Freescale 56F8345, 56F8145 DATA SHEET

56F8345/56F8145
Data Sheet
Preliminary Technical Data
56F8300
16-bit Digital Signal Controllers
MC56F8345
Rev. 14.0
12/2005
freescale.com
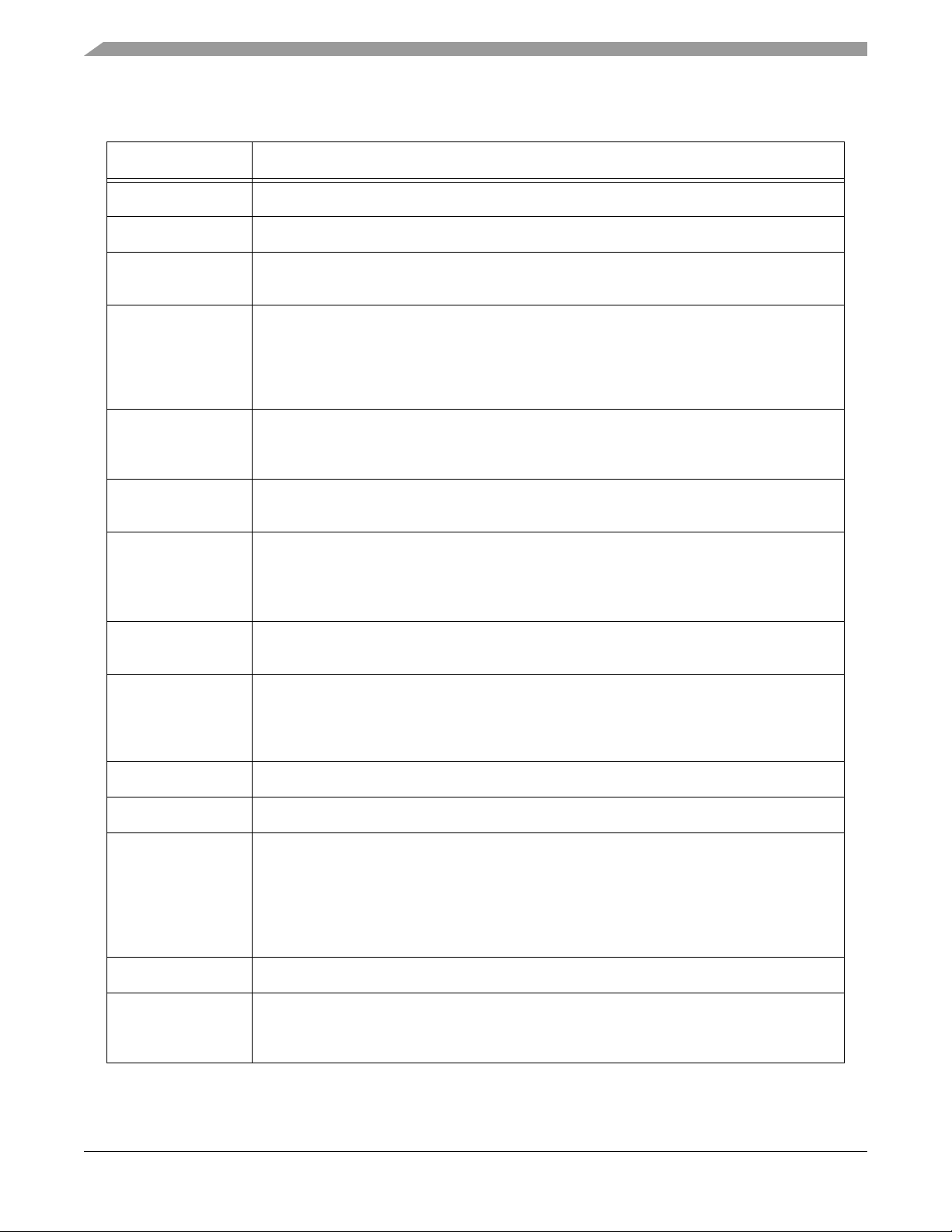
Document Revision History
Version History Description of Change
Rev 1.0 Pre-Release version, Alpha customers only
Rev 2.0 Initial Public Release
Rev 3.0 Corrected typo in Table 10-4, Flash Endurance is 10,000 cycles. Addressed additional
grammar issues.
Rev 4.0 Added “Typical Min” values to Table 10-16. Edited grammar, spelling, consistency of
language throughout family. Updated values in Current Consumption per Power Supply Pin,
Table 10-7, Regulator Parameters, Table 10-9, External Clock Operation Timing
Requirements Table 10-13, SP I Timing, Table 10-17, ADC Parameters, Table 10-23, and IO
Loading Coefficients at 10MHz, Table 10-24.
Rev 5.0 Added Part 4.8. Added the word “access” to FM Error Interrupt in Table 4-5. Removed min
and max numbers. Clarified CSBAR 0 and CSBAR 1 reset values in Table 4-10. Removed
min and max numbers, only documenting Typ. numbers for LVI in Table 10-6.
Rev 6.0 Updated numbers in Table 10-7 and Table 10-8 with more recent data. Corrected typo in
Table 10-3 in Pd characteristics.
Rev 7.0 Replaced any reference to Flash Interface Unit with Flash Memory Module. Added note to
V
pin in Table 2-3. Removed unneccessary notes in Table 10-12. Corrected temperature
CAP
range in Table 10-14. Added ADC calibration information to Table 10-23 and new graphs in
Figure 10-21.
Rev 8.0 Clarified Table 10-22. Corrected Digital Input Current Low (pull-up enabled) numbers in
Table 10-5. Removed text and Table 10-2. Replaced with note to Table 10-1.
Rev 9.0 Added 56F8145 information; edited to indicate differences in 56F8345 and 56F8145 .
Reformatted for Freescale look and feel. Updated Temperature Sensor and ADC tables;
updated balance of electrical tables for consistency throughout family. Clarified I/O power
description in Table 2-3, added note to Table 10-7 and clarified Section 12.3.
Rev 10.0 Corrected beginning address for On-Chip Data RAM, Table 4-6.
Rev 11.0 Corrected addresses in Table 4-6.
Rev 12.0 Corrected Figure 10-21. Added output voltage maximum value and note to clarify in
Table 10-1; also removed overall life expectancy note, since life expectancy is dependent on
customer usage and must be determined by reliability engineering. Clarified value and unit
measure for Maximum allowed P
Flash Data Retention in Table 10-4. Added new RoHS-compliant orderable part numbers in
Table 13-1.
Rev 13.0 Updated Table 10-23 to reflect new value for maximum Uncalibrated Gain Error
Rev 14.0 Deleted RSTO from Pin Group 2 (listed after Table 10-1). Deleted formula for Max Ambient
Operating Temperature (Automotive) and Max Ambient Operating Temperature (Industrial) in
Table 10-4. Added RoHS-compliance and “pb-free” language to back cover.
in Table 10-3. Corrected note about average value for
D
Please see http://www.freescale.com for the most current Data Sheet revision.
56F8345 Technical Data, Rev. 14.0
2 Freescale Semiconductor
Preliminary
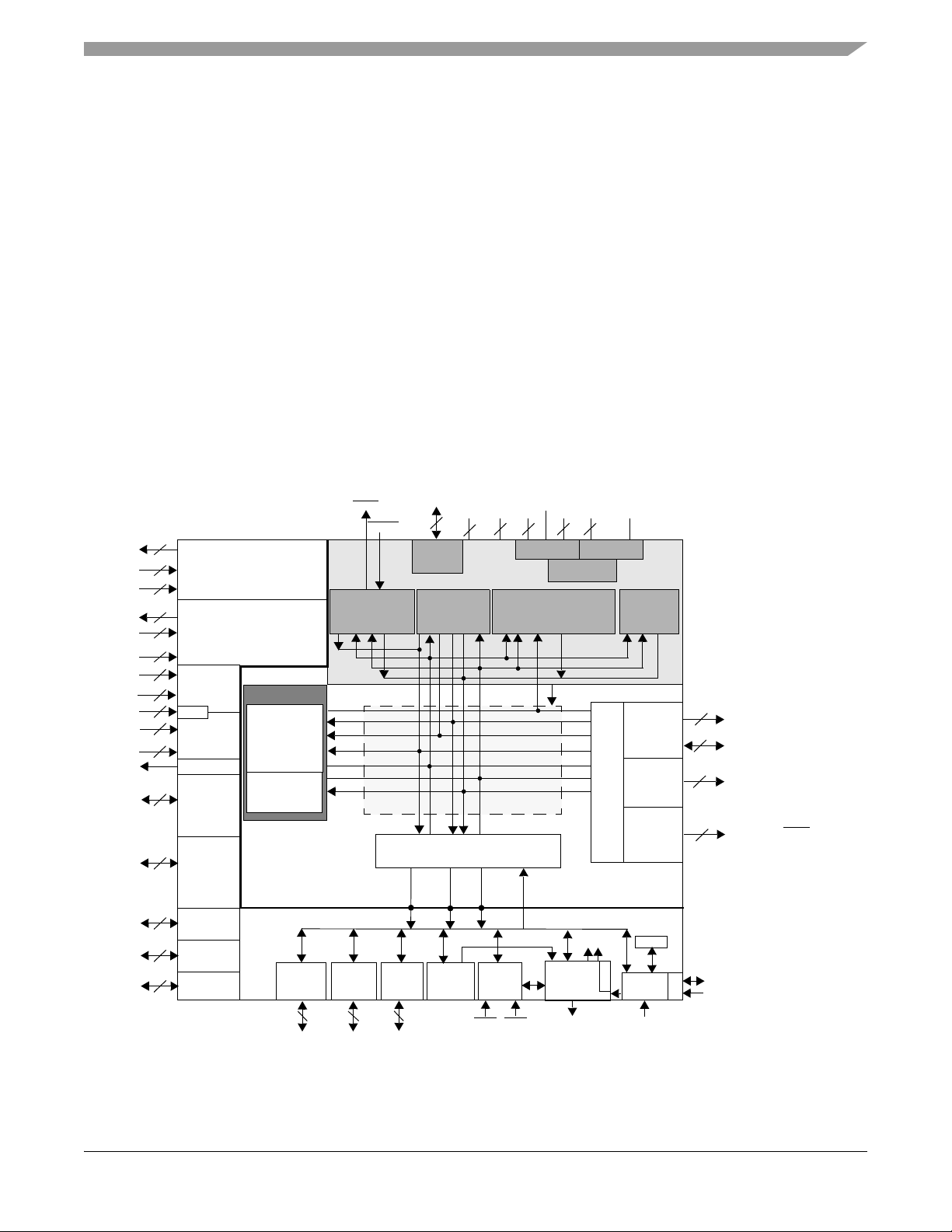
56F8345/56F8145 General Description
Note: Features in italics are NOT available in the 56F8145 device.
