Page 1

Freescale Semiconductor
LQFP–64
10 mm x 10 mm
MAPBGA–81
10 mm x 10 mm
LQFP–100
14 mm x 14 mm
QFN–64
9mmx9mm
Data Sheet
MCF5213 ColdFire Microcontroller
Supports MCF5213,
MCF5212, & MCF5211
The MCF5213 is a member of the ColdFire® family of
reduced instruction set computing (RISC) microprocessors.
This document provides an overview of the 32-bit MCF5213
microcontroller, focusing on its highly integrated and diverse
feature set.
This 32-bit device is based on the Version 2 ColdFire core
operating at a frequency up to 80 MHz, offering high
performance and low power consumption. On-chip memories
connected tightly to the processor core include up to
256 Kbytes of flash memory and 32 Kbytes of static random
access memory (SRAM). On-chip modules include:
• V2 ColdFire core delivering 76 MIPS (Dhrystone 2.1) at
80 MHz running from internal flash memory with Multiply
Accumulate (MAC) Unit and hardware divider
• FlexCAN controller area network (CAN) module
• Three universal asynchronous/synchronous
receiver/transmitters (UARTs)
• Inter-integrated circuit (I2C™) bus controller
• Queued serial peripheral interface (QSPI) module
• Eight-channel 12-bit fast analog-to-digital converter
(ADC)
• Four-channel direct memory access (DMA) controller
• Four 32-bit input capture/output compare timers with
DMA support (DTIM)
• Four-channel general-purpose timer (GPT) capable of
input capture/output compare, pulse width modulation
(PWM), and pulse accumulation
• Eight-channel/Four-channel, 8-bit/16-bit pulse width
modulation timer
• Two 16-bit periodic interrupt timers (PITs)
• Programmable software watchdog timer
• Interrupt controller capable of handling 57 sources
• Clock module with 8 MHz on-chip relaxation oscillator
and integrated phase-locked loop (PLL)
• Test access/debug port (JTAG, BDM)
Document Number: MCF5213EC
Rev. 3, 05/2007
MCF5213
This document contains information on a product under development. Freescale reserves the
right to change or discontinue this product without notice.
© Freescale Semiconductor, Inc., 2007. All rights reserved.
Page 2

Table of Contents
1 MCF5213 Family Configurations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3
1.1 Block Diagram. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4
1.2 Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4
1.3 Reset Signals . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .20
1.4 PLL and Clock Signals . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .20
1.5 Mode Selection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .20
1.6 External Interrupt Signals . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .21
1.7 Queued Serial Peripheral Interface (QSPI). . . . . . . . . .21
2
1.8 I
C I/O Signals . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .21
1.9 UART Module Signals. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .22
1.10 DMA Timer Signals . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .22
1.11 ADC Signals . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .22
1.12 General Purpose Timer Signals . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .23
1.13 Pulse Width Modulator Signals . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
1.14 Debug Support Signals . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .23
1.15 EzPort Signal Descriptions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .24
1.16 Power and Ground Pins . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .25
2 Electrical Characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .25
2.1 Maximum Ratings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .26
2.2 Current Consumption . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .27
2.3 Thermal Characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .28
2.4 Flash Memory Characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .30
2.5 ESD Protection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .31
2.6 DC Electrical Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
2.7 Clock Source Electrical Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . .32
2.8 General Purpose I/O Timing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .33
2.9 Reset Timing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .34
2
2.10 I
C Input/Output Timing Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . .35
2.11 Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC) Parameters . . . . . .36
2.12 Equivalent Circuit for ADC Inputs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .37
2.13 DMA Timers Timing Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
2.14 QSPI Electrical Specifications. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .38
2.15 JTAG and Boundary Scan Timing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .39
2.16 Debug AC Timing Specifications. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .41
3 Mechanical Outline Drawings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .43
3.1 64-pin LQFP Package. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .43
3.2 64 QFN Package. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
3.3 81 MAPBGA Package. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .50
3.4 100-pin LQFP Package. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .52
4 Revision History . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .54
List of Figures
Figure 1.MCF5213 Block Diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
Figure 2.100 LQFP Pin Assignments . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Figure 3.81 MAPBGA Pin Assignments . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Figure 4.64 LQFP and 64 QFN Pin Assignments . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Figure 5.GPIO Timing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Figure 6.RSTI and Configuration Override Timing . . . . . . . . . . 34
Figure 7.I
2
C Input/Output Timings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
Figure 8.Equivalent Circuit for A/D Loading. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
Figure 9.QSPI Timing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
Figure 10.Test Clock Input Timing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Figure 11.Boundary Scan (JTAG) Timing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
Figure 12.Test Access Port Timing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
Figure 13.TRST Timing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
Figure 14.Real-Time Trace AC Timing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
Figure 15.BDM Serial Port AC Timing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
List of Tables
Table 1. MCF5213 Family Configurations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
Table 2. Orderable Part Number Summary. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Table 3. Pin Functions by Primary and Alternate Purpose . . . . 16
Table 4. Reset Signals . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Table 5. PLL and Clock Signals . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Table 6. Mode Selection Signals . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Table 7. Clocking Modes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Table 8. External Interrupt Signals . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Table 9. Queued Serial Peripheral Interface (QSPI) Signals. . . 21
Table 10.I
Table 11.UART Module Signals . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Table 12.DMA Timer Signals . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Table 13.ADC Signals . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Table 14.GPT Signals . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Table 15.PWM Signals . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Table 16.Debug Support Signals . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Table 17.EzPort Signal Descriptions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Table 18.Power and Ground Pins. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Table 19.Absolute Maximum Ratings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Table 20.Current Consumption in Low-Power Mode
Table 21.Typical Active Current Consumption Specifications. . . 28
Table 22.Thermal Characteristics. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
Table 23.SGFM Flash Program and Erase Characteristics . . . . 30
Table 24.SGFM Flash Module Life Characteristics . . . . . . . . . . 30
Table 25.ESD Protection Characteristics, . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Table 26.DC Electrical Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Table 27.PLL Electrical Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Table 28.GPIO Timing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Table 29.Reset and Configuration Override Timing . . . . . . . . . . 34
Table 30.I
Table 31.I
Table 32.ADC Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
Table 33.Timer Module AC Timing Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . 38
Table 34.QSPI Modules AC Timing Specifications. . . . . . . . . . . 38
Table 35.JTAG and Boundary Scan Timing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Table 36.Debug AC Timing Specification . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
Table 37.Revision History. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
2
C I/O Signals. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
,
. . . . . . . . . 27
2
C Input Timing Specifications between I2C_SCL
and I2C_SDA. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
2
C Output Timing Specifications between I2C_SCL
and I2C_SDA. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
MCF5213 ColdFire Microcontroller, Rev. 3
Freescale Semiconductor2
Page 3

1 MCF5213 Family Configurations
Table 1. MCF5213 Family Configurations
Module 5211 5212 5213
MCF5213 Family Configurations
ColdFire Version 2 Core with MAC
(Multiply-Accumulate Unit)
System Clock 66, 80 MHz
Performance (Dhrystone 2.1 MIPS) 63 up to 76
Flash / Static RAM (SRAM) 128/16 Kbytes 256/32 Kbytes
Interrupt Controller (INTC)
Fast Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC)
FlexCAN 2.0B Module See note
Four-channel Direct-Memory Access (DMA)
Watchdog Timer Module (WDT)
Programmable Interval Timer Module (PIT) 2 2 2
Four-Channel General-Purpose Timer 3 3 3
32-bit DMA Timers 4 4 4
QSPI
UARTs 3 3 3
2
C
I
PWM 8 8 8
General Purpose I/O Module (GPIO)
•••
•••
•••
1
—
•••
•••
•••
•••
•••
•
Chip Configuration and Reset Controller Module
Background Debug Mode (BDM)
JTAG - IEEE 1149.1 Test Access Port
Package 64 LQFP
1
FlexCAN is available on the MCF5211 only in the 64 QFN package.
2
The full debug/trace interface is available only on the 100-pin packages. A reduced debug interface is
bonded on smaller packages.
2
•••
•••
•••
64 QFN
81 MAPBGA
64 LQFP
81 MAPBGA
81 MAPBGA
100 LQFP
Figure 1 shows a top-level block diagram of the MCF5213. Package options for this family are described later in this document.
MCF5213 ColdFire Microcontroller, Rev. 3
Freescale Semiconductor 3
Page 4
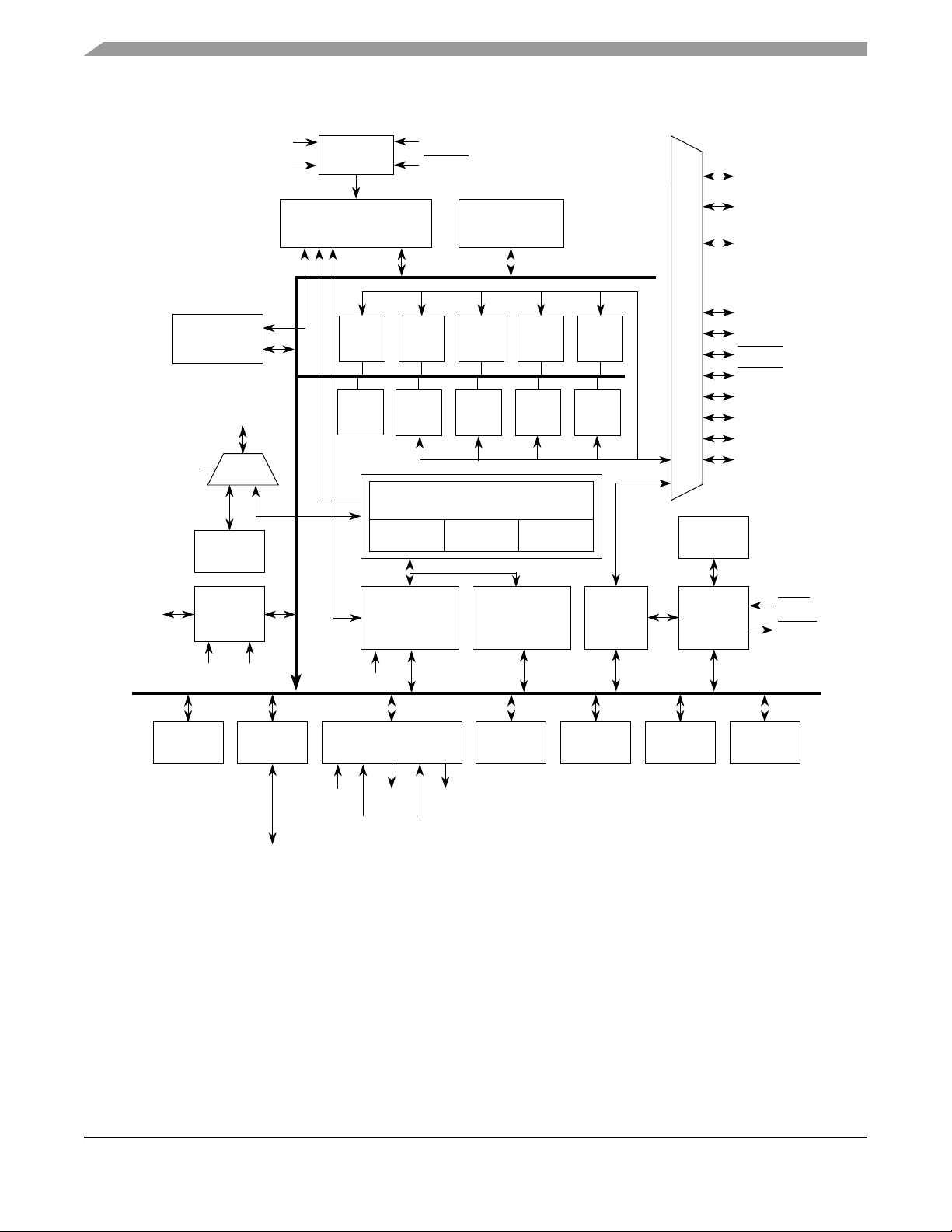
MCF5213 Family Configurations
Arbiter
Interrupt
Controller
UART
0
QSPI
UART
1
UART
2
I2C
DTIM0DTIM1DTIM2DTIM
3
V2 ColdFire CPU
IFP OEP MAC
4 CH DMA
MUX
JTAG
TAP
To/From PADI
32 Kbytes
SRAM
(4K×16)×4
256 Kbytes
Flash
(32K×16)×4
PORTS
(GPIO)
CIM
RSTI
RSTO
UTXDn
URXDn
U
RTSn
DTINn/DTOUTn
CANRX
JTAG_EN
ADCAN[7:0]
V
RHVRL
PLL OCO
CLKGEN
Edge
Port
FlexCAN
EXTAL XTAL CLKOUT
PIT0 PIT1 GPT PWM
To/From Interrupt Controller
CANTX
U
CTSn
PMM
V
STBY
P AD I – Pi n Mu xin g
EzPort
EzPCS
CLKMOD0 CLKMOD1
QSPI_CLK,
QSPI_CSn
PWMn
QSPI_DIN,
QSPI_DOUT
GPTn
EzPCK
EzPD
EzPQ
SWT
1.1 Features
Figure 1. MCF5213 Block Diagram
This document contains information on a new product under development. Freescale reserves the right to change or discontinue
this product without notice. Specifications and information herein are subject to change without not ice.
1.1.1 Feature Overview
The MCF5213 family includes the following features:
MCF5213 ColdFire Microcontroller, Rev. 3
Freescale Semiconductor4
Page 5

