Foundry Networks FGS648P-POE, FGS648P, FGS624XGP, FGS624P-POE, FGS624XGP-POE User Manual
...
Foundry FastIron GS
Compact Layer 2 Switch
POE and POE-Upgradeable
Hardware Installation Guide
FGS624P
FGS624P-POE
FGS648P
FGS648P-POE
FGS624XGP
FGS624XGP-POE
FGS Release 04.0.00
™
4980 Great America Parkway
Santa Clara, CA 95054
Tel 408.207.1700
www.foundrynetworks.com
September 2007

Copyright © 2007 Foundry Networks, Inc. All rights reserved.
No part of this work may be reproduced in any form or by any means – graphic, electronic or mechanical, including
photocopying, recording, taping or storage in an information retrieval system – without prior written permission of the
copyright owner.
The trademarks, logos and service marks ("Marks") displayed herein are the property of Foundry or other third parties.
You are not permitted to use these Marks without the prior written consent of Foundry or such appropriate third party.
Foundry Networks, BigIron, FastIron, IronView, JetCore, NetIron, ServerIron, TurboIron, IronWare, EdgeIron, IronPoint,
the Iron family of marks and the Foundry Logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Foundry Networks, Inc. in
the United States and other countries.
F-Secure is a trademark of F-Secure Corporation. All other trademarks mentioned in this document are the property of
their respective owners.

Contents
CHAPTER 1
BOUT THIS GUIDE..................................................................................... 1-1
A
INTRODUCTION ...........................................................................................................................................1-1
W
HAT’S INCLUDED IN THIS EDITION? ...........................................................................................................1-1
A
UDIENCE ..................................................................................................................................................1-1
N
OMENCLATURE .........................................................................................................................................1-1
R
ELATED PUBLICATIONS .............................................................................................................................1-2
H
OW TO GET HELP .....................................................................................................................................1-2
W
EB ACCESS .......................................................................................................................................1-2
E
MAIL ACCESS .....................................................................................................................................1-2
T
ELEPHONE ACCESS ............................................................................................................................1-2
W
ARRANTY COVERAGE ...............................................................................................................................1-2
CHAPTER 2
RODUCT OVERVIEW .................................................................................. 2-1
P
PRODUCT OVERVIEW ..................................................................................................................................2-1
S
OFTWARE FEATURES ................................................................................................................................2-2
H
ARDWARE FEATURES ...............................................................................................................................2-2
FGS624P
FGS624XGP
FGS648P
C
ONTROL FEATURES ............................................................................................................................2-4
F
IBER OPTIC MODULES ......................................................................................................................2-12
P
OWER SUPPLIES ..............................................................................................................................2-12
C
OOLING SYSTEM AND FANS ..............................................................................................................2-13
AND FGS624P-POE ...........................................................................................................2-2
AND FGS624XGP-POE ................................................................................................2-3
AND FGS648P-POE ...........................................................................................................2-3
CHAPTER 3
NSTALLING THE FASTIRON GS CHASSIS..................................................... 3-1
I
UNPACKING A SYSTEM ................................................................................................................................3-1
P
ACKAGE CONTENTS ...........................................................................................................................3-1
September 2007 © 2007 Foundry Networks, Inc. iii

FastIron GS Compact Layer 2 Switch Hardware Installation Guide
GENERAL REQUIREMENTS ....................................................................................................................3-1
S
UMMARY OF INSTALLATION TASKS .............................................................................................................3-2
I
NSTALLATION PRECAUTIONS .......................................................................................................................3-3
G
ENERAL PRECAUTIONS .......................................................................................................................3-3
L
IFTING PRECAUTIONS .........................................................................................................................3-3
P
OWER SUPPLY PRECAUTIONS .............................................................................................................3-4
P
REPARING THE INSTALLATION SITE ............................................................................................................3-5
C
ABLING INFRASTRUCTURE ..................................................................................................................3-5
I
NSTALLATION LOCATION ......................................................................................................................3-5
I
NSTALLING AN ADDITIONAL POWER SUPPLY ................................................................................................3-5
I
NSTALLING AN AC POWER SUPPLY ......................................................................................................3-6
I
NSTALLING A DC POWER SUPPLY ..............................................................................................................3-8
I
NSTALLING THE DEVICE ............................................................................................................................3-11
D
ESKTOP INSTALLATION .....................................................................................................................3-11
R
ACK MOUNT INSTALLATION ...............................................................................................................3-11
W
ALL MOUNT INSTALLATION ...............................................................................................................3-13
P
OWERING ON THE SYSTEM .....................................................................................................................3-14
P
OWERING OFF THE SYSTEM .............................................................................................................3-15
V
ERIFYING PROPER OPERATION ...............................................................................................................3-15
O
BSERVING THE POWER STATUS LEDS ..............................................................................................3-16
A
TTACHING A PC OR TERMINAL ................................................................................................................3-16
CHAPTER 4
ONNECTING NETWORK DEVICES AND
C
HECKING CONNECTIVITY ...........................................................................4-1
C
ASSIGNING PERMANENT PASSWORDS .........................................................................................................4-1
R
ECOVERING FROM A LOST PASSWORD ................................................................................................4-2
C
ONFIGURING IP ADDRESSES .....................................................................................................................4-3
D
EVICES RUNNING LAYER 2 SOFTWARE ...............................................................................................4-3
C
ONNECTING NETWORK DEVICES ...............................................................................................................4-4
C
ABLE SPECIFICATIONS ........................................................................................................................4-4
C
ONNECTING TO ETHERNET OR FAST ETHERNET HUBS .........................................................................4-4
C
ONNECTING TO WORKSTATIONS, SERVERS, OR ROUTERS ...................................................................4-5
C
ONNECTING A NETWORK DEVICE TO A FIBER PORT .............................................................................4-5
T
ESTING CONNECTIVITY ..............................................................................................................................4-6
P
INGING AN IP ADDRESS ......................................................................................................................4-6
O
BSERVING LEDS ................................................................................................................................4-7
T
RACING A ROUTE ...............................................................................................................................4-8
T
ROUBLESHOOTING NETWORK CONNECTIONS .............................................................................................4-8
U
SING VIRTUAL CABLE TESTING TO DIAGNOSE A CABLE .......................................................................4-8
CHAPTER 5
ANAGING THE FASTIRON GS CHASSIS...................................................... 5-1
M
MANAGING TEMPERATURE SETTINGS ..........................................................................................................5-1
U
SING THE TEMPERATURE SENSOR ......................................................................................................5-1
iv © 2007 Foundry Networks, Inc. September 2007

Contents
DISPLAYING THE TEMPERATURE ...........................................................................................................5-1
D
ISPLAYING TEMPERATURE MESSAGES ................................................................................................5-2
C
HANGING THE TEMPERATURE WARNING LEVEL ...................................................................................5-2
C
HANGING THE CHASSIS TEMPERATURE POLLING INTERVAL ..................................................................5-3
D
ISPLAYING MANAGEMENT MODULE CPU USAGE .......................................................................................5-3
R
EMOVING MAC ADDRESS ENTRIES ...........................................................................................................5-3
CHAPTER 6
ARDWARE SPECIFICATIONS....................................................................... 6-1
H
CHASSIS SPECIFICATIONS ...........................................................................................................................6-2
P
HYSICAL DIMENSIONS AND WEIGHT ....................................................................................................6-2
E
NVIRONMENTAL CONSIDERATIONS ......................................................................................................6-2
C
OOLING .............................................................................................................................................6-3
R
EGULATORY COMPLIANCE ..................................................................................................................6-3
P
OWER SOURCE INTERRUPTIONS .........................................................................................................6-4
M
EAN TIME BETWEEN FAILURE .............................................................................................................6-4
P
OWER DRAW SPECIFICATIONS ............................................................................................................6-5
P
INOUTS AND SIGNALLING ....................................................................................................................6-6
C
ABLE SPECIFICATIONS ........................................................................................................................6-7
P
OWER CORDS ....................................................................................................................................6-9
W
ARRANTY ..........................................................................................................................................6-9
P
OWER SUPPLY SPECIFICATIONS ................................................................................................................6-9
O
VERVIEW ...........................................................................................................................................6-9
K
EY FEATURES ...................................................................................................................................6-10
P
HYSICAL DIMENSIONS AND WEIGHT ..................................................................................................6-10
E
NVIRONMENTAL CONSIDERATIONS ....................................................................................................6-10
P
OWER SUPPLY CONSUMPTION ..........................................................................................................6-11
I
NPUT CONNECTOR AND PLUG ............................................................................................................6-12
R
EGULATORY COMPLIANCE ................................................................................................................6-13
S
AFETY WARNINGS ............................................................................................................................6-13
E
LECTRICAL SPECIFICATIONS .............................................................................................................6-14
CHAPTER 7
AINTAINING THE FASTIRON GS HARDWARE .............................................. 7-1
M
HARDWARE MAINTENANCE SCHEDULE .........................................................................................................7-1
R
EPLACING A POWER SUPPLY ....................................................................................................................7-1
I
NSTALLATION PRECAUTIONS AND WARNINGS ........................................................................................7-2
D
ETERMINING WHICH POWER SUPPLY FAILED ......................................................................................7-2
AC P
OWER SUPPLIES ..........................................................................................................................7-2
DC P
OWER SUPPLIES ..........................................................................................................................7-5
I
NSTALLING OR REPLACING A 2-PORT 10-GBE MODULE ...............................................................................7-9
R
EMOVING A 2-PORT 10-GBE MODULE .................................................................................................7-9
I
NSTALLING A 2-PORT 10-GBE MODULE ................................................................................................7-9
I
NSTALLING OR REPLACING A POE DAUGHTER CARD ................................................................................7-10
D
ISASSEMBLING THE CHASSIS ............................................................................................................7-11
I
NSTALLING A POE DAUGHTER CARD .................................................................................................7-12
September 2007 © 2007 Foundry Networks, Inc. v

FastIron GS Compact Layer 2 Switch Hardware Installation Guide
RE-ASSEMBLING THE CHASSIS ............................................................................................................7-14
R
EPLACING A FIBER OPTIC MODULE .........................................................................................................7-15
R
EMOVING A FIBER OPTIC MODULE ....................................................................................................7-15
I
NSTALLING A NEW FIBER OPTIC MODULE ...........................................................................................7-16
C
ABLING A FIBER OPTIC MODULE .......................................................................................................7-16
C
LEANING THE FIBER-OPTIC CONNECTORS ...............................................................................................7-16
D
IGITAL OPTICAL MONITORING ...........................................................................................................7-17
APPENDIX A
REGULATORY STATEMENTS ........................................................................A-1
U.S.A. ...................................................................................................................................................... A-1
I
NDUSTRY CANADA STATEMENT ................................................................................................................. A-1
E
UROPE AND AUSTRALIA ........................................................................................................................... A-1
J
APAN ....................................................................................................................................................... A-1
APPENDIX B
AUTIONS AND WARNINGS..........................................................................B-1
C
CAUTIONS ................................................................................................................................................. B-1
W
ARNINGS ................................................................................................................................................ B-6
vi © 2007 Foundry Networks, Inc. September 2007