• Up to 60 MIPS at 60MHz core frequency
• DSP and MCU functionality in a unified,
C-efficient architecture
• 128KB Program Flash
• 4KB Program RAM
• 8KB Data Flash
• 8KB Data RAM
• 8KB Boot Flash
• Up to two 6-channel PWM modules
• Four 4-channel, 12-bit ADCs
• Temperature Sensor
RSTO
6
PWM Outputs
Current Sense Inputs
3
or GPIOC
4
Fault Inputs
6
PWM Outputs
3
Current Sense Inputs
or GPIOD
4
Fault Inputs
4
AD0
4
AD1
5
VREF
4
AD0
4
AD1
TEMP_SENSE
Decoder 0 or
4
4
2
4
2
ADCA
ADCB
Quadrature
Quad
Timer A or
GPIOC
Quadrature
Decoder 1 or
Quad
Timer B or
SP1I or
GPIOC
Quad Timer
C or GPIOE
Quad Timer
D or GPIOE
FlexCAN
PWMA
PWMB
Memory
Program Memory
64K x 16 Flash
2K x 16 RAM
4K x 16 Boot
Flash
Data Memory
4K x 16 Flash
4K x 16 RAM
Decoding
Peripherals
SPI0 or
GPIOE
Program Controller
and Hardware
XDB2
XAB1
XAB2
PAB
PDB
CDBR
CDBW
Peripheral
Device Selects
SCI1 or
GPIOD
4
Looping Unit
2
PAB
PDB
CDBR
CDBW
5
JTAG/
EOnCE
Port
Address
Generation Unit
RESET
IPBus Bridge (IPBB)
RW
Control
2
COP/
Watchdog
SCI0 or
GPIOE
• Up to two Quadrature Decoders
• FlexCAN module
• Optional On-Chip Regulator
• Two Serial Communication Interfaces (SCIs)
• Up to two Serial Peripheral Interface (SPIs)
• Up to four general-purpose Quad Timers
• Computer Operating Properly (COP)/Watchdog
• JTAG/Enhanced On-Chip Emulation (OnCE™) for
unobtrusive, real-time debugging
• Up to 49 GPIO lines
• 128-pin LQFP Package
V
PP
2
56800E Core
IPAB IPWDB IPRDB
IRQA
OCR_DIS
V
CAPVDDVSSVDDAVSSA
47 52
Digital Reg
16-Bit
Data ALU
16 x 16 + 36 -->36-Bit MAC
Three 16-bit Input Registers
Four 36-bit Accumulators
System Bus
Control
Interrupt
Controller
IRQB
Low Voltage
Supervisor
R/W Control
System
Integration
Module
CLKO
Analog Reg
External Bus
Clock
resets
P
O
R
Bit
Manipulation
Unit
* External
Address Bus
Switch
* External
Data
Bus Switch
Interface Unit
* Bus
Control
PLL
Clock
Generator
CLKMODE
6
5
4
6
* EMI not functional in
this package; use as
GPIO pins
O
XTAL
S
EXTAL
C
A8-13 or GPIOA0-5
GPIOB0-4 or A16-20
D7-10 or GPIOF0-3
GPIOD0-5 or CS2-7
56F8345/56F8145 Block Diagram - 128 LQFP
56F8345 Technical Data, Rev. 14.0
Freescale Semiconductor 3
Preliminary

Table of Contents
Part 1: Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .5
1.1. 56F8345/56F8145 Fea tu r es . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .5
1.2. Device Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7
1.3. Award-Winning Development Environment . . .9
1.4. Architecture Block Diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . .10
1.5. Product Documentation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .14
1.6. Data Sheet Conventions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .14
Part 2: Signal/Connection Descriptions . . .15
2.1. Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .15
2.2. Signal Pins . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1 8
Part 3: On-Chip Clock Synthesis (OCCS) . .33
3.1. Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .33
3.2. External Clock Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .33
3.3. Registers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3 5
Part 4: Memory Map . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .35
4.1. Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .35
4.2. Program Map . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .36
4.3. Interrupt Vector Table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .38
4.4. Data Map . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .41
4.5. Flash Memory Map . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .41
4.6. EOnCE Memory Map . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .43
4.7. Peripheral Memory Mapped Registers . . . . . .44
4.8. Factory Programmed Memory . . . . . . . . . . . .70
Part 5: Interrupt Controller (ITCN) . . . . . . . .70
5.1. Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .70
5.2. Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .70
5.3. Functional Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .70
5.4. Block Diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .72
5.5. Operating Modes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .72
5.6. Register Descriptions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .73
5.7. Resets . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9 9
Part 6: System Integration Module (SIM) .100
6.1. Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .100
6.2. Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .100
6.3. Operating Modes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .101
6.4. Operating Mode Register . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .101
6.5. Register Descriptions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .102
6.6. Clock Generation Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . .115
6.7. Power-Down Modes Overview . . . . . . . . . . .116
6.8. Stop and Wait Mode Disable Func tion . . . . .117
6.9. Resets . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .117
Part 8: General Purpose Input/Output
(GPIO) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 121
8.1. Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .121
8.2. Memory Maps . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 121
8.3. Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 121
Part 9: Joint Test Action Group (JTAG) . 127
9.1. JTAG Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .127
Part 10: Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 128
10.1. General Characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .128
10.2. DC Electrical Characteristics . . . . . . . . . . .132
10.3. AC Electrical Characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . 136
10.4. Flash Memory Characteristics . . . . . . . . . .136
10.5. External Clock Operation Timing . . . . . . . . 137
10.6. Phase Locked Loop Timing . . . . . . . . . . . .137
10.7. Crystal Oscillator Timing . . . . . . . . . . . . . .138
10.8. Reset, Stop, Wait, Mode Select, and
Interrupt Timing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 138
10.9. Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) Timing . . . 140
10.10. Quad Timer Timing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .143
10.11. Quadrature Decoder Timing . . . . . . . . . . . 144
10.12. Serial Communication Interface (SCI)
Timing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 145
10.13. Controller Area Network (CAN) Timing . . 145
10.14. JTAG Timing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 146
10.15. Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC)
Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .147
10.16. Equivalent Circuit for ADC Inputs . . . . . . .150
10.17. Power Consumption . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 150
Part 11: Packaging . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 152
11.1. 56F8345 Package and Pin-Out
Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .152
11.2. 56F8145 Package and Pin-Out
Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .155
Part 12: Design Considerations . . . . . . . . 159
12.1. Thermal Design Considerations . . . . . . . . .159
12.2. Electrical Design Considerations . . . . . . . .160
12.3. Power Distribution and I/O Ring
Implementation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .161
Part 13: Ordering Information . . . . . . . . . 162
Part 7: Security Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . .118
7.1. Operat ion with Security Enabled . . . . . . . . .118
7.2. Flash Access Blocking Mechanisms . . . . . .118
56F8345 Technical Data, Rev. 14.0
4 Freescale Semiconductor
Preliminary
Part 1 Overview
1.1 56F8345/56F8145 Features
1.1.1 Core
• Efficient 16-bit 56800E family controller engine with dual Harvard architecture
• Up to 60 Million Instructions Per Second (MIPS) at 60MHz core frequency
• Single-cycle 16 × 16-bit parallel Multiplier-Accumulator (MAC)
• Four 36-bit accumulators, including extension bits
• Arithmetic and logic multi-bit shifter
• Parallel instruction set with unique DSP addressing modes
• Hardware DO and REP loops
• Three internal address buses
• Four internal data buses
• Instruction set supports both DSP and controller functions
• Controller-style addressing modes and instructions for compact code
• Efficient C compiler and local variable support
• Software subroutine and interrupt stack with depth limited only by memory
• JTAG/EOnCE debug programming interface
56F8345/56F8145 Features
1.1.2 Differences Between Devices
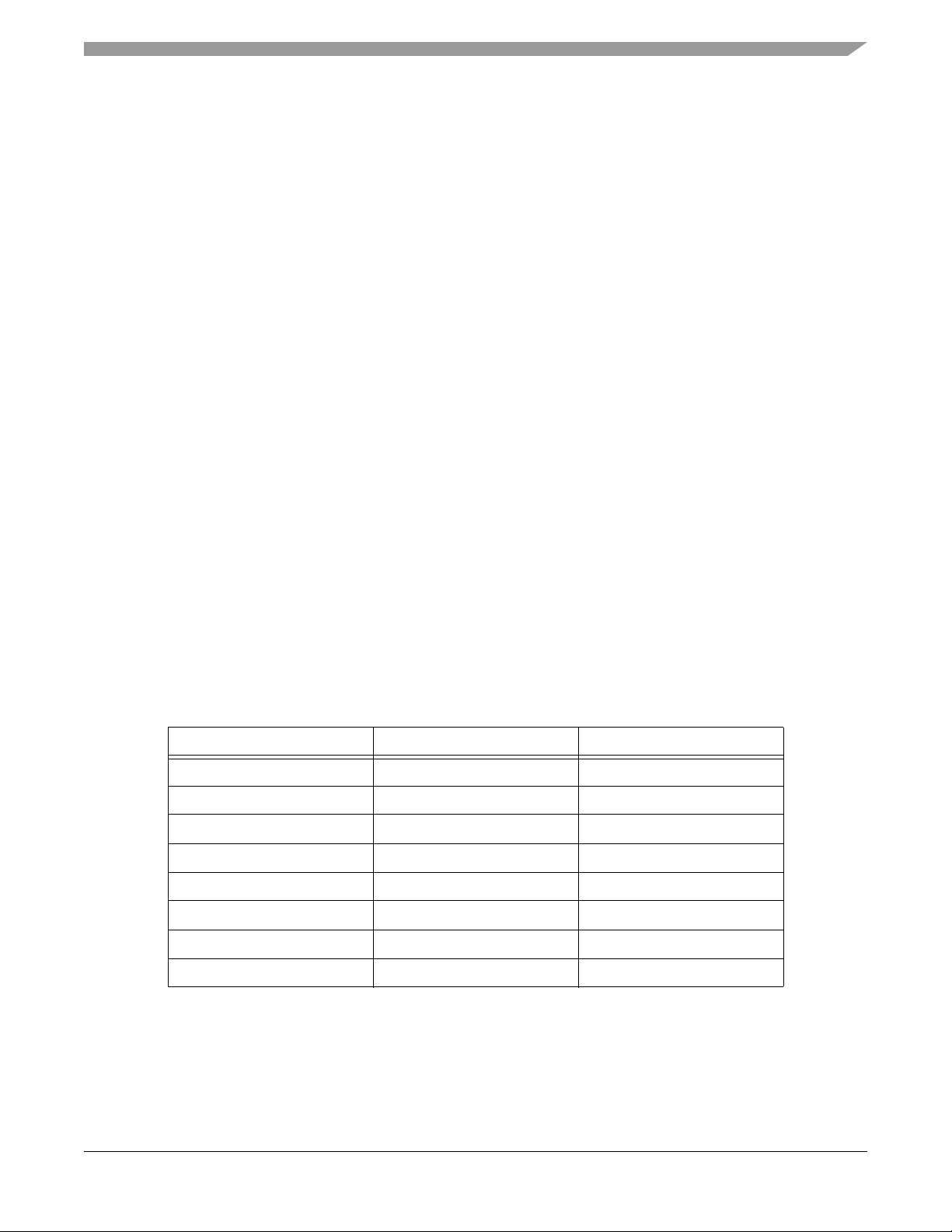
Table 1-1 outlines the key differences between the 56F8345 and 56F8145 devices.
Table 1-1 Device Differences
Feature 56F8345 56F8145
Guaranteed Speed 60MHz/60 MIPS 40MHz/40MIPS
Program RAM 4KB Not Available
Data Flash 8KB Not Available
PWM 2 x 6 1 x 6
CAN 1 Not Available
Quad Timer 4 2
Quadrature Decoder 2 x 4 1 x 4
Temperature Sensor 1 Not Available
56F8345 Technical Data, Rev. 14.0
Freescale Semiconductor 5
Preliminary

1.1.3 Memory
Note: Features in italics are NOT available in the 56F8145 device.
• Harvard architecture permits as many as three simultaneous accesses to program and data memory
• Flash security protection feature
• On-chip memory, including a low-cost, high-volume Flash solution
— 128KB of Program Flash
— 4KB of Program RAM
— 8KB of Data Flash
—8KB of Data RAM
— 8KB of Boot Flash
• EEPROM emulation capability
1.1.4 Peripheral Circuits
Note: Features in italics are NOT available in the 56F8145 device.
• Pulse Width Modulator module:
— In the 56F8345, two P ulse W idth Modulator mod ules, each with six PWM out puts, three Current Sense
inputs, and four Fault inputs; fault-tolerant design with dead time insertion; supports both center-aligned
and edge-aligned modes
— In the 56F8145, one Pulse W idth Modulato r module with six PWM outputs, three Current Sense inputs
and three Fault inputs; fault-tolerant design with dead time insertion; supports both center-aligned and
edge-aligned modes
• Four 12-bit, Analog-to-Digital Converters (ADCs), which support four simultane ous conversions with
quad, 4-pin multiplexed inputs; ADC and PWM modules can be synchronized through Timer C, channels
2 and 3
• Quadrature Decoder:
— In the 56F8345, two four-input Quadrature Decoders or two additional Quad Timers
— In the 56F8145, one four-input Quadrature Decoder, which works in conjunction with Quad Timer A
• Temperature Sensor can be connected, on the board, to any of the ADC inputs to monitor the on-chip
temperature
•Quad Timer:
— In the 56F8345, four dedicated general-purpose Quad Timers totaling six dedicated pins: Timer C with
two pins and Timer D with four pins
— In the 56F8145, two Quad Timers; Timer A and Timer C both work in conjunction with GPIO
• Optional On-Chip Regulator
• FlexCAN (CAN Version 2.0 B-compliant) module with 2-pin port for transmit and receive
• Two Serial Communication Interfaces (SCIs), each with two pins (or four additional GPIO lines)
• Up to two Serial Peripheral Interfaces (SPIs), both with configurable 4-pin port (or eight additional GPIO
lines); SPI 1 can also be used as Quadrature Decoder 1 or Quad Timer B
• Computer Operating Properly (COP)/Watchdog timer
56F8345 Technical Data, Rev. 14.0
6 Freescale Semiconductor
Preliminary

Device Description
• Two dedicated external interrupt pins
• 49 General Purpose I/O (GPIO) pins; 28 pins dedicated to GPIO
• External reset input pin for hardware reset
• External reset output pin for system reset
• Integrated low-voltage interrupt module
• JTAG/Enhanced On-Ch ip Emulation (OnCE) for unobtrusive, processor speed-independent, real-time
debugging
• Software-programmable, Phase Lock Loop-based frequency synthesizer for the core clock
1.1.5 Energy Information
• Fabricated in high-density CMOS with 5V-tolerant, TTL-compatible digital inputs
• On-board 3.3V down to 2.6V voltage regulator for powering internal logic and memories; can be disabled
• On-chip regulators for digital and analog circuitry to lower cost and reduce noise
• Wait and Stop modes available
• ADC smart power management
• Each peripheral can be individually disabled to save power
1.2 Device Description
The 56F8345 and 56F8145 are members of the 56800E core-based family of controllers. Each combines,
on a single chip, the processing power of a Digital Signal Processor (DSP) and the functionality of a
microcontroller with a flexible set of peripherals to create an extremely cost-effective solution. Because
of their low cost, configuration flexibility, and compact program code, the 56F8345 and 56F8145 are
well-suited for many applications. The devices include many peripherals that are especially useful for
motion control, smart appliances, steppers, encoders, tachometers, limit switches, power supply and
control, automotive control (56F8345 only), engine management, noise suppression, remote utility
metering, industrial control for power, lighting, and automation applications.
The 56800E core is based on a Harvard-style architecture consisting of three execution units operating in
parallel, allowing as many as six operations per instruction cycle. The MCU-style programming model and
optimized instruction set allow straightforward generation of efficient, compact DSP and control code.
The instruction set is also highly efficient for C/C++ Compilers to enable rapid development of optimized
control applications.
The 56F8345 and 56F8145 support program execution from internal memories. Two data operands can be
accessed from the on-chip data RAM per instruction cycle. These devices also provide two external
dedicated interrupt lines and up to 49 General Purpose Input/Output (GPIO) lines, depending on peripheral
configuration.
1.2.1 56F8345 Features
The 56F8345 controller includes 128KB of Program Flash and 8KB of Data Flash (each programmable
through the JTAG port) with 4KB of Program RAM and 8KB of Data RAM. A total of 8KB of Boot Flash
is incorporated for easy customer inclusion of field-programmable software routines that can be used to
56F8345 Technical Data, Rev. 14.0
Freescale Semiconductor 7
Preliminary

program the main Program and Data Flash memory areas. Both Program and Data Flash memories can be
independently bulk erased or erased in pages. Program Flash page erase size is 1KB. Boot and Data Flash
page erase size is 512 bytes. The Boot Flash memory can also be either bulk or page erased.
