Page 1
Fly Development department
Repair Manual
Item: Fly PC 100
0
File NO
Secrecy Grade
Secret
Total:
Effected Date
2006-10-27
Version Ver1.0
text
Charge NO
Department
HW
Addenda
Originator Check Approval
Centel Internal Use Only
Page 2
AMENDMENT HISTORY
S/N Rev
1 V1.0
2
V1.0 RUS Check 2007-10-27
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
File
Department
Description of
Change
Repair Manual――PC 100-
HW
Version
Date Originator Check Approval
2006-10-27
薛辰宇
E. Kozlov
Ver1.0
Page
File style
ATTENTION
Report
DCR
No.
Page 3

The product must be repaired by the experienced engineers, we will not responsible for the damage caused
by any other person using this manual as instruction to repair products.
The manual owned by TechFaith Wireless Communication Technology (BeiJing) Limited, no part may be
reproduced except as authorized by written permission. The copyright and the foregoing restriction extend to
reproduction in all media.
Whilst every care has been taken in the preparation and publication of this document, errors in content,
typographical or otherwise, may occur. If you have comments concerning its accuracy, please write to:
Beijing Techfaith R&D CO.,LTD.
1/F M8 East No.1 Jiu Xian Qiao Dong Road, Chao Yang District.
Beijing, China.
P.C: 100016
1. Foreword
Page 4

1.1. The purpose of the manual
The manual is just used for the experienced engineer not the general publication, providing basic
reference for electric and mechanic repairing.
1.2. General safety notice
For protecting safety of individual and commonality, everybody should pay attention to the items hereinafter:
z The mobile phone should not close too much with exposed body especially face and eye. Don’t touch the
antenna part(right top of the phone) when using the phone, make sure it is under the best signal condition.
z Don’t use mobile phone on the airplane. Lest should disturb communication of aviation and navigation
system, lead to accident, endanger flying safety
z Don’t use mobile phone in he building site, avoid the contact bomb caused by radio signal. Pay attention
to the sign that forbid radio signal around before use mobile phone
z Don’t use mobile phone near flammable gas or oil(including fuel section, under the board on the ship, fuel
or other transfer and deposited area). For preventing the bomb caused by electromagnetic harmonic
z Don’t use the mobile phone in the operating room and other area with electric medical treatment. For
protect the electronic treatment from interference and medical accident
z Please don’t use mobile phone when driving Connect outer antenna on the car when using hand over
z Don’t give the mobile phone to children. Some other people should use the mobile phone cautiously
(pregnant woman, neurasthenia sufferer, people with heart pacemaker in body etc.)
Page 5

2. General character
2.1. Product description
PC 100 mobile phone is full duplex, using digital dem odulation technology, controlled by microprocessor.
Support 900MHz/1800MHz/1900MHz cell radio system compatible and GPRS. Handset provide land connect
telephone service to user through single base station when using it correct. All the base stations connect to a
centre control room.
Primary chips in PC 100 contain below (according to the way of encapsulation)
BGA encapsulation:OMAP730-DBB(DBB-Digital BaseBand,encapsulate CPU and DSP manage
function)、TWL3016B2GQW-ABB(ABB-Analog BaseBand,providing the interface between system analog
and digital signal, and power manage function)、K4S51163PF-Y(P)F75 Memory(8M x 16Bit x 4 Banks
Mobile-SDRAM); 、-MD4832-D512-V3Q18-X Memory(512Mbit Flash) 、和 BC41B143AXX-IXB-E42-Single
Chip Bluetooth;
QFN encapsulation:TRF6151BRGZR-TRANSCEIVER 、BQ24020DRCR-smart charge
Special encapsulation: PF09016B-TB-PA、
Radio Frequency and Base band in PEAN is isolated by screen, micro SIM card box is protected by the
battery
PC 100 has the same power step as usual
Radio Frequency circuit of antenna on the top of the mobile phone will cut automaticly when PEAN using
RF accessory plug
2.2. Introduction of character and function
Character:
Supporting trio band:The mobile phone can automatic switch in GSM900 network, DCS1800 network and
PCS1900 network. Choose best channel for calling. The mobile phone can also automatic switch during the
call without disturbing users. And the ratio of connecting improves with the automatic switch. Using trio method
GSM900/DCS1800/PCS1900 networks,not only ease up the high dense radio channel, but also provide
wilder users for network operation vendor. Both user and operation vendor gain more benefit. Using of GPRS
(General Packet Radio Service)change the mind of GSM network, which can provide more than circuit
switch, It can combine mobile communication with digital network together through add corresponding function
entities and limited changes about network. Import IP service in wild mobile market, bring wilder and faster
message space for mobile phone user too
Function:
z GSM850 / GSM900 / DCS1800 / PCS1900 automatic switching
z Full-rate/enhanced full-rate/half-rate coders
z GPRS Class 10
z Inter antenna
z 65K color 2.4” TFT display screen, 320×240
z Inter 200,0000 pixel camera
z 64 tones ring bell
z Microsoft operation system
z Enhanced phone number book
z WAP Explorer Ver 2.0
z MMS/SMS
z Inter 2Games
z Inter ring bell and wallpaper
z WI-FI
z Blue Tooth
z MP3;MPG4
z STK Service
Page 6
3. Technical Reference:
Function
Frequency
Range
Channel
Interval
Channel
Modulate
Transfer
phase error
Full duplex
interval
Frequency
stabilization
Battery voltage:3.7V Battery voltage:3.7V Battery voltage:3.7V Battery voltage:3.7V
Voltage
Transmit
current
Antenna
impedance
RF export
power
SIM Insert only Insert only Insert only Insert only
Temperature
Range
Table 3.1: basic technique parameter
RF power
export
Interference
radiation
Table 3.2: Transmitter
RF voltage < -102 dBm < -100 dBm < -100 dBm
Receive error
ratio (100
kbits )
Channel jump
time
Insert time around10 s
Table 3.3: Receiver
Sound coding
style
Ratio 13.0 kbps 13.0 kbps 13.0 kbps
GSM850
Technical Reference
Transmit Frequency
824-849 MHz
Receiver Frequency
869-894 MHz
200 KHz 200 KHz 200 KHz 200 KHz
119channel,
Every channel
contains 8 short
GMSK ( BT = 0.3) GMSK ( BT = 0.3) GMSK ( BT = 0.3) GMSK ( BT = 0.3)
RMS<5°, peak<20 RMS<5°, peak<20 RMS<5°, Peak<20 RMS<5°, Peak<°
45 MHz 45 MHz 95 MHz 85 MHz
±1ppm ±1ppm ±1ppm ±1ppm
Operation voltage:
3.4~4.2V
Peak value≤1.5A Peak value≤1.5A
50Ω 50Ω
most 2W most 2W most 1W most 1W
-10 °C to +55°C -10 °C to +55°C -10 °C to +55°C -10 °C to +55°C
33 dBm +/- 2dBm 30 dBm +/- 2dBm 30 dBm +/- 2dBm
1GHz should <-36 dBm, (>
1GHz should <-30dBm )
< 2% < 2% < 2%
500us
规则脉冲激励 /长时预测线性预
测编码。(采用 LTP 的 RPE )
Technical Reference
Transmit Frequency
Receiver Frequency
Operation voltage:
EGSM
880-915 MHz
925-960 MHz
174channel,
Every channel
contains 8 short
3.4~4.2V
规则脉冲激励 /长时预测线性预
测编码。(采用 LTP 的 RPE )
DCS
Technical Reference
Transmit Frequency
1710-1785MHz
Receiver Frequency
1805-1880 MHz
374channel,
Every channel
contains 8 short
Operation voltage:
3.4~4.2V
规则脉冲激励 /长时预测线性预
测编码。(采用 LTP 的 RPE )
PCS
Technical Reference
Transmit Frequency
1850~1910MHz
Receiver Frequency
1930~1990MHz
299channel,
Every channel
contains 8 short
Operation voltage:
3.4~4.2V
Page 7

Frame
duration
Code length 260 bit 260 bit 260 bit
Kind
使用前向纠错
码的编码比特
率
Table 3.4: Sound Coding
kind 1 为 182 bit,kind 2 为 78
20 ms 20 ms 20 ms
kind 1 为 182 bit,kind 2 为 78
bit
22.8 kbps 22.8 kbps 22.8 kbps
bit
kind 1 为 182 bit,kind 2 为 78
bit
Page 8
4. Marking and Security:
4.1 Marking:
In order to protecting legitimate rights and interests of user, economic profit of manufacturer, and attacking
smuggles and counterfeit, the domestic and foreign mobile phone manufacturers (according to the regulation
of government department) should paste series of security marks on the production when after producing, for
distinguishing and protection. There are two among them is the most important:
1) CMII
The abbreviation of CMII is the license issued by the information industries department. Both the domestic
and foreign productions factory must apply this license to the information industries department if there mobile
phone will sells in China (besides HongKong, Macao and Taiwan). The productions must paste the mark that
accesses the net when they leave factory after acquiring the license. The actual mark (use after 1st Feb.1999)
could be identified from these aspects as follow:
z The symbol is the rectangle, the bottom grain for the light blue net grain.
z Four Chinese character ‘the permit of access the net’ are printed on right side relative to the middle. The
symbol is the only group of Chinese characters.
z “CMII” is printed on the left side of the symbol "The permit of access the net ". There are three lines of
contents under the symbol "The permit of access the net": The first line permit number (each production
factory homogeneous model handset access net card number is only), its form is 02-XXXX-XXXXXX,
3-6th common representative factory serial number, second line handset model: Form like V998, N5110
and so on. The third line of form is group of numerical codes (each access net symbol not to be all same).
z The typeface on the true symbol usually printed by the needle printer, the number is clear, and the color is
shallower. It is can be seen that hits by needle if carefully look on it. The imitate symbol usually printed by
common spray-ink printer, the number is unclear, the color is darker, and no hits by needle
z The symbol uses the safety line to guard against false paper printing. This kind of paper touches different,
there is obvious convex-concave feeling on the safety line place, There is vertical lines obviously under
the ultraviolet lamp (e.g. 验钞机). Simultaneously, red fluorescence typeface ‘CMII’ appears on the right
side of the symbol (which is can not see with naked eye). There is non on the imitate one.
2)IMEI:
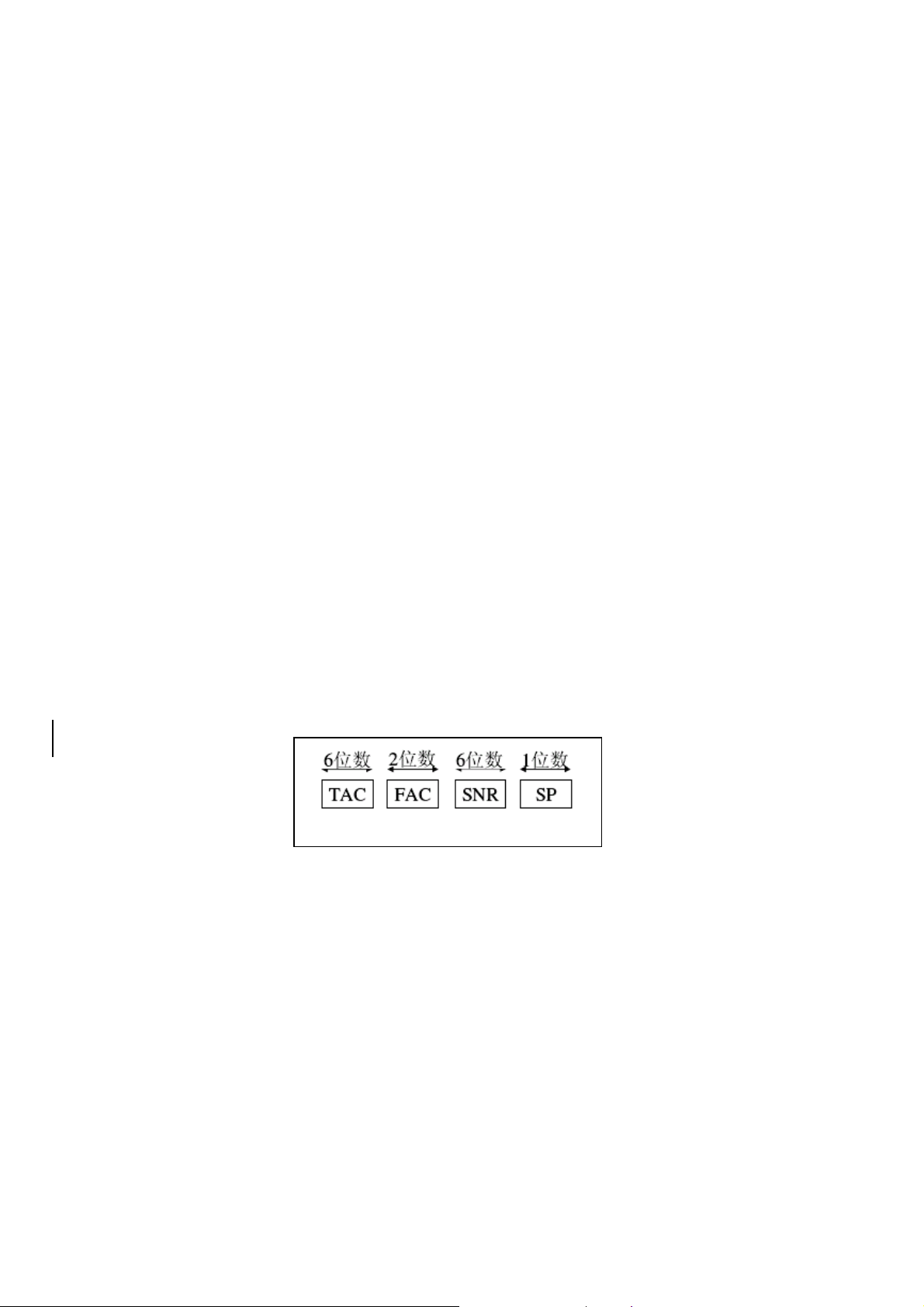
IMEI is the abbreviation of International Mobile Equipment Identification. The IMEI code is a kind of
electrical character code made up of 15 digit number. Every code is unique in the world corresponds only one
mobile phone. Every mobile phone will be match a unique IMEI code after assembly. This code will be
recorded by manufacturer in the whole production. Its composition is as follows:
The first 6 digit (TAC) is the "model approves code", standing for the type of a mobile phone. The follow 2
digit (FAC) is "final assembly number", standing for the production factory or the final assembly place. The
afterwards 6 digit (SNR) is "bunch number", standing for the production sequence number. The last 1 digit (SP)
is set to "0" which is the examination code that standby temporarily usually now.
The IMEI code is pasted on the symbol at the back of the mobile phone, and saved in the memory. It is
also the "file" and "ID card number" of the mobile phone in factory. The IMEI code can be read by pressing
"*#06#" on the keyboard. The IMEI code will be changed when displace new main board. It is necessary to
refresh new symbol for the equipment.
4.2 SIM card:
1)Brief introduction of SIM card
SIM is the abbreviation of Subscriber Identity Model (customer recognition module). SIM card is also
called smart card, ID card of user. The GSM digital mobile phone can be used when inserting this card only.
There are three kind of materials in the SIM card: Surface metallic circuit board, IC integrated circuit, black
protective hard glue. The work of surface metallic circuit board is transmitting information between IC and the
mobile phone. The black protective hard glue purely for protects IC. And IC is the important part in SIM card.
IC saved user's information, encryption key and other information in the SIM card. It identify user for GSM
network and encrypte voice information for user during the call. The work of the six blocks on the metallic
Page 9

circuit is record input information, voice, instruction of network operation business respectively and so on. The
using of SIM card prevent simultaneous calling and wire tapping. Facture of SIM card is according to GSM
international standard and criterion strictly. It ensure common communication for user reliably. The using of
SIM card divides card and mobile phone in the GSM system. One SIM card marks one user. SIM card can be
inserted in every GSM mobile phone, and the fee of communication can be recorded to the marked account of
the user. SIM card contain personal data of accessing GSM service that must be needed, they are:
z International mobile subscriber recognition
z Temporarily mobile subscriber recognition
z Main system
z Registration service
z The PIN reconciliation locks the code
z The call limits the code
z The user stores individual data. For instance, the short news, the fixed digit dialing, shrink the position
digit dialing, the performance parameter, the speech spends the register and so on
z Will access the net the numeral mobile phone, otherwise will have the possibility to cause the card to
receive the damage.
2)Security function
There is mobile phone SIM card lock function to prevent other people use the SIM card random. To
unblocking it, just input PIN code easily. The PIN code (personal Identity Number) is called individual
identification code. It is 4digit long, established by user himself. It belongs to the password of SIM card that
protect security of SIM card. Its original estate is not activating. After its starting up, GSM system will identify
the mobile phone automatically after turn on the phone every time. It will estimate validity of the SIM card, in
other words, it will check password with mobile phone. It provides services to user after approving by the
system only. There are 3 times of opportunities for input PIN code. It will lock automatically if the 3 times of
opportunities failed all. The way of unblocking it is input PUK only. PUK (PIN Unblocking Key) is the master key
for unblock the PIN code. Every SIM card has its corresponding PUK code. It is 8digit long, managed by user
himself. It is controlled by network operation business too. At present, the domestic motion bureau has opened
PUK inquire service that user could manage PUK code by themselves. There are 10 times of opportunities for
input PUK code. The SIM card will start up self-destruction program automatically if the 10 of opportunities
failed all. Then invalidate the SIM card. In this case, it is necessary to transact a new SIM card. Therefore,
please do not decode without correct PUK code
Setting calling restriction is another way of protect the SIM card. The calling restriction is away of restrict
call in and call out through establishing password. User could establish or cancel every kind of restriction of the
mobile phone at will, preventing call out by mistake, stealing call, especially international long distance call,
avoiding unnecessary loss. The password of calling restriction is 4digit long which the original estate is 0000.
The user who transacts this service should modify the original password, for improving the security. The calling
restriction could be set according to both file way and coding way. These two ways of setting have the same
effect. It is noticed that this kind of service is for user only who use international long distance service, and it
can not be used with calling diversion service at the same time
Page 10