Chapter 1
About This Guide
Introduction
This guide describes the following FastIron GS® (FGS) Compact Layer 2 POE (Power over Ethernet) and POEupgradeable switches from Foundry Networks:
• FGS624P-POE – 24-port POE
• FGS624P – 24-port POE-upgradeable
• FGS624XGP – 24-port POE-upgradeable with 1-port 10-GbE (new in release 02.5.00)
• FGS624XGP-POE – 24-port POE with 1-port 10-GbE (new in release 02.5.00)
• FGS648P-POE – 48-port POE
• FGS648P – 48-port POE-upgradeable
This guide includes procedures for installing the hardware and configuring essential, basic parameters such as
permanent passwords and IP addresses. The basic software configuration procedures show how to perform
tasks using the CLI. This guide also includes instructions for managing and maintaining the hardware.
What’s Included in This Edition?
This edition includes the following FastIron GS releases:
• 02.5.00
• 02.4.00
• 03.0.00
Audience
This guide is designed for network installers, system administrators, and resellers who will install the FGS
hardware. This guide assumes a working knowledge of Layer 2 switching.
Nomenclature
This guide uses the following typographical conventions to show information:
Italic highlights the title of another publication and occasionally emphasizes a word or phrase.
Bold highlights a CLI command.
Bold Italic highlights a term that is being defined.
September 2007 © 2007 Foundry Networks, Inc. 1 - 1

FastIron GS Compact Layer 2 Switch Hardware Installation Guide
NOTE: A note emphasizes an important fact or calls your attention to a dependency.
CAUTION: A caution calls your attention to a possible hazard that can damage equipment.
WARNING: A warning calls your attention to a possible hazard that can cause injury or death.
Related Publications
The following Foundry Networks documents supplement the information in this guide.
• Foundry FastIron Configuration Guide – for FastIron Edge Switch X Series (FESX), FastIron SuperX Switch
(FSX), FastIron SX 800, FastIron SX 1600, FastIron Workgroup Switch X Series (FWSX), and FastIron GS
(FGS), provides configuration procedures for system-level features, Layer 2 features, and configuration
information for Layer 3 enterprise routing protocols including IP, RIP, IP multicast, OSPF, BGP4, VRRP and
VRRPE. This guide also provides procedures for securing management access to Foundry devices and for
protecting against Denial of Service (DoS) attacks.
• Foundry Management Information Base Reference – contains the Simple Network Management Protocol
(SNMP) Management Information Base (MIB) objects supported on Foundry devices.
• Release Notes for the FastIron GS Switch (FGS) – describes features introduced in each software release,
lists features that are supported on the FGS, and describes how configuration procedures or defaults differ
from those on other Foundry devices, due to the FGS’s hardware architecture.
To order additional copies of these manuals, do one of the following:
• Call 1.877.TURBOCALL (887.2622) in the United States or 1.408.207.1600 outside the United States.
• Send email to info@foundrynet.com.
NOTE: For the latest edition of this document, which contains the most up-to-date information, see
kp.foundrynet.com.
How to Get Help
Foundry Networks technical support will ensure that the fast and easy access that you have come to expect from
your Foundry Networks products will be maintained.
Web Access
• kp.foundrynet.com
Email Access
Technical requests can also be sent to the following email address:
• support@foundrynet.com
Telephone Access
• 1.877.TURBOCALL (887.2622) United States
• 1.408.207-1600 Outside the United States
Warranty Coverage
Contact Foundry Networks using any of the methods listed above for information about the standard and extended
warranties.
1 - 2 © 2007 Foundry Networks, Inc. September 2007

This chapter contains the following information:
• “Product Overview” on page 2-1
• “Software Features” on page 2-2
• “Hardware Features” on page 2-2
Chapter 2
Product Overview
Product Overview
This chapter contains an overview of the following Foundry Networks FastIron GS® (FGS) products:
• FGS624P-POE – 24-port POE
• FGS624P – 24-port POE-upgradeable
• FGS624XGP – 24-port POE-upgradeable with 1-port 10-GbE (new in release 02.5.00)
• FGS624XGP-POE – 24-port POE with 1-port 10-GbE (new in release 02.5.00)
• FGS648P-POE – 48-port POE
• FGS648P – 48-port POE-upgradeable
The FGS provides high port density within a compact form factor. All devices provide 128 MB of SDRAM when
shipped from the factory.
You can order the FGS
device, you can later upgrade your device to a POE device.
The FGS delivers a full complement of standards-based, feature-rich Layer 2 switching and Base Layer 3
capability. The extensive feature set supports network requirements ranging from basic connectivity to multicastenabled full streaming audio and video applications for converged services such as Voice over IP (VoIP).
The FGS, together with Foundry’s FastIron X Series devices, provide an integral range of network connectivity
within the entire enterprise network. The FGS provides high port density and Gigabit Ethernet (GbE) uplinks in a
compact form factor. All models optionally support two 10-GbE uplink ports. The FGS624XGP and FGS624XGPPOE, introduced in release 02.5.00, come with one 10-GbE uplink port.
The POE devices provide electrical power over existing Ethernet cables, supporting the need for integrated data,
voice, and video applications.
with or without Power over Ethernet (POE) installed. If you order a POE-upgradeable
September 2007 © 2007 Foundry Networks, Inc. 2 - 1

FastIron GS Compact Layer 2 Switch Hardware Installation Guide
Software Features
Software features differ depending on the software version that is loaded on the device. When first shipped, the
FGS devices support full Layer 2 Switching and Base Layer 3 Switching.
For a complete list of software features supported on the FGS, see the release notes or the Foundry FastIron
Configuration Guide.
Hardware Features
This section describes the physical characteristics of Foundry’s FGS models. For details about physical
dimensions, power supply specifications, and pinouts, see the chapter “Hardware Specifications” on page 6-1.
FGS624P and FGS624P-POE
The FGS624P is POE-upgradeable. You can upgrade it by installing a POE daughter card.
The FGS624P-POE already has the POE daughter card installed.
Figure 2.1 shows the FGS624P and FGS624P-POE.
Figure 2.1 FGS624P and RGS624P-POE
26
FGS-2XG
25
The FGS624P and FGS624P-POE have the following ports:
• 24 10/100/1000 Mbps Copper ports that support 100Base-TX and 1000Base-T RJ-45 connectors
• Four Gigabit Fiber ports for mini-GBIC optical transceivers (also called Small Form Factor Pluggable (SFP)
MultiSource Agreement (MSA)-compliant optical transceivers)
Note that ports 1 – 4 of the copper ports and 1F – 4F of the fiber ports are combination ports, meaning either
the copper port or its corresponding fiber port can be active at a time. For example, for copper port 1 and
fiber port 1F, only one of these ports can be active at any given time. The same applies to copper port 2 and
fiber port 2F, and so forth. You can use a combination of fiber and copper ports or all four copper or all four
fiber ports, as needed. For more information, see “Combination Ports” on page 2-7.
• Optionally, two 10-GbE ports. See “10 Gbps Ports” on page 2-7.
2 - 2 © 2007 Foundry Networks, Inc. September 2007

