Page 1

HC16
HC16
HC16
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
nc...
I
Order this document by
MC68HC16ZUM/AD
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
M68HC16Z Series
MC68HC16Z1
MC68CK16Z1
MC68CM16Z1
MC68HC16Z2
MC68HC16Z3
MC68HC16Z4
MC68CK16Z4
User’s Manual
NON-DISCLOSURE AGREEMENT REQUIRED
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 2

User’s Manual
nc...
I
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
Motorola reserves the right to make changes without further notice to
any products herein to improve reliability, function or design. Motorola
does not assume any liability arising out of the application or use of any
product or circuit described herein; neither does it convey any license
under its patent rights nor the rights of others. Motorola products are not
designed, intended, or authorized for use as components in systems
intendedforsurgicalimplant intothe body,or otherapplications intended
to support or sustain life, or for any other application in which the failure
of the Motorola product could create a situation where personal injury or
death may occur. Should Buyer purchase or use Motorola products for
any such unintended or unauthorized application, Buyer shall indemnify
and hold Motorola and its officers, employees, subsidiaries, affiliates,
and distributors harmless against all claims, costs, damages, and
expenses, and reasonable attorney fees arising out of, directly or
indirectly, any claim of personal injury or death associated with such
unintended or unauthorized use, even if such claim alleges that Motorola
was negligent regarding the design or manufacture of the part.
© Motorola, Inc., 1997
NON-DISCLOSURE AGREEMENT REQUIRED
User’s Manual M68HC16Z Series
2 MOTOROLA
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 3

Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Paragraph Title Page
SECTION 1
INTRODUCTION
SECTION 2
NOMENCLATURE
2.1 Symbols and Operators .............................................................................2-1
2.2 CPU16 Register Mnemonics .....................................................................2-2
2.3 Register Mnemonics ..................................................................................2-3
2.4 Conventions ..............................................................................................2-6
nc...
I
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
SECTION 3
OVERVIEW
3.1 M68HC16 Z-Series MCU Features ...........................................................3-1
3.1.1 Central Processor Unit (CPU16/CPU16L) .........................................3-1
3.1.2 System Integration Module (SIM/SIML) ............................................3-1
3.1.3 Standby RAM (SRAM) ......................................................................3-1
3.1.4 Masked ROM Module (MRM) — (MC68HC16Z2/Z3 Only) ...............3-2
3.1.5 Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC) ....................................................3-2
3.1.6 Queued Serial Module (QSM) ...........................................................3-2
3.1.7 Multichannel Communication Interface (MCCI) —
(MC68HC16Z4/CKZ4 Only) ..............................................................3-2
3.1.8 General-Purpose Timer (GPT) ..........................................................3-2
3.2 Intermodule Bus ........................................................................................3-2
3.3 System Block Diagram and Pin Assignment Diagrams .............................3-2
3.4 Pin Descriptions ......................................................................................3-11
3.5 Signal Descriptions ..................................................................................3-13
3.6 Internal Register Map ..............................................................................3-16
3.7 Address Space Maps ..............................................................................3-19
SECTION 4
CENTRAL PROCESSOR UNIT
4.1 General ......................................................................................................4-1
4.2 Register Model ..........................................................................................4-1
4.2.1 Accumulators .....................................................................................4-3
4.2.2 Index Registers .................................................................................4-3
4.2.3 Stack Pointer .....................................................................................4-3
4.2.4 Program Counter ...............................................................................4-3
4.2.5 Condition Code Register ...................................................................4-4
4.2.6 Address Extension Register and Address Extension Fields .............4-5
M68HC16 Z SERIES MOTOROLA
USER’S MANUAL i
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 4

nc...
I
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
(Continued)
Paragraph Title Page
4.2.7 Multiply and Accumulate Registers ...................................................4-5
4.3 Memory Management ...............................................................................4-5
4.3.1 Address Extension ............................................................................4-6
4.3.2 Extension Fields ................................................................................4-6
4.4 Data Types ................................................................................................4-6
4.5 Memory Organization ................................................................................4-7
4.6 Addressing Modes .....................................................................................4-8
4.6.1 Immediate Addressing Modes ...........................................................4-9
4.6.2 Extended Addressing Modes ..........................................................4-10
4.6.3 Indexed Addressing Modes .............................................................4-10
4.6.4 Inherent Addressing Mode ..............................................................4-10
4.6.5 Accumulator Offset Addressing Mode .............................................4-10
4.6.6 Relative Addressing Modes .............................................................4-10
4.6.7 Post-Modified Index Addressing Mode ............................................4-10
4.6.8 Use of CPU16 Indexed Mode to Replace M68HC11 Direct Mode ..4-11
4.7 Instruction Set .........................................................................................4-11
4.7.1 Instruction Set Summary .................................................................4-11
4.8 Comparison of CPU16 and M68HC11 CPU Instruction Sets ..................4-31
4.9 Instruction Format ...................................................................................4-33
4.10 Execution Model ......................................................................................4-34
4.10.1 Microsequencer ...............................................................................4-35
4.10.2 Instruction Pipeline ..........................................................................4-35
4.10.3 Execution Unit .................................................................................4-35
4.11 Execution Process ...................................................................................4-36
4.11.1 Changes in Program Flow ...............................................................4-36
4.12 Instruction Timing ....................................................................................4-36
4.13 Exceptions ...............................................................................................4-37
4.13.1 Exception Vectors ...........................................................................4-37
4.13.2 Exception Stack Frame ...................................................................4-38
4.13.3 Exception Processing Sequence .....................................................4-39
4.13.4 Types of Exceptions ........................................................................4-39
4.13.4.1 Asynchronous Exceptions .......................................................4-39
4.13.4.2 Synchronous Exceptions .........................................................4-39
4.13.5 Multiple Exceptions .........................................................................4-40
4.13.6 RTI Instruction .................................................................................4-40
4.14 Development Support ..............................................................................4-40
4.14.1 Deterministic Opcode Tracking .......................................................4-40
4.14.1.1 IPIPE0/IPIPE1 Multiplexing .....................................................4-41
4.14.1.2 Combining Opcode Tracking with Other Capabilities ..............4-41
4.14.2 Breakpoints .....................................................................................4-41
4.14.3 Opcode Tracking and Breakpoints ..................................................4-42
MOTOROLA M68HC16 Z SERIES
ii USER’S MANUAL
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 5

nc...
I
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
(Continued)
Paragraph Title Page
4.14.4 Background Debug Mode ................................................................4-42
4.14.4.1 Enabling BDM .........................................................................4-42
4.14.4.2 BDM Sources ..........................................................................4-42
4.14.4.3 Entering BDM ..........................................................................4-42
4.14.4.4 BDM Commands .....................................................................4-43
4.14.4.5 Returning from BDM ...............................................................4-43
4.14.4.6 BDM Serial Interface ...............................................................4-44
4.15 Recommended BDM Connection ............................................................4-45
4.16 Digital Signal Processing .........................................................................4-45
SECTION 5
SYSTEM INTEGRATION MODULE
5.1 General ......................................................................................................5-1
5.2 System Configuration ................................................................................5-2
5.2.1 Module Mapping ................................................................................5-2
5.2.2 Interrupt Arbitration ............................................................................5-3
5.2.3 Show Internal Cycles .........................................................................5-3
5.2.4 Register Access ................................................................................5-3
5.2.5 Freeze Operation ..............................................................................5-3
5.3 System Clock ............................................................................................5-4
5.3.1 Clock Sources ...................................................................................5-5
5.3.2 Clock Synthesizer Operation .............................................................5-6
5.3.3 External Bus Clock ..........................................................................5-21
5.3.4 Low-Power Operation ......................................................................5-21
5.4 System Protection ...................................................................................5-24
5.4.1 Reset Status ....................................................................................5-24
5.4.2 Bus Monitor .....................................................................................5-24
5.4.3 Halt Monitor .....................................................................................5-25
5.4.4 Spurious Interrupt Monitor ...............................................................5-25
5.4.5 Software Watchdog .........................................................................5-25
5.4.6 Periodic Interrupt Timer ...................................................................5-27
5.4.7 Interrupt Priority and Vectoring ........................................................5-28
5.4.8 Low-Power STOP Operation ...........................................................5-29
5.5 External Bus Interface .............................................................................5-29
5.5.1 Bus Control Signals .........................................................................5-31
5.5.1.1 Address Bus ............................................................................5-31
5.5.1.2 Address Strobe .......................................................................5-31
5.5.1.3 Data Bus .................................................................................5-31
5.5.1.4 Data Strobe .............................................................................5-31
5.5.1.5 Read/Write Signal ...................................................................5-32
5.5.1.6 Size Signals ............................................................................5-32
M68HC16 Z SERIES MOTOROLA
USER’S MANUAL iii
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 6

nc...
I
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
(Continued)
Paragraph Title Page
5.5.1.7 Function Codes .......................................................................5-32
5.5.1.8 Data Size Acknowledge Signals .............................................5-32
5.5.1.9 Bus Error Signal ......................................................................5-33
5.5.1.10 Halt Signal ...............................................................................5-33
5.5.1.11 Autovector Signal ....................................................................5-33
5.5.2 Dynamic Bus Sizing ........................................................................5-33
5.5.3 Operand Alignment .........................................................................5-35
5.5.4 Misaligned Operands ......................................................................5-35
5.5.5 Operand Transfer Cases .................................................................5-35
5.6 Bus Operation .........................................................................................5-36
5.6.1 Synchronization to CLKOUT ...........................................................5-36
5.6.2 Regular Bus Cycle ...........................................................................5-37
5.6.2.1 Read Cycle ..............................................................................5-37
5.6.2.2 Write Cycle ..............................................................................5-38
5.6.3 Fast Termination Cycles ..................................................................5-39
5.6.4 CPU Space Cycles ..........................................................................5-40
5.6.4.1 Breakpoint Acknowledge Cycle ...............................................5-41
5.6.4.2 LPSTOP Broadcast Cycle .......................................................5-42
5.6.5 Bus Exception Control Cycles .........................................................5-43
5.6.5.1 Bus Errors ...............................................................................5-44
5.6.5.2 Double Bus Faults ...................................................................5-45
5.6.5.3 Halt Operation .........................................................................5-45
5.6.6 External Bus Arbitration ...................................................................5-46
5.6.6.1 Show Cycles ...........................................................................5-47
5.7 Reset .......................................................................................................5-48
5.7.1 Reset Exception Processing ...........................................................5-48
5.7.2 Reset Control Logic .........................................................................5-48
5.7.3 Reset Mode Selection .....................................................................5-49
5.7.3.1 Data Bus Mode Selection ........................................................5-50
5.7.3.2 Clock Mode Selection .............................................................5-52
5.7.3.3 Breakpoint Mode Selection .....................................................5-52
5.7.4 MCU Module Pin Function During Reset ........................................5-52
5.7.5 Pin State During Reset ....................................................................5-53
5.7.5.1 Reset States of SIM Pins ........................................................5-54
5.7.5.2 Reset States of Pins Assigned to Other MCU Modules ..........5-54
5.7.6 Reset Timing ...................................................................................5-55
5.7.7 Power-On Reset ..............................................................................5-55
5.7.8 Use of the Three-State Control Pin .................................................5-56
5.7.9 Reset Processing Summary ............................................................5-57
5.7.10 Reset Status Register .....................................................................5-57
5.8 Interrupts .................................................................................................5-58
MOTOROLA M68HC16 Z SERIES
iv USER’S MANUAL
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 7

nc...
I
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
(Continued)
Paragraph Title Page
5.8.1 Interrupt Exception Processing .......................................................5-58
5.8.2 Interrupt Priority and Recognition ....................................................5-58
5.8.3 Interrupt Acknowledge and Arbitration ............................................5-59
5.8.4 Interrupt Processing Summary ........................................................5-60
5.8.5 Interrupt Acknowledge Bus Cycles ..................................................5-61
5.9 Chip-Selects ............................................................................................5-61
5.9.1 Chip-Select Registers ......................................................................5-63
5.9.1.1 Chip-Select Pin Assignment Registers ...................................5-64
5.9.1.2 Chip-Select Base Address Registers ......................................5-65
5.9.1.3 Chip-Select Option Registers ..................................................5-66
5.9.1.4 PORTC Data Register .............................................................5-67
5.9.2 Chip-Select Operation .....................................................................5-67
5.9.3 Using Chip-Select Signals for Interrupt Acknowledge .....................5-68
5.9.4 Chip-Select Reset Operation ...........................................................5-69
5.10 Parallel Input/Output Ports ......................................................................5-70
5.10.1 Pin Assignment Registers ...............................................................5-70
5.10.2 Data Direction Registers .................................................................5-70
5.10.3 Data Registers .................................................................................5-71
5.11 Factory Test ............................................................................................5-71
SECTION 6
STANDBY RAM MODULE
6.1 SRAM Register Block ................................................................................6-1
6.2 SRAM Array Address Mapping .................................................................6-2
6.3 SRAM Array Address Space Type ............................................................6-2
6.4 Normal Access ..........................................................................................6-2
6.5 Standby and Low-Power Stop Operation ..................................................6-2
6.6 Reset .........................................................................................................6-3
SECTION 7
MASKED ROM MODULE
7.1 MRM Register Block ..................................................................................7-1
7.2 MRM Array Address Mapping ...................................................................7-1
7.3 MRM Array Address Space Type ..............................................................7-2
7.4 Normal Access ..........................................................................................7-2
7.5 Low-Power Stop Mode Operation .............................................................7-3
7.6 ROM Signature ..........................................................................................7-3
7.7 Reset .........................................................................................................7-3
M68HC16 Z SERIES MOTOROLA
USER’S MANUAL v
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 8

nc...
I
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
(Continued)
Paragraph Title Page
SECTION 8
ANALOG-TO-DIGITAL CONVERTER
8.1 General ......................................................................................................8-1
8.2 External Connections ................................................................................8-1
8.2.1 Analog Input Pins ..............................................................................8-2
8.2.2 Analog Reference Pins ......................................................................8-3
8.2.3 Analog Supply Pins ...........................................................................8-3
8.3 Programmer’s Model .................................................................................8-3
8.4 ADC Bus Interface Unit .............................................................................8-3
8.5 Special Operating Modes ..........................................................................8-3
8.5.1 Low-Power Stop Mode ......................................................................8-3
8.5.2 Freeze Mode .....................................................................................8-4
8.6 Analog Subsystem ....................................................................................8-4
8.6.1 Multiplexer .........................................................................................8-4
8.6.2 Sample Capacitor and Buffer Amplifier .............................................8-5
8.6.3 RC DAC Array ...................................................................................8-5
8.6.4 Comparator .......................................................................................8-6
8.7 Digital Control Subsystem .........................................................................8-6
8.7.1 Control/Status Registers ...................................................................8-6
8.7.2 Clock and Prescaler Control ..............................................................8-6
8.7.3 Sample Time .....................................................................................8-7
8.7.4 Resolution .........................................................................................8-7
8.7.5 Conversion Control Logic ..................................................................8-7
8.7.5.1 Conversion Parameters ............................................................8-8
8.7.5.2 Conversion Modes ....................................................................8-8
8.7.6 Conversion Timing ..........................................................................8-12
8.7.7 Successive Approximation Register ................................................8-13
8.7.8 Result Registers ..............................................................................8-13
8.8 Pin Considerations ..................................................................................8-14
8.8.1 Analog Reference Pins ....................................................................8-14
8.8.2 Analog Power Pins ..........................................................................8-14
8.8.3 Analog Supply Filtering and Grounding ...........................................8-16
8.8.4 Accommodating Positive/Negative Stress Conditions .....................8-18
8.8.5 Analog Input Considerations ...........................................................8-19
8.8.6 Analog Input Pins ............................................................................8-21
8.8.6.1 Settling Time for the External Circuit .......................................8-22
8.8.6.2 Error Resulting from Leakage .................................................8-23
MOTOROLA M68HC16 Z SERIES
vi USER’S MANUAL
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 9

nc...
I
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
(Continued)
Paragraph Title Page
SECTION 9
QUEUED SERIAL MODULE
9.1 General ......................................................................................................9-1
9.2 QSM Registers and Address Map .............................................................9-2
9.2.1 QSM Global Registers .......................................................................9-2
9.2.1.1 Low-Power Stop Mode Operation .............................................9-2
9.2.1.2 Freeze Operation ......................................................................9-3
9.2.1.3 QSM Interrupts ..........................................................................9-3
9.2.2 QSM Pin Control Registers ...............................................................9-4
9.3 Queued Serial Peripheral Interface ...........................................................9-5
9.3.1 QSPI Registers ..................................................................................9-6
9.3.1.1 Control Registers ......................................................................9-6
9.3.1.2 Status Register ..........................................................................9-7
9.3.2 QSPI RAM .........................................................................................9-7
9.3.2.1 Receive RAM ............................................................................9-7
9.3.2.2 Transmit RAM ...........................................................................9-7
9.3.2.3 Command RAM .........................................................................9-8
9.3.3 QSPI Pins ..........................................................................................9-8
9.3.4 QSPI Operation .................................................................................9-8
9.3.5 QSPI Operating Modes .....................................................................9-9
9.3.5.1 Master Mode ...........................................................................9-16
9.3.5.2 Master Wrap-Around Mode .....................................................9-19
9.3.5.3 Slave Mode .............................................................................9-20
9.3.5.4 Slave Wrap-Around Mode .......................................................9-21
9.3.6 Peripheral Chip Selects ...................................................................9-21
9.4 Serial Communication Interface ..............................................................9-21
9.4.1 SCI Registers ..................................................................................9-24
9.4.1.1 Control Registers ....................................................................9-24
9.4.1.2 Status Register ........................................................................9-24
9.4.1.3 Data Register ..........................................................................9-24
9.4.2 SCI Pins ..........................................................................................9-25
9.4.3 SCI Operation ..................................................................................9-25
9.4.3.1 Definition of Terms ..................................................................9-25
9.4.3.2 Serial Formats .........................................................................9-25
9.4.3.3 Baud Clock ..............................................................................9-26
9.4.3.4 Parity Checking .......................................................................9-26
9.4.3.5 Transmitter Operation .............................................................9-27
9.4.3.6 Receiver Operation .................................................................9-28
9.4.3.7 Idle-Line Detection ..................................................................9-29
9.4.3.8 Receiver Wake-Up ..................................................................9-29
9.4.3.9 Internal Loop Mode .................................................................9-30
M68HC16 Z SERIES MOTOROLA
USER’S MANUAL vii
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 10

nc...
I
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
(Continued)
Paragraph Title Page
SECTION 10
MULTICHANNEL COMMUNICATION INTERFACE
10.1 General ....................................................................................................10-1
10.2 MCCI Registers and Address Map ..........................................................10-2
10.2.1 MCCI Global Registers ....................................................................10-2
10.2.1.1 Low-Power Stop Mode ............................................................10-2
10.2.1.2 Privilege Levels .......................................................................10-3
10.2.1.3 MCCI Interrupts .......................................................................10-3
10.2.2 Pin Control and General-Purpose I/O .............................................10-4
10.3 Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) ..............................................................10-4
10.3.1 SPI Registers ..................................................................................10-6
10.3.1.1 SPI Control Register (SPCR) ..................................................10-6
10.3.1.2 SPI Status Register (SPSR) ....................................................10-6
10.3.1.3 SPI Data Register (SPDR) ......................................................10-6
10.3.2 SPI Pins ...........................................................................................10-6
10.3.3 SPI Operating Modes ......................................................................10-7
10.3.3.1 Master Mode ...........................................................................10-7
10.3.3.2 Slave Mode .............................................................................10-8
10.3.4 SPI Clock Phase and Polarity Controls ...........................................10-8
10.3.4.1 CPHA = 0 Transfer Format .....................................................10-9
10.3.4.2 CPHA = 1 Transfer Format ...................................................10-10
10.3.5 SPI Serial Clock Baud Rate ..........................................................10-11
10.3.6 Wired-OR Open-Drain Outputs .....................................................10-11
10.3.7 Transfer Size and Direction ...........................................................10-11
10.3.8 Write Collision ...............................................................................10-12
10.3.9 Mode Fault ....................................................................................10-12
10.4 Serial Communication Interface (SCI) ...................................................10-13
10.4.1 SCI Registers ................................................................................10-13
10.4.1.1 SCI Control Registers ...........................................................10-13
10.4.1.2 SCI Status Register ...............................................................10-16
10.4.1.3 SCI Data Register .................................................................10-16
10.4.2 SCI Pins ........................................................................................10-16
10.4.3 Receive Data Pins (RXDA, RXDB) ...............................................10-17
10.4.4 Transmit Data Pins (TXDA, TXDB) ...............................................10-17
10.4.5 SCI Operation ................................................................................10-17
10.4.5.1 Definition of Terms ................................................................10-17
10.4.5.2 Serial Formats .......................................................................10-18
10.4.5.3 Baud Clock ............................................................................10-18
10.4.5.4 Parity Checking .....................................................................10-19
10.4.5.5 Transmitter Operation ...........................................................10-19
10.4.5.6 Receiver Operation ...............................................................10-20
MOTOROLA M68HC16 Z SERIES
viii USER’S MANUAL
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 11

nc...
I
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
(Continued)
Paragraph Title Page
10.4.5.7 Idle-Line Detection ................................................................10-21
10.4.5.8 Receiver Wake-Up ................................................................10-22
10.4.5.9 Internal Loop .........................................................................10-22
10.5 MCCI Initialization .................................................................................10-23
SECTION 11
GENERAL-PURPOSE TIMER
11.1 General ....................................................................................................11-1
11.2 GPT Registers and Address Map ............................................................11-2
11.3 Special Modes of Operation ....................................................................11-3
11.3.1 Low-Power Stop Mode ....................................................................11-3
11.3.2 Freeze Mode ...................................................................................11-3
11.3.3 Single-Step Mode ............................................................................11-4
11.3.4 Test Mode .......................................................................................11-4
11.4 Polled and Interrupt-Driven Operation .....................................................11-4
11.4.1 Polled Operation ..............................................................................11-4
11.4.2 GPT Interrupts .................................................................................11-5
11.5 Pin Descriptions ......................................................................................11-7
11.5.1 Input Capture Pins ...........................................................................11-7
11.5.2 Input Capture/Output Compare Pin .................................................11-7
11.5.3 Output Compare Pins ......................................................................11-7
11.5.4 Pulse Accumulator Input Pin ...........................................................11-7
11.5.5 Pulse-Width Modulation ..................................................................11-8
11.5.6 Auxiliary Timer Clock Input ..............................................................11-8
11.6 General-Purpose I/O ...............................................................................11-8
11.7 Prescaler .................................................................................................11-8
11.8 Capture/Compare Unit ..........................................................................11-10
11.8.1 Timer Counter ...............................................................................11-10
11.8.2 Input Capture Functions ................................................................11-10
11.8.3 Output Compare Functions ...........................................................11-13
11.8.3.1 Output Compare 1 .................................................................11-14
11.8.3.2 Forced Output Compare .......................................................11-14
11.9 Input Capture 4/Output Compare 5 .......................................................11-14
11.10 Pulse Accumulator ................................................................................11-14
11.11 Pulse-Width Modulation Unit .................................................................11-16
11.11.1 PWM Counter ................................................................................11-18
11.11.2 PWM Function ...............................................................................11-18
M68HC16 Z SERIES MOTOROLA
USER’S MANUAL ix
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 12

Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
(Continued)
Paragraph Title Page
APPENDIX A
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
APPENDIX B
MECHANICAL DATA AND ORDERING INFORMATION
B.1 Obtaining Updated M68HC16 Z-Series MCU Mechanical Information .... B-8
B.2 Ordering Information ................................................................................ B-8
APPENDIX C
DEVELOPMENT SUPPORT
nc...
I
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
C.1 M68MMDS1632 Modular Development System ...................................... C-1
C.2 M68MEVB1632 Modular Evaluation Board ..............................................C-2
APPENDIX D
REGISTER SUMMARY
D.1 Central Processing Unit ............................................................................D-1
D.1.1 Condition Code Register ..................................................................D-3
D.2 System Integration Module .......................................................................D-4
D.2.1 SIM Module Configuration Register ................................................. D-6
D.2.2 System Integration Test Register .....................................................D-7
D.2.3 Clock Synthesizer Control Register .................................................. D-7
D.2.4 Reset Status Register ...................................................................... D-8
D.2.5 System Integration Test Register E .................................................. D-9
D.2.6 Port E Data Register ........................................................................ D-9
D.2.7 Port E Data Direction Register .........................................................D-9
D.2.8 Port E Pin Assignment Register .....................................................D-10
D.2.9 Port F Data Register ....................................................................... D-10
D.2.10 Port F Data Direction Register ....................................................... D-11
D.2.11 Port F Pin Assignment Register .....................................................D-11
D.2.12 System Protection Control Register ...............................................D-12
D.2.13 Periodic Interrupt Control Register .................................................D-13
D.2.14 Periodic Interrupt Timer Register ................................................... D-14
D.2.15 Software Watchdog Service Register ............................................. D-15
D.2.16 Port C Data Register ......................................................................D-15
D.2.17 Chip-Select Pin Assignment Registers ........................................... D-15
D.2.18 Chip-Select Base Address Register Boot ....................................... D-17
D.2.19 Chip-Select Base Address Registers .............................................D-17
D.2.20 Chip-Select Option Register Boot .................................................. D-18
D.2.21 Chip-Select Option Registers .........................................................D-18
MOTOROLA M68HC16 Z SERIES
x USER’S MANUAL
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 13

nc...
I
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
(Continued)
Paragraph Title Page
D.2.22 Master Shift Registers ....................................................................D-22
D.2.23 Test Module Shift Count Register .................................................. D-22
D.2.24 Test Module Repetition Count Register ......................................... D-22
D.2.25 Test Module Control Register ......................................................... D-22
D.2.26 Test Module Distributed Register ...................................................D-22
D.3 Standby RAM Module ............................................................................D-23
D.3.1 RAM Module Configuration Register .............................................. D-23
D.3.2 RAM Test Register .........................................................................D-24
D.3.3 Array Base Address Register High ................................................. D-24
D.3.4 Array Base Address Register Low ................................................. D-24
D.4 Masked ROM Module .............................................................................D-25
D.4.1 Masked ROM Module Configuration Register ................................ D-25
D.4.2 ROM Array Base Address Registers .............................................. D-27
D.4.3 ROM Signature Registers High ......................................................D-27
D.4.4 ROM Bootstrap Words ...................................................................D-28
D.5 Analog-to-Digital Converter Module ....................................................... D-29
D.5.1 ADC Module Configuration Register ..............................................D-30
D.5.2 ADC Test Register ......................................................................... D-30
D.5.3 Port ADA Data Register ................................................................. D-30
D.5.4 ADC Control Register 0 .................................................................. D-31
D.5.5 ADC Control Register 1 .................................................................. D-32
D.5.6 ADC Status Register ......................................................................D-36
D.5.7 Right Justified, Unsigned Result Register ......................................D-36
D.6 Queued Serial Module ............................................................................D-38
D.6.1 QSM Configuration Register .......................................................... D-38
D.6.2 QSM Test Register ......................................................................... D-39
D.6.3 QSM Interrupt Level Register/Interrupt Vector Register ................. D-39
D.6.4 SCI Control Register ...................................................................... D-40
D.6.5 SCI Control Register 1 ................................................................... D-41
D.6.6 SCI Status Register ........................................................................ D-43
D.6.7 SCI Data Register .......................................................................... D-44
D.6.8 Port QS Data Register .................................................................... D-44
D.6.9 Port QS Pin Assignment Register/Data Direction Register ............D-45
D.6.10 QSPI Control Register 0 ................................................................. D-46
D.6.11 QSPI Control Register 1 ................................................................. D-48
D.6.12 QSPI Control Register 2 ................................................................. D-49
D.6.13 QSPI Control Register 3 ................................................................. D-50
D.6.14 Receive Data RAM ......................................................................... D-51
D.6.15 Transmit Data RAM ........................................................................ D-52
D.6.16 Command RAM .............................................................................. D-52
D.7 Multichannel Communication Interface Module ..................................... D-54
M68HC16 Z SERIES MOTOROLA
USER’S MANUAL xi
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 14

nc...
I
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
(Continued)
Paragraph Title Page
D.7.1 MCCI Module Configuration Register ............................................. D-54
D.7.2 MCCI Test Register ........................................................................ D-55
D.7.3 SCI Interrupt Level Register/MCCI Interrupt Vector Register ......... D-55
D.7.4 MCCI Interrupt Vector Register ......................................................D-56
D.7.5 SPI Interrupt Level Register ...........................................................D-56
D.7.6 MCCI Pin Assignment Register ...................................................... D-57
D.7.7 MCCI Data Direction Register ........................................................D-58
D.7.8 MCCI Port Data Registers .............................................................. D-59
D.7.9 SCI Control Register 0 ................................................................... D-59
D.7.11 SCI Status Register ........................................................................ D-62
D.7.12 SCI Data Register .......................................................................... D-63
D.7.13 SPI Control Register ....................................................................... D-64
D.7.14 SPI Status Register ........................................................................D-65
D.7.15 SPI Data Register ........................................................................... D-66
D.8 General-Purpose Timer ..........................................................................D-67
D.8.1 GPT Module Configuration Register .............................................. D-67
D.8.2 GPT Test Register .......................................................................... D-68
D.8.3 GPT Interrupt Configuration Register ............................................. D-68
D.8.4 Port GP Data Direction Register/Data Register ............................. D-69
D.8.5 OC1 Action Mask Register/Data Register ......................................D-69
D.8.6 Timer Counter Register ..................................................................D-70
D.8.7 Pulse Accumulator Control Register/Counter ................................. D-70
D.8.8 Input Capture Registers 1–3 .......................................................... D-71
D.8.9 Output Compare Registers 1–4 ...................................................... D-71
D.8.10 Input Capture 4/Output Compare 5 Register .................................. D-72
D.8.11 Timer Control Registers 1 and 2 .................................................... D-72
D.8.12 Timer Interrupt Mask Registers 1 and 2 .........................................D-72
D.8.13 Timer Interrupt Flag Registers 1 and 2 ........................................... D-74
D.8.14 Compare Force Register/PWM Control Register C ........................ D-74
D.8.15 PWM Registers A/B ........................................................................ D-76
D.8.16 PWM Count Register ...................................................................... D-76
D.8.17 PWM Buffer Registers A/B .............................................................D-76
D.8.18 GPT Prescaler ................................................................................ D-77
APPENDIX E
INITIALIZATION AND PROGRAMMING EXAMPLES
E.1 Initialization Programs .............................................................................. E-1
E.1.1 EQUATES.ASM ............................................................................... E-2
E.1.2 ORG00000.ASM .............................................................................. E-6
E.1.3 ORG00008.ASM .............................................................................. E-6
E.1.4 INITSYS.ASM ................................................................................. E-11
MOTOROLA M68HC16 Z SERIES
xii USER’S MANUAL
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 15

Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
(Continued)
Paragraph Title Page
E.1.5 INITRAM.ASM ................................................................................ E-11
E.1.6 INITSCI.ASM .................................................................................. E-12
E.2 Programming Examples ......................................................................... E-12
E.2.1 SIM Programming Examples .......................................................... E-13
E.2.1.1 Example 1 - Using Ports E and F ........................................... E-13
E.2.1.2 Example 2 - Using Chip-Selects ............................................ E-14
E.2.1.3 Example 3 - Changing Clock Frequencies ............................. E-16
E.2.1.4 Example 4 - Software Watchdog, Periodic Interrupt,
and Autovector Demo ............................................................ E-18
E.2.2 CPU16 Programming Example ...................................................... E-23
E.2.2.1 Example 5 - Indexed and Extended Addressing .................... E-23
nc...
I
E.2.3 QSM/SCI Programming Example ................................................... E-24
E.2.3.1 Example 6 - Using an SCI Port .............................................. E-24
E.2.4 GPT Programming Example .......................................................... E-25
E.2.4.1 Example 7 - Basic GPT Functions ......................................... E-25
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
M68HC16 Z SERIES MOTOROLA
USER’S MANUAL xiii
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 16

Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
nc...
I
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
MOTOROLA M68HC16 Z SERIES
xiv USER’S MANUAL
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 17

nc...
I
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
LIST OF ILLUSTRATIONS
Figure Title Page
3-1 MC68HC16Z1/CK16Z1/CM16Z1 Block Diagram ...........................................3-4
3-2 MC68HC16Z2/Z3 Block Diagram ...................................................................3-5
3-3 MC68HC16Z4/CK16Z4 Block Diagram ..........................................................3-6
3-4 MC68HC16Z1/CKZ1/CMZ1/Z2/Z3 Pin Assignments
for 132-Pin Package .......................................................................................3-7
3-5 MC68HC16Z1/CKZ1/CMZ1/Z2/Z3 Pin Assignments
for 144-Pin Package .......................................................................................3-8
3-6 MC68HC16Z4/CKZ4 Pin Assignments for 132-Pin Package .........................3-9
3-7 MC68HC16Z4/CKZ4 Pin Assignments for 144-Pin Package .......................3-10
3-8 MC68HC16Z1/CKZ1/CMZ1 Address Map ................................................... 3-17
3-9 MC68HC16Z2/Z3 Address Map ...................................................................3-18
3-10 MC68HC16Z4/CKZ4 Address Map ..............................................................3-18
3-11 MC68HC16Z1/CKZ1/CMZ1 Combined Program
and Data Space Map ....................................................................................3-20
3-12 MC68HC16Z2/Z3 Combined Program and Data Space Map ...................... 3-21
3-13 MC68HC16Z4/CKZ4 Combined Program and Data Space Map ................. 3-22
3-14 MC68HC16Z1/CKZ1/CMZ1 Separate Program
and Data Space Map ....................................................................................3-23
3-15 MC68HC16Z2/Z3 Separate Program and Data Space Map ........................3-24
3-16 MC68HC16Z4/CKZ4 Separate Program and Data Space Map ...................3-25
4-1 CPU16 Register Model ...................................................................................4-2
4-2 Condition Code Register ................................................................................ 4-4
4-3 Data Types and Memory Organization ...........................................................4-8
4-4 Basic Instruction Formats .............................................................................4-34
4-5 Instruction Execution Model ......................................................................... 4-35
4-6 Exception Stack Frame Format ....................................................................4-38
4-7 BDM Serial I/O Block Diagram .....................................................................4-44
4-8 BDM Connector Pinout .................................................................................4-45
5-1 System Integration Module Block Diagram .................................................... 5-2
5-2 System Clock Block Diagram .........................................................................5-4
5-3 Slow Reference Crystal Circuit .......................................................................5-5
5-4 Fast Reference Crystal Circuit .......................................................................5-5
5-5 System Clock Filter Networks ........................................................................5-7
5-6 SIM LPSTOP Flowchart ............................................................................... 5-22
5-7 SIML LPSTOP Flowchart ............................................................................. 5-23
5-8 System Protection ........................................................................................ 5-24
5-9 Periodic Interrupt Timer and Software Watchdog Timer .............................. 5-27
5-10 MCU Basic System ......................................................................................5-30
5-11 Operand Byte Order .....................................................................................5-34
M68HC16 Z SERIES MOTOROLA
USER’S MANUAL xv
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 18

nc...
I
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
LIST OF ILLUSTRATIONS
(Continued)
Figure Title Page
5-12 Word Read Cycle Flowchart .........................................................................5-38
5-13 Write Cycle Flowchart ..................................................................................5-39
5-14 CPU Space Address Encoding ....................................................................5-41
5-15 Breakpoint Operation Flowchart ...................................................................5-42
5-16 LPSTOP Interrupt Mask Level ......................................................................5-43
5-17 Bus Arbitration Flowchart for Single Request ...............................................5-47
5-18 Preferred Circuit for Data Bus Mode Select Conditioning ............................ 5-50
5-19 Alternate Circuit for Data Bus Mode Select Conditioning .............................5-51
5-20 Power-On Reset ...........................................................................................5-56
5-21 Basic MCU System ......................................................................................5-62
5-22 Chip-Select Circuit Block Diagram ............................................................... 5-63
5-23 CPU Space Encoding for Interrupt Acknowledge .........................................5-68
8-1 ADC Block Diagram .......................................................................................8-2
8-2 8-Bit Conversion Timing ...............................................................................8-12
8-3 10-Bit Conversion Timing .............................................................................8-13
8-4 Analog Input Circuitry ...................................................................................8-15
8-5 Errors Resulting from Clipping .....................................................................8-16
8-6 Star-Ground at the Point of Power Supply Origin .........................................8-17
8-7 Input Pin Subjected to Negative Stress ........................................................8-18
8-8 Voltage Limiting Diodes in a Negative Stress Circuit ................................... 8-19
8-9 External Multiplexing of Analog Signal Sources ...........................................8-20
8-10 Electrical Model of an A/D Input Pin .............................................................8-21
9-1 QSM Block Diagram .......................................................................................9-1
9-2 QSPI Block Diagram ......................................................................................9-5
9-3 QSPI RAM ......................................................................................................9-7
9-4 Flowchart of QSPI Initialization Operation ....................................................9-10
9-5 Flowchart of QSPI Master Operation (Part 1) ..............................................9-11
9-6 Flowchart of QSPI Master Operation (Part 2) ..............................................9-12
9-7 Flowchart of QSPI Master Operation (Part 3) ..............................................9-13
9-8 Flowchart of QSPI Slave Operation (Part 1) ................................................9-14
9-9 Flowchart of QSPI Slave Operation (Part 2) ................................................9-15
9-10 SCI Transmitter Block Diagram ....................................................................9-22
9-11 SCI Receiver Block Diagram ........................................................................9-23
10-1 MCCI Block Diagram ....................................................................................10-1
10-2 SPI Block Diagram ....................................................................................... 10-5
10-3 CPHA = 0 SPI Transfer Format .................................................................... 10-9
10-4 CPHA = 1 SPI Transfer Format .................................................................. 10-10
10-5 SCI Transmitter Block Diagram ..................................................................10-14
MOTOROLA M68HC16 Z SERIES
xvi USER’S MANUAL
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 19

nc...
I
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
LIST OF ILLUSTRATIONS
(Continued)
Figure Title Page
10-6 SCI Receiver Block Diagram ......................................................................10-15
11-1 GPT Block Diagram ......................................................................................11-2
11-2 Prescaler Block Diagram ..............................................................................11-9
11-3 Capture/Compare Unit Block Diagram .......................................................11-11
11-4 Input Capture Timing Example ...................................................................11-13
11-5 Pulse Accumulator Block Diagram .............................................................11-15
11-6 PWM Block Diagram .................................................................................. 11-17
A-1 CLKOUT Output Timing Diagram .................................................................A-28
A-2 External Clock Input Timing Diagram ...........................................................A-28
A-3 ECLK Output Timing Diagram ......................................................................A-28
A-4 Read Cycle Timing Diagram ........................................................................A-29
A-5 Write Cycle Timing Diagram .........................................................................A-30
A-6 Fast Termination Read Cycle Timing Diagram ............................................A-31
A-7 Fast Termination Write Cycle Timing Diagram .............................................A-32
A-8 Bus Arbitration Timing Diagram — Active Bus Case ...................................A-33
A-9 Bus Arbitration Timing Diagram — Idle Bus Case .......................................A-34
A-10 Show Cycle Timing Diagram ........................................................................A-35
A-11 Chip-Select Timing Diagram ........................................................................A-36
A-12 Reset and Mode Select Timing Diagram ......................................................A-36
A-13 Background Debug Mode Timing Diagram (Serial Communication) ............A-39
A-14 Background Debug Mode Timing Diagram (Freeze Assertion) ....................A-39
A-15 ECLK Timing Diagram ..................................................................................A-44
A-16 QSPI Timing — Master, CPHA = 0 ..............................................................A-47
A-17 QSPI Timing — Master, CPHA = 1 ..............................................................A-47
A-18 QSPI Timing — Slave, CPHA = 0 ................................................................A-48
A-19 QSPI Timing — Slave, CPHA = 1 ................................................................A-48
A-20 SPI Timing — Master, CPHA = 0 .................................................................A-51
A-21 SPI Timing — Master, CPHA = 1 .................................................................A-51
A-22 SPI Timing — Slave, CPHA = 0 ...................................................................A-52
A-23 SPI Timing — Slave, CPHA = 1 ...................................................................A-52
A-24 Input Signal Conditioner Timing ...................................................................A-53
A-25 Pulse Accumulator — Event Counting Mode (Leading Edge) ......................A-54
A-26 Pulse Accumulator — Gated Mode (Count While Pin High) ........................A-55
A-27 Pulse Accumulator — Using TOF as Gated Mode Clock .............................A-56
A-28 PWMx (PWMx Register = 01, Fast Mode) ...................................................A-56
A-29 Output Compare (Toggle Pin State) .............................................................A-57
A-30 Input Capture (Capture on Rising Edge) ......................................................A-58
A-31 General-Purpose Input .................................................................................A-59
A-32 General-Purpose Output (Causes Input Capture) ........................................A-60
M68HC16 Z SERIES MOTOROLA
USER’S MANUAL xvii
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 20

Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
LIST OF ILLUSTRATIONS
(Continued)
Figure Title Page
A-33 Force Compare (CLEAR) .............................................................................A-61
A-34 Low Voltage 8-Bit ADC Conversion Accuracy ..............................................A-68
A-35 8-Bit ADC Conversion Accuracy ..................................................................A-69
A-36 Low Voltage 10-Bit ADC Conversion Accuracy ............................................A-70
A-37 10-Bit ADC Conversion Accuracy ................................................................A-71
B-1 MC68HC16Z1/CKZ1/CMZ1/Z2/Z3 Pin Assignments
for 132-Pin Package .......................................................................................B-2
B-2 MC68HC16Z4/CKZ4 Pin Assignments for 132-Pin Package .........................B-3
B-3 Case 831A-01 — 132-Pin Package Dimensions ............................................B-4
B-4 MC68HC16Z1/CKZ1/CMZ1/Z2/Z3 Pin Assignments
nc...
I
B-5 MC68HC16Z4/CKZ4 Pin Assignments for 144-Pin Package .........................B-6
B-6 Case 918 — 144-Pin Package Dimensions ...................................................B-7
for 144-Pin Package .......................................................................................B-5
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
D-1 CPU16 Register Model ...................................................................................D-2
MOTOROLA M68HC16 Z SERIES
xviii USER’S MANUAL
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 21

Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
LIST OF TABLES
Table Title Page
1-1 M68HC16 Z-Series MCUs...............................................................................1-1
1-2 Z-Series MCU Reference Frequencies...........................................................1-2
3-1 M68HC16 Z-Series Pin Characteristics.........................................................3-11
3-2 M68HC16 Z-Series Driver Types..................................................................3-12
3-3 M68HC16 Z-Series Power Connections....................................................... 3-13
3-4 M68HC16 Z-Series Signal Characteristics.................................................... 3-13
3-5 M68HC16 Z-Series Signal Function.............................................................. 3-15
4-1 Addressing Modes...........................................................................................4-9
4-2 Instruction Set Summary...............................................................................4-12
nc...
I
4-3 Instruction Set Abbreviations and Symbols................................................... 4-30
4-4 CPU16 Implementation of M68HC11 CPU Instructions................................4-32
4-5 Exception Vector Table.................................................................................4-38
4-6 IPIPE0/IPIPE1 Encoding...............................................................................4-41
4-7 Command Summary.....................................................................................4-43
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
5-1 Show Cycle Enable Bits..................................................................................5-3
5-2 16.78-MHz Clock Control Multipliers...............................................................5-9
5-3 20.97-MHz Clock Control Multipliers.............................................................5-11
5-4 25.17-MHz Clock Control Multipliers.............................................................5-13
5-5 16.78-MHz System Clock Frequencies.........................................................5-15
5-6 System Clock Frequencies for a 20.97-MHz System.................................... 5-17
5-7 System Clock Frequencies for a 25.17-MHz System.................................... 5-19
5-8 Bus Monitor Period........................................................................................ 5-25
5-9 MODCLK Pin and SWP Bit During Reset..................................................... 5-26
5-10 Software Watchdog Divide Ratio...................................................................5-27
5-11 MODCLK Pin and PTP Bit at Reset..............................................................5-28
5-12 Periodic Interrupt Priority............................................................................... 5-29
5-13 Size Signal Encoding....................................................................................5-32
5-14 Address Space Encoding..............................................................................5-32
5-15 Effect of
5-16 Operand Alignment.......................................................................................5-36
5-17
5-18 Reset Source Summary................................................................................5-49
5-19 Reset Mode Selection...................................................................................5-49
5-20 Module Pin Functions.................................................................................... 5-53
5-21 SIM Pin Reset States....................................................................................5-54
5-22 Chip-Select Pin Functions.............................................................................5-64
5-23 Pin Assignment Field Encoding.....................................................................5-64
5-24 Block Size Encoding......................................................................................5-65
DSACK, BERR, and HALT Assertion Results ...............................................5-44
DSACK Signals...............................................................................5-34
M68HC16 Z SERIES MOTOROLA
USER’S MANUAL xix
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 22

nc...
I
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
LIST OF TABLES
(Continued)
Table Title Page
5-25 Chip-Select Base and Option Register Reset Values...................................5-69
5-26
6-1 SRAM Configuration........................................................................................6-1
6-2 SRAM Array Address Space Type..................................................................6-2
7-1 ROM Array Space Field..................................................................................7-2
7-2 Wait States Field.............................................................................................7-3
8-1 FRZ Field Selection......................................................................................... 8-4
8-2 Multiplexer Channel Sources..........................................................................8-5
8-3 Prescaler Output.............................................................................................8-7
8-4 TS Field Selection...........................................................................................8-7
8-5 Conversion Parameters Controlled by ADCTL1..............................................8-8
8-6 ADC Conversion Modes.................................................................................. 8-8
8-7 Single-Channel Conversions (MULT = 0)......................................................8-10
8-8 Multiple-Channel Conversions (MULT = 1)................................................... 8-11
8-9 Result Register Formats................................................................................8-14
8-10 External Circuit Settling Time (10-Bit Conversions)......................................8-23
8-11 Error Resulting From Input Leakage (IOFF)..................................................8-23
9-1 Effect of DDRQS on QSM Pin Function..........................................................9-4
9-2 QSPI Pins........................................................................................................ 9-8
9-3 Bits Per Transfer...........................................................................................9-18
9-4 Serial Frame Formats....................................................................................9-26
9-5 Effect of Parity Checking on Data Size.........................................................9-27
10-1 MCCI Interrupt Vectors..................................................................................10-3
10-2 Pin Assignments............................................................................................10-4
10-3 SPI Pin Functions.......................................................................................... 10-7
10-4 SCK Frequencies........................................................................................10-11
10-5 SCI Pins......................................................................................................10-17
10-6 Serial Frame Formats..................................................................................10-18
10-7 Effect of Parity Checking on Data Size.......................................................10-19
CSBOOT Base and Option Register Reset Values....................................... 5-70
11-1 GPT Status Flags..........................................................................................11-5
11-2 GPT Interrupt Sources..................................................................................11-6
11-3 PWM Frequency Ranges............................................................................11-18
A-1 Maximum Ratings............................................................................................A-1
A-2 Typical Ratings, 2.7 to 3.6V, 16.78-MHz Operation........................................A-2
MOTOROLA M68HC16 Z SERIES
xx USER’S MANUAL
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 23

nc...
I
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
LIST OF TABLES
(Continued)
Table Title Page
A-3 Typical Ratings, 5V, 16.78-MHz Operation.....................................................A-3
A-4 Typical Ratings, 20.97-MHz Operation ...........................................................A-3
A-5 Typical Ratings, 25.17-MHz ............................................................................A-4
A-6 Thermal Characteristics ..................................................................................A-5
A-7 Low Voltage Clock Control Timing ..................................................................A-6
A-8 16.78-MHz Clock Control Timing ....................................................................A-7
A-9 20.97-MHz Clock Control Timing ....................................................................A-8
A-10 25.17-MHz Clock Control Timing ....................................................................A-9
A-11 Low Voltage 16.78-MHz DC Characteristics.................................................A-10
A-12 16.78-MHz DC Characteristics......................................................................A-12
A-13 20.97-MHz DC Characteristics......................................................................A-14
A-14 25.17-MHz DC Characteristics......................................................................A-16
A-15 Low Voltage 16.78-MHz AC Timing..............................................................A-19
A-16 16.78-MHz AC Timing...................................................................................A-21
A-17 20.97-MHz AC Timing...................................................................................A-23
A-18 25.17-MHz AC Timing...................................................................................A-25
A-19 Low Voltage 16.78-MHz Background Debug Mode Timing ..........................A-37
A-20 16.78-MHz Background Debug Mode Timing...............................................A-37
A-21 20.97-MHz Background Debug Mode Timing...............................................A-38
A-22 25.17-MHz Background Debug Mode Timing...............................................A-38
A-23 Low Voltage ECLK Bus Timing.....................................................................A-40
A-24 16.78-MHz ECLK Bus Timing .......................................................................A-41
A-25 20.97-MHz ECLK Bus Timing .......................................................................A-42
A-26 25.17-MHz ECLK Bus Timing .......................................................................A-43
A-27 Low Voltage QSPI Timing.............................................................................A-45
A-28 QSPI Timing..................................................................................................A-46
A-29 Low Voltage SPI Timing................................................................................A-49
A-30 SPI Timing.....................................................................................................A-50
A-31 General-Purpose Timer AC Characteristics..................................................A-53
A-32 ADC Maximum Ratings.................................................................................A-62
A-33 Low Voltage ADC DC Electrical Characteristics (Operating) ........................A-63
A-34 Low Voltage ADC AC Characteristics (Operating)........................................A-63
A-35 5V ADC DC Electrical Characteristics (Operating)........................................A-64
A-36 ADC AC Characteristics (Operating).............................................................A-65
A-37 Low Voltage ADC Conversion Characteristics (Operating)...........................A-66
A-38 ADC Conversion Characteristics (Operating)................................................A-67
B-1 M68HC16 Z-Series Ordering Information........................................................B-8
D-1 Module Address Map ......................................................................................D-1
D-2 SIM Address Map............................................................................................D-4
M68HC16 Z SERIES MOTOROLA
USER’S MANUAL xxi
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 24

nc...
I
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
LIST OF TABLES
(Continued)
Table Title Page
D-3 Show Cycle Enable Bits..................................................................................D-6
D-4 Port E Pin Assignments.................................................................................D-10
D-5 Port F Pin Assignments.................................................................................D-11
D-6 Software Watchdog Divide Ratio...................................................................D-12
D-7 Bus Monitor Time-Out Period........................................................................D-13
D-8 Pin Assignment Field Encoding.....................................................................D-16
D-9 CSPAR0 Pin Assignments............................................................................D-16
D-10 CSPAR1 Pin Assignments............................................................................D-17
D-11 Reset Pin Function of CS[10:6].....................................................................D-17
D-12 Block Size Field Bit Encoding........................................................................D-18
D-13 BYTE Field Bit Encoding...............................................................................D-19
D-14 Read/Write Field Bit Encoding......................................................................D-19
D-15
D-16 Memory Access Times at 16.78, 20.97, and 25.17 MHz...............................D-20
D-17 Address Space Bit Encodings.......................................................................D-21
D-18 Interrupt Priority Level Field Encoding..........................................................D-21
D-19 SRAM Address Map......................................................................................D-23
D-20 SRAM Array Address Space Type................................................................D-23
D-21 MRM Address Map........................................................................................D-25
D-22 ROM Array Space Field................................................................................D-26
D-23 Wait States Field...........................................................................................D-26
D-24 ADC Module Address Map............................................................................D-29
D-25 Freeze Encoding...........................................................................................D-30
D-26 Sample Time Selection.................................................................................D-31
D-27 Prescaler Output...........................................................................................D-32
D-28 ADC Conversion Mode..................................................................................D-33
D-29 Single-Channel Conversions (MULT = 0)......................................................D-34
D-30 Multiple-Channel Conversions (MULT = 1)...................................................D-35
D-31 QSM Address Map........................................................................................D-38
D-32 Examples of SCI Baud Rates........................................................................D-41
D-33 PQSPAR Pin Assignments............................................................................D-45
D-34 Effect of DDRQS on QSM Pin Function........................................................D-46
D-35 Bits Per Transfer...........................................................................................D-47
D-36 Examples of SCK Frequencies.....................................................................D-48
D-37 MCCI Address Map.......................................................................................D-54
D-38 Interrupt Vector Sources...............................................................................D-56
D-39 MPAR Pin Assignments................................................................................D-57
D-40 Effect of MDDR on MCCI Pin Function.........................................................D-58
D-41 Examples of SCI Baud Rates........................................................................D-60
D-42 GPT Address Map.........................................................................................D-67
D-43 GPT Interrupt Sources..................................................................................D-69
DSACK Field Encoding.................................................................................D-20
MOTOROLA M68HC16 Z SERIES
xxii USER’S MANUAL
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 25

Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
LIST OF TABLES
(Continued)
Table Title Page
D-44 PAMOD and PEDGE Effects.........................................................................D-71
D-45 PACLK[1:0] Effects........................................................................................D-71
D-46 OM/OL[5:2] Effects........................................................................................D-72
D-47 EDGE[4:1] Effects.........................................................................................D-72
D-48 CPR[2:0]/Prescaler Select Field....................................................................D-73
D-49 PPR[2:0] Field...............................................................................................D-75
D-50 PWM Frequency Ranges..............................................................................D-76
nc...
I
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
M68HC16 Z SERIES MOTOROLA
USER’S MANUAL xxiii
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 26

Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
nc...
I
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
MOTOROLA M68HC16 Z SERIES
xxiv USER’S MANUAL
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 27
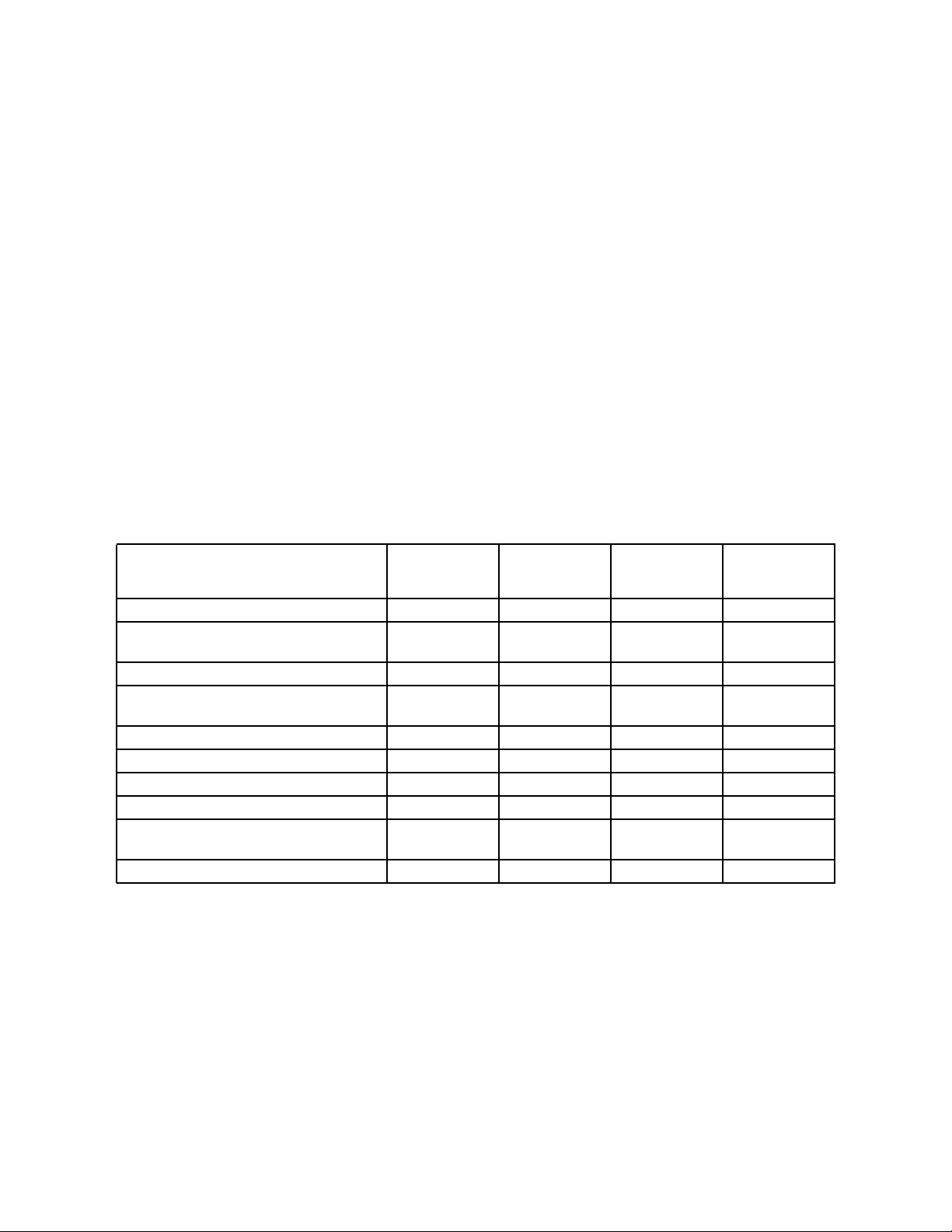
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
SECTION 1
INTRODUCTION
M68HC16 Z-series microcontrollers (including the MC68HC16Z1, MC68CM16Z1,
MC68CK16Z1, MC68HC16Z2, MC68HC16Z3, MC68HC16Z4, and MC68CK16Z4)
are high-speed 16-bit control units that are upwardly code compatible with M68HC11
controllers. All are members of the M68HC16 Family of modular microcontrollers.
M68HC16 microcontroller units (MCUs) are built from standard modules that interface
via a common internal bus. Standardization facilitates rapid development of devices
tailored for specific applications.
M68HC16 Z-series MCUs incorporate a number of different modules. Refer to Table
nc...
I
1-1 for information on the contents of a specific Z-series MCU. (
module is used in the MCU. All of these modules are interconnected by the intermodule bus (IMB).
X) indicates that the
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
Table 1-1 M68HC16 Z-Series MCUs
Modules
Central Processor Unit (CPU16) X X X —
Low-Power Central Processor
Unit (CPU16L)
System Integration Module (SIM) X X X —
Low-Power System Integration
Module (SIML)
Standby RAM (SRAM) 1 Kbyte 2 Kbytes 4 Kbytes 1 Kbyte
Masked ROM Module (MRM) — 8 Kbytes 8 Kbytes —
Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC) XXXX
Queued Serial Module (QSM) X X X —
Multichannel Communication
Interface (MCCI)
General-Purpose Timer (GPT) XXXX
NOTES:
1. “C” designator indicates a 2.7V to 3.6V part; “M” indicates a fast reference frequency and “K” indicates a slow
reference frequency. “HC” stands for HCMOS.
MC68HC16Z1
MC68CK16Z1
MC68CM16Z1
———X
———X
———X
1
MC68HC16Z2 MC68HC16Z3
1
MC68HC16Z4
MC68CK16Z4
1
The maximum system clock for M68HC16 Z-series MCUs can be either 16.78 MHz,
20.97 MHz, or 25.17 MHz. An internal phase-locked loop circuit synthesizes the system clock from a slow (typically 32.768 kHz) or fast (typically 4.194 MHz) reference, or
uses an external frequency source. Refer to Table 1-2 for information on which reference frequency is applied to a particular MCU. (
X) indicates the reference frequency
applicable to the MCU.
M68HC16 Z SERIES INTRODUCTION MOTOROLA
USER’S MANUAL 1-1
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 28
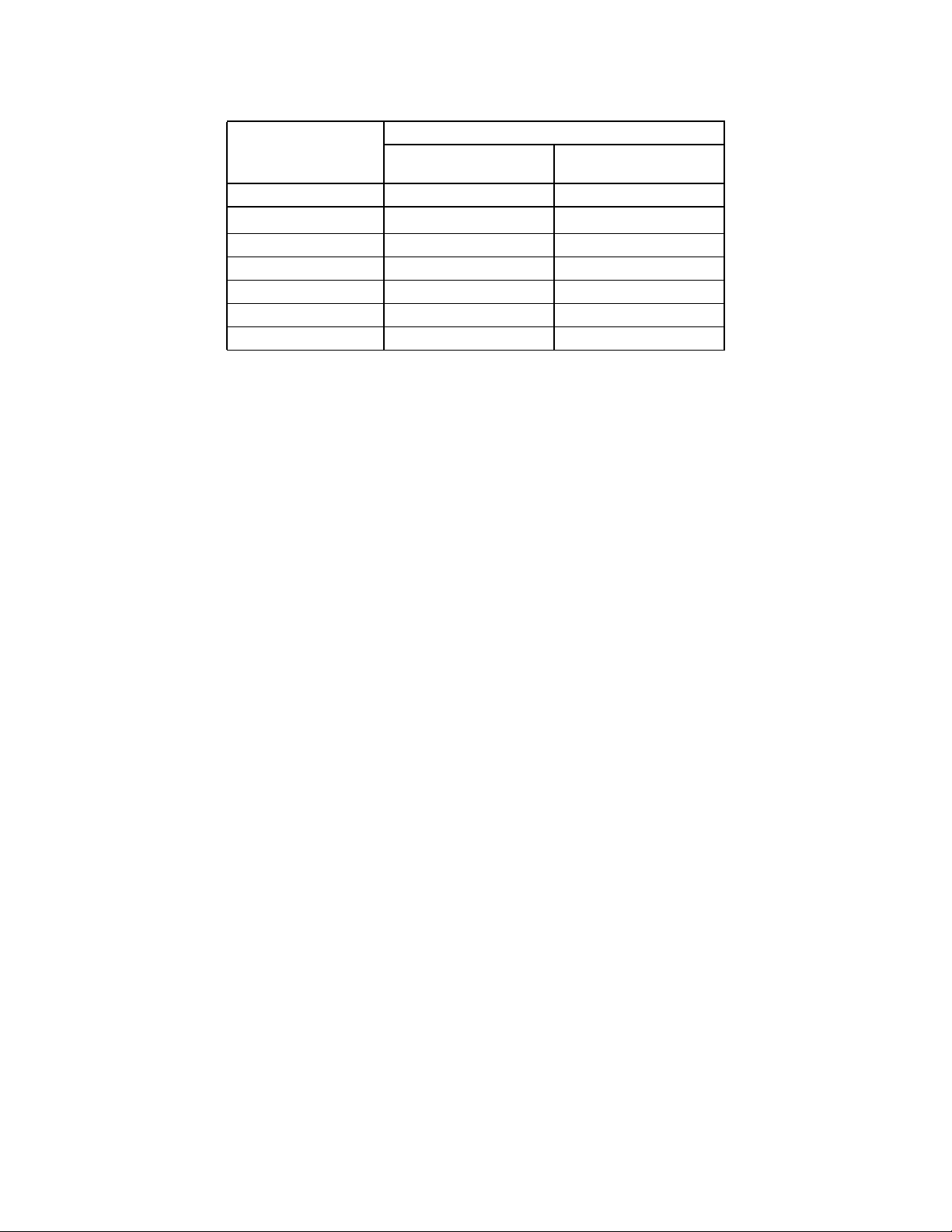
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
Table 1-2 Z-Series MCU Reference Frequencies
Nominal Reference Frequency
MCU
MC68HC16Z1 X —
MC68CM16Z1
MC68CK16Z1 X —
MC68HC16Z2 — X
MC68HC16Z3 — X
MC68HC16Z4 X —
MC68CK16Z4 X —
NOTES:
1. The nominal slow reference frequency is 32.768 kHz, but can range from
20 to 50 kHz. The nominal fast reference frequency is 4.194 MHz, but can
range from 1MHz to 6.25 MHz.
nc...
I
Slow
(32.768 kHz)
—X
(4.194 MHz)
1
Fast
System hardware and software allow changes in clock rate during operation. Because
the MCUs are a fully static design, register and memory contents are not affected by
clock rate changes.
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
High-density complementary metal-oxide semiconductor (HCMOS) architecture
makes the basic power consumption low. Power consumption can be minimized by
stopping the system clocks. The M68HC16 instruction set includes a low-power stop
(LPSTOP) command that efficiently implements this capability. Individual stop bits in
each module allow for selective power reduction.
Documentation for the Modular Microcontroller Family follows the modular construction of the devices in the product line. Each device has a comprehensive user’s manual that provides sufficient information for normal operation of the device. The user’s
manual is supplemented by module reference manuals that provide detailed information about module operation and applications. Refer to Motorola publication
Microcontroller Unit (AMCU) Literature
(BR1116/D) for a complete list of documenta-
Advanced
tion to supplement this manual.
MOTOROLA INTRODUCTION M68HC16 Z SERIES
1-2 USER’S MANUAL
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 29
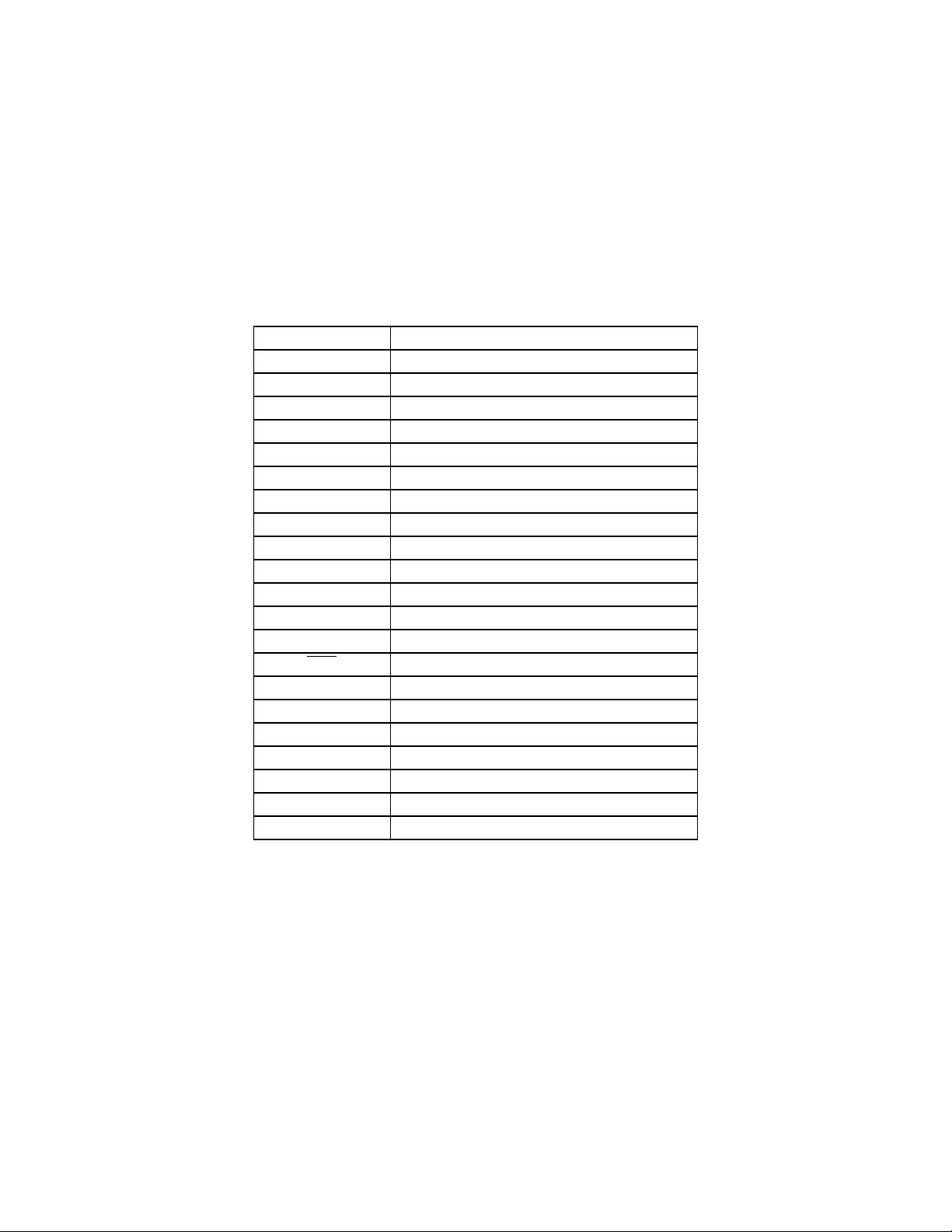
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
SECTION 2
NOMENCLATURE
The following tables show the nomenclature used throughout the M68HC16 Z-series
manual.
2.1 Symbols and Operators
Symbol Function
+ Addition
- Subtraction (two’s complement) or negation
* Multiplication
nc...
I
cale Semiconductor,
/ Division
> Greater
< Less
= Equal
≥ Equal or greater
≤ Equal or less
≠ Not equal
• AND
✛ Inclusive OR (OR)
⊕ Exclusive OR (EOR)
NOT Complementation
: Concatenation
⇒ Transferred
⇔ Exchanged
± Sign bit; also used to show tolerance
« Sign extension
% Binary value
$ Hexadecimal value
Frees
M68HC16 Z SERIES NOMENCLATURE MOTOROLA
USER’S MANUAL 2-1
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 30
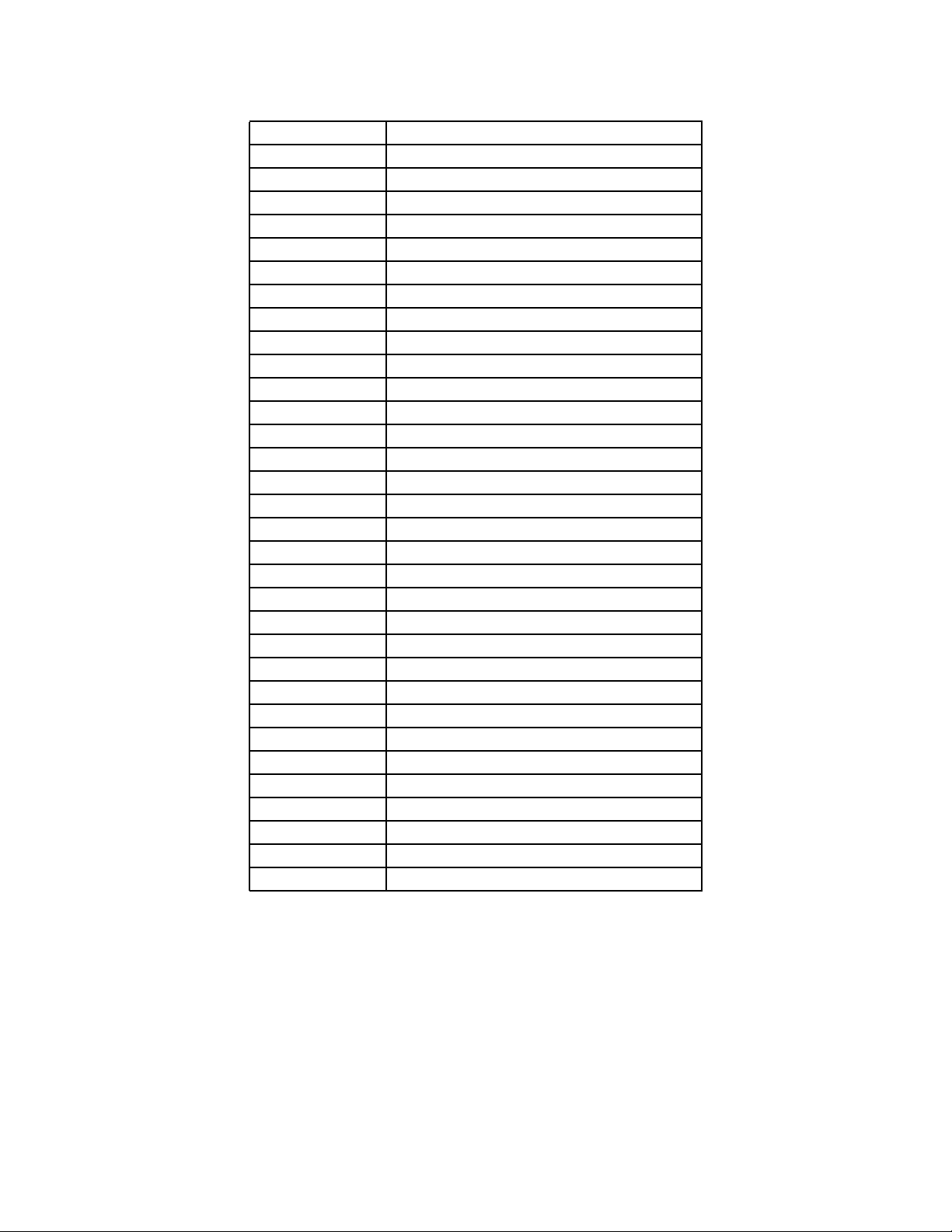
nc...
I
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
2.2 CPU16 Register Mnemonics
Mnemonic Register
A Accumulator A
AM Accumulator M
B Accumulator B
CCR Condition code register
D Accumulator D
E Accumulator E
EK Extended addressing extension field
HR MAC multiplier register
IR MAC multiplicand register
IX Index register X
IY Index register Y
IZ Index register Z
K Address extension register
PC Program counter
PK Program counter extension field
SK Stack pointer extension field
SP Stack pointer
XK Index register X extension field
YK Index register Y extension field
ZK Index register Z extension field
XMSK Modulo addressing index register X mask
YMSK Modulo addressing index register Y mask
S LPSTOP mode control bit
MV AM overflow flag
H Half carry flag
EV AM extended overflow flag
N Negative flag
Z Zero flag
V Two’s complement overflow flag
C Carry/borrow flag
IP Interrupt priority field
SM Saturation mode control bit
MOTOROLA NOMENCLATURE M68HC16 Z SERIES
2-2 USER’S MANUAL
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 31

nc...
I
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
2.3 Register Mnemonics
Mnemonic Register
ADCMCR ADC Module Configuration Register
ADCTEST ADC Test Register
ADCTL[0:1] ADC Control Registers [0:1]
ADCSTAT ADC Status Register
CFORC GPT Compare Force Register
CREG SIM Test Module Control Register
CR[0:F] QSM Command RAM [0:F]
CSBARBT SIM Chip-Select Base Address Register Boot
CSBAR[0:10] SIM Chip-Select Base Address Registers [0:10]
CSORBT SIM Chip-Select Option Register Boot
CSOR[0:10] SIM Chip-Select Option Registers [0:10]
CSPAR[0:1] SIM Chip-Select Pin Assignment Registers [0:1]
DDRE SIM Port E Data Direction Register
DDRF SIM Port F Data Direction Register
DDRGP GPT Port GP Data Direction Register
DDRM MCCI Data Direction Register
DDRQS QSM Port QS Data Direction Register
DREG SIM Test Module Distributed Register
GPTMCR GPT Module Configuration Register
GPTMTR GPT Module Test Register
ICR GPT Interrupt Configuration Register
ILSCI MCCI SCI Interrupt Register
ILSPI MCCI SPI Interrupt Register
LJSRR[0:7] ADC Left-Justified Signed Result Registers [0:7]
LJURR[0:7] ADC Left-Justified Unsigned Result Registers [0:7]
MIVR MCCI Interrupt Vector Register
MMCR MCCI Module Configuration Register
MPAR MCCI Pin Assignment Register
MRMCR Masked ROM Module Configuration Register
MTEST MCCI Test Register
OC1D GPT Output Compare 1 Action Data Register
OC1M GPT Output Compare 1 Action Mask Register
PACNT GPT Pulse Accumulator Counter Register
PACTL GPT Pulse Accumulator Control Register
PEPAR SIM Port E Pin Assignment Register
PFPAR SIM Port F Pin Assignment Register
M68HC16 Z SERIES NOMENCLATURE MOTOROLA
USER’S MANUAL 2-3
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 32

nc...
I
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
Mnemonic Register
PICR SIM Periodic Interrupt Control Register
PITR SIM Periodic Interrupt Timer Register
PORTADA ADC Port ADA Data Register
PORTC SIM Port C Data Register
PORTE SIM Port E Data Register [0:1]
PORTF SIM Port F Data Register [0:1]
PORTGP GPT Port GP Data Register
PORTMC MCCI Port Data Register
PORTMCP MCCI Port Pin State Register
PORTQS QSM Port QS Data Register
PQSPAR QSM Port QS Pin Assignment Register
PRESCL GPT Prescaler Register
PWMA GPT PWM Control Register A
PWMB GPT PWM Control Register B
PWMBUFA GPT PWM Buffer Register A
PWMBUFB GPT PWM Buffer Register B
PWMC GPT PWM Control Register C
PWMCNT GPT PWM Counter Register
QILR QSM Interrupt Level Register
QIVR QSM Interrupt Vector Register
QSMCR QSM Module Configuration Register
QTEST QSM Test Register
RAMBAH RAM Array Base Address Register High
RAMBAL RAM Array Base Address Register Low
RAMMCR RAM Module Configuration Register
RAMTST RAM Test Register
RJURR[0:7] ADC Right-Justified Unsigned Result Registers [0:7]
ROMBAH ROM Array Base Address Register High
ROMBAL ROM Array Base Address Register Low
ROMBS[0:3] ROM Bootstrap Word Registers [0:3]
RR[0:F] QSM Receive Data RAM [0:F]
RSR SIM Reset Status Register
SCCR[0:1] QSM SCI Control Registers [0:1]
SCCR0[A:B] MCCI SCIA/B Control Registers 0 [A:B]
SCCR1[A:B] MCCI SCIA/B Control Registers 1 [A:B]
SCDR QSM SCI Data Register
SCDR[A:B] MCCI SCIA/B Data Registers [A:B]
MOTOROLA NOMENCLATURE M68HC16 Z SERIES
2-4 USER’S MANUAL
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 33

Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
Mnemonic Register
SCSR QSM SCI Status Register
SCSR[A:B] MCCI SCIA/B Status Registers [A:B]
SIGHI ROM Signature Register High
SIGLO ROM Signature Register Low
SIMCR SIM Module Configuration Register
SIMTR SIM Test Register
SIMTRE SIM Test Register E
SPCR MCCI SPI Control Register
SPCR[0:3] QSM SPI Control Registers [0:3]
SPDR MCCI SPI Data Register
SPSR QSM SPI Status Register
SPSR MCCI SPI Status Register
SWSR SIM Software Watchdog Service Register
nc...
I
SYNCR SIM Clock Synthesizer Control Register
SYPCR SIM System Protection Control Register
TCNT GPT Timer Counter Register
TCTL[1:2] GPT Timer Control Registers [1:2]
TFLG[1:2] GPT Timer Flag Registers [1:2]
TI4/O5 GPT Timer Input Capture 4/Output Compare 5 Register
TIC[1:3] GPT Timer Input Capture Registers [1:3]
TMSK[1:2] GPT Timer Mask Register [1:2]
TOC[1:4] GPT Timer Output Compare Registers [1:4]
TR[0:F] QSM Transmit RAM [0:F]
TSTMSRA SIM Test Module Master Shift Register A
TSTMSRB SIM Test Module Master Shift Register B
TSTRC SIM Test Module Repetition Count Register
TSTSC SIM Test Module Shift Count Register
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
M68HC16 Z SERIES NOMENCLATURE MOTOROLA
USER’S MANUAL 2-5
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 34

Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
2.4 Conventions
Logic level one is the voltage that corresponds to a Boolean true (1) state.
Logic level zero is the voltage that corresponds to a Boolean false (0) state.
Set refers specifically to establishing logic level one on a bit or bits.
Clear refers specifically to establishing logic level zero on a bit or bits.
Asserted means that a signal is in active logic state. An active low signal changes
from logic level one to logic level zero when asserted, and an active high signal changes from logic level zero to logic level one.
Negated means that an asserted signal changes logic state. An active low signal
changes from logic level zero to logic level one when negated, and an active high signal changes from logic level one to logic level zero.
nc...
I
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
A specific mnemonic within a range is referred to by mnemonic and number. A15 is
bit 15 of accumulator A; ADDR7 is line 7 of the address bus; CSOR0 is chip-select option register 0. A range of mnemonics is referred to by mnemonic and the numbers
that define the range. VBR[4:0] are bits four to zero of the vector base register;
CSOR[0:5] are the first six chip-select option registers.
Parentheses are used to indicate the content of a register or memory location, rather
than the register or memory location itself. For example, (A) is the content of accumulator A. (M : M + 1) is the content of the word at address M.
LSB means least significant bit or bits. MSB means most significant bit or bits. References to low and high bytes are spelled out.
LSW means least significant word or words. MSW means most significant word or
words.
ADDR is the address bus. ADDR[7:0] are the eight LSB of the address bus.
DATA is the data bus. DATA[15:8] are the eight MSB of the data bus.
MOTOROLA NOMENCLATURE M68HC16 Z SERIES
2-6 USER’S MANUAL
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 35

Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
SECTION 3
OVERVIEW
This section provides general information on M68HC16 Z-series MCUs. It lists features of each of the modules, shows device functional divisions and pin assignments,
summarizes signal and pin functions, discusses the intermodule bus, and provides
system memory maps. Timing and electrical specifications for the entire microcontroller and for individual modules are provided in APPENDIX A ELECTRICAL CHARAC-
TERISTICS. Comprehensive module register descriptions and memory maps are
provided in APPENDIX D REGISTER SUMMARY.
3.1 M68HC16 Z-Series MCU Features
nc...
I
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
The following paragraphs highlight capabilities of each of the MCU modules. Each
module is discussed separately in a subsequent section of this manual.
3.1.1 Central Processor Unit (CPU16/CPU16L)
• 16-bit architecture
• Full set of 16-bit instructions
• Three 16-bit index registers
• Two 16-bit accumulators
• Control-oriented digital signal processing capability
• Addresses up to 1 Mbyte of program memory; 1 Mbyte of data memory
• Background debug mode
• Fully static operation
• Expanded LPSTOP operation on CPU16L (MC68HC16Z4, MC68CK16Z4 only)
3.1.2 System Integration Module (SIM/SIML)
• External bus support
• Programmable chip-select outputs
• System protection logic
• Watchdog timer, clock monitor, and bus monitor
• Two 8-bit dual function input/output ports
• One 7-bit dual function output port
• Phase-locked loop (PLL) clock system
• Expanded LPSTOP operation on SIML (MC68HC16Z4, MC68CK16Z4 only)
3.1.3 Standby RAM (SRAM)
• 1-Kbyte static RAM (MC68HC16Z1/Z4 only)
• 2-Kbyte static RAM (MC68HC16Z2 only)
• 4-Kbyte static RAM (MC68HC16Z3 only)
• External standby voltage supply input
M68HC16 Z SERIES OVERVIEW MOTOROLA
USER’S MANUAL 3-1
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 36

Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
3.1.4 Masked ROM Module (MRM) — (MC68HC16Z2/Z3 Only)
• 8-Kbyte array, accessible as bytes or words
• User-selectable default base address
• User-selectable bootstrap ROM function
• User-selectable ROM verification code
3.1.5 Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC)
• Eight channels, eight result registers
• Eight automated modes
• Three result alignment modes
3.1.6 Queued Serial Module (QSM)
• Enhanced serial communication interface
• Queued serial peripheral interface
nc...
I
3.1.7 Multichannel Communication Interface (MCCI) — (MC68HC16Z4/CKZ4 Only)
• One 8-bit dual function port
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
• Two channels of enhanced SCI (UART)
• One channel of SPI
3.1.8 General-Purpose Timer (GPT)
• Two 16-bit free-running counters with prescaler
• Three input capture channels
• Four output compare channels
• One input capture/output compare channel
• One pulse accumulator/event counter input
• Two pulse width modulation outputs
• Optional external clock input
3.2 Intermodule Bus
The intermodule bus (IMB) is a standardized bus developed to facilitate the design of
modular microcontrollers. It contains circuitry that supports exception processing, address space partitioning, multiple interrupt levels, and vectored interrupts. The standardized modules in M68HC16 Z-series MCUs communicate with one another via the
IMB. Although the full IMB supports 24 address and 16 data lines, M68HC16 Z-series
MCUs use only 20 address lines. ADDR[23:20] follow the state of ADDR19.
3.3 System Block Diagram and Pin Assignment Diagrams
Figure 3-1 is a functional diagram of the MC68HC16Z1/CKZ1/CMZ1 MCU. Refer to
Figure 3-2 for a functional diagram of the MC68HC16Z2/Z3 MCU. Figure 3-3 is a
functional diagram of the MC68HC16Z4/CKZ4 MCU. Although diagram blocks represent the relative size of the physical modules, there is not a one-to-one correspondence between location and size of blocks in the diagram and location and size of
integrated-circuit modules.
MOTOROLA OVERVIEW M68HC16 Z SERIES
3-2 USER’S MANUAL
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 37

Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
M68HC16 Z-series microcontrollers are available in both 132- and 144-pin packages.
Figure 3-4 shows an MC68HC16Z1/CKZ1/CMZ1/Z2/Z3 pin assignment drawing
based on a 132-pin plastic surface-mount package. Figure 3-5 shows an
MC68HC16Z1/CKZ1/CMZ1/Z2/Z3 pin assignment drawing based on a 144-pin plastic
surface-mount package. Figure 3-6 shows an MC68HC16Z4/CKZ4 pin assignment
drawing based on a 132-pin plastic surface-mount package. Figure 3-7 shows an
MC68HC16Z4/CKZ4 pin assignment drawing based on a 144-pin plastic surfacemount package. Refer to APPENDIX B MECHANICAL DATA AND ORDERING IN-
FORMATION for information on how to obtain package dimensions. Refer to subse-
quent paragraphs in this section for pin and signal descriptions.
nc...
I
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
M68HC16 Z SERIES OVERVIEW MOTOROLA
USER’S MANUAL 3-3
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 38

Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
nc...
I
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
PWMA
PWMB
PCLK
PAI
IC4/OC5/OC1/PGP7
OC4/OC1/PGP6
OC3/OC1/PGP5
OC2/OC1/PGP4
OC1/PGP3
IC3/PGP2
IC2/PGP1
IC1/PGP0
RXD
TXD/PQS7
PCS3/PQS6
PCS2/PQS5
PCS1/PQS4
PCS0/
SS/PQS3
SCK/PQS2
MOSI/PQS1
MISO/PQS0
V
DD
V
SS
V
DDA
V
SSA
AN7/PADA7
AN6/PADA6
AN5/PADA5
AN4/PADA4
AN3/PADA3
AN2/PADA2
AN1/PADA1
AN0/PADA0
V
RH
V
RL
BKPT/DSCLK
IPIPE1/DSI
IPIPE0/DSO
V
STBY
PORT GP
CONTROL
CONTROL
PORT QS
PORT AD
CONTROL
CONTROL
IC4/OC5/OC1
OC4/OC1
OC3/OC1
OC2/OC1
OC1
IC3
IC2
IC1
TXD
PCS3
PCS2
PCS1
PCS0
SCK
MOSI
MISO
AN7
AN6
AN5
AN4
AN3
AN2
AN1
AN0
BKPT
IPIPE0
IPIPE1
DSI
DSO
DSCLK
ADC
GPT
QSM
IMB
1K
SRAM
CPU16
CHIP
SELECT
SIM
EBI
CLOCK
TEST
CS[10:0]
ECLK
BGACK
BG
BR
FC2
FC1
FC0
ADDR[23:19]
SIZ1
SIZ0
AS
DS
PE3
AVEC
DSACK1
DSACK0
IRQ[7:1]
MODCLK
TSC
QUOT
FREEZE
ADDR23/CS10/ECLK
ADDR22/
ADDR21/
ADDR20/
ADDR19/CS6/PC3
PORT C
FC2/
CONTROL
CONTROL
CONTROL
CONTROL
FC1/
FC0/
PORT E
DSACK1/PE1
DSACK0/PE0
PORT F
MODCLK/PF0
FREEZE/QUOT
BGACK/CS2
ADDR[18:0]
AVEC/PE2
DATA[15:0]
IRQ7/PF7
IRQ6/PF6
IRQ5/PF5
IRQ4/PF4
IRQ3/PF3
IRQ2/PF2
IRQ1/PF1
CSBOOT
CS9/PC6
CS8/PC5
CS7/PC4
CS5/PC2
CS4/PC1
CS3/PC0
BG/CS1
BR/CS0
SIZ1/PE7
SIZ0/PE6
AS/PE5
DS/PE4
R/W
RESET
HALT
BERR
CLKOUT
XTAL
EXTAL
XFC
V
DDSYN
TSC
HC16Z1/CKZ1/CMZ1 BLOCK
Figure 3-1 MC68HC16Z1/CK16Z1/CM16Z1 Block Diagram
MOTOROLA OVERVIEW M68HC16 Z SERIES
3-4 USER’S MANUAL
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 39

Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
nc...
I
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
PWMA
PWMB
PCLK
PAI
IC4/OC5/OC1/PGP7
OC4/OC1/PGP6
OC3/OC1/PGP5
OC2/OC1/PGP4
OC1/PGP3
IC3/PGP2
IC2/PGP1
IC1/PGP0
RXD
TXD/PQS7
PCS3/PQS6
PCS2/PQS5
PCS1/PQS4
PCS0/
SS/PQS3
SCK/PQS2
MOSI/PQS1
MISO/PQS0
V
DD
V
SS
V
DDA
V
SSA
AN7/PADA7
AN6/PADA6
AN5/PADA5
AN4/PADA4
AN3/PADA3
AN2/PADA2
AN1/PADA1
AN0/PADA0
V
RH
V
RL
BKPT/DSCLK
IPIPE1/DSI
IPIPE0/DSO
V
STBY
PORT GP
CONTROL
CONTROL
PORT QS
PORT AD
CONTROL
CONTROL
IC4/OC5/OC1
OC4/OC1
OC3/OC1
OC2/OC1
OC1
IC3
IC2
IC1
TXD
PCS3
PCS2
PCS1
PCS0
SCK
MOSI
MISO
AN7
AN6
AN5
AN4
AN3
AN2
AN1
AN0
BKPT
IPIPE0
IPIPE1
DSI
DSO
DSCLK
ADC
2K/Z2
4K/Z3
GPT
QSM
IMB
MRM
CSBOOT
ADDR23/CS10/ECLK
CS9/PC6
CHIP
SELECT
SIM
EBI
CPU16SRAM
CLOCK
TEST
CS[10:0]
ECLK
BGACK
BG
BR
FC2
FC1
FC0
ADDR[23:19]
SIZ1
SIZ0
AS
DS
PE3
AVEC
DSACK1
DSACK0
IRQ[7:1]
MODCLK
TSC
QUOT
FREEZE
ADDR22/
ADDR21/
ADDR20/
ADDR19/CS6/PC3
PORT C
CONTROL
PORT E
CONTROL
PORT F
CONTROL
FREEZE/QUOT
CONTROL
CS8/PC5
CS7/PC4
CS5/PC2
FC2/
FC1/
CS4/PC1
CS3/PC0
FC0/
BGACK/CS2
BG/CS1
BR/CS0
ADDR[18:0]
SIZ1/PE7
SIZ0/PE6
AS/PE5
DS/PE4
AVEC/PE2
DSACK1/PE1
DSACK0/PE0
DATA[15:0]
R/W
RESET
HALT
BERR
IRQ7/PF7
IRQ6/PF6
IRQ5/PF5
IRQ4/PF4
IRQ3/PF3
IRQ2/PF2
IRQ1/PF1
MODCLK/PF0
CLKOUT
XTAL
EXTAL
XFC
V
DDSYN
TSC
Z2/Z3 BLOCK
Figure 3-2 MC68HC16Z2/Z3 Block Diagram
M68HC16 Z SERIES OVERVIEW MOTOROLA
USER’S MANUAL 3-5
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 40

Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
nc...
I
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
PWMA
PWMB
PCLK
PAI
IC4/OC5/OC1/PGP7
OC4/OC1/PGP6
OC3/OC1/PGP5
OC2/OC1/PGP4
OC1/PGP3
IC3/PGP2
IC2/PGP1
IC1/PGP0
TXDA/PMC7
RXDA/PMC6
TXDB/PMC5
RXDB/PMC4
SS/PMC3
SCK/PMC2
MOSI/PMC1
MISO/PMC0
V
DD
V
SS
V
DDA
V
SSA
AN7/PADA7
AN6/PADA6
AN5/PADA5
AN4/PADA4
AN3/PADA3
AN2/PADA2
AN1/PADA1
AN0/PADA0
V
RH
V
RL
BKPT/DSCLK
IPIPE1/DSI
IPIPE0/DSO
V
STBY
PORT GP
CONTROL
CONTROL
PORT MCCI
PORT AD
CONTROL
CONTROL
IC4/OC5/OC1
OC4/OC1
OC3/OC1
OC2/OC1
OC1
IC3
IC2
IC1
TXDA
RXDA
TXDB
RXDB
SS
SCK
MOSI
MISO
AN7
AN6
AN5
AN4
AN3
AN2
AN1
AN0
BKPT
IPIPE0
IPIPE1
DSI
DSO
DSCLK
ADC
GPT
MCCI
IMB
1K
SRAM
CPU16L
CHIP
SELECT
SIML
EBI
CLOCK
TEST
CS[10:0]
ECLK
BGACK
BG
BR
FC2
FC1
FC0
ADDR[23:19]
SIZ1
SIZ0
AS
DS
PE3
AVEC
DSACK1
DSACK0
IRQ[7:1]
MODCLK
TSC
QUOT
FREEZE
ADDR23/CS10/ECLK
ADDR22/
ADDR21/
ADDR20/
ADDR19/CS6/PC3
PORT C
FC2/
CONTROL
CONTROL
CONTROL
CONTROL
FC1/
FC0/
PORT E
DSACK1/PE1
DSACK0/PE0
PORT F
MODCLK/PF0
FREEZE/QUOT
BGACK/CS2
ADDR[18:0]
AVEC/PE2
DATA[15:0]
IRQ7/PF7
IRQ6/PF6
IRQ5/PF5
IRQ4/PF4
IRQ3/PF3
IRQ2/PF2
IRQ1/PF1
CSBOOT
CS9/PC6
CS8/PC5
CS7/PC4
CS5/PC2
CS4/PC1
CS3/PC0
BG/CS1
BR/CS0
SIZ1/PE7
SIZ0/PE6
AS/PE5
DS/PE4
R/W
RESET
HALT
BERR
CLKOUT
XTAL
EXTAL
XFC
V
DDSYN
TSC
HC16Z4/CK16Z4 BLOCK
Figure 3-3 MC68HC16Z4/CK16Z4 Block Diagram
MOTOROLA OVERVIEW M68HC16 Z SERIES
3-6 USER’S MANUAL
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 41

Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
nc...
I
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
TXD/PQS7 18
ADDR1 19
ADDR2 20
VDD 21
VSS 22
ADDR3 23
ADDR4 24
ADDR5 25
ADDR6 26
ADDR7 27
ADDR8 28
VSS 29
ADDR9 30
ADDR10 31
ADDR11 32
ADDR12 33
ADDR13 34
ADDR14 35
ADDR15 36
ADDR16 37
ADDR17 38
ADDR18 39
VDD 40
VSS 41
VDDA 42
VSSA 43
AN0/PADA0 44
AN1/PADA1 45
AN2/PADA2 46
AN3/PADA3 47
AN4/PADA4 48
AN5/PADA5 49
VRH 50
NOTES:
1. MMMMM = MASK OPTION NUMBER
2. ATWLYYWW = ASSEMBLY TEST LOCATION/YEAR, WEEK
PCLK126
VSS125
CS10/ECLK123
VDD124
ADDR23/
SS/PQS313
RXD17
PCS3/PQS616
PCS2/PQS515
PCS1/PQS414
PCS0/
SCK/PQS212
MOSI/PQS111
MISO/PQS010
VSS9
VDD8
IC1/PGP07
IC2/PGP16
IC3/PGP25
OC1/PGP34
OC2/OC1/PGP43
VSS2
VDD1
OC3/OC1/PGP5132
OC4/OC1/PGP6131
IC4/OC5/OC1/PGP7130
PAI129
PWMA128
PWMB127
MC68HC16Z1
MC68CK16Z1
MC68CM16Z1
MC68HC16Z2
MC68HC16Z3
MMMMM
ATWLYYWW
VRL 51
VSTBY 54
AN6/PADA6 52
AN7/PADA7 53
VSS 58
XFC 60
VSS 62
VDD 59
XTAL 55
EXTAL 57
VDDSYN 56
VDD 61
TSC 65
CLKOUT 63
FREEZE/QUOT 64
1
2
HALT 70
BERR 71
RESET 69
IRQ7/PF7 72
IRQ6/PF6 73
IRQ5/PF5 74
IRQ4/PF4 75
IRQ3/PF3 76
IPIPE1/DSI 68
IPIPE0/DSO 67
BKPT/DSCLK 66
IRQ2/PF2 77
ADDR22/CS9/PC6122
IRQ1/PF1 78
ADDR21/CS8/PC5121
MODCLK/PF0 79
CS6/PC3119
ADDR20/CS7/PC4120
ADDR19/
BGACK/CS2118
BG/CS1117
R/W80
VSS 83
SIZ1/PE7 81
SIZ0/PE6 82
HC16Z1/CKZ1/CMZ1/Z2/Z3 132-PIN QFP
BR/CS0116
FC2/CS5/PC2115
FC1/CS4/PC1114
VDD113
VSS112
FC0/CS3/PC0111
CSBOOT110
DATA0109
DATA1108
DATA2107
DATA3106
VSS105
DATA4104
DATA5103
DATA6102
DATA7101
DATA8100
DATA999
VDD98
VSS97
DATA1096
DATA1195
DATA1294
DATA1393
DATA1492
DATA1591
ADDR090
DSACK0/PE089
DSACK1/PE188
AVEC/PE287
DS/PE486
AS/PE585
VDD84
Figure 3-4 MC68HC16Z1/CKZ1/CMZ1/Z2/Z3 Pin Assignments for 132-Pin Package
M68HC16 Z SERIES OVERVIEW MOTOROLA
USER’S MANUAL 3-7
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 42

VSS108
SIZ0/PE6107
SIZ1/PE7106
R/W105
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
MODCLK/PF0104
IRQ1/PF1103
IRQ2/PF2102
IRQ3/PF3101
IRQ4/PF4100
IRQ5/PF599
IRQ6/PF698
IRQ7/PF797
BERR96
HALT95
RESET94
IPIPE1/DSI93
IPIPE0/DSO92
BKPT/DSCLK91
NC90
TSC89
FREEZE/QUOT88
CLKOUT87
VSS86
VDD85
XFC84
NC83
VDD82
VSS81
EXTAL80
VDDSYN79
XTAL78
VSTBY77
AN7/PADA776
AN6/PADA675
VRLP74
NC73
nc...
I
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
VDD 109
AS/PE5 110
DS/PE4 111
AVEC/PE2 112
DSACK1/PE1 113
DSACK0/PE0 114
ADDR0 115
DATA15 116
DATA14 117
DATA13 118
DATA12 119
DATA11 120
DATA10 121
VSS 122
NC 123
VDD 124
DATA9 125
DATA8 126
DATA7 127
DATA6 128
DATA5 129
DATA4 130
NC 131
VSS 132
NC 133
DATA3 134
DATA2 135
DATA1 136
DATA0 137
CSBOOT 138
FC0/CS3/PC0 139
VSS 140
VDD 141
FC1/CS4/PC1 142
FC2/CS5/PC2 143
BR/CS0 144
MC68HC16Z1
MC68CK16Z1
MC68CM16Z1
MC68HC16Z2
MC68HC16Z3
MMMMM
ATWLYYWW
1234567891011121314151617181920212223242526272829303132333435
NC
BG/CS1
BGACK/CS2
ADDR19/CS6/PC5
CS7/PC4
ADDR20/
ADDR21/CS8/PC5
ADDR22/CS9/PC6
ADDR23/CS10
VDD
VSS
PCLK
PWMB
PWMA
PAI
OC4/OC1/PGP6
IC4/OC5/OC1/PGP7
1
2
NC
VSS
VDD
OC2/PGP4
OC3/OC1/PCP5
IC3/PGP2
IC2/PGP1
OC1/PGP3
VSS
VDD
IC1/PGP0
SCK/PQS2
MISO/PQS0
MOSI/PQS1
SS/PQS3
PCS1/PQS4
PCS2/PQS5
PCS0/
PCS3/PQS6
RXD
36
NC
VRHP72
AN5/PADA571
AN4/PADA470
AN3/PADA369
AN2/PADA268
AN1/PADA167
AN0/PADA066
VSSA65
VDDA64
VSS63
VDD62
ADDR1861
ADDR1760
ADDR1659
ADDR1558
NC57
ADDR1456
ADDR1355
ADDR1254
ADDR1153
ADDR1052
ADDR951
NC50
VSS49
NC48
ADDR847
ADDR746
ADDR645
ADDR544
ADDR443
ADDR342
VSS41
VDD40
ADDR239
ADDR138
TXD/PQS737
NOTES:
1. MMMMM = MASK OPTION NUMBER
2. ATWLYYWW = ASSEMBLY TEST LOCATION/YEAR, WEEK
HC16Z1/CKZ1/CMZ1/Z2/Z3 144-PIN QFP
Figure 3-5 MC68HC16Z1/CKZ1/CMZ1/Z2/Z3 Pin Assignments for 144-Pin Package
MOTOROLA OVERVIEW M68HC16 Z SERIES
3-8 USER’S MANUAL
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 43

Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
nc...
I
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
NC17
RXDA/PMC616
TXDB/PMC515
RXDB/PMC414
SS/PMC313
SCK/PMC212
MOSI/PMC111
MISO/PMC010
VSS9
TXDA/PMC7 18
ADDR1 19
ADDR2 20
VDD 21
VSS 22
ADDR3 23
ADDR4 24
ADDR5 25
ADDR6 26
ADDR7 27
ADDR8 28
VSS 29
ADDR9 30
ADDR10 31
ADDR11 32
ADDR12 33
ADDR13 34
ADDR14 35
ADDR15 36
ADDR16 37
ADDR17 38
ADDR18 39
VDD 40
VSS 41
VDDA 42
VSSA 43
AN0/PADA0 44
AN1/PADA1 45
AN2/PADA2 46
AN3/PADA3 47
AN4/PADA4 48
AN5/PADA5 49
VRH 50
VRL 51
VSTBY 54
AN6/PADA6 52
AN7/PADA7 53
NOTES:
1. MMMMM = MASK OPTION NUMBER
2. ATWLYYWW = ASSEMBLY TEST LOCATION/YEAR, WEEK
VSS 58
XTAL 55
VDD 59
EXTAL 57
VDDSYN 56
CS10/ECLK123
VDD8
IC1/PGP07
IC2/PGP16
IC3/PGP25
OC1/PGP34
OC2/OC1/PGP43
VSS2
VDD1
OC3/OC1/PGP5132
OC4/OC1/PGP6131
IC4/OC5/OC1/PGP7130
PAI129
PWMA128
PWMB127
PCLK126
VSS125
VDD124
ADDR23/
MC68HC16Z4
MC68CK16Z4
MMMMM
ATWLYYWW
XFC 60
VSS 62
VDD 61
TSC 65
CLKOUT 63
FREEZE/QUOT 64
1
2
HALT 70
BERR 71
RESET 69
IRQ7/PF7 72
IRQ6/PF6 73
IRQ5/PF5 74
IRQ4/PF4 75
IRQ3/PF3 76
IPIPE1/DSI 68
IPIPE0/DSO 67
BKPT/DSCLK 66
IRQ2/PF2 77
ADDR22/CS9/PC6122
IRQ1/PF1 78
ADDR21/CS8/PC5121
MODCLK/PF0 79
CS6/PC3119
ADDR20/CS7/PC4120
ADDR19/
R/W80
SIZ1/PE7 81
BGACK/CS2118
BG/CS1117
VSS 83
SIZ0/PE6 82
HC16Z4/CK16Z4 132-PIN QFP
BR/CS0116
FC2/CS5/PC2115
FC1/CS4/PC1114
VDD113
VSS112
FC0/CS3/PC0111
CSBOOT110
DATA0109
DATA1108
DATA2107
DATA3106
VSS105
DATA4104
DATA5103
DATA6102
DATA7101
DATA8100
DATA999
VDD98
VSS97
DATA1096
DATA1195
DATA1294
DATA1393
DATA1492
DATA1591
ADDR090
DSACK0/PE089
DSACK1/PE188
AVEC/PE287
DS/PE486
AS/PE585
VDD84
Figure 3-6 MC68HC16Z4/CKZ4 Pin Assignments for 132-Pin Package
M68HC16 Z SERIES OVERVIEW MOTOROLA
USER’S MANUAL 3-9
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 44

VSS108
SIZ0/PE6107
SIZ1/PE7106
R/W105
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
MODCLK/PF0104
IRQ1/PF1103
IRQ2/PF2102
IRQ3/PF3101
IRQ4/PF4100
IRQ5/PF599
IRQ6/PF698
IRQ7/PF797
BERR96
HALT95
RESET94
IPIPE1/DSI93
IPIPE0/DSO92
BKPT/DSCLK91
NC90
TSC89
FREEZE/QUOT88
CLKOUT87
VSS86
VDD85
XFC84
NC83
VDD82
VSS81
EXTAL80
VDDSYN79
XTAL78
VSTBY77
AN7/PADA776
AN6/PADA675
VRLP74
NC73
nc...
I
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
VDD 109
AS/PE5 110
DS/PE4 111
AVEC/PE2 112
DSACK1/PE1 113
DSACK0/PE0 114
ADDR0 115
DATA15 116
DATA14 117
DATA13 118
DATA12 119
DATA11 120
DATA10 121
VSS 122
NC 123
VDD 124
DATA9 125
DATA8 126
DATA7 127
DATA6 128
DATA5 129
DATA4 130
NC 131
VSS 132
NC 133
DATA3 134
DATA2 135
DATA1 136
DATA0 137
CSBOOT 138
FC0/CS3/PC0 139
VSS 140
VDD 141
FC1/CS4/PC1 142
FC2/CS5/PC2 143
BR/CS0 144
MC68HC16Z4
MC68CK16Z4
MMMMM
ATWLYYWW
1234567891011121314151617181920212223242526272829303132333435
NC
BG/CS1
BGACK/CS2
ADDR19/CS6/PC5
CS7/PC4
ADDR20/
ADDR21/CS8/PC5
ADDR22/CS9/PC6
ADDR23/CS10
VDD
VSS
PCLK
PWMB
PWMA
PAI
OC4/OC1/PGP6
IC4/OC5/OC1/PGP7
1
2
NC
VSS
VDD
OC2/PGP4
OC3/OC1/PCP5
IC3/PGP2
IC2/PGP1
OC1/PGP3
VSS
VDD
IC1/PGP0
SS/PMC3
SCK/PMC2
MISO/PMC0
MOSI/PMC1
NC
TXDB/PMC5
RXDB/PMC4
36
NC
RXDA/PMC6
VRHP72
AN5/PADA571
AN4/PADA470
AN3/PADA369
AN2/PADA268
AN1/PADA167
AN0/PADA066
VSSA65
VDDA64
VSS63
VDD62
ADDR1861
ADDR1760
ADDR1659
ADDR1558
NC57
ADDR1456
ADDR1355
ADDR1254
ADDR1153
ADDR1052
ADDR951
NC50
VSS49
NC48
ADDR847
ADDR746
ADDR645
ADDR544
ADDR443
ADDR342
VSS41
VDD40
ADDR239
ADDR138
TXDA/PMC737
NOTES:
1. MMMMM = MASK OPTION NUMBER
2. ATWLYYWW = ASSEMBLY TEST LOCATION/YEAR, WEEK
HC16Z4/CK16Z4 144-PIN QFP
Figure 3-7 MC68HC16Z4/CKZ4 Pin Assignments for 144-Pin Package
MOTOROLA OVERVIEW M68HC16 Z SERIES
3-10 USER’S MANUAL
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 45

Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
3.4 Pin Descriptions
The following tables are a summary of the functional characteristics of M68HC16 Zseries MCU pins. Table 3-1 shows all inputs and outputs. Digital inputs and outputs
use CMOS logic levels. An entry in the “Discrete I/O” column indicates that a pin can
also be used for general-purpose input, output, or both. The I/O port designation is given when it applies. Refer to Figure 3-1 for port organization. Table 3-2 shows types
of output drivers. Table 3-3 shows characteristics of power pins.
Table 3-1 M68HC16 Z-Series Pin Characteristics
nc...
I
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
Pin
Mnemonic
ADDR23/
ADDR[22:19]/
CS10/ECLK A Y N O —
CS[9:6] A Y N O PC[6:3]
ADDR[18:0] A Y N — —
1
AN[7:0]
AS B Y Y I/O PE5
AVEC B Y N I/O PE2
BERR B Y N — —
BG/CS1 B — — — —
BGACK/CS2 B Y N — —
BKPT/DSCLK — Y Y — —
BR/CS0 B Y N O —
CLKOUT A — — — —
CSBOOT B — — — —
DATA[15:0]
DSACK[1:0] B Y N I/O PE[1:0]
DSI/IPIPE1 A Y Y — —
DSO/IPIPE0 A — — — —
EXTAL
FC[2:0]/CS[5:3] A Y N O PC[2:0]
FREEZE/QUOT A — — — —
HALT Bo Y N — —
IC4/OC5 A Y Y I/O PGP7
IC[3:1] A Y Y I/O PGP[2:0]
IRQ[7:1] B Y Y I/O PF[7:1]
MISO Bo Y Y I/O PQS0
MISO
MODCLK
MOSI Bo Y Y I/O PQS1
MOSI
OC[4:1] A Y Y I/O PGP[6:3]
PAI
1
DS B Y Y I/O PE4
2
3
1
3
4
Output
Driver
— Y N I PADA[7:0]
AW Y N — —
— — Special — —
Bo Y Y I/O PMC0
B Y N I/O PF0
Bo Y Y I/O PMC1
—Y Y I —
Input
Synchronized
Input
Hysteresis
Discrete
I/O
Designation
Port
M68HC16 Z SERIES OVERVIEW MOTOROLA
USER’S MANUAL 3-11
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 46

Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
Table 3-1 M68HC16 Z-Series Pin Characteristics (Continued)
nc...
I
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
Pin
Mnemonic
4
PCLK
PCS0/SS Bo Y Y I/O PQS3
PCS[3:1] Bo Y Y I/O PQS[6:4]
PWMA, PWMB
R/WAYN——
RESET Bo Y Y — —
RXD — N N — —
RXDA
RXDB
SCK
SCK Bo Y Y I/O PQS2
SIZ[1:0] B Y Y I/O PE[7:6]
SS
TSC — Y Y — —
TXD Bo Y Y I/O PQS7
TXDA
TXDB
XFC
XTAL
NOTES:
1. DATA[15:0] are synchronized during reset only. MODCLK, QSM, MCCI and ADC pins are synchronized
only when used as input port pins.
2. EXTAL, XFC, and XTAL are clock reference connections.
3. MCCI pins used only on the MC68HC16Z4/CK16Z4.
4. PAI and PCLK can be used for discrete input, but are not part of an I/O port.
5. PWMA and PWMB can be used for discrete output, but are not part of an I/O port.
5
3
3
3
3
3
3
2
2
Output
Driver
—Y Y I —
A— — O—
Bo Y Y — PMC6
Bo Y Y — PMC4
Bo Y Y — PMC2
Bo Y Y — PMC3
Bo Y Y — PMC7
Bo Y Y — PMC5
— — — Special —
— — — Special —
Input
Synchronized
Input
Hysteresis
Discrete
I/O
Designation
Table 3-2 M68HC16 Z-Series Driver Types
Type I/O Description
A O Three-state capable output signals
Aw O Type A output with weak p-channel pull-up during reset
BO
Bo O Type B output that can be operated in an open-drain mode
Three-state output that includes circuitry to pull up output before high impedance is established,
to ensure rapid rise time
Port
MOTOROLA OVERVIEW M68HC16 Z SERIES
3-12 USER’S MANUAL
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 47

Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
Table 3-3 M68HC16 Z-Series Power Connections
Pin Mnemonic Description
V
STBY
V
DDSYN
V
DDA/VSSA
V
RH/VRL
V
SS/VDD
Standby RAM power
Clock synthesizer power
A/D converter power
A/D reference voltage
Microcontroller power
3.5 Signal Descriptions
The following tables define the M68HC16 Z-series MCU signals. Table 3-4 shows signal origin, type, and active state. Table 3-5 describes signal functions. Both tables are
sorted alphabetically by mnemonic. MCU pins often have multiple functions. More
than one description can apply to a pin.
nc...
I
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
Table 3-4 M68HC16 Z-Series Signal Characteristics
Signal
Name
ADDR[23:0] SIM Bus —
AN[7:0] ADC Input —
AS SIM Output 0
AVEC SIM Input 0
BERR SIM Input 0
BG SIM Output 0
BGACK SIM Input 0
BKPT CPU16 Input 0
BR SIM Input 0
CLKOUT SIM Output —
CS[10:0] SIM Output 0
CSBOOT SIM Output 0
DATA[15:0] SIM Bus —
DS SIM Output 0
DSACK[1:0] SIM Input 0
DSCLK CPU16 Input Serial Clock
DSI CPU16 Input Serial Data
DSO CPU16 Output Serial Data
EXTAL SIM Input —
FC[2:0] SIM Output —
FREEZE SIM Output 1
HALT SIM Input/Output 0
IC[4:1] GPT Input —
IPIPE0 CPU16 Output —
IPIPE1 CPU16 Output —
IRQ[7:1] SIM Input 0
MCU
Module
Signal
Type
Active
State
M68HC16 Z SERIES OVERVIEW MOTOROLA
USER’S MANUAL 3-13
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 48

Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
Table 3-4 M68HC16 Z-Series Signal Characteristics (Continued)
nc...
I
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
Signal
Name
MISO QSM Input/Output —
1
MISO
MODCLK SIM Input —
MOSI QSM Input/Output —
1
MOSI
OC[5:1] GPT Output —
PADA[7:0] ADC Input —
PAI GPT Input —
PC[6:0] SIM Output —
PE[7:0] SIM Input/Output —
PF[7:0] SIM Input/Output —
PGP[7:0] GPT Input/Output —
PQS[7:0] QSM Input/Output —
PCLK GPT Input —
PCS[3:0] QSM Input/Output —
PWMA, PWMB GPT Output —
PMC[7:0]
RESET SIM Input/Output 0
RXDA
RXDB
SIZ[1:0] SIM Output 1/0
NOTES:
1. Used only in the MC68HC16Z4/CK16Z4.
1
QUOT SIM Output —
W SIM Output 1/0
R/
RXD QSM Input —
1
1
SCK QSM Input/Output —
1
SCK
SS QSM Input 0
1
SS
TSC SIM Input 1
TXD QSM Output —
1
TXDA
1
TXDB
XFC SIM Input —
XTAL SIM Output —
MCU
Module
MCCI Input/Output —
MCCI Input/Output —
MCCI Input/Output —
MCCI Input —
MCCI Input —
MCCI Input/Output —
MCCI Input 0
MCCI Output —
MCCI Output —
Signal
Type
Active
State
MOTOROLA OVERVIEW M68HC16 Z SERIES
3-14 USER’S MANUAL
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 49

nc...
I
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
Table 3-5 M68HC16 Z-Series Signal Function
Mnemonic Signal Name Function
ADDR[19:0] Address Bus 20-bit address bus used by CPU16
AN[7:0] ADC Analog Input Inputs to ADC multiplexer
AS Address Strobe Indicates that a valid address is on the address bus
AVEC Autovector Requests an automatic vector during interrupt acknowledge
BERR Bus Error Indicates that a bus error has occurred
BG Bus Grant Indicates that the MCU has relinquished the bus
BGACK
BKPT Breakpoint Signals a hardware breakpoint to the CPU
BR Bus Request Indicates that an external device requires bus mastership
CLKOUT System Clockout System clock output
CS[10:0] Chip-Selects Select external devices at programmed addresses
CSBOOT Boot Chip Select Chip select for external boot start-up ROM
DATA[15:0] Data Bus 16-bit data bus
DS Data Strobe
DSACK[1:0]
DSI, DSO,
DSCLK
EXTAL, XTAL Crystal Oscillator
FC[2:0] Function Codes Identify processor state and current address space
FREEZE Freeze Indicates that the CPU has entered background mode
HALT Halt Suspend external bus activity
IRQ[7:1] Interrupt Request Level Provides an interrupt priority level to the CPU
IPIPE[1:0] Instruction Pipeline Indicate instruction pipeline activity
MISO Master In Slave Out
1
MISO
MODCLK Clock Mode Select Selects the source and type of system clock
MOSI Master Out Slave In
1
MOSI
PADA[7:0] Port ADA ADC digital input port signals
PAI Pulse Accumulator Input Input to the GPT pulse accumulator
PCLK Auxiliary Timer Clock GPT external clock input
PC[6:0] Port C Port C digital output port signals
PCS[3:0] Peripheral Chip Select QSPI peripheral chip-selects
PE[7:0] Port E Port E digital I/O port signals
Bus Grant
Acknowledge
Data and Size
Acknowledge
Development Serial In,
Out, Clock
Master In Slave Out
Master Out Slave In
Indicates that an external device has assumed bus mastership
During a read cycle, indicates that an external device should
place valid data on the data bus. During a write cycle, indicates
that valid data is on the data bus.
Provide asynchronous data transfers and dynamic bus sizing
Serial I/O and clock for background debug mode
Connections for clock synthesizer circuit reference a crystal or
an external oscillator can be used
Serial input to QSPI in master mode; serial output from QSPIin
slave mode
Serial input to SPI in master mode; serial output from SPI in
slave mode
Serial output from QSPI in master mode; serial input to QSPIin
slave mode
Serial output from SPI in master mode; serial input to SPI in
slave mode
M68HC16 Z SERIES OVERVIEW MOTOROLA
USER’S MANUAL 3-15
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 50

nc...
I
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
Table 3-5 M68HC16 Z-Series Signal Function (Continued)
Mnemonic Signal Name Function
PF[7:0] Port F Port F digital I/O port signals
PGP[7:0] Port GP GPT digital I/O port signals
PQS[7:0] Port QS QSM digital I/O port signals
PWMA, PWMB Pulse Width Modulation Output for PWM
QUOT Quotient Out Provides the quotient bit of the polynomial divider
W Read/Write Indicates the direction of data transfer on the bus
R/
RESET Reset System reset
RXD Receive Data (SCI) Serial input to the SCI
1
RXDA
1
RXDB
SCK Serial Clock (QSPI)
1
SCK
SIZ[1:0] Size
SS Slave Select (QSPI)
1
SS
TSC Three-State Control Places all output drivers in a high-impedance state
TXD SCI Transmit Data Serial output from the SCI
1
TXDA
1
TXDB
XFC External Filter Capacitor Connection for external phase-locked loop filter capacitor
NOTES:
1. MCCI signals present only in MC68HC16Z4/CK16Z4.
SCI A Receive Data Serial input from SCI A
SCI B Receive Data Serial input from SCI B
Clock output from QSPI in master mode; clock input to QSPI in
slave mode
Serial Clock (SPI)
Slave Select (SPI)
SCI A Transmit Data Serial output from SCI A
SCI B Transmit Data Serial output from SCI B
Clock output from SPI in master mode; clock input to SPI in
slave mode
Indicates the number of bytes to be transferred during a bus
cycle
Causes serial transmission when QSPI is in slave mode;
causes mode fault in master mode
Causes serial transmission when the SPI is in slave mode;
causes mode fault in master mode
3.6 Internal Register Map
In Figures 3-8, 3-9, and 3-10, IMB ADDR[23:20] are represented by the letter Y. The
value represented by Y determines the base address of MCU module control registers. Y is equal to M111, where M is the logic state of the module mapping (MM) bit in
the system integration module configuration register (SIMCR). Since the CPU16 uses
only ADDR[19:0], and ADDR[23:20] follow the logic state of ADDR19 when CPU driven, the CPU cannot access IMB addresses from $080000 to $F7FFFF. In order for the
MCU to function correctly, MM must be set (Y must equal $F). If M is cleared, internal
registers are mapped to base address $700000, and are inaccessible until a reset occurs. The SRAM array is positioned by a base address register in the SRAM CTRL
block. Unimplemented blocks are mapped externally.
MOTOROLA OVERVIEW M68HC16 Z SERIES
3-16 USER’S MANUAL
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 51

$000000
$YFF700
$YFF73F
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
ADC
64 BYTES
$YFF900
$YFF93F
$YFFA00
$YFFA7F
$YFFB00
$YFFB07
$YFFC00
nc...
I
$YFFDFF
$FFFFFF
Figure 3-8 MC68HC16Z1/CKZ1/CMZ1 Address Map
cale Semiconductor,
GPT
64 BYTES
SIM
128 BYTES
SRAM CONTROL
8 BYTES
QSM
512 BYTES
1K SRAM ARRAY
(MAPPED TO 1K BOUNDARY)
HC16Z1/CKZ1/CMZ1 ADDRESS MAP
Frees
M68HC16 Z SERIES OVERVIEW MOTOROLA
USER’S MANUAL 3-17
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 52

Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
$000000
$YFF700
$YFF73F
$YFF820
$YFF83F
$YFF900
$YFF93F
$YFFA00
$YFFA7F
$YFFB00
$YFFB07
$YFFC00
nc...
I
SRAM CONTROL
ADC
64 BYTES
ROM CONTROL
32 BYTES
GPT
64 BYTES
SIM
128 BYTES
8 BYTES
QSM
512 BYTES
8K ROM ARRAY
(MAPPED TO 8K BOUNDARY)
2K SRAM ARRAY
(MAPPED TO 2K BOUNDARY)
Z2 ONLY
4K SRAM ARRAY
(MAPPED TO 4K BOUNDARY)
Z3 ONLY
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
$YFFDFF
$FFFFFF
$000000
$YFF700
$YFF73F
$YFF900
$YFF93F
$YFFA00
$YFFA7F
$YFFB00
$YFFB07
$YFFC00
$YFFC3F
Figure 3-9 MC68HC16Z2/Z3 Address Map
ADC
64 BYTES
GPT
64 BYTES
SIML
128 BYTES
SRAM CONTROL
8 BYTES
MCCI
64 BYTES
1K SRAM ARRAY
(MAPPED TO 1K BOUNDARY)
HC16Z2/Z3 ADDRESS MAP
$FFFFFF
HC16Z4/CKZ4 ADDRESS MAP
Figure 3-10 MC68HC16Z4/CKZ4 Address Map
MOTOROLA OVERVIEW M68HC16 Z SERIES
3-18 USER’S MANUAL
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 53

Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
3.7 Address Space Maps
Figures 3-11 through 3-16 show CPU16 address space for M68HC16 Z-series MCUs.
Address space can be split into physically distinct program and data spaces by decoding the MCU function code outputs.
Figures 3-11, 3-12, and 3-13 show the memory map of a system that has combined
program and data spaces. Figures 3-14, 3-15, and 3-16 show the memory map when
MCU function code outputs are decoded.
Reset and exception vectors are mapped into bank 0 and cannot be relocated. The
CPU16 program counter, stack pointer, and Z index register can be initialized to any
address in pseudolinear memory, but exception vectors are limited to 16-bit addresses. To access locations outside of bank 0 during exception handler routines (including
interrupt exceptions), a jump table must be used. Refer to SECTION 4 CENTRAL
PROCESSOR UNIT for more information concerning memory management, extend-
ed addressing, and exception processing. Refer to SECTION 5 SYSTEM INTEGRA-
nc...
I
TION MODULE for more information concerning function codes, address space types,
resets, and interrupts.
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
M68HC16 Z SERIES OVERVIEW MOTOROLA
USER’S MANUAL 3-19
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 54

nc...
I
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
512 KBYTE
UNDEFINED
512 KBYTE
$000000
$010000
$020000
$030000
$040000
$050000
$060000
$070000
$07FFFF
$080000
1
$F7FFFF
$F80000
$F90000
$FA0000
$FB0000
$FC0000
$FD0000
$FE0000
$FF0000
$FFFFFF
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
BANK 0
RESET AND EXCEPTION
BANK 1
BANK 2
BANK 3
BANK 4
BANK 5
BANK 6
PROGRAM
BANK 7
AND DATA
UNDEFINED
VECTORS
SPACE
VECTOR
ADDRESS
0000
0002
0004
0006
0008
000A
000C
000E
0010
0012–001C
001E
0020
0022
0024
0026
0028
002A
002C
002E
0030
0032–006E
0070–01FE
VECTOR
NUMBER
0
4
5
6
7
8
9–E
F
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19–37
38–FF
ADC
BANK 8
BANK 9
BANK 10
GPT
BANK 11
BANK 12
BANK 13
SIM
SRAM
(CONTROL)
BANK 14
BANK 15
INTERNAL REGISTERS
QSM
TYPE OF
EXCEPTION
RESET — INITIAL ZK, SK, AND PK
RESET — INITIAL PC
RESET — INITIAL SP
RESET — INITIAL IZ (DIRECT PAGE)
BKPT (BREAKPOINT)
BERR (BUS ERROR)
SWI (SOFTWARE INTERRUPT)
ILLEGAL INSTRUCTION
DIVISION BY ZERO
UNASSIGNED, RESERVED
UNINITIALIZED INTERRUPT
UNASSIGNED, RESERVED
LEVEL 1 INTERRUPT AUTOVECTOR
LEVEL 2 INTERRUPT AUTOVECTOR
LEVEL 3 INTERRUPT AUTOVECTOR
LEVEL 4 INTERRUPT AUTOVECTOR
LEVEL 5 INTERRUPT AUTOVECTOR
LEVEL 6 INTERRUPT AUTOVECTOR
LEVEL 7 INTERRUPT AUTOVECTOR
SPURIOUS INTERRUPT
UNASSIGNED, RESERVED
USER-DEFINED INTERRUPTS
$YFF700
$YFF73F
$YFF900
$YFF93F
$YFFA00
$YFFA7F
$YFFB00
$YFFB07
$YFFC00
$YFFDFF
$000000
$0001FE
NOTE:
1. THE ADDRESSES DISPLAYED IN THIS MEMORY MAP ARE THE FULL 24-BIT IMB ADDRESSES. THE CPU16
ADDRESS BUS IS 20 BITS WIDE, AND CPU16 ADDRESS LINE 19 DRIVES IMB ADDRESS LINES [23:20]. THE
BLOCK OF ADDRESSES FROM $080000 TO $F7FFFF MARKED AS UNDEFINED WILL NEVER APPEAR ON THE
IMB. MEMORY BANKS 0 TO 15 APPEAR FULLY CONTIGUOUS IN THE CPU16’S FLAT 20-BIT ADDRESS SPACE.
THE CPU16 NEED ONLY GENERATE A 20-BIT EFFECTIVE ADDRESS TO ACCESS ANY LOCATION IN THIS RANGE.
HC16Z1/CK/CM MEM MAP (C)
Figure 3-11 MC68HC16Z1/CKZ1/CMZ1 Combined Program and Data Space Map
MOTOROLA OVERVIEW M68HC16 Z SERIES
3-20 USER’S MANUAL
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 55

nc...
I
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
512 KBYTE
UNDEFINED
512 KBYTE
$000000
$010000
$020000
$030000
$040000
$050000
$060000
$070000
$07FFFF
$080000
1
$F7FFFF
$F80000
$F90000
$FA0000
$FB0000
$FC0000
$FD0000
$FE0000
$FF0000
$FFFFFF
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
BANK 0
RESET AND EXCEPTION
BANK 1
BANK 2
BANK 3
BANK 4
BANK 5
BANK 6
PROGRAM
BANK 7
AND DATA
UNDEFINED
VECTORS
SPACE
VECTOR
ADDRESS
0000
0002
0004
0006
0008
000A
000C
000E
0010
0012–001C
001E
0020
0022
0024
0026
0028
002A
002C
002E
0030
0032–006E
0070–01FE
VECTOR
NUMBER
0
4
5
6
7
8
9–E
F
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19–37
38–FF
ADC
BANK 8
BANK 9
BANK 10
ROM
(CONTROL)
GPT
BANK 11
BANK 12
BANK 13
SIM
SRAM
(CONTROL)
BANK 14
BANK 15
INTERNAL REGISTERS
QSM
TYPE OF
EXCEPTION
RESET — INITIAL ZK, SK, AND PK
RESET — INITIAL PC
RESET — INITIAL SP
RESET — INITIAL IZ (DIRECT PAGE)
BKPT (BREAKPOINT)
BERR (BUS ERROR)
SWI (SOFTWARE INTERRUPT)
ILLEGAL INSTRUCTION
DIVISION BY ZERO
UNASSIGNED, RESERVED
UNINITIALIZED INTERRUPT
UNASSIGNED, RESERVED
LEVEL 1 INTERRUPT AUTOVECTOR
LEVEL 2 INTERRUPT AUTOVECTOR
LEVEL 3 INTERRUPT AUTOVECTOR
LEVEL 4 INTERRUPT AUTOVECTOR
LEVEL 5 INTERRUPT AUTOVECTOR
LEVEL 6 INTERRUPT AUTOVECTOR
LEVEL 7 INTERRUPT AUTOVECTOR
SPURIOUS INTERRUPT
UNASSIGNED, RESERVED
USER-DEFINED INTERRUPTS
$YFF700
$YFF73F
$YFF820
$YFF83F
$YFF900
$YFF93F
$YFFA00
$YFFA7F
$YFFB00
$YFFB07
$YFFC00
$YFFDFF
$000000
$0001FE
NOTE:
1. THE ADDRESSES DISPLAYED IN THIS MEMORY MAP ARE THE FULL 24-BIT IMB ADDRESSES. THE CPU16
ADDRESS BUS IS 20 BITS WIDE, AND CPU16 ADDRESS LINE 19 DRIVES IMB ADDRESS LINES [23:20]. THE
BLOCK OF ADDRESSES FROM $080000 TO $F7FFFF MARKED AS UNDEFINED WILL NEVER APPEAR ON THE
IMB. MEMORY BANKS 0 TO 15 APPEAR FULLY CONTIGUOUS IN THE CPU16’S FLAT 20-BIT ADDRESS SPACE.
THE CPU16 NEED ONLY GENERATE A 20-BIT EFFECTIVE ADDRESS TO ACCESS ANY LOCATION IN THIS RANGE.
HC16 Z2/Z3 MEM MAP (C)
Figure 3-12 MC68HC16Z2/Z3 Combined Program and Data Space Map
M68HC16 Z SERIES OVERVIEW MOTOROLA
USER’S MANUAL 3-21
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 56

nc...
I
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
512 KBYTE
UNDEFINED
512 KBYTE
$000000
$010000
$020000
$030000
$040000
$050000
$060000
$070000
$07FFFF
$080000
1
$F7FFFF
$F80000
$F90000
$FA0000
$FB0000
$FC0000
$FD0000
$FE0000
$FF0000
$FFFFFF
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
BANK 0
RESET AND EXCEPTION
BANK 1
BANK 2
BANK 3
BANK 4
BANK 5
BANK 6
PROGRAM
BANK 7
AND DATA
UNDEFINED
VECTORS
SPACE
VECTOR
ADDRESS
0000
0002
0004
0006
0008
000A
000C
000E
0010
0012–001C
001E
0020
0022
0024
0026
0028
002A
002C
002E
0030
0032–006E
0070–01FE
VECTOR
NUMBER
0
4
5
6
7
8
9–E
F
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19–37
38–FF
ADC
BANK 8
BANK 9
BANK 10
GPT
BANK 11
BANK 12
BANK 13
SIML
SRAM
(CONTROL)
BANK 14
MCCI
BANK 15
INTERNAL REGISTERS
TYPE OF
EXCEPTION
RESET — INITIAL ZK, SK, AND PK
RESET — INITIAL PC
RESET — INITIAL SP
RESET — INITIAL IZ (DIRECT PAGE)
BKPT (BREAKPOINT)
BERR (BUS ERROR)
SWI (SOFTWARE INTERRUPT)
ILLEGAL INSTRUCTION
DIVISION BY ZERO
UNASSIGNED, RESERVED
UNINITIALIZED INTERRUPT
UNASSIGNED, RESERVED
LEVEL 1 INTERRUPT AUTOVECTOR
LEVEL 2 INTERRUPT AUTOVECTOR
LEVEL 3 INTERRUPT AUTOVECTOR
LEVEL 4 INTERRUPT AUTOVECTOR
LEVEL 5 INTERRUPT AUTOVECTOR
LEVEL 6 INTERRUPT AUTOVECTOR
LEVEL 7 INTERRUPT AUTOVECTOR
SPURIOUS INTERRUPT
UNASSIGNED, RESERVED
USER-DEFINED INTERRUPTS
$YFF700
$YFF73F
$YFF900
$YFF93F
$YFFA00
$YFFA7F
$YFFB00
$YFFB07
$YFFC00
$YFFC3F
$YFFDFF
$000000
$0001FE
NOTE:
1. THE ADDRESSES DISPLAYED IN THIS MEMORY MAP ARE THE FULL 24-BIT IMB ADDRESSES. THE CPU16
ADDRESS BUS IS 20 BITS WIDE, AND CPU16 ADDRESS LINE 19 DRIVES IMB ADDRESS LINES [23:20]. THE
BLOCK OF ADDRESSES FROM $080000 TO $F7FFFF MARKED AS UNDEFINED WILL NEVER APPEAR ON THE
IMB. MEMORY BANKS 0 TO 15 APPEAR FULLY CONTIGUOUS IN THE CPU16’S FLAT 20-BIT ADDRESS SPACE.
THE CPU16 NEED ONLY GENERATE A 20-BIT EFFECTIVE ADDRESS TO ACCESS ANY LOCATION IN THIS RANGE.
HC16Z4/CKZ4 MEM MAP (C)
Figure 3-13 MC68HC16Z4/CKZ4 Combined Program and Data Space Map
MOTOROLA OVERVIEW M68HC16 Z SERIES
3-22 USER’S MANUAL
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 57

$000000
$000008
$010000
BANK 0
BANK 1
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
VECTOR
ADDRESS
0000
0002
0004
0006
VECTOR
NUMBER
0
RESET — INITIAL ZK, SK, AND PK
1
2
3
RESET — INITIAL PC
RESET — INITIAL SP
RESET — INITIAL IZ (DIRECT PAGE)
TYPE OF
EXCEPTION
BANK 0
EXCEPTION VECTORS
BANK 1
$000000
$000008
$010000
nc...
I
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
$020000
$030000
512 KBYTE
$040000
$050000
$060000
$070000
$07FFFF
$080000
UNDEFINED
$F7FFFF
$F80000
$F90000
$FA0000
$FB0000
512 KBYTE
$FC0000
$FD0000
$FE0000
BANK 2
BANK 3
BANK 4
BANK 5
BANK 6
BANK 7
PROGRAM
SPACE
VECTOR
ADDRESS
0008
000A
000C
000E
0010
0012–001C
001E
0020
0022
0024
0026
0028
002A
002C
002E
0030
0032–006E
0070–01FE
VECTOR
NUMBER
4
5
6
7
8
9–E
F
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19–37
38–FF
BKPT (BREAKPOINT)
BERR (BUS ERROR)
SWI (SOFTWARE INTERRUPT)
ILLEGAL INSTRUCTION
DIVISION BY ZERO
UNASSIGNED, RESERVED
UNINITIALIZED INTERRUPT
UNASSIGNED, RESERVED
LEVEL 1 INTERRUPT AUTOVECTOR
LEVEL 2 INTERRUPT AUTOVECTOR
LEVEL 3 INTERRUPT AUTOVECTOR
LEVEL 4 INTERRUPT AUTOVECTOR
LEVEL 5 INTERRUPT AUTOVECTOR
LEVEL 6 INTERRUPT AUTOVECTOR
LEVEL 7 INTERRUPT AUTOVECTOR
SPURIOUS INTERRUPT
UNASSIGNED, RESERVED
USER-DEFINED INTERRUPTS
TYPE OF
EXCEPTION
BANK 2
BANK 3
BANK 4
BANK 5
BANK 6
DATA
SPACE
BANK 7
$020000
$030000
$040000
$050000
$060000
$070000
$07FFFF
UNDEFINED
1
UNDEFINED
$YFF700
ADC
BANK 8
BANK 9
BANK 10
BANK 11
BANK 12
$YFF73F
$YFF900
$YFF93F
$YFFA00
GPT
SIM
BANK 8
BANK 9
BANK 10
BANK 11
BANK 12
$YFFA7F
BANK 13
BANK 14
$YFFB00
$YFFB07
$YFFC00
SRAM
(CONTROL)
BANK 13
BANK 14
$080000
UNDEFINED
$F7FFFF
$F80000
$F90000
$FA0000
$FB0000
$FC0000
$FD0000
$FE0000
1
$FF0000
BANK 15
$YFFDFF
$FFFFFF
NOTE:
1. THE ADDRESSES DISPLAYED IN THIS MEMORY MAP ARE THE FULL 24-BIT IMB ADDRESSES. THE CPU16
ADDRESS BUS IS 20 BITS WIDE, AND CPU16 ADDRESS LINE 19 DRIVES IMB ADDRESS LINES [23:20]. THE
BLOCK OF ADDRESSES FROM $080000 TO $F7FFFF MARKED AS UNDEFINED WILL NEVER APPEAR ON THE
IMB. MEMORY BANKS 0 TO 15 APPEAR FULLY CONTIGUOUS IN THE CPU16’S FLAT 20-BIT ADDRESS SPACE.
THE CPU16 NEED ONLY GENERATE A 20-BIT EFFECTIVE ADDRESS TO ACCESS ANY LOCATION IN THIS RANGE.
QSM
BANK 15
INTERNAL REGISTERS
$FF0000
$FFFFFF
HC16Z1/CK/CM MEM MAP (S)
Figure 3-14 MC68HC16Z1/CKZ1/CMZ1 Separate Program and Data Space Map
M68HC16 Z SERIES OVERVIEW MOTOROLA
USER’S MANUAL 3-23
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 58

$000000
$000008
$010000
BANK 0
BANK 1
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
VECTOR
ADDRESS
0000
0002
0004
0006
VECTOR
NUMBER
0
RESET — INITIAL ZK, SK, AND PK
1
2
3
RESET — INITIAL PC
RESET — INITIAL SP
RESET — INITIAL IZ (DIRECT PAGE)
TYPE OF
EXCEPTION
BANK 0
EXCEPTION VECTORS
BANK 1
$000000
$000008
$010000
nc...
I
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
$020000
$030000
512 KBYTE
$040000
$050000
$060000
$070000
$07FFFF
$080000
UNDEFINED
$F7FFFF
$F80000
$F90000
$FA0000
$FB0000
512 KBYTE
$FC0000
$FD0000
$FE0000
$FF0000
$FFFFFF
BANK 2
BANK 3
BANK 4
BANK 5
BANK 6
BANK 7
PROGRAM
SPACE
VECTOR
ADDRESS
0008
000A
000C
000E
0010
0012–001C
001E
0020
0022
0024
0026
0028
002A
002C
002E
0030
0032–006E
0070–01FE
VECTOR
NUMBER
4
5
6
7
8
9–E
F
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19–37
38–FF
BKPT (BREAKPOINT)
BERR (BUS ERROR)
SWI (SOFTWARE INTERRUPT)
ILLEGAL INSTRUCTION
DIVISION BY ZERO
UNASSIGNED, RESERVED
UNINITIALIZED INTERRUPT
UNASSIGNED, RESERVED
LEVEL 1 INTERRUPT AUTOVECTOR
LEVEL 2 INTERRUPT AUTOVECTOR
LEVEL 3 INTERRUPT AUTOVECTOR
LEVEL 4 INTERRUPT AUTOVECTOR
LEVEL 5 INTERRUPT AUTOVECTOR
LEVEL 6 INTERRUPT AUTOVECTOR
LEVEL 7 INTERRUPT AUTOVECTOR
SPURIOUS INTERRUPT
UNASSIGNED, RESERVED
USER-DEFINED INTERRUPTS
TYPE OF
EXCEPTION
BANK 2
BANK 3
BANK 4
BANK 5
BANK 6
DATA
SPACE
BANK 7
$020000
$030000
$040000
$050000
$060000
$070000
$07FFFF
UNDEFINED
1
UNDEFINED
$YFF700
ADC
BANK 8
BANK 9
$YFF73F
$YFF820
ROM
(CONTROL)
BANK 8
BANK 9
$YFF83F
BANK 10
BANK 11
BANK 12
$YFF900
$YFF93F
$YFFA00
GPT
SIM
BANK 10
BANK 11
BANK 12
$YFFA7F
BANK 13
BANK 14
BANK 15
$YFFB00
$YFFB07
$YFFC00
$YFFDFF
SRAM
(CONTROL)
QSM
BANK 13
BANK 14
BANK 15
INTERNAL REGISTERS
$080000
UNDEFINED
$F7FFFF
$F80000
$F90000
$FA0000
$FB0000
$FC0000
$FD0000
$FE0000
$FF0000
1
$FFFFFF
NOTE:
1. THE ADDRESSES DISPLAYED IN THIS MEMORY MAP ARE THE FULL 24-BIT IMB ADDRESSES. THE CPU16
ADDRESS BUS IS 20 BITS WIDE, AND CPU16 ADDRESS LINE 19 DRIVES IMB ADDRESS LINES [23:20]. THE
BLOCK OF ADDRESSES FROM $080000 TO $F7FFFF MARKED AS UNDEFINED WILL NEVER APPEAR ON THE
IMB. MEMORY BANKS 0 TO 15 APPEAR FULLY CONTIGUOUS IN THE CPU16’S FLAT 20-BIT ADDRESS SPACE.
THE CPU16 NEED ONLY GENERATE A 20-BIT EFFECTIVE ADDRESS TO ACCESS ANY LOCATION IN THIS RANGE.
HC16 Z2/Z3 MEM MAP (S)
Figure 3-15 MC68HC16Z2/Z3 Separate Program and Data Space Map
MOTOROLA OVERVIEW M68HC16 Z SERIES
3-24 USER’S MANUAL
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 59

$000000
$000008
$010000
BANK 0
BANK 1
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
VECTOR
ADDRESS
0000
0002
0004
0006
VECTOR
NUMBER
0
RESET — INITIAL ZK, SK, AND PK
1
2
3
RESET — INITIAL PC
RESET — INITIAL SP
RESET — INITIAL IZ (DIRECT PAGE)
TYPE OF
EXCEPTION
BANK 0
EXCEPTION VECTORS
BANK 1
$000000
$000008
$010000
nc...
I
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
$020000
$030000
512 KBYTE
$040000
$050000
$060000
$070000
$07FFFF $07FFFF
$080000
UNDEFINED
$F7FFFF
$F80000
$F90000
$FA0000
$FB0000
512 KBYTE
$FC0000
$FD0000
$FE0000
$FF0000
$FFFFFF
VECTOR
BANK 2
BANK 3
BANK 4
BANK 5
BANK 6
PROGRAM
SPACE
BANK 7
UNDEFINED
1
0012–001C
0032–006E
0070–01FE
ADDRESS
0008
000A
000C
000E
0010
001E
0020
0022
0024
0026
0028
002A
002C
002E
0030
VECTOR
NUMBER
4
5
6
7
8
9–E
F
10
LEVEL 1 INTERRUPT AUTOVECTOR
11
LEVEL 2 INTERRUPT AUTOVECTOR
12
LEVEL 3 INTERRUPT AUTOVECTOR
13
LEVEL 4 INTERRUPT AUTOVECTOR
14
LEVEL 5 INTERRUPT AUTOVECTOR
15
LEVEL 6 INTERRUPT AUTOVECTOR
16
LEVEL 7 INTERRUPT AUTOVECTOR
17
18
19–37
38–FF
TYPE OF
EXCEPTION
BKPT (BREAKPOINT)
BERR (BUS ERROR)
SWI (SOFTWARE INTERRUPT)
ILLEGAL INSTRUCTION
DIVISION BY ZERO
UNASSIGNED, RESERVED
UNINITIALIZED INTERRUPT
UNASSIGNED, RESERVED
SPURIOUS INTERRUPT
UNASSIGNED, RESERVED
USER-DEFINED INTERRUPTS
BANK 2
BANK 3
BANK 4
BANK 5
BANK 6
DATA
SPACE
BANK 7
UNDEFINED
$YFF700
ADC
BANK 8
BANK 9
BANK 10
BANK 11
$YFF73F
$YFF900
$YFF93F
GPT
BANK 8
BANK 9
BANK 10
BANK 11
$YFFA00
BANK 12
SIML
BANK 12
$YFFA7F
BANK 13
BANK 14
$YFFB00
$YFFB07
$YFFC00
SRAM
(CONTROL)
BANK 13
BANK 14
$020000
$030000
$040000
$050000
$060000
$070000
$080000
UNDEFINED
$F7FFFF
$F80000
$F90000
$FA0000
$FB0000
$FC0000
$FD0000
$FE0000
1
MCCI
BANK 15
$YFFC3F
$YFFDFF
BANK 15
INTERNAL REGISTERS
$FF0000
$FFFFFF
NOTE:
1. THE ADDRESSES DISPLAYED IN THIS MEMORY MAP ARE THE FULL 24-BIT IMB ADDRESSES. THE CPU16
ADDRESS BUS IS 20 BITS WIDE, AND CPU16 ADDRESS LINE 19 DRIVES IMB ADDRESS LINES [23:20]. THE
BLOCK OF ADDRESSES FROM $080000 TO $F7FFFF MARKED AS UNDEFINED WILL NEVER APPEAR ON THE
IMB. MEMORY BANKS 0 TO 15 APPEAR FULLY CONTIGUOUS IN THE CPU16’S FLAT 20-BIT ADDRESS SPACE.
THE CPU16 NEED ONLY GENERATE A 20-BIT EFFECTIVE ADDRESS TO ACCESS ANY LOCATION IN THIS RANGE.
HC16Z4/CKZ4 MEM MAP (S)
Figure 3-16 MC68HC16Z4/CKZ4 Separate Program and Data Space Map
M68HC16 Z SERIES OVERVIEW MOTOROLA
USER’S MANUAL 3-25
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 60

Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
nc...
I
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
MOTOROLA OVERVIEW M68HC16 Z SERIES
3-26 USER’S MANUAL
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 61

Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
SECTION 4
CENTRAL PROCESSOR UNIT
This section is an overview of the central processor unit (CPU16). For detailed information, refer to the
4.1 General
The CPU16 provides compatibility with the M68HC11 CPU and also provides additional capabilities associated with 16- and 32-bit data sizes, 20-bit addressing, and digital
signal processing. CPU16 registers are an integral part of the CPU and are not addressed as memory locations.
CPU16 Reference Manual
(CPU16RM/AD).
nc...
I
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
The CPU16 treats all peripheral, I/O, and memory locations as parts of a linear one
Megabyte address space. There are no special instructions for I/O that are separate
from instructions for addressing memory. Address space is made up of sixteen 64Kbyte banks. Specialized bank addressing techniques and support registers provide
transparent access across bank boundaries.
The CPU16 interacts with external devices and with other modules within the microcontroller via a standardized bus and bus interface. There are bus protocols used for
memory and peripheral accesses, as well as for managing a hierarchy of interrupt
priorities.
4.2 Register Model
Figure 4-1 shows the CPU16 register model. Refer to the paragraphs that follow for a
detailed description of each register.
M68HC16 Z SERIES CENTRAL PROCESSOR UNIT MOTOROLA
USER’S MANUAL 4-1
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 62

Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
1620 15 08 7 BIT POSITION
nc...
I
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
A B
D
E
XK IX INDEX REGISTER X
YK IY INDEX REGISTER Y
ZK IZ INDEX REGISTER Z
SK SP STACK POINTER SP
PK PC PROGRAM COUNTER PC
CCR PK
EK XK YK ZK
K
SK STACK EXTENSION FIELD SK
HR
IR
ACCUMULATORS A AND B
ACCUMULATOR D (A:B)
ACCUMULATOR E
CONDITION CODE REGISTER CCR
PC EXTENSION FIELD PK
ADDRESS EXTENSION REGISTER K
MAC MULTIPLIER REGISTER HR
MAC MULTIPLICAND REGISTER IR
AM MAC ACCUMULATOR MSB[35:16] AM
XMSK
AM
YMSK MAC XY MASK REGISTER
MAC ACCUMULATOR LSB[15:0] AM
CPU16 REGISTER MODEL
Figure 4-1 CPU16 Register Model
MOTOROLA CENTRAL PROCESSOR UNIT M68HC16 Z SERIES
4-2 USER’S MANUAL
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 63

Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
4.2.1 Accumulators
The CPU16 has two 8-bit accumulators (A and B) and one 16-bit accumulator (E). In
addition, accumulators A and B can be concatenated into a second 16-bit double accumulator (D).
Accumulators A, B, and D are general-purpose registers that hold operands and results during mathematical and data manipulation operations.
Accumulator E, which can be used in the same way as accumulator D, also extends
CPU16 capabilities. It allows more data to be held within the CPU16 during operations,
simplifies 32-bit arithmetic and digital signal processing, and provides a practical 16bit accumulator offset indexed addressing mode.
4.2.2 Index Registers
The CPU16 has three 16-bit index registers (IX, IY, and IZ). Each index register has
nc...
I
an associated 4-bit extension field (XK, YK, and ZK).
Concatenated registers and extension fields provide 20-bit indexed addressing and
support data structure functions anywhere in the CPU16 address space.
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
IX and IY can perform the same operations as M68HC11 registers of the same names,
but the CPU16 instruction set provides additional indexed operations.
IZ can perform the same operations as IX and IY. IZ also provides an additional indexed addressing capability that replaces M68HC11 direct addressing mode. Initial IZ
and ZK extension field values are included in the RESET exception vector, so that
ZK:IZ can be used as a direct page pointer out of reset.
4.2.3 Stack Pointer
The CPU16 stack pointer (SP) is 16 bits wide. An associated 4-bit extension field (SK)
provides 20-bit stack addressing.
Stack implementation in the CPU16 is from high to low memory. The stack grows
downward as it is filled. SK:SP are decremented each time data is pushed on the
stack, and incremented each time data is pulled from the stack.
SK:SP point to the next available stack address rather than to the address of the latest
stack entry. Although the stack pointer is normally incremented or decremented by
word address, it is possible to push and pull byte-sized data. Setting the stack pointer
to an odd value causes data misalignment, which reduces performance.
4.2.4 Program Counter
The CPU16 program counter (PC) is 16 bits wide. An associated 4-bit extension field
(PK) provides 20-bit program addressing.
CPU16 instructions are fetched from even word boundaries. Address line 0 always
has a value of zero during instruction fetches to ensure that instructions are fetched
from word-aligned addresses.
M68HC16 Z SERIES CENTRAL PROCESSOR UNIT MOTOROLA
USER’S MANUAL 4-3
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 64

Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
4.2.5 Condition Code Register
The 16-bit condition code register is composed of two functional blocks. The eight
MSB, which correspond to the CCR on the M68HC11, contain the low-power stop control bit and processor status flags. The eight LSB contain the interrupt priority field, the
DSP saturation mode control bit, and the program counter address extension field.
Figure 4-2 shows the condition code register. Detailed descriptions of each status in-
dicator and field in the register follow the figure.
15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
S MV H EV N Z V C IP[2:0] SM PK[3:0]
Figure 4-2 Condition Code Register
S — STOP Enable
nc...
I
0 = Stop clock when LPSTOP instruction is executed.
1 = Perform NOP when LPSTOP instruction is executed.
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
MV — Accumulator M overflow flag
MV is set when an overflow into AM35 has occurred.
H — Half Carry Flag
H is set when a carry from A3 or B3 occurs during BCD addition.
EV — Accumulator M Extension Overflow Flag
EV is set when an overflow into AM31 has occurred.
N — Negative Flag
N is set under the following conditions:
• When the MSB is set in the operand of a read operation.
• When the MSB is set in the result of a logic or arithmetic operation.
Z — Zero Flag
Z is set under the following conditions:
• When all bits are zero in the operand of a read operation.
• When all bits are zero in the result of a logic or arithmetic operation.
V — Overflow Flag
V is set when a two’s complement overflow occurs as the result of an operation.
C — Carry Flag
C is set when a carry or borrow occurs during an arithmetic operation. This flag is also
used during shift and rotate to facilitate multiple word operations.
IP[2:0] — Interrupt Priority Field
The priority value in this field (0 to 7) is used to mask interrupts.
MOTOROLA CENTRAL PROCESSOR UNIT M68HC16 Z SERIES
4-4 USER’S MANUAL
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 65

Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
SM — Saturate Mode Bit
When SM is set and either EV or MV is set, data read from AM using TMER or TMET
is given maximum positive or negative value, depending on the state of the AM sign
bit before overflow.
PK[3:0] — Program Counter Address Extension Field
This field is concatenated with the program counter to form a 20-bit address.
4.2.6 Address Extension Register and Address Extension Fields
There are six 4-bit address extension fields. EK, XK, YK, and ZK are contained by the
address extension register (K), PK is part of the CCR, and SK stands alone.
Extension fields are the bank portions of 20-bit concatenated bank:byte addresses
used in the CPU16 linear memory management scheme.
All extension fields except EK correspond directly to a register. XK, YK, and ZK extend
nc...
I
registers IX, IY, and IZ. PK extends the PC; and SK extends the SP. EK holds the four
MSB of the 20-bit address used by the extended addressing mode.
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
4.2.7 Multiply and Accumulate Registers
The multiply and accumulate (MAC) registers are part of a CPU submodule that performsrepetitive signed fractional multiplication and stores the cumulative result. These
operations are part of control-oriented digital signal processing.
There are four MAC registers. Register H contains the 16-bit signed fractional multiplier. Register I contains the 16-bit signed fractional multiplicand. Accumulator M is a
specialized 36-bit product accumulation register. XMSK and YMSK contain 8-bit mask
values used in modulo addressing.
The CPU16 has a special subset of signal processing instructions that manipulate the
MAC registers and perform signal processing calculations.
4.3 Memory Management
The CPU16 providesa 1-Mbyte address space. There are 16 banks within the address
space. Each bank is made up of 64 Kbytes addressed from $0000 to $FFFF. Banks
are selected by means of the address extension fields associated with individual
CPU16 registers.
In addition, address space can be split into discrete 1-Mbyte program and data spaces
by externally decoding the MCU’s function code outputs. When this technique is used,
instruction fetches and reset vector fetches access program space, while exception
vector fetches (other than for reset), data accesses, and stack accesses are made in
data space.
M68HC16 Z SERIES CENTRAL PROCESSOR UNIT MOTOROLA
USER’S MANUAL 4-5
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 66

Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
4.3.1 Address Extension
All CPU16 resources used to generate addresses are effectively 20 bits wide. These
resources include the index registers, program counter, and stack pointer. All addressing modes use 20-bit addresses.
Twenty-bit addresses are formed from a 16-bit byte address generated by an individual CPU16 register and a 4-bit address extension contained in an associated extension field. The byte address corresponds to ADDR[15:0] and the address extension
corresponds to ADDR[19:16].
4.3.2 Extension Fields
Each of the six address extension fields is used for a different type of access. All but
EK are associated with particular CPU16 registers. There are several ways to manipulate extension fields and the address map. Refer to the
(CPU16RM/AD) for detailed information.
nc...
I
4.4 Data Types
CPU16 Reference Manual
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
The CPU16 uses the following types of data:
• Bits
• 4-bit signed integers
• 8-bit (byte) signed and unsigned integers
• 8-bit, 2-digit binary coded decimal (BCD) numbers
• 16-bit (word) signed and unsigned integers
• 32-bit (long word) signed and unsigned integers
• 16-bit signed fractions
• 32-bit signed fractions
• 36-bit signed fixed-point numbers
• 20-bit effective addresses
There are eight bits in a byte and 16 bits in a word. Bit set and clear instructions use
both byte and word operands. Bit test instructions use byte operands.
Negative integers are represented in two’s complement form. Four-bit signed integers,
packed two to a byte, are used only as X and Y offsets in MAC and RMAC operations.
32-bit integers are used only by extended multiply and divide instructions, and by the
associated LDED and STED instructions.
BCD numbers are packed, two digits per byte. BCD operations use byte operands.
Signed 16-bit fractions are used by the fractional multiplication instructions, and as
multiplicand and multiplier operands in the MAC unit. Bit 15 is the sign bit, and there
is an implied radix point between bits 15 and 14. There are 15 bits of magnitude. The
range of values is –1 ($8000) to 1 – 2
Signed 32-bit fractions are used only by the fractional multiplication and division instructions. Bit 31 is the sign bit. An implied radix point lies between bits 31 and 30.
There are 31 bits of magnitude. The range of values is –1 ($80000000) to 1 – 2
($7FFFFFFF).
MOTOROLA CENTRAL PROCESSOR UNIT M68HC16 Z SERIES
4-6 USER’S MANUAL
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
-15
($7FFF).
-31
Page 67

Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
Signed 36-bit fixed-point numbers are used only by the MAC unit. Bit 35 is the sign bit.
Bits [34:31] are sign extension bits. There is an implied radix point between bits 31 and
30. There are 31 bits of magnitude, but use of the extension bits allows representation
of numbers in the range –16 ($800000000) to 15.999969482 ($7FFFFFFFF).
4.5 Memory Organization
Both program and data memory are divided into sixteen 64-Kbyte banks. Addressing
is linear. A 20-bit extended address can access any byte location in the appropriate
address space.
A word is composed of two consecutive bytes. A word address is normally an even
byte address. Byte 0 of a word has a lower 16-bit address than byte 1. Long words and
32-bit signed fractions consist of two consecutive words, and are normally accessed
at the address of byte 0 in word 0.
Instruction fetches always access word addresses. Word operands are normally ac-
nc...
I
cessed at even byte addresses, but can be accessed at odd byte addresses, with a
substantial performance penalty.
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
To permit compatibility with the M68HC11, misaligned word transfers and misaligned
stack accesses are allowed. Transferring a misaligned word requires two successive
byte transfer operations.
Figure 4-3 shows how each CPU16 data type is organized in memory. Consecutive
even addresses show size and alignment.
M68HC16 Z SERIES CENTRAL PROCESSOR UNIT MOTOROLA
USER’S MANUAL 4-7
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 68

Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
Address Type
$0000
$0002 BYTE0 BYTE1
$0004 ± X OFFSET ± Y OFFSET ± X OFFSET ± Y OFFSET
$0006 BCD1 BCD0 BCD1 BCD0
$0008 WORD 0
$000A WORD 1
$000C MSW LONG WORD 0
$000E LSW LONG WORD 0
$0010 MSW LONG WORD 1
$0012 LSW LONG WORD 1
$0014 ±⇐ (Radix Point) 16-BIT SIGNED FRACTION 0
$0016 ±⇐ (Radix Point) 16-BIT SIGNED FRACTION 1
nc...
I
$0018 ±⇐ (Radix Point) MSW 32-BIT SIGNED FRACTION 0
$001A LSW 32-BIT SIGNED FRACTION 0 0
$001C ±⇐ (Radix Point) MSW 32-BIT SIGNED FRACTION 1
$001E LSW 32-BIT SIGNED FRACTION 1 0
BIT15BIT14BIT13BIT12BIT11BIT10BIT9BIT8BIT7BIT6BIT5BIT4BIT3BIT2BIT1BIT
0
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
MAC Data Types
35 32 31 16
± ««««⇐ (Radix Point) MSW 32-BIT SIGNED FRACTION
15 0
LSW 32-BIT SIGNED FRACTION
±⇐ (Radix Point) 16-BIT SIGNED FRACTION
Address Data Type
19 16 15 0
4-Bit Address Extension 16-Bit Byte Address
Figure 4-3 Data Types and Memory Organization
4.6 Addressing Modes
The CPU16 uses nine types of addressing. There are one or more addressing modes
within each type. Table 4-1 shows the addressing modes.
MOTOROLA CENTRAL PROCESSOR UNIT M68HC16 Z SERIES
4-8 USER’S MANUAL
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 69

Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
Table 4-1 Addressing Modes
Mode Mnemonic Description
E,X Index register X with accumulator E offset
Accumulator Offset
Extended
Immediate
Indexed 8-Bit
Indexed 16-Bit
nc...
I
Indexed 20-Bit
Inherent INH Inherent
Post-Modified Index IXP
Relative
E,Y Index register Y with accumulator E offset
E,Z Index register Z with accumulator E offset
EXT Extended
EXT20 20-bit extended
IMM8 8-bit immediate
IMM16 16-bit immediate
IND8, X Index register X with unsigned 8-bit offset
IND8, Y Index register Y with unsigned 8-bit offset
IND8, Z Index register Z with unsigned 8-bit offset
IND16, X Index register X with signed 16-bit offset
IND16, Y Index register Y with signed 16-bit offset
IND16, Z Index register Z with signed 16-bit offset
IND20, X Index register X with signed 20-bit offset
IND20, Y Index register Y with signed 20-bit offset
IND20, Z Index register Z with signed 20-bit offset
Signed 8-bit offset added to index register
X after effective address is used
REL8 8-bit relative
REL16 16-bit relative
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
All modes generate ADDR[15:0]. This address is combined with ADDR[19:16] from an
operand or an extension field to form a 20-bit effective address.
NOTE
Access across 64-Kbyte address boundaries is transparent. ADDR[19:16] of the effective address are changed to make an access
across a bank boundary. Extension field values will not change as a
result of effective address computation.
4.6.1 Immediate Addressing Modes
In the immediate modes, an argument is contained in a byte or word immediately following the instruction. For IMM8 and IMM16 modes, the effective address is the address of the argument.
There are three specialized forms of IMM8 addressing.
• The AIS, AIX, AIY, AIZ, ADDD, and ADDE instructions decrease execution time
by sign-extending the 8-bit immediate operand to 16 bits, then adding it to an appropriate register.
• The MAC and RMAC instructions use an 8-bit immediate operand to specify two
signed 4-bit index register offsets.
• The PSHM and PULM instructions use an 8-bit immediate mask operand to indicate which registers must be pushed to or pulled from the stack.
M68HC16 Z SERIES CENTRAL PROCESSOR UNIT MOTOROLA
USER’S MANUAL 4-9
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 70

Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
4.6.2 Extended Addressing Modes
Regular extended mode instructions contain ADDR[15:0] in the word following the opcode.The effective address is formedby concatenating the EK fieldand the 16-bit byte
address. EXT20 mode is used only by the JMP and JSR instructions. These instructions contain a 20-bit effective address that is zero-extended to 24 bits to give the instruction an even number of bytes.
4.6.3 Indexed Addressing Modes
In the indexed modes, registers IX, IY, and IZ, together with their associated extension
fields, are used to calculate the effective address.
For 8-bit indexed modes an 8-bit unsigned offset contained in the instruction is added
to the value contained in an index register and its extension field.
For 16-bit modes, a 16-bit signed offset contained in the instruction is added to the val-
nc...
I
ue contained in an index register and its extension field.
For 20-bit modes, a 20-bit signed offset (zero-extended to 24 bits) is added to the val-
ue contained inan index register. These modes are used for JMP and JSR instructions
only.
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
4.6.4 Inherent Addressing Mode
Inherent mode instructions use information directly available to the processor to determine the effective address. Operands, if any, are system resources and are thus not
fetched from memory.
4.6.5 Accumulator Offset Addressing Mode
Accumulator offset modes form an effective address by sign-extending the content of
accumulator E to 20 bits, then adding the result to an index register and its associated
extension field. This mode allows use of an index register and an accumulator within
a loop without corrupting accumulator D.
4.6.6 Relative Addressing Modes
Relative modes are used for branch and long branch instructions. If a branch condition
is satisfied, a byte or word signed two’s complement offset is added to the concatenated PK field and program counter. The new PK : PC value is the effective address.
4.6.7 Post-Modified Index Addressing Mode
Post-modified index mode is used by the MOVB and MOVW instructions. A signed 8bit offset is added to index register X after the effective address formed by XK : IX is
used.
MOTOROLA CENTRAL PROCESSOR UNIT M68HC16 Z SERIES
4-10 USER’S MANUAL
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 71

Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
4.6.8 Use of CPU16 Indexed Mode to Replace M68HC11 Direct Mode
In M68HC11 systems, the direct addressing mode can be used to perform rapid accesses to RAM or I/O mapped from $0000 to $00FF. The CPU16 uses the first 512
bytes of bank 0 for exception vectors. To provide an enhanced replacement for the
M68HC11’s direct addressing mode, the ZK field and index register Z have been assigned reset initialization vectors. By resetting the ZK field to a chosen page and using
indexed mode addressing, a programmer can access useful data structures anywhere
in the address map.
4.7 Instruction Set
The CPU16 instruction set is based on the M68HC11 instruction set, but the opcode
map has been rearranged to maximize performance with a 16-bit data bus. Most
M68HC11 code can run on the CPU16 following reassembly. The user must take into
accountchanged instruction times, the interrupt mask, andthe changed interrupt stack
frame (refer to
nc...
I
gramming Note M68HC16PN01/D, for more information).
Transporting M68HC11 Code to M68HC16 Devices
, Motorola Pro-
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
4.7.1 Instruction Set Summary
Table 4-2 is a quick reference to the entire CPU16 instruction set. Refer to the
Reference Manual
sembler syntax, and condition code evaluation. Table 4-3 provides a key to the table
nomenclature.
(CPU16RM/AD) for detailed information about each instruction, as-
CPU16
M68HC16 Z SERIES CENTRAL PROCESSOR UNIT MOTOROLA
USER’S MANUAL 4-11
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 72

nc...
I
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
Table 4-2 Instruction Set Summary
Mnemonic Operation Description Address Instruction Condition Codes
Mode Opcode Operand Cycles S MV H EV N Z V C
ABA Add B to A (A ) + (B) ⇒ A INH 370B — 2 — — ∆ — ∆∆∆∆
ABX Add B to IX (XK :IX) +(000 :B)⇒ XK: IX INH 374F — 2 — — — — ————
ABY Add B to IY (YK :IY) +(000 : B)⇒ YK: IY INH 375F — 2 — — — — ————
ABZ Add B to IZ (ZK :IZ) +(000 :B) ⇒ ZK : IZ INH 376F — 2 — — — — ————
ACE Add E to AM (AM[31:16])+ (E) ⇒ AM INH 3722 — 2 — ∆ — ∆ ————
ACED Add E : D to AM (AM) + (E : D) ⇒ AM INH 3723 — 4 — ∆ — ∆ ————
—— ∆ — ∆∆∆∆
ADCA Add with Carry to A (A) + (M) + C⇒ A IND8, X
IND8, Y
IND8, Z
IMM8
IND16, X
IND16, Y
IND16, Z
EXT
E, X
E, Y
E, Z
ADCB Add with Carry to B (B) + (M) + C⇒ B IND8, X
IND8, Y
IND8, Z
IMM8
IND16, X
IND16, Y
IND16, Z
EXT
E, X
E, Y
E, Z
ADCD Add with Carry to D (D) + (M : M + 1)+ C ⇒ D IND8, X
IND8, Y
IND8, Z
IMM16
IND16, X
IND16, Y
IND16, Z
EXT
E, X
E, Y
E, Z
ADCE Add with Carry to E (E) + (M : M+ 1) + C ⇒ E IMM16
IND16, X
IND16, Y
IND16, Z
EXT
ADDA Add to A (A) + (M) ⇒ A IND8, X
IND8, Y
IND8, Z
IMM8
IND16, X
IND16, Y
IND16, Z
EXT
E, X
E, Y
E, Z
43
53
63
73
1743
1753
1763
1773
2743
2753
2763
C3
D3
E3
F3
17C3
17D3
17E3
17F3
27C3
27D3
27E3
83
93
A3
37B3
37C3
37D3
37E3
37F3
2783
2793
27A3
3733
3743
3753
3763
3773
41
51
61
71
1741
1751
1761
1771
2741
2751
2761
ff
ff
ff
ii
gggg
gggg
gggg
hh ll
—
—
—
ff
ff
ff
ii
gggg
gggg
gggg
hh ll
—
—
—
ff
ff
ff
jj kk
gggg
gggg
gggg
hh ll
—
—
—
jj kk
gggg
gggg
gggg
hh ll
ff
ff
ff
ii
gggg
gggg
gggg
hh ll
—
—
—
6
6
6
2
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
—— ∆ — ∆∆∆∆
6
6
6
2
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
———— ∆∆∆∆
6
6
6
4
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
———— ∆∆∆∆
4
6
6
6
6
—— ∆ — ∆∆∆∆
6
6
6
2
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
MOTOROLA CENTRAL PROCESSING UNIT M68HC16 Z SERIES
4-12 USER’S MANUAL
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 73

nc...
I
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
Table 4-2 Instruction Set Summary (Continued)
Mnemonic Operation Description Address Instruction Condition Codes
Mode Opcode Operand Cycles S MV H EV N Z V C
—— ∆ — ∆∆∆∆
ADDB Add to B (B) + (M) ⇒ B IND8, X
ADDD Add to D (D) + (M : M+ 1) ⇒ D IND8, X
ADDE Add to E (E) + (M : M+ 1) ⇒ E IMM8
ADE Add D to E (E) + (D) ⇒ E INH 2778 — 2 — — — — ∆∆∆∆
ADX Add D to IX INH 37CD — 2 — — — — ————
ADY Add D to IY INH 37DD — 2 — — — — ————
ADZ Add D to IZ INH 37ED — 2 — — — — ————
AEX Add E to IX INH 374D — 2 — — — — ————
AEY Add E to IY INH 375D — 2 — — — — ————
AEZ Add E to IZ INH 376D — 2 — — — — ————
AIS Add Immediate Data
to Stack Pointer
AIX Add Immediate Value
to IX
AIY Add Immediate Value
to IY
AIZ Add Immediate Value
to IZ
ANDA AND A (A) • (M) ⇒ A IND8, X
XK : IX()20 D«()
XK : IX
YK : IY()20 D«()
YK : IY
ZK : IZ()20 D«()
ZK : IZ
XK : IX()20 E«()
XK : IX
YK : IY()20 E«()
YK : IY
ZK : IZ()20 E«()
ZK : IZ
(SK : SP) + (20 « IMM)⇒
SK : SP
(XK : IX) + (20 « IMM) ⇒
XK : IX
(YK : IY) + (20 « IMM)⇒
YK : IY
(ZK : IZ) + (20 « IMM)⇒
ZK : IZ
⇒+
⇒+
⇒+
⇒+
⇒+
⇒+
IND8, Y
IND8, Z
IMM8
IND16, X
IND16, Y
IND16, Z
EXT
E, X
E, Y
E, Z
IND8, Y
IND8, Z
IMM8
IMM16
IND16, X
IND16, Y
IND16, Z
EXT
E, X
E, Y
E, Z
IMM16
IND16, X
IND16, Y
IND16, Z
EXT
IMM8
IMM163F373F
IMM8
IMM163C373C
IMM8
IMM163D373D
IMM8
IMM163E373E
IND8, Y
IND8, Z
IMM8
IND16, X
IND16, Y
IND16, Z
EXT
E, X
E, Y
E, Z
C1
D1
E1
F1
17C1
17D1
17E1
17F1
27C1
27D1
27E1
81
91
A1
FC
37B1
37C1
37D1
37E1
37F1
2781
2791
27A1
7C
3731
3741
3751
3761
3771
46
56
66
76
1746
1756
1766
1776
2746
2756
2766
ff
ff
ff
ii
gggg
gggg
gggg
hh ll
—
—
—
ff
ff
ff
ii
jj kk
gggg
gggg
gggg
hh ll
—
—
—
ii
jj kk
gggg
gggg
gggg
hh ll
ii
jj kk
ii
jj kk
ii
jj kk
ii
jj kk
ff
ff
ff
ii
gggg
gggg
gggg
hh ll
—
—
—
6
6
6
2
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
———— ∆∆∆∆
6
6
6
2
4
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
———— ∆∆∆∆
2
4
6
6
6
6
24—— — —————
24—————∆ ——
24—————∆ ——
24—————∆ ——
———— ∆∆0—
6
6
6
2
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
M68HC16 Z SERIES CENTRAL PROCESSING UNIT MOTOROLA
USER’S MANUAL 4-13
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 74

Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
Table 4-2 Instruction Set Summary (Continued)
Mnemonic Operation Description Address Instruction Condition Codes
Mode Opcode Operand Cycles S MV H EV N Z V C
———— ∆∆0—
ANDB AND B (B) • (M) ⇒ B IND8, X
ANDD AND D (D) • (M : M + 1) ⇒ D IND8, X
nc...
I
ANDE AND E (E) • (M : M + 1) ⇒ E IMM16
1
ANDP
ASL Arithmetic Shift Left IND8, X
ASLA Arithmetic Shift Left A INH 3704 — 2 — — — — ∆∆∆∆
ASLB Arithmetic Shift Left B INH 3714 — 2 — — — — ∆∆∆∆
cale Semiconductor,
ASLD Arithmetic Shift Left D INH 27F4 — 2 — — — — ∆∆∆∆
ASLE Arithmetic Shift Left E INH 2774 — 2 — — — —
AND CCR (CCR) • IMM16⇒ CCR IMM16 373A jj kk 4 ∆ ∆ ∆ ∆∆∆∆∆
IND8, Y
IND8, Z
IMM8
IND16, X
IND16, Y
IND16, Z
EXT
E, X
E, Y
E, Z
IND8, Y
IND8, Z
IMM16
IND16, X
IND16, Y
IND16, Z
EXT
E, X
E, Y
E, Z
IND16, X
IND16, Y
IND16, Z
EXT
IND8, Y
IND8, Z
IND16, X
IND16, Y
IND16, Z
EXT
C6
D6
E6
F6
17C6
17D6
17E6
17F6
27C6
27D6
27E6
86
96
A6
37B6
37C6
37D6
37E6
37F6
2786
2796
27A6
3736
3746
3756
3766
3776
04
14
24
1704
1714
1724
1734
ff
ff
ff
ii
gggg
gggg
gggg
hh ll
—
—
—
ff
ff
ff
jj kk
gggg
gggg
gggg
hh ll
—
—
—
jj kk
gggg
gggg
gggg
hh ll
ff
ff
ff
gggg
gggg
gggg
hh ll
6
6
6
2
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
———— ∆∆0—
6
6
6
4
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
———— ∆∆0—
4
6
6
6
6
———— ∆∆∆∆
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
Frees
ASLM Arithmetic Shift Left
AM
ASLW Arithmetic Shift Left
Word
ASR Arithmetic Shift Right IND8, X
INH 27B6 — 4 — — — —
IND16, X
IND16, Y
IND16, Z
EXT
IND8, Y
IND8, Z
IND16, X
IND16, Y
IND16, Z
EXT
2704
2714
2724
2734
0D
1D
2D
170D
171D
172D
173D
gggg
gggg
gggg
hh ll
ff
ff
ff
gggg
gggg
gggg
hh ll
8
————
8
8
8
————
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
MOTOROLA CENTRAL PROCESSING UNIT M68HC16 Z SERIES
4-14 USER’S MANUAL
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 75

Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
Table 4-2 Instruction Set Summary (Continued)
Mnemonic Operation Description Address Instruction Condition Codes
Mode Opcode Operand Cycles S MV H EV N Z V C
ASRA Arithmetic Shift Right
A
INH 370D — 2 — — — —
nc...
I
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
ASRB Arithmetic Shift Right
ASRD Arithmetic Shift Right
ASRE Arithmetic Shift Right
ASRM Arithmetic Shift Right
ASRW Arithmetic Shift Right
2
BCC
BCLR Clear Bit(s) (M) • (
BCLRW Clear Bit(s) in a Word (M : M + 1) • (
BCS
BEQ
BGE
BGND Enter Background
BGT
BHI
BITA Bit Test A (A) • (M) IND8, X
Branch if Carry Clear If C = 0, branch REL8 B4 rr 6, 2 — — — — ————
2
2
2
BranchifGreater Than
2
BranchifGreater Than
2
B
D
E
AM
Word
Mask) ⇒ M IND8, X
Mask) ⇒
M : M + 1
Branch if Carry Set If C = 1, branch REL8 B5 rr 6, 2 — — — — ————
Branch if Equal If Z = 1, branch REL8 B7 rr 6, 2 — — — — ————
or Equal to Zero
Debug Mode
Zero
Branch if Higher If C ✛ Z = 0, branch REL8 B2 rr 6, 2 — — — — ————
If N ⊕ V = 0, branch REL8 BC rr 6, 2 — — — — ————
If BDM enabled,
begin debug;
else, illegal instruction trap
If Z ✛ (N ⊕ V) = 0, branch REL8 BE rr 6, 2 — — — — ————
INH 371D — 2 — — — —
INH 27FD — 2 — — — —
INH 277D — 2 — — — —
INH 27BA — 4 — — — — —
IND16, X
IND16, Y
IND16, Z
EXT
IND8, Y
IND8, Z
IND16, X
IND16, Y
IND16, Z
EXT
IND16, X
IND16, Y
IND16, Z
EXT
INH 37A6 — — — — — — ————
IND8, Y
IND8, Z
IMM8
IND16, X
IND16, Y
IND16, Z
EXT
E, X
E, Y
E, Z
270D
271D
272D
273D
1708
1718
1728
08
18
28
38
2708
2718
2728
2738
49
59
69
79
1749
1759
1769
1779
2749
2759
2769
gggg
gggg
gggg
hh ll
mm ff
mm ff
mm ff
mm gggg
mm gggg
mm gggg
mm hh ll
gggg
mmmm
gggg
mmmm
gggg
mmmm
hh ll
mmmm
ff
ff
ff
ii
gggg
gggg
gggg
hh ll
—
—
—
8
————
8
8
8
———— ∆∆0—
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
———— ∆∆0—
10
10
10
10
———— ∆∆0—
6
6
6
2
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
M68HC16 Z SERIES CENTRAL PROCESSING UNIT MOTOROLA
USER’S MANUAL 4-15
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 76

nc...
I
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
Table 4-2 Instruction Set Summary (Continued)
Mnemonic Operation Description Address Instruction Condition Codes
Mode Opcode Operand Cycles S MV H EV N Z V C
———— ∆∆0—
BITB Bit Test B (B) • (M) IND8, X
2
BLE
BLS
BLT
BMI
BNE
BPL
BRCLR
BRSET
BSET Set Bit(s) (M) ✛ (Mask) ⇒ M IND8, X
BSETW Set Bit(s) in Word (M : M + 1) ✛ (Mask)
Branchif LessThan or
Equal to Zero
2
Branch if Lower or
Same
2
Branch if Less Than
Zero
2
BRA Branch Always If 1 = 1, branch REL8 B0 rr 6 — — — — ————
BRN Branch Never If 1 = 0, branch REL8 B1 rr 2 — — — — ————
Branch if Minus If N = 1, branch REL8 BB rr 6, 2 — — — — ————
2
Branch if Not Equal If Z = 0, branch REL8 B6 rr 6, 2 — — — — ————
2
Branch if Plus If N = 0, branch REL8 BA rr 6, 2 — — — — ————
2
Branch if Bit(s) Clear If (M) • (Mask) = 0, branch IND8, X
2
Branch if Bit(s) Set If (M) • (Mask) = 0, branch IND8, X
If Z ✛ (N ⊕ V) = 1, branch REL8 BF rr 6, 2 — — — — ————
If C ✛ Z = 1, branch REL8 B3 rr 6, 2 — — — — ————
If N ⊕ V = 1, branch REL8 BD rr 6, 2 — — — — ————
⇒ M : M + 1
IND8, Y
IND8, Z
IMM8
IND16, X
IND16, Y
IND16, Z
EXT
E, X
E, Y
E, Z
IND8, Y
IND8, Z
IND16, X
IND16, Y
IND16, Z
EXT
IND8, Y
IND8, Z
IND16, X
IND16, Y
IND16, Z
EXT
IND8, Y
IND8, Z
IND16, X
IND16, Y
IND16, Z
EXT
IND16, X
IND16, Y
IND16, Z
EXT
C9
D9
E9
F9
17C9
17D9
17E9
17F9
27C9
27D9
27E9
CB
DB
EB
0A
1A
2A
3A
8B
9B
AB
0B
1B
2B
3B
1709
1719
1729
09
19
29
39
2709
2719
2729
2739
ff
ff
ff
ii
gggg
gggg
gggg
hh ll
—
—
—
mm ff rr
mm ff rr
mm ff rr
mmgggg
rrrr
mmgggg
rrrr
mmgggg
rrrr
mm hh ll
rrrr
mm ff rr
mm ff rr
mm ff rr
mmgggg
rrrr
mmgggg
rrrr
mmgggg
rrrr
mm hh ll
rrrr
mm ff
mm ff
mm ff
mm gggg
mm gggg
mm gggg
mm hh ll
gggg
mmmm
gggg
mmmm
gggg
mmmm
hh ll
mmmm
6
6
6
2
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
10, 12
10, 12
10, 12
10, 14
10, 14
10, 14
10, 14
10, 12
10, 12
10, 12
10, 14
10, 14
10, 14
10, 14
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
10
10
10
10
—— — —————
—— — —————
———— ∆∆0 ∆
———— ∆∆0 ∆
MOTOROLA CENTRAL PROCESSING UNIT M68HC16 Z SERIES
4-16 USER’S MANUAL
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 77

nc...
I
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
Table 4-2 Instruction Set Summary (Continued)
Mnemonic Operation Description Address Instruction Condition Codes
Mode Opcode Operand Cycles S MV H EV N Z V C
BSR Branch to Subroutine (PK : PC) - 2 ⇒ PK : PC
2
BVC
BVS
CBA Compare A to B (A) − (B) INH 371B — 2 — — — — ∆∆∆∆
CLR Clear a Byte in
CLRA Clear A $00 ⇒ A INH 3705 — 2 — — — — 0100
CLRB Clear B $00 ⇒ B INH 3715 — 2 — — — — 0100
CLRD Clear D $0000 ⇒ D INH 27F5 — 2 — — — — 0100
CLRE Clear E $0000 ⇒ E INH 2775 — 2 — — — — 0100
CLRM Clear AM $000000000⇒ AM[35:0] INH 27B7 — 2 — 0 — 0 ————
CLRW Clear a Word in
CMPA Compare A toMemory (A) − (M) IND8, X
CMPB Compare B toMemory (B) − (M) IND8, X
COM One’s Complement $FF − (M) ⇒ M, or
COMA One’s Complement A $FF − (A) ⇒ A, or
COMB One’s Complement B $FF − (B) ⇒ B, or
COMD One’s Complement D $FFFF− (D) ⇒ D, or
COME One’s Complement E $FFFF − (E) ⇒ E, or
COMW One’s Complement
Branch if Overflow
Clear
2
Branch if Overflow Set If V = 1, branch REL8 B9 rr 6, 2 — — — — ————
Memory
Memory
Word
Push (PC)
(SK : SP) - 2 ⇒ SK : SP
Push (CCR)
(SK : SP) - 2 ⇒ SK : SP
(PK :PC) +Offset ⇒PK:PC
If V = 0, branch REL8 B8 rr 6, 2 — — — — ————
$00 ⇒ M IND8, X
$0000 ⇒ M : M+ 1 IND16, X
M ⇒ M IND8, X
M ⇒ A INH 3700 — 2 — — — — ∆∆01
B ⇒ B INH 3710 — 2 — — — — ∆∆01
D ⇒ D INH 27F0 — 2 — — — — ∆∆01
E ⇒ E INH 2770 — 2 — — — — ∆∆01
$FFFF − M : M + 1⇒
M : M + 1, or (
M : M + 1) ⇒
M : M + 1
REL8 36 rr 10 — — — — ————
————0100
IND8, Y
IND8, Z
IND16, X
IND16, Y
IND16, Z
EXT
IND16, Y
IND16, Z
EXT
IND8, Y
IND8, Z
IMM8
IND16, X
IND16, Y
IND16, Z
EXT
E, X
E, Y
E, Z
IND8, Y
IND8, Z
IMM8
IND16, X
IND16, Y
IND16, Z
EXT
E, X
E, Y
E, Z
IND8, Y
IND8, Z
IND16, X
IND16, Y
IND16, Z
EXT
IND16, X
IND16, Y
IND16, Z
EXT
05
15
25
1705
1715
1725
1735
2705
2715
2725
2735
48
58
68
78
1748
1758
1768
1778
2748
2758
2768
C8
D8
E8
F8
17C8
17D8
17E8
17F8
27C8
27D8
27E8
00
10
20
1700
1710
1720
1730
2700
2710
2720
2730
ff
ff
ff
gggg
gggg
gggg
hh ll
gggg
gggg
gggg
hh ll
ff
ff
ff
ii
gggg
gggg
gggg
hh ll
—
—
—
ff
ff
ff
ii
gggg
gggg
gggg
hh ll
—
—
—
ff
ff
ff
gggg
gggg
gggg
hh ll
gggg
gggg
gggg
hh ll
4
4
4
6
6
6
6
6
————0100
6
6
6
———— ∆∆∆∆
6
6
6
2
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
———— ∆∆∆∆
6
6
6
2
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
———— ∆∆01
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
———— ∆∆01
8
8
8
M68HC16 Z SERIES CENTRAL PROCESSING UNIT MOTOROLA
USER’S MANUAL 4-17
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 78

