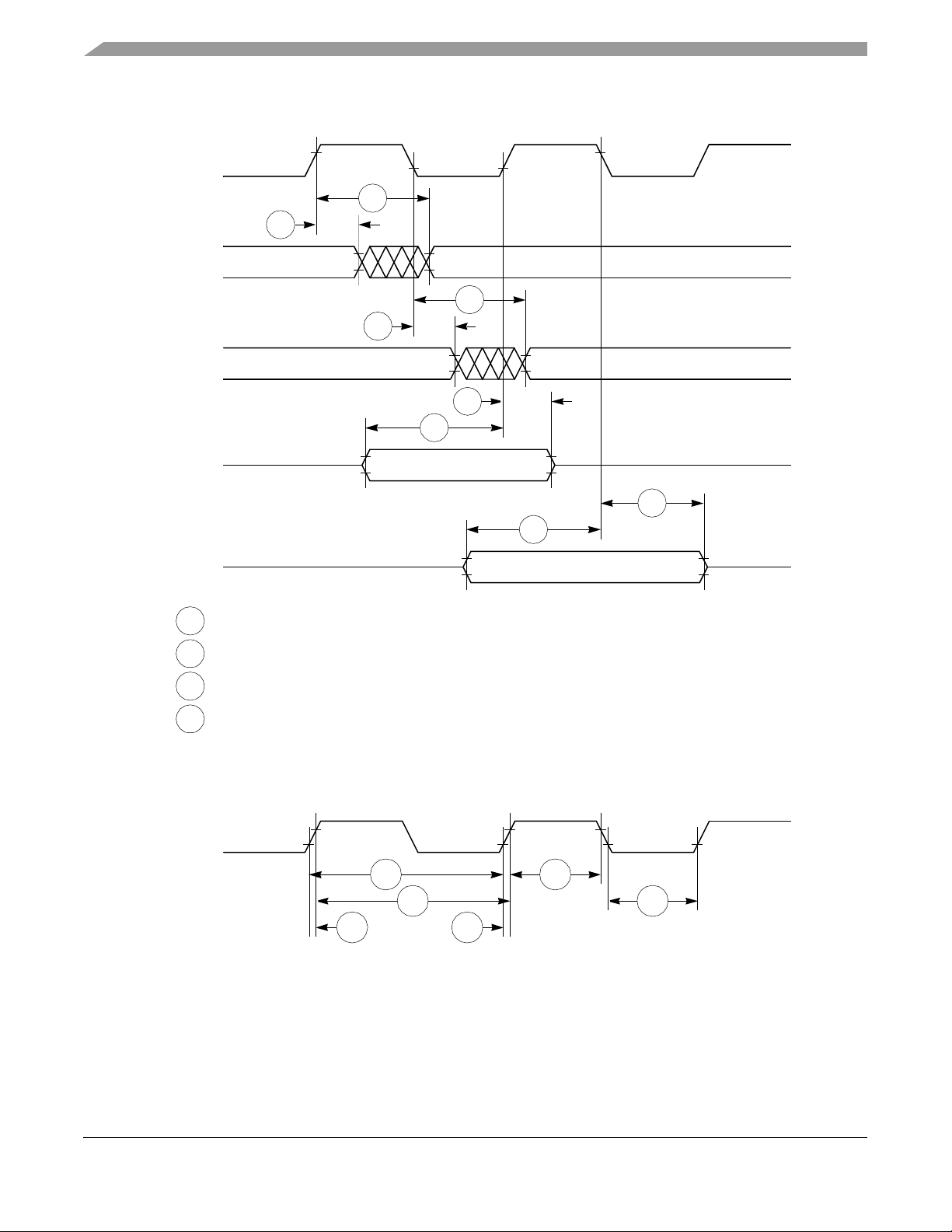
Figure 6 provides the timing for the synchronous output signals.
CLKOUT
B8
B7 B9
Output
Signals
B8a
Output
Signals
B8b
B7b
Output
Signals
Figure 6. Synchronous Output Signals Timing
Bus Signal Timing
B9B7a
Figure 7 provides the timing for the synchronous active pull-up and open-drain output signals.
CLKOUT
B13
B12B11
TS
, BB
B13a
B11a B12a
TA , BI
B14
B15
TEA
Figure 7. Synchronous Active Pull-Up Resistor and Open-Drain Outputs
Signals Timing
MPC862/857T/857DSL PowerQUICC™ Family Hardware Specifications, Rev. 3
Freescale Semiconductor 25
Page 26
Bus Signal Timing
Figure 8 provides the timing for the synchronous input signals.
CLKOUT
B16
, BI
TA
B16a
TEA, KR,
RETRY
, CR
B16b
BB, BG, BR
Figure 8. Synchronous Input Signals Timing
B17
B17a
B17
Figure 9 provides normal case timing for input data. It also applies to normal read accesses under the
control of the UPM in the memory controller.
CLKOUT
B16
B17
TA
B18
B19
D[0:31],
DP[0:3]
Figure 9. Input Data Timing in Normal Case
MPC862/857T/857DSL PowerQUICC™ Family Hardware Specifications, Rev. 3
26 Freescale Semiconductor
Page 27
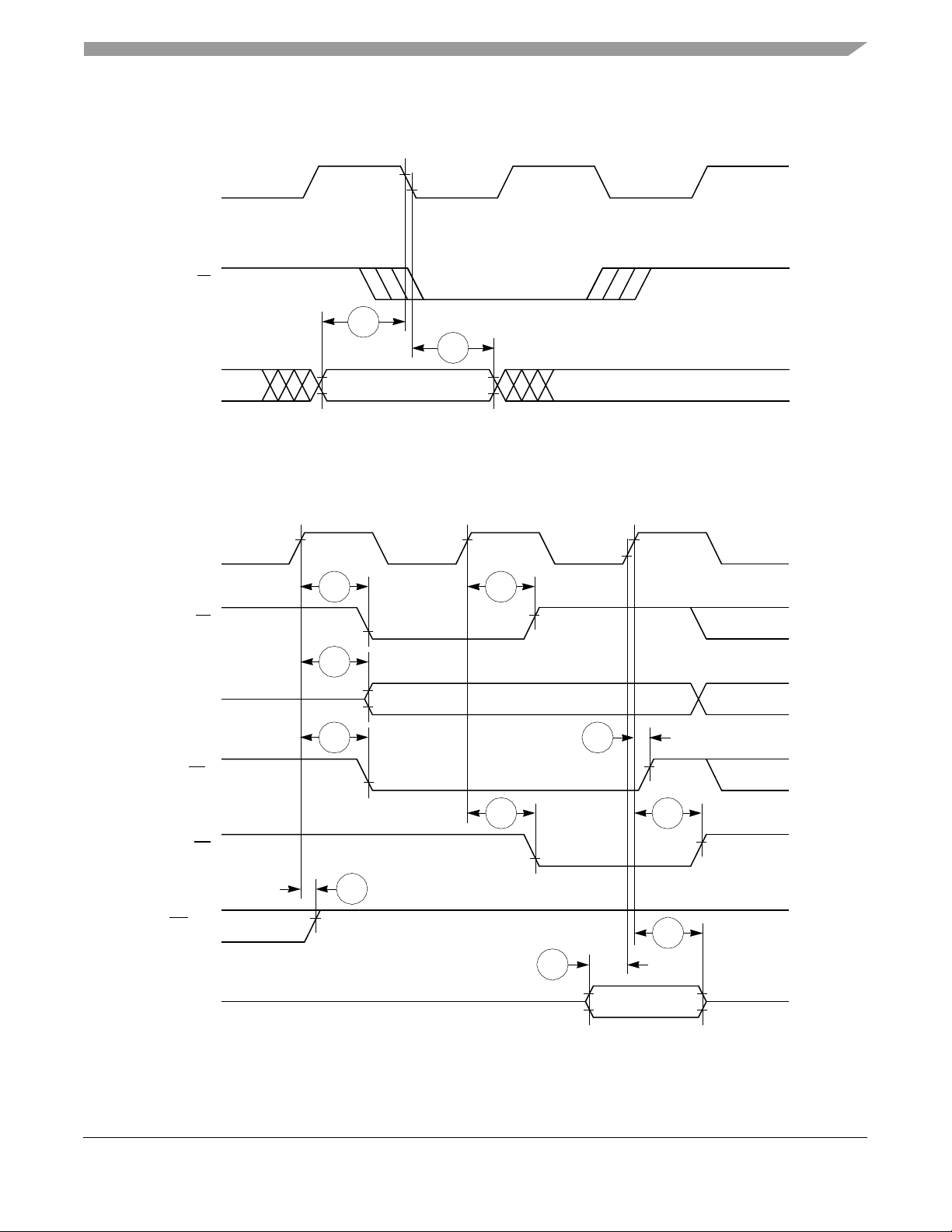
Bus Signal Timing
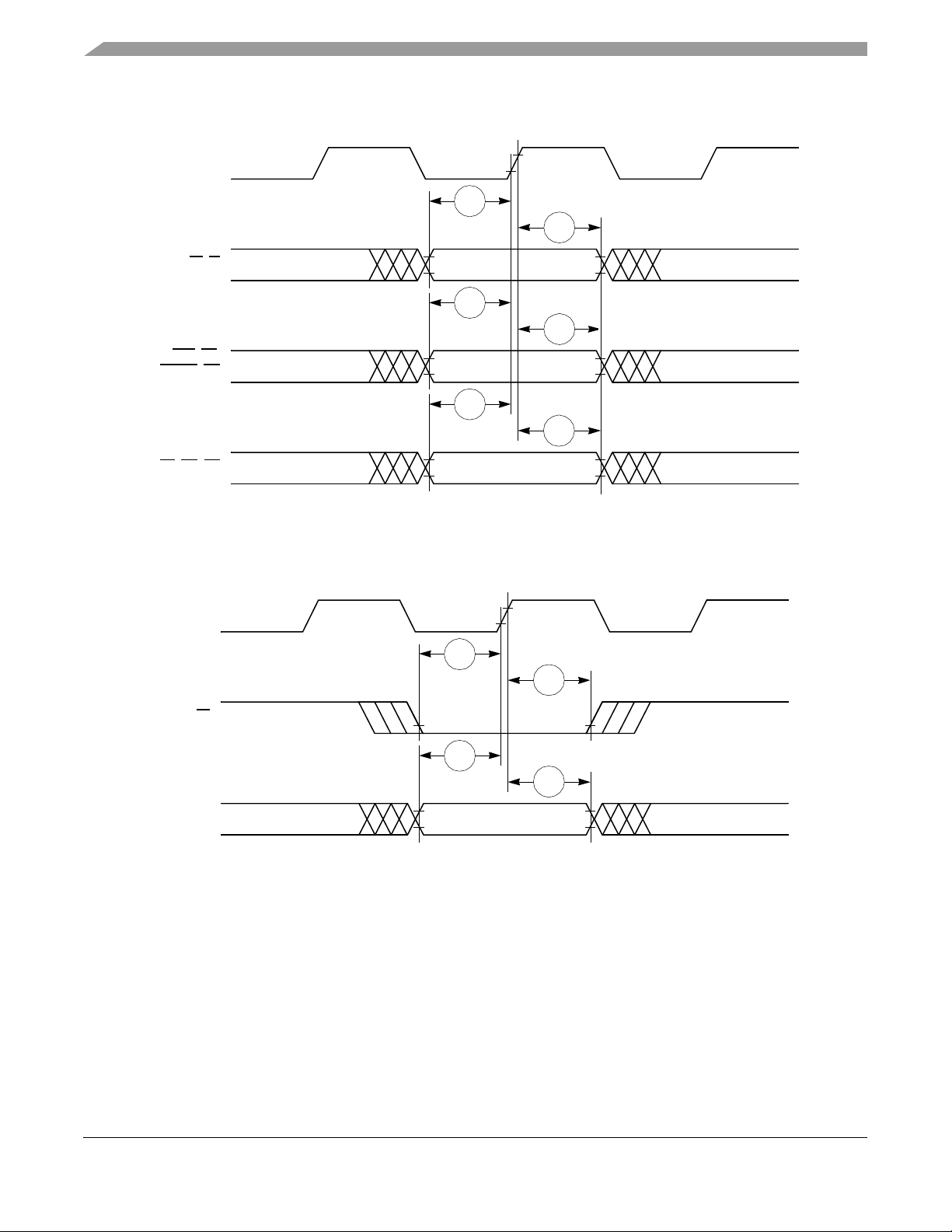
Figure 10 provides the timing for the input data controlled by the UPM for data beats where DLT3 = 1 in
the UPM RAM words. (This is only the case where data is latched on the falling edge of CLKOUT.)
CLKOUT
TA
B20
B21
D[0:31],
DP[0:3]
Figure 10. Input Data Timing when Controlled by UPM in the
Memory Controller and DLT3 = 1
Figure 11 through Figure 14 provide the timing for the external bus read controlled by various GPCM
factors.
CLKOUT
TS
A[0:31]
CSx
OE
WE[0:3]
D[0:31],
DP[0:3]
B11 B12
B8
B22
B25
B28
B23
B26
B19
B18
Figure 11. External Bus Read Timing (GPCM Controlled—ACS = 00)
MPC862/857T/857DSL PowerQUICC™ Family Hardware Specifications, Rev. 3
Freescale Semiconductor 27
Page 28

