Page 1
Freescale Semiconductor
Technical Data
±1.5g Three Axis Low-g
Document Number: MMA7368L
Rev 0, 05/2008
Micromachined Accelerometer
The MMA7368L is a low power, low profile capacitive micromachined
accelerometer featuring signal conditioning, a 1-pole low pass filter,
temperature compensation, and self test. Zero-g offset and sensitivity are
factory set and require no external devices. The MMA7368L includes a Sleep
Mode that makes it ideal for handheld battery powered electronics.
Features
• 3mm x 5mm x 1.0mm LGA-14 Package
• Low Current Consumption: 400 μA
• Sleep Mode: 3 μA
• Low Voltage Operation: 2.2 V – 3.6 V
• High Sensitivity (800 mV/g @ 1.5g)
• Fast Turn On Time (0.5 ms Enable Response Time)
• Self Test for Freefall Detect Diagnosis
• Signal Conditioning with Low Pass Filter
• Robust Design, High Shocks Survivability
• RoHS Compliant
• Environmentally Preferred Product
• Low Cost
Typical Applications
• 3D Gaming: Tilt and Motion Sensing, Event Recorder
• HDD MP3 Player: Freefall Detection
• Laptop PC: Freefall Detection, Anti-Theft
• Cell Phone: Image Stability, Text Scroll, Motion Dialing, E-Compass
• Pedometer: Motion Sensing
• PDA: Text Scroll
• Navigation and Dead Reckoning: E-Compass Tilt Compensation
• Robotics: Motion Sensing
ORDERING INFORMATION
Part Number
MMA7368LR2
Temperature
Range
–40 to +85°C 1977-01 LGA-14 13” Tape & Reel
Package
Drawing
Package Shipping
MMA7368L
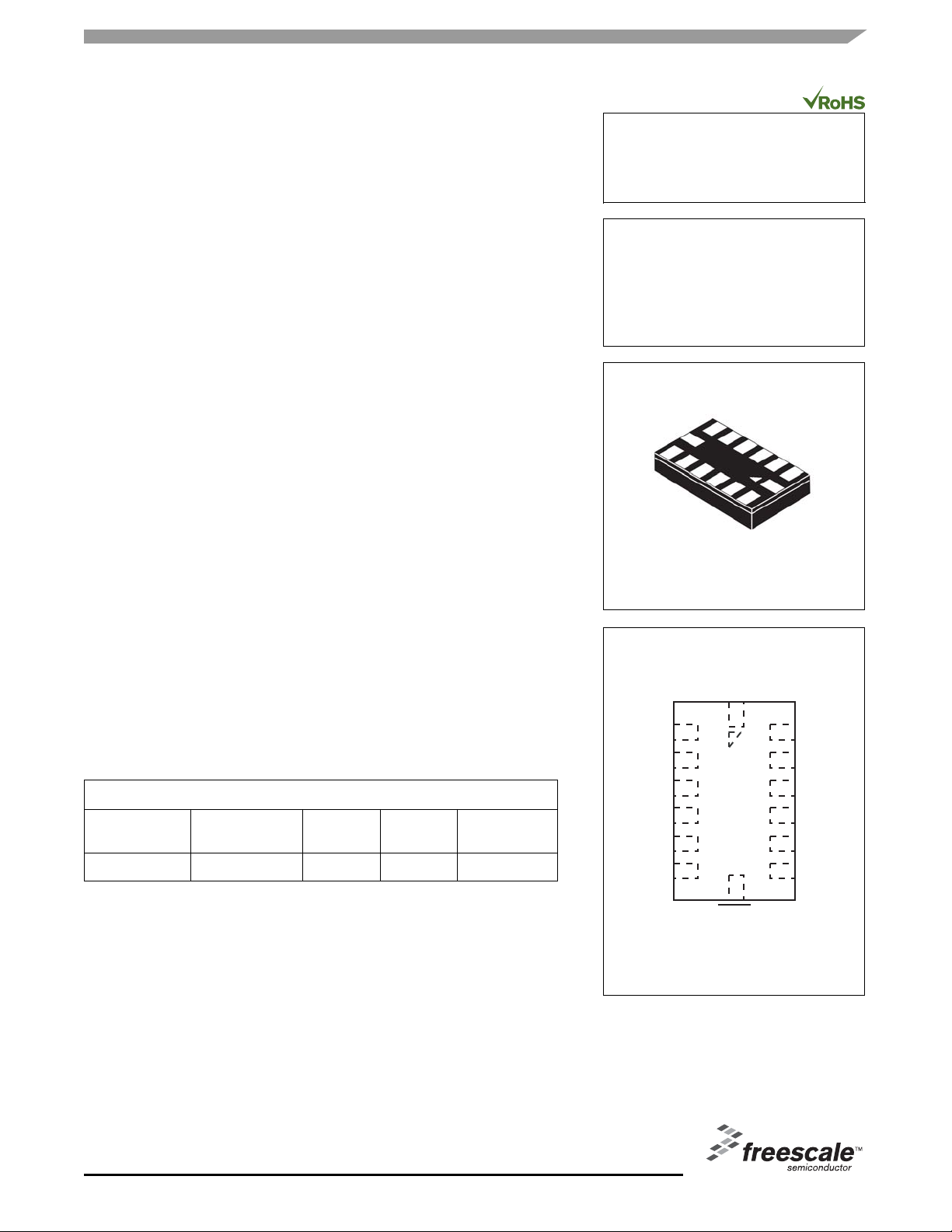
MMA7368L: XYZ AXIS
ACCELEROMETER
±1.5g
Bottom View
14 LEAD
LGA
CASE 1977-01
Top View
N/C
14
7
X
Y
Z
N/C
OUT
OUT
OUT
V
SS
V
DD
123456
Self Test
N/C
N/C
N/C
N/C
8 9 10 11 12 13
N/C
© Freescale Semiconductor, Inc., 2008. All rights reserved.
Sleep
Figure 1. Pin Connections
Page 2
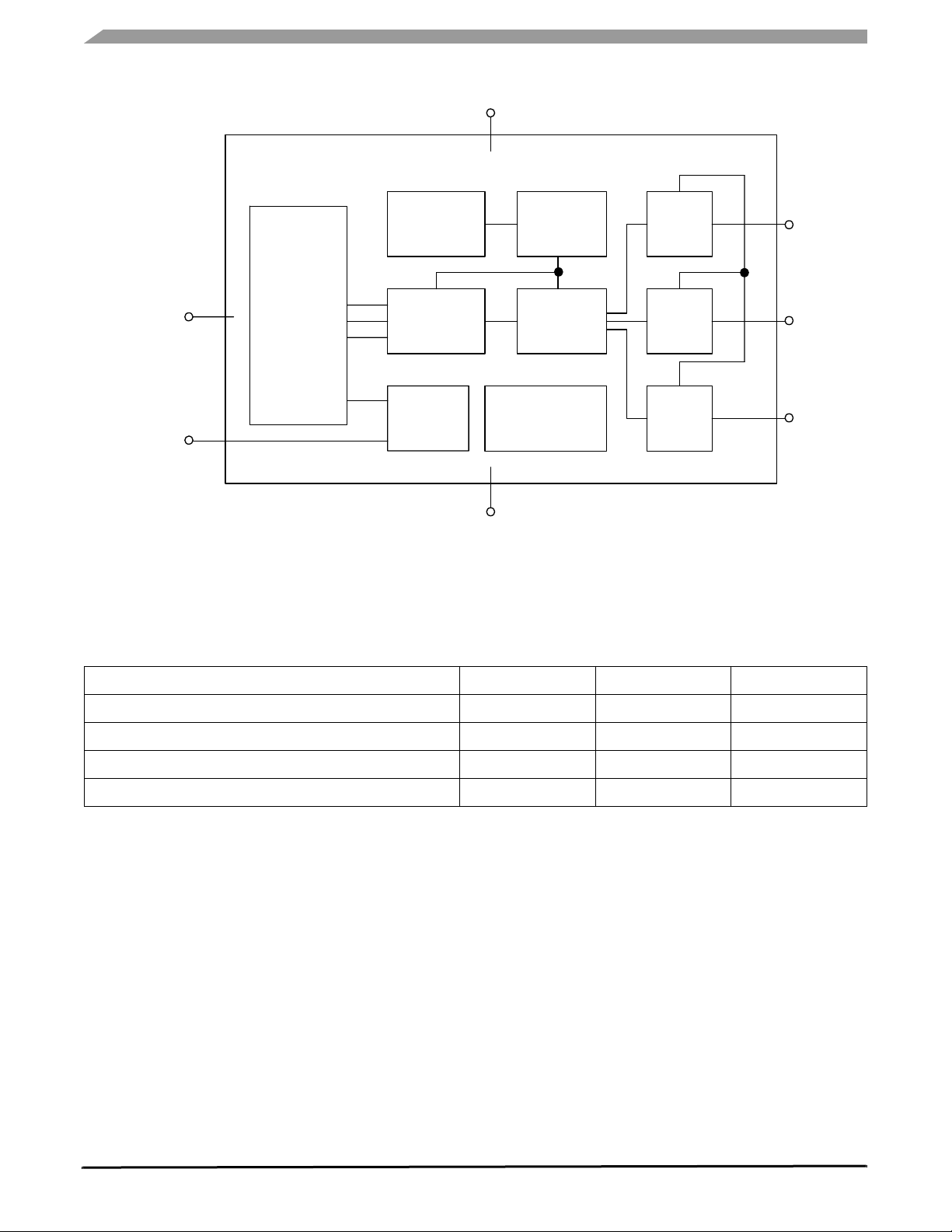
OSCILLATOR
CLOCK
GEN
X-TEMP
COMP
X
OUT
Sleep Mode
Selftest
G-CELL
SENSOR
C to V
CONVERTER
SELFTEST
CONTROL LOGIC
V
SS
GAIN
+
FILTER
NVM TRIM
CIRCUITS
Y-TEMP
COMP
Z-TEMP
COMP
Figure 2. Simplified Accelerometer Functional Block Diagram
Table 1. Maximum Ratings
(Maximum ratings are the limits to which the device can be exposed without causing permanent damage.)