FGS624XGP and FGS624XGP-POE
The FGS624XGP is POE-upgradeable. You can upgrade it by installing a POE daughter card.
The FGS624XGP-POE already has the POE daughter cards installed.
Figure 2.2 shows the FGS624XGP and FGS624XGP-POE.
Figure 2.2 FGS624XGP and FGS624XGP-POE
3
Slot
Product Overview
Slot 1
The FGS624XGP and FGS624XGP-POE have the following ports:
• 24 10/100/1000 Copper ports that support 100Base-TX and 1000Base-T RJ-45 connectors
• Four Gigabit Fiber uplink ports (1F – 4F) for mini-GBIC optical transceivers (also called Small Form Factor
Pluggable (SFP) Multisource Agreement (MSA)-compliant optical transceivers)
Note that ports 1 – 4 of the copper ports and 1F – 4F of the fiber ports are combination ports, meaning either
the copper port or its corresponding fiber port can be active at a time. For example, for copper port 1 and
fiber port 1F, only one of these ports can be active at any given time. The same applies to copper port 2 and
fiber port 2F, and so forth. You can use a combination of fiber and copper ports or all four copper or all four
fiber ports, as needed. For more information, see “Combination Ports” on page 2-7.
• One built-in 10-GbE port. See “10 Gbps Ports” on page 2-7.
• Optionally, two additional 10-GbE ports. See “10 Gbps Ports” on page 2-7.
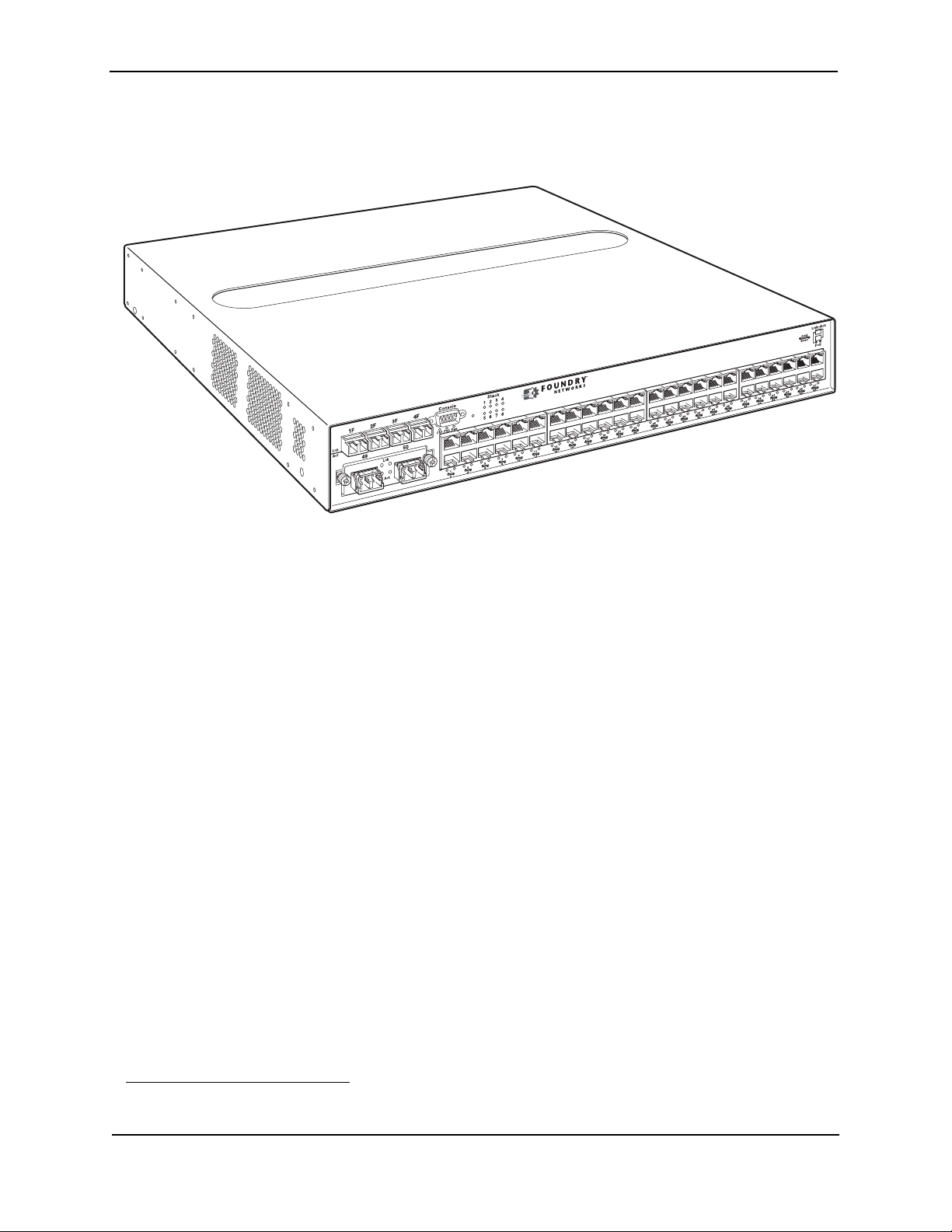
FGS648P and FGS648P-POE
The FGS648P is POE-upgradeable. You can upgrade it to a POE device by installing one or two POE daughter
cards. A single POE daughter card supports 24 POE ports. Two POE daughter cards support 48 POE ports.
The FGS648P-POE already has the POE daughter cards installed.
September 2007 © 2007 Foundry Networks, Inc. 2 - 3
FastIron GS Compact Layer 2 Switch Hardware Installation Guide
Figure 2.3 shows the FGS648P and FGS648P-POE
Figure 2.3 FGS648P and FGS648P-POE
FGS-2XG
.
The FGS648P and FGS648P-POE have the following ports:
• 48 10/100/1000 Copper ports that support 100Base-TX and 1000Base-T RJ-45 connectors
• Four Gigabit Fiber uplink ports (1F – 4F) for mini-GBIC optical transceivers (also called Small Form Factor
Pluggable (SFP) Multisource Agreement (MSA)-compliant optical transceivers)
Note that ports 1 – 4 of the copper ports and 1F – 4F of the fiber ports are combination ports, meaning either
the copper port or its corresponding fiber port can be active at a time. For example, for copper port 1 and
fiber port 1F, only one of these ports can be active at any given time. The same applies to copper port 2 and
fiber port 2F, and so forth. You can use a combination of fiber and copper ports or all four copper or all four
fiber ports, as needed. For more information, see “Combination Ports” on page 2-7.
• Optionally, two 10-GbE ports. See “10 Gbps Ports” on page 2-7.
Control Features
Each device’s front panel has the following control features:
• Serial management interface (the port labeled Console)
• Reset button
• 10/100/1000 ports with RJ-45 copper connectors
• 100/1000 ports with mini-GBIC slots for SFP MSA-compliant fiber transceivers
• The FGS624XGP and FGS624XGP-POE have one 10-Gigabit Ethernet port for XFP MSA compliant fiber
connector(s)
• Optionally, two 10 Gigabit Ethernet ports for XFP MSA-compliant fiber connectors
• LEDs for ports, power supplies, and stacking
1.Reserved for possible use in the future.
2 - 4 © 2007 Foundry Networks, Inc. September 2007
1
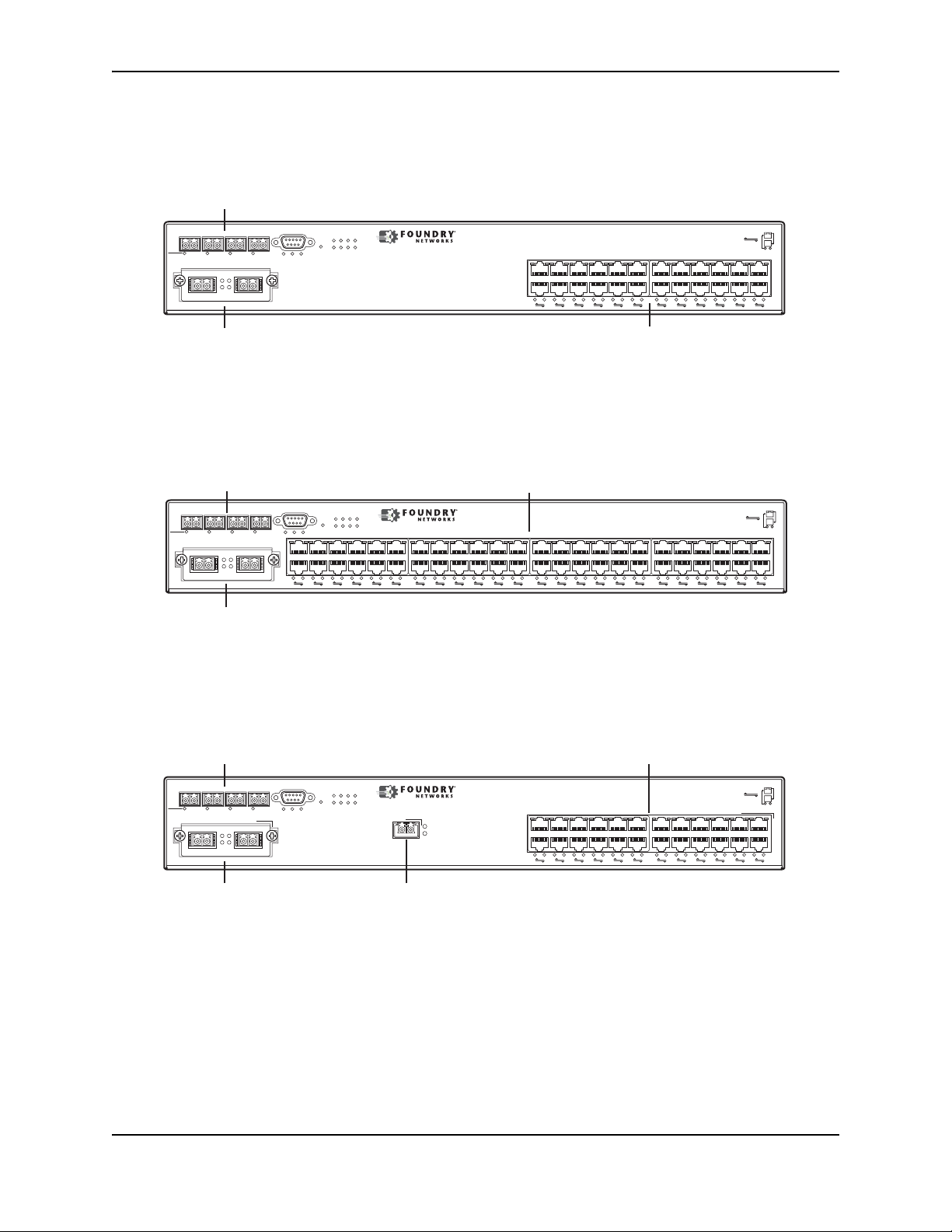
Figure 2.4 shows the front panel of the FGS624P and FGS624P-POE.
Figure 2.4 FGS624P and FGS624P-POE Front Panel
Ports 1-4
Product Overview
1F 2F 3F4F
Lnk
Act
25 26
Lnk
Act
Console
PS1PS2Pwr
FGS-2XG
Stack
2 3
1
5678
4
1
34567891011121314151617181920212223
2
Ports 25 and 26 Ports 1-24
Figure 2.5 shows the front panel of the FGS648P and FGS648P-POE.
Figure 2.5 FGS648P and FGS648P-POE Front Panel
GbE Fiber Ports (1F - 4F)
1F 2F 3F 4F
Lnk
Act
49
Lnk
Act
Console
PS1 PS2 Pwr
50
1
2
Stack
1
23
4
5678
34567891011121314151617181920212223242526272829303132333435363738394041424344454647
GbE Copper Ports (1 - 48)
Optional 2-port 10-GbE Module
(port 49 and 50)
Figure 2.6 shows the front panel of the FGS624XGP and FGS624XGP-POE.
Lnk-Act
Odd
Even
PoE
24
Lnk-Act
Odd
Even
PoE
48
Figure 2.6 FGS624XGP and FGS624XGP-POE Front Panel
GbE Fiber Ports (slot 1, ports 1F - 4F) GbE Copper Ports (slot 1, ports 1 - 24)
Slot 1
Lnk-Act
Odd
Even
PoE
24
FGS-2XG
Slot 2
Console
PS1PS2 Pwr
1F 2F 3F4F
Lnk
Act
12
Lnk
Act
Optional 2-port 10-GbE Module
(slot 2, ports 1 and 2)
Stack
2 3
4
1
5678
Slot 3
1-port 10-GbE Module
(slot 3, port 1)
Lnk
Act
1
34567891011121314151617181920212223
2
Serial Management Interface (Console Port)
The serial management interface (the port labelled Console) enables you to configure and manage the device
using a third-party terminal emulation application on a directly connected PC. A straight-through EIA/TIA DB-9
serial cable (M/F) ships with the device. The serial management interface is located in the left corner of the front
panel.
September 2007 © 2007 Foundry Networks, Inc. 2 - 5

FastIron GS Compact Layer 2 Switch Hardware Installation Guide
Reset Button
The reset button allows you to restart the system without switching the power supplies off and on or using the CLI
or Web management interface. The button is located to the right of the serial management interface and is
recessed to prevent it from being pushed accidentally.
Network Interfaces
Table 2.1 describes the network interfaces supported on the FGS devices. For network interface specifications,
see Table 6.7 on page 6-7.
Table 2.1: Network Interfaces
Interface Show Media
Description
1000Base-BX-D M-GBXD
1000Base-BX-U M-GBXU
1000Base-LHA M-LHA
1000Base-LHB M-LHB
1000Base-LX M-LX
1000Base-SX M-SX
1000Base-SX2 M-SX2
1000Base-T C
100Base-BX M-FBX
100Base-FX M-FX
10GBase-ER XG-ER
10GBase-LR XG-LR
10GBase-SR XG-SR
10GBase-ZR XG-ZR
10GBase-ZRD XG-ZRD
CX4 10GbE module CX4
10GbE XFP and CX4 module CX4
1310-MMF 10GbE 1310-NM
Viewing the Media Types Installed in the Ports
The output of the show media command displays the type of media (copper or fiber) installed in the ports. The
output differs between devices running software release 02.4.00 and release 02.5.00 or later. Starting in software
release 02.5.00, the software uses a stacking nomenclature.
The following shows an example of the show media output in pre-release 02.5.00.
FastIron(config)# show media
1:M-GBXD 2:M-LHB 3:M-FBX 4:M-SX2 5: C 6: C 7: C 8: C 9: C 10: C 11: C 12: C 13:
C 14: C 15: C 16: C 17: C 18: C 19: C 20: C 21: C 22: C 23: C 24: C 25:XG-ZR
1550.0 nm 26:XG-SR 27:
2 - 6 © 2007 Foundry Networks, Inc. September 2007

