Page 1

56F8367
Evaluation Module User Manual
56F8300
16-bit Digital Signal Controllers
MC56F8367EVMUM
Rev. 2
07/2005
freescale.com
Page 2

Document Revision History
Version History Description of Change
Rev 1.0 Initial Public Release
Rev 2.0 Updated look and feel
Page 3

TABLE OF CONTENTS
Preface Preface-vii
Chapter 1
Introduction
1.1 56F8367EVM Architecture. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-2
1.2 56F8367EVM Configuration Jumpers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-3
1.3 56F8367EVM Connections. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-5
Chapter 2
Technical Summary
2.1 MC56F8367 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-4
2.2 Program and Data Memory. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-4
2.2.1 SRAM Bank 0 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-5
2.2.2 SRAM Bank 1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-6
2.3 RS-232 Serial Communications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-7
2.4 Clock Source . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-8
2.5 Operating Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-9
2.5.1 EXTBOOT. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-9
2.5.2 EMI_MODE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-9
2.5.3 CLKMODE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-10
2.6 Debug LEDs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-10
2.7 Debug Support . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-11
2.7.1 JTAG Connector . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-12
2.7.2 Parallel JTAG Interface Connector . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-13
2.8 External Interrupts. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-15
2.9 Reset . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-16
2.10 Power Supply . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-17
2.11 Daughter Card Connectors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-18
2.11.1 Peripheral Daughter Card Connector . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-18
2.11.2 Memory Daughter Card Connector . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-20
2.12 Motor Control PWM Signals and LEDs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-22
Table of Contents, Rev. 2
Freescale Semiconductor i
Preliminary
Page 4

2.13 CAN Interfaces . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-23
2.13.1 FlexCAN #1 Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-23
2.13.2 FlexCAN #2 Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-24
2.14 Software Feature Jumpers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-26
2.15 Peripheral Expansion Connectors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-27
2.15.1 Address Bus Expansion Connector . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-28
2.15.2 Data Bus Expansion Connector. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-29
2.15.3 External Memory Control Signal Expansion Connector. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-30
2.15.4 Encoder #0 / Quad Timer Channel A Expansion Connector. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-30
2.15.5 Encoder #1 / SPI #1 Expansion Connector . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-31
2.15.6 Timer Channel C Expansion Connector . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-31
2.15.7 Timer Channel D Expansion Connector . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-32
2.15.8 A/D Port A Expansion Connector . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-33
2.15.9 A/D Port B Expansion Connector . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-34
2.15.10 Serial Communications Port #0 Expansion Connector . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-34
2.15.11 Serial Communications Port #1 Expansion Connector . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-35
2.15.12 Serial Peripheral Interface #0 Expansion Connector. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-35
2.15.13 FlexCAN #1 Expansion Connector . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-36
2.15.14 FlexCAN #2 Expansion Connector . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-36
2.15.15 PWM Port A Expansion Connector. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-37
2.15.16 PWM Port B Expansion Connector. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-37
2.16 Test Points. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-38
Appendix A
56F8367EVM Schematics
Appendix B
56F8367EVM Bill of Material
MC56F8367EVM User Manual, Rev. 2
ii Freescale Semiconductor
Preliminary
Page 5

LIST OF FIGURES
1-1 Block Diagram of the 56F8367EVM . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-2
1-2 MC56F8367 Default Jumper Options . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-3
1-3 Connecting the 56F8367EVM Cables. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-5
2-1 Schematic Diagram of the External CS0 Memory Interface. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-5
2-2 Schematic Diagram of the External CS1 / CS4 Memory Interface. . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-6
2-3 Schematic Diagram of the RS-232 Interface. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-7
2-4 Schematic Diagram of the Clock Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-8
2-5 Schematic Diagram of the Debug LED Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-11
2-6 Block Diagram of the Parallel JTAG Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-13
2-7 Schematic Diagram of the User Interrupt Interface. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-15
2-8 Schematic Diagram of the Reset Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-16
2-9 Schematic Diagram of the Power Supply . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-17
2-10 PWM Group A Interface and LEDs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-22
2-11 CAN #1 Interface. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-23
2-12 CAN #2 Interface. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-25
2-13 Software Feature Jumpers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-26
2-14 Typical Analog Input RC Filter. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-33
List of Figures, Rev. 2
Freescale Semiconductor iii
Preliminary
Page 6

MC56F8367EVM User Manual, Rev. 2
iv Freescale Semiconductor
Preliminary
Page 7

LIST OF TABLES
1-1 56F8367EVM Default Jumper Options. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-4
2-1 SCI #0 Jumper Options . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-7
2-2 RS-232 Serial Connector Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-8
2-3 EXTBOOT Operating Mode Selection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-9
2-4 EMI Operating Mode Selection. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-9
2-5 EMI Operating Mode Selection. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-10
2-6 LED Control. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-10
2-7 JTAG Connector Description. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-12
2-8 Parallel JTAG Interface Disable Jumper Selection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-12
2-9 Parallel JTAG Interface Connector Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-14
2-10 Parallel JTAG Interface Voltage Jumper Selection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-14
2-11 Peripheral Daughter Card Connector Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-18
2-12 Memory Daughter Card Connector Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-20
2-13 CAN #1 Header Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-24
2-14 CAN #2 Header Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-25
2-15 CAN #2 Pass-Through Jumper Description. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-25
2-16 External Memory Address Bus Connector Description. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-28
2-17 External Memory Address Bus Connector Description. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-29
2-18 External Memory Control Signal Connector Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-30
2-19 Timer A Signal Connector Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-30
2-20 SPI #1 Signal Connector Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-31
2-21 Timer Channel C Connector Description. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-31
2-22 Timer Channel D Connector Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-32
2-23 A/D Port A Connector Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-33
2-24 A/D Port B Connector Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-34
2-25 SCI #0 Connector Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-34
List of Tables, Rev. 2
Freescale Semiconductor v
Preliminary
Page 8

2-26 SCI #1 Connector Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-35
2-27 SPI #0 Connector Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-35
2-28 CAN #1 Connector Description. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-36
2-29 CAN #2 Connector Description. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-36
2-30 PWM Port A Connector Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-37
2-31 PWM Port B Connector Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-37
MC56F8367EVM User Manual, Rev. 2
vi Freescale Semiconductor
Preliminary
Page 9

Preface
This reference manual describes in detail the hardware on the 56F8367 Evaluation Module.
Audience
This document is intended for application developers who are creating software for devices using
the Freescale 56F8367 part or a member of the 56F8300 family that is compatible with this part.
Examples would include the 56F8346 and the 56F8357 devices.
Organization
This manual is organized into two chapters and two appendices:
• Chapter 1, Introduction provides an overview of the EVM and its features.
• Chapter 2, Technical Summary describes in detail the 56F8367 hardware.
• Appendix A, "56F8367EVM Schematics"contains the schematics of the
MC56F8367EVM.
• Appendix B, "56F8367EVM Bill of Material" provides a list of the materials used on the
MC56F8367EVM board.
Suggested Reading
More documentation on the 56F8367 and the MC56F8367EVM kit may be found at URL:
www.freescale.com
Preface, Rev. 2
Freescale Semiconductor vii
Preliminary
Page 10
Notation Conventions
This manual uses the following notational conventions:
Term or Value Symbol Examples Exceptions
Active High Signals
(Logic One)
Active Low Signals
(Logic Zero)
Hexadecimal Values Begin with a “$” sym-
Decimal Values No special symbol
Binary Values Begin with the letter “b”
Numbers Considered positive
Blue Text Linkable on-line ...refer to Chapter 7, License
Bold Reference sources,
No special symbol
attached to the signal
name
Noted with an
overbar in text and in
most figures
bol
attached to the
number
attached to the number
unless specifically
noted as a negative
value
paths, emphasis
A0
CLKO
WE
OE
$0FF0
$80
10
34
b1010
b0011
5
-10
...see: www.freescale.com/
In schematic drawings,
Active Low Signals may be
noted by a backslash: /WE
Voltage is often shown as
positive: +3.3V
MC56F8367EVM User Manual, Rev. 2
viii Freescale Semiconductor
Preliminary
Page 11

Definitions, Acronyms, and Abbreviations
Definitions, acronyms and abbreviations for terms used in this document are defined below for
reference.
A/D Analog-to-Digital; a method of converting Analog signals to Digital values
ADC Analog-to-Digital Converter; a peripheral on the 56F8367 part
CAN Controller Area Network; serial communications peripheral and method
CiA CAN in Automation; an international CAN user’s group that coordinates
standards for CAN communications protocols
D/A Digital-to-Analog; a method of converting Digital values to an Analog form
56F8367
EOnCE
Controller with motor control peripherals
Enhanced On-Chip Emulation; a debug bus and port was created to enable a
designer to create a low-cost hardware interface for a professional-quality
debug environment
EVM
Evaluation Module; a hardware platform which allows a customer to evaluate
the silicon and develop his application
FlexCAN
GPIO
Flexable CAN Interface Module; a peripheral on the 56F8367 part
General Purpose Input and Output port on Freescale’s family of controllers;
does not share pin functionality with any other peripheral on the chip and can
only be set as an input, output or level-sensitive interrupt input
IC
JTAG
LED
Integrated Circuit
Joint Test Action Group; a bus protocol/interface used for test and debug
Light Emitting Diode
LQFP Low-profile Quad Flat Package
MPIO
Multi-Purpose Input and Output port on Freescale’s family of controllers;
shares package pins with other peripherals on the chip and can function as a
GPIO
OnCE
TM
On-Chip Emulation, a debug bus and port created to allow a means for low-cost
hardware to provide a professional-quality debug environment
PCB
PLL
PWM
QuadDec
Freescale Semiconductor ix
Preliminary
Printed Circuit Board
Phase Locked Loop
Pulse Width Modulation
Quadrature Decoder; a peripheral on the 56F8367 part
Preface, Rev. 2
Page 12

RAM
Random Access Memory
R/C
ROM
SCI
Resistor/Capacitor Network
Read-Only Memory
Serial Communications Interface; a peripheral on Freescale’s family of
controllers
SPI
SRAM
WS
Serial Peripheral Interface; a peripheral on Freescale’s family of controllers
Static Random Access Memory
Wait State
References
The following sources were referenced to produce this manual:
[1] DSP56800E Reference Manual, DSP56800ERM, Freescale Semiconductor
[2] 56F8300 Peripheral User Manual, MC56F8300UM, Freescale Semiconductor
[3] 56F8367 Technical Data, MC56F8367, Freescale Semiconductor
[4] CiA Draft Recommendation DR-303-1, Cabling and Connector Pin Assignment,
Version 1.0, CAN in Automation
[5] CAN Specification 2.0B, BOSCH or CAN in Automation
MC56F8367EVM User Manual, Rev. 2
x Freescale Semiconductor
Preliminary
Page 13