A key application-specific feature of the 56F8345 is the inclusion of two Pulse Width Modulator (PWM)
modules. These modules each incorporate three complementary, individually programmable PWM signal
output pairs (each module is also capable of supporting six independent PWM functions, for a total of 12
PWM outputs) to enhance motor control functionality. Complementary operation permits programmable
dead time insertion, distortion correction via current sensing by software, and separate top and bottom
output polarity control. The up-counter value is programmable to support a continuously variable PWM
frequency. Edge-aligned and center-aligned synchronous pulse width control (0% to 100% modulation) is
supported. The device is capable of controlling most motor types: ACIM (AC Induction Motors); both
BDC and BLDC (Brush and Brushless DC motors); SRM and VRM (Switched and Variable Reluctance
Motors); and stepper motors. The PWMs incorporate fault protection and cycle-by-cycle current limiting
with sufficient output drive capability to directly drive standard optoisolators. A “smoke-inhibit”,
write-once protection feature for key parameters is also included. A patented PWM waveform distortion
correction circuit is also provided. Each PWM is double-buffered and includes interrupt controls to permit
integral reload rates to be programmable from 1 to 16. The PWM modules provide reference outputs to
synchronize the Analog-to-Digital Converters through two channels of Quad Timer C.
The 56F8345 incorporates two Quadrature Decoders capable of capturing all four transitions on the
two-phase inputs, permitting generation of a number proportional to actual position. Speed computation
capabilities accommodate both fast- and slow-moving shafts. An integrated watchdog timer in the
Quadrature Decoder can be programmed with a time-out value to alert when no shaft motion is detected.
Each input is filtered to ensure only true transitions are recorded.
This controller also provides a full set of standard programmable peripherals that include two Serial
Communications Interfaces (SCIs); two Serial Peripheral Interfaces (SPIs); and four Quad Timers. Any of
these interfaces can be used as General Purpose Input/Outputs (GPIOs) if that function is not required. A
Flex Controller Area Network (FlexCAN) interface (CAN Version 2.0 B-compliant) and an internal
interrupt controller are also a part of the 56F8345.
1.2.2 56F8145 Features
The 56F8145 controller includes 128KB of Program Flash, programmable through the JTAG port, and
8KB of Data RAM. A total of 8KB of Boot Flash is incorporated for easy customer inclusion of
field-programmable software routines that can be used to program the main Program Flash memory area.
The Program Flash memory can be independently bulk erased or erased in pages; Program Flash page
erase size is 1KB. The Boot Flash page erase size is 512 bytes; Boot Flash memory can also be either bulk
or page erased.
A key application-specific feature of the 56F8145 is the inclusion of one Pulse Width Modulator (PWM)
module. This module incorporates three complementary, individually programmable PWM signal output
pairs and can also support six independent PWM functions to enhance motor control functionality.
Complementary operation permits programmable dead time insertion, distortion correction via current
sensing by software, and separate top and bottom output polarity control. The up-counter value is
programmable to support a continuously variable PWM frequency. Edge-aligned and center-aligned
56F8345 Technical Data, Rev. 14.0
8 Freescale Semiconductor
Preliminary

Award-Winning Development Environment
synchronous pulse width control (0% to 100% modulation) is supported. The device is capable of
controlling most motor types: ACIM (AC Induction Motors); both BDC and BLDC (Brush and Brushless
DC motors); SRM and VRM (Switched and Variable Reluctance Motors); and stepper motors. The PWM
incorporates fault protection and cycle-by-cycle current limiting with sufficient output drive capability to
directly drive standard optoisolators. A “smoke-inhibit”, write-once protection feature for key parameters
is also included. A patented PWM waveform distortion correction circuit is also provided. The PWM is
double-buffered and includes interrupt controls to permit integral reload rates to be programmable from 1
to 16. The PWM module provides reference outputs to synchronize the Analog-to-Digital Converters
through two channels of Quad Timer C.
The 56F8145 incorporates a Quadrature Decoder capable of capturing all four transitions on the two-phase
inputs, permitting generation of a number proportional to actual position. Speed computation capabilities
accommodate both fast- and slow-moving shafts. An integrated watchdog timer in the Quadrature Decoder
can be programmed with a time-out value to alert when no shaft motion is detected. Each input is filtered
to ensure only true transitions are recorded.
This controller also provides a full set of standard programmable peripherals that include two Serial
Communications Interfaces (SCIs); two Serial Peripheral Interfaces (SPIs); and two Quad Timers. Any of
these interfaces can be used as General Purpose Input/Outputs (GPIOs) if that function is not required. An
internal interrupt controller is also a part of the 56F8145.
1.3 Award-Winning Development Environment
Processor ExpertTM (PE) provides a Rapid Application Design (RAD) tool that combines easy-to-use
component-based software application creation with an expert knowledge system.
The CodeWarrior Integrated Development Environment is a sophisticated tool for code navigation,
compiling, and debugging. A complete set of evaluation modules (EVMs) and development system cards
will support concurrent engineering. Together, PE, CodeWarrior and EVMs create a complete, scalable
tools solution for easy, fast, and efficient development.
56F8345 Technical Data, Rev. 14.0
Freescale Semiconductor 9
Preliminary

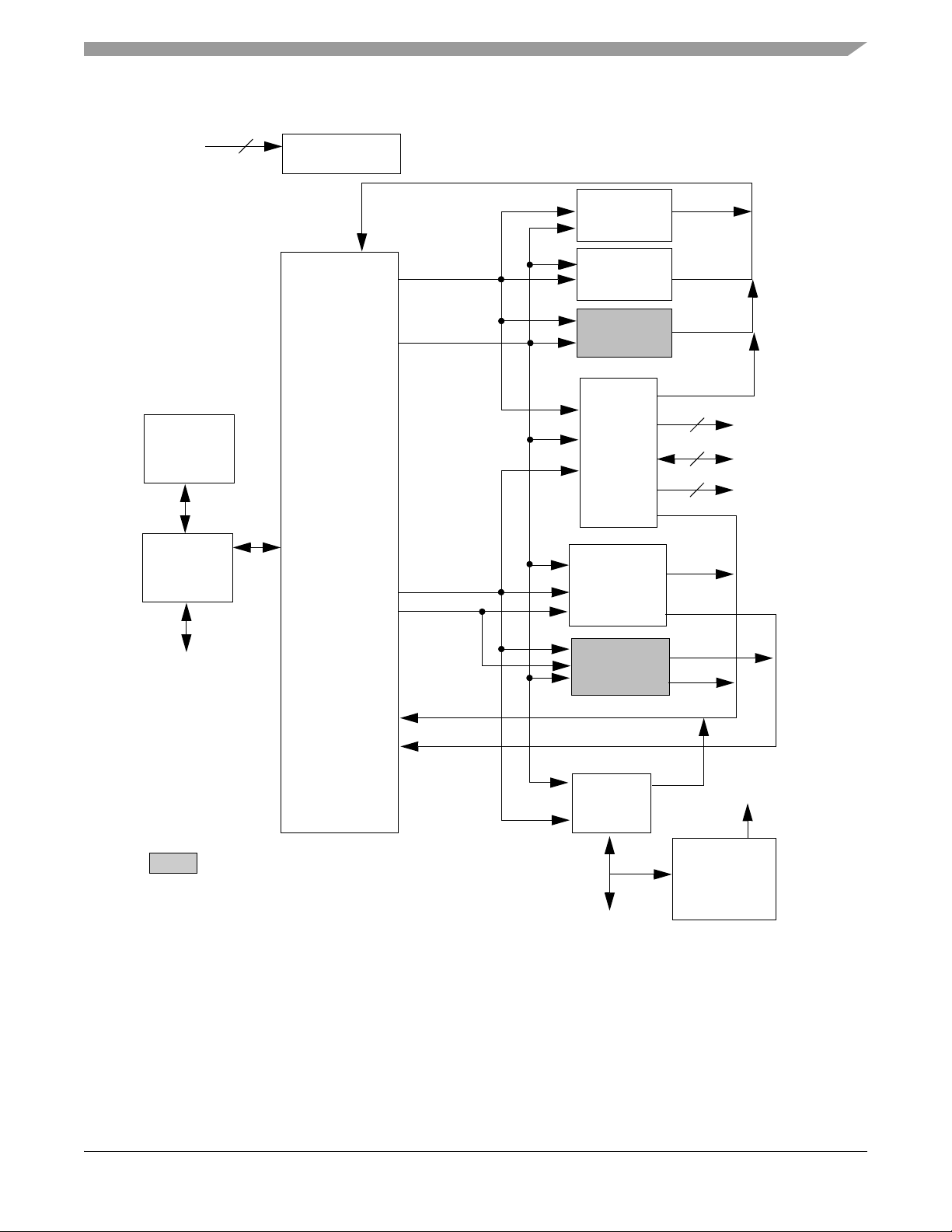
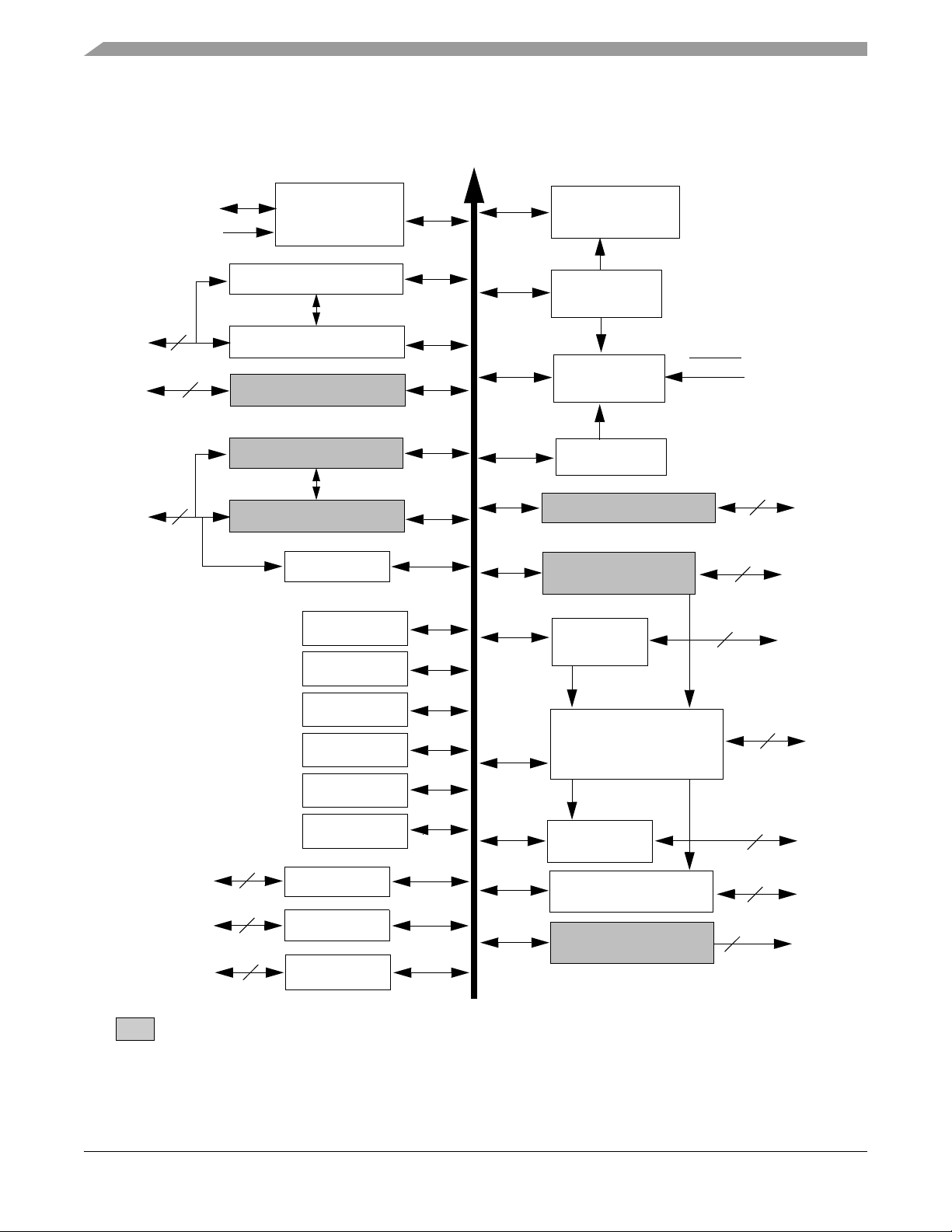
1.4 Architecture Block Diagram
Note: Features in italics are NOT available in the 56F8145 device and are shaded in the following figures.
The 56F8345/56F8145 architecture is shown in Figure 1-1 and Figure 1-2. Figure 1-1 illustrates how the
56800E system buses communicate with internal memories and the IPBus Bridge. Table 1-2 lists the
internal buses in the 56800E architecture and provides a brief description of their function. Figure 1-2
shows the peripherals and control blocks connected to the IPBus Bridge. The figures do not show the
on-board regulator and power and ground signals. They also do not show the multiplexing between
peripherals or the dedicated GPIOs. Please see Part 2, Signal/Connection Descriptions, to see which
signals are multiplexed with those of other peripherals.
Also shown in Figure 1-2 are connections between the PWM, Timer C and ADC blocks. These
connections allow the PWM and/or Timer C to control the timing of the start of ADC conversions. The
Timer C channel indicated can generate periodic start (SYNC) signals to the ADC to start its conversions.
In another operating mode, the PWM load interrupt (SYNC output) signal is routed internally to the Timer
C input channel as indicated. The timer can then be used to introduce a controllable delay before
generating its output signal. The timer output then triggers the ADC. To fully understand this interaction,
please see the 56F8300 Peripheral User’s Manual for clarification on the operation of all three of these
peripherals.
56F8345 Technical Data, Rev. 14.0
10 Freescale Semiconductor
Preliminary
Architecture Block Diagram
CHIP
TAP
Controller
TAP
Linking
Module
5
JTAG / EOnCE
Boot
Flash
pdb_m[15:0]
pab[20:0]
Program
Flash
Program
cdbw[31:0]
RAM
56800E
xab1[23:0]
xab2[23:0]
EMI*
Data RAM
11
Address
4
6
Data
Control
External
JTAG Port
cdbr_m[31:0]
xdb2_m[15:0
Data
Flash
To Flash
Control
IPBus
Logic
Bridge
NOT available on the 56F8145 device.
Flash
Memory
* EMI not functional in this package; since only part of
the address/data bus is bonded out, use as GPIO pins
IPBus
Module
Figure 1-1 System Bus Interfaces
Note: Flash memories are encapsulated within the Flash Memory (FM) Module. Flash control is
accomplished by the I/O to the FM over the peripheral bus, while reads and writes are completed
between the core and the Flash memories.