Product Overview
The following shows an example of the show media output in release 02.5.00 and later.
FastIron(config)# show media
0/1/1:M-SX 0/1/2: C 0/1/3: C 0/1/4: C 0/1/5: C 0/1/6: C 0/1/7: C 0/1/8: C 0/1/9:
C 0/1/10: C 0/1/11: C 0/1/12: C 0/1/13: C 0/1/14: C 0/1/15: C 0/1/16: C 0/1/17:
C 0/1/18: C 0/1/19: C 0/1/20: C 0/1/21: C 0/1/22: C 0/1/23: C 0/1/24: C
0/2/1:XG-LMR 0/2/2:1310-NM
The “Show Media Description” column in Table 2.1 shows the text that displays in the output of the show media
command for each connector type.
10/100/1000 Mbps Ports
The 10/100/1000 copper ports use auto-sensing and auto-negotiating to determine the speed (10 Mbps, 100
Mbps, or 1000 Mbps) and mode (full-duplex or half-duplex) of the port at the other end of the link and adjust port
speed accordingly.
10/100/1000 ports on the FGS devices support RJ-45 copper connectors. The output of the show media
command displays C next to the ports that have copper connectors installed.
Gigabit copper ports on the FGS models support auto MDI/MDIX detection. For more information about this
feature, see "Configuring MDI/MDIX" in the Foundry FastIron Configuration Guide.
100/1000 Mbps Ports
The 100/1000 fiber ports (ports 1F – 4F) on the FGS devices support the SFP fiber connectors listed in Table 2.1.
Combination Ports
Ports 1 – 4 of the copper ports and 1F – 4F of the fiber ports are combination ports, meaning either the copper
port or its corresponding fiber port can be active at a time. For example, for copper port 1 and fiber port 1F, only
one of these ports can be active at any given time. The same applies to copper port 2 and fiber port 2F, and so
forth. You can use a combination of fiber and copper ports or all four copper or all four fiber ports, as needed.
If you attach both the copper and fiber connectors for a port to the network, the fiber connectors take precedence
over the copper connectors. These ports support true media automatic detection, meaning the device will select
the fiber or copper connector based on link availability. If a fiber link cannot be established, the device will select
the copper media.
10 Gbps Ports
This section describes the 10-GbE modules
1-Port 10-GbE Module
The 1-port 10-GbE module is installed in the FGS624XGP and FGS624XGP-POE (shown in Figure 2.4). This
module is factory-installed only. It is not a field-upgradeable module. This module is a 10-GbE fiber uplink for 10Gigabit Small Form Factor Pluggable (XFP) MSA-compliant optical transceiver.
Figure 2.7 shows the 1-port 10-GbE module. This port supports the 10-GbE connector types (10GBase) listed in
Table 2.1.
Figure 2.7 1-port 10-GbE Module
1 XFP port
2-port 10-GbE Module
The 2-port 10-GbE module on the FGS is optional. You can order the FGS with one of these 2-port 10-Gigabit
module installed at the factory, or you can later upgrade your device.
The following 2-port 10-Gigabit Ethernet module is supported:
• 2-port 10-GbE fiber uplinks for 10-Gigabit Small Form Factor Pluggable (XFP) MSA-compliant optical
September 2007 © 2007 Foundry Networks, Inc. 2 - 7

