Page 1

MicroScanner
January 2007 Rev. 1 7/07
©2007 Fluke Corporation. All rights reserved.
All product names are trademarks of their respective companies.
TM
2
Cable Verifier
Users Manual
Page 2

LIMITED WARRANTY AND LIMITATION OF LIABILITY
Each Fluke Networks product is warranted to be free from defects in material and workmanship under normal use and service. The
warranty period for the mainframe is one year and begins on the date of purchase. Parts, accessories, product repairs and services are
warranted for 90 days, unless otherwise stated. Ni-Cad, Ni-MH and Li-Ion batteries, cables or other peripherals are all considered parts
or accessories. The warranty extends only to the original buyer or end user customer of a Fluke Networks authorized reseller, and does
not apply to any product which, in Fluke Networks’ opinion, has been misused, abused, altered, neglected, contaminated, or damaged
by accident or abnormal conditions of operation or handling. Fluke Networks warrants that software will operate substantially in
accordance with its functional specifications for 90 days and that it has been properly recorded on non-defective media. Fluke Networks
does not warrant that software will be error free or operate without interruption.
Fluke Networks authorized resellers shall extend this warranty on new and unused products to end-user customers only but have no
authority to extend a greater or different warranty on behalf of Fluke Networks. Warranty support is available only if product is
purchased through a Fluke Networks authorized sales outlet or Buyer has paid the applicable international price. Fluke Networks
reserves the right to invoice Buyer for importation costs of repair/replacement parts when product purchased in one country is
submitted for repair in another country.
Fluke Networks warranty obligation is limited, at Fluke Networks option, to refund of the purchase price, free of charge repair, or
replacement of a defective product which is returned to a Fluke Networks authorized service center within the warranty period.
To obtain warranty service, contact your nearest Fluke Networks authorized service center to obtain return authorization information,
then send the product to that service center, with a description of the difficulty, postage and insurance prepaid (FOB destination). Fluke
Networks assumes no risk for damage in transit. Following warranty repair, the product will be returned to Buyer, transportation
prepaid (FOB destination). If Fluke Networks determines that failure was caused by neglect, misuse, contamination, alteration, accident
or abnormal condition of operation or handling, or normal wear and tear of mechanical components, Fluke Networks will provide an
estimate of repair costs and obtain authorization before commencing the work. Following repair, the product will be returned to the
Buyer transportation prepaid and the Buyer will be billed for the repair and return transportation charges (FOB Shipping point).
THIS WARRANTY IS BUYER’S SOLE AND EXCLUSIVE REMEDY AND IS IN LIEU OF ALL OTHER WARRANTIES, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED,
INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO ANY IMPLIED WARRANTY OR MERCHANTABILITY OR FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. FLUKE
NETWORKS SHALL NOT BE LIABLE FOR ANY SPECIAL, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES OR LOSSES, INCLUDING
LOSS OF DATA, ARISING FROM ANY CAUSE OR THEORY.
Since some countries or states do not allow limitation of the term of an implied warranty, or exclusion or limitation of incidental or
consequential damages, the limitations and exclusions of this warranty may not apply to every buyer. If any provision of this Warranty
is held invalid or unenforceable by a court or other decision-maker of competent jurisdiction, such holding will not affect the validity or
enforceability of any other provision.
4/04
Fluke Networks
PO Box 777
Everett, WA 98206-0777
USA
Page 3

Table of Contents
Title Page
Introduction .......................................................................................................................................................................... 1
Registration ........................................................................................................................................................................... 2
Contacting Fluke Networks .................................................................................................................................................. 2
Unpacking ............................................................................................................................................................................. 3
MicroScanner
MicroScanner2 Cable Verifier (MS2-100) ...................................................................................................................... 3
Safety Information ................................................................................................................................................................ 4
MicroScanner
Display Features .................................................................................................................................................................... 8
Auto Shutoff ......................................................................................................................................................................... 9
Changing the Length Units .................................................................................................................................................. 9
Using the Wiremap Adapter and Remote ID Locators ....................................................................................................... 10
Testing Twisted Pair Cabling ................................................................................................................................................ 11
Twisted Pair Test Results ............................................................................................................................................... 12
Open on Twisted Pair Cabling ............................................................................................................................... 12
Short on Twisted Pair Cabling ............................................................................................................................... 13
Crossed Wires .......................................................................................................................................................... 13
Crossed Pairs ........................................................................................................................................................... 14
2
Professional Kit (MS2-KIT) .................................................................................................................... 3
2
Features ........................................................................................................................................................ 6
i
Page 4

