
SGA10GD
Dual 10Gbps PCI Expressx8
Ethernet adapter
REFERENCE MANUAL
Ver.: 2009.09.29., Ver. 1.1
(C) BUDAPEST UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY AND ECONOMICS
DEPARTMENT OF TELECOMMUNICATIONS AND MEDIA
INFORMATICS
1

Contents
Contents...........................................................................................................................................................................................2
1. Introduction..................................................................................................................................................................................3
1.1 What is SGA10GD?...............................................................................................................................................................3
1.2 What is on-board?..................................................................................................................................................................3
1.3 Conformity.............................................................................................................................................................................4
2. Architecture..................................................................................................................................................................................5
2.1 Power Supply.........................................................................................................................................................................6
2.2 Clock sources.........................................................................................................................................................................7
2.3 Dual XFPs for 10Gbps Ethernet............................................................................................................................................8
2.4 PCI Express x8 endpoint......................................................................................................................................................10
2.5 DDR2 SODIMM RAM........................................................................................................................................................12
2.6 Feature Connector................................................................................................................................................................14
2.7 FPGA Programming.............................................................................................................................................................16
2.7.1 Programming through JTAG.........................................................................................................................................16
2.7.2 Programming from FLASH..........................................................................................................................................16
2.7.3 Partial reconfiguration...................................................................................................................................................17
2.8 Status LEDs.........................................................................................................................................................................17
4. FPGA test Cores.........................................................................................................................................................................18
4.1 PCIEX4 - Endpoint Block for PCI Express v. 1.6...............................................................................................................18
4.2 XAUI v. 8.1..........................................................................................................................................................................18
4.3 DDR2 - MIG v. 2.0 generated SODIMM teszt core............................................................................................................18
4.4 Clock domains......................................................................................................................................................................19
2
1. Introduction
1.1 What is SGA10GD?
SGA10GD is a PCI-Express x8 adapter card, primarily developed for 10Gbits
Ethernet network monitoring. It's on-board resources, and reconfigurability of its
FPGA extends its functionality beyond the 10G application,
1.2 What is on-board?
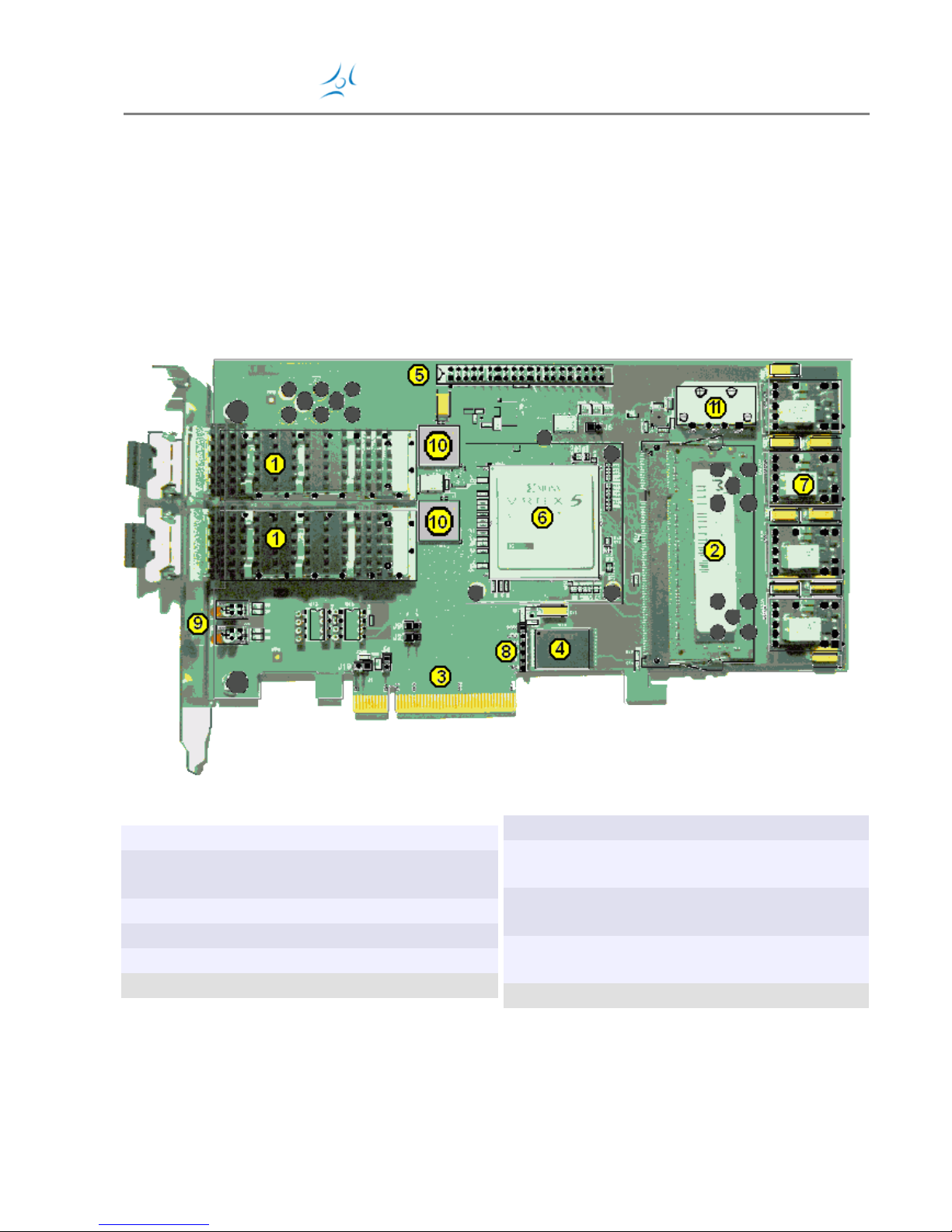
The figures below show the major on-board components.
Top side components:
1: Dual 10 Gigabit/sec XFP receptacle
2:
DDR2 RAM SODIMM Receptacle 1.8V
(Notebook RAM)
3: PCI Express x8 Edge Connector
4: Platform FLASH with initial FPGA core
5: 40 pin Berg type Feature Connector
10: XAUI/XFI converters
6: Xilinx Virtex-5 family FPGA device
7:
Switching regulators for 1.0, 1.8, 2.5,
3.3 Volts
8:
JTAG connector for programming the
FPGA or Flash
9:
Interface status LED's, RED/GREEN
pairs
11: Power connector
3