Chapter 1 Introduction
The 56F8367EVM is used to demonstrate the abilities of the 56F8367 controller and to provide a
hardware tool allowing the development of applications.
The 56F8367EVM is an evaluation module board that includes a 56F8367 part, peripheral
expansion connectors, a CAN interface, 512KB of external memory and a pair of daughter card
connectors. The daughter card connectors are for signal monitoring and user feature
expandability.
The 56F8367EVM is designed for the following purposes:
• Allowing new users to become familiar with the features of the 56800E architecture. The
tools and examples provided with the 56F8367EVM facilitate evaluation of the feature set
and the benefits of the family.
• Serving as a platform for real-time software development. The tool suite enables the user
to develop and simulate routines, download the software to on-chip or on-board RAM, run
it, and debug it using a debugger via the JTAG/Enhanced OnCE (EOnCE) port. The
breakpoint features of the EOnCE port enable the user to easily specify complex break
conditions and to execute user-developed software at full speed until the break conditions
are satisfied. The ability to examine and modify all user-accessible registers, memory and
peripherals through the EOnCE port greatly facilitates the task of the developer.
• Serving as a platform for hardware development. The hardware platform enables the user
to connect external hardware peripherals. The on-board peripherals can be disabled,
providing the user with the ability to reassign any and all of the processor's peripherals.
The EOnCE port's unobtrusive design means that all memory on the board and on the
processor is available to the user.
Introduction, Rev. 2
Freescale Semiconductor 1-1
Preliminary
Page 14
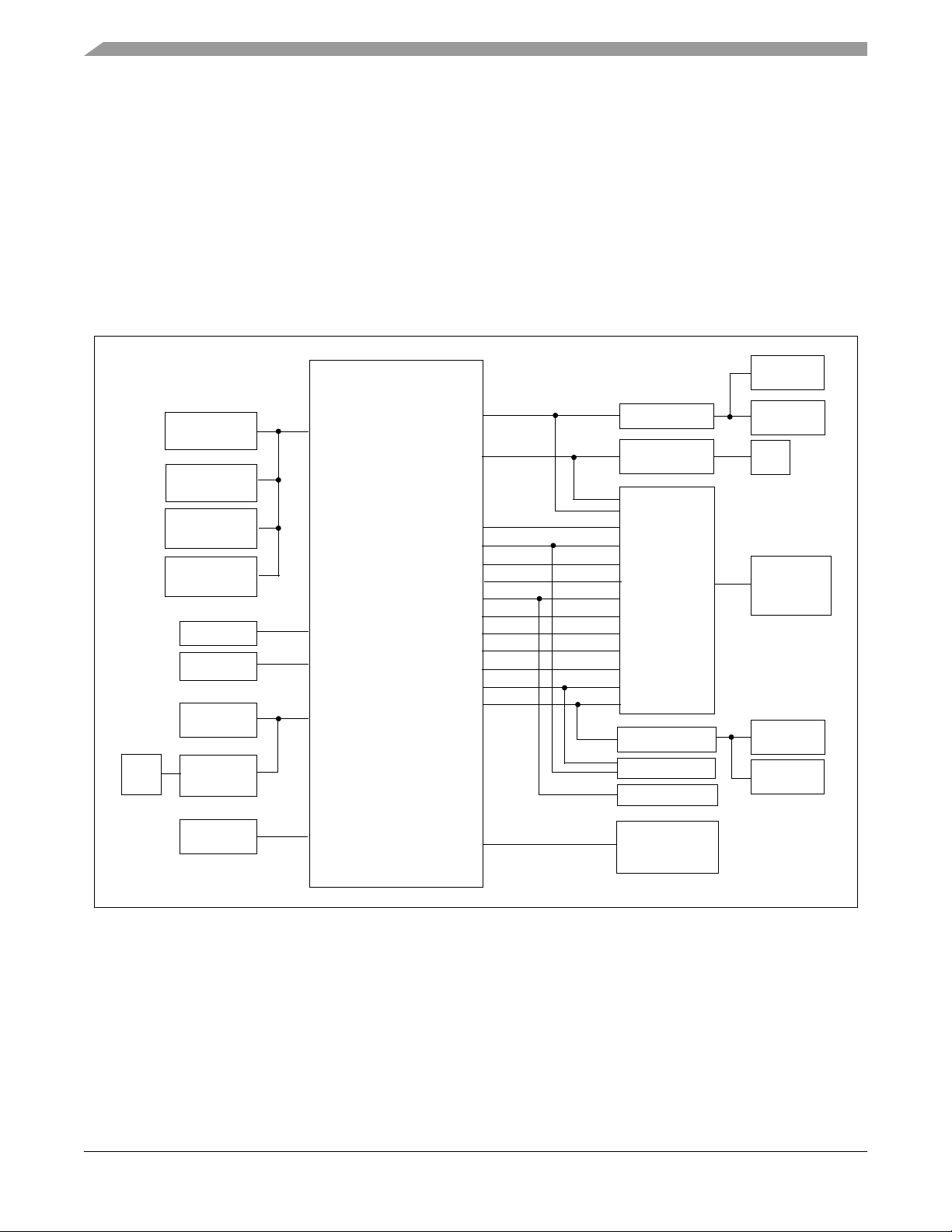
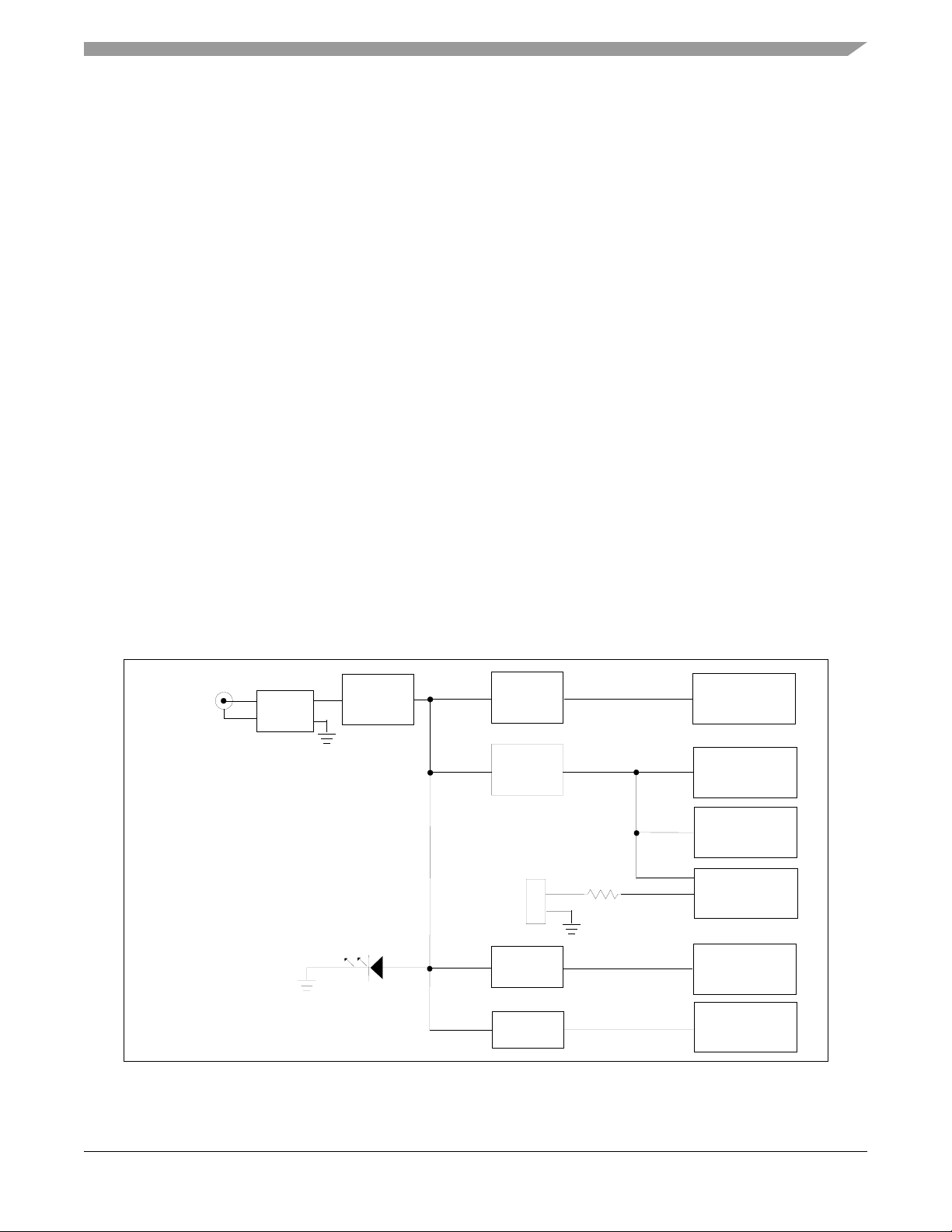
1.1 56F8367EVM Architecture
The 56F8367EVM facilitates the evaluation of various features present in the 56F8367 part. The
56F8367EVM can be used to develop real-time software and hardware products. The
56F8367EVM provides the features necessary for a user to write and debug software,
demonstrate the functionality of that software and interface with the user's application-specific
device(s). The 56F8367EVM is flexible enough to allow a user to fully exploit the 56F8367's
features to optimize the performance of his product, as shown in
Figure 1-1.
DSub
25-Pin
Program Memory
128K x 16-bit
SRAM
Data Memory
128K x 16-bit
SRAM
Memory
Expansion
Connector
Memory
Daughter Card
Connector
Reset Logic
Mode/IRQ
Logic
JTAG
Connector
Parallel
JTAG
Interface
56F8367
Address,
Data &
Control
RESET
MODE/IRQ
JTAG/EOnCE
FlexCAN #1
SCI #0
SPI #0
SCI #1
Timer C
Timer D
PWMA
ADCA
QuadDec #0
PWMB
ADCB
QuadDec #1
FlexCAN #2
CAN #1 Interface
RS-232
Interface
Peripheral
Expansion
Connectors
CAN #2 Interface
Debug LEDs
PWM LEDs
CAN #1 Bus
DaisyChain
CAN #1 Bus
Header
DSub
9-Pin
Peripheral
Daughter Card
Connector
CAN #2 Bus
Header
CAN #2 Bus
DaisyChain
8.00MHz
Crystal
XTAL/
EXTAL
+3.3V & GND
+3.3V A &
AGND
+3.3V
REF
Power Supply
+3.3V, +3.3V A,
+5V & +3.3V
REF
Figure 1-1. Block Diagram of the 56F8367EVM
MC56F8367EVM User Manual, Rev. 2
1-2 Freescale Semiconductor
Preliminary
Page 15
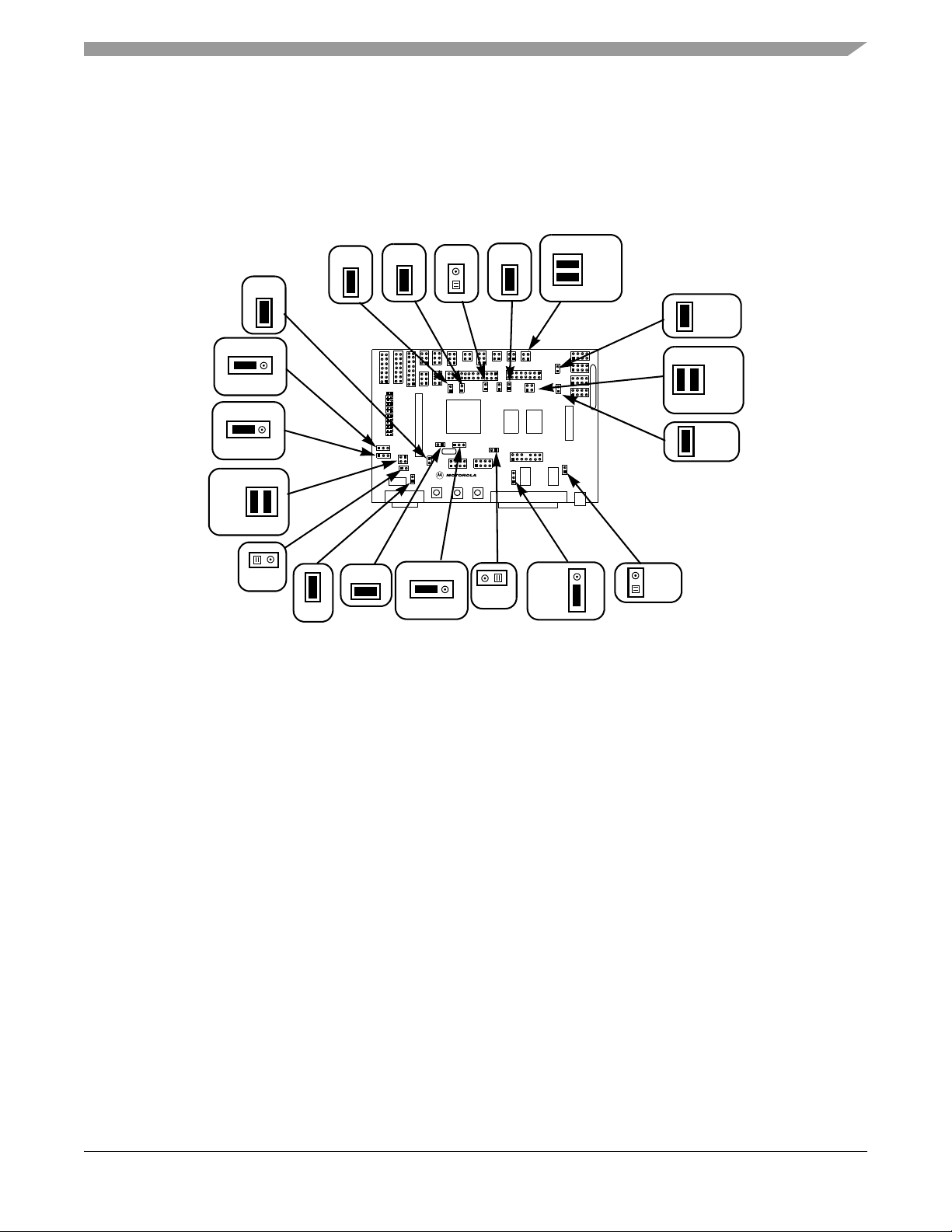
56F8367EVM Configuration Jumpers
1.2 56F8367EVM Configuration Jumpers
Ninteen jumper groups, (JG1-JG19), shown in Figure 1-2, are used to configure various features
on the 56F8367EVM board. Table 1-1 describes the default jumper group settings.
3
4
JG14
2
1
JG13
J19
J3
J20
J14
J5
J21
JG13
J22
JG8
JG17
J23
J2
U3
JTAG
U8
S/N
U9
JG3
P3
4
2
JG8
3
1
JG17
JG9
JG12
1
JG15
1
JG16
JG6
JG4
JG5
JG7
3
J18
J16
J13
J15
J14
JG6
JG2
JG1
Y1
J9
MC56F8357EVM
IRQA
J17
J4
JG7
JG5
J24
JG4
U1
S2
U2
JG18
J10
JG19
S1
P1
IRQB
J11
J8
J7
J12
J6
PC0
J1
PC1
PC2
PC3
PD6
3
3
1
4
2
PD7
PWMA0
PWMA1
PWMA2
PWMA3
PWMA4
PWMA5
JG15
JG9
JG16
JG12
JG10
U4
S3
JG11
P2
LED3
RESET
JG10
JG2
JG11
JG1
1
JG18
3
JG19
1
3
Figure 1-2. MC56F8367 Default Jumper Options
JG3
Introduction, Rev. 2
Freescale Semiconductor 1-3
Preliminary
Page 16
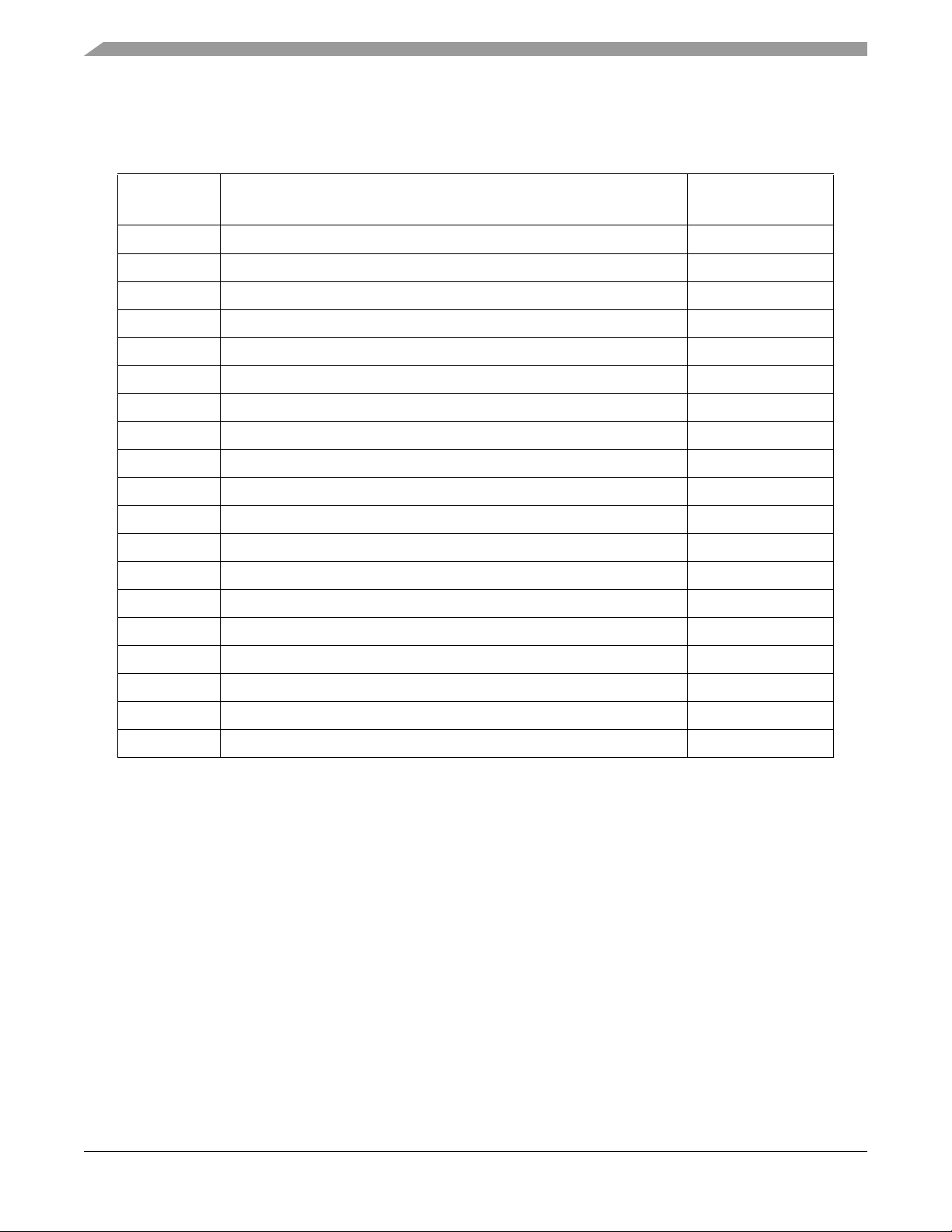
Table 1-1. 56F8367EVM Default Jumper Options
Jumper
Group
JG1 Use on-board EXTAL crystal input for oscillator 1–2
JG2 Use on-board XTAL crystal input for oscillator 1–2
JG3 Enable on-board Parallel JTAG Host/Target Interface NC
JG4 Enable Internal Boot Mode 1–2
JG5 Enable A0 - A23 for external memory accesses NC
JG6 Enable Crystal Mode 1–2
JG7 Enable SRAM Memory Bank 0 (use CS0) 1–2
JG8 Enable SRAM Memory Bank 1 (use CS1 & CS4) 1–2 & 3–4
JG9 Pass RXD0 & TXD0 to RS-232 level converter 1–2 & 3–4
JG10 Enable RS-232 output NC
JG11 Pass RS-232 RST to CTS 1–2
JG12 Pass Temperature Diode to ANA7 1–2
JG13 CAN #1 termination selected 1–2
JG14 Pass CAN2_TX & CAN2_RX to CAN tranceiver 1–2 & 3–4
JG15 High selected on User Jumper #0 1–2
Comment
Jumpers
Connections
JG16 High selected on User Jumper #1 1–2
JG17 CAN2 termination selected 1–2
JG18 Analog Ground to Digital Ground not reconnected NC
JG19 Use +3.3V for Printer Interface to on-board Parallel JTAG Host/Target 1-2
MC56F8367EVM User Manual, Rev. 2
1-4 Freescale Semiconductor
Preliminary
Page 17
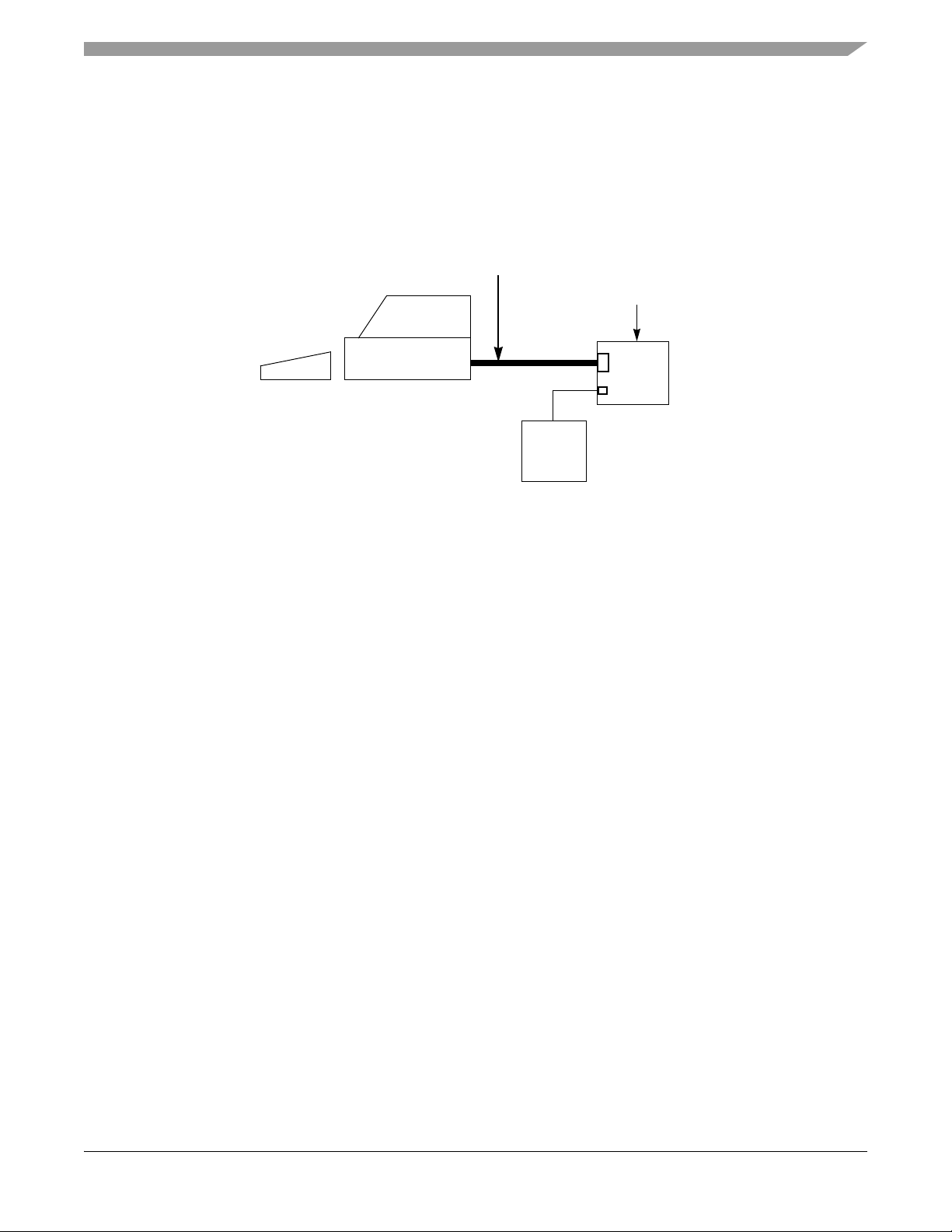
56F8367EVM Connections
1.3 56F8367EVM Connections
An interconnection diagram is shown in Figure 1-3 for connecting the PC and the external
+12.0V DC/AC power supply to the 56F8367EVM board.
Parallel extension
cable
MC56F8367EVM
PC-compatible
computer
P1
Connect cable
to parallel / printer port
External
+12V
power
P3
with 2.1mm,
receptacle
connector
Figure 1-3. Connecting the 56F8367EVM Cables
Perform the following steps to connect the 56F8367EVM cables:
1. Connect the parallel extension cable to the parallel port of the host computer.
2. Connect the other end of the parallel extension cable to P1, shown in Figure 1-3, on the
56F8367EVM board. This provides the connection which allows the host computer to
control the board.
3. Make sure that the external +12V DC, 1.2A power supply is not plugged into a +120V AC
power source.
4. Connect the 2.1mm output power plug from the external power supply into P3, shown in
Figure 1-3, on the 56F8367EVM board.
5. Apply power to the external power supply. The green Power-On LED, LED13, will
illuminate when power is correctly applied.
Introduction, Rev. 2
Freescale Semiconductor 1-5
Preliminary
Page 18

MC56F8367EVM User Manual, Rev. 2
1-6 Freescale Semiconductor
Preliminary
Page 19

Chapter 2 Technical Summary
The 56F8367EVM is designed as a versatile development card using the 56F8367 processor,
allowing the creation of real-time software and hardware products to support a new generation of
applications in servo and motor control, digital and wireless messaging, digital answering
machines, feature phones, modems, and digital cameras. The power of the 16-bit 56F8367
processor, combined with the on-board 128K x 16-bit external Program/Data Static RAM
(SRAM), 128K x 16-bit external Data/Program SRAM, RS-232 interface, CAN interface,
daughter card interface, peripheral expansion connectors and parallel JTAG interface, makes the
56F8367EVM ideal for developing and implementing many motor controlling algorithms, as
well as for learning the architecture and instruction set of the 56F8367 processor.
The main features of the 56F8367EVM, with board and schematic reference designators, include:
• MC56F8367VPY60, a 16-bit +3.3V/+2.5V controller operating at 60MHz [U1]
• External Fast Static RAM (FSRAM) memory, configured as:
— 128K x 16-bit of memory [U2] with 0 wait state at 60MHz via CS0
— 128K x 16-bit of memory [U3] with 0 wait state at 60MHz via CS1/CS4
• 8.00MHz crystal oscillator, for base processor frequency generation [Y1]
• Optional external oscillator frequency input connectors [JG1 and JG2]
• Joint Test Action Group (JTAG) port interface connector, for an external debug Host
Target Interface [J3]
• On-board parallel JTAG host target interface, with a connector for a PC printer port cable
[P1], including a disable jumper [JG3] and a printer port voltage selection jumper [JG19]
• RS-232 interface, for easy connection to a host processor [U4 and P2], including a disable
jumper [JG10]
• RTS and CTS RS-232 control signal access [JG11]
• CAN interface, for high speed, 1.0Mbps, FlexCAN communications [U10 and J20]
• CAN bypass and bus termination [J21 and JG13]
Technical Summary, Rev. 2
Freescale Semiconductor 2-1
Preliminary
Page 20

• CAN #2 interface, for high speed, 1.0Mbps, FlexCAN communications [U11 and J22]
• CAN #2 bypass and bus termination [J23 and JG17]
• CAN #2 interface signal isolation [JG14]
• Peripheral Daughter Card connector, to allow the user to connect his own SCI, SPI or
GPIO-compatible peripheral to the controller [J1]
• Memory Daughter Card connector, to allow the user to connect his own memory or
memory device to the device [J2]
• SCI #0 expansion connector, to allow the user to connect his own SCI #0 /
MPIO-compatible peripheral [J13]
• SCI #1 expansion connector, to allow the user to connect his own SCI #1 /
MPIO-compatible peripheral [J14]
• SPI #0 expansion connector, to allow the user to connect his own SPI #0 /
MPIO-compatible peripheral [J11]
• SPI #1 expansion connector, to allow the user to connect his own SPI #1 /
MPIO-compatible peripheral [J12]
• PWMA expansion connector, to allow the user to connect his own PWMA-compatible
peripheral [J7]
• PWMB expansion connector, to allow the user to connect his own PWMB-compatible
peripheral [J8]
• CAN #1 expansion connector, to allow the user to connect his own CAN physical layer
peripheral [J18]
• CAN #2 expansion connector, to allow the user to connect his own CAN physical layer
peripheral [J19]
• Timer A expansion connector, to allow the user to connect his own Timer A / Encoder
#0-compatible peripheral [J15]
• Timer C expansion connector, to allow the user to connect his own Timer C-compatible
peripheral [J16]
• Timer D expansion connector, to allow the user to connect his own Timer D-compatible
peripheral [J17]
• ADC A expansion connector, to allow the user to attach his own A/D Port A-compatible
peripheral [J9]
• ADC B expansion connector, to allow the user to attach his own A/D Port B-compatible
peripheral [J10]
MC56F8367EVM User Manual, Rev. 2
2-2 Freescale Semiconductor
Preliminary
Page 21

