Freedom9 2420 User Manual
freeConnect Smart 2420
24-Port 10/100Mbps + 2-Port Combo-SFP
Web Smart Switch
USER’S MANUAL
P/N: S102411200
Rev. 1.0

Copyright and Trademark Information
Freedom9 makes no warranty or representation, expressed or implied, with respect to the
contents or use of this documentation. Freedom9 reserves the right to modify this
documentation at any time without obligation to notify any individual or entity of such
modifications.
© Copyright 2006, freeConnect Smart and the freedom9 company logo are trademarks or
registered trademarks of Freedom9 Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this document may be
photocopied, reproduced, or translated into another language without express prior to written
consent of Freedom9 Inc. Windows is a trademark or registered trademark of Microsoft
Corporation. Other trademarks or registered trademarks are the property of their respective
holders.

TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 ABOUT THIS GUIDE........................................................................................................................... 1
1.1 PURPOSE ....................................................................................................................................... 1
1.2 TERMS/USAGE ............................................................................................................................... 1
2 INTRODUCTION ................................................................................................................................. 2
2.1 GIGABIT ETHERNET TECHNOLOGY................................................................................................... 2
2.2 FAST ETHERNET TECHNOLOGY........................................................................................................ 2
2.3 VLAN (VIRTUAL LOCAL AREA NETWORK)......................................................................................... 2
2.4 FEATURES...................................................................................................................................... 3
3 UNPACKING AND INSTALLATION.................................................................................................... 4
3.1 UNPACKING .................................................................................................................................... 4
3.2 INSTALLATION ................................................................................................................................. 4
3.3 RACK MOUNTING ............................................................................................................................ 4
3.4 CONNECTING NETWORK CABLE....................................................................................................... 5
3.5 AC POWER .................................................................................................................................... 5
4 IDENTIFYING EXTERNAL COMPONENTS....................................................................................... 6
4.1 FRONT PANEL................................................................................................................................. 6
4.2 REAR PANEL .................................................................................................................................. 6
5 UNDERSTANDING LED INDICATORS .............................................................................................. 8
5.1 POWER AND SYSTEM LEDS ............................................................................................................ 8
5.2 PORTS 1~24 STATU S LEDS ............................................................................................................ 8
5.3 PORTS 25~26 STATU S LEDS .......................................................................................................... 8
6 CONFIGURATION............................................................................................................................. 10
6.1 INSTALLING THE WEB MANAGEMENT UTILITY.................................................................................. 10
6.2 DISCOVERY LIST........................................................................................................................... 10
6.3 MONITOR LIST ...............................................................................................................................11
6.4 DEVICE SETTING .......................................................................................................................... 12
6.5 TOOLBAR ..................................................................................................................................... 13
6.6 CONFIGURING THE SWITCH ........................................................................................................... 14
6.7 LOGIN .......................................................................................................................................... 14
6.8 MAIN MENU.................................................................................................................................. 16
6.9 CONFIGURING SETUP SETTING...................................................................................................... 16
6.10 MAINTENANCE SETTINGS .............................................................................................................. 21
6.11 LOGOUT ....................................................................................................................................... 23
7 TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS ....................................................................................................... 24
8 CERTIFICATIONS ............................................................................................................................. 25

freeConnect Smart 2420 User’s Manual
1 About This Guide
Thank you for purchasing the freeConnect Smart 2420. This device integrates 1000Mbps Gigabit
Ethernet, 100Mbps Fast Ethernet and 10Mbps Ethernet network capabilities in a highly flexible
package.
1.1 Purpose
This guide discusses how to install your freeConnect Smart 2420.
1.2 Terms/Usage
In this guide, the term “Switch” (first letter upper case) refers to your freeConnect Smart 2420, and
“switch” (first letter lower case) refers to Ethernet switches in general.
1

