Page 1

Foundry AR-Series Router User Guide
For AR1202, AR1204, AR1208, AR1216, AR3201-CH/CL, and AR3202-CH/CL Routers
June 2004 © 2004 Foundry Networks, Inc.
2100 Gold Street
P.O. Box 649100
San Jose, CA 95164-9100
Tel 408.586.1700
Fax 408.586.1900
June 2004
Page 2

Copyright © 2004 Foundry Networks, Inc. All rights reserved.
No part of this work may be reproduced in any form or by any means – graphic, electronic or mechanical, including
photocopying, recording, taping or storage in an information retrieval system – without prior written permission of the
copyright owner.
The trademarks, logos and servi ce marks (“M arks”) displ ayed he rein are the pro perty of Fou ndry or othe r third p arties.
You are not permitted to use these Marks without the prior written consent of Foundry or such appropriate third party.
Foundry Networks, BigIron, FastIron, IronView, JetCore, NetIron, ServerIron, TurboIron, IronWare, EdgeIron,
IronPoint, AccessIron, the Iron family of marks and the Foundry Logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of
Foundry Networks, Inc. in the United States and other countries.
F-Secure is a trademark of F-Se cure Corporat ion. All other trademar ks mentio ned in this doc ument are the property of
their respective owners.
Page 3

Contents
CHAPTER 1
G
ETTING STARTED...................................................................................... 1-1
INTRODUCTION ...........................................................................................................................................1-1
A
UDIENCE ..................................................................................................................................................1-1
OMENCLATURE ............................... ................................................................ ..........................................1-1
N
R
ELATED PUBLICATIONS .............................................................................................................................1-2
L
IST OF FEATURES .....................................................................................................................................1-2
OW TO GET HELP ........................................................... ....... ...... ...... ....... ....................................... .........1-5
H
W
EB ACCESS ...................... ....... ...... ....... ...... ....... ...... ....... ...... ...... ....... ...... ..........................................1-5
E
MAIL ACCESS .............................................. .......................... ................................ .............................1-5
ELEPHONE ACCESS ............................................................... ............................................................. 1-5
T
W
ARRANTY COVERAGE ........................................ ............. ............. ...... ............. ............. ............. ............. ...1-5
CHAPTER 2
C
OMMAND LINE INTERFACE ........................................................................ 2-1
COMMAND TYPES .......................................................................................................................................2-1
ONTEXT-SENSITIVE COMMANDS .......................... ...... ....... ...... ...... ....... ...... ....... ...... ....... ......................2-1
C
C
OMMAND CONVENTIONS ...........................................................................................................................2-2
A
BBREVIATED COMMANDS .......... ................................................... .................................................... ...2-3
AVIGATION ............................................................... .......................... ................................ ................2-4
CLI N
N
AVIGATION KEYS ................................................ ......................... .......................... .......................... ...2-4
C
OMMAND HELP ............................................ ................................................... ..........................................2-4
ELP ...................................................................................................................................................2-4
H
T
REE ..................................................................................................................................................2-5
Q
UESTION MARK HELP SCREEN ...........................................................................................................2-5
LOBAL COMMANDS ............................................................................................................................2-6
G
CHAPTER 3
P
OLICY COMMANDS.................................................................................... 3-1
June 2004 © 2004 Foundry Networks, Inc. iii
Page 4

Foundry AR-Series Router User Guide
CONFIGURE POLICY ........................... ............................................. ............................................. ................3-1
CONFIGURE POLICY AS_PATH ......................................................................................................................3-2
CONFIGURE POLICY COMMUNITY_LIST ................................ ....................................................................... ...3-3
CONFIGURE POLICY COMMUNITY_LIST EXTENDED_COMMUNITY ............................ ....... ...... ....... ...... ....... ...... ...3-4
CONFIGURE POLICY COMMUNITY_LIST STANDARD_COMMUNITY .....................................................................3-5
CONFIGURE POLICY IP_ACCESS_LIST ...........................................................................................................3-6
CONFIGURE POLICY ROUTE_MAP .................................................................................................................3-8
CONFIGURE POLICY ROUTE_MAP MATCH ....................................................................................................3-10
CONFIGURE POLICY ROUTE_MAP MATCH AS_PATH ........................................ ....................................... .......3-11
CONFIGURE POLICY ROUTE_MAP MATCH COMMUNITY .................................................................................3-12
CONFIGURE POLICY ROUTE_MAP MATCH IP IP_ADDRESS ........................ ..................................................... 3-13
CONFIGURE POLICY ROUTE_MAP SET .................................................... ..................................................... 3-14
CONFIGURE POLICY ROUTE_MAP SET AS_PATH ..........................................................................................3-15
CONFIGURE POLICY ROUTE_MAP SET COMMUNITY ......................................................................................3-16
CONFIGURE POLICY ROUTE_MAP SET DISTANCE .........................................................................................3-17
CONFIGURE POLICY ROUTE_MAP SET LOCAL_PREFERENCE ........................... ....................................... .......3-18
CONFIGURE POLICY ROUTE_MAP SET METRIC .................................. ............................................. ..............3-19
CONFIGURE POLICY ROUTE_MAP SET METRIC_TYPE ...................................................................................3-20
CONFIGURE POLICY ROUTE_MAP SET ORIGIN ................................................................... .................... ....... 3-2 1
CHAPTER 4
P
ROTOCOLS OVERVIEW .............................................................................. 4-1
BGP4 ................................................................. .......................................................................................4-1
RFC C
OMPLIANCE ...............................................................................................................................4-2
OSPF .......................... .............................................. ............................................. ...................................4-2
RFC C
OMPLIANCE ...............................................................................................................................4-3
RIP .............................. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. ...................................4-3
RFC C
ULTICASTING ......................................................................... ...... ...... ....... ...... ....... ...... ....... ...... ................4-4
M
P
S
ECURING REMOTE ACCESS USING IPSEC VPN .........................................................................................4-4
OMPLIANCE ...............................................................................................................................4-3
ROTOCOL INDEPENDENT MULTICAST (PIM) .........................................................................................4-4
CHAPTER 5
BGP4 C
CLEAR IP BGP .............................................................................................................................................5-1
CLEAR IP BGP ALL .......................................................................................................................................5-2
CLEAR IP BGP GROUP ........................................... .................... ................... ................... .................... .........5-3
CLEAR IP BGP NEIGHBOR ............................................. ................................................... ............................. 5-4
LEAR COMMANDS ..........................................................................5-1
CHAPTER 6
G
ENERIC ROUTING COMMANDS...................................................................6-1
CONFIGURE ROUTER ...................................................................................................................................6-1
CONFIGURE ROUTER ROUTERID ...................................................................................................................6-2
SHOW IP ROUTES .............................................................. ..........................................................................6-3
iv © 2004 Foundry Networks, Inc. June 2004
Page 5

Contents
CHAPTER 7
BGP4 C
CONFIGURE ROUTER BGP ............................................................................................................................7-1
CONFIGURE ROUTER BGP AGGREGATE_ADDRESS ............................................................ .............................7-2
CONFIGURE ROUTER BGP ALWAYS_COMPARE_MED ......................................................................................7-4
CONFIGURE ROUTER BGP DEFAULT_METRIC .............................................................. ...................................7-5
CONFIGURE ROUTER BGP DISTANCE ...................... ....... ...... ....... ...... ...... ....... ...... ....... ...... ....... ......................7-6
CONFIGURE ROUTER BGP GROUP .............................................. ...... ...... ....... ...... ....... ...... ....... ...... ....... .........7-7
CONFIGURE ROUTER BGP GROUP DISTRIBUTE_LIST ......................................................................................7-8
CONFIGURE ROUTER BGP GROUP FILTER_LIST .................... ............. ............. ............. ............. ............. .........7-9
CONFIGURE ROUTER BGP GROUP NEXT_HOP_SELF ....................................................................................7-10
CONFIGURE ROUTER BGP GROUP PASSWORD ..................... ....................................... ................................. 7-11
CONFIGURE ROUTER BGP GROUP REMOVE_PRIVATE_AS ................. ........................................................... 7-12
CONFIGURE ROUTER BGP GROUP ROUTE_MAP ...........................................................................................7-13
CONFIGURE ROUTER BGP NEIGHBOR ......................................... ................................ ................................ .7-14
CONFIGURE ROUTER BGP NEIGHBOR ADVERTISEMENT_INTERVAL ................................................................7-16
CONFIGURE ROUTER BGP NEIGHBOR ALLOWBADID ........................... .......................................................... .7-17
CONFIGURE ROUTER BGP NEIGHBOR DEFAULT_ORIGINATE ............................................................ ..............7-1 8
CONFIGURE ROUTER BGP NEIGHBOR DESCRIPTION .....................................................................................7-19
CONFIGURE ROUTER BGP NEIGHBOR DISTRIBUTE_LIST .................................. ...... ....... ...... ....... ...... ....... ...... .7-20
CONFIGURE ROUTER BGP NEIGHBOR EBGP_MULTIHOP ............................................................ ....................7-21
CONFIGURE ROUTER BGP NEIGHBOR FILTER_LIST ............................ ................................ ........................... 7-22
CONFIGURE ROUTER BGP NEIGHBOR KEEP .................................................................................................7-23
CONFIGURE ROUTER BGP NEIGHBOR LOGUPDOWN ..................................................... ............. ............. ....... 7 -24
CONFIGURE ROUTER BGP NEIGHBOR MAXIMUM_PREFIX ..............................................................................7-25
CONFIGURE ROUTER BGP NEIGHBOR NEIGHBOR_GROUP ........................ .................................................... .7-26
CONFIGURE ROUTER BGP NEIGHBOR NEXT_HOP_SELF .................................. ................... .................... ....... 7-27
CONFIGURE ROUTER BGP NEIGHBOR PASSWORD ................ ................................................................. .......7-28
CONFIGURE ROUTER BGP NEIGHBOR ROUTE_MAP ......................................................................................7-29
CONFIGURE ROUTER BGP NEIGHBOR TIMERS ................ ................................................... ...........................7 -30
CONFIGURE ROUTER BGP NEIGHBOR UPDATE_SOURCE .............................................. ................................. 7-31
CONFIGURE ROUTER BGP REDISTRIBUTE ......................................... ........................................................... 7-32
CONFIGURE ROUTER BGP REDISTRIBUTE CONNECTED ......................................... ....................................... .7-33
CONFIGURE ROUTER BGP REDISTRIBUTE OSPF ...........................................................................................7-34
CONFIGURE ROUTER BGP REDISTRIBUTE RIP ..............................................................................................7-35
CONFIGURE ROUTER BGP REDISTRIBUTE STATIC .............................. ....................................... .................... 7-36
ONFIGURE COMMANDS................................................................... 7-1
CHAPTER 8
BGP4
SHOW IP BGP .................................... ................................................... .......................................................8-1
SHOW IP BGP AGGREGATE_ADDRESS .............. ................................ ................................ ............................. 8-2
SHOW IP BGP COMMUNITY ...........................................................................................................................8-3
SHOW IP BGP GROUPS ................................................................................................................................8-5
SHOW IP BGP NEIGHBORS ..................................... ............. ............. ...... ............. ............. ............. ............. ...8-6
SHOW IP BGP PATHS ...................................................................................................................................8-9
June 2004 © 2004 Foundry Networks, Inc. v
SHOW COMMANDS ...........................................................................8-1
Page 6

Foundry AR-Series Router User Guide
SHOW IP BGP REGEXP .................................... ................................................... ........................................8-10
SHOW IP BGP SUMMARY ............................................................................................................................8-11
SHOW IP BGP TABLE .................................................... ...................................... ........................................8-12
SHOW POLICY ...........................................................................................................................................8-13
SHOW POLICY AS_PATH ........................................ ....... ...... ....... ...... ....................................... ...... ....... ...... .8-14
SHOW POLICY COMMUNITY_LIST ................................................................................................................8-15
SHOW POLICY IP_ACCESS_LIST .................................................................................................................8-16
SHOW POLICY ROUTE_MAP ................................................ ....................................... ................................. 8-17
CHAPTER 9
OSPF C
CONFIGURE ROUTER OSPF ..........................................................................................................................9-2
CONFIGURE ROUTER OSPF 1583 COMPATIBILITY ................................... ....................................................... 9-3
CONFIGURE ROUTER OSPF AREA .................................................................................................................9-4
CONFIGURE ROUTER OSPF AREA AREA_TYPE ...............................................................................................9-5
CONFIGURE ROUTER OSPF AREA AREA_TYPE NORMAL .................................................................. ................9- 6
CONFIGURE ROUTER OSPF AREA AREA_TYPE NSSA ......................................................................................9-7
CONFIGURE ROUTER OSPF AREA AREA_TYPE NSSA NO_SUMMARY ................................................................9-8
CONFIGURE ROUTER OSPF AREA AREA_TYPE STUB ......................................................................................9-9
CONFIGURE ROUTER OSPF AREA AREA_TYPE STUB NO_SUMMARY ..............................................................9-10
CONFIGURE ROUTER OSPF AREA DEFAULT_COST .......................................................................................9-11
CONFIGURE ROUTER OSPF AREA RANGE ....................................................................................................9-12
CONFIGURE ROUTER OSPF AREA VIRTUAL_LINK ............ ....................................................................... .......9-13
CONFIGURE ROUTER OSPF AREA VIRTUAL_LINK AUTHENTICATION ............................... ................................ .9-1 4
CONFIGURE ROUTER OSPF AREA VIRTUAL_LINK DEAD_INTERVAL ...................................... ...........................9-1 5
CONFIGURE ROUTER OSPF AREA VIRTUAL_LINK HELLO_INTERVAL ...............................................................9-16
CONFIGURE ROUTER OSPF AREA VIRTUAL_LINK RETRANSMIT_INTERVAL ......................................................9-17
CONFIGURE ROUTER OSPF AREA VIRTUAL_LINK TRANSMIT_DELAY ................. ....................................... .......9-18
CONFIGURE ROUTER OSPF DISTANCE .............................................. ............................................. ..............9-19
CONFIGURE ROUTER OSPF DISTANCE OSPF ............................................................... .................................9-20
CONFIGURE ROUTER OSPF DISTANCE OSPF EXTERNAL .................................. ....................................... .......9-21
CONFIGURE ROUTER OSPF DISTANCE OSPF NON_EXTERNAL .......................................................................9-22
CONFIGURE ROUTER OSPF INTERFACE ......................................................................................... ..............9-23
CONFIGURE ROUTER OSPF INTERFACE AUTHENTICATION ........................ ....................................... ..............9 -24
CONFIGURE ROUTER OSPF INTERFACE COST ..............................................................................................9-25
CONFIGURE ROUTER OSPF INTERFACE DEAD_INTERVAL ................... ........................................................... 9-26
CONFIGURE ROUTER OSPF INTERFACE HELLO_INTERVAL .................. ...... ....... ...... ....... ...... ....... ...... ....... ...... .9-27
CONFIGURE ROUTER OSPF INTERFACE NEIGHBOR ............... .......................... .......................... ................... .9 -28
CONFIGURE ROUTER OSPF INTERFACE NETWORK .......................................................................................9-29
CONFIGURE ROUTER OSPF INTERFACE POLL_INTERVAL .............. ................... ................... .................... ....... 9-31
CONFIGURE ROUTER OSPF INTERFACE PRIORITY ........................................................................................9-32
CONFIGURE ROUTER OSPF INTERFACE RETRANSMIT_INTERVAL ...................................................................9-33
CONFIGURE ROUTER OSPF INTERFACE TRANSMIT_DELAY ................. .......................................................... .9-34
CONFIGURE ROUTER OSPF REDISTRIBUTE ..................................................................................................9-35
CONFIGURE ROUTER OSPF REDISTRIBUTE BGP ...........................................................................................9-36
ONFIGURE COMMANDS................................................................... 9-1
vi © 2004 Foundry Networks, Inc. June 2004
Page 7