1.3 Conformity
SGA10GD aims the following Standards/Recommendations:
XFP 10 Gigabit Small Form Factor Pluggable Module
SFF Committee INF-8077i 10 Gigabit Small Form Factor Pluggable Module
...GBE Gigabit Ethernet (Optical/Copper)
IEEE Std 802.3 Carrier sense multiple access with collision detection
(CSMA/CD) access method and physical layer specifications
PCIE PCI Express
PCI-SIG PCI Express Base Specification Revision 1.0a
PCI-SIG PCI Express Card Electromechanical Specification Revision 1.0a
DDR2 Dual DataRate II. SDRAM and Modules
JEDEC JESD79-2D DDR2 SDRAM SPECIFICATION
JEDEC No.21C 4.20.11 200-Pin DDR2 SDRAM Unbuffered SODIMM Design
Specification. (Item #2017.10) Release No. 17
FC 40 pin Feature Connector
...PDH
ITU-T G.703 Physical/electrical characteristics of hierarchical digital interfaces
(.9 with passive feature card)
...HDD
NCITS 361-2002 AT Attachment with Packet Interface - 6
(ATA/ATAPI-6/UDMA5/UDMA100/UATA100 interface)
4
2. Architecture
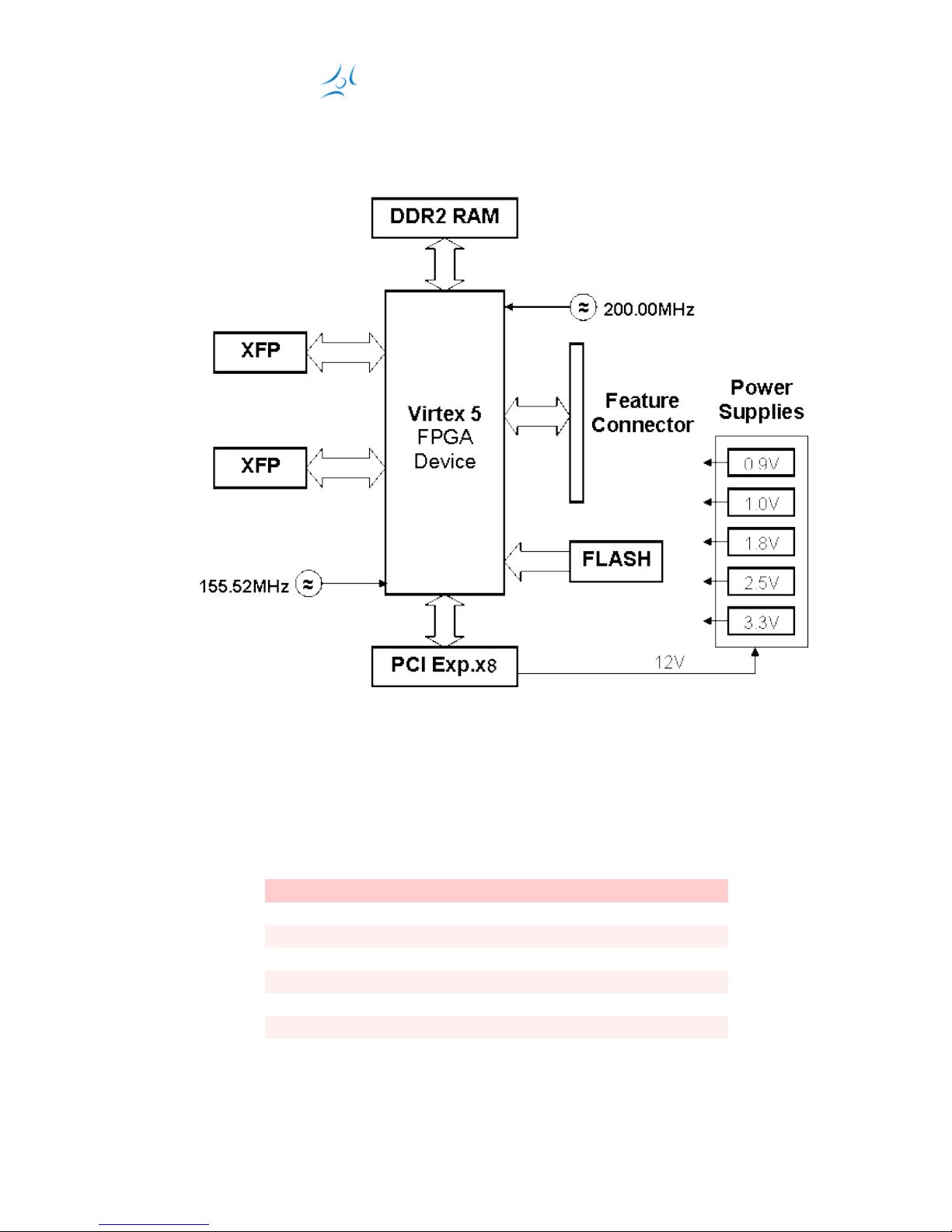
The simple and robust architecture of SGA10GD is shown on the block diagram
below.
The heart of the board is a Xilinx Virtex-5 family FPGA device.
The PCB can accomodate two types of devices:
XC5VLX110T-2FF1136C (for SGA10GD board)
XC5VLX50T-1FF1136C (for SGA10GDL board)
The main characteristics of the devices are shown in the table below:
XC5VLX110TXC5VLX50T
Array metric 160x54 120x30
Slices 17280 7200
LUT RAM 1120 kBytes 480 kBytes
Block RAM 5.32 MBytes 2.16 MBytes
DSP slices 64 48
GTP Transceivers 16 (8 pairs) 12 (6 pairs)
Clock Management Tiles8 6
5
In addition, both types have
Clock Management Tiles (CMTs) having two Digital Clock Managers (DCM)
and a Phase Locked Loop per CMT
One PCI Express Endpoint Controller
4 Tri-mode (10/100/1000)Ethernet Media Access Controller (MAC)
2 Internal Configuration Acces Ports (ICAP)
Core logic can run at 550MHz internal clock speed
Two SGA10GD models can be produced depending on the insertion of FPGA type as
shown below:
Model FPGA
SGA10GD XC5VLX110T
SGA10GDLXC5VLX50T
The following sections detail the rest of the board's architectual elements.
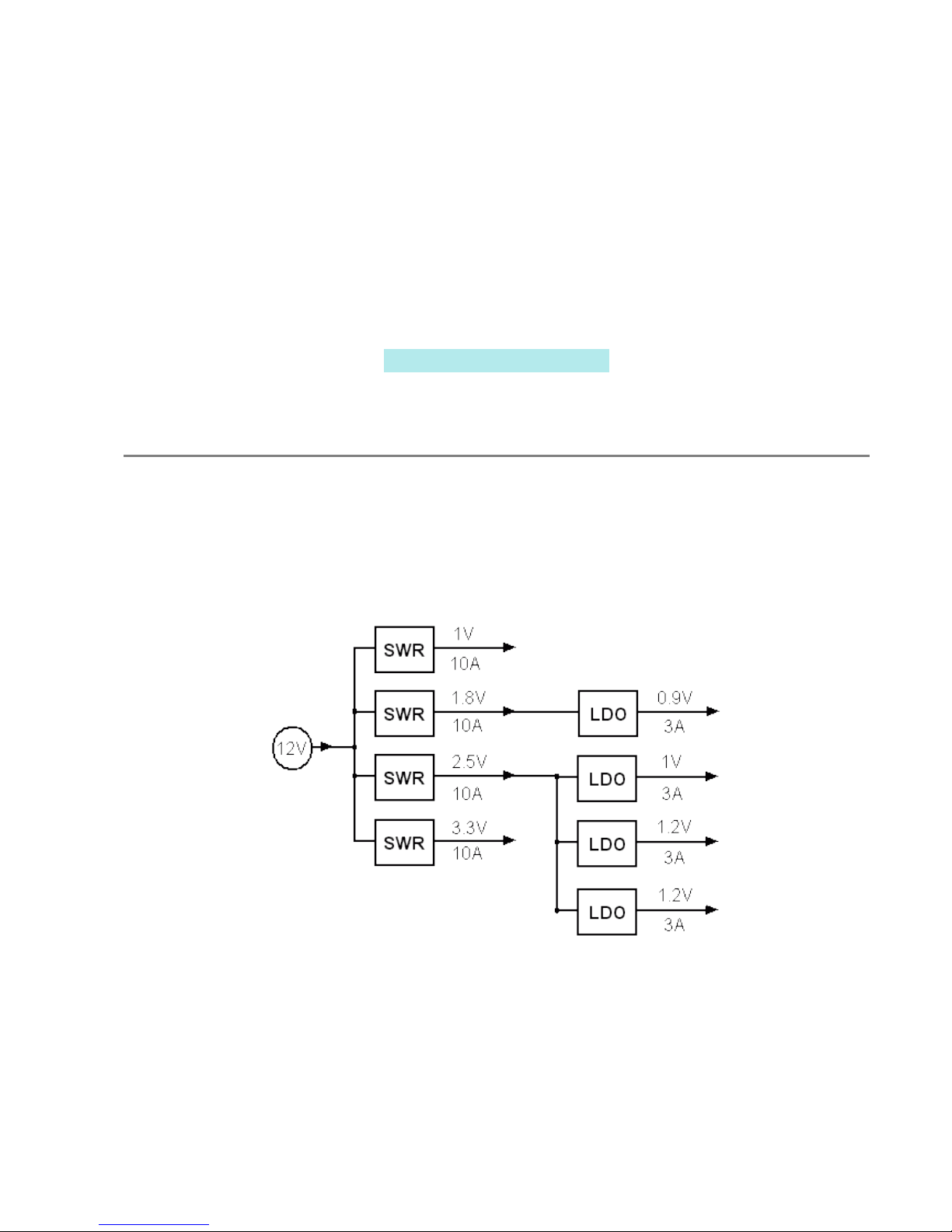
2.1 Power Supply
The figure below shows the power distribution tree for SGA10GD.
The first stages consist of switching regulator modules (SWR), since on second
stages there are low drop-out (LDO) point of load (POL) type regulators.
6