Note: The primary data RAM port is 32 bits wide. Other data ports are 16 bits.
56F8345 Technical Data, Rev. 14.0
Freescale Semiconductor 11
Preliminary
To/From IPBus Bridge
CLKGEN
(OSC / PLL)
Interrupt
Controller
Low-Voltage Interrupt
Timer A
POR & LVI
4
4
Quadrature Decoder 0
Timer D
System POR
SIM
RESET
COP Reset
Timer B
4
Quadrature Decoder 1
SPI1
COP
FlexCAN
PWMA
2
13
SYNC Output
GPIOA
PWMB
13
GPIOB
SYNC Output
GPIOC
GPIOD
GPIOE
GPIOF
4
2
2
SPI0
SCI0
SCI1
NOT available on the 56F8145 device.
Figure 1-2 Peripheral Subsystem
56F8345 Technical Data, Rev. 14.0
IPBus
ch3i ch2i
Timer C
ch3o ch2o
ADCB
ADCA
, V
1
REFN
TEMP_SENSE
Note: ADC A and ADC B use the same
voltage reference circuit with V
V
REFP, VREFMID
pins.
2
8
8
, and V
REFH
REFLO
,
12 Freescale Semiconductor
Preliminary
Architecture Block Diagram
Table 1-2 Bus Signal Names
Name Function
Program Memory Interface
pdb_m[15:0] Program data bus for instruction word fetches or read operations.
cdbw[15:0] Primary core data bus used for program memory writes. (Only these 16 bits of the cdbw[31:0] bus
are used for writes to program memory.)
pab[20:0] Program memory address bus. Data is returned on pdb_m bus.
Primary Data Memory Interface Bus
cdbr_m[31:0] Primary core data bus for memory reads. Addressed via xab1 bus.
cdbw[31:0] Primary core data bus for memory writes. Addressed via xab1 bus.
xab1[23:0]
xdb2_m[15:0] Secondary data bus used for secondary data address bus xab2 in the dual memory reads.
xab2[23:0] Secondary data address bus used for the second of two simultaneous accesses. Capable of
IPBus [15:0] Peripheral bus accesses all on-chip peripherals registers. This bus operates at the same clock rate
1. Byte accesses can only occur in the bottom half of the memory address space. The MSB of the address will be forced
to 0.
Primary data address bus. Capable of addressing bytes1, words, and long data types. Data is written
on cdbw and returned on cdbr_m. Also used to access memory-mapped I/O.
Secondary Data Memory Interface
addressing only words. Data is returned on xdb2_m.
Peripheral Interface Bus
as the Primary Data Memory and therefore generates no delays when accessing the processor.
Write data is obtained from cdbw. Read data is provided to cdbr_m.
56F8345 Technical Data, Rev. 14.0
Freescale Semiconductor 13
Preliminary
1.5 Product Documentation
The documents listed in Table 1-3 are required for a complete description and proper design with the
56F8345 and 56F8145 devices. Documentation is available from local
Semiconductor sales offices,
Freescale
Literature Distribution Centers, or online at
http://www.freescale.com.
Table 1-3 Chip Documentation
Topic Description Order Number
Freescale
distributors,
Freescale
DSP56800E
Reference Manual
56F8300 Peripheral User
Manual
56F8300 SCI/CAN
Bootloader User Manual
56F8345/56F8145
Technical Data Sheet
Errata Details any chip issues that might be present MC56F8345E
Detailed description of the 56800E family architecture,
16-bit controller core processor, and the instruction set
Detailed description of peripherals of the 56F8300
family of devices
Detailed description of the SCI/CAN Bootloaders
56F8300 family of devices
Electrical and timing specifications, pin descriptions,
device specific peripheral information and package
descriptions (this document)
DSP56800EERM
MC56F8300UM
MC56F83xxBLUM
MC56F8345
MC56F8145E
1.6 Data Sheet Conventions
This data sheet uses the following conventions:
OVERBAR
“asserted” A high true (active high) signal is high or a low true (active low) signal is low.
This is used to indicate a signal that is active when pulled low. For example, the RESET pin is
active when low.
“deasserted” A high true (active high) signal is low or a low true (active low) signal is high.
Examples:
1. Values for VIL, VOL, VIH, and VOH are defined by individual product specifications.
14 Freescale Semiconductor
Signal/Symbol Logic State Signal State
PIN True Asserted VIL/V
PIN False Deasserted VIH/V
PIN True Asserted VIH/V
PIN False Deasserted VIL/V
56F8345 Technical Data, Rev. 14.0
Voltage
1
OL
OH
OH
OL
Preliminary

Introduction
Part 2 Signal/Connection Descriptions
2.1 Introduction
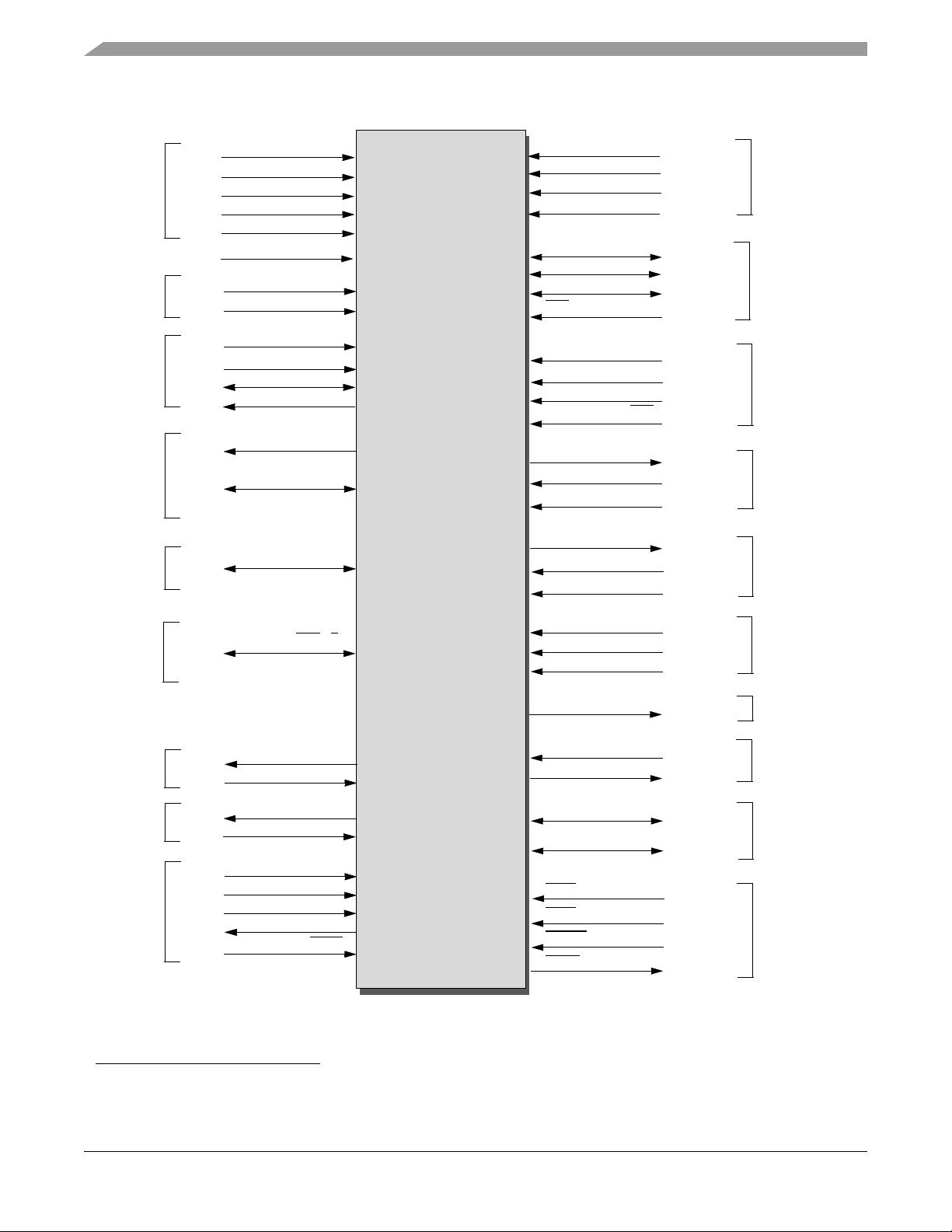
The input and output signals of the 56F8345 and 56F8145 are organized into functional groups, as detailed
in Table 2-1 and as illustrated in Figure 2-1. In Table 2-2, each table row describes the signal or signals
present on a pin.
Table 2-1 Functional Group Pin Allocations
Functional Group
Power (V
Power Option Control
Ground (V
Supply Capacitors1 & V
PLL and Clock
Bus Control
Interrupt and Program Control
Pulse Width Modulator (PWM) Ports
Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) Port 0
Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) Port 1
Quadrature Decoder Port 0
Quadrature Decoder Port 1
Serial Communications Interface (SCI) Ports
CAN Ports
DD
or V
SS
or V
DDA
SSA
)
)
PP
2
3
Number of Pins in Package
56F8345 56F8145
99
11
66
66
44
66
44
26 13
44
—4
44
4—
44
2—
Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC) Ports
Timer Module Ports
JTAG/Enhanced On-Chip Emulation (EOnCE)
Temperature Sense
4
Dedicated GPIO ( Address Bus = 11; Data Bus = 4
1. If the on-chip regulator is disabled, the V
2. Alternately, can function as Quad Timer pins or GPIO
3. Pins in this section can function as Quad Timer, SPI 1, orGPIO
4. EMI not functional in these packages; use as GPIO pins.
Note: See Table 1-1 for 56F8145 functional differences.
Freescale Semiconductor 15
Preliminary
pins serve as 2.5V V
CAP
56F8345 Technical Data, Rev. 14.0
)
DD_CORE
21 21
64
55
1—
28 28
power inputs
Power
Power
Power
Ground
Ground
Other
Supply
Ports
PLL
and
Clock
*External
Address
Bus
or GPIO
*External
Data Bus
V
DD_IO
V
DDA_ADC
V
DDA_OSC_PLL
V
SS
V
SSA_ADC
OCR_DIS
V
1 - V
CAP
V
PP
CAP
1 & VPP2
CLKMODE
EXTAL
XTAL
CLKO
A8 - A13 (GPIOA0 - 5)
GPIOB0-4 (A16 - 20)
D7 - D10 (GPIOF0 - 3)
PHASEA0 (TA0, GPIOC4)
7
7
1
1
1
5
1
1
56F8345
1
4
4
2
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
6
6
5
4
4
1
PHASEB0(TA1, GPIOC5 )
1
INDEX0 (TA2, GPIOC6)
1
HOME0 (TA3, GPIOC7)
1
SCLK0 (GPIOE4)
1
MOSI0 (GPIOE5)
1
MISO0 (GPIOE6)
1
SS0
1
1
1
1
1
6
3
4
6
3
4
(GPIOE7)
PHASEA1(TB0, SCLK1, GPIOC0)
PHASEB1 (TB1, MOSI1, GPIOC1)
INDEX1 (TB2, MISO1, GPIOC2)
HOME1 (TB3, SS1
PWMA0 - 5
ISA0 - 2 (GPIOC8 - 10)
FAULTA0 - 3
PWMB0 - 5
ISB0 - 2 (GPIOD10 - 12)
FAULTB0-3
, GPIOC3)
Quadrature
Decoder 0
or Quad
Timer A or
GPIO
SPI0 or
GPIO
Quadrature
Decoder 1 or
Quad Timer B
or SPI1 or
GPIO
PWMA
PWMB
ANA0 - 7
*External
Bus
GPIOD0 - 5 (CS2 - 7)
Control
SCI0 or
GPIOE
SCI1 or
GPIO
TXD0 (GPIOE0)
RXD0 (GPIOE1)
TXD1 (GPIOD6)
RXD1 (GPIOD7)
JTAG/
EOnCE
Port
* EMI not functional in this package; use as GPIO pins
TCK
TMS
TDI
TDO
TRST
6
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
8
V
5
8
1
1
1
2
4
1
1
1
1
REF
ANB0 - 7
TEMP_SENSE
CAN_RX
CAN_TX
TC0 - 1 (GPIOE8 - 9)
TD0 - 3 (GPIOE10 - 13)
IRQA
IRQB
RESET
RSTO
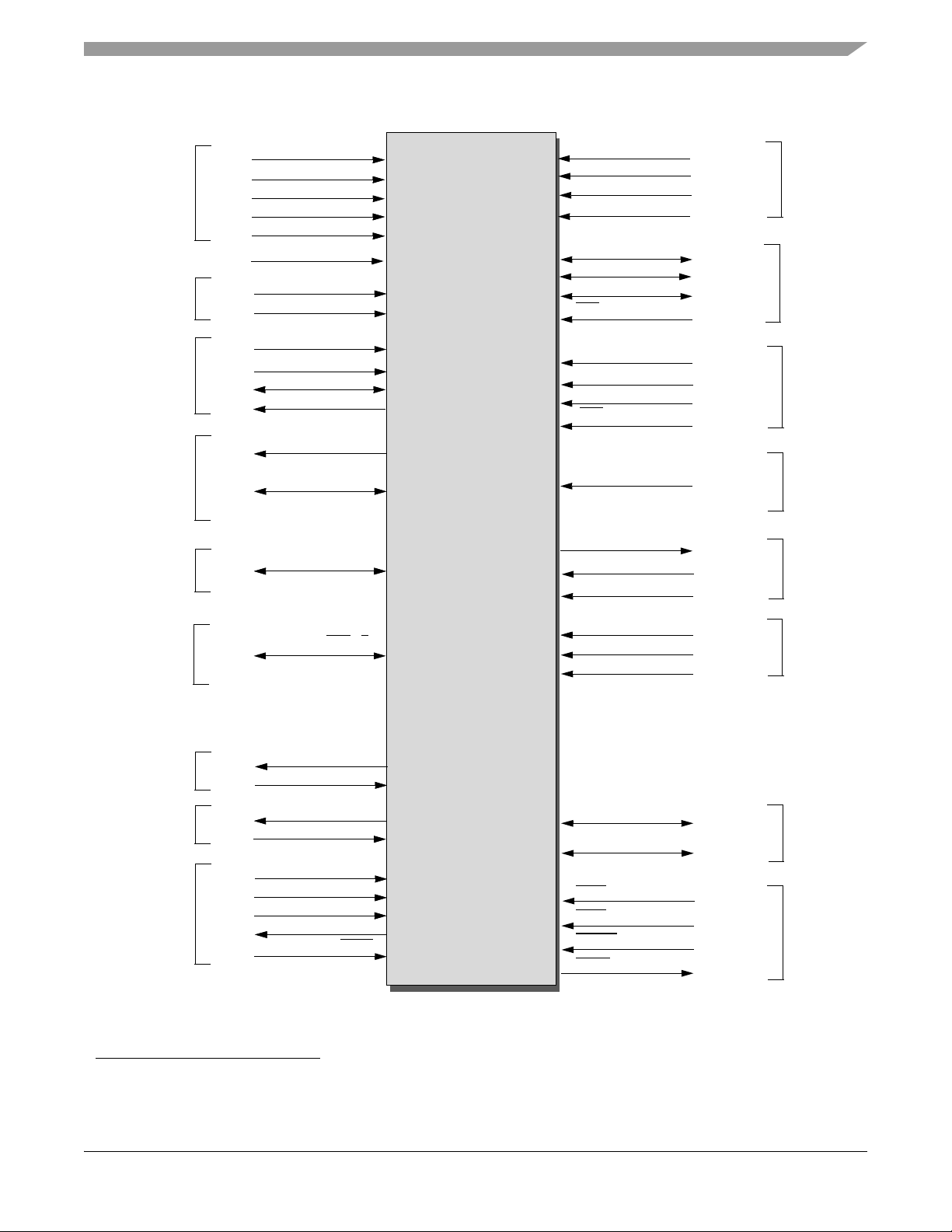
Figure 2-1 56F8345 Signals Identified by Functional Group1 (128-Pin LQFP)
