Page 1

FortiLog
Administration Guide
FortiLog-400
FortiLog-100
1
FortiLog-800
8
4
FortiLog Administration Guide
Version 1.6
January 15, 2004
05-16000-0082-20050115
Page 2

© Copyright 2005 Fortinet Inc. All rights reserved.
No part of this publication including text, examples, diagrams or illustrations may be reproduced,
transmitted, or translated in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, manual, optical or
otherwise, for any purpose, without prior written permission of Fortinet Inc.
FortiLog Administration Guide
Version 1.6
January 15, 2005
05-16000-0082-20050115
Trademarks
Products mentioned in this document are trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective
holders.
Regulatory Compliance
FCC Class A Part 15, UL, CE
CAUTION: RISK OF EXPLOSION IF BATTERY IS REPLACED BY AN INCORRECT TYPE.
DISPOSE OF USED BATTERIES ACCORDING TO THE INSTRUCTIONS.
For technical support, please visit http://www.fortinet.com.
Send information about errors or omissions in this document or any Fortinet technical documentation to
techdoc@fortinet.com.
Page 3

Table of Contents
Introduction............................................................................................................ 7
Operational Modes.............................................................................................................. 8
Active Mode .................................................................................................................... 8
Passive Mode ................................................................................................................. 9
About this guide ................................................................................................................ 10
FortiLog documentation .................................................................................................... 10
Related documentation ..................................................................................................... 11
FortiGate documentation .............................................................................................. 11
FortiManager documentation ........................................................................................ 12
FortiClient documentation ............................................................................................. 12
FortiMail documentation................................................................................................ 12
Fortinet Knowledge Center ........................................................................................... 12
Comments on Fortinet technical documentation........................................................... 12
Customer service and technical support........................................................................... 13
Setting up the FortiLog unit................................................................................ 15
Contents
Checking the package contents........................................................................................ 15
Hardware specifications................................................................................................ 16
Dimensions ............................................................................................................... 16
Weight....................................................................................................................... 16
Power requirements.................................................................................................. 17
Environmental specifications..................................................................................... 17
Air flow ...................................................................................................................... 17
Mechanical loading ................................................................................................... 17
Planning the installation.................................................................................................... 17
Connecting the FortiLog unit............................................................................................. 18
Configuring the FortiLog unit............................................................................................. 19
Using the web-based manager ..................................................................................... 19
Using the command line interface................................................................................. 20
Using the front panel buttons and LCD......................................................................... 21
Connecting to the FortiLog Unit......................................................................... 23
Sending device logs to the FortiLog unit........................................................................... 23
Configuring FortiGate unit running FortiOS 2.8 ............................................................ 23
Configuring FortiGate devices running FortiOS 2.5 ...................................................... 24
Configuring FortiMail devices........................................................................................ 25
Configuring the FortiLog unit............................................................................................. 26
Adding a device ............................................................................................................ 26
Defining device port interfaces.................................................................................. 27
Creating Device Groups................................................................................................ 28
FortiLog Administration Guide 05-16000-0082-20050115 3
Page 4

Contents
Managing the FortiLog unit................................................................................. 29
Status................................................................................................................................ 29
Status............................................................................................................................ 29
Changing the FortiLog host name............................................................................. 31
Changing operating modes....................................................................................... 31
Viewing system resources information...................................................................... 32
Changing the firmware.................................................................................................. 32
Installing firmware from a system reboot .................................................................. 33
Testing a new firmware image .................................................................................. 35
Installing a backup firmware image........................................................................... 36
Switching to a backup firmware image...................................................................... 38
Switching to the default firmware image ................................................................... 38
Backing up system settings .......................................................................................... 39
Downlading the FortiLog debug log .............................................................................. 39
Restoring system settings............................................................................................. 40
Restore factory default system settings ........................................................................ 40
Restoring a FortiLog unit............................................................................................... 40
RAID ............................................................................................................................. 41
Config................................................................................................................................ 42
Network......................................................................................................................... 42
RAID ............................................................................................................................. 43
Log settings................................................................................................................... 44
Log policy.................................................................................................................. 45
Time .............................................................................................................................. 46
Options.......................................................................................................................... 46
Admin............................................................................................................................ 46
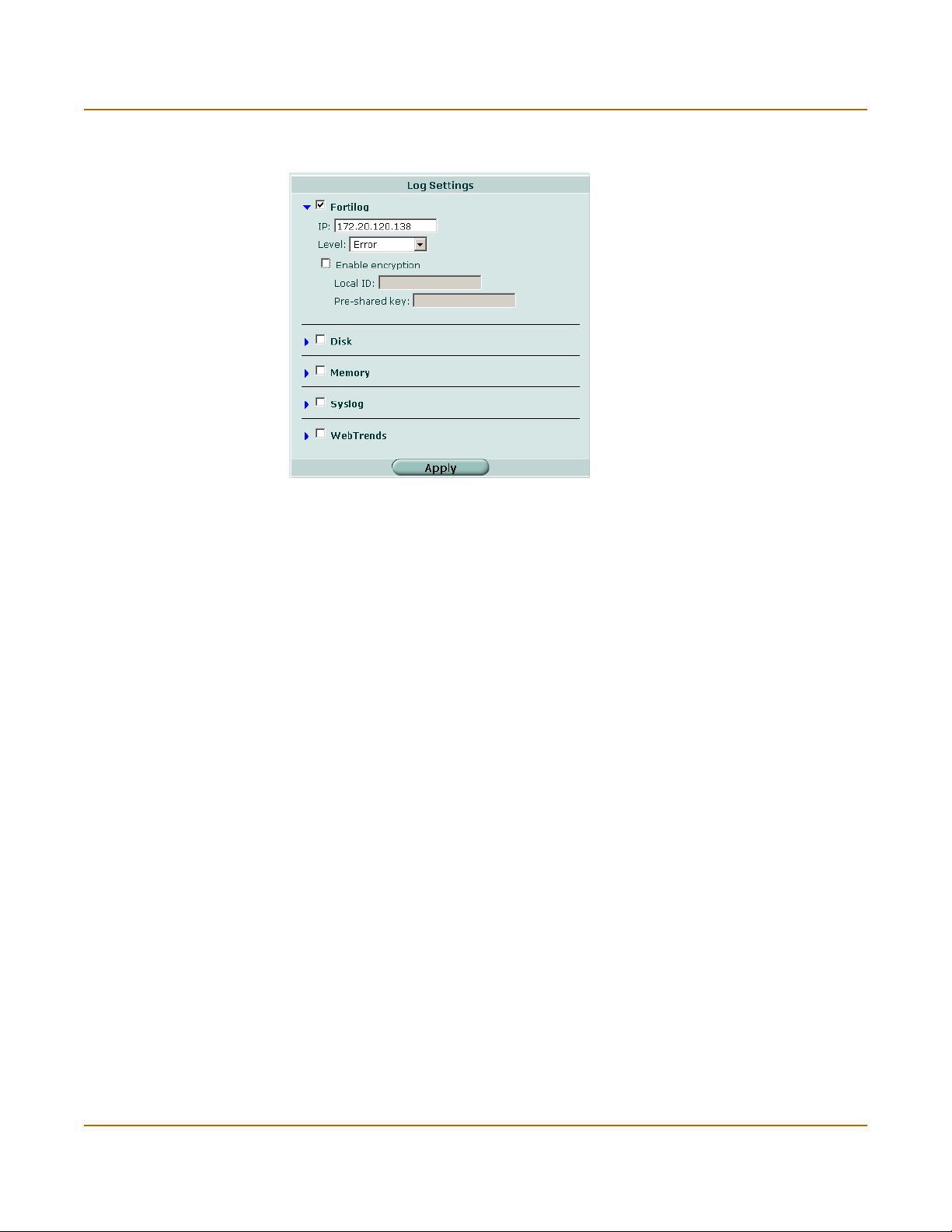
Configure Administrator access ................................................................................ 47
Administrator account levels ..................................................................................... 48
Administrator options ................................................................................................ 48
Changing the Administrator password ...................................................................... 49
Devices (Active mode)...................................................................................................... 49
Device list...................................................................................................................... 50
Adding and registering a device.................................................................................... 50
Editing device information............................................................................................. 50
Alert Email......................................................................................................................... 51
Server ........................................................................................................................... 51
Local ............................................................................................................................. 52
Device (Active mode).................................................................................................... 52
Creating a new device alert....................................................................................... 52
Alerts................................................................................................................................. 54
Network Sharing ............................................................................................................... 55
Defining IP aliases ............................................................................................................ 55
4 05-16000-0082-20050115 Fortinet Inc.
Page 5

Reports ................................................................................................................. 57
Creating and generating a report...................................................................................... 57
Configuring report parameters ...................................................................................... 58
Configuring a report query ............................................................................................ 59
Creating a query profile............................................................................................. 60
Selecting the devices for the report .............................................................................. 60
Creating a device profile ........................................................................................... 61
Select filtering options................................................................................................... 61
Creating a filter profile............................................................................................... 62
Setting a report schedule .............................................................................................. 62
Creating a report schedule profile ............................................................................. 63
Choosing the report destination and format.................................................................. 63
Creating a report destination and format profile........................................................ 64
Reports on demand ...................................................................................................... 64
Viewing reports ................................................................................................................. 65
Roll up report ................................................................................................................ 66
Individual reports........................................................................................................... 66
Vulnerability reports .......................................................................................................... 67
Creating and generating a report .................................................................................. 67
Selecting report result parameters................................................................................ 68
Selecting plug-ins.......................................................................................................... 68
Creating a plug-in profile........................................................................................... 69
Selecting the scan targets for the report ....................................................................... 69
Creating a scan target profile.................................................................................... 70
Choosing the report destination and format.................................................................. 71
Creating a report destination and format profile........................................................ 71
Viewing the vulnerability report ..................................................................................... 72
Contents
Using Logs ........................................................................................................... 73
The Log view interface...................................................................................................... 74
Viewing logs...................................................................................................................... 74
Finding log information.................................................................................................. 75
Importing log files.............................................................................................................. 77
Log Search........................................................................................................................ 78
Log watch (Active mode) .................................................................................................. 78
Event correlation (Active mode)........................................................................................ 79
Using the FortiLog unit as a NAS....................................................................... 81
Connecting to the FortiLog file system.............................................................................. 81
Providing access to the FortiLog hard disk....................................................................... 82
Selecting a file sharing protocol .................................................................................... 82
Adding and modifying user accounts ............................................................................ 82
FortiLog Administration Guide 05-16000-0082-20050115 5
Page 6

Contents
Adding and modifying group accounts.......................................................................... 83
Assigning access to folders .......................................................................................... 83
Modifying the user or group folder access ................................................................ 85
Setting folder and file properties ....................................................................................... 86
FortiLog CLI reference ........................................................................................ 87
CLI documentation conventions........................................................................................ 87
Connecting to the CLI ....................................................................................................... 88
Connecting to the FortiLog-800 console ....................................................................... 88
Setting administrative access for SSH or Telnet........................................................... 89
Connecting to the FortiLog CLI using SSH ................................................................... 90
Connecting to the FortiLog CLI using Telnet ................................................................ 90
CLI commands.................................................................................................................. 91
execute branch ............................................................................................................. 91
get branch ..................................................................................................................... 92
set branch ..................................................................................................................... 94
set alertemail............................................................................................................. 94
set console................................................................................................................ 97
set log........................................................................................................................ 98
set NAS................................................................................................................... 103
set report................................................................................................................. 104
set system............................................................................................................... 104
unset branch ............................................................................................................... 110
Appendix A: Log Report Types ........................................................................ 113
Network Activity....................................................................................................... 113
Web Activity ............................................................................................................ 113
FTP Activity ............................................................................................................. 114
Terminal Activity...................................................................................................... 115
Mail Activity ............................................................................................................. 115
Intrusion Activity...................................................................................................... 116
Antivirus Activity ...................................................................................................... 116
Web Filter Activity ................................................................................................... 116
Mail Filter Activity .................................................................................................... 117
VPN Activity ............................................................................................................ 118
Content Activity ....................................................................................................... 118
Index .................................................................................................................... 121
6 05-16000-0082-20050115 Fortinet Inc.
Page 7

Introduction
FortiLog units are network appliances that provide integrated log collection, analysis
tools and data storage. Detailed log reports provide historical as well as current
analysis of network and email activity to help identify security issues and reduce
network misuse and abuse.
FortiLog units operate in one of two modes:
• In Active mode as a log collection and analysis tool to collect logs from FortiGate
and FortiMail devices and generate reports based on log data.
• In Passive mode as a Network Attached Storage (NAS) server to act as an
additional storage device.
The models in the FortiLog family:
FortiLog Administration Guide Version 1.6
• FortiLog-100, desktop model with one hard drive.
• FortiLog-400, desktop model with four hard drives.
• FortiLog-800, rackmount model with four hard drives.
Figure 1: FortiLog models
FortiLog-400
FortiLog-100
1
4
FortiLog-800
8
FortiLog Administration Guide 05-16000-0082-20050115 7
Page 8
Operational Modes Introduction
Operational Modes
The FortiLog device can operate in two modes: Active mode or Passive mode. The
web-based interface provides an interface that reflects each models’ functionality.
Active Mode
Active mode is the default mode for the FortiLog unit. In Active mode, the FortiLog unit
can receive log files from FortiGate, FortiClient, FortiMail and syslog devices. Using
the reporting features, you can use the FortiLog unit to view the log files and generate
more than 130 different reports for hourly, daily, weekly, monthly, and even quarterly
reviews of any device traffic.
Figure 2: FortiLog unit in Active mode
Using FortiLog to analyze logs and generate reports enables you to proactively secure
networks before threats arise, avoid network abuses, manage bandwidth
requirements, monitor Web site visits, and ensure appropriate usage of the network by
employees.
The FortiLog unit also acts as a Network Attached Storage (NAS) device. Use the
FortiLog unit as a means of backing up or storing important information or using the
extra hard disk space as a file server or repository. Any computer using NFS or
Windows sharing can mount the FortiLog hard drive to save and retrieve files.
8 05-16000-0082-20050115 Fortinet Inc.
Page 9
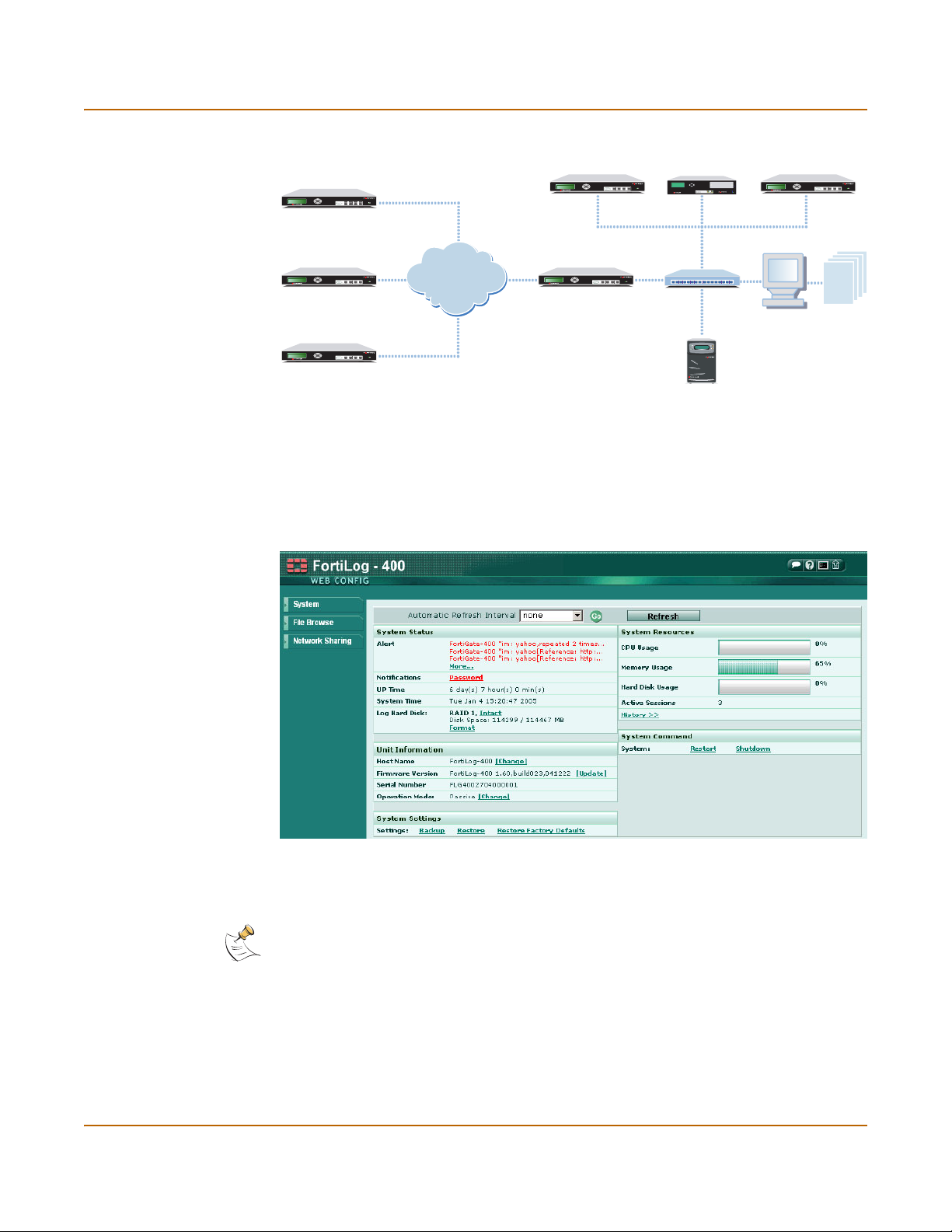
Introduction Operational Modes
Figure 3: FortiLog Active mode network architecture
1
CONSOLE
Esc Enter
FortiGate Unit
FortiMail UnitFortiGate Unit
4 / HA3
1
CONSOLE
2
4 / HA3
2
Esc Enter
1
2
CONSOLE
PWE
FortiGate Unit
1
CONSOLE
Esc Enter
4 / HA3
2
Passive Mode
1
CONSOLE
Esc Enter
FortiGate Unit
1
CONSOLE
Esc Enter
FortiGate Unit
4 / HA3
2
Internet
FortiGate Unit
4 / HA3
2
4 / HA3
1
CONSOLE
2
Esc Enter
Switch
Management PC
4
Reports
FortiLog Unit
Passive mode enables you to use the FortiLog unit solely as a Network Attached
Server (NAS) storage device. The collection of device log files and the log reporting
features are not available in passive mode.
Figure 4: FortiLog unit in Passive mode
FortiLog units running in Passive mode provide secure storage space. Using the
integrated RAID (Redundant Arrays of Inexpensive Disks) functionality provides better
data security.
Note: RAID functionality is only available on the FortiLog-400 and 800. These units contain four
hard disks and support RAID level 0, 1, and 5.
FortiLog Administration Guide 05-16000-0082-20050115 9
Page 10

About this guide Introduction
About this guide
This document describes how to set up and configure the FortiLog unit. The
configuration and features of the FortiLog unit are similar in either mode. Section titles
indicate where the features or configuration differs or is unique to each mode. For
example, Devices (Active mode).
This document has the following sections:
• Setting up the FortiLog unit describes how to set up and install the FortiLog unit in
your network.
• Connecting to the FortiLog Unit describes how to connect a FortiGate and
FortiMail device to the FortiLog unit to for collecting log files. It also discusses the
requirements to help users to connect and view files on the FortiLog hard disk.
• Managing the FortiLog unit describes how to view and configure the FortiLog
system settings, such as system time, session information, and user management.
• Reports describes how to generate, customize and view log reports and generate
vulnerability reports for selected devices.
• Using Logs describes how to select, and view device and FortiLog log files. It also
describes customizing the log views to find information in the logs easier, as well
as watch logs in real time.
• Using the FortiLog unit as a NAS describes how to use the FortiLog unit as a file
storage device and how to provide access to users and groups.
• FortiLog CLI reference is a source for commands when accessing the FortiLog unit
from the CLI.
• Appendix A: Log Report Types provides an extensive list of the more than 130 log
reports that the FortiLog unit can generate.
This document is available in online help format from the web-based manager. To
access the online help, select the question mark icon in the upper-right corner of the
web-based manager window.
FortiLog documentation
• FortiLog Administration Guide
Describes how to install and configure a FortiLog unit to collect FortiGate and
FortiMail log files. It also describes how to view FortiGate and FortiMail log files,
generate and view log reports, and use the FortiLog unit as a NAS server.
• FortiLog online help
Provides a searchable version of the Administration Guide in HTML format. You
can access online help from the web-based manager as you work.
• FortiLog QuickStart Guide
Explains how to install and set up the FortiLog unit.
10 05-16000-0082-20050115 Fortinet Inc.
Page 11