Bus Signal Timing
CLKOUT
A[0:31]
B11 B12
TS
B8
B22a
CSx
B25B24
OE
D[0:31],
DP[0:3]
B23
B26
B19B18
Figure 12. External Bus Read Timing (GPCM Controlled—TRLX = 0, ACS = 10)
CLKOUT
B11 B12
TS
B22bB8
A[0:31]
B22c B23
CSx
B24a B25 B26
OE
B19B18
D[0:31],
DP[0:3]
Figure 13. External Bus Read Timing (GPCM Controlled—TRLX = 0, ACS = 11)
MPC862/857T/857DSL PowerQUICC™ Family Hardware Specifications, Rev. 3
28 Freescale Semiconductor
Page 29

CLKOUT
TS
A[0:31]
Bus Signal Timing
B11 B12
B8
CSx
OE
D[0:31],
DP[0:3]
B22a
B27
B27a
B22b B22c B19B18
B23
Figure 14. External Bus Read Timing (GPCM Controlled—TRLX = 1,
ACS = 10, ACS = 11)
B26
MPC862/857T/857DSL PowerQUICC™ Family Hardware Specifications, Rev. 3
Freescale Semiconductor 29
Page 30

Bus Signal Timing
Figure 15 through Figure 17 provide the timing for the external bus write controlled by various GPCM
factors.
CLKOUT
TS
A[0:31]
CSx
WE[0:3]
OE
D[0:31],
DP[0:3]
B11
B8
B22 B23
B26
B12
B8 B9
B30
B28B25
B29b
B29
Figure 15. External Bus Write Timing (GPCM Controlled—TRLX = 0,1 CSNT = 0)
MPC862/857T/857DSL PowerQUICC™ Family Hardware Specifications, Rev. 3
30 Freescale Semiconductor
Page 31

CLKOUT
Bus Signal Timing
B11
B12
TS
B8
B30a B30c
A[0:31]
B22
B28b B28d
B23
CSx
B25
B29c B29g
WE[0:3]
OE
B26
B28aB9B28c
B29a B29f
B8
D[0:31],
DP[0:3]
Figure 16. External Bus Write Timing (GPCM Controlled—TRLX = 0,1 CSNT = 1)
MPC862/857T/857DSL PowerQUICC™ Family Hardware Specifications, Rev. 3
Freescale Semiconductor 31
Page 32

Bus Signal Timing
CLKOUT
B12B11
TS
B8
B30dB30b
A[0:31]
B28b B28d
B23B22
CSx
B25 B29e B29i
WE[0:3]
B26 B29d B29h
OE
B29b
B28a B28c B9B8
D[0:31],
DP[0:3]
Figure 17. External Bus Write Timing (GPCM Controlled—TRLX = 0,1, CSNT = 1)
MPC862/857T/857DSL PowerQUICC™ Family Hardware Specifications, Rev. 3
32 Freescale Semiconductor
Page 33

Figure 18 provides the timing for the external bus controlled by the UPM.
CLKOUT
B8
A[0:31]
B31a
B31d
B31
CSx
B34
B34a
B34b
B32a B32d
B32
B31b
B32b
Bus Signal Timing
B31c
B32c
[0:3],
BS_A
BS_B
[0:3]
GPL_A[0:5],
GPL_B
[0:5]
B36
B35
B35a
B35b
B33
B33a
Figure 18. External Bus Timing (UPM Controlled Signals)
MPC862/857T/857DSL PowerQUICC™ Family Hardware Specifications, Rev. 3
Freescale Semiconductor 33
Page 34

Bus Signal Timing
Figure 19 provides the timing for the asynchronous asserted UPWAIT signal controlled by the UPM.
CLKOUT
B37
UPWAIT
B38
CSx
BS_A[0:3],
BS_B
[0:3]
GPL_A
[0:5],
GPL_B
[0:5]
Figure 19. Asynchronous UPWAIT Asserted Detection in UPM Handled
Cycles Timing
Figure 20 provides the timing for the asynchronous negated UPWAIT signal controlled by the UPM.
CLKOUT
B37
UPWAIT
B38
CSx
BS_A[0:3],
[0:3]
BS_B
[0:5],
GPL_A
[0:5]
GPL_B
Figure 20. Asynchronous UPWAIT Negated Detection in UPM Handled
Cycles Timing
MPC862/857T/857DSL PowerQUICC™ Family Hardware Specifications, Rev. 3
34 Freescale Semiconductor
Page 35

Bus Signal Timing
Figure 21 provides the timing for the synchronous external master access controlled by the GPCM.
CLKOUT
B41 B42
TS
B40
A[0:31],
TSIZ[0:1],
, BURST
R/W
B22
CSx
Figure 21. Synchronous External Master Access Timing
(GPCM Handled ACS = 00)
Figure 22 provides the timing for the asynchronous external master memory access controlled by the
GPCM.
CLKOUT
B39
AS
B40
A[0:31],
TSIZ[0:1],
R/W
B22
CSx
Figure 22. Asynchronous External Master Memory Access Timing
(GPCM Controlled—ACS = 00)
Figure 23 provides the timing for the asynchronous external master control signals negation.
AS
B43
CSx, WE[0:3],
OE
, GPLx,
BS
[0:3]
Figure 23. Asynchronous External Master—Control Signals Negation Timing
MPC862/857T/857DSL PowerQUICC™ Family Hardware Specifications, Rev. 3
Freescale Semiconductor 35
Page 36

Bus Signal Timing
Table 8 provides interrupt timing for the MPC862/857T/857DSL.
Table 8. Interrupt Timing
Num Characteristic
I39 IRQ
I40 IRQ
I41 IRQ
I42 IRQ
I43 IRQ
1
The timings I39 and I40 describe the testing conditions under which the IRQ lines are tested when being
defined as level sensitive. The IRQ
negated with reference to the CLKOUT.
The timings I41, I42, and I43 are specified to allow the correct function of the IRQ
and has no direct relation with the total system interrupt latency that the MPC862/857T/857DSL is able to
support.
x valid to CLKOUT rising edge (set up time) 6.00 ns
x hold time after CLKOUT 2.00 ns
x pulse width low 3.00 ns
x pulse width high 3.00 ns
x edge-to-edge time 4xT
lines are synchronized internally and do not have to be asserted or
1
All Frequencies
Min Max
CLOCKOUT
lines detection circuitry,
Figure 24 provides the interrupt detection timing for the external level-sensitive lines.
CLKOUT
I39
I40
Unit
—
x
IRQ
Figure 24. Interrupt Detection Timing for External Level Sensitive Lines
Figure 25 provides the interrupt detection timing for the external edge-sensitive lines.
CLKOUT
I41 I42
x
IRQ
I43
I43
Figure 25. Interrupt Detection Timing for External Edge Sensitive Lines
MPC862/857T/857DSL PowerQUICC™ Family Hardware Specifications, Rev. 3
36 Freescale Semiconductor
Page 37

Table 9 shows the PCMCIA timing for the MPC862/857T/857DSL.
Table 9. PCMCIA Timing
33 MHz 40 MHz 50 MHz 66 MHz
Num Characteristic
Min Max Min Max Min Max Min Max
Bus Signal Timing
Unit
A(0:31), REG
P44
Strobe asserted.
B1 - 2.00)
P45
A(0:31), REG
negation.
1
(MIN = 1.00 x B1 -
2.00)
CLKOUT to REG
P46
0.25 x B1 + 8.00)
CLKOUT to REG
P47
0.25 x B1 + 1.00)
CLKOUT to CE1
P48
(MAX = 0.25 x B1 + 8.00)
CLKOUT to CE1
P49
(MAX = 0.25 x B1 + 8.00)
CLKOUT to PCOE
IOWR
P50
assert time. (MAX = 0.00 x
B1 + 11.00)
CLKOUT to PCOE
IOWR
P51
negate time. (MAX = 0.00 x
B1 + 11.00)
CLKOUT to ALE assert time
P52
(MAX = 0.25 x B1 + 6.30)
valid to PCMCIA
1
(MIN = 0.75 x
valid to ALE
valid (MAX =
Invalid. (MIN =
, CE2 asserted.
, CE2 negated.
, IORD, PCWE,
, IORD, PCWE,
20.70 — 16.70 — 13.00 — 9.40 — ns
28.30 — 23.00 — 18.00 — 13.20 — ns
7.60 15.60 6.30 14.30 5.00 13.00 3.80 11.80 ns
8.60 — 7.30 — 6.00 — 4.80 — ns
7.60 15.60 6.30 14.30 5.00 13.00 3.80 11.80 ns
7.60 15.60 6.30 14.30 5.00 13.00 3.80 11.80 ns
— 11.00 — 11.00 — 11.00 — 11.00 ns
2.00 11.00 2.00 11.00 2.00 11.00 2.00 11.00 ns
7.60 13.80 6.30 12.50 5.00 11.30 3.80 10.00 ns
CLKOUT to ALE negate time
P53
(MAX = 0.25 x B1 + 8.00)
, IOWR negated to D(0:31)
PCWE
P54
P55
1
invalid.
WAITA
(MIN = 0.25 x B1 - 2.00)
and WAITB valid to
CLKOUT rising edge.
1
(MIN =
— 15.60 — 14.30 — 13.00 — 11.80 ns
5.60 — 4.30 — 3.00 — 1.80 — ns
8.00 — 8.00 — 8.00 — 8.00 — ns
0.00 x B1 + 8.00)
2.00 — 2.00 — 2.00 — 2.00 — ns
CLKOUT rising edge to WAITA
and WAITB
P56
invalid.1 (MIN = 0.00 x
B1 + 2.00)
1
PSST = 1. Otherwise add PSST times cycle time.
PSHT = 0. Otherwise add PSHT times cycle time.
These synchronous timings define when the WAITx
current cycle. The WAITx
PCMCIA Interface in the
assertion will be effective only if it is detected 2 cycles before the PSL timer expiration. See
MPC862 PowerQUICC User s Manual
signals are detected in order to freeze (or relieve) the PCMCIA
.
MPC862/857T/857DSL PowerQUICC™ Family Hardware Specifications, Rev. 3
Freescale Semiconductor 37
Page 38