Rating Symbol Value Unit
Maximum Acceleration (all axis) g
Supply Voltage V
Drop Test
Storage Temperature Range T
1. Dropped onto concrete surface from any axis.
(1)
max
DD
D
drop
stg
±5000 g
–0.3 to +3.6 V
1.8 m
–40 to +125 °C
Y
OUT
Z
OUT
ELECTRO STATIC DISCHARGE (ESD)
WARNING: This device is sensitive to electrostatic
discharge.
Although the Freescale accelerometer contains internal
2000 V ESD protection circuitry, extra precaution must be
taken by the user to protect the chip from ESD. A charge of
over 2000 volts can accumulate on the human body or
associated test equipment. A charge of this magnitude can
MMA7368L
2 Freescale Semiconductor
alter the performance or cause failure of the chip. When
handling the accelerometer, proper ESD precautions should
be followed to avoid exposing the device to discharges which
may be detrimental to its performance.
Sensors
Page 3
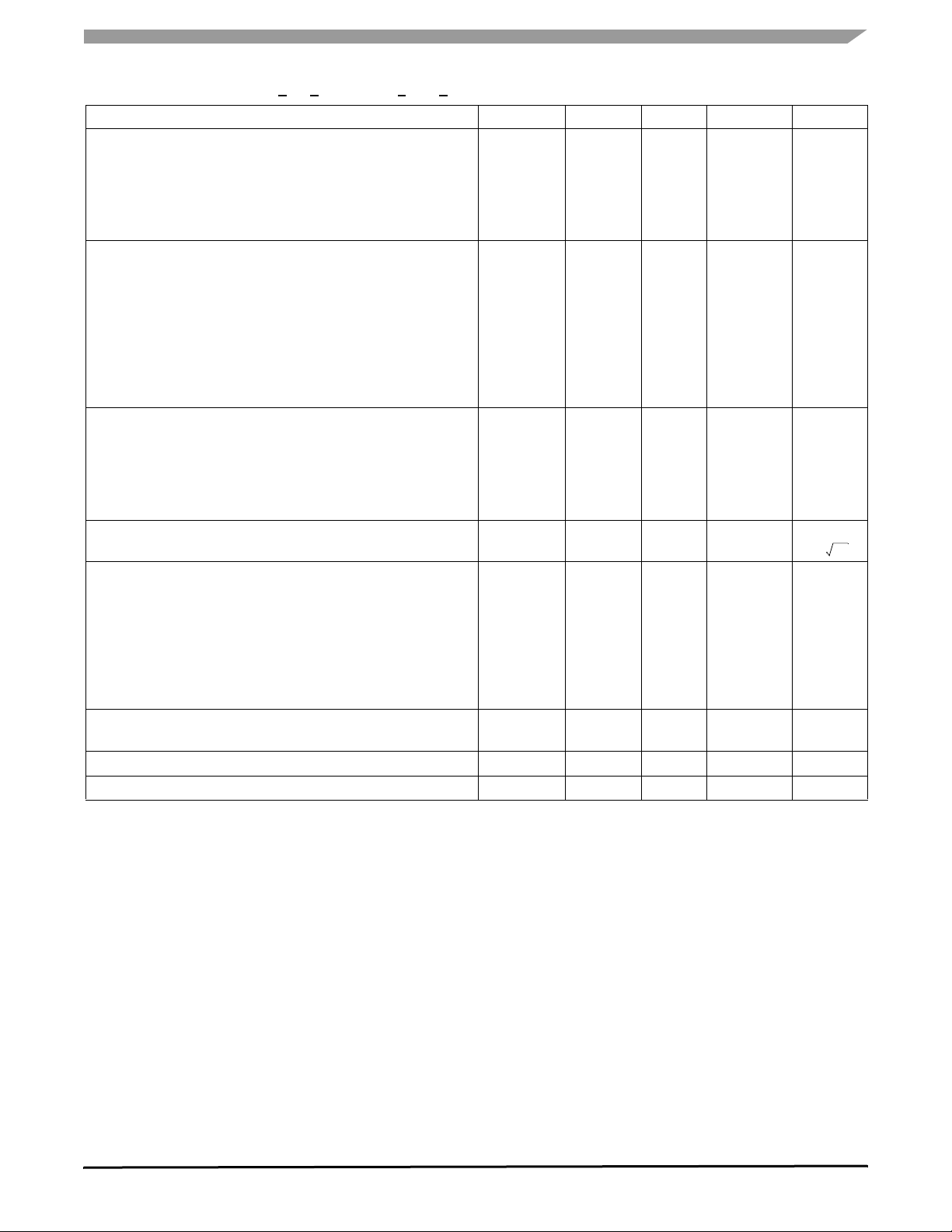
Table 2. Operating Characteristics
Unless otherwise noted: -40°C < TA < 85°C, 2.2 V < VDD < 3.6 V, Acceleration = 0g, Loaded output
(1)
Characteristic Symbol Min Typ Max Unit
Operating Range
Supply Voltage
Supply Current
Supply Current at Sleep Mode
Operating Temperature Range
Acceleration Range, X-Axis, Y-Axis, Z-Axis
(2)
(3)
(4)
(4)
V
DD
I
DD
I
DD
T
A
g
FS
2.2
—
—
-40
—
3.3
400
3
—
±1.5
3.6
600
10
+85
—
V
μA
μA
°C
g
Output Signal