Introduction Related documentation
Related documentation
Additional information about Fortinet products is available from the following related
documentation.
FortiGate documentation
Information about FortiGate products is available from the following guides:
• FortiGate QuickStart Guide
Provides basic information about connecting and installing a FortiGate unit.
• FortiGate Installation Guide
Describes how to install a FortiGate unit. Includes a hardware reference, default
configuration information, installation procedures, connection procedures, and
basic configuration procedures. Choose the guide for your product model number.
• FortiGate Administration Guide
Provides basic information about how to configure a FortiGate unit, including how
to define FortiGate protection profiles and firewall policies; how to apply intrusion
prevention, antivirus protection, web content filtering, and spam filtering; and how
to configure a VPN.
• FortiGate online help
Provides a context-sensitive and searchable version of the Administration Guide in
HTML format. You can access online help from the web-based manager as you
work.
• FortiGate CLI Reference Guide
Describes how to use the FortiGate CLI and contains a reference to all FortiGate
CLI commands.
• FortiGate Log Message Reference Guide
Describes the structure of FortiGate log messages and provides information about
the log messages that are generated by FortiGate units.
• FortiGate High Availability Guide
Contains in-depth information about the FortiGate high availability feature and the
FortiGate clustering protocol.
• FortiGate IPS Guide
Describes how to configure the FortiGate Intrusion Prevention System settings and
how the FortiGate IPS deals with some common attacks.
• FortiGate VPN Guide
Explains how to configure VPNs using the web-based manager.
FortiLog Administration Guide 05-16000-0082-20050115 11
Page 12

Related documentation Introduction
FortiManager documentation
• FortiManager QuickStart Guide
Explains how to install the FortiManager Console, set up the FortiManager Server,
and configure basic settings.
• FortiManager System Administration Guide
Describes how to use the FortiManager System to manage FortiGate devices.
• FortiManager System online help
Provides a searchable version of the Administration Guide in HTML format. You
can access online help from the FortiManager Console as you work.
FortiClient documentation
• FortiClient Host Security User Guide
Describes how to use FortiClient Host Security software to set up a VPN
connection from your computer to remote networks, scan your computer for
viruses, and restrict access to your computer and applications by setting up firewall
policies.
• FortiClient Host Security online help
Provides information and procedures for using and configuring the FortiClient
software.
FortiMail documentation
• FortiMail Administration Guide
Describes how to install, configure, and manage a FortiMail unit in gateway mode
and server mode, including how to configure the unit; create profiles and policies;
configure antispam and antivirus filters; create user accounts; and set up logging
and reporting.
• FortiMail online help
Provides a searchable version of the Administration Guide in HTML format. You
can access online help from the web-based manager as you work.
• FortiMail Web Mail Online Help
Describes how to use the FortiMail web-based email client, including how to send
and receive email; how to add, import, and export addresses; and how to configure
message display preferences.
Fortinet Knowledge Center
The most recent Fortinet technical documentation is available from the Fortinet
Knowledge Center. The knowledge center contains short how-to articles, FAQs,
technical notes, product and feature guides, and much more. Visit the Fortinet
Knowledge Center at http://kc.forticare.com.
Comments on Fortinet technical documentation
You can send information about errors or omissions in this document, or any Fortinet
technical documentation, to techdoc@fortinet.com.
12 05-16000-0082-20050115 Fortinet Inc.
Page 13

Introduction Customer service and technical support
Customer service and technical support
For antivirus and attack definition updates, firmware updates, updated product
documentation, technical support information, and other resources, please visit the
Fortinet technical support web site at http://support.fortinet.com.
You can also register FortiGate Antivirus Firewalls from http://support.fortinet.com and
change your registration information at any time.
Fortinet email support is available from the following addresses:
amer_support@fortinet.com For customers in the United States, Canada, Mexico, Latin
apac_support@fortinet.com For customers in Japan, Korea, China, Hong Kong, Singapore,
eu_support@fortinet.com For customers in the United Kingdom, Scandinavia, Mainland
America and South America.
Malaysia, all other Asian countries, and Australia.
Europe, Africa, and the Middle East.
For information on Fortinet telephone support, see http://support.fortinet.com.
When requesting technical support, please provide the following information:
• Your name
• Company name
•Location
• Email address
• Telephone number
• FortiGate unit serial number
• FortiGate model
• FortiGate FortiOS firmware version
• Detailed description of the problem
FortiLog Administration Guide 05-16000-0082-20050115 13
Page 14

Customer service and technical support Introduction
14 05-16000-0082-20050115 Fortinet Inc.
Page 15

FortiLog Administration Guide Version 1.6
Setting up the FortiLog unit
This chapter includes:
• Checking the package contents
• Hardware specifications
• Planning the installation
• Connecting the FortiLog unit
• Configuring the FortiLog unit
Checking the package contents
The FortiLog family includes three models. Check the model number on the front
panel of your FortiLog unit. All three models are shown in the picture below.
• FortiLog-100, desktop model with one hard drive.
• FortiLog-400, desktop model with four hard drives.
• FortiLog-800, rackmount model with four hard drives.
Table 1: FortiLog unit connectors
Connector Type Speed Protocol Description
LAN for FortiLog-100
LAN1 for
FortiLog-400
and 800
CONSOLE
(FortiLog-800 only)
RJ-45 10/100Base-T
(FortiLog-100 and
400)
10/100/1000Base-T
(FortiLog-800)
DB-9 9600 bps RS-232
Ethernet Connection to the network.
serial
Connection to the
management computer.
Provides access to the
command line interface
(CLI).
FortiLog Administration Guide 05-16000-0082-20050115 15
Page 16
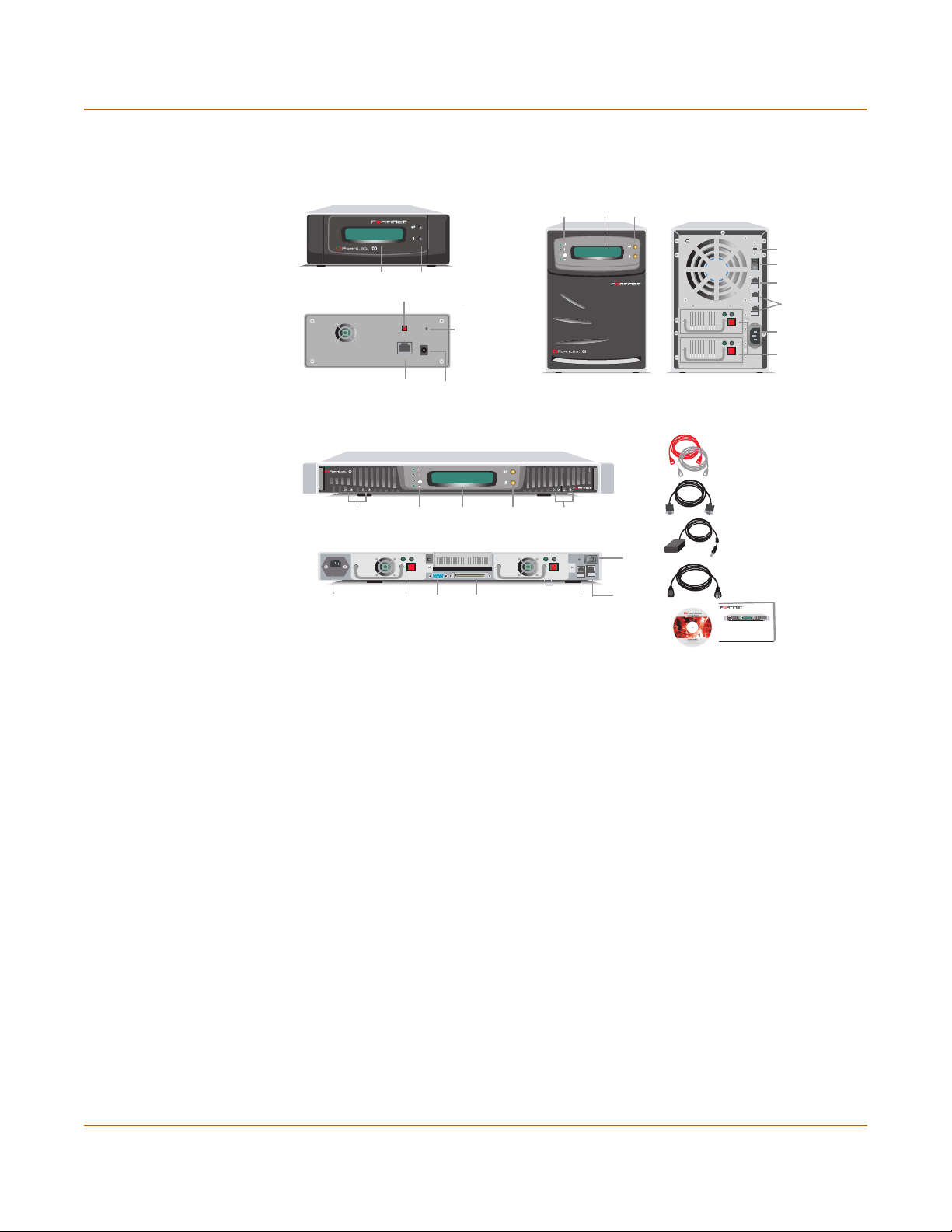
Checking the package contents Setting up the FortiLog unit
Figure 5: FortiLog front and back diagrams
FortiLog-100 FortiLog-400
Front
LED indicators:
Power, Error, Network,
and Disk Access
LCD
Panel
Setting
Switches
A and B
Hard Disk
Power
Connection
1
LCD
Panel
Back
8
LED indicators:
Power, Error, Network,
LEDs
and Disk Access
ATX Redundant
Power Supplies
Setting Switches
A and B
Power
Switch
LAN
Power
Connection
FortiLog-800
Front
Back
RS-232
Serial
Connection
Reset
Switch
LCD
Panel
SCSI Connector
For Tape Drive
For Future Use
Setting
Switches
A and B
Hard Disk
LEDs
(Network
Connection)
LAN1
4
Front
Rack-Mount
Back
Accessories for each model
Orange - Crossover
Grey - Straight-through
Brackets
Power
Switch
LAN2
For Future Use
USER MANUAL
Null-Modem Cable
Copyright 2004 Fortinet Incorporated. All rights reserved.
Trademarks
Products mentioned in this document are trademarks.
Ethernet Cables:
(RS-232)
for FortiLog-800
AC Adapter
for FortiLog-100
Power Cable
FortiLog-100,400, 800
8
QuickStart Guide
Documentation
Reset
Switch
Power
Switch
LAN1
(Network Connection)
LAN2 and LAN3
For Future Use
Power
Connection
ATX
Redundant
Power
Supplies
Hardware specifications
Dimensions
• FortiLog-100: 38 x 17 x 31 cm
• FortiLog-400: 54 x 33 x 44 cm
• FortiLog-800: 78 x 65 x 25 cm
Weight
• FortiLog-100: 2.5 kg
• FortiLog-400: 11 kg
• FortiLog-800:14 kg
16 05-16000-0082-20050115 Fortinet Inc.
Page 17

Setting up the FortiLog unit Planning the installation
Power requirements
• FortiLog-100
• AC input voltage: 100 to 240 VAC
• AC input current: 1.0 A
• Frequency: 47 to 63 Hz
• FortiLog-400 and 800
• AC input voltage: 115 to 230 VAC
• AC input current: 4 to 2 A
• Frequency: 47 to 63 Hz
Environmental specifications
• Operating temperature: 41 to 95°F (5 to 35°C)
If you install the FortiLog unit in a closed or multi-unit rack assembly, the
operating ambient temperature of the rack environment may be greater than room
ambient temperature. Therefore, make sure to install the equipment in an
environment
compatible with the manufacturer's maximum rated ambient temperature.
• Storage temperature: -4 to 176°F (-20 to 80°C)
• Humidity: 10 to 90% non-condensing
Air flow
• For rack installation, make sure that the amount of air flow required for safe
operation of the equipment is not compromised.
• For free-standing installation, make sure that the appliance has at least 1.5 in.
(3.75 cm) of clearance on each side to allow for adequate air flow and cooling.
Mechanical loading
For rack installation, ensure an even mechanical loading of the FortiLog unit to avoid a
hazardous condition.
Planning the installation
You can add the FortiLog unit to your local network to receive log messages from your
local FortiGate and FortiMail devices or act as a NAS server.
You can also connect the FortiLog unit to devices remotely through the Internet.
To connect the FortiLog unit to devices remotely, you must configure the DNS server
and the default gateway.
To manage the FortiLog unit, you can use a computer within the local network or over
the Internet.
FortiLog Administration Guide 05-16000-0082-20050115 17
Page 18
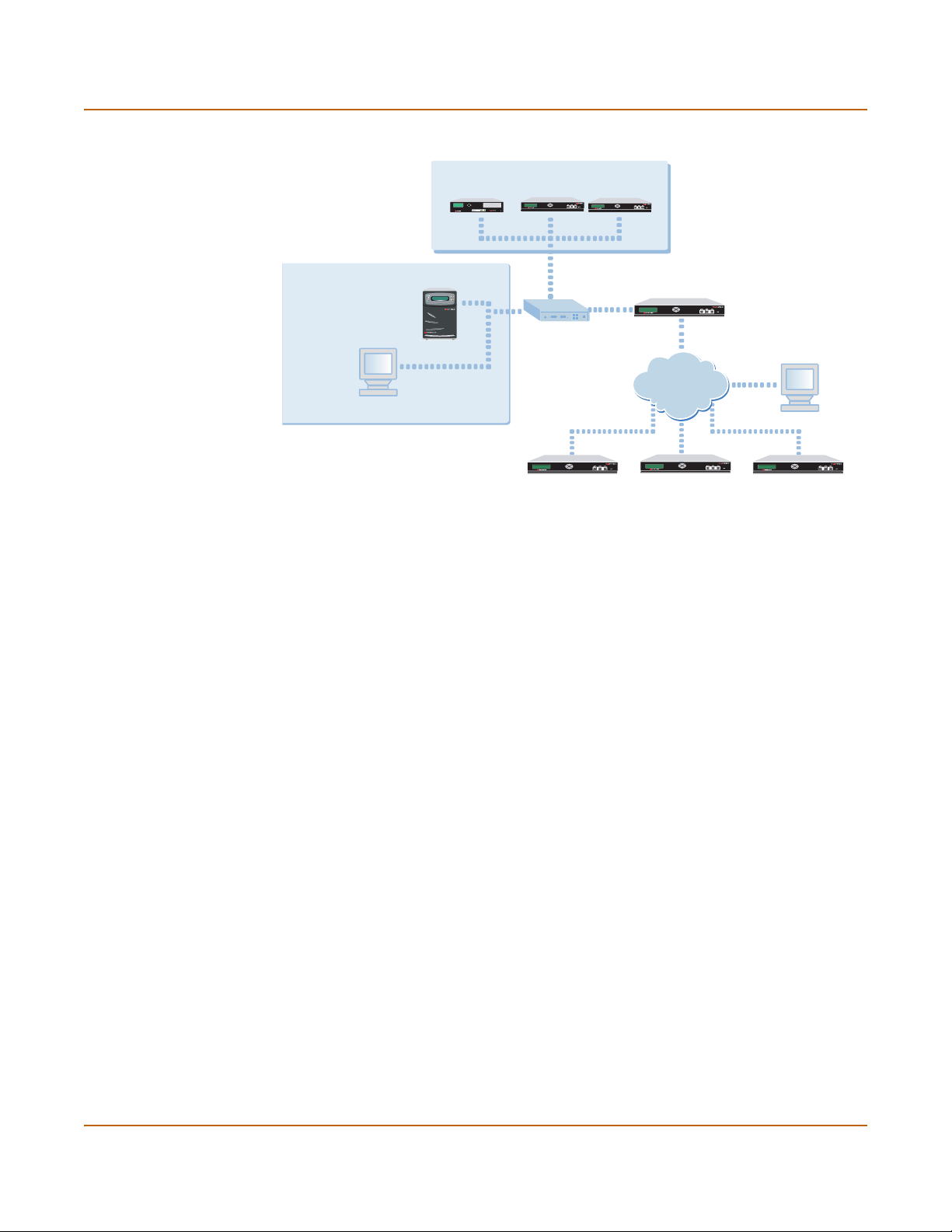
Connecting the FortiLog unit Setting up the FortiLog unit
C
Figure 6: FortiLog connection option
Internal Network
FortiLog unit
Management PC
Connecting the FortiLog unit
You can install the FortiLog unit as a free-standing appliance on any stable surface.
You can mount the FortiLog-800 unit in a standard 19-inch rack. It requires 1 U of
vertical space in the rack.
FortiMail unit
CONSOLE
4
FortiGate units
1
2
PWE
Esc Enter
Esc Enter
FortiGate unit
Esc Enter
Management P
Internet
Esc Enter Esc Enter
FortiGate unit
Esc Enter
FortiGate unit
FortiGate unit
To connect the FortiLog unit to the network
1 Place the unit on a stable surface.
2 If you have a FortiLog-800 unit, you can also mount it in a 19-inch rack. The units
require 1.5 inches (3.75 cm) clearance on each side to allow for cooling.
3 Make sure the power of the unit is turned off.
4 Connect the network cable to the LAN interface.
5 Connect the power cable to a power outlet.
6 Turn on the power switch.
18 05-16000-0082-20050115 Fortinet Inc.
Page 19
Setting up the FortiLog unit Configuring the FortiLog unit
Configuring the FortiLog unit
Use the web-based manager or the Command Line Interface (CLI) to configure the FortiLog unit
IP address, netmask, DNS server IP address, and default gateway IP address.
Table 2: Factory defaults
Administrator
account
LAN
User name: admin
Password: (none)
IP: 192.168.1.99
Netmask: 255.255.255.0
Management Access: HTTPS, Ping
Using the web-based manager
The web-based manager provides a GUI interface to configure and administer the
FortiLog unit. The web-based manager has a similar look and feel as the FortiGate 2.8
family.
You can use the web-based manager to configure most FortiLog settings. You can
also use the web-based manager to monitor the status of the FortiLog unit, administer
users, groups and set access rights.The web-based manager has a similar look and
feel as a FortiGate 2.8 web-based manager.
Using a secure HTTPS connection from any computer running Internet Explorer, you
can configure and manage the FortiLog unit.
Configuration changes made using the web-based manager are effective immediately
without resetting the firewall or interrupting service. Once you are satisfied with a
configuration, you can download and save it. You can restore the saved configuration
at any time.
For all the three FortiLog models, use the following procedure to connect to the
web-based manager for the first time.
To connect to the web-based manager, you need:
• An Ethernet connection between the FortiLog unit and management computer.
• Internet Explorer version 4.0 or higher on the management computer.
To connect to the web-based manager
1 Connect the LAN interface of the FortiLog unit to the Ethernet port of the management
computer.
2 Use a cross-over Ethernet cable to connect the devices directly. Use straight-through
Ethernet cables to connect the devices through a hub or switch.
3 Configure the management computer to be on the same subnet as the FortiLog LAN
interface.
4 To do this, change the IP address of the management computer to 192.168.1.2 and
the netmask to 255.255.255.0.
5 To access the FortiLog web-based manager, start Internet Explorer and browse to
https://192.168.1.99 (remember to include the “s” in https://).
FortiLog Administration Guide 05-16000-0082-20050115 19
Page 20