5. Introduction of GSM System:
5.1:The history and development of GSM:
1981 Analogue cellular introduced
Franco-German study of digital pan-European cellular system
1987 MoU signed by over 18 countries
1989 GSM was moved into the ETSI organization
GSM name changed to Global System for Mobile communications.
1990 DCS1800(edited GSM900) specification developed
In 1981 analogue cellular was introduced and at about the same time there was a joint Franco-German
study looking at digital cellular technology and the possibility of making a pan-European system..
In 1982 a special working committee, Groupe Spécial Mobile (GSM), was formed within the CEPT to look
at and continue the Franco-German study. In 1986 the working committee was taken a step further by
establishment of a permanent nucleus of people to continue the work and create standards for a digital system
of the future. About a year later, the memorandum of understanding, or MoU, as it is referred to, was signed by
over 18 countries. It stated that they would participate in the GSM system and get it into operation by 1991.
In 1989 GSM was moved into the ETSI (European Telecommunications Standards Institute) organization.
Once under the control of ETSI, the GSM system had it's name changed to Global System for Mobile
communications. The committees working on the system changed from GSM to SMG (Special Mobile Group).
These changes avoided confusion between the system name (GSM), and the people working the specification
(SMG). It also brought the naming in line with the official working language of ETSI (English).
In 1990 the GSM specification developed an offshoot - DCS1800. The Original DCS1800 specifications
were developed simply as edited versions of the GSM900 documents. Interest in GSM quickly spread outside
Europe. In 1992 Australia became the first non-European country to join the MoU. Since then, many other
Asian countries have adopted GSM. There's now a Pan-Asian MoU, investigating international roaming
agreements.
The Phase II specification for GSM has now been defined, merging GSM900 and DCS1800 documents,
number of new features are added to the system, along with many minor adjustments. The next step, Phase
II+ defines the addition of specific new services such as data and fax to GSM and DCS1800.
5.2: GSM Network
This is the GSM system. The Mobile Stations (MS), both hand held (portables) and traditional mobiles in a
car, talk to the Base Station System (BSS) over the RF air interface. The Base Station System (BSS) consists
of a Base Transceiver Station (BTS), and a Base Station Controller (BSC). It's typical for several BTS to be
located at the same site, producing 2 to 4 sectored cells around a common antenna tower. BSC's are often
connected to BTS via microwave links.
The BSC to BTS link is called the Abis interface. Typically 20 to 30 BTS will be controlled by one BSC. A
number of BSS's would then report back to the Mobile Switching Center (MSC) which controls the traffic
among a number of different cells. Each (MSC) will have a Visitors Location Register (VLR) in which mobiles
that are out of their home cell will be listed, so that the network will know where to find them. The MSC will also
be connected to the Home Location Register (HLR), the Authentication Center (AUC), and the Equipment
Identity Register (EIR) so the system can verify that users and equipment are legal subscribers. This helps
avoid the use of stolen or fraud mobiles. There are also facilities within the system for Operations and
Maintenance (OMC) and Network Management (NMC) organizations. The Mobile Switching Center (MSC)
also has the interface to other networks such as Private Land Mobile Networks (PLMN) and Public Switched
Telephone Networks (PSTN) and ISDN networks.
5.3 :GSM Air Interface:
In GSM, the GSM transmission between MS and BS is Radio Communication, let’s introduce the GSM Air
Interface.
1):Channel Plans:
Page 11
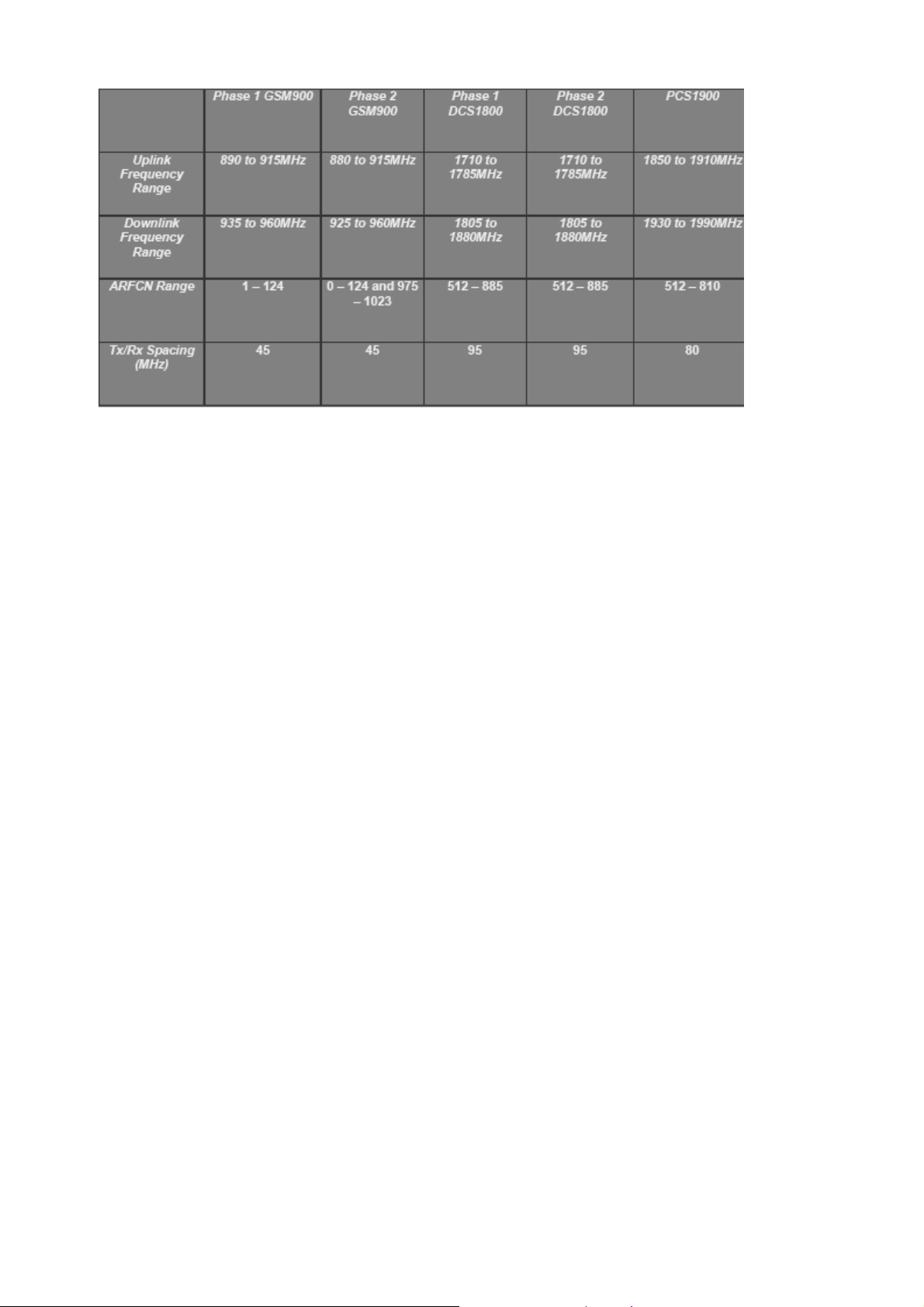
Above is a table that shows the relative frequency plans of the three GSM networks: GSM900, DCS1800
and PCS1900.
The frequency range of the Uplink and Downlink show how the two bands are split into the two directions,
rather than an uplink being followed by a downlink 200kHz later. Another difference is that the channel
numbers are different. Remember this if you write any test control software and want to port from one system
to another, as the channel numbers must be changed for correct operation.
2):GSM FDMA and TDMA:
GSM uses TDMA (Time Division Multiple Access) and FDMA (Frequency Division Multiple Access). The
slide shows part of one of these bands. Each band is divided into 200kHz slots called ARFCN’s (Absolute
Radio Frequency Channel Numbers).
As well as dividing up the frequency, the ARFCN is also divided in time into 8 Timeslots (TS), each TS
being used in turn by a different MS. The 8 TS’s together are known as a Frame.
3):Physical Channel:
The combination of a TS number and ARFCN is called a physical channel. The corresponding Number is
called ARFCN (Absoluteness RF Channel Number). One ARFCN assert a pair of channels, one is uplink, the
other is downlink. This pair of channels is called physical channel.
In GSM system , the frequency interval is 200kHz.
The ARFCN of PGSM is 1~124,the center frequency of CH1 uplink is 890.2MHz. When the value of
ARFCN is equal to n, center frequency uplink channel is fn=f1+(n-1) 200kHz 。The center frequency of
corresponding downlink channel need to add duplex frequency separation, PGSM is 45MHz.
We need declare that, because of the PCD system is only used in North American, and no DCS system
used, these two systems can not be exist at the same area, the ARFCN of DCS and PCS system can overlap
with each other.
Modulation Mode:
4):
Now the signal can be modulated with a 0.3GMSK modulation scheme.
5):TDMA Burst:
The burst can be divided into three distinct areas:
• Ramp Up
• Useful Part of the Burst
• Ramp Down
All of these levels are controlled by the GSM standard.
The Useful Part of the Burst is the area where the modulated data is present. There are 148 bits (each bit is
represented by a single symbol in 0.3GMSK modulation) which will be examined more closely in a later
section.
GSM is part of
6):
Duplex Timing:
TDMA system,
Downlink and Uplink
¦Uplink Lags Downlink by 3 Timeslot periods
¦Uplink and Downlink use same Timeslot Number
¦Uplink and Downlink use same Channel Number (ARFCN)
Page 12
¦Uplink and Downlink use different bands (45MHz apart for GSM900)
In the previous example we can see that the timeslots are offset by 3 between the downlink and the
uplink. We receive information in timeslot two in the downlink we have two timeslots in which to switch to
the uplink frequency and be ready to transmit information. Then, we have to get ready to receive our next
time slot of information in the next frame.
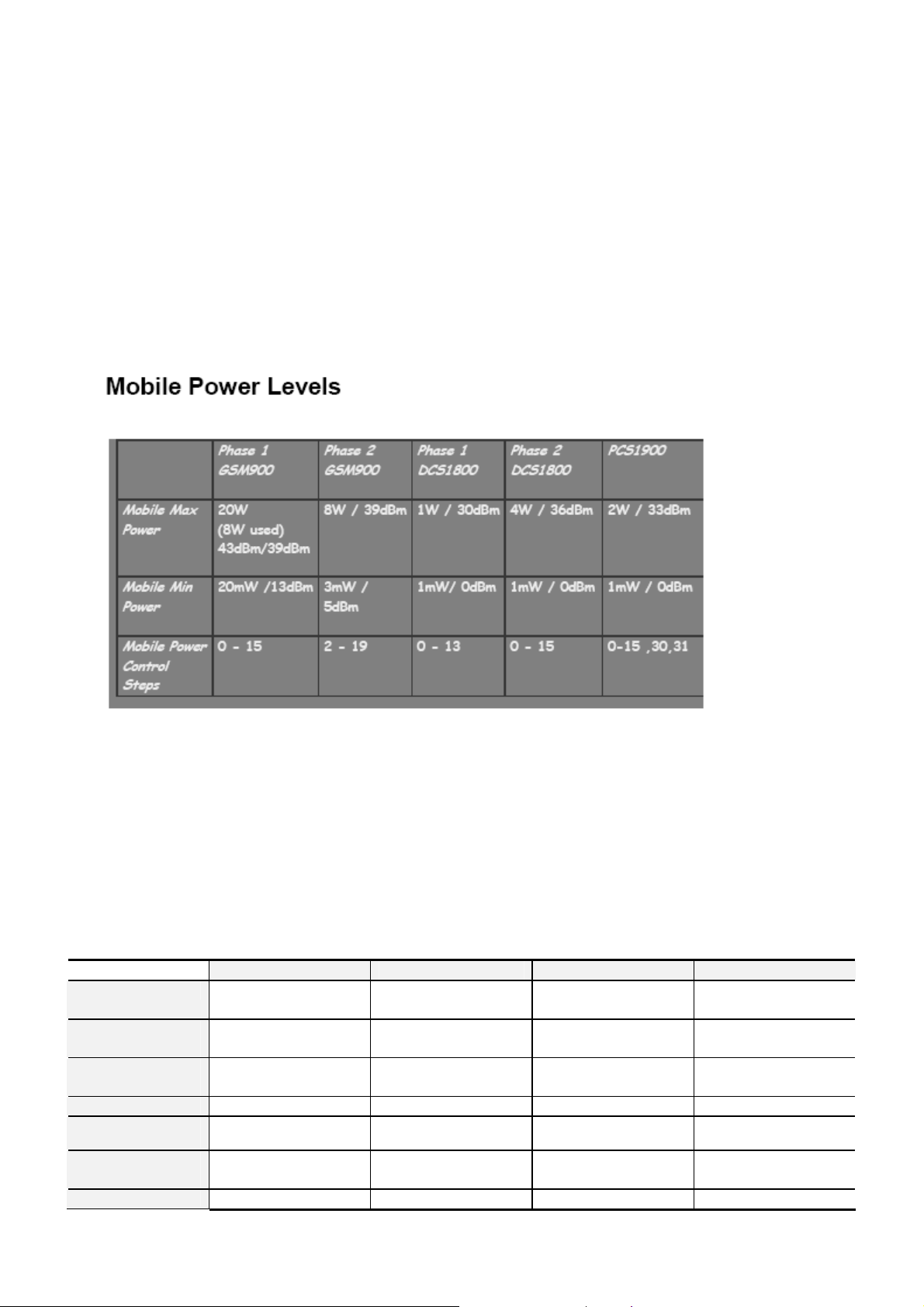
7):Power Control:
As the mobile moves around the cell, its transmitter power needs to be varied. When it's close to the base
station, power levels are set low to reduce the interference to other users. When the mobile is further from the
base station, its power level needs to increase to overcome the increased path loss. However, if too much
power is used, the user’s battery will run down too quickly. All GSM mobiles are able to control their output
power in 2dB steps. The base station commands the mobile to a particular MS TX Level (power level) by
watching the power level of the received signal at the BS.
There may be man y users in the same cell. If every Mobile phone has the same emission power,
ones closer to Base Station can block the ones which are farther; On the other hand, because if closer ones
emit more power
The table above shows the maximum and minimum power levels on the mobiles in different systems. The final
row shows the power steps, which are all numbered, and how they relate to the max and min powers.
8):Timing Control:
If the burst arrives at the correct time, it will fit into its physical channel and not disturb any other burst that may
follow it in the next timeslot. However, if it is delayed, due to a long distance to travel, it may arrive late and
impact the following burst from another user. In this case the mobile is instructed by the BS to burst earlier
which will correctly align the burst in the timeslot. The message sent by the BS is called the Timing Advance.
The base station monitors the burst to see when it arrives at the base station. If it arrives late or early, the base
station will note how many times it has changed since the last Timing Advance adjustment, and if there have
been more than 4 x ¼ bit periods change in one direction, the adjustment will be made again.
Main parameter of GSM is showed as follows:
ARFCN Range 1~124 975~1023, 0,
PGSM EGSM DCS PCS
512~885 512~810
1~124
Uplink Band
Range
Downlink Band
Range
Bandwidth
duplex Interval
Frequency
TDMA User
890MHz~915MHz 880MHz~915MHz 1710MHz~1785MHz 1850MHz~1910MH
z
935MHz~960MHz 925MHz~960MHz 1805MHz~1880MHz 1930MHz~1990MH
z
200kHz 200kHz 200kHz 200kHz
45MHz 45MHz 95MHz 85MHz
8 8 8 8
Number
Modulation Mode
0.3GMSK 0.3GMSK 0.3GMSK 0.3GMSK
Page 13