Contents
CONFIGURE ROUTER OSPF REDISTRIBUTE CONNECTED ...............................................................................9-37
CONFIGURE ROUTER OSPF REDISTRIBUTE RIP ............................................................................................9-38
CONFIGURE ROUTER OSPF REDISTRIBUTE STATIC ......................................... ..............................................9 -39
CONFIGURE ROUTER OSPF REF_BW ................................... ................................................................. .......9-40
CONFIGURE ROUTER OSPF TIMERS ............................................................................................................9-41
CHAPTER 10
OSPF S
SHOW IP OSPF AREA .................................................................................................................................10-1
SHOW IP OSPF DATABASE ..... ................................ ................................ ................................. .................... 10-3
SHOW IP OSPF DATABASE ALL ..... .................... ................... ................... .................... ................... .............. 1 0-4
SHOW IP OSPF DATABASE ASBR_SUMMARY ................................................................................................10-5
SHOW IP OSPF DATABASE DATABASE_SUMMARY ........... ......................... .......................... .......................... .1 0-6
SHOW IP OSPF DATABASE EXTERNAL ........ ....................................... ...... ....... ...... ....... ...... ....... ...... ....... ...... .10-7
SHOW IP OSPF DATABASE NETWORK ..........................................................................................................10-8
SHOW IP OSPF DATABASE NSSA_EXTERNAL ........... ................................ ................................. .................... 10-9
SHOW IP OSPF DATABASE ROUTER ........... ............. ....... ............. ............ ............. ............. ............. ............10-10
SHOW IP OSPF DATABASE SELF_ORIGINATE .................................................. ................................ ............ 10-11
SHOW IP OSPF DATABASE SUMMARY ............................ ............................................................................10-12
SHOW IP OSPF GLOBAL ................................................ ...... ....... ...... ....................................... ...... ....... .....10-13
SHOW IP OSPF INTERFACE ........................................... ...................................... ...................................... 10-14
SHOW IP OSPF INTERFACE ALL ........................................... .......................... .......................... .................. 10 -15
SHOW IP OSPF INTERFACE BUNDLE ..........................................................................................................10-16
SHOW IP OSPF INTERFACE ETHERNET ......................................................................................................10-17
SHOW IP OSPF NEIGHBOR ..................................... ....................................... ....................................... .....10-1 8
SHOW IP OSPF NEIGHBOR DETAIL .............................................. ................... .......................... .................. 10-19
SHOW IP OSPF NEIGHBOR ID .................... .......................................................... ......................................10 -20
SHOW IP OSPF NEIGHBOR INTERFACE ......................................................................................................10-21
SHOW IP OSPF NEIGHBOR INTERFACE BUNDLE .................... ....................................... ............................... 10-22
SHOW IP OSPF NEIGHBOR INTERFACE ETHERNET ....................... ............................................................... 10-23
SHOW IP OSPF NEIGHBOR LIST ..................................... ......................... .......................... .................... ..... 10-24
SHOW IP OSPF REQUEST_LIST .................................................................................................................10-25
SHOW IP OSPF RETRANSMISSION_LIST .....................................................................................................10-26
SHOW IP OSPF VIRTUAL_LINKS ..................................... ................... ................... .................... ..................10-27
HOW COMMANDS .........................................................................10-1
CHAPTER 11
RIP C
CONFIGURE ROUTER RIP ...........................................................................................................................11-2
CONFIGURE ROUTER RIP DEFAULT_METRIC ................................................................................................11-3
CONFIGURE ROUTER RIP DISTANCE ........................................... ................................................... ..............11-4
CONFIGURE ROUTER RIP INTERFACE .......................................................................................................... 11-5
CONFIGURE ROUTER RIP INTERFACE AUTHENTICATION ............................................................ .................... 11-6
CONFIGURE ROUTER RIP INTERFACE DISTRIBUTE_LIST ............................................... .................................1 1-7
CONFIGURE ROUTER RIP INTERFACE METRIC ..............................................................................................11-8
CONFIGURE ROUTER RIP INTERFACE MODE ................................................................................................11-9
June 2004 © 2004 Foundry Networks, Inc. vii
ONFIGURE COMMANDS .................................................................... 11-1
Page 8

Foundry AR-Series Router User Guide
CONFIGURE ROUTER RIP INTERFACE NEIGHBOR ..................................... ................................. .................. 11-10
CONFIGURE ROUTER RIP INTERFACE PASSIVE ..................................................... ................................. .....11 -11
CONFIGURE ROUTER RIP INTERFACE SPLIT_HORIZON .............................................................. ..................11 -12
CONFIGURE ROUTER RIP MODE .................................... ...................................... ...................................... 11-13
CONFIGURE ROUTER RIP PACING .............................................................................................................11-14
CONFIGURE ROUTER RIP PASSIVE ............................................................................................................11-15
CONFIGURE ROUTER RIP REDISTRIBUTE ...................................................................................................11-16
CONFIGURE ROUTER RIP REDISTRIBUTE BGP ............................................................................................11-17
CONFIGURE ROUTER RIP REDISTRIBUTE CONNECTED ................................................................................11-18
CONFIGURE ROUTER RIP REDISTRIBUTE OSPF ..........................................................................................11-19
CONFIGURE ROUTER RIP REDISTRIBUTE STATIC ........................................................................................11-20
CONFIGURE ROUTER RIP TIMERS .............. ....... ...... ....... ...... ....................................... ...... ....... ...... ....... .....11-21
CONFIGURE ROUTER RIP TIMERS FLUSH ...................................................................................................11-22
CONFIGURE ROUTER RIP TIMERS HOLDDOWN ...........................................................................................11-23
CONFIGURE ROUTER RIP TIMERS UPDATE .............................................. ................................................... 11-24
CHAPTER 12
RIP
SHOW COMMANDS .............................................................................12-1
SHOW IP RIP .............................................................................................................................................12-2
SHOW IP RIP GLOBAL ......................................................... ................... .................... ................... ..............12-3
SHOW IP RIP INTERFACE ....... .................................................... ................................................... ..............12-4
SHOW IP RIP INTERFACE ALL .............. .......................... ................................ ................................ ..............1 2-5
SHOW IP RIP INTERFACE BUNDLE ...............................................................................................................12-6
SHOW IP RIP INTERFACE ET HERNE T ...........................................................................................................12-7
SHOW IP RIP INTERFACE STATISTICS ..........................................................................................................12-8
SHOW IP RIP STATISTICS ...........................................................................................................................12-9
CHAPTER 13
AS P
MATCHING AS PATHS .......................................... ....................................... ................................ ..............13-1
AS P
AS P
ATH REGULAR EXPRESSIONS............................................................13-1
ATH REGULAR EXPRESSIONS (REGEX) ................................................. ................... .................... ....... 13-1
ATH TERMS ......................................................................................................................................13-1
CHAPTER 14
M
ULTICASTING..........................................................................................14-1
MULTICASTING OVERVIEW ........................................................................................................................14-1
P
ROTOCOL INDEPENDENT MULTICAST (PIM) .......................................................................................14-1
OMMANDS ................................................................................................................................14-1
PIM C
P
ROTOCOL INDEPENDENT MULTICAST - SOURCE SPECIFIC MULTICAST (PIM-SSM) ....................................14-3
I
NTERNET GROUP MANAGEMENT PROTOCOL (IGMP) ................................................................................14-4
IGMP C
T
RACEROUTE FACILITY FOR IP MULTICAST ........................................................ ........................................ 14-6
M
ULTICAST MULTIPATH ............................................... ...................................... ....................................... .14-6
ULTIPATH COMMANDS ............................................................................................................................14-7
M
viii © 2004 Foundry Networks, Inc. June 2004
OMMANDS .............................................................................................................................14-4
Page 9

Contents
GENERIC ROUTING ENCAPSULATION (GRE) ..............................................................................................14-7
CHAPTER 15
S
ECURITY FEATURES ................................................................................ 15-1
INTRODUCTION TO SECURITY ....................................................................................................................15-1
E
NABLING SECURITY FEATURES .........................................................................................................15-1
ECURING REMOTE ACCESS USING IPSEC VPN .......................................................................................15-2
S
A
CCESS METHODS ............................................................ ............................................. ....................1 5-2
E
XAMPLE 1: SECURELY MANAGING THE FOUNDRY AR1204 OVER AN IPSEC TUNNEL ................... .......15-3
XAMPLE 2: JOINING TWO PRIVATE NETWORKS WITH AN IP SECURITY TUNNEL .................................15-10
E
E
XAMPLE 3: JOINING TWO NETWORKS WITH AN IPSEC TUNNEL USING MULTIPLE IPSEC PROPOSALS .15-19
E
XAMPLE 4: SUPPORTING REMOTE USER ACCESS ................................................................ ............15-28
E
XAMPLE 5: CONFIGURING IPSEC REMOTE ACCESS TO CORPORATE LAN WITH MODE-CONFIGURATION
ETHOD ................................................. ....... ...... ....... ...... ....................................... ...... ............15-37
M
C
ONFIGURING GRE ................................................................................................................................15-45
F
IREWALLS ................................ .............................................. ...............................................................15-50
IREWALL CONFIGURATION EXAMPLES .................................................. ................... .................... ..... 15-50
F
S
TOPPING DOS ATTACKS ................. ....................................... ....................................... .................. 15-56
P
ACKET REASSEMBLY ......................................................................................................................15-57
NAT C
NAT C
S
ECURITY PROTOCOL DEFAULTS ............................................................................................................15-61
IPS
F
F
IREWALL DEFAULT VALUES ...................................................................................................................15-63
UNNELING DEFAULT VALUES ................................................................................................................. 15-65
T
ONFIGURATIONS ....................................................................................................................15-57
ONFIGURATION EXAMPLES .....................................................................................................15-58
EC SUPPORTED PROTOCOLS AND ALGORITHMS ........................ .............................................. .....15-61
OUNDRY IKE AND IPSEC DEFAULTS ...............................................................................................15-62
June 2004 © 2004 Foundry Networks, Inc. ix
Page 10

