Freescale Semiconductor
Technical Data
Single Gauge Driver
Document Number: MC33977
Rev. 2.0, 1/2007
The 33977 is a Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) Controlled, stepper
motor gauge driver Integrated Circuit (IC). This monolithic IC consists
of a dual H-Bridge coil driver and its associated control logic. The HBridge drivers are used to automatically control the speed, direction,
and magnitude of current through the coils of a two-phase
instrumentation stepper motor, similar to an MMT-licensed AFIC 6405
of Switec MS-X156.xxx motor.
The 33977 is ideal for use in instrumentation systems requiring
distributed and flexible stepper motor gauge driving. The device also
eases the transition to stepper motors from air core motors by
emulating the damped air core pointer movement.
Features
• MMT-Licensed Two-Phase Stepper Motor Compatible
• Switec MS-X15.xxx Stepper Motor Compatible
• Minimal Processor Overhead Required
• Fully Integrated Pointer Movement and Position State Machine
with Air Core Movement Emulation
• 4096 Possible Steady State Pointer Positions
• 340° Maximum Pointer Sweep
• Maximum Acceleration of 4500°/s
2
• Maximum Pointer Velocity of 400°/s
• Analog Microstepping (12 Steps/Degrees of Pointer Movement)
• Pointer Calibration and Return to Zero (RTZ)
• Controlled via 16-Bit SPI Messages
• Internal Clock Capable of Calibration
• Low Sleep Mode Current
• Pb-Free Packaging Designated by suffix code EG
SINGLE GAUGE DRIVER
ORDERING INFORMATION
Device
MC33977DW/R2
MCZ33977EG/R2
33977
DW SUFFIX
EG SUFFIX (Pb-FREE)
98ASB42344B
24-PIN SOICW
Temperature
Range (T
- 40°C to 125°C 24 SOICW
)
A
Package
V
PWR
33977
V
5.0 V
DD
Regulator
MCU
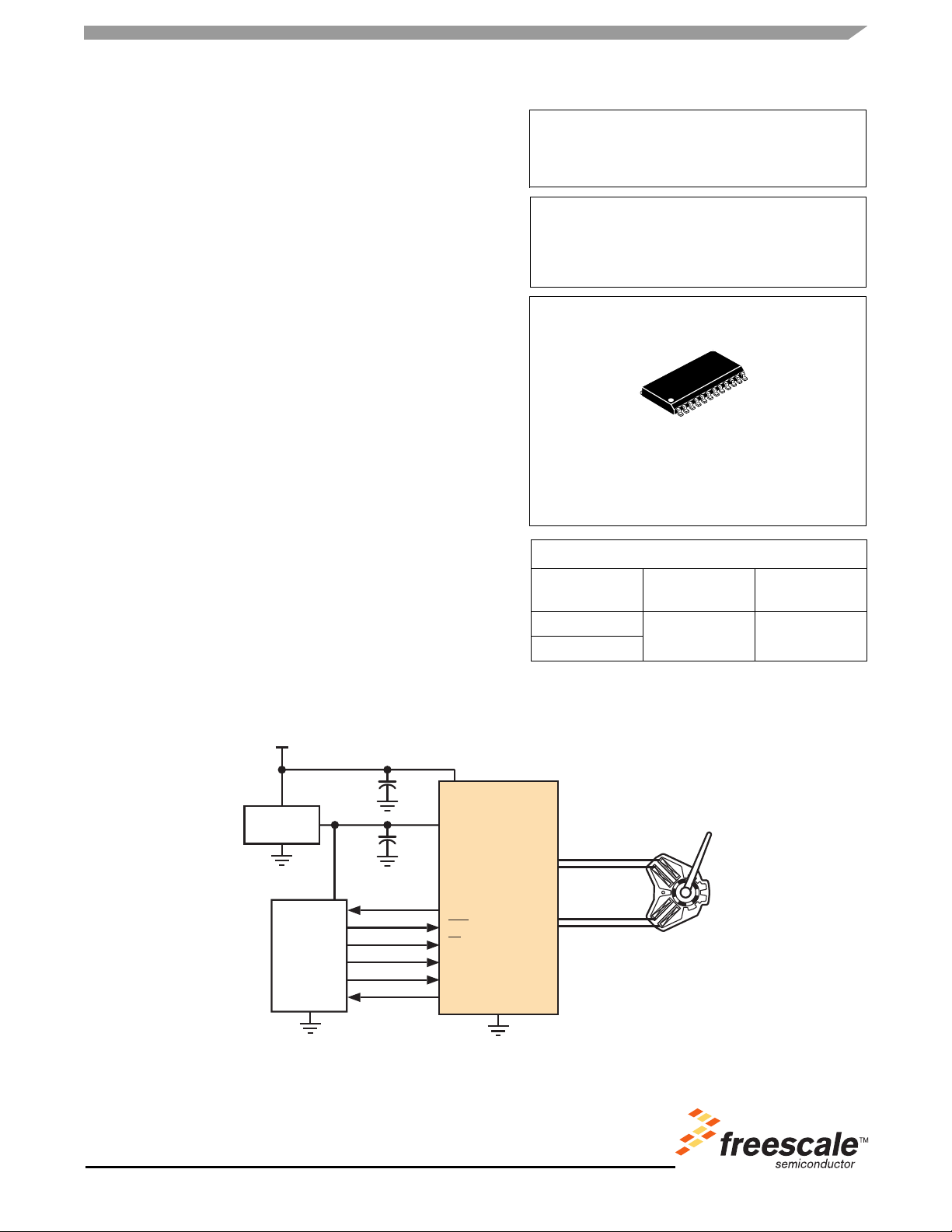
Figure 1. 33977 Simplified Application Diagram
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. reserves the right to change the detail specifications,
as may be required, to permit improvements in the design of its products.