nc...
I
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
Table 4-2 Instruction Set Summary (Continued)
Mnemonic Operation Description Address Instruction Condition Codes
Mode Opcode Operand Cycles S MV H EV N Z V C
———— ∆∆∆∆
CPD CompareD toMemory (D) − (M : M + 1) IND8, X
CPE Compare E toMemory (E) − (M : M + 1) IMM16
CPS Compare Stack
Pointer to Memory
CPX Compare IX to
Memory
CPY Compare IY to
Memory
CPZ Compare IZ to
Memory
DAA Decimal Adjust A (A)
DEC Decrement Memory (M) − $01 ⇒ M IND8, X
DECA Decrement A (A) − $01 ⇒ A INH 3701 — 2 — — — — ∆∆∆—
DECB Decrement B (B) − $01 ⇒ B INH 3711 — 2 — — — — ∆∆∆—
DECW Decrement Memory
Word
EDIV Extended Unsigned
Integer Divide
(SP) − (M : M+ 1) IND8, X
(IX) − (M : M + 1) IND8, X
(IY) − (M : M + 1) IND8, X
(IZ) − (M : M+ 1) IND8, X
10
(M : M + 1) − $0001
⇒ M : M + 1
(E : D) / (IX)
Quotient ⇒ IX
Remainder ⇒ D
IND8, Y
IND8, Z
IMM16
IND16, X
IND16, Y
IND16, Z
EXT
E, X
E, Y
E, Z
IND16, X
IND16, Y
IND16, Z
EXT
IND8, Y
IND8, Z
IMM16
IND16, X
IND16, Y
IND16, Z
EXT
IND8, Y
IND8, Z
IMM16
IND16, X
IND16, Y
IND16, Z
EXT
IND8, Y
IND8, Z
IMM16
IND16, X
IND16, Y
IND16, Z
EXT
IND8, Y
IND8, Z
IMM16
IND16, X
IND16, Y
IND16, Z
EXT
INH 3721 — 2 — — — — ∆∆U ∆
IND8, Y
IND8, Z
IND16, X
IND16, Y
IND16, Z
EXT
IND16, X
IND16, Y
IND16, Z
EXT
INH 3728 — 24 — — — — ∆∆∆∆
88
98
A8
37B8
37C8
37D8
37E8
37F8
2788
2798
27A8
3738
3748
3758
3768
3778
4F
5F
6F
377F
174F
175F
176F
177F
4C
5C
6C
377C
174C
175C
176C
177C
4D
5D
6D
377D
174D
175D
176D
177D
4E
5E
6E
377E
174E
175E
176E
177E
01
11
21
1701
1711
1721
1731
2701
2711
2721
2731
ff
ff
ff
jj kk
gggg
gggg
gggg
hh ll
—
—
—
jjkk
gggg
gggg
gggg
hhll
ff
ff
ff
jj kk
gggg
gggg
gggg
hh ll
ff
ff
ff
jj kk
gggg
gggg
gggg
hh ll
ff
ff
ff
jj kk
gggg
gggg
gggg
hh ll
ff
ff
ff
jj kk
gggg
gggg
gggg
hh ll
ff
ff
ff
gggg
gggg
gggg
hh ll
gggg
gggg
gggg
hh ll
6
6
6
4
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
———— ∆∆∆∆
4
6
6
6
6
———— ∆∆∆∆
6
6
6
4
6
6
6
6
———— ∆∆∆∆
6
6
6
4
6
6
6
6
———— ∆∆∆∆
6
6
6
4
6
6
6
6
————
6
6
6
4
6
6
6
6
———— ∆∆∆—
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
———— ∆∆∆—
8
8
8
MOTOROLA CENTRAL PROCESSING UNIT M68HC16 Z SERIES
4-18 USER’S MANUAL
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 79

nc...
I
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
Table 4-2 Instruction Set Summary (Continued)
Mnemonic Operation Description Address Instruction Condition Codes
Mode Opcode Operand Cycles S MV H EV N Z V C
EDIVS Extended Signed
Integer Divide
EMUL Extended Unsigned
Multiply
EMULS Extended Signed
Multiply
EORA Exclusive OR A (A) ⊕ (M) ⇒ A IND8, X
EORB Exclusive OR B (B) ⊕ (M) ⇒ B IND8, X
EORD Exclusive OR D (D) ⊕ (M : M + 1) ⇒ D IND8, X
EORE Exclusive OR E (E) ⊕ (M : M + 1) ⇒ E IMM16
FDIV Fractional
Unsigned Divide
FMULS Fractional Signed
Multiply
IDIV Integer Divide (D) / (IX) ⇒ IX
INC Increment Memory (M) + $01 ⇒ M IND8, X
INCA Increment A (A) + $01 ⇒ A INH 3703 — 2 — — — — ∆∆∆—
INCB Increment B (B) + $01 ⇒ B INH 3713 — 2 — — — — ∆∆∆—
INCW Increment Memory
Word
(E : D) / (IX)
Quotient ⇒ IX
Remainder ⇒ D
(E) ∗(D) ⇒ E : D INH 3725 — 10 — — — — ∆∆— ∆
(E) ∗(D) ⇒ E : D INH 3726 — 8 — — — — ∆∆— ∆
(D) / (IX) ⇒ IX
Remainder ⇒ D
(E) ∗ (D) ⇒ E : D[31:1]
0 ⇒ D[0]
Remainder ⇒ D
(M : M + 1) + $0001
⇒ M : M + 1
INH 3729 — 38 — — — — ∆∆∆∆
———— ∆∆0—
44
IND8, Y
IND8, Z
IMM8
IND16, X
IND16, Y
IND16, Z
EXT
E, X
E, Y
E, Z
IND8, Y
IND8, Z
IMM8
IND16, X
IND16, Y
IND16, Z
EXT
E, X
E, Y
E, Z
IND8, Y
IND8, Z
IMM16
IND16, X
IND16, Y
IND16, Z
EXT
E, X
E, Y
E, Z
IND16, X
IND16, Y
IND16, Z
EXT
INH 372B — 22 — — — — — ∆∆∆
INH 3727 — 8 — — — — ∆∆∆∆
INH 372A — 22 — — — — — ∆ 0 ∆
IND8, Y
IND8, Z
IND16, X
IND16, Y
IND16, Z
EXT
IND16, X
IND16, Y
IND16, Z
EXT
54
64
74
1744
1754
1764
1774
2744
2754
2764
C4
D4
E4
F4
17C4
17D4
17E4
17F4
27C4
27D4
27E4
84
94
A4
37B4
37C4
37D4
37E4
37F4
2784
2794
27A4
3734
3744
3754
3764
3774
03
13
23
1703
1713
1723
1733
2703
2713
2723
2733
ff
ff
ff
ii
gggg
gggg
gggg
hh ll
—
—
—
ff
ff
ff
ii
gggg
gggg
gggg
hh ll
—
—
—
ff
ff
ff
jj kk
gggg
gggg
gggg
hh ll
—
—
—
jj kk
gggg
gggg
gggg
hh ll
ff
ff
ff
gggg
gggg
gggg
hh ll
gggg
gggg
gggg
hh ll
6
6
6
2
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
———— ∆∆0—
6
6
6
2
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
———— ∆∆0—
6
6
6
4
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
———— ∆∆0—
4
6
6
6
6
———— ∆∆∆—
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
———— ∆∆∆—
8
8
8
M68HC16 Z SERIES CENTRAL PROCESSING UNIT MOTOROLA
USER’S MANUAL 4-19
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 80

nc...
I
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
Table 4-2 Instruction Set Summary (Continued)
Mnemonic Operation Description Address Instruction Condition Codes
Mode Opcode Operand Cycles S MV H EV N Z V C
JMP Jump 〈ea〉⇒ PK : PC EXT20
JSR Jump to Subroutine Push (PC)
2
LBCC
LBCS
LBEQ
LBEV
LBGE
LBGT
LBHI
LBLE
LBLS
LBLT
LBMI
LBMV
LBNE
LBPL
LBRA Long Branch Always If 1 = 1, branch REL16 3780 rrrr 6 — — — — ————
LBRN Long Branch Never If 1 = 0, branch REL16 3781 rrrr 6 — — — — ————
LBSR Long Branch to
LBVC
LBVS
LDAA Load A (M) ⇒ A IND8, X
Long Branch if Carry
Clear
2
Long Branch if Carry
Set
2
Long Branch if Equal
to Zero
2
Long Branch if EV Set If EV = 1, branch REL16 3791 rrrr 6, 4 — — — — ————
2
LongBranch if Greater
Than or Equal to Zero
2
LongBranch if Greater
Than Zero
2
Long Branch if Higher If C ✛ Z = 0, branch REL16 3782 rrrr 6, 4 — — — — ————
2
Long Branch if Less
Than or Equal to Zero
2
Long Branch ifLower
or Same
2
Long Branch if Less
Than Zero
2
Long Branch if Minus If N = 1, branch REL16 378B rrrr 6, 4 — — — — ————
2
Long Branch ifMV Set If MV = 1, branch REL16 3790 rrrr 6, 4 — — — — ————
2
Long Branch if Not
Equal to Zero
2
Long Branch if Plus If N = 0, branch REL16 378A rrrr 6, 4 — — — — ————
Subroutine
2
Long Branch if
Overflow Clear
2
Long Branch if
Overflow Set
(SK : SP) −$0002 ⇒SK :SP
Push (CCR)
(SK : SP) −$0002 ⇒SK :SP
〈ea〉⇒ PK : PC
If C = 0, branch REL16 3784 rrrr 6, 4 — — — — ————
If C = 1, branch REL16 3785 rrrr 6, 4 — — — — ————
If Z = 1, branch REL16 3787 rrrr 6, 4 — — — — ————
If N ⊕ V = 0, branch REL16 378C rrrr 6, 4 — — — — ————
If Z ✛ (N ⊕ V) = 0, branch REL16 378E rrrr 6, 4 — — — — ————
If Z ✛ (N ⊕ V) = 1, branch REL16 378F rrrr 6, 4 — — — — ————
If C ✛ Z = 1, branch REL16 3783 rrrr 6, 4 — — — — ————
If N ⊕ V = 1, branch REL16 378D rrrr 6, 4 — — — — ————
If Z = 0, branch REL16 3786 rrrr 6, 4 — — — — ————
Push (PC)
(SK : SP) − 2 ⇒ SK : SP
Push (CCR)
(SK : SP) − 2 ⇒ SK : SP
(PK : PC) + Offset ⇒
PK : PC
If V = 0, branch REL16 3788 rrrr 6, 4 — — — — ————
If V = 1, branch REL16 3789 rrrr 6, 4 — — — — ————
IND20, X
IND20, Y
IND20, Z
EXT20
IND20, X
IND20, Y
IND20, Z
REL16 27F9 rrrr 10 — — — — ————
IND8, Y
IND8, Z
IMM8
IND16, X
IND16, Y
IND16, Z
EXT
E, X
E, Y
E, Z
7A
4B
5B
6B
FA
89
99
A9
45
55
65
75
1745
1755
1765
1775
2745
2755
2765
zb hh ll
zg gggg
zg gggg
zg gggg
zb hh ll
zg gggg
zg gggg
zg gggg
ff
ff
ff
ii
gggg
gggg
gggg
hh ll
—
—
—
6
—— — —————
8
8
8
10
—— — —————
12
12
12
———— ∆∆0—
6
6
6
2
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
MOTOROLA CENTRAL PROCESSING UNIT M68HC16 Z SERIES
4-20 USER’S MANUAL
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 81

nc...
I
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
Table 4-2 Instruction Set Summary (Continued)
Mnemonic Operation Description Address Instruction Condition Codes
Mode Opcode Operand Cycles S MV H EV N Z V C
———— ∆∆0 ∆
LDAB Load B (M) ⇒ B IND8, X
LDD Load D (M : M + 1) ⇒ D IND8, X
LDE Load E (M : M + 1) ⇒ E IMM16
LDED Load Concatenated
E and D
LDHI Initialize H and I (M : M + 1)X⇒ H R
LDS Load SP (M : M + 1)⇒ SP IND8, X
LDX Load IX (M : M + 1) ⇒ IX IND8, X
LDY Load IY (M : M + 1) ⇒ IY IND8, X
LDZ Load IZ (M : M + 1)⇒ IZ IND8, X
(M : M + 1)⇒ E
(M + 2 : M + 3)⇒ D
(M : M + 1)Y⇒ I R
IND8, Y
IND8, Z
IMM8
IND16, X
IND16, Y
IND16, Z
EXT
E, X
E, Y
E, Z
IND8, Y
IND8, Z
IMM16
IND16, X
IND16, Y
IND16, Z
EXT
E, X
E, Y
E, Z
IND16, X
IND16, Y
IND16, Z
EXT
EXT 2771 hh ll 8 — — — — ————
INH 27B0 — 8 — — — — ————
IND8, Y
IND8, Z
IND16, X
IND16, Y
IND16, Z
EXT
IMM16
IND8, Y
IND8, Z
IMM16
IND16, X
IND16, Y
IND16, Z
EXT
IND8, Y
IND8, Z
IMM16
IND16, X
IND16, Y
IND16, Z
EXT
IND8, Y
IND8, Z
IMM16
IND16, X
IND16, Y
IND16, Z
EXT
C5
D5
E5
F5
17C5
17D5
17E5
17F5
27C5
27D5
27E5
85
95
A5
37B5
37C5
37D5
37E5
37F5
2785
2795
27A5
3735
3745
3755
3765
3775
CF
DF
EF
17CF
17DF
17EF
17FF
37BF
CC
DC
EC
37BC
17CC
17DC
17EC
17FC
CD
DD
ED
37BD
17CD
17DD
17ED
17FD
CE
DE
EE
37BE
17CE
17DE
17EE
17FE
ff
ff
ff
ii
gggg
gggg
gggg
hh ll
—
—
—
ff
ff
ff
jj kk
gggg
gggg
gggg
hh ll
—
—
—
jj kk
gggg
gggg
gggg
hh ll
ff
ff
ff
gggg
gggg
gggg
hh ll
jj kk
ff
ff
ff
jj kk
gggg
gggg
gggg
hh ll
ff
ff
ff
jj kk
gggg
gggg
gggg
hh ll
ff
ff
ff
jj kk
gggg
gggg
gggg
hh ll
6
6
6
2
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
———— ∆∆0—
6
6
6
4
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
———— ∆∆0—
4
6
6
6
6
———— ∆∆0—
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
4
———— ∆∆0—
6
6
6
4
6
6
6
6
———— ∆∆0—
6
6
6
4
6
6
6
6
———— ∆∆0—
6
6
6
4
6
6
6
6
M68HC16 Z SERIES CENTRAL PROCESSING UNIT MOTOROLA
USER’S MANUAL 4-21
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 82

Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
Table 4-2 Instruction Set Summary (Continued)
Mnemonic Operation Description Address Instruction Condition Codes
Mode Opcode Operand Cycles S MV H EV N Z V C
LPSTOP Low Power Stop If S
LSR Logical Shift Right IND8, X
LSRA Logical Shift Right A INH 370F — 2 — — — — 0 ∆∆∆
LSRB Logical Shift Right B INH 371F — 2 — — — — 0 ∆∆∆
LSRD Logical Shift Right D INH 27FF — 2 — — — — 0 ∆∆∆
nc...
I
LSRE Logical Shift Right E INH 277F — 2 — — — — 0 ∆∆∆
then STOP
else NOP
INH 27F1 — 4, 20 — — — — ————
———— 0∆∆∆
IND8, Y
IND8, Z
IND16, X
IND16, Y
IND16, Z
EXT
0F
1F
2F
170F
171F
172F
173F
ff
ff
ff
gggg
gggg
gggg
hh ll
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
LSRW Logical Shift Right
MAC Multiply and
MOVB Move Byte (M
MOVW Move Word (M : M + 11) ⇒ M : M + 12IXP to EXT
MUL Multiply (A) ∗ (B) ⇒ D INH 3724 — 10 — — — — — — — ∆
NEG Negate Memory $00 − (M) ⇒ M IND8, X
NEGA Negate A $00 − (A) ⇒ A INH 3702 — 2 — — — — ∆∆∆∆
NEGB Negate B $00 − (B) ⇒ B INH 3712 — 2 — — — — ∆∆∆∆
NEGD Negate D $0000 − (D)⇒ D INH 27F2 — 2 — — — — ∆∆∆∆
NEGE Negate E $0000 − (E)⇒ E INH 2772 — 2 — — — — ∆∆∆∆
NEGW Negate MemoryWord $0000 − (M : M + 1)
NOP Null Operation — INH 274C — 2 — — — — ————
Word
Accumulate
Signed 16-Bit
Fractions
(HR) ∗ (IR) ⇒ E : D
(AM) + (E : D) ⇒AM
Qualified (IX) ⇒ IX
Qualified (IY) ⇒ IY
(HR) ⇒ IZ
(M : M + 1)
(M : M + 1)Y⇒ IR
⇒ HR
X
) ⇒ M
1
⇒ M : M + 1
2
IND16, X
IND16, Y
IND16, Z
EXT
IMM8 7B xoyo 12 — ∆ — ∆ —— ∆ —
IXP to EXT
EXT to IXP
EXT to
EXT
EXT to IXP
EXT to
EXT
IND8, Y
IND8, Z
IND16, X
IND16, Y
IND16, Z
EXT
IND16, X
IND16, Y
IND16, Z
EXT
270F
271F
272F
273F
30
32
37FE
31
33
37FF
02
12
22
1702
1712
1722
1732
2702
2712
2722
2732
gggg
gggg
gggg
hh ll
ff hh ll
ff hh ll
hh ll hh ll
ff hh ll
ff hh ll
hh ll hh ll
ff
ff
ff
gggg
gggg
gggg
hh ll
gggg
gggg
gggg
hh ll
8
———— 0∆∆∆
8
8
8
8
———— ∆∆0—
8
10
8
———— ∆∆0—
8
10
———— ∆∆∆∆
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
———— ∆∆∆∆
8
8
8
MOTOROLA CENTRAL PROCESSING UNIT M68HC16 Z SERIES
4-22 USER’S MANUAL
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 83

nc...
I
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
Table 4-2 Instruction Set Summary (Continued)
Mnemonic Operation Description Address Instruction Condition Codes
Mode Opcode Operand Cycles S MV H EV N Z V C
———— ∆∆0—
ORAA OR A (A) ✛ (M) ⇒ A IND8, X
ORAB OR B (B) ✛ (M) ⇒ B IND8, X
ORD OR D (D) ✛ (M : M + 1) ⇒ D IND8, X
ORE OR E (E) ✛ (M : M + 1) ⇒ E IMM16
1
ORP
PSHA Push A (SK : SP) + $0001 ⇒ SK : SP
PSHB Push B (SK : SP) + $0001 ⇒ SK : SP
PSHM Push Multiple
PSHMAC Push MAC Registers MAC Registers ⇒ Stack INH 27B8 — 14 — — — — ————
PULA Pull A (SK :SP) + $0002 ⇒ SK : SP
PULB Pull B (SK :SP) + $0002 ⇒ SK : SP
OR Condition Code
Register
Registers
Mask bits:
0 = D
1 = E
2 = IX
3 = IY
4 = IZ
5 = K
6 = CCR
7 = (Reserved)
(CCR) ✛ IMM16 ⇒ CCR IMM16 373B jj kk 4 ∆∆ ∆ ∆∆∆∆∆
Push (A)
(SK : SP) −$0002 ⇒SK:SP
Push (B)
(SK : SP) −$0002 ⇒SK:SP
For mask bits 0 to 7:
If mask bit set
Push register
(SK : SP) − 2 ⇒ SK : SP
Pull (A)
(SK : SP) –$0001 ⇒SK :SP
Pull (B)
(SK : SP) –$0001 ⇒SK :SP
IND8, Y
IND8, Z
IMM8
IND16, X
IND16, Y
IND16, Z
EXT
E, X
E, Y
E, Z
IND8, Y
IND8, Z
IMM8
IND16, X
IND16, Y
IND16, Z
EXT
E, X
E, Y
E, Z
IND8, Y
IND8, Z
IMM16
IND16, X
IND16, Y
IND16, Z
EXT
E, X
E, Y
E, Z
IND16, X
IND16, Y
IND16, Z
EXT
INH 3708 — 4 — — — — ————
INH 3718 — 4 — — — — ————
IMM8 34 ii 4 + 2N
INH 3709 — 6 — — — — ————
INH 3719 — 6 — — — — ————
47
57
67
77
1747
1757
1767
1777
2747
2757
2767
C7
D7
E7
F7
17C7
17D7
17E7
17F7
27C7
27D7
27E7
87
97
A7
37B7
37C7
37D7
37E7
37F7
2787
2797
27A7
3737
3747
3757
3767
3777
ff
ff
ff
ii
gggg
gggg
gggg
hh ll
—
—
—
ff
ff
ff
ii
gggg
gggg
gggg
hh ll
—
—
—
ff
ff
ff
jj kk
gggg
gggg
gggg
hh ll
—
—
—
jj kk
gggg
gggg
gggg
hh ll
6
6
6
2
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
2
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
4
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
4
6
6
6
6
N =
numberof
registers
pushed
———— ∆∆0—
———— ∆∆0—
———— ∆∆0—
—— — —————
M68HC16 Z SERIES CENTRAL PROCESSING UNIT MOTOROLA
USER’S MANUAL 4-23
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 84

nc...
I
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
Table 4-2 Instruction Set Summary (Continued)
Mnemonic Operation Description Address Instruction Condition Codes
Mode Opcode Operand Cycles S MV H EV N Z V C
1
PULM
PULMAC Pull MAC State Stack ⇒ MAC Registers INH 27B9 — 16 — — — — ————
RMAC Repeating
ROL Rotate Left IND8, X
ROLA Rotate Left A INH 370C — 2 — — — — ∆∆∆∆
ROLB Rotate Left B INH 371C — 2 — — — — ∆∆∆∆
ROLD Rotate Left D INH 27FC — 2 — — — — ∆∆∆∆
ROLE Rotate Left E INH 277C — 2 — — — — ∆∆∆∆
ROLW Rotate Left Word IND16, X
ROR Rotate Right Byte IND8, X
RORA Rotate Right A INH 370E — 2 — — — — ∆∆∆∆
Pull Multiple Registers
Mask bits:
0 = CCR[15:4]
1 = K
2 = IZ
3 = IY
4 = IX
5 = E
6 = D
7 = (Reserved)
Multiply and
Accumulate
Signed 16-Bit
Fractions
For mask bits 0 to 7:
If mask bit set
(SK : SP) + 2 ⇒ SK : SP
Pull register
Repeat until (E) < 0
(AM) + (H) ∗ (I) ⇒AM
Qualified (IX) ⇒ IX;
Qualified (IY) ⇒ IY;
(M : M + 1)
(M : M + 1)
Until (E) < $0000
X
Y
(E) − 1 ⇒ E
⇒ H;
⇒ I
IMM8 35 ii 4+2(N+1)
numberof
registers
pulled
IMM8 FB xoyo 6 + 12
iteration
IND8, Y
IND8, Z
IND16, X
IND16, Y
IND16, Z
EXT
IND16, Y
IND16, Z
EXT
IND8, Y
IND8, Z
IND16, X
IND16, Y
IND16, Z
EXT
0C
1C
2C
170C
171C
172C
173C
270C
271C
272C
273C
0E
1E
2E
170E
171E
172E
173E
ff
ff
ff
gggg
gggg
gggg
hh ll
gggg
gggg
gggg
hh ll
ff
ff
ff
gggg
gggg
gggg
hh ll
∆∆ ∆ ∆∆∆∆∆
N =
— ∆ — ∆ ————
per
———— ∆∆∆∆
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
———— ∆∆∆∆
8
8
8
———— ∆∆∆∆
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
RORB Rotate Right B INH 371E — 2 — — — — ∆∆∆∆
RORD Rotate Right D INH 27FE — 2 — — — — ∆∆∆∆
RORE Rotate Right E INH 277E — 2 — — — — ∆∆∆∆
MOTOROLA CENTRAL PROCESSING UNIT M68HC16 Z SERIES
4-24 USER’S MANUAL
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 85
nc...
I
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
Table 4-2 Instruction Set Summary (Continued)
Mnemonic Operation Description Address Instruction Condition Codes
Mode Opcode Operand Cycles S MV H EV N Z V C
RORW Rotate Right Word IND16, X
3
RTI
RTS
SBA Subtract B from A (A) − (B) ⇒ A INH 370A — 2 — — — — ∆∆∆∆
SBCA Subtract with Carry
SBCB Subtract with Carry
SBCD Subtract with Carry
SBCE Subtract with Carry
SDE Subtract D from E (E) − (D)⇒ E INH 2779 — 2 — — — — ∆∆∆∆
STAA Store A (A) ⇒ M IND8, X
Return from Interrupt (SK : SP) + 2 ⇒ SK : SP
4
Return from Subrou-
tine
from A
from B
from D
from E
Pull CCR
(SK : SP) + 2 ⇒ SK: SP
(PK : PC) − 6⇒ PK : PC
(SK : SP) + 2 ⇒ SK : SP
(SK : SP) + 2 ⇒ SK : SP
(PK : PC) − 2 ⇒ PK: PC
(A) − (M) − C⇒ A IND8, X
(B) − (M) − C⇒ B IND8, X
(D) − (M : M + 1) − C⇒ D IND8, X
(E) − (M : M + 1) − C⇒ E IMM16
Pull PC
Pull PK
Pull PC
IND16, Y
IND16, Z
EXT
INH 2777 — 12 ∆∆ ∆ ∆∆∆∆∆
INH 27F7 — 12 — — — — ————
IND8, Y
IND8, Z
IMM8
IND16, X
IND16, Y
IND16, Z
EXT
E, X
E, Y
E, Z
IND8, Y
IND8, Z
IMM8
IND16, X
IND16, Y
IND16, Z
EXT
E, X
E, Y
E, Z
IND8, Y
IND8, Z
IMM16
IND16, X
IND16, Y
IND16, Z
EXT
E, X
E, Y
E, Z
IND16, X
IND16, Y
IND16, Z
EXT
IND8, Y
IND8, Z
IND16, X
IND16, Y
IND16, Z
EXT
E, X
E, Y
E, Z
270E
271E
272E
273E
42
52
62
72
1742
1752
1762
1772
2742
2752
2762
C2
D2
E2
F2
17C2
17D2
17E2
17F2
27C2
27D2
27E2
82
92
A2
37B2
37C2
37D2
37E2
37F2
2782
2792
27A2
3732
3742
3752
3762
3772
4A
5A
6A
174A
175A
176A
177A
274A
275A
276A
gggg
gggg
gggg
hh ll
ff
ff
ff
ii
gggg
gggg
gggg
hh ll
—
—
—
ff
ff
ff
ii
gggg
gggg
gggg
hh ll
—
—
—
ff
ff
ff
jj kk
gggg
gggg
gggg
hh ll
—
—
—
jj kk
gggg
gggg
gggg
hh ll
ff
ff
ff
gggg
gggg
gggg
hh ll
—
—
—
8
———— ∆∆∆∆
8
8
8
———— ∆∆∆∆
6
6
6
2
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
———— ∆∆∆∆
6
6
6
2
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
———— ∆∆∆∆
6
6
6
4
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
———— ∆∆∆∆
4
6
6
6
6
———— ∆∆0—
4
4
4
6
6
6
6
4
4
4
M68HC16 Z SERIES CENTRAL PROCESSING UNIT MOTOROLA
USER’S MANUAL 4-25
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 86

nc...
I
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
Table 4-2 Instruction Set Summary (Continued)
Mnemonic Operation Description Address Instruction Condition Codes
Mode Opcode Operand Cycles S MV H EV N Z V C
———— ∆∆0—
STAB Store B (B) ⇒ M IND8, X
STD Store D (D) ⇒ M : M + 1 IND8, X
STE Store E (E) ⇒ M : M + 1 IND16, X
STED Store Concatenated
D and E
STS Store Stack Pointer (SP) ⇒ M : M + 1 IND8, X
STX Store IX (IX) ⇒ M : M+ 1 IND8, X
STY Store IY (IY) ⇒ M : M+ 1 IND8, X
STZ Store Z (IZ) ⇒ M : M + 1 IND8, X
SUBA Subtract from A (A) − (M) ⇒ A IND8, X
(E) ⇒ M : M+ 1
(D) ⇒ M + 2: M + 3
IND8, Y
IND8, Z
IND16, X
IND16, Y
IND16, Z
EXT
E, X
E, Y
E, Z
IND8, Y
IND8, Z
IND16, X
IND16, Y
IND16, Z
EXT
E, X
E, Y
E, Z
IND16, Y
IND16, Z
EXT
EXT 2773 hh ll 8 — — — — ————
IND8, Y
IND8, Z
IND16, X
IND16, Y
IND16, Z
EXT
IND8, Y
IND8, Z
IND16, X
IND16, Y
IND16, Z
EXT
IND8, Y
IND8, Z
IND16, X
IND16, Y
IND16, Z
EXT
IND8, Y
IND8, Z
IND16, X
IND16, Y
IND16, Z
EXT
IND8, Y
IND8, Z
IMM8
IND16, X
IND16, Y
IND16, Z
EXT
E, X
E, Y
E, Z
CA
DA
EA
17CA
17DA
17EA
17FA
27CA
27DA
27EA
8A
9A
AA
37CA
37DA
37EA
37FA
278A
279A
27AA
374A
375A
376A
377A
8F
9F
AF
178F
179F
17AF
17BF
8C
9C
AC
178C
179C
17AC
17BC
8D
9D
AD
178D
179D
17AD
17BD
8E
9E
AE
178E
179E
17AE
17BE
40
50
60
70
1740
1750
1760
1770
2740
2750
2760
ff
ff
ff
gggg
gggg
gggg
hh ll
—
—
—
ff
ff
ff
gggg
gggg
gggg
hh ll
—
—
—
gggg
gggg
gggg
hh ll
ff
ff
ff
gggg
gggg
gggg
hh ll
ff
ff
ff
gggg
gggg
gggg
hh ll
ff
ff
ff
gggg
gggg
gggg
hh ll
ff
ff
ff
gggg
gggg
gggg
hh ll
ff
ff
ff
ii
gggg
gggg
gggg
hh ll
—
—
—
4
4
4
6
6
6
6
4
4
4
———— ∆∆0—
4
4
4
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
———— ∆∆0—
6
6
6
———— ∆∆0—
4
4
4
6
6
6
6
———— ∆∆0—
4
4
4
6
6
6
6
———— ∆∆0—
4
4
4
6
6
6
6
———— ∆∆0—
4
4
4
6
6
6
6
———— ∆∆∆∆
6
6
6
2
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
MOTOROLA CENTRAL PROCESSING UNIT M68HC16 Z SERIES
4-26 USER’S MANUAL
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 87