Chapter 1
Getting Started
Introduction
This guide describes how to configure the AccessIron routers in typical scenarios using information presented in
the configurations and user guides.
Audience
This manual is desi gned f or system ad ministrat ors with a working kn owledg e of Layer 2 and Layer 3 switchin g and
routing.
If you are using a Foundry Layer 3 Switch, you should be familiar with the following protocols if applicable to your
network – IP, RIP, OSPF, BGP4, PIM, and VRRP.
Nomenclature
This guide uses the following typographical conventions to show information:
Italic highlights the title of another publication and occasionally emphasizes a word or phrase.
Bold highlights a CLI command.
Bold Italic highlights a term that is being defined.
Underline
Capitals highlights field names and buttons that appear in the Web management interface.
NOTE: A note emphasizes an important fact or calls your attention to a dependency.
WARNING: A warning calls your attention to a possible hazard that can cause injury or death.
CAUTION: A caution calls your attention to a possible hazard that can damage equipment.
highlights a link on the Web management interface.
June 2004 © 2004 Foundry Networks, Inc. 1 - 1
Page 11
Foundry AR-Series Router User Guide
Related Publications
The following Foundry Networks documents supplement the information in this guide.
• Release Notes
Printed release notes provide th e latest i nformatio n. If releas e notes a re provide d with you r product, fo llow th e
instructions contained within them instead of those provided in other documentation.
• Foundry AR-Series AR1202 and AR1204 Installation Guide
This guide is designed to assist users with the initial installation and deployment of the Foundry AR1202 two-
port and AR1204 four-port router. The guide provides a brief overview of the installation and initial
configuration proces se s.
• Foundry AR-Series AR1202 and AR1204 Quick Installation Guide
This detailed guide provides an abbreviated install guide for those experienced with installing Foundry
AccessIron routers.
• Foundry AR-Series Rack-Mounted Router Installation Guide
This guide is designed to assist users with the initial installation and deployment of Foundry rack-mounted
routers. The guide provides a brief overview of the installation and initial configuration processes.
• Foundry AR-Series Rack-Mounted Router Quick Installation Guide
This detailed guide provides an abbreviated install guide for those experienced with installing Foundry
AccessIron rack-mounted routers.
• Foundry AR-Series Router Configurations Guide
This guide provides examples of AccessIron configurations.
• Foundry AR-Series Router Command Reference Guide
This guide explains the syntax and application of AccessIron router CLI commands.
To order additional copies of these manuals, do one of the following:
• Call 1.877.TURBOCALL (887.2622) in the United States or 1.408.586.1881 outside the United States.
• Send email to info@foundrynet.com.
List of Features
Table 1.1 shows the features supported on AccessIron devices.
T a ble 1.1: Fea ture Supporte d in AccessIro n Device s
Category Feature AR1202
AR1204
AR1208
AR1216
Interfaces
WAN/LAN 10/100 Fast Ethernet 2 2 2
T1/E1 Yes - Channelized T3 - - Yes
AR3201-T-CL
AR3202-T-CL
AR3201-T-CH
AR3202-T-CH
Clear Channel T3 - Yes -
WAN Protocols
1 - 2 © 2004 Foundry Networks, Inc. June 2004
Page 12
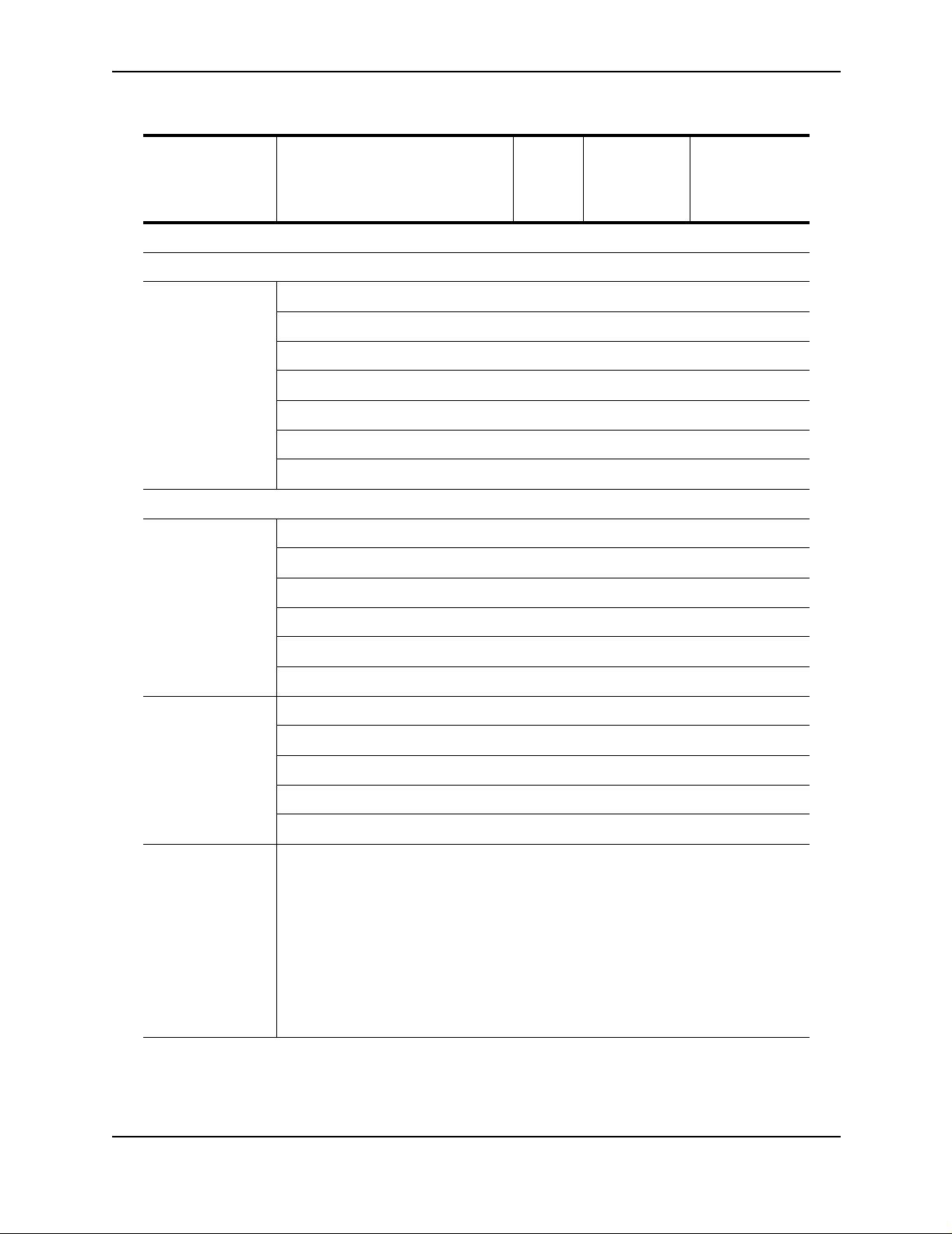
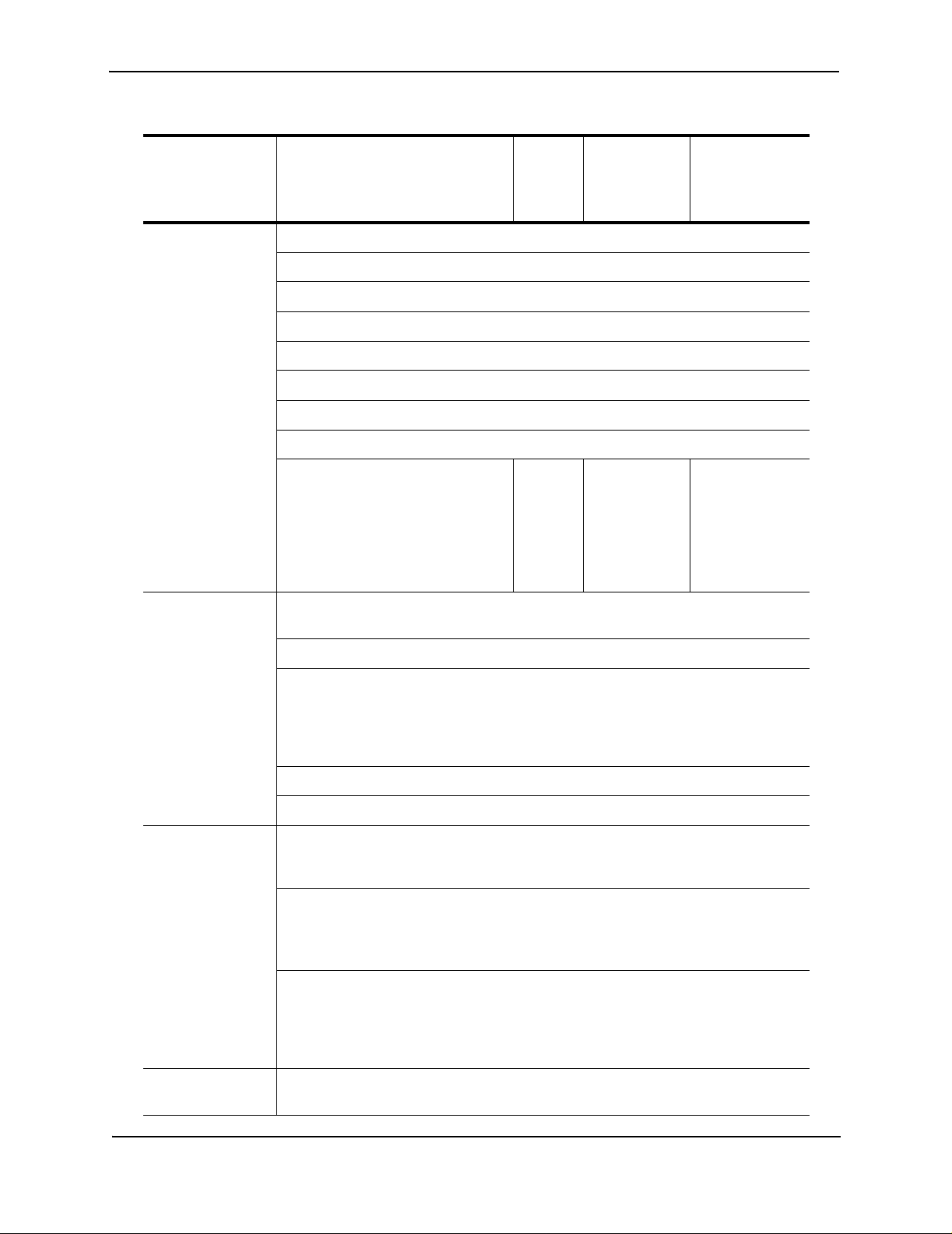
Table 1.1: Feature Supported in AccessIron Devices (Continued)
Getting Started
Category Feature AR1202
AR1204
AR1208
AR1216
PPP, PAP, Multilink PPP, Frame Relay, Multilink Frame Relay, (FRF.15, FRF.16.1) BCP, HDLC
Layer 2 Features
802.1Q VLAN tagging and forwarding over WLAN
Virtual LAN Domain (VLD) VLAN Double Tagging
Transparent Bridging
Jumbo Frames (4072 bytes)
IP Multiplexing
NAT mode
Transparent Layer 3 packet forwarding
Layer 3 Features
Routing RIPv1/v2
OSPF
BGP4
AR3201-T-CL
AR3202-T-CL
AR3201-T-CH
AR3202-T-CH
Static Routing
ECMP (IP load balancing)
Multicast (PIM-SM, PIM-SSM, IGMP v2/v3)
High Availabi lit y VRRP
BGP4 Multi-homing
Bundle Tracking
MLPPP Bundle Thresholding
LAN Interface Load Sharing with Failover
Security/
Management
Stateful Packet Inspection Firewall with:
Layer-3 mode (router and NAT)
Policy-based NAT/PAT
Policy-based filters
URL and application content filtering
Time and rate limiting
Denial of Service protection
Network attack detection
Application Level Gateway support
Packet-level logging and syslog support
June 2004 © 2004 Foundry Networks, Inc. 1 - 3
Page 13
Foundry AR-Series Router User Guide
Table 1.1: Feature Supported in AccessIron Devices (Continued)
Category Feature AR1202
AR1204
AR1208
AR1216
ACLs
DHCP
TFTP
PAP
RADIUS
TACACS+
SSH v2
GRE Tunneling
IPSec VPN with integrated IKE
Site-to-site VPN
Site-to-remote VPN
MD5 & SHA-1 authentication
Hardware accelerated encryp tio n
3DES (168 bit), DES (56 bit), AES
VPN
optional
on the
AR1202
and
AR1204
(256 bit) encryption
AR3201-T-CL
AR3202-T-CL
AR3201-T-CH
AR3202-T-CH
--
QoS/Traffic
Management
Service
Provisioning
RED
DiffServ
Class-based Queuing per:
IP address
Flow
VLAN tag
Application port
Frame Relay traffic shaping and policing
VLAN-802.1P 8 queue prioritization of VLAN frames
Management (in-band, serial, Telnet, or modem) by:
CLI
SNMP
Monitoring
syslog
Statistics
Alarms
Diagnostics
BERT
Loopback testing
Traceroute
Reverse Telnet
Specialized
Hospitality Web Redirection
Features
1 - 4 © 2004 Foundry Networks, Inc. June 2004
Page 14
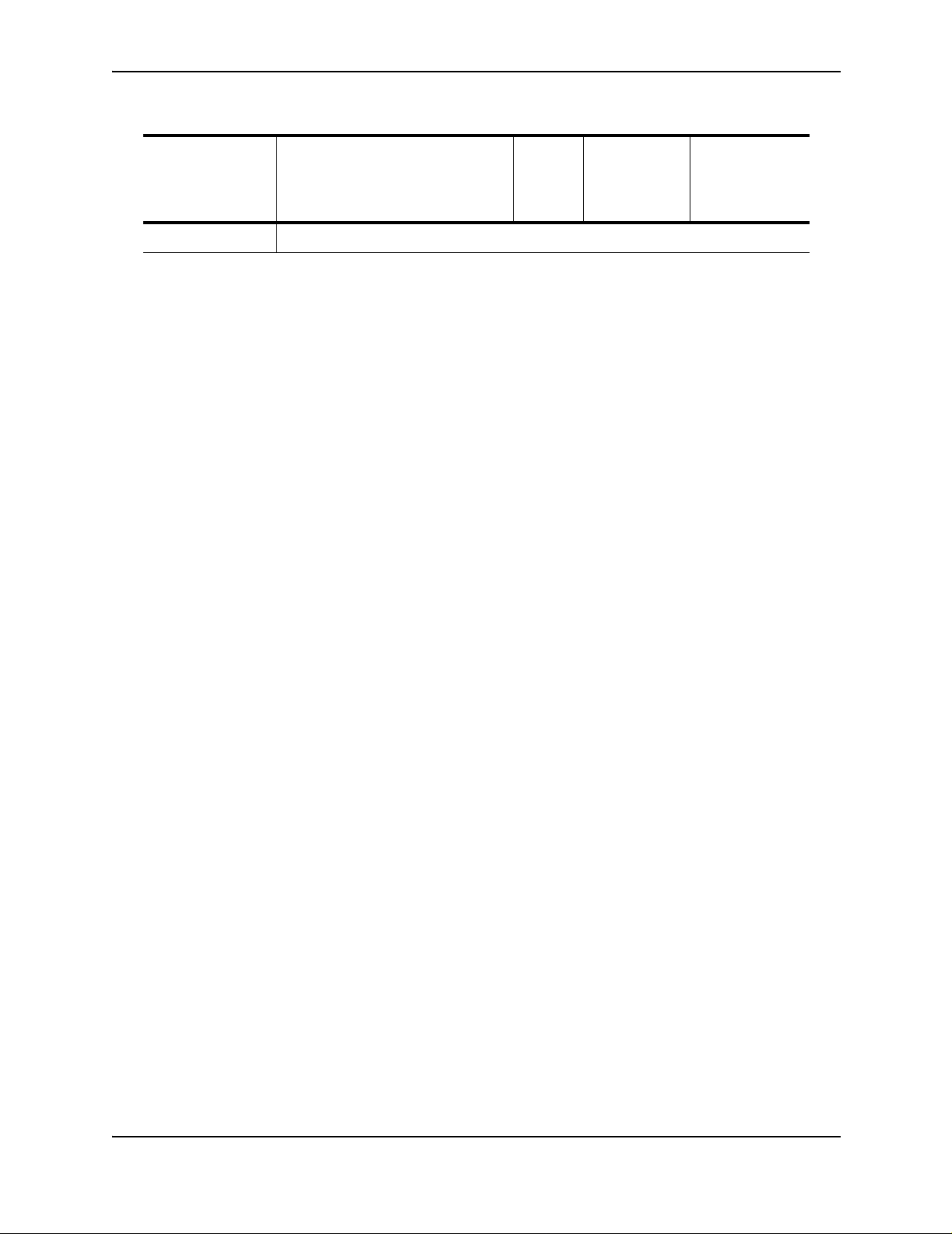
Table 1.1: Feature Supported in AccessIron Devices (Continued)
Getting Started
Category Feature AR1202
AR1204
AR1208
AR1216
Timed Access List
AR3201-T-CL
AR3202-T-CL
AR3201-T-CH
AR3202-T-CH
How to Get Help
Foundry Networks technical support will ensure that the fast and easy access that you have come to expect from
your Foundry Networks products will be maintained.
Web Access
• http://www.foundrynetworks.com
Email Access
Technical requests can also be sent to the following email address:
• support@foundrynet.com
Teleph one Access
• 1.877.TURBOCALL (887.2622) United States
• 1.408.586.1881 Outside the United States
Warranty Cove rage
Contact Foundry Networks using a ny of the methods listed above for informati on about t he sta ndard and extended
warranties.
June 2004 © 2004 Foundry Networks, Inc. 1 - 5
Page 15