MCF5213 Family Configurations
• Version 2 ColdFire variable-length RISC processor core
— Static operation
— 32-bit address and data paths on-chip
— Up to 80 MHz processor core frequency
— Sixteen general-purpose, 32-bit data and address registers
— Implements ColdFire ISA_A with extensions to support the user stack pointer register and four new instructions
for improved bit processing (ISA_A+)
— Multiply-Accumulate (MAC) unit with 32-bit accumulator to support 16×16 → 32 or 32×32 → 32 operations
— Illegal instruction decode that allows for 68-Kbyte emulation support
• System debug support
— Real-time trace for determining dynamic execution path
— Background debug mode (BDM) for in-circuit debugging (DEBUG_B+)
— Real-time debug support, with six hardware breakpoints (4 PC, 1 address and 1 data) configurable into a 1- or
2-level trigger
• On-chip memories
— 32-Kbyte dual-ported SRAM on CPU internal bus, supporting core and DMA access with standby power supply
support
— 256 Kbytes of interleaved flash memory supporting 2-1-1-1 accesses
• Power management
— Fully static operation with processor sleep and whole chip stop modes
— Rapid response to interrupts from the low-power sleep mode (wake-up feature)
— Clock enable/disable for each peripheral when not used
• FlexCAN 2.0B module
— Based on and includes all existing features of the Freescale TouCAN module
— Full implementation of the CAN protocol specification version 2.0B
– Standard data and rem ot e frames (up to 109 bit s long)
– Extended data and remote frames (up to 127 bits long)
– Zero to eight bytes data length
– Programmable bit rate up to 1 Mbit/sec
— Flexible message buffers (MBs), totalling up to 16 message buffers of 0–8 byte data length each, configurable as
Rx or Tx, all supporting standard and extended messages
— Unused MB space can be used as general purpose RAM space
— Listen-only mode capability
— Content-related addressing
— No read/write semaphores
— Three programmable mask registers: global for MBs 0-13, special for MB14, and special for MB15
— Programmable transmit-first scheme: lowest ID or lowest buffer number
— Time stamp based on 16-bit free-running timer
— Global network time, synchronized by a specific message
— Maskable interrupts
• Three universal asynchronous/synchronous receiver transmitters (UARTs)
— 16-bit divider for clock generation
— Interrupt control logic with maskable interrupts
— DMA support
— Data formats can be 5, 6, 7 or 8 bits with even, odd, or no parity
— Up to two stop bits in 1/16 increments
MCF5213 ColdFire Microcontroller, Rev. 3
Freescale Semiconductor 5
Page 6

MCF5213 Family Configurations
— Error-detection capabilities
— Modem support includes request-to-send (RTS) and clear-to-send (CTS) lines for two UARTs
— Transmit and receive FIFO buffers
2
•I
C module
— Interchip bus interface for EEPROMs, LCD controllers, A/D converters, and keypads
— Fully compatible with industry-standard I
— Master and slave modes support multiple masters
— Automatic interrupt generation with programmable level
• Queued serial peripheral interface (QSPI)
— Full-duplex, three-wire synchronous transfers
— Up to four chip selects available
— Master mode operation only
— Programmable bit rates up to half the CPU clock frequency
— Up to 16 pre-programmed transfers
• Fast analog-to-digital converter (ADC)
— Eight analog input channels
— 12-bit resolution
— Minimum 1.125 μs conversion time
— Simultaneous sampling of two channels for motor control applications
— Single-scan or continuous operation
— Optional interrupts on conversion complete, zero crossing (sign change), or under/over low/high limit
— Unused analog channels can be used as digital I/O
• Four 32-bit timers with DMA support
— 12.5 ns resolution at 80 MHz
— Programmable sources for clock input, including an external clock option
— Programmable prescaler
— Input capture capability with programmable trigger edge on input pin
— Output compare with programmable mode for the output pin
— Free run and restart modes
— Maskable interrupts on input capture or output compare
— DMA trigger capability on input capture or output compare
• Four-channel general purpose timer
— 16-bit architecture
— Programmable prescaler
— Output pulse-widths variable from microseconds to seconds
— Single 16-bit input pulse accumulator
— Toggle-on-overflow feature for pulse-width modulator (PWM) generation
— One dual-mode pulse accumulation channel
• Pulse-width modulation timer
— Operates as eight channels with 8-bit resolution or four channels with 16-bit resolution
— Programmable period and duty cycle
— Programmable enable/disable for each channel
— Software selectable polarity for each channel
— Period and duty cycle are double buffered. Change takes effect when the end of the current period is reached
(PWM counter reaches zero) or when the channel is disabled.
2
C bus
MCF5213 ColdFire Microcontroller, Rev. 3
Freescale Semiconductor6
Page 7

MCF5213 Family Configurations
— Programmable center or left aligned outputs on individual channels
— Four clock sources (A, B, SA, and SB) provide for a wide range of frequencies
— Emergency shutdown
• Two periodic interrupt timers (PITs)
— 16-bit counter
— Selectable as free running or count down
• Software watchdog timer
— 32-bit counter
— Low-power mode support
• Clock generation features
— One to 48 MHz crystal, 8 MHz on-chip relaxation oscillator, or external oscillator reference options
— Trimmed relaxation oscillator
— Two to 10 MHz reference frequency for normal PLL mode with a pre-divider programmable from 1 to 8
— System can be clocked from PLL or directly from crystal oscillator or relaxation oscillator
— Low power modes supported
n
—2
(n ≤ 0 ≤ 15) low-power divider for extremely low frequency operation
• Interrupt controller
— Uniquely programmable vectors for all interrupt sources
— Fully programmable level and priority for all peripheral interrupt sources
— Seven external interrupt signals with fixed level and priority
— Unique vector number for each interrupt source
— Ability to mask any individual interrupt source or all interrupt sources (global mask-all)
— Support for hardware and software interrupt acknowledge (IACK) cycles
— Combinatorial path to provide wake-up from low-power modes
• DMA controller
— Four fully programmable channels
— Dual-address transfer support with 8-, 16-, and 32-bit data capability, along with support for 16-byte (4×32-bit)
burst transfers
— Source/destination address pointers that can increment or remain constant
— 24-bit byte transfer counter per channel
— Auto-alignment transfers supported for efficient block movement
— Bursting and cycle steal support
— Software-programmable DMA requesters for the UARTs (3) and 32-bit timers (4)
• Reset
— Separate reset in and reset out signals
— Seven sources of reset:
– Power-on reset (POR)
– External
–Software
– Watchdog
– Loss of clock
– Loss of lock
– Low-voltage detection (LVD)
— Status flag indication of source of last reset
• Chip integration module (CIM)
MCF5213 ColdFire Microcontroller, Rev. 3
Freescale Semiconductor 7
Page 8

MCF5213 Family Configurations
— System configuration during reset
— Selects one of six clock modes
— Configures output pad drive strength
— Unique part identification number and part revision number
• General purpose I/O interface
— Up to 56 bits of general purpose I/O
— Bit manipulation supported via set/clear functions
— Programmable drive strengths
— Unused peripheral pins may be used as extra GPIO
• JTAG support for system level board testing
1.1.2 V2 Core Overview
The version 2 ColdFire processor core is comprised of two separate pipelines decoupled by an instruction buffer . The two-stage
instruction fetch pipeline (IFP) is responsible for instruction-address generation and instruction fetch. The instruction buffer is
a first-in-first-out (FIFO) buffer that holds prefetched instructions awaiting execution in the operand execution pipeline (OEP).
The OEP includes two pipeline stages. The first stage decodes instructions and selects operands (DSOC); the second stage
(AGEX) performs instruction execution and calculates operand effective addresses, if needed.
The V2 core implements the ColdFire instruction set architecture revision A+ with added support for a separate user stack
pointer register and four new instructions to assist in bit processing. Additionally, the MCF5213 core includes the
multiply-accumulate (MAC) unit for improved signal processing capabilities. The MAC implements a three-stage arithmetic
pipeline, optimized for 16×16 bit operations, with support for one 32-bit accumulator. Supported operands include 16- and
32-bit signed and unsigned integers, signed fractional operands, and a complete set of instructions to process these data types.
The MAC provides support for execution of DSP operations within the context of a single processor at a minimal hardware cost.
1.1.3 Integrated Debug Module
The ColdFire processor core debug interface is provided to support system debugging with low-cost debug and emulator
development tools. Through a standard debug interface, access to debug information and real-time tracing capability is provided
on 100-lead packages. This allows the processor and system to be debugged at full speed without the need for costly in-circuit
emulators.
The on-chip breakpoint resources include a total of nine programmable 32-bit registers: an address and an address mask register,
a data and a data mask register, four PC registers, and one PC mask register. These registers can be accessed through the
dedicated debug serial communication channel or from the processor’s supervisor mode programming model. The breakpoint
registers can be configured to generate triggers by combining the address, data, and PC conditions in a variety of single- or
dual-level definitions. The trigger event can be programmed to generate a processor halt or initiate a debug interrupt exception.
The MCF5213 implements revision B+ of the ColdFire Debug Architecture.
The MCF5213’s interrupt servicing options during emulator mode allow real-time critical interrupt service routines to be
serviced while processing a debug interrupt event. This ensures the system continues to operate even during debugging.
To support program trace, the V2 debug module provides processor status (PST[3:0]) and debug data (DDATA [3:0]) ports .
These buses and the PSTCLK output provid e execu tion status, captured operand data, and branch target addresses defining
processor activity at the CPU’s clock rate. The MCF5213 includes a new debug signal, ALLPST . This signal is the logical AND
of the processor status (PST[3:0]) signals and is useful for detecting when the processor is in a halted state (PST[3:0] = 1111).
The full debug/trace interface is available only on the 100-pin packages. However, every product features the dedicated debug
serial communication channel (DSI, DSO, DSCLK) and the ALLPST signal.
MCF5213 ColdFire Microcontroller, Rev. 3
Freescale Semiconductor8
Page 9

MCF5213 Family Configurations
1.1.4 JTAG
The MCF5213 supports circuit board test strategies based on the Test T echnology Committee of IEEE and the Joint T est Action
Group (JTAG). The test logic includes a test access port (TAP) consisting of a 16-state controller, an instruction register, and
three test registers (a 1-bit bypass register, a 256-bit boundary-scan register, and a 32-bit ID register). The boundary scan register
links the device’s pins into one shift register. Test logic, implemented using static logic design, is independent of the device
system logic.
The MCF5213 implementation can:
• Perform boundary-scan operations to test circuit board electrical continuity
• Sample MCF5213 system pins during operation and transparently shift out the result in the boundary scan register
• Bypass the MCF5213 for a given circuit board test by effectively reducing the boundary-scan register to a single bit
• Disable the output drive to pins during circuit-board testing
• Drive output pins to stable levels
1.1.5 On-Chip Memories
1.1.5.1 SRAM
The dual-ported SRAM module provides a general-purpose 32-Kbyte memory block that the ColdFire core can access in a
single cycle. The location of the memory block can be set to any 32-Kbyte boundary within the 4-Gbyte address space. This
memory is ideal for storing critical code or data structures and for use as the system stack. Because the SRAM module is
physically connected to the processor's high-speed local bus, it can quickly service core-initiated accesses or
memory-referencing commands from the debug module.
The SRAM module is also accessible by the DMA. The dual-ported nature of the SRAM makes it ideal for implementing
applications with double-buffer schemes, where the processor and a DMA device operate in alternate regions of the SRAM to
maximize system performance.
1.1.5.2 Flash Memory
The ColdFire flash module (CFM) is a non-volatile memory (NVM) module that connects to the processor’s high-speed local
bus. The CFM is constructed with four banks of 32-Kbyte×16-bit flash memory arrays to generate 256 Kbytes of 32-bit flash
memory. Th ese electrically erasable and programmable arrays serve as non-volatile program and data memory. The flash
memory is ideal for program and data storage for single-chip applications, allowing for field reprogramming without requiring
an external high voltage source. The CFM interfaces to the ColdFire core through an optimized read-only memory controller
that supports interleaved accesses from the 2-cycle flash memory arrays. A backdoor mapping of the flash memory is used for
all program, erase, and verify operations, as well as providing a read datapath for the DMA. Flash memory may also be
programmed via the EzPort, which is a serial flash memory programming interface that allows the flash memory to be read,
erased and programmed by an external controller in a format compatible with most SPI bus flash memory chips.
1.1.6 Power Management
The MCF5213 incorporates several low-power modes of operation entered under program control and exited by several external
trigger events. An integrated power-on reset (POR) circuit monitors the input supply and forces an MCU reset as the supply
voltage rises. The low voltage detector (LVD) mon itors the supply voltage and is configurable to force a reset or interrupt
condition if it falls below the LVD trip point. The RAM standby switch provides power to RAM when the supply voltage to the
chip falls below the standby battery voltage.
MCF5213 ColdFire Microcontroller, Rev. 3
Freescale Semiconductor 9
Page 10

MCF5213 Family Configurations
1.1.7 FlexCAN
The FlexCAN module is a communication controller implementing version 2.0 of the CAN protocol parts A and B. The CAN
protocol can be used as an industrial control serial data bus, meeting the specific requirements of reliable operation in a harsh
EMI environment with high bandwidth. This instantiation of FlexCAN has 16 message buffers.
1.1.8 UARTs
The MCF5213 has three full-duplex UARTs that function independently. The three UARTs can be clocked by the system bus
clock, eliminating the need for an external clock source. On smaller packages, the third UART is multiplexed with other digital
I/O functions.
1.1.9 I2C Bus
The I2C bus is a two-wire, bidirectional serial bus that provides a simple, efficient method of data exchange and minimizes the
interconnection between devices. This bus is suitable for applications requiring occasional communications over a short
distance between many devices.
1.1.10 QSPI
The queued serial peripheral interface (QSPI) provides a synchronous serial peripheral interface with queued transfer capability.
It allows up to 16 transfers to be queued at once, minimizing the need for CPU intervention between transfers.
1.1.11 Fast ADC
The fast ADC consists of an eight-channel input select multiplexer and two independent sample and hold (S/H) circuits feeding
separate 12-bit ADCs. The two separate converters store their results in accessible buffers for further processing.
The ADC can be configured to perform a single scan and halt, a scan when triggered, or a programmed scan sequence repeatedly
until manually stopped.
The ADC can be configured for sequential or simultaneous conversion. When configured for sequential conversions, up to eight
channels can be sampled and stored in any order specified by the channel list register. Both ADCs may be required during a
scan, depending on the inputs to be sampled.
During a simultaneous conversion, both S/H circuits are used to capture two different channels at the same time. This
configuration requires that a single channel may not be sampled by both S/H circuits simultaneously.
Optional interrupts can be generated at the end of the scan sequence if a channel is out of range (measures below the low
threshold limit or above the high threshold limit set in the limit registers) or at several different zero crossing conditions.
1.1.12 DMA Timers (DTIM0–DTIM3)
There are four independent, DMA transfer capable 32-bit timers (DTIM0, DTIM1, DTIM2, and DTIM3) on the MCF5213.
Each module incorporates a 32-bit timer with a separate register set for configuration and control. The timers can be configured
to operate from the system clock or from an external clock source using one of the DTINn signals. If the system clock is selected,
it can be divided by 16 or 1. The input clock is further divided by a user-programmable 8-bit prescaler that clocks the actual
timer counter register (TCRn). Each of these timers can be configured for input capture or reference (output) compare mode.
Timer events may optionally cause interrupt requests or DMA transfers.
MCF5213 ColdFire Microcontroller, Rev. 3
Freescale Semiconductor10
Page 11