Bus Signal Timing
Figure 26 provides the PCMCIA access cycle timing for the external bus read.
CLKOUT
TS
P44
A[0:31]
REG
CE1/CE2
PCOE, IORD
ALE
D[0:31]
P46 P45
P48 P49
P53P52 P52
P47
P51P50
Figure 26. PCMCIA Access Cycles Timing External Bus Read
B19B18
MPC862/857T/857DSL PowerQUICC™ Family Hardware Specifications, Rev. 3
38 Freescale Semiconductor
Page 39

Figure 27 provides the PCMCIA access cycle timing for the external bus write.
CLKOUT
TS
P44
A[0:31]
Bus Signal Timing
P46 P45
REG
P48 P49
CE1/CE2
PCOE, IOWR
P53P52 P52
ALE
D[0:31]
Figure 27. PCMCIA Access Cycles Timing External Bus Write
Figure 28 provides the PCMCIA W A IT signals detection timing.
P47
P51P50
P54
B19B18
CLKOUT
P55
P56
x
WAI T
Figure 28. PCMCIA WAIT Signals Detection Timing
MPC862/857T/857DSL PowerQUICC™ Family Hardware Specifications, Rev. 3
Freescale Semiconductor 39
Page 40

Bus Signal Timing
Table 10 shows the PCMCIA port timing for the MPC862/857T/857DSL.
Table 10. PCMCIA Port Timing
33 MHz 40 MHz 50 MHz 66 MHz
Num Characteristic
Min Max Min Max Min Max Min Max
Unit
CLKOUT to OPx Valid (MAX = 0.00 x
P57
B1 + 19.00)
HRESET
P58
(MIN = 0.75 x B1 + 3.00)
IP_Xx valid to CLKOUT rising edge
P59
(MIN = 0.00 x B1 + 5.00)
CLKOUT rising edge to IP_Xx invalid
P60
(MIN = 0.00 x B1 + 1.00)
1
OP2 and OP3 only.
negated to OPx drive
1
— 19.00 — 19.00 — 19.00 — 19.00 ns
25.70 — 21.70 — 18.00 — 14.40 — ns
5.00 — 5.00 — 5.00 — 5.00 — ns
1.00 — 1.00 — 1.00 — 1.00 — ns
Figure 29 provides the PCMCIA output port timing for the MPC862/857T/857DSL.
CLKOUT
P57
Output
Signals
HRESET
P58
OP2, OP3
Figure 29. PCMCIA Output Port Timing
Figure 30 provides the PCMCIA output port timing for the MPC862/857T/857DSL.
CLKOUT
P59
P60
Input
Signals
Figure 30. PCMCIA Input Port Timing
MPC862/857T/857DSL PowerQUICC™ Family Hardware Specifications, Rev. 3
40 Freescale Semiconductor
Page 41

Table 11 s hows the debug port timing for the MPC862/857T/857DSL.
Table 11. Debug Port Timing
All Frequencies
Num Characteristic
Min Max
Bus Signal Timing
Unit
D61 DSCK cycle time 3 x T
D62 DSCK clock pulse width 1.25 x T
D63 DSCK rise and fall times 0.00 3.00 ns
D64 DSDI input data setup time 8.00 ns
D65 DSDI data hold time 5.00 ns
D66 DSCK low to DSDO data valid 0.00 15.00 ns
D67 DSCK low to DSDO invalid 0.00 2.00 ns
CLOCKOUT
Figure 31 provides the input timing for the debug port clock.
DSCK
D61
D61
D63
D62
Figure 31. Debug Port Clock Input Timing
Figure 32 provides the timing for the debug port.
CLOCKOUT
D62
-
-
D63
DSCK
D64
D65
DSDI
D66
D67
DSDO
Figure 32. Debug Port Timings
MPC862/857T/857DSL PowerQUICC™ Family Hardware Specifications, Rev. 3
Freescale Semiconductor 41
Page 42

Bus Signal Timing
Table 12 shows the reset timing for the MPC862/857T/857DSL.
Table 12. Reset Timing
33 MHz 40 MHz 50 MHz 66 MHz
Num Characteristic
Min Max Min Max Min Max Min Max
Unit
CLKOUT to HRESET
R69
(MAX = 0.00 x B1 + 20.00)
CLKOUT to SRESET
R70
(MAX = 0.00 x B1 + 20.00)
RSTCONF
R71
(MIN = 17.00 x B1)
R72— —————————
Configuration data to HRESET rising
R73
edge set up time
(MIN = 15.00 x B1 + 50.00)
Configuration data to RSTCONF
edge set up time
R74
(MIN = 0.00 x B1 + 350.00)
Configuration data hold time after
R75
RSTCONF
(MIN = 0.00 x B1 + 0.00)
Configuration data hold time after
R76
HRESET
(MIN = 0.00 x B1 + 0.00)
HRESET
R77
data out drive (MAX = 0.00 x B1 + 25.00)
pulse width
negation
negation
and RSTCONF asserted to
high impedance
high impedance
rising
— 20.00 — 20.00 — 20.00 — 20.00 ns
— 20.00 — 20.00 — 20.00 — 20.00 ns
515.20 — 425.00 — 340.00 — 257.60 — ns
504.50 — 425.00 — 350.00 — 277.30 — ns
350.00 — 350.00 — 350.00 — 350.00 — ns
0.00 — 0.00 — 0.00 — 0.00 — ns
0.00 — 0.00 — 0.00 — 0.00 — ns
— 25.00 — 25.00 — 25.00 — 25.00 ns
RSTCONF
R78
impedance. (MAX = 0.00 x B1 + 25.00)
CLKOUT of last rising edge before chip
R79
three-states HRESET
impedance. (MAX = 0.00 x B1 + 25.00)
R80 DSDI, DSCK set up (MIN = 3.00 x B1) 90.90 — 75.00 — 60.00 — 45.50 — ns
DSDI, DSCK hold time
R81
(MIN = 0.00 x B1 + 0.00)
SRESET
edge for DSDI and DSCK sample
R82
(MIN = 8.00 x B1)
negated to data out high
to data out high
negated to CLKOUT rising
MPC862/857T/857DSL PowerQUICC™ Family Hardware Specifications, Rev. 3
— 25.00 — 25.00 — 25.00 — 25.00 ns
— 25.00 — 25.00 — 25.00 — 25.00 ns
0.00 — 0.00 — 0.00 — 0.00 — ns
242.40 — 200.00 — 160.00 — 121.20 — ns
42 Freescale Semiconductor
Page 43

Figure 33 shows the reset timing for the data bus configuration.
HRESET
R71
R76
RSTCONF
R73
R74
D[0:31] (IN)
R75
Figure 33. Reset Timing—Configuration from Data Bus
Figure 34 provides the reset timing for the data bus weak drive during configuration.
CLKOUT
Bus Signal Timing
HRESET
RSTCONF
D[0:31] (OUT)
(Weak)
R69
R79
R77 R78
Figure 34. Reset Timing—Data Bus Weak Drive during Configuration
MPC862/857T/857DSL PowerQUICC™ Family Hardware Specifications, Rev. 3
Freescale Semiconductor 43
Page 44

IEEE 1149.1 Electrical Specifications
Figure 35 provides the reset timing for the debug port configuration.
CLKOUT
R70
R82
SRESET
R80R80
R81
DSCK, DSDI
R81
Figure 35. Reset Timing—Debug Port Configuration
10 IEEE 1149.1 Electrical Specifications
Table 13 provides the JTAG timings for the MPC862/857T/857DSL shown in Figure 36 though Figure 39.
Table 13. JTAG Timing
All Frequencies
Num Characteristic
Min Max
J82 TCK cycle time 100.00 — ns
J83 TCK clock pulse width measured at 1.5 V 40.00 — ns
J84 TCK rise and fall times 0.00 10.00 ns
J85 TMS, TDI data setup time 5.00 — ns
J86 TMS, TDI data hold time 25.00 — ns
J87 TCK low to TDO data valid — 27.00 ns
J88 TCK low to TDO data invalid 0.00 — ns
J89 TCK low to TDO high impedance — 20.00 ns
J90 TRST
J91 TRST
J92 TCK falling edge to output valid — 50.00 ns
J93 TCK falling edge to output valid out of high impedance — 50.00 ns
J94 TCK falling edge to output high impedance — 50.00 ns
J95 Boundary scan input valid to TCK rising edge 50.00 — ns
assert time 100.00 — ns
setup time to TCK low 40.00 — ns
Unit
J96 TCK rising edge to boundary scan input invalid 50.00 — ns
MPC862/857T/857DSL PowerQUICC™ Family Hardware Specifications, Rev. 3
44 Freescale Semiconductor
Page 45

TCK
TCK
TMS, TDI
TDO
IEEE 1149.1 Electrical Specifications
J82 J83
J82 J83
J84 J84
Figure 36. JTAG Test Clock Input Timing
J85
J86
J87
J88 J89
TCK
TRST
TCK
Output
Signals
Output
Signals
Figure 37. JTAG Test Access Port Timing Diagram
J91
J90
Figure 38. JTAG TRST
J92 J94
J93
Timing Diagram
J95 J96
Output
Signals
Figure 39. Boundary Scan (JTAG) Timing Diagram
MPC862/857T/857DSL PowerQUICC™ Family Hardware Specifications, Rev. 3
Freescale Semiconductor 45
Page 46

CPM Electrical Characteristics
11 CPM Electrical Characteristics
This section provides the AC and DC electrical specifications for the communications processor module
(CPM) of the MPC862/857T/857DSL.
11.1 PIP/PIO AC Electrical Specifications
Table 14 provides the PIP/PIO AC timings as shown in Figure 40 though Figure 44.
Table 14. PIP/PIO Timing
All Frequencies
Num Characteristic
Min Max
21 Data-in setup time to STBI low 0 — ns
22 Data-in hold time to STBI high 2.5 – t3
23 STBI pulse width 1.5 — clk
24 STBO pulse width 1 clk – 5 ns — ns
25 Data-out setup time to STBO low 2 — clk
1
—clk
Unit
26 Data-out hold time from STBO high 5 — clk
27 STBI low to STBO low (Rx interlock) — 2 clk
28 STBI low to STBO high (Tx interlock) 2 — clk
29 Data-in setup time to clock high 15 — ns
30 Data-in hold time from clock high 7.5 — ns
31 Clock low to data-out valid (CPU writes data, control, or direction) — 25 ns
1
t3 = Specification 23
DATA-IN
21
23
STBI
27
24
STBO
22
Figure 40. PIP Rx (Interlock Mode) Timing Diagram
MPC862/857T/857DSL PowerQUICC™ Family Hardware Specifications, Rev. 3
46 Freescale Semiconductor
Page 47