Foundry AR-Series Router User Guide
1 - 6 © 2004 Foundry Networks, Inc. June 2004
Page 16
Chapter 2
Command Line Interface
This chapter introduces the Command Line Interface (CLI) hierarchy and the conventions used to describe it. It
also introduces the CLI navigation keys and methods, as well as the available help screens.
Command Types
This guide contains two types of commands: transition, or mode change, commands and standard commands.
Transition commands do not affect the syst em configuration, they are used to ga in access to lower- or next-level
commands in the CLI hierarchy. Following each transition command is a brief description, a syntax and usage
example, a list of next-level commands, and a list of systems for which the command is applicable.
NOTE: In certain instances, transition commands will select an interface for configuration and access next-level
commands. For example, the configure interface bundle dallas command accesses the configure interface
bundle mode and selects or creates the bundle dallas.
Stan da rd comma nds a re u sed t o conf igure t he syst em. Fo llowing ea ch st and ard co mman d is a brie f desc ript ion, a
list of parameters and definitions, a syntax and usage example, a list of related commands, and a list of systems
for which the command is applicable.
Context-Sensitive Commands
Some commands are context-sensitive. Once a module, bundle, or Ethernet port has been selected for
configuration, all further configuration applies only to the selected interface. Table 2.1: shows a context-sensitive
command string for a AR1208 system. In this example, T1 link 1 remains selected for configuration until you exit
from the Foundry-AR1208/con fig ure / mo dul e/t1 # prom pt.
Table 2.1: Context-Sensitive Command Sequence
Context-Sensitive Command String Example
1 Go into the configuration mode.
1 Specify the type of interface (T1). Foundry-AR1208/configure#module t1
Foundry-AR1208#configure terminal
1 Choose the specific interface (T1 link 1). Foundry-AR1208/configure#module t1 1
1 From now on, al l con figurat ion co mman ds
are for T1 link 1 until y ou exi t from mo dule
configuration or choose another T1 link.
June 2004 © 2004 Foundry Networks, Inc. 2 - 1
Foundry-AR1208/configure/module/t1 1#
Page 17
Foundry AR-Series Router User Guide
NOTE: Command strings that require identification of a specific interface are context-sensitive.
Command Conventions
Each command is briefly described and then followed by the complete syntax, which is essentially a map of the
command that shows mandatory and optional parameters.
The following tables provide details of the conventions used for syntaxes and examples.
Table 2.2: Syntax Conventions
For Syntaxes What it means
normal type Within syntaxes, “normal type” represents required words
that must be entered by the user — except when follo wed by
a parameter setting that is enclosed in angled brackets. In
that case, only enter the parameter setting enclosed in the
angled brackets .
Example 1: Normal type only.
In this example, the user enters the word or argument
(module) appearing in the syntax in “normal type.”
Syntax:
module
Command execution:
module
Example 2: Normal type word or argument that is followed
by a second normal type word or argument, which is
followed by a p aram eter setting enclose d i n a ngl ed bra ck et s .
In this example, the user enters the first word or argument
“connections,” appearing in normal type, and then only
enters the value “4” of the second word or argument.
Syntax:
connections connections < n >
Command execution:
connections 4
In other words, the first occurence of “connections” must be
entered because it is not followed by a setting enclosed in
angled brackets. The second occurence of the word
“connections” must NOT be entered bec au se it is followed
by a setting enclosed in angled brackets. This value of the
setting must be entered to execute the command.
2 - 2 © 2004 Foundry Networks, Inc. June 2004
Page 18
Command Line Interface
Table 2.2: Syntax Conventions (Continued)
[ a | b | c ] Normal brackets “[ ]” indicate optional keywords or
arguments.
A vertical bar “ | “ separates individual settings.
Example:
In this example, the user enters the word “timeout;” must
specify either for “tcp” or “udp” for a protocol type; and
optionally enters a timeout value “n.”
Syntax:
timeout protocol_ty pe < tcp | udp > [ s econds < n > ]
Command execution:
timeout udp 3600
< # Angled brackets. All parameter settings are enclosed in
angled brackets. The user is directed to choose an
appropriate setting. In some cases, the parameter name
accompanies the required setting.
[ ] Optional parameter settings in each syntax are indicated by
normal brackets.
Table 2.3: Example Conventions
For Examples What it means
normal type Prompts and comman ds that are p art of th e main prompt a re
shown in normal type.
Examples:
Foundry-AR1208#
Foundry-AR1208/show#
bold type All character strings that a user must enter to execute a
command are in bold type.
Example:
Foundry-AR1208# configure term
Abbreviated Commands
You may enter commands by typing the first few characters of each word in a command string. The Foundry
system recognizes the unique abbreviated entry and executes the command exactly as if you had entered it fully.
For example, to view the currently running system configuration, you may type show configuration running at
the Foundry# prompt. You may also type dis con run to get the same result. Similarly, you may abbreviate the
optional parameter names required by some commands.
For example, a typical entry may be as follows:
mlppp mrru 1600 sequence short seg_threshold 1000 differential_delay 100 discriminator 10.1.100.22
To save time, you may type the following equivalent abbreviated string:
mlppp m 1600 seq short seg 1000 diff 100 dis 10.1.100.22
June 2004 © 2004 Foundry Networks, Inc. 2 - 3
Page 19

Foundry AR-Series Router User Guide
CLI Navigation
The Tab, Esc, and Ctrl keyboard keys may be used to:
• Move backwards or forwards in the CLI
• Edit entered command strings
• Or acceler ate the command entry process
Navigation Keys
You may use the Tab key to quickly enter each word of a command without typing its full name. For example, to
enter the configure command, you may type its first two letters and then press Tab to complete the entire word.
Then, you may specify an item to configure by pressing the Spacebar and then pressing Tab repeatedly until the
desired sub-command appears. Repeat this sequence for each successive sub-command string until the entire
command string appears.
You may also use the other keystrokes shown in during command entry. For example, to back up the cursor
without deleting any charac ters, type Ctrl-B. To repeat the last command that yo u entered , type Ctrl-P. T o go back
several commands, type Ctrl-P repeatedly until the desired previous command appears. Or, you may go directly
back to the main CLI# prompt from anywhere in the command hierarchy by typing Ctrl-Z.
Figure 2.1 Navigation Keys
# help edit
key stroke -- action
---------- -- ----- TAB -- command completion
Esc-B -- go back one word
Esc-F -- forward one word
Esc-DEL -- delete one word left to cursor
BackSpace -- go back and delete one char
Ctrl-A -- start of line
Ctrl-B / <- -- go back one char
Ctrl-D / DEL -- delete a char
-- go up one level if empty command
Ctrl-E -- end of line
Ctrl-F / -# -- forward one char
Ctrl-K -- delete line ahead of cursor
Ctrl-L -- refresh line
Ctrl-N / DN ARROW -- next command in history
Ctrl-P / UP ARROW -- previous command in history
Ctrl-U -- delete entire line
Ctrl-W -- delete one word left to cursor
#
Command Help
Command help is availa ble for navi gating the C LI command hi erarchy and for assist ance w ith specific command s.
You may obtain help by using any of the three commands described below.
Help
Type help at the main CLI prompt to see the basic Foundry system help information. Or, type help followed by a
command name to view information about that command. shows the help screen.
2 - 4 © 2004 Foundry Networks, Inc. June 2004
Page 20
Command Line Interface
Figure 2.2 Help Screen
# help
? -- display commands under this tree
exit [level] -- exit (level nos ) from the current tree
-- 'exit' from "top level" terminates CLI
Ctrl-Z -- exit to top level
tree -- display tree under current node
type 'help edit' to see editing features
type 'help <cmd#' to get help for that command
#
Tree
You may view a tree that shows all CLI commands, or a tree that shows only the commands associated with the
current command mode (or th e rout ing mode for example). Figure 2.3 sh ow s two comma nd tree ex am ple s. If y ou
type tree at the main (Foundry-AR1208# or equivalent) prompt, the entire list of system commands appears. If
you type tree within a com ma nd mo de, such as Foundry-AR3201-CH/clear# tree, the com mand s associa ted with
this command mode are displayed.
Figure 2.3 Foundry CLI Command Tree
# tree
xcli
|-- ping
|-- clear
| |-- cfg_file
| |-- arp
| |-- cfg_log
| |-- command_log
| |-- snmp_stats
| |-- counters
| | |-- all
| | |-- ethernet
| | |-- ethernets
| | |-- bundle
| | |-- bundles
| | |-- avc
| | |-- avcs
| | |-- tunnel
| | |-- tunnels
| |-- interface
| | |-- all
| | |-- ethernet
Press any key to continue (q : quit) :
Question Mark Help Screen
To view help information for a command cate gory, specific command, or a parameter, type the associated word
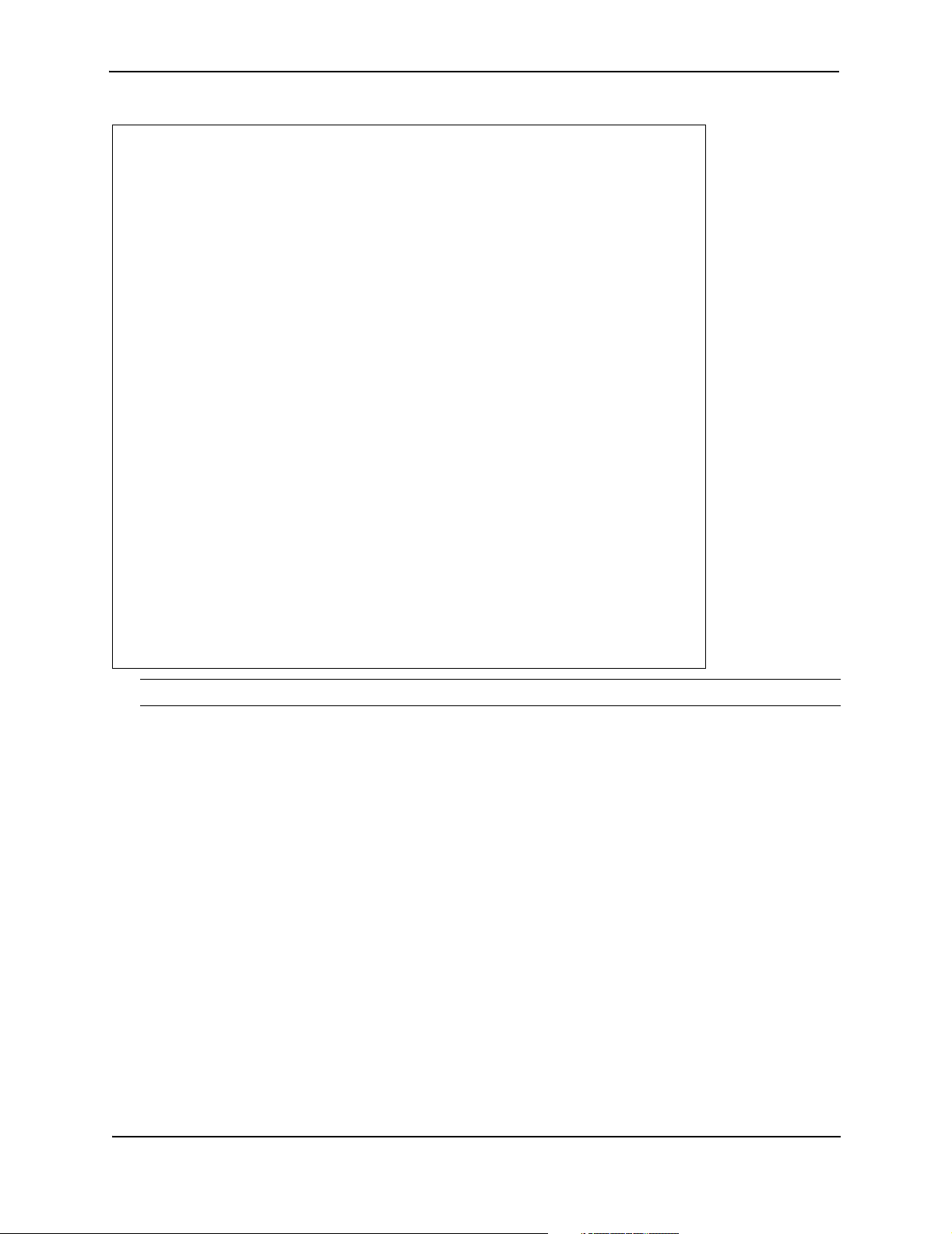
followed by a space and a question mark (?). For example, if you type a question mark at the main command
prompt, the system command categories appear. Shows a display of these top-level commands.
June 2004 © 2004 Foundry Networks, Inc. 2 - 5
Page 21
Foundry AR-Series Router User Guide
Figure 2.4 ? Help Screen
# ?
NAME
xcli -- This is root and not a command
SYNTAX
COMMANDS <cr#
DESCRIPTION
COMMANDS -- Any of the following commands can be used
clear -- access clear commands
configure -- configure from ( flash / network / terminal )
debug -- accesses debug commands
dir -- directory of files in flash
erase -- access erase filesystem commands
file -- access file commands
mtrace -- multicast trace route to source address
password -- Change the user password
ping -- invoke ping
reboot -- reboot the system
reload -- reboot the system
save -- save configuration to ( local / network )
show -- access show commands
tclsh -- To invoke TCL shell
telnet -- open a telnet connection
test -- access test commands
trace -- trace route to destination address or host name
write -- write to terminal/network/flash
#
NOTE: The default parameters for specific commands appear in parenthesis.
Global Commands
All show, ping, and save commands are available from any level of the CLI. For example, the global show
commands allow the user to view current configuration settings, alarms, or tests without exiting the configure
mode. In Figure 2.5 on page 2-7, a user has displayed a bundle summary while configuring a new bundle.
Similarly, the ping and save commands are available at any level of the CLI command. The ping command
verifies connectivity between the Foundry system and other network hosts; access to the save commands from
anywhere in the CLI ensur es that your c onfigurati ons may be save d periodically.
2 - 6 © 2004 Foundry Networks, Inc. June 2004
Page 22

Figure 2.5 Global show Command
# show configuration
: Select type of 'configuration' ( Hit Tab )
# dir
CONTENTS OF /flash1:
size date time name
-------- ------ ------ ------- 6467513 FEB-04-2004 13:51:22 AR0x_###x
6771268 APR-01-2004 11:38:42 AR0x_###y
1908 APR-01-2004 11:56:18 system.cfg
0 FEB-05-2004 07:12:30 oldsystem.cfg
6500329 APR-01-2004 11:49:22 AR0x_###z
Total bytes: 19741018
Bytes Free: 12713984
#
NOTE: The CLI commands show and display can be used interchangeably.
NOTE: The tab completion feature is not currently available for global commands.
Command Line Interface
June 2004 © 2004 Foundry Networks, Inc. 2 - 7
Page 23