© Freescale Semiconductor, Inc., 2007. All rights reserved.
VPWR
VDD
RTZ
RST
CS
SCLK
SI
SO
GND
SIN+
SIN-
COS+
COS-
Motor
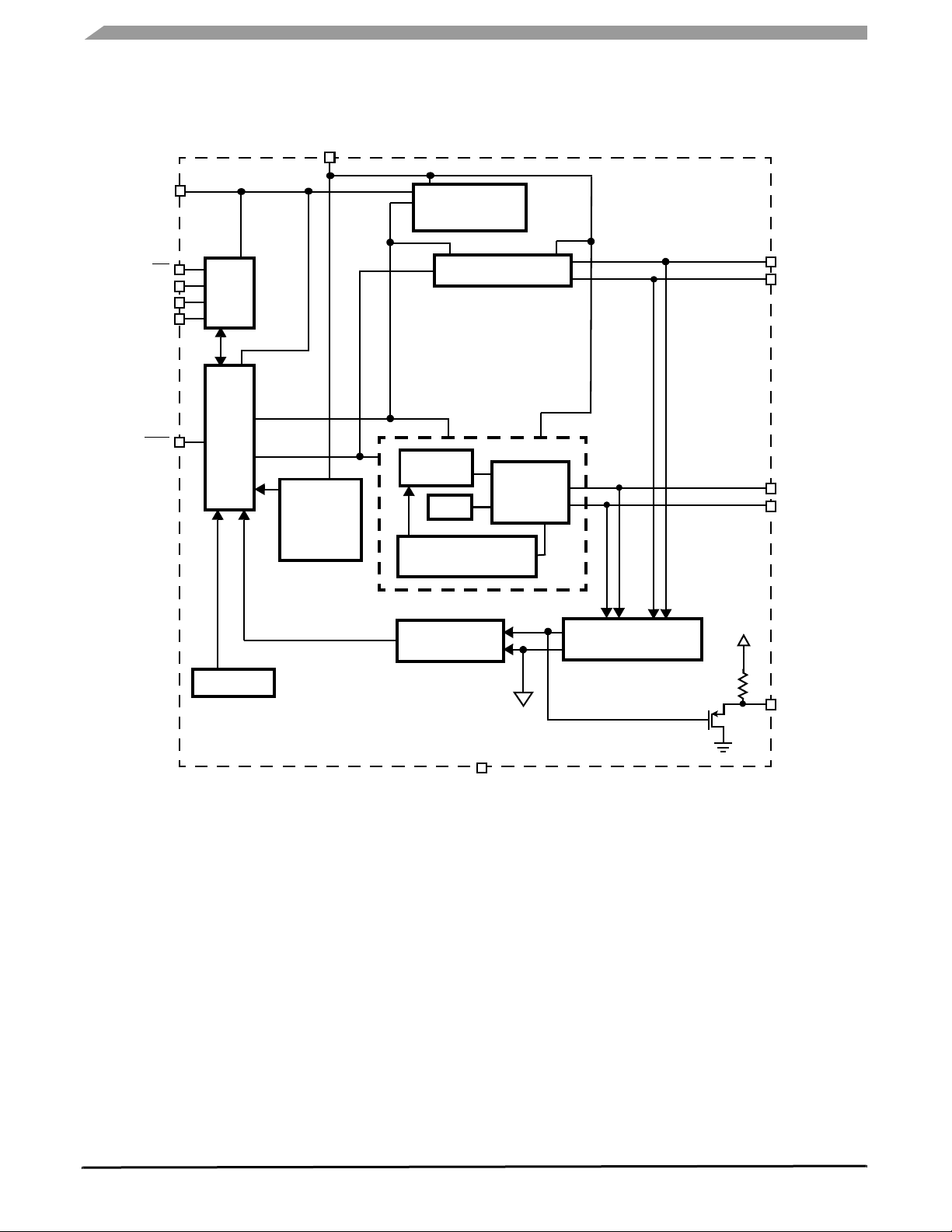
INTERNAL BLOCK DIAGRAM
INTERNAL BLOCK DIAGRAM
VPWR
VDD
CS
SCLK
SO
RST
INTERNAL
REGULATOR
COS
SPI
SI
LOGIC
UNDER
-
AND
OVERVOLTAGE
DETECT
STATE
MACHINE
ILIM
OVERTEMPERATURE
DETECT
SIGMA-DELTA
ADC
H-BRIDGE
AND
CONTROL
SIN
VDD
MULTIPLEXER
COS+
COS-
SIN+
SIN-
OSCILLATOR
AGND
GND (8)
Figure 2. 33977 Simplified Internal Block Diagram
RTZ
33977
Analog Integrated Circuit Device Data
2 Freescale Semiconductor
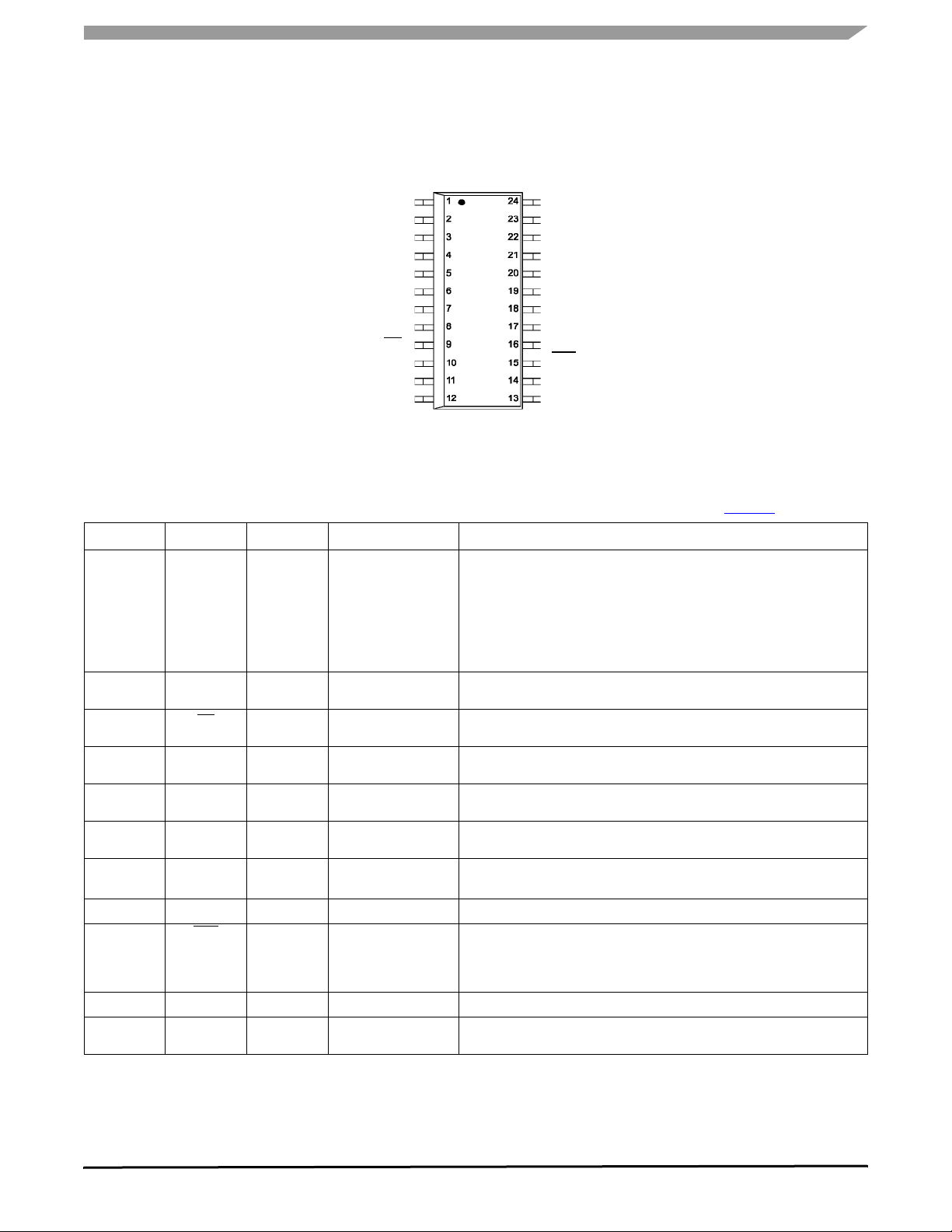
PIN CONNECTIONS
PIN CONNECTIONS
COS+
COS-
SIN+
SINGND
GND
GND
GND
CS
SCLK
SO
SI
NC
NC
NC
NC
GND
GND
GND
GND
VPWR
RST
VDD
RTZ
Figure 3. 33977 Pin Connections
Table 1. 33977 Pin Definitions
A functional description of each pin can be found in the Functional Pin Descri ption section beginning onpage 10.
Pin Pin Name Pin Function Formal Name Definition
1
2
3
4
5 to 8,
17 to 20
9
10 SCLK
11 SO
12
13 RTZ
14 VDD
15 RST
16 VPWR
21, 22, 23, 24
(MS Motor
Pin #)
COS+ (MS #4)
COS- (MS #3)
SIN+ (MS #1)
SIN- (MS #2)
GND
CS
SI
NC
Output
N/A
Input
Input
Output
Input
Multiplexed
Output
Input
Input
Input
–
H-Bridge Outputs 0 Each pin is the output of a half-bridge, designed to source or sink current.
Ground Ground pins
Chip Select This pin is connected to a chip select output of a Large Scale Integration
(LSI) Master IC and controls which device is addressed.
Serial Clock This pin is connected to the SCLK pin of the master device and acts as a
bit clock for the SPI port.
Serial Output This pin is connected to the SPI Serial Data Input pin of the Master device
or to the SI pin of the next device in a daisy chain.
Serial Input This pin is connected to the SPI Serial Data Output pin of the Master