FastIron GS Compact Layer 2 Switch Hardware Installation Guide
transceivers (part number FGS-2XG).
Figure 2.8 shows the 2-port 10-GbE module. These ports support the 10-GbE connector types (10GBase) listed
in Table 2.1.
Figure 2.8 2-port 10-GbE Module
2 XFP ports
10 Gbps CX4 and XFP Ports
This section describes the 10-GbE CX4 modules.
2-port CX4 Module (Release 02.6.00)
The 2-port CX4 module on the FGS is optional. You can order the FGS with a 2-port CX4 module installed at the
factory, or you can later upgrade your device.
The following 2-port CX4 module is supported:
• 2-port CX4 uplinks for 10-Gigabit Small Form Factor Pluggable (XFP) MSA-compliant optical transceivers
(part number FGS-2XGC).
When this module is installed, the show media command returns the following display:
FGS648 Switch#sh media
0/2/1:CX4 0/2/2:CX4
2-port 10-GbE Hybrid Interface Module (Release 02.6.00)
The 2-port 10-GbE hybrid interface module contains a CX4 port and an XFP port. You can order the FGS with one
a 2-port hybrid module installed at the factory, or you can later upgrade your device.
The following 2-port 10-GbE hybrid interface module is supported:
• 2-port 10-GbE hybrid uplinks; one for a 10-Gigabit Small Form Factor Pluggable (XFP) MSA-compliant optical
transceiver and one for a 2-port CX4 10-Gigabit Small Form Factor Pluggable (XFP) MSA-compliant optical
transceiver (part number FGS-1XG1XGC).
When this module is installed, the show media command returns the following display:
FGS648 Switch#sh media
0/2/1:<depends on transceiver installed> 0/2/2:CX4
10GbE XFP Transceiver (FGS624XGP Models Only)
Release 02.6.00 introduced support for a 10GbE XFP transceiver specifically in port 1, slot 3..
The following 2-port CX4 module is supported:
• 2-port CX4 uplinks for 10-Gigabit Small Form Factor Pluggable (XFP) MSA-compliant optical transceivers
(part number FGS-2XGC).
Link and Activity LEDs on the module faceplates indicate operational status:
• If the Lnk LED is on, the port is connected. If the Lnk LED is off, no connection exists, or the link is down.
• If the Act LED is on or blinking, traffic is being transmitted and received on the port. If the Act LED is off, no
traffic is being transmitted or received on the port.
Figure 2.9 shows the faceplates of both modules:
2 - 8 © 2007 Foundry Networks, Inc. September 2007
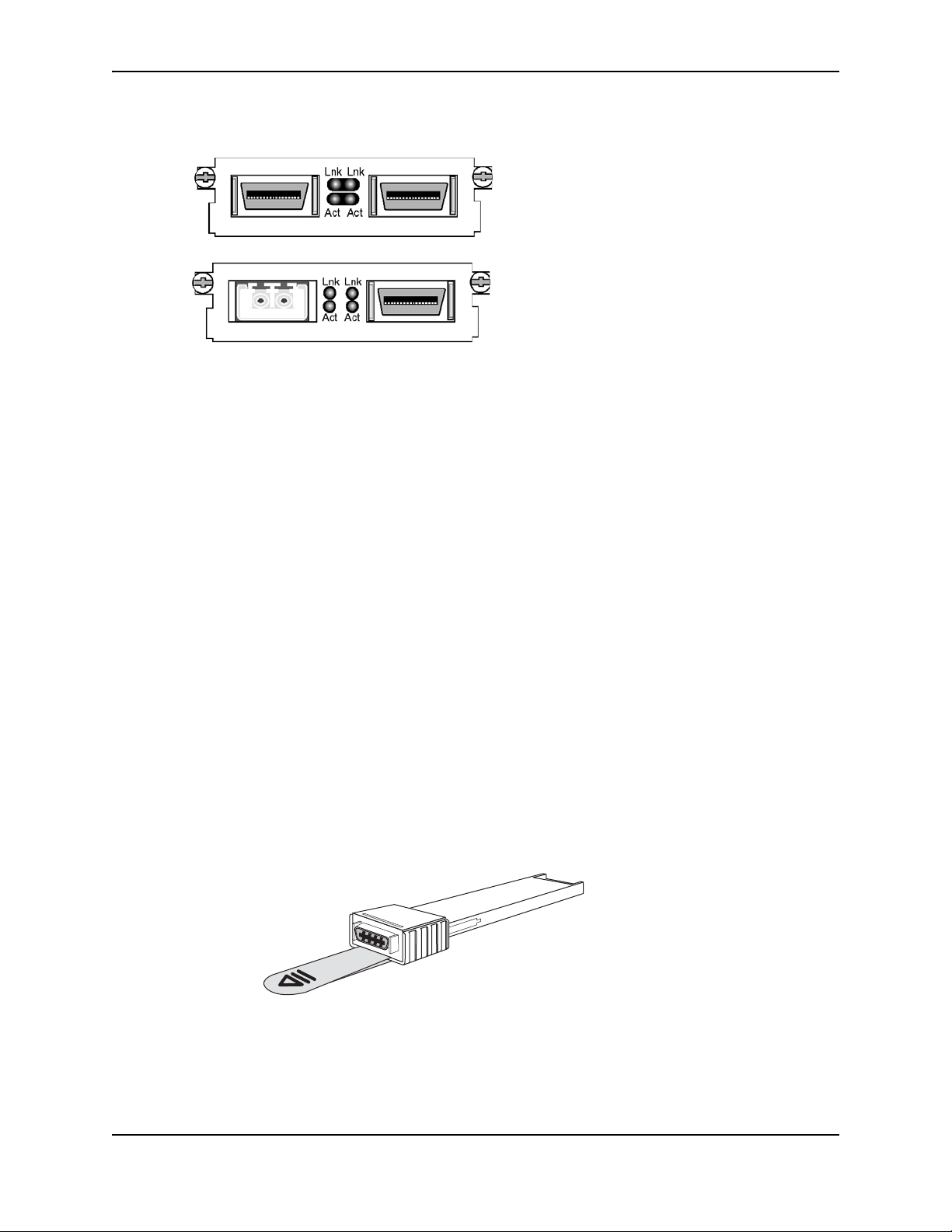
Figure 2.9 2-port CX4 10GbE Module and 10GbE and CX4 Module
Lnk
Lnk
Product Overview
Act
Lnk
Act
Lnk
10GbE 2-port CX4 Module
10GbE XG and CX4 Module
Act
Act
Cable Specifications for New Optics Modules
The following cable specifications apply to the CX4 ports, which are included in the new 10GbE interface modules
(FGS-2XGC and FGS-1XG1XGC):
• Support for 802.3ak or 10 Gigabit Ethernet CX4 standard
• Support of up to 15m in length
• Requires latch-style receptacle or SFF-8470 plug
• Recommended CX4 cable: Manufactured by WL Gore, part number IBN6600-15, CX4 Assembly - 26AWG
SPC 15.0m
CX4 10Gbps XFP Transceiver
This release introduces a twin-axial 10G copper CX4 XFP transceiver that can be installed in any 10G port. For a
link to operate properly, both sides must use identical CX4 transceivers.
The show media command identifies the CX4 as XG-CX4 as shown here:
FGS624P Switch#sh media
0/1/1: C 0/1/2:M-SX 0/1/3: C 0/1/4: C 0/1/5: C 0/1/6: C 0/1/7: C 0/1/8: C 0/1/9:
C 0/1/10: C 0/1/11: C 0/1/12: C 0/1/13: C 0/1/14: C 0/1/15: C 0/1/16: C 0/1/17:
C 0/1/18: C 0/1/19: C 0/1/20: C 0/1/21: C 0/1/22: C 0/1/23: C 0/1/24: C
0/2/1:XG-SR 0/2/2:XG-SR 0/3/1:XG-CX4
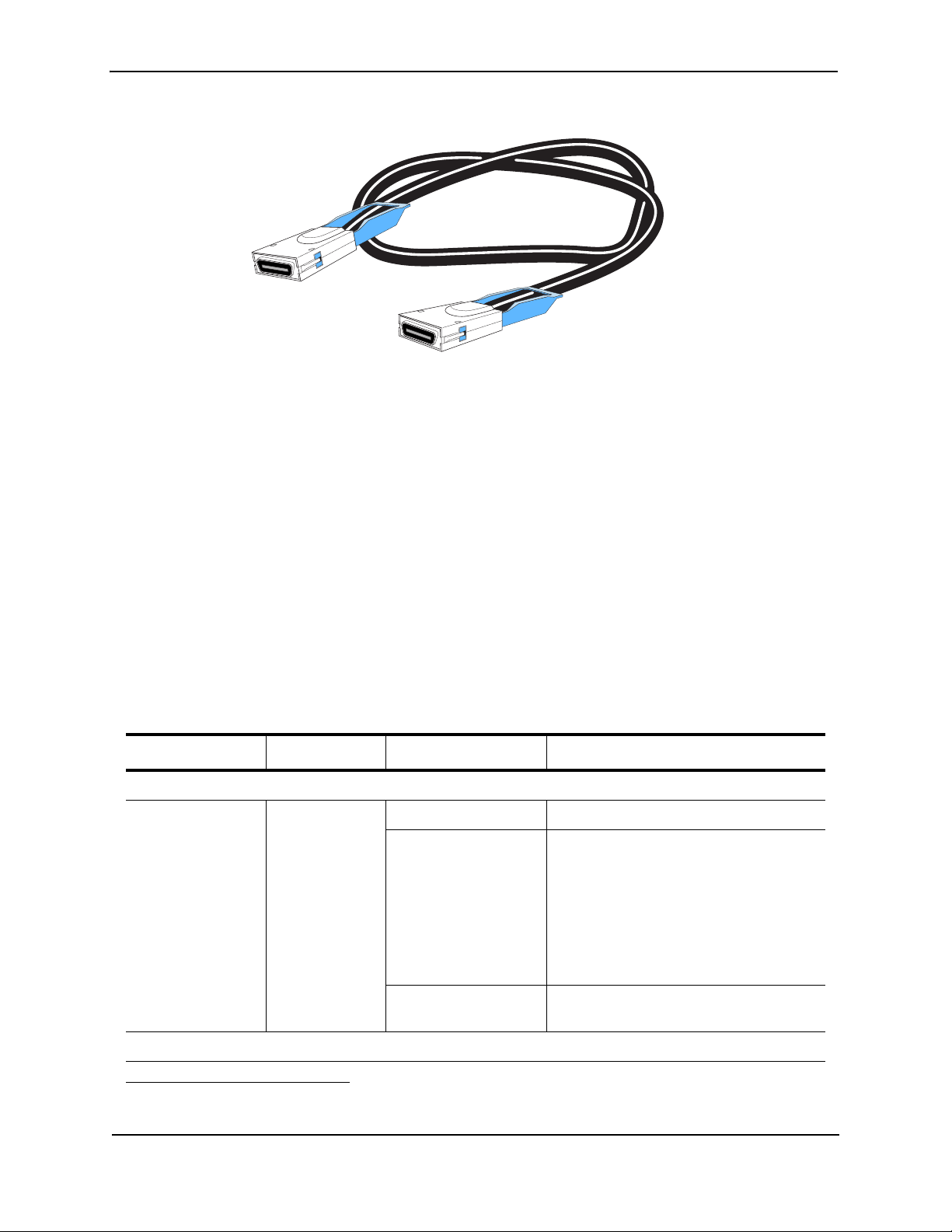
The CX4 transceiver requires a 15 meter CX4-grade cable, which may be purchased from Foundry Networks.
Refer to part number CAB-CX4-0050 when ordering.
Figure 2.10 shows the CX4 transceiver. Figure 2.11 shows the CX4-grade cable.
Figure 2.10 CX4 Transceiver
September 2007 © 2007 Foundry Networks, Inc. 2 - 9
FastIron GS Compact Layer 2 Switch Hardware Installation Guide
Figure 2.11 CX4 Transceiver Cable
CX4 Transceiver Infiniband cable
LEDs for Network Interfaces and Power Supplies
The fiber and copper ports on the FGS provide status information using the LEDs listed in Table 2.2.
• The 10/100/1000 copper ports (1 – 24 or 1 – 48) use the LEDs located on the top left and top right of the
upper copper connectors. The LEDs are combined Link/Activity (Lnk/Act) LEDs. The LED on the left side is
for the upper copper connector. The LED on the right side is for the lower copper connector.
• The 100/1000 fiber ports (1F – 4F) use the LEDs located beneath the fiber connectors. The LEDs are
combined Link/Activity (Lnk/Act) LEDs.
• The POE ports (1 – 24) use the round LEDs located beneath the copper ports. The first (left-most) LED is for
port 1, the second LED is for port 2, the third LED is for port 3, and so forth.
• The 10 Gbps fiber ports use the LEDs located beside them.
• The FastIron GS with stacking1 use the Stack LEDs (1 – 8) located to the right of the console port.
• The power supplies use the Pwr, PS1, and PS2 LEDs on the left side of the front panel, beneath the console
port.
Table 2.2: LEDs
LED Position State Meaning
10/100/1000 Copper Port LEDs
Lnk/Act Located along
the top of the
copper ports
Left for upper
copper
connector
Right for lower
copper
connector
100/1000 Fiber Port LEDs
On The link is up.
Off The link is down.
Blinking The port is transmitting and/or receiving
traffic
1.Reserved for possible use in the future.
2 - 10 © 2007 Foundry Networks, Inc. September 2007
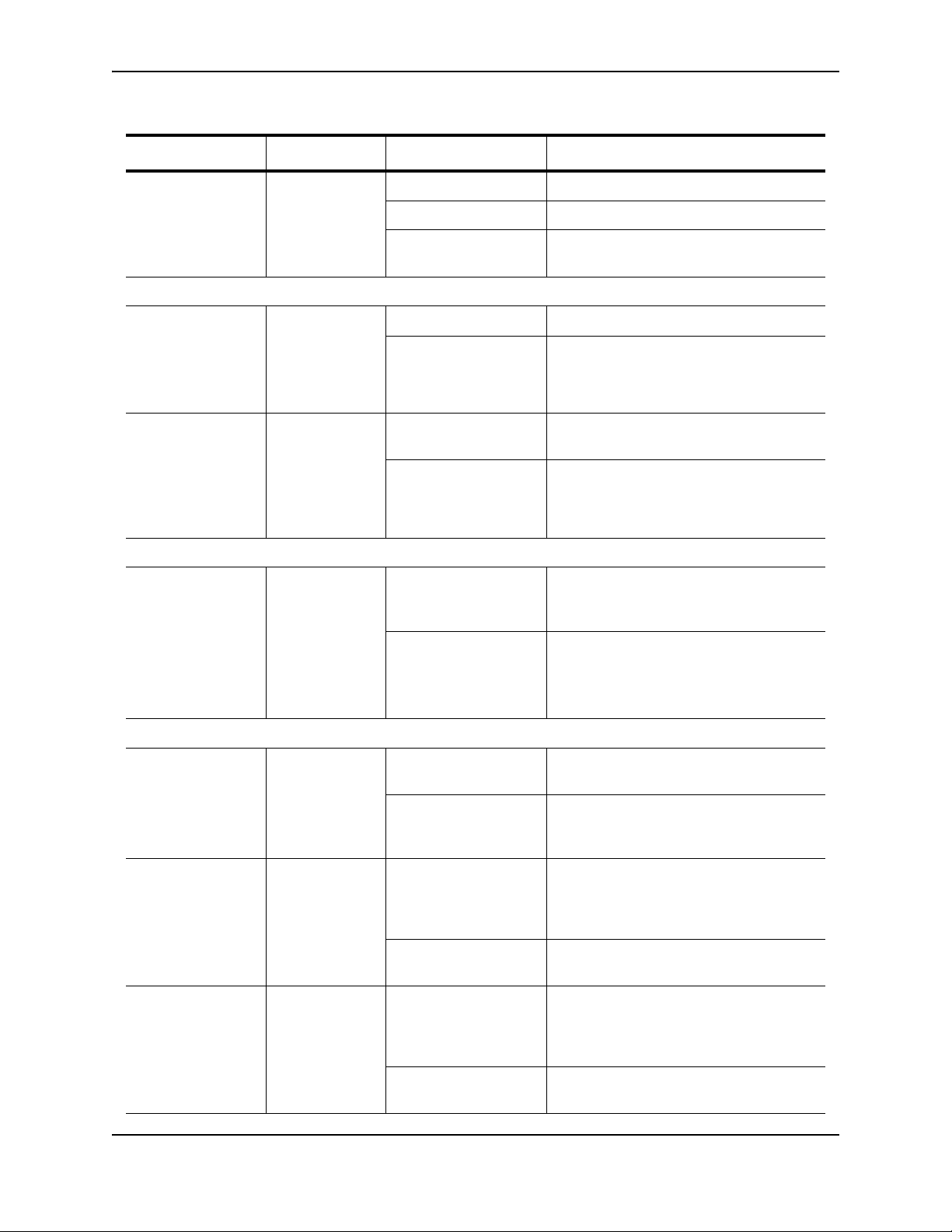
Table 2.2: LEDs (Continued)
LED Position State Meaning
Lnk/Act Bottom left On The link is up.
Off The link is down.
Blinking The port is transmitting and/or receiving
traffic.
10 Gbps Port LEDs
Product Overview
Lnk Located beside
the 10-GbE
port.
This is the topmost LED.
Act Located beside
the 10-GbE
port.
This is the
bottom-most
LED.
POE Port LEDs
POE Located along
the bottom of
the copper ports
Left for upper
port
Right for lower
port
Power Supply LEDs
Power Right-most LED
beneath the
console port
On The port is connected.
Off No fiber port connection exists or the link
is down.
On or Blinking Traffic is being transmitted and/or received
on the fiber port.
Off No traffic is being transmitted or received
on the fiber port.
On (Green) The port is enabled, a power-consuming
device has been detected, and the
module is supplying power to the device.
Off The port is not providing in-line power.
On The device is powered on and has enough
power to operate.
Off The device is not powered on, or has
been powered on but does not have
sufficient power to operate.
PS1 Left-most LED
beneath the
console port
PS2 Middle LED
beneath the
console port
September 2007 © 2007 Foundry Networks, Inc. 2 - 11
On Power supply 1 is installed and is
functioning normally. Power supply 1 is
located in the right-hand bay (when you
are facing the rear of the device).
Off Power supply 1 is not installed or is not
providing power.
On Power supply 2 is installed and is
functioning normally. Power supply 2 is
located in the left-hand bay (when you are
facing the rear of the device).
Off Power supply 2 is not installed or is not
providing power.
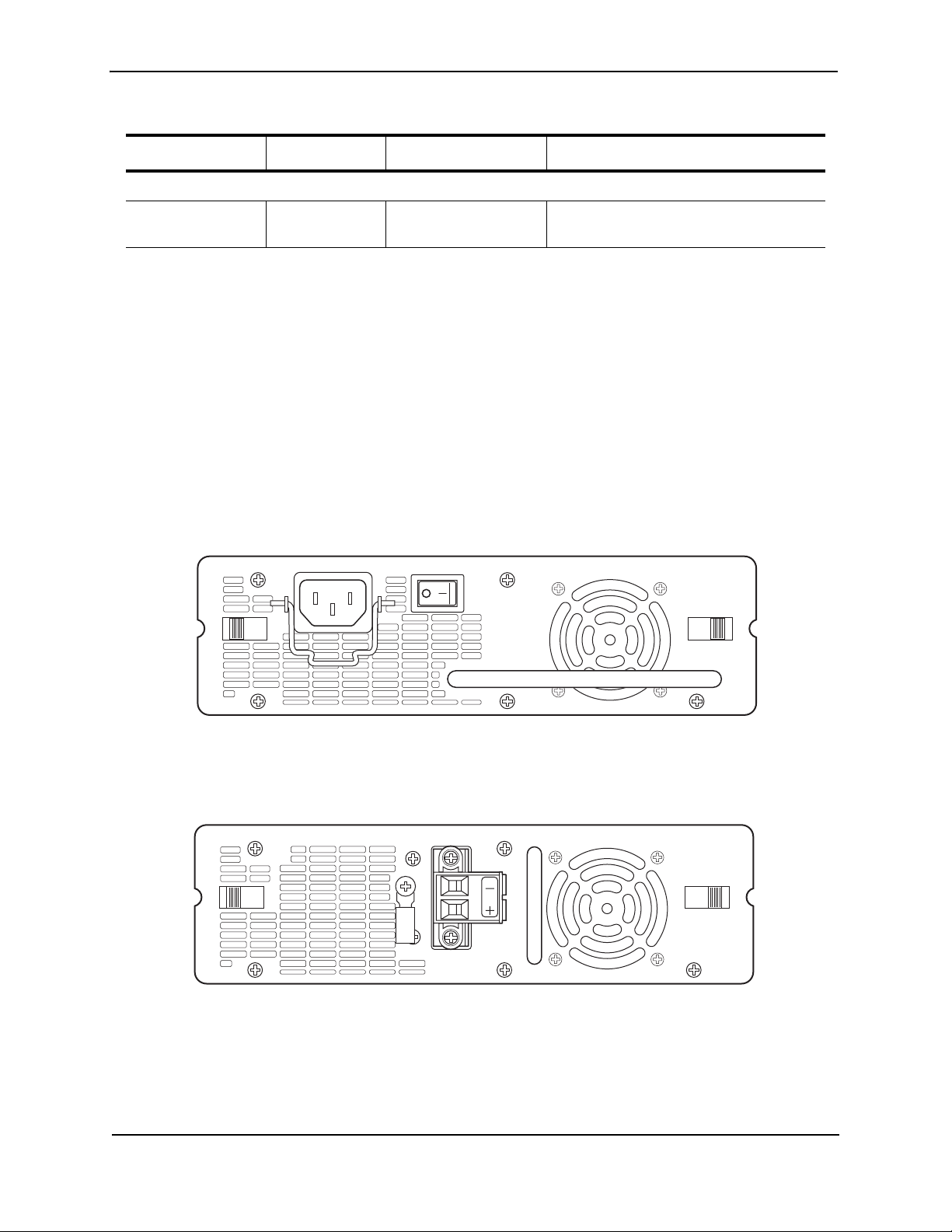
FastIron GS Compact Layer 2 Switch Hardware Installation Guide
Table 2.2: LEDs (Continued)
LED Position State Meaning
Stacking LEDs
Reserved for future
use
Fiber Optic Modules
Table 6.7 in the chapter “Hardware Specifications” lists the types of fiber optic modules (SFPs and XFPs)
supported on Foundry’s FGS devices.
Table 2.1 lists the description that displays in the output of the show media command for each media type.
Power Supplies
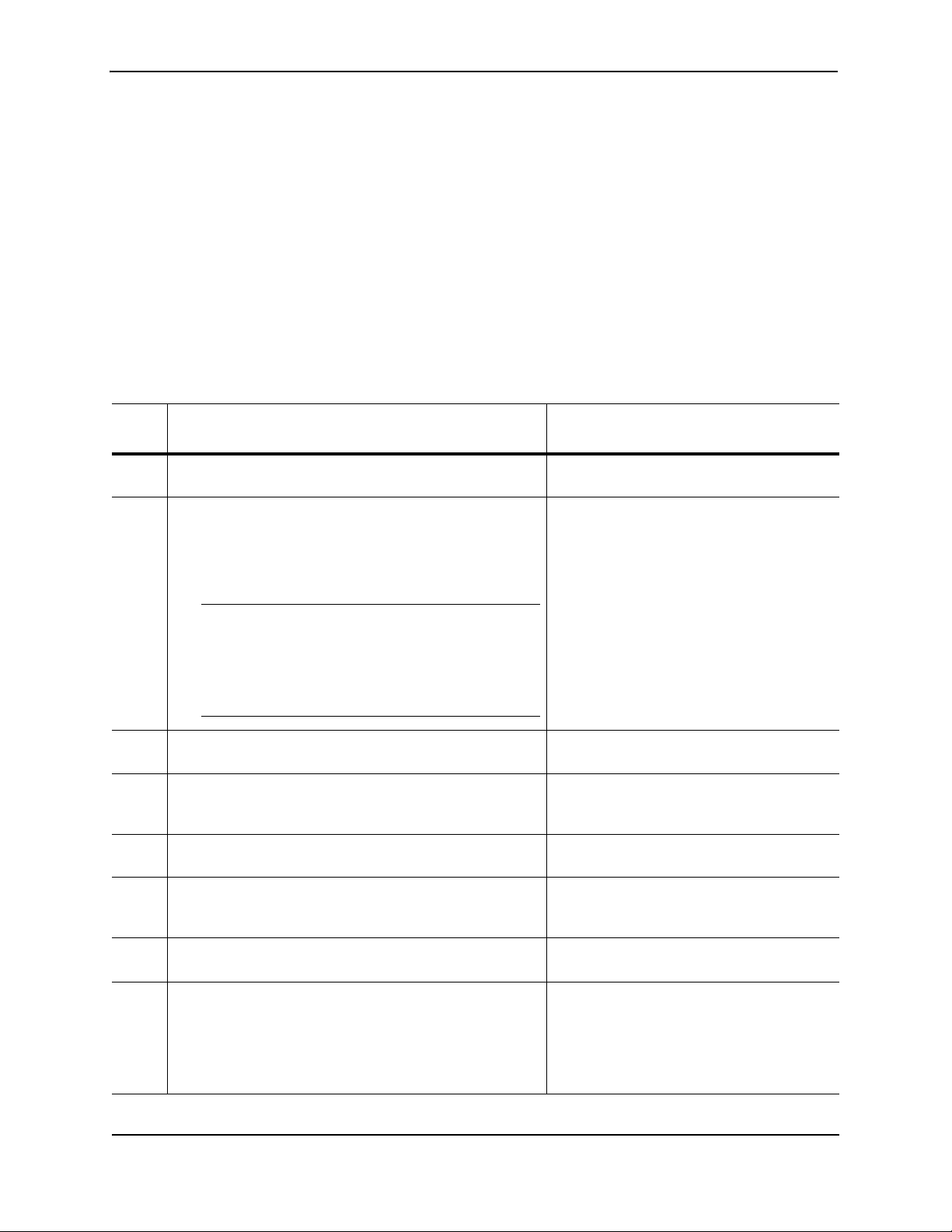
Each FGS device comes with one alternating-current (AC) power supply (part number RPS-FGS) or direct-current
(DC) power supply (part number RPSDC-FGS), depending on how it was ordered from the factory. All models
have two power supply slots, enabling you to install a second power supply for redundancy (if applicable) or for
additional POE power. You can use any combination of AC and DC supplies in the same device.
Figure 2.12 shows the AC power supply used with the FastIron GS.
Figure 2.12 RPS-FGS AC power supply
Figure 2.13 shows the DC power supply used with the FastIron GS.
Figure 2.13 RPSDC-FGS DC power supply
The power supplies are auto-sensing and auto-switching. The supplies provide 600 watts of total output power,
including +12VDC @ 10A to the system and -48VDC@ 10A for Power over Ethernet applications. The supplies
provide 100-240 VAC input, 50-60Hz @ 8A to 3.2A.
The power supplies can be swapped in or out of the device while the device is running. You can remove and insert
a power supply without opening the chassis. If the device contains redundant power supplies, you can remove
2 - 12 © 2007 Foundry Networks, Inc. September 2007