Foundry AR-Series Router User Guide
2 - 8 © 2004 Foundry Networks, Inc. June 2004
Page 24
Policy Commands
This chapter provides information about routing policy commands that are supported by Foundry.
configure policy
This command provides access to the next-level commands.
Chapter 3
related commands:
configure policy as_path
configure policy communi ty_list
configure policy ip_access_list
configure policy route_map
June 2004 © 2004 Foundry Networks, Inc. 3 - 1
Page 25

Foundry AR-Series Router User Guide
configure policy as_path
This command configures the autonomous system path filter for BGP.
AS path access li sts are used for matching the AS path attribute in a BGP route. An AS path access lis t s ucce eds
if any “permit” line in the list m atches, o r fails if a ny “deny” l ine matc hes. Matchin g proceed s sequen tially an d stops
at the first match.
The regular expressio n p a ram ete r is an a s path regular expression. (For regular expressio n syntax, see “AS Path
Regular Expressions” on page 13-1.) Note that the regular expression must be enclosed in quotation marks. The
AS number is the smallest element of a Foundry regular expression. It is an integer ranging from 0 to 65536; the
Foundry regular expression matcher is AS number-based.
Any number of AS path access list lines may be declared. They are evaluated in the order declared. If neither
permit nor deny is specified, the default is “permit.”
Parameter Description
access_list Access list number
Range is 1 - 199.
number Sequence to insert or delete from an existing AS path entry.
Range is 0 - 65535.
action
deny Deny AS path.
permit Permit AS path.
regular_expression Regular expression to match the AS paths.
Enter a quot ed string.
Refer to “AS Path Regular Expressions” on page 13-1 for more
information about regular expressions.
syntax:
[ no ] policy as_path access_list < n > number < n > action < deny | permit > regular_expression < “string” >
example:
Foundry-AR1208/configure# policy as_path 1 120 permit “100”
example:
Foundry-AR1208/configure# policy as_path 1 121 deny “.* 101 .*”
applicable systems:
All models.
3 - 2 © 2004 Foundry Networks, Inc. June 2004
Page 26
Policy Commands
configure policy community_list
This command accesses next-level commands for adding extended or standard community lists.
Community list s are used for m atchin g the “com muni ty” attrib ute in a BGP rou te. A comm unity list su cceed s if any
“permit” line in the list matches, or fails if any “deny” line matches. Matching proceeds sequentially and stops at
the first match. A line in a community list is normally said to match if the route being tested contains at least all of
the communities listed in the line. That is, it may contain additional communities as well. If the exact-match
keyword is used, then it must contai8n exactly the same communities as listed.
The communities pa rameter can be:
• local_as
• no_advertise
• no_export
• aa:nn (an integer between 0 and 65,535)
• community (an integer between 1 and 4294967295
Note that “exact_m atc h” is su ppo rted in the community_list as well as at the route_map lev el. If n ei ther permit nor
deny is specified, the default is pe rmi t. If n o community is specified, any route w il l b e ma tch ed, regardless of what
communities are present. The route will even be matched if the community path attribute is not present. Any
number of community list lines may be declared. They are evaluated in the order declared.
related commands:
configure policy community_list extended_community
configure policy community_list standard_community
June 2004 © 2004 Foundry Networks, Inc. 3 - 3
Page 27

Foundry AR-Series Router User Guide
configure policy community_list extended_community
This command configures an extended community list as part of the policy.
Parameter Description
community_list Extended community list number
The range is 100 - 199.
community_index Community index number
The range is 0 - 65535.
action
deny Specify a community to reject.
permit Specify a community to permit.
community A list of community numbers
The range is 1 - 4294967295.
This list can contain a maximum of 32 numbers.
generate_local_as
local_as Do not send out local AS.
aa_nn Community number in aa:nn format
This list can contain a maximum of 32 numbers.
generate_no_advertise
no_advertise Do not advertise to any neighbor.
generate_no_export
no_export Do not send to next AS
syntax:
[ no ] policy community_list extended_community community_list < n > community_index < n > action < deny |
permit > [ community < n > ] [ generate _local_as < local_as > ]
[ aa_nn < n > ] [ generate_no_advertise < no_advertise > ] [ generate_no_export < no_export > ]
example:
Foundry-AR1208/configure# policy community_list extended_community 100 1 deny community 44 45
local_as aa_nn 400:500 no_advertise
applicable systems:
All models.
3 - 4 © 2004 Foundry Networks, Inc. June 2004
Page 28

configure policy community_list standard_community
This command configures a standard community list as part of the routing policy.
Parameter Description
community_list Extended community list number
The range is 100 - 199.
community_index Community index number
The range is 0 - 65535.
action
deny Specify a community to reject.
permit Specify a community to permit.
community A list of community numbers
The range is 1 - 4294967295.
This list can contain a maximum of 32 numbers.
generate_local_as
local_as Do not send out local AS.
aa_nn Community number in aa:nn format
This list can contain a maximum of 32 numbers.
generate_no_advertise
no_advertise Do not advertise to any neighbor.
generate_no_export
no_export Do not send to next AS
Policy Commands
syntax:
[ no ] policy community_list standard_community community_list < n > community_index < n > action < deny |
permit > [ community < n > ] [ generate_local_as < local_as > ]
[ aa_nn < n > ] [ generate_no_advertise <no_advertise > ] [ generate_no_export
< no_export > ]
example:
Foundry-AR1208/configure# policy community_list standard_community 90 150 permit community 40 45
local_as aa_nn 655:232592 no_advertise
example:
Foundry-AR1208/configure/policy# community_list standard_community 90 150 permit community
42949672 no_advertise
applicable systems:
All models.
June 2004 © 2004 Foundry Networks, Inc. 3 - 5
Page 29

Foundry AR-Series Router User Guide
configure policy ip_access_list
This command configures the IP access list for routes.
Ip access lists are used for matching any type of route prefix. An IP access list is said to succeed if any “permit”
line in the list matc hes, or fails, if any “deny” line matches. Matching proceeds sequentially and stops at the first
match. A line in an IP access list is said to match according to the rules listed below.
• network netmask
Matches addresses as fo llow s: The bi t s in t he add ress p art of the ro ute be ing ma sked that ar e not c overed by
“one” bits in net mask must be equal to the corresponding bits in network. The “one” bits in net mask are
sometimes referred to as “don’t care” bits, because the policy engine does not care what their values are.
• network netmask mask maskmask
Matches addresses as follows: The first pair of parameters (network, maskmask) match the address part of
the route just as in the previous (network netmask) form. The second pair of parameters (mask, maskmask)
are used to match against the mask part of the route being matched in a similar fashion. That is, the route is
matched if the address part matches and the bits in the mask that are not covered by “one” bits in net mask
are equal to the corresponding bits in mask.
If neither permit nor deny is specified, the default is permit. All kinds of access_list entries may be mixed freely
within a list, and there are no restrictions on what the access_list number may be. Any number of IP access list
lines may be declared. They are evaluated in the order declared.
Parameter Description
access_list Access list number
The range is 1 - 99
number Sequence to insert to or delete from an existing access list entry.
The range is 0 - 65535.
action
deny Route map deny set operation.
permit Route map permit set operation.
network Network route (IP address in dotted notation)
netmask Network mask as wildcard bits (IP address in dotted notation)
mask Network route’s mask (IP address in dotted notation)
maskmask Wildcard mask for network route’s mask ( in dotted notation)
syntax:
[ no ] policy ip_access_list access_list < n > number < n > action < deny | permit > [ network < IP address > ] [
netmask < IP address > ] [ mask < IP address > ] [ maskmask < IP address > ]
example:
Foundry-AR1208/configure# policy ip_access_list 1 1 permit network 10.0.0.0 netmask 0.255.255.255
This example permits prefixes 10.0.0.0/8, 10.0.0.0/9 and so on.
3 - 6 © 2004 Foundry Networks, Inc. June 2004
Page 30

Policy Commands
example:
Foundry-AR1208/configure# policy ip_access_list 1 1 permit network 10.0.0.0 netmask 0.255.255.255 mask
255.0.0.0 maskmask 0.255.255.255
This example restricts the prefixes to 10.0.0.0/8 only.
applicable systems:
All models.
June 2004 © 2004 Foundry Networks, Inc. 3 - 7
Page 31

Foundry AR-Series Router User Guide
configure policy route_map
This command configures the policy for router route maps.
Route maps are used for general-purpose matching of routes and setting of route attributes. Each route_map is
comprised of one or more route_map clauses, of the form shown below.
route_map name number [ permit | deny ]
match statements
set statements
A route_map clause is said to match if each of its match statements matches, according to the rules given below.
A route_map is said to succeed if one of its permit clauses clauses matches, and fails if one of its deny clauses
matches. Matching proceeds sequentially and stops at the first match. If the route_map succeeds, the actions
specified by the set statements in the matched clause are performed.
If neither permit nor deny is specified, the default is permit.
Match statements can be:
• match as_path
• match community
• match ip ip_address
Set statements can be:
• set as_path
• set community
• set local_preference
•set metric
• set origin
• set distance
• set metric_type
Parameter Description
name Route map name
number A sequence to insert to or delete from exiting route map.
The range is 0 - 65535.
action
deny Deny the rout e map.
This is the default value.
permit Permit the route map.
syntax:
[ no ] policy route_map name number [ action < deny | permit > ]
example:
Foundry-AR1208/configure# policy route_map Block100 1 permit
3 - 8 © 2004 Foundry Networks, Inc. June 2004
Page 32

related commands:
configure policy route_map commit
configure policy route_map match
configure policy route_map set
applicable systems:
All models.
Policy Commands
June 2004 © 2004 Foundry Networks, Inc. 3 - 9
Page 33

Foundry AR-Series Router User Guide
configure policy route_map match
This command accesses next-level commands for configuring the policy for matching parameters of the routes.
related commands:
configure policy route_map match as_path
configure policy route_map match community
configure policy route_map match ip
3 - 10 © 2004 Foundry Networks, Inc. June 2004
Page 34

configure policy route_map match as_pat h
This command matches any of the specified BGP AS path access lists.
Parameter Description
path_list AS path access list
The range is 1 - 199; the maximum list size is 32.
syntax:
[ no ] policy match as_path path_list < n >
example:
Foundry-AR1208/configure#/policy/route _m ap Bloc k1 00 1# match as_path 1
related commands:
configure policy route_map match ip
configure policy route_map match community
Policy Commands
applicable systems:
All models.
June 2004 © 2004 Foundry Networks, Inc. 3 - 11
Page 35

Foundry AR-Series Router User Guide
configure policy route_map match community
This command matches any of the specified BGP community lists.
syntax:
[ no ] policy match community
example:
Foundry-AR1208/configure/policy/route_map Block100 1# match community
related commands:
configure policy route_map match as_path
configure policy route_map match ip
applicable systems:
All models.
3 - 12 © 2004 Foundry Networks, Inc. June 2004
Page 36

configure policy route_map match ip ip_address
This command distributes routes matching the prefix against any of the specified IP access lists.
Parameter Description
ip_list Ip access list number(s)
Enter a list of numbers.
The range is 1 - 199.
A maximum of 32 numbers can be in the list.
syntax:
[ no ] match ip ip_address ip_list < n >
example:
Foundry-AR1208/configure/policy/route_map Block100 1# match ip ip_address 20
Policy Commands
applicable systems:
All models.
June 2004 © 2004 Foundry Networks, Inc. 3 - 13
Page 37

Foundry AR-Series Router User Guide
configure policy route_map set
This command provides access to next-level commands to set parameters for the routes.
related commands:
configure policy route_map set as_pat h
configure policy route_map set community
configure policy route_map set distance
configure policy route_map set local_preference
configure policy route_map set metric
configure policy route_map set metric_type
configure policy route_map set origin
3 - 14 © 2004 Foundry Networks, Inc. June 2004
Page 38

configure policy route_map set as_pat h
This command configures a character string for a BGP AS-path attribute.
Parameter Description
prepend AS path access list
Enter a list of numbers.
The range is 1 - 65535; the maximum list size is 32.
tag Set tag as an AS path attribute.
Enter a number.
syntax:
[ no ] set as_path [ prepend < n > ] [ tag < n > ]
example:
Foundry-AR1208/configure/policy/route_map Block100 1# set as_path prepend 100 250 tag 0
Policy Commands
related commands:
configure policy route_map set community
configure policy route_map set distance
configure policy route_map set local_preference
configure policy route_map set metric
configure policy route_map set metric_type
configure policy route_map set origin
applicable systems:
All models.
June 2004 © 2004 Foundry Networks, Inc. 3 - 15
Page 39

Foundry AR-Series Router User Guide
configure policy route_map set community
This command configures the policy for community attributes.
Set the community attribute to the given value or list of values. If the additive keyword is specified, the list of
values augments any communities already present. If the additive keyword is not specified, the list of values
overwrites any communities already present.
Parameter Descriptiongenerate_
number Community number (unsigned)
The range is 1 - 4294967294
The maximum numbers in the list is 32.
aa_nn Community number in aa:nn format
Enter a number or a list of numbers separated by spaces.
The maximum numbers in the list is 32
generate_additive
additive Add to the existing community.
generate_local_as
local_as Do not send outside local AS.
gemerate_no_advertise
no_advertise Do not advertise to any neighbor.
generate_no_export
no_export Do not send to next AS
syntax:
[ no ] set community number [ < n > ] [aa_nn < n > ] [ generate_additive < additive > ]
[ generate_local_as < local_as > ] [ generate_no_advertise < no_advertise > ]
[ generate_no_export < no_export > ]
example:
Foundry-AR1208/configure/policy/route_map Block100 1# set community aa:nn 500:60
related commands:
configure policy route_map set as_pat h
configure policy route_map set distance
configure policy route_map set local_preference
configure policy route_map set metric
configure policy route_map set metric_type
configure policy route_map set origin
applicable systems:
All models.
3 - 16 © 2004 Foundry Networks, Inc. June 2004
Page 40

configure policy route_map set distance
This command sets the BGP protocol preference for the path attribute.
Parameter Description
distance Default preference value
The range is 0 - 255.
syntax:
[ no ] set distance distance < n >
example:
Foundry-AR1208/configure/policy/route_map Block100 1# set distan ce 20
related commands:
configure policy route_map set as_pat h
configure policy route_map set community
configure policy route_map set local_preference
configure policy route_map set metric
configure policy route_map set metric_type
configure policy route_map set origin
Policy Commands
applicable systems:
All models.
June 2004 © 2004 Foundry Networks, Inc. 3 - 17
Page 41