The signal names, nominal voltages, maximum load current, and designated targets
are the following:
Signal name V A Targets Notes
VCC1 1.010FPGA Core voltage
VCC1V8 1.810DDR2 RAM Main supply
. . LDO Feed for DDR2 Ref.
. . FPGA I/O Bank 11,13,15,17,(19,21)
. . FLASH Internal voltage
VCC2V5 2.510LDO Feed For MGT LDOs
. . FPGA Auxiliary voltage
. . XFP/XAUI Auxiliary voltage
VCC3V3 3.310XFPs .
. . FPGA I/O Bank 20,1,3,0,2,4,(12,5,23,18,6,25)
. . Feature Conn.for I/O std. only
. . FLASH/JTAG I/O voltage
. . DDR2 Supply SPD ROM
VCC0V9 0.93 DDR2 Reference voltage
AVCC1 1.03 FPGA MGT MGT's core voltage
AVCPLL1V2 1.23 FPGA MGT MGT's PLL supply
VCC5 5 . XFP aux. XPF aux. power
VCC1V2 1.222XFP/XAUI XFP/XAUI converter Main supply
2.2 Clock sources
There are three clock sources available on SGA10GD for the FPGA cores. The
following tables shows their name, nominal frequencies, designated FPGA pins, and
their application.
Signal f [MHz]FPGA# Application
GCLKN 200.00 L18 System/Global Clock, and
GCLKP (XO) K17 DDR2 reference clock
REF2CKN *156.25 H3 XFP Gigabit Ethernet App.
REF2CKP (XO) H4
GT3RCKN *100.00 Y3 PCI Express Hosts reference
GT3RCKP - Y4 .
* These clock references are routed to MGT clock pins.
XO designates LVPECL Crystal Oscillators.
7