DATA-OUT
CPM Electrical Characteristics
STBO
(Output)
STBI
(Input)
DATA-IN
STBI
(Input)
25
24
28
23
26
Figure 41. PIP Tx (Interlock Mode) Timing Diagram
2221
23
24
STBO
(Output)
DATA-OUT
STBO
(Output)
STBI
(Input)
Figure 42. PIP Rx (Pulse Mode) Timing Diagram
2625
24
23
Figure 43. PIP TX (Pulse Mode) Timing Diagram
MPC862/857T/857DSL PowerQUICC™ Family Hardware Specifications, Rev. 3
Freescale Semiconductor 47
Page 48

CPM Electrical Characteristics
CLKO
29
30
DATA-I N
31
DATA-OUT
Figure 44. Parallel I/O Data-In/Data-Out Timing Diagram
11.2 Port C Interrupt AC Electrical Specifications
Table 15 provides the timings for port C interrupts.
Table 15. Port C Interrupt Timing
Num Characteristic
33.34 MHz
Unit
Min Max
35 Port C interrupt pulse width low (edge-triggered mode) 55 — ns
36 Port C interrupt minimum time between active edges 55 — ns
Figure 45 shows the port C interrupt detection timing.
36
Port C
(Input)
35
Figure 45. Port C Interrupt Detection Timing
11.3 IDMA Controller AC Electrical Specifications
Table 16 provides the IDMA controller timings as shown in Figure 46 though Figure 49.
Table 16. IDMA Controller Timing
All Frequencies
Num Characteristic
Min Max
40 DREQ
setup time to clock high 7 — ns
Unit
41 DREQ
42 SDACK
48 Freescale Semiconductor
hold time from clock high 3 — ns
assertion delay from clock high — 12 ns
MPC862/857T/857DSL PowerQUICC™ Family Hardware Specifications, Rev. 3
Page 49

CPM Electrical Characteristics
Table 16. IDMA Controller Timing (continued)
All Frequencies
Num Characteristic
Min Max
43 SDACK negation delay from clock low — 12 ns
Unit
44 SDACK
45 SDACK
46 TA
assertion to falling edge of the clock setup time (applies to external TA)7 — ns
CLKO
(Output)
DREQ
(Input)
CLKO
(Output)
TS
(Output)
negation delay from TA low — 20 ns
negation delay from clock high — 15 ns
41
40
Figure 46. IDMA External Requests Timing Diagram
R/W
(Output)
DATA
TA
(Input)
SDACK
Figure 47. SDACK
MPC862/857T/857DSL PowerQUICC™ Family Hardware Specifications, Rev. 3
42
43
46
Timing Diagram—Peripheral Write, Externally-Generated TA
Freescale Semiconductor 49
Page 50

CPM Electrical Characteristics
CLKO
(Output)
TS
(Output)
R/W
(Output)
DATA
TA
(Output)
SDACK
42 44
Figure 48. SDACK Timing Diagram—Peripheral Write, Internally-Generated TA
CLKO
(Output)
TS
(Output)
R/W
(Output)
42 45
DATA
TA
(Output)
SDACK
Figure 49. SDACK
MPC862/857T/857DSL PowerQUICC™ Family Hardware Specifications, Rev. 3
50 Freescale Semiconductor
Timing Diagram—Peripheral Read, Internally-Generated TA
Page 51

CPM Electrical Characteristics
11.4 Baud Rate Generator AC Electrical Specifications
Table 17 provides the baud rate generator timings as shown in Figure 50.
Table 17. Baud Rate Generator Timing
All Frequencies
Num Characteristic
Min Max
50 BRGO rise and fall time — 10 ns
51 BRGO duty cycle 40 60 %
52 BRGO cycle 40 — ns
Unit
50
BRGOX
51
52
50
51
Figure 50. Baud Rate Generator Timing Diagram
11.5 Timer AC Electrical Specifications
Table 18 provides the general-purpose timer timings as shown in Figure 51.
Num Characteristic
61 TIN/TGATE
62 TIN/TGATE
63 TIN/TGATE
64 TIN/TGATE
rise and fall time 10 — ns
low time 1 — clk
high time 2 — clk
cycle time 3 — clk
Table 18. Timer Timing
All Frequencies
Unit
Min Max
65 CLKO low to TOUT
MPC862/857T/857DSL PowerQUICC™ Family Hardware Specifications, Rev. 3
Freescale Semiconductor 51
valid 3 25 ns
Page 52

CPM Electrical Characteristics
CLKO
TIN/TGATE
(Input)
60
626361
61
64
65
TOUT
(Output)
Figure 51. CPM General-Purpose Timers Timing Diagram
11.6 Serial Interface AC Electrical Specifications
Table 19 provides the s erial interface timings as shown in Figure 52 though Figure 56.
Num Characteristic
70 L1RCLK, L1TCLK frequency (DSC = 0)
71 L1RCLK, L1TCLK width low (DSC = 0)
71a L1RCLK, L1TCLK width high (DSC = 0)
72 L1TXD, L1ST(1–4), L1RQ
, L1CLKO rise/fall time — 15.00 ns
73 L1RSYNC, L1TSYNC valid to L1CLK edge (SYNC setup time) 20.00 — ns
Table 19. SI Timing
All Frequencies
Min Max
1, 2
— SYNCCLK/2.5 MHz
2
3
P + 10 — ns
P + 10 — ns
Unit
74 L1CLK edge to L1RSYNC, L1TSYNC, invalid (SYNC hold
35.00 — ns
time)
75 L1RSYNC, L1TSYNC rise/fall time — 15.00 ns
76 L1RXD valid to L1CLK edge (L1RXD setup time) 17.00 — ns
77 L1CLK edge to L1RXD invalid (L1RXD hold time) 13.00 — ns
78 L1CLK edge to L1ST(1–4) valid
4
10.00 45.00 ns
78A L1SYNC valid to L1ST(1–4) valid 10.00 45.00 ns
79 L1CLK edge to L1ST(1–4) invalid 10.00 45.00 ns
80 L1CLK edge to L1TXD valid 10.00 55.00 ns
80A L1TSYNC valid to L1TXD valid
4
10.00 55.00 ns
81 L1CLK edge to L1TXD high impedance 0.00 42.00 ns
82 L1RCLK, L1TCLK frequency (DSC =1) — 16.00 or
MHz
SYNCCLK/2
83 L1RCLK, L1TCLK width low (DSC =1) P + 10 — ns
MPC862/857T/857DSL PowerQUICC™ Family Hardware Specifications, Rev. 3
52 Freescale Semiconductor
Page 53

CPM Electrical Characteristics
Table 19. SI Timing (continued)
All Frequencies
Num Characteristic
Min Max
83a L1RCLK, L1TCLK width high (DSC = 1)
84 L1CLK edge to L1CLKO valid (DSC = 1) — 30.00 ns
85 L1RQ
86 L1GR setup time
valid before falling edge of L1TSYNC
2
87 L1GR hold time 42.00 — ns
3
4
P + 10 — ns
1.00 — L1TCL
42.00 — ns
Unit
K
88 L1CLK edge to L1SYNC valid (FSD = 00) CNT = 0000, BYT =
—0.00ns
0, DSC = 0)
1
The ratio SyncCLK/L1RCLK must be greater than 2.5/1.
2
These specs are valid for IDL mode only.
3
Where P = 1/CLKOUT. Thus for a 25-MHz CLKO1 rate, P = 40 ns.
4
These strobes and TxD on the first bit of the frame become valid after L1CLK edge or L1SYNC, whichever is later.
L1RCLK
(FE=0, CE=0)
(Input)
71
70 71a
72
L1RCLK
(FE=1, CE=1)
(Input)
RFSD=1
75
L1RSYNC
(Input)
73
74 77
L1RXD
(Input)
BIT0
76
78
79
L1ST(4-1)
(Output)
Figure 52. SI Receive Timing Diagram with Normal Clocking (DSC = 0)
MPC862/857T/857DSL PowerQUICC™ Family Hardware Specifications, Rev. 3
Freescale Semiconductor 53
Page 54

CPM Electrical Characteristics
L1RCLK
(FE=1, CE=1)
(Input)
82
L1RCLK
(FE=0, CE=0)
(Input)
L1RSYNC
(Input)
72
RFSD=1
75
73
74 77
83a
L1RXD
(Input)
L1ST(4-1)
(Output)
L1CLKO
(Output)
BIT0
76
78
79
84
Figure 53. SI Receive Timing with Double-Speed Clocking (DSC = 1)
MPC862/857T/857DSL PowerQUICC™ Family Hardware Specifications, Rev. 3
54 Freescale Semiconductor
Page 55

L1TCLK
(FE=0, CE=0)
(Input)
L1TCLK
(FE=1, CE=1)
(Input)
L1TSYNC
(Input)
73
71 70
72
TFSD=0
75
74
80a
CPM Electrical Characteristics
81
L1TXD
(Output)
L1ST(4-1)
(Output)
BIT0
80
78
Figure 54. SI Transmit Timing Diagram (DSC = 0)
79
MPC862/857T/857DSL PowerQUICC™ Family Hardware Specifications, Rev. 3
Freescale Semiconductor 55
Page 56

CPM Electrical Characteristics
L1RCLK
(FE=0, CE=0)
(Input)
L1RCLK
(FE=1, CE=1)
(Input)
L1RSYNC
(Input)
73
75
74
72
82
TFSD=0
83a
81
L1TXD
(Output)
L1ST(4-1)
(Output)
L1CLKO
(Output)
BIT0
80
78a
79
78
84
Figure 55. SI Transmit Timing with Double Speed Clocking (DSC = 1)
MPC862/857T/857DSL PowerQUICC™ Family Hardware Specifications, Rev. 3
56 Freescale Semiconductor
Page 57

81
CPM Electrical Characteristics
78
87
72
71
71
74
73
12345678910 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20
B17 B16 B15 B14 B13 B12 B11 B10 D1 A B27 B26 B25 B24 B23 B22 B21 B20 D2 M
76
B17 B16 B14 B13 B12 B11 B10 D1 A B27 B26 B25 B24 B23 B22 B21 B20 D2 MB15
85
86
77
80
(Input)
L1RCLK
(Input)
L1RSYNC
L1TXD
(Output)
(Input)
L1RXD
(Output)
L1ST(4-1)
L1RQ
(Output)
L1GR
(Input)
Figure 56. IDL Timing
MPC862/857T/857DSL PowerQUICC™ Family Hardware Specifications, Rev. 3
Freescale Semiconductor 57
Page 58