MicroScanner2 Cable Verifier
Users Manual
Split Pair ..................................................................................................................................................................15
Telephone Voltages Detected ................................................................................................................................16
Bridge Tap Detected ............................................................................................................................................... 17
Ethernet Port Detected ........................................................................................................................................... 18
Viewing Individual Results .............................................................................................................................................20
Using Multiple Remote ID Locators ..............................................................................................................................22
Connecting to Telephone Networks Wired in Star Topologies ...................................................................................24
Connecting to Telephone Networks Wired in Bus Topologies ................................................................................... 26
Testing Coaxial Cabling .........................................................................................................................................................28
Coaxial Results ................................................................................................................................................................ 29
Open on Coaxial Cabling ........................................................................................................................................29
Short on Coaxial Cabling ........................................................................................................................................ 30
Unknown Termination on Coaxial Cabling ........................................................................................................... 30
Detecting Power Over Ethernet ...........................................................................................................................................31
Using the Toner .....................................................................................................................................................................32
Toning in IntelliTone Mode (optional IntelliTone probe required) ............................................................................32
Analog Toner Mode (optional tone probe required) ..................................................................................................35
Using the SmartTone Function ......................................................................................................................................36
Using the IntelliTone Cable Map Function (optional IP200 probe required) ....................................................................36
Calibrating Length Measurements .......................................................................................................................................38
Setting the NVP to a Specified Value ............................................................................................................................ 38
Determining a Cable’s Actual NVP ................................................................................................................................38
Maintenance ..........................................................................................................................................................................39
Cleaning .......................................................................................................................................................................... 40
Battery Life, Status, and Replacement .......................................................................................................................... 40
Checking the Tester’s Version and Serial Number ....................................................................................................... 41
If Something Seems Wrong .................................................................................................................................................. 41
Options and Accessories ........................................................................................................................................................42
ii
Page 5

Table of Contents
Specifications ......................................................................................................................................................................... 43
Environmental Specifications ........................................................................................................................................ 43
General Specifications ................................................................................................................................................... 44
Test Modes ..................................................................................................................................................................... 44
Performance Specifications ........................................................................................................................................... 45
Regulatory Information ................................................................................................................................................. 46
Appendix A: Diagnosing Wiremap Faults ........................................................................................................................... 47
Open ............................................................................................................................................................................... 47
Split Pair ......................................................................................................................................................................... 47
Reversed Pairs ................................................................................................................................................................ 47
Crossed Pairs ................................................................................................................................................................... 47
Short ............................................................................................................................................................................... 48
Index ...................................................................................................................................................................................... 49
iii
Page 6

MicroScanner2 Cable Verifier
Users Manual
iv
Page 7

List of Figures
Figure Title Page
1 High Voltage Display Example ...................................................................................................................... 5
2 MicroScanner
3 Display Features ............................................................................................................................................. 8
4 Connecting a Remote ID Locator in a Confined Area or to an RJ11 Jack................................................... 10
5 Connecting to Twisted Pair Network Cabling.............................................................................................. 11
6 Open on Twisted Pair Cabling....................................................................................................................... 12
7 Short on Twisted Pair Cabling....................................................................................................................... 13
8 Crossed Wires ................................................................................................................................................. 13
9 Crossed Pairs................................................................................................................................................... 14
10 Split Pair.......................................................................................................................................................... 15
11 Telephone Voltages Detected ....................................................................................................................... 16
12 Bridge Tap Detected ...................................................................................................................................... 17
13 Ethernet Port Detected.................................................................................................................................. 19
14 Results Screens for Individual Wire Pairs ...................................................................................................... 21
15 Using Multiple Remote ID Locators............................................................................................................... 23
16 Connecting to a Telephone Network Wired in a Star Topology................................................................. 25
17 Connecting to a Telephone Network Wired in a Bus Topology.................................................................. 27
18 Connecting to Coaxial Cabling...................................................................................................................... 28
2
Features ................................................................................................................................. 6
v
Page 8