Power Grade
Range
Max Power 33dBm 33dBm 30dBm 30dBm
Power Grade
Difference
5.4:Identity:
If user want to connect to network, GSM need affirm users’ legality identity. Users’ identity information
recorded in SIM. According to these information, network affirm user’s validity. Important Digital Identification
used in GSM include:
1. IMSI(International Mobile Subscriber Identification)
This number is the exclusive number to indicate user’s identity. When user enter network, the system find
user’s information according to this number. It is composed by three parts:
MCC(Mobile Country Code)Country Number, three digits, indicate user’s country.
MNC(Mobile Network Code)Mobile Network, two digits, indicate Network Operator.
MSIN(Mobile Subscriber Identification Number)User Identity Number, eleven digits, indicate Mobile
Subscriber in network.
2. TMSI(Temporary Mobile Subscriber Identification)To safeties, we use TMSI instead of IMSI when
transmitted IMSI, TMSI is valid only in local area. Its structure is selected by manage department, and the
whole size is not more than 4 bits.
3. IMEI(International Mobile Equipment Identity)exclusive number, system also can distinguish validity of
equipment by this number.
5.5:GSM Voice Path :
There needs to be some way to encode the voice into data
Next the data must have error protection added to it
The Data has further error protection
It is modulated
It is bursted
Again, this is very simplistic and other steps will be explored during this section.
5.6:logical channels
TCH :Mobiles on a call use a Traffic Channel (TCH). The TCH is a two way channel used to exchange
speech information between the mobile and base-station.
SACCH :When the MS is on a call, it is constantly monitoring the Received Signal Quality (a bit error rate
measurement known as RxQual) and the Received Signal Level (a power measurement call RxLev). These
are constantly being sent back to the BS on a Slow Associated Control Channel (SACCH).
FACCH:The Fast Associated Control Channel is used to pass critical information to the mobile during a
call, by taking over the TCH from the callers.
BCH:All BTS produce a Broadcast Channel (BCH). The BCH is like a lighthouse or beacon. It's on all the
time and allows mobile to find the GSM network. The network for a variety of user functions also uses the BCH
signal strength. It's a useful way of telling which is the closest BTS to the mobile. It also has information coded
onto it, such as the identity of the network (e.g. Mannesmann, Detecon, or Optus), paging messages for any
mobiles needing to accept a phone call, and a variety of other information. Each mobile will monitor the power
of adjacent cell BCH’s to aid the network in making hand-off decisions.
FCH:Frequency Correction Channel
SCH:Synchronization Channel
BCCH:Broadcast Control Channel
CCCH:Common Control Channel
The base-station posts a PCH (paging channel) on the CCCH part of the BCH. When the mobile receives the
PCH, it responds by sending a RACH. The remainder of the process is identical to the mobile originated case.
AGCH:Access Grant Channel
RACH:Random Access Channel, When the mobile sends out a RACH, to start a call, to avoid collisions
with bursts in adjacent TS, RACH bursts, that are shorter than normal are sent.
The Stand-Alone Dedicated Control Channel (SDCCH) is used during call set up as a stepping stone to
the Traffic Channel. It is also used to pass signaling when the mobile is in IDLE mode. This is used for example
for SMS Point-to-Point messages as well as Location Updates that we will look at later.
5~19 5~19 0~15 0~15
2dBm 2dBm 2dBm 2dBm
Page 14

5.7 Mobile Turn-On
1)Mobile Searches for Broadcast Channels (BCH)
2)Synchronizes Frequency and Timing
3)Decodes BCH sub-channels (BCCH)
4)Checks if Network Allowed by SIM
5)Location Update
6)Authentication
When a mobile first turns on, it searches all 124 channels in the downlink for signals. It will then order the
channels by received signal strengths and check to determine if the channel was a BCH (Broadcast CHannel).
Once the MS finds a BCH, it adjusts internal frequency and timing from the FCH and SCH, then checks to
determine if the BCH is from its PLMN (Public Land Mobile Network). This involves comparing the allowed
network and country codes stored on the SIM card with the information encoded on the BCCH. The mobile
repeats this cycle until a good broadcast channel is found. If the mobile recognizes that it's in a different cell
from the last time it was used, it needs to tell the network where it is. The network has to keep track of where
every mobile is so that it can route calls to the correct cell for any particular mobile. This process of telling the
network "here I am" is called a location update. The mobile sends a RACH, gets assigned to an SDCCH,
exchanges control information, then ends the call. The user will typically not be aware that this process is
taking place.
For Location Updates, this time showing which part of the network is involved in transactions.
The IMSI attach/detach process is a way of forcing all mobiles to inform the network when they have
camped and when they have turned off (or just before they turn off!). The SIM stores the last location Area
Code (LAC) when it is powered down and it compares this to the camping LAC on Power up and if they are
different it will perform an IMSI attach.
Mobile Originated Call
Mobile Sends RACH
Channel Assignment Posted on BCH (AGCH)
Mobile and Base Station communicate on SDCCH
Authentication
Mobile Assigned to Traffic Channel (TCH)
Speech Data sent and received
Once camped, the mobile is ready to send or receive calls.
When a user dials a number, and presses the send button on the mobile, call origination takes place. The
mobile transmits a short RACH burst on the uplink, using the same ARFCN as the BCH is using on the
downlink. The base station responds to the RACH by posting an AGCH (Access Grant CHannel) on the CCCH.
These are logical channels on the BCH physical channel. The mobile listens on the BCH for the AGCH, when it
receives it and decodes the instructions, it re-tunes to another ARFCN and/or timeslot and begins a two-way
dialogue with the base station on an SDCCH. One of the first things that the mobile will mreceive is the SACCH
associated with the SDCCH. Once it receives the SACCH, it will get timing advance and transmitter power
information from the base station. The base station will have calculated the correct timing advance from the
arrival time of the RACH. Once the mobile gets timing advance information, it can send normal length bursts.
The SDCCH is used to send messages back and forth, taking care of alerting (making the mobile ring) and
authentication (verifying that this mobile is allowed to use the network). After a short period of time (1 to 2
seconds), the mobile is commanded over the SDCCH to re-tune to a TCH. Once on the TCH, speech data is
transferred on the uplink and downlink.
Mobile Terminated Call
Mobile Sees Page
Mobile Sends RACH
Channel Assignment Posted on BCH (AGCH)
Mobile and Base Station communicate on SDCCH
Authentication
Mobile Assigned to Traffic Channel (TCH)
Speech Data sent and received
The process for base station originated calls is very similar. The base-station posts a PCH (paging CHannel)
on the CCCH part of the BCH. When the mobile receives the PCH, it responds by sending a RACH. The
remainder of the process is identical to the mobile originated case. If you can find a way to translate the GSM
bursts into audio tones (AM demodulate), it's interesting to hear the difference between the channel types as a
call is set up. A good way to do this is to use a GSM phone near an old TV set or a conventional wired phone.
Page 15