nc...
I
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
Table 4-2 Instruction Set Summary (Continued)
Mnemonic Operation Description Address Instruction Condition Codes
Mode Opcode Operand Cycles S MV H EV N Z V C
———— ∆∆∆∆
SUBB Subtract from B (B) − (M) ⇒ B IND8, X
SUBD Subtract from D (D) − (M : M + 1) ⇒ D IND8, X
SUBE Subtract from E (E) − (M : M + 1) ⇒ E IMM16
SWI Software Interrupt (PK: PC)+ $0002 ⇒PK :PC
SXT Sign Extend B into A If B7 = 1
TAB Transfer A to B (A) ⇒ B INH 3717 — 2 — — — — ∆∆0—
TAP Transfer A to CCR (A[7:0]) ⇒ CCR[15:8] INH 37FD — 4 ∆∆ ∆ ∆∆∆∆∆
TBA Transfer B to A (B) ⇒ A INH 3707 — 2 — — — — ∆∆0—
TBEK Transfer B to EK (B[3:0]) ⇒ EK INH 27FA — 2 — — — — ————
TBSK Transfer B to SK (B[3:0]) ⇒ SK INH 379F — 2 — — — — ————
TBXK Transfer B to XK (B[3:0]) ⇒ XK INH 379C — 2 — — — — ————
TBYK Transfer B to YK (B[3:0]) ⇒ YK INH 379D — 2 — — — — ————
TBZK Transfer B to ZK (B[3:0]) ⇒ ZK INH 379E — 2 — — — — ————
TDE Transfer D to E (D) ⇒ E INH 277B — 2 — — — — ∆∆0—
TDMSK Transfer D to
1
TDP
TED Transfer E to D (E) ⇒ D INH 27FB — 2 — — — — ∆∆0—
TEDM Transfer E and D to
TEKB Transfer EK to B (EK) ⇒ B[3:0]
TEM Transfer E to
TMER Transfer Rounded AM
XMSK : YMSK
Transfer D to CCR (D) ⇒ CCR[15:4] INH 372D — 4 ∆∆ ∆ ∆∆∆∆∆
AM[31:0]
Sign Extend AM
AM[31:16]
Sign Extend AM
Clear AM LSB
to E
Push (PC)
(SK : SP) −$0002 ⇒SK :SP
Push (CCR)
(SK : SP) −$0002 ⇒SK :SP
$0 ⇒ PK
SWI Vector ⇒ PC
then $FF ⇒A
else $00 ⇒A
(D[15:8]) ⇒ X MASK
(D[7:0]) ⇒ Y MASK
(E) ⇒ AM[31:16]
(D) ⇒ AM[15:0]
AM[35:32] = AM31
$0 ⇒ B[7:4]
(E) ⇒ AM[31:16]
$00 ⇒ AM[15:0]
AM[35:32] = AM31
Rounded (AM) ⇒ Temp
If (SM • (EV ✛ MV))
then Saturation Value ⇒ E
else Temp[31:16] ⇒ E
IND8, Y
IND8, Z
IMM8
IND16, X
IND16, Y
IND16, Z
EXT
E, X
E, Y
E, Z
IND8, Y
IND8, Z
IMM16
IND16, X
IND16, Y
IND16, Z
EXT
E, X
E, Y
E, Z
IND16, X
IND16, Y
IND16, Z
EXT
INH 3720 — 16 — — — — ————
INH 27F8 — 2 — — — — ∆∆——
INH 372F — 2 — — — — ————
INH 27B1 — 4 — 0 — 0 ————
INH 27BB — 2 — — — — ————
INH 27B2 — 4 — 0 — 0 ————
INH 27B4 — 6 — ∆ — ∆∆∆——
C0
D0
E0
F0
17C0
17D0
17E0
17F0
27C0
27D0
27E0
80
90
A0
37B0
37C0
37D0
37E0
37F0
2780
2790
27A0
3730
3740
3750
3760
3770
ff
ff
ff
ii
gggg
gggg
gggg
hh ll
—
—
—
ff
ff
ff
jj kk
gggg
gggg
gggg
hh ll
—
—
—
jj kk
gggg
gggg
gggg
hh ll
6
6
6
2
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
———— ∆∆∆∆
6
6
6
4
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
———— ∆∆∆∆
4
6
6
6
6
M68HC16 Z SERIES CENTRAL PROCESSING UNIT MOTOROLA
USER’S MANUAL 4-27
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 88

nc...
I
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
Table 4-2 Instruction Set Summary (Continued)
Mnemonic Operation Description Address Instruction Condition Codes
Mode Opcode Operand Cycles S MV H EV N Z V C
TMET Transfer Truncated
AM to E
TMXED Transfer AM to
IX : E : D
TPA Transfer CCR to A (CCR[15:8]) ⇒ A INH 37FC — 2 — — — — ————
TPD Transfer CCR to D (CCR) ⇒ D INH 372C — 2 — — — — ————
TSKB Transfer SK to B (SK) ⇒ B[3:0]
TST Test Byte
Zero or Minus
TSTA Test A for
Zero or Minus
TSTB Test B for
Zero or Minus
TSTD Test D for
Zero or Minus
TSTE Test E for
Zero or Minus
TSTW Test for
Zero or Minus Word
TSX Transfer SP to X (SK : SP)+ $0002 ⇒ XK : IX INH 274F — 2 — — — — ————
TSY Transfer SP to Y (SK : SP)+ $0002 ⇒ YK : IY INH 275F — 2 — — — — ————
TSZ Transfer SP to Z (SK : SP)+ $0002 ⇒ ZK : IZ INH 276F — 2 — — — — ————
TXKB Transfer XK to B (XK) ⇒ B[3:0]
TXS Transfer X to SP (XK : IX) − $0002⇒ SK : SP INH 374E — 2 — — — — ————
TXY Transfer X to Y (XK : IX) ⇒ YK : IY INH 275C — 2 — — — — ————
TXZ Transfer X to Z (XK : IX) ⇒ ZK : IZ INH 276C — 2 — — — — ————
TYKB Transfer YK to B (YK) ⇒ B[3:0]
TYS Transfer Y to SP (YK : IY) − $0002⇒ SK : SP INH 375E — 2 — — — — ————
TYX Transfer Y to X (YK : IY) ⇒ XK : IX INH 274D — 2 — — — — ————
TYZ Transfer Y to Z (YK : IY) ⇒ ZK : IZ INH 276D — 2 — — — — ————
TZKB Transfer ZK to B (ZK) ⇒ B[3:0]
TZS Transfer Z to SP (ZK : IZ) − $0002⇒ SK : SP INH 376E — 2 — — — — ————
TZX Transfer Z to X (ZK : IZ) ⇒ XK : IX INH 274E — 2 — — — — ————
TZY Transfer Z to Y (ZK : IZ) ⇒ YK : IY INH 275E — 2 — — — — ————
WAI Wait for Interrupt WAIT INH 27F3 — 8 — — — — ————
XGAB Exchange A with B (A) ⇔(B) INH 371A — 2 — — — — ————
XGDE Exchange D with E (D) ⇔(E) INH 277A — 2 — — — — ————
XGDX Exchange D with IX (D) ⇔ (IX) INH 37CC — 2 — — — — ————
If (SM • (EV ✛ MV))
then Saturation Value ⇒ E
else AM[31:16] ⇒ E
AM[35:32] ⇒ IX[3:0]
AM35 ⇒ IX[15:4]
AM[31:16] ⇒ E
AM[15:0] ⇒ D
$0 ⇒ B[7:4]
(M) − $00 IND8, X
(A) − $00 INH 3706 — 2 — — — — ∆∆00
(B) − $00 INH 3716 — 2 — — — — ∆∆00
(D) − $0000 INH 27F6 — 2 — — — — ∆∆00
(E) − $0000 INH 2776 — 2 — — — — ∆∆00
(M : M + 1)− $0000 IND16, X
$0 ⇒ B[7:4]
$0 ⇒ B[7:4]
$0 ⇒ B[7:4]
INH 27B5 — 2 — — — — ∆∆——
INH 27B3 — 6 — — — — ————
INH 37AF — 2 — — — — ————
———— ∆∆00
06
IND8, Y
IND8, Z
IND16, X
IND16, Y
IND16, Z
EXT
IND16, Y
IND16, Z
EXT
INH 37AC — 2 — — — — ————
INH 37AD — 2 — — — — ————
INH 37AE — 2 — — — — ————
16
26
1706
1716
1726
1736
2706
2716
2726
2736
ff
ff
ff
gggg
gggg
gggg
hh ll
gggg
gggg
gggg
hh ll
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
———— ∆∆00
6
6
6
MOTOROLA CENTRAL PROCESSING UNIT M68HC16 Z SERIES
4-28 USER’S MANUAL
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 89

Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
Table 4-2 Instruction Set Summary (Continued)
Mnemonic Operation Description Address Instruction Condition Codes
Mode Opcode Operand Cycles S MV H EV N Z V C
XGDY Exchange D with IY (D) ⇔ (IY) INH 37DC — 2 — — — — ————
XGDZ Exchange D with IZ (D) ⇔(IZ) INH 37EC — 2 — — — — ————
XGEX Exchange E with IX (E) ⇔(IX) INH 374C — 2 — — — — ————
XGEY Exchange E with IY (E) ⇔(IY) INH 375C — 2 — — — — ————
XGEZ Exchange E with IZ (E) ⇔ (IZ) INH 376C — 2 — — — — ————
NOTES:
1. CCR[15:4] change according to the results of the operation. The PK field is not affected.
2. Cycle times for conditional branches are shown in “taken, not taken” order.
3. CCR[15:0] change according to the copy of the CCR pulled from the stack.
4. PK field changes according to the state pulled from the stack. The rest of the CCR is not affected.
nc...
I
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
M68HC16 Z SERIES CENTRAL PROCESSING UNIT MOTOROLA
USER’S MANUAL 4-29
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 90

nc...
I
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
Table 4-3 Instruction Set Abbreviations and Symbols
A — Accumulator A X — Register used in operation
AM — Accumulator M M — Address of one memory byte
B — Accumulator B M +1 — Address of byte at M + $0001
CCR — Condition code register M : M + 1 — Address of one memory word
D — Accumulator D (…)X — Contents of address pointed to by IX
E — Accumulator E (...)Y — Contents of address pointed to by IY
EK — Extended addressing extension field (...)Z — Contents of address pointed to by IZ
IR — MAC multiplicand register E, X — IX with E offset
HR — MAC multiplier register E, Y — IY with E offset
IX — Index register X E, Z — IZ with E offset
IY — Index register Y EXT — Extended
IZ — Index register Z EXT20 — 20-bit extended
K — Address extension register IMM8 — 8-bit immediate
PC — Program counter IMM16 — 16-bit immediate
PK — Program counter extension field IND8, X — IX with unsigned 8-bit offset
SK — Stack pointer extension field IND8, Y — IY with unsigned 8-bit offset
SL — Multiply and accumulate sign latch IND8, Z — IZ with unsigned 8-bit offset
SP — Stack pointer IND16, X — IX with signed 16-bit offset
XK — Index register X extension field IND16, Y — IY with signed 16-bit offset
YK — Index register Y extension field IND16, Z — IZ with signed 16-bit offset
ZK — Index register Z extension field IND20, X — IX with signed 20-bit offset
XMSK — Modulo addressing index register X mask IND20, Y — IY with signed 20-bit offset
YMSK — Modulo addressing index register Y mask IND20, Z — IZ with signed 20-bit offset
S — Stop disable control bit INH — Inherent
MV — AM overflow indicator IXP — Post-modified indexed
H — Half carry indicator REL8 — 8-bit relative
EV — AM extended overflow indicator REL16 — 16-bit relative
N — Negative indicator b — 4-bit address extension
Z — Zero indicator ff — 8-bit unsigned offset
V — Two’s complement overflow indicator gggg — 16-bit signed offset
C — Carry/borrow indicator hh — High byte of 16-bit extended address
IP — Interrupt priority field ii — 8-bit immediate data
SM — Saturation mode control bit jj — High byte of 16-bit immediate data
PK — Program counter extension field kk — Low byte of 16-bit immediate data
— — Bit not affected ll — Low byte of 16-bit extended address
∆ — Bit changes as specified mm — 8-bit mask
0 — Bit cleared mmmm — 16-bit mask
1 — Bit set rr — 8-bit unsigned relative offset
M — Memory location used in operation rrrr — 16-bit signed relative offset
R — Result of operation xo — MAC index register X offset
S — Source data yo — MAC index register Y offset
z — 4-bit zero extension
+ — Addition • — AND
− — Subtraction or negation (two’s complement) ✛ — Inclusive OR (OR)
∗ — Multiplication ⊕ — Exclusive OR (EOR)
/ — Division
> — Greater : — Concatenation
< — Less ⇒ — Transferred
= — Equal ⇔ — Exchanged
≥ — Equal or greater ± — Sign bit; also used to show tolerance
≤ — Equal or less « — Sign extension
≠ — Not equal % — Binary value
NOT — Complementation
$ — Hexadecimal value
MOTOROLA CENTRAL PROCESSING UNIT M68HC16 Z SERIES
4-30 USER’S MANUAL
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 91

Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
4.8 Comparison of CPU16 and M68HC11 CPU Instruction Sets
Most M68HC11 CPU instructions are a source-code compatible subset of the CPU16
instruction set. However, certain M68HC11 CPU instructions have been replaced by
functionally equivalent CPU16 instructions, and some CPU16 instructions with the
same mnemonics as M68HC11 CPU instructions operate differently.
Table 4-4 shows the M68HC11 CPU instructions that either have been replaced by
CPU16 instructions or that operate differently on the CPU16. Replacement instructions are not identical to M68HC11 CPU instructions. M68HC11 code must be altered
to establish proper preconditions.
All CPU16 instruction execution times differ from those of the M68HC11.
M68HC11 Code to M68HC16 Devices
mation about differences between the two instruction sets. Refer to the
ence Manual
nc...
I
(CPU16RM/AD) for further details about CPU operations.
, (M68HC16PN01/D), contains detailed infor-
cale Semiconductor,
Transporting
CPU16 Refer-
Frees
M68HC16 Z SERIES CENTRAL PROCESSING UNIT MOTOROLA
USER’S MANUAL 4-31
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 92

nc...
I
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
Table 4-4 CPU16 Implementation of M68HC11 CPU Instructions
M68HC11 Instruction CPU16 Implementation
BHS BCC only
BLO BCS only
BSR Generates a different stack frame
CLC Replaced by ANDP
CLI Replaced by ANDP
CLV Replaced by ANDP
DES Replaced by AIS
DEX Replaced by AIX
DEY Replaced by AIY
INS Replaced by AIS
INX Replaced by AIX
INY Replaced by AIY
JMP IND8 and EXT addressing modes replaced by IND20 and EXT20 modes
JSR
LSL, LSLD Use ASL instructions
PSHX Replaced by PSHM
PSHY Replaced by PSHM
PULX Replaced by PULM
PULY Replaced by PULM
RTI Reloads PC and CCR only
RTS Uses two-word stack frame
SEC Replaced by ORP
SEI Replaced by ORP
SEV Replaced by ORP
STOP Replaced by LPSTOP
TAP
TPA
TSX Adds two to SK : SP before transfer to XK : IX
TSY Adds two to SK : SP before transfer to YK : IY
TXS Subtracts two from XK : IX before transfer to SK : SP
TXY Transfers XK field to YK field
TYS Subtracts two from YK : IY before transfer to SK : SP
TYX Transfers YK field to XK field
WAI
NOTES:
1. Motorola assemblers automatically translate ASL mnemonics.
IND8 and EXT addressingmodesreplacedbyIND20 and EXT20 modes.
Generates a different stack frame
1
CPU16 CCR bits differ from M68HC11
CPU16 interrupt priority scheme differs from M68HC11
CPU16 CCR bits differ from M68HC11
CPU16 interrupt priority scheme differs from M68HC11
Waits indefinitely for interrupt or reset
Generates a different stack frame
MOTOROLA CENTRAL PROCESSING UNIT M68HC16 Z SERIES
4-32 USER’S MANUAL
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 93

Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
4.9 Instruction Format
CPU16instructions consist of an 8-bitopcode that can be precededby an 8-bit prebyte
and followed by one or more operands.
Opcodes are mapped in four 256-instruction pages. Page 0 opcodes stand alone.
Page 1, 2, and 3 opcodes are pointed to by a prebyte code on page 0. The prebytes
are $17 (page 1), $27 (page 2), and $37 (page 3).
Operands can be four bits, eight bits or sixteen bits in length. Since the CPU16 fetches
16-bit instruction words from even-byte boundaries, each instruction must contain an
even number of bytes.
Operands are organized as bytes, words, or a combination of bytes and words. Operands of four bits are either zero-extended to eight bits, or packed two to a byte. The
largest instructions are six bytes in length. Size, order, and function of operands are
evaluated when an instruction is decoded.
nc...
I
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
A page 0 opcode and an 8-bit operand can be fetched simultaneously. Instructions
that use 8-bit indexed, immediate, and relative addressing modes have this form.
Code written with these instructions is very compact.
Figure 4-4 shows basic CPU16 instruction formats.
M68HC16 Z SERIES CENTRAL PROCESSING UNIT MOTOROLA
USER’S MANUAL 4-33
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 94

Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
8-Bit Opcode with 8-Bit Operand
15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Opcode Operand
8-Bit Opcode with 4-Bit Index Extensions
15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Opcode X Extension Y Extension
8-Bit Opcode, Argument(s)
15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Opcode Operand
Operand(s)
Operand(s)
8-Bit Opcode with 8-Bit Prebyte, No Argument
15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
nc...
I
8-Bit Opcode with 8-Bit Prebyte, Argument(s)
15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Prebyte Opcode
Prebyte Opcode
Operand(s)
Operand(s)
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
8-Bit Opcode with 20-Bit Argument
15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Opcode $0 Extension
Operand
Figure 4-4 Basic Instruction Formats
4.10 Execution Model
This description builds up a conceptual model of the mechanism the CPU16 uses to
fetch and execute instructions. The functional divisions in the model do not necessarily
correspond to physical subunits of the microprocessor.
As shown in Figure 4-5, there are three functional blocks involved in fetching, decoding, and executing instructions. These are the microsequencer, the instruction pipeline, and the execution unit. These elements function concurrently. All three may be
active at any given time.
MOTOROLA CENTRAL PROCESSING UNIT M68HC16 Z SERIES
4-34 USER’S MANUAL
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 95

Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
nc...
I
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
IPIPE0
IPIPE1
DATA
BUS
A
MICROSEQUENCER
INSTRUCTION PIPELINE
B
EXECUTION UNIT
C
16 EXEC UNIT MODEL
Figure 4-5 Instruction Execution Model
4.10.1 Microsequencer
The microsequencer controls the order in which instructions are fetched, advanced
through the pipeline, and executed. It increments the program counter and generates
multiplexed external tracking signals IPIPE0 and IPIPE1 from internal signals that control execution sequence.
4.10.2 Instruction Pipeline
The pipeline is a three stage FIFO that holds instructions while they are decoded and
executed. Depending upon instruction size, as many as three instructions can be in
the pipeline at one time (single-word instructions, one held in stage C, one being executed in stage B, and one latched in stage A).
4.10.3 Execution Unit
The execution unit evaluates opcodes, interfaces with the microsequencer to advance
instructions through the pipeline, and performs instruction operations.
M68HC16 Z SERIES CENTRAL PROCESSING UNIT MOTOROLA
USER’S MANUAL 4-35
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 96

Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
4.11 Execution Process
Fetched opcodes are latched into stage A, then advanced to stage B. Opcodes are
evaluated in stage B. The execution unit can access operands in either stage A or
stage B (stage B accesses are limited to 8-bit operands). When execution is complete,
opcodes are moved from stage B to stage C, where they remain until the next instruction is complete.
A prefetch mechanism in the microsequencer reads instruction words from memory
and increments the program counter. When instruction execution begins, the program
counter points to an address six bytes after the address of the first word of the instruction being executed.
The number of machine cycles necessary to complete an execution sequence varies
according to the complexity of the instruction. Refer to the
(CPU16RM/AD) for details.
CPU16 Reference Manual
nc...
I
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
4.11.1 Changes in Program Flow
When program flow changes, instructions are fetched from a new address. Before execution can begin at the new address, instructions and operands from the previous instruction stream must be removed from the pipeline. If a change in flow is temporary,
a return address must be stored, so that execution of the original instruction stream
can resume after the change in flow.
When an instruction that causes a change in program flow executes, PK : PC point to
the address of the first word of the instruction + $0006. During execution of the instruction, PK : PC is loaded with the address of the first instruction word in the new instruction stream. However, stages A and B still contain words from the old instruction
stream. Extra processing steps must be performed before execution from the new instruction stream.
4.12 Instruction Timing
The execution time of CPU16 instructions has three components:
• Bus cycles required to prefetch the next instruction
• Bus cycles required for operand accesses
• Time required for internal operations
A bus cycle requires a minimum of two system clock periods. If the access time of a
memory device is greater than two clock periods, bus cycles are longer. However, all
bus cycles must be an integer number of clock periods. CPU16 internal operations are
always an integer multiple of two clock periods.
Dynamic bus sizing affects bus cycle time. The integration module manages all accesses. Refer to SECTION 5 SYSTEM INTEGRATION MODULE for more information.
The CPU16 does not execute more than one instruction at a time. The total time required to execute a particular instruction stream can be calculated by summing the individual execution times of each instruction in the stream.
MOTOROLA CENTRAL PROCESSING UNIT M68HC16 Z SERIES
4-36 USER’S MANUAL
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 97

Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
Total execution time is calculated using the expression:
nc...
I
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
()CL
CL
Where:
(CLT) = Total clock periods per instruction
(CLI) = Clock periods used for internal operation
(CLP) = Clock periods used for program access
(CLO) = Clock periods used for operand access
Refer to the
topic.
4.13 Exceptions
An exception is an event that preempts normal instruction processing. Exception processing makes the transition from normal instruction execution to execution of a routine that deals with the exception.
Each exception has an assigned vector that points to an associated handler routine.
Exception processing includes all operations required to transfer control to a handler
routine, but does not include execution of the handler routine itself. Keep the distinction between exception processing and execution of an exception handler in mind
while reading this section.
4.13.1 Exception Vectors
An exception vector is the address of a routine that handles an exception. Exception
vectors are contained in a data structure called the exception vector table, which is located in the first 512 bytes of bank 0. Refer to Table 4-5 for the exception vector table.
All vectors except the reset vector consist of one word and reside in data space. The
reset vector consists of four words that reside in program space. Refer to SECTION 5
SYSTEM INTEGRATION MODULE for information concerning address space types
and the function code outputs. There are 52 predefined or reserved vectors, and 200
user-defined vectors.
CPU16 Reference Manual
()CLO()CL
T
P
(CPU16RM/AD) for more information on this
()++=
I
Each vector is assigned an 8-bit number. Vector numbers for some exceptions are
generated by external devices; others are supplied by the processor. There is a direct
mapping of vector number to vector table address. The processor left shifts the vector
number one place (multiplies by two) to convert it to an address.
M68HC16 Z SERIES CENTRAL PROCESSING UNIT MOTOROLA
USER’S MANUAL 4-37
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 98
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
Table 4-5 Exception Vector Table
Vector
Number
0 0000 P Reset — Initial ZK, SK, and PK
4 0008 D Breakpoint
5 000A D Bus Error
6 000C D Software Interrupt
7 000E D Illegal Instruction
8 0010 D Division by Zero
9 – E 0012 – 001C D Unassigned, Reserved
F 001E D Uninitialized Interrupt
nc...
I
10 0020 D Unassigned, Reserved
11 0022 D Level 1 Interrupt Autovector
12 0024 D Level 2 Interrupt Autovector
13 0026 D Level 3 Interrupt Autovector
14 0028 D Level 4 Interrupt Autovector
15 002A D Level 5 Interrupt Autovector
16 002C D Level 6 Interrupt Autovector
17 002E D Level 7 Interrupt Autovector
18 0030 D Spurious Interrupt
19 – 37 0032 – 006E D Unassigned, Reserved
38 – FF 0070 – 01FE D User-Defined Interrupts
4.13.2 Exception Stack Frame
During exception processing, the contents of the program counter and condition code
register are stacked at a location pointed to by SK : SP. Unless it is altered during ex-
cale Semiconductor,
ception processing, the stacked PK : PC value is the address of the next instruction in
the current instruction stream, plus $0006. Figure 4-6 shows the exception stack
frame.
Vector
Address
0002 P Reset — Initial PC
0004 P Reset — Initial SP
0006 P Reset — Initial IZ (Direct Page)
Address
Space
Type of
Exception
Frees
Low Address ⇐ SP After Exception Stacking
Condition Code Register
High Address Program Counter ⇐ SP Before Exception Stacking
Figure 4-6 Exception Stack Frame Format
MOTOROLA CENTRAL PROCESSING UNIT M68HC16 Z SERIES
4-38 USER’S MANUAL
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 99

Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
4.13.3 Exception Processing Sequence
Exception processing is performed in four phases. Priority of all pending exceptions is
evaluated and the highest priority exception is processed first. Processor state is
stacked, then the CCR PK extension field is cleared. An exception vector number is
acquired and converted to a vector address. The content of the vector address is loaded into the PC and the processor jumps to the exception handler routine.
There are variations within each phase for differing types of exceptions. However, all
vectors except RESET are 16-bit addresses, and the PK field is cleared during exception processing. Consequently, exception handlers must be located within bank 0 or
vectors must point to a jump table in bank 0.
4.13.4 Types of Exceptions
Exceptions can be either internally or externally generated. External exceptions, which
are defined as asynchronous, include interrupts, bus errors, breakpoints, and resets.
nc...
I
Internal exceptions, which are defined as synchronous, include the software interrupt
(SWI) instruction, the background (BGND) instruction, illegal instruction exceptions,
and the divide-by-zero exception.
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
4.13.4.1 Asynchronous Exceptions
Asynchronous exceptions occur without reference to CPU16 or IMB clocks, but exception processing is synchronized. For all asynchronous exceptions except RESET, exception processing begins at the first instruction boundary following recognition of an
exception. Refer to 5.8.1 Interrupt Exception Processing for more information concerning asynchronous exceptions.
Because of pipelining, the stacked return PK : PC value for all asynchronous exceptions, other than reset, is equal to the address of the next instruction in the current instruction stream plus $0006. The RTI instruction, which must terminate all exception
handler routines, subtracts $0006 from the stacked value to resume execution of the
interrupted instruction stream.
4.13.4.2 Synchronous Exceptions
Synchronous exception processing is part of an instruction definition. Exception processing for synchronous exceptions is always completed, and the first instruction of
the handler routine is always executed, before interrupts are detected.
Because of pipelining, the value of PK : PC at the time a synchronous exception executes is equal to the address of the instruction that causes the exception plus $0006.
Because RTI always subtracts $0006 upon return, the stacked PK : PC must be adjusted by the instruction that caused the exception so that execution resumes with the
following instruction. For this reason, $0002 is added to the PK : PC value before it is
stacked.
M68HC16 Z SERIES CENTRAL PROCESSING UNIT MOTOROLA
USER’S MANUAL 4-39
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Page 100

Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
4.13.5 Multiple Exceptions
Each exception has a hardware priority based upon its relative importance to system
operation. Asynchronous exceptions have higher priorities than synchronous exceptions. Exception processing for multiple exceptions is completed by priority, from highest to lowest. Priority governs the order in which exception processing occurs, not the
order in which exception handlers are executed.
Unless a bus error, a breakpoint, or a reset occurs during exception processing, the
first instruction of all exception handler routines is guaranteed to execute before another exception is processed. Because interrupt exceptions have higher priority than
synchronous exceptions, the first instruction in an interrupt handler is executed before
other interrupts are sensed.
Bus error, breakpoint, and reset exceptions that occur during exception processing of
a previous exception are processed before the first instruction of that exception’s handler routine. The converse is not true. If an interrupt occurs during bus error exception
nc...
I
processing, for example, the first instruction of the exception handler is executed before interrupts are sensed. This permits the exception handler to mask interrupts during execution.
cale Semiconductor,
Frees
Refer to SECTION 5 SYSTEM INTEGRATION MODULE for detailed information concerning interrupts and system reset. For information concerning processing of specific
exceptions, refer to the
4.13.6 RTI Instruction
The return-from-interrupt instruction (RTI) must be the last instruction in all exception
handlers except the RESET handler. RTI pulls the exception stack frame that was
pushed onto the system stack during exception processing, and restores processor
state. Normal program flow resumes at the address of the instruction that follows the
last instruction executed before exception processing began.
RTI is not used in the RESET handler because RESET initializes the stack pointer and
does not create a stack frame.
4.14 Development Support
The CPU16 incorporates powerful tools for tracking program execution and for system
debugging. These tools are deterministic opcode tracking, breakpoint exceptions, and
background debug mode. Judicious use of CPU16 capabilities permits in-circuit emulation and system debugging using a bus state analyzer, a simple serial interface, and
a terminal.
CPU16 Reference Manual
(CPU16RM/AD).
4.14.1 Deterministic Opcode Tracking
The CPU16 has two multiplexed outputs, IPIPE0 and IPIPE1, that enable external
hardwareto monitor the instruction pipeline during normal program execution. The signals IPIPE0 and IPIPE1 can be demultiplexed into six pipeline state signals that allow
a state analyzer to synchronize with instruction stream activity.
MOTOROLA CENTRAL PROCESSING UNIT M68HC16 Z SERIES
4-40 USER’S MANUAL
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
 Loading...
Loading...