Configuring the FortiLog unit Setting up the FortiLog unit
6 Type admin in the Name field and select Login.
After connecting to the Web-based manager, you can configure the FortiLog unit IP
address, DNS server IP address, and default gateway to connect the FortiLog unit to
the network.
To configure the FortiLog unit using the web-based manager
1 In the web-based manager, go to System > Config > Network.
2 Enter the IP address, netmask, primary DNS server IP address, secondary DNS
server IP address (optional), and the default gateway IP address if the FortiLog unit
connects to the Internet.
Using the command line interface
You can use a terminal emulation software to connect to the command line interface
(CLI) from any network that is connected to the FortiLog unit, including the Internet.
This applies to all FortiLog models.
You can also access the FortiLog-800 CLI by using the null-modem cable provided to
connect to the unit’s console port.
The CLI supports the same configuration and monitoring functionality as the
web-based manager. In addition, you can use the CLI for advanced configuration
options that are not available from the web-based manager.
To connect to the FortiLog-800 unit
1 Use a null modem cable to connect the FortiLog-800 serial port to the management
computer serial port.
2 Start a terminal emulation program (such as HyperTerminal) on the management
computer. Use these settings:
• Baud Rate (bps) 9600
• Data bits 8,
• Parity None
• Stop bits 1
• Flow Control None.
3 At the login: prompt, type admin and press Enter twice.
4 (The
1 Set the IP address and netmask of the LAN interface:
2 Confirm that the address is correct:
login
prompt is preceded by the server IP address.)
After connecting to the CLI, you can configure the FortiLog-800 unit IP address, DNS
server IP address, and default gateway to connect the FortiLog-800 unit to the
network.
To configure the FortiLog unit using the CLI
set system interface port1 mode static ip <IP_address>
<netmask>
get system interface
20 05-16000-0082-20050115 Fortinet Inc.
Page 21

Setting up the FortiLog unit Configuring the FortiLog unit
3 Set the primary DNS server IP address:
set system dns primary <IP_address>
4 Optionally set the secondary DNS server IP address:
set system dns secondary <IP_address>
5 Set the default gateway:
set system route number <route_no> dst 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 gw1
<gw_ip>
Using the front panel buttons and LCD
You can use the front panel buttons to set up the FortiLog unit’s IP address, netmask,
and default gateway.
FortiLog Administration Guide 05-16000-0082-20050115 21
Page 22

Configuring the FortiLog unit Setting up the FortiLog unit
22 05-16000-0082-20050115 Fortinet Inc.
Page 23

FortiLog Administration Guide Version 1.6
Connecting to the FortiLog Unit
In order for FortiLog to receive log files, you need to configure the FortiGate, FortiMail
or syslog devices to send log files to the FortiLog unit. You also need to configure the
FortiLog unit to accept the log files from these devices.
This chapter explains how to set up your devices to send log files to the FortiLog unit
running in Active mode. If you are using the FortiLog device in Passive mode, you do
not have to read this chapter.
This chapter includes:
• Sending device logs to the FortiLog unit
• Configuring the FortiLog unit
Sending device logs to the FortiLog unit
When running in Active mode, the FortiLog unit collects log files from FortiGate,
FortiMail and syslog devices and uses those logs to generate detailed reports. Before
this can occur, you need to configure the devices to send the log files to the FortiLog
unit. You also need to configure the FortiLog unit to receive the log files.
Configuring FortiGate unit running FortiOS 2.8
To configure the FortiGate unit to send log files to the FortiLog unit
1 Log on to the FortiGate unit.
2 Go to Log&Report > Log Config.
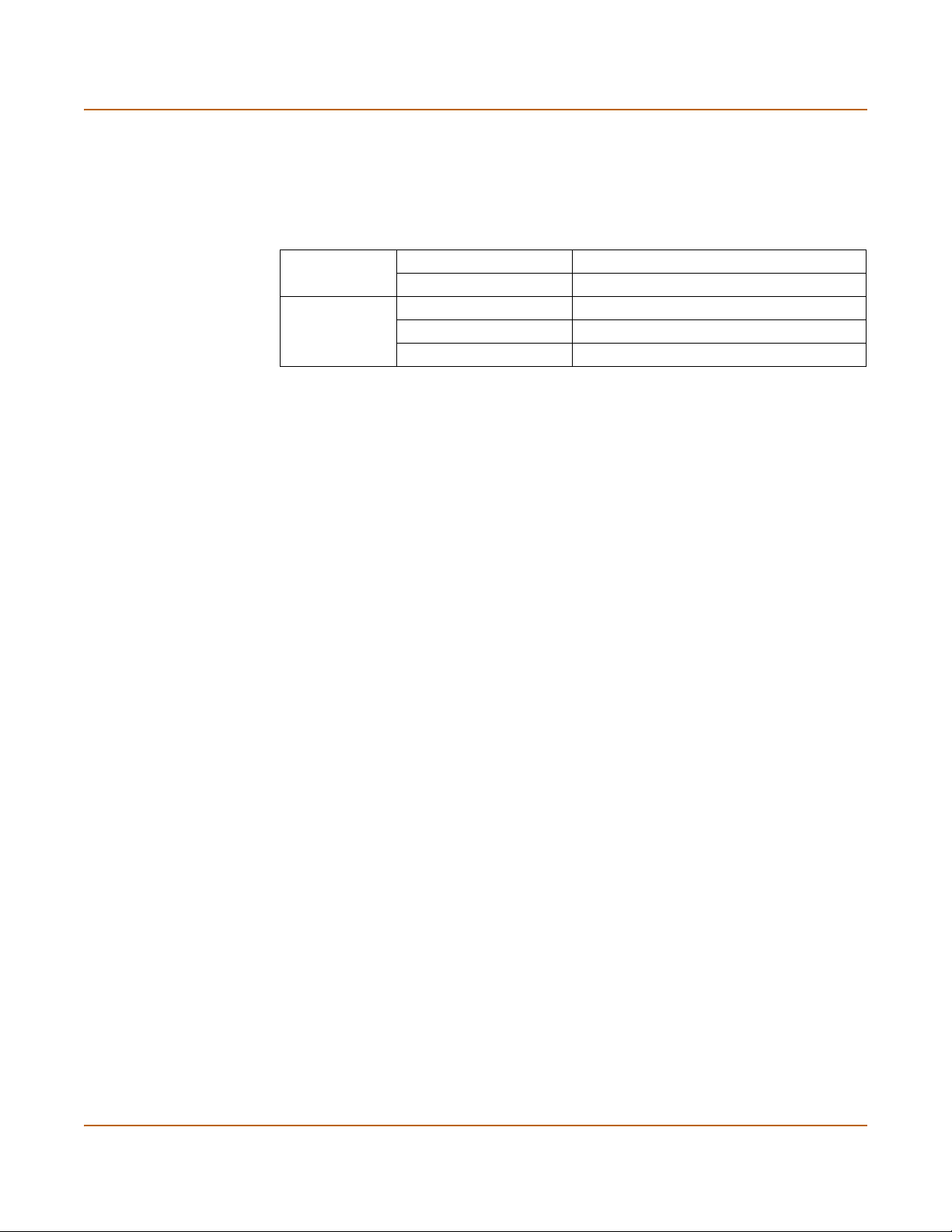
3 Select FortiLog.
4 Select the blue arrow beside the FortiLog selection.
FortiLog Administration Guide 05-16000-0082-20050115 23
Page 24
Sending device logs to the FortiLog unit Connecting to the FortiLog Unit
Figure 7: FortiGate 2.8 log settings
5 Enter the IP address of the FortiLog unit.
6 Set the level that the FortiGate unit logs messages to the FortiLog unit.
The FortiGate unit logs all messages at and above the logging severity you select. For
example, if you select Error, the device logs Error, Critical, Alert and Emergency level
messages. For a list of severity levels, see “Log policy” on page 45.
7 Select Enable encryption to send the log files through an IPsec connection.
If you choose to send encrypted log files:
• Enter a Local ID for the FortiGate unit. Use an ID that represents the FortiGate
unit. For example, FGT-500A. You will use this entry on the FortiLog unit as the
device name when registering the FortiGate unit.
• Enter an encryption key. You must also specify the identical value on the FortiLog
unit. For security reasons, the encryption key should be more than six characters
in length and contain a mixture of alpha and numeric characters.
Configuring FortiGate devices running FortiOS 2.5
If your FortiGate unit is running with FortiOS version 2.5, use the following procedure
to configure the FortiGate unit to record log messages on a remote system.
To configure the FortiGate unit to send log files to the FortiLog unit
1 Go to Log&Report > Log Setting.
24 05-16000-0082-20050115 Fortinet Inc.
Page 25

Connecting to the FortiLog Unit Sending device logs to the FortiLog unit
Figure 8: FortiGate 2.5 Log settings
2 Select Log to Remote Host to send the logs to a syslog server.
3 Enter the IP address of the FortiLog unit.
4 Enter the port number of the FortiLog unit.
5 Select the severity level for which you want to record log messages.
The FortiGate device logs all messages at and above the logging severity you select.
For example, if you select Error, the device logs Error, Critical, Alert and Emergency
level messages. For a list of severity levels, see “Log policy” on page 45.
6 Select Config Policy to select log types and activities.
7 Select Apply.
Configuring FortiMail devices
To configure a FortiMail device to send log files to a FortiLog unit
1 On the FortiMail web-based manager, go to Log&Report > Log Setting.
2 Select the Log to Remote Host check box.
3 Enter the FortiLog IP address.
4 Select the severity level for which you want to record log messages.
The FortiMail device logs all messages at and above the logging severity you select.
For example, if you select Error, the device logs Error, Critical, Alert and Emergency
level messages. For a list of severity levels, see “Log policy” on page 45.
5 Select Config Policy.
• Select the Log type for which you want the FortiMail Server to record logs.
• For each Log type, select the activities for which you want the FortiMail Server to
record log messages.
6 Select OK.
7 Select Apply.
FortiLog Administration Guide 05-16000-0082-20050115 25
Page 26

Configuring the FortiLog unit Connecting to the FortiLog Unit
Configuring the FortiLog unit
When you configure a device to send logs to the FortiLog unit, an entry for the device
appears automatically in the Unregistered Devices tab.
Adding a device
The Devices screen provides a easy access to all devices currently sending log files
to the FortiLog unit. It also provides a way to add unregistered or other new devices to
the FortiLog unit so it can receive log files.
Figure 9: FortiLog device tabs
All Displays all registered devices available to the FortiLog unit.
Groups Displays the groups available. You can also edit, delete and create new
Unregistered Displays a list of unregistered devices available to the FortiLog unit. This
Device tabs A tab is available for each device supported by the FortiLog unit.
To add a device
1 For a FortiGate device, go to System > Devices > Unregistered.
For devices that are not automatically registered, such as a syslog server, select the
device tab and select Create New.
2 In the Register column, select Add for the device you wish to add.
Figure 10: Adding/registering a new device to the FortiLog unit
groups from this tab.
does not indicate that a FortiGate device is not registered with Fortinet.
26 05-16000-0082-20050115 Fortinet Inc.
Page 27

Connecting to the FortiLog Unit Configuring the FortiLog unit
3 Enter a device name.
For a FortiGate device, this is the same entry as entered as the Local ID set in the
Log&Config settings for FortiLog. For example, FGT-500A.
4 Select a group to add the device to if desired. For details on creating a group see
“Creating Device Groups” on page 28.
5 For Secure Connection, select Yes.
If you select secure connection between the FortiLog unit and the FortiGate unit, the
device name must match the local ID you entered on the FortiGate unit. For
information about how to configure the FortiGate unit, see “Configuring FortiGate unit
running FortiOS 2.8” and “Configuring FortiGate devices running FortiOS 2.5” on
page 24.
6 If you select Secure connection, enter the Pre-shared Key. The preshared key must
be the same as what you entered on the device. You must enter the key in the exact
same way including upper and lower case.
7 Enter the Allocated Disk Space. Set disk quota from 0 to 4000 MB. A disk quota of 0 is
unlimited.
8 Enter the size limit for the log files.
9 For Max Logfile Age, enter the time limit for the FortiLog unit to keep the log files.
10 Select what the FortiLog unit should do when the allocated disk space for the
FortiGate device is used up.
11 When adding a FortiGate unit, expand the device Interface Specification to set the
default port settings for the device.
Define the port interface options using the arrow buttons. For details on port interface
settings see “Defining device port interfaces” on page 27.
If you want to add a VLAN or other interface, type the name of the interface and select
Add.
12 Select Apply.
Defining device port interfaces
FortiLog Network activity log reports include information on inbound and outbound
traffic flow. Traffic flow information is based on the source and destination interfaces
of the device and how they are configured to send and receive information.
To ensure that the traffic information is represented correctly in these reports, you
need to assign the FortiGate interfaces to an interface type. The device interface can
include an interface name or a defined VLAN on the device.
FortiLog Administration Guide 05-16000-0082-20050115 27
Page 28

Configuring the FortiLog unit Connecting to the FortiLog Unit
You can classify the device interfaces as one of None, LAN, WAN or DMZ to match
the type of traffic the interface will process. When the FortiLog unit generates the
traffic log report, the FortiLog unit compares the source and destination interface
classifications and determines the traffic direction. The traffic direction is one of:
• Incoming
• Outgoing
• Internal
• External
• Unclassified.
The table below illustrates how the source and destination interface types are
represented in the log report as traffic direction.
Table 3: Log report traffic direction identification
Source Destination Traffic Direction
None All types Unclassified
All types None Unclassified
WAN LAN, DMZ Incoming
WAN WAN External
LAN, DMZ LAN, DMZ Internal
LAN, DMZ WAN Outgoing
Creating Device Groups
if you have a number of devices belonging to a department or section of the company,
you can create groups to keep these devices together for easier access. Once you
create a group you can add or remove devices from the groups as required.
To create a device group
1 Go to System > Devices > Groups.
2 Select Create New.
3 Enter a group name.
4 Select the devices you wish to add to the group.
5 Select OK.
You do not have to add device to the group when you first create the group. There are
a number of alternate ways of adding a device to a group:
• add devices when registering them
• select Edit to add or remove devices when required.
• In the selected devices tab, select the device and select Assign Selected.
28 05-16000-0082-20050115 Fortinet Inc.
Page 29

FortiLog Administration Guide Version 1.6
Managing the FortiLog unit
Using the FortiLog system settings, you can view the operating status of the FortiLog
unit and configure the FortiLog unit for your network. You can also use system
settings to configure RAID (Redundant Arrays of Inexpensive Disks) settings for the
FortiLog unit (for the FortiLog-400 and FortiLog-800), set email alerts and set system
time. This chapter includes topics on:
• Status
• Config
• Devices (Active mode)
• Alert Email
• Network Sharing
Status
Status
Use system status pages to view and monitor the status of the FortiLog unit. The
status information includes basic system information, alerts information, CPU usage,
memory usage, hard disk usage and network utilization, RAID information (for the
FortiLog-400 and FortiLog-800), and a list of all of the communication sessions with
the FortiLog unit.
• Status
• RAID
• Config
You can connect to the web-based manager and view the current system status of the
FortiLog unit. The status information displays basic system information such as the
host name, firmware version, and serial number of the FortiLog unit.
FortiLog Administration Guide 05-16000-0082-20050115 29
Page 30

Status Managing the FortiLog unit
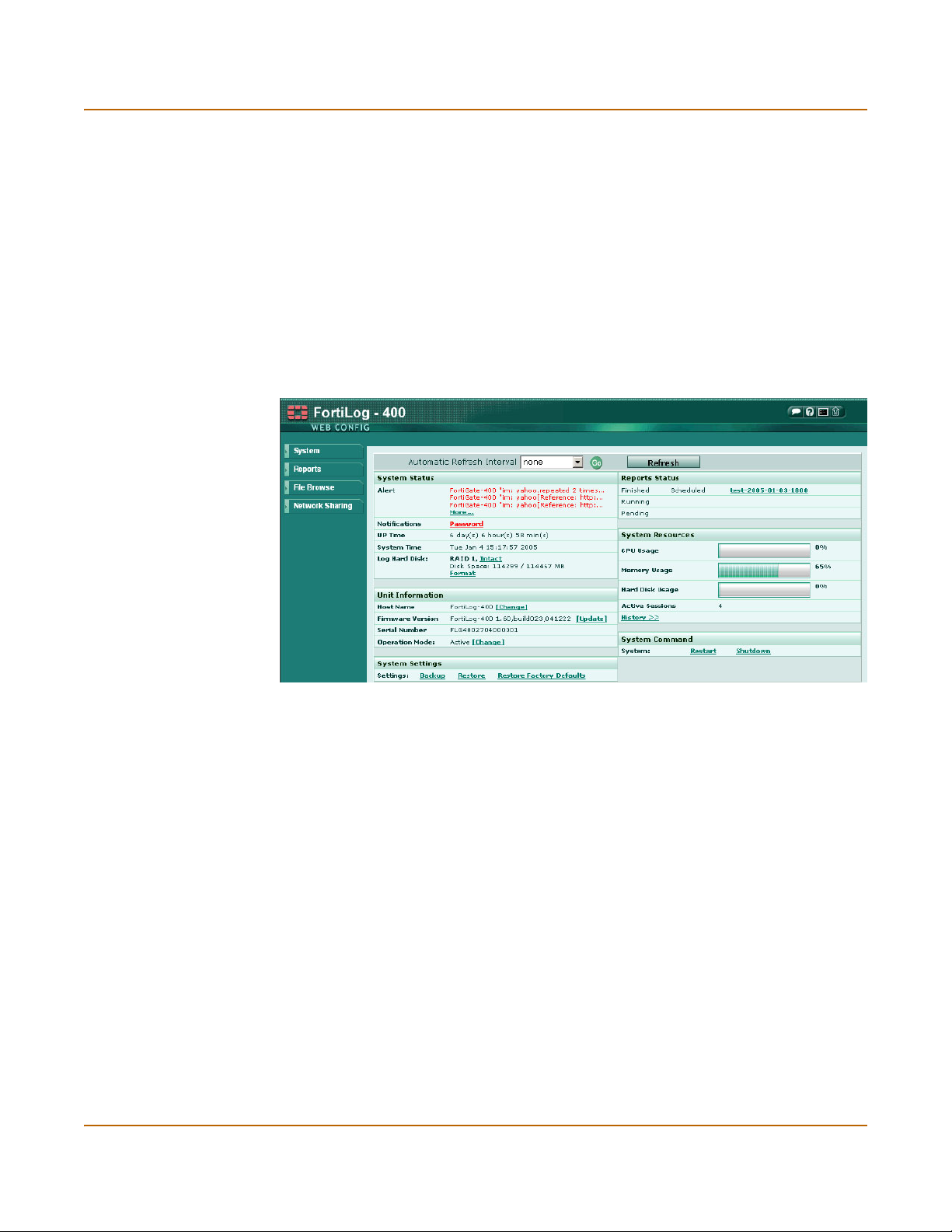
Figure 11: System status (Active mode)
Automatic Refresh
Interval
Go Select to set the selected automatic refresh interval.
Refresh Select to manually update the system status display.
Alerts Provides immediate information on any system alerts from connected
Notifications Select Password to change the password for administrative access. See
Up time The time in days, hours, and minutes since the FortiLog unit was last
System Time The current time according to the FortiLog unit internal clock.
Log Hard Disk The current RAID status. Select Intact to set automatic refresh interval and
Host Name The current host name of the FortiLog unit. See “Changing the FortiLog
Operating Mode The current mode for the FortiLog unit. The mode is either Active or
Firmware version The current FortiLog firmware version. To upgrade the firmware, see
Serial number The serial number of the FortiLog unit. The serial number is a unique
System Settings Backup and restore system settings. See “Backing up system settings” on
Reports Status List the generated log reports, log reports being generated, and the
Select to control how often the web-based manager updates the system
status display.
devices. Select More when available to view the details of the alerts for the
FortiLog unit and connected devices. For details on the alert messages
see “Alerts” on page 54.
“To change the admin account password” on page 49.
started.
view the detailed log device configuration and status information. See
“RAID” on page 41.
host name” on page 31.
Passive. For details on the different modes see “Operational Modes” on
page 8. To change the operating mode for the FortiLog unit, see “To
change the operating mode in the CLI” on page 31.
“Changing the firmware” on page 32.
identifier for the FortiLog unit and is required when you register the
FortiLog unit.
page 39 and “Restoring system settings” on page 40. Restore system
settings to factory defaults, “Restore factory default system settings” on
page 40. You can also download a debug log, see “Downlading the
FortiLog debug log” on page 39.
scheduled time to generate next log report.
30 05-16000-0082-20050115 Fortinet Inc.
Page 31