The interference created in these devices amounts to AM demodulation.
The RACH burst can be heard as a single 'Tick' sound. It's quickly followed by the SDCCH 'Tat, Tat-tattat,
tat-tat-tat ...'. After a few seconds, the TCH is connected 'Buzzzzzzzzz'.
Mobile Handoff
We have covered mobile power on and call establishment, but there is one other important area. During
a call the mobile may have to change base stations. If the call is between faces of the same base station, this
is performed locally. The case shown here is that where the base station is not the same. The mobile reports
its measurements and the serving BSC determines that it is time to perform a handoff. It will contact the new
base station and get the information on the new channel and timeslot (along with midamble and timing
information) and send this to the mobile. It then commends the mobile to switch base stations and then once
the new call is established, close down the old link and reallocate it to another user if necessary.
Page 16
6. Summary introduction of mostly chips used in PEAN
Chips used in PEAN can be divided into flat and application manage according to function. There is the
introduction of these two chips
6.1:Flat Chip:
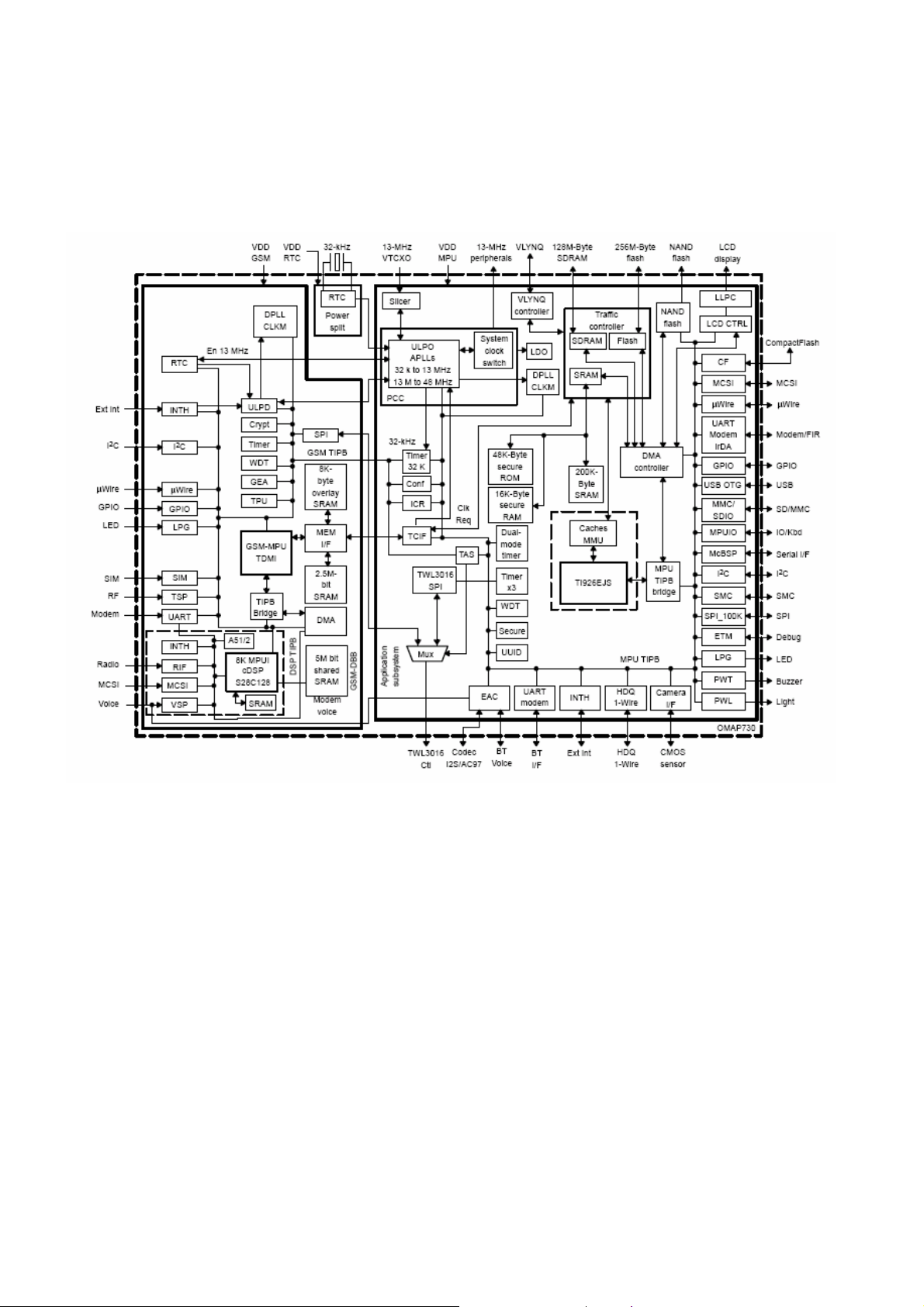
U201:DBB——Digital Base Band, composed of ARM7 TDMIE CPU and TMS320C54X DSP dual inter
core. The chip integrate 4Mbit Memory inside、provide multi control interface outside. There is the basic
structure as follows:
Figure6.1: DBB basic structure
Main structure characteristic and function of DBB (Part Number is D751992AGHHR ) including:
Nuclear working voltage 1.5V (1.35-1.65V ), IO voltage 2.8V( 2.5V-3V )
Working temperature range -40~ +85℃
CPU working at 52MHz, DSP working at 104MHz
Integrate 4Mbit SPAM Memory inside
289 pin uStarBGA encapsulation
U201:ABB——Analog Base Band, is the bridge of digital and analog signal in the system. Audio, IQ and
other exterior analog signal can connect with DBB control centre through ABB. ABB controls system clock, A/D
D/A conversion, background light of keyboard, provide system power and charge interface etc. There is the
basic structure as follows:
Page 17
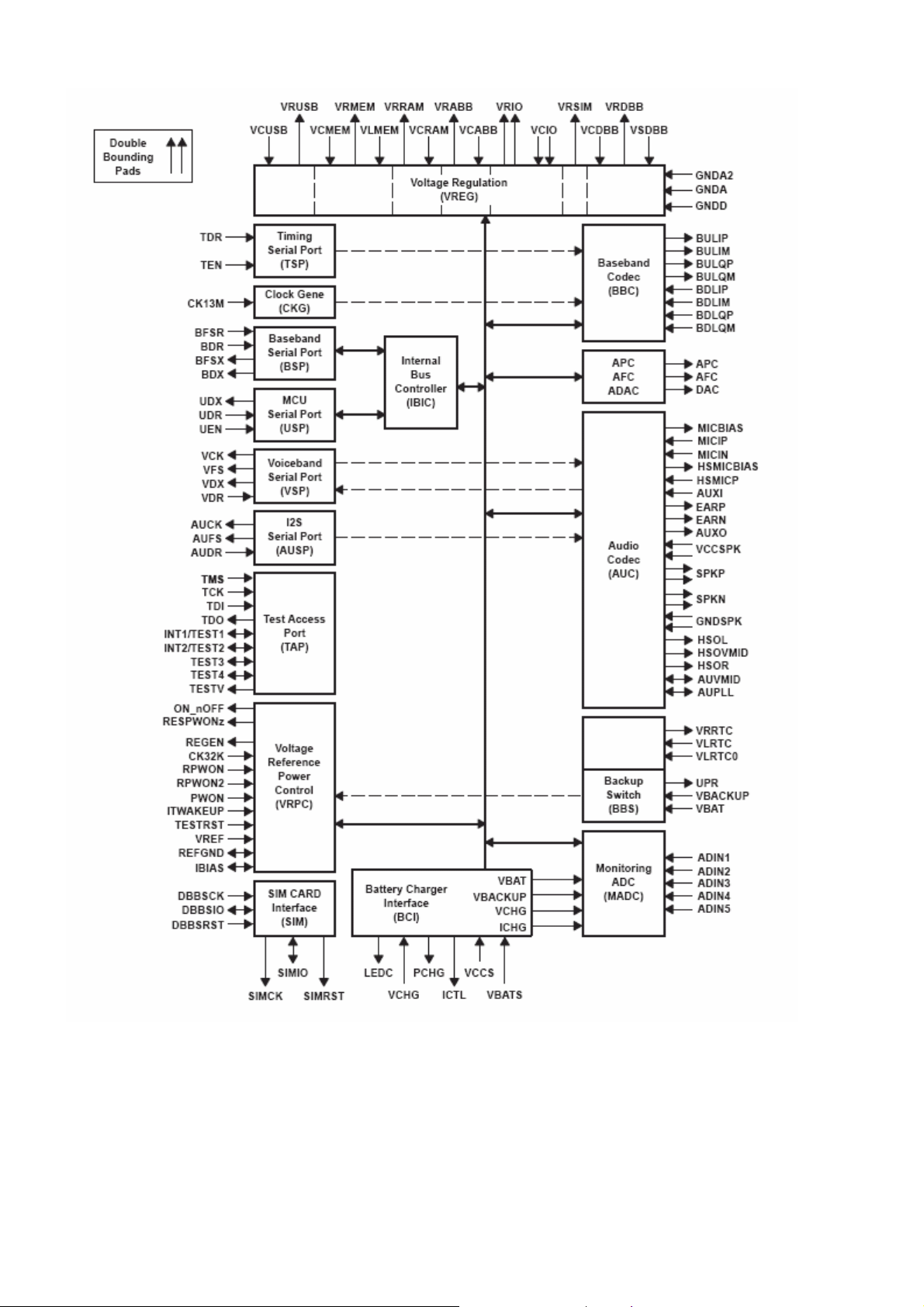
Figure 6.2: ABB basic structure
U682:Transceiver: is a high integrated multi frequency low power cost transceiver, there is the structure
as follows:
Page 18
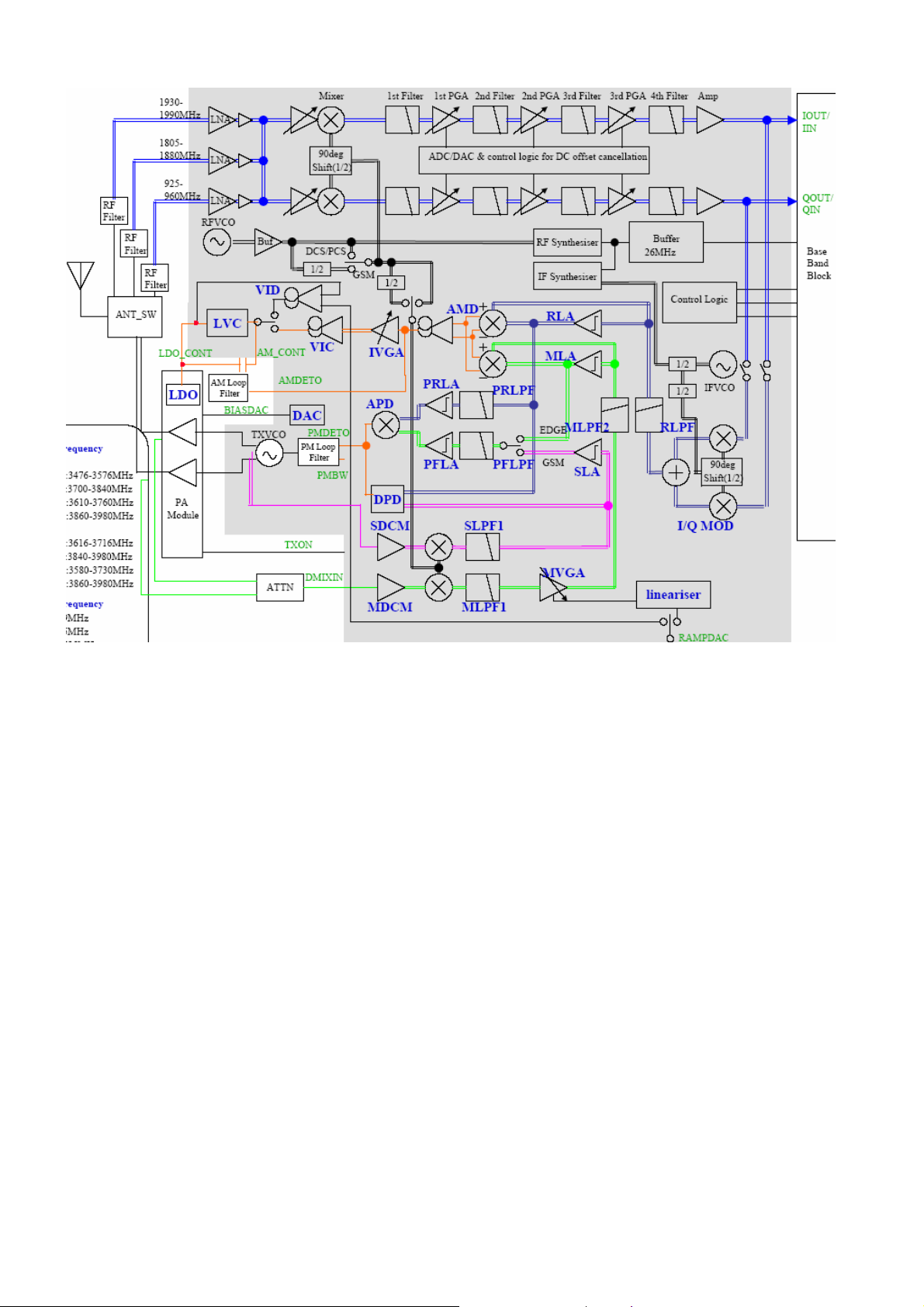
Figure 6.3: Transceiver structure
Main function and characteristic of U682:
Support GSM850, GSM900, DCS1800, PCS1900 multi frequency cell system
Support GPRS Class 12 and EDGE operation
Contained a synthesizer, 4 fully compositive VCO, 3 regulator and PA controller
3 bios serial interface
48pin QFN48 encapsulation
IO working voltage 2.8V(2.7-2.9V)
Working temperature -30℃~ +85℃
U603:U603(PF09016B-TB),is a 3 band power amplifier module integration with power control function.
With its control part, signal’s amplify and signal’s power control can be made by itself only. It is divided to low
frequency band(GSM850/EGSM900) and high frequency band(DCS1800/PCS1900). Every part of the
amplifier is combined with 3 sect amplifier. Export power is controlled by a inter power control module, which
realize the control function through changing 3 sect amplifier’s deflection set. Power export of low frequency
band could reach 37dB, power export of high frequency band could reach 34dB. Spec value of working voltage
is 3.5V, in/out impedance is 50 ohm. There is the structure as follows:
Page 19
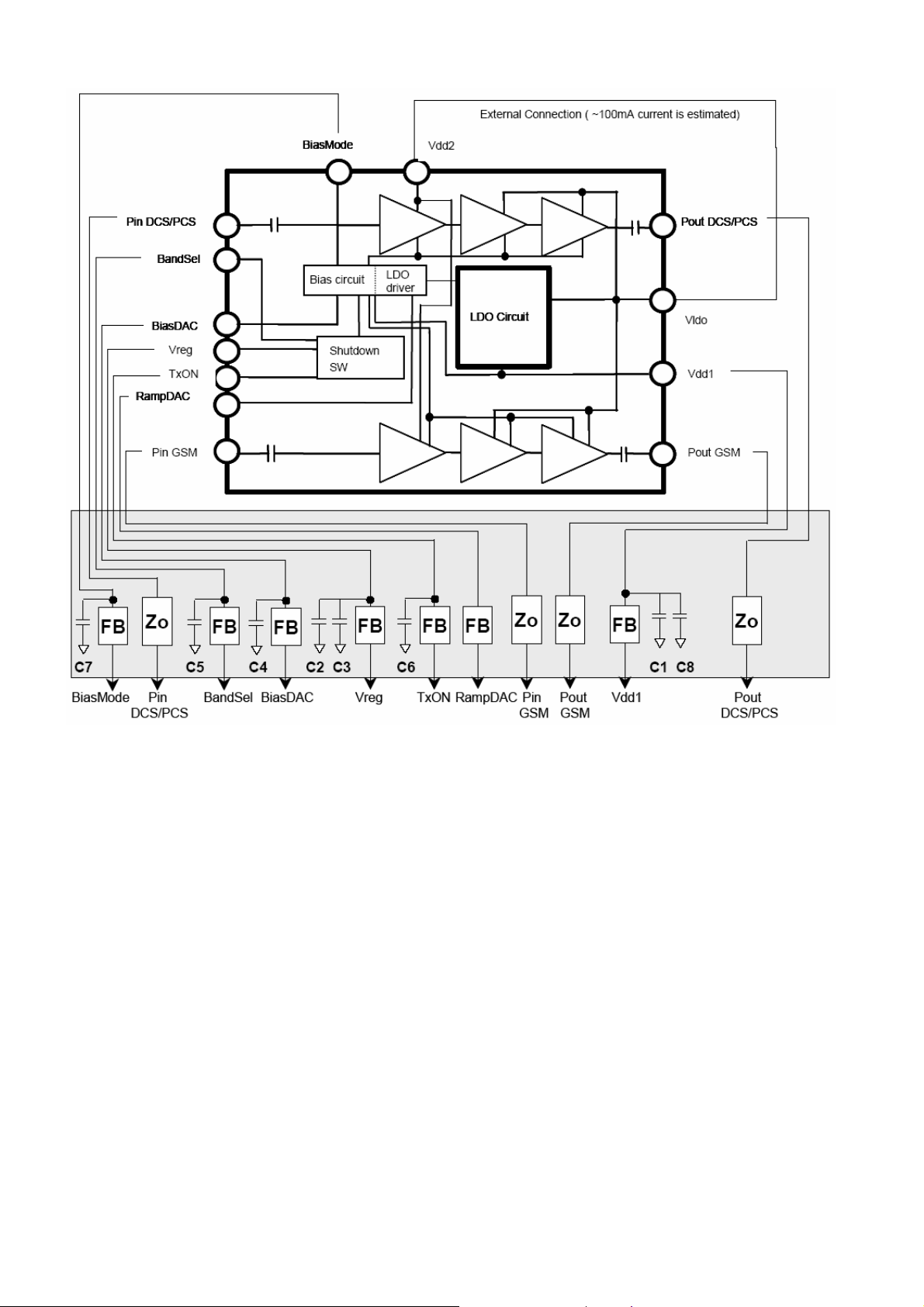
Figure 6.4: PA structure
Definition of main pin: spec value of working voltage VBAT1、VBAT2 is 3.5V, provided by battery of mobile
phone. TX-ON is the power set of amplifier, at high level is (1.5V~2.8V,spec level 2.0V) amplificatory state; at
low level is (0V~0.5V,spec value 0V) idle state. Bandsel is band selecting signal, GSM band select pass at
low level (0V~0.5V,spec value 0V), DCS band select pass at high level(1.9V~3.0V,spec value 2.0V).
VRAMP is frequency modulate control level, around 0.2V-1.8V
Page 20
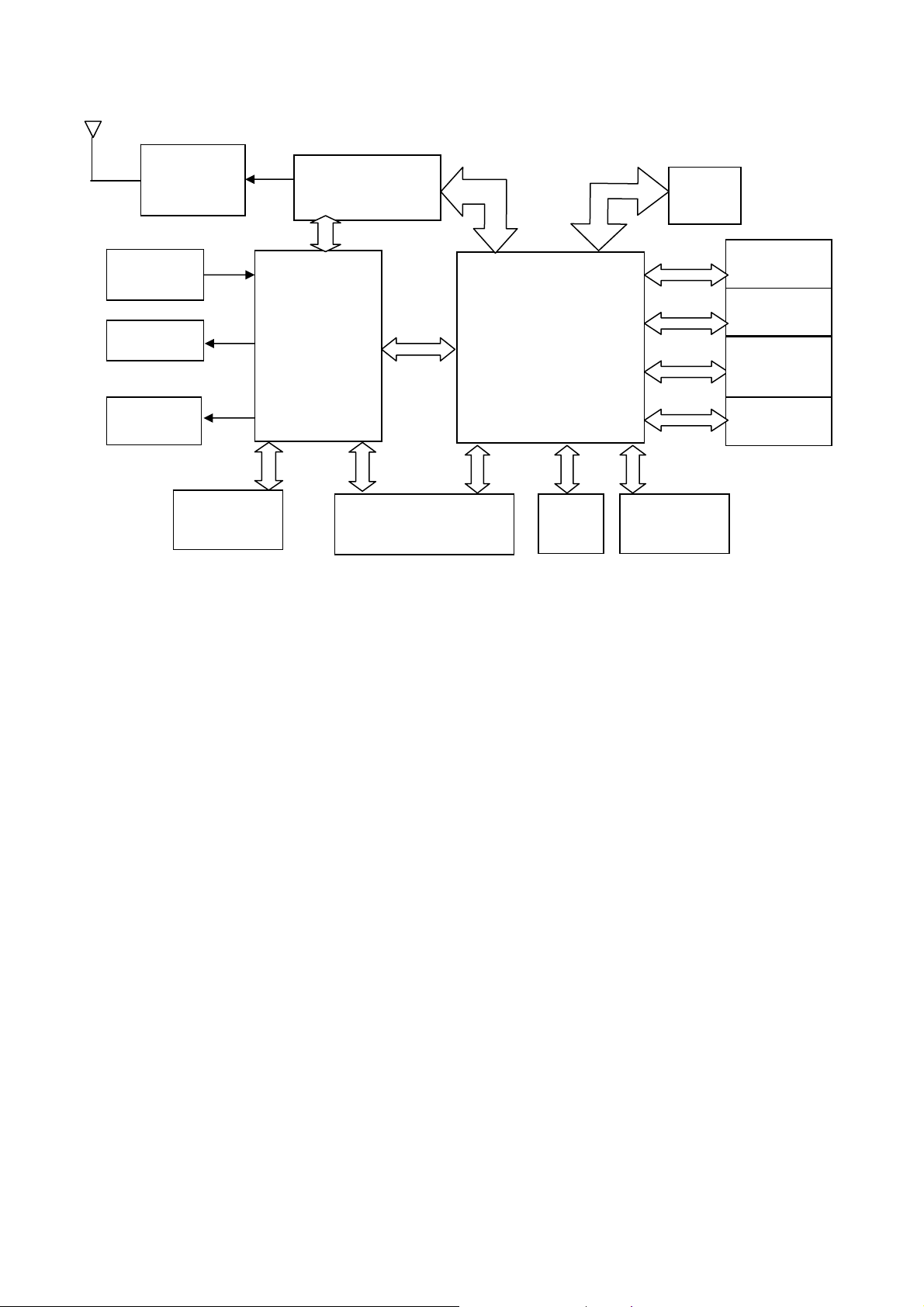
图 7.1:PEAN 基带电路原理示意图
Figure 7.1 shows basic control flow of PEAN mobile phone
It is shown in the picture that U201 is the core of control in the whole system. It carries out all programs
storage in U307, and control the whole system through U202, U5(M-DOC), U4(SDRAM)
According to the difference of function, PEAN can be divided as: RF process circuit (including receiver
part and transmit part), audio interface circuit (Mic、Receiver、ear phone Mic and ear phone Receiver) and
charge circuit, Sim card interface circuit, backlight control circuit, display circuit and camera process circuit etc.
Before introduce these circuit cell, it is necessary to know clock circuit and power management in the
system——because these two are the base or working
7.2 System clock circuit introduction:
Clock is the base of system control in every control system. So, it is necessary to know the output and
control theory of clock in PEAN mobile phone.
There are 2 kind of clock in the system: one is 32.768KHz for display time — —provided by
Y201(32.768KHz crystal); the other is work clock for system working——provided by(26MHz crystal)
1. RTC——Real Time Clock
Y201 connect to U200 through the matching network combined with C201, C204, C203, C204 and
R201, provide RTC for U200
Power supply of Y203 is provided by H1 in U202, it is V-RTC in the theory structure
V-RTC can be defined as 1.8V, 1.5V and 1.3V by software (There is 1.5V in PEAN)
Power supply of RTC circuit provided by main battery VBAT usually, and provided by standby battery
(standby battery provide V-RTC only) when main battery lack of electric power or take off the main battery (e.g.
when changing Sim card) . Electric power provided by standby battery is limited (support RTC circuit for only a
few hours). Therefore, it is necessary to keep power supply provided by VBAT in sure time interval that prevent
RTC information missing.
2. System clock circuit
Y202 (26MHz crystal) provide base value for system clock
connect to pin C12 of U202, which provide AFC (AFC:Automatic Frequency Control) for 26MHz crystal; the
PF09016B
(PA)
MIC
Speaker
Receiver T-Flash
Earphone
C206, R201, D201, C202, R220 and C205 provide matching circuit for Y202. One side of this circuit
155154NPTEBE (transcevier)
U202
TWL3027B2G
WQ
(ANALOG
BASEBAND)
Supply Management
BQ24070
Figure 7.1: PEAN base band circuit structure
U201
OMAP 850
LCD
WI-FI
Bluetooth
M-DOC
DDR
-SDRAM
2M
Camera
Page 21

other side of this circuit pass through a more complicated path to provide system working clock:
a: first, input 48pin on U682, provide working clock for U682
b: then, processed in U682, pass through 47pin on U682 input Y9 on U200——provide 26MHz working
clock for DBB
c: and then, processed in U201, pass through N1 output 13MHz clock for other exterior equipments:
pass through E1 on U202 provide ABB clock
7.3: System power management introduction:
In the mobile phone system, because of using many equipment and interface, lead to considering many
kinds of power is necessary (generally 6 or 7). As the technology improved, now, most of these electrical
source are provided by flat chip. Using power management provide additional power only when the flat chip
can not match design conditions
According to the classify principle above, introduce power management of PEAN follows:
a: Source from flat
Source from flat is provided by U202(ABB), its power and use are in the table:
Title Pin voltage Current Benefited Chip
V_DBB
V_ABB H10 2.8V 80mA
V_IO
V_FLASH G1 2.8V 60mA
V_SRAM F1 2.8V 50mA
V_SIM B4 2.9V 10mA
V_RTC D1 1.5/1.3V
Table 7.1: A19 system flat power distribute
b: Source outside the flat
PEAN use U309,U301,U303——LDO(Low Dropout) provide system additional power needing 2.8V,
1.8V and 1.578V, for prevent lack of power in system
J1、H2
B1、B2
1.5V 170mA
2.8V 100mA
U201:main working voltage
U202:analog circuit working voltage
U104、U200、U301、U302 和 U305:system digital
IO interface working voltage
U300:Flash working voltage
U300:RAM working voltage
U201:Sim interface working voltage
U203:RTC circuit working voltage
U200(CPU) VDDSHV9,VDDSHV2,VDDSHV6,VDDSHV4,VDDSHV8
1
U309
(V-1O-2)
2 U310(LDO enable)
3 U307(SDRAM)
4 J403( T-FLASH)
5 Q430(EARPHONE) R481,SDMC-DAT0,SDMC-DAT1,SDMC-DAT2,SDMC-DAT3
6 U500(IRDA) VIO,VCC
7 CN1(LCD) CN700
8 J740(KEYPAD) KBR0,KBR1,KBR2,KBR3,KBR4
SW720(UP)
9
SW721(DOWN)
SW723(CAMERA)
U490,VCC,2.8V
U491,VCC,2.8V
1 OMAP(CPU) VDDSH1,VDDSH3
U301
(MEMARY)
2 U302(SDRAM)
3 U307(M-DOC)
4 U402(CHARGE)
Page 22