1. Alternate pin functionality is shown in parenthesis; pin direction/type shown is the default functionality.
ADCA
ADCB
Temperature
Sensor
CAN
Quad
Timer C
and D or
GPIO
Interrupt/
Program
Control
56F8345 Technical Data, Rev. 14.0
16 Freescale Semiconductor
Preliminary
Introduction
Power
Power
Power
Ground
Ground
Other
Supply
Ports
PLL
and
Clock
*External
Address
Bus
or GPIO
*External
Data Bus
V
DD_IO
V
DDA_ADC
V
DDA_OSC_PLL
V
SS
V
SSA_ADC
OCR_DIS
V
1 - V
CAP
V
PP
CAP
1 & VPP2
CLKMODE
EXTAL
XTAL
CLKO
A8 - A13 (GPIOA0 - 5)
GPIOB0-4 (A16 - 20)
D7 - D10 (GPIOF0 - 3)
PHASEA0 (TA0, GPIOC4)
7
7
1
1
1
5
1
1
56F8145
1
4
4
2
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
6
6
5
4
4
1
PHASEB0(TA1, GPIOC5 )
1
INDEX0 (TA2, GPIOC6)
1
HOME0 (TA3, GPIOC7)
1
SCLK0 (GPIOE4)
1
MOSI0 (GPIOE5)
1
MISO0 (GPIOE6)
1
SS0
1
1
1
1
1
3
6
3
4
(GPIOE7)
(SCLK1, GPIOC0)
(MOSI1, GPIOC1)
(MISO1, GPIOC2)
(S
S1,GPIOC3)
(GPIOC8 - 10)
PWMB0 - 5
ISB0 - 2 (GPIOD10 - 12)
FAULTB0-3
Quadrature
Decoder 0
or Quad
Timer A or
GPIO
SPI0 or
GPIO
SPI1 or
GPIO
GPIO
PWMB
ANA0 - 7
*External
Bus
Control
SCI0 or
GPIOE
SCI1 or
GPIO
JTAG/
EOnCE
Port
GPIOD0 - 5 (CS2 - 7)
TXD0 (GPIOE0)
RXD0 (GPIOE1)
TXD1 (GPIOD6)
RXD1 (GPIOD7)
TCK
TMS
TDI
TDO
TRST
6
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
8
V
5
8
2
4
1
1
1
1
REF
ANB0 - 7
TC0 - 1 (GPIOE8 - 9)
(GPIOE10 - 13)
IRQA
IRQB
RESET
RSTO
* EMI not functional in this package; use as GPIO pins
Figure 2-2 56F8145 Signals Identified by Functional Group1 (128-Pin LQFP)
1. Alternate pin functionality is shown in parenthesis; pin direction/type shown is the default functionality.
ADCA
ADCB
QUAD
Timer C or
GPIO
Interrupt/
Program
Control
56F8345 Technical Data, Rev. 14.0
Freescale Semiconductor 17
Preliminary
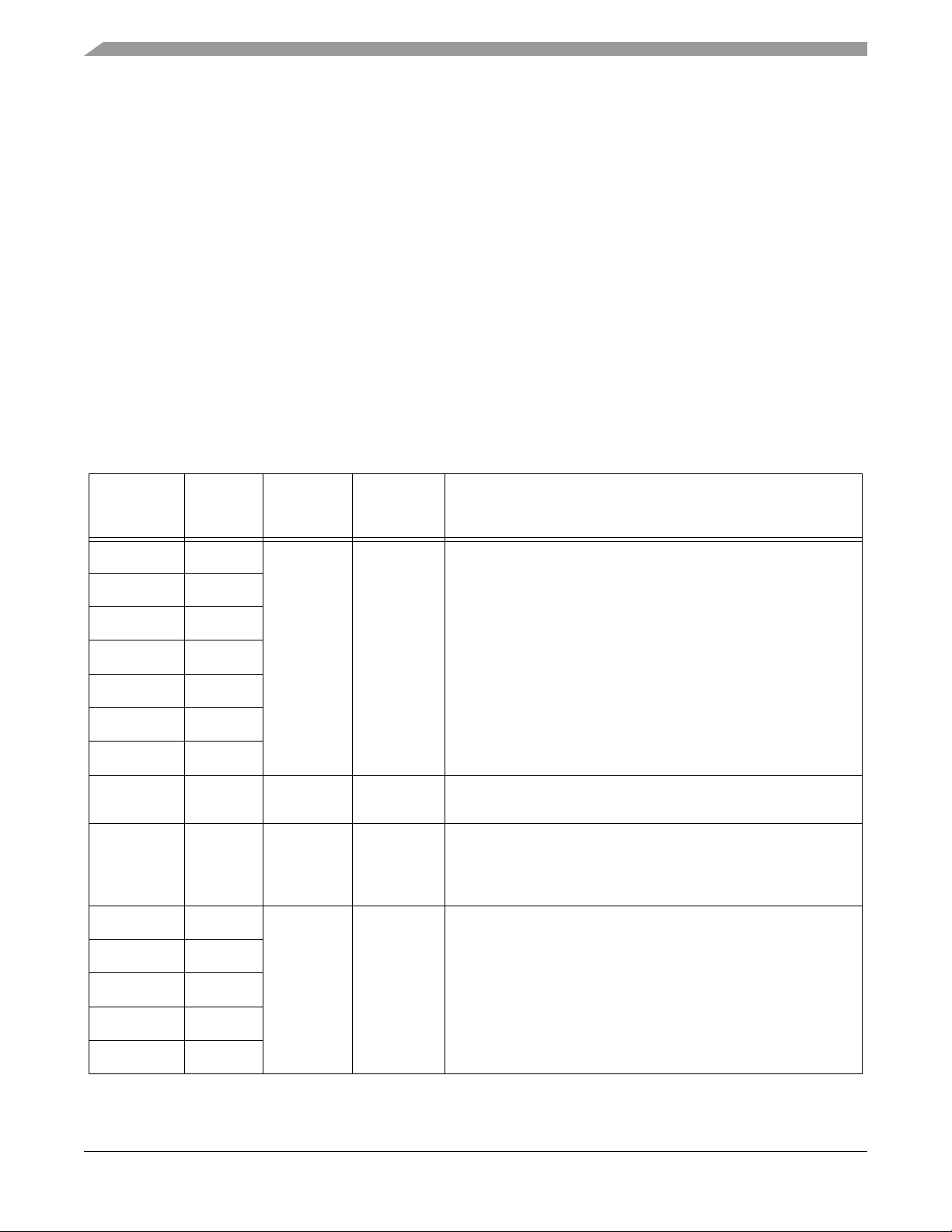
2.2 Signal Pins
After reset, each pin is configured for its primary function (listed first). Any alternate functionality must
be programmed.
EMI is not functional in this package; since only part of the address/data bus is bonded out, use as GPIO
pins.
Note: Signals in italics are NOT available in the 56F8145 device.
If the “State During Reset” lists more than one state for a pin, the first state is the actual reset state. Other
states show the reset condition of the alternate function, which you get if the alternate pin function is
selected without changing the configuration of the alternate peripheral. For example, the A8/GPIOA0 pin
shows that it is tri-stated during reset. If the GPIOA_PER is changed to select the GPIO function of the
pin, it will become an input if no other registers are changed.
Table 2-2 Signal and Package Information for the 128-Pin LQFP
Signal
Name
V
DD_IO
V
DD_IO
V
DD_IO
V
DD_IO
V
DD_IO
V
DD_IO
V
DD_IO
V
DDA_ADC
V
DDA_OSC_
PLL
V
SS
V
SS
State
Pin No. Type
4 Supply I/O Power — This pin supplies 3.3V power to the chip I/O
14
25
36
62
76
112
94 Supply ADC Power — This pin supplies 3.3V power to the ADC
72 Supply Oscillator and PLL Power — This pin supplies 3.3V power to
3 Supply Ground — These pins provide ground for chip logic and I/O
21
During
Reset
Signal Description
interface and also the Processor core throught the on-chip
voltage regulator, if it is enabled.
modules. It must be connected to a clean analog power supply.
the OSC and to the internal regulator that in turn supplies the
Phase Locked Loop. It must be connected to a clean analog
power supply.
drivers.
V
SS
V
SS
V
SS
18 Freescale Semiconductor
35
59
65
56F8345 Technical Data, Rev. 14.0
Preliminary
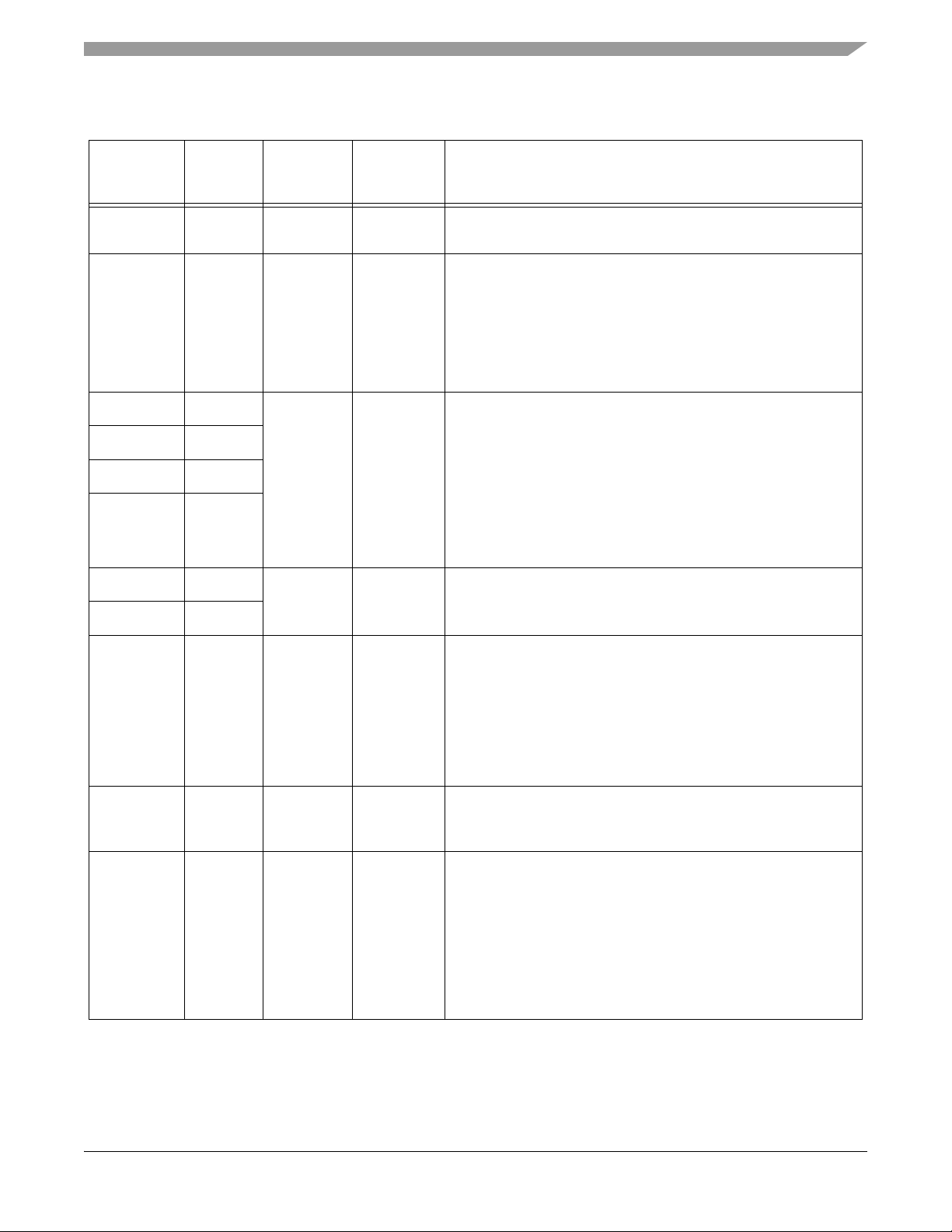
Table 2-2 Signal and Package Information for the 128-Pin LQFP
Signal Pins
Signal
Name
V
SSA_ADC
Pin No. Type
95 Supply ADC Analog Ground — This pin supplies an analog ground to
State
During
Reset
Signal Description
the ADC modules.