Managing the FortiLog unit Status
CPU Usage The current CPU status. The web-based manager displays CPU usage for
Memory Usage The current memory status. The web-based manager displays memory
Hard Disk Usage The current status on the hard disk. The web-based manager displays
Active Sessions The number of communications sessions being processed by the FortiLog
History Select History to view a graphical representation of the last minute of CPU,
System Command Restart or shutdown the FortiLog unit.
core processes only. CPU usage for management processes (for
example, for HTTPS connections to the web-based manager) is excluded.
usage for core processes only. Memory usage for management processes
(for example, for HTTPS connections to the web-based manager) is
excluded.
how much hard disk space is free and how much is used.
unit.
memory, sessions, and network usage.
Changing the FortiLog host name
The FortiLog host name appears on the Status page and in the FortiLog CLI prompt.
To change the FortiLog unit host name
1 Go to System > Status > Status.
2 Select Change.
3 Enter a new host name.
4 Select OK.
Changing operating modes
The FortiLog unit can operate in two modes; Active mode and Passive mode. The
default is Active mode. For details see “Operational Modes” on page 8.
To change the operating mode in the web-based manager
1 Go to System > Status > Status.
2 Select Change.
3 Select the desired mode.
4 Select OK.
To change the operating mode in the CLI
1 For all three FortiLog models, use a terminal emulation software to access the
unit’s CLI.
For the FortiLog-800 unit, you can also access the unit’s CLI by connecting the
null-modem cable provided to the unit’s console port.
2 Enter the following command:
set system opmode {active|passive}
where {active|passive} is the mode you want to use. The FortiLog unit informs
you that log collection and reporting will not be available in Passive mode.
3 Enter y to change the mode or n to leave the FortiLog unit in its current mode.
FortiLog Administration Guide 05-16000-0082-20050115 31
Page 32

Status Managing the FortiLog unit
Viewing system resources information
On the Status page, you can view the CPU, memory and hard disk usage information
and the session information.
By selecting the History link under System Resources, you can also view the statistics
for the previous minute.
If CPU and memory use is low, the FortiLog unit is able to process much more traffic
than is currently running. If CPU and memory use is high, the FortiLog unit is
performing near its full capacity. Putting additional demands on the system might
cause log message processing delays.
Changing the firmware
Use the following procedure to upgrade the FortiLog unit to a newer firmware version
or revert to a previous firmware version.
If you are reverting to a previous firmware version, the procedure reverts the FortiLog
unit to its factory default configuration and deletes all configuration on the unit. When
you upgrade the firmware, the FortiLog unit maintains the configurations you define.
Back up the FortiLog unit configuration before beginning this procedure. For
information, see “Backing up system settings” on page 39.
Note: If you revert to a previous firmware version, because the configuration is reset, you will
need to reconfigure the IP address from the front panel of the FortiLog-100 and FortiLog-400,
and the console for the FortiLog-800.
To change the firmware using the web-based manager
1 Copy the firmware image file to your management computer.
2 Log on to the web-based manager as the administrative user.
3 Go to System > Status > Status.
4 Select Update.
5 Type the path and filename of the firmware image file, or select Browse and locate the
firmware image file.
6 Select OK.
If you are reverting to a previous version of the firmware, a message appears
informing you that the system configuration will be set to default and all the original
configuration will be lost.
7 Select OK.
• If you upgrade the firmware, the FortiLog unit uploads the firmware image file,
upgrades to the new firmware version, resets the configuration, restarts, and
displays the FortiLog login. This process takes a few minutes.
• If you revert to a previous firmware version, the FortiLog unit uploads the firmware
image file, reverts to the old firmware version, resets the configuration, restarts,
and displays the FortiLog unit login. This process takes a few minutes.
8 Restore your configuration. See “Restoring system settings” on page 40.
32 05-16000-0082-20050115 Fortinet Inc.
Page 33

Managing the FortiLog unit Status
To change the firmware using the CLI
Use the following procedure to upgrade the FortiLog unit to a newer firmware version
or revert to a previous firmware version.
To use the following procedure you must have a TFTP server that the FortiLog unit
can connect to.
This procedure reverts your FortiLog unit to its factory default configuration and
deletes all configuration on the unit.
Back up the FortiLog unit configuration before beginning this procedure using the
command execute backup config.
1 Make sure that the TFTP server is running.
2 Copy the new firmware image file to the root directory of the TFTP server.
3 Log into the CLI as the admin administrative user.
4 Make sure the FortiLog unit can connect to the TFTP server.
Use the following command to ping the computer running the TFTP server. For
example, if the IP address of the TFTP server is 192.168.1.168:
execute ping 192.168.1.168
5 Enter the following command to copy the firmware image from the TFTP server to the
FortiLog unit:
execute restore image <name_str> <tftp_ip>
Where <name_str> is the name of the firmware image file on the TFTP server and
<tftp_ip> is the IP address of the TFTP server. For example, if the firmware image
file name is FortiLog_400-v120.out and the IP address of the TFTP server is
192.168.1.168, enter:
execute restore image FortiLog_400-v120.out 192.168.1.168
• If you upgrade the firmware, the FortiLog unit uploads the firmware image file,
upgrades to the new firmware version, resets the configuration, restarts, and
displays the FortiLog login. This process takes a few minutes.
• If you revert to a previous firmware version, the FortiLog unit uploads the firmware
image file, reverts to the old firmware version, resets the configuration, restarts,
and displays the FortiLog unit login. This process takes a few minutes.
6 Reconnect to the CLI.
7 To confirm that the new firmware image is successfully installed, enter:
get system status
8 Restore your previous configuration. Use the following command:
execute restore config
Installing firmware from a system reboot
This procedure installs a specified firmware image and resets the FortiLog unit to
default settings. You can use this procedure to upgrade to a new firmware version,
revert to an older firmware version, or re-install the current firmware version.
FortiLog Administration Guide 05-16000-0082-20050115 33
Page 34

Status Managing the FortiLog unit
To perform this procedure you need to install a TFTP server that you can connect to
from the FortiLog unit LAN port. The TFTP server should be on the same subnet as
the LAN port.
Before beginning this procedure you can back up the FortiLog unit configuration. For
information, see “Backing up system settings” on page 39.
To install firmware from a system reboot
1 For all three FortiLog models, use a terminal emulation software to access the
unit’s CLI.
For the FortiLog-800 unit, you can also access the unit’s CLI by connecting the
null-modem cable provided to the unit’s console port.
2 Make sure that the TFTP server is running.
3 Copy the new firmware image file to the root directory of the TFTP server.
4 Make sure that the LAN port is connected to the same network as the TFTP server.
5 To confirm that the FortiLog unit can connect to the TFTP server, use the following
command to ping the computer running the TFTP server. For example, if the IP
address of the TFTP server is 192.168.1.168, enter:
execute ping 192.168.1.168
6 Enter the following command to restart the FortiLog unit:
execute reboot
As the FortiLog unit starts, a series of system startup messages is displayed.
When the following message appears:
Press any key to enter configuration menu.....
7 Immediately press any key to interrupt the system startup.
Note: You have only 3 seconds to press any key. If you do not press a key soon enough, the
FortiLog unit reboots and you must log in and repeat the
execute reboot command.
If you successfully interrupt the startup process, the following message appears:
[G]: Get firmware image from TFTP server.
[F]: Format boot device.
[B]: Boot with backup firmware and set as default.
[Q]: Quit menu and continue to boot with default firmware.
[H]: Display this list of options.
Enter G,F,B,Q,or H:
8 Type G to get the new firmware image from the TFTP server.
9 Type the address of the TFTP server and press Enter.
The following message appears:
Enter Local Address [192.168.1.188]:
10 Type the address of the LAN port and press Enter.
34 05-16000-0082-20050115 Fortinet Inc.
Page 35

Managing the FortiLog unit Status
Note: The local IP address is used only to download the firmware image. After the firmware is
installed, the address of this interface is changed back to the default IP address for this
interface.
The following message appears:
Enter File Name [image.out]:
11 Enter the firmware image filename and press Enter.
The TFTP server uploads the firmware image file to the FortiLog unit and a message
similar to the following is displayed:
Save as Default firmware/Run image without saving:[D/R]
Save as Default firmware/Backup firmware/Run image without
saving:[D/B/R]
12 Type D.
The FortiLog unit installs the new firmware image and restarts. The installation might
take a few minutes to complete.
Testing a new firmware image
You can test a new firmware image by installing the firmware image from a system
reboot and saving it to system memory. After completing this procedure, the FortiLog
unit operates using the new firmware image with the current configuration. This new
firmware image is not permanently installed. The next time the FortiLog unit restarts, it
operates with the originally installed firmware image using the current configuration. If
the new firmware image operates successfully, you can install it permanently.
To run this procedure you need to install a TFTP server that you can connect to from
the FortiLog unit LAN port. The TFTP server should be on the same subnet as the
LAN port.
To test a new firmware image before installing it
1 For all three FortiLog models, use a terminal emulation software to access the unit’s
CLI.
For the FortiLog-800 unit, you can also access the unit’s CLI by connecting the
null-modem cable provided to the unit’s console port.
2 Make sure the TFTP server is running.
3 Copy the new firmware image file to the root directory of the TFTP server.
4 Make sure that the LAN port is connected to the same network as the TFTP server.
You can use the following command to ping the computer running the TFTP server.
For example, if the TFTP server's IP address is 192.168.1.168:
execute ping 192.168.1.168
5 Enter the following command to restart the FortiLog unit:
execute reboot
6 As the FortiLog unit reboots, press any key to interrupt the system startup.
As the FortiLog unit starts, a series of system startup messages are displayed.
When the following message appears:
Press any key to enter configuration menu.....
FortiLog Administration Guide 05-16000-0082-20050115 35
Page 36

Status Managing the FortiLog unit
7 Immediately press any key to interrupt the system startup.
Note: You have only 3 seconds to press any key. If you do not press a key soon enough, the
FortiLog unit reboots and you must log in and repeat the execute reboot command.
If you successfully interrupt the startup process, the following message appears:
[G]: Get firmware image from TFTP server.
[F]: Format boot device.
[Q]: Quit menu and continue to boot with default firmware.
[H]: Display this list of options.
Enter G,F,Q,or H:
8 Type G to get the new firmware image from the TFTP server.
9 Type the address of the TFTP server and press Enter.
The following message appears:
Enter Local Address [192.168.1.188]:
10 Type the address of the LAN port and press Enter.
Note: The local IP address is used only to download the firmware image. After the firmware is
installed, the address of this interface is changed back to the default IP address for this
interface.
The following message appears:
Enter File Name [image.out]:
11 Enter the firmware image file name and press Enter.
The TFTP server uploads the firmware image file to the FortiLog unit and a message
similar to the following appears.
Save as Default firmware/Run image without saving:[D/R]
12 Type R.
The FortiLog unit image is installed to system memory and the FortiLog unit starts
running the new firmware image but with its current configuration.
13 You can log into the CLI or the web-based manager using any administrative account.
14 To confirm that the new firmware image has been loaded, from the CLI enter:
get system status
You can test the new firmware image as required.
Installing a backup firmware image
If the FortiLog unit is running BIOS version v3.x, you can install a backup firmware
image. Once the backup firmware image is installed you can switch to this backup
image when required.
To run this procedure you need to install a TFTP server that you can connect to from
the FortiLog unit LAN port. The TFTP server should be on the same subnet as the
LAN port.
36 05-16000-0082-20050115 Fortinet Inc.
Page 37

Managing the FortiLog unit Status
To install a backup firmware image
1 For all three FortiLog models, use a terminal emulation software to access the
unit’s CLI.
For the FortiLog-800 unit, you can also access the unit’s CLI by connecting the
null-modem cable provided to the unit’s console port.
2 Make sure that the TFTP server is running.
3 Copy the new firmware image file to the root directory of your TFTP server.
4 To confirm that the FortiLog unit can connect to the TFTP server, use the following
command to ping the computer running the TFTP server. For example, if the IP
address of the TFTP server is 192.168.1.168:
execute ping 192.168.1.168
5 Enter the following command to restart the FortiLog unit:
execute reboot
As the FortiLog unit starts, a series of system startup messages are displayed.
When the following message appears:
Press any key to enter configuration menu.....
6 Immediately press any key to interrupt the system startup.
Note: You have only 3 seconds to press any key. If you do not press a key soon enough, the
FortiLog unit reboots and you must log in and repeat the
execute reboot command.
If you successfully interrupt the startup process, the following message appears:
[G]: Get firmware image from TFTP server.
[F]: Format boot device.
[B]: Boot with backup firmware and set as default.
[Q]: Quit menu and continue to boot with default firmware.
[H]: Display this list of options.
Enter G,F,B,Q,or H:
7 Type G to get the new firmware image from the TFTP server.
8 Type the address of the TFTP server and press Enter.
The following message appears:
Enter Local Address [192.168.1.188]:
9 Type the address of the interface of the FortiLog unit that can connect to the TFTP
server and press Enter.
The following message appears:
Enter File Name [image.out]:
10 Enter the firmware image file name and press Enter.
The TFTP server uploads the firmware image file to the FortiLog unit and a message
similar to the following appears.
Save as Default firmware/Backup firmware/Run image without
saving:[D/B/R]
11 Type B.
FortiLog Administration Guide 05-16000-0082-20050115 37
Page 38

Status Managing the FortiLog unit
The FortiLog unit saves the backup firmware image and restarts. When the FortiLog
unit restarts it is running the previously installed firmware version.
Switching to a backup firmware image
Use this procedure to switch the FortiLog unit to operating with a backup firmware
image that you previously installed. When you switch the FortiLog unit to the backup
firmware image, the FortiLog unit operates using the configuration that was saved with
that firmware image.
If you install a new backup image from a reboot, the configuration saved with this
firmware image is the factory default configuration. If you use the procedure
“Switching to the default firmware image” on page 38 to switch to a backup firmware
image that was previously running as the default firmware image, the configuration
saved with this firmware image is restored.
To switch to the backup firmware image
1 For all three FortiLog models, use a terminal emulation software to access the unit’s
CLI.
For the FortiLog-800 unit, you can also access the unit’s CLI by connecting the
null-modem cable provided to the unit’s console port.
2 Enter the following command to restart the FortiLog unit:
execute reboot
As the FortiLog unit starts, a series of system startup messages are displayed.
When the following message appears:
Press any key to enter configuration menu.....
3 Immediately press any key to interrupt the system startup.
Note: You have only 3 seconds to press any key. If you do not press a key soon enough, the
FortiLog unit reboots and you must log in and repeat the execute reboot command.
If you successfully interrupt the startup process, the following message appears:
[G]: Get firmware image from TFTP server.
[F]: Format boot device.
[B]: Boot with backup firmware and set as default.
[Q]: Quit menu and continue to boot with default firmware.
[H]: Display this list of options.
Enter G,F,B,Q,or H:
4 Type B to load the backup firmware image.
The FortiLog unit loads the backup firmware image and restarts. When the FortiLog
unit restarts, it is running the backup firmware version and the configuration is set to
factory default.
Switching to the default firmware image
Use this procedure to switch the FortiLog unit to operating with the backup firmware
image that had been running as the default firmware image. When you switch to this
backup firmware image, the configuration saved with this firmware image is restored.
38 05-16000-0082-20050115 Fortinet Inc.
Page 39

Managing the FortiLog unit Status
To switch back to the default firmware image
1 For all three FortiLog models, use a terminal emulation software to access the
unit’s CLI.
For the FortiLog-800 unit, you can also access the unit’s CLI by connecting the
null-modem cable provided to the unit’s console port.
2 Enter the following command to restart the FortiLog unit:
execute reboot
As the FortiLog unit starts, a series of system startup messages are displayed.
When the following message appears:
Press any key to enter configuration menu.....
3 Immediately press any key to interrupt the system startup.
Note: You have only 3 seconds to press any key. If you do not press a key soon enough, the
FortiLog unit reboots and you must log in and repeat the
If you successfully interrupt the startup process, the following message appears:
[G]: Get firmware image from TFTP server.
[F]: Format boot device.
[B]: Boot with backup firmware and set as default.
[Q]: Quit menu and continue to boot with default firmware.
[H]: Display this list of options.
execute reboot command.
Enter G,F,B,Q,or H:
4 Type B to load the backup firmware image.
5 The FortiLog unit loads the backup firmware image and restarts. When the FortiLog
unit restarts it is running the backup firmware version with a restored configuration.
Backing up system settings
You can back up system settings by downloading them to a text file on the
management computer.
To backup up system settings
1 Go to System > Status > Status.
2 For System Settings, select Backup.
3 Select Backup system settings.
4 Type a name and location for the file.
The system settings file is backed up to the management computer.
5 Select Return to go back to the Status page.
Downlading the FortiLog debug log
Download a debug log to send debug information to Fortinet Tech Support to help
diagnose a problem with the FortiLog unit.
FortiLog Administration Guide 05-16000-0082-20050115 39
Page 40

Status Managing the FortiLog unit
!
To download a FortiLog debug log
1 Go to System > Status > Status.
2 For System Settings, select Backup.
3 Select download debug log.
4 Type a name and location for the file.
The debug log file is backed up to the management computer.
5 Select Return to go back to the Status page.
Restoring system settings
Restore system settings by uploading a previously downloaded system settings text
file.
To restore system settings
1 Go to System > Status > Status.
2 For System Settings, select Restore.
3 Enter the path and filename of the system settings file, or select Browse and locate
the file.
4 Select OK to restore the system settings file to the FortiLog unit.
The FortiLog restarts, loading the new system settings.
5 Reconnect to the web-based manager and review your configuration to confirm that
the uploaded system settings have taken effect.
Restore factory default system settings
Use the following procedure to restore system settings to the values set at the factory.
This procedure does not change the firmware version.
Caution: This procedure deletes all changes that you have made to the FortiLog configuration
and reverts the system to its original configuration, including resetting interface addresses.
To restore system settings to factory defaults
1 Go to System > Status > Status.
2 For System Settings, select Restore Factory Defaults.
3 Select OK to confirm.
The FortiLog unit restarts with the configuration that it had when it was first
powered on.
Restoring a FortiLog unit
Use the following procedure if the FortiLog unit cannot complete the startup
procedure. When this event occurs, you cannot connect to the FortiLog unit through
the web-based manager or the CLI. The cause may be a corrupted firmware image.
To use the following procedure you must have a TFTP server that the FortiLog unit
can connect to. The TFTP server IP address must be set to 192.168.1.168
40 05-16000-0082-20050115 Fortinet Inc.
Page 41

Managing the FortiLog unit Status
To upload the firmware image to the FortiLog unit
1 Make sure the TFTP server is running.
2 Copy the firmware image file to the root directory of the TFTP server. Ensure the file
name is image.out.
3 Start the FortiLog unit.
As the FortiLog unit starts, the following message appears:
Press any key to begin download.....
4 Immediately press any key to begin the automatic download.
The FortiLog unit connects to the TFTP server and begin downloading the firmware
image. Once downloaded, the FortiLog will load the firmware and proceed with the
system startup.
RAID
Use the RAID (Redundant Arrays of Inexpensive Disks) tab to set automatic refresh
interval and view detailed log device information.
Note: RAID functionality is only available on the FortiLog-400 and 800. These units have four
hard disks and support RAID level 0, 1, and 5.
Figure 12: RAID
Automatic Refresh
Interval
Go Select to set the selected automatic refresh interval.
Refresh Select to manually update the RAID information.
Create Date Date and time when the RAID was created. This information may be
Select to control how often the web-based manager updates the RAID
information.
incorrect if the FortiLog clock is changed after creating the RAID.
FortiLog Administration Guide 05-16000-0082-20050115 41
Page 42