Product Overview
one of the supplies without interrupting operation. The remaining redundant supply provides enough power for all
the ports.
For power supply hardware specifications, see “Hardware Specifications” on page 6-1.
NOTE: A FastIron GS POE device with dual power supplies may not provide redundancy, depending on how
much power the POE ports are consuming. See “Power Specifications for POE” on page 2-13.
CAUTION: Remove the power cord from a power supply before you install it in or remove it from the device.
Otherwise, the power supply or the device could be damaged as a result. (The device can be running while a
power supply is being installed or removed, but the power supply itself should not be connected to a power
source.)
CAUTION: The FGS power supply is designed exclusively for use with the FGS devices. The power supply produces extensive power to support 802.3af applications. Installing the power supply in a device other than the FGS
will cause extensive damage to your equipment.
Power Specifications for POE
The actual implementation of the 802.3af standard limits power to 15.4W (44V to 57V) from the power sourcing
device. This is in compliance with safety standards and existing wiring limitations. Though limited by the 802.3af
standard, 15.4 watts of power is ample, as most powered devices consume an average of 5 to 12 watts of power.
IP phones, wireless LAN access points, and network surveillance cameras each consume an average of 3.5 to 9
watts of power.
Foundry’s 48-volt power supplies provide power to the POE daughter card, and ultimately to POE powerconsuming devices. The number of POE power-consuming devices that one 48-volt power supply can support
depends on the number of watts required by each power-consuming device. Each 48-volt power supply provides
480 watts of power for POE, and each POE port supports a maximum of 15.4 watts of power per POE powerconsuming device. For example, if each POE power-consuming device attached to the FastIron GS consumes 12
watts of power, one 48-volt supply will power up to 40 POE ports. You can install a second 48-volt supply for
additional POE power.
NOTE: If your FastIron GS POE chassis has 48 ports and only one power supply, and each POE-enabled port
needs 15.4 watts, then a maximum of 31 ports can supply power to connected devices.
For power supply specifications, see “Hardware Specifications” on page 6-1. For POE configuration procedures,
see the Foundry FastIron Configuration Guide.
Precautions
The following precautions apply to the FastIron GS POE with 48 ports:
• If your FastIron GS POE chassis has 48 ports and two power supplies, and the POE ports are consuming
more than 480 watts of power, a single power supply failure will cause both power supplies to shut down.
• If your FastIron GS POE chassis has 48 ports and only one power supply, and the power consuming devices
connected to POE-enabled ports consume a total of more than 480 watts of power, the power supply may
shut down.
Cooling System and Fans
The FGS chassis has two single-speed fans that operate simultaneously. If one fan fails, it does not affect the
operation of the other fan.
September 2007 © 2007 Foundry Networks, Inc. 2 - 13

FastIron GS Compact Layer 2 Switch Hardware Installation Guide
2 - 14 © 2007 Foundry Networks, Inc. September 2007