CPM Electrical Characteristics
11.7 SCC in NMSI Mode Electrical Specifications
Table 20 provides the NMSI external clock timing.
Table 20. NMSI External Clock Timing
All Frequencies
Num Characteristic
Min Max
100 RCLK1 and TCLK1 width high
101 RCLK1 and TCLK1 width low 1/SYNCCLK +5 — ns
102 RCLK1 and TCLK1 rise/fall time — 15.00 ns
103 TXD1 active delay (from TCLK1 falling edge) 0.00 50.00 ns
1
1/SYNCCLK — ns
Unit
104 RTS1
105 CTS1
active/inactive delay (from TCLK1 falling edge) 0.00 50.00 ns
setup time to TCLK1 rising edge 5.00 — ns
106 RXD1 setup time to RCLK1 rising edge 5.00 — ns
107 RXD1 hold time from RCLK1 rising edge
108 CD1
1
The ratios SyncCLK/RCLK1 and SyncCLK/TCLK1 must be greater than or equal to 2.25/1.
2
Also applies to CD and CTS hold time when they are used as an external sync signal.
setup Time to RCLK1 rising edge 5.00 — ns
2
5.00 — ns
Table 21 provides the NMSI internal clock timing.
Table 21. NMSI Internal Clock Timing
All Frequencies
Num Characteristic
Min Max
100 RCLK1 and TCLK1 frequency
102 RCLK1 and TCLK1 rise/fall time — — ns
103 TXD1 active delay (from TCLK1 falling edge) 0.00 30.00 ns
104 RTS1
105 CTS1
active/inactive delay (from TCLK1 falling edge) 0.00 30.00 ns
setup time to TCLK1 rising edge 40.00 — ns
1
0.00 SYNCCLK/3 MHz
Unit
106 RXD1 setup time to RCLK1 rising edge 40.00 — ns
107 RXD1 hold time from RCLK1 rising edge
108 CD1
1
The ratios SyncCLK/RCLK1 and SyncCLK/TCLK1 must be greater or equal to 3/1.
2
Also applies to CD and CTS hold time when they are used as an external sync signals.
setup time to RCLK1 rising edge 40.00 — ns
2
0.00 — ns
MPC862/857T/857DSL PowerQUICC™ Family Hardware Specifications, Rev. 3
58 Freescale Semiconductor
Page 59

Figure 57 through Figure 59 show the NMSI timings.
RCLK1
CPM Electrical Characteristics
RxD1
(Input)
CD1
(Input)
CD1
(SYNC Input)
TCLK1
106
102
102
102 101
100
107
Figure 57. SCC NMSI Receive Timing Diagram
102 101
100
108
107
TxD1
(Output)
RTS1
(Output)
CTS1
(Input)
CTS1
(SYNC Input)
103
105
104
Figure 58. SCC NMSI Transmit Timing Diagram
104
107
MPC862/857T/857DSL PowerQUICC™ Family Hardware Specifications, Rev. 3
Freescale Semiconductor 59
Page 60

CPM Electrical Characteristics
TCLK1
102
TxD1
(Output)
RTS1
(Output)
CTS1
(Echo Input)
102 101
100
103
104
105
Figure 59. HDLC Bus Timing Diagram
11.8 Ethernet Electrical Specifications
Table 22 provides the E thernet timings as shown in Figure 60 though Figure 64.
Table 22. Ethernet Timing
All Frequencies
Num Characteristic
Min Max
104107
Unit
120 CLSN width high 40 — ns
121 RCLK1 rise/fall time — 15 ns
122 RCLK1 width low 40 — ns
123 RCLK1 clock period
124 RXD1 setup time 20 — ns
125 RXD1 hold time 5 — ns
126 RENA active delay (from RCLK1 rising edge of the last data bit) 10 — ns
127 RENA width low 100 — ns
128 TCLK1 rise/fall time — 15 ns
129 TCLK1 width low 40 — ns
130 TCLK1 clock period
131 TXD1 active delay (from TCLK1 rising edge) 10 50 ns
132 TXD1 inactive delay (from TCLK1 rising edge) 10 50 ns
133 TENA active delay (from TCLK1 rising edge) 10 50 ns
MPC862/857T/857DSL PowerQUICC™ Family Hardware Specifications, Rev. 3
1
1
80 120 ns
99 101 ns
60 Freescale Semiconductor
Page 61

CPM Electrical Characteristics
Table 22. Ethernet Timing (continued)
All Frequencies
Num Characteristic
Min Max
134 TENA inactive delay (from TCLK1 rising edge) 10 50 ns
Unit
135 RSTRT
136 RSTRT
137 REJECT
138 CLKO1 low to SDACK
139 CLKO1 low to SDACK
1
The ratios SyncCLK/RCLK1 and SyncCLK/TCLK1 must be greater or equal to 2/1.
2
SDACK is asserted whenever the SDMA writes the incoming frame DA into memory.
active delay (from TCLK1 falling edge) 10 50 ns
inactive delay (from TCLK1 falling edge) 10 50 ns
width low 1 — CLK
asserted
negated
2
2
CLSN(CTS1)
(Input)
120
Figure 60. Ethernet Collision Timing Diagram
RCLK1
121
124 123
RxD1
(Input)
121
—20ns
—20ns
Last Bit
125
126
127
RENA(CD1)
(Input)
Figure 61. Ethernet Receive Timing Diagram
MPC862/857T/857DSL PowerQUICC™ Family Hardware Specifications, Rev. 3
Freescale Semiconductor 61
Page 62

CPM Electrical Characteristics
TCLK1
(Output)
TENA(RTS1)
RENA(CD1)
(NOTE 2)
RCLK1
TxD1
(Input)
(Input)
128
128
129
131 121
132
133 134
NOTES:
Transmit clock invert (TCI) bit in GSMR is set.
1.
If RENA is deasserted before TENA, or RENA is not asserted at all during transmit, then the
2.
CSL bit is set in the buffer descriptor at the end of the frame transmission.
Figure 62. Ethernet Transmit Timing Diagram
RxD1
(Input)
RSTRT
(Output)
REJECT
0
Start Frame Delimiter
1 1 BIT1 BIT2
136
125
Figure 63. CAM Interface Receive Start Timing Diagram
137
Figure 64. CAM Interface REJECT
MPC862/857T/857DSL PowerQUICC™ Family Hardware Specifications, Rev. 3
Timing Diagram
62 Freescale Semiconductor
Page 63

CPM Electrical Characteristics
11.9 SMC Transparent AC Electrical Specifications
Table 23 provides the SMC transparent timings as shown in Figure 65.
Table 23. SMC Transparent Timing
All Frequencies
Num Characteristic
Min Max
150 SMCLK clock period
151 SMCLK width low 50 — ns
151A SMCLK width high 50 — ns
152 SMCLK rise/fall time — 15 ns
153 SMTXD active delay (from SMCLK falling edge) 10 50 ns
154 SMRXD/SMSYNC setup time 20 — ns
155 RXD1/SMSYNC hold time 5 — ns
1
SyncCLK must be at least twice as fast as SMCLK.
1
100 — ns
Unit
SMCLK
SMTXD
(Output)
SMSYNC
SMRXD
(Input)
NOTE:
152
This delay is equal to an integer number of character-length clocks.1.
152 151
NOTE 1
154 153
155
154
155
151A
150
Figure 65. SMC Transparent Timing Diagram
MPC862/857T/857DSL PowerQUICC™ Family Hardware Specifications, Rev. 3
Freescale Semiconductor 63
Page 64

CPM Electrical Characteristics
11.10 SPI Master AC Electrical Specifications
Table 24 provides the SPI master timings as shown in Figure 66 though Figure 67.
Table 24. SPI Master Timing
All Frequencies
Num Characteristic
Min Max
Unit
160 MASTER cycle time 4 1024 t
161 MASTER clock (SCK) high or low time 2 512 t
162 MASTER data setup time (inputs) 15 — ns
163 Master data hold time (inputs) 0 — ns
164 Master data valid (after SCK edge) — 10 ns
165 Master data hold time (outputs) 0 — ns
166 Rise time output — 15 ns
167 Fall time output — 15 ns
SPICLK
(CI=0)
(Output)
166167161
161 160
SPICLK
(CI=1)
(Output)
163
162
166
167
cyc
cyc
SPIMISO
(Input)
SPIMOSI
(Output)
msb Data lsb msb
165 164
167 166
msb lsb msb
Data
Figure 66. SPI Master (CP = 0) Timing Diagram
MPC862/857T/857DSL PowerQUICC™ Family Hardware Specifications, Rev. 3
64 Freescale Semiconductor
Page 65

SPICLK
(CI=0)
(Output)
SPICLK
(CI=1)
(Output)
161 160
163
162
CPM Electrical Characteristics
166167161
167
166
SPIMISO
(Input)
SPIMOSI
(Output)
msb Data lsb msb
165 164
167 166
msb lsb msb
Data
Figure 67. SPI Master (CP = 1) Timing Diagram
11.11 SPI Slave AC Electrical Specifications
Table 25 provides the SPI slave timings as shown in Figure 68 though Figure 69.
Table 25. SPI Slave Timing
All Frequencies
Num Characteristic
Min Max
170 Slave cycle time 2 — t
171 Slave enable lead time 15 — ns
172 Slave enable lag time 15 — ns
173 Slave clock (SPICLK) high or low time 1 — t
174 Slave sequential transfer delay (does not require deselect) 1 — t
175 Slave data setup time (inputs) 20 — ns
Unit
cyc
cyc
cyc
176 Slave data hold time (inputs) 20 — ns
177 Slave access time — 50 ns
MPC862/857T/857DSL PowerQUICC™ Family Hardware Specifications, Rev. 3
Freescale Semiconductor 65
Page 66

CPM Electrical Characteristics
SPISEL
(Input)
SPICLK
(CI=0)
(Input)
SPICLK
(CI=1)
(Input)
181182173
173 170
177 182
181
180
171172
174
178
SPIMISO
(Output)
SPIMOSI
(Input)
SPISEL
(Input)
SPICLK
(CI=0)
(Input)
SPICLK
(CI=1)
(Input)
Datamsb lsb msbUndef
175 179
176 182
msb lsb msb
Data
181
Figure 68. SPI Slave (CP = 0) Timing Diagram
172
171 170
173
173
177 182
181
180
181182
174
178
SPIMISO
(Output)
SPIMOSI
(Input)
msb
175 179
176 182
msb lsb
Data
181
Data
lsbUndef
msb
msb
Figure 69. SPI Slave (CP = 1) Timing Diagram
MPC862/857T/857DSL PowerQUICC™ Family Hardware Specifications, Rev. 3
66 Freescale Semiconductor
Page 67