• Address bus expansion connector, to allow the user to monitor the external address bus
[J4]
• Data bus expansion connector, to allow the user to monitor the external data bus [J5]
• External memory bus control signal connector, to allow the user to monitor the external
memory bus [J6]
• On-board power regulation provided from an external +12V DC-supplied power input
[P3]
• Light Emitting Diode (LED) power indicator [LED13]
• Six on-board real-time user debugging LEDs [LED1 - 6]
• Six on-board Port A PWM monitoring LEDs [LED7 - 12]
• Internal/external (EXTBOOT) boot mode selector [JG4]
• Address range (EMI_MODE) boot mode selector [JG5]
• Clock mode (CLKMODE) boot selector [JG6]
• Temperature sense diode to ANA7 selector [JG12]
• Manual reset push button [S1]
• Manual interrupt push button for IRQA [S2]
• Manual interrupt push button for IRQB [S3]
• General-purpose jumper on GPIO PE4 [JG15]
• General-purpose jumper on GPIO PE7 [JG16]
Technical Summary, Rev. 2
Freescale Semiconductor 2-3
Preliminary
Page 22

2.1 MC56F8367
The 56F8367EVM uses a Freescale MC56F8367VPY60 part, designated as U1 on the board and
in the schematics. This part will operate at a maximum external bus speed of 60MHz. A full
description of the 56F8367, including functionality and user information, is provided in these
documents:
• 56F8367 Technical Data Sheet, (MC56F8367): Electrical and timing specifications, pin
descriptions, device-specific peripheral information and package descriptions (this
document)
• 56F8300 Peripheral User Manual, (MC56F8300UM): Detailed description of peripherals
of the 56F8300 family of devices
• DSP56800E Reference Manual, (DSP56800ERM): Detailed description of the 56800E
family architecture, 16-bit core processor, and the instruction set
Refer to these documents for detailed information about chip functionality and operation. They
can be found on this URL:
www.freescale.com
2.2 Program and Data Memory
The 56F8367EVM contains two 128K x 16-bit Fast Static RAM banks. SRAM bank 0 is
controlled by CS0 and SRAM bank 1 is controlled by CS1 and CS4. This provides a total of
256K x 16 bits of external memory.
MC56F8367EVM User Manual, Rev. 2
2-4 Freescale Semiconductor
Preliminary
Page 23
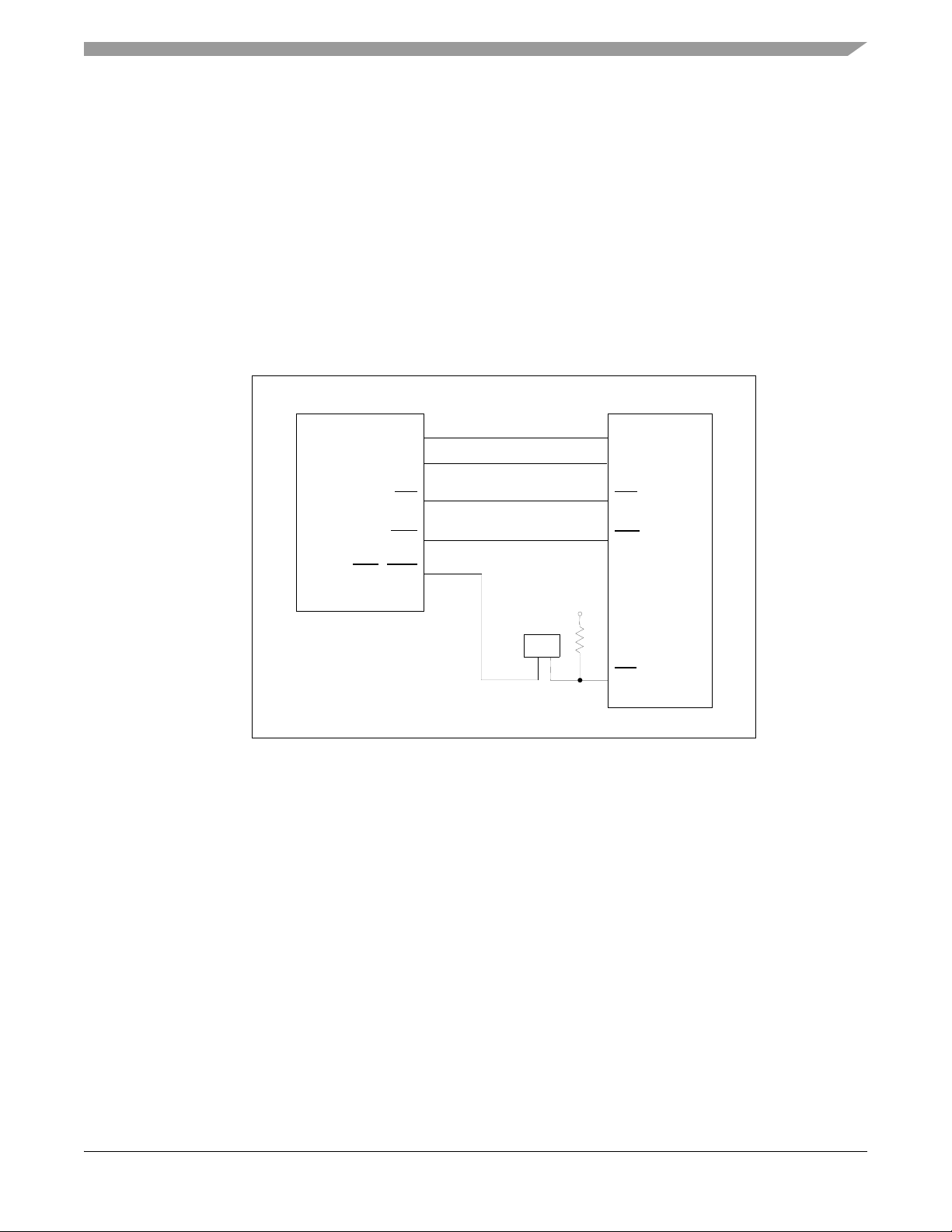
Program and Data Memory
2.2.1 SRAM Bank 0
SRAM bank 0, which is controlled by CS0, uses a 128K x 16-bit Fast Static RAM (GSI
GS72116, labeled U2) for external memory expansion; see the FSRAM schematic diagram in
Figure 2-1. CS0 can be configured to use this memory bank as 16 bits of Program memory, Data
memory, or both. Additionally, CS0 can be configured to assign this memory’s size and starting
address to any modulo address space.
This memory bank will operate with zero wait state access while the 56F8367 is running at
60MHz and can be disabled by removing the jumper at JG7.
MC56F8367 GS72116
A0 - A16
D0 - D15
RD
WR
PS / CS0
Jumper Pin 1-2:
Enable SRAM
Jumper Removed:
Disable SRAM
JG7
+3.3V
1
2
A0 - A16
DQ0 - DQ15
OE
WE
CE
Figure 2-1. Schematic Diagram of the External CS0 Memory Interface
Technical Summary, Rev. 2
Freescale Semiconductor 2-5
Preliminary
Page 24
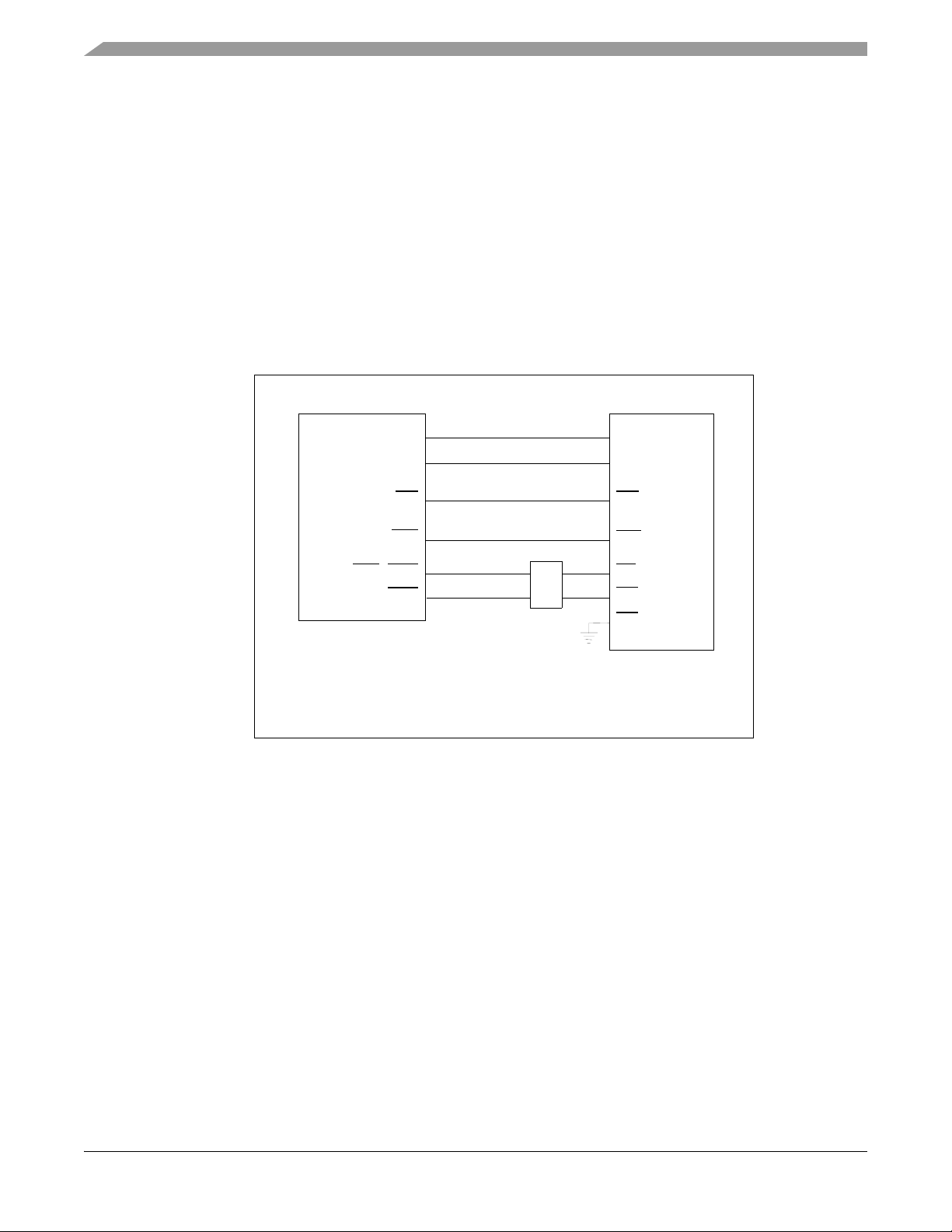
2.2.2 SRAM Bank 1
SRAM bank 1, which is controlled by CS1 and CS2, uses a 128K x 16-bit Fast Static RAM (GSI
GS72116, labeled U3) for external memory expansion; see the FSRAM schematic diagram in
Figure 2-2. Using CS1 and CS4, this memory bank can be configured as byte (8-bit) or word
(16-bit) accessable Program memory, Data memory, or both. Additionally, CS1 and CS4 can be
configured to assign this memory’s size and starting address to any modulo address space.
This memory bank will operate with zero wait state access while the 56F8367 is running at
60MHz and can be disabled by removing the jumpers at JG8.
MC56F8367 GS72116
A0 - A16
D0 - D15
RD
WR
DS / CS1
PD2 / CS4
Jumper Pin 1-2:
Enable SRAM Low Byte
Jumper Pin 3-4:
Enable SRAM High Byte
JG8
1
3
2
4
A0 - A16
DQ0 - DQ15
OE
WE
LB
HB
CE
Figure 2-2. Schematic Diagram of the External CS1 / CS4 Memory Interface
MC56F8367EVM User Manual, Rev. 2
2-6 Freescale Semiconductor
Preliminary
Page 25

RS-232 Serial Communications
2.3 RS-232 Serial Communications
The 56F8367EVM provides an RS-232 interface by the use of an RS-232 level converter, Maxim
MAX3245EEAI, designated as U4. Refer to the RS-232 schematic diagram in
RS-232 level converter transitions the SCI port’s +3.3V signal levels to RS-232-compatible
signal levels and connects to the host’s serial port via connector P2. RTS/CTS flow control is
provided on JG11 as a jumper, but could be implemented using uncommitted GPIO signals. The
SCI port #0 signals can be isolated from the RS-232 level converter by removing the jumpers in
JG9; see
Table 2-1. The pin-out of connector P2 is listed in Table 2-2. The RS-232 level
converter/transceiver can be disabled by placing a jumper at JG10.
Figure 2-3. The
MC56F8367
RS-232
Level Converter
Interface
JG9
TXD0
RXD0
1
3
JG11
1
2
TXD
2
RXD
4
RTS
CTS
+3.3V
T1 in
R1 out
T2 in
R2 out
T1 out
R1 in
R2 in
T2 out
x
FORCEOFF
Jumper Removed:
Enable RS-232
Jumper Pin 1-2:
Disable RS-232
JG10
1
2
Figure 2-3. Schematic Diagram of the RS-232 Interface
P2
1
6
2
7
3
8
4
9
5
Table 2-1. SCI #0 Jumper Options
JG9
Pin # Signal Pin # Signal
1 TXD0 2 RS-232 TXD
3 RXD0 4 RS-232 RXD
Technical Summary, Rev. 2
Freescale Semiconductor 2-7
Preliminary
Page 26

Table 2-2. RS-232 Serial Connector Description
P2
Pin # Signal Pin # Signal
1 Jumper to 6 & 4 6 Jumper to 1 & 4
2 TXD 7 CTS
3 RXD 8 RTS
4 Jumper to 1 & 6 9 NC
5 GND
2.4 Clock Source
The 56F8367EVM uses an 8.00MHz crystal, Y1, connected to its external crystal inputs, EXTAL
and XTAL. To achieve its maximum internal operating frequency, the 56F8367 uses its internal
PLL to multiply the input frequency. An external oscillator source can be connected to the
processor by using the oscillator bypass connectors, JG1 and JG2; see
frequency is above 8MHz, then the EXTAL input should be jumpered to ground by adding a
jumper between JG1 pins 2 and 3. The input frequency would then be injected on JG2’s pin 2. If
the input frequency is below 4MHz, then the input frequency can be injected on JG1’s pin 2.
Figure 2-4. If the input
External
8.00MHz
Oscillator
Headers
JG1
1
2
3
JG2
1
2
MC56F8367
EXTAL
XTAL
Figure 2-4. Schematic Diagram of the Clock Interface
MC56F8367EVM User Manual, Rev. 2
2-8 Freescale Semiconductor
Preliminary
Page 27

Operating Mode
2.5 Operating Mode
The 56F8367EVM provides three boot mode selection jumpers, EXTBOOT, EMI_MODE and
CLKMODE, to provide boot-up mode options.
2.5.1 EXTBOOT
The 56F8367EVM provides an external/internal boot mode jumper, JG4. This jumper is used to
select the internal or external memory operation of the processor as it exits reset. Refer to the
56F8300 Peripheral User Manual and the 56F8367 Technical Data Sheet for a complete
description of the chip’s operating modes.
modes available on the 56F8367.
Table 2-3. EXTBOOT Operating Mode Selection
Operating Mode JG4 Comment
0 1 - 2 Bootstrap from internal memory (GND)
Table 2-3 shows the two external boot operation
3 No Jumper Bootstrap from external memory (+3.3V)
2.5.2 EMI_MODE
The 56F8367EVM provides an EMI boot mode jumper, JG5. This jumper is used to select the
external memory addressing range operating mode of the processor as it exits reset. The user can
select between a 64K address space or an 8M address space. Refer to the 56F8300 Peripheral
User Manual and the 56F8367 Technical Data Sheet for a complete description of the chip’s
operating modes.
Table 2-4 shows the two EMI operation modes available on the 56F8367.
Table 2-4. EMI Operating Mode Selection
Operating Mode JG5 Comment
V1 1 - 2 A0 - A15 (64K) available for external memory bus (GND)
V2 No Jumper A0 - A23 (8M) available for external memory bus (+3.3V)
Technical Summary, Rev. 2
Freescale Semiconductor 2-9
Preliminary
Page 28
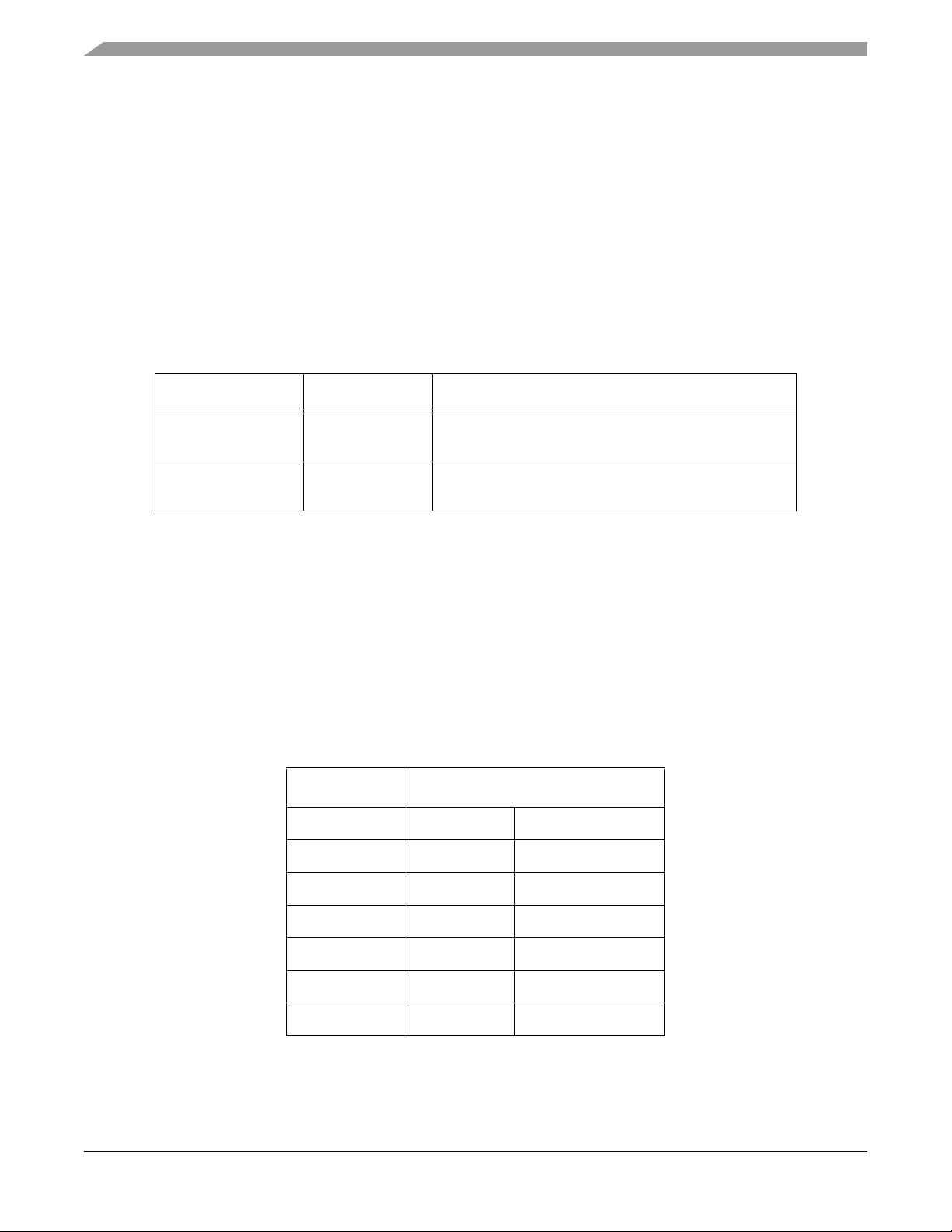
2.5.3 CLKMODE
The 56F8367EVM provides a clock boot mode jumper, JG6. This jumper is used to select the
type of clock source being provided to the processor as it exits reset. The user can select between
the use of a crystal or an oscillator as the clock source for the processor. Refer to the 56F8300
Peripheral User Manual and the 56F8367 Technical Data Sheet for a complete description of
the chip’s operating modes.
Table 2-5 shows the two CLKMODE operation modes available on
the 56F8367.
Table 2-5. EMI Operating Mode Selection
Operating Mode JG6 Comment
Crystal 1 - 2 Enables the external clock drive logic so an external
crystal can be used as the input clock source. (GND)
Oscillator No Jumper Disables the external clock drive logic. Use oscillator
input on XTAL and Ground on EXTAL. (3.3V)
2.6 Debug LEDs
Six on-board Light Emitting Diodes, (LEDs), are provided to allow real-time debugging for user
programs. These LEDs will allow the programmer to monitor program execution without having
to stop the program during debugging; refer to
Figure 2-5. Table 2-6 describes the control of
each LED.
Table 2-6. LED Control
Controlled by
User LED Color Signal
LED1 RED Port C Bit 0 (PC0)
LED2 YELLOW Port C Bit 1 (PC1)
LED3 GREEN Port C Bit 2 (PC2)
LED4 RED Port C Bit 3 (PC3)
LED5 YELLOW Port D Bit 6 (PD6)
LED6 GREEN Port D Bit 7 (PD7)
MC56F8367EVM User Manual, Rev. 2
2-10 Freescale Semiconductor
Preliminary
Page 29