device from which it receives output command data.
Return to Zero This is a multiplexed output pin for the non-driven coil, during a Return to
Zero (RTZ) event.
Voltage This SPI and logic power supply input will work with 5.0 V supplies.
Reset This pin is connected to the Master and is used to reset the device, or
place it into a sleep state by driving it to Logic [1]. When this pin is driven
to Logic [0], all internal logic is forced to the default state. This input has
an internal active pull-up.
Battery Voltage Power supply
No Connect These pins are not connected to any internal circuitry, or any other pin,
and may be connected to the board where convenient.
33977
Analog Integrated Circuit Device Data
Freescale Semiconductor 3
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
MAXIMUM RATINGS
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
MAXIMUM RATINGS
Table 2. Maximum Ratings
All voltages are with respect to ground unless otherwise noted. Exceeding these ratings may cause a malfunction or
permanent damage to the device.
Ratings Symbol Value Unit
ELECTRICAL RATINGS
Power Supply Voltage
Steady-State
Input Pin Voltage
SIN± COSI± Continuous Current Per Output
ESD Voltage
(1)
(2)
(3)
Human Body Model (HBM)
Machine Model (MM)
Charge Device Model (CDM)
THERMAL RATINGS
Operating Temperature
Ambient
Junction
Storage Temperature T
Thermal Resistance
Junction-to-Ambient
Junction-to-Lead
Peak Package Reflow Temperature During Reflow
(4), (5)
Notes
1. Exceeding voltage limits on Input pins may cause permanent damage to the device.
2. Output continuous output rating so long as maximum junction temperature is not exceeded. Operation at 125°C ambient temperature
will require maximum output current computation using package thermal resistances.