2.3 Dual XFPs for 10Gbps Ethernet
The SGA10GD board has two XFP module cages (P1,P2) that support user-installed
XFP modules for Gigabit Ethernet (10Gbps) interfaces.
Dedicated 156.25 MHz reference clock source is available for FPGA reference, and
and other XO reference for XAUI/XFI converter chips.
The SGA10GD board provides filtered 1,8V, 3.3V, 5V, power to both XFP modules as
per the XFP specification.
The table below lists the connectors pins and any associated FPGA connectivity.
Status LED's are also listed here.
Signal (P1) XFP#FPGA# Signal (P2) XFP#FPGA#
HSTDP[0] 029 G12 * HSTDP[1] 029 G12 *
HSTDN[0] 028 F12 * HSTDN[1] 028 F12 *
HSRDP[0] 018 C12 * HSRDP[1] 018 C12 *
HSRDN[0] 017 B12 * HSRDN[1] 017 B12 *
HSTCLKP[0]024 G12 * HSTCLKP[1]024 G12 *
HSTCLKN[0]025 F12 * HSTCLKN[1]025 F12 *
GND 001 - GND 001 GND 007 - GND 007 GND 015 - GND 015 GND 016 - GND 016 GND 019 - GND 019 GND 023 - GND 023 GND 026 - GND 026 GND 027 - GND 027 GND 030 - GND 030 VCC5 006 - VCC5 006 VCC3V3 008 - VCC3V3 008 VCC3V3 009 - VCC3V3 009 VCC1V8 020 - VCC1V8 020 VCC1V8 022 - VCC1V8 022 XINTN[0] 004 E13 XINTN[1] 004 D11
XTXDIS[0] 005 G12 XTXDIS[1] 005 E11
XSCSN[0] 003 E12 XSCSN[1] 003 D10
XSCLK 010 D12 010
XSDIO 011 B12 011
XPLUGN[0] 012 C13 XPLUGN[1] 012 F9
XLOS[0] 014 B13 XLOS[1] 014 E8
XNRDY[0] 013 C12 XNRDY[1] 013 E9
LEDACTN[0]- G13 LEDACTN[1]- G11
LEDLOSN[0]- F13 LEDLOSN[1]- F11
* Routed to the XFAUI/XFI converters U12, U14
8