Zero-g (T
(4)
Zero-g
= 25°C, VDD = 3.3 V)
A
(5), (6)
V
OFF
V
, T
OFF
A
1.485
-2.0
1.65
±0.5
1.815
+2.0
V
mg/°C
Sensitivity (TA = 25°C, VDD = 3.3 V)
1.5g
Sensitivity
S
(4)
S,T
1.5g
A
740
-0.0075
800
±0.002
860
+0.0075
mV/g
%/°C
Bandwidth Response
XY
Z
f
-3dBXY
f
-3dBZ
—
—
400
300
—
—
Hz
Hz
Self Test
Output Response
X
, Y
OUT
Z
OUT
Input Low
Input High
OUT
Δg
Δg
STXY
STZ
V
IL
V
IH
-0.05
+0.8
V
0.7 V
SS
DD
-0.1
+1.0
—
—
—
+1.2
0.3 V
V
DD
DD
g
g
V
V
Noise
Power Spectral Density RMS (0.1 Hz – 1 kHz)
(4)
n
PSD
— 350 — μg/
Hz
Control Timing
Power-Up Response Time
Enable Response Time
(8)
Self Test Response Time
(7)
(9)
t
RESPONSE
t
ENABLE
t
ST
—
—
—
1.0
0.5
2.0
2.0
2.0
5.0
ms
ms
ms
Sensing Element Resonant Frequency
XY
Z
Internal Sampling Frequency
f
GCELLXY
f
GCELLZ
f
CLK
—
—
—
6.0
3.4
11
—
—
—
kHz
kHz
kHz
Output Stage Performance
Full-Scale Output Range (I
Nonlinearity, X
Cross-Axis Sensitivity
OUT
, Y
OUT
(10)
= 3 µA) V
OUT
, Z
OUT
FSO
NL
OUT
V
XY, XZ, YZ
VSS+0.1 — VDD–0.1 V
-1.0 — +1.0 %FSO
-5.0 — +5.0 %
1. For a loaded output, the measurements are observed after an RC filter consisting of an internal resistor and an external 0.1uF capacitor
(recommended as a minimum to filter clock noise) on the analog output for each axis and a 0.1μF capacitor on V
2. These limits define the range of operation for which the part will meet specification.
- GND.