3. ESD testing is performed in accordance with the Human Body Model (HBM) (C
(C
ZAP
= 200 pF, R
= 0 Ω), and the Charge Device Model (CDM).
ZAP
4. Pin soldering temperature limit is for 10 seconds maximum duration. Not designed for immersion soldering. Exceeding these limits may
cause malfunction or permanent damage to the device.
5. Freescale’s Package Reflow capability meets Pb-free requirements for JEDEC standard J-STD-020C. For Peak Package Reflow
Temperature and Moisture Sensitivity Levels (MSL),
Go to www.freescale.com, search by part number [e.g. remove prefixes/suffixes and enter the core ID to view all orderable parts. (i.e.
MC33xxxD enter 33xxx), and review parametrics.
V
PWRSS
V
IN
I
OUTMAX
V
ESD
T
A
T
J
STG
R
ΘJA
R
ΘJL
T
PPRT
= 100 pF, R
ZAP
-0.3 to 41
-0.3 to 7.0 V
40 mA
±2000
±2000
±200
-40 to 125
-40 to 150
-55 to 150 °C
°C/W
60
20
Note 5
= 1500 Ω), the Machine Model (MM)
ZAP
V
V
°C
°C
33977
Analog Integrated Circuit Device Data
4 Freescale Semiconductor
STATIC ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
STATIC ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
Table 3. Static Electrical Characteristics
Characteristics noted under conditions 4.75 V < VDD < 5.25 V, and - 40°C < TA< 125°C, unless otherwise noted. Typical
values noted reflect the approximate parameter means at T
Characteristic Symbol Min Typ Max Unit
POWER INPUT (VDD)
Battery Supply Voltage Range
Fully Operational
Limited Operation
V
Supply Current
PWR
Gauge Outputs ON, No Output Loads
VPWR Supply Current (All Outputs Disabled)
Reset = Logic [0], V
Reset = Logic [0], V
Overvoltage Detection Level
Undervoltage Detection Level
Logic Supply Voltage Range (5.0 V Nominal Supply)
Under VDD Logic Reset
VDD Supply Current
Sleep: Reset Logic [0]
Outputs Enabled
POWER OUTPUT (SIN-, SIN+, COS-, COS+)
Microstep Output (Measured Across Coil Outputs)
SIN± (COS±) (Refer to Pin Definitions onpage 3)
R
= 200 Ω, PE6 = 0
OUT
Steps Pin Definitions
6, 18, 0, 12
5, 7, 17, 19 1, 11, 13, 23
4, 8, 16, 20 2, 10, 14, 22
3, 9, 15, 21 3, 9, 15, 21
2, 10, 14, 22 5, 7, 17, 19
1, 11, 13, 23 5, 7, 17, 19
0, 12 6, 18
Full Step Active Output (Measured Across Coil Outputs)
SIN± (COS±), Steps 1,3 (Pin Definitions 0 and 2)
Notes
6. Outputs and logic remain active; however, the larger coil voltage levels may be clipped. The reduction in drive voltage may result in a
loss of position control.
7. The logic will reset at some level below the specified Limited Operational minimum.
8. Outputs will disable and must be re-enabled via the PECCR command.
9. Outputs remain active; however, the reduction in drive voltage may result in a loss of position control.
10. See Figure 7.
(6), (7)
DD
DD
= 5.0 V
= 0 V
(8)
(9)
(10)
= 25°C under nominal conditions unless otherwise noted.
A
V
PWR
I
PWR
6.5
4.0
– 26
26
– 4.0 6.0
I
PWRSLP1
I
PWRSLP2
V
PWROV
V
PWRUV
V
DD
V
DDUV
I
DDOFF
I
DDON
V
ST6
V
ST5
V
ST4
V
ST3
V
ST2
V
ST1
V
ST0
V
FS
–
–
42
15
60
25
26 32 38 V
5.0 5.6 6.2 V
4.5 5.0 5.5 V
– – 4.5 V
4.82
0.94 V
0.84 V
0.68 V
0.47 V
0.23 V
0.1
–
–
ST6
ST6
ST6
ST6
ST6
40
1.0
5.3
0.97 V
0.87 V
0.71 V
0.50 V
0.26 V
0.0
ST6
ST6
ST6
ST6
ST6
65
1.8
6.0
1.0 V
0.96 V
0.8 V
0.57 V
0.31 V
0.1
ST6
ST6
ST6
ST6
ST6
4.9 5.3 6.0
V
mA
µA
µV
mA
V
V
33977
Analog Integrated Circuit Device Data
Freescale Semiconductor 5
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
STATIC ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
Table 3. Static Electrical Characteristics (continued)
Characteristics noted under conditions 4.75 V < VDD < 5.25 V, and - 40°C < TA< 125°C, unless otherwise noted. Typical
values noted reflect the approximate parameter means at TA = 25°C under nominal conditions unless otherwise noted.