2 Introduction
This chapter describes the features of the freeConnect Smart 2420 and some background information
about Ethernet/Fast Ethernet/Gigabit Ethernet switching technology.
2.1 Gigabit Ethernet Technology
Gigabit Ethernet is an extension of IEEE 802.3 Ethernet utilizing the same packet structure, format,
and support for CSMA/CD protocol, full duplex, flow control, and management objects, but with a
tenfold increase in theoretical throughput over 100-Mbps Fast Ethernet and a hundredfold increase
over 10-Mbps Ethernet. Since it is compatible with all 10-Mbps and 100-Mbps Ethernet environments,
Gigabit Ethernet provides a straightforward upgrade without wasting a company’s existing investment
in hardware, software, and trained personnel.
The increased speed and extra bandwidth offered by Gigabit Ethernet is essential to coping with the
network bottlenecks that frequently develop as computers and their busses get faster and more users
use applications that generate more traffic. Upgrading key components, such as your backbone and
servers to Gigabit Ethernet can greatly improve network response times as well as significantly speed
up the traffic between your subnets.
Gigabit Ethernet enables fast optical fiber connections to support video conferencing, complex
imaging, and similar data-intensive applications. Likewise, since data transfers occur 10 times faster
than Fast Ethernet, servers outfitted with Gigabit Ethernet NIC’s are able to perform 10 times the
number of operations in the same amount of time.
In addition, the phenomenal bandwidth delivered by Gigabit Ethernet is the most cost-effective method
to take advantage of today’s and tomorrow’s rapidly improving switching and routing internetworking
technologies.
2.2 Fast Ethernet Technology
The growing importance of LANs and the increasing complexity of desktop computing applications are
fueling the need for high performance networks. A number of high-speed LAN technologies have
been proposed to provide greater bandwidth and improve client/server response times. Among them,
100BASE-T (Fast Ethernet) provides a non-disruptive, smooth evolution from the current 10BASE-T
technology. The non-disruptive and smooth evolution nature, and the large installed market base,
virtually guarantees cost-effective and high performance Fast Ethernet solutions.
100Mbps Fast Ethernet is a standard specified by the IEEE 802.3 LAN committee. It is an extension of
the 10Mbps Ethernet standard with the ability to transmit and receive data at 100Mbps, while
maintaining the CSMA/CD Ethernet protocol. Since the 100Mbps Fast Ethernet is compatible with all
other 10Mbps Ethernet environments, it provides a straightforward upgrade and takes advantage of
the existing investment in hardware, software, and personnel training.
2.3 VLAN (Virtual Local Area Network)
A VLAN is a group of end-stations that are not constrained by their physical location and can
communicate as if a common broadcast domain, a LAN. The primary utility of using VLAN is to
reduce latency and need for routers, using faster switching instead. Other VLAN uses include:
Security: Security is increased with the reduction of opportunity in eavesdropping on a broadcast
network because data will be switched to only the users within the same VLAN.

freeConnect Smart 2420 User’s Manual
Cost Reduction: VLANs can be used to create multiple broadcast domains, thus eliminating the need
of expensive routers.
Port-based (or port-group) VLAN is the common method of implementing a VLAN, and is the one
supplied in the Switch.
2.4 Features
• 24x10/100Mbps Auto-negotiation Fast Ethernet ports
• 2x10/100/1000Mbps Auto-negotiation Gigabit Ethernet ports
• 2xmini-GBIC (shared with two Gigabit Ethernet ports)
• All RJ45 ports support auto MDI/MDIX, so there is no need to use cross-over cables or an up-link
port
• Half duplex transfer mode for connection speed 10Mbps and 100Mbps
• Full duplex transfer mode for connection speed of 10Mbps, 100Mbps and 1000Mbsps
• Wire speed reception and transmission
• Store-and-Forward switching scheme capability to support rate adaptation and ensure data
integrity
• Up to 8k unicast addresses entities per device, self-learning, and table aging
• 2Mbits packet buffer
• Supports IEEE 802.3x flow control for full-duplex mode ports
• Supports Port-based VLAN
• Supports Port-based QoS / IEEE 802.1P based QoS
• Supports Port-based Trunking
• Supports Port-Mirroring
• Supports Port-setting for Speed/Disable, Flow control
• Easy configuration via Web Browser
• Easy setting via Web Management Utility
• Standard 19” Rack-mount size
3