The table below lists the XAUI/XFI converter vs. FPGA connectivity.
Common Signal Function FPGA#
PRTAD[0] Port base address 0AJ11
PRTAD[1] Port base address 1AP12
PRTAD[2] Port base address 2AK11
PRTAD[3] Port base address 3AN12
PRTAD[4] Port base address 4AM11
U12 Signals Function FPGA# U14 Signals Function FPGA#
TRSTN[0] Reset (active low) AN14 TRSTN[1] Reset (active low) AF11
MDIO[0] MDIO data AM13 MDIO[1] MDIO data AL10
MDC[0] MDIO clock AM12 MDC[1] MDIO clock AJ10
CDRLOL[0] Loss of Lock in CDR AP14 CDRLOL[1] Loss of Lock in CDR AE11
CMULOL[0] Loss of Lock in CMUAN13 CMULOL[1] Loss of Lock in CMUAH10
TTXON[0] TX enable AL11 TTXON[1] TX enable AG11
RXDP[0][0] XAUI RX lane 0 D1 RXDP[1][0] XAUI RX lane 0 T1
RXDN[0][0] C1 RXDN[1][0] R1
RXDP[0][1] XAUI RX lane 1 A3 RXDP[1][1] XAUI RX lane 1 N1
RXDN[0][1] A2 RXDN[1][1] P1
RXDP[0][2] XAUI RX lane 2 A6 RXDP[1][2] XAUI RX lane 2 K1
RXDN[0][2] A7 RXDN[1][2] J1
RXDP[0][3] XAUI RX lane 3 A9 RXDP[1][3] XAUI RX lane 3 G1
RXDN[0][3] A8 RXDN[1][3] H1
TXDP[0][0] XAUI TX lane 0 E2 TXDP[1][0] XAUI TX lane 0 U2
TXDN[0][0] D2 TXDN[1][0] T2
TXDP[0][1] XAUI TX lane 1 B4 TXDP[1][1] XAUI TX lane 1 M2
TXDN[0][1] B3 TXDN[1][1] N2
TXDP[0][2] XAUI TX lane 2 B5 TXDP[1][2] XAUI TX lane 2 L2
TXDN[0][2] B6 TXDN[1][2] K2
TXDP[0][3] XAUI TX lane 3 B10 TXDP[1][3] XAUI TX lane 3 F2
TXDN[0][3] B9 TXDN[1][3] G2
* RXPOLARITY attribute for the MGT has to be changed
** TXPOLARITY attribute for the MGT has to be changed
9

2.4 PCI Express x8 endpoint
The PCI Express endpoint connector (designated as J1 on-board) allows an FPGA
design to support x1, x4 and x8 gigabit lanes to communicate with the host, at the
speed of 2.5 Gbps of each.
Caution! There are jumpers - designated as J2, J9 - on board to select the proper
presence detect lane configuration (close J2 for x4, plus close J9 for x8) for the
actual design.
The table below lists the connectors pins and any associated FPGA connectivity.
Signal (P1) Side A FPGA# Signal (P2) Side B FPGA#
PRESENT_NA1 - +12 VOLTS B1 To PWR
+12 VOLTS A2 To PWR +12 VOLTS B2 To PWR
+12 VOLTS A3 To PWR +12 VOLTS B3 To PWR
GND A4 - GND B4 JTAG_TCK A5 - SMCLK B5 JTAG_TDI A6 - SMDAT B6 JTAG_TDO A7 - GND B7 JTAG_TMS A8 - +3.3 VOLTS B8 +3.3 VOLTS A9 - JTAG_TRST_N B9 +3.3 VOLTS A10 - +3.3 VAUX B10 PXPERST A11 - PCIE_WAKE_NB11 KEY KEY KEY KEY KEY KEY
GND A12 - RESERVED B12 PXCLKP A13 Y4 GND B13 PXCLKN A14 Y3 PETP0 B14 W1
GND A15 - PETN0 B15 Y1
PERP0 A16 V2 GND B16 PERN0 A17 W2 PRESENT_N B17 GND A18 - GND B18 RESERVED A19 - PETP1 B19 AA1 **
GND A20 - PETN1 B20 AB1
PERP1 A21 AB2 * GND B21 PERN1 A22 AC2 GND B22 GND A23 - PETP2 B23 AE1
GND A24 - PETN2 B24 AF1
PERP2 A25 AD2 GND B25 PERN2 A26 AE2 GND B26 GND A27 - PETP3 B27 AG1 **
GND A28 - PETN3 B28 AH1
PERP3 A29 AH2 * GND B29 PERN3 A30 AJ2 --- B30 GND A31 - PRESENT4_N B31 To J2
--- --- - GND B32 -
--- --- - PETP4 B33 AL1
GND A34 - PETN4 B34 AM1
PERP4 A35 AK2 GND B35 PERN4 A36 AL2 GND B36 GND A37 - PETP5 B37 AP2 **
10