MCF5213 Family Configurations
1.1.13 General Purpose Timer (GPT)
The general purpose timer (GPT) is a four-channel timer module consisting of a 16-bit programmable counter driven by a
seven-stage programmable prescaler. Each of the four channels can be configured for input capture or output compare.
Additionally , channel th ree, can be configured as a pulse accumulator.
A timer overflow function allows software to extend the timing capability of the system beyond the 16-bit range of the counter.
The input capture and output compare functions allow simultaneous input waveform measurements and output waveform
generation. The input capture function can capture the time of a selected transition edge. The output compare function can
generate output waveforms and timer software delays. The 16-bit pulse accumulator can operate as a simple event counter or a
gated time accumulator.
1.1.14 Periodic Interrupt Timers (PIT0 and PIT1)
The two periodic interrupt timers (PIT0 and PIT1) are 16-bit timers that provide interrupts at regular intervals with minimal
processor intervention. Each timer can count down from the value written in its PIT modulus register or it can be a free-running
down-counter.
1.1.15 Pulse-Width Modulation (PWM) Timers
The MCF5213 has an 8-channel, 8-bit PWM timer. Each channel has a programmable period and duty cycle as well as a
dedicated counter. Each of the modulators can create independent continuous waveforms with software-selectable duty rates
from 0% to 100%. The PWM outputs have programmable polarity, and can be programmed as left aligned outputs or center
aligned outputs. For higher period and duty cycle resolution, each pair of adjacent channels ([7:6], [5:4], [3:2], and [1:0]) can
be concatenated to form a single 16-bit channel. The module can, therefore, be configured to support 8/0, 6/1, 4/2, 2/3, or 0/4
8-/16-bit channels.
1.1.16 Software Watchdog Timer
The watchdog timer is a 32-bit timer that facilitates recovery from runaway code. The watchdog counter is a free-running
down-counter that generates a reset on underflow. To prevent a reset, software must periodically restart the countdown.
1.1.17 Phase-Locked Loop (PLL)
The clock module contains a crystal oscillator, 8 MHz on-chip relaxation oscillator (OCO), phase-locked loop (PLL), reduced
frequency divider (RFD), low-power divider status/control registers, and control logic. To improve noise immunity, the PLL,
crystal oscillator, and relaxation oscillator have their own power supply inputs: VDDPLL and VSSPLL. All other circuits are
powered by the normal supply pins, VDD and VSS.
1.1.18 Interrupt Controller (INTC)
The MCF5213 has a single interrupt controller that supports up to 63 interrupt sources. There are 56 programmable sources, 49
of which are assigned to unique peripheral interrupt requests. The remaining seven sources are unassigned and may be used for
software interrupt requests.
1.1.19 DMA Controller
The direct memory access (DMA) controller provides an efficient way to move blocks of data with minimal processor
intervention. It has four channels that allow byte, word, longword, or 16-byte burst line transfers. These transfers are triggered
by software explicitly setting a DCRn[START] bit or by the occurrence of certain UART or DMA timer events.
MCF5213 ColdFire Microcontroller, Rev. 3
Freescale Semiconductor 11
Page 12
MCF5213 Family Configurations
1.1.20 Reset
The reset controller determines the source of reset, asserts the appropriate reset signals to the system, and keeps track of what
caused the last reset. There are seven sources of reset:
• External reset input
• Power-on reset (POR)
• Watchdog timer
• Phase locked-loop (PLL) loss of lock
• PLL loss of clock
•Software
• Low-voltage detector (LVD)
Control of the L VD and its associated reset and interrupt are managed by the reset controller . Other registers provide status flags
indicating the last source of reset and a control bit for software assertion of the RSTO
pin.
1.1.21 GPIO
Nearly all pins on the MCF5213 have general purpose I/O capability and are grouped into 8-bit ports. Some ports do not use all
eight bits. Each port has registers that configure, monitor, and control the port pins.
1.1.22 Part Numbers and Packaging
This product is RoHS-compliant. Refer to the product page at freescale.com or contact your sales office for up-to-date RoHS
information.
Table 2. Orderable Part Number Summary
Freescale Part
Number
MCF5211CAE66 MCF5211 ColdFire Microcontroller 66 MHz 64 LQFP -40 to +85
MCF5211CEP66 MCF5211 ColdFire Microcontroller, FlexCAN 66 MHz 64 QFN -40 to +85
MCF5211LCEP66 MCF5211 ColdFire Microcontroller 66 MHz 64 QFN -40 to +85
MCF5211LCVM66 MCF5211 ColdFire Microcontroller 66 MHz 81 MAPBGA -40 to +85
MCF5211LCVM80 MCF5211 ColdFire Microcontroller 80 MHz 81 MAPBGA -40 to +85
MCF5212CAE66 MCF5212 ColdFire Microcontroller 66 MHz 64 LQFP -40 to +85
MCF5212LCVM66 MCF5212 ColdFire Microcontroller 66 MHz 81 MAPBGA -40 to +85
MCF5212LCVM80 MCF5212 ColdFire Microcontroller 80 MHz 81 MAPBGA -40 to +85
MCF5213CAF66 MCF5213 ColdFire Microcontroller, FlexCAN 66 MHz 100 LQFP -40 to +85
MCF5213CAF80 MCF5213 ColdFire Microcontroller, FlexCAN 80 MHz 100 LQFP -40 to +85
MCF5213LCVM66 MCF5213 ColdFire Microcontroller, FlexCAN 66 MHz 81 MAPBGA -40 to +85
MCF5213LCVM80 MCF5213 ColdFire Microcontroller, FlexCAN 80 MHz 81 MAPBGA -40 to +85
Description Speed Package Temperature
°C
°C
°C
°C
°C
°C
°C
°C
°C
°C
°C
°C
MCF5213 ColdFire Microcontroller, Rev. 3
Freescale Semiconductor12
Page 13
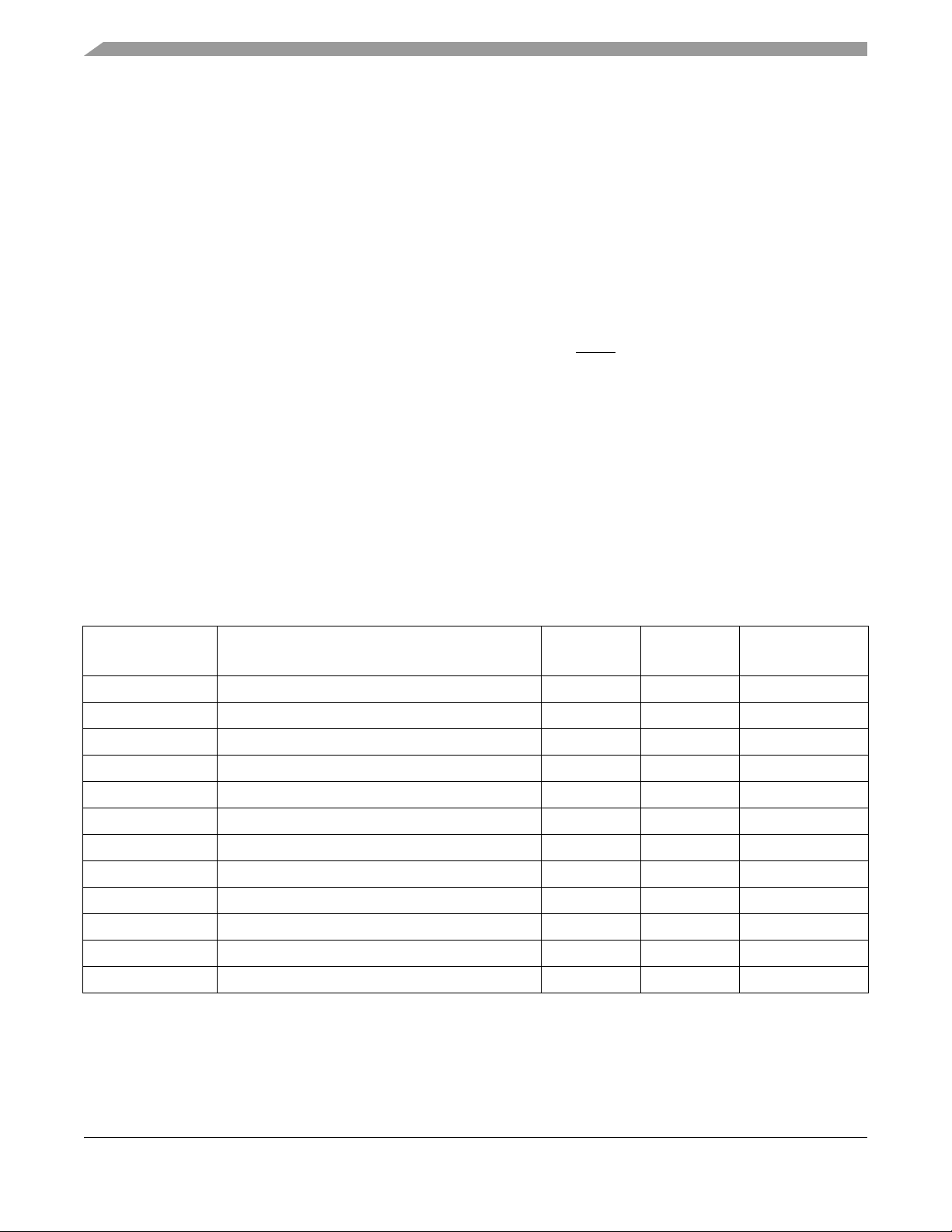
Figure 2 shows the pinout configuration for the 100 LQFP.
AN5
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
V
DD
V
DD
V
SS
URTS1
TEST
UCTS0
UTXD0
URTS0
SCL
SDA
QSPI_CS3
QSPI_CS2
V
DD
V
SS
QSPI_DIN
QSPI_DOUT
QSPI_CLK
QSPI_CS1
QSPI_CS0
RCON
V
DD
V
DD
V
SS
100 LQFP
75
74
73
72
71
70
69
68
67
66
65
64
63
62
61
60
59
58
57
56
55
54
53
52
51
V
SS
V
DDPLL
EXTAL
XTAL
V
SSPLL
PST3
PST2
V
DD
V
SS
PST1
PST0
PSTCLK
PWM7
GPT3
GPT2
PWM5
GPT1
GPT0
V
DD
V
SS
V
STBY
AN6
AN7
100
9998979695949392919089888786858483828180797877
76
URXD1
UTXD1
UCTS1
RSTO
RSTI
IRQ7
IRQ6
VDDVSSIRQ5
IRQ4
IRQ3
IRQ2
IRQ1
ALLPST
DDATA3
DDATA2
VSSVDDDSO
DSI
DDATA1
DDATA0
BKPT
26272829303132333435363738394041424344454647484950
JTAG_EN
UCTS2
URXD2
UTXD2
URTS2
DTIN2
DTIN3
PWM3
V
DD
V
SS
DTIN0
DTIN1
PWM1
CLKMOD1
CLKMOD0
V
DD
V
SS
AN0
AN1
AN2
AN3
V
SSA
V
RL
V
RH
V
DDA
V
SS
URXD0
AN4
DSCLK
MCF5213 Family Configurations
Figure 2. 100 LQFP Pin Assignments
MCF5213 ColdFire Microcontroller, Rev. 3
Freescale Semiconductor 13
Page 14
MCF5213 Family Configurations
V
SS
UTXD1 RSTI IRQ5 IRQ3 ALLPST TDO TMS V
SS
A
123456789
URTS1 URXD1 RSTO IRQ6 IRQ2 TRST TDI VDDPLL EXTALB
UCTS0 TEST UCTS1 IRQ7 IRQ4 IRQ1 TCLK VSSPLL XTALC
URXD0 UTXD0 URTS0 V
SS
V
DD
V
SS
PWM7 GPT3 GPT2D
SCL SDA V
DD
V
DD
V
DD
V
DD
V
DD
PWM5 GPT1E
QSPI_CS3 QSPI_CS2 QSPI_DIN V
SS
V
DD
V
SS
GPT0 V
STBY
AN4F
QSPI_DOUT QSPI_CLK RCON DTIN1 CLKMOD0 AN2 AN3 AN5 AN6G
QSPI_CS0 QSPI_CS1 DTIN3 DTIN0 CLKMOD1 AN1 V
SSA
V
DDA
AN7H
V
SS
JTAG_EN DTIN2 PWM3 PWM1 AN0 V
RL
V
RH
V
SSA
J
Figure 3 shows the pinout configuration for the 81 MAPBGA.
Figure 3. 81 MAPBGA Pin Assignments
MCF5213 ColdFire Microcontroller, Rev. 3
Freescale Semiconductor14
Page 15
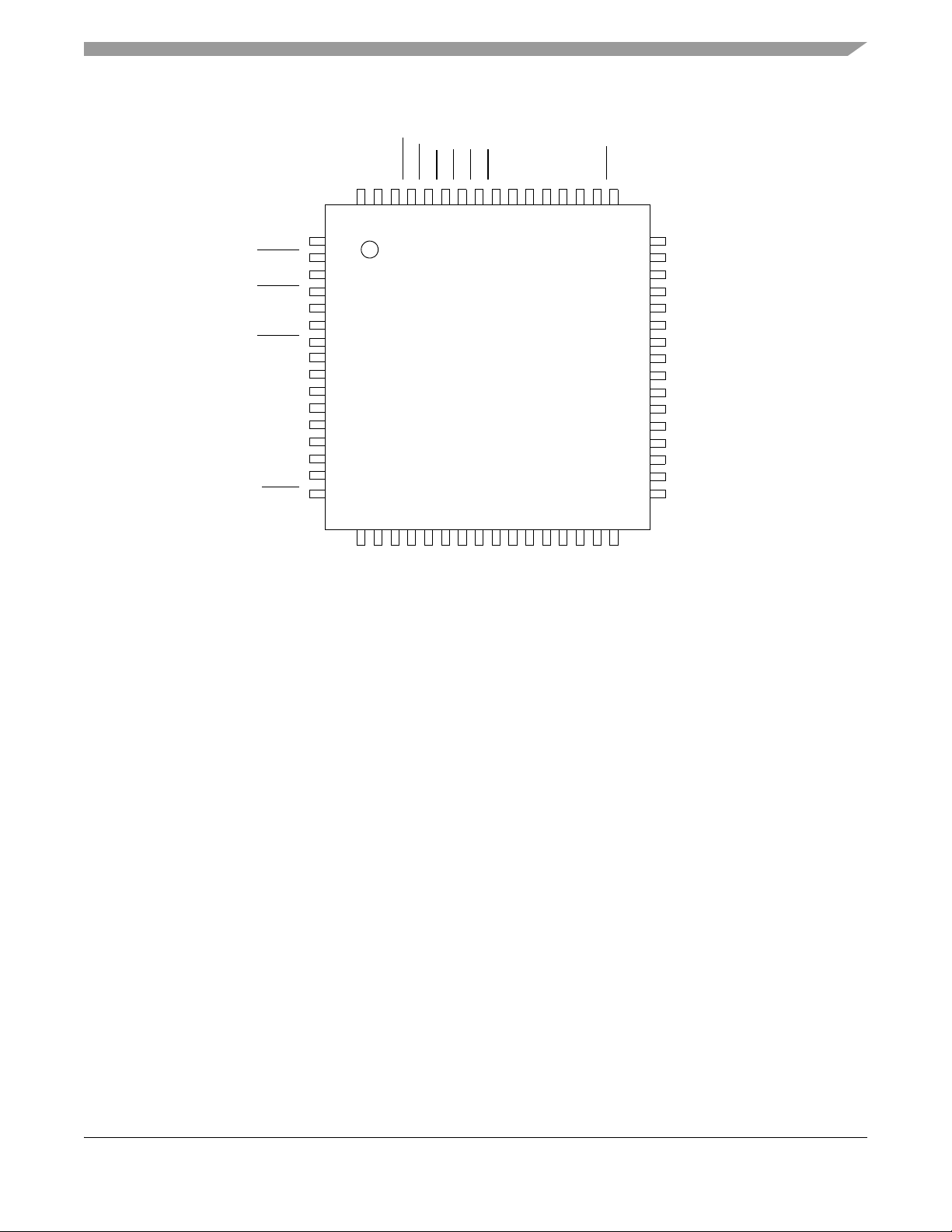
Figure 4 shows the pinout configuration for the 64 LQFP and 64 QFN.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
V
DD
URTS1
TEST
UCTS0
URXD0
UTXD0
SCL
SDA
V
DD
V
SS
QSPI_DIN
QSPI_DOUT
QSPI_CLK
QSPI_CS0
RCON
64-Pin Packages
646362616059585756555453525150
49
V
SS
URXD1
UTXD1
UCTS1
RSTO
RSTI
IRQ7
IRQ4
IRQ1
ALLPST
DSCLK
VSSVDDDSO
DSI
BKPT
URTS0
171819202122232425262728293031
32
JTAG_EN
DTIN2
DTIN3
V
DD
V
SS
DTIN0
DTIN1
CLKMOD0
AN0
AN1
AN2
AN3
V
SSA
V
RL
V
RH
V
DDA
48
47
46
45
44
43
42
41
40
39
38
37
36
35
34
33
V
DDPLL
EXTAL
XTAL
V
SSPLL
PSTCLK
GPT3
GPT2
GPT1
GPT0
V
DD
V
SS
V
STBY
AN4
AN5
AN6
AN7
MCF5213 Family Configurations
Figure 4. 64 LQFP and 64 QFN Pin Assignments
Table 3 shows the pin functions by primary and alternate purpose, and illustrates which packages contain each pin.
Freescale Semiconductor 15
MCF5213 ColdFire Microcontroller, Rev. 3
Page 16
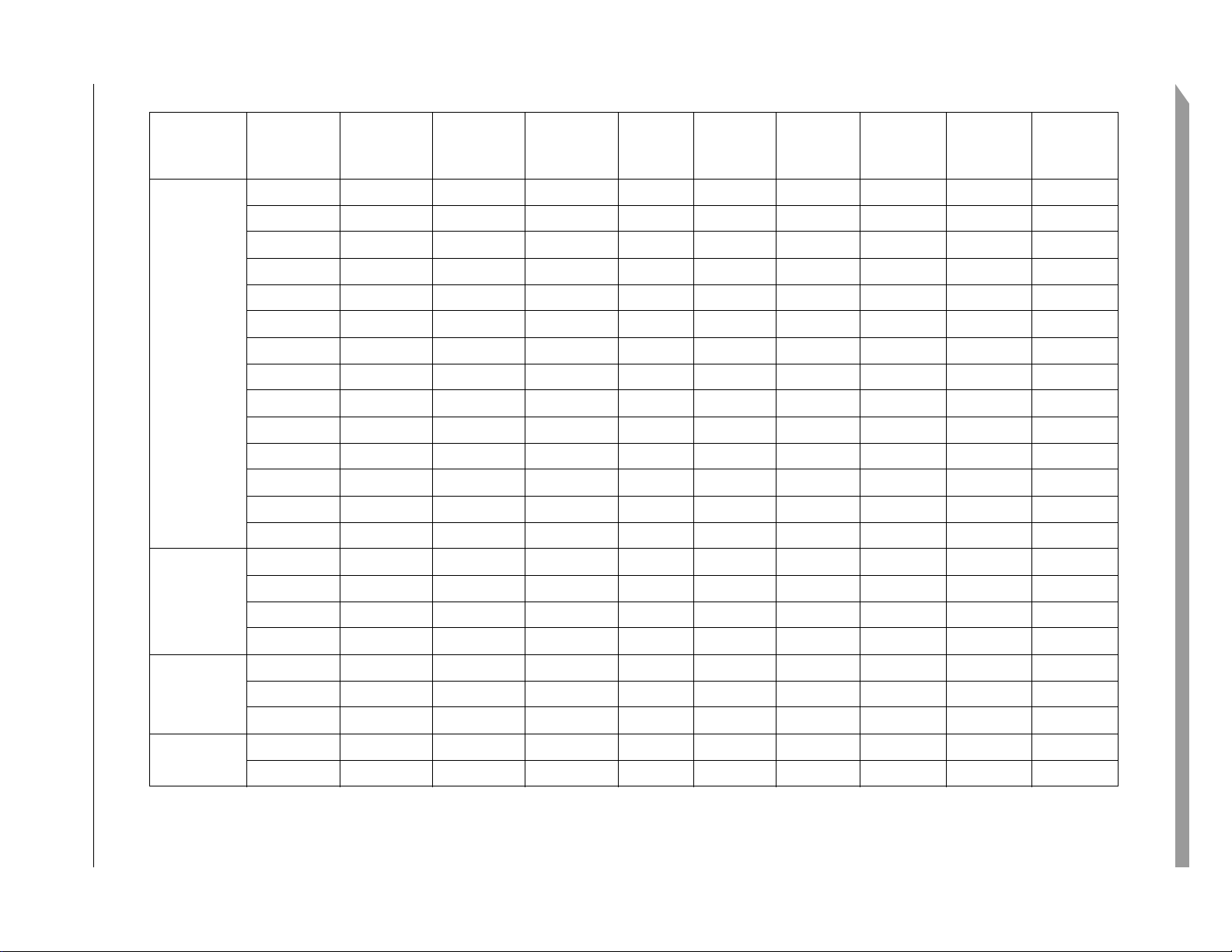
Table 3. Pin Functions by Primary and Alternate Purpose
MCF5213 Family Configurations
Pin
Group
Primary
Function
Secondary
Function
Ter tia r y
Function
Quaternary
Function
Drive
Strength /
Control
1
Slew Rate /
Control
1
Pull-up /
Pull-down
2
100 LQFP
Pin on
Pin on 81
MAPBGA
Pin on 64
LQFP/QFN
ADC AN7 — — GPIO Low FAST — 51 H9 33
AN6 — — GPIO Low FAST — 52 G9 34
AN5 — — GPIO Low FAST — 53 G8 35
AN4 — — GPIO Low FAST — 54 F9 36
AN3 — — GPIO Low FAST — 46 G7 28
MCF5213 ColdFire Microcontroller, Rev. 3
AN2 — — GPIO Low FAST — 45 G6 27
AN1 — — GPIO Low FAST — 44 H6 26
AN0 — — GPIO Low FAST — 43 J6 25
SYNCA
SYNCB
3
3
— — —N/AN/A————
— — —N/AN/A————
VDDA — — — N/A N/A — 50 H8 32
VSSA — — — N/A N/A — 47 H7, J9 29
VRH — — — N/A N/A — 49 J8 31
VRL — — — N/A N/A — 48 J7 30
Clock
Generation
EXTAL — — — N/A N/A — 73 B9 47
XTAL — — — N/A N/A — 72 C9 46
Freescale Semiconductor16
VDDPLL — — — N/A N/A — 74 B8 48
VSSPLL — — — N/A N/A — 71 C8 45
Debug Data ALLPST — — — High FAST — 86 A6 55
DDATA[3:0] — — GPIO High FAST — 84,83,78,77 — —
PST[3:0] — — GPIO High FAST — 70,69,66,65 — —
2
C SCL CANTX
I
SDA CANRX
4
3
UTXD2 GPIO PDSR[0] PSRR[0] pull-up
URXD2 GPIO PDSR[0] PSRR[0] pull-up
5
5
10 E1 8
11 E2 9
Page 17
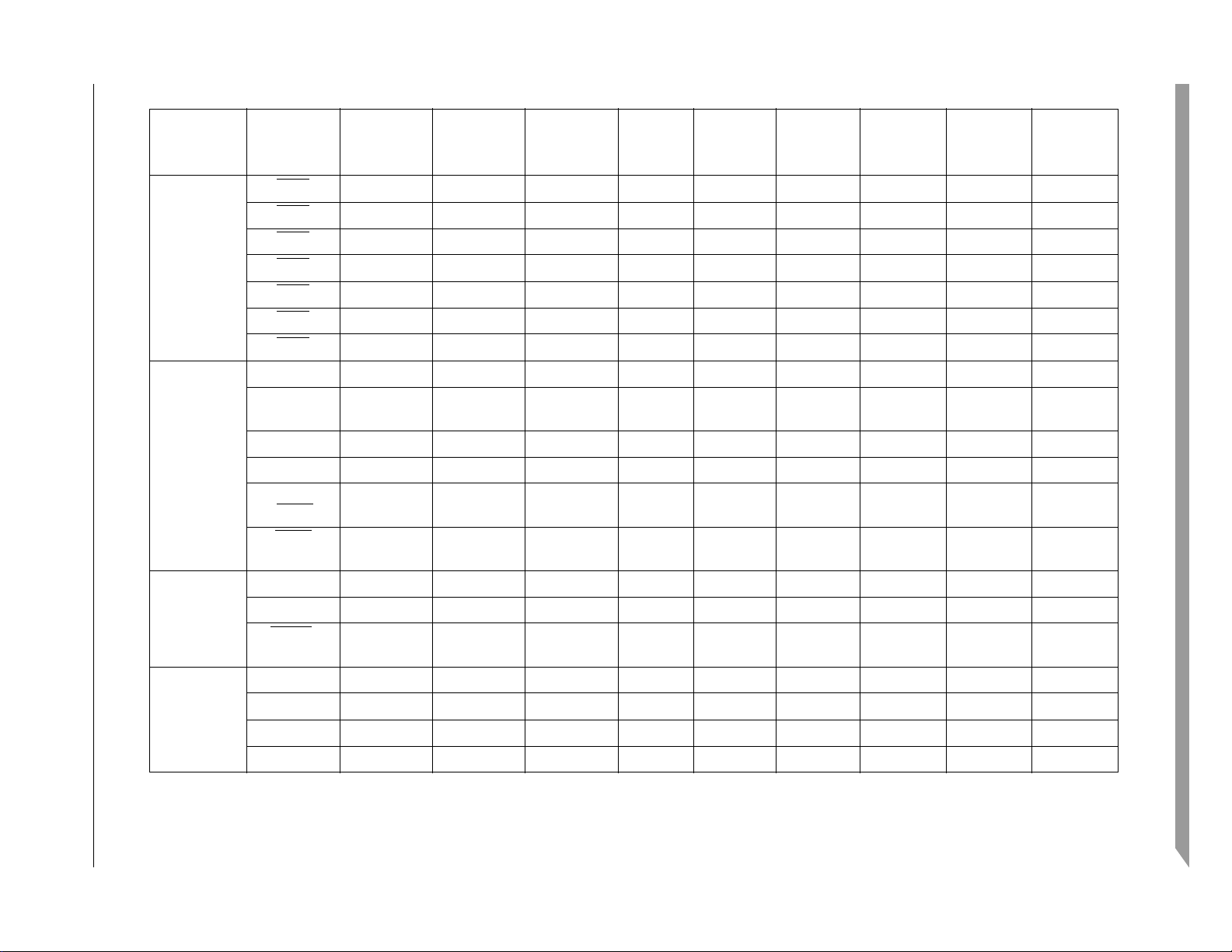
Freescale Semiconductor 17
Table 3. Pin Functions by Primary and Alternate Purpose (continued)
Pin
Group
Primary
Function
Secondary
Function
Ter tia r y
Function
Quaternary
Function
Drive
Strength /
Control
1
Slew Rate /
Control
1
Pull-up /
Pull-down
2
100 LQFP
Pin on
Pin on 81
MAPBGA
Pin on 64
LQFP/QFN
Interrupts IRQ7 — — GPIO Low FAST pull-up 95 C4 58
IRQ6
IRQ5
IRQ4
IRQ3
IRQ2
MCF5213 ColdFire Microcontroller, Rev. 3
IRQ1
— — GPIO Low FAST pull-up 94 B4 —
— — GPIO Low FAST pull-up 91 A4 —
— — GPIO Low FAST pull-up 90 C5 57
— — GPIO Low FAST pull-up 89 A5 —
— — GPIO Low FAST pull-up 88 B5 —
SYNCA PWM1 GPIO High FAST pull-up
5
87 C6 56
JTAG/BDM JTAG_EN — — — N/A N/A pull-down 26 J2 17
TCLK/
CLKOUT — — High FAST pull-up
6
64 C7 44
PSTCLK
TDI/DSI — — — N/A N/A pull-up
6
79 B7 50
TDO/DSO— — —HighFAST—80A751
TMS
— — — N/A N/A pull-up
6
76 A8 49
/BKPT
TRST
— — — N/A N/A pull-up
6
85 B6 54
/DSCLK
Mode
Selection
CLKMOD0 — — — N/A N/A pull-down
7
CLKMOD1 — — — N/A N/A pull-down
RCON
/
— — — N/A N/A pull-up 21 G3 16
EZPCS
7
7
40 G5 24
39 H5 —
MCF5213 Family Configurations
PWM PWM7 — — GPIO PDSR[31] PSRR[31] — 63 D7 —
PWM5 — — GPIO PDSR[30] PSRR[30] — 60 E8 —
PWM3 — — GPIO PDSR[29] PSRR[29] — 33 J4 —
PWM1 — — GPIO PDSR[28] PSRR[28] — 38 J5 —
Page 18