Characteristic Symbol Min Typ Max Unit
POWER OUTPUT (SIN-, SIN+, COS-, COS+) (Continued)
Microstep Full Step Output (Measured from Coil Low Side to Ground)
SIN± (COS±) I
Output Flyback Clamp
Output Current Limit (Output - V
Overtemperature Shutdown
Overtemperature Hysteresis
OUT
= 30 mA
(11)
(12)
(12)
ST6
)
CONTROL I/O (SI, SCLK, CS, RST, SO)
Input Logic High Voltage
Input Logic Low Voltage
Input Logic Voltage Hysteresis
(12)
(12)
(12)
Input Logic Pull-Down Current (SI, SCLK)
Input Logic Pull-Up Current (CS, RST)
SO High State Output Voltage (IOH = 1.0 mA)
SO Low State Output Voltage (IOL = 1.6 mA)
SO Tri-State Leakage Current (CS = 3.5 V)
Input Capacitance
SO Tri-State Capacitance
(13)
(13)
ANALOG TO DIGITAL CONVERTER (RTZ ACCUMULATOR COUNT)
ADC Gain
(12), (14)
Notes
11. Outputs remain active; however, the reduction in drive voltage may result in a loss of position control.
12. This parameter is guaranteed by design; however, it is not production tested.
13. Capacitance not measured. This parameter is guaranteed by design; however, it is not production tested.
14. Reference RTZ Accumulator (Typical) on page 30
V
V
I
LIM
T
T
HYST
V
V
V
INHYST
I
DWN
I
V
SOH
V
I
SOLK
C
C
G
ADC
LS
FB
SD
IH
IL
UP
SOL
IN
SO
0.0 0.1 0.3
– V
ST6
+ 0.5 V
+ 1.0 V
ST6
40 100 170 mA
155 – 180 °C
8.0 – 16 °C
2.0 – – V
– – 0.8 V
– 100 – mV
3.0 – 20 µA
5.0 – 20 µA
0.8 V
DD
– – V
– 0.2 0.4 V
-5.0 0.0 5.0 µA
– 4.0 12 pF
– – 20 pF
100 188 270 Counts/V/
V
ms
33977
Analog Integrated Circuit Device Data
6 Freescale Semiconductor
DYNAMIC ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
DYNAMIC ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
Table 4. Dynamic Electrical Characteristics
Characteristics noted under conditions 4.75 V < VDD < 5.25 V, and - 40°C < TA < 125°C, unless otherwise noted. Typical
values noted reflect the approximate parameter means at T
Characteristic Symbol Min Typ Max Unit
POWER OUTPUT AND CLOCK TIMINGS (SIN+, SIN-, COS+, COS-) CS
SIN± (COS±) Output Turn ON Delay Time (Time from Rising CS
Enabling Outputs to Steady State Coil Voltages and Currents)
SIN± (COS±) Output Turn OFF Delay Time (Time from Rising CS
Disables Outputs to Steady State Coil Voltages and Currents)
Uncalibrated Oscillator Cycle Time
Calibrated Oscillator Cycle Time
Calibration Pulse = 8.0 µs, PECCR D4 = Logic [0]
Calibration Pulse = 8.0 µs, PECCR D4 = Logic [1]
Maximum Pointer Speed
Maximum Pointer Acceleration
SPI INTERFACE TIMING (CS, SCLK, SO, SI, RST)
Recommended Frequency of SPI Operation
Falling Edge of CS to Rising Edge of SCLK (Required Setup Time)
Falling Edge of SCLK to Rising Edge of CS (Required Setup Time)
SI to Falling Edge of SCLK (Required Setup Time)
Falling Edge of SCLK to SI (Required Hold Time)
SO Rise Time
CL = 200 pF
SO Fall Time
CL = 200 pF
SI, CS, SCLK, Incoming Signal Rise Time
SI, CS, SCLK, Incoming Signal Fall Time
Falling Edge of RST to Rising Edge of RST (Required Setup Time)
Rising Edge of CS to Falling Edge of CS (Required Setup Time)
Falling Edge of RST to Rising Edge of CS (Required Setup Time)
Notes
15. Maximum specified time for the 33977 is the minimum guaranteed time needed from the microcontroller.
16. The minimum and maximum value will vary proportionally to the internal clock tolerance. These numbers are based on an ideally
calibrated clock frequency of 1.0 MHz. These are not 100 percent tested.
17. The 33977 shall meet all SPI interface timing requirements specified in the SPI Interface Timing section of this table, over the specified
temperature range. Digital interface timing is based on a symmetrical 50 percent duty cycle SCLK Clock Period of 33 ns. The device shall
be fully functional for slower clock speeds. Reference
18. The required setup times specified for the 33977 are the minimum time needed from the microcontroller to guarantee correct operation.
19. Rise and Fall time of incoming SI, CS, and SCLK signals suggested for design consideration to prevent the occurrence of double pulsing.
20. The value is for a 1.0 MHz calibrated internal clock. The value will change proportionally as the internal clock frequency changes.
(16)
(16)
(17)
(18)
(18)
(19)
(19)
= 25°C under nominal conditions unless otherwise noted.
A
t
(15)
(15)
(18)
(18)
DLYON
t
DLYOFF
t
CLU
t
CLC
V
MAX
A
MAX
f
SPI
t
LEAD
t
LAG
t
SISU
t
SIHOLD
t
RSO
– – 1.0
– – 1.0
0.65 1.0 1.7 µs
1.0
0.9
1.1
1.0
– – 400 °/s
– – 4500 °/s
– 1.0 2.0 MHz
167 – – ns
167 – – ns
– 25 83 ns
– 25 83 ns
– 25 50
t
FSO
– 25 50
(18)
(18), (20)
(18)
t
RSI
t
FIS
t
RST
W
t
CS
t
EN
– – 50 ns
– – 50 ns
– – 3.0 µs
– – 5.0 µs
– – 5.0 µs
Figure 4 and 5.
ms
ms
µs
1.2
1.1
ns
ns
2
33977
Analog Integrated Circuit Device Data
Freescale Semiconductor 7
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
DYNAMIC ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
Table 4. Dynamic Electrical Characteristics (continued)
Characteristics noted under conditions 4.75 V < VDD < 5.25 V, and - 40°C < TA < 125°C, unless otherwise noted. Typical
values noted reflect the approximate parameter means at TA = 25°C under nominal conditions unless otherwise noted.