U303(V-CORD) 1 U200(OMAP730) VDDOMPE,VDD
Note: This LDO encapsulation is very small, it may weld unstable when jointing, then lead system working
abnormally. Therefore, make sure this LDO output normally first before adjusting hardware
7.4: RF process circuit----receiver circuit
Figure 7.2: PEAN receiver structure
As the figure shows: downlink from base station to mobile phone leaded into receiver circuit by antenna.
The receiver circuit mainly contains Antenna, RF-Connector(CN600), RF-Switch(FE601), Transceiver(U682),
DBB(U201) and ABB(U202) etc.
PEAN use inter antenna. The antenna is paste on back cover of the mobile phone in the antenna area
through glue on back of antenna. After main board’s assemble, feed point of antenna must be pressed well
with input of antenna on main board. Signal intension rest with connecting between antenna and main board,
so make sure of the two contacts well
CN600 is test jack match with factory when calibrating RF. The switching inside is mechanical, break up
when the test probe insert, signal input to mobile phone or output from mobile phone through probe. After
probe exiting, switching close up, signal output from antenna. The max impedance of CN600 is 50 ohm, max
insert loss is 0.1dB
FE601 is a RD-switch controlled by DBB(U200), its working band is GSM, DCS and PCS, structure as
follows:
Page 23

DDB(U201) set voltage for V_TX_LOW and V_TX_HIGH which is two control unit of FE601 through
external gate circuit Q601_A and Q601_A indirect. Control signal TSPACT01 and TSPACT02 from U200
control if set high to V_TX_lOW and V_TX_HIGH for RF source V-TX through estate (connect/cut off) of
Q601-A and Q601-B. Then realize to control working estate of U101
Logic of control is as follows:
When the mobile working, high frequency signals are divided into two paths balanceable output by FE601
after received by antenna. These two paths of signals input U682 from pin GSMLNA1 and GSMLNA1B (or
PCSLNA1 and PCSLNA1B or DCSLNA1 and DCSLNA1B) respective. First, do low noise magnify, after
magnify input I.Q mixer (which contains high/low paratactic two mixer part), mix with surge signal caused by
local oscillator in U104, these surge signals must match the currently working frequency of mobile phone.
Modulate them into four low frequency I.Q signal around 100KHz after mix (there is phase relation in these four
paths of signal). Second, I.Q must input in low pass filter for eliminate syntonic interfere. After this process,
input signals into channel filter. Channel filter is a five-class belt passes filter with self adjust function. Its center
frequency is 100KHz. For avoid leading distortion caused by signal attenuated too much after many times
sieve, before sieve, it should match 8dB step magnify for each class. Signals after sieve match 4dB step
magnify for compensate direct current excursion. Finally, these signals input intermediate frequency buffer
waiting for input U201 ABB which will manage them.
I.Q signal is transfer into digital signal by ADC when input in ABB, then output from ABB to U201 DBB.
DBB do farther digital sieve to these signals, GMSK demodulating, complect removing, decoding, channel
decoding, PCM decoding etc. voice decode arithmetic manage. Then the signals passes VSP port (Voiceband
serial port) between U201 and U202 into U202 and managed by DAC in U202. Finally, analogy signal are sent
to earphone or headphone and transfer them into voice signal.
Page 24

7.5: RF manage circuit----transmit circuit:
As the picture shows: transmit circuit is made up of: DBB(U201)、ABB(U202)、Transceiver(U682)、
PA(U603),RF-Switch(FE601),RF-Connector(CN600),Antenna etc.
Voice signal from user is transmit into analogy electronic signal, and then input in ABB U202. After
transferred by ADC in U202, pass VSP port into DBB U201. In U201, signals will be impulse sampling, PCM
coding, channel coding, coding, complecting, GMSK modulating etc. voice demodulating manage, and then
pass BSP path into ABB U202. Managed signals by DAC in ABB, divided into four paths of analogy base band
I.Q signal after passing low frequency filter. Finally, input these signals into transceiver U682
In U682, base band signal is modulated to transmit intermediate frequency by I.Q modulation. This I.Q
modulation with low harmonic wave distortion, low carrier wave divulge, high syntonic interference restrain etc.
can reduce phase error furthest. Then pass high frequency modulate, signal are modulated to final frequency
needed. Finally, the signals are sent to PA for magnifying.
Page 25

RF signal after PA magnifying pass RF-Switch (Now RF-Switch should be transmit elect connect estate)
to antenna then send out.
Mini USB connector:
Charging circuit:
SIM card interface circuit:
Page 26

Definition of SiM card reader pin is as follows:
GND: grounding port
SIM_Vcc: SIM card power supply, normally 3V (U202 can supply two mode that 2.9V/1.8V)
RST: SIM card reset signal
I/O: Input/Output port of user’s information in SIM card, signal should be square wave
CLK: clock in SIM card
SIM card is voucher of network of a mobile phone. Mobile will display ‘please insert a SIM card’ when
there is no SIM card in mobile phone. Only if the user’s information in SIM card is legal, could the mobile phone
do networking, finish user’s operation, and record other kinds of information. U201 as interface circuit and
management circuit, provide working voltage, clock, reset spring for SIM card, and connect its BSP to U201,
achieve operation of input/output user’s information in SIM card
SD card circuit:
As the picture shows, pins of SD card I/O circuit are:
1. SDMC_DAT0, SDMC_DAT1, SDMC_DAT2, SDMC_DAT3 are 4 data line of SD card
2. SDMC_CMD is control line of SD card
3. V_SDMMC is power source
4. SDMC_CLK is transmission clock signal
5. VSS is voltage of zero
Page 27

There are two modes of SD card data transmission, 1digit and 4digit. This mobile phone use 1digit mode
Headphone circuit of mobile phone:
Loudspeaker circuit of mobile phone:
Mic circuit of mobile phone:
Earphone circuit of mobile phone:
Page 28

3 LDO circuit:
Page 29

Cameramodule control circuit:
As figure 7.1 shows: cameramodule control circuit is achieved Preview and take photo function through U201
PEAN’s inter cameramodule is 200,0000 pixel. It is connected to main board through CN702. The working
voltages are 2.8V and 1.8V, provided by 2 LDO as follows:
Data from cameramodule is paste up on LCD display indirect when Previewing. Base band processor
controls simple task only. After taking photo, it is need base band processor to move data from U201 to U302
for saving, if user saves the photo
Vibrator circuit control structure:
Page 30

PEAN use SMT motor pasted on the bracket of speaker. SMT motor is propitious to mass production, and
connect with main board well, provide optimal shake effect. Drive voltage of Motor is provided by VBAT. The
use of Motor can be controlled by FADD22 in the system: source pole and drip pole of Q750 will connect when
FADD22 is set at high level, then the Vibrator begin to work; source pole and drip pole cut off when FADD19 is
set at low level, then Vibrator stop working. Resistance R751 and R752 are use to limit current when Vibrator
working
Page 31

8. Frequently malfunction analyse
It is needed to connect LCD_PXL11,LCD_PXL1 and V-USB,V-IO-2. USB line should add VBAT and GND.
BlueTooth should pass two path that both MPU-RX1 and MPR-TX1, connect to BASEBAND, add VBAT and
GND.
8.1: Can not download program
1. First check U201 and U10, is there weld connective or weld weakly between them
2. Check voltage, 5V at VCUSB, 1.2V at USB-VM in U201, 1.8V at USB-VP. Check R416A, R146B,
R330, R331, R334 normal or not and if U420 disabled when the voltage above getting normal. If all of them
getting normal, then weld U201 again.
8.2: Can not turn on
1. Check battery. If the battery voltage is under 3.5V, then it is needed to charge. On the contray, it may
be connect weakly between battery and battery seat
2. Check if there is weld weakly on the battery seat
3. Check U201, U202, U603, U10 and the resistances and capacitance around, is them weld weakly or
excursion, and is there weld connective on PCB board
4. Connect an external power source (set at 3.8V) to +/- pole of the battery seat. If there is current
passing the powermeter before ON, it is illuminated that the mobile is creepaged. Check voltage for power
supply LDO when turn on the mobile, the voltage value of U309 (V-IO-2), U301(V-MEMORY), U303 (V-CORD)
should be 2.8V, 1.8V, 1.5V respectively. Check creepaged or not after extirpating the abnormal one
5. Check VRUSB, if there is no voltage on it or abnormol with it, then the malfunction may be at U202
6. Check V-SIM, if there is no voltage on it or abnormol with it, then the malfunction may be at U202
7. Check V-RTC, if there is no voltage on it or abnormol with it, then the malfunction may be at U202
8. Check V-IO, if there is no voltage on it or abnormol with it, then the malfunction may be at U202
9. Check VABB, if there is no voltage on it or abnormol with it, then the malfunction may be at U202
10. Check 26MHz clock output, if it is normal, may be malfunction is caused by U202
11. Measure 32.768 clock, check C201, C203, C204, R212, if all of them getting normal, may be
malfunction is caused by U202
12. Validate download software normal or not again
8.3: No display, No background light
1. Check connection between main board and LCD. Refix it if the connection failed
2. Install a new LCD instead of the old one. If it getting normal, then the old one must be damaged
3. Check the pin of the connector. Reweld if there is weld connective or weakly
4. No background light. Check U730 and D730, D731, L730, C731, C732, R731, R732, Q730 around,
the voltage at LED+ pole should be 10V, if the voltage is abnormal, then the malfunction may be at U730, then
it must be displaced
8.4: Can not identify the SIM card
1. Check the weld of SIM card, reweld if it weakly
2. Displace an eligible SIM card instead, affirm the malfunction that is caused by SIM card or not
3. Measure the voltage of V-SIM after insert SIM card, if the value is not 2.8V, then the malfunction may
be at U202, then it must be displaced
4. Check and measure spring low level for V-RST, if there is no spring low level, then the malfunction
may be at U202, then it must be displaced
5. Measure SIM-I/O signal, if the signal is not square wave, then the malfunction may be at U202, then it
must be displaced
6. Download the software again, if the problem occurs still, then the malfunction may be at U201, then it
must be displaced
8.5: Can not charge
1. Displace an eligible battery with the voltage higher than 3.6V instead. If it charge normal, maybe the
charge response is slow caused by lower voltage in the battery, or the battery is damaged
2. Check the charger. Displace another charger if the light down, affirm the charger is not disabled
3. Check U10 and elements around, is there weld weakly exist
4. Check the voltage for V-MEMORY. If the output value is not 2.8V, then displace another V-MEMORY
5. Check output voltage for GPIO73. STATE1 in U10 denotes charge or not. If GPIO output none, then
the malfunction may be at U201
Page 32

8.6: No bell or bell abnormal
1. Check the setting of the mobile, if the bell is set at close, then turn it on
2. Test it after download software again. If it gets normal, then the malfunction may be at software
3. Check weld for Speaker, reweld if it weakly
4. Measure the resistance of Speaker. If the value is not 8ohm, then displace the Speaker----Speaker is
damaged, or its line is break off
8.7: The motor can not vibrate
1. Check the setting of the mobile, if the vibrate is set at close, then turn it on
2. Check weld for R751, R752, Q750, reweld if it weakly
3. Measure the voltage of Pin1 on Q750 when the vibrator working. If its value is not high level----2.8V,
then displace U201
8.8: Can not take photo or abnormal
1. Check the installation of the cameramodule, installate it again if the installation failed
2. Check the installation of the side key, installate it again if the installation failed
3. Download software again. If it gets normal, then the malfunction may be at the version of software
4. Installate an eligible cameramodule. If it gets normal, then the former one must be damaged
5. Check the weld for CN702. Reweld if it weld weakly
6. Check the pin of CN702. Displace it if pins are damaged: weld new CN702 on the board
7. Check input voltage of U710 and U712 under the photographic mode. If the value is not 2.8V, then
U201 may be damaged. On the contray, check output voltage of U710 and U712. The value should be 1.8V
and 2.8V respectively. The one failed that the one damaged
8. Displace an eligible U202. If it gets normal, then maybe the U202 is damaged or weld weakly
8.9: Keyboard function error or no function (especially the side key)
1. Check the installation of the side key FPC, installate it again if the installation failed
2. Check the pasted position of Dome, appropriated with PCB board and the elasticity of it. Cleanout it
with alcohol and wipe off the goo, then displace Dome
3. Check weld for D740, D741, D742. Exchange or adjust the polarity of diode if it is welded reverse or
damaged
4. Check short circuit for keyboard. Wipe out eyewinker cause to short circuit
5. Displace U201. If it gets normal, then maybe the U201 is damaged----caused by ESD maybe
8.10: Signal weakly
1. Choose a no impedient environment for testing signal estate. If it gets normal, then it maybe the
envirment that infect the communication condition
2. Switch to another network to check the signal estate. If it gets normal, then the problem is caused by
the coverage of network
3. Check receiver access of the mobile phone. If it gets abnormal, please consult 8.16
8.11: Can not deliver voice signal (Receive call is able)
1. Check connection of Mic. Or else connect it again
2. Check weld for Mic and elements around. Or else weld again
3. Check conducting of D747 and D748. Displace new if the conduction is reverse
4. Measure deflection voltage of Mic. If it get abnormal, then maybe the U202 is damaged
5. Displace an eligible Mic. The former Mic maybe damaged if the new one get normal
6. Check transmitter access of the mobile phone. If it get abnormal, please consult 8.15
7. Displace an eligible U202. The former one maybe damaged if the new one gets normal, or the
interface of Mic is damaged
8.12: Drop call
1. Check inserted estate of SIM card. Insert it again if it is abnormal
2. Check the contact estate of interfaces on the mobile. Installate them if they are abnormal
3. Tune electric capability again. The reason is tune windaged or the data missin If it gets normal
4. Check transmitter and receiver access for the mobile phone. If it gets abnormal, please consult
8.15--8.16
8.13: Transmit abnormally
1): Antenna part
Page 33