Debug Support
Setting PC0, PC1, PC2, PC3, PD6, or PD7 to a Logic One value will turn on the associated LED.
MC56F8367
PC0
PC1
PC2
PC3
PD6
PD7
INVERTING BUFFER
+3.3V
RED LED
YELLOW LED
GREEN LED
RED LED
YELLOW LED
GREEN LED
Figure 2-5. Schematic Diagram of the Debug LED Interface
2.7 Debug Support
The 56F8367EVM provides an on-board parallel JTAG host target interface and a JTAG
interface connector for external target interface support. Two interface connectors are provided to
support each of these debugging approaches. These two connectors are designated the JTAG
connector and the host parallel interface connector.
Technical Summary, Rev. 2
Freescale Semiconductor 2-11
Preliminary
Page 30

2.7.1 JTAG Connector
The JTAG connector on the 56F8367EVM allows the connection of an external host target
interface for downloading programs and working with the 56F8367’s registers. This connector is
used to communicate with an external host target interface, which passes information and data
back and forth with a host processor running a debugger program.
for this connector.
Table 2-7. JTAG Connector Description
J3
Pin # Signal Pin # Signal
1 TDI 2 GND
3 TDO 4 GND
5 TCK 6 GND
7 NC 8 KEY
9 RESET 10 TMS
Table 2-7 shows the pin-out
11 +3.3V 12 NC
13 DE 14 TRST
When this connector is used with an external host target interface, the parallel JTAG interface
should be disabled by placing a jumper in jumper block JG3. Reference
Table 2-8 for this
jumper’s selection options.
Table 2-8. Parallel JTAG Interface Disable Jumper Selection
JG3 Comment
No jumpers Enables On-board Parallel JTAG Interface
1 - 2 Disables on-board Parallel JTAG Interface
MC56F8367EVM User Manual, Rev. 2
2-12 Freescale Semiconductor
Preliminary
Page 31

Debug Support
2.7.2 Parallel JTAG Interface Connector
The Parallel JTAG Interface Connector, P1, allows the 56F8367 to communicate with a parallel
printer port on a Windows PC; reference
download programs and work with the 56F8367’s registers. Table 2-9 shows the pin-out for this
connector. When using the parallel JTAG interface, the jumper at JG3 should be removed, as
shown in
Table 2-8. The printer port interface voltage of +3.3V or +5.0V can be selected by a
jumper on JG19, as shown in Table 2-10.
DB-25 Connector Parallel JTAG Interface MC56F8367
TDI
TDO
P_TRST
TMS
TCK
P_RESET
P_DE
+3.3V
Jumper Removed:
Enable JTAG I/F
Jumper Pin 1-2:
Disable JTAG I/F
JG3
1
2
Figure 2-6. Using this connector, the user can
OUT
IN
OUT
IN
IN
IN
IN
IN
EN
IN
OUT
OUT
OUT
OUT
OUT
V
cc
JG19
TDI
TDO
TRST
TMS
TCK
RESET
DE
+3.3V
1
2
3
+5.0V
Figure 2-6. Block Diagram of the Parallel JTAG Interface
Technical Summary, Rev. 2
Freescale Semiconductor 2-13
Preliminary
Page 32

Table 2-9. Parallel JTAG Interface Connector Description
P1
Pin # Signal Pin # Signal
1 NC 14 NC
2 PORT_RESET 15 PORT_IDENT
3 PORT_TMS 16 NC
4 PORT_TCK 17 NC
5 PORT_TDI 18 GND
6 PORT_TRST 19 GND
7 PORT_DE 20 GND
8 PORT_IDENT 21 GND
9 PORT_VCC 22 GND
10 NC 23 GND
11 PORT_TDO 24 GND
12 NC 25 GND
13 PORT_CONNECT
Table 2-10. Parallel JTAG Interface Voltage Jumper Selection
JG19 Comment
1 - 2 Interface with the PC’s printer port using +3.3V signals
2 - 3 Interface with the PC’s printer port using +5.0V signals
MC56F8367EVM User Manual, Rev. 2
2-14 Freescale Semiconductor
Preliminary
Page 33
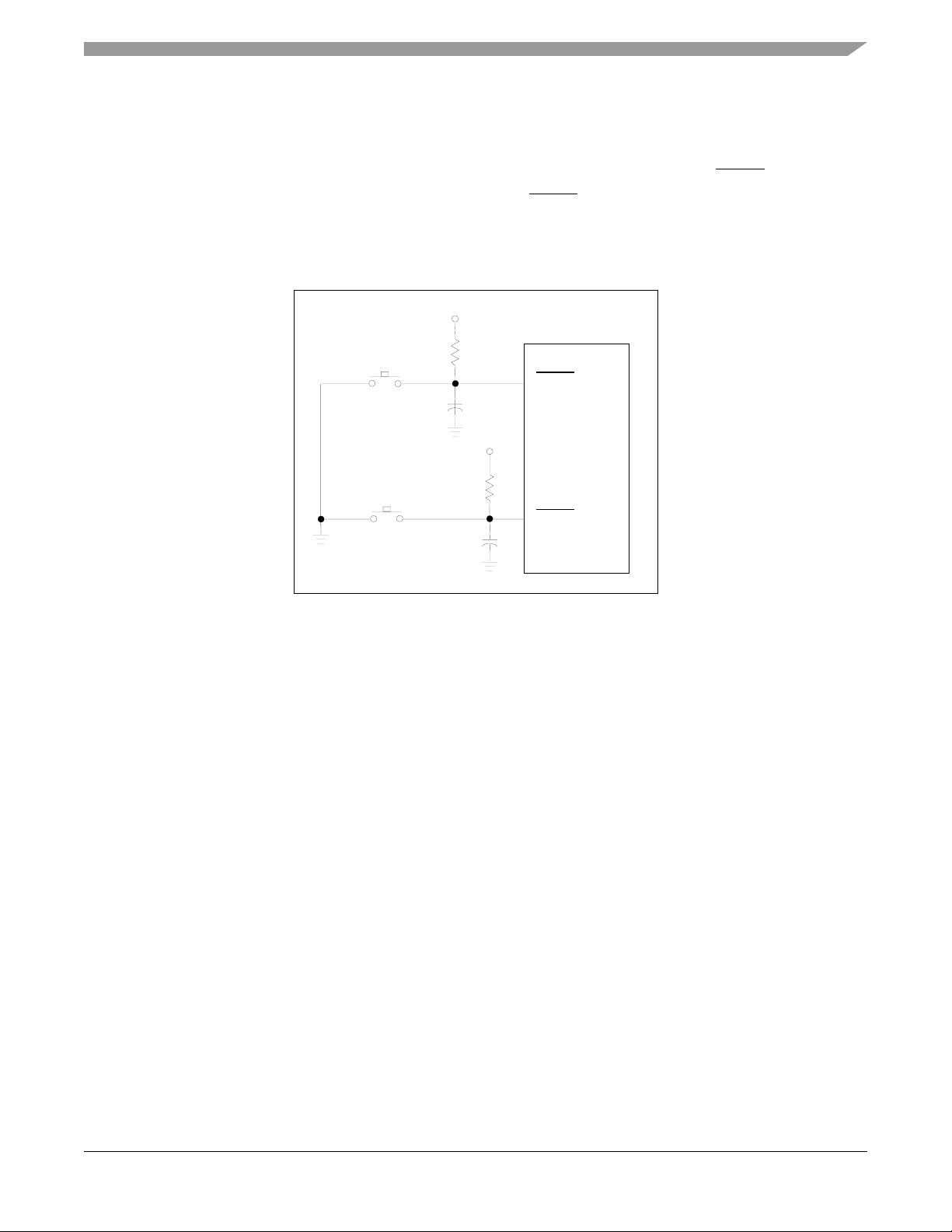
External Interrupts
2.8 External Interrupts
Two on-board push button switches are provided for external interrupt generation, as shown in
Figure 2-7. S2 allows the user to generate a hardware interrupt for signal line IRQA. S3 allows
the user to generate a hardware interrupt for signal line IRQB. These two switches allow the user
to generate interrupts for his user-specific programs.
+3.3V
MC56F8367
S2
0.1µF
10K
IRQA
+3.3V
S3
0.1µF
10K
IRQB
Figure 2-7. Schematic Diagram of the User Interrupt Interface
Technical Summary, Rev. 2
Freescale Semiconductor 2-15
Preliminary
Page 34

2.9 Reset
Logic is provided on the 56F8367 to generate an internal power-on reset. Additional reset logic is
provided to support the reset signals from the JTAG connector, the parallel JTAG interface and
the user reset push button, S1; refer to
Figure 2-8.
RESET
PUSHBUTTON
S1
JTAG_RESET
MANUAL RESET
JTAG_TAP_RESET
RESET
TRST
Figure 2-8. Schematic Diagram of the Reset Interface
MC56F8367EVM User Manual, Rev. 2
2-16 Freescale Semiconductor
Preliminary
Page 35
Power Supply
2.10 Power Supply
The main power input to the 56F8367EVM, +12V DC at 1.2A, is through a 2.1mm coax power
jack. This input power is rectified to provide a DC supply input. This allows a user the option to
use a +12V AC power supply. A 1.2 Amp power supply is provided with the 56F8367EVM;
however, less than 500mA is required by the EVM. The remaining current is available for custom
control applications when connected to the daughter card connectors. The 56F8367EVM
provides +5.0V DC regulation for the CAN interface and additional regulators. The
56F8367EVM provides +3.3V DC voltage regulation for the processor, memory, D/A, ADC,
parallel JTAG interface and supporting logic; refer to
logic provides a low-noise +3.3V DC voltage reference to the processor’s A/D V
JG18, and resistor, R66, are provided to allow the analog and digital grounds to be isolated on the
56F8367EVM board. This allows the analog ground reference point to be provided on a custom
board attached to the 56F8367EVM daughter card connectors. By removing R66, the AGND
reference is disconnected from the 56F8367EVM’s digital ground. By placing a jumper on JG18,
the AGND is reconnected to the 56F8367EVM’s digital ground. Power applied to the
56F8367EVM is indicated with a power-on LED, referenced as LED13. Optionally, the user can
provide the +2.5 DC voltage needed by the processor’s core on connector J24 and disable the
on-chip core voltage regulator by moving the resistor at R72 to R71. Additonally, four zero ohm
resistors or shorting wires must be added at R67, R68, R69, and R70 to allow the external +2.5V
DC to pass to the 56F8367.
Figure 2-9. Additional voltage regulation
. A jumper,
REFH
+12V DC/AC
Input
P3
Bridge
Rectifier
+5.0V
Regulator
Power On
Power
Condition
+3.3V
Regulator
+2.5V DC
Ext In
+3.3V
Regulator
U15
+3.3V
Regulator
J24
2
1
+5.0V DC
+3.3V DC
R67 - R70
+3.3VA DC
+3.3VA DC
Figure 2-9. Schematic Diagram of the Power Supply
CAN
56F8367
& PLL
V
DD_IO
56F8367EVM
Parts
56F8367
V
Core
DD
56F8367
ADC
56F8367
V
REFH
Technical Summary, Rev. 2
Freescale Semiconductor 2-17
Preliminary
Page 36

2.11 Daughter Card Connectors
The EVM board contains two daughter card connectors. One connector, J1, contains the
processor’s peripheral port signals. The second connector, J2, contains the processor’s external
memory bus signals.
2.11.1 Peripheral Daughter Card Connector
The processor’s peripheral port signals are connected to the peripheral daughter card connector,
J1. The peripheral daughter card connector is used to connect a daughter card or a user-specific
daughter card to the processor’s peripheral port signals. The peripheral port daughter card
connector is a 100-pin high-density connector with signals for the IRQs, reset, SPI, SCI, PWM,
ADC and Quad Timer ports.
signal-to-pin assignments.
Table 2-11. Peripheral Daughter Card Connector Description
Pin # Signal Pin # Signal
Table 2-11 shows the peripheral daughter card connector’s
J1
1 +12V 2 +12V
3 GND 4 GND
5 +5.0V 6 +5.0V
7 GND 8 GND
9 +3.3V 10 +3.3V
11 GND 12 GND
13 PHASEA0 / TA0 / PC4 14 PHASEB0 / TA1 / PC5
15 INDEX0 / TA2 / PC6 16 HOME0 / TA3 / PC7
17 GND 18 GND
19 PHASEA1 / PC0 / TB0 / SCLK1 20 PHASEB1 / PC1 / TB1 / MOSI1
21 INDEX1 / PC2 / TB2 / MISO1 22 HOME1 / PC3 / TB3 / SS1
23 TXD0 / PE0 24 TXD1 / PD6
25 TXD0 / PE0 26 TXD1 / PD6
27 RXD0 / PE1 28 RXD1 / PD7
MC56F8367EVM User Manual, Rev. 2
2-18 Freescale Semiconductor
Preliminary
Page 37

Daughter Card Connectors
Table 2-11. Peripheral Daughter Card Connector Description (Continued)
J1
Pin # Signal Pin # Signal
29 IRQA 30 IRQB
31 RXD0 / PE1 32 RXD1 / PD7
33 PWMB0 34 PWMB1
35 PWMB2 36 PWMB3
37 PWMB4 38 PWMB5
39 GND 40 GND
41 ISB0 / PD10 42 ISB1 / PD11
43 ISB2 / PD12 44 GND
45 FAULTB1 46 FAULTB0
47 FAULTB3 48 FAULTB2
49 GND 50 GND
51 PWMA0 52 PWMA1
53 PWMA2 54 PWMA3
55 PWMA4 56 PWMA5
57 GND 58 GND
59 FAULTA0 60 FAULTA1
61 FAULTA2 62 MISO0 / PE6
63 ISA0 / PC8 64 ISA1 / PC9
65 ISA2 / PC10 66 RSTO
67 MOSI0 / PE5 68 SS0 / PE7
69 TD0 / PE10 70 TD1 / PE11
71 SCLK0 / PE7 72 TC0 / PE8
73 CAN_TX 74 CAN_RX
75 MOSI0 / PE5 76 MISO0 / PE6
77 SCLK0 / PE4 78 SS0 / PE7
79 GND 80 GND
Technical Summary, Rev. 2
Freescale Semiconductor 2-19
Preliminary
Page 38

Table 2-11. Peripheral Daughter Card Connector Description (Continued)
J1
Pin # Signal Pin # Signal
81 +V
83 GNDA 84 GNDA
85 AN0 86 AN1
87 AN2 88 AN3
89 AN4 90 AN5
91 AN6 92 AN7
93 AN8 94 AN9
95 AN10 96 AN11
97 AN12 98 AN13
99 AN14 100 AN15
REFH
82 +V
REFH
2.11.2 Memory Daughter Card Connector
The processor’s external memory bus signals are connected to the memory daughter card
connector, J2.
Table 2-12 shows the port signal-to-pin assignments.
Table 2-12. Memory Daughter Card Connector Description
J2
Pin # Signal Pin # Signal
1 A4 / PA12 2 A5 / PA13
3 A3 / PA11 4 A6 / PE2
5 A2 / PA10 6 A7 / PE3
7 A1 / PA9 8 RD
9 GND 10 GND
11 A0 / PA8 12 DS / CS1
13 PS / CS0 14 PD0 / CS2 / CAN2_TX
MC56F8367EVM User Manual, Rev. 2
2-20 Freescale Semiconductor
Preliminary
Page 39
Daughter Card Connectors
Table 2-12. Memory Daughter Card Connector Description (Continued)
J2
Pin # Signal Pin # Signal
15 D0 / PF9 16 D15 / PF8
17 D1 / PF10 18 D14 / PF7
19 GND 20 GND
21 GND 22 GND
23 D2 / PF11 24 D13 / PF6
25 D3 / PF12 26 D12 / PF5
27 D4 / PF13 28 D11 / PF4
29 D5 / PF14 30 D10 / PF3
31 GND 32 GND
33 GND 34 GND
35 D6 / PF15 36 D9 / PF2
37 D7 / PF0 38 D8 / PF1
39 WR 40 PD1 / CS3 / CAN2_RX
41 A15 / PA7 42 A8 / PA0
43 GND 44 GND
45 A14 / PA6 46 A9 / PA1
47 A13 / PA5 48 A10 / PA2
49 A12 / PA4 50 A11 / PA3
51 PB0 / A16 52 GND
53 GND 54 GND
55 +3.3V 56 +3.3V
57 GND 58 GND
59 +5.0V 60 +5.0V
Technical Summary, Rev. 2
Freescale Semiconductor 2-21
Preliminary
Page 40
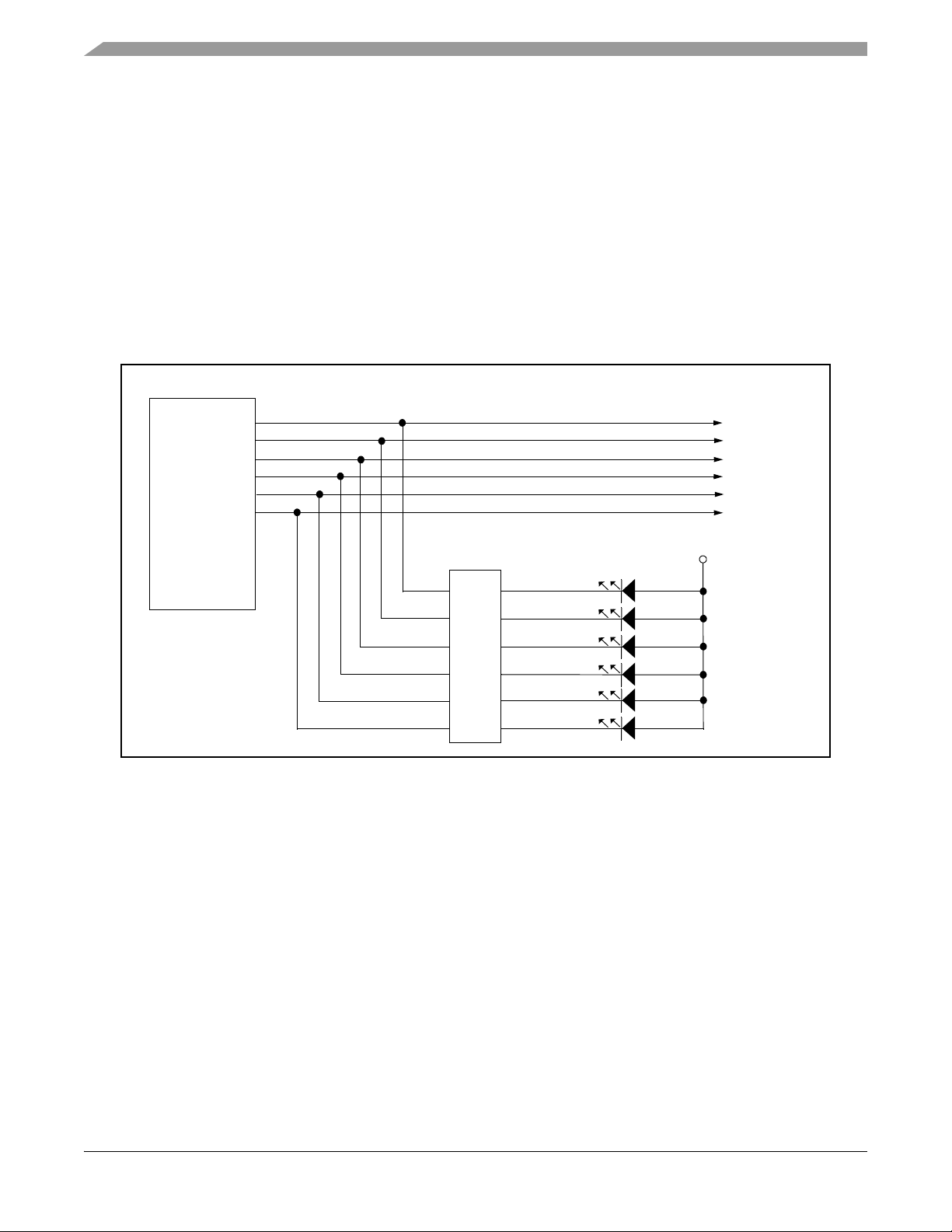
2.12 Motor Control PWM Signals and LEDs
The 56F8367 has two independent groups of dedicated PWM units. Each unit contains six PWM,
three phase current sense inputs and four fault input lines. PWM group A’s PWM lines are
connected to a set of six PWM LEDs via inverting buffers. The buffers are used to isolate and
drive the Processor’s PWM group A’s outputs to the PWM LEDs. The PWM LEDs indicate the
status of PWM group A signals; refer to
out to headers, J7 and J8 respectively, and to the peripheral daughter card connector for easy use
by the end user.
56F8367
Figure 2-10. PWM Group A and B signals are routed
PWMA0
PWMA1
PWMA2
PWMA3
PWMA4
PWMA5
LED7
LED8
LED9
LED10
LED11
LED12
LED
Buffer
Yellow LED
Green LED
Yellow LED
Green LED
Yellow LED
Green LED
Figure 2-10. PWM Group A Interface and LEDs
PWMA0
PWMA1
PWMA2
PWMA3
PWMA4
PWMA5
+3.3V
Phase A Top
Phase A Bottom
Phase B Top
Phase B Bottom
Phase C Top
Phase C Bottom
MC56F8367EVM User Manual, Rev. 2
2-22 Freescale Semiconductor
Preliminary
Page 41