Characteristic Symbol Min Typ Max Unit
SPI INTERFACE TIMING (CS, SCLK, SO, SI, RST) ‘ (CONTINUED)
(24)
(22)
(23)
t
SOEN
t
SODIS
t
VALID
– – 145 ns
– 1.3 4.0 µs
ns
– 90 150
Time from Falling Edge of CS to SO Low Impedance
Time from Falling Edge of CS to SO High Impedance
Time from Rising Edge of SCLK to SO Data Valid
0.2 VDD = SO = 0.8 VDD, CL = 200 pF
Notes
21. The 33977 shall meet all SPI interface timing requirements specified in the SPI Interface Timing section of this table, over the specified
temperature range. Digital interface timing is based on a symmetrical 50 percent duty cycle SCLK Clock Period of 33 ns. The device shall
be fully functional for slower clock speeds.
22. Time required for output status data to be terminated at SO 1.0 kΩ load on SO.
23. Time required for output status data to be available for use at SO 1.0 kΩ load on SO.
24. Time required to obtain valid data out from SO following the rise of SCLK.
33977
Analog Integrated Circuit Device Data
8 Freescale Semiconductor
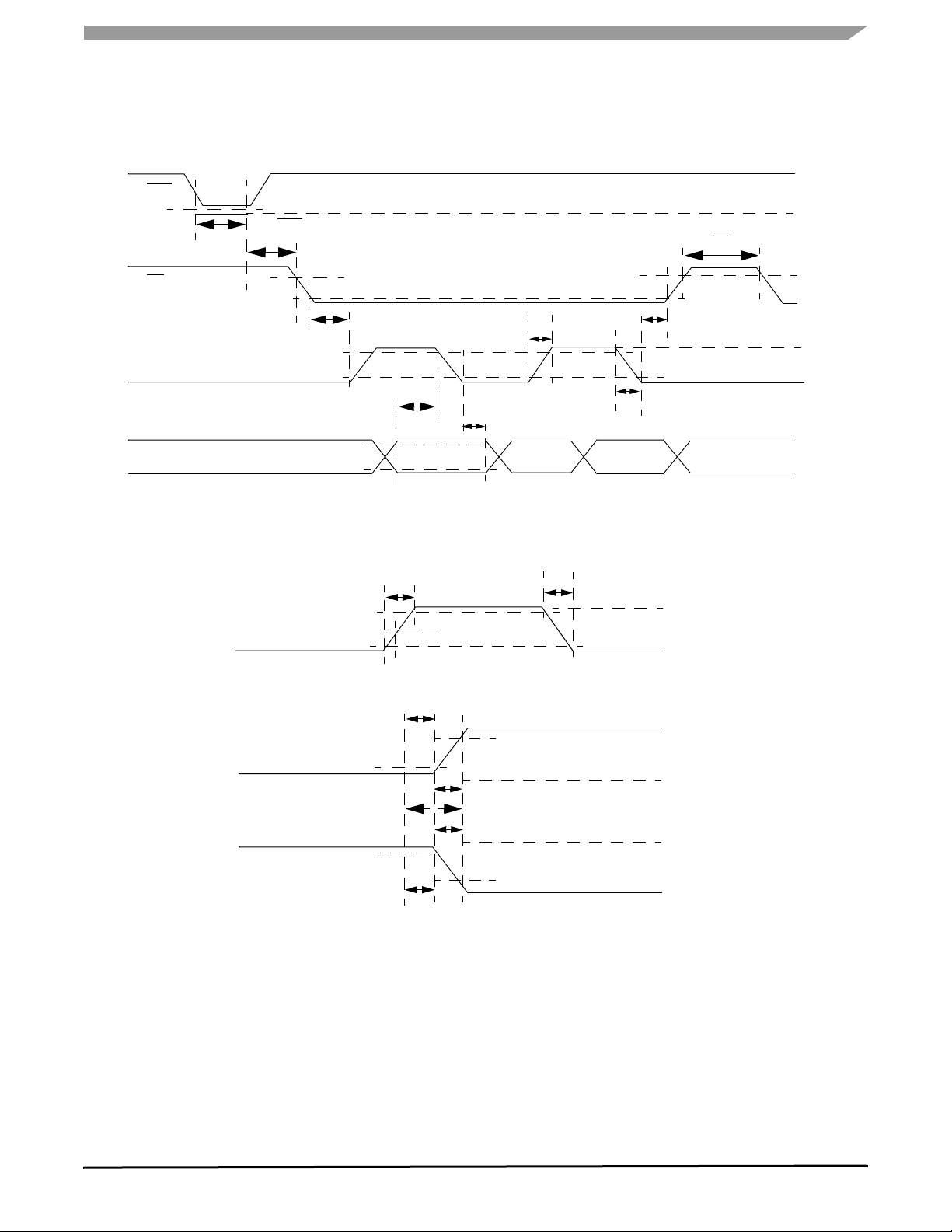
RST
t
WRST
0.2 V
DD
TIMING DIAGRAMS
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
TIMING DIAGRAMS
t
CS
V
IN
V
IL
CS
SCLK
SI
0.7 V
DD
SCLK
SO
Low-to-High
SO
High-to-Low
0.7 V
0.2 V
0.2 V
t
LEAD
DD
DD
0.7 V
DD
DD
t
SISU
Valid Don’t Care Valid Don’t CareDon’t Care
t
SI(HOLD)
t
RSI
Figure 4. Input Timing Switching Characteristics
t
FIS
3.5V
0.2 VDD
V
DD
0.7
t
SO(DIS)
t
SO(EN)
t
VALID
t
RSI
50%
t
RSO
t
RSO
0.7 VDD
0.2 VDD
0.7 V
1.0V
DD
t
FIS
V
IH
V
IL
t
LAG
V
OH
V
OL
V
OH
V
OL
V
OH
V
OL
V
IH
Figure 5. Valid Data Delay Time and Valid Time Waveforms
33977
Analog Integrated Circuit Device Data
Freescale Semiconductor 9

FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
FUNCTIONAL PIN DESCRIPTION
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
INTRODUCTION
This 33977 is a single-packaged, Serial Peripheral
INterface (SPI) controlled, single stepper motor gauge driver
integrated circuit (IC). This monolithic stepper IC consists of
[deleted two per D. Mortensen] a dual output H-Bridge coil
driver [deleted plural s for accurate tense] and the
FUNCTIONAL PIN DESCRIPTION
COSINE POSITIVE (COS0+)
The H-Bridge pins linearly drive the sine and cosine coils
of a stepper motor, providing four-quadrant operation.