3 Unpacking and Installation
This chapter provides unpacking and installation information for the Switch.
3.1 Unpacking
Open the box and carefully unpacks its contents. The box should contain the following items:
• One freeConnect Smart 2420
• One AC power cord, suitable for your area’s electrical power connections
• Four rubber feet to be used for shock cushioning
• Screws and two mounting brackets
• CD-ROM with Web Management Utility and User’s Guide
If any item is found missing or damaged, please contact your local reseller for replacement.
3.2 Installation
The site where you install the hub stack may greatly affect its performance. When installing the unit,
consider the following pointers:
• Install the Switch in a fairly cool and dry place. See Technical Specifications for the acceptable
temperature and humidity operating ranges.
• Install the Switch in a site free from strong electromagnetic field generators (such as motors),
vibration, dust, and direct exposure to sunlight.
• Leave at least 4” (10cm) of space at the front and rear of the Switch for ventilation.
• Install the Switch on a sturdy, level surface that can support its weight, or in an EIA standard-size
equipment rack. For information on rack installation, see the next section, Rack Mounting.
• When installing the Switch on a level surface, attach the rubber feet to the bottom of each device.
The rubber feet cushion the Switch and protect the case and surface from scratching.
3.3 Rack Mounting
The Switch can be mounted in an EIA standard-size, 19-inch rack, which can be placed in a wiring
closet with other equipment. Attach the mounting brackets to the switch’s front panel (one on each
side), and secure them with the screws provided (Figure 1).
Figure 1: Attach the brackets to the Switch
Then, use the screws provided with the rack to mount each switch in the rack (Figure 2).