GND A38 - PETN5 B38 AP3
PERP5 A39 AN3 * GND B39 PERN5 A40 AN4 GND B40 GND A41 - PETP6 B41 AP6
GND A42 - PETN6 B42 Ap7
PERP6 A43 AN5 GND B43 PERN6 A44 AN6 GND B44 GND A45 - PETP7 B45 AP8 **
GND A46 - PETN7 B46 AP9
PERP7 A47 AN9 * GND B47 PERN7 A48 AN10 PRESENT8_N B48 To J9
GND A49 - GND B49 -
* RXPOLARITY attribute for the MGT has to be changed
** TXPOLARITY attribute for the MGT has to be changed
Although the PCI identification codes are FPGA core dependeant, defaults are the
following:
Vendor ID........ 15C6 ..... Technical University of
Budapest
Device ID........ 106D ..... SGA10GD dual 10Gbps Ethernet
adapter
Revision ID...... 1 ..... Rev. 1. (SGA10GD)
Base Class....... 02 ..... Network controller
Sub-Class........ 80 ..... Other network controller
Interface........ 0 ..... Base model, XC5VLX110T
Interface........ 1 ..... Lite model, XC5VLX50T
11

2.5 DDR2 SODIMM RAM
The SGA10GD board contains a 200-pin, small-outline dual in-line memory module
(SODIMM) receptacle ( J3 ) that supports installation of DDR2 SDRAM SODIMMs of
128MB, 256MB, or 512 MB.
Dual-rank SODIMMs may not be supported. Also, the speed grade of -1 of the default
FPGA installation limits the DDR2 memory clock support to a range of 200-233MHz
(400-466 million transfers per second - double rate).
A 256MB DDR2-667 SODIMM (Micron Semiconductor part number MT4HTF3264HY667D3) is shipped with SGA10GD - by default.
The SODIMM interface may support customer installation of DDR2-533 and/or
DDR2-400 SODIMMs too.
The table below provides a description of the memory interface signals SODIMM
connector pin assignments, and the associated FPGA pin assignments.
Signal (Front)DIMM#FPGA# Signal (Back)DIMM#FPGA#
VCC0V9 001 - GND 002 GND 003 - DQ[4] 004 H29
DQ[0] 005 L29 DQ[5] 006 G30
DQ[1] 007 J29 GND 008 GND 009 - DM[0] 010 H30
DQS_N[0] 011 F29 GND 012 DQS[0] 013 E29 DQ[6] 014 F30
GND 015 - DQ[7] 016 G31
DQ[2] 017 P29 GND 018 DQ[3] 019 P30 DQ[12] 020 L30
GND 021 - DQ[13] 022 K31
DQ[8] 023 F31 GND 024 DQ[9] 025 E31 DM[1] 026 J31
GND 027 - GND 028 DQS_N[1] 029 N30 CK[0] 030 B32
DQS[1] 031 M31 CK_N[0] 032 A33
GND 033 - GND 034 DQ[10] 035 P31 DQ[14] 036 M30
DQ[11] 037 R31 DQ[15] 038 N29
GND 039 - GND 040 GND 041 - GND 042 DQ[16] 043 B33 DQ[20] 044 C34
DQ[17] 045 C33 DQ[21] 046 D34
GND 047 - GND 048 DQS_N[2] 049 E34 NC/EVENT_N050 DQS[2] 051 F33 DM[2] 052 E33
GND 053 - GND 054 DQ[18] 055 F34 DQ[22] 056 C32
DQ[19] 057 E32 DQ[23] 058 D32
GND 059 - GND 060 DQ[24] 061 H34 DQ[28] 062 G33
12