1. Measure the output power of antenna. Test again if it gets normal
2. Measure the output power of RF Switch. Check connection estate between antenna and main board
if the power is normal, or else, please consult RF Switch part
2): RF Switch part
1. Measure the input power of RF Switch. Please consult PA part if it is abnormal
2. Measure the voltage of VREG. It may be mulfunction at Transceiver or the capacitance is damaged if
the voltage value is not 2.8V
3. Measure the logic of TSPACT00 and TSPACT04. it may be mulfunction at DBB if the logic is
abnormal. Or else, displace new RF Switch
3): PA part
1. Measure the input power of PA. Please consult Transceiver if it is abnormal
2. Measure VBAT. It may be mulfunction at ABB or the capacitance is damaged if VBAT gets abnormal
3. Measure level of TX-EN, and Band select that under GSM mode and DCS mode. The value of TX-EN
should be high level, the one of Band select under GSM mode should be low and under DCS mode should be
high. It may be mulfunction at DBB or capacitance is damaged
4. Measure APC signal. It should be analogous square wave with occupation/unoccupied is 1/8, and the
changes with power’s change. It may be mulfunction at ABB if the wave and is abnormal. Or else, diplace
new PA
4): Transceiver part
1. Measure VBAT and V_IO. It may be mulfunction at ABB or capacitance is damaged if they are
abnormal
2. Measure 26MHz. It may be damaged of Transceiver if 26MHz is abnormal. Please consult Can not
turn on
3. Measure STROBE. It is mulfunction at DBB if STROBE is normal, or else, just caused by DBB maybe
8.14: Receive abnormal
1. Check the element connection among antenna to Switch. Weld missing ones if there is absent
2. Measure input signal of RF Switch. If there is none, please check elements’ absent
3. Measure VREG. It may be mulfunction at ABB if VREG is abnormal
4. Measure the logic of TSPACT00 and TSPACT04. it may be mulfunction at DBB if the logic is
abnormal
5. Measure output of RF Switch. Displace RF Switch if it is normal
6. Measure output of filter. Displace it if its attenuation too much or no signal
7. Measure signal IA, IB, QA and QB. Displace Transceiver if they are normal, or else, displace DBB
Note: RF/Logic element that used to displace mulfunction one during the maintain process must
be test and melody in addvance
Page 34

9. Introdution of each station test item
1.BT station
Accomplish initialization of mobile phone (as file system, parameter insert etc.), test of base band (as
battery adjust, all kinds of current test) and RF test mainly.
1 Scan Serial Number
2 Initialize System Test initialize system
3 Off Current Test off current
4 Run Mini Kernel Run mini kernel
5 Enter Test Mode
6 Power On Current Test power on current
7 Check MS SW Version Check MS software version
8 Set MS Date/Time Set MS date/time
9 Create Directories Create directories
10 Save Batt/Chg Files Save batt/chg files
11 Save RF Files Save RF initialize files
12 Save BlueTooth Address Save Bluetooth address
13 Save Setting Files Save setting files
14 Check vibrator current Check vibrator current
15 Read ADC value at 3.4v Read ADC value at 3.4v
16 Read ADC value at 4.2v Read ADC value at 4.2v
17 Calculate battery coefficients Calculate battery coefficients
18 Charger OFF Flag Check Charger OFF Flag
19 Start Charger Start Charger
20 Charger ON Flag Charger ON Flag
21 Charge Current Test Charge Current
22 Stop-Charge Stop-Charge
23 Check SIM Card Check SIM Card
AFC Calibration
24
Initialize Test set Initialize Test set
25
Switch to GSM900 NSIG Mode Switch to GSM900 NSIG Mode
26
Switch RF Path to connector Switch RF Path to connector
27
Config to BCH+TCH Mode Config to BCH+TCH Mode
28
Initialize AFC Initialize AFC
29
Measure FreqError at 2048 Measure FreqError at 2048
30
Calculate F1&F2 Calculate F1&F2
31
Check DAC Low Limit Check DAC Low Limit
32
Check DAC Up Limit Check DAC Up Limit
33
Measure FreqError at 100 Measure FreqError at 100
34
Calculate F3&F4 Calculate F3&F4
35
Save AFC Parameters Save AFC Parameters
36
Check AFC Check AFC error
37
AGC Calibration
38
Switch GSM Measure Object Switch GSM Measure Object
39
Config Test set to CW Mode Config Test set to CW Mode
40
Initialize GSM AGC Initialize GSM AGC
41
Measure GSM Rx Level Measure GSM Rx Level
42
Page 35

CalSavAGC CalSavAGC
43
Check Rx Level Check Rx Level
44
GSM850
45
Switch to GSM850 NSIG Mode Switch to GSM850 NSIG Mode
46
Initialize GSM AGC Initialize GSM AGC
47
Measure GSM850 Rx Level Measure GSM850 Rx Level
48
Calculate & Save GSM850 G-Magic Calculate & Save GSM850 G-Magic
49
Check Rx Level Check Rx Level
50
DCS
51
Switch to DCS NSIG Mode Switch to DCS NSIG Mode
52
Initialize DCS AGC Initialize DCS AGC
53
Measure DCS Rx Level Measure DCS Rx Level
54
Calculate & Save DCS G-Magic Calculate & Save DCS G-Magic
55
Check Rx Level Check Rx Level
56
PCS
57
Switch to PCS NSIG Mode Switch to PCS NSIG Mode
58
Initialize PCS AGC Initialize PCS Auto Gain Control
59
Measure PCS Rx Level Measure PCS Rx Level
60
Calculate & Save PCS G-Magic Calculate & Save PCS G-Magic
61
Check Rx Level Check Rx Level
62
GSM900
63
Switch to GSM900 NSIG Mode Switch to GSM900 NSIG Mode
64
Init GSM AGC vs Channel Init GSM AGC vs Channel
65
GSM Rx Compensation at Ch1
66
GSM Rx Compensation at Ch20
67
GSM Rx Compensation at Ch40
68
GSM Rx Compensation at Ch62
69
GSM Rx Compensation at Ch80
70
GSM Rx Compensation at Ch100
71
GSM Rx Compensation at Ch124
72
GSM Rx Compensation at Ch975
73
GSM Rx Compensation at Ch1000
74
GSM Rx Compensation at Ch1017
75
Save GSM Rx vs Chan Compensation
76
GSM850
77
Switch to GSM850 NSIG Mode Switch to GSM850 NSIG Mode
78
Init GSM AGC vs Channel Init GSM AGC vs Channel
79
GSM Rx Compensation at Ch128
80
GSM Rx Compensation at Ch148
81
GSM Rx Compensation at Ch168
82
GSM Rx Compensation at Ch190
83
GSM Rx Compensation at Ch208
84
GSM Rx Compensation at Ch228
85
GSM Rx Compensation at Ch251
86
Save GSM Rx vs Chan Compensation Save GSM Rx vs Chan Compensation
87
DCS
88
Switch to DCS NSIG Node Switch to DCS NSIG Node
89
Init DCS AGC vs Channel Init DCS AGC vs Channel
90
DCS Rx Compensation at Ch512
91
GSM Rx Compensation
GSM Rx Compensation
DCS Rx Compensation
Page 36

DCS Rx Compensation at Ch585
92
DCS Rx Compensation at Ch660
93
DCS Rx Compensation at Ch700
94
DCS Rx Compensation at Ch790
95
DCS Rx Compensation at Ch835
96
DCS Rx Compensation at Ch885
97
Save DCS Rx vs Chan Compensation Save DCS Rx vs Chan Compensation
98
PCS
99
Switch to PCS NSIG Node Switch to PCS NSIG Node
100
Init PCS AGC vs Channel Init PCS AGC vs Channel
101
PCS Rx Compensation at Ch512
102
PCS Rx Compensation at Ch585
103
PCS Rx Compensation at Ch660
104
PCS Rx Compensation at Ch700
105
PCS Rx Compensation at Ch780
106
Save PCS Rx vs Chan Compensation Save PCS Rx vs Chan Compensation
107
APC Calibration
108
Switch GSM900 NSIG Mode Switch GSM900 NSIG Mode
109
Config to BCH+TCH Mode Config to BCH+TCH Mode
110
Initial GSM APC Calibration Initial GSM APC Calibration
111
Get GSM900 APC Power Get GSM900 APC Power
112
Calculate & save GSM APC table Calculate & save GSM APC table
113
Switch GSM850 NSIG Mode Switch GSM850 NSIG Mode
114
Initial GSM APC Calibration Initial GSM APC Calibration
115
Get GSM850 APC Power Get GSM850 APC Power
116
Calculate & save GSM APC table Calculate & save GSM APC table
117
Switch DCS NSIG Mode Switch DCS NSIG Mode
118
Initial DCS APC Calibration Initial DCS APC Calibration
119
Get DCS APC Power Get DCS APC Power
120
Calculate & save DCS APC table Calculate & save DCS APC table
121
Switch PCS NSIG Mode Switch PCS NSIG Mode
122
Initial PCS APC Calibration Initial PCS APC Calibration
123
Get PCS APC Power Get PCS APC Power
124
Calculate & save PCS APC table Calculate & save PCS APC table
125
Tx vs Channel Calibration
126
Switch to GSM900 NSIG Mode Switch to GSM900 NSIG Mode
127
Initial GSM Tx vs Channel Initial GSM Tx vs Channel
128
GSM Tx Compensation at Ch14
129
GSM Tx Compensation at Ch40
130
GSM Tx Compensation at Ch57
131
GSM Tx Compensation at Ch76
132
GSM Tx Compensation at Ch95
133
GSM Tx Compensation at Ch114
134
GSM Tx Compensation at Ch985
135
GSM Tx Compensation at Ch1009
136
Save GSM Tx vs Chan Compensation Save GSM Tx vs Chan Compensation
137
GSM850
138
Switch to GSM850 NSIG Mode Switch to GSM850 NSIG Mode
139
Initial GSM Tx vs Channel Initial GSM Tx vs Channel
140
PCS Rx Compensation
GSM Tx Compensation
Page 37

GSM Tx Compensation at Ch128
141
GSM Tx Compensation at Ch143
142
GSM Tx Compensation at Ch159
143
GSM Tx Compensation at Ch175
144
GSM Tx Compensation at Ch190
145
GSM Tx Compensation at Ch206
146
GSM Tx Compensation at Ch222
147
GSM Tx Compensation at Ch241
148
Save GSM Tx vs Chan Compensation Save GSM Tx vs Chan Compensation
149
DCS
150
Switch to DCS NSIG Mode Switch to DCS NSIG Mode
151
152 Initial DCS Tx vs Channel Initial DCS Tx vs Channel
153 DCS Tx Compensation at Ch533
154 DCS Tx Compensation at Ch574
155 DCS Tx Compensation at Ch615
156 DCS Tx Compensation at Ch657
157 DCS Tx Compensation at Ch700
158 DCS Tx Compensation at Ch740
159 DCS Tx Compensation at Ch781
160 DCS Tx Compensation at Ch844
161 Save DCS Tx vs Chan Compensation Save DCS Tx vs Chan Compensation
162 PCS
163 Switch to PCS NSIG Mode Switch to PCS NSIG Mode
164 Initial PCS Tx vs Channel Initial PCS Tx vs Channel
165 PCS Tx Compensation at Ch531
166 PCS Tx Compensation at Ch568
167 PCS Tx Compensation at Ch605
168 PCS Tx Compensation at Ch660
169 PCS Tx Compensation at Ch712
170 PCS Tx Compensation at Ch740
171 PCS Tx Compensation at Ch768
172 PCS Tx Compensation at Ch796
173 Save PCS Tx vs Chan Compensation Save PCS Tx vs Chan Compensation
174 Rx Check
175 Switch to GSM900 NSIG Mode Switch to GSM900 NSIG Mode
176 Config to BCH+TCH Mode Config to BCH+TCH Mode
177 Initial GSM Rx Check Initial GSM Rx Check
178 Check GSM Rx Ch976
179 Check GSM Rx Ch1023
180 Check GSM Rx Ch80
181 Check GSM Rx Ch124
182 Switch to GSM850 NSIG Mode Switch to GSM850 NSIG Mode
183 Initial GSM Rx Check Initial GSM Rx Check
184 Check GSM Rx Ch128
185 Check GSM Rx Ch178
186 Check GSM Rx Ch208
187 Check GSM Rx Ch251
188 Switch to DCS NSIG Mode Switch to DCS NSIG Mode
189 Initial DCS Rx Check Initial DCS Rx Check
190 Check DCS Rx Ch512
191 Check DCS Rx Ch606
192 Check DCS Rx Ch794
193 Check DCSRx Ch885
194 Switch to PCS NSIG Mode Switch to PCS NSIG Mode
195 Initial PCS Rx Check Initial PCS Rx Check
196 Check PCS Rx Ch512
197 Check PCS Rx Ch586
GSM Tx Compensation
DCS Tx Compensation
PCS Tx Compensation
Check GSM Rx
Check GSM Rx
Check DCS Rx
Check PCS Rx
Page 38

198 Check PCS Rx Ch735
199 Check PCS Rx Ch810
200 Tx Check
201 Switch to GSM900 NSIG Mode Switch to GSM900 NSIG Mode
202 Config to BCH+TCH Mode Config to BCH+TCH Mode
203 GSM Tx Check(976,5) GSM Tx Check(976,5)
204 Tx Power(976,5) Check Tx Power(976,5)
205 Time Mask(976,5) Check Time Mask(976,5)
206 Peak Phase Error(976,5) Check Peak Phase Error(976,5)
207 RMS Phase Error(976,5) Check RMS Phase Error(976,5)
208 GSM Tx Check(976,19) GSM Tx Check(976,19)
209 Tx Power(976,19) Check Tx Power(976,19)
210 Time Mask(976,19) Check Time Mask(976,19)
211 Peak Phase Error(976,19) Check Peak Phase Error(976,19)
212 RMS Phase Error(976,19) Check RMS Phase Error(976,19)
213 GSM Tx Check(124,5) GSM Tx Check(124,5)
214 Tx Power(124,5) Check Tx Power(124,5)
215 Time Mask(124,5) Check Time Mask(124,5)
216 Peak Phase Error(124,5) Check Peak Phase Error(124,5)
217 RMS Phase Error(124,5) Check RMS Phase Error(124,5)
218 GSM Tx Check(124,19) GSM Tx Check(124,19)
219 Tx Power(124,19) Check Tx Power(124,19)
220 Time Mask(124,19) Check Time Mask(124,19)
221 Peak Phase Error(124,19) Check Peak Phase Error(124,19)
222 RMS Phase Error(124,19) Check RMS Phase Error(124,19)
223 GSM850
224 Switch to GSM850 NSIG Mode Switch to GSM850 NSIG Mode
225 GSM Tx Check(128,5) Check GSM Tx Check(128,5)
226 Tx Power(128,5) Check Tx Power(128,5)
227 Time Mask(128,5) Check Time Mask(128,5)
228 Peak Phase Error(128,5) Check Peak Phase Error(128,5)
229 RMS Phase Error(128,5) Check RMS Phase Error(128,5)
230 GSM Tx Check(128,19) GSM Tx Check(128,19)
231 Tx Power(128,19) Check Tx Power(128,19)
232 Time Mask(128,19) Check Time Mask(128,19)
Peak Phase Error(128,19) Check Peak Phase Error(128,19)
233
RMS Phase Error(128,19) Check RMS Phase Error(128,19)
234
GSM Tx Check(251,5) GSM Tx Check(251,5)
235
Tx Power(251,5) Check Tx Power(251,5)
236
Time Mask(251,5) Check Time Mask(251,5)
237
Peak Phase Error(251,5) Check Peak Phase Error(251,5)
238
RMS Phase Error(251,5) Check RMS Phase Error(251,5)
239
GSM Tx Check(251,19) GSM Tx Check(251,19)
240
Tx Power(251,19) Check Tx Power(251,19)
241
Time Mask(251,19) Check Time Mask(251,19)
242
Peak Phase Error(251,19) Check Peak Phase Error(251,19)
243
244 RMS Phase Error(251,19) Check RMS Phase Error(251,19)
245 DCS
246 Switch to DCS NSIG Mode Switch to DCS NSIG Mode
247 DCS Tx Check(512,0) DCS Tx Check(512,0)
248 Tx Power(512,0) Check Tx Power(512,0)
249 Time Mask(512,0) Check Time Mask(512,0)
250 Peak Phase Error(512,0) Check Peak Phase Error(512,0)
251 RMS Phase Error(512,0) Check RMS Phase Error(512,0)
252 DCS Tx Check(512,15) DCS Tx Check(512,15)
253 Tx Power(512,15) Check Tx Power(512,15)
254 Time Mask(512,15) Check Time Mask(512,15)
Page 39