Table 3. Pin Functions by Primary and Alternate Purpose (continued)
MCF5213 Family Configurations
Pin
Group
Primary
Function
QSPI QSPI_DIN/
Secondary
Function
CANRX
4
Ter tia r y
Function
Quaternary
Function
URXD1 GPIO PDSR[2] PSRR[2] — 16 F3 12
Drive
Strength /
Control
1
Slew Rate /
Control
1
Pull-up /
Pull-down
2
100 LQFP
Pin on
Pin on 81
MAPBGA
Pin on 64
LQFP/QFN
EZPD
QSPI_DOUT/
CANTX
4
UTXD1 GPIO PDSR[1] PSRR[1] — 17 G1 13
EZPQ
QSPI_CLK/
SCL URTS1
GPIO PDSR[3] PSRR[3] pull-up
8
18 G2 14
EZPCK
QSPI_CS3 SYNCA SYNCB GPIO PDSR[7] PSRR[7] — 12 F1 —
MCF5213 ColdFire Microcontroller, Rev. 3
QSPI_CS2 — — GPIO PDSR[6] PSRR[6] — 13 F2 —
QSPI_CS1 — — GPIO PDSR[5] PSRR[5] — 19 H2 —
8
9
20 H1 15
96 A3 59
Reset
QSPI_CS0 SDA UCTS1 GPIO PDSR[4] PSRR[4] pull-up
9
RSTI — — — N/A N/A pull-up
RSTO
— — —highFAST—97B360
Test TEST — — — N/A N/A pull-down 5 C2 3
Timers, 16-bit GPT3 — PWM7 GPIO PDSR[23] PSRR[23] pull-up
GPT2 — PWM5 GPIO PDSR[22] PSRR[22] pull-up
GPT1 — PWM3 GPIO PDSR[21] PSRR[21] pull-up
GPT0 — PWM1 GPIO PDSR[20] PSRR[20] pull-up
10
10
10
10
62 D8 43
61 D9 42
59 E9 41
58 F7 40
Freescale Semiconductor18
Timers, 32-bit DTIN3 DTOUT3 PWM6 GPIO PDSR[19] PSRR[19] — 32 H3 19
DTIN2 DTOUT2 PWM4 GPIO PDSR[18] PSRR[18] — 31 J3 18
DTIN1 DTOUT1 PWM2 GPIO PDSR[17] PSRR[17] — 37 G4 23
DTIN0 DTOUT0 PWM0 GPIO PDSR[16] PSRR[16] — 36 H4 22
UART 0 UCTS0
URTS0
CANRX — GPIO PDSR[11] PSRR[11] — 6 C1 4
CANTX — GPIO PDSR[10] PSRR[10] — 9 D3 7
URXD0 — — GPIO PDSR[9] PSRR[9] — 7 D1 5
UTXD0 — — GPIO PDSR[8] PSRR[8] — 8 D2 6
Page 19