MicroScanner2 Cable Verifier
Users Manual
19 Coaxial Results ................................................................................................................................................ 29
20 Open on Coaxial Cabling ...............................................................................................................................29
21 Short on Coaxial Cabling................................................................................................................................ 30
22 Unknown Termination on Coaxial Cabling...................................................................................................30
23 PoE Display......................................................................................................................................................31
24 IntelliTone Toner Mode Display ....................................................................................................................33
25 Using the Toner in IntelliTone Mode............................................................................................................ 34
26 Analog Toner Mode Display.......................................................................................................................... 35
27 Using the Toner with the IP200 IntelliTone Cable Map Function ...............................................................37
28 Replacing the Tester’s Batteries.....................................................................................................................40
vi
Page 9

MicroScanner2 Cable Verifier
Introduction
2
The MicroScanner
instrument that lets you verify and troubleshoot the wiring
of twisted pair and coaxial cables and detect network
services.
The tester does the following:
•
Measures length up to 1500 ft (457 m) and detects
opens and shorts on twisted pair and coaxial cabling.
•
Detects split pairs on twisted pair cabling.
•
Displays wiremap, cable length, proportional distance
to opens, and the remote ID number all on one screen.
Cable Verifier is a hand-held test
•
Detects Ethernet ports on twisted pair cabling and
reports the port speed.
•
Detects PoE (Power over Ethernet) and telephone
voltages on twisted pair cabling.
•
IntelliTone™ function works with an optional Fluke
Networks IntelliTone probe to help you locate and
isolate cables behind walls, at patch panels, or in
bundles. The analog toner works with standard analog
probes and includes the SmartTone
positive identification of cables in bundles.
™
function for
1
Page 10

MicroScanner2 Cable Verifier
Users Manual
Registration
Registering your product with Fluke Networks gives you
access to valuable information on product updates,
troubleshooting tips, and other support services. To register,
fill out the online registration form on the Fluke Networks
website at www.flukenetworks.com/registration.
Contacting Fluke Networks
www.flukenetworks.com
support@flukenetworks.com
+1-425-446-4519
•
Australia: 61 (2) 8850-3333 or 61 (3) 9329 0244
•
Beijing: 86 (10) 6512-3435
•
Brazil: 11 3044 1277
•
Canada: 1-800-363-5853
•
Europe: +44-(0)1923 281 300
•
Hong Kong: 852 2721-3228
•
Japan: 03-3434-0510
•
Korea: 82 2 539-6311
•
Singapore: +65-6799-5566
•
Taiwan: (886) 2-227-83199
•
USA: 1-800-283-5853
Visit our website for a complete list of phone numbers.
2
Page 11