2. FT station
255 Peak Phase Error(512,15) Check Peak Phase Error(512,15)
256 RMS Phase Error(512,15) Check RMS Phase Error(512,15)
257 DCS Tx Check(885,0) DCS Tx Check(885,0)
258 Tx Power(885,0) Check Tx Power(885,0)
259 Time Mask(885,0) Check Time Mask(885,0)
260 Peak Phase Error(885,0) Check Peak Phase Error(885,0)
261 RMS Phase Error(885,0) Check RMS Phase Error(885,0)
262 DCS Tx Check(885,15) DCS Tx Check(885,15)
263 Tx Power(885,15) Check Tx Power(885,15)
264 Time Mask(885,15) Check Time Mask(885,15)
265 Peak Phase Error(885,15) Check Peak Phase Error(885,15)
266 RMS Phase Error(885,15) Check RMS Phase Error(885,15)
267 PCS
268 Switch to PCS NSIG Mode Switch to PCS NSIG Mode
269 PCS Tx Check(512,0) PCS Tx Check(512,0)
270 Tx Power(512,0) Check Tx Power(512,0)
271 Time Mask(512,0) Check Time Mask(512,0)
272 Peak Phase Error(512,0) Check Peak Phase Error(512,0)
273 RMS Phase Error(512,0) Check RMS Phase Error(512,0)
274 PCS Tx Check(512,15) PCS Tx Check(512,15)
275 Tx Power(512,15) Check Tx Power(512,15)
276 Time Mask(512,15) Check Time Mask(512,15)
277 Peak Phase Error(512,15) Check Peak Phase Error(512,15)
278 RMS Phase Error(512,15) Check RMS Phase Error(512,15)
279 PCS Tx Check(810,0) PCS Tx Check(810,0)
280 Tx Power(810,0) Check Tx Power(810,0)
281 Time Mask(810,0) Check Time Mask(810,0)
282 Peak Phase Error(810,0) Check Peak Phase Error(810,0)
283 RMS Phase Error(810,0) Check RMS Phase Error(810,0)
284 PCS Tx Check(810,15) Check PCS Tx Check(810,15)
285 Tx Power(810,15) Check Tx Power(810,15)
286 Time Mask(810,15) Check Time Mask(810,15)
287 Peak Phase Error(810,15) Check Peak Phase Error(810,15)
288 RMS Phase Error(810,15) Check RMS Phase Error(810,15)
289 End Of Test End Of Test
290 Check RTC Check RTC
291 Set Phase Version Set Phase Version
292 Write FFS to Flash Write FFS to Flash
293
1 Init
2 Initialize System Initialize System
3 Off Current Off Current
4 Run Mini Kernel Run Mini Kernel
5 Check Phase Version Check Phase Version
6 Call Test
7 Initialize GSM Test set Initialize GSM Test set
8 Switch to GSM900 signalling mode Switch to GSM900 signalling mode
9 Switch RF Path to connector Switch RF Path to connector
10 Setup BCCH Setup BCCH
11 Setup TCH Setup TCH
12 Wait for MS Registering Wait for MS Registering
13 Ms call to BS Ms call to BS
Page 40

14 Check Call connection Check Call connection
15 Change PLC(975,19) Change PLC(975,19)
16 Start Tx Measurement(975,19) Start Tx Measurement(975,19)
17 Average Power(975,19) Check Average Power(975,19)
18 Peak Phs Error(975,19) Check Peak Phs Error(975,19)
19 RMS Phs Error(975,19) Check RMS Phs Error(975,19)
20 Frequency Error(975,19) Check Frequency Error(975,19)
21 Time Mask(975,19) Check Time Mask(975,19)
22 Change PCL(975,5) Change PCL(975,5)
23 Start Tx Measurement(975,5) Start Tx Measurement(975,5)
24 Average Power(975,5) Check Average Power(975,5)
25 Peak Phs Error(975,5) Check Peak Phs Error(975,5)
26 RMS Phs Error(975,5) Check RMS Phs Error(975,5)
27 Frequency Error(975,5) Check Frequency Error(975,5)
28 Time Mask(975,5) Check Time Mask(975,5)
29 Switching spectrum(975,5) Check Switching spectrum(975,5)
30 ORFS Offset -1200Khz(975,5)
ORFS Offset - 800Khz(975,5)
31
ORFS Offset - 400Khz(975,5)
32
ORFS Offset - 400Khz(975,5)
33
ORFS Offset + 400Khz(975,5)
34
ORFS Offset + 600Khz(975,5)
35
ORFS Offset + 800Khz(975,5)
36
ORFS Offset + 1200Khz(975,5)
37
38 Start BER Measurement(975,-106) Start BER Measurement(975,-106)
39 RBER ClassII(975,-106) RBER ClassII(975,-106)
40 FER(975,-106) FER(975,-106)
41 Rx Level(975,-106) Rx Level(975,-106)
42 Rx Quality(975,-106) Rx Quality(975,-106)
43 Change TCH(40,19) Change TCH(40,19)
44 Start Tx Measurement(40,19) Start Tx Measurement(40,19)
45 Average Power(40,19) Measurement Average Power(40,19)
46 Peak Phs Error(40,19) Measurement Peak Phs Error(40,19)
47 RMS Phs Error(40,19) Measurement RMS Phs Error(40,19)
48 Frequency Error(40,19) Measurement Frequency Error(40,19)
49 Time Mask(40,19) Measurement Time Mask(40,19)
50 Change PCL(40,5) Change PCL(40,5)
51 Start Tx Measurement(40,5) Start Tx Measurement(40,5)
52 Average Power(40,5) Measurement Average Power(40,5)
53 Peak Phs Error(40,5) Measurement Peak Phs Error(40,5)
54 RMS Phs Error(40,5) Measurement RMS Phs Error(40,5)
55 Frequency Error(40,5) Measurement Frequency Error(40,5)
56 Time Mask(40,5) Measurement Time Mask(40,5)
57 Switching spectrum(40,5) Switching spectrum(40,5)
58 ORFS Offset -1200Khz(40,5)
ORFS Offset - 800Khz(40,5)
59
Check Switching spectrum(975,5)
Check ORFS Offset at 40channel
Page 41

ORFS Offset - 400Khz(40,5)
60
ORFS Offset - 400Khz(40,5)
61
ORFS Offset + 400Khz(40,5)
62
ORFS Offset + 600Khz(40,5)
63
ORFS Offset + 800Khz(40,5)
64
65 ORFS Offset + 1200Khz(40,5)
66 Tx Max current(GSM) Tx Max current(GSM)
67 Start BER Measurement(40,-106) Start BER Measurement(40,-106)
68 RBER ClassII(40,-106) RBER ClassII(40,-106)
69 FER(40,-106) FER(40,-106)
70 Rx Level(40,-106) Rx Level(40,-106)
71 Rx Quality(40,-106) Rx Quality(40,-106)
72 Change TCH(124,19) Change TCH(124,19)
73 Start Tx Measurement(124,19) Start Tx Measurement(124,19)
74 Average Power(124,19) Measurement Average Power(124,19)
75 Peak Phs Error(124,19) Measurement Peak Phs Error(124,19)
76 RMS Phs Error(124,19) Measurement RMS Phs Error(124,19)
77 Frequency Error(124,19) Measurement Frequency Error(124,19)
78 Time Mask(124,19) vTime Mask(124,19)
79 Change PCL(124,5) Measurement Change PCL(124,5)
80 Start Tx Measurement(124,5) Start Tx Measurement(124,5)
81 Average Power(124,5) Measurement Average Power(124,5)
82 Peak Phs Error(124,5) Measurement Peak Phs Error(124,5)
83 RMS Phs Error(124,5) Measurement RMS Phs Error(124,5)
84 Frequency Error(124,5) Measurement Frequency Error(124,5)
85 Time Mask(124,5) Measurement Time Mask(124,5)
86 Switching spectrum(124,5) Switching spectrum(124,5)
87 ORFS Offset -1200Khz(124,5)
ORFS Offset - 800Khz(124,5)
88
ORFS Offset - 400Khz(124,5)
89
ORFS Offset - 400Khz(124,5)
90
ORFS Offset + 400Khz(124,5)
91
ORFS Offset + 600Khz(124,5)
92
ORFS Offset + 800Khz(124,5)
93
ORFS Offset + 1200Khz(124,5)
94
95 Start BER Measurement(124,-106) Start BER Measurement(124,-106)
96 RBER ClassII(124,-106) RBER ClassII(124,-106)
97 FER(124,-106) FER(124,-106)
98 Rx Level(124,-106) Rx Level(124,-106)
99 Rx Quality(124,-106) Rx Quality(124,-106)
100 DCS measurement
101 Handover to DCS band Handover to DCS band
102 Check Call connected(DCS) Check Call connected(DCS)
103 Change TCH(512,15) Change TCH(512,15)
104 Start Tx Measurement(512,15) Start Tx Measurement(512,15)
105 Average Power(512,15) Measurement Average Power(512,15)
106 Peak Phs Error(512,15) Measurement Peak Phs Error(512,15)
107 RMS Phs Error(512,15) Measurement RMS Phs Error(512,15)
Check ORFS Offset at 124channel
Page 42

108 Frequency Error(512,15) Measurement Frequency Error(512,15)
109 Time Mask(512,15) Measurement Time Mask(512,15)
110 Change PCL(512,0) Measurement Change PCL(512,0)
111 Start Tx Measurement(512,0) Start Tx Measurement(512,0)
112 Average Power(512,0) Measurement Average Power(512,0)
113 Peak Phs Error(512,0) Measurement Peak Phs Error(512,0)
114 RMS Phs Error(512,0) Measurement RMS Phs Error(512,0)
115 Frequency Error(512,0) Measurement Frequency Error(512,0)
116 Time Mask(512,0) Measurement Time Mask(512,0)
117 Switching spectrum(512,0) Switching spectrum(512,0)
118 ORFS Offset -1200Khz(512,0)
119 ORFS Offset - 800Khz(512,0)
120 ORFS Offset - 400Khz(512,0)
121 ORFS Offset - 400Khz(512,0)
122 ORFS Offset + 400Khz(512,0)
123 ORFS Offset + 600Khz(512,0)
124 ORFS Offset + 800Khz(512,0)
125 ORFS Offset + 1200Khz(512,0)
126 Start BER Measurement(512,-106) Start BER Measurement(512,-106)
127 RBER ClassII(512,-106) RBER ClassII(512,-106)
128 FER(512,-106) FER(512,-106)
129 Rx Level(512,-106) Rx Level(512,-106)
130 Rx Quality(512,-106) Rx Quality(512,-106)
131 Change TCH(698,15) Change TCH(698,15)
132 Start Tx Measurement(698,15) Start Tx Measurement(698,15)
133 Average Power(698,15) Measurement Average Power(698,15)
134 Peak Phs Error(698,15) Measurement Peak Phs Error(698,15)
135 RMS Phs Error(698,15) Measurement RMS Phs Error(698,15)
136 Frequency Error(698,15) Measurement Frequency Error(698,15)
137 Time Mask(698,15) Measurement Time Mask(698,15)
138 Change PCL(698,0) Measurement Change PCL(698,0)
139 Start Tx Measurement(698,0) Start Tx Measurement(698,0)
140 Average Power(698,0) Measurement Average Power(698,0)
141 Peak Phs Error(698,0) Measurement Peak Phs Error(698,0)
142 RMS Phs Error(698,0) Measurement RMS Phs Error(698,0)
143 Frequency Error(698,0) Measurement Frequency Error(698,0)
144 Time Mask(698,0) Measurement Time Mask(698,0)
145 Switching spectrum(698,0) Switching spectrum(698,0)
146 ORFS Offset -1200Khz(698,0)
147 ORFS Offset - 800Khz(698,0)
148 ORFS Offset - 400Khz(698,0)
149 ORFS Offset - 400Khz(698,0)
150 ORFS Offset + 400Khz(698,0)
151 ORFS Offset + 600Khz(698,0)
152 ORFS Offset + 800Khz(698,0)
153 ORFS Offset + 1200Khz(698,0)
154 Tx Max current(DCS) Tx Max current(DCS)
155 Start BER Measurement(698,-106) Start BER Measurement(698,-106)
156 RBER ClassII(698,-106) RBER ClassII(698,-106)
157 FER(698,-106) FER(698,-106)
158 Rx Level(698,-106) Rx Level(698,-106)
159 Rx Quality(698,-106) Rx Quality(698,-106)
160 Change TCH(885,15) Change TCH(885,15)
161 Start Tx Measurement(885,15) Start Tx Measurement(885,15)
162 Average Power(885,15) Measurement Average Power(885,15)
163 Peak Phs Error(885,15) Measurement Peak Phs Error(885,15)
164 RMS Phs Error(885,15) Measurement RMS Phs Error(885,15)
Check ORFS Offset at 512channel
检查 698 信道最大功率级开关频谱
Page 43

165 Frequency Error(885,15) Measurement Frequency Error(885,15)
166 Time Mask(885,15) Measurement Time Mask(885,15)
167 Change PCL(885,0) Measurement Change PCL(885,0)
168 Start Tx Measurement(885,0) Start Tx Measurement(885,0)
169 Average Power(885,0) Measurement Average Power(885,0)
170 Peak Phs Error(885,0) Measurement Peak Phs Error(885,0)
171 RMS Phs Error(885,0) Measurement RMS Phs Error(885,0)
172 Frequency Error(885,0) Measurement Frequency Error(885,0)
173 Time Mask(885,0) Measurement Time Mask(885,0)
174 Switching spectrum(885,0) Switching spectrum(885,0)
175 ORFS Offset -1200Khz(885,0)
176 ORFS Offset - 800Khz(885,0)
177 ORFS Offset - 400Khz(885,0)
178 ORFS Offset - 400Khz(885,0)
179 ORFS Offset + 400Khz(885,0)
180 ORFS Offset + 600Khz(885,0)
181 ORFS Offset + 800Khz(885,0)
182 ORFS Offset + 1200Khz(885,0)
183 Start BER Measurement(885,-106) Start BER Measurement(885,-106)
184 RBER ClassII(885,-106) RBER ClassII(885,-106)
185 FER(885,-106) FER(885,-106)
186 Rx Level(885,-106) Rx Level(885,-106)
187 Rx Quality(885,-106) Rx Quality(885,-106)
188 PCS measurement
189 Initialize System Initialize System
190 Run Mini Kernel Run Mini Kernel
191 Initialize GSM Test set Initialize GSM Test set
192 Switch RF Path to connector Switch RF Path to connector
193 Setup BCCH Setup BCCH
194 Setup TCH Setup TCH
195 Wait for MS Registering Wait for MS Registering
196 Ms call to BS Ms call to BS
197 Check Call connection Check Call connection
198 Change TCH(512,15) Change TCH(512,15)
199 Start Tx Measurement(512,15) Start Tx Measurement(512,15)
200 Average Power(512,15) Measurement Average Power(512,15)
201 Peak Phs Error(512,15) Measurement Peak Phs Error(512,15)
202 RMS Phs Error(512,15) Measurement RMS Phs Error(512,15)
203 Frequency Error(512,15) Measurement Frequency Error(512,15)
204 Time Mask(512,15) Measurement Time Mask(512,15)
205 Change PCL(512,0) Measurement Change PCL(512,0)
206 Start Tx Measurement(512,0) Start Tx Measurement(512,0)
207 Average Power(512,0) Measurement Average Power(512,0)
208 Peak Phs Error(512,0) Measurement Peak Phs Error(512,0)
209 RMS Phs Error(512,0) Measurement RMS Phs Error(512,0)
210 Frequency Error(512,0) Measurement Frequency Error(512,0)
211 Time Mask(512,0) Measurement Time Mask(512,0)
212 Switching spectrum(512,0) Switching spectrum(512,0)
213 ORFS Offset -1200Khz(512,0)
214 ORFS Offset - 800Khz(512,0)
215 ORFS Offset - 400Khz(512,0)
216 ORFS Offset - 400Khz(512,0)
217 ORFS Offset + 400Khz(512,0)
218 ORFS Offset + 600Khz(512,0)
219 ORFS Offset + 800Khz(512,0)
220 ORFS Offset + 1200Khz(512,0)
221 Start BER Measurement(512,-106) Start BER Measurement(512,-106)
Check ORFS Offset at 885channel
Check ORFS Offset at 512channel
Page 44