Config Managing the FortiLog unit
Level The RAID level. See “RAID” on page 43.
Array Size The total disk space available.
Device Size The disk space used on each drive of the array.
RAID Disks The number of disks used by the array for data storage.
Total Disks Total Disks include spare and failed disks.
Update Time The time of the last status change.
State State of the log device includes dirty, clean, no-errors, and errors. Dirty
Working Drives Active and spare drives. Display color is black.
Active Drives Drives used for data storage and are trusted. Display color is green.
Failed Drives Drives used for data storage and are not trusted. Display color is red.
Spare Drives Drives never used for data storage. Display color is yellow.
means that parts of a redundant array (RAID1 and RAID5) need to be
synchronized (which is automated). No-errors indicates that the log device
is usable.
Config
Network
Use system config to configure the FortiLog network settings, RAID settings, log
message settings, time settings, and other options. You can also add and remove
FortiLog administrator accounts and change administrator passwords.
• Network
• RAID
• Log settings
• Time
• Options
• Admin
To configure the FortiLog network settings, go to System > Config > Network. You
can configure the FortiLog unit IP address, netmask, DNS server, and default
gateway.
Figure 13: Network settings
42 05-16000-0082-20050115 Fortinet Inc.
Page 43

Managing the FortiLog unit Config
RAID
IP Address Enter the static IP address required by the FortiLog unit to be able to
connect to your network.
Netmask Enter the netmask required by the FortiLog unit to connect to your
network.
Primary DNS Server Enter the primary DNS server IP address. Several FortiLog functions
use DNS. Add the IP address of the DNS servers that your FortiLog unit
can connect to.
Second DNS Server Enter the secondary DNS server IP address.
Default Gateway Enter the IP address of the default gateway for the network that your
FortiLog is connected to.
To configure the FortiLog RAID level and check the RAID disk space, go to System >
Config > RAID.
Figure 14: RAID settings
Note: RAID functionality is only available on the FortiLog-400 and 800. These units have four
hard disks and support RAID level 0, 1, and 5.
RAID Level Select the RAID level. The FortiLog unit supports the linear, 0, 1, and 5
Linear Linear disk volume. Combines two or more disks into one larger disk.
Level 0 Striping disk volume. Combines two or more disks into one larger disk.
RAID levels. The default RAID level is linear. Changing the RAID level
deletes all log messages from the FortiLog hard disk.
During file saving, the files are saved on physical disks sequentially but
do not have a disk failure file protection function. The overall capacity of
linear disks is the sum of all disks. Linear disks are generally used for
storing large amounts of data and not for protection of important data.
Stripping disk RAID offers the fastest disk access but does not provide
data protection of the data when the striped array fails. The disk capacity
equals the number of disks in the array times the size of the smallest disk.
Select striping disk to maximize disk capacity or for fast disk access but
not for protection of important data.
FortiLog Administration Guide 05-16000-0082-20050115 43
Page 44

Config Managing the FortiLog unit
Log settings
Level 1 Mirroring disk volume. Protects data by automatically backing up the
contents of one disk onto the second disk of a mirrored pair. Mirroring
protects data if one disks fails. Disk capacity is equal to a single hard disk
because the second hard disk is used to automatically back up the first.
Use Level 1 to protect important personal or corporate data.
Level 5 RAID 5 disk group. Three or more hard disks can be teamed up to form a
large-capacity RAID 5 disk group. RAID 5 distributes and stores data
among member disks as it is received. At the same time RAID uses an
amount of space roughly equivalent to a whole disk to store reference
numbers with the same elements. If one of the disks in the group is
damaged, you can shut down the computer and install a new disk, and
the FortiLog unit can restore the data on the new disk using the reference
information.
If you have a system with four disks but use only three in your RAID 5
group, the fourth serves as a backup disk. If one of the three disks is
damaged the FortiLog unit automatically reverts to the fourth disk without
powering down.
The approximate capacity of a RAID 5 disk group is one hard disk worth
of space less than the total rated capacity of the group.
To configure the FortiLog unit to log locally or to send FortiLog log messages to a
remote syslog server, go to System > Config > Log Settings. You can configure the
log level and you can use config policy to record event log messages. See “Log
policy” on page 45 for information about the types of logs and how to configure them.
Figure 15: Log settings
Log Locally Select this option to save the log messages on its own hard disks.
Level Select the severity for which you want to record log messages locally. The
Config Policy Select Config policy for which activities you want the FortiLog unit to
Log to Host Select Log to Host to configure the FortiLog unit to send log messages to
IP The IP address of the remote syslog server.
Port The port that the remote syslog server uses to receive log messages. The
FortiLog unit logs all levels of severity down to, but not lower than, the
level you select. For example, if you want to record emergency, critical,
and error messages, select Error. “Log policy” on page 45 lists the log
message levels.
record log messages.
a remote syslog server.
default port is 514.
44 05-16000-0082-20050115 Fortinet Inc.
Page 45

Managing the FortiLog unit Config
Level Select the severity level for which you want to record log messages to a
Config Policy Select Config policy for which activities you want the FortiLog unit to
CSV format Enable CSV format to record log messages in comma-separated value
remote syslog server. The FortiLog unit logs all levels of severity down to,
but not lower than, the level you select. For example, if you want to record
emergency, alert, critical, and error messages, select Error. “Log policy”
on page 45 lists the log message levels.
record log messages.
(CSV) formatted files. Log message fields are separated by commas.
Log policy
Levels Description Generated by
0 - Emergency The system has become unstable. Emergency messages not
1 - Alert Immediate action is required. NIDS attack log messages.
2 - Critical Functionality is affected. DHCP
3 - Error An error condition exists and functionality
could be affected.
4 - Warning Functionality could be affected. Antivirus, Web filter, email filter,
5 - Notice Information about normal events. Antivirus, Web filter, and email
6 - Information General information about system
operations.
available.
Error messages not available.
and system event log messages.
filter log messages.
Antivirus, Web filter, email filter log
messages, and other event log
messages.
Select Config Policy to configure the FortiLog unit to send event log messages to a
local or remote syslog server.
Enable Event Log to record management and activity events. Management events
include changes to the FortiLog unit configuration as well as administrator and user
logins and logouts. Activity events include system activities such as IPSec negotiation
events
Figure 16: Config log policy
FortiLog Administration Guide 05-16000-0082-20050115 45
Page 46

Config Managing the FortiLog unit
Time
To change the FortiLog unit time, go to System > Config > Time. For effective
scheduling and logging, the FortiLog system time must be accurate. You can either
manually set the FortiLog system time or you can configure the FortiLog unit to
automatically keep its system time correct by synchronizing with a Network Time
Protocol (NTP) server.
Figure 17: Time settings
Options
Admin
To change the FortiLog administration options, go to System > Config > Options. On
the System Config Options page, you can set:
• the system idle timeout.
• the language for the web-based manager.
Figure 18: Options
Idle Timeout Enter an idle timeout number in minutes. Idle Timeout controls the
amount of inactive time that the web-based manager waits before
requiring the administrator to log in again.
The recommend idle time out is 5 minutes. The maximum idle time out is
480 minutes (8 hours).
Language Select a language for the web-based manager to use. You can choose
English, Simplified Chinese, Japanese, Korean, or Traditional Chinese.
To change the FortiLog administrator settings, go to System > Config > Admin. Use
admin options to add and configure FortiLog administrators. For information on
FortiLog administrators, see “Devices (Active mode)” on page 49.
46 05-16000-0082-20050115 Fortinet Inc.
Page 47
Managing the FortiLog unit Config
Figure 19: Admin
Create New Select Create New to add an administrator account.
Name The login name for the administrator account.
Trusted host The trusted host IP address for the location from which the administrator can
Netmask The trusted host netmask for the location from which the administrator can log
Permission The permission level for the administrator. Permission can be all, read & write,
Modify Select Edit to change an administrator account. Select Change Password to
Administrative
Access
HTTPS To allow secure HTTPS connections to the FortiLog web-based manager.
PING If you want the FortiLog unit to respond to pings. Use this setting to verify your
HTTP To allow HTTP connections to the FortiLog web-based manager. HTTP
SSH To allow secure SSH connections to the FortiLog CLI.
SNMP To allow a remote SNMP manager to request SNMP information by connecting
TELNET To allow Telnet connections to the FortiLog CLI. Telnet connections are not
log into the web-based manager. If Trusted Host is 0.0.0.0 the administrator
can log in from any IP address.
into the web-based manager. If Netmask is 0.0.0.0 there is no restriction on the
netmask.
or read only.
change an administrator account password.
Configure administrative access to control how administrators access the
FortiLog unit.
installation and for testing.
connections are not secure and can be intercepted by a third party.
to this interface.
secure and can be intercepted by a third party.
Configure Administrator access
Configure administrative access to allow remote administration of the FortiLog unit.
However, allowing remote administration could compromise the security of your
FortiLog unit. To improve the security of a FortiLog unit use the following principles
when configuring administrative access:
• Use secure administrator passwords,
• Change these passwords regularly,
• Enable secure administrative access to this interface using only HTTPS or SSH,
• Do not change the system idle timeout from the default value of 5 minutes.
FortiLog Administration Guide 05-16000-0082-20050115 47
Page 48

Config Managing the FortiLog unit
To configure administrative access to the FortiLog unit
1 Go to System > Config > Admin.
2 Select the Administrative Access methods for the FortiLog unit.
3 Select Apply.
Administrator account levels
When the FortiLog unit is initially installed, it is configured with a single administrator
account with the user name of “admin”. From this administrator account, you can add
and edit administrator accounts. You can also control the access level of each of
these administrator accounts and control the IP address from which the administrator
can connect to the FortiLog unit.
There are three administration account access levels:
admin Has all permissions. Can view, add, edit, and delete administrator accounts.
Read & Write Can view and change the FortiLog configuration. Can view but cannot add,
Read Only Can view the FortiLog configuration.
Can view and change the FortiLog configuration. The admin user is the only
user who can go to the System Status page and manually update firmware,
restore the FortiLog unit to factory defaults, restart the FortiLog unit, and shut
down the FortiLog unit. There is only one admin user.
edit, or delete administrator accounts. Can change own administrator account
password. Cannot make changes to system settings from the System Status
page.
Administrator options
When you add an administrator you can configure the following options.
Figure 20: Administrator options
Administrator The login name for the administrator account. The login name can contain
Password/
Confirm
Password
numbers (0-9), uppercase and lowercase letters (A-Z, a-z), and the special
characters - and _. Other special characters and spaces are not allowed.
The password for the administrator account.
For improved security, the password should be at least 6 characters long. The
password can contain any characters except spaces.
48 05-16000-0082-20050115 Fortinet Inc.
Page 49

Managing the FortiLog unit Devices (Active mode)
Trusted host The trusted host IP address for the location from which the administrator can
Netmask The trusted host netmask for the location from which the administrator can log
Permission The permission level for the administrator.
log into the FortiLog unit.
If you want the administrator to be able to access the FortiLog unit from any
address, set the trusted host to 0.0.0.0 and the netmask to 0.0.0.0.
To limit the administrator to only access the FortiLog unit from a specific
network, set the trusted host to the address of the network and set the netmask
to the netmask for the network.
For example, to limit an administrator to accessing the FortiLog unit from your
internal network, set the trusted host to the address of your internal network
(for example, 192.168.1.0) and set the netmask to 255.255.255.0.
into the web-based manager. If Netmask is 0.0.0.0 there is no restriction on the
netmask.
To add an administrator account
1 Go to System > Config > Admin.
2 Select New.
3 Enter a login name for the administrator account.
4 Enter and confirm a password for the administrator account.
5 Optionally type a Trusted Host IP address and netmask for the location from which the
administrator can log into the web-based manager.
6 Set permission to Read Only or Read & Write.
7 Select OK.
Changing the Administrator password
The admin administrator and administrators with read & write permissions can change
their administrator account password.
To change the admin account password
1 Go to System > Config > Admin.
2 For your administrator account, select Change Password.
3 Enter and confirm a new password.
4 Select OK.
Devices (Active mode)
When using the FortiLog unit in Active mode, you can add the FortiGate, FortiMail and
Syslog devices for the FortiLog unit to collect log files.
• Device list
• Adding and registering a device
• Editing device information
FortiLog Administration Guide 05-16000-0082-20050115 49
Page 50

Devices (Active mode) Managing the FortiLog unit
Device list
To add and manage devices connecting to the FortiLog unit, go to System > Devices.
Figure 21: Device list
Adding and registering a device
Add FortiGate, FortiMail and Syslog devices to the FortiLog configuration so that the
FortiLog unit can receive logs from the devices. For details on adding a device, see
“Sending device logs to the FortiLog unit” on page 23.
The unregistered devices on the network that you configured to send logs to the
FortiLog unit are listed at the bottom of the devices page. Before the FortiLog unit can
generate log reports for the unregistered devices, you must register them.
To register an unregistered device, select Add to the right of the device name. For
complete details on registering a device, see “Configuring the FortiLog unit” on
page 26.
Editing device information
After adding a FortiGate, FortiMail or Syslog device to the FortiLog unit, you can
modify the device information as required.
Figure 22: Editing a device
50 05-16000-0082-20050115 Fortinet Inc.
Page 51

Managing the FortiLog unit Alert Email
To edit a device
1 Go to System > Devices.
2 For the device you want to edit, select Edit.
3 Modify the device information and select an Interface Type for each interface, as
required.
4 Select OK.
Alert Email
Use Alert Email to configure the FortiLog unit to monitor logs for specific alert
messages, and to send an email to inform an Administrator of the problem
encountered. You can apply these settings to the local FortiLog unit and selected
registered devices. FortiLog will also monitor its own log as well.
• Server
• Local
• Device (Active mode)
Server
Set the mail server options so the FortiLog unit can connect to and use the SMTP mail
facilities to alert a user of any attack issues. You must configure at least one DNS
server. The FortiLog unit uses the SMTP server name to connect to the mail server,
and must look up this name on your DNS server.
To set the mail server options go to System > Alert Email > Server. Set the SMTP
mail server connection information for sending alert messages to specified recipients.
Figure 23: Alert email settings
Authentication Enable or disable SMTP authentication for sending alert email.
SMTP Server Enter the IP address of the SMTP server for sending alert email.
SMTP User Enter the user name for logging on to the SMTP server to send alert
mails. You only need to do this if you have enabled the SMTP
authentication.
Password Enter the password for logging on to the SMTP server to send alert
email. You only need to do this if you selected SMTP authentication.
FortiLog Administration Guide 05-16000-0082-20050115 51
Page 52

Alert Email Managing the FortiLog unit
Local
Testing E-mail
Address
Test Select to verify that the SMTP information you entered is correct.
Enter the email address where the FortiLog unit sends an email message
to verify the mail server settings.
To set the email alert notification for the FortiLog unit, go to System > Alert Email >
Local. Set the options when the FortiLog unit alerts an individual or group of
individuals.
Figure 24: Local alert settings
Enable Select to toggle the FortiLog alert email settings on and off.
Email Address(es) Enter a recipient or number of recipients to receive alert email.
Level The FortiLog unit sends alert email for all messages at and above the
When N or more
events
In N hours Select the wait time for the number of events to occur within before
logging severity level you select.
Select the number events at the specified level before the FortiLog unit
sends an alert email. Use this setting in conjunction with the setting
below.
sending an alert email for the specified level log messages. Use this
setting in conjunction with the setting above.
Device (Active mode)
To set alert messages for specific FortiGate and FortiMail devices, select System >
Alert Email > Device. You can define log alert messages for specific devices
connected to the FortiLog unit. The FortiLog unit monitors all log messages and when
a device log contains specific alert messages, the FortiLog unit sends an email to the
specified recipients.
Creating a new device alert
When you add a new device alert, you can set the following options.
52 05-16000-0082-20050115 Fortinet Inc.
Page 53

Managing the FortiLog unit Alert Email
Figure 25: Device alert settings
Alert Name Enter a name to identify the alert settings.
Devices to Monitor Select the device logs the FortiLog unit monitors. Expand the device
Level Set the level of message that the FortiLog unit monitors for. The FortiLog
Level wait interval Set the number of events and the time frame. The FortiLog unit will send
Attack Type Set the type of attack that the FortiLog device should look for. Select any
Attack Type Entry
and listing
Level of wait
interval
FortiLog Administration Guide 05-16000-0082-20050115 53
groups to select individual devices.
unit sends alert email for all messages at and above the logging severity
level you select.
an alert email when the conditions are satisfied. For example, if you set
the alert to three events in one hour, after three events within that time the
FortiLog unit sends an alert email.
attack or specific attack identifiers.
When you select “Just these” for the attack type, enter the names of the
virus and select Insert.
Set the number of attacks and the time frame. The FortiLog unit will not
send an alert email until the conditions are met.
Page 54

Alerts Managing the FortiLog unit
Single Source Only Set to have the FortiLog unit send and alert email only when the defined
Virus Type Set the type of virus that the FortiLog device should look for. Select any
Virus Type Entry
and listing
Level of wait
interval
Single Source Only Set to have the FortiLog unit send and alert email only when the defined
Email Address(es) Enter the email addresses of the recipients to receive the alert warning
attack settings originate from a single source IP rather than many
different sources. A single source attack can indicate a targeted attack on
the network.
virus or specific virus identifiers.
When you select “Just these” for the virus type, enter the names of the
virus and select Insert.
Set the number of virus attacks and the time frame. The FortiLog unit will
send an alert email when the conditions are met.
virus settings originate from a singe source IP. A single source virus
attack can indicate a targeted attack on the network.
messages. For multiple addresses, separate each address with either a
semi-colon, comma or a space.
To add a device alert
1 Go to System > Alert Email > Device.
2 Select Create New.
3 Set the Alert email options as required.
4 Select Enable to set the FortiLog unit to send alert email messages for selected
devices.
5 Select OK.
Alerts
Use Alerts to view the system alert messages for the FortiLog unit and any other
systems monitored by the FortiLog unit.
54 05-16000-0082-20050115 Fortinet Inc.
Page 55

Managing the FortiLog unit Network Sharing
Figure 26: Device alert messages
Alert Inclusion Select the minimum level of alert messages you would like displayed. The
Keep
unacknowledge
alerts for
Acknowledge
check box
Device Displays the name of the device with the alert message.
Event The type of alert message logged.
Severity The severity of the alert message
Time The date and time when the alert message was logged.
Network Sharing
Use Network Sharing to configure the FortiLog unit to use file sharing (Windows
workgroups or NFS) to view and share log reports and other files. You can define the
users, groups and file access privileges.
For details on setting protocols adding user and group access to the FortiLog hard
disk see “Using the FortiLog unit as a NAS” on page 81.
selection you make and any messages with higher priority will appear in
the window.
Select the number of days of alert messages you want to keep. If you
change the number of days from a longer period to a shorter period, the
FortiLog unit removes the older alert messages. You will not be able to
change back to a longer period and see the older messages again.
Select the check boxes for those alert messages and select acknowledge
at the bottom of the column to remove the selected alert messages.
Defining IP aliases
The IP Aliases list provides a means of mapping a meaningful name to hosts,
networks or IP ranges. The names you add here appear in the log report filters.
FortiLog Administration Guide 05-16000-0082-20050115 55
Page 56

Defining IP aliases Managing the FortiLog unit
Figure 27: IP aliases
To set host alias names
1 Go to Reports > IP Aliases.
2 Select Create New.
3 Enter a name of the host, network or IP address range in the Alias text box.
4 Enter the IP address of the host, network or the IP range. For example:
• 10.1.1.1
• 10.1.1.1/24 10.1.1.0/24
• 10.1.0.0/16-10.9.0.0
• 10.1.0.0/16-10.9.0.0/16.
5 Select OK.
56 05-16000-0082-20050115 Fortinet Inc.
Page 57

Reports
FortiLog Administration Guide Version 1.6
The FortiLog unit collates information collected from device log files and presents the
information in tables and graphs. There are over 130 different reports, in 11
categories. The reports provide detailed information on the type of traffic, attacks and
preventative actions occurred during a specific period on your network. For a full list of
report types see “Appendix A: Log Report Types” on page 113.
Using reports you can:
• manage your network more effectively and to make informed decisions.
• view the network usage and security information.
• discover and address vulnerabilities across dispersed device installations.
• minimize the effort required to monitor and maintain acceptable user policies,
identify attack patterns and prevent attacks.
• monitor Internet surfing patterns for compliance with company policy.
• identify visitors to your web site for potential customers.
Reports are available in multiple file formats including HTML, PDF, RTF and
ASCII text.
Note: In Passive mode, the FortiLog unit does not receive logs or generate reports. To create
reports the FortiLog unit must be set to Active mode.
This chapter describes:
• Creating and generating a report
• Viewing reports
• Vulnerability reports
Creating and generating a report
To generate a report, begin by creating and saving a report configuration. You can
use this report configuration for a scheduled report or for generating reports on
demand.
To create a report
1 Go to Reports > Config.
2 Select New and enter a name for the report.
FortiLog Administration Guide 05-16000-0082-20050115 57
Page 58