DD
3. Within the supply range of 2.2 and 3.6 V, the device operates as a fully calibrated linear accelerometer. Beyond these supply limits the device
may operate as a linear device but is not guaranteed to be in calibration.
4. This value is measured with g-Select in 1.5g mode.
5. The device can measure both + and – acceleration. With no input acceleration the output is at midsupply. For positive acceleration the output
will increase above V
/2. For negative acceleration, the output will decrease below VDD/2.
DD
6. For optimal 0g offset performance, adhere to AN3484 and AN3447
7. The response time between 10% of full scale V
8. The response time between 10% of full scale Sleep Mode input voltage and 90% of the final operating output voltage.
input voltage and 90% of the final operating output voltage.
DD
9. The response time between 10% of the full scale self test input voltage and 90% of the self test output voltage.
10. A measure of the device’s ability to reject an acceleration applied 90° from the true axis of sensitivity.
MMA7368L
Sensors
Freescale Semiconductor 3
Page 4
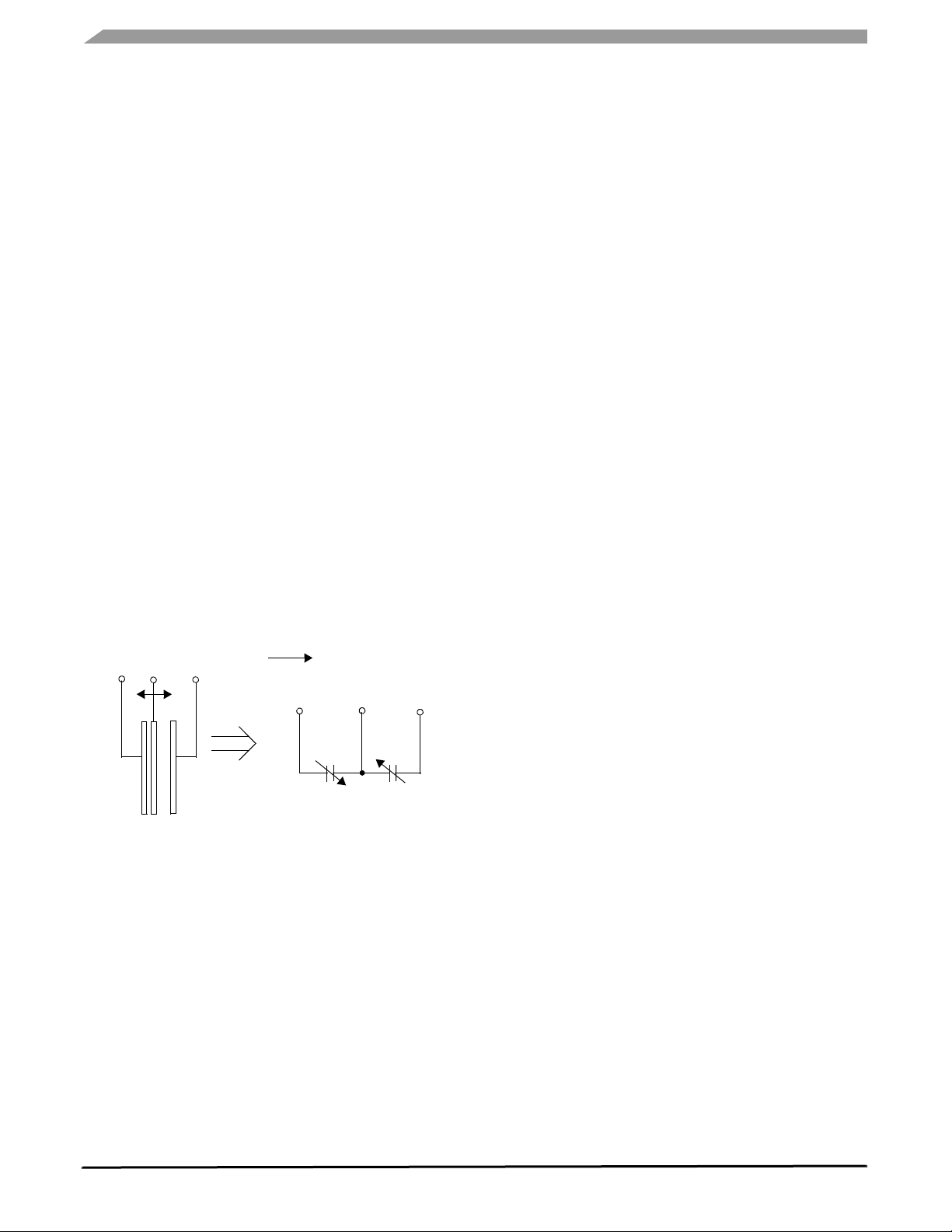
PRINCIPLE OF OPERATION
The Freescale accelerometer is a surf ace-micromachined
integrated-circuit accelerometer.