CAN Interfaces
2.13 CAN Interfaces
The 56F8367EVM board contains two FlexCAN interfaces. The primary CAN interface uses the
CAN1_RX and CAN1_TX pins on the 56F8367. The secondary CAN interface uses the
CAN2_RX and CAN2_TX pins on the 56F8367.
2.13.1 FlexCAN #1 Interface
The 56F8367EVM board contains a CAN physical-layer interface chip that is attached to the
FlexCAN port’s CAN1_RX and CAN1_TX pins on the 56F8367. The EVM board uses a Phillips
high-speed, 1.0Mbps, physical layer interface chip, PCA82C250. Due to the +5.0V operating
voltage of the CAN interface chip, a pull-up to +5.0V is required to level shift the transmit data
output line from the 56F8367. The CANH and CANL signals pass through inductors before
attaching to the CAN bus connectors. A primary, J20, and daisy-chain, J21, CAN connector are
provided to allow easy daisy-chaining of CAN devices. CAN bus termination of 120 ohms can be
provided by adding a jumper to JG13. Refer to
Figure 2-12 for a connection diagram.
Table 2-14 for the CAN connector signals and
MC56F8367
CAN1_TX
CAN1_RX
+5.0V
1K
CAN Transceiver
TXD
CANH
CANL
RXD
PCA82C250
Figure 2-11. CAN #1 Interface
120
J20
4
3
J21
4
3
5
5
JG13
CAN #1 Bus
Connector
Daisy-Chain CAN #1
Connector
1
CAN Bus #1
2
Terminator
Technical Summary, Rev. 2
Freescale Semiconductor 2-23
Preliminary
Page 42

Table 2-13. CAN #1 Header Description
J20 and J21
Pin # Signal Pin # Signal
1 NC 2 NC
3 CANL 4 CANH
5 GND 6 NC
7 NC 8 NC
9 NC 10 NC
2.13.2 FlexCAN #2 Interface
The 56F8367EVM board contains a second FlexCAN port, the CAN2_RX and CAN2_TX pins
on the 56F8367. These signals pass through an isolation jumper, JG14, before going to the CAN
physical layer interface. The EVM board uses a Phillips high-speed, 1.0Mbps, physical layer
interface chip, PCA82C250. Due to the +5.0V operating voltage of the CAN interface chip, a pull
up to +5.0V is required to level shift the transmit data output line from the 56F8367. The CAN2H
and CAN2L signals pass through inductors before attaching to the CAN bus connectors. A
primary, J22, and daisy-chain, J23, CAN connector are provided to allow easy daisy-chaining of
CAN devices. CAN bus termination of 120 ohms can be provided by adding a jumper to JG17.
Refer to Figure 2-12 for a connection diagram and to Table 2-14 and Table 2-15 for the CAN
connector signals.
MC56F8367EVM User Manual, Rev. 2
2-24 Freescale Semiconductor
Preliminary
Page 43
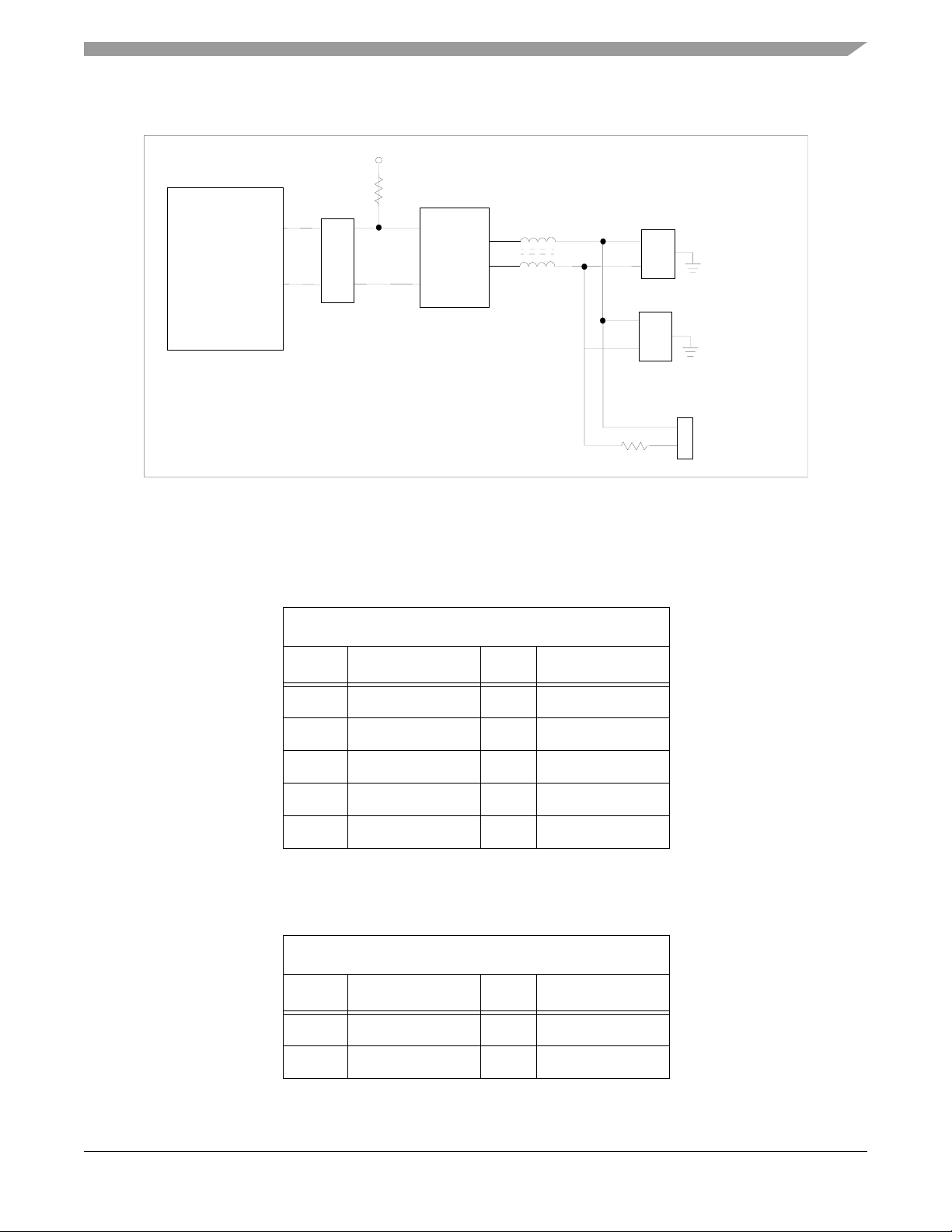
+5.0V
CAN Interfaces
MC56F8367
PD0 / CAN2_TX
PD1 / CAN2_RX
JG14
1
3
1K
2
4
CAN Transceiver
TXD
CANH
CANL
RXD
PCA82C250
J22
4
3
J23
4
3
120
Figure 2-12. CAN #2 Interface
Table 2-14. CAN #2 Header Description
J22 and J23
5
5
JG17
1
2
CAN #2 Bus
Connector
Daisy-Chain
CAN #2
Connector
CAN #2 Bus
Terminator
Pin # Signal Pin # Signal
1 NC 2 NC
3 CAN2L 4 CAN2H
5 GND 6 NC
7 NC 8 NC
9 NC 10 NC
Table 2-15. CAN #2 Pass-Through Jumper Description
JG14
Pin # Signal Pin # Signal
1 PD0 2 CAN2_TX
3 PD1 4 CAN2_RX
Technical Summary, Rev. 2
Freescale Semiconductor 2-25
Preliminary
Page 44
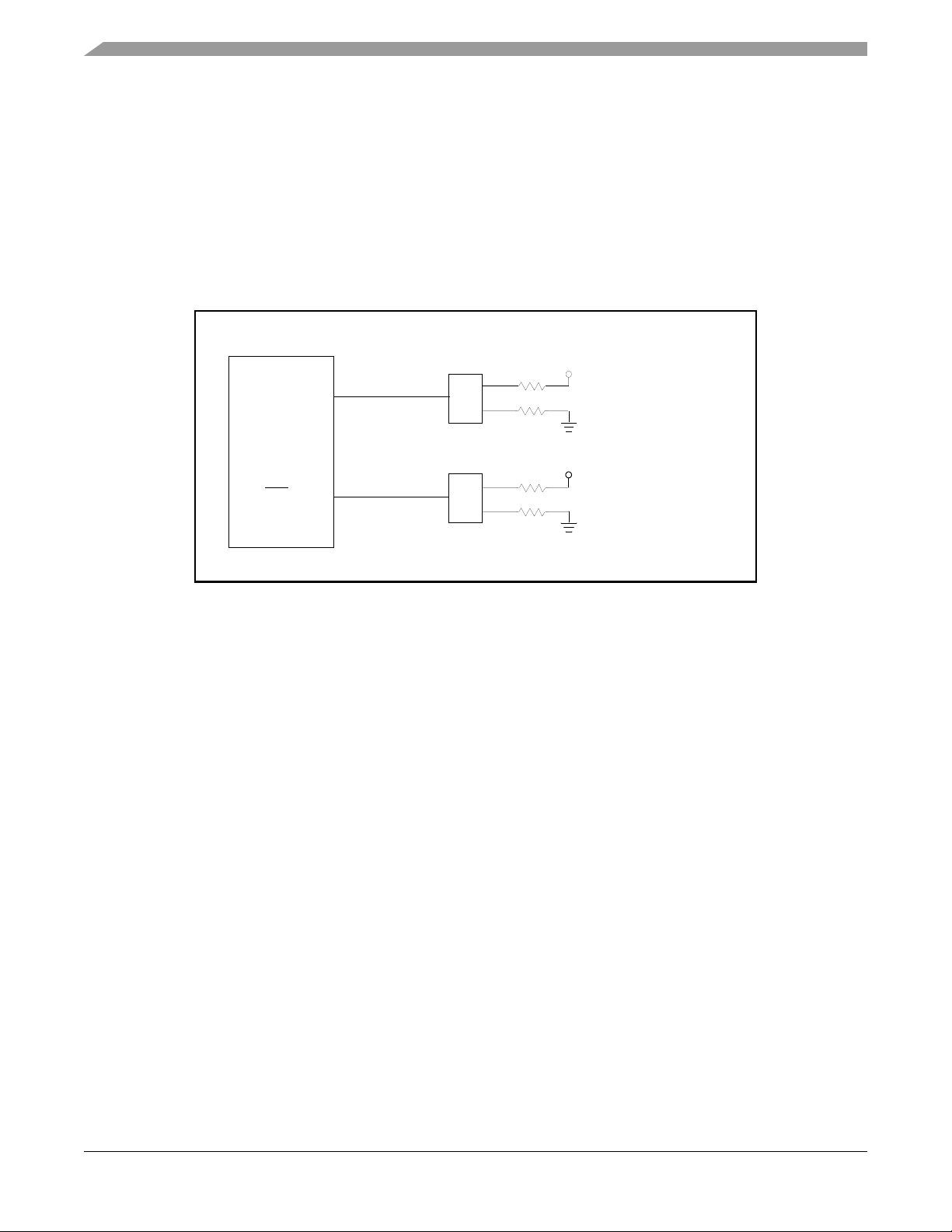
2.14 Software Feature Jumpers
The 56F8367EVM board contains two software feature jumpers that allow the user to select
user-defined software features. Two GPIO port pins, PE4 and PE7, are pulled high or low with
10K ohm resistors on JG15 and JG16. Attaching a jumper between pins 1 and 2 will place a high
or 1 on the port pin. Attaching a jumper between pins 2 and 3 will place a low or 0 on the port
pin; see
Figure 2-13.
MC56F8367
SCLK0 / PE4
SS0
/ PE7
Figure 2-13. Software Feature Jumpers
JG15
1
2
JG16
1
2
+3.3V
10K
3
3
10K
10K
10K
+3.3V
User Jumper
#0
User Jumper
#1
MC56F8367EVM User Manual, Rev. 2
2-26 Freescale Semiconductor
Preliminary
Page 45

Peripheral Expansion Connectors
2.15 Peripheral Expansion Connectors
The EVM board contains a group of peripheral expansion connectors used to gain access to the
resources of the 56F8367. The following signal groups have expansion connectors:
• External Memory Address Bus (A0 - A23)
General Purpose Port A (bits 0 - 13)
General Purpose Port E (bits 2 & 3)
General Purpose Port B (bit 0 - 7)
• External Memory Data Bus (D0 - D15)
General Purpose Port F (bits 0 - 15)
• External Memory Control
General Purpose Port D (bits 0 - 5, 8 & 9)
• Quadrature Decoder #0
Quad Timer Channel A
• Quadrature Decoder #1
Serial Peripheral Interface Port #1
Quad Timer Channel B
General Purpose Port C (bits 0 - 3)
• Quad Timer Channel C
General Purpose Port E (bits 8 & 9)
• Quad Timer Channel D
General Purpose Port E (bits 10 - 13)
• A/D Input Port A
• A/D Input Port B
• Serial Communications Port #0 / General Purpose Port E (bits 0 and 1)
• Serial Communications Port #1 / General Purpose Port D (bits 6 and 7)
• Serial Peripheral Interface Port #0 / General Purpose Port E (bits 4 - 7)
• PWM Port A / General Purpose Port C (bits 8 - 10)
• PWM Port B / General Purpose Port C (bits 0 - 3)
• CAN Port #1
• CAN Port #2
Technical Summary, Rev. 2
Freescale Semiconductor 2-27
Preliminary
Page 46

2.15.1 Address Bus Expansion Connector
The address bus expansion connector contains the 56F8367’s 24 external memory address signal
lines. Address lines A6 and A7 can optionally be used as GPIO Port E lines (bits 2 and 3).
Address lines A8 - A15 can optionally be used as GPIO Port A lines (bits 0 - 7). Address lines
- A5 can optionally be used as GPIO Port A lines (bits 8 - 13). Address lines A16 - A23 are
A0
MPIO signals, which can be configured as A16 - A23 or GPIO Port B bits 0 - 7. Refer to
Table 2-16 for the address bus connector information.
Table 2-16. External Memory Address Bus Connector Description
J4
Pin # Signal Pin # Signal
1 A0 / PA8 2 A1 / PA9
3 A2 / PA10 4 A3 / PA11
5 A4 / PA12 6 A5 / PA13
7 A6 / PE2 8 A7 / PE3
9 A8 / PA0 10 A9 / PA1
11 A10 / PA2 12 A11 / PA3
13 A12 / PA4 14 A13 / PA5
15 A14 / PA6 16 A15 / PA7
17 PB0 / A16 18 PB1 / A17
19 PB2 / A18 20 PB3 / A19
21 PB4 / A20 22 PB5 / A21
23 PB6 / A22 24 PB7 / A23
19 GND 20 +3.3V
MC56F8367EVM User Manual, Rev. 2
2-28 Freescale Semiconductor
Preliminary
Page 47

Peripheral Expansion Connectors
2.15.2 Data Bus Expansion Connector
The data bus expansion connector contains the 56F8367’s 16 external memory data signal lines.
Refer to
as GPIO Port F lines (bits 0 - 15).
Table 2-17 for the data bus connector information. Data lines D0 - D15 can also be used
Table 2-17. External Memory Address Bus Connector Description
J5
Pin # Signal Pin # Signal
1 D0 / PF9 2 D1 / PF10
3 D2 / PF11 4 D3 / PF12
5 D4 / PF13 6 D5 / PF14
7 D6 / PF15 8 D7 / PF0
9 D8 / PF1 10 D9 / PF2
11 D10 / PF3 12 D11 / PF4
13 D12 / PF5 14 D13 / PF6
15 D14 / PF7 16 D15 / PF8
17 GND 18 +3.3V
Technical Summary, Rev. 2
Freescale Semiconductor 2-29
Preliminary
Page 48

2.15.3 External Memory Control Signal Expansion Connector
The external memory control signal connector contains the 56F8367’s external memory control
signal lines. CS2 and CS3 are MPIO signals, which can be configured as GPIO Port D lines (bits
0 and 1). Refer to
Table 2-18. External Memory Control Signal Connector Description
Table 2-18 for the names of these signals.
J6
Pin # Signal Pin # Signal
1 RD 2 IRQA
3 WR 4 IRQB
5 PS / CS0 6 DS / CS1
7 PD0 / CS2 / CAN2_TX 8 PD1 / CS3 / CAN2_RX
PD2 / CS4 PD3 / CS5
PD4 / CS6 PD5 / CS7
9 CLKO 10 RESET
11 GND 12 RSTO
2.15.4 Encoder #0 / Quad Timer Channel A Expansion Connector
The Encoder #0 / Quad Timer Channel A port is an MPIO port attached to the Timer A expansion
connector. This port can be configured as a Quadrature Decoder interface port or as a Quad
Timer port. Refer to
Table 2-19 for the signals attached to the connector.
Table 2-19. Timer A Signal Connector Description
J15
Pin # Signal Pin # Signal
1 PHASEA0 / TA0 2 PHASEB0 / TA1
3 INDEX0 / TA2 4 HOME0 / TA3
5 GND 6 +3.3V
MC56F8367EVM User Manual, Rev. 2
2-30 Freescale Semiconductor
Preliminary
Page 49