Creating and generating a report Reports
3 Set the following:
• “Configuring report parameters” on page 58
• “Configuring a report query” on page 59
• “Selecting the devices for the report” on page 60
• “Select filtering options” on page 61
• “Setting a report schedule” on page 62
• “Choosing the report destination and format” on page 63.
4 Select Run now.
Configuring report parameters
Report parameters defines the reporting period the FortiLog unit uses when gathering
the information from the device logs. Report parameters include:
• the reporting period.
• the specific device or all device logs submitted to the FortiLog unit.
• the top ranked values for specific report categories.
Figure 28: Report parameter settings
To define report parameters
1 Go to Reports > Config.
2 Select new.
3 Enter a report name and select OK.
4 Configure the following options:
Time Period Select a date range from the list or select a specific reporting period.
When making a time selection, some times include variables. For example,
Last N days. When you select this setting, a text box appears. Enter the
numeric value for N.
From Date Select the year, month, day and hour for the start of the reporting period.
To Dat e Select the year, month, day and hour for the ending of the reporting period.
58 05-16000-0082-20050115 Fortinet Inc.
Page 59

Reports Creating and generating a report
Per Virtual
Domain
For all devices Select to generate the report for all devices.
Per device Select to generate a separate report for each device.
Resolve Host
Names
Resolve Service
Names
In 'Ranked
Reports' show
top
5 Select Apply.
Configuring a report query
Select the specific information you need to generate a more concise report. Each
report category includes a refined list of sub-categories that reports specific
information. For example, you can generate an extensive intrusion activity report, or
only generate intrusion activity by attacks by top types, or by hour of the day.
The default is to run a report for all information in the log files. Select the specific
information you want to include in the report. Reports are listed by categories and
sub-categories.You can save the report query selections to use in other reports.
Select to generate the report based on the virtual domains configured on the
FortiGate devices.
Select to display host names by name rather than IP addresses. For
details on configuring IP address host names see “Defining IP
aliases” on page 55.
Select to display network service names rather than port numbers.
For example, HTTP rather than port 80.
For some report types, you can set the top ranked items for the
report. When setting top ranked items, the report will only include the
most active content. For example, report the most active mail clients
within the organization rather than all mail clients.
Figure 29: Report query options
To set the report queries
1 Go to Reports > Config.
2 Select a report from the list.
3 Select Queries.
FortiLog Administration Guide 05-16000-0082-20050115 59
Page 60

Creating and generating a report Reports
4 Select the plus sign next to a category to expand and view the sub categories.
5 Select the content from the sub-categories to include in the reports.
6 Select Apply.
Creating a query profile
You can save the selections as a query profile. After creating a query profile, you can
select the profile for use in other reports.
To create a query profile
1 Select New.
or
Start with an existing profile by selecting the profile and selecting Clone.
2 Enter a name for the profile and select OK.
3 Select the log information to include in the query profile.
4 Select Apply.
Selecting the devices for the report
Specify the devices to include in the report. If you have many devices sending log files
to the FortiLog unit, you can to run reports for specific devices or groups of devices.
The default is to run a report for all devices. You can save the device selections to use
in other reports.
Figure 30: Selecting devices
To select the devices
1 Go to Reports > Config.
2 Select a report from the list.
3 Select Devices.
4 Select These to select specific devices or groups of devices.
5 Select the Plus sign to expand the list of devices for a specific group.
60 05-16000-0082-20050115 Fortinet Inc.
Page 61

Reports Creating and generating a report
6 Select the group or individual devices to use in the report.
7 Select Apply.
Creating a device profile
You can save the selections as a device profile. After creating a device profile, you
can select the profile for use in other reports.
To create a device profile
1 Select New.
or
Start with an existing profile by selecting the profile and selecting Clone.
2 Enter a name for the profile and select OK.
3 Select the devices to include in the profile.
4 Select Apply.
Select filtering options
Filtering enables you to view or remove information from a report to provide a more
concise report. For example, you only want reports on specific error messages, or you
do not want include certain IP address destinations.
Figure 31: Filter options
To set the filtering on a log report
1 Go to Reports > Config.
2 Select a report from the list.
3 Select Filter.
FortiLog Administration Guide 05-16000-0082-20050115 61
Page 62

Creating and generating a report Reports
4 Select the type of matching for the filter criteria:
• Select Any to find any matches for the criteria specified.
• Select All to find all criteria. All criteria must match to display in the results.
5 Select whether to have log messages less than and equal, equal or greater than and
equal to the level you selected. For a list of log policies levels and how they relate to
each other, see “Log policy” on page 42.
6 Select the filtering criteria for the remaining fields. The number of fields and the
information you can filter on depends on the type of log you are filtering.
Select the Not option when you want to exclude specific information. For example, for
the Source IP field, do not include any information from a specific source IP address in
the log report.
Creating a filter profile
You can save the filter options as a filter profile. After creating a filter profile, you can
select the profile for use in other reports.
To create a report filter profile
1 Select New.
or
Start with an existing profile by selecting the profile and selecting Clone.
2 Enter a name for the profile and select OK.
3 Select the filter options for the report.
4 Select Apply.
Setting a report schedule
Set a schedule so that FortiLog generates reports at a consistent time. The default is
to run a report for daily at 6pm. You can save a schedule to use in other reports.
Figure 32: Report scheduling
To create a scheduled report
1 Go to Reports > Config.
2 Select a report from the list.
62 05-16000-0082-20050115 Fortinet Inc.
Page 63

Reports Creating and generating a report
3 Select Schedule.
4 Select a day from the following:
Not Scheduled Select to not run a daily report. Use this setting when you only want to run
Daily Select to run the report every day at the same time.
These Days Select specific days of the week to run reports.
These Dates Select specific days of the month to run the report. For example, to run
the reports as needed. For details on running on demand reports see
“Reports on demand” on page 64.
reports on the first and fifteenth of every month, enter 1,15.
5 Select a specified time of the day to run the report, up to three times per day.
6 Select Apply.
Creating a report schedule profile
You can save the schedule as a schedule profile. After creating a schedule profile,
you can select the profile for use in other reports.
To create a report schedule profile
1 Select New.
or
Start with an existing profile by selecting the profile and selecting Clone.
2 Enter a name for the profile and select OK.
3 Select the schedule for the report.
4 Select Apply.
Choosing the report destination and format
Select destination and format for the report. Configure the FortiLog unit to either save
the reports to the FortiLog hard disk or email the report to any number of recipients or
both. The default is to save the report to the FortiLog hard disk in HTML format.
You can save the output options for use in other reports.
Figure 33: Select a file format
FortiLog Administration Guide 05-16000-0082-20050115 63
Page 64

Creating and generating a report Reports
To select the report destination and format
1 Go to Reports > Config.
2 Select a report from the list.
3 Select Output.
4 Set the following options:
File
Browse/Reports
Email it Select the file formats for the generated reports that the FortiLog unit sends
Email address
list
Select the file format for the generated reports that are saved to the FortiLog
hard disk. To access the reports on the hard disk, see “Viewing reports” on
page 65.
as an email attachment.
Enter the email addresses of the recipients of the report. Add multiple
recipients by pressing Enter after each email address.
5 Select Apply.
Creating a report destination and format profile
You can save the selections in a output profile. After creating an output profile, you
can select the profile for use in other reports.
To create a pre-defined output selection
1 Select New.
or
Start with an existing profile by selecting the profile and selecting Clone.
2 Enter a name for the profile and select OK.
3 Select the destination and format options.
4 Select Apply.
Reports on demand
Reports on demand provides an instant report. When requesting a report, the FortiLog
unit compiles the data from the available device logs and immediately generates a
report based on your requirements and the log data available.
The on demand reports include the same information and options as a scheduled
report.
To generate a report on demand
1 Go to Reports > Config.
2 Select a report from the list or select options for the report.
3 Select Run now.
64 05-16000-0082-20050115 Fortinet Inc.
Page 65
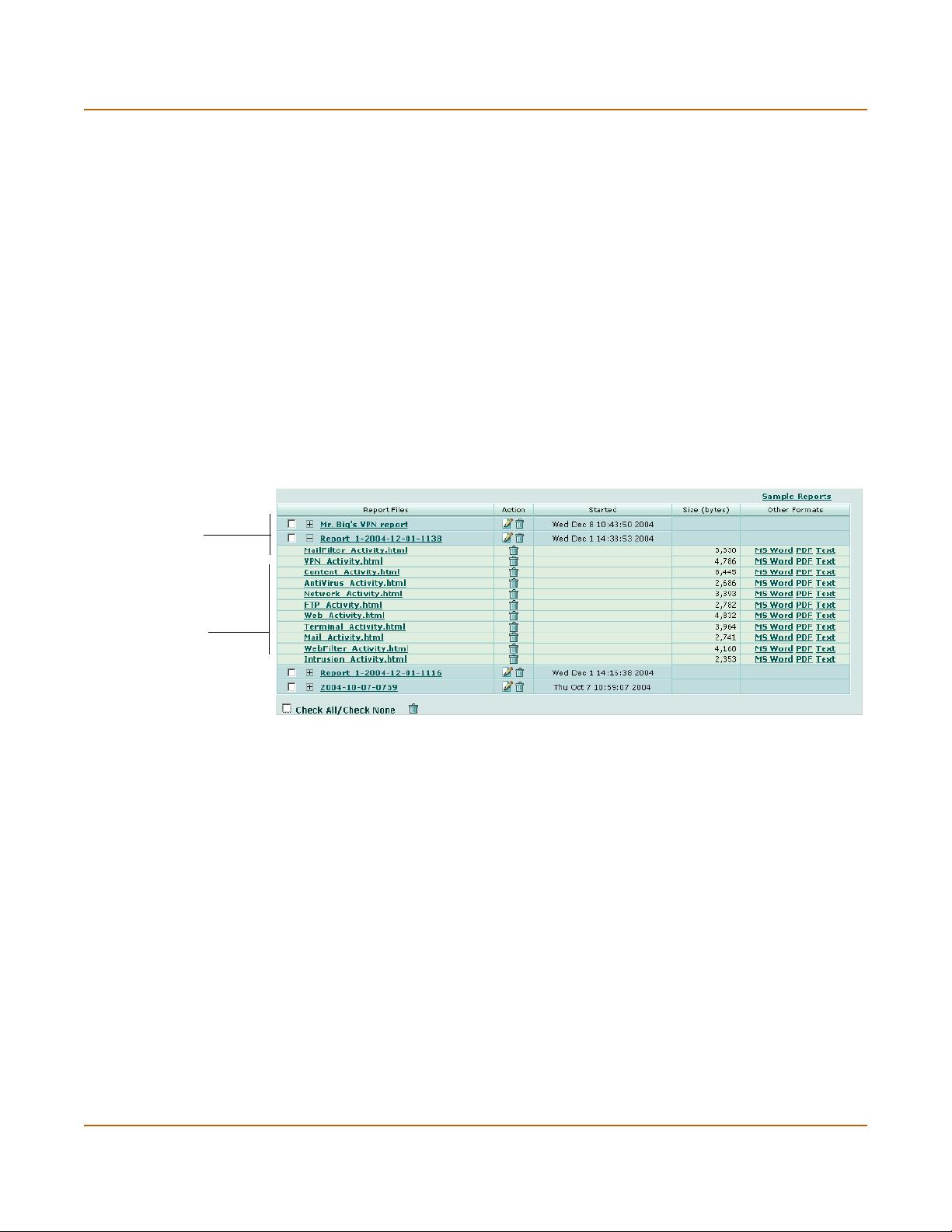
Reports Viewing reports
Viewing reports
Use the FortiLog web-based manager to view a list of the generated reports. The
generated reports are available in HTML, PDF, RTF and ASCII text formats,
depending on the output configuration. For details on setting output options see
“Choosing the report destination and format” on page 63.
There are two ways of viewing reports from the web-based manager; a roll up of all
reports selected or individual reports.
Reports are categorized by the date and time the FortiLog unit generated the reports.
The report appears in the reports list with the report name, date and time the report
was generated.
For example, a report name of “Report 1-2004-12-15-2112”, is a report called “Report
1”, generated on December 15, 2004 at 9:12pm.
To view a generated report
1 Go to File Browse > Reports.
Figure 34: Viewing reports
Report
categories
Report
sub-categories
2 Do one of the following:
Report Files Select the report name to view a roll up of all reports in HTML format.
Select the Plus sign to expand the report to view the individual reports in
HTML format.
Action Select Edit to rename the report.
Select Delete to remove the report from the FortiLog hard disk.
Check
All/Check None
Other Formats
Select to select all reports for removal from the FortiLog hard disk.
Select an alternate format to view the report.
FortiLog Administration Guide 05-16000-0082-20050115 65
Page 66

Viewing reports Reports
Roll up report
The roll up report contains all reports that you selected for the FortiLog unit to
generate. Select the report name to view the report roll up in HTML format.
Figure 35: Roll up report
Report title
Report information
compiled from
device logs.
Select a report category to expand the list of report sub-categories. Selecting a report
name in the left frame displays the report in the right frame.
Individual reports
Individual reports have the same look and functionality as the roll up reports when
viewing the HTML file format. When you view the report in one of the alternate
formats, only the right frame with the report information is included.
66 05-16000-0082-20050115 Fortinet Inc.
Page 67

Reports Vulnerability reports
Figure 36: VPN activity report in PDF
Vulnerability reports
Vulnerability reports show any potential weaknesses to attacks that may exist for
selected devices by displaying the available ports on a FortiGate device. Rather than
using the device logs for this report, the FortiLog unit queries for open ports and
where possible and gathers information about the services running. Any known
vulnerabilities that exist for the specific service or version of the service, are included
in the reports.
Creating and generating a report
To generate a vulnerability report, begin by creating and saving a report configuration.
You can use this report configuration for a scheduled report or for generating reports
on demand.
To create a report
1 Go to Reports > Config > Vulnerability.
2 Select New and enter a name for the report.
FortiLog Administration Guide 05-16000-0082-20050115 67
Page 68

Vulnerability reports Reports
3 Set the following:
• “Selecting report result parameters” on page 68
• “Selecting plug-ins” on page 68
• “Selecting the scan targets for the report” on page 69
• “Choosing the report destination and format” on page 71.
4 Select Run now.
Selecting report result parameters
Report results parameters define how the FortiLog unit displays the vulnerability
report results. Report results parameters include:
• the specific device or all device logs submitted to the FortiLog unit.
• the device IP addresses or alias names.
Figure 37: Vulnerability report parameters
To define report result parameters
1 Go to Reports > Config > Vulnerabilities.
2 Select new.
3 Enter a report name and select OK.
4 Configure the following options:
For all devices Select to generate the report for all devices.
Per device Select to generate a separate report for each device.
Resolve Host
Names
Resolve Service
Names
Select to display host names by name rather than IP addresses. For details
on configuring IP address host names see “Defining IP aliases” on page 55.
Select to display network service names rather than port numbers. For
example, HTTP rather than port 80.
5 Select Apply.
Selecting plug-ins
Select the port scans the FortiLog unit will perform on the selected device(s).
68 05-16000-0082-20050115 Fortinet Inc.
Page 69

Reports Vulnerability reports
Figure 38: Vulnerability plugin options
To select the plug-ins
1 Go to Reports > Config > Vulnerabilities.
2 Select a report from the list.
3 Select Plug-ins.
4 Select the plug-ins to include in the report.
5 Select Apply.
Creating a plug-in profile
You can save the selections as a plug-in profile. After creating a plug-in profile, you
can select the profile for use in other vulnerability reports.
To create a plug-in profile
1 Select New.
2 Enter a name for the profile and select OK.
3 Select the plug-ins to include in the query profile.
4 Select Apply.
Selecting the scan targets for the report
Scan targets are the devices the FortiLog scans for vulnerability threats. You can save
the device selections to use in other reports.
FortiLog Administration Guide 05-16000-0082-20050115 69
Page 70

Vulnerability reports Reports
Figure 39: Selecting scan targets
To select the scan targets
1 Go to Reports > Config > Vulnerability.
2 Select a report from the list.
3 Select Scan Targets.
4 Select devices from the Available IP Aliases list.
5 Select the right arrow to move the device to the Selected IP Aliases list.
6 To add additional devices, select Create New, and repeat step 4 and 5.
7 Select Apply.
To add additional devices
1 Select Create New.
2 Enter a name of the host, network or IP address range in the Alias text box.
3 Enter the IP address of the host, network or the IP range.
4 Select OK.
5 Select the device from the Available IP Aliases list.
6 Select the right arrow to move the device to the Selected IP Aliases list.
7 Select Apply.
Creating a scan target profile
You can save the selections as a scan target profile. After creating a scan target
profile, you can select the profile for use in other vulnerability reports.
To create a scan target profile
1 Select New.
2 Enter a name for the profile and select OK.
3 Select the devices to include in the profile.
70 05-16000-0082-20050115 Fortinet Inc.
Page 71

Reports Vulnerability reports
4 Select Apply.
Choosing the report destination and format
Select destination and format for the vulnerability report. Configure the FortiLog unit to
either save the reports to the FortiLog hard disk or email the report to any number of
recipients or both. The default is to save the report to the FortiLog hard disk in HTML
format.
You can save the output options for use in other reports.
Figure 40: Selecting report output
To select the report destination and format
1 Go to Reports > Config > Vulnerability.
2 Select a report from the list.
3 Select Output.
4 Set the following options:
File
Browse/Reports
Email list Select the file formats for the generated reports that the FortiLog unit sends
Email address
list
Select the file format for the generated reports that are saved to the FortiLog
hard disk.
as an email attachment.
Enter the email addresses of the recipients of the report. Add multiple
recipients by pressing Enter after each email address.
5 Select Apply.
Creating a report destination and format profile
You can save the selections in a output profile. After creating an output profile, you
can select the profile for use in other vulnerability reports.
To create a pre-defined output selection
1 Select New.
2 Enter a name for the profile and select OK.
3 Select the destination and format options.
4 Select Apply.
FortiLog Administration Guide 05-16000-0082-20050115 71
Page 72

Vulnerability reports Reports
Viewing the vulnerability report
The FortiLog unit saves the vulnerability report either to it hard disk or sends the
report as an email attachment.
Figure 41: Viewing the list of vulnerability reports
To view the vulnerability report saved to the FortiLog hard disk
1 Go to File Browse > Reports > Vulnerability.
2 Select the report name from the list of completed reports.
Report Files The name of the report. Select the report name to view the vulnerability
Action Select Edit to rename the report. Select Delete to remove the report from the
Started The date and time the FortiLog unit started running the report.
Size The size of the report file in bytes.
Alternate
Formats
Check
All/Check None
report file. Select the check box next to the report name to select it for
removal from the list.
list.
Select an alternate file format for the report. The default format is HTML and
the alternate format is ASCII text.
Select the checkbox to select all reports in the list to quickly delete all
reports from the list.
Select Delete to delete the reports you selected to delete by selecting the
report’s check box.
72 05-16000-0082-20050115 Fortinet Inc.
Page 73