11.12 I2C AC Electrical Specifications
Table 26 provides the I2C (SCL < 100 KHz) timings.
Table 2 6 . I2C Timing (SCL < 100 KHZ)
CPM Electrical Characteristics
Num Characteristic
200 SCL clock frequency (slave) 0 100 kHz
200 SCL clock frequency (master)
202 Bus free time between transmissions 4.7 — μs
203 Low period of SCL 4.7 — μs
204 High period of SCL 4.0 — μs
205 Start condition setup time 4.7 — μs
206 Start condition hold time 4.0 — μs
207 Data hold time 0 — μs
208 Data setup time 250 — ns
209 SDL/SCL rise time — 1 μs
210 SDL/SCL fall time — 300 ns
211 Stop condition setup time 4.7 — μs
1
SCL frequency is given by SCL = BRGCLK_frequency / ((BRG register + 3) * pre_scaler * 2).
The ratio SyncClk/(BRGCLK/pre_scaler) must be greater or equal to 4/1.
1
All Frequencies
Min Max
1.5 100 kHz
Table 27 provides the I2C (SCL > 100 kHz) timings.
Table 27. I2C Timing (SCL > 100 kHZ)
Unit
Num Characteristic Expression
200 SCL clock frequency (slave) fSCL 0 BRGCLK/48 Hz
200 SCL clock frequency (master)
202 Bus free time between transmissions — 1/(2.2 * fSCL) — s
203 Low period of SCL — 1/(2.2 * fSCL) — s
204 High period of SCL — 1/(2.2 * fSCL) — s
205 Start condition setup time — 1/(2.2 * fSCL) — s
206 Start condition hold time — 1/(2.2 * fSCL) — s
207 Data hold time — 0 — s
208 Data setup time — 1/(40 * fSCL) — s
209 SDL/SCL rise time — — 1/(10 * fSCL) s
210 SDL/SCL fall time — — 1/(33 * fSCL) s
211 Stop condition setup time — 1/2(2.2 * fSCL) — s
1
SCL frequency is given by SCL = BrgClk_frequency / ((BRG register + 3) * pre_scaler * 2).
The ratio SyncClk/(Brg_Clk/pre_scaler) must be greater or equal to 4/1.
MPC862/857T/857DSL PowerQUICC™ Family Hardware Specifications, Rev. 3
1
fSCL BRGCLK/16512 BRGCLK/48 Hz
All Frequencies
Min Max
Unit
Freescale Semiconductor 67
Page 68

UTOPIA AC Electrical Specifications
Figure 70 shows the I2C bus timing.
SDA
202
205
SCL
206 209 211210
203
207
204
208
Figure 70. I2C Bus Timing Diagram
12 UTOPIA AC Electrical Specifications
Table 28 shows the AC electrical specifications for the UTOPIA interface.
Table 28. UTOPIA AC Electrical Specifications
Num Signal Characteristic Direction Min Max Unit
U1 UtpClk rise/fall time (Internal clock option) Output 4 ns ns
Duty cycle 50 50 %
Frequency 33 MHz
U1a UtpClk rise/fall time (external clock option) Input 4ns ns
Duty cycle 40 60 %
Frequency 33 MHz
U2 RxEnb
U3 UTPB, SOC, Rxclav and Txclav setup time Input 4 ns ns
U4 UTPB, SOC, Rxclav and Txclav hold time Input 1 ns ns
U5 UTPB, SOC active delay (and PHREQ and PHSEL active
and TxEnb active delay Output 2 ns 16 ns ns
Output 2 ns 16 ns ns
delay in MPHY mode)
MPC862/857T/857DSL PowerQUICC™ Family Hardware Specifications, Rev. 3
68 Freescale Semiconductor
Page 69

Figure 71 shows signal timings during UTOPIA receive operations.
FEC Electrical Characteristics
U1
UtpClk
U5
PHREQn
U3 U4
3
RxClav
RxEnb
UTPB
SOC
HighZ at MPHY
U2
2
Figure 71. UTOPIA Receive Timing
Figure 72 shows signal timings during UTOPIA transmit operations.
U1
1
UtpClk
U5
5
U1
4
HighZ at MPHY
U3
U1
U4
3
4
PHSELn
U3 U4
TxClav
TxEnb
UTPB
SOC
HighZ at MPHY
U2
2
U5
5
3
4
HighZ at MPHY
Figure 72. UTOPIA Transmit Timing
13 FEC Electrical Characteristics
This section provides the AC electrical specifications for the Fast Ethernet controller (FEC). Note that the
timing specifications for the MII signals are independent of system clock frequency (part speed
designation). Furthermore, MII signals use TTL signal levels compatible with devices operating at eithe r
5.0 or 3.3 V.
MPC862/857T/857DSL PowerQUICC™ Family Hardware Specifications, Rev. 3
Freescale Semiconductor 69
Page 70

FEC Electrical Characteristics
13.1 MII Receive Signal Timing (MII_RXD[3:0], MII_RX_DV, MII_RX_ER, MII_RX_CLK)
The receiver functions correctly up to a MII_RX_CLK maximum frequency of 25MHz +1%. There is no
minimum frequency requirement. In addition, the processor clock frequency must exceed the
MII_RX_CLK frequency - 1%.
Table 29 provides information on the MII receive signal timing.
Table 29. MII Receive Signal Timing
Num Characteristic Min Max Unit
M1 MII_RXD[3:0], MII_RX_DV, MII_RX_ER to MII_RX_CLK setup 5 — ns
M2 MII_RX_CLK to MII_RXD[3:0], MII_RX_DV, MII_RX_ER hold 5 — ns
M3 MII_RX_CLK pulse width high 35% 65% MII_RX_CLK period
M4 MII_RX_CLK pulse width low 35% 65% MII_RX_CLK period
Figure 73 shows MII receive signal timing.
M3
MII_RX_CLK (input)
M4
MII_RXD[3:0] (inputs)
MII_RX_DV
MII_RX_ER
M1
Figure 73. MII Receive Signal Timing Diagram
M2
13.2 MII Transmit Signal Timing (MII_TXD[3:0], MII_TX_EN, MII_TX_ER, MII_TX_CLK)
The transmitter functions correctly up to a MII_TX_CLK maximum fr equency of 25 MHz +1%. There is
no minimum frequency requirement. In addition, the processor clock frequency must exceed the
MII_TX_CLK frequency - 1%.
Table 30 provides information on the MII transmit signal timing.
Table 30. MII Transmit Signal Timing
Num Characteristic Min Max Unit
M5 MII_TX_CLK to MII_TXD[3:0], MII_TX_EN, MII_TX_ER invalid 5 — ns
M6 MII_TX_CLK to MII_TXD[3:0], MII_TX_EN, MII_TX_ER valid — 25
MPC862/857T/857DSL PowerQUICC™ Family Hardware Specifications, Rev. 3
70 Freescale Semiconductor
Page 71

FEC Electrical Characteristics
Table 30. MII Transmit Signal Timing (continued)
Num Characteristic Min Max Unit
M7 MII_TX_CLK pulse width high 35% 65% MII_TX_CLK period
M8 MII_TX_CLK pulse width low 35% 65% MII_TX_CLK period
Figure 74 shows the MII trans mit signal timing diagram.
M7
MII_TX_CLK (input)
M5
M8
MII_TXD[3:0] (outputs)
MII_TX_EN
MII_TX_ER
M6
Figure 74. MII Transmit Signal Timing Diagram
13.3 MII Async Inputs Signal Timing (MII_CRS, MII_COL)
Table 31 provides information on the MII async inputs signal timing.
Table 31. MII Async Inputs Signal Timing
Num Characteristic Min Max Unit
M9 MII_CRS, MII_COL minimum pulse width 1.5 — MII_TX_CLK period
Figure 75 shows the MII asynchronous inputs signal timing diagram.
MII_CRS, MII_COL
M9
Figure 75. MII Async Inputs Timing Diagram
13.4 MII Serial Management Channel Timing (MII_MDIO, MII_MDC)
Table 32 provides information on the MII serial management channel signal timing. The FEC functions
correctly with a maximum MDC frequency in excess of 2.5 MHz. The exact upper bound is under
investigation.
MPC862/857T/857DSL PowerQUICC™ Family Hardware Specifications, Rev. 3
Freescale Semiconductor 71
Page 72

Mechanical Data and Ordering Information
Table 32. MII Serial Management Channel Timing
Num Characteristic Min Max Unit
M10 MII_MDC falling edge to MII_MDIO output invalid (minimum
propagation delay)
M11 MII_MDC falling edge to MII_MDIO output valid (max prop delay) — 25 ns
M12 MII_MDIO (input) to MII_MDC rising edge setup 10 — ns
M13 MII_MDIO (input) to MII_MDC rising edge hold 0 — ns
M14 MII_MDC pulse width high 40% 60% MII_MDC period
M15 MII_MDC pulse width low 40% 60% MII_MDC period
0— ns
Figure 76 shows the MII serial management channel timing diagram.
M14
MM15
MII_MDC (output)
M10
MII_MDIO (output)
M11
MII_MDIO (input)
M12
M13
Figure 76. MII Serial Management Channel Timing Diagram
14 Mechanical Data and Ordering Information
Table 33 provides information on the MPC862/857T/857DSL derivative devices.
Table 33. MPC862/857T/857DSL Derivatives
Number
Device
MPC862T Four 10/100 Mbps Yes Yes 4 Kbytes 4 Kbytes
MPC862P Four 10/100 Mbps Yes Yes 16 Kbytes 8 Kbytes
of
SCCs
1
Ethernet
Support
Multi-Channel
HDLC Support
ATM Support
Instruction Data
Cache Size
MPC862/857T/857DSL PowerQUICC™ Family Hardware Specifications, Rev. 3
72 Freescale Semiconductor
Page 73

Mechanical Data and Ordering Information
Table 33. MPC862/857T/857DSL Derivatives (continued)
Number
Device
MPC857T One (SCC1) 10/100 Mbps Yes Yes 4 Kbytes 4 Kbytes
MPC857DSL One (SCC1) 10/100 Mbps No Up to 4 addresses 4 Kbytes 4 Kbytes
1
Serial communications controller (SCC)
of
SCCs
1
Ethernet
Support
Multi-Channel
HDLC Support
ATM Support
Instruction Data
Cache Size
Table 34 identifies the packages and operating frequencies orderable for the MPC862/857T/857DSL
derivative devices.
Plastic ball grid array
(ZP suffix)
Table 34. MPC862/857T/857DSL Package/Frequency Orderable
Package Type Temperature (Tj) Frequency (MHz) Order Number
0°C to 105°C 50 XPC862PZP50B
XPC862TZP50B
XPC857TZP50B
XPC857DSLZP50B
66 XPC862PZP66B
XPC862TZP66B
XPC857TZP66B
XPC857DSLZP66B
80 XPC862PZP80B
XPC862TZP80B
XPC857TZP80B
100 XPC862PZP100B
XPC862TZP100B
XPC857TZP100B
Plastic ball grid array
(CZP suffix)
1
Additional extended temperature devices can be made available at 50MHz, 66MHz, and
80MHz
-40°C to 115°C 66
1
XPC862PCZP66B
XPC857TCZP66B
14.1 .Pin Assignments
Figure 77 shows the top view pinout of the PBGA package. For additional information, see the MPC862
PowerQUICC Family User s Manual.
MPC862/857T/857DSL PowerQUICC™ Family Hardware Specifications, Rev. 3
Freescale Semiconductor 73
Page 74