Peripheral Expansion Connectors
2.15.5 Encoder #1 / SPI #1 Expansion Connector
The Encoder #1 / SPI #1 port is an MPIO port attached to the SPI #1 expansion connector. This
port can be configured as a Quadrature Decoder interface port, a Serial Peripherial Interface,
Quad Timer port or General Purpose I/O port. Refer to
connector.
Table 2-20. SPI #1 Signal Connector Description
J12
Pin # Signal Pin # Signal
1 PHASEB1 / MOSI1 / TB1 / PC1 2 INDEX1 / MISO1 / TB2 / PC2
3 PHASEA1 / SCLK1 / TB0 / PC0 4 HOME1 / SS1 / TB3 / PC3
5 GND 6 +3.3V
Table 2-20 for the signals attached to the
2.15.6 Timer Channel C Expansion Connector
The Timer Channel C port is a Quad Timer port attached to the Timer C expansion connector.
This port can be configured as a Quad Timer port or a General Purpose I/O port. Refer to
Table 2-21 for the signals attached to the connector.
Table 2-21. Timer Channel C Connector Description
J16
Pin # Signal Pin # Signal
1 TC0 / PE8 2 TC1 / PE9
3 GND 4 +3.3V
Technical Summary, Rev. 2
Freescale Semiconductor 2-31
Preliminary
Page 50

2.15.7 Timer Channel D Expansion Connector
The Timer Channel D port is a Quad Timer attached to the Timer D expansion connector. This
port can be configured as a Quad Timer port or a General Purpose I/O port. Refer to
for the signals attached to the connector.
Table 2-22. Timer Channel D Connector Description
J17
Pin # Signal Pin # Signal
1 TD0 / PE10 2 TD1 / PE11
3 TD2 / PE12 4 TD3 / PE13
3 GND 4 +3.3V
Table 2-22
MC56F8367EVM User Manual, Rev. 2
2-32 Freescale Semiconductor
Preliminary
Page 51

Peripheral Expansion Connectors
2.15.8 A/D Port A Expansion Connector
The eight-channel Analog-to-Digital conversion Port A is attached to this connector. Refer to
Table 2-23 for connection information. There is a Resistor/Connector (R/C) network on each of
the Analog Port A input signals; see Figure 2-14.
Table 2-23. A/D Port A Connector Description
J9
Pin # Signal Pin # Signal
1 AN0 2 AN1
3 AN2 4 AN3
5 AN4 6 AN5
7 AN6 8 AN7
9 GNDA 10 +V
100 ohm
Analog Input
REFH
To Processor’s Analog
Port
0.0022uF
Figure 2-14. Typical Analog Input RC Filter
Technical Summary, Rev. 2
Freescale Semiconductor 2-33
Preliminary
Page 52

2.15.9 A/D Port B Expansion Connector
The eight-channel Analog-to-Digital conversion Port B is attached to this connector. Refer to
Table 2-24 for connection information. There is an R/C network on each of the Analog Port B
input signals; see Figure 2-14.
Table 2-24. A/D Port B Connector Description
J10
Pin # Signal Pin # Signal
1 AN8 2 AN9
3 AN10 4 AN11
5 AN12 6 AN13
7 AN14 8 AN15
9 GNDA 10 +V
REFH
2.15.10 Serial Communications Port #0 Expansion Connector
The Serial Communications Port #0 is an MPIO port attached to the SCI #0 expansion connector.
This port can be configured as a Serial Communications Interface or as a General Purpose I/O
port. Refer to
Table 2-25 for connection information.
Table 2-25. SCI #0 Connector Description
J13
Pin # Signal Pin # Signal
1 TXD0 / PE0 2 RXD0 / PE1
3 GND 4 +3.3V
5 GND 6 +5.0V
MC56F8367EVM User Manual, Rev. 2
2-34 Freescale Semiconductor
Preliminary
Page 53

Peripheral Expansion Connectors
2.15.11 Serial Communications Port #1 Expansion Connector
The Serial Communications Port #1 is an MPIO port attached to the SCI #1 expansion connector.
This port can be configured as a Serial Communications Interface or as a General Purpose I/O
port. Refer to
Table 2-26 for connection information.
Table 2-26. SCI #1 Connector Description
J14
Pin # Signal Pin # Signal
1 TXD1 / PD6 2 RXD1 / PD7
3 GND 4 +3.3V
5 GND 6 +5.0V
2.15.12 Serial Peripheral Interface #0 Expansion Connector
The Serial Peripheral Interface #0 is an MPIO port attached to this connector. This port can be
configured as a Serial Peripheral Interface or as a General Purpose I/O port. Refer to
Table 2-27
for the connection information.
Table 2-27. SPI #0 Connector Description
J11
Pin # Signal Pin # Signal
1 MOSI0 / PE5 2 MISO0 / PE6
3 SCLK0 / PE4 4 SS0 / PE7
5 GND 6 +3.3V
Technical Summary, Rev. 2
Freescale Semiconductor 2-35
Preliminary
Page 54

2.15.13 FlexCAN #1 Expansion Connector
The FlexCAN Port #1 is attached to this connector. Refer to Table 2-28 for connection
information.
Table 2-28. CAN #1 Connector Description
J18
Pin # Signal Pin # Signal
1 CAN1_TX 2 GND
3 CAN1_RX 4 GND
2.15.14 FlexCAN #2 Expansion Connector
The FlexCAN Port #2 is attached to this connector. Refer to Table 2-29 for connection
information.
Table 2-29. CAN #2 Connector Description
J19
Pin # Signal Pin # Signal
1 CAN2_TX 2 GND
3 CAN2_RX 4 GND
MC56F8367EVM User Manual, Rev. 2
2-36 Freescale Semiconductor
Preliminary
Page 55
Peripheral Expansion Connectors
2.15.15 PWM Port A Expansion Connector
The PWM Port A is attached to this connector. Refer to Table 2-30 for connection information.
Table 2-30. PWM Port A Connector Description
J7
Pin # Signal Pin # Signal
1 PWMA0 2 PWMA1
3 PWMA2 4 PWMA3
5 PWMA4 6 PWMA5
7 FAULTA0 8 FAULTA1
9 FAULTA2 10 FAULTA3
11 ISA0 / PC8 12 ISA1 / PC9
13 ISA2 / PC10 14 GND
2.15.16 PWM Port B Expansion Connector
The PWM Port B is attached to this connector. Refer to Table 2-31 for connection information.
Table 2-31. PWM Port B Connector Description
J8
Pin # Signal Pin # Signal
1 PWMB0 2 PWMB1
3 PWMB2 4 PWMB3
5 PWMB4 6 PWMB5
7 FAULTB0 8 FAULTB1
9 FAULTB2 10 FAULTB3
11 ISB0 / PD10 12 ISB1 / PD11
13 ISB2 / PD12 14 GND
Technical Summary, Rev. 2
Freescale Semiconductor 2-37
Preliminary
Page 56

2.16 Test Points
The 56F8367EVM board has a total of seven test points:
• Analog Ground (AGND)
• Three Digital Grounds (GND)
• +3.3V
• +3.3VA
• +5.0V
MC56F8367EVM User Manual, Rev. 2
2-38 Freescale Semiconductor
Preliminary
Page 57

Appendix A 56F8367EVM Schematics
56F8367EVM Schematics, Rev. 2
Freescale Semiconductor Appendix A-1
Preliminary
Page 58

Rev.
1.0
+3.3VA
Single trace
to GNDA
C58
E
100pF
C57
0.001uF
C14
0.1uF
+3.3V_PLL
92
114
+VREFH
VREFN
VREFMID
VREFP
113
115
112
111
Single trace
to GNDA
C17
0.1uF
47K
47K
47K
R19
R20
C16
0.1uF
C15
0.1uF
FAULTB0
R21
FAULTB1
47K
R22
FAULTB3
FAULTB2
2100 East Elliot Road
Tempe, Arizona 85284
(512) 895-7215 FAX: (480) 413-2510
Digital Signal Controller Operation
110
109
114Thursday, September 02, 2004
E
DSCO Design
Designer: Sheet of
VREFP
VREFH
VREFN
VSSA_ADC
VDDA_ADC
VDDA_OSC_PLL
D
C
U1B
1
VDD_IO1
VDD_IO2
VDD_IO3
1631427796
+3.3V
VPP1
VPP2
VDD_IO4
VDD_IO5
VDD_IO6
VDD_IO7
2
134
141
R70
0 Ohm
DNP
R69
0 Ohm
DNP
R68
0 Ohm
DNP
R67
0 Ohm
DNP
+2.5V
VREFMID
VCAPC3
VCAPC4
VSS_IO1
VCAPC1
VCAPC2
274174
62
95
15
144
VCAPC1
VCAPC3
VCAPC4
VCAPC2
C7
C6
2.2uF
VREFLO
MC56F8367VPY60
Use on-chip
regulators
OCR_DIS
VSS_IO6
VSS_IO2
VSS_IO3
VSS_IO4
VSS_IO5
80
91
R72
OCR_DIS
R71
+3.3V
0 Ohm
0 Ohm
DNP
Use external
+2.5V Supply
125
160
C9
2.2uF
C8
2.2uF
2.2uF
47K
47K
47K
R15
R16
R17
FAULTA1
FAULTA0
47K
R18
FAULTA2
FAULTA3
D
MC56F8367EVM.DSN
C77
0.1uF
TEMP_SENSE
ANA7
2
1
JG12
Number
Document
Date:
MC56F8367 Processor
B
Title
Size
C
B
U1A
A
PWMA1
PWMA2
PWMA5
ISA1
ISA0
ISA2
FAULTA0
FAULTA1
PWMA0
PWMA4
PWMA3
737576787981828485
PWMA0
PWMA1
PWMA2
PWMA3
PWMA4
A0/PA8
A1/PA9
A2/PA10
A3/PA11
A4/PA12
101112131417181920212223242526
154
A0A1A2A3A4A5A6A7A8
FAULTA2
126
127
128
PWMA5
ISA0/PC8
ISA1/PC9
FAULTA0
FAULTA1
FAULTA2
ISA2/PC10
A5/PA13
A6/PE2
A7/PE3
A8/PA0
A9/PA1
A10/PA2
A11/PA3
A9
A10
A11
4 4
PHASEA0
HOME0
INDEX0
PHASEB0
FAULTA3
87
FAULTA3
A12/PA4
A12
ANA0
ANA1
155
156
157
158
100
101
102
ANA0
ANA1
HOME0/TA3/PC7
INDEX0/TA2/PC6
PHASEA0/TA0/PC4
PHASEB0/TA1/PC5
PB0/A16
PB1/A17
PB2/A18
PB3/A19
A13/PA5
A13
PB4/A20/Prescaler_Clock
A14/PA6
A15/PA7
33
343536
37
464748
PB0
A14
A15
PB1
PB2
PB3
PB4
ANA6
ANA7
ANA2
ANA5
ANA4
ANA3
103
104
105
106
107
ANA2
ANA3
ANA4
ANA5
ANA6
ANA7
PB5/A21/SYS_CLK
PB6/A22/SYS_CLKx2
PB7/A23/OSC_CLOCK
D0/PF9
D1/PF10
7071838688899028293032
D0D1D2D3D4D5D6D7D8
PB5
PB6
PB7
PWMB0
383940434445616364
D2/PF11
ISB1
PWMB2
PWMB1
PWMB3
PWMB0
PWMB1
PWMB2
PWMB3
D3/PF12
D4/PF13
D5/PF14
D6/PF15
3 3
FAULTB1
FAULTB0
PWMB4
PWMB5
ISB0
FAULTB2
FAULTB3
ISB2
676869
72
PWMB4
PWMB5
FAULTB0
FAULTB1
FAULTB2
FAULTB3
ISB0/PD10
ISB1/PD11
ISB2/PD12
D7/PF0
D8/PF1
D9/PF2
D10/PF3
D11/PF4
D12/PF5
D13/PF6
D14/PF7
D15/PF8
149
150
151
152
153
D9
D10
D11
D12
D13
D14
D15
ANB6
ANB5
ANB1
ANB4
ANB0
ANB2
ANB3
ANB7
INDEX1
PHASEB1
HOME1
TC0
TC1
PHASEA1
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
ANB0
ANB1
ANB2
ANB3
ANB4
ANB5
ANB6
PD0/CS2/CAN2_TX
DS/CS1/PD9
PD1/CS3/CAN2_RX
PD2/CS4
PD3/CS5
PD4/CS6
PS/CS0/PD8
53
54
55
56
575859
60
/DS
/PS
PD0
PD1
PD2
PD3
PD4
133
786
9
135
ANB7
PD5/CS7
PD5
TC1/PE9
TC0/PE8
HOME1/TB3/SS1/PC3
INDEX1/TB2/MISO1/PC2
PHASEB1/TB1/MOSI1/PC1
PHASEA1/TB0/SCLK1/PC0
EXTBOOT
XTAL
EXTAL
EMI_MODE
WR
RD
51
52
93
949798
124
159
/RD
/WR
XTAL
EXTAL
EXTBOOT
EMI_MODE
2 2
CAN_RX
CAN_TX
TXD0
RXD0
TXD1
TD0
TD1
TD2
TD3
129
130
142
143
131
132
CAN1_TX
TD2/PE12
TD3/PE13
TD0/PE10
TD1/PE11
CAN1_RX
RSTO
CLKO
RESET
CLKMODE
3
99
147
CLKO
/RSTO
MISO0
/RESET
CLKMODE
RXD1
/IRQA
/IRQB
TEMP_SENSE
49
50
65
TXD0/PE0
SS0/PE7
/SS0
66
5
IRQB
IRQA
TXD1/PD6
RXD0/PE1
RXD1/PD7
MC56F8367VPY60
TRST
TCK
TMS
TDI
TDO
136
137
138
139
140
TDI
TMS
TCK
TDO
/TRST
1 1
108
4
TEMP_SENSE
SCLK0/PE4
MISO0/PE6
MOSI0/PE5
145
146
148
MOSI0
SCLK0
Figure A-1. 56F8367 Processor
B
A
MC56F8367EVM User Manual, Rev. 2
Appendix A-2 Freescale Semiconductor
Preliminary
Page 59
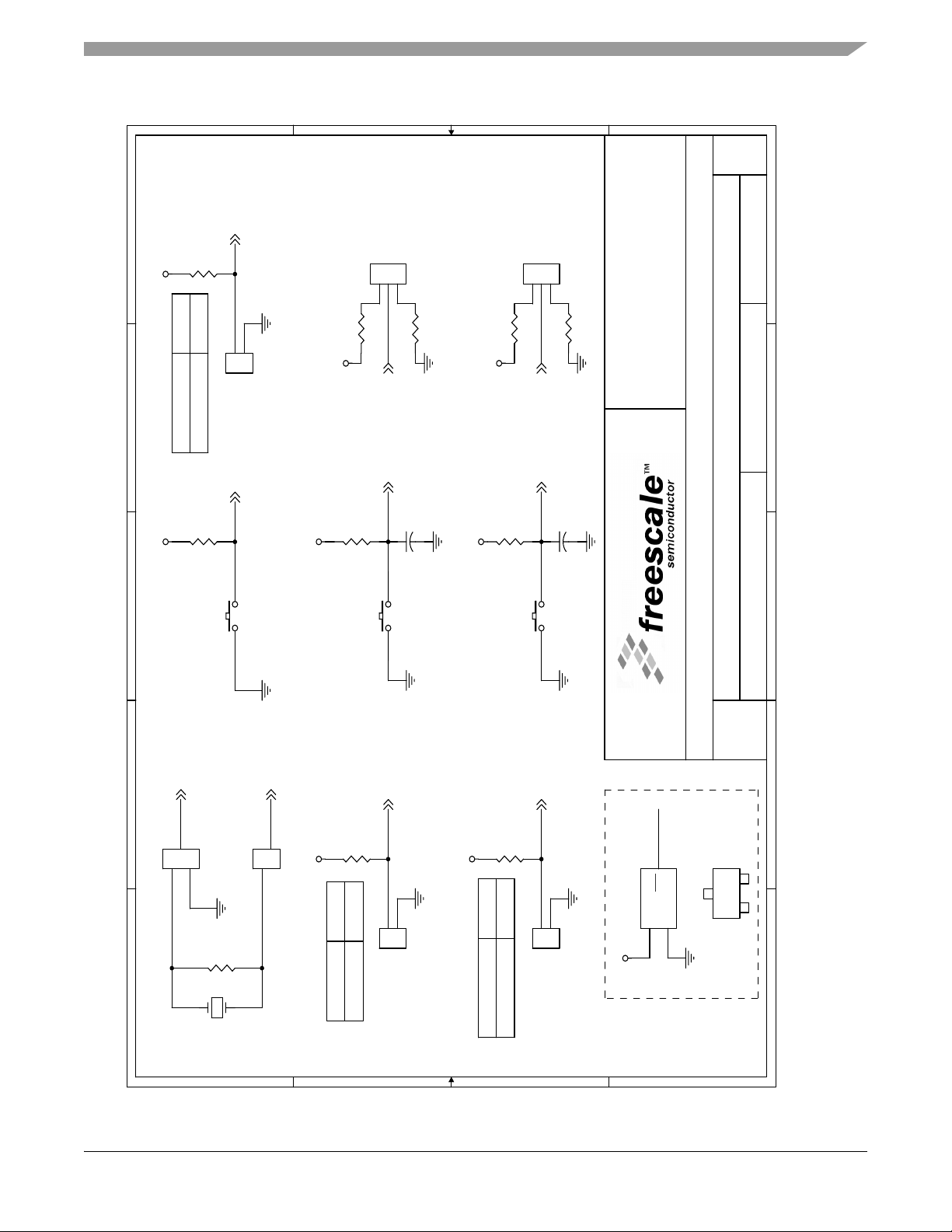
Rev.
1.0
E
R7
10K
NC
1 - 2
D
C
EXT OSC
CLOCK MODE JUMPER
USE CRYSTAL
R2
10K
+3.3V +3.3V
CLKMODE
1
2
/POR
S1 JG6
RESET PUSHBUTTON
+3.3V
+3.3V
#0
User
Jumper
123
JG15
R8
10K
R9
PE4
SCLK0
/IRQA
R3
10K
C18
S2
IRQA PUSHBUTTON
JG16
10K
SOFTWARE FEATURE JUMPERS
0.1uF
R10
+3.3V
10K
R4
+3.3V
IRQB PUSHBUTTON
User
123
10K
S3
#1
Jumper
R11
PE7
/SS0
/IRQB
C19
0.1uF
2100 East Elliot Road
10K
Tempe, Arizona 85284
(512) 895-7215 FAX: (480) 413-2510
Digital Signal Controller Operation
RESET, MODE, CLOCK & IRQS
E
214Thursday, September 02, 2004
DSCO Design
D
Designer: Sheet of
MC56F8367EVM.DSN
C
Document
Date:
Number
3
A
Size
DS1818
12
Figure A-2. Reset, Mode, Clock & IRQs
B
A
Title
B
EXTAL
123
JG1
OSC BYPASS
R1
1M
A
Y1
8.00MHz
4 4
XTAL
2
1
JG2
+3.3V
NC
EXT BOOT
BOOT MODE JUMPER
EXTBOOT
R5
10K
1 - 2
2
JG4
INT BOOT
3 3
EMI_MODE
R6
10K
+3.3V
NC
1
1 - 2
EMI A0-A23
EMI MODE JUMPER
EMI A0-A15
2
JG5
2 2
1
OPTIONAL
/POR
RST
U16
DS1818
Vcc
GND
213
+3.3V
1 1
56F8367EVM Schematics, Rev. 2
Freescale Semiconductor Appendix A-3
Preliminary
Page 60