Using Logs
The FortiLog unit collects log files from various sources and stores them on its hard
disk. With the log viewer you can:
• view log files collected from FortiGate, FortiManager, FortiMail and syslog devices
• customize the log file view
• download log files to your hard disk
• filter the logs for specific information using various criteria
• search multiple log files for unique entries
• import older log files
• watch active log files for real-time logging information of a selected device.
This chapter includes:
• The Log view interface
• Viewing logs
• Importing log files
• Log Search
• Log watch (Active mode)
• Event correlation (Active mode)
FortiLog Administration Guide Version 1.6
FortiLog Administration Guide 05-16000-0082-20050115 73
Page 74
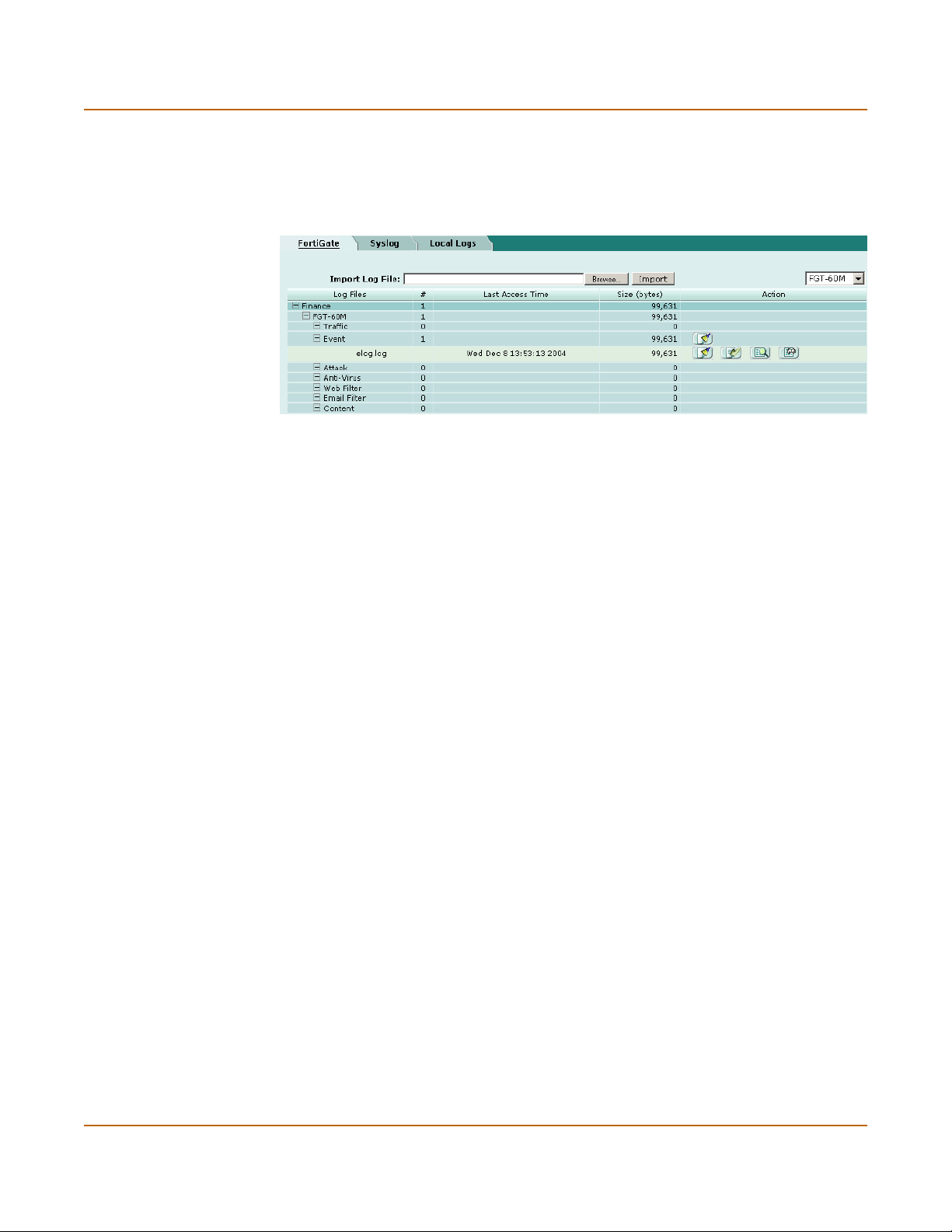
The Log view interface Using Logs
The Log view interface
The log viewer interface provides a means of viewing device log files.
Figure 42: Viewing the logs
Viewing logs
Device Tabs Access to the specific device logs. Selecting a tab will display the available
Import Log file Use this field to import older log files to view and run log reports. For details
Log files A list of log files on the FortiLog unit. Any device groups you create also
# The number of devices in a group, and the number of logs for a device.
Last Access
Time
Size (bytes) The size of the log file.
Action Select Delete to remove the log file from the FortiLog hard disk.
Device List Provides quick access to a specific device’s logs.
logs for any device within a group.
on importing log files see “Importing log files” on page 77.
appear here. Select the group name to expand the list of devices within the
group.
Select the device name to see the available log files.
The last time the log was updated from the device.
Select Download to save the log file to your local hard disk.
Select Display to view the contents of the log file. For details on viewing the
log file see “Viewing logs” on page 74.
Select Watch to view the log file updates in real time. For details on
watching log files see “Log watch (Active mode)” on page 78.
The log viewer interface provides a display of log data that you can organize and
format.
74 05-16000-0082-20050115 Fortinet Inc.
Page 75

Using Logs Viewing logs
Figure 43: Viewing a device log
To view the device log files
1 Go to File Browse > Logs.
2 Select a device tab.
3 Expand the group name and device name to see the list of available logs.
4 In the Action column, select Display for the desired log file.
5 Do one of the following to change the views of the log information”
Page Select Page forward or Page back to move through the log entries.
Enter the page number to jump to a specific page.
Raw Select to view the log information as it appears in the log. Select Formatted
Column
headers
to return to the column view.
Select the column header to change the sort order between
ascending and descending order.
For information about log messages, see the FortiGate Log Message Reference
Guide.
Finding log information
You can filter the contents of the log file to find specific information within a large log
file. There are two methods of finding information in the log:
• Basic filter - provides a simple filtering mechanism to search the log file for a
specific keyword. The keyword search applies to all columns of the log file.
• Standard filter - perform a more detailed search of the log. With a standard search,
you can set specific search criteria for each column of information in the log. You
can also enable or disable a filter for greater search accuracy.
To perform a basic search of the log contents
1 Go to File Browse > Logs.
2 Select a device and log file.
3 In the log view, select Column Settings at the top of the page.
4 Set the Search to Basic.
FortiLog Administration Guide 05-16000-0082-20050115 75
Page 76

Viewing logs Using Logs
Figure 44: Basic log filter
5 Do the following to search the log using the Basic log filter:
Show Select the columns of information you want to view in the log.
Lines per page Enter the number of entries of the log you want to see on each page.
Keyword
Enter the words you want to find in the log.
6 Select Apply.
To perform a standard search of the log contents
1 Go to File Browse > Logs.
2 Select a device and log file.
3 In the log view, select Column Settings at the top of the page.
4 Set the Search to Standard.
Figure 45: Standard log filter
5 Do the following to search the log using the Standard log filter:
Show Select the columns of information you want to view in the log.
Lines per page Enter the number of entries of the log you want to see on each page.
76 05-16000-0082-20050115 Fortinet Inc.
Page 77

Using Logs Importing log files
Match Select Any to find any matches for the criteria specified.
Select All to find all criteria. All criteria must match to display in the results.
Up and Down
arrows
Select a row and select the up and down arrows to reposition the column
within the display.
6 Select each row in the Filter column.
7 Each row of information provides criteria for the search:
Device time Set the time span .
Log time Set the time span of the logged information.
Level
Service The type of service, such as POP3.
Source The source IP address
Destination The destination IP address
Sent The volume of information sent.
Received The volume of information received.
The alert level.
The row criteria available reflect the content within the selected log file.
8 Select Enable for each row you want the search criteria to use.
9 Select Apply.
Importing log files
If you have older log files from various devices, you can import these logs onto the
FortiLog unit to generate log reports.
Importing log files is also useful when changing your RAID configuration (for the
FortiLog-400 and FortiLog-800). Changing your RAID configuration wipes the hard
disk. If you backup your FortiLog log, you can import the FortiLog log onto the device.
Figure 46: Import log file
To import a log file
1 Go to File Browse > Logs.
2 Enter the path and file name of the log file, or select Browse.
3 Select the device name from the list above the Action column.
4 Select Import.
FortiLog Administration Guide 05-16000-0082-20050115 77
Page 78

Log Search Using Logs
Log Search
Use the Log Search, to perform a simple search of all log files on the FortiLog unit.
The FortiLog unit maintains a search history for future use. If you need to clean out a
long search history, select Clear History.
To search the log files for specific information
1 Go to File Browse > Log Search.
2 Enter the keywords for the search and select Search.
The search results appear below the search fields.
Log watch (Active mode)
Log watch enables you to monitor a device log as it is updated to the FortiLog unit.The
FortiLog unit refreshes the view of the device log for the selected interval.
Note: The feature is only available to active log files. That is, log files that are continually
updated from a registered device.
To set log watching
1 Go to File Browse > Logs.
2 Select the device you wish to monitor from the device list.
3 Select Watch in the Action column.
Figure 47: Log watch settings
4 Select Column Settings to set the log information you want to view:
Refresh Select an automatic refresh rate between zero (none) and 30 seconds.
Select Refresh to manually refresh the screen.
Raw Select to view the log information as it appears in the log. Select Formatted
Show Select the columns of information you want to view in the log.
Up and Down
arrows
to return to the column view.
Select a row and select the up and down arrows to reposition the column
within the display.
78 05-16000-0082-20050115 Fortinet Inc.
Page 79

Using Logs Event correlation (Active mode)
5 Select Apply.
Event correlation (Active mode)
Event correlation is a data mining feature that provides a way of reviewing attacks on
multiple devices in one location. The FortiLog unit collates attack events from all
submitted logs and displays the information in a table. With even Correlation you can
view:
• all attacks on your network.
• attacks targeted to specific devices.
• the target and source of the attack.
• when the attack occurred.
• details on the type of attack.
To run an event correlation:
1 Go to File Browse > Event Correlation.
2 Select an attack type from the list
3 Select Next.
4 From the drop list, select to view the attacks from the same source IP or targets of the
same attack.
5 Select Show me.
Figure 48: Event Correlation results
Page Use the page arrows or enter the page number to move to a different page
Sort list Select an attack sort for viewing the results. You can choose from Attacks
of the event correlation results.
from the same source or other targets of the same attack.
FortiLog Administration Guide 05-16000-0082-20050115 79
Page 80

Event correlation (Active mode) Using Logs
Show me Select Show me to view the selection from the sort list.
# The number of entries for the attack report.
Log time The date and time of the attack.
Device ID The name of the device subjected to the attack.
Source The source IP address of the attack.
Destination The IP address of the device subjected to the attack.
Message The attack message logged for the device. The message also includes a
link to the FortiProtect web site for further details on the type of attack.
80 05-16000-0082-20050115 Fortinet Inc.
Page 81

FortiLog Administration Guide Version 1.6
Using the FortiLog unit as a NAS
Users can save, store and access information on the FortiLog hard disk as an
alternate means of storing important files and work. To provide users with access to
the FortiLog file system you must:
• configure the FortiLog unit to use Windows sharing or Network File System (NFS)
• configure users and user groups with access to read and write files on the FortiLog
hard disk.
This chapter includes:
• Connecting to the FortiLog file system
• Providing access to the FortiLog hard disk
• Setting folder and file properties
Use the FortiLog web-based manager to view and manage files on the FortiLog hard
disk. You can also use the web-based manager to set up and manage user and group
access to the FortiLog hard disk directories and files.
To view and manage files stored on the FortiLog hard drive
1 Go to File Browse > Files.
2 Navigate the folder structure by double-clicking the folders.
Connecting to the FortiLog file system
Before a user can access files on the FortiLog hard disk, create user and group
accounts and set their access permissions.
When users connect to the FortiLog unit, consider the following:
• Microsoft Windows users connect to the FortiLog hard disk by mapping a drive
letter to a network folder.
• For Macintosh users, enable the FortiLog Windows networking selection.
Macintosh users can use the SMB sharing protocol to connect to the FortiLog unit.
• UNIX or Linux users:
• mount the FortiLog hard disk as smbfs if you are using Windows Networking.
• mount the FortiLog hard disk as nfs if you select Network File System.
FortiLog Administration Guide 05-16000-0082-20050115 81
Page 82

Providing access to the FortiLog hard disk Using the FortiLog unit as a NAS
Providing access to the FortiLog hard disk
To enable user access to the FortiLog hard disk to store and access files you need to
add user and group accounts to the FortiLog unit. Along with user and group
accounts, you define the write or read/write access to files and folders.
Selecting a file sharing protocol
Enable sharing protocols before providing user and group access to the FortiLog hard
disk folders and files.
To set the file sharing for the FortiLog unit
1 Go to Network Sharing > Protocols.
2 Select Enable for a file sharing protocol.
Windows
Networking
Workgroup Enter a workgroup name that the users can identify on the Windows network.
NFS A means file sharing native to Unix and Linux.
A means of file sharing native to Microsoft Windows.
3 Select Apply.
Adding and modifying user accounts
When you add user accounts, you add the user name and set a password. You can
then add the user to a group or set specific access rights to folders on the FortiLog
hard disk. The users you add will not have administrative access to the FortiLog hard
disk or FortiLog unit. To add administrative users see “Configure Administrator
access” on page 47.
To add a user account
1 Go to Network Sharing > Users.
2 Select Create New.
3 Enter the following information for the user account:
User name Enter a user name. For example, twhite. The name cannot include spaces.
UID Enter a user ID.
Use this field only if you are using the NFS protocol. The NFS protocol uses
the UID to determine the permissions on files and folders.
Password Enter a password for the user.
Display Name Enter the user name to identify who the user is. For example, Terry White.
If you are using the Windows Networking protocol, you only need to complete the
information for the User name, Password and Display Name.
You can include spaces in this field.
4 Select OK.
5 Select Edit in the Modify column to update the user name or password.
82 05-16000-0082-20050115 Fortinet Inc.
Page 83

Using the FortiLog unit as a NAS Providing access to the FortiLog hard disk
Adding and modifying group accounts
Create user groups to assign directory access to many users at once rather than
individually.
To add a user group
1 Go to Network Sharing > Groups.
2 Select Create New.
3 Enter the following information for the group account:
Group Enter a user name. For example, Finance. The name cannot include spaces.
GID Enter a Group ID. Use this field if you are using Network File System.
4 Select the users from the Available members area and select the Right arrow to add
them to the group.
To remove a member, select a user from the Members area and select the Left arrow.
5 Select OK.
6 Select Edit in the Modify column to add or remove users from the group.
Assigning access to folders
With users, groups and a file sharing protocol defined, you can apply access rights to
users and groups. You can apply read only and read/write access for users and
groups to the folder structure of the FortiLog hard disk.
To add a new Windows share configuration
1 Go to Network Shares > Access > Windows Shares.
2 Select Create New.
FortiLog Administration Guide 05-16000-0082-20050115 83
Page 84

Providing access to the FortiLog hard disk Using the FortiLog unit as a NAS
Figure 49: Windows sharing configuration
Local Path
Button
3 Select the Local Path button to select the folder for the users or groups to access.
Note: The default permissions for files and folders is read and execute privileges. The owner of
the document also has write privileges. To enable write permissions for users and groups, you
must select the write permission for the folder and for the user and the group. For details see
“Setting folder and file properties” on page 86.
4 Select OK.
5 Enter the Share Name to describe the shared folder.
6 Select user and group names from the Available Users & Groups box. Hold the Ctrl
key to select multiple users.
7 Select the type of access rights the users and groups will have and select the
appropriate right arrow to move the user or group name to the Read-Only Access or
Read-Write Access boxes.
8 Select Ok.
To add a new NFS share configuration
1 Go to Network Shares > Access > NFS Exports.
2 Select Create New.
84 05-16000-0082-20050115 Fortinet Inc.
Page 85

Using the FortiLog unit as a NAS Providing access to the FortiLog hard disk
Figure 50: NFS share configuration
Local Path
Button
3 Select the Local Path button to select the folder for the users or groups to access.
Note: The default permissions for files and folders is read and execute privileges. The owner of
the document also has write privileges. To enable write permissions for users and groups, you
must select the write permission for the folder and for the user and the group. For details see
“Setting folder and file properties” on page 86.
4 Select OK.
5 Enter the IP address of the remote system or user ID.
6 Select user and group names from the Available Users & Groups box. Hold the Ctrl
key to select multiple users.
7 Select the type of access rights the users and groups will have and select the
appropriate right arrow to move the user or group name to the Read-Only Access or
Read-Write Access boxes.
8 Select Ok.
Modifying the user or group folder access
At any time you can modify a user or group folder access to the FortiLog unit. You can
also delete the access rights.
To modify the FortiLog folder access
1 Go to Network Sharing > Access.
2 In the Modify column, select Edit to update the access rights for a user or group.
or
In the Modify column, select Delete to remove the user or group access from the
FortiLog unit.
FortiLog Administration Guide 05-16000-0082-20050115 85
Page 86

Setting folder and file properties Using the FortiLog unit as a NAS
Setting folder and file properties
The FortiLog unit enables you to administer the folders and files on the FortiLog hard
disk. Using the file browser you can:
• rename and delete files and folders
• set the access permissions
• download files to your local hard disk.
Figure 51: Set file and folder properties
Each folder and file has its own access permissions. You can set three types of
permissions:
Owner The original user for the file or folder. This is the user who creates or
Group A group of users you define. The default group is the Admin group.
Other All other users that are not otherwise the owner of the file or within a group.
uploads the file to the FortiLog hard disk.
By default, when a user adds a new file or folder, the access rights are Read, Write,
Execute for the owner (user), and Read and Execute for the Admin group and Others.
To set file and folder permissions
1 Go to File Browse > Files.
2 Navigate to the folder or file you wish to set the permissions and select Edit.
3 Set the read, write and execute permissions for the folder.
4 Select OK.
For example, if you wanted only users in the Finance group to view a folder with
financial information, create a user group called Finance that includes the users from
the Finance department. Set the following permissions to the folder:
Owner Select the user name or Admin and Read, Write, Execute
Group Select Finance from the list and select Read
Other No selections
86 05-16000-0082-20050115 Fortinet Inc.
Page 87

FortiLog Administration Guide Version 1.6
FortiLog CLI reference
This chapter explains how to connect to and use the FortiLog command line interface
(CLI). You can use CLI commands to view all system information and to change all
system configuration settings.
• CLI documentation conventions
• Connecting to the CLI
• CLI commands
CLI documentation conventions
This guide uses the following conventions to describe CLI command syntax.
• angle brackets < > to indicate variable keywords
For example:
execute restore config <filename_str>
You enter restore config myfile.bak
<xxx_str> indicates an ASCII string variable keyword.
<xxx_integer> indicates an integer variable keyword.
<xxx_ip> indicates an IP address variable keyword.
• vertical bar and curly brackets {|} to separate alternative, mutually exclusive
required keywords
For example:
set system opmode {active | passive}
You can enter set system opmode active or set system opmode
passive
FortiLog Administration Guide 05-16000-0082-20050115 87
Page 88

Connecting to the CLI FortiLog CLI reference
Connecting to the CLI
The FortiLog-800 model has serial port and you can use the null modem cable to connect it to
your management computer.
The FortiLog-100 and 400 models do not support serial cable connections. You can use a
t
erminal emulation software such as HyperTerminal for Windows to access the CLI.
• Connecting to the FortiLog-800 console
• Setting administrative access for SSH or Telnet
• Connecting to the FortiLog CLI using SSH
• Connecting to the FortiLog CLI using Telnet
Connecting to the FortiLog-800 console
You require:
• A computer with an available communications port,
• A null modem cable to connect the FortiLog console port and a communications
port on your computer,
• Terminal emulation software such as HyperTerminal for Windows.
Note: The following procedure describes how to connect to the FortiLog CLI using
Windows HyperTerminal software. You can use any terminal emulation program.
To connect to the FortiLog-800 console
1 Connect the
FortiLog console port to the available communications port on your
computer.
2 Make sure the
FortiLog unit is powered on.
3 Start HyperTerminal, enter a name for the connection, and select OK.
4 Configure HyperTerminal to connect directly to the communications port on the
computer to which you have connected the
FortiLog console port.
5 Select OK.
6 Select the following port settings and select OK.
Bits per second 9600
Data bits 8
Parity None
Stop bits 1
Flow control None
7 Press Enter to connect to the
FortiLog CLI.
8 A prompt appears:
FortiLog-800 login:
9 Type a valid administrator name and press Enter.
88 05-16000-0082-20050115 Fortinet Inc.
Page 89