Foundry AR-Series Router User Guide
configure policy route_map set local_preference
This command configures the BGP local preference path attribute.
Parameter Description
local_preference Preference value
The range is 1 - 4292967294.
syntax:
[ no ] set local_preference local_preference < n >
example:
Foundry-1450configure/policy/route_map Block100 1# set local_preference 50
related commands:
configure policy route_map set as_pat h
configure policy route_map set community
configure policy route_map set distance
configure policy route_map set metric
configure policy route_map set metric_type
configure policy route_map set origin
applicable systems:
All models.
3 - 18 © 2004 Foundry Networks, Inc. June 2004
Page 42

configure policy route_map set metric
This command configures the metric value for the destination routing protocol.
Parameter Description
metric Metric value
The range is 1 - 4294967294.
syntax:
[ no ] set metric metric < n >
example:
Foundry-AR1208/configure/policy/route_map Block100 1# set metric 120
related commands:
configure policy route_map set as_pat h
configure policy route_map set community
configure policy route_map set distance
configure policy route_map set local_preference
configure policy route_map set metric_type
configure policy route_map set origin
Policy Commands
applicable systems:
All models.
June 2004 © 2004 Foundry Networks, Inc. 3 - 19
Page 43

Foundry AR-Series Router User Guide
configure policy route_map set metric_type
This command configures the metric type for a route.
Parameter Description
type Internal
internal Use the IGP metric as the MED for BGP.
syntax:
[ no ] set metric_type type < internal >
example:
Foundry-AR1208/configure/policy/route_map Block100 1# set metric_type i nternal
related commands:
configure policy route_map set as_pat h
configure policy route_map set community
configure policy route_map set distance
configure policy route_map set local_preference
configure policy route_map set metric
configure policy route_map set origin
applicable systems:
All models.
3 - 20 © 2004 Foundry Networks, Inc. June 2004
Page 44

configure policy route_map set origin
This command configures the origin value for the BGP route.
Parameter Description
origin
egp EGP protocol
igp IGP protoc ol
incomplete Unknown protocol type
syntax:
[ no ] set origin origin < egp | igp | incomplete >
example:
Foundry-AR1208/configure/policy/route_map Block100 1# set origin igp
Policy Commands
applicable systems:
All models.
related commands:
configure policy route_map set origin egp
configure policy route_map set origin igp
configure policy route_map set origin incomplete
June 2004 © 2004 Foundry Networks, Inc. 3 - 21
Page 45

Foundry AR-Series Router User Guide
3 - 22 © 2004 Foundry Networks, Inc. June 2004
Page 46

Chapter 4
Protocols Overview
BGP4
Border Gateway Protocol Version 4 (also referred to as simply BGP) is an exterior routing protocol used for the
global Internet.
Once configured, BGP peers first exchange co mp le te c opi es of their routing tables (in cl udi ng BGP version, router
ID, and keep alive hold time), which are usually very large. Thereafter, only incremental updates (deltas) are sent
as changes occur to the routing tables. BGP keeps a current version of the routing table for all peers, keep alive
packets ar e s en t to ens ure tha t th e c onn ec tion between BGP peers, and n oti fic ati on packets are sent in response
to problems and irregularities. This enables longer running BGP sessions to be more efficient than shorter
sessions.
BGP's basic unit of routing information is the BGP path, a route to a certain set of classless interdomain routing
prefixes. Paths are t agged with various path attri butes, inc luding an aut onomous sys tems (AS) path an d next-hop.
In fact, one of BGP's most imp ort a nt fu nct ion s is lo op de tec tio n at the AS level, using the AS p ath attrib ute , whic h
is a list of autonomous systems used for data transport.
The syntax of this attribute is made more co mplex by its need to suppor t path agg regation w hen multip le paths are
collapsed into one in order to simplify further route advertisements. A more simplified view of an AS path is that it
is a list of autonomous sy stems that a route go es through to rea ch its de stina tion. Loop s are detec ted and avoid ed
by checking for your own AS number in the AS path' s receiv ed from neigh boring auto nomous s ystems. Every time
a BGP path advertisement crosses an AS boundary, the next-hop attribute is changed on the boundary router.
Conversely, as a BGP path advertisement is pa ssed am ong BGP speake rs in the sa me AS, the next-h op attrib ute
is left untouched. Consequently, BGP's next-hop is always the IP address of the first router in the next
autonomous system, even though this may actually be several hops away. The AS's interior routing protocol is
responsible for computing an interior route to reach the BGP next-hop.
This leads to the di stinction b etween i nternal BGP (IBG P) sessions (b etween route rs in the same AS) an d external
BGP (EBGP) sessions (between routers in different AS's). Next-hops are only changed across EBGP sessions,
but left inta ct acro ss IBGP sess ions. The two m ost im port ant co nsequ ences of this desig n are th e need f or interi or
routing protocols to reach one hop beyond the AS boundary, and for BGP sessions to be fully meshed within an
AS.
Since the next-hop contains the IP address of a router interface in the next AS, and this IP address is used to
perform routing, the inte rio r rou ting pro toc ol mu st be able to route to this ad dres s. Thi s m ea ns that int erior routing
tables must include entries one hop beyond the AS boundary. Furthermore, since BGP does not relay routing
traffic from one interio r BGP se ssion to anot her (onl y from a n exter ior BGP ses sion to an IBGP session or anoth er
EBGP session), BGP speakers must be fully meshed.
June 2004 © 2004 Foundry Networks, Inc. 4 - 1
Page 47

Foundry AR-Series Router User Guide
RFC Compliance
The following table provides Foundry Network’s BGP RFC compliance information.
Table 4.1: BGP RFC Compliance
RFC Description
2385 Protection of BGP sessions via the TCP MD5 signature option
1998 An application of the BGP community attribute in multi-home routing
1997 BGP communities attribute
1775 BGP OSPF interaction
1771 Border Gateway Protocol 4 (BGP-4)
OSPF
Open Shortest Path First (OSPF), a link-state routing protocol, is used for routing IP packets. OSPF offers the
following advantages:
• Scalability
OSPF is designed to operate with larger networks. It does not impose a hop-count restriction and permits its
domain to be split into areas for easier management.
• Full subnetting support
OSPF can fully support subnetting, including Variable Length Subnet Mask (VLSM).
• Tagged routes
Routes can be tag ged with arbitrary values. T his ea ses in teroperation with Exterior Gateway Protocols
(EGPs), which can tag OSPF routes with AS numbers.
• Meshed networks
OSPF provides the ability to support complex meshed networks.
The following features are incorporated in Foundry’ implementation of OSPF.
• Intra- and inter-area routing
• Broadcast and point-to-point
• Type 1 & Type 2 AS external routes
• Stub areas
• NSSA – Not-So-Stubby-Area
• Route re-distribution
• Authentication – simple & MD5
• RFC 1583 backwards compatibility
• Equal cost multipath
• Configurable routing interface parameters
• Non-intrusive reconfiguration
4 - 2 © 2004 Foundry Networks, Inc. June 2004
Page 48

Protocols Overview
RFC Compliance
The following table provides Foundry Network’s OSPF RFC compliance information.
Ta ble 4.2: OS PF RFC Compliance
RFC Description
2328 OSPF version 2
1587 OSPF NSSA option
1850 OSPF Version 2 Management Informa tio n Base
RIP
Routing Information Protocol (RIP) is an interior gateway protocol (IGP), i.e., it routes traffic within a single
autonomous system (AS). RIP uses a d istan ce-vector al gorithm w ith hop cou nt as the m etric to d etermine t he best
route to a destination.
Update messages are sent at configured intervals and when changes occur in the network topology. These
messages are used by routers to update their routing tables to maintain currency with the state of the network.
When a router updates its routing table, it transmits update messages to other routers in the network to enable
them to update their routing tables.
The following list identifies architectural characteristics of RIP:
• The network path is limited to 15 hops. A destination with a greater number of hops is considered
unreachable.
• The time required to determine a next hop and bandwidth could be substantial in a large network.
• A fixed metric is used to select routes. Only the best route with the lowest metric is maintained for a specific
destination.
The following features are incorporated into Foundry’ implementation of RIP:
• RIP v1, v2, and v1 compatibility modes
• Configurable timers
•VLSM
• Split-horizon and split-horizon with poison reverse
• Clear text and MD5 authentication
• Redistribution of connected, static, and OSPF routes
• Inbound and outbound filtering policies
RFC Compliance
The following table provides Foundry Network’s RIP RFC compliance information.
Table 4.3: RIP RFC Compliance
RFC Description
1058 Routing Information Protocol
2453/
STD0056
1724 RIP Version 2 MIB extension
June 2004 © 2004 Foundry Networks, Inc. 4 - 3
RIP Version 2
Page 49

Table 4.3: RIP RFC Compliance
2082 RIP-II MD5 Authentication
Multicasting
Traditiona l multic ast routi ng mech anisms such as Dist ance Vector Multicast Routing Protocol (DVM RP) and Multicas t Open
Shortest Path First (MOSPF) were intended for use within regions where groups are densely populated or bandwidth is
universally ple ntif ul. Whe n g r ou p s , an d s en ders to these groups, are distri but ed sp arsely across a wide area, thes e “dense
mode” schemes do not perform efficiently.
Protocol Independent Multicast (PIM)
Protocol Independent Multicast (PIM) protocols route multicast packets to multicast groups. PIM is protocol independent
because it can leverage whichever unicast routing protocol is used to populate unicast routing table. There are two modes
of PIM protocol – Dense mode (DM) and Sparse mode (SM). Foundry supports SM only.
PIM-DM floods multicast traffic throughout the network initially and then generates prune messages as required. PIM-SM
attempts to send multicast data only to networks which have active receivers. This is achieved by having a common
Rendezvous Point (RP) known to the senders and receivers and by forming shared trees from the RP to the receivers.
PIM-SM is described in RFC 2362.
Securing Remote Access Using IPSec VPN
This feature allows AR-series router administrators to form a security tunnel to join two private networks over the Internet.
The following examples show how to set up an end-to-end tunnel with a single proposal and pre-shared key authentication,
with multiple proposals and pre-shared key authentication, and with an SA Bundle, and pre-shared key authentication.
The corporate network no longer has a clearly defined perimeter inside secure building and locked equipment closets.
Increasingly, companies have a need to provide remote access to their corporate resources for the employees on the
move.
Traditionally, remote users could access the corporate LAN through dial-up and ISDN lines which were terminated in the
corporate remote access servers. However, these point-to-point connection t echnologies do not scale w ell to the growing
number of remote users and the corresponding increase in the infrastructure investments and maintenance costs.
A solution to meeting the needs of increasing numbers of remote users and for controlling access costs is to provide
remote access through the Internet using firewalls and a Virtual Private Network (VPN). Internet Protocol Security (IPSec)
keeps the connection safe from unauthorized users.
In a typical IPSec remot e ac c ess s ce nari o, th e m ob ile us er h as con nectivity to Internet an d a n IPSe c VPN c li ent loaded on
their PC. The remote user connects to the Internet through their Internet service provider and then initiates a VPN
connection to the IPSec security gateway (the VPN server) of the corporate office, which is typically an always-on Internet
connection.
One of the main limitations in providing remote access is the typical remote user connects with a dynamically assigned IP
address provided by th e ISP. IPSec uses t he IP address o f users as an index to a pply th e Intern et Key Ex chang e (IKE ) and
IPSec policies to be used for negotiation with each peer. When the VPN client has a dynamic IP address, the VPN server
cannot access the poli cies bas ed on the IP add ress of the clie nt. Inst ead, the VPN serv er uses the iden tity of the VPN cl ient
to access the policies.
Page 50

Use BGP clear commands to clear bgp configuration settings.
clear ip bgp
This command provides access to the following next-level commands.
Chapter 5
BGP4 Clear Commands
syntax:
clear ip bgp
related commands:
clear ip bgp all
clear ip bgp group
clear ip bgp neighbor
example:
Foundry-AR1208# clear ip bgp
applicable systems:
All models.
June 2004 © 2004 Foundry Networks, Inc. 5 - 1
Page 51

Foundry AR-Series Router User Guide
clear ip bgp all
This command removes all BGP neighbor connections.
syntax:
clear ip bgp all
example:
Foundry-AR1208# clear ip bgp all
related commands:
clear ip bgp group
clear ip bgp neighbor
applicable systems:
All models.
5 - 2 © 2004 Foundry Networks, Inc. June 2004
Page 52

clear ip bgp group
This command removes all connections for a BGP group.
Parameter Description
group_name Name of the group
syntax:
clear ip bgp group group_name < name >
example:
Foundry-AR1208# clear ip bgp group north
In this example, all BGP connections that belong to neighbor group north will be cleared.
related commands:
clear ip bgp all
clear ip bgp neighbor
BGP4 Clear Commands
applicable systems:
All models.
June 2004 © 2004 Foundry Networks, Inc. 5 - 3
Page 53

Foundry AR-Series Router User Guide
clear ip bgp neighbor
This command removes a specified BGP neighbor connection.
Parameter Description
ip_address The IP address of the neighbor
Enter an IP address (in dotted notation) to be cleared.
remote_as The AS number of the remote neighbor to be cleared.
The range is from 1 - 65535.
syntax:
clear ip bgp neighbor ip_address < IP address > remote_as < n >
example:
Foundry-AR1208# clear ip bgp neighbor 10.1.1.1 200
related commands:
clear ip bgp all
clear ip bgp group
applicable systems:
All models.
5 - 4 © 2004 Foundry Networks, Inc. June 2004
Page 54

Generic Routing Commands
This chapter contains routing commands that are not protocol specific. These commands can be used
interchangeably with the three routing protocols supported by Foundry.
configure router
This command provides access to next-level commands.
Chapter 6
related commands:
configure router routerid
June 2004 © 2004 Foundry Networks, Inc. 6 - 1
Page 55