OCR_DIS 71 Input Input On-Chip Regulator Disable —
Tie this pin to V
Tie this pin to V
to enable the on-chip regulator
SS
to disable the on-chip regulator
DD
This pin is intended to be a static DC signal from powe r-up
to shut down. Do not try to toggle this pin for power savings
during operation.
1 49 Supply Supply V
V
CAP
1 - 4 — When OCR_DIS is tied to VSS (regulator enabled),
CAP
connect each pin to a 2.2µF or greater bypass capacitor in order
2 122
V
CAP
3 75
V
CAP
4 13
V
CAP
to bypass the core logic voltage regulator, required for proper
chip operation. When OCR_DIS is tied to V
disabled), these pins become V
DD_CORE
(regulator
DD
and should be
connected to a regulated 2.5V power supply.
Note: This bypass is required even if the chip is powered
with an external supply.
V
1 119 Input Input VPP1 - 2 — These pins should be left unconnected as an open
PP
circuit for normal functionality.
2 5
V
PP
CLKMODE 79 Input Input Clock Input Mode Selection — This input determines the
function of the XTAL and EXTAL pins.
1 = External clock input on XTAL is used to directly drive the
input clock of the chip. The EXTAL pin should be grounded.
0 = A crystal or ceramic resonator should be connected between
XTAL and EXTAL.
EXTAL 74 Input Input External Crystal Oscillator Input — This input can be
connected to an 8MHz external crystal. Tie this pin low if XTAL is
driven by an external clock source.
XTAL 73 Input/
Output
Chip-driven Crystal Oscillator Output — This output connects the internal
crystal oscillator output to an external crystal.
If an external clock is used, XTAL must be used as the input and
EXTAL connected to GND.
The input clock can be selected to provide the clock directly to
the core. This input clock can also be selected as the input clock
for the on-chip PLL.
56F8345 Technical Data, Rev. 14.0
Freescale Semiconductor 19
Preliminary
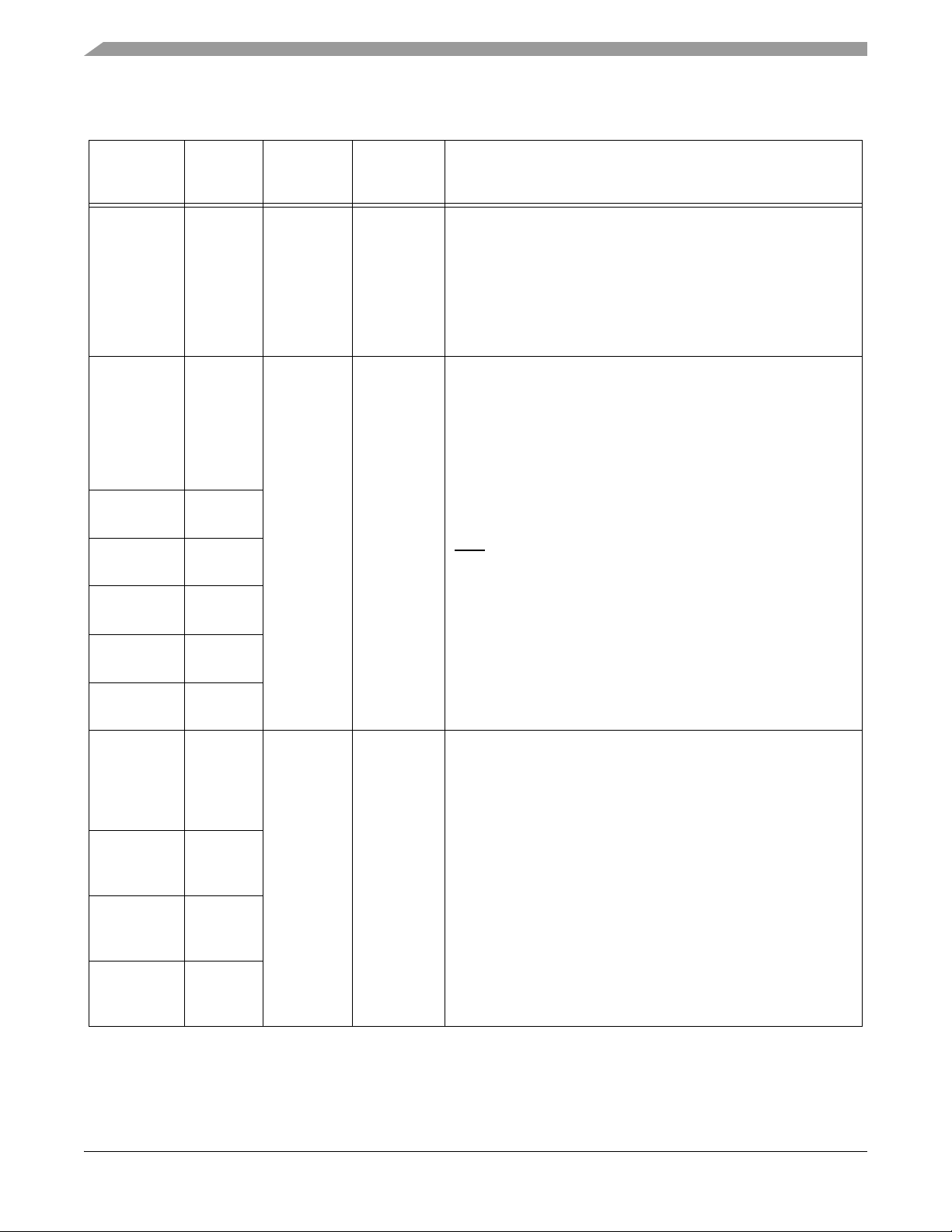
Table 2-2 Signal and Package Information for the 128-Pin LQFP
Signal
Name
CLKO 6 Output Tri-Stated Clock Output — This pin outputs a buffered clock signal. Using
A8
(GPIOA0)
A9
(GPIOA1)
A10
(GPIOA2)
A11
(GPIOA3)
A12
(GPIOA4)
A13
(GPIOA5)
Pin No. Type
15 Output
Schmitt
16
17
18
19
20
Input/
Output
State
During
Reset
Tri-stated
Input
Signal Description
the SIM CLKO Select Register (SIM_CLKOSR), this pin can be
programmed as any of the following: disabled, CLK_MSTR
(system clock), IPBus clock, oscillator output, prescaler clock
and postscaler clock. Other signals are also available for test
purposes.
See Part 6.5.7 for details.
Address Bus — A8 - A13 specify six of the address lines for
external program or data memory accesses. Depending upon
the state of the DRV bit in the EMI bus control register (BCR), A8
- A13 and EMI control signals are tri-stated when the external
bus is inactive.
Port A GPIO — These six GPIO pins can be individually
programmed as input or output pins.
After reset, these pins default to address bus functionality and
be programmed as GPIO.
must
To deactivate the internal pull-up resistor, clear the appropriate
GPIO bit in the GPIOA_PUR register.
Example: GPIOA0, clear bit 0 in the GPIOA_PUR register.
Note: Primary function is not available in this package
configuration; GPIO function must be used instead.
GPIOB0
(A16)
GPIOB1
(A17)
GPIOB2
(A18)
GPIOB3
(A19)
20 Freescale Semiconductor
27 Schmitt
Input/
Output
Output
28
29
30
Input
Tri-stated
56F8345 Technical Data, Rev. 14.0
Port B GPIO — These four GPIO pins can be individually
programmed as an input or output pin.
Address Bus — A16 - A19 specify four of the address lines for
external program or data memory accesses. Depending upon
the state of the DRV bit in the EMI bus control register (BCR),
A16 - A19 and EMI control signals are tri-stated when the
external bus is inactive.
After reset, the default state is GPIO.
To deactivate the internal pull-up resistor, clear bit 0 in the
GPIOB_PUR register.
Example: GPIOB1, clear bit 1 in the GPIOB_PUR register.
Preliminary
Table 2-2 Signal and Package Information for the 128-Pin LQFP
Signal Pins
Signal
Name
GPIOB4
(A20)
(prescaler_
clock)
Pin No. Type
31 Schmitt
Input/
Output
Output
Output
State
During
Reset
Input
Tri-stated
Output
Signal Description
Port B GPIO — This GPIO pin can be individually programmed
as an input or output pin.
Address Bus — A20 specifies one of the address lines for
external program or data memory accesses. Depending upon
the state of the DRV bit in the EMI bus control register (BCR),
A20 and EMI control signals are tri-stated when the external bus
is inactive.
Clock Output — can be used to monitor the prescaler_clock on
GPIOB4.
After reset, the default state is GPIO.
This pin can also be used to view the prescaler_clock. In these
cases, the GPIOB_PER can be used to disable the GPIO. The
CLKOSR register in the SIM can then be used to choose
between address and clock functions; see
Part 6.5.7 for details.
To deactivate the internal pull-up resistor, clear bit 4 in the
GPIOB_PUR register.
D7
(GPIOF0)
D8
(GPIOF1)
D9
(GPIOF2)
D10
(GPIOF3)
22 Input/
Output
Input/
Output
23
24
26
Tri-stated
Input
Data Bus — D7 - D10 specify part of the data for external
program or data memory accesses. Depending upon the state of
the DRV bit in the EMI bus control register (BCR), D7 - D10 are
tri-stated when the external bus is inactive
Port F GPIO — These four GPIO pins can be individually
programmed as input or output pins.
After reset, these pins default to data bus functionality and
should be programmed as GPIO.
To deactivate the internal pull-up resistor, clear the appropriate
GPIO bit in the GPIOF_PUR register.
Example: GPIOF0, clear bit 0 in the GPIOF_PUR register.
Note: Primary function is not available in this package
configuration; GPIO function must be used instead.
56F8345 Technical Data, Rev. 14.0
Freescale Semiconductor 21
Preliminary
Table 2-2 Signal and Package Information for the 128-Pin LQFP
Signal
Name
GPIOD0
)
(CS2
GPIOD1
)
(CS3
GPIOD2
)
(CS4
GPIOD3
(CS5)
GPIOD4
(CS6)
GPIOD5
(CS7)
TXD0
(GPIOE0)
Pin No. Type
42 Input/
Output
Output
43
44
45
46
47
7 Output
Input/
Output
State
During
Reset
Input
Input
Tri-stated
Input
Signal Description
Port D GPIO — These six GPIO pins can be individually
programmed as input or output pins.
Chip Select — CS2 - CS7 may be programmed within the EMI
module to act as chip selects for specific areas of the external
memory map. Depending upon the state of the DRV bit in the
EMI bus control register (BCR), CS2
the external bus is inactive.
After reset, these pins are configured as GPIO.
To deactivate the internal pull-up resistor, clear the appropriate
GPIO bit in the GPIOD_PUR register.
Example: GPIOD0, clear bit 0 in the GPIOD_PUR register.
Transmit Data — SCI0 transmit data output
Port E GPIO — This GPIO pin can be individually programmed
as an input or output pin.
- CS7 are tri-stated when
RXD0
(GPIOE1)
TXD1
(GPIOD6)
8 Input
Input/
Output
40 Output
Input/
Output
Input
Input
Tri-stated
Input
After reset, the default state is SCI output.
To deactivate the internal pull-up resistor, clear bit 0 in the
GPIOE_PUR register.
Receive Data — SCI0 receive data input
Port E GPIO — This GPIO pin can be individually programmed
as an input or output pin.
After reset, the default state is SCI output.
To deactivate the internal pull-up resistor, clear bit 1 in the
GPIOE_PUR register.
Transmit Data — SCI1 transmit data output
Port D GPIO — This GPIO pin can be individually programmed
as an input or output pin.
After reset, the default state is SCI output.
To deactivate the internal pull-up resistor, clear bit 6 in the
GPIOD_PUR register.
56F8345 Technical Data, Rev. 14.0
22 Freescale Semiconductor
Preliminary
Table 2-2 Signal and Package Information for the 128-Pin LQFP
Signal Pins
Signal
Name
RXD1
(GPIOD7)
TCK 115 Schmitt
TMS 116 Schmitt
TDI 117 Schmitt
Pin No. Type
41 Input
Input/
Output
Input
Input
Input
State
During
Reset
Input
Input
Input,
pulled low
internally
Input,
pulled high
internally
Input,
pulled high
internally
Signal Description
Receive Data — SCI1 receive data input
Port D GPIO — This GPIO pin can be individually programmed
as an input or output pin.
After reset, the default state is SCI input.
To deactivate the internal pull-up resistor, clear bit 7 in the
GPIOD_PUR register.
Test Clock Input — This input pin provides a gated clock to
synchronize the test logic and shift serial data to the
JTAG/EOnCE port. The pin is connected internally to a
pull-down resistor.
Test Mode Select Input — This input pin is used to sequence
the JTAG TAP controller’s state machine. It is sampled on the
rising edge of TCK and has an on-chip pull-up resistor.
To deactivate the internal pull-up resistor, set the JTAG bit in the
SIM_PUDR register.
Test Data Input — This input pin provides a serial input data
stream to the JTAG/EOnCE port. It is sampled on the rising edge
of TCK and has an on-chip pull-up resistor.
To deactivate the internal pull-up resistor, set the JTAG bit in the
SIM_PUDR register.
TDO 118 Output Tri-stated Test Data Output — This tri-stateable output pin provides a
serial output data stream from the JTAG/EOnCE port. It is driven
in the shift-IR and shift-DR controller states, and changes on the
falling edge of TCK.
TRST
114 Schmitt
Input
Input,
pulled high
internally
Test Reset — As an input, a low signal on this pin provides a
reset signal to the JTAG TAP controller. To ensure complete
hardware reset, TRST
asserted. The only exception occurs in a debugging environment
when a hardware device reset is required and the JTAG/EOnCE
module must not be reset. In this case, assert RESET
assert TRST
To deactivate the internal pull-up resistor, set the JTAG bit in the
SIM_PUDR register.