freeConnect Smart 2420 User’s Manual
Figure 2: Mount the Switch in the rack
3.4 Connecting Network Cable
The Switch supports 1000Mbs Gigabit Ethernet that runs in Auto-negotiation mode and 10Mbps
Ethernet or 100Mbps Fast Ethernet that runs both in half and full duplex mode and 1000Mbps Gigabit
Ethernet runs in full duplex mode using four pair of Category 5 Cable (Category 5e Cable or better is
required for Gigabit Ethernet).
These RJ-45 ports support Auto-MDIX meaning that the Switch can automatically switch between
MDI-II and MDI-X types, allowing you to use any cable without worrying about whether it is a straightthrough or crossover RJ-45 cable.
3.5 AC Power
The Switch uses an AC power supply operating at 100-240V AC, 50-60 Hz. The power switch is
located at the rear of the unit adjacent to the AC power connector and the system fan. The switch’s
power supply will adjust to the local power source automatically and the unit can be turned on any
number of Ethernet cable connected to it.
5
4 Identifying External Components
This chapter describes the front panel, rear panel, and LED indicators of the Switch.
4.1 Front Panel
The figure below (Figure 3) shows the front panels of the Switch.
Figure 3: Front panel of the Switch
LED Indicator:
Comprehensive LED indicators display the status of the switch and the network (see the LED
Indicators section below).
Fast Ethernet Ports (Port 1~24):
These ports support network speeds of 10Mbps and 100Mbps, and can operate in half- and full-duplex
transfer modes. These ports also support automatic MDI/MDIX crossover functionality providing true
“plug and play” capability. You only have to a device to the switch using a straight-through cable,
regardless of whether the device is a computer, switch and hub.
Gigabit Ethernet Ports (Port 25~26):
The Switch is equipped with two Gigabit twisted pair ports, supported auto negotiable
10/100/1000Mbps and auto MDI/MDIX crossover detection function. These two ports can operate in
half-duplex mode for 10/100Mbps and full-duplex mode for 10/100/1000Mbps.
Mini-GBIC Ports (Port 25~26):
The Switch is equipped with two mini-GBIC ports, supporting standard fiber mini-GBIC modules.
These ports use the same ports as the gigabit Ethernet ports. When a mini-GBIC module is plugged
into the switch, the corresponding gigabit Ethernet port will be disabled.
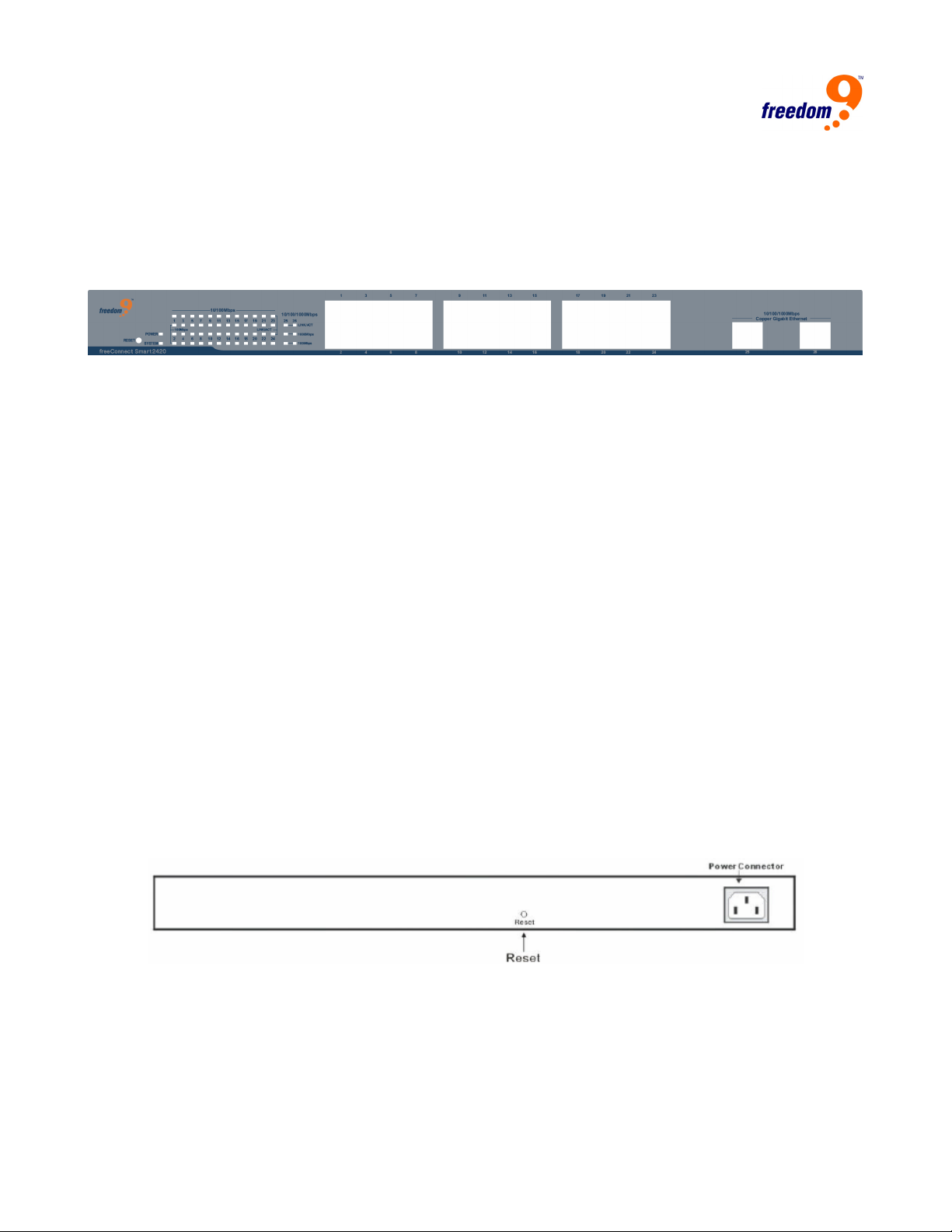
4.2 Rear Panel
Figure 4: Rear panel of the Switch
AC Power Connector:
This is a three-pronged connector that supports the power cord. Plug in the female connector of the
provided power cord into this connector, and the male into a power outlet. Supported input voltage
range is 100-240V AC at 50-60Hz.
 Loading...
Loading...