222 RBER ClassII(512,-106) RBER ClassII(512,-106)
223 FER(512,-106) FER(512,-106)
224 Rx Level(512,-106) Rx Level(512,-106)
225 Rx Quality(512,-106) Rx Quality(512,-106)
226 Change TCH(660,15) Change TCH(660,15)
227 Start Tx Measurement(660,15) Start Tx Measurement(660,15)
228 Average Power(660,15) Measurement Average Power(660,15)
229 Peak Phs Error(660,15) Measurement Peak Phs Error(660,15)
230 RMS Phs Error(660,15) Measurement RMS Phs Error(660,15)
231 Frequency Error(660,15) Measurement Frequency Error(660,15)
232 Time Mask(660,15) Measurement Time Mask(660,15)
233 Change PCL(660,0) Measurement Change PCL(660,0)
234 Start Tx Measurement(660,0) Start Tx Measurement(660,0)
235 Average Power(660,0) Measurement Average Power(660,0)
236 Peak Phs Error(660,0) Measurement Peak Phs Error(660,0)
237 RMS Phs Error(660,0) Measurement RMS Phs Error(660,0)
238 Frequency Error(660,0) Measurement Frequency Error(660,0)
239 Time Mask(660,0) Measurement Time Mask(660,0)
240 Switching spectrum(660,0) Switching spectrum(660,0)
241 ORFS Offset -1200Khz(660,0)
242 ORFS Offset - 800Khz(660,0)
243 ORFS Offset - 400Khz(660,0)
244 ORFS Offset - 400Khz(660,0)
245 ORFS Offset + 400Khz(660,0)
246 ORFS Offset + 600Khz(660,0)
247 ORFS Offset + 800Khz(660,0)
248 ORFS Offset + 1200Khz(660,0)
249 Tx Max current(PCS) Tx Max current(PCS)
250 Start BER Measurement(660,-106) Start BER Measurement(660,-106)
251 RBER ClassII(660,-106) RBER ClassII(660,-106)
252 FER(660,-106) FER(660,-106)
253 Rx Level(660,-106) Rx Level(660,-106)
254 Rx Quality(660,-106) Rx Quality(660,-106)
255 Change TCH(810,15) Change TCH(810,15)
256 Start Tx Measurement(810,15) Start Tx Measurement(810,15)
257 Average Power(810,15) Measurement Average Power(810,15)
258 Peak Phs Error(810,15) Measurement Peak Phs Error(810,15)
259 RMS Phs Error(810,15) Measurement RMS Phs Error(810,15)
260 Frequency Error(810,15) Measurement Frequency Error(810,15)
261 Time Mask(810,15) Measurement Time Mask(810,15)
262 Change PCL(810,0) Measurement Change PCL(810,0)
263 Start Tx Measurement(810,0) Start Tx Measurement(810,0)
264 Average Power(810,0) Measurement Average Power(810,0)
265 Peak Phs Error(810,0) Measurement Peak Phs Error(810,0)
266 RMS Phs Error(810,0) Measurement RMS Phs Error(810,0)
267 Frequency Error(810,0) Measurement Frequency Error(810,0)
268 Time Mask(810,0) Measurement Time Mask(810,0)
269 Switching spectrum(810,0) Switching spectrum(810,0)
270 ORFS Offset -1200Khz(810,0)
271 ORFS Offset - 800Khz(810,0)
272 ORFS Offset - 400Khz(810,0)
273 ORFS Offset - 400Khz(810,0)
274 ORFS Offset + 400Khz(810,0)
275 ORFS Offset + 600Khz(810,0)
276 ORFS Offset + 800Khz(810,0)
277 ORFS Offset + 1200Khz(810,0)
278 Start BER Measurement(810,-106) Start BER Measurement(810,-106)
Check ORFS Offset at 660channel
Check ORFS Offset at 810channel
Page 45

3. ANT station
1 Init
2 Initialize System Initialize System
3 Run Mini Kernel Run Mini Kernel
4 Enter Test Mode Enter Test Mode
5 Check Phase Version Check Phase Version
6 TX Check
7 Switch to GSM900 NSIG Mode Switch to GSM900 NSIG Mode
8 Switch RF Path to connector Switch RF Path to connector
9 Config to BCH+TCH Mode Config to BCH+TCH Mode
10 GSM Tx Check(40,5) GSM Tx Check(40,5)
11 Tx Power(40,5) Check Tx Power(40,5)
12 Time Mask(40,5) Check Time Mask(40,5)
13 Peak Phase Error(40,5) Check Peak Phase Error(40,5)
14 Switch to DCS NSIG Mode Switch to DCS NSIG Mode
15 DCS Tx Check(700,0) DCS Tx Check(700,0)
16 Tx Power(700,0) Check Tx Power(700,0)
17 Time Mask(700,0) Check Time Mask(700,0)
18 Peak Phase Error(700,0) Check Peak Phase Error(700,0)
19 Switch to PCS NSIG Mode Switch to PCS NSIG Mode
20 PCS Tx Check(660,0) PCS Tx Check(660,0)
21 Tx Power(660,0) Check Tx Power(660,0)
22 Time Mask(660,0) Check Time Mask(660,0)
23 Peak Phase Error(660,0) Check Peak Phase Error(660,0)
24 End Test
25 SetPhaseVersion SetPhaseVersion
26 Write FFS to Flash Write FFS to Flash
279 RBER ClassII(810,-106) RBER ClassII(810,-106)
280 FER(810,-106) FER(810,-106)
281 Rx Level(810,-106) Rx Level(810,-106)
282 Rx Quality(810,-106) Rx Quality(810,-106)
283 End Call End Call
284 End of Test
285 Re-Enter Test Mode Re-Enter Test Mode
286 Set Phase Version Set Phase Version
287 Write FFS to Flash Write FFS to Flash
Page 46

10. reference information and notice:
10.1 test reference value:
1: GSM frequency band
The number of Low band channel is 975, transmit frequency of low band channel is 880.2MHz, receive
frequency is 925.2MHz
The number of Intermediate band channel is 37, transmit frequency of intermediate band channel is
897.4MHz, receive frequency is 942.4MHz
The number of High band channel is 124, transmit frequency of high band channel is 914.8MHz, receive
frequency is 959.8MHz
Test parameter:
Executive EGSM Test Lower limit Upper limit
Transmitting average phase error when at min and max
power transmit (均方根值)
Transmitting average phase error when at min and max
power transmit (peak value)
Transmitting average frequency error when at min and max
power transmit
Transmitting power error at NO.7 power class (29dBm) on
CH62
Transmitting power error at NO.10 power class (23dBm) on
CH62
Transmitting power error at NO.15 power class (13dBm) on
CH62
Transmitting average power error when at min and max
power transmit
Receive bit error test of RES II ( at -103 dBm) 2%
Receive frame erasure rate of RES II ( at -103 dBm) 0.12%
Indication of RX_LEV at -100 dBm -104 dB -96 dB
Indication of RX_LEV at -45 dBm -49 dB -41 dB
Quality of RX_LEV (RX_QUAL) No more than 2
Table 10.1: GSM frequency band test parameter
2: DCS frequency band
The number of Low band channel is 512, transmit frequency of low band channel is 1710.2MHz, receive
frequency is 1805.2MHz
The number of Intermediate band channel is 700, transmit frequency of intermediate band channel is
1747.8MHz, receive frequency is 1842.8MHz
The number of High band channel is 885, transmit frequency of high band channel is 1785MHz, receive
frequency is 1880MHz
Test parameter:
Ready to executive EGSM Test Lower limit Upper limit
Transmitting average phase error when at min and max power
transmit (均方根值)
Transmitting average phase error when at min and max power
transmit (peak value)
Transmitting average frequency error when at min and max
power transmit
Transmitting power error at NO.5 power class (20dBm) on
CH700
Transmitting power error at NO.10 power class (10dBm) on
CH62
Transmitting power error at NO.15 power class (0dBm) on
CH62
Transmitting average power error when at min and max power
transmit
Receive bit error test of RES II ( at -102 dBm) 2%
0 5 degree
0 20 degree
-91Hz +91Hz
-2db +2db
-3db +3db
-3db +3db
In GSM technique guideline
5 degree
20 degree
-171Hz +171Hz
-2db +2db
-3db +3db
-3db +3db
In DCS technique guideline
Page 47

Receive frame erasure rate of RES II ( at -102 dBm) 0.12%
Indication of RX_LEV at -100 dBm -104 dB -96 dB
Indication of RX_LEV at -45 dBm -49 dB -41 dB
Quality of RX_LEV (RX_QUAL) No more than 2
Table 10.2: DCS frequency band test parameter
3: PCS frequency band
The number of Low band channel is 512, transmit frequency of low band channel is 1850MHz, receive
frequency is 1930MHz
The number of Intermediate band channel is 665, transmit frequency of intermediate band channel is
1880.6MHz, receive frequency is 1960.6MHz
The number of High band channel is 810, transmit frequency of high band channel is 1910MHz, receive
frequency is 1990MHz
Test parameter:
Ready to executive EGSM Test Lower limit Upper limit
Transmitting average phase error when at min and max power
transmit (均方根值)
Transmitting average phase error when at min and max power
transmit (peak value)
Transmitting average frequency error when at min and max
power transmit
Transmitting power error at NO.5 power class (20dBm) on
CH700
Transmitting power error at NO.10 power class (10dBm) on
CH62
Transmitting power error at NO.15 power class (0dBm) on
CH62
Transmitting average power error when at min and max power
transmit
Receive bit error test of RES II ( at -102 dBm) 2%
Receive frame erasure rate of RES II ( at -102 dBm) 0.12%
Indication of RX_LEV at -100 dBm -104 dB -96 dB
Indication of RX_LEV at -45 dBm -49 dB -41 dB
Quality of RX_LEV (RX_QUAL) No more than 2
Table 10.2: PCS frequency band test parameter
10.2: analyse equipment and maintain tool in common use:
CMU200 / HP8960 / CMD55 -- -- signal generator
HP8594E -- -- 频谱分析仪
HP854810 / HP54520 -- -- oscillograph
HP34410A -- -- multimeter
HP6623A / LPS-105-AMRFL -- -- DC
ERSA 60A / HAKO926 -- -- electric iron
STEINEL-HL2305LCD / HAKO851 -- -- 热风枪
10.3:Notice:
z Products with power should be repaired by the experienced engineer, any other person use this
manual to repair product nonstandard may cause electric damage or even person wound
z There should be a credible working zone----ESDs (Electro-Static sense discharge), then it could be
used safety to avoid danger of Electro-Static discharge. This working zone must be set according to
these as follows:
Working flat ---- Each working flat must lay contradict Electro-Static mat. For the safety of equipment
with power, it should connect to the commonality ground through a resistance of 1.2M
Hand ring ---- A device made of soft line that can release Electro-Static fast. Hand ring’s soft line
5 degree
20 degree
-171Hz +171Hz
-2db +2db
-3db +3db
-3db +3db
In PCS technique guideline
Page 48

connect to commonality ground with a resistance of 5.2K to 1.2M inter
Container ---- all of the container must be conductor
z Maintain engineer should take care of self-protect, such as using blinker, glove, avoid inbreathe gas
within plumbum or powder etc.
11.Abbreviation:
ABB:Analog Base Band
AFC:Automatic Frequency Control
APC:Automatic Power Control
BGA:Ball Grid Array:a kind of encapsulation of chip in common
CMII:Ministry of Information Industry, China. Abbreviation of The Information Industries Department which
issues permit to enters the net
CPU:Central Process Unit
CSTN:Color Super Twisted Nematic
DBB:Digital Base Band
DNP:Don’t Process,as the same meaning with NC, denote element which no need to jointing in the
structure figure
DSP:Digital Signal Processor
GSM:Global System for Mobile communications
H/W:HardWare
I2C:Inter IC Control:A bunch communication protocol standard that advanced by Philps, contains two
circuitry which are clock and data
IMEI:International Mobile Equipment Identity
IMSI:International Mobile Subscriber Identification
I/O:Input/Output
ISO:International Standards Organization
JTAG:Joint Test Action Group
Flash:Flash E2PROM
LCD:Liquid Crystal Display
LCM:LCD Module:Indicate a module in mobile phone----it not only contain LCD display function, but also
contain backlight control function, Speaker, Receiver and Motor (even Sensor) and any other interface
commonly. It is an important composing module in mobile phone
MCC:Mobile Country Code:3digit, stand for country code that user in
MCU:Micro-Controller Unit
MNC:Mobile Network Code:2digit, stand for network code user in
MSIN :
communication network
NC: Not Connect:As the same meaning of DNP, denote element which no need to jointing in the
structure figure
PLL:Phase Loop Lock
PWL:Pseudo-noise pulse Width Light :A function module in U201 DBB, output pulse width modulated
signal
PWT:Pulse Width Tone Generator:Similar with PWL, output pulse width modulated signal too
RISC:Reduced Instruction Set Computer
RAM:Random Access Memory
ROM:Read Only Memory
RTC:Real Time Clock
SIM:Subscriber Identity Module
S/W:SoftWare
TDMA:Time Division Multiple Access
TMSI:Temporary Mobile Subscriber Identification
TPU:Time Processing Unit——A function processing unit in U200 DBB unit
TSP:Time Serial Port——A function processing unit in U200 DBB unit
USART:Universal Synchronous/Asynchronous Receiver Transmitter
USB:Universal Serial Bus
Mobile Subscriber Identification Number : Use to identify mobile subscriber in mobile
Page 49

12.Disassembling and Assembling
Overview
This section describes how to Disassembling and Assembling before debug.
12.1 Disassembling
Tools using of Disassembling and
Assembling Pean
List of the left picture
1. Tweeze
2. Screw Driver T5
Remove the stylus, battery and
battery_cover_asm
Push the base_deco_right and
remove it.
Release 6 screws from back of the
phone.
Page 50

According to left diagram make for
the rear housing separate from the
front housing.
`
The housing_rear_asm was
separated from the front housing.
Remove the T-flash cover.
Unlock the connector of keypad
FPC.
Then separated the PCBA.
Page 51

The PCBA was separated from
the front housing.
Remove the Power key, Fun key
Volume key, Camera key and unlock
the Keypad FPC.
Rive off the Copper.
Page 52

Release 2 screws
from the Keypcb.
Then remove the
Keypcb.
```
According to left
diagram prize up
keypad assembly
(can not make for the
keypad distortion)
Then remove the
keypad assembly.
Page 53

According to left
diagram prize up
speaker and vibrator
with tweeze.
The speaker and
vibrator were
separated from the
frame
Page 54

Use tweeze or
fingers to
scratch 3
hooks make for
frame
separated.(
reference
left diagram)
Unclose the foam of
camera connector
with tweeze, and
remove it.
Page 55

Then unlock the
camera connector
and remove it.
Unclose the foam of
LCD_FPC connector
with tweeze.
Then unlock the LCD
connector and touch
panel connector with
tweeze.
Page 56

Unlock 4 buckles
arrowhead denotes with
tweeze or finger.(or
unlock 2 buckles in the
same side)
Then remove the LCM.
From boundary of LCD
prize up it,and remove
it.
Thus the whole phone
is downright
disassembled into PCB
and mechanical parts.
The Unit Disassembly is done
Page 57

12.2 Assembling
Lock the connector of
the FPC of camera
module and paste the
foam.
Put frame of antenna
installed to PCBA
board.
(Attention to the
details of the left
diagram)
Attention this
details:
①At first install this
hook
② Then press this
area
The legs of antenna
can not be
distortion.
The frame was
installed.
Page 58

Release the paper of
speaker and vibrator
with tweeze, then
install it to the frame.
①
②
③
④
Install the LCM to
PCBA board.(lock 4
hooks with finger)
(Attention to the
details of the left
diagram , close 4
hooks)
Lock the FPC of LCD
and touch panel, then
paste a piece of foam
on the LCD connect.
Page 59

Attention this
details:
Put keypad installed to
front housing.
(Attention to the
details of the left
diagram)
① At first aim
the two holes
② Then press the two
The keypad was
installed.
Page 60

Fixing the PCB of
keypad into front
housing with two
screws.
The PCB of keypad
was installed.
Lock the FPC of
keypad to the PCBA.
The FPC of keypad
was installed.
Page 61

Put the volume key,
camera key, power
key and fun key into
the front housing.
These keys were
installed.
Page 62

Assembly the PCBA in
the front housing. And
then lock the Key
FPC.
Key
FPC
Install the T-flash
cover to the rear
housing.
Install the Audio cap to
the rear housing.
Page 63

Install the rear housing
to the front housing.
The housing was
installed.
Fixing the housing use
6 screws, as left
diagram.
Page 64

Install the decoration
to rear housing.
The battery installed,
and then cover the
battery cover
Put stylus into the rear
housing.
Page 65

The Unit assembly is done and ready for further tests.
Assembly process is
done.
Now the unit is ready
for performing TEST.
 Loading...
Loading...