FortiLog CLI reference Connecting to the CLI
10 Type the password for this administrator and press Enter.
The following prompt appears:
Welcome!
You have connected to the FortiLog CLI, and you can enter CLI commands.
Setting administrative access for SSH or Telnet
To configure the FortiLog unit to accept SSH or Telnet connections, you must set
administrative access to SSH or Telnet for the FortiLog interface to which your
management computer connects. To use the web-based manager to configure
FortiLog interfaces for SSH or Telnet access, see “Admin” on page 46.
To use the CLI to configure SSH or Telnet access
1 Connect and log into the CLI using the FortiLog console port and your terminal
emulation software.
2 Use the following command to configure an interface to accept SSH connections:
set system interface port1 config allowaccess ssh
3 Use the following command to configure an interface to accept Telnet connections:
set system interface port1 config allowaccess telnet
Note: Remember to press Enter at the end of command. As well, remember to type end and
press Enter to commit the changes to the FortiLog configuration.
FortiLog Administration Guide 05-16000-0082-20050115 89
Page 90

Connecting to the CLI FortiLog CLI reference
!
4 To confirm that you have configured SSH or Telnet access correctly, enter the
following command to view the access settings for the interface:
get system interface
The CLI displays the settings, including the management access settings, for the
port1 interface.
Connecting to the FortiLog CLI using SSH
Secure Shell (SSH) provides strong secure authentication and secure
communications to the FortiLog CLI from your internal network or the internet. Once
the FortiLog unit is configured to accept SSH connections, you can run an SSH client
on your management computer and use this client to connect to the FortiLog CLI.
Note: The Fortilog unit supports the following encryption algorithms for SSH access: 3DES and
Blowfish.
To connect to the CLI using SSH
1 Install and start an SSH client.
2 Connect to the FortiLog port1 interface that is configured for SSH connections.
3 Type a valid administrator name and press Enter.
4 Type the password for this administrator and press Enter.
The FortiLog model name followed by a # is displayed.
You have connected to the FortiLog CLI, and you can enter CLI commands.
Connecting to the FortiLog CLI using Telnet
You can use Telnet to connect to the FortiLog CLI from your internal network or the
Internet. Once the FortiLog unit is configured to accept Telnet connections, you can
run a Telnet client on your management computer and use this client to connect to the
FortiLog CLI.
Caution: Telnet is not a secure access method. SSH should be used to access the FortiLog CLI
from the internet or any other unprotected network.
To connect to the CLI using Telnet
1 Install and start a Telnet client.
2 Connect to the FortiLog port1 interface that is configured for Telnet connections.
3 Type a valid administrator name and press Enter.
4 Type the password for this administrator and press Enter.
You have connected to the FortiLog CLI, and you can enter CLI commands.
90 05-16000-0082-20050115 Fortinet Inc.
Page 91

FortiLog CLI reference CLI commands
CLI commands
The FortiLog CLI commands include:
• execute branch
• get branch
• set branch
• unset branch
execute branch
Use execute to run static commands, to reset the FortiLog unit to factory defaults, to
back up or restore FortiLog configuration files, and to reboot or shut down the FortiLog
system.
Table 4: execute command architecture
reload <return>
config <string> <xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx> <return>
image <string> <xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx> <return>
execute
restore
backup config <name_str> <xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx> <return>
reboot <return>
factoryreset <return>
save config <return>
shutdown <return>
formatlogdisk <return>
Commands Description
execute reload If you set your console to batch mode, use this command to flush the
execute restore config <string>
<xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx>
execute restore image <string>
<xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx>
execute backup config <name_str>
<xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx>
execute reboot Restart the FortiLog system.
execute factoryreset Set the FortiLog system back to factory defaults.
execute save config Save the FortiLog system configuration.
execute shutdown Shut down the FortiLog system.
execute formatlogdisk Format the local log hard disk.
FortiLog Administration Guide 05-16000-0082-20050115 91
current configuration from system memory and reload the configuration
from a saved configuration file.
Restore system settings from tftp server.
• <string> is the configuration file name on the tftp server.
•<xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx> is the IP address of the tftp server.
Restore system images from tftp server.
• <string> is the image file name on the tftp server.
•<xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx> is the IP address of the tftp server.
Backup system settings to tftp server.
• <name_str> is the system configuration file name.
•<xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx> is the IP address of the tftp server.
Page 92
CLI commands FortiLog CLI reference
get branch
Use get to display settings, logs, or system information.
Table 5: get command architecture
alertemail
config <return> <keyword_str> <return>
console <return>
report
log
get
system
configuration <return>
setting <return>
resolve
alias
client <return>
elog <return>
logsetting <return>
query <return>
report <return>
raid <return>
policy <return> destination {syslog | local | console} <return> event <return>
status <return>
serialno <return>
performance <return>
interface <return>
dns <return>
route table <return>
time
session_ttl
option <return>
mainregpage <return>
admin <return>
name <string>
querysets
devicesets
filters
schedules
otuputs
time <return>
ntp <return>
Commands Description
get alertemail configuration Display alert email configuration.
get alertemail setting Display alert email setting status.
get config Display system configuration.
get console Display console information, including page number, mode and baudrate.
92 05-16000-0082-20050115 Fortinet Inc.
Page 93

FortiLog CLI reference CLI commands
get report resolve Display the settings (what is turned on) for resolving host and service
get report aliases Display a list of IP aliases and their IP address.
get log client Display the FortiGate units connected to the FortiLog unit.
get log elog Display event logs.
get log logsetting Display log settings.
get log query Display log queries.
get log report Display a matrix of all set reports.
get log report name <string> Display information on a specific report name.
get log report querysets Display information on the queries set for each report.
get log report devicesets Display information on the devices sets for each report.
get log report filters Display the information on the filtering options for the reports.
get log report schedules Display the scheduling information for the reports.
get log report outputs Display the output options for the reports.
get log raid Display RAID levels.
get log policy destination {syslog | local |
console}
get log policy destination event Display log policy event setting of the selected destination.
get system status Display system status.
get system serialno Display the FortiLog unit serial number.
get system performance Display the FortiLog unit system performance, including CPU, memory, and
get system interface Display port1 interface information.
get system dns Display domain name server configuration.
get system brctl Display system interface information and MAC address.
get system route table Display system route table information, including table number, destination,
get system time time Display current system time.
get system time ntp Display NTP server name and information.
get system session_ttl Display the idle time length for a session.
get system option Display system options, including system idle timeout, authentication
get system mainregpage Display main registration message.
get system admin Display admin user information.
names.
Display log policies of the remote syslog server, the FortiLog hard disk, or
the console.
if the system is up.
gateway, and interface.
timeout, and language for the web-base manager.
FortiLog Administration Guide 05-16000-0082-20050115 93
Page 94

CLI commands FortiLog CLI reference
set branch
Use set to configure settings, logs, or system information.
set alertemail
Use set alertemail to configure alert mails.
Table 6: set alertemail command architecture
auth {enable | disable} <return>
set alertemail
mailto <string> <string> <string>
<return>
configuration
setting option
local
device {enable |
disable}
passwd <string> <return>
server <server_address>
<return>
user <name_str> <return>
alert {enable disable} <return>
localmailaddr <string><return>
level {emergency | alert | critical |
error | warning | notification |
information}
eventnum {1 | 5 | 10 | 20 | 50 | 100
| 500 | 1000} <return>
time {0.5 | 1.0 | 3.0 | 6.0 |12.0 |
24.0 | 72.0 | 168.0}
add
none <return>
critical <return>
diskfull <return>
none <return>
name <string><return>
devlist <string><return>
levelalert {enable | disable}<return>
levelnum {emergency | alert | critical | error |
warning | notification | information} <return>
eventnum {1 | 5 | 10 | 20 | 50 | 100 | 500 |
1000} <return>
leveltime {0.5 | 1.0 | 3.0 | 6.0 |12.0 | 24.0 |
72.0 | 168.0} <return>
leveldevice {all | per } <return>
attackalert {enable | disable}<return>
attackany {any | some} <return>
attackeywords <keyword1 | keyword2>
<return>
attacknum {1 | 5 | 10 | 20 | 50 | 100 | 500 |
1000} <return>
attacktime {0.5 | 1.0 | 3.0 | 6.0 |12.0 | 24.0 |
72.0 | 168.0} <return>
attackdevice {all | per } <return>
attacksingle {y | n} <return>
94 05-16000-0082-20050115 Fortinet Inc.
Page 95
FortiLog CLI reference CLI commands
Table 6: set alertemail command architecture
virusalert {enable | disable}<return>
virusany {any |some| <return>
viruskeywords <keyword1 | keyword2>
<return>
set alertemail
Commands Description
set alertemail configuration auth {enable |
disable}
set alertemail configuration mailto <string>
<string> <string>
set alertemail configuration mailto none Clear all email addresses of the alert email recipients.
set alertemail configuration passwd <string> Set the password for logging on to the SMTP server to send alert emails.
set alertemail configuration server
<server_address>
set alertemail configuration user <name_str> Set the user name for logging on to the SMTP server to send alert emails.
set alertemail setting option critical Configure the alertemail to report critical incidents.
set alertemail setting option diskfull Configure the alertemail to report if the FortiLog hard disk is full.
set alertemail setting option none Clear all alert email option configuration.
set alertmail local alert {enable | disable} Enable the alert messages for the FortiLog unit.
set alertmail local localmailaddr <string> Set the email address where the FortiLog unit will send the alert
set alertmail local level {emergency | alert |
critical | error | warning | notification |
information}
set alertmail local eventnum {1 | 5 | 10 | 20 | 50 |
100 | 500 | 1000}
set alertmail local time {0.5 | 1.0 | 3.0 | 6.0 |12.0 |
24.0 | 72.0 | 168.0}
set alertmail device {enable | disable} Enable or disable the monitoring of device logs for alert messages.
set alertmail device enable add name <string> Add a device name to the alertmail list.
set alertmail device enable add devlist <string> Add a device group to the alertmail list.
set alertmail device enable add levelalert
{enable | disable}
device {enable |
disable}
add
Enable or disable SMTP authentication for sending alert emails.
Enter the email addresses of three alert email recipients.
• <string> is the email address of an alert email recipient.
• <string> is the password.
Set the IP address of the SMTP server for sending alert emails.
• <server_address> is the IP address of the SMTP server.
• <name_str> is the user name.
messages.
Set the level to monitor before sending an alert message. The FortiLog
unit sends alert email for all messages at and above the logging severity
level you set.
Set the number of selected events that occur before the FortiLog unit
sends an alert message. Use this setting in conjunction with the setting
below.
Set the wait time for the number of events to occur within before sending
an alert email for the specified level log messages. Use this setting in
conjunction with the setting above.
Enable the level alert option to set the level the FortiLog unit will monitor
before sending an alert message.
virusnum {1 | 5 | 10 | 20 | 50 | 100 | 500 |
1000} <return>
virustime {0.5 | 1.0 | 3.0 | 6.0 |12.0 | 24.0 |
72.0 | 168.0} <return>
virusdevice {all | per } <return>
virussingle {y | n} <return
devicemailaddr <string>
FortiLog Administration Guide 05-16000-0082-20050115 95
Page 96

CLI commands FortiLog CLI reference
set alertmail device enable add levelnum
{emergency | alert | critical | error | warning |
notification | information}
set alertmail device enable add eventnum
{1 | 5 | 10 | 20 | 50 | 100 | 500 | 1000}
set alertmail device enable add leveltime
{0.5 | 1.0 | 3.0 | 6.0 |12.0 | 24.0 | 72.0 | 168.0}
set alertmail device enable add leveldevice
{all | per}
set alertmail device enable add attackalert
{enable | disable}
set alertmail device enable add attackany
{any | some}
set alertmail device enable add attackeywords
<keyword1 | keyword2}
set alertmail device enable add attacknum
{1 | 5 | 10 | 20 | 50 | 100 | 500 | 1000}
set alertmail device enable add attacktime
{0.5 | 1.0 | 3.0 | 6.0 |12.0 | 24.0 | 72.0 | 168.0}
set alertmail device enable add attackdevice
{all | per}
set alertmail device enable add attacksingle
{y | n}
set alertmail device enable add virusalert
{enable | disable}
set alertmail device enable add virusany
{any | some}
set alertmail device enable add viruskeywords
<keyword1 | keyword2}
set alertmail device enable add virusnum
{1 | 5 | 10 | 20 | 50 | 100 | 500 | 1000}
set alertmail device enable add virustime
{0.5 | 1.0 | 3.0 | 6.0 |12.0 | 24.0 | 72.0 | 168.0}
set alertmail device enable add virusdevice
{all | per}
set alertmail device enable add virussingle
{y | n}
set alertmail device enable add devicemailaddr
<string>
Set the level to monitor before sending an alert message. The FortiLog
unit sends alert email for all messages at and above the logging severity
level you set.
Set the number of selected events that occur before the FortiLog unit
sends an alert message. Use this setting in conjunction with the setting
below.
Set the wait time for the number of events to occur within before sending
an alert email for the specified level log messages. Use this setting in
conjunction with the setting above.
Set level setting to monitor each device separately or as a group.
Enable or disable the monitoring of specific attack types.
Set the FortiLog to monitor for any attack types or specific attacks. Use in
conjunction with the next command.
Set the attack types the Fortilog should monitor for in the device logs. Use
in conjunction with the command above.
Set the number of attack events that occur before the FortiLog unit sends
an alert message. Use this setting in conjunction with the setting below.
Set the wait time for the number of attack events to occur within before
sending an alert email for the specified level log messages. Use this
setting in conjunction with the setting above.
Set level setting to monitor each device separately or as a group.
Set to the FortiLog unit send and alert email only when the defined attack
settings originate from a singe source IP.
Enable or disable the monitoring of specific virus types.
Set the FortiLog to monitor for any virus types or specific attacks. Use in
conjunction with the next command.
Set the virus types the Fortilog should monitor for in the device logs. Use
in conjunction with the command above.
Set the number of virus events that occur before the FortiLog unit sends
an alert message. Use this setting in conjunction with the setting below.
Set the wait time for the number of virus events to occur within before
sending an alert email for the specified level log messages. Use this
setting in conjunction with the setting above.
Set level setting to monitor each device separately or as a group.
Set to the FortiLog unit send and alert email only when the defined virus
settings originate from a singe source IP.
Set the email addresses of the recipients to receive the alert warning
messages.
96 05-16000-0082-20050115 Fortinet Inc.
Page 97
FortiLog CLI reference CLI commands
set console
Use set console to set console configuration.
Table 7: set console command architecture
baudrate {9600 | 19200 |
38400 | 57600 | 115200}
<return>
set console
Commands Description
set console baudrate {9600 | 19200 |
38400 | 57600 | 115200}
set console mode {batch | line} Set the console mode to batch or line. The default setting is line.
set console page <integer/0> Set the number of lines that appear on each page of command line console output.
mode
page <integer/0> <return>
Set the console baudrate to one of the five values.
The default setting is 25.
Set this value to 0 to allow output to flow without paging.
• <integer/0> is the number of lines that appear on each page of command line
console output.
batch <return>
line <return>
FortiLog Administration Guide 05-16000-0082-20050115 97
Page 98

CLI commands FortiLog CLI reference
set log
Use set log to configure log settings
Table 8: set log command architecture
set log
client
<string>
raid
<raid
level>
<return>
devicegr
oup
<string>
setting
policy destination
deviceid
<string>
uuid <raid_
uuid>
console status {enable |
local
memory
<enable |
disable>
<return>
syslog
<syslog |
local |
console>
secure {yes | no} psk <string> space
disable} <return>
status {enable |
disable} <return>
diskfull
loglevel
<severity_integer>
remote {enable |
disable} <return>
local status {enable |
event status <enable |
loglevel
<severity_integer>
<return>
loglevel
<severity_integer>
<return>
server <server_ip>
<return>
disable} <return>
disable> <return>
<number>
<return>
csv {enable |
disable}
port
<port_integer>
<return>
loglevel
<severity_integ
er> <return>
category configura
filesz
<integer>
<return>
loglevel
<severity
_integer>
<return>
csv
{enable |
disable}
tion
fileage
<integer>
<return>
csv
{enable |
disable}
ipsec
login
ipmac
system
routegate
way
none
spacefull
{overwrite
_oldest |
stop_
logging}
98 05-16000-0082-20050115 Fortinet Inc.
Page 99

FortiLog CLI reference CLI commands
Table 8: set log command architecture
from <YY-MMDD-HH> to
<YY-MM-DDHH>
today |
yesterday
this {year
|quarter|month|
week}
last
{year|quarter|m
onth|week}
vdom
dev
all
x <integer
0..99>
y <integer
0..99>
ip
port
schedule
<return>
<string>
output <string>
run
none
hours <hour>
daily
days <mon, tue,
wed...>
dates <1,2,3..>
nweeks<
weeks>
ndays<d
ays>nho
urs<hour
s>
storage formats
mail
<return>
address
formats
<return>
<html,pdf
,rtf,text>
<html,pdf
,rtf,text>
set
log
devtype
<string>
report
period
name <report
name><Return>
queryset <name of
queryset><return>
deviceset <string><return>
filters<return> <string><return>
schedule <string><return>
output <string><return> destination
results
top
resolve
queryset <string>
deviceset <string>
filters<return>
<string>
<qry_indexes>
{all | 0,4,5}
FortiLog Administration Guide 05-16000-0082-20050115 99
Page 100

CLI commands FortiLog CLI reference
Commands Description
set log client <client_string> deviceid <id_string>
secure {yes | no} psk <psk_string> space
<number> filesz <filesz_integer> fileage
<fileage_integer> spacefull {overwrite_oldest |
stop_logging}
set log raid <raid_level> Set the log RAID level: linear, 0, 1, or 5. There is no default value for this
set log raid uuid <raid_uuid> Set the log RAID universal unique identifier.
set log devicegroup <string> Create a device group to add devices to.
set log setting console loglevel
<severity_integer>
set log setting local status {enable | disable} Enable or disable logging to the FortiLog unit hard disks.
set log setting local filesz <file-sz_integer> Set the maximum size for the Fortilog local log file.
set log setting local logtime <days_integer> Set the number of days before the FortiLog unit starts a new log file.
set log setting local diskfull
set log setting local memory status <enable |
disable>
set log setting local memory loglevel
<severity_integer>
set log setting syslog local status loglevel
<severity_integer>
set log setting syslog local status loglevel
<severity_integer> csv {enable | disable}
set log setting syslog remote {enable | disable} Enable or disable logging to the remote syslog server.
set log setting syslog remote server <server_ip> Configure the remote syslog server log setting.
set log setting syslog remote server <server_ip>
port <port_integer>
Configure the FortiLog to log a FortiGate client.
• <client_string> is the name of the client.
• <id_string> is the FortiGate client ID, for example, the serial number.
• {yes | no} provides the option to configure secured connection or not.
• <psk_string> is the pre-shared key number.
• <number> is the amount of the allocated disk space. Set disk quota
from 0 to 4000 MB. A disk quota of 0 is unlimited
• <filesz_integer> is the size limit for the log files. The default log file size
is 10 MB.
• <fileage> is the time limit for the FortiLog unit to keep the log files. The
default log file age is 10 days.
• {overwrite_oldest | stop_logging} allows you to select what you want
the FortiLog unit to do when the allocated disk space for the FortiGate
device is used up.
option.
Set the console log severity level
0 = Emergency, 1 = Alert, 2 = Critical, 3 = Error, 4 = Warning, 5 =
Notification, 6 = Information
The log levels will be up to but not higher than the value you set.
Configure the FortiLog unit to log to the local memory.
Set the local FortiLog unit log severity level
0 = Emergency, 1 = Alert, 2 = Critical, 3 = Error, 4 = Warning, 5 =
Notification, 6 = Information
The log levels will be up to but not higher than the value you set.
Set the local FortiLog unit log severity level
0 = Emergency, 1 = Alert, 2 = Critical, 3 = Error, 4 = Warning, 5 =
Notification, 6 = Information
The log levels will be up to but not higher than the value you set.
Enable or disable CSV format to record log messages to the FortiLog
unit hard disk in comma-separated value (CSV) formatted files. Log
message fields are separated by commas.
• <server_ip> is the IP address of the remote server.
Configure the port that the remote syslog server uses to receive log
messages.
• <port_integer> is the port number of the server.
The default port is 514.
.
100 05-16000-0082-20050115 Fortinet Inc.
 Loading...
Loading...