COSINE NEGATIVE (COS0-)
The H-Bridge pins linearly drive the sine and cosine coils
of a stepper motor, providing four-quadrant operation.
SINE POSITIVE (SIN+)
The H-Bridge pins linearly drive the sine and cosine coils
of a stepper motor, providing four-quadrant operation.
SINE NEGATIVE (SIN-)
The H-Bridge pins linearly drive the sine and cosine coils
of a stepper motor, providing four-quadrant operation.
GROUND (GND)
Ground pins.
CHIP SELECT (CS)
The pin enables communication with the master device.
When this pin is in a logic [0] state, the 33977 is capable of
transferring information to, and recei vi n g i nf ormation from,
the master. The 33977 latches data in from the Input Shift
registers to the addressed registers on the rising edge of
The output driver on the SO pin is enabled when CS is
logic [0]. When CS is logic high, signals at the SCLK and SI
pins are ignored and the SO pin is tri-stated (high
impedance).
to a logic [0] state when SCLK is logic [0].
pull-up (I
of the Static Electrical Characteristics Table.
CS will only be transitioned from a logic [1] state
CS has an internal
) connected to the pin, as specified in the section
UP
CS.
associated control logic. The dual H-Bridge driver is used to
automatically control the speed, direction, and magnitude of
current through the coils of a two-phase instrumentation
stepper motor, similar to an MMT-licensed AFIC 6405 of
Switec MS-X 156.xxx motor.
SCLK has an internal pull down (l
section of the Static Electrical Characteristics Table. When
CS is logic [1], signals at the SCLK and SI pins are ignored
and SO is tri-stated (high impedance). Refer to the data
transfer
Timing Diagrams on page 9.
), as specified in the
DWN
SERIAL OUTPUT (SO)
The SO data pin is a tri-stateable output from the Shift
register. The Status register bits are the first 16 bits shifted
out. Those bits are followed by the message bits clocked in
FIFO, when the device is in a daisy chain connection or being
sent words that are multiples of 16 bits. Data is shifted on the
rising edge of the SCLK signal. The SO pin will remain in a
high impedance state until the
state.
CS pin is put into a logic low
SERIAL INPUT (SI)
The SI pin is the input of the SPI. Serial input information
is read on the falling edge of SCLK. A 16-bit stream of serial
data is required on the SI pin, beginning with the most
significant bit (MSB). Messages that are not multiples of 16
bits (e.g., daisy chained device messages) are ignored. After
transmitting a 16-bit word, the
(logic [1]) before transmitting a new word. SI information is
ignored when
CS is in a logic high state.
CS pin must be de-asserted
RETURN TO ZERO (RTZ)
This is a multiplexed output pin for the non-driven coil,
during a Return to Zero (RTZ) event.
VOLTAGE (VDD)
The SPI and logic power supply input will work with 5.0 V
supplies.
SERIAL CLOCK (SCLK)
SCLK clocks the Internal Shift registers of the 33977
device. The SI pin accepts data into the Input Shift register on
the falling edge of the SCLK signal, while the Serial Output
pin (SO) shifts data information out of the SO Line Driver on
the rising edge of the SCLK signal. It is important that the
SCLK pin be in a logic [0] state whenever the
transition.
33977
10 Freescale Semiconductor
CS makes any
RESET (RST)
If the master decides to reset the device, or place it into a
sleep state, the
the RST pin forces all internal logic to the known default state.
This input has an internal active pull-up.
RST pin is driven to a Logic [0]. A Logic [0] on
VOLTAGE POWER (VPWR)
This is the power supply pin.
Analog Integrated Circuit Device Data

FUNCTIONAL INTERNAL BLOCK DESCRIPTION (OPTIONAL)
FUNCTIONAL INTERNAL BLOCK DESCRIPTION (OPTIONAL)
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
SPI Logic
Under and
Overvoltage
Detect
Figure 6. Functional Internal 33977 Block Illustration
SERIAL PERIPHERAL INTERFACE (SPI)
This circuitry manages incoming messages and outgoing
status data.
LOGIC
This design element includes internal logic including state
machines and message decoding.
INTERNAL REFERENCE
This design element is used for step value levels.
UNDER AND OVERVOLTAGE DETECTION
This design element detects when V
normal operating range.
is out of the
PWR
Internal
Reference
Oscillator
RTZ
H-Bridge
and Control
OSCILLATOR
The internal oscillator generates the internal clock for all
timing critical features.
H-BRIDGE AND CONTROL
This circuitry contains the output coil drivers and the
multiplexers necessary for four quadrant operation and RTZ
sequencing. This circuitry is repeated for the Sine and Cosine
coils.
• Overtemperature — Each output includes an
overtemperature sensing circuit
• ILIM — Each output is current limited
RETURN TO ZERO (RTZ)
This circuitry outputs the voltage present on the non-driven
coil during RTZ operation.