DQ[25] 063 H33 DQ[29] 064 G32
GND 065 - GND 066 DM[3] 067 J34 DQS_N[3] 068 K34
NC/RESET_N 069 - DQS[3] 070 L34
GND 071 - GND 072 DQ[26] 073 K32 DQ[30] 074 J32
DQ[27] 075 L33 DQ[31] 076 K33
GND 077 - GND 078 CKE[0] 079 N32 CKE[1] 080 M32
VCC1V8 081 - VCC1V8 082 NC/CSN[2] 083 - A[15] 084 R32
BA[2] 085 P32 A[14] 086 R33
VCC1V8 087 - VCC1V8 088 A[12] 089 U31 A[11] 090 T33
A[9] 091 P34 A[7] 092 U32
A[8] 093 V25 A[6] 094 U33
VCC1V8 095 - VCC1V8 096 A[5] 097 W29 A[4] 098 Y28
A[3] 099 R34 A[2] 100 V29
A[1] 101 V24 A[0] 102 AA30
VCC1V8 103 - VCC1V8 104 A[10] 105 W26 BA[1] 106 W31
BA[0] 107 V27 RAS_N 108 AA31
WE_N 109 V28 CS_N[0] 110 Y31
VCC1V8 111 - VCC1V8 112 CAS_N 113 Y29 ODT[0] 114 T34
CS_N[1] 115 AA29 A[13] 116 AB31
VCC1V8 117 - VCC1V8 118 ODT[1] 119 V30 NC/CSN[3] 120 GND 121 - GND 122 DQ[32] 123 V32 DQ[36] 124 Y33
DQ[33] 125 V33 DQ[37] 126 Y32
GND 127 - GND 128 DQS_N[4] 129 V34 DM[4] 130 AB32
DQS[4] 131 W34 GND 132 GND 133 - DQ[38] 134 Y34
DQ[34] 135 AA33 DQ[39] 136 AA34
DQ[35] 137 AB33 GND 138 GND 139 - DQ[44] 140 AD32
DQ[40] 141 AC32 DQ[45] 142 AK32
DQ[41] 143 AC33 GND 144 GND 145 - DQS_N[5] 146 AD34
DM[5] 147 AE33 DQS[5] 148 AC34
GND 149 - GND 150 DQ[42] 151 AE32 DQ[46] 152 AF33
DQ[43] 153 AE34 DQ[47] 154 AF34
GND 155 - GND 156 DQ[48] 157 AH34 DQ[52] 158 AM33
DQ[49] 159 AJ34 DQ[53] 160 AK34
GND 161 - GND 162 -
13

NC/TEST 163 - CK[1] 164 AN34
GND 165 - CK_N[1] 166 AN33
DQS_N[6] 167 AL33 GND 168 DQS[6] 169 AL34 DM[6] 170 AN32
GND 171 - GND 172 DQ[50] 173 AK33 DQ[54] 174 AP32
DQ[51] 175 AJ32 DQ[55] 176 AM32
GND 177 - GND 178 DQ[56] 179 AF31 DQ[60] 180 AK31
DQ[57] 181 AG30 DQ[61] 182 AD30
GND 183 - GND 184 DM[7] 185 AF30 DQS_N[7] 186 AH30
GND 187 - DQS[7] 188 AJ30
DQ[58] 189 AD29 GND 190 DQ[59] 191 AE29 DQ[62] 192 AH29
GND 193 - DQ[63] 194 AF29
SDA 195 AH19 GND 196 SCL 197 AF19 SA0 198 (GND)
VCC3V3 199 - SA1 200 (GND)
2.6 Feature Connector
Mainly for historical reason, a 40 pins BERG type Feature Connector ( designated as
J5 ) is used for SGA10GD.
The table below shows the pinout assignment for FPGA cores implementing
IDE/HDD applications.
Signal (even)J5#FPGA#.Signal (odd)J5#FPGA#
FRST 01 H14 GND 02 FD[7] 03 J14 FD[8] 04 H20
FD[6] 05 K14 FD[9] 06 J20
FD[5] 07 L14 FD[10] 08 L20
FD[4] 09 G15 FD[11] 10 J21
FD[3] 11 H15 FD[12] 12 K21
FD[2] 13 J15 FD[13] 14 L21
FD[1] 15 L15 FD[14] 16 G22
FD[0] 17 G16 FD[15] 18 H22
GND 19 - FKEY 20 J22
FDRQ 21 J16 GND 22 FIOWN 23 K16 GND 24 FIORN 25 L16 GND 26 FIORDY 27 H17 FBALE 28 K22
FDACKN 29 J17 GND 30 FIRQ 31 H18 FIOCSN 32 G23
FA[1] 33 K18 GND 34 FA[0] 35 H19 FA[2] 36 H23
FCSN[0] 37 J19 FCSN[1] 38 L19
FACT 39 K19 GND 40 -
14

For PDH applications, a passive child board (type D1558001-LIU) has to be
connected to J5. The pinout can be found in the table below.
Signal (even)J5#FPGA#.Signal (odd)J5#FPGA#
NC 01 H14 GND 02 TTXA[0] 03 J14 TTXB[0] 04 H20
RTXA[0] 05 K14 TTXB[0] 06 J20
TTXA[1] 07 L14 TTXA[1] 08 L20
RTXA[1] 09 G15 RTXA[1] 10 J21
TTXA[2] 11 H15 TTXA[2] 12 K21
RTXA[2] 13 J15 RTXA[2] 14 L21
TTXA[3] 15 L15 TTXA[3] 16 G22
RTXA[3] 17 G16 RTXA[3] 18 H22
GND 19 - NC 20 J22
TRX[0] 21 J16 GND 22 NC 23 K16 GND 24 RRX[0] 25 L16 GND 26 NC 27 H17 NC 28 K22
RRX[1] 29 J17 GND 30 TRX[1] 31 H18 NC 32 G23
TRX[2] 33 K18 GND 34 RRX[2] 35 H19 NC 36 H23
TRX[3] 37 J19 NC 38 L19
RRX[3] 39 K19 GND 40 -
TTX signals drives the TIP side pulses, RTX signals drives RING.
RRX and TRX signals carry received pulses (RING and TIP).
Note that TTXA and TTXB signals are bound together on the child board to achive
the 3 volts peak voltage of the transmitted pulses. (conforming ITU-T Rec. G.703)
Crosscurrent glitches are limited by serial resistors on SGA10GD card.
The child board has four interfaces with RJ12 connectors, as shown below.
15