1.0
Rev.
+3.3V
E
10K
10K
R14
R13
/ECS4
/ECS1
2100 East Elliot Road
Tempe, Arizona 85284
7
D1
DQ1
D2
819
DQ2A4DQ3
D5
D4D0D6
1021314315
DQ4A3
DQ5
DQ6A2DQ7
D7
16429
DQ8A1DQ9
D8
D9
30531
DQ10A0DQ11
D11D3D10
321835
DQ12
D12
D13
36
DQ13
D14
DQ14
D15
DQ16
11
VDD1
33
VDD2
12
VSS1
34
VSS2
E
314Thursday, September 02, 2004
U3
D
A5
A10A3A14
A5A9A6
A2
A8A0A7
A4
A15
A14 DQ15
A13
A12
A11
A10A9A8A7A6
A11A1A12
A17
A18
A16
19 3738202124252627424344
22
23
28
/RD
PB1
PB2
A15
A13
PB0
GS72116TP-7
UB
LBOEWE
CE
6
394117
/WR
/ECS1
/CE
Note: A17 & A18 are
40
/ECS4
R32
1K
N/C on GS72116.
3-4
1-2SRAM WORD ENABLE
3-4
NC
NC
1-2
NC
Digital Signal Controller Operation
NC
(512) 895-7215 FAX: (480) 413-2510
DSCO Design
D
Designer: Sheet of
2
4
1
3
JG8
/DS
PD2
C
D0D1D2D3D4D5D6D7D8D9D10
7
819
1021314315
DQ1
DQ2A4DQ3
DQ4A3
DQ5
DQ6A2DQ7
B
U2
A5
16429
DQ8A1DQ9
30531
DQ10A0DQ11
A10A9A8A7A6
D11
321835
DQ12
A11
D12
36
DQ13
A12
D13
DQ14
A13
19 3738202124252627424344
D14
A14 DQ15
D15
DQ16
A15
22
A16
+3.3V +3.3V
34
12
33
11
VSS2
VSS1
VDD2
VDD1
A17
A18
A16
23
28
A17
A18
GS72116TP-7
LBOEWE
CE
UB
Note: A17 & A18 are
6
40
394117
/UB
/LB
N/C on GS72116.
R31
1K
OPTION JG8
CS1/CS4 ENABLE JUMPER
SRAM DISABLE
SRAM UPPER BYTE ENABLE
SRAM LOWER BYTE ENABLE
MC56F8367EVM.DSN
C
Document
Date:
Number
PROGRAM [WORD] (CS0) and DATA [BYTE] (CS1/CS4) SRAM MEMORY
Size
A
B
Title
A0A1A2A3A4A5A6A7A8
128Kx16-bit Program Memory (CS0) 128Kx16-bit Data Memory (CS1/CS4)
A
4 4
A9
A10
A11
A12
A13
A14
A15
PB0
PB1
PB2
/RD
/WR
10K
/ECS0
2
1
JG7
/PS
3 3
R12
+3.3V
R30
1K
CS0 ENABLE JUMPER
JG7
OPTION
2 2
NC
1-2SRAM ENABLE
SRAM DISABLE
Note:
GS71116ATP 64Kx16-bit
GS72116ATP 128Kx16-bit
GS74116ATP 256Kx16-bit
IS61LV51216 512Kx16-bit
1 1
A
Figure A-3. Program [Word] (CS0) & Data [Byte] (CS1/CS4) SRAM Memory
MC56F8367EVM User Manual, Rev. 2
Appendix A-4 Freescale Semiconductor
Preliminary
Page 61

1.0
+3.3V
Rev.
1K
1K
R36
1K
R37
R35
E
R34
1K
1K
R38
E
414Thursday, September 02, 2004
R4IN
R5IN
2100 East Elliot Road
Tempe, Arizona 85284
DCD
DSR
TXD
CTS
RXD
RTS
DTR
GND
/EN
R3IN
T3IN
(512) 895-7215 FAX: (480) 413-2510
P2
D
SCI #0
594837261
RS-232
CONNECTOR
Digital Signal Controller Operation
DSCO Design
D
Designer: Sheet of
C13
1.0uF
C12
1.0uF
+3.3V
27
3
25
C
V-
V+
VCC
GND
1
TXD
RTS
T2OUT
T1OUT
R3IN
RXD
CTS
4
11109
R2IN
R1IN
T3OUT
1
R4IN
R5IN
765
21
MC56F8367EVM.DSN
R4IN
R3IN
INVALID
C
/EN
FORCEON
23
22
R33
MAX3245EEAI
FORCEOFF
RS232EN
1K
1
JG10
N/C
RS-232 SHUTDOWN JUMPER
RS-232 ENABLE
2
JG11
1 - 2
RS-232 DISABLE
2 2
RTS1
CTS1
1
2
U4
B
A
C2+
C1-
1262
24
C11
C2-
1.0uF
JG9
C1+
28
C10
1.0uF
4 4
R2OUTB
T1IN
T2IN
T3IN
R1OUT
R2OUT
14131219181716
20
CTS1
RTS1
T3IN
1
TX_IN
RX_OUT
2
4
1
3
RXD0
TXD0
3 3
R3OUT
R4OUT
15 8
111
+3.3V
R5OUT R5IN
Document
RS-232 AND SCI CONNECTORS
Title
Size
1 1
Date:
Number
A
B
A
Figure A-4. RS-232 and SCI Connectors
56F8367EVM Schematics, Rev. 2
Freescale Semiconductor Appendix A-5
Preliminary
Page 62

Rev.
1.0
E
E
514Thursday, September 02, 2004
2100 East Elliot Road
USER
LEDS
Tempe, Arizona 85284
(512) 895-7215 FAX: (480) 413-2510
Digital Signal Controller Operation
D
+3.3V
DSCO Design
D
Designer: Sheet of
RED LED
LED1
C
270
R58
YELLOW LED
LED2
270
R59
GREEN LED
LED3
270
R60
RED LED
LED4
R61
270
YELLOW LED
LED5
270
R62
GREEN LED
LED6
270
R63
MC56F8367EVM.DSN
C
Document
Date:
Number
USER DEBUG LEDS
Size
A
Figure A-5. User Debug LEDs
B
A
U6B
74AC04
U6C
74AC04
U6D
U6A
74AC04
1 2
B
PC0
PHASEA1
A
3 4
PC1
PHASEB1
4 4
5 6
PC2
INDEX1
74AC04
U6E
9 8
PC3
HOME1
3 3
11 10
PD6
74AC04
U6F
74AC04
13 12
PD7
TXD1
RXD1
2 2
Title
1 1
MC56F8367EVM User Manual, Rev. 2
Appendix A-6 Freescale Semiconductor
Preliminary
Page 63

Rev.
1.0
E
E
614Thursday, September 02, 2004
LEDS
2100 East Elliot Road
Tempe, Arizona 85284
PWM STATE
+3.3V
D
270
GREEN LED
LED8
R53
YELLOW LED
LED7
R52
C
270
YELLOW LED
LED9
R54
270
GREEN LED
LED10
R55
270
LED11
YELLOW LED
R56
270
GREEN LED
LED12
270
R57
Digital Signal Controller Operation
(512) 895-7215 FAX: (480) 413-2510
DSCO Design
D
Designer: Sheet of
MC56F8367EVM.DSN
C
Document
Date:
Number
U5A
74AC04
U5B
74AC04
U5C
74AC04
U5D
1 2
3 4
5 6
U5E
74AC04
U5F
74AC04
9 8
11 10
74AC04
13 12
PWM PORT A STATE LEDS
Size
A
Title
Figure A-6. PWM Port A State LEDs
B
PWMA0
A
4 4
PWMA1
PWMA2
PWMA3
3 3
PWMA4
PWMA5
2 2
1 1
B
A
56F8367EVM Schematics, Rev. 2
Freescale Semiconductor Appendix A-7
Preliminary
Page 64

Rev.
1.0
E
E
714Thursday, September 02, 2004
CAN BUS
TERMINATION
2100 East Elliot Road
Tempe, Arizona 85284
1
2
JG13
D
BCANL
R40
120
1/4W
Digital Signal Controller Operation
BCANH
BCANL
(512) 895-7215 FAX: (480) 413-2510
DSCO Design
D
Designer: Sheet of
L6
T11
CANL
3
567
VCC
CANH BCANH
2
GND
VREF
CANL
CANH
+5.0V
C
BCANHBCANL
246
J211357
8
10
9
MC56F8367EVM.DSN
C
U10
TXD
RXD
1
4
R28
1K
+5.0V
B
SLOPE
8
PCA82C250T
DAISY-CHAIN
CAN BUS CONNECTOR
HIGH-SPEED CAN PORT #1 INTERFACE
Title
Document
Number
Size
Date:
A
B
Figure A-7. High-Speed CAN Port #1 Interface
CAN_TX
CAN_RX
246
8
10
J201357
A
4 4
3 3
CAN BUS CONNECTOR
9
BCANL BCANH
2 2
1 1
A
MC56F8367EVM User Manual, Rev. 2
Appendix A-8 Freescale Semiconductor
Preliminary
Page 65

Rev.
1.0
E
E
814Thursday, September 02, 2004
CAN BUS
TERMINATION
2100 East Elliot Road
Tempe, Arizona 85284
1
2
JG17
D
BCAN2L
R41
120
1/4W
Digital Signal Controller Operation
BCAN2H
BCAN2L
(512) 895-7215 FAX: (480) 413-2510
DSCO Design
D
Designer: Sheet of
L7
T21
+5.0V
C
3
VCC
567
VREF
CAN2H BCAN2H
CAN2L
2
GND
CANL
CANH
BCAN2HBCAN2L
246
J231357
8
10
9
MC56F8367EVM.DSN
C
U11
TXD
RXD
1
R29
+5.0V
B
4
1K
CAN2_RX
CAN2_TX
2
4
1
3
JG14
SLOPE
8
PCA82C250T
DAISY-CHAIN
CAN BUS CONNECTOR
HIGH-SPEED CAN PORT #2 INTERFACE
Title
Document
Number
Size
Date:
A
B
Figure A-8. High-Speed CAN Port #2 Interface
PD1
PD0
A
4 4
3 3
246
8
10
J221357
CAN BUS CONNECTOR
9
BCAN2L BCAN 2H
A
2 2
1 1
56F8367EVM Schematics, Rev. 2
Freescale Semiconductor Appendix A-9
Preliminary
Page 66
Rev.
1.0
E
E
914Thursday, September 02, 2004
2100 East Elliot Road
A5A6A7
D
246
PD0
/DS
D15
D14
D12
D13
D10
D11
/CS1
/CS2/CAN2_TX
GND
8
101214161820222426283032343638404244464850
GNDGND
PD2PD3
GNDGND
PD1
A8
D8
PB2PB3
/CS3/CAN2_RX
A11D9A10
A9
PB1
+3.3V
+5.0V
GNDGND
GNDGNDA
Tempe, Arizona 85284
(512) 895-7215 FAX: (480) 413-2510
Digital Signal Controller Operation
DSCO Design
D
Designer: Sheet of
J2
135791113151719212325272931333537394143454749
A20
/CS0
/CS6 /CS7
A4A3A2
A1 /RD
A0
D0
D1
/PS
PB4
C
PD4 PD5
D3D2D5
D4
/CS5 /CS4
D7
D6
/WR
51 52
53 54
55 56
57 58
59 60
A16 A17
A19 A18
GND GND
Daughter Address/Data Connector
+5.0V
+3.3V
A15
A12
A13
A14
PB0
MC56F8367EVM.DSN
C
Document
Date:
Number
DAUGHTER CARD CONNECTORS
Size
A
Figure A-9. Daughter Card Connectors
B
A
Title
ISB1
ISB0
GND
ISB2
PWMA1
PWMA3
FAULTB0
FAULTB2
GND
GND
FAULTB3
FAULTB1
51 52
PWMA0
53 54
PWMA2
PWMA5
55 56
PWMA4
GND
GND
FAULTA1
/RSTO
ISA1
MISO0
PE6
PE7
GND
GND
57 58
59 60
61 62
63 64
65 66
GND
PE5
ISA2
ISA0
FAULTA0
FAULTA2
PWMB3
RXD1
PHASEB1
/IRQB/IRQA
PHASEB0
HOME1
TXD1
HOME0
TXD1
B
A
+12V+12V
+5.0V
+3.3V
GND
GND
GND
246
8
101214161820222426283032343638404244464850
J1
135791113151719212325272931333537394143454749
GND
GND
GND
+5.0V
+3.3V
4 4
TA1
TA0
PHASEA0
TA3
TA2
GND
GND
INDEX0
PD6
PC1/TB1/MOSI1
PC3/TB3/SS1
GNDGND
PE0
PC0/TB0/SCLK1
PC2/TB2/MISO1
TXD0
TXD0
INDEX1
PHASEA1
PWMB5
PWMB1
RXD1
PD7
GND
GND
GND
GND
PE1
RXD0
RXD0
PWMB2
PWMB4
PWMB0
3 3
/SS0
67 68
MOSI0
/SS0
TD1
TC0
CAN_RX
MISO0
AN1
+3.3VA
GND
GNDA
69 70
71 72
73 74
75 76
77 78
79 80
81 82
83 84
85 86
GNDA
GND
GND
PE4
TD0
+3.3VA
AN0
SCLK0
SCLK0
MOSI0
CAN_TX
2 2
AN13
AN11
AN9
AN7
AN5
AN3
87 88
AN2
AN15
89 90
91 92
93 94
95 96
97 98
99 100
AN6
AN4
Daughter Peripheral Port Connector
AN8
AN12
AN10
AN14
1 1
MC56F8367EVM User Manual, Rev. 2
Appendix A-10 Freescale Semiconductor
Preliminary
Page 67

1.0
Rev.
10 14Thursday, September 02, 2004
E
246
8
10
J101357
9
A/D PORT B
RXD1
+3.3V
246
J14
135
2100 East Elliot Road
Tempe, Arizona 85284
(512) 895-7215 FAX: (480) 413-2510
Digital Signal Controller Operation
E
DSCO Design
D
C
B
/IRQB
/IRQA
/DS
/RESETCLKO
PD1
PD3
PD5
/CS5
/CS7
246
8
101214
J613579111315
/CS4
/CS6
/CS2 /CS3
/CS0 /CS1
/RD
/PS
PD0
PD2
PD4
/WR
J5
12
34
56
78
910
11 12
13 14
D2 D3
D4 D5
D6 D7
D8 D9
D10 D11
D12 D13
/RSTO
16
ADDRESS CONTROL
+3.3V
15 16
17 18
DATA BUS
D14 D15
AN8 AN9
AN10 AN 11
AN12 AN 13
246
J91357
AN0 AN1
AN2 AN3
AN4 AN5
PWMB1
PWMB3
PWMB5
246
J8
135791113
PWMB0
PWMB2
PWMB4
AN14 AN 15
+3.3VA +3.3VA
8
10
9
AN6 AN7
FAULTB3
ISB1
FAULTB1
8
101214
ISB0
FAULTB0
FAULTB2
A/D PORT A
PWMB
ISB2
TXD1
RXD0
+3.3V
+5.0V +5.0V
246
J13
135
SCI #0
+3.3V
246
J17
135
TIMER CHANNEL DTIMER CHANNEL A
TD0 TD1TC0
TXD0
+3.3V
/SS1
246
&
J12
135
SPI #1 SCI #1
QUAD-DECODER #1
SCLK1
MOSI1 MISO1
PHASEB1 INDEX1
PHASEA1 HOME1
TD2 TD3
TC1
+3.3V
2
4
J16
1
3
TIMER CHANNEL C
J19
2
4
1
3
CAN2_TX
CAN2_RX
PD0
PD1
CAN #2
Designer: Sheet of
D
MC56F8367EVM.DSN
Number
Document
Date:
PROCESSOR PORT EXPANSION CONNECTORS
B
Title
Size
C
B
Figure A-10. Processor Port Expansion Connectors
A1A3A5A7A9
A11
A13
A15
PB1
PB3
PB5
A
A17
A19
A21
246
8
101214161820222426
J41357911131517192123
A18
A20
A16
A4A6A8
A2
A0 D0 D1
PB0
A10
A12
A14
PB2
PB4
4 4
PB7PB6
+3.3V
A23
25
A22
ADDRESS BUS
PWMA1
PWMA3
PWMA5
246
J7
135791113
PWMA0
PWMA2
PWMA4
FAULTA1
FAULTA3
8
101214
PWMA
ISA0 ISA1
ISA2
FAULTA0
FAULTA2
3 3
+3.3V
246
J11
135
SPI #0
MOSI0 MISO0
SCLK0 /SS0
2 2
56F8367EVM Schematics, Rev. 2
Freescale Semiconductor Appendix A-11
Preliminary
PHASEB0PHASEA0
+3.3V
TA3TA2
TA1
246
&
J15
135
QUAD-DECODER #0
TA0
INDEX0 HOME0
2
4
J18
1
3
CAN #1
CAN_TX
CAN_RX
1 1
A
Page 68
1.0
Rev.
+3.3V
5.1K
47K
R47
47K
47K
R24
R25
R26
E
TDO
PWR
/DE
R27
47K
P_DE
/J_TRST
TMS
2100 East Elliot Road
Tempe, Arizona 85284
11 14Thursday, September 02, 2004
E
/J_TRST
KEY
246
8
101214
J3
TMS
TCK
/J_TRST
TDI
P_RESET
181614129
1Y1
1Y2
1Y3
1Y4
D
C
U9
1A1
1A2
1A3
246
0 Ohm
R74
0 Ohm
R73
R75
181614129
1Y1
1Y2
1Y3
U8
1A1
1A2
1A3
246
R76
8
0 Ohm
8
1A4
1Y4
1A4
Parallel JTAG Interface
B
0 Ohm
R77
2Y1
2A1
11
2Y1
2A1
11
R43
TDO
P_DE
131517
2A2
2Y2
753
11
0 Ohm
7
15
2Y2
2A2
13
+Vsel
JG19
5.1K
PWR
2A3
2A4
2Y3
2Y42G1G
1720
2A3
2A4VCC
123
+3.3V
10
GND
VCC
MC74LCX244DW
1
19
20
R46
5.1K
/CCEN
1
2
+3.3V
JG3
On-Board
Host Target Interface
10
GND
2Y4
3
5.1K
5.1K
51 Ohm
Disable
MC74HC244DW
R45
R44
19
1
2G
1G
2Y3
5
+5.0V
R51
51 Ohm
R50
/RESET
6
U7B
4
3
U7A
1
/J_RESET
135791113
JTAG Connector
/DE
/J_RESET
TDI
TCK
TDO
+3.3V
/TRST
8
74AC00
U7C
5
74AC00
2
/POR
74AC00
9
10
11
U7D
74AC00
12
13
/J_TRST
(512) 895-7215 FAX: (480) 413-2510
Digital Signal Controller Operation
DSCO Design
Designer: Sheet of
D
MC56F8367EVM.DSN
Number
Document
Date:
PARALLEL JTAG HOST TARGET INTERFACE AND JTAG CONNECTOR
B
Title
Size
+Vsel
1K
DNP
1K
R95
R94
PORT_PU
C
PORT_CONNECT
B
/J_RESET
R42
5.1K
Q1
PORT_TMS
/PORT_TRST
PORT_TCK
PORT_TDI
PORT_RESET
132
P1
PORT_IDENT
A
4 4
151416417518619720821922102311241225
PORT_DE
PORT_TDO
PORT_CONNECT
PORT_PU
PORT_VCC
13
3 3
+3.3V
2 2
2N2222A
R48
5.1K
Figure A-11. Parallel JTAG Host Target Interface and JTAG Connector
R23
47K
P_RESET
A
1 1
MC56F8367EVM User Manual, Rev. 2
Appendix A-12 Freescale Semiconductor
Preliminary
Page 69