Freescale Semiconductor 19
Table 3. Pin Functions by Primary and Alternate Purpose (continued)
Pin
Group
Primary
Function
Secondary
Function
Ter tia r y
Function
Quaternary
Function
Drive
Strength /
Control
1
Slew Rate /
Control
1
Pull-up /
Pull-down
2
100 LQFP
Pin on
Pin on 81
MAPBGA
Pin on 64
LQFP/QFN
UART 1 UCTS1 SYNCA URXD2 GPIO PDSR[15] PSRR[15] — 98 C3 61
URTS1
SYNCB UTXD2 GPIO PDSR[14] PSRR[14] — 4 B1 2
URXD1 — — GPIO PDSR[13] PSRR[13] — 100 B2 63
UTXD1 — — GPIO PDSR[12] PSRR[12] — 99 A2 62
UART 2 UCTS2
URTS2
MCF5213 ColdFire Microcontroller, Rev. 3
URXD2 — — GPIO PDSR[25] PSRR[25] — 28 — —
— — GPIO PDSR[27] PSRR[27] — 27 — —
— — GPIO PDSR[26] PSRR[26] — 30 — —
UTXD2 — — GPIO PDSR[24] PSRR[24] — 29 — —
FlexCAN CANRX
CANTX
4,11
4,11
N/AN/A————
N/AN/A————
VSTBY VSTBY — — — N/A N/A — 55 F8 37
VDD VDD — — — N/A N/A — 1,2,14,22,
23,34,41,
D5,E3–E7, F51,10,20,39,5
2
57,68,81,93
VSS VSS — — — N/A N/A — 3,15,24,25,3
5,42,56,
A1,A9,D4,D
6,F4,F6,J1
11,21,38,
53,64
67,75,82,92
1
The PDSR and PSSR registers are described in the General Purpose I/O chapter. All programmable signals default to 2 mA drive and FAST slew rate in
normal (single-chip) mode.
2
All signals have a pull-up in GPIO mode.
3
These signals are multiplexed on other pins.
4
The multiplexed CANTX and CANRX signals are not available on the MCF5211 or MCF5212.
5
For primary and GPIO functions only.
6
Only when JTAG mode is enabled.
7
CLKMOD0 and CLKMOD1 have internal pull-down resistors; however, the use of external resistors is very strongly recommended.
8
For secondary and GPIO functions only.
9
RSTI has an internal pull-up resistor; however, the use of an external resistor is very strongly recommended.
10
For GPIO function. Primary Function has pull-up control within the GPT module.
11
CANTX and CANRX are secondary functions only.
MCF5213 Family Configurations
Page 20

MCF5213 Family Configurations
1.2 Reset Signals
Table 4 describes signals used to reset the chip or as a reset indication.
Table 4. Reset Signals
Signal Name Abbreviation Function I/O
Reset In RSTI
Reset Out RSTO
Primary reset input to the device. Asserting RSTI for at least 8 CPU
clock cycles immediately resets the CPU and peripherals.
Driven low for 1024 CPU clocks after the reset source has deasserted. O
1.3 PLL and Clock Signals
Table 5 describes signals used to support the on-chip clock generation circuitry.
Table 5. PLL and Clock Signals
Signal Name Abbreviation Function I/O
External Clock In EXTAL Crystal oscillator or external clock input except when the on-chip
relaxation oscillator is used.
Crystal XTAL Crystal oscillator output except when CLKMOD1=1, then sampled as
part of the clock mode selection mechanism.
Clock Out CLKOUT This output signal reflects the internal system clock. O
1.4 Mode Selection
Table 6 describes signals used in mode selection; Table 7 describes the particu lar clocking modes.
Table 6. Mode Selection Signals
Signal Name Abbreviation Function I/O
I
I
O
Clock Mode Selection CLKMOD[1:0] Selects the clock boot mode. I
Reset Configuration RCON The Serial Flash Programming mode is entered by asserting the
RCON pin (with the TEST pin negated) as the chip comes out of
reset. During this mode, the EzPort has access to the flash memory
which can be programmed from an external device.
Test TEST Reserved for factory testing only and in normal modes of operation
should be connected to VSS to prevent unintentional activation of
test functions.
Table 7. Clocking Modes
CLKMOD[1:0] XTAL Configure the clock mode.
00 0 PLL disabled, clock driven by external oscillator
00 1 PLL disabled, clock driven by on-chip oscillator
01 N/A PLL disabled, clock driven by crystal
10 0 PLL in normal mode, clock driven by external oscillator
10 1 PLL in normal mode, clock driven by on-chip oscillator
11 N/A PLL in normal mode, clock driven by crystal
MCF5213 ColdFire Microcontroller, Rev. 3
Freescale Semiconductor20
I
Page 21

1.5 External Interrupt Signals
Table 8 describes the external interrupt signals.
Table 8. External Interrupt Signals
Signal Name Abbreviation Function I/O
MCF5213 Family Configurations
External Interrupts IRQ
[7:1] External interrupt sources. I
1.6 Queued Serial Peripheral Interface (QSPI)
Table 9 describes the QSPI signals.
Table 9. Queued Serial Peripheral Interface (QSPI) Signals
Signal Name Abbreviation Function I/O
QSPI Synchronous
Serial Output
QSPI Synchronous
Serial Data Input
QSPI Serial Clock QSPI_CLK Provides the serial clock from the QSPI. The polarity and phase of
Synchronous Peripheral
Chip Selects
QSPI_DOUT Provides the serial data from the QSPI and can be programmed to be
driven on the rising or falling edge of QSPI_CLK.
QSPI_DIN Provides the serial data to the QSPI and can be programmed to be
sampled on the rising or falling edge of QSPI_CLK.
QSPI_CLK are programmable.
QSPI_CS[3:0] QSPI peripheral chip select; can be programmed to be active high or
low.
1.7 I2C I/O Signals
Table 10 describes the I2C serial interface module signals.
Table 10. I2C I/O Signals
O
I
O
O
Signal Name Abbreviation Function I/O
Serial Clock SCL Open-drain clock signal for the for the I
In master mode, this clock is driven by the I2C module; when the bus
is in slave mode, this clock becomes the clock input.
Serial Data SDA Open-drain signal that serves as the data input/output for the I
interface.
MCF5213 ColdFire Microcontroller, Rev. 3
2
C interface. When the bus is
2
C
I/O
I/O
Freescale Semiconductor 21
Page 22

MCF5213 Family Configurations
1.8 UART Module Signals
Table 11 describes the UART module signals.
Table 11. UART Module Signals
Signal Name Abbreviation Function I/O
Transmit Serial Data
Output
Receive Serial Data
Input
Clear-to-Send UCTS
Request-to-Send URTS
UTXDn Transmitter serial data outputs for the UART modules. The output is
held high (mark condition) when the transmitter is disabled, idle, or in
the local loopback mode. Data is shifted out, LSB first, on this pin at
the falling edge of the serial clock source.
URXDn Receiver serial data inputs for the UART modules. Data is received on
this pin LSB first. When the UART clock is stopped for power-down
mode, any transition on this pin restarts the clock.
n Indication to the UART modules that they can begin data
transmission.
n Automatic request-to-send outputs from the UART modules. This
signal can also be configured to be asserted and negated as a
function of the RxFIFO level.
1.9 DMA Timer Signals
Table 12 describes the signals of the four DMA timer modules.
Table 12. DMA Timer Signals
Signal Name Abbreviation Function I/O
DMA Timer Input DTIN Event input to the DMA timer modules. I
DMA Timer Output DTOUT Programmable output from the DMA timer modules. O
O
I
I
O
1.10 ADC Signals
Table 13 describes the signals of the Analog-to-Digital Converter.
Table 13. ADC Signals
Signal Name Abbreviation Function I/O
Analog Inputs AN[7:0] Inputs to the analog-to-digital converter. I
Analog Reference V
Analog Supply V
ADC Sync Inputs SYNCA /
RH
V
RL
DDA
V
SSA
SYNCB
MCF5213 ColdFire Microcontroller, Rev. 3
Reference voltage high and low inputs. I
Isolate the ADC circuitry from power supply noise. —
These signals can initiate an analog-to-digital conversion
process.
I
—
I
Freescale Semiconductor22
Page 23

MCF5213 Family Configurations
1.11 General Purpose Timer Signals
Table 14 describes the general purpose timer signals.
Table 14. GPT Signals
Signal Name Abbreviation Function I/O
General Purpose Timer
Input/Output
GPT[3:0] Inputs to or outputs from the general purpose timer module. I/O
1.12 Pulse Width Modulator Signals
Table 15 describes the PWM signals.
Table 15. PWM Signals
Signal Name Abbreviation Function I/O
PWM Output Channels PWM[7:0] Pulse width modulated output for PWM channels. O
1.13 Debug Support Signals
These signals are used as the interface to the on-chip JTAG controller and the BDM logic.
Table 16. Debug Support Signals
Signal Name Abbreviation Function I/O
JTAG Enable JTAG_EN Select between debug module and JTAG signals at reset. I
Test Reset TRST This active-low signal is used to initialize the JTAG logic
asynchronously.
Test Clock TCLK Used to synchronize the JTAG logic. I
Test Mode Select TMS Used to sequence the JTAG state machine. TMS is sampled on the
rising edge of TCLK.
I
I
Test Data Input TDI Serial input for test instructions and data. TDI is sampled on the rising
edge of TCLK.
Test Data Output TDO Serial output for test instructions and data. TDO is tri-stateable and is
actively driven in the shift-IR and shift-DR controller states. TDO
changes on the falling edge of TCLK.
Development Serial
Clock
Breakpoint BKPT
Freescale Semiconductor 23
DSCLK Development Serial Clock - Internally synchronized input. (The logic
level on DSCLK is validated if it has the same value on two
consecutive rising bus clock edges.) Clocks the serial communication
port to the debug module during packet transfers. Maximum frequency
is PSTCLK/5. At the synchronized rising edge of DSCLK, the data
input on DSI is sampled and DSO changes state.
Breakpoint - Input used to request a manual breakpoint. Assertion of
puts the processor into a halted state after the current
BKPT
instruction completes. Halt status is reflected on processor
status/debug data signals (PST[3:0] and PSTDDATA[7:0]) as the
value 0xF. If CSR[BKD] is set (disabling normal BKPT
asserting BKPT
processor.
MCF5213 ColdFire Microcontroller, Rev. 3
generates a debug interrupt exception in the
functionality),
I
O
I
I
Page 24