Chapter 3
Installing the FastIron GS Chassis
WARNING: The procedures in this manual are for qualified service personnel.
This chapter describes how to physically install the FastIron GS.
This chapter contains the following information:
• “Unpacking a System” on page 3-1
• “Summary of Installation Tasks” on page 3-2
• “Installation Precautions” on page 3-3
• “Installing an Additional Power Supply” on page 3-5
• “Installing the Device” on page 3-11
• “Powering On the System” on page 3-14
• “Verifying Proper Operation” on page 3-15
• “Attaching a PC or Terminal” on page 3-16
Information about configuring IP addresses and connecting network devices is in the chapter “Connecting
Network Devices and Checking Connectivity” on page 4-1.
Unpacking a System
Foundry systems ship with all of the following items. Please review the list below and verify the contents. If any
items are missing, please contact the place of purchase.
Package Contents
• Foundry Networks FastIron GS POE or POE-upgradeable device with one AC or DC power supply installed
• 115V AC power cable (for AC sourced devices)
• Rack mount brackets and mounting screws
• CD-ROM containing software images and the user documentation (including this guide)
• Warranty card
General Requirements
To manage the system, you need the following items for serial connection to the switch or router:
September 2007 © 2007 Foundry Networks, Inc. 3 - 1
FastIron GS Compact Layer 2 Switch Hardware Installation Guide
• A management station, such as a PC running a terminal emulation application.
• A straight-through EIA/TIA DB-9 serial cable (F/F). This cable can be ordered separately from Foundry
Networks. If you prefer to build your own cable, see the pinout information in “Attaching a PC or Terminal” on
page 3-16.
You use the serial connection to perform basic configuration tasks such as assigning an IP address and network
mask to the system. This information is required for managing the system using the Web management interface
or IronView Network Manager, or using the CLI through Telnet.
Summary of Installation Tasks
Follow the steps listed below to install your FGS device. Details for each of these steps are provided in this
chapter and in the following chapter.
Table 3.1: Summary of Installation Tasks
Task
No.
1 Ensure that the physical environment that will host the
2 Optionally insert an additional power supply. If you need to
4 Install the Foundry device on a desktop, in an equipment
5 When the device is installed, plug the power cord into a
6 Verify that the system LEDs are registering the proper LED
7 Attach a terminal or PC to the Foundry device. This
8 No default password is assigned to the CLI. For additional
Task Where to Find More Information
device has the proper cabling and ventilation.
install a power supply, it may be easier to install it before
mounting the device, although power supplies are “hot
swappable”, and can be installed or removed after the
device is mounted and powered-on.
CAUTION: Remove the power cord from a power
supply before you install or remove it from the device.
Otherwise, the power supply or the device could be
damaged. (The device can be running while a power
supply is installed or removed, but the power supply
itself must be disconnected from the power source.)
rack, or on the wall.
nearby power source that adheres to the regulatory
requirements outlined in this manual.
state after power-on of the system.
enables you to configure the device via the Command Line
Interface (CLI).
access security, assign a password.
“Preparing the Installation Site” on page 3-5
“Installing an Additional Power Supply” on
page 3-5
“Installing the Device” on page 3-11
“Powering On the System” on page 3-14
“Verifying Proper Operation” on page 3-15
“Attaching a PC or Terminal” on page 3-16
“Assigning Permanent Passwords” on
page 4-1
9 Before attaching equipment to the device, you must
configure an interface IP address to the subnet on which it
will be located. Initial IP address configuration is performed
using the CLI with a direct serial connection. Subsequent
IP address configuration can be performed using the Web
management interface.
3 - 2 © 2007 Foundry Networks, Inc. September 2007
“Configuring IP Addresses” on page 4-3
Installing the FastIron GS Chassis
Table 3.1: Summary of Installation Tasks (Continued)
Task
No.
10 Once you power on the device and assign IP addresses,
11 Test IP connectivity by pinging other devices and tracing
12 Continue configuration using the CLI or the Web
13 Secure access to the device. Foundry FastIron Configuration Guide.
Task Where to Find More Information
“Connecting Network Devices” on page 4-4
the system is ready to accept network equipment.
“Testing Connectivity” on page 4-6
routes.
Foundry FastIron Configuration Guide
management interface. You also can use IronView Network
Manager to manage the device. See the Foundry IronView
Network Management User’s Guide for information.
Installation Precautions
Follow these precautions when installing a Foundry device.
General Precautions
WARNING: All fiber-optic interfaces use Class 1 lasers.
CAUTION: Do not install the device in an environment where the operating ambient temperature might exceed
40o C (104o F).
CAUTION: Make sure the air flow around the front, sides, and back of the device is not restricted.
CAUTION: Never leave tools inside the chassis.
Lifting Precautions
WARNING: Make sure the rack or cabinet housing the device is adequately secured to prevent it from becoming
unstable or falling over.
WARNING: Do not use the handles on the power supply units to lift or carry a Foundry device.
WARNING: Mount the devices you install in a rack or cabinet as low as possible. Place the heaviest device at
the bottom and progressively place lighter devices above.
September 2007 © 2007 Foundry Networks, Inc. 3 - 3