Mechanical Data and Ordering Information
NOTE: This is the top view of the device.
PD10 PD8
PD14
PD13 PD6 IRQ0
PB14 PD4 IRQ1 D8 D23 D11 D16 D19 D21 D26 D30 IPA5 IPA2 N/CIPA4PD15 PD5 VSSSYNPA 0
P C5 P D1 1 V D DH D 1 2 D 1 7 D 9 D 15 D2 2 D 2 5 D 3 1 I PA6 I PA0 I PA 7 X FCIPA1PC4 PD7 VDDSYNPA 1
PA 2 P D 12
PB17 VDDL GND
PA5 PB16
PC8 PC7
PA 7
PC9 PB20 AS
PA9 PB21 GND IPB6 ALEABADDR30PB23 IRQ4PC10
PB24 PB25 IPB1 IPB2IPB5PA1 0 ALEBPC11
M_MDIO
TMS PA11 IRQ6
PC12 VDDL
PC13 PB29
PC14 PC15 N/C N/C A15 A19 A25 A18 BSA0
PA15 A3 A12 A16 A20 A24 A26 TSIZ1 BSA1
A1 A6 A13 A17 A21 A23 A22 TSIZ0 BSA3
A2 A7 A14 A27 A29 A30 A28 A31 VDDL BSA2
18 16 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 3 2417 15 119
PD3 IR Q7 D0 D4 D1 D2 D3 D5 VDDL D6 D7 D29 CLKOUT IPA3DP2
D13D27D10D14D18D20D24D28DP1 DP0N/CDP3PD9 M_Tx_EN
PB15
PB18 EXTALPB19
PA 6
TCK IRQ2 IPB0M_COLTDI IPB7VDDL
VDDH
GND GND
VDDH VDDH
GPLA0 N/ C CS6 GPLA5 BDIPCS2PA 14 A 8 TEAPB28
WE0 GPLA1 GPLA3 CS0 TACS7PB31 A9 GPLA4PB30
M_CRS WE2 GPLA2 CE1A WRCS5A4 A10 GPLB4A0
VDDH
WE1 WE3 CE2A CS1CS4A5 A11
WAIT _B
VDDLPA3 G N D XTALPA4
HRESET
MODCK2
WAIT _A
RSTCONF
TEXP
BADDR28
TS
BI
PORESE T
SRESET
EXTCLK
BADDR29
OP1OP0PA 8 MODCK1PB22
IPB4BRTDO IPB3TRST
IRQ3VDDLPA 12 BURSTPB26
BGCS3PA1 3 BBPB27
W
V
VSSSYN1
U
T
R
KAPWRPC6
P
N
M
VDDL
L
K
J
H
G
F
E
D
C
B
A
Figure 77. Pinout of the PBGA Package
MPC862/857T/857DSL PowerQUICC™ Family Hardware Specifications, Rev. 3
74 Freescale Semiconductor
Page 75

Mechanical Data and Ordering Information
Table 35 contains a list of the MPC862 input and output signals and shows multiplexing and pin
assignments.
Table 35. Pin Assignments
Name Pin Number Type
A[0:31] B19, B18, A18, C16, B17, A17, B16, A16, D15, C15, B15, A15, C14,
B14, A14, D12, C13, B13, D9, D11, C12, B12, B10, B11, C11, D10,
C10, A13, A10, A12, A11, A9
TSIZ0
REG
TSIZ1 C9 Bidirectional
RD/WR
BURST
BDIP
GPL_B5
TS
TA
TEA
BI
B2 Bidirectional
B9 Bidirectional
F1 Bidirectional
D2 Output
F3 Bidirectional
C2 Bidirectional
D1 Open-drain
E3 Bidirectional
Bidirectional
Three-state
Three-state
Three-state
Three-state
Three-state
Active Pull-up
Active Pull-up
Active Pull-up
IRQ2
RSV
IRQ4
KR
RETRY
SPKROUT
CR
IRQ3
D[0:31] W14, W12, W11, W10, W13, W9, W7, W6, U13, T11, V11, U11,
DP0
IRQ3
DP1
IRQ4
DP2
IRQ5
DP3
IRQ6
H3 Bidirectional
K1 Bidirectional
F2 Input
T13, V13, V10, T10, U10, T12, V9, U9, V8, U8, T9, U12, V7, T8, U7,
V12, V6, W5, U6, T7
V3 Bidirectional
V5 Bidirectional
W4 Bidirectional
V4 Bidirectional
MPC862/857T/857DSL PowerQUICC™ Family Hardware Specifications, Rev. 3
Three-state
Three-state
Bidirectional
Three-state
Three-state
Three-state
Three-state
Three-state
Freescale Semiconductor 75
Page 76

Mechanical Data and Ordering Information
Table 35. Pin Assignments (continued)
Name Pin Number Type
BR G4 Bidirectional
BG
BB
FRZ
IRQ6
IRQ0
IRQ1
M_TX_CLK
IRQ7
[0:5] C3, A2, D4, E4, A4, B4 Output
CS
CS6
CE1_B
CS7
CE2_B
WE0
BS_B0
IORD
WE1
BS_B1
IOWR
E2 Bidirectional
E1 Bidirectional
G3 Bidirectional
V14 Input
U14 Input
W15 Input
D5 Output
C4 Output
C7 Output
A6 Output
Active Pull-up
WE2
BS_B2
PCOE
WE3
BS_B3
PCWE
BS_A
[0:3] D8, C8, A7, B8 Output
GPL_A0
GPL_B0
OE
GPL_A1
GPL_B1
GPL_A
[2:3]
GPL_B
[2:3]
CS
[2–3]
UPWAITA
GPL_A4
UPWAITB
GPL_B4
B6 Output
A5 Output
D7 Output
C6 Output
B5, C5 Output
C1 Bidirectional
B1 Bidirectional
MPC862/857T/857DSL PowerQUICC™ Family Hardware Specifications, Rev. 3
76 Freescale Semiconductor
Page 77

Mechanical Data and Ordering Information
Table 35. Pin Assignments (continued)
Name Pin Number Type
GPL_A5 D3 Output
PORESET
RSTCONF
HRESET
SRESET
R2 Input
P3 Input
N4 Open-drain
P2 Open-drain
XTAL P1 Analog Output
EXTAL N1 Analog Input (3.3 V only)
XFC T2 Analog Input
CLKOUT W3 Output
EXTCLK N2 Input (3.3 V only)
TEXP N3 Output
ALE_A
K2 Output
MII-TXD1
CE1_A
B3 Output
MII-TXD2
CE2_A
A3 Output
MII-TXD3
WAI T_A
SOC_Split
2
R3 Input
WAI T_B
IP_A0
UTPB_Split0
MII-RXD3
IP_A1
UTPB_Split1
MII-RXD2
IP_A2
IOIS16_A
UTPB_Split2
MII-RXD1
IP_A3
UTPB_Split3
MII-RXD0
IP_A4
UTPB_Split4
MII-RXCLK
IP_A5
UTPB_Split5
MII-RXERR
R4 Input
2
2
T5 Input
T4 Input
U3 Input
2
2
2
2
W2 Input
U4 Input
U5 Input
MPC862/857T/857DSL PowerQUICC™ Family Hardware Specifications, Rev. 3
Freescale Semiconductor 77
Page 78

Mechanical Data and Ordering Information
Name Pin Number Type
Table 35. Pin Assignments (continued)
IP_A6
UTPB_Split6
MII-TXERR
IP_A7
UTPB_Split7
MII-RXDV
ALE_B
DSCK/AT1
IP_B[0:1]
IWP[0:1]
VFLS[0:1]
IP_B2
IOIS16_B
AT 2
IP_B3
IWP2
VF2
IP_B4
LWP0
VF0
IP_B5
LWP1
VF1
2
2
T6 Input
T3 Input
J1 Bidirectional
Three-state
H2, J3 Bidirectional
J2 Bidirectional
Three-state
G1 Bidirectional
G2 Bidirectional
J4 Bidirectional
IP_B6
DSDI
K3 Bidirectional
Three-state
AT 0
IP_B7
PTR
H1 Bidirectional
Three-state
AT 3
OP0
MII-TXD0
UtpClk_Split
2
L4 Bidirectional
OP1 L2 Output
OP2
L1 Bidirectional
MODCK1
STS
OP3
M4 Bidirectional
MODCK2
DSDO
BADDR30
K4 Output
REG
BADDR[28:29] M3, M2 Output
AS
L3 Input
MPC862/857T/857DSL PowerQUICC™ Family Hardware Specifications, Rev. 3
78 Freescale Semiconductor
Page 79

Mechanical Data and Ordering Information
Table 35. Pin Assignments (continued)
Name Pin Number Type
PA 1 5
RXD1
RXD4
PA 1 4
TXD1
TXD4
PA 1 3
RXD2
PA 1 2
TXD2
PA 1 1
L1TXDB
RXD3
PA 1 0
L1RXDB
TXD3
PA 9
L1TXDA
RXD4
PA 8
L1RXDA
TXD4
C18 Bidirectional
D17 Bidirectional
(Optional: Open-drain)
E17 Bidirectional
F17 Bidirectional
(Optional: Open-drain)
G16 Bidirectional
(Optional: Open-drain)
J17 Bidirectional
(Optional: Open-drain)
K18 Bidirectional
(Optional: Open-drain)
L17 Bidirectional
(Optional: Open-drain)
PA 7
CLK1
L1RCLKA
BRGO1
TIN1
PA 6
CLK2
TOU T1
PA 5
CLK3
L1TCLKA
BRGO2
TIN2
PA 4
CLK4
TOU T2
PA 3
CLK5
BRGO3
TIN3
M19 Bidirectional
M17 Bidirectional
N18 Bidirectional
P19 Bidirectional
P17 Bidirectional
MPC862/857T/857DSL PowerQUICC™ Family Hardware Specifications, Rev. 3
Freescale Semiconductor 79
Page 80

Mechanical Data and Ordering Information
Name Pin Number Type
Table 35. Pin Assignments (continued)
PA 2
CLK6
TOU T3
L1RCLKB
PA 1
CLK7
BRGO4
TIN4
PA 0
CLK8
TOU T4
L1TCLKB
PB31
SPISEL
REJECT1
PB30
SPICLK
RSTRT2
PB29
SPIMOSI
PB28
SPIMISO
BRGO4
R18 Bidirectional
T19 Bidirectional
U19 Bidirectional
C17 Bidirectional
(Optional: Open-drain)
C19 Bidirectional
(Optional: Open-drain)
E16 Bidirectional
(Optional: Open-drain)
D19 Bidirectional
(Optional: Open-drain)
PB27
I2CSDA
BRGO1
PB26
I2CSCL
BRGO2
PB25
RXADDR3
SMTXD1
PB24
TXADDR3
SMRXD1
PB23
TXADDR2
SDACK1
SMSYN1
PB22
TXADDR4
SDACK2
SMSYN2
E19 Bidirectional
(Optional: Open-drain)
F19 Bidirectional
(Optional: Open-drain)
2
2
2
2
J16 Bidirectional
(Optional: Open-drain)
J18 Bidirectional
(Optional: Open-drain)
K17 Bidirectional
(Optional: Open-drain)
L19 Bidirectional
(Optional: Open-drain)
MPC862/857T/857DSL PowerQUICC™ Family Hardware Specifications, Rev. 3
80 Freescale Semiconductor
Page 81

Mechanical Data and Ordering Information
Table 35. Pin Assignments (continued)
Name Pin Number Type
PB21
SMTXD2
L1CLKOB
PHSEL1
1
TXADDR1
PB20
SMRXD2
L1CLKOA
PHSEL0
1
TXADDR0
PB19
RTS1
L1ST1
PB18
RXADDR4
RTS2
L1ST2
PB17
L1RQb
L1ST3
RTS3
PHREQ1
RXADDR1
PB16
L1RQa
L1ST4
RTS4
PHREQ0
RXADDR0
K16 Bidirectional
(Optional: Open-drain)
2
L16 Bidirectional
(Optional: Open-drain)
2
N19 Bidirectional
(Optional: Open-drain)
2
N17 Bidirectional
(Optional: Open-drain)
P18 Bidirectional
(Optional: Open-drain)
1
2
N16 Bidirectional
(Optional: Open-drain)
1
2
PB15
R17 Bidirectional
BRGO3
TxClav
PB14
RXADDR2
2
U18 Bidirectional
RSTRT1
PC15
D16 Bidirectional
DREQ0
RTS1
L1ST1
RxClav
PC14
D18 Bidirectional
DREQ1
RTS2
L1ST2
MPC862/857T/857DSL PowerQUICC™ Family Hardware Specifications, Rev. 3
Freescale Semiconductor 81
Page 82