Foundry AR-Series Router User Guide
configure router routerid
This command configures a router for routing operation.
syntax:
[ no ] router routerid < IP address#
example:
Foundry-AR1208/configure# router routerid 10.10.10.10
applicable systems:
All models.
6 - 2 © 2004 Foundry Networks, Inc. June 2004
Page 56

show ip routes
This command displays IP routing information for Ethernet ports.
Parameter Description
network Network IP address
Enter an IP address.
mask Network mask
Enter a netmask address
protocol
all All protocols
bgp Border Gateway protocol (BGP)
connected Connected routes
ospf Open Shortest Path First protocol (OSPF)
rip Routing Information Protocol (RIP)
static Static routes
database
rib RIB routes
fib FIB routes
Generic Routing Commands
syntax:
show ip routes [ network < IP address > ] [ mask < netmask > ] [ protocol < all | bgp | connected | ospf | rip | static
> ] [ database < rib | fib > ]
The following table provides parameter definitions for the following screen display examples.
Table 6.1: Parameter Definitions
term definition
Network Indicates the address of the remote network.
Next Hop Specifies the address of the next router to the remote network
Interface Specifies the in terface through which the specifi ed network can be
reached.
PVC > Virtual (logical) circuit identification number.
Distance The administrative distance for the route.
Metric The metric for the route.
By default, information is displayed for all routes in the routing table. To display only specific route information,
specify the appropriate protocol or the network mask.
June 2004 © 2004 Foundry Networks, Inc. 6 - 3
Page 57

Foundry AR-Series Router User Guide
example:
To display all routes, issue the show ip routes command.
example:
To display the route for a specific network and subnet, issue the show ip routes netw ork 123 .1.2 .0 mas k
255.255.255.0 command.
example:
To display the connected ip routes, issue the show ip routes connected command.
example:
To display static routes, issue the show ip routes static command.
example:
To display RIP routes, issue the show ip routes rip command.
example:
To display ospf routes, issue the show ip routes ospf command.
example:
Foundry-AR1208/show# ip routes bgp
The following sc reen d ispla y ex ample is a typi cal d ispla y showing the destin ation IP a ddress, met ric, n etmas k and
gateway, status, Ethernet interface, and type of route.
applicable systems:
All models.
6 - 4 © 2004 Foundry Networks, Inc. June 2004
Page 58

BGP4 Config ure Commands
Chapter 7
BGP4 Configure Commands
Use BGP configure commands to configure all BGP4 parameters.
configure router bgp
This command configures BGP routing protocol on a router and provides access to the next-level commands
listed below.
Parameter Description
as_number The number of an autonomous system.
The range is 1 - 65535.
syntax:
[ no ] router bgp as_number < n >
example:
Foundry-AR1208/configure# router bgp 10
related commands:
configure router bgp aggregate_address
configure router bgp always_compare_med
configure router bgp distance
configure router bgp default_metric
configure router bgp group
configure router bgp neighbor
configure router bgp redistribute
applicable systems:
All models.
June 2004 © 2004 Foundry Networks, Inc. 7 - 1
Page 59

Foundry AR-Series Router User Guide
configure router bgp aggregate_address
This command is used to aggregate routes.
Parameter Description
network Network IP address in dotted notation
mask Network subnet mask address in dotted notation
generate_as_set
as_set Generates AS path information
Form a verbose aggregate, whose AS path contains a leading AS
sequence representing the com m on lea din g seq uen ce of all
contributing routes, and whose AS path contains a trailing AS set
representing all ASes in all contributing paths that could not be
included in the AS sequ ence. By de fault, thi s feature is of f, and the AS
path is truncated when the aggregate is formed.
generate_summary_only
summary_only Filters more specific routes from updates
Suppresses transmission of any contributing routes if an aggregate
exists. Note that the contributing route will not be sent even if an
outgoing route_map blocks the sending of the aggregate itself. This
cannot be combined with the suppress_map parameter.
suppress_map Name of the route map to suppress
Uses the named route_map to suppress the transmission of selected
contributing routes. Contributing routes that do not match the
route_map will not be suppressed. This cannot be combined with the
summary_only parameter.
advertise_map Name of route map to control attribute advertisement
Selects the routes that co ntribute to the aggre gate. The aggregate will
only be formed if matching routes exist. Only the matching routes will
be suppressed if summary_only or suppress_map are configured.
attribute_map Name of route map for setting attributes
Specifies attributes to be set on the aggregate when it is transmitted.
syntax:
[ no ] aggregate_address network < IP address > mask < subnet mask > [ generate_as_set
< as_set > ] [ generate_summ ary_on ly < sum mary_ only > ] [ su ppress_m ap < name > ] [adverti se_ma p < name >
] [ attribute_map < name > ]
example:
Foundry-AR1208/configure/router/bgp 10# a ggregate_address 100.3.0.0 255.255.0.0
related commands:
configure router bgp always_compare_med
configure router bgp distance
7 - 2 © 2004 Foundry Networks, Inc. June 2004
Page 60

configure router bgp default_metric
configure router bgp group
configure router bgp neighbor
configure router bgp redistribute
applicable systems:
All models.
BGP4 Config ure Commands
June 2004 © 2004 Foundry Networks, Inc. 7 - 3
Page 61

Foundry AR-Series Router User Guide
configure router bgp always_compare_med
This command con fig ures a rou ter to allow the comparison of the mu lti-exit discriminator fo r p a ths fro m nei ghb ors
in different autonomous systems.
Normally, MED comparison is done on paths within the same autonomous system. This command allows the
comparison to be made for paths received from other autonomous systems.
syntax:
[ no ] always_compare_med
example:
Foundry-AR1208/configure/router/bgp 10# always_compare_med
related commands:
configure router bgp aggregate_address
configure router bgp distance
configure router bgp default_metric
configure router bgp group
configure router bgp neighbor
configure router bgp redistribute
applicable systems:
All models.
7 - 4 © 2004 Foundry Networks, Inc. June 2004
Page 62

BGP4 Config ure Commands
configure router bgp default_metric
This command configures the default metric value for redistributed BGP routes.
This command forces the routing protocol to use the same metric value for all redistributed routes.
Parameter Description
default_metric The default metric value.
The range is 1 - 4294967294.
syntax:
[ no ] default_metric default_metric < n >
example:
Foundry-AR1208/configure/router/bgp 10# d efau lt_m etric 200 0
related commands:
configure router bgp aggregate_address
configure router bgp always_compare_med
configure router bgp distance
configure router bgp group
configure router bgp neighbor
configure router bgp redistribute
applicable systems:
All models.
June 2004 © 2004 Foundry Networks, Inc. 7 - 5
Page 63

Foundry AR-Series Router User Guide
configure router bgp distance
This command changes the default distance value on a router.
Higher values are preferred.
Parameter Description
distance Default preference value
The range i s 0-255; the default is 170.
syntax:
[ no ] distance distance < n >
example:
Foundry-AR1208/configure/router/bgp 10# distance 20
T abl e 7.1: Def ault Route Pref eren ce (A dmin istrative Distance) Values
How Route is Learned Default
Preferenc
e
Directly connected
network
Static 1 Not configurable.
OSPF non-external route 10 configure router ospf distance ospf non_external
RIP 100 configure router rip distance
Generated or aggregate 130 Applicable to BGP only, and is not configurable.
OSPF AS external
routes
BGP 170 configure router bgp distance
0 Not configurable.
150 configure router ospf distance ospf exter nal
related commands:
configure router bgp aggregate_address
configure router bgp always_compare_med
configure router bgp default_metric
configure router bgp group
configure router bgp neighbor
configure router bgp redistribute
Command to Modify Default Preference
applicable systems:
All models.
7 - 6 © 2004 Foundry Networks, Inc. June 2004
Page 64

BGP4 Config ure Commands
configure router bgp group
This command configures BGP groups.
Neighbors with the same update policies are more easily managed when they are in groups. Group organization
simplifies configuration and streamlines the update process. Neighbor group members inherit all configuration
options of a group. The BG P group sub comman ds are simil ar to those foun d under the n eighbor tree , but they a re
applied to all neighbors in the group.
Parameter Description
name Group name to be configured
group_type
external External routing group
Default group name = FoundryBgpExternal
external_rt External routing group
Default group name = FoundryBgpExternalRt
internal Internal routing group
Default group name = FoundryBgpInternal
syntax:
[ no ] group name < name > group_type < external | external_rt | internal |
internal_ rt >
example:
Foundry-AR1208/configure/router/bgp 10# group toronto internal
related commands:
configure router bgp group distribute_list
configure router bgp group filter_list
configure router bgp group next_hop_self
configure router bgp group password
configure router bgp group remove_private_AS
configure router bgp group route_map
applicable systems:
All models.
June 2004 © 2004 Foundry Networks, Inc. 7 - 7
Page 65

Foundry AR-Series Router User Guide
configure router bgp group distribute_list
This command configures filter updates to this group.
Parameter Description
access_list IP access list number
The range is 1-199.
filter_option
out Outbound direction
syntax:
[ no ] distribute_list access_list < n > filter_option < out >
example:
Foundry-AR1208/conf igu r e/ro ute r/bg p 10/gro up toro nto int erna l# distribute_ list 101 out
related commands:
configure router bgp group filter_list
configure router bgp group next_hop_self
configure router bgp group password
configure router bgp group remove_private_AS
configure router bgp group route_map
applicable systems:
All models.
7 - 8 © 2004 Foundry Networks, Inc. June 2004
Page 66

configure router bgp group filter_list
This command configures BGP filters for a specified group.
Parameter Description
access list AS path access list
The range is 1-199.
filter_option
out Outbound direction
syntax:
[ no ] filter_list access list < n > filter_option < out >
example:
Foundry-AR1208/conf igu r e/ro ute r/bg p 10/gro up toro nto int erna l# filter_list 103 out
BGP4 Config ure Commands
related commands:
configure router bgp group distribute_list
configure router bgp group next_hop_self
configure router bgp group password
configure router bgp group remove_private_AS
configure router bgp group route_map
applicable systems:
All models.
June 2004 © 2004 Foundry Networks, Inc. 7 - 9
Page 67

Foundry AR-Series Router User Guide
configure router bgp group next_hop_self
This command disables the next hop calculation for all peers in the group.
syntax:
next_hop_self
example:
Foundry-AR1208/configure/router/bgp 10/group blue external# next_hop_self
related commands:
configure router bgp group distribute_list
configure router bgp group filter_list
configure router bgp group password
configure router bgp group remove_private_AS
configure router bgp group route_map
applicable systems:
All models.
7 - 10 © 2004 Foundry Networks, Inc. June 2004
Page 68

BGP4 Config ure Commands
configure router bgp group password
This command configures the TCP MD5 password to enable MD5 au thentication for a BGP group.
Parameter Description
md5_password TCP MD5 password (string) for the group
Enter a word.
syntax:
[ no ] password md5_password < string >
example:
Foundry-AR1208/conf igu r e/ro ute r/bg p 10/gro up toro nto int erna l# password rt56htd
related commands:
configure router bgp group distribute_list
configure router bgp group filter_list
configure router bgp group next_hop_self
configure router bgp group remove_private_AS
configure router bgp group route_map
applicable systems:
All models.
June 2004 © 2004 Foundry Networks, Inc. 7 - 11
Page 69

Foundry AR-Series Router User Guide
configure router bgp group remove_private_AS
This command removes the private AS number from updates that are sent out.
syntax:
[ no ] remove_private_AS
example:
Foundry-AR1208/conf igu r e/ro ute r/bg p 10/gro up toro nto int erna l# remove_private_AS
related commands:
configure router bgp group distribute_list
configure router bgp group filter_list
configure router bgp group next_hop_self
configure router bgp group password
configure router bgp group route_map
applicable systems:
All models.
7 - 12 © 2004 Foundry Networks, Inc. June 2004
Page 70

configure router bgp group route_map
This command configures a route map to a BGP group.
This command can only be applied in the outbound direction.
Parameter Description
route_map Route map name
route_map_options
out Outbound direction
syntax:
[ no ] route_map route_map < name > route_map_options < out >
example:
Foundry-AR1208/configure/router bgp 10/group toronto internal# route_map foo out
BGP4 Config ure Commands
related commands:
configure router bgp group distribute_list
configure router bgp group filter_list
configure router bgp group next_hop_self
configure router bgp group password
configure router bgp group remove_private_AS
applicable systems:
All models.
June 2004 © 2004 Foundry Networks, Inc. 7 - 13
Page 71

Foundry AR-Series Router User Guide
configure router bgp neighbor
This command configures a BGP neighbor.
Parameter Description
IP address The IP address of the neighbor in dotted notation
remote_as The AS number
The range is 1 - 65535.
syntax:
[ no ] neighbor IP address < IP address > remote_as < n >
example:
Foundry-AR1208/configure/router/bgp 10# neighbor 101.101.1.2 4
related commands:
configure router bgp neighbor advertisement_interval
configure router bgp neighbor allowbadid
configure router bgp neighbor default_originate
configure router bgp neighbor description
configure router bgp neighbor distribute_list
configure router bgp neighbor ebgp_multihop
configure router bgp neighbor filter_list
configure router bgp neighbor keep
configure router bgp neighbor logupdown
configure router bgp neighbor maximum_prefix
configure router bgp neighbor neighbor_group
configure router bgp neighbor next_hop_self
configure router bgp neighbor password
configure router bgp neighbor route_map
configure router bgp neighbor timers
configure router bgp neighbor update_source
related commands:
configure router bgp aggregate_address
configure router bgp always_compare_med
configure router bgp distance
configure router bgp default_metric
configure router bgp group
7 - 14 © 2004 Foundry Networks, Inc. June 2004
Page 72

configure router bgp redistribute
applicable systems:
All models.
BGP4 Config ure Commands
June 2004 © 2004 Foundry Networks, Inc. 7 - 15
Page 73

Foundry AR-Series Router User Guide
configure router bgp neighbor advertisement_interval
This command configures the minimum time interval for sending BGP route updates.
Parameter Description
advertisement_interv al Time, in seconds
The range is 1 - 600 seconds.
syntax:
[ no ] advertisement_interval advertisement_interval < n >
example:
Foundry-AR1208/configure/router/bgp 10/neighbor 101.101.1.2 4# advertisement_interval 60
applicable systems:
All models.
7 - 16 © 2004 Foundry Networks, Inc. June 2004
Page 74

BGP4 Config ure Commands
configure router bgp neighbor allowbadid
This command permits BGP sessions to be established with routers that represent their router ID as 0.0.0.0 or
255.255.255.255.
syntax:
[ no ] allowbadid
example:
Foundry-AR1208/configure/router/bgp 10/neighbor 101.101.1.2 4# allowbadid
applicable systems:
All models.
June 2004 © 2004 Foundry Networks, Inc. 7 - 17
Page 75