MCF5213 Family Configurations
Signal Name Abbreviation Function I/O
Table 16. Debug Support Signals (continued)
Development Serial
Input
Development Serial
Output
Debug Data DDATA[3:0] Display captured processor data and breakpoint status. The CLKOUT
Processor Status Clock PSTCLK Processor Status Clock - Delayed version of the processor clock. Its
Processor Status
Outputs
All Processor Status
Outputs
DSI Development Serial Input - Internally synchronized input that provides
data input for the serial communication port to the debug module, after
the DSCLK has been seen as high (logic 1).
DSO Development Serial Output - Provides serial output communication for
debug module responses. DSO is registered internally. The output is
delayed from the validation of DSCLK high.
signal can be used by the development system to know when to
sample DDATA[3:0].
rising edge appears in the center of valid PST and DDATA output.
PSTCLK indicates when the development system should sample PST
and DDATA values.
If real-time trace is not used, setting CSR[PCD] keeps PSTCLK, and
PST and DDATA outputs from toggling without disabling triggers.
Non-quiescent operation can be reenabled by clearing CSR[PCD],
although the external development systems must resynchronize with
the PST and DDATA outputs.
PSTCLK starts clocking only when the first non-zero PST value (0xC,
0xD, or 0xF) occurs during system reset exception processing.
PST[3:0] Indicate core status. Debug mode timing is synchronous with the
processor clock; status is unrelated to the current bus transfer. The
CLKOUT signal can be used by the development system to know
when to sample PST[3:0].
ALLPST Logical AND of PST[3:0]. The CLKOUT signal can be used by the
development system to know when to sample ALLPST.
I
O
O
O
O
O
1.14 EzPort Signal Descriptions
Table contains a list of EzPort external signals.
Table 17. EzPort Signal Descriptions
Signal Name Abbreviation Function I/O
EzPort Clock EZPCK Shift clock for EzPort transfers. I
EzPort Chip Select EZPCS Chip select for signalling the start and end of
EzPort Serial Data In EZPD EZPD is sampled on the rising edge of
EzPort Serial Data Out EZPQ EZPQ transitions on the falling edge of
MCF5213 ColdFire Microcontroller, Rev. 3
I
serial transfers.
I
EZPCK.
O
EZPCK.
Freescale Semiconductor24
Page 25

Electrical Characteristics
1.15 Power and Ground Pins
The pins described in Table 18 provide system power and ground to the chip. Multiple pins are provided for adequate current
capability. All power supply pins must have adequate bypass capacitance for high-frequency noise suppression.
Table 18. Power and Ground Pins
Signal Name Abbreviation Function
PLL Analog Supply VDDPLL,
VSSPLL
Positive Supply VDD These pins supply positive power to the core logic.
Ground VSS This pin is the negative supply (ground) to the chip.
Dedicated power supply signals to isolate the sensitive PLL analog
circuitry from the normal levels of noise present on the digital power
supply.
2 Electrical Characteristics
This section contains electrical specification tables and reference timing diagrams for the MCF5213 microcontroller unit,
including detailed information on power considerations, DC/AC electrical characteristics, and AC timing specifications.
NOTE
The parameters specified in this data sheet supersede any values found in the module
specifications.
MCF5213 ColdFire Microcontroller, Rev. 3
Freescale Semiconductor 25
Page 26

Electrical Characteristics
2.1 Maximum Ratings
Table 19. Absolute Maximum Ratings
Rating Symbol Value Unit
1, 2
Supply voltage V
Clock synthesizer supply voltage V
DDPLL
RAM standby supply voltage V
Digital input voltage
EXTAL pin voltage V
3
EXTAL
XTAL pin voltage V
Instantaneous maximum current
Single pin limit (applies to all pins)
4, 5
Operating temperature range (packaged) T
DD
STBY
V
IN
XTAL
I
DD
A
–0.3 to +4.0 V
–0.3 to +4.0 V
–0.3 to +4.0 V
–0.3 to +4.0 V
0 to 3.3 V
0 to 3.3 V
25 mA
–40 to 85 °C
(TL - TH)
Storage temperature range T
1
Functional operating conditions are given in DC Electrical Specifications. Absolute Maximum Ratings
stg
–65 to 150 °C
are stress ratings only, and functional operation at the maxima is not guaranteed. Stress beyond
those listed may affect device reliability or cause permanent damage to the device.
2
This device contains circuitry protecting against damage due to high static voltage or electrical fields;
however, it is advised that normal precautions be taken to avoid application of any voltages higher
than maximum-rated voltages to this high-impedance circuit. Reliability of operation is enhanced if
unused inputs are tied to an appropriate logic voltage level (V
3
Input must be current limited to the IDD value specified. To determine the value of the required
or VDD).
SS
current-limiting resistor, calculate resistance values for positive and negative clamp voltages, then
use the larger of the two values.
4
All functional non-supply pins are internally clamped to VSS and VDD.
5
The power supply must maintain regulation within operating VDD range during instantaneous and
operating maximum current conditions. If positive injection current (Vin > VDD) is greater than IDD, the
injection current may flow out of V
regulation. Ensure that the external V
and could result in the external power supply going out of
DD
load shunts current greater than maximum injection current.
DD
This is the greatest risk when the MCU is not consuming power (e.g., no clock).
MCF5213 ColdFire Microcontroller, Rev. 3
Freescale Semiconductor26
Page 27

2.2 Current Consumption
0.00
5.00
10.00
15.00
20.00
25.00
30.00
35.00
40.00
45.00
50.00
0 8 16 24 32 40 48 56 64 72 80
System Clock (MHz)
mA @ 3.3V
Stop 0 - Flash
Stop 1 - Flash
Stop 2 - Flash
Stop 3 - Flash
Wait/Doze - Flash
Run - Flash
Table 20. Current Consumption in Low-Power Mode
Electrical Characteristics
1,2
Mode 8MHz (Typ)
Stop mode 3 (Stop 11)
Stop mode 2 (Stop 10)
Stop mode 1 (Stop 01)
Stop mode 0 (Stop 00)
4,5
3
16MHz (Typ)
4
4
2.80 3.08 4.76 5.38
4
2.80 3.08 4.76 5.39
2
64MHz (Typ)280MHz (Typ)2Units
0.13 mA
2.29
Wait / Doze 11.12 20.23 30.17 33.36
Run 12.40 22.74 39.92 45.47
1
All values are measured with a 3.30 V power supply
2
Refer to the Power Management chapter in the MCF5213 Reference Manual for more information on
low-power modes.
3
CLKOUT and all peripheral clocks except UART0 and CFM off before entering low power mode. CLKOUT
is disabled. All code executed from flash memory. Code run from SRAM reduces power consumption
further. Tests performed at room temperature.
4
See the description of the Low-Power Control Register (LPCR) in the MCF5213 Reference Manual for
more information on stop modes 0–3.
5
Results are identical to STOP 00 for typical values because they only differ by CLKOUT power
consumption. CLKOUT is already disabled in this instance prior to entering low power mode.
Typical Current Consumption in Low-Power Modes
MCF5213 ColdFire Microcontroller, Rev. 3
Freescale Semiconductor 27
Page 28

Electrical Characteristics
Table 21. Typical Active Current Consumption Specifications
Characteristic Symbol
1 MHz core & I/O I
DD
Typica l1
Typical
Active
(SRAM)
—3.48—mA
Active
(Flash)
1
2
Peak
8 MHz core & I/O 7.28 13.37 19.02
16 MHz core & I/O 12.08 25.08 35.66
64 MHz core & I/O 40.14 54.62 85.01
80 MHz core & I/O 49.2 64.09 100.03
RAM standby supply current
• Normal operation: V
• Transient condition: V
• Standby operation: V
DD
STBY
DD
> V
< V
- 0.3 V
STBY
- 0.3 V > V
+ 0.5 V
SS
DD
> V
SS
+ 0.5 V
Analog supply current
• Normal operation
• Low-power stop
1
Tested at room temperature with CPU polling a status register. All clocks were off except the UART and CFM (when
I
STBY
I
DDA
—
—
N/A
N/A
N/A
3
3
3
—
—
N/A
N/A
N/A
16
50
3
3
3
running from flash memory).
2
Peak current measured with all modules active, and default drive strength with matching load.
3
Due to the errata “Non-functional RAM Standby Supply” in the MCF5213 Device Errata, V
directly to V
and cannot be used for RAM standby operation.
DD
should be connected
STBY
Unit
μA
mA
μA
mA
μA
2.3 Thermal Characteristics
Table 22 lists thermal resistance values.
Table 22. Thermal Characteristics
Characteristic Symbol Value Unit
100 LQFP Junction to ambient, natural convection Single layer board (1s) θ
Junction to ambient, natural convection Four layer board (2s2p) θ
Junction to ambient, (@200 ft/min) Single layer board (1s) θ
Junction to ambient, (@200 ft/min) Four layer board (2s2p) θ
Junction to board — θ
Junction to case — θ
Junction to top of package Natural convection Ψ
Maximum operating junction temperature — T
JA
JA
JMA
JMA
JB
JC
1,2
53
1,3
39
1,3
42
1,3
33
4
25
5
9
6
jt
j
2
105
°C / W
°C / W
°C / W
°C / W
°C / W
°C / W
°C / W
o
C
MCF5213 ColdFire Microcontroller, Rev. 3
Freescale Semiconductor28
Page 29

Electrical Characteristics
Table 22. Thermal Characteristics (continued)
Characteristic Symbol Value Unit
1,2
81 MAPBGA Junction to ambient, natural convection Single layer board (1s) θ
Junction to ambient, natural convection Four layer board (2s2p) θ
Junction to ambient, (@200 ft/min) Single layer board (1s) θ
Junction to ambient, (@200 ft/min) Four layer board (2s2p) θ
Junction to board — θ
Junction to case — θ
Junction to top of package Natural convection Ψ
Maximum operating junction temperature — T
64 LQFP Junction to ambient, natural convection Single layer board (1s) θ
Junction to ambient, natural convection Four layer board (2s2p) θ
Junction to ambient (@200 ft/min) Single layer board (1s) θ
Junction to ambient (@200 ft/min) Four layer board (2s2p) θ
Junction to board — θ
Junction to case — θ
Junction to top of package Natural convection Ψ
Maximum operating junction temperature — T
64 QFN Junction to ambient, natural convection Single layer board (1s) θ
Junction to ambient, natural convection Four layer board (2s2p) θ
Junction to ambient (@200 ft/min) Single layer board (1s) θ
Junction to ambient (@200 ft/min) Four layer board (2s2p) θ
Junction to board — θ
Junction to case (bottom) — θ
Junction to top of package Natural convection Ψ
Maximum operating junction temperature — T
1
θJA and Ψjt parameters are simulated in conformance with EIA/JESD Standard 51-2 for natural convection. Freescale
JA
JA
JMA
JMA
JB
JC
jt
j
JA
JA
JMA
JMA
JB
JC
jt
j
JA
JA
JMA
JMA
JB
JC
jt
j
61
35
50
31
20
12
105
62
43
50
36
26
105
68
24
55
19
0.6
105
2,3
2,3
2,3
4
5
6
2
1,2
1,3
1,3
1,3
4
5
9
6
2
1,2
1,3
1,3
1,3
4
8
5
6
3
recommends the use of θJA and power dissipation specifications in the system design to prevent device junction
temperatures from exceeding the rated specification. System designers should be aware that device junction temperatures
can be significantly influenced by board layout and surrounding devices. Conformance to the device junction temperature
specification can be verified by physical measurement in the customer’s system using the Ψ
parameter, the device power
jt
dissipation, and the method described in EIA/JESD Standard 51-2.
2
Per JEDEC JESD51-2 with the single-layer board (JESD51-3) horizontal.
3
Per JEDEC JESD51-6 with the board JESD51-7) horizontal.
4
Thermal resistance between the die and the printed circuit board in conformance with JEDEC JESD51-8. Board
temperature is measured on the top surface of the board near the package.
5
Thermal resistance between the die and the case top surface as measured by the cold plate method (MIL SPEC-883
Method 1012.1).
6
Thermal characterization parameter indicating the temperature difference between package top and the junction
temperature per JEDEC JESD51-2. When Greek letters are not available, the thermal characterization parameter is written
in conformance with Psi-JT.
°C / W
°C / W
°C / W
°C / W
°C / W
°C / W
°C / W
°C / W
°C / W
°C / W
°C / W
°C / W
°C / W
°C / W
°C / W
°C / W
°C / W
°C / W
°C / W
°C / W
°C / W
o
C
o
C
o
C
MCF5213 ColdFire Microcontroller, Rev. 3
Freescale Semiconductor 29
Page 30

Electrical Characteristics
TJTAP
DΘJMA
×()+=
PDKTJ273°C+()÷=
The average chip-junction temperature (TJ) in °C can be obtained from:
(1)
Where:
T
A
Θ
JA
P
D
P
INT
P
I/O
For most applications P
= ambient temperature, °C
= package thermal resistance, junction-to-ambient, °C/W
= P
+ P
INT
I/O
= chip internal power, IDD × VDD, watts
= power dissipation on input and output pins — user determined, watts
< P
I/O
and can be ignored. An approximate relationship between PD and TJ (if P
INT
is neglected) is:
I/O
(2)
Solving equations 1 and 2 for K gives:
2
K = PD × (TA + 273 °C) + Θ
JMA
× P
where K is a constant pertaining to the particular part. K can be determined from equation (3) by measuring P
(3)
D
(at equilibrium)
D
for a known TA. Using this value of K, the values of PD and TJ can be obtained by solving equations (1) and (2) iteratively for
any value of T
.
A
2.4 Flash Memory Characteristics
The flash memory characteristics are shown in Table 23 and Table 24.
Table 23. SGFM Flash Program and Erase Characteristics
(V
= 2.7 to 3.6 V)
DDF
Parameter Symbol Min Typ Max Unit
System clock (read only) f
System clock (program/erase)
1
Depending on packaging; see Ta bl e 2 .
2
Refer to the flash memory section for more information
2
sys(R)
f
sys(P/E)
0—66.67 or 80
0.15 — 66.67 or 80
Table 24. SGFM Flash Module Life Characteristics
(V
= 2.7 to 3.6 V)
DDF
Parameter Symbol Value Unit
Maximum number of guaranteed program/erase cycles
1
before failure
P/E 10,000
Data retention at average operating temperature of 85°C Retention 10 Years
1
A program/erase cycle is defined as switching the bits from 1 → 0 → 1.
2
Reprogramming of a flash memory array block prior to erase is not required.
2
1
1
Cycles
MHz
MHz
MCF5213 ColdFire Microcontroller, Rev. 3
Freescale Semiconductor30
Page 31