Mechanical Data and Ordering Information
Name Pin Number Type
Table 35. Pin Assignments (continued)
PC13
L1RQb
L1ST3
RTS3
PC12
L1RQa
L1ST4
RTS4
PC11
CTS1
PC10
CD1
TGATE1
PC9
CTS2
PC8
CD2
TGATE2
PC7
CTS3
L1TSYNCB
SDACK2
E18 Bidirectional
F18 Bidirectional
J19 Bidirectional
K19 Bidirectional
L18 Bidirectional
M18 Bidirectional
M16 Bidirectional
PC6
CD3
L1RSYNCB
PC5
CTS4
L1TSYNCA
SDACK1
PC4
CD4
L1RSYNCA
PD15
L1TSYNCA
MII-RXD3
UTPB0
PD14
L1RSYNCA
MII-RXD2
UTPB1
PD13
L1TSYNCB
MII-RXD1
UTPB2
R19 Bidirectional
T18 Bidirectional
T17 Bidirectional
U17 Bidirectional
V19 Bidirectional
V18 Bidirectional
MPC862/857T/857DSL PowerQUICC™ Family Hardware Specifications, Rev. 3
82 Freescale Semiconductor
Page 83

Mechanical Data and Ordering Information
Table 35. Pin Assignments (continued)
Name Pin Number Type
PD12
L1RSYNCB
MII-MDC
UTPB3
PD11
RXD3
MII-TXERR
RXENB
PD10
TXD3
MII-RXD0
TXENB
PD9
RXD4
MII-TXD0
UTPCLK
PD8
TXD4
MII-MDC
MII-RXCLK
PD7
RTS3
MII-RXERR
UTPB4
R16 Bidirectional
T16 Bidirectional
W18 Bidirectional
V17 Bidirectional
W17 Bidirectional
T15 Bidirectional
PD6
RTS4
MII-RXDV
UTPB5
PD5
REJECT2
MII-TXD3
UTPB6
PD4
REJECT3
MII-TXD2
UTPB7
PD3
REJECT4
MII-TXD1
SOC
TMS G18 Input
TDI
DSDI
TCK
DSCK
V16 Bidirectional
U15 Bidirectional
U16 Bidirectional
W16 Bidirectional
H17 Input
H16 Input
MPC862/857T/857DSL PowerQUICC™ Family Hardware Specifications, Rev. 3
Freescale Semiconductor 83
Page 84

Mechanical Data and Ordering Information
Table 35. Pin Assignments (continued)
Name Pin Number Type
TRST G19 Input
TDO
DSDO
M_CRS B7 Input
M_MDIO H18 Bidirectional
M_TXEN V15 Output
M_COL H4 Input
KAPWR R1 Power
GND F6, F7, F8, F9, F10, F11, F12, F13, F14, G6, G7, G8, G9, G10, G11,
VDDL A8, M1, W8, H19, F4, F16, P4, P16 Power
VDDH E5, E6, E7, E8, E9, E10, E11, E12, E13, E14, E15, F5, F15, G5,
N/C D6, D13, D14, U2, V2 No-connect
1
Classic SAR mode only
2
ESAR mode only
G17 Output
Power
G12, G13, G14, H6, H7, H8, H9, H10, H11, H12, H13, H14, J6, J7,
J8, J9, J10, J11, J12, J13, J14, K6, K7, K8, K9, K10, K11, K12, K13,
K14, L6, L7, L8, L9, L10, L11, L12, L13, L14, M6, M7, M8, M9, M10,
M11, M12, M13, M14, N6, N7, N8, N9, N10, N11, N12, N13, N14,
P6, P7, P8, P9, P10, P11, P12, P13, P14
Power
G15, H5, H15, J5, J15, K5, K15, L5, L15, M5, M15, N5, N15, P5,
P15, R5, R6, R7, R8, R9, R10, R11, R12, R13, R14, R15, T14
14.2 Mechanical Dimensions of the PBGA Package
For more information on the pr inted circuit board layout of the PBGA package, including thermal via
design and suggested pad layout, please refer to Plastic Ball Grid Array Applic ation Note (order number:
AN1231/D) available from your local Freescale sales office. Figure 78 shows the mechanical dimensions
of the PBGA package.
MPC862/857T/857DSL PowerQUICC™ Family Hardware Specifications, Rev. 3
84 Freescale Semiconductor
Page 85

Mechanical Data and Ordering Information
D
D2
TOP VIEW
D1
W
V
U
T
R
P
N
M
L
K
J
H
G
F
E
D
C
B
A
12345678910111213141516171819
BOTTOM VIEW
Figure 78. Mechanical Dimensions and Bottom Surface Nomenclature
4X
18X
E1
357X b
0.3
0.15MC
0.2
A
EE2
B
e
NOTES:
1. Dimensions and tolerancing per ASME Y14.5M,
1994.
2. Dimensions in millimeters.
3. Dimension b is the maximum solder bal
measured parallel to datum C.
M
C
AB
of the PBGA Package
0.2 C
0.25 C
0.35 C
A2
A3
A1
A
SIDE VIEW
MILLIMETERS
DIM MIN MAX
A --- 2.05
A1
0.50 0.70
A2 0.95 1.35
A3 0.70 0.90
b 0.60 0.90
D 25.00 BSC
D1 22.86 BSC
D2 22.40 22.60
e 1.27 BSC
E 25.00 BSC
E1 22.86 BSC
E2 22.40 22.60
C
l diameter
Case No. 1103-01
MPC862/857T/857DSL PowerQUICC™ Family Hardware Specifications, Rev. 3
Freescale Semiconductor 85
Page 86

Document Revision History
15 Document Revision History
Table 36 lists significant changes between revisions of this document.
Table 36. Document Revision History
Rev. No. Date Substantive Changes
0 2001 Initial revision
0.1 9/2001 Change extended temperature from 95 to 105
0.2 11/2001 Revised for new template, changed Ta bl e 7 B23 max value @ 66 MHz from 2 ns to 8 ns.
0.3 4/2002 • Timing modified and equations added, for Rev. A and B devices.
• Modified power numbers and temperature ranges. Added ESAR UTOPIA timing.
1.0 9/2002 • Specification changed to include the MPC857T and MPC857DSL.
• Changed maximum operating frequency from 80 MHz to 100 MHz.
• Removed MPC862DP, DT, and SR derivatives and part numbers.
• Corrected power dissipation numbers.
• Changed UTOPIA maximum frequency from 50 MHz to 33 MHz.
• Changed part number ordering information to Rev. B devices only.
• To maximum ratings for temperature, added frequency ranges.
1.1 5/2003 Changed SPI Master Timing Specs. 162 and 164
1.2 8/2003 • Changed B28a through B28d and B29b to show that TRLX can be 0 or 1.
• Non-technical reformatting
2.0 11/2004 • Added a table footnote to Tabl e 5 DC Electrical Specifications about meeting the VIL Max
of the I2C Standard.
• Updated document template.
3.0 2/2006 • Changed Tj from 95C to 105C in table 34
MPC862/857T/857DSL PowerQUICC™ Family Hardware Specifications, Rev. 3
86 Freescale Semiconductor
Page 87

THIS PAGE INTENTIONALLY LEFT BLANK
Document Revision History
MPC862/857T/857DSL PowerQUICC™ Family Hardware Specifications, Rev. 3
Freescale Semiconductor 87
Page 88

How to Reach Us:
Home Page:
www.freescale.com
email:
support@freescale.com
USA/Europe or Locations Not Listed:
Freescale Semiconductor
Technical Information Center, CH370
1300 N. Alma School Road
Chandler, Arizona 85224
(800) 521-6274
480-768-2130
support@freescale.com
Europe, Middle East, and Africa:
Freescale Halbleiter Deutschland GmbH
Technical Information Center
Schatzbogen 7
81829 Muenchen, Germany
+44 1296 380 456 (English)
+46 8 52200080 (English)
+49 89 92103 559 (German)
+33 1 69 35 48 48 (French)
support@freescale.com
Japan:
Freescale Semiconductor Japan Ltd.
Headquarters
ARCO Tower 15F
1-8-1, Shimo-Meguro, Meguro-ku
Tokyo 153-0064, Japan
0120 191014
+81 2666 8080
support.japan@freescale.com
Asia/Pacific:
Freescale Semiconductor Hong Kong Ltd.
Technical Information Center
2 Dai King Street
Tai Po Industrial Estate,
Tai Po, N.T., Hong Kong
+800 2666 8080
support.asia@freescale.com
For Literature Requests Only:
Freescale Semiconductor
Literature Distribution Center
P.O. Box 5405
Denver, Colorado 80217
(800) 441-2447
303-675-2140
Fax: 303-675-2150
LDCForFreescaleSemiconductor
@hibbertgroup.com
Information in this document is provided solely to enable system and software
implementers to use Freescale Semiconductor products. There are no express or
implied copyright licenses granted hereunder to design or fabricate any integrated
circuits or integrated circuits based on the information in this document .
Freescale Semiconductor reserves the right to make changes without fur ther notice to
any products herein. Freescale Semiconductor makes no warranty, representation or
guarantee regarding the suitability of its products for any particular purpose, nor does
Freescale Semiconductor assume any liability arising out of the application or use of
any product or circuit, and specifically disclaims any and all liability, including without
limitation consequential or incidental damages. “Typical” parameters which may be
provided in Freescale Semiconductor data sheets and/or specifications can and do
vary in different applications and actual performance may vary over time. All operating
parameters, including “Typicals” must be validated for each customer application by
customer’s technical experts. Freescale Semiconductor does not convey any license
under its patent rights nor the rights of others. Freescale Semiconductor products are
not designed, intended, or authorized for use as components in systems intended for
surgical implant into the body, or other applications intended to support or sustain life,
or for any other application in which the failure of the Freescale Semiconductor product
could create a situation where personal injury or death may occur. Should Buyer
purchase or use Freescale Semiconductor products for any such unintended or
unauthorized application, Buyer shall indemn ify and hold Freescale Semiconductor
and its officers, employees, subsidiaries, affiliates, and distributors har mless against all
claims, costs, damages, and expenses, and reasonable attorney fees arising out of,
directly or indirectly, any claim of personal injury or death a ssociated with such
unintended or unauthorized use, even if such claim alleges that Freescale
Semiconductor was negligent regarding the design or manufacture of the par t.
Freescale™ and the Freescale logo are trademarks of Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
The described product contains a PowerPC processor core. The PowerPC name is a
trademark of IBM Corp. and used under license. All other product or ser vice names are
the property of their respective owners.
© Freescale Semiconductor, Inc., 2006.
Document Number: MPC862EC
Rev. 3
2/2006
 Loading...
Loading...