2.7 FPGA Programming
Three configuration methods are available on SGA10GD to upload (program) the
FPGA core.
2.7.1 Programming through JTAG
FPGA core can be loaded directly through the JTAG port (designated as J7 on-board)
as shown in the figure below
2.7.2 Programming from FLASH
From the Platform FLASH (designated as U11), the FPGA can be loaded
automatically.
If J4 jumper is open - it happens one time during the power-up.
If J4 is closed, every fundamental reset causes reconfiguration of the FPGA from the
Platform FLASH.
The FLASH itself has to be burned through the JTAG with a valid configuration
stream.
16

2.7.3 Partial reconfiguration
If the Platform FLASH contains the proper core implementing a PCI Express
endpoint, and a controller core for ICAP (Internal Configuration Access Port) - this
RESIDENT core allows the Partial reconfiguration of the FPGA.
TRANSIENT cores can be loaded that way.
J6 jumper controls HSWAPEN.
2.8 Status LEDs
There are two status LEDs assigned to an interface on board.
One red colored LOS (Loss of Signal) and one green colored ACT (Activity). The
table below summarizes the assignment:
Signal LED InterfaceFPGA#
LEDACT_N[0]GreenXFP1 G13
LEDLOS_N[0]Red XFP1 F13
LEDACT_N[1]GreenXFP2 G11
LEDLOS_N[1]Red XFP2 F11
17

4. FPGA test Cores
The on-board subsystems have been successfully tested using the Xilinx's Coregen
generated cores. User Constraints files were modified according to the boards metric.
Further modifications are discussed below on a per-Core bases.
These test Cores are available in the Distribution media:
4.1 PCIEX4 - Endpoint Block for PCI Express v. 1.6
This core implements a PCI Express x4 endpoint, with a completer allowing R/W
access to the on-chip RAM block.
Little modifications were made to the orignal top level design. Red LED's above P1,
P2, and P3 signal failures.
P1 - PLLLKDET lit if the GTP's PLL is not locked.
P2 - LINKUP lit if link training have failed for the lanes.
P3 - CLKLOCK lit if the on-chip PLL_ADV did not locked.
In order to report the presence of all four lanes, J2 has to be closed. Closing J4
forces the FPGA to be reloaded from the Platform Flash when the OS restarts, or the
reset button is pushed on the PC.
Using the Microsoft Windows XP operating system, SGA10GD is found as a new
hardware with the following ID's:
Vendor: 15C6 - BUTE
Device: 106D - 10 Gbps Dual Ethernet Adapter
Revision: 1
Base Class: 02 - Network
Subclass: 80 - Other
4.2 XAUI v. 8.1
The dual-XFP subystems are currently being tested.
4.3 DDR2 - MIG v. 2.0 generated SODIMM teszt core
SGA10GD has a 256 MBytes DDR2-400 SODIMM type MT4HTF3264HY-667
installed by default. The Memory Interface Generator produced a test core that
initialize the module, and performs continuous R/W tests.
Little modifications were made to the orignal top level design.
Red LED's above P1 signals failure.
P1 - phy_init_done lit if failed to initialize the module.
Green LED's above P1, P2 acts as described below.
P1 - error lit if the R/W test does not reveal bit errors. This signal is latched. Close
pin 1 and 20 on the feature connector to reset the core in order to restart the test.
P2 - testcnt(26) Blinks slowly if 200 MHz global clock is OK.
18

The test is passed if SGA10GD shows green lit for all LEDs (P2 blinks slowly).
4.4 Clock domains
The following table summarizes the proposed clock domains to help devloping
new/combined FPGA Cores.
It can also be used for estimating the performace of core by using the data bits
column for a given clock rate.
Signal f [MHz] FPGA Res. Core D bits Source
core_clk250.00 1 PLL_ADV pciex8n.a. Slot clock (100MHz)
user_clk125.00 see above pciex864 Slot clock (100MHz)
clk200 200.00 see below ddr2 n.a. Crystal Osc. X4
clk0 200.00 1 DCM_ADVddr2 128 Crystal Osc. X4
clk90 200.00 see above ddr2 n.a. Crystal Osc. X4
clkdiv0 100.00 see above ddr2 Cal. Crystal Osc. X4
clk156 156.25 n.a. XAUI 8 Crystal Osc. X2
19
 Loading...
Loading...