.
should be asserted whenever RESET is
, but do not
56F8345 Technical Data, Rev. 14.0
Freescale Semiconductor 23
Preliminary
Table 2-2 Signal and Package Information for the 128-Pin LQFP
Signal
Name
PHASEA0
(TA0)
(GPIOC4)
PHASEB0
(TA1)
(GPIOC5)
Pin No. Type
127 Schmitt
Input
Schmitt
Input/
Output
Schmitt
Input/
Output
128 Schmitt
Input
Schmitt
Input/
Output
Schmitt
Input/
Output
State
During
Reset
Input
Input
Input
Input
Input
Input
Signal Description
Phase A — Quadrature Decoder 0, PHASEA input
TA0 — Timer A, Channel 0
Port C GPIO — This GPIO pin can be individually programmed
as an input or output pin.
After reset, the default state is PHASEA0.
To deactivate the internal pull-up resistor, clear bit 4 of the
GPIOC_PUR register.
Phase B — Quadrature Decoder 0, PHASEB input
TA1 — Timer A, Channel 1
Port C GPIO — This GPIO pin can be individually programmed
as an input or output pin.
After reset, the default state is PHASEB0.
INDEX0
(TA2)
(GPIOC6)
1Schmitt
Input
Schmitt
Input/
Output
Schmitt
Input/
Output
Input
Input
Input
To deactivate the internal pull-up resistor, clear bit 5 of the
GPIOC_PUR register.
Index — Quadrature Decoder 0, INDEX input
TA2 — Timer A, Channel 2
Port C GPIO — This GPIO pin can be individually programmed
as an input or output pin.
After reset, the default state is INDEX0.
To deactivate the internal pull-up resistor, clear bit 6 of the
GPIOC_PUR register.
56F8345 Technical Data, Rev. 14.0
24 Freescale Semiconductor
Preliminary
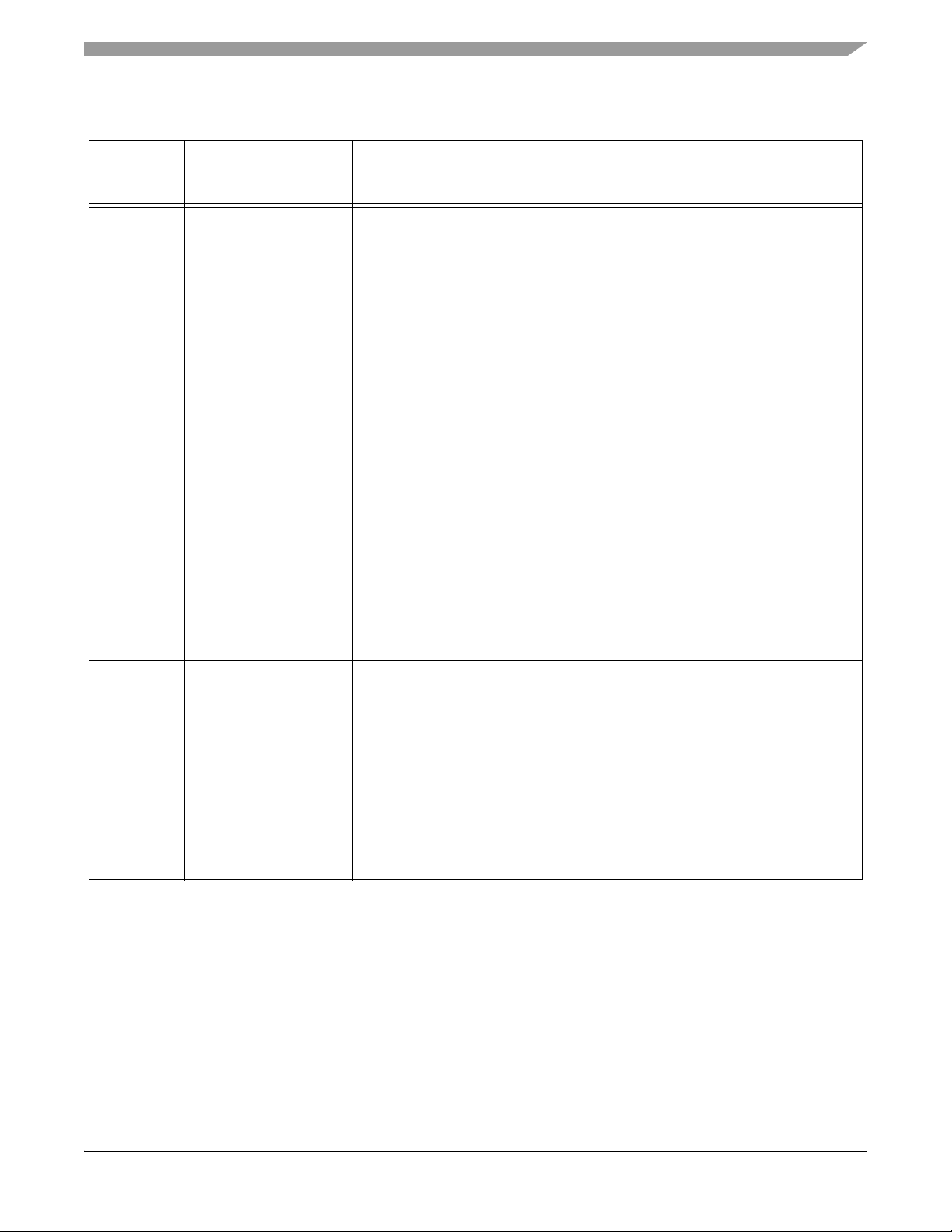
Table 2-2 Signal and Package Information for the 128-Pin LQFP
Signal Pins
Signal
Name
HOME0
(TA3)
(GPIOC7)
SCLK0
(GPIOE4)
Pin No. Type
2Schmitt
Input
Schmitt
Input/
Output
Schmitt
Input/
Output
124 Schmitt
Input/
Output
Schmitt
Input/
Output
State
During
Reset
Input
Input
Input
Input
Input
Signal Description
Home — Quadrature Decoder 0, HOME input
TA3 — Timer A ,Channel 3
Port C GPIO — This GPIO pin can be individually programmed
as an input or output pin.
After reset, the default state is HOME0.
To deactivate the internal pull-up resistor, clear bit 7 of the
GPIOC_PUR register.
SPI 0 Serial Clock — In the master mode, this pin serves as an
output, clocking slaved listeners. In slave mode, this pin serves
as the data clock input.
Port E GPIO — This GPIO pin can be individually programmed
as an input or output pin.
After reset, the default state is SCLK0.
MOSI0
(GPIOE5)
126 Input/
Output
Input/
Output
Tri-stated
Input
To deactivate the internal pull-up resistor, clear bit 4 in the
GPIOE_PUR register.
SPI 0 Master Out/Slave In — This serial data pin is an output
from a master device and an input to a slave device. The master
device places data on the MOSI line a half-cycle before the clock
edge the slave device uses to latch the data.
Port E GPIO — This GPIO pin can be individually programmed
as an input or output pin.
After reset, the default state is MOSI0.
To deactivate the internal pull-up resistor, clear bit 5 in the
GPIOE_PUR register.
56F8345 Technical Data, Rev. 14.0
Freescale Semiconductor 25
Preliminary
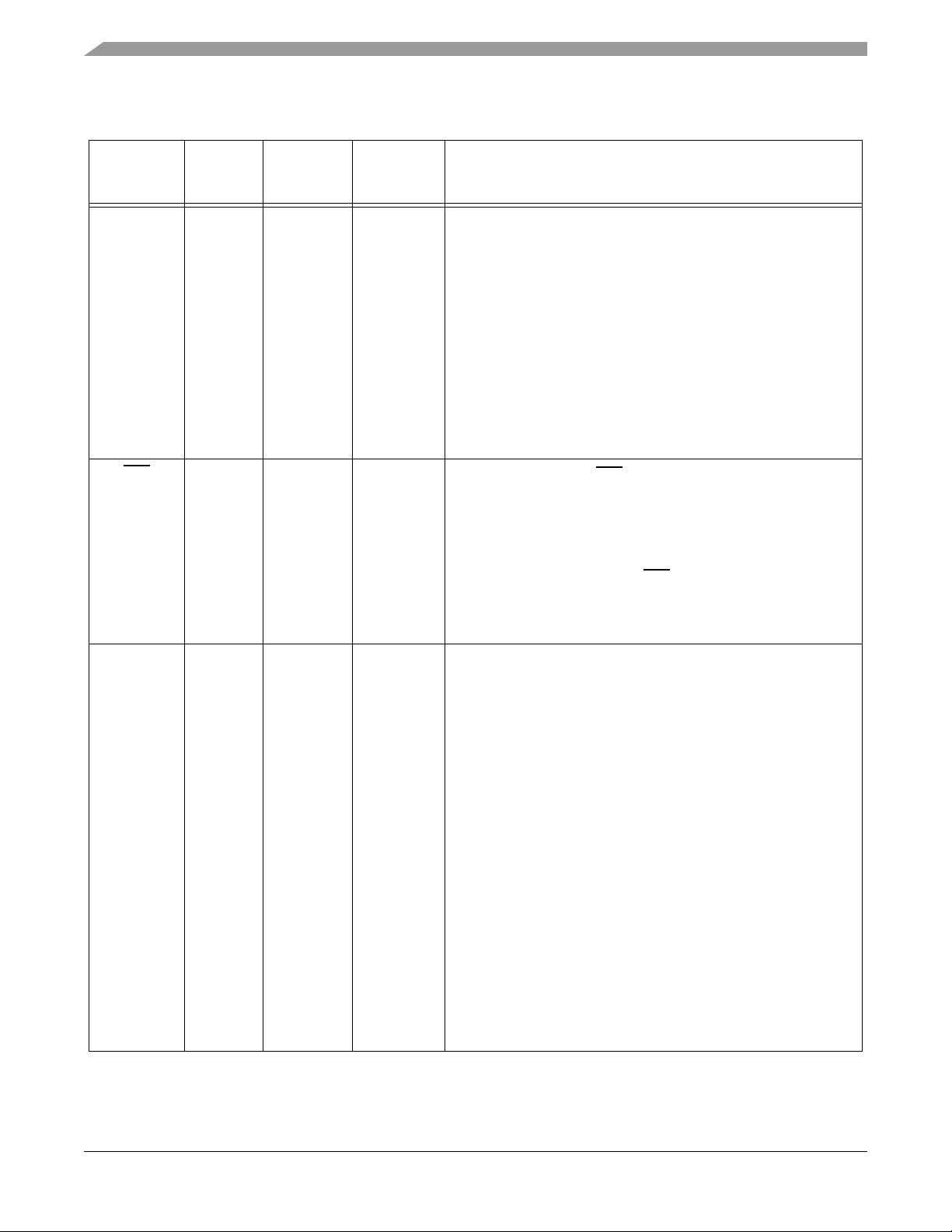
Table 2-2 Signal and Package Information for the 128-Pin LQFP
Signal
Name
MISO0
(GPIOE6)
SS0
(GPIOE7)
Pin No. Type
125 Input/
Output
Input/
Output
123 Input
Input/
Output
State
During
Reset
Input
Input
Input
Input
Signal Description
SPI 0 Master In/Slave Out — This serial data pin is an input to a
master device and an output from a slave device. The MISO line
of a slave device is placed in the high-impedance state if the
slave device is not selected. The slave device places data on the
MISO line a half-cycle before the clock edge the master device
uses to latch the data.
Port E GPIO — This GPIO pin can be individually programmed
as an input or output pin.
After reset, the default state is MISO0.
To deactivate the internal pull-up resistor, clear bit 6 in the
GPIOE_PUR register.
SPI 0 Slave Select — SS0
the SPI module that the current transfer is to be received.
Port E GPIO — This GPIO pin can be individually programmed
as an input or output pin.
After reset, the default state is SS0
is used in slave mode to indicate to
.
PHASEA1
(TB0)
(SCLK1)
(GPIOC0)
9Schmitt
Input
Schmitt
Input/
Output
Schmitt
Input/
Output
Schmitt
Input/
Output
Input
Input
Input
Input
To deactivate the internal pull-up resistor, clear bit 7 in the
GPIOE_PUR register.
Phase A1 — Quadrature Decoder 1, PHASEA input for decoder
1.
TB0 — Timer B, Channel 0
SPI 1 Serial Clock — In the master mode, this pin serves as an
output, clocking slaved listeners. In slave mode, this pin serves
as the data clock input. To activate the SPI function, set the
PHSA_ALT bit in the SIM_GPS register. For details, see Part
6.5.8.
Port C GPIO — This GPIO pin can be individually programmed
as an input or output pin.
In the 56F8345, the default state after reset is PHASEA1.
In the 56F8145, the default state is not one of the functions
offered and must be reconfigured.
To deactivate the internal pull-up resistor, clear bit 0 in the
GPIOC_PUR register.