FastIron GS Compact Layer 2 Switch Hardware Installation Guide
Power Supply Precautions
The following precautions apply to FastIron GS POE 48-port devices:
• If your FastIron GS POE chassis has 48 ports and only one power supply, and each POE-enabled port needs
15.4 watts, then a maximum of 31 ports can supply power to connected devices.
• If your FastIron GS POE chassis has 48 ports and two power supplies, and the POE ports are consuming
more than 480 watts of power, a single power supply failure will cause both power supplies to shut down.
• If your FastIron GS POE chassis has 48 ports and only one power supply, and the power consuming devices
connected to POE-enabled ports consume a total of more than 480 watts of power, the power supply may
shut down.
CAUTION: Use a separate branch circuit for each AC power cord, which provides redundancy in case one of the
circuits fails.
CAUTION: Ensure that the device does not overload the power circuits, wiring, and over-current protection. To
determine the possibility of overloading the supply circuits, add the ampere (amp) ratings of all devices installed
on the same circuit as the device. Compare this total with the rating limit for the circuit. The maximum ampere ratings are usually printed on the devices near the input power connectors.
CAUTION: All devices with DC power supplies are intended for installation in restricted access areas only. A
restricted access area is where access can be gained only by service personnel through the use of a special tool,
lock and key, or other means of security, and is controlled by the authority responsible for the location.
CAUTION: For a DC system (DC power supply part number RPSDC-FGS), use a grounding wire of at least 10
American Wire Gauge (AWG). The 10 AWG wire should be attached to an agency-approved crimp connector,
crimped with the proper tool.
CAUTION: For the DC input circuit to the system (DC power supply part number RPSDC-FGS), make sure
there is a Listed 30 amp circuit breaker, minimum -48Vdc, double pole, on the input to the terminal block. The
input wiring for connection to the product should be Listed copper wire, 10 AWG, marked VW-1, and rated minimum 90 degrees celcius.
CAUTION: Make sure you insert the power supply right-side up. It is possible to insert the supply upside down,
although the supply will not engage with the power backplane when upside down. The power supply is right-side
up when the power connector is on the left and the fan vent is on the right.
CAUTION: Remove the power cord from a power supply before you install it in or remove it from the device.
Otherwise, the power supply or the device could be damaged as a result. (The device can be running while a
power supply is being installed or removed, but the power supply itself should not be connected to a power
source.)
CAUTION: The FGS power supply is designed exclusively for use with the FGS devices. The power supply produces extensive power to support 802.3af applications. Installing the power supply in a device other than the FGS
will cause extensive damage to your equipment.
WARNING: Disconnect the power cord from all power sources to completely remove power from the device.
WARNING: Make sure to choose the appropriate circuit device depending on the number of AC power supplies
installed in the chassis. The minimum current draw for the system is one AC power supply.
3 - 4 © 2007 Foundry Networks, Inc. September 2007
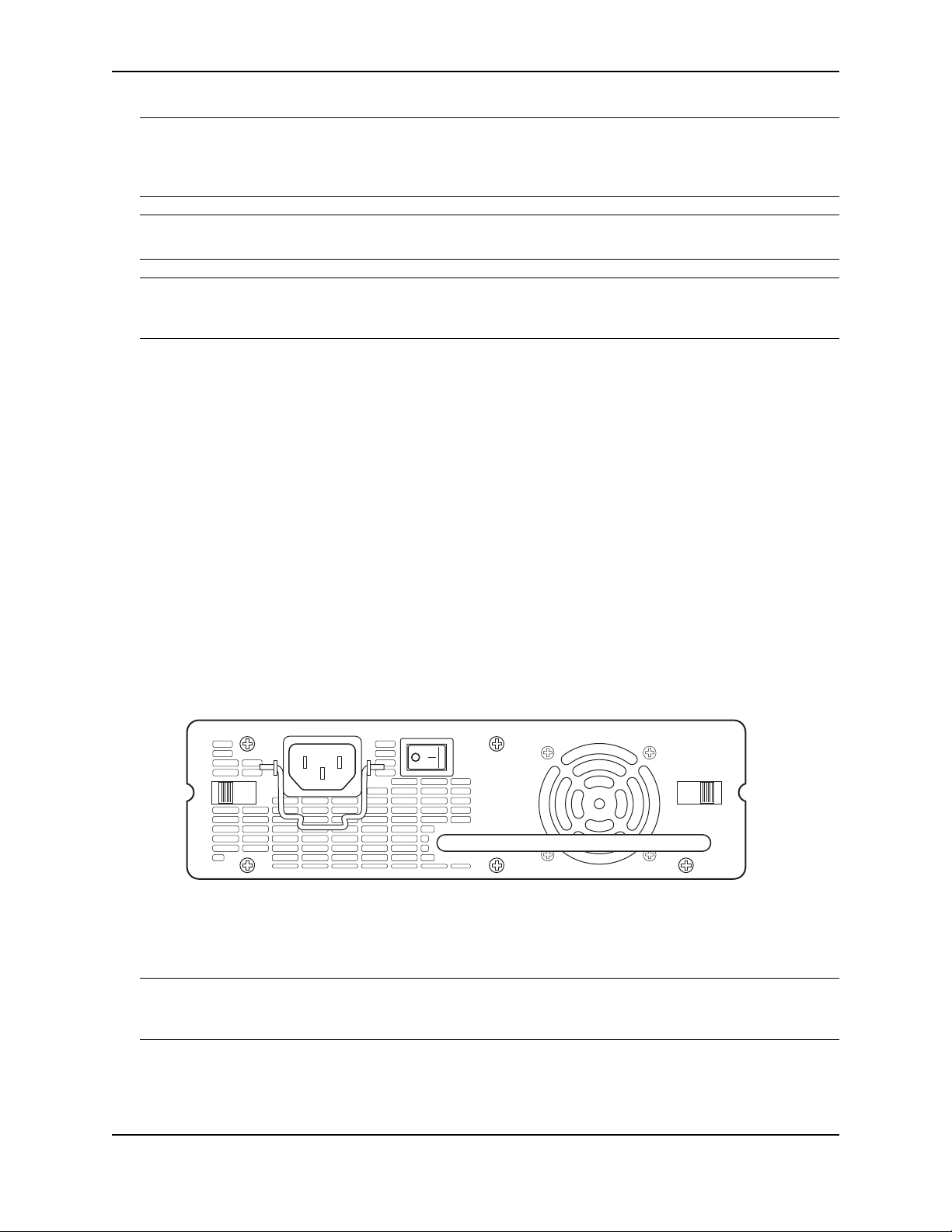
Installing the FastIron GS Chassis
WARNING: Power supplies are hot swappable. However, Foundry Networks recommends that you disconnect
the power supply from AC power before installing or removing the supply. The device can be running while a
power supply is being installed or removed, but the power supply itself should not be connected to a power source.
Otherwise, you could be injured or the power supply or other parts of the device could be damaged.
WARNING: Make sure that the power source circuits are properly grounded, then use the power cord supplied
with the device to connect it to the power source.
WARNING: If the installation requires a different power cord than the one supplied with the device, make sure
you use a power cord displaying the mark of the safety agency that defines the regulations for power cords in your
country. The mark is your assurance that the power cord can be used safely with the device.
Preparing the Installation Site
Cabling Infrastructure
Ensure that the proper cabling is installed in the site. See “Chassis Specifications” on page 6-2 or
www.foundrynetworks.com for a summary of supported cabling types and their specifications.
Installation Location
Before installing the device, plan its location and orientation relative to other devices and equipment. Allow at
least 3" of space at the front of the device for the twisted-pair, fiber-optic, and power cabling. Also, allow a
minimum of 3" of space between the sides and the back of the device and walls or other obstructions.
Installing an Additional Power Supply
The FGS ships with one AC or DC power supply. If desired, you can install a second supply for added power or for
redundancy (if applicable). The illustration below shows the rear panel of an AC power supply.
If you need to install a second power supply, it may be easier to install it before mounting the device, although the
power supplies are “hot swappable” and can be installed or removed after the device is mounted and powered on.
CAUTION: Remove the power cord from a power supply before you install it in or remove it from the device.
Otherwise, the power supply or the device could be damaged. The device can be running while a power supply is
being installed or removed, but the power supply itself should be disconnected from the power source.
This section provides the following procedures:
• “Installing an AC Power Supply” on page 3-6
• “Installing a DC Power Supply” on page 3-8
September 2007 © 2007 Foundry Networks, Inc. 3 - 5
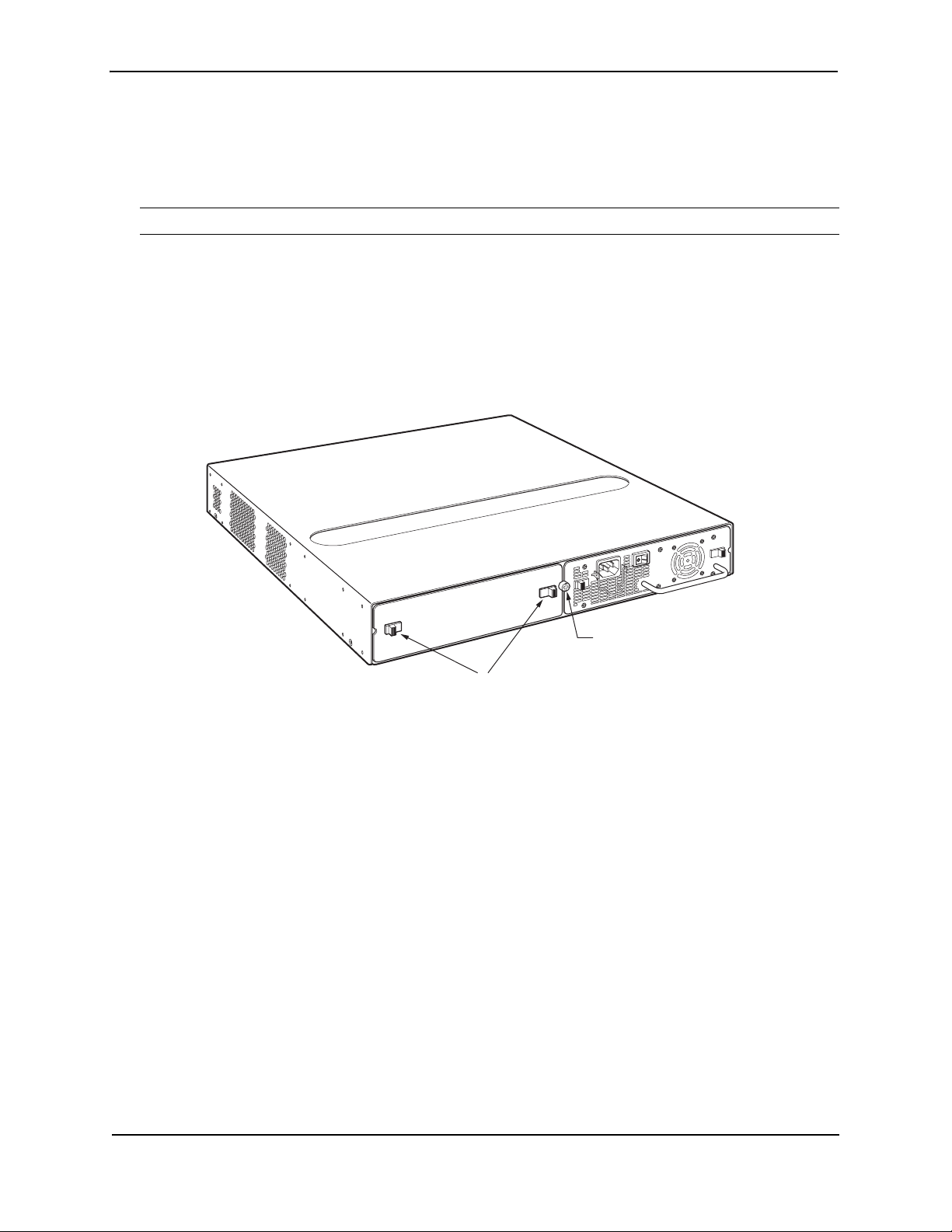
FastIron GS Compact Layer 2 Switch Hardware Installation Guide
You will need the following tools to perform these procedures:
• #2 Phillips-head screwdriver
Installing an AC Power Supply
WARNING: Before beginning the installation, see the precautions in “Power Supply Precautions” on page 3-4.
Use the following procedures for installing AC power supplies in the FastIron GS.
To install an AC power supply, do the following:
1. If necessary, remove the power supply locking screw located in the center rear of the device (illustrated
below).
2. If the empty power supply bay has a cover plate, press inward on the two latches near the left and right edges
of the cover plate to unlock the plate (illustrated below), then remove the plate.
Latches
3. Remove the new power supply from its packaging.
Power supply
locking screw
3 - 6 © 2007 Foundry Networks, Inc. September 2007
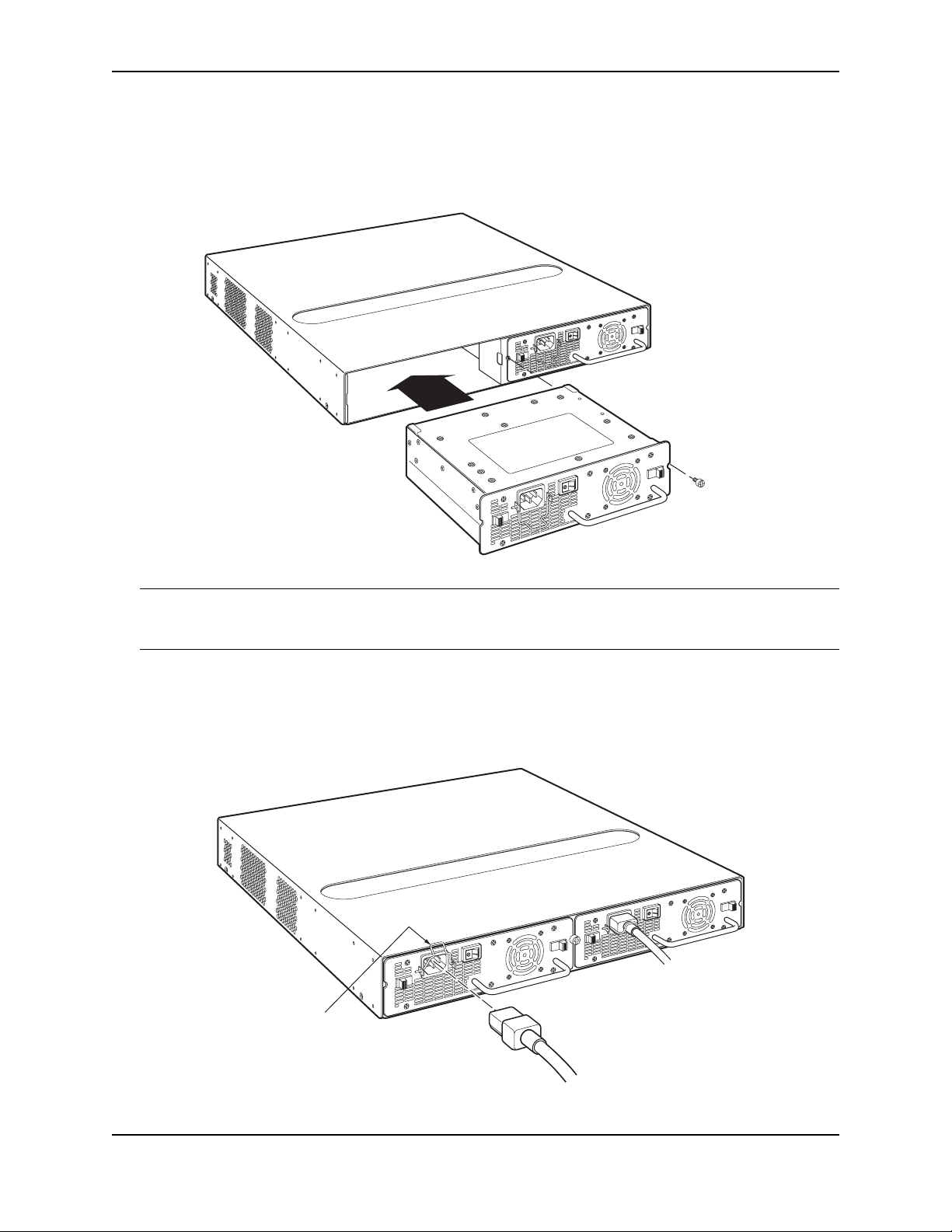
Installing the FastIron GS Chassis
4. With one hand, hold the bar on the front panel of the power supply. With the other hand, support the
underside of the power supply, and insert the power supply into the empty power supply slot. Press until the
supply is completely in the slot, so that the connectors on the back of the supply fully engage with the pins on
the power backplane.
CAUTION: Make sure you insert the power supply right-side up. It is possible to insert the supply upside down,
although the supply will not engage with the power backplane when upside down. The power supply is right-side
up when the power connector is on the left and the fan vent is on the right.
5. Press the two latches near the edges of the supply outward to lock the supply in place.
6. Replace the power supply locking screw.
7. Install the power cord, as shown below.
Retaining Bale AC Power Cord
September 2007 © 2007 Foundry Networks, Inc. 3 - 7
 Loading...
Loading...