Foundry AR-Series Router User Guide
configure router bgp neighbor default_originate
This command sends the default route to the neighbor.
Parameter Description
route_map The name of the route map
syntax:
[ no ] default_originate [ route_map < name > ]
example:
Foundry-AR1208/configure/router/bgp 10/neighbor 101.101.1.2 4# default_originate altmap5
applicable systems:
All models.
7 - 18 © 2004 Foundry Networks, Inc. June 2004
Page 76

configure router bgp neighbor description
This command describes or identifies a neighbor router.
Parameter Description
neighbor_description Text string in quotes describing nei ghbor
syntax:
[ no ] description neighbor_description < “string” >
example:
Foundry-AR1208/configure/router/bgp 10/neighbor 101.101.1.2 4# de scrip tion “foo 1”
applicable systems:
All models.
BGP4 Config ure Commands
June 2004 © 2004 Foundry Networks, Inc. 7 - 19
Page 77

Foundry AR-Series Router User Guide
configure router bgp neighbor distribute_list
This command configures filter updates to or from this neighbor.
Parameter Description
access_list The IP access list number.
The range is 1 - 199.
filter_option
in Inbound filter list
syntax:
[ no ] distribute_list access_list < n > filter_option < in >
example:
Foundry-AR1208/configure/router/bgp 10/neighbor 101.101.1.2 4# distribute_list 101 in
applicable systems:
All models.
7 - 20 © 2004 Foundry Networks, Inc. June 2004
Page 78

configure router bgp neighbor ebgp_multihop
This command configures multihop EBGP on a neighbor.
syntax:
[ no ] ebgp_multihop
example:
Foundry-AR1208/configure/router/bgp 10/neighbor 101.101.1.2 4# ebgp_multihop
applicable systems:
All models.
BGP4 Config ure Commands
June 2004 © 2004 Foundry Networks, Inc. 7 - 21
Page 79

Foundry AR-Series Router User Guide
configure router bgp neighbor filter_list
This command configures BGP filters.
Parameter Description
access_list AS path access list
The range is 1 - 199.
access_list_option
in Inbound filter list
syntax:
[ no ] filter_list access_list < n > access_list_option < in >
example:
Foundry-AR1208/configure/router/bgp 10/neighbor 101.101.1.2 4# filter_list 103 in
applicable systems:
All models.
7 - 22 © 2004 Foundry Networks, Inc. June 2004
Page 80

configure router bgp neighbor keep
This command configures neighbor route storage options.
Parameter Description
keep_option
all Keep all non-active routes
none Don’t store non-active routes
syntax:
keep keep_option < all | none >
example:
Foundry-AR1208/configure/router/bgp 10/neighbor 10.10.20.1 2# keep all
BGP4 Config ure Commands
applicable systems:
All models.
June 2004 © 2004 Foundry Networks, Inc. 7 - 23
Page 81

Foundry AR-Series Router User Guide
configure router bgp neighbor logupdown
This command configures logging of established state transition changes of a neighbor.
syntax:
[ no ] logupdown
example:
Foundry-AR1208/configure/router/bgp10/neighbor 101.101.1.2 4# logupdown
applicable systems:
All models.
7 - 24 © 2004 Foundry Networks, Inc. June 2004
Page 82

BGP4 Config ure Commands
configure router bgp neighbor maximum_prefix
This command configures the maximum number of BGP routes to be accepted.
If the neighbor sends more prefixes than are configured, the connection to this neighbor will be broken.
Parameter Description
prefix_number Maximu m prefix limit
The range is 1 - 1000000.
syntax:
maximum_prefix prefix_number < n >
example:
Foundry-AR1208/configure/router/bgp 10/neighbor 101.101.1.2 4# maximum_prefix 100000
applicable systems:
All models.
June 2004 © 2004 Foundry Networks, Inc. 7 - 25
Page 83

Foundry AR-Series Router User Guide
configure router bgp neighbor neighbor_group
This command configures a neighbor to a specific group.
Parameter Description
neighbor_group The name of a neighbor group.
syntax:
[ no ] neighbor_group neighbor_group < name >
example:
Foundry-AR1208/configure/router/bgp 10/neighbor 101.101.1.2 4# neighbor_group internal-group
applicable systems:
All models.
7 - 26 © 2004 Foundry Networks, Inc. June 2004
Page 84

configure router bgp neighbor next_hop_self
This command disables the next hop calculation for this neighbor.
syntax:
next_hop_self
example:
Foundry-AR1208/configure/router/bgp 10/neighbor 10.10.20.1 2# next_hop_self
applicable systems:
All models.
BGP4 Config ure Commands
June 2004 © 2004 Foundry Networks, Inc. 7 - 27
Page 85

Foundry AR-Series Router User Guide
configure router bgp neighbor password
This command configures a password for md5 authentication.
Parameter Description
md5_password TCP MD5 password for the BGP session
Enter a word (maximum 80 characters) .
syntax:
md5_password < string >
example:
Foundry-AR1208/configure/router/bgp 10/neighbor 10.10.20.1 2# md5_password asdf
applicable systems:
All models.
7 - 28 © 2004 Foundry Networks, Inc. June 2004
Page 86

BGP4 Config ure Commands
configure router bgp neighbor route_map
This command applies a route map to a neighbor.
A similar command exists under the group tree for applying route_map to a group of neighbors in the outbound
direction.
Parameter Description
route_map The name of a route map
route_map_options Filter options
in Inbound direction
syntax:
[ no ] route_map route_map < name > route_map_options < in >
example:
Foundry-AR1208/configure/router/bgp 10/neighbor 100.50.23.3 4# route_map B01 in
applicable systems:
All models.
June 2004 © 2004 Foundry Networks, Inc. 7 - 29
Page 87

Foundry AR-Series Router User Guide
configure router bgp neighbor timers
This command configure keepalive timers for a neighbor (peer).
The holdtime timer value is calculated as three times the value of the keepalive timer.
Parameter Description
keepalive The keepalive interval
The range is 2 - 21845; the default is 60.
syntax:
[ no ] timers keepalive < n >
example:
Foundry-AR1208/configure/router/bgp 10/neighbor 101.101.1.2 4# tim ers 120
applicable systems:
All models.
7 - 30 © 2004 Foundry Networks, Inc. June 2004
Page 88

BGP4 Config ure Commands
configure router bgp neighbor update_source
This command configures the source of BGP TCP connections for a specified neighbor as the IP address
specified, instead of the IP address of a physical interface.
This address will be used as the source address for routing updates.
syntax:
[ no ] update_source < IP address >
example:
Foundry-AR1208/configure/router/bgp 10/neighbor 101.101.1.2 4# update_source 10.10.2.1
applicable systems:
All models.
June 2004 © 2004 Foundry Networks, Inc. 7 - 31
Page 89

Foundry AR-Series Router User Guide
configure router bgp redistribute
This command provides access to the following next-level commands.
Redistribution causes rou tes from other protocols to be exporte d vi a th e c urren t pro toc ol. Routes from the current
protocol are alw a ys e xpo rted , s om e pro toc ols may prov id e additional policy f eat ures that allow the suppression of
protocol routes.
related commands:
configure router bgp redistribute connected
configure router bgp redistribute ospf
configure router bgp redistribute rip
configure router bgp redistribute static
related commands:
configure router bgp aggregate_address
configure router bgp always_compare_med
configure router bgp distance
configure router bgp default_metric
configure router bgp group
configure router bgp neighbor
7 - 32 © 2004 Foundry Networks, Inc. June 2004
Page 90

configure router bgp redistribute connected
This command redistributes interface routes.
Parameter Description
metric Default metric
The range is 0 - 4294967294.
route_map Name of the route map to use
syntax:
[ no ] redistribute connected [ metric < n > ] [ route_map < name > ]
example:
Foundry-AR1208/configure/router/bgp 10# redistribute connected metric 5000
BGP4 Config ure Commands
related commands:
configure router bgp redistribute ospf
configure router bgp redistribute rip
configure router bgp redistribute static
applicable systems:
All models.
June 2004 © 2004 Foundry Networks, Inc. 7 - 33
Page 91

Foundry AR-Series Router User Guide
configure router bgp redistribute ospf
This command configures the router to redistribute OSPF routes.
Parameter Description
metric The default metric
The range is 0 - 4294967294.
route_map Name of the route map to use
syntax:
[ no ] redistribute ospf [ metric < n > ] [ route_map < name > ]
example:
Foundry-AR1208/configure/router/bgp 10# redistribute ospf metric AR1208
related commands:
configure router bgp redistribute connected
configure router bgp redistribute rip
configure router bgp redistribute static
applicable systems:
All models.
7 - 34 © 2004 Foundry Networks, Inc. June 2004
Page 92

configure router bgp redistribute rip
This command configures a router to redistribute RIP routes.
Parameter Description
metric The default metric
The range is 0 - 4294967294.
route_map Name or ID of the route map to use
syntax:
[ no ] redistribute rip [ metric < n > ] [ route_map < name > ]
example:
Foundry-AR1208/configure/router/bgp 10# redistribute rip route_map east8
BGP4 Config ure Commands
related commands:
configure router bgp redistribute connected
configure router bgp redistribute ospf
configure router bgp redistribute static
applicable systems:
All models.
June 2004 © 2004 Foundry Networks, Inc. 7 - 35
Page 93

Foundry AR-Series Router User Guide
configure router bgp redistribute static
This command configures a router to redistribute static routes.
Parameter Description
metric The default metric
The range is 0 - 4294967294.
route_map Name of the route map to use
syntax:
[ no ] redistribute static [ metric < n > ] [ route_map < name > ]
example:
Foundry-AR1208/configure/router/bgp 10# redistribute static metric 25
related commands:
configure router bgp redistribute connected
configure router bgp redistribute ospf
configure router bgp redistribute rip
applicable systems:
All models.
7 - 36 © 2004 Foundry Networks, Inc. June 2004
Page 94

BGP4 show Commands
Use BGP show commands to display all configured BGP information.
NOTE: The CLI commands “show” and “display” can be used interchangeably.
show ip bgp
Chapter 8
This command accesses the following next-level display (show) commands.
related commands:
show ip bgp aggregate_address
show ip bgp community
show ip bgp groups
show ip bgp neighbors
show ip bgp paths
show ip bgp regexp
show ip bgp summary
show ip bgp table
June 2004 © 2004 Foundry Networks, Inc. 8 - 1
Page 95

Foundry AR-Series Router User Guide
show ip bgp aggregate_address
This command displays a list of configured aggregate addresses.
Parameter Description
address Aggregate address
Enter an IP address.
mask Aggregate mask
Enter a subnet mask.
syntax:
show ip bgp aggregate_address [ address < IP add res s > [ mask < subnet mask > ] ]
example:
Foundry-AR1208# show ip bgp aggregate_address address 100.12.23.0 mask 255.255.255.0
applicable systems:
All models.
8 - 2 © 2004 Foundry Networks, Inc. June 2004
Page 96

show ip bgp community
This command displays routes that match BGP communities.
Parameter Description
number Community number (enter a list of unsigned numbers)
The maximum list size is 10.
The range is 1 - 4294967294
aa:nn Community number in aa:nn format
Enter a list of strings separated by spaces.
The maximum list size is 10 numbers.
match_local_as
local_as Do not send outside local AS (well-known community)
match_no_advertise
no_advertise Do not advertise to any peer (well-known community)
match_no_export
no_export Do not export to next AS (well-known community)
match_exact_match
exact_match
Exact match of the communities
BGP4 show Commands
syntax:
show ip bgp community [ number < n > ] [ aa:nn < n > ] [ match_local_as < local_as > ]
[ match_no_advertise < no_advertise > ] [ match_no_export < no_export > ]
[ match_exact_match < exact_m atc h > ]
example:
Foundry-AR1208# show ip bgp community aa:nn 0:999
June 2004 © 2004 Foundry Networks, Inc. 8 - 3
Page 97

Foundry AR-Series Router User Guide
Status codes
* ( valid ) The table entry is valid.
# ( best ) The table entry is the best entry to use for that network.
i ( internal ) The table entry was learned via an internal BGP session.
Origin codes
i ( IGP) Internal BGP
e (EGP) Externa l BGP
? ( incomplete) Protocol of unknown origi n. T ypically redistributed into BGP from an
applicable systems:
All models.
Table 8.1: Status and Origin Codes
IGP.
8 - 4 © 2004 Foundry Networks, Inc. June 2004
Page 98

show ip bgp groups
This command provides information about BGP groups.
syntax:
show ip bgp g roups [ < name > ]
example:
Foundry-AR1208# show ip bgp groups north
applicable systems:
All models.
BGP4 show Commands
June 2004 © 2004 Foundry Networks, Inc. 8 - 5
Page 99

Foundry AR-Series Router User Guide
show ip bgp neighbors
This command displays detailed information and status on all BGP neighbors, including:
• peer group and AS affiliations
• configured and negotiated timers
• minimum times between advertisements
• receive and transmit updates
• BGP state status
• TCP connection ( active or inactive)
Parameter Description
group Neighbors belonging to a group
Enter a name or word.
address Neighbor to display information about
Enter an IP address.
routes
advertised_routes Display the routes advertised to a BGP neighbor.
received_routes Display the routes receiv ed from a neighbor.
syntax:
show ip bgp neighbors [ group < name > ] [ address < IP address# ]
[ routes < advertised_routes | received_routes > ]
example:
Foundry-AR1208# show ip bgp neighbors
8 - 6 © 2004 Foundry Networks, Inc. June 2004
Page 100

Table 8.2: Status and Origin Codes
Status codes
* ( valid ) The table entry is valid.
# ( best ) The table entry is the best entry to use for that network.
i ( internal ) The table entry was learned via an internal BGP session.
Origin codes
i ( IGP) Internal BGP
e (EGP) Externa l BGP
? ( incomplete) Protocol of unknown origin.
Table 8.3: Other BGP show Descriptions
BGP neighbor IP address of the BGP neighbor
BGP4 show Commands
peer group Displays the name of the peer group.
remote AS The remote AS number of the neighbor
local AS The local AS number of the neighbor
link Identifies the link as internal or external.
BGP version Identifies the BGP version
local router ID BGP identifier of the local router
remote router ID BGP identifier of the remote router
current state Current BGP protocol state
last state Previous BGP protocol state
last event Previous BGP protocol event
configured hold time Configured BGP hold time
keepalive interval Configured BGP keepalive interval
minimum time Minimum time between advertisements
received
messages Number of received BGP messages
notifications Number of received BGP notifications
updates Number of received BGP updates
sent
messages Number of sent BGP messages
notifications Number of sent BGP notifications
June 2004 © 2004 Foundry Networks, Inc. 8 - 7
 Loading...
Loading...