33977
Analog Integrated Circuit Device Data
Freescale Semiconductor 11
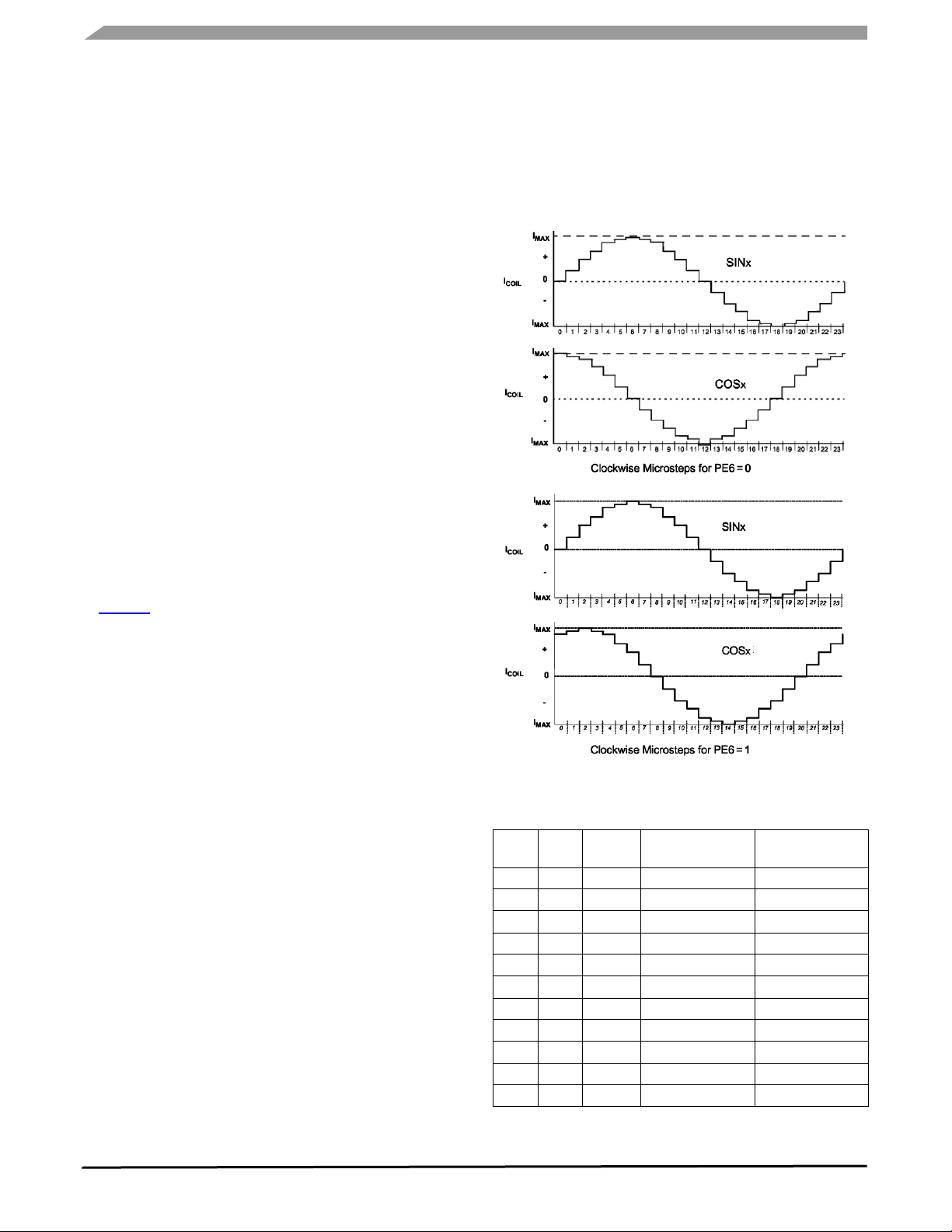
FUNCTIONAL DEVICE OPERATION
OPERATIONAL MODES
FUNCTIONAL DEVICE OPERATION
OPERATIONAL MODES
STATE MACHINE OPERATION
The 33977 is ideal for use in instrumentation systems
requiring distributed and flexible stepper motor gauge driving.
The device also eases the transition to stepper motors from
air core motors by emulating the air core pointer movement
with little additional processor bandwidth utilization. The twophase stepper motor has maximum allowable velocities and
acceleration and deceleration. The purpose of the stepper
motor state machine is to drive the motor with the maximum
performance while remaining within the motor’s voltage,
velocity, and acceleration constraints.
A requirement of the state machine is to ensure the
deceleration phase begins at the correct time and pointer
position. When commanded, the motor [will deleted PV]
accelerates constantly to the maximum velocity, and then it
moves toward the commanded position at the maximum
velocity. Eventually, the pointer reaches the calculated
location where the movement has to decelerate, safely
slowing to a stop at the desired position. During the
deceleration phase, the motor does [will deleted PV] not
exceed the maximum deceleration.
During normal operation, both stepper motor rotors are
microstepped at 24 steps per electrical revolution, illustrated
in Figure 7. A complete electrical revolution results in two
degrees of pointer movement. There is a second smaller
[parentheses removed-unnecessary] state machine in the IC
controlling these microsteps. The smaller state machine
receives clockwise or counter-clockwise index commands at
timed intervals, thereby stepping the motor in the appropriate
direction by adjusting the current in each coil. Normalized
values are provided in
Table 5.
Figure 7. Clockwise Microsteps
Table 5. Coil Step Value
33977
Step
Angle
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
105 0.966 -0.259 0.259
8
120 0.866 -0.5 0.0
9
135 0.707 -0.707 -0.259
10
150 0.5 -0.866 -0.500
SINE
(Angle)*
0.0 0.0 1.0 0.866
15 0.259 0.965 0.966
30 0.5 0.866 1.0
45 0.707 0.707 0.966
60 0.866 0.5 0.866
75 0.966 0.259 0.707
90 1.0 0.0 0.500
COS (Angle -30)*
PE6=0
COS (Angle -30)*
PE6=1
Analog Integrated Circuit Device Data
12 Freescale Semiconductor
 Loading...
Loading...