Unpacking
The tester comes with the accessories listed below. If
something is damaged or missing, contact the place of
purchase immediately.
•
MicroScanner2 Getting Started Guide
•
IntelliTone Quick Reference Guide
•
CD-ROM with MicroScanner2 manuals
•
CD-ROM with IntelliTone manuals
Unpacking
MicroScanner2 Professional Kit (MS2-KIT)
•
MicroScanner2 tester with detachable wiremap
adapter
•
2 AA alkaline batteries
•
ITK200 IntelliTone probe
•
9 V alkaline battery
•
Six remote ID adapters (numbers 2 through 7)
•
Two shielded patch cords, 8-pin modular plug to 8-pin
modular plug (RJ45 to RJ45), 2 m
•
Two patch cords, 4-pin modular plug to 4-pin modular
plug (RJ11 to RJ11), 15 cm
•
Coaxial patch cord, F-connector to F-connector, 75 Ω,
with push-on adapters, 1.8 m
•
Test lead, 8-pin modular plug (RJ45) to 8 alligator clips
•
Wrist strap
•
Carrying case
•
Folding pouch for accessories
MicroScanner2 Cable Verifier (MS2-100)
•
MicroScanner2 tester with detachable wiremap
adapter
•
2 AA alkaline batteries
•
Carrying pouch
•
MicroScanner2 Getting Started Guide
•
CD-ROM with MicroScanner2 manuals
3
Page 12
MicroScanner2 Cable Verifier
Users Manual
Safety Information
Table 1 describes the international electrical symbols used
on the tester and in this manual.
Table 1. International Electrical Symbols
Warning or Caution: risk of damage or
destruction to equipment or software. See
W
X
j
explanations in the manual.
On the tester’s display this symbol indicates a
cable fault or voltage on the cable.
Warning: Risk of electric shock.
This equipment not for connection to public
communications networks, such as active
telephone systems.
Do not put products containing circuit boards
into the garbage. Dispose of circuits boards in
~
accordance with local regulations.
WWarningX
To avoid possible fire, electric shock, or personal
injury:
•
Do not open the case; no user-serviceable parts
are inside.
•
Do not modify the tester.
•
Do not use the tester if it is damaged. Inspect
the tester before use.
•
If this equipment is used in a manner not
specified by the manufacturer, the protection
provided by the equipment may be impaired.
•