The device consists of a surface micromachined
capacitive sensing cell (g-cell) and a signal conditioning ASIC
contained in a single package. The sensing element is sealed
hermetically at the wafer level using a bulk micromachined
cap wafer.
The g-cell is a mechanical structure formed from
semiconductor materials (polysilicon) using semiconductor
processes (masking and etching). It can be modeled as a set
of beams attached to a movable central mass that move
between fixed beams. The movable beams can be deflected
from their rest position by subjecting the system to an
acceleration (Figure 3).
As the beams attached to the central mass move, the
distance from them to the fixed beams on one side will
increase by the same amount that the distance to the fixed
beams on the other side decreases. The change in distance
is a measure of acceleration.
The g-cell beams form two back-to-back capacitors
(Figure 3). As the center beam moves with acceleration, the
distance between the beams changes and each capacitor's
value will change, (C = Aε/D). Where A is the area of the
beam, ε is the dielectric constant, and D is the distance
between the beams.
The ASIC uses switched capacitor techniques to measure
the g-cell capacitors and extract the acceleration data from
the difference between the two capacitors. The ASIC also
signal conditions and filters (switched capacitor) the signal,
providing a high level output voltage that is ratiometric and
proportional to acceleration.
Acceleration
SPECIAL FEATURES
Self Test
The sensor provides a self test feature that allows the
verification of the mechanical and electrical integrity of the
accelerometer at any time before or after installation.
feature is critical in applications such as hard disk drive
protection where system integrity must be ensured over the
life of the product. Customers can use self test to verify the
solderability to confirm that the part was mounted to the PCB
correctly. To use this feature to verify the 0g-Detect function,
the accelerometer should be held upside down so that the
z-axis experiences -1g. When the self test function is
initiated, an electrostatic force is applied to each axis to
cause it to deflect. The x- and y-axis are deflected slightly
while the z-axis is trimmed to deflect 1g. This procedure
assures that both the mechanical (g-cell) and electronic
sections of the accelerometer are functioning.
Sleep Mode
The 3 axis accelerometer provides a Sleep Mode that is
ideal for battery operated products. When Sleep Mode is
active, the device outputs are turned off, providing significant
reduction of operating current. A low input signal on pin 7
(Sleep Mode) will place the device in this mode and reduce
the current to 3 μA typ. For lower power consumption, it is
recommended to set g-Select to 1.5g mode. By placing a high
input signal on pin 7, the device will resume to normal mode
of operation.
Filtering
The 3 axis accelerometer contains an onboard single-pole
switched capacitor filter. Because the filter is realized using
switched capacitor techniques, there is no requirement for
external passive components (resistors and capacitors) to set
the cut-off frequency.
This
Ratiometricity
Ratiometricity simply means the output offset voltage and
sensitivity will scale linearly with applied supply voltage. That
is, as supply voltage is increased, the sensitivity and offset
increase linearly; as supply voltage decreases, offset and
sensitivity decrease linearly. This is a key feature when
Figure 3. Simplified Transducer Physical Model
MMA7368L
4 Freescale Semiconductor
interfacing to a microcontroller or an A/D converter because
it provides system level cancellation of supply induced errors
in the analog to digital conversion process.
Sensors
Page 5

BASIC CONNECTIONS
Pin Descriptions
Top View
N/C
N/C
X
OUT
Y
OUT
Z
OUT
V
SS
V
DD
14
123456
Sleep
Self Test
N/C
N/C
N/C
N/C
8 9 10 11 12 13
N/C
7
Figure 4. Pinout Description
Table 3. Pin Descriptions
Pin No.