2.5 ESD Protection
Table 25. ESD Protection Characteristics1,
Electrical Characteristics
2
Characteristics
Symbol Value Units
ESD target for Human Body Model HBM 2000 V
ESD target for Machine Model MM 200 V
HBM circuit description R
series
1500 Ω
C 100 pF
MM circuit description R
series
0 Ω
C 200 pF
Number of pulses per pin (HBM)
• Positive pulses
• Negative pulses
Number of pulses per pin (MM)
• Positive pulses
• Negative pulses
—
—
—
—
1
1
3
3
—
—
Interval of pulses — 1 sec
1
All ESD testing is in conformity with CDF-AEC-Q100 Stress Test Qualification for
Automotive Grade Integrated Circuits.
2
A device is defined as a failure if after exposure to ESD pulses the device no longer
meets the device specification requirements. Complete DC parametric and functional
testing is performed per applicable device specification at room temperature followed by
hot temperature, unless specified otherwise in the device specification.
2.6 DC Electrical Specifications
Characteristic Symbol Min Max Unit
Supply voltage V
Standby voltage V
Input high voltage V
Input low voltage V
Input hysteresis V
Low-voltage detect trip voltage (VDD falling) V
Low-voltage detect hysteresis (VDD rising) V
Input leakage current
V
= VDD or VSS, digital pins
in
Output high voltage (all input/output and all output pins)
= –2.0 mA
I
OH
Output low voltage (all input/output and all output pins)
= 2.0mA
I
OL
Table 26. DC Electrical Specifications
DD
STBY
IH
IL
HYS
LV D
LV DH Y S
I
in
V
OH
V
OL
1
3.0 3.6 V
3.0 3.6 V
0.7 × V
DD
V
– 0.3 0.35 × V
SS
0.06 × V
DD
4.0 V
DD
—mV
2.15 2.3 V
60 120 mV
–1.0 1.0 μA
V
– 0.5 — V
DD
—0.5V
V
MCF5213 ColdFire Microcontroller, Rev. 3
Freescale Semiconductor 31
Page 32

Electrical Characteristics
Table 26. DC Electrical Specifications (continued)
Characteristic Symbol Min Max Unit
Output high voltage (high drive)
= -5 mA
I
OH
Output low voltage (high drive)
= 5 mA
I
OL
Output high voltage (low drive)
= -2 mA
I
OH
Output low voltage (low drive)
= 2 mA
I
OL
Weak internal pull Up device current, tested at VIL Max.
Input Capacitance
3
2
V
V
V
V
I
APU
C
• All input-only pins
• All input/output (three-state) pins
1
Refer to Table 27 for additional PLL specifications.
2
Refer to Ta bl e 3 for pins having internal pull-up devices.
3
This parameter is characterized before qualification rather than 100% tested.
2.7 Clock Source Electrical Specifications
Table 27. PLL Electrical Specifications
(VDD and V
= 2.7 to 3.6 V, VSS = V
DDPLL
SSPLL
OH
OL
OH
OL
in
V
= 0 V)
1
– 0.5 — V
DD
—0.5V
V
- 0.5 — V
DD
—0.5V
–10 –130 μA
pF
—
—
7
7
Characteristic Symbol Min Max Unit
PLL reference frequency range
• Crystal reference
• External reference
System frequency
1
• External clock mode
• On-chip PLL frequency
Loss of reference frequency
3, 5
Self clocked mode frequency
Crystal start-up time
5, 6
EXTAL input high voltage
• External reference
EXTAL input low voltage
• External reference
PLL lock time
Duty cycle of reference
4,7
4
MHz
f
ref_crystal
f
ref_ext
f
sys
2
2
0
f
/ 32
ref
f
LOR
4
f
SCM
V
IHEXT
t
cst
100 1000 kHz
15MHz
—10ms
2.0 V
V
ILEXT
t
lpll
t
dc
V
SS
—500μs
40 60 % f
10.0
10.0
66.67 or 80
66.67 or 80
DD
0.8
MHz
2
2
V
V
ref
MCF5213 ColdFire Microcontroller, Rev. 3
Freescale Semiconductor32
Page 33

Electrical Characteristics
Table 27. PLL Electrical Specifications (continued)
(VDD and V
Characteristic Symbol Min Max Unit
= 2.7 to 3.6 V, VSS = V
DDPLL
SSPLL
= 0 V)
Frequency un-LOCK range f
Frequency LOCK range f
CLKOUT period jitter
4, 5, 8 ,9
, measured at f
SYS
Max
C
UL
LCK
jitter
• Peak-to-peak (clock edge to clock edge)
• Long term (averaged over 2 ms interval)
On-chip oscillator frequency f
1
All internal registers retain data at 0 Hz.
2
Depending on packaging; see Ta b l e 2 .
3
Loss of Reference Frequency is the reference frequency detected internally, which transitions the PLL into self clocked mode.
4
Self clocked mode frequency is the frequency at which the PLL operates when the reference frequency falls below f
oco
–1.5 1.5 % f
–0.75 0.75 % f
—
—
10
.01
% f
7.84 8.16 MHz
LOR
default MFD/RFD settings.
5
This parameter is characterized before qualification rather than 100% tested.
6
Proper PC board layout procedures must be followed to achieve specifications.
7
This specification applies to the period required for the PLL to relock after changing the MFD frequency control bits in the
synthesizer control register (SYNCR).
8
Jitter is the average deviation from the programmed frequency measured over the specified interval at maximum f
sys
.
Measurements are made with the device powered by filtered supplies and clocked by a stable external clock signal. Noise
injected into the PLL circuitry via V
DDPLL
and V
and variation in crystal oscillator frequency increase the C
SSPLL
percentage
jitter
for a given interval.
9
Based on slow system clock of 40 MHz measured at f
sys
max.
2.8 General Purpose I/O Timing
ref
ref
sys
with
GPIO can be configured for certain pins of the QSPI, DDR Control, timer, UAR T , and Interrupt interfaces. When in GPIO mode,
the timing specification for these pins is given in Table 28 and Figure 5.
The GPIO timing is met under the following load test conditions:
•50pF/50Ω for high drive
•25pF/25Ω for low drive
Table 28. GPIO Timing
NUM Characteristic Symbol Min Max Unit
G1 CLKOUT High to GPIO Output Valid t
G2 CLKOUT High to GPIO Output Invalid t
G3 GPIO Input Valid to CLKOUT High t
G4 CLKOUT High to GPIO Input Invalid t
CHPOV
CHPOI
PVCH
CHPI
—10ns
1.5 — ns
9—ns
1.5 — ns
MCF5213 ColdFire Microcontroller, Rev. 3
Freescale Semiconductor 33
Page 34

Electrical Characteristics
G1
CLKOUT
GPIO Outputs
G2
G3 G4
GPIO Inputs
1R1
R2
CLKOUT
RSTI
RSTO
R3
R4 R4
Figure 5. GPIO Timing
2.9 Reset Timing
Table 29. Reset and Configuration Override Timing
(V
= 2.7 to 3.6 V, V
DD
SS
= 0 V, T
= TL to TH)
A
NUM Characteristic Symbol Min Max Unit
1
R1 RSTI
R2 CLKOUT High to RSTI
R3 RSTI
R4 CLKOUT High to RSTO Val i d t
1
All AC timing is shown with respect to 50% VDD levels unless otherwise noted.
2
During low power STOP, the synchronizers for the RSTI input are bypassed and RSTI is asserted asynchronously to the
system. Thus, RSTI
input valid to CLKOUT High t
Input invalid t
input valid time
2
must be held a minimum of 100 ns.
RVCH
CHRI
t
RIVT
CHROV
9—ns
1.5 — ns
5—t
—10ns
Figure 6. RSTI and Configuration Override Timing
CYC
MCF5213 ColdFire Microcontroller, Rev. 3
Freescale Semiconductor34
Page 35

2.10 I2C Input/Output Timing Specifications
Table 30 lists specifications for the I2C input timing parameters shown in Figure 7.
Table 30. I2C Input Timing Specifications between I2C_SCL and I2C_SDA
Num Characteristic Min Max Units
Electrical Characteristics
11 Start condition hold time 2 × t
I2 Clock low period 8 × t
I3 SCL/SDA rise time (V
I4 Data hold time 0 — ns
I5 SCL/SDA fall time (VIH= 2.4 V to VIL= 0.5 V) — 1 ms
I6 Clock high time 4 × t
I7 Data setup time 0 — ns
I8 Start condition setup time (for repeated start condition only) 2 × t
I9 Stop condition setup time 2 × t
Table 31 lists specifications for the I
1
2
3
Table 31 . I2C Output Timing Specifications between I2C_SCL and I2C_SDA
Num Characteristic Min Max Units
1
11
Start condition hold time 6 × t
1
Clock low period 10 × t
I2
2
I2C_SCL/I2C_SDA rise time
I3
= 0.5 V to VIH= 2.4 V)
(V
IL
1
I4
Data hold time 7 × t
3
I5
I2C_SCL/I2C_SDA fall time
= 2.4 V to VIL= 0.5 V)
(V
IH
1
I6
Clock high time 10 × t
1
Data setup time 2 × t
I7
1
I8
Start condition setup time (for repeated start
condition only)
1
Stop condition setup time 10 × t
I9
Output numbers depend on the value programmed into the IFDR; an IFDR programmed with the
maximum frequency (IFDR = 0x20) results in minimum output timings as shown in Ta bl e 31 . The I2C
interface is designed to scale the actual data transition time to move it to the middle of the SCL low
period. The actual position is affected by the prescale and division values programmed into the IFDR;
however, the numbers given in Ta b l e 3 1 are minimum values.
Because SCL and SDA are open-collector-type outputs, which the processor can only actively drive
low, the time SCL or SDA take to reach a high level depends on external signal capacitance and pull-up
resistor values.
Specified at a nominal 50-pF load.
CYC
CYC
= 0.5 V to VIH= 2.4 V) — 1 ms
IL
CYC
CYC
CYC
2
C output timing parameters shown in Figure 7.
—ns
CYC
CYC
—ns
—ns
—ns
—ns
—ns
—ns
——µs
CYC
—ns
—3ns
—ns
—ns
—ns
—ns
20 × t
CYC
CYC
CYC
CYC
MCF5213 ColdFire Microcontroller, Rev. 3
Freescale Semiconductor 35
Page 36

Electrical Characteristics
I2 I6
I1 I4
I7
I8 I9
I5
I3
SCL
SDA
Figure 7 shows timing for the values in Table 30 and Table 31.
Figure 7. I
2
C Input/Output Timings
2.11 Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC) Parameters
Table 32 lists specifications for the analog-to-digital converter.
Table 32. ADC Parameters
Name Characteristic Min Typical Max Unit
V
V
V
V
REFL
REFH
DDA
ADIN
Low reference voltage V
High reference voltage V
ADC analog supply voltage 3.0 3.3 3.6 V
Input voltages V
RES Resolution 12 — 12 Bits
INL Integral non-linearity (full input signal range)
INL Integral non-linearity (10% to 90% input signal range)
2
4
DNL Differential non-linearity — –1 < DNL < +1<+1LSB
Monotonicity GUARANTEED
f
ADIC
R
t
ADPU
t
REC
t
ADC
t
ADS
C
X
I
ADI
I
VREFHVREFH
V
OFFSET
E
GAIN
V
OFFSET
ADC internal clock 0.1 — 5.0 MHz
Conversion range V
AD
ADC power-up time
5
Recovery from auto standby — 0 1 t
Conversion time — 6 — t
Sample time — 1 — t
Input capacitance — See Figure 8 —pF
ADI
Input impedance — See Figure 8 —W
IN
Input injection current7, per pin — — 3 mA
current — 0 — m
Offset voltage internal reference — ±8 ±15 mV
Gain error (transfer path) .99 1 1.01 —
Offset voltage external reference — ±3TBDmV
SNR Signal-to-noise ratio — 62 to 66 — dB
1
SS
REFL
REFL
—V
—V
—V
REFH
DDA
REFH
V
V
V
— ±2.5 ±3LSB
— ±2.5 ±3LSB
REFL
—V
REFH
—613t
AIC
AIC
AIC
AIC
V
cycles
cycles
cycles
cycles
3
6
MCF5213 ColdFire Microcontroller, Rev. 3
Freescale Semiconductor36
Page 37