Rev.
1.0
E
ANB4
ANB5
ANB6
ANB7
E
12 14Thursday, September 02, 2004
C71
R90
0.0022uF
100
R91
100
C72
0.0022uF
R92
100
C73
0.0022uF
R93
100
C74
0.0022uF
2100 East Elliot Road
Tempe, Arizona 85284
(512) 895-7215 FAX: (480) 413-2510
NOTE: Use a single trace
for GNDA signals to the
D
AN12
AN13
AN14
AN15
common GNDA point.
Digital Signal Controller Operation
DSCO Design
D
Designer: Sheet of
ANA7
C66
0.0022uF
C
R85
100
R86
ANB0
C67
0.0022uF
100
R87
ANB1
C68
0.0022uF
100
R88
ANB2
C69
0.0022uF
100
R89
ANB3
C70
0.0022uF
MC56F8367EVM.DSN
C
100
Document
Date:
Number
A/D INPUT FILTERS
AN7
B
ANA0
C59
0.0022uF
R78
100
A
AN0
4 4
R79
AN8
ANA1
C60
0.0022uF
100
AN1
R80
AN9
ANA2
C61
0.0022uF
100
AN2
3 3
R81
AN10
ANA3
C62
0.0022uF
100
AN3
R82
AN11
ANA4
C63
0.0022uF
100
AN4
2 2
R83
ANA5
C64
0.0022uF
100
AN5
R84
Title
ANA6
C65
100
AN6
1 1
0.0022uF
Size
A
B
A
Figure A-12. A/D Input Filters
56F8367EVM Schematics, Rev. 2
Freescale Semiconductor Appendix A-13
Preliminary
Page 70

1.0
Rev.
4
123
REGULATOR
Single trace
to GNDA.
U15
1
3.3V AND 5.0V
3.3V REF
REGULATOR
+VREFH
10 Ohm
R65
C75
10uF
6VDC
+
+3.3V
C76
0.01uF
5
4
NR
VOUT
VIN
GND
EN
REG113NA-3.3/3K
2
3
E
+5.0V
+2.5V Input
+2.5V Ground Reference
1
2
J24
D
+5.0V
C
+2.5V
L1
External +2.5V
C2
47uF
10VDC
+
FERRITE BEAD
POWER GOOD LED
R64
270
Power Supply
Input
DNP
D3
FM4001
LED13
GREEN LED
NOTE: Remove 0 OHM
resistor to use Analog
GND isolation jumper.
1
2
JG18
+3.3VA
C4
47uF
10VDC
R66
+
L2
FERRITE BEAD
C22
0.1uF
41
VOUTGND
U13
MC33269DT-3.3
VIN VOUT
3 2
0 Ohm
L3
FERRITE BEAD
MC33269
5
1234
REG113NA3/3K
2100 East Elliot Road
Tempe, Arizona 85284
(512) 895-7215 FAX: (480) 413-2510
Digital Signal Controller Operation
TP7
1
13 14Thursday, September 02, 2004
DSCO Design
Designer: Sheet of
MC56F8367EVM.DSN
Number
Document
Date:
POWER SUPPLIES
B
Title
Size
+5.0V
E
D
C
TP6
1
TP3
1
GROUND
TEST POINT TEST POINT TEST POINT
TP2
1
GROUND
TEST POINT
TP1
1
TP5
1
TEST POINT TEST POINT
TP4
1
Figure A-13. Power Supplies
B
+3.3VA+3.3V
A
DNP
FM4001
+5.0V
+3.3V
Typ 135mA
C3
47uF
10VDC
+
VCC
L4
FERRITE BEAD
41
VOUTGND
NOTE: To measure +3.3V supply
current, remove L2 and replace
U14
MC33269DT-3.3
VIN VOUT
3 2
with amp meter.
41
VOUTGND
D2
FM4001
U12
B
+12V
D1
3
1
3
P3
2
MC33269DT-5.0
VIN VOUT
3 2
C20
0.1uF
C1
470uF
16VDC
+
1
4
-+
2
D4
7-12V DC/AC
A
EXTERNAL POWER INPUT
+5.0V
+5.0V
+3.3V_PLL
C21
0.1uF
C5
47uF
10VDC
+
L5
FERRITE BEAD
+3.3V
+3.3V +3.3VA GROUND ANALOG GROUND +5.0V
TEST POINT
4 4
3 3
2 2
1 1
MC56F8367EVM User Manual, Rev. 2
Appendix A-14 Freescale Semiconductor
Preliminary
Page 71

1.0
Rev.
14 14Thursday, September 02, 2004
E
C32
U11
PCA82C250
U10
0.1uF
C50
J10
C31
0.1uF
0.1uF
+3.3VA
A/D CONNECTOR
2100 East Elliot Road
Tempe, Arizona 85284
(512) 895-7215 FAX: (480) 413-2510
Digital Signal Controller Operation
PCA82C250
C35
U9U8
D
0.1uF
J9
C49
0.1uF
+3.3VA
E
DSCO Design
Designer: Sheet of
D
MC56F8367EVM.DSN
A/D CONNECTOR
C36
0.1uF
74HC244
C48
0.1uF
C37
U7
C
+VREFH
B
C28
0.1uF
C27
0.1uF
C54
0.01uF
C53
0.01uF
C52
0.01uF
74AC04
U5 U6
74AC04 74AC00 74LCX244
U4
MAX3245GS72116
U1
MC56F8367
C26
0.1uF
C25
0.1uF
C24
0.1uF
A
C23
0.1uF
+3.3V
U3
U2
GS72116
0.1uF
C39
0.1uF
C38
0.1uF
+3.3V +3.3V +3.3V+3.3V +Vsel +5.0V +5.0V
C51
0.1uF
DNP
+3.3V
C56
0.01uF
C30
0.1uF
+3.3V +3.3V
C55
0.01uF
C29
0.1uF
+3.3V +3.3V
+3.3V+3.3V
DATA BUS
CONNECTOR
C47
J4 J5
CONNECTOR
ADDRESS BUS
MEMORY CONNECTOR
J1 J2
PERIPHERAL CONNECTOR
0.1uF
C46
0.1uF
C45
0.1uF
C44
0.1uF
+5.0V +3.3V +3.3V
C43
0.1uF
+3.3VA
C42
0.1uF
C41
0.1uF
C40
0.1uF
+5.0V +3.3V +12V
Number
Document
Date:
BYPASS CAPACITORS
B
Title
Size
C
Figure A-14. Bypass Capacitors
B
A
4 4
3 3
2 2
1 1
56F8367EVM Schematics, Rev. 2
Freescale Semiconductor Appendix A-15
Preliminary
Page 72

MC56F8367EVM User Manual, Rev. 2
Appendix A-16 Freescale Semiconductor
Preliminary
Page 73

Appendix B 56F8367EVM Bill of Material
Qty Description Ref. Designators Vendor Part #
Integrated Circuits
1 MC56F8367 U1 Freescale, MC56F8367VPY60
2 128K x 16-Bit SRAM U2, U3 GSI, GS72116ATP-8
1 RS-232 Transceiver U4 Maxim, MAX3245EEAI
2 74AC04 U5, U6 ON Semiconductor, MC74AC04AD
1 74AC00 U7 Fairchild, 74AC00SC
1 74HC244 U8 ON Semiconductor, MC74LHC44AADW
1 74LCX244 U9 ON Semiconductor, MC74LCX244ADW
2 CAN Transceiver U10, U11 Philips Semiconductor, PCA82C250T
1 +5.0V Voltage Regulator U12 ON Semiconductor, MC33269DT-5
2 +3.3V Voltage Regulator U13, U14 ON Semiconductor, MC33269DT-3.3
1 +3.3V Voltage Regulator U15 Burr-Brown, REG113NA-3.3
0 Power-On Reset U16 (Optional) Dallas Semiconductor, DS1818
Resistors
1 1MΩ R1 SMEC, RC73L2A105OHMJT
13 10KΩ R2 - R14 SMEC, RC73L2A103OHMJT
13 47KΩ R15 - R27 SMEC, RC73L2A473OHMJT
12 1KΩ R28 - R38, R94 SMEC, RC73L2A103OHMJT
0 1KΩ R95 (Optional) SMEC, RC73L2A103OHMJT
2 120Ω, 1/4W R40, R41 YAGEO, CFR 120QBK
56F8367EVM Bill of Material, Rev. 2
Freescale Semiconductor Appendix B-1
Preliminary
Page 74

Qty Description Ref. Designators Vendor Part #
Resistors (Continued)
7 5.1KΩ R42 - R48 SMEC, RC73L2A512OHMJT
2 51Ω R50, R51 SMEC, RC73L2A51OHMJT
13 270Ω R52 - R64 SMEC, RC73L2A271OHMJT
1 10Ω R65 SMEC, RC73L2A100OHMJT
7 0Ω R66, R72 - R77 SMEC, RC73JP2A
0 0Ω R67 - R71 (Optional) SMEC, RC73JP2A
16 100Ω R78 - R93 SMEC, RC73L2A101OHMJT
Inductors
5 1.0mH FERRITE BEAD L1 - L5 Panasonic, EXC-ELSA35V
2 CAN Bus Filter L6, L7 EPCOS, B82790-S0513-N201
LEDs
2 Red LED LED1, LED4 Hewlett-Packard, HSMS-C650
5 Yellow LED LED2, LED5, LED7, LED9,
LED11
6 Green LED LED3, LED6, LED8, LED10,
LED12, LED13
Diode
1 +50V 1A BRIDGE RECT D1 DIODES, DF02S
1 S2B-FM401 D2 Vishay, DL4001DICT
0 S2B-FM401 D3, D4 (Optional) Vishay, DL4001DICT
Capacitors
1 470µF, +16V DC C1 ELMA, RV-16V471MH10R
4 47µF, +16V DC C2 - C5 ELMA, RV2-16V470M-R
4 2.2µF, +25V DC
(Low ESR)
4 1.0µF, +25V DC C10 - C13 SMEC, MCCE105K3NR-T1
37 0.1µF C14 - C32, C35 - C51, C77 SMEC, MCCE104K2NR-T1
6 0.01µF C52 - C56, C76 SMEC, MCCE103K2NR-T1
C6 - C9 TAIYO YUDEN, CELMK212BJ225MG-T
Hewlett-Packard, HSMY-C650
Hewlett-Packard, HSMG-C650
MC56F8367EVM User Manual, Rev. 2
Appendix B-2 Freescale Semiconductor
Preliminary
Page 75

Qty Description Ref. Designators Vendor Part #
Capacitors (Continued)
1 0.001µF C57 SMEC, MCCE102K2NR-T1
1 100pF C58 SMEC, MCCE101K2NR-T1
16 0.0022µF C59 - C74 SMEC, MCCE222K2NR-T1
1 10µF, +10V DC C75 KEMET, T494B106M010AS
Jumpers
4 3 × 1 Bergstick JG1, JG15, JG16, JG19 SAMTEC, TSW-103-07-S-S
12 1 × 2 Bergstick JG2 - JG7, JG10 - JG13, JG17,
JG18
3 2 × 2 Bergstick JG8, JG9, JG14 SAMTEC, TSW-102-07-S-D
Test Points
3 GND Test Point TP1, TP2, TP3 KEYSTONE, 5001, BLACK
1 +3.3V Test Point TP4 KEYSTONE, 5000, RED
1 +3.3V A Test Point TP5 KEYSTONE, 5004, YELLOW
1 GNDA Test Point TP6 KEYSTONE, 5002, WHITE
1 +5.0V Test Point TP7 KEYSTONE, 5003, ORANGE
Crystals
1 8.00MHz Crystal Y1 CTS, ATS08ASM-T
Connectors
1 DB25M Connector P1 AMPHENOL, 617-C025P-AJ121
1 DE9S Connector P2 AMPHENOL, 617-C009S-AJ120
1 2.1mm coax
Power Connector
P3 Switchcraft, RAPC-722
SAMTEC, TSW-102-07-S-S
1 Peripheral Daughter Card
Connector
1 Memory Bus Daughter
Card Connector
1 7 x 2 JTAG Header J3 SAMTEC, TSW-106-07-S-D
1 13 x 2 Header J4 SAMTEC, TSW-106-13-S-D
56F8367EVM Bill of Material, Rev. 2
Freescale Semiconductor Appendix B-3
Preliminary
J1 HRS, FX6-100P-0.8SV2
J2 HRS, FX6-60P-0.8SV2
Page 76

Qty Description Ref. Designators Vendor Part #
Connectors (Continued)
1 9 x 2 Header J5 SAMTEC, TSW-106-09-S-D
1 8 x 2 Header J6 SAMTEC, TSW-106-08-S-D
2 7 x 2 Header J7, J8 SAMTEC, TSW-106-07-S-D
6 5 x 2 Header J9, J10, J20 - J23 SAMTEC, TSW-106-05-S-D
6 3 x 2 Header J11 - J15, J17 SAMTEC, TSW-106-03-S-D
3 2 x 2 Header J16, J18, J19 SAMTEC, TSW-106-02-S-D
Switches
3 SPST Push button S1 - S3 Panasonic, EVQ-PAD05R
Transistors
1 2N2222A Q1 ZETEX, FMMT2222ACT
Miscellaneous
18 Shunt SH1 - SH13 Samtec, SNT-100-BL-T
4 Rubber Feet RF1 - RF4 3M, SJ5018BLKC
MC56F8367EVM User Manual, Rev. 2
Appendix B-4 Freescale Semiconductor
Preliminary
Page 77

INDEX
Numerics
1.2 Amp power supply 2-17
56F8300 Peripheral User Manual 2-4
56F8357 Technical Data Sheet 2-4
8.00MHz crystal oscillator 2-1
A
A/D Preface-ix
ADC Preface-ix
Analog-to-Digital
A/D Preface-ix
Analog-to-Digital Converter
ADC Preface-ix
C
CAN Preface-ix
bus termination 2-1, 2-2
bypass 2-1, 2-2
interface 2-1
CAN in Automation
CiA Preface-ix
CAN physical layer peripheral 2-2
CiA Preface-ix
Controller Area Network
CAN Preface-ix
D
D/A Preface-ix
Daughter Card Expansion
interface 2-1
Debugging 2-10
Digital-to-Analog
D/A Preface-ix
DSP56800E Reference Manual 2-4
E
Enhanced On-Chip Emulation
EOnCE Preface-ix
EOnce Preface-ix
Evaluation Module
EVM Preface-ix
EVM Preface-ix
External oscillator frequency input 2-1
F
FlexCAN Preface-ix
FlexCAN Interface Module
FlexCAN Preface-ix
FSRAM 2-1, 2-5, 2-6
G
General Purpose Input and Output
GPIO Preface-ix
GPIO Preface-ix, 2-28
H
Host Parallel Interface Connector 2-11
Host Target Interface 2-11
I
IC Preface-ix
Integrated Circuit
IC Preface-ix
J
Joint Test Action Group
JTAG Preface-ix
JTAG Preface-ix, 2-1
JTAG/Enhanced OnCE (EOnCE) 1-1
Jumper Group 1-4
JG1 1-4
JG10 1-4
JG11 1-4
JG12 1-4
JG13 1-4
JG14 1-4
JG15 1-4
JG16 1-4
JG17 1-4
JG18 1-4
JG19 1-4
JG2 1-4
JG3 1-4
JG4 1-4
JG5 1-4
JG6 1-4
JG7 1-4
JG8 1-4
JG9 1-4
Index, Rev. 2
Freescale Semiconductor Index-1
Preliminary
Page 78

L
R
LED Preface-ix
Light Emitting Diode
LED Preface-ix
Low-profile Quad Flat Package
LQFP Preface-ix
LQFP Preface-ix
M
MPIO Preface-ix, 2-31
Multi Purpose Input and Output
MPIO Preface-ix
O
On-board power regulation 2-3
OnCE Preface-ix
On-Chip Emulation
OnCE Preface-ix
P
Parallel JTAG Host Target Interface 2-1
PCB Preface-ix
peripheral port signals 2-18
Phase Locked Loop
PLL Preface-ix
PLL Preface-ix
Printed Circuit Board
PCB Preface-ix
Pulse Width Modulation
PWM Preface-ix
PWM Preface-ix
PWMA-compatible peripheral 2-2
PWMB-compatible peripheral 2-2
R/C Preface-x
RAM Preface-x
Random Access Memory
RAM Preface-x
Read-Only Memory
ROM Preface-x
real-time debugging 2-10
Resistor/Capacitor Network
R/C Preface-x
ROM Preface-x
RS-232 2-1
level converter 2-7
schematic diagram 2-7
S
SCI Preface-x
SCI/MPIO-compatible peripheral 2-2
Serial Communications Interface
SCI Preface-x
Serial Peripheral Interface
SPI Preface-x
SPI Preface-x
SPI/MPIO-compatible peripheral 2-2
SRAM Preface-x
external data 2-1
external program 2-1
Static Random Access Memory
SRAM Preface-x
T
Timer-compatible peripheral 2-2
W
Q
QuadDec Preface-ix
Quadrature Decoder
interface port 2-30
QuadDec Preface-ix
MC56F8367EVM User Manual, Rev. 2
Index-2 Freescale Semiconductor
Wait State
WS Preface-x
WS Preface-x
Preliminary
Page 79

Page 80

How to Reach Us:
Home Page:
www.freescale.com
E-mail:
support@freescale.com
USA/Europe or Locations Not Listed:
Freescale Semiconductor
Technical Information Center, CH370
1300 N. Alma School Road
Chandler, Arizona 85224
+1-800-521-6274 or +1-480-768-2130
support@freescale.com
Europe, Middle East, and Africa:
Freescale Halbleiter Deutschland GmbH
Technical Information Center
Schatzbogen 7
81829 Muenchen, Germany
+44 1296 380 456 (English)
+46 8 52200080 (English)
+49 89 92103 559 (German)
+33 1 69 35 48 48 (French)
support@freescale.com
Japan:
Freescale Semiconductor Japan Ltd.
Headquarters
ARCO Tower 15F
1-8-1, Shimo-Meguro, Meguro-ku,
Tokyo 153-0064, Japan
0120 191014 or +81 3 5437 9125
support.japan@freescale.com
Asia/Pacific:
Freescale Semiconductor Hong Kong Ltd.
Technical Information Center
2 Dai King Street
Tai Po Industrial Estate
Tai Po, N.T., Hong Kong
+800 2666 8080
support.asia@freescale.com
For Literature Requests Only:
Freescale Semiconductor Literature Distribution Center
P.O. Box 5405
Denver, Colorado 80217
1-800-441-2447 or 303-675-2140
Fax: 303-675-2150
LDCForFreescaleSemiconductor@hibbertgroup.com
Information in this document is provided solely to enable system and
software implementers to use Freescale Semiconductor products. There are
no express or implied copyright licenses granted hereunder to design or
fabricate any integrated circuits or integrated circuits based on the
information in this document.
Freescale Semiconductor reserves the right to make changes without further
notice to any products herein. Freescale Semiconductor makes no warranty,
representation or guarantee regarding the suitability of its products for any
particular purpose, nor does Freescale Semiconductor assume any liability
arising out of the application or use of any product or circuit, and specifically
disclaims any and all liability, including without limitation consequential or
incidental damages. “Typical” parameters that may be provided in Freescale
Semiconductor data sheets and/or specifications can and do vary in different
applications and actual performance may vary over time. All operating
parameters, including “Typicals”, must be validated for each customer
application by customer’s technical experts. Freescale Semiconductor does
not convey any license under its patent rights nor the rights of others.
Freescale Semiconductor products are not designed, intended, or authorized
for use as components in systems intended for surgical implant into the body,
or other applications intended to support or sustain life, or for any other
application in which the failure of the Freescale Semiconductor product could
create a situation where personal injury or death may occur. Should Buyer
purchase or use Freescale Semiconductor products for any such unintended
or unauthorized application, Buyer shall indemnify and hold Freescale
Semiconductor and its officers, employees, subsidiaries, affiliates, and
distributors harmless against all claims, costs, damages, and expenses, and
reasonable attorney fees arising out of, directly or indirectly, any claim of
personal injury or death associated with such unintended or unauthorized
use, even if such claim alleges that Freescale Semiconductor was negligent
regarding the design or manufacture of the part.
Freescale™ and the Freescale logo are trademarks of Freescale Semiconductor,
Inc. All other product or service names are the property of their respective owners.
This product incorporates SuperFlash® technology licensed from SST.
© Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. 2005. All rights reserved.
MC56F8367EVMUM
Rev. 2
07/2005
 Loading...
Loading...