Pin Name Description
1 N/C No internal connection
2X
3Y
4Z
5 V
6V
OUT
OUT
OUT
SS
DD
7 Sleep
8 NC No internal connection
Leave unconnected
X direction output voltage
Y direction output voltage
Z direction output voltage
Power Supply Ground
Power Supply Input
Logic input pin to enable product or Sleep Mode
Leave unconnected
9 NC Leave unconnected
10 NC Leave unconnected
11 N/C Unused for factory trim
12 N/C Unused for factory trim
Leave unconnected
Leave unconnected
13 Self Test Input pin to initiate Self Test
14 N/C Unused for factory trim
Logic
Input
V
DD
Leave unconnected
13
Self Test
X
OUT
MMA7368L
6
V
DD
0.1 μF
5
V
SS
Y
OUT
2
3
0.1 μF
0.1 μF
PCB Layout
POWER SUPPLY
V
Accelerometer
V
Sleep
Self Test
X
OUT
Y
OUT
Z
OUT
DD
C
SS
C
C
C
V
RH
C
C
P0
V
V
P1
A/D
IN
Microcontroller
A/D
IN
A/D
IN
Figure 6. Recommended PCB Layout for Interfacing
Accelerometer to Microcontroller
NOTES:
1. Use 0.1 µF capacitor on V
to decouple the power
DD
source.
2. Physical coupling distance of the accelerometer to
the microcontroller should be minimal.
3. Place a ground plane beneath the accelerometer to
reduce noise, the ground plane should be attached to
all of the open ended terminals shown in Figure 6.
4. Use a 0.1uF capacitor on the outputs of the
accelerometer to minimi ze clock noise (from the
switched capacitor filter circuit).
5. PCB layout of power and ground should not couple
power supply noise.
6. Accelerometer and microcontroller should not be a
high current path.
7. A/D sampling rate and any external power supply
switching frequency should be selected such that
they do not interfere with the internal accelerometer
sampling frequency (11 kHz for the sampling
frequency). This will prevent aliasing errors.
DD
C
C
SS
Logic
Input
7
Sleep
Z
4
OUT
0.1 μF
Figure 5. Accelerometer with Recommended
Connection Diagram
MMA7368L
Sensors
Freescale Semiconductor 5
Page 6

Top View
DYNAMIC ACCELERATION
7
8 9 10 11 12 13
-Y
14-Pin LGA Package
Top View
+Y
123456
14
+X +Z-X
STATIC ACCELERATION
Side View
Top
Bottom
: Arrow indicates direction of package movement.
Direction of Earth's gravity field.*
-Z
123456
@ +1g = 2.45 V
X
OUT
@ 0g = 1.65 V
Y
OUT
@ 0g = 1.65 V
Z
OUT
123456
7
14
Side View
8 9 10 11 12 13
14
8 9 10 11 12 13
7
X
@ 0g = 1.65 V
OUT
@ +1g = 2.45 V
Y
OUT
@ 0g = 1.65 V
Z
OUT
13 12 11 10 9 8
14 7
1234 56
X
@ 0g = 1.65 V
OUT
@ -1g = 0.85 V
Y
OUT
@ 0g = 1.65 V
Z
OUT
X
Y
Z
8 9 10 11 12 13
@ -1g = 0.85 V
OUT
@ 0g = 1.65 V
OUT
@0g=1.65V
OUT
7
123456
14
* When positioned as shown, the Earth’s gravity will result in a positive 1g output.
Bottom
X
@ 0g = 1.65 V
OUT
@ 0g = 1.65 V
Y
OUT
@ +1g = 2.45 V
Z
OUT
Bottom
X
@ 0g = 1.65 V
OUT
@ 0g = 1.65 V
Y
OUT
@ -1g =0.85 V
Z
OUT
Top
Top
MMA7368L
Sensors
6 Freescale Semiconductor
Page 7

X-T C O mg/ degC
X-TCS %/degC
LSL USLTarget
-2 -1 0 1 2
Y-T C O mg/ degC
LSL USLTarget
-2 -1 0 1 2
Z-TCO mg/degC
LSL USLTarget
-0.01 -0.005 0 .005 .01
Y-TCS %/degC
LSL USLTarget
-0.01 -0.005 0 .005 .01
Z-TCS %/degC
LSL USLTarget
-2 -1 0 1 2
LSL USLTarget
-0.01 -0.005 0 .005 .01
Figure 7. MMA7368L Temperature Coefficient of Offset (TCO) and
Temperature Coefficient of Sensitivity (TCS) Distribution Charts
MMA7368L
Sensors
Freescale Semiconductor 7
Page 8

MINIMUM RECOMMENDED FOOTPRINT FOR SURFACE MOUNTED APPLICATIONS
PCB Mounting Recommendations
MEMS based sensors are sensitive to Printed Circuit
Board (PCB) reflow processes. For optimal zero-g offset after
PCB mounting, care must be taken to PCB layout and reflow
conditions. Reference application note AN3484 for best
practices to minimize the zero-g offset shift after PCB
mounting.