56F8345 Technical Data, Rev. 14.0
26 Freescale Semiconductor
Preliminary
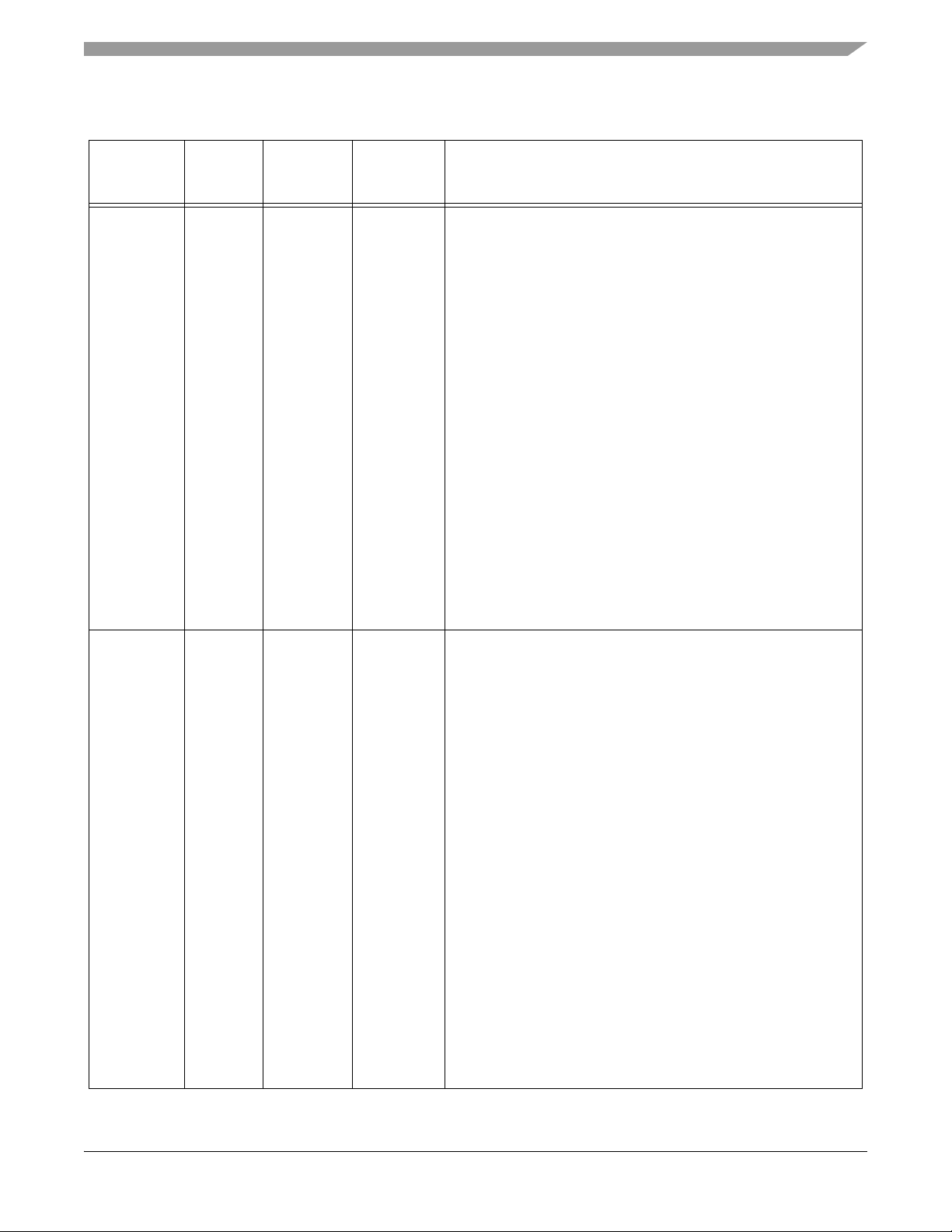
Table 2-2 Signal and Package Information for the 128-Pin LQFP
Signal Pins
Signal
Name
PHASEB1
(TB1)
(MOSI1)
(GPIOC1)
Pin No. Type
10 Schmitt
Input
Schmitt
Input/
Output
Schmitt
Input/
Output
Schmitt
Input/
Output
State
During
Reset
Input
Input
Tri-stated
Input
Signal Description
Phase B1 — Quadrature Decoder 1, PHASEB input for decoder
1.
TB1 — Timer B, Channel 1
SPI 1 Master Out/Slave In — This serial data pin is an output
from a master device and an input to a slave device. The master
device places data on the MOSI line a half-cycle before the clock
edge the slave device uses to latch the data. To activate the SPI
function, set the PHSB_ALT bit in the SIM_GPS register. For
details, see Part 6.5.8.
Port C GPIO — This GPIO pin can be individually programmed
as an input or output pin.
In the 56F8345, the default state after reset is PHASEB1.
In the 56F8145, the default state is not one of the functions
offered and must be reconfigured.
To deactivate the internal pull-up resistor, clear bit 1 in the
GPIOC_PUR register.
INDEX1
(TB2)
(MISO1)
(GPIOC2)
11 Schmitt
Input
Schmitt
Input/
Output
Schmitt
Input/
Output
Schmitt
Input/
Output
Input
Input
Input
Input
Index1 — Quadrature Decoder 1, INDEX input
TB2 — Timer B, Channel 2
SPI 1 Master In/Slave Out — This serial data pin is an input to a
master device and output from a slave device. The MISO line of
a slave device is placed in the high-impedance state if the slave
device is not selected. The slave device places data on the
MISO line a half-cycle before the clock edge the master device
uses to latch the data. To activate the SPI function, set the
INDEX_ALT bit in the SIM_GPS register. See Part 6.5.8 for
details.
Port C GPIO — This GPIO pin can be individually programmed
as an input or output pin.
In the 56F8345, the default state after reset is INDEX1.
In the 56F8145, the default state is not one of the functions
offered and must be reconfigured.
To deactivate the internal pull-up resistor, clear bit 2 in the
GPIOC_PUR register.
56F8345 Technical Data, Rev. 14.0
Freescale Semiconductor 27
Preliminary
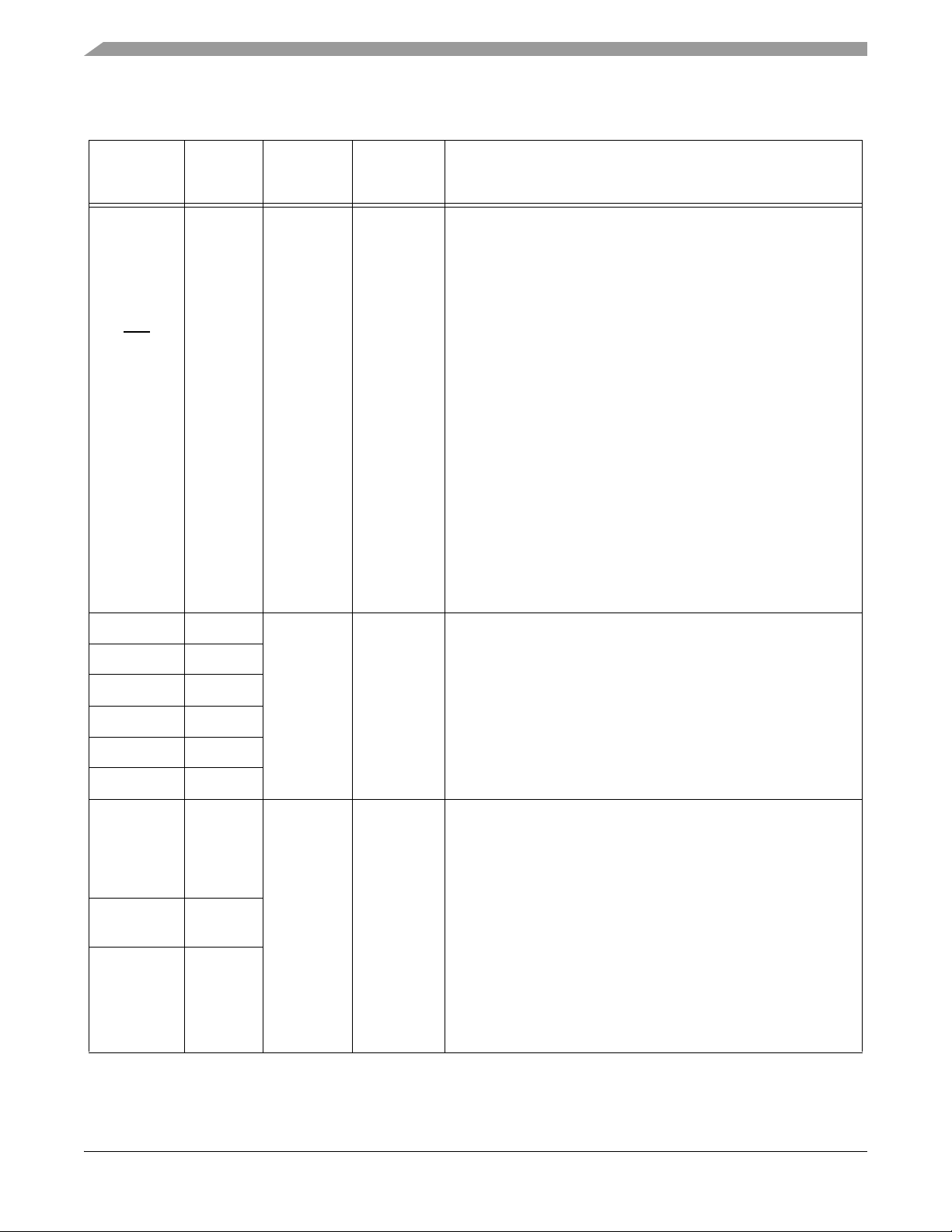
Table 2-2 Signal and Package Information for the 128-Pin LQFP
Signal
Name
HOME1
(TB3)
(SS1)
(GPIOC3)
Pin No. Type
12 Schmitt
Input
Schmitt
Input/
Output
Schmitt
Input
Schmitt
Input/
Output
State
During
Reset
Input
Input
Input
Input
Signal Description
Home — Quadrature Decoder 1, HOME input
TB3 — Timer B, Channel 3
SPI 1 Slave Select — In the master mode, this pin is used to
arbitrate multiple masters. In slave mode, this pin is used to
select the slave. To activate the SPI function, set the
HOME_ALT bit in the SIM_GPS register. See Part 6.5.8 for
details.
Port C GPIO — This GPIO pin can be individually programmed
as input or output pin.
In the 56F8345, the default state after reset is HOME1.
In the 56F8145, the default state is not one of the functions
offered and must be reconfigured.
To deactivate the internal pull-up resistor, clear bit 3 in the
GPIOC_PUR register.
PWMA0 58 Output Tri-State PWMA0 - 5 — These are six PWMA output pins.
PWMA1 60
PWMA2 61
PWMA3 63
PWMA4 64
PWMA5 66
ISA0
(GPIOC8)
ISA1
(GPIOC9)
ISA2
(GPIOC10)
104 Schmitt
Input
Schmitt
105
106
Input/
Output
Input
Input
ISA0 - 2 — These three input current status pins are used for
top/bottom pulse width correction in complementary channel
operation for PWMA.
Port C GPIO — These GPIO pins can be individually
programmed as input or output pins.
In the 56F8345, these pins default to ISA functionality.
In the 56F8145, the default state is not one of the functions
offered and must be reconfigured.
To deactivate the internal pull-up resistor, clear the appropriate
bit of the GPIOC_PUR register. See Part 6.5.6 for details.
56F8345 Technical Data, Rev. 14.0
28 Freescale Semiconductor
Preliminary
Table 2-2 Signal and Package Information for the 128-Pin LQFP
Signal Pins
Signal
Name
FAULTA0 67 Schmitt
FAULTA1 68
FAULTA2 69
FAULTA3 70 Schmitt
PWMB0 32 Output Tri-State PWMB0 - 5 — Six PWMB output pins.
PWMB1 33
PWMB2 34
PWMB3 37
PWMB4 38
PWMB5 39
Pin No. Type
Input
Input
State
During
Reset
Input FAULTA0 - 2 — These three fault input pins are used for
disabling selected PWMA outputs in cases where fault
conditions originate off-chip.
To deactivate the internal pull-up resistor, set the PWMA0 bit in
the SIM_PUDR register. See Part 6.5.6 for details.
Input FAULTA3 — This fault input pin is used for disabling selected
PWMA outputs in cases where fault conditions originate off-chip.
To deactivate the internal pull-up resistor, set the PWMA1 bit in
the SIM_PUDR register. See Part 6.5.6 for details.
Signal Description
ISB0
(GPIOD10)
ISB1
(GPIOD11)
ISB2
(GPIOD12)
FAULTB0 54 Schmitt
FAULTB1 55
FAULTB2 56
FAULTB3 57
ANA0 80 Input Input ANA0 - 3 — Analog inputs to ADC A, channel 0
ANA1 81
ANA2 82
ANA3 83
48 Schmitt
Input
Schmitt
50
51
Input/
Output
Input
Input
Input
Input FAULTB0 - 3 — These four fault input pins are used for
ISB0 - 2 — These three input current status pins are used for
top/bottom pulse width correction in complementary channel
operation for PWMB.
Port D GPIO — These GPIO pins can be individually
programmed as input or output pins.
At reset, these pins default to ISB functionality.
To deactivate the internal pull-up resistor, clear the appropriate
bit of the GPIOD_PUR register. See Part 6.5.6 for details.
disabling selected PWMB outputs in cases where fault
conditions originate off-chip.
To deactivate the internal pull-up resistor, set the PWMB bit in
the SIM_PUDR register. See Part 6.5.6 for details.
56F8345 Technical Data, Rev. 14.0
Freescale Semiconductor 29
Preliminary
Table 2-2 Signal and Package Information for the 128-Pin LQFP
Signal
Name
Pin No. Type
State
During
Reset
Signal Description
ANA4 84 Input Input ANA4 - 7 — Analog inputs to ADC A, channel 1
ANA5 85
ANA6 86
ANA7 87
V
REFH
V
REFP
V
REFMID
V
REFN
V
REFLO
93 Input Input V
92 Input/
Output
Input/
Output
91
90
89 Input Input V
— Analog Reference Voltage High. V
REFH
than or equal to V
V
, V
REFP
REFMID
DDA_ADC.
& V
REFN
— Internal pins for voltage reference
which are brought off-chip so that they can be bypassed.
Connect to a 0.1 µF low ESR capacitor.
— Analog Reference Voltage Low. This should normally
REFLO
be connected to a low-noise V
SSA
.
ANB0 96 Input Input ANB0 - 3 — Analog inputs to ADC B, channel 0
ANB1 97
must be less
REFH
ANB2 98
ANB3 99
ANB4 100 Input Input ANB4 - 7 — Analog inputs to ADC B, channel 1
ANB5 101
ANB6 102
ANB7 103
TEMP_
SENSE
88 Temperature Sense Diode — This signal connects to an
on-chip diode that can be connected to one of the ADC inputs
and is used to monitor the temperature of the die. Must be
bypassed with a 0.01 µF capacitor.
CAN_RX 121 Schmitt
Input
Input FlexCAN Receive Data — This is the CAN input. This pin has
an internal pull-up resistor.
To deactivate the internal pull-up resistor, set the CAN bit in the
SIM_PUDR register.
CAN_TX 120 Open
Output FlexCAN Transmit Data — CAN output
Drain
Output
56F8345 Technical Data, Rev. 14.0
30 Freescale Semiconductor
Preliminary
 Loading...
Loading...