Electrical Characteristics
1
2
3
Analog Input
4
S1
S2
S3
C1
C2
S/H
C1 = C2 = 1pF
(V
REFH
- V
REFL
)/ 2
125W ESD Resistor
8pF noise damping capacitor
1
(ADC Clock Rate) × (1.4×10
-12
)
Table 32. ADC Parameters1 (continued)
Name Characteristic Min Typical Max Unit
THD Total harmonic distortion — −75 — dB
SFDR Spurious free dynamic range — 67 to 70.3 — dB
SINAD Signal-to-noise plus distortion — 61 to 63.9 — dB
ENOB Effective number of bits 9.1 10.6 — Bits
1
All measurements are preliminary pending full characterization, and made at VDD = 3.3V, V
2
INL measured from VIN = V
3
LSB = Least Significant Bit
4
INL measured from VIN = 0.1V
5
Includes power-up of ADC and V
6
ADC clock cycles
7
Current that can be injected or sourced from an unselected ADC signal input without impacting the performance of the ADC
REFL
to VIN = V
to VIN = 0.9V
REFH
REF
REFH
REFH
= 3.3V, and V
REFH
REFL
= ground
2.12 Equivalent Circuit for ADC Inputs
Figure 10-17 shows the ADC input circuit during sample and hold. S1 and S2 are always open/closed at the same time that S3
is closed/open. When S1/S2 are closed & S3 is open, one input of the sample and hold circuit moves to (V
REFH-VREFL
the other charges to the analog input voltage. When the switches are flipped, the charge on C1 and C2 are averaged via S3, with
the result that a single-ended analog input is switched to a differential voltage centered about (V
REFH-VREFL
)/2. The switches
switch on every cycle of the ADC clock (open one-half ADC clock, closed one-half ADC clock). There are additional
capacitances associated with the analog input pad, routing, etc., but these do not filter into the S/H output voltage, as S1 provides
isolation during the charge-sharing phase. One aspect of this circuit is that there is an on-going input current, which is a function
of the analog input voltage, V
and the ADC clock frequency.
REF
)/2, while
1. Parasitic capacitance due to package, pin-to-pin and pin-to-package base coupling; 1.8pF
2. Parasitic capacitance due to the chip bond pad, ESD protection devices and signal routi ng; 2.04 pF
3. Equivalent resistance for the channel select mux; 100 Ωs
4. Sampling capacitor at the sample and hold circuit. Capacitor C1 is normally disconnected from the input and is only
connected to it at sampling time; 1.4pF
5. Equivalent input imp edance, when the input is selected =
Freescale Semiconductor 37
Figure 8. Equivalent Circuit for A/D Loading
MCF5213 ColdFire Microcontroller, Rev. 3
Page 38

Electrical Characteristics
QSPI_CS[3:0]
QSPI_CLK
QSPI_DOUT
QS5
QS1
QSPI_DIN
QS3
QS4
QS2
2.13 DMA Timers Timing Specifications
Table 33 lists timer module AC timings.
Table 33. Timer Module AC Timing Specifications
Name Characteristic
T1 DTIN0 / DTIN1 / DTIN2 / DTIN3 cycle time 3 × t
T2 DTIN0 / DTIN1 / DTIN2 / DTIN3 pulse width 1 × t
1
All timing references to CLKOUT are given to its rising edge.
1
Min Max Unit
CYC
CYC
—ns
—ns
2.14 QSPI Electrical Specifications
Table 34 lists QSPI timings.
Table 34. QSPI Modules AC Timing Specifications
Name Characteristic Min Max Unit
QS1 QSPI_CS[3:0] to QSPI_CLK 1 510 t
QS2 QSPI_CLK high to QSPI_DOUT valid — 10 ns
QS3 QSPI_CLK high to QSPI_DOUT invalid (Output hold) 2 — ns
QS4 QSPI_DIN to QSPI_CLK (Input setup) 9 — ns
QS5 QSPI_DIN to QSPI_CLK (Input hold) 9 — ns
The values in Table 34 correspond to Figure 9.
CYC
Figure 9. QSPI Timing
MCF5213 ColdFire Microcontroller, Rev. 3
Freescale Semiconductor38
Page 39

2.15 JTAG and Boundary Scan Timing
TCLK
V
IL
V
IH
J3 J3
J4 J4
J2
(input)
Table 35. JTAG and Boundary Scan Timing
Electrical Characteristics
Num Characteristics
J1 TCLK frequency of operation f
J2 TCLK cycle period t
J3 TCLK clock pulse width t
J4 TCLK rise and fall times t
J5 Boundary scan input data setup time to TCLK rise t
J6 Boundary scan input data hold time after TCLK rise t
J7 TCLK low to boundary scan output data valid t
J8 TCLK low to boundary scan output high Z t
J9 TMS, TDI input data setup time to TCLK rise t
J10 TMS, TDI Input data hold time after TCLK rise t
J11 TCLK low to TDO data valid t
J12 TCLK low to TDO high Z t
J13 TRST
J14 TRST
1
JTAG_EN is expected to be a static signal. Hence, it is not associated with any timing.
assert time t
setup time (negation) to TCLK high t
1
Symbol Min Max Unit
JCYC
JCYC
JCW
JCRF
BSDST
BSDHT
BSDV
BSDZ
TAPBST
TAPBHT
TDODV
TDODZ
TRSTAT
TRSTST
DC 1/4 f
4 × t
CYC
—ns
sys/2
26 — ns
03ns
4—ns
26 — ns
033ns
033ns
4—ns
10 — ns
026ns
08ns
100 — ns
10 — ns
Figure 10. Test Clock Input Timing
MCF5213 ColdFire Microcontroller, Rev. 3
Freescale Semiconductor 39
Page 40

Electrical Characteristics
Input Data Valid
Output Data Valid
Output Data Valid
TCLK
Data Inputs
Data Outputs
Data Outputs
Data Outputs
V
IL
V
IH
J5 J6
J7
J8
J7
Input Data Valid
Output Data Valid
Output Data Valid
TCLK
TDI
TDO
TDO
TDO
TMS
V
IL
V
IH
J9 J10
J11
J12
J11
TCLK
TRST
14
13
Figure 11. Boundary Scan (JTAG) Timing
Figure 12. Test Access Port Timing
Figure 13. TRST Timing
MCF5213 ColdFire Microcontroller, Rev. 3
Freescale Semiconductor40
Page 41

2.16 Debug AC Timing Specifications
CLKOUT
PST[3:0]
D2D1
DDATA[3:0]
Table 36 lists specifications for the debug AC timing parameters shown in Figure 15.
Table 36. Debug AC Timing Specification
Num Characteristic
Min Max
D1 PST, DDATA to CLKOUT setup 4 — ns
D2 CLKOUT to PST, DDATA hold 1.5 — ns
D3
DSI-to-DSCLK setup 1 × t
1
D4
DSCLK-to-DSO hold 4 × t
D5 DSCLK cycle time 5 × t
D6 BKPT
D7 BKPT
input data setup time to CLKOUT rise 4 — ns
input data hold time to CLKOUT rise 1.5 — ns
66/80 MHz
CYC
CYC
CYC
Electrical Characteristics
Units
—ns
—ns
—ns
D8 CLKOUT high to BKPT
1
DSCLK and DSI are synchronized internally. D4 is measured from the synchronized DSCLK input relative to
high Z 0.0 10.0 ns
the rising edge of CLKOUT.
Figure 14 shows real-time trace timing for the values in Table 36.
Figure 14. Real-Time Trace AC Timing
MCF5213 ColdFire Microcontroller, Rev. 3
Freescale Semiconductor 41
Page 42

Electrical Characteristics
DSI
DSO
Current Next
CLKOUT
Past Current
DSCLK
D3
D4
D5
Figure 15 shows BDM serial port AC timing for the values in Table 36.
Figure 15. BDM Serial Port AC Timing
MCF5213 ColdFire Microcontroller, Rev. 3
Freescale Semiconductor42
Page 43

3 Mechanical Outline Drawings
This section describes the physical properties of the MCF5213 and its derivatives.
3.1 64-pin LQFP Package
Mechanical Outline Drawings
MCF5213 ColdFire Microcontroller, Rev. 3
Freescale Semiconductor 43
Page 44

Mechanical Outline Drawings
MCF5213 ColdFire Microcontroller, Rev. 3
Freescale Semiconductor44
Page 45

Mechanical Outline Drawings
MCF5213 ColdFire Microcontroller, Rev. 3
Freescale Semiconductor 45
Page 46

Mechanical Outline Drawings
3.2 64 QFN Package
MCF5213 ColdFire Microcontroller, Rev. 3
Freescale Semiconductor46
Page 47

Mechanical Outline Drawings
MCF5213 ColdFire Microcontroller, Rev. 3
Freescale Semiconductor 47
Page 48

Mechanical Outline Drawings
MCF5213 ColdFire Microcontroller, Rev. 3
Freescale Semiconductor48
Page 49

Mechanical Outline Drawings
MCF5213 ColdFire Microcontroller, Rev. 3
Freescale Semiconductor 49
Page 50

Mechanical Outline Drawings
3.3 81 MAPBGA Package
MCF5213 ColdFire Microcontroller, Rev. 3
Freescale Semiconductor50
Page 51

Mechanical Outline Drawings
MCF5213 ColdFire Microcontroller, Rev. 3
Freescale Semiconductor 51
Page 52

Mechanical Outline Drawings
3.4 100-pin LQFP Package
MCF5213 ColdFire Microcontroller, Rev. 3
Freescale Semiconductor52
Page 53

Mechanical Outline Drawings
MCF5213 ColdFire Microcontroller, Rev. 3
Freescale Semiconductor 53
Page 54

Revision History
4 Revision History
Table 37. Revision History
Revision Description
2 • Formatting, layout, spelling, and grammar corrections.
• Added revision history.
• Corrected signal names in block diagram to match those in signal description table.
• Added the following footnote to the MCF5211 FlexCAN entry:
“FlexCAN is available on the MCF5211 only in the 64 QFN package.”
• Added an entry for standby voltage (V
• Deleted the PSTCLK cycle time row in the “Debug AC timing specifications” table.
• Changed the frequency above the “Min” and “Max” column headings in the “Debug AC timing
specifications” table (was 166 MHz, is 66/80 MHz).
• Changed the minimum value for SNR, THD, SFDR, and SINAD in the “ADC parameters” table (was
TBD, is “—”).
• In the “Pin Functions by Primary and Alternate Purpose” table, changed the value in the
“Pull-up/pull-down” column for IRQ2
• Added values for I
and IOL to the “DC electrical specifications” table.
OH
• Added load test condition information to the “General Purpose I/O Timing” section.
• Deleted the “80 MHz (Peak)” column from the “Current Consumption in Low-Power Mode” table.
• In the “Typical Active Current Consumption Specifications” table, changed the typical active (SRAM)
and peak I
• Changed the I
values for the 1 MHz core & I/O entry (were TBD, are “—”).
DD
values In the “Typical Active Current Consumption Specifications” table (were 0 or
STBY
TBD, are “—”) and added an explanatory footnote referring to the MCF5213 Device Errata.
• Changed the I
values In the “Typical Active Current Consumption Specifications” table (were TBD,
DDA
are 16 mA for normal operation and 50 μA for low-power stop).
STBY
-IRQ6 (was “—”, is “pull-up”).
) to the “DC electrical specifications” table.
3 • Formatting, layout, spelling, and grammar corrections.
• Synchronized the “Pin Functions by Primary and Alternate Purpose” table in this document and the
reference manual.
• Restructured the part number summary table to include full orderable parts, and changed its name (was
“Part Number Summary”, is “Orderable Part Number Summary”).
• Updated the family configurations table to show that FlexCAN is not available on the MCF5212.
• Added specifications for V
LV D
and V
to the “DC electrical specifications” table.
LV DH Y S
MCF5213 ColdFire Microcontroller, Rev. 3
Freescale Semiconductor54
Page 55

Revision History
MCF5213 ColdFire Microcontroller, Rev. 3
Freescale Semiconductor 55
Page 56

How to Reach Us:
Home Page:
www.freescale.com
Web Support:
http://www.freescale.com/support
USA/Europe or Locations Not Listed:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
Technical Information Center, EL516
2100 East Elliot Road
Tempe, Arizona 85284
+1-800-521-6274 or +1-480-768-2130
www.freescale.com/support
Europe, Middle East, and Africa:
Freescale Halbleiter Deutschland GmbH
Technical Information Center
Schatzbogen 7
81829 Muenchen, Germany
+44 1296 380 456 (English)
+46 8 52200080 (English)
+49 89 92103 559 (German)
+33 1 69 35 48 48 (French)
www.freescale.com/support
Japan:
Freescale Semiconductor Japan Ltd.
Headquarters
ARCO Tower 15F
1-8-1, Shimo-Meguro, Meguro-ku,
Tokyo 153-0064
Japan
0120 191014 or +81 3 5437 9125
support.japan@freescale.com
Asia/Pacific:
Freescale Semiconductor Hong Kong Ltd.
Technical Information Center
2 Dai King Street
Tai Po Industrial Estate
Tai Po, N.T., Hong Kong
+800 2666 8080
support.asia@freescale.com
For Literature Requests Only:
Freescale Semiconductor Literature Distribution Center
P.O. Box 5405
Denver, Colorado 80217
1-800-441-2447 or 303-675-2140
Fax: 303-675-2150
LDCForFreescaleSemiconductor@hibbertgroup.com
Information in this document is provided solely to enable system and software
implementers to use Freescale Semiconductor products. There are no express or
implied copyright licenses granted hereunder to design or fabricate any integrated
circuits or integrated circuits based on the information in this document.
Freescale Semiconductor reserves the right to make changes without further notice to
any products herein. Freescale Semiconductor makes no warranty, representation or
guarantee regarding the suitability of its products for any particular purpose, nor does
Freescale Semiconductor assume any liability arising out of the application or use of any
product or circuit, and specifically disclaims any and all liability, including without
limitation consequential or incidental damages. “Typical” parameters that may be
provided in Freescale Semiconductor data sheets and/or specifications can and do vary
in different applications and actual performance may vary over time. All operating
parameters, including “Typicals”, must be validated for each customer application by
customer’s technical experts. Freescale Semiconductor does not convey any license
under its patent rights nor the rights of others. Freescale Semiconductor products are
not designed, intended, or authorized for use as components in systems intended for
surgical implant into the body, or other applications intended to support or sustain life,
or for any other application in which the failure of the Freescale Semiconductor product
could create a situation where personal injury or death may occur. Should Buyer
purchase or use Freescale Semiconductor products for any such unintended or
unauthorized application, Buyer shall indemnify and hold Freescale Semiconductor and
its officers, employees, subsidiaries, affiliates, and distributors harmless against all
claims, costs, damages, and expenses, and reasonable attorney fees arising out of,
directly or indirectly, any claim of personal injury or death associated with such
unintended or unauthorized use, even if such claim alleges that Freescale
Semiconductor was negligent regarding the design or manufacture of the part.
RoHS-compliant and/or Pb-free versions of Freescale products have the functionality
and electrical characteristics as their non-RoHS-compliant and/or non-Pb-free
counterparts. For further information, see http://www.freescale.com or contact your
Freescale sales representative.
For information on Freescale’s Environmental Products program, go to
http://www.freescale.com/epp.
Freescale™ and the Freescale logo are trademarks of Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
All other product or service names are the property of their respective owners.
© Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. 2007. All rights reserved.
Document Number: MCF5213EC
Rev. 3
05/2007
 Loading...
Loading...