Surface mount board layout is a critical portion of the total
design. The footprint for the surface mount packages must be
the correct size to ensure proper solder connection interface
between the board and the package.
With the correct footprint, the packages will self-align when
subjected to a solder reflow process. It is always
recommended to design boards with a solder mask layer to
avoid bridging and shorting between solder pads.
10x0.8
1
6
13
6x2
8
14x0.6
14x0.9
12x1
MMA7368L
Sensors
8 Freescale Semiconductor
Page 9

PACKAGE DIMENSIONS
CASE 1977-01
ISSUE A
14-LEAD LGA
MMA7368L
Sensors
Freescale Semiconductor 9
Page 10

PACKAGE DIMENSIONS
CASE 1977-01
ISSUE A
14-LEAD LGA
MMA7368L
Sensors
10 Freescale Semiconductor
Page 11

How to Reach Us:
Home Page:
www.freescale.com
Web Support:
http://www.freescale.com/support
USA/Europe or Locations Not Listed:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
Technical Information Center, EL516
2100 East Elliot Road
Tempe, Arizona 85284
+1-800-521-6274 or +1-480-768-2130
www.freescale.com/support
Europe, Middle East, and Africa:
Freescale Halbleiter Deutschland GmbH
Technical Information Center
Schatzbogen 7
81829 Muenchen, Germany
+44 1296 380 456 (English)
+46 8 52200080 (English)
+49 89 92103 559 (German)
+33 1 69 35 48 48 (French)
www.freescale.com/support
Japan:
Freescale Semiconductor Japan Ltd.
Headquarters
ARCO Tower 15F
1-8-1, Shimo-Meguro, Meguro-ku,
Tokyo 153-0064
Japan
0120 191014 or +81 3 5437 9125
support.japan@freescale.com
Asia/Pacific:
Freescale Semiconductor Hong Kong Ltd.
Technical Information Center
2 Dai King Street
Tai Po Industrial Estate
Tai Po, N.T., Hong Kong
+800 2666 8080
support.asia@freescale.com
For Literature Requests Only:
Freescale Semiconductor Literature Distribution Center
P.O. Box 5405
Denver, Colorado 80217
1-800-441-2447 or 303-675-2140
Fax: 303-675-2150
LDCForFreescaleSemiconductor@hibbertgroup.com
Information in this document is provided solely to enable system and software
implementers to use Freescale Semiconductor products. There are no express or
implied copyright licenses granted hereunder to design or fabricate any integrated
circuits or integrated circuits base d on the information in this document.
Freescale Semiconductor reserves the right to make changes without further notice to
any products herein. Freescale Semiconductor makes no warranty, representation or
guarantee regarding the suitability of its products for any particular purpose, nor does
Freescale Semiconductor assume any liability arising out of the application o r use of any
product or circuit, and specifically disclaims any and all liability, including without
limitation consequential or incidental damages. “Typical” parameters that may be
provided in Freescale Semiconductor data sheet s and/or specifications can and do vary
in different applications and actual performance may vary over time. All operating
parameters, including “Typicals”, must be validated for each customer application by
customer’s technical experts. Freescale Semiconductor does not convey any license
under its patent rights nor the rights of others. Freescale Semiconductor products are
not designed, intended, or authorized for use as components in systems intended for
surgical implant into the body, or other applications intended to support or sustain life,
or for any other application in which the failure of the Freescale Semiconduct or product
could create a situation where personal injury or death may occur. Should Buyer
purchase or use Freescale Semiconductor products for any such unintended or
unauthorized application, Buyer shall indemnify and hold Freescale Semiconductor and
its officers, employees, subsidiaries, affiliates, and distributors harmless against all
claims, costs, damages, and expenses, and reasonable attorney fee s arising out of,
directly or indirectly, any claim of personal injury or death associated with such
unintended or unauthorized use, even if such claim alleges that Freescale
Semiconductor was negligent regarding the design or manufacture of the part.
Freescale™ and the Freescale logo are trademarks of Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
All other product or service names are the property of their respective owners.
© Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. 2008. All rights reserved.
MMA7368L
Rev. 0
05/2008
RoHS-compliant and/or Pb-free versions of Freescale products have the functionality and electrical
characteristics of their non-RoHS-compliant and/or non-Pb-free counterparts. For further
information, see http:/www.freescale.com or contact your Freescale sales representative.
For information on Freescale’s Environment al Product s program, go to http://www.freescale.com/epp.
 Loading...
Loading...