The tester is not intended to be connected to
active telephone inputs, systems, or equipment,
including ISDN devices. Prolonged exposure to
the voltages applied by these interfaces may
damage the tester. The tester shows a warning
symbol (
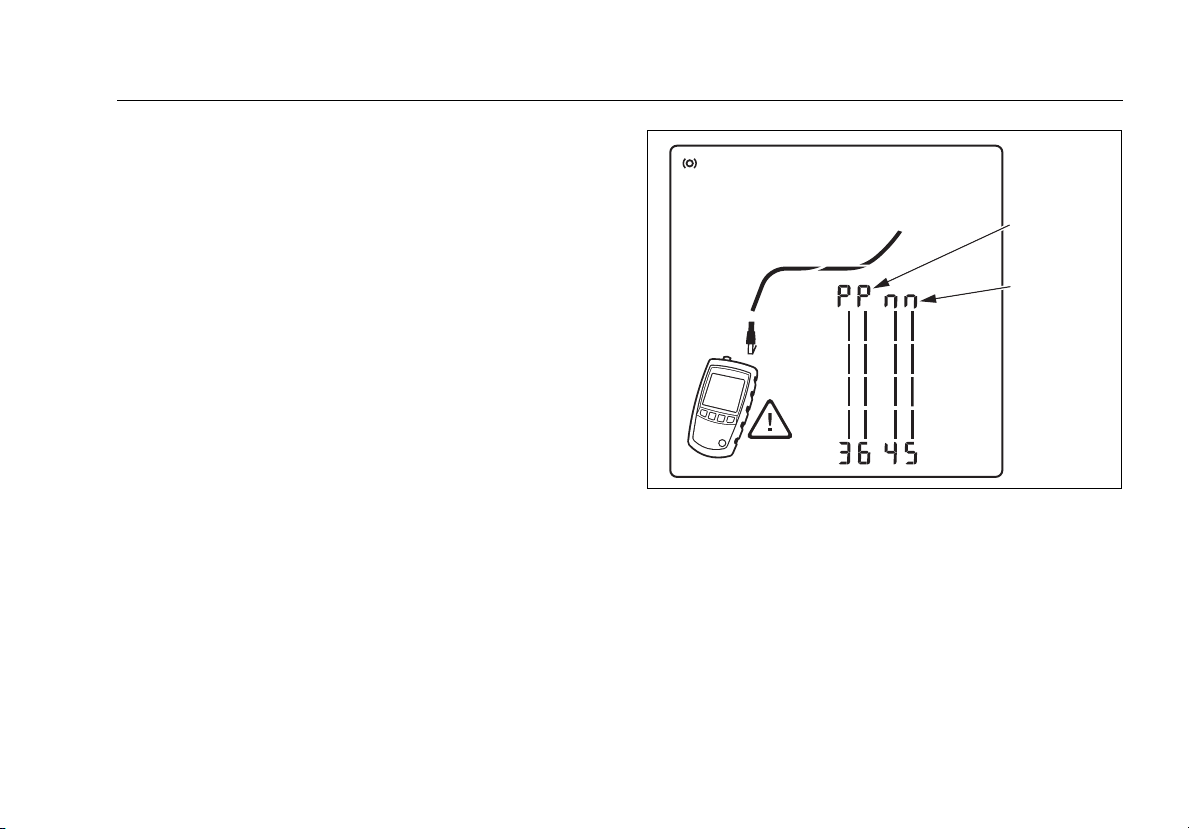
detects high voltage. Figures 1 and 11 show
examples of this display.
W) and the voltage polarities when it
4
Page 13
•
Before using the optional IntelliTone probe, read
the safety information in the probe’s
documentation provided on the IntelliTone
manuals CD.
•
Do not use the tester if it operates abnormally.
Protection may be impaired.
WCaution
To ensure maximum accuracy of test results
replace the batteries as soon as the low battery
indicator appears (see "Battery Life, Status, and
Replacement" on page 40).
Safety Information
Positive
Negative
egk29.eps
Figure 1. High Voltage Display Example
5
Page 14
MicroScanner2 Cable Verifier
Users Manual
MicroScanner2 Features
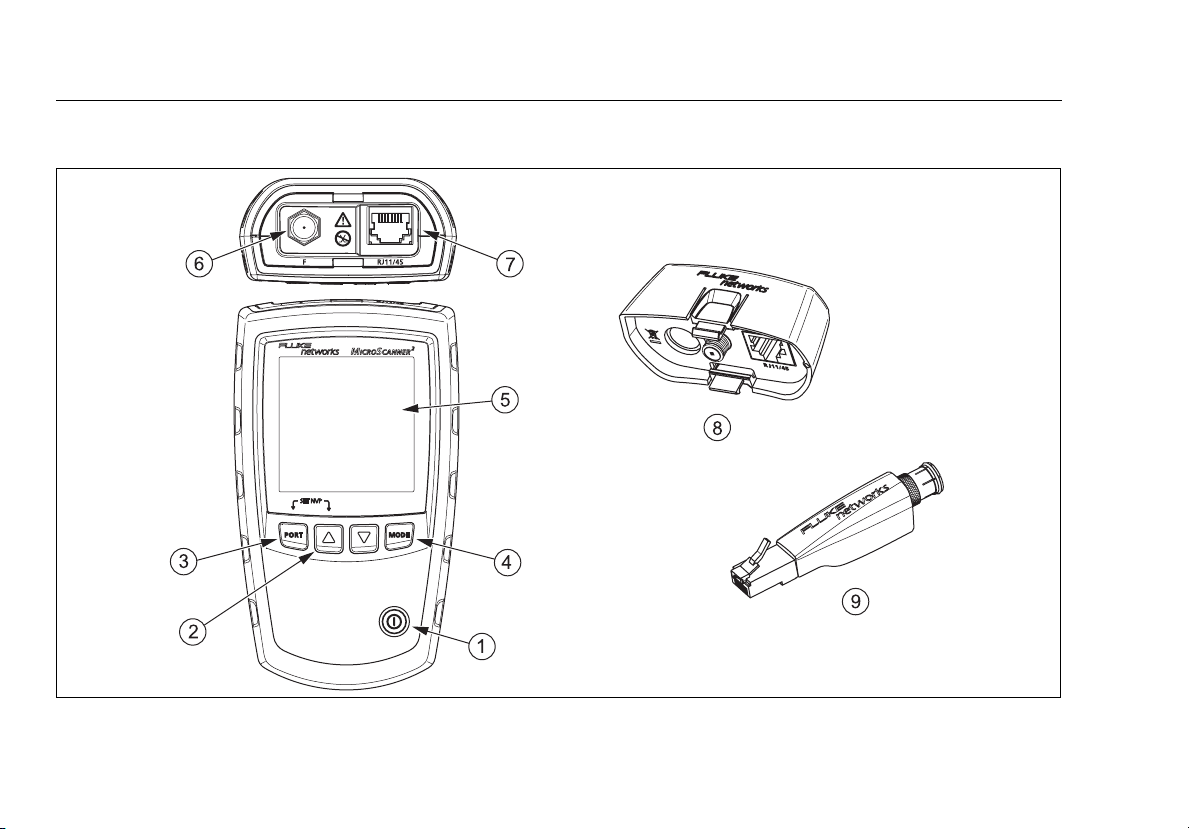
egk01.eps
Figure 2. MicroScanner2 Features
6
Page 15

A
On/off key.
B
E, D: Navigates through screens and changes
settings. In toner mode, these keys cycle through the
IntelliTone and analog toner songs.
C
Y: Selects the RJ45 or coaxial connector as the active
port.
D
M: Cycles through the cable test, toner, and PoE
detect modes.
For additional modes, hold down keys while turning the
tester on:
•
Y + E: Lets you calibrate length measurements and
select meters or feet as the length unit.
•
M + D: Activates a demonstration mode where the
tester shows examples of test result screens.
Note
Auto shutoff is disabled in demonstration mode.
•
E + D: Displays the version and serial number
screens.
MicroScanner2 Features
E
LCD display with backlight.
F
F-connector for connecting to 75 Ω coaxial cable.
G
Modular jack for connecting to telephone and twisted
pair network cable. The jack accepts 8-pin modular
(RJ45) and
6-pin modular (RJ11) connectors.
H
Wiremap adapter with F-connector and 8-pin modular
jack. See page 10.
I
Optional remote ID locator with F-connector and 8-pin
modular jack. See page 10.
7
Page 16
MicroScanner2 Cable Verifier
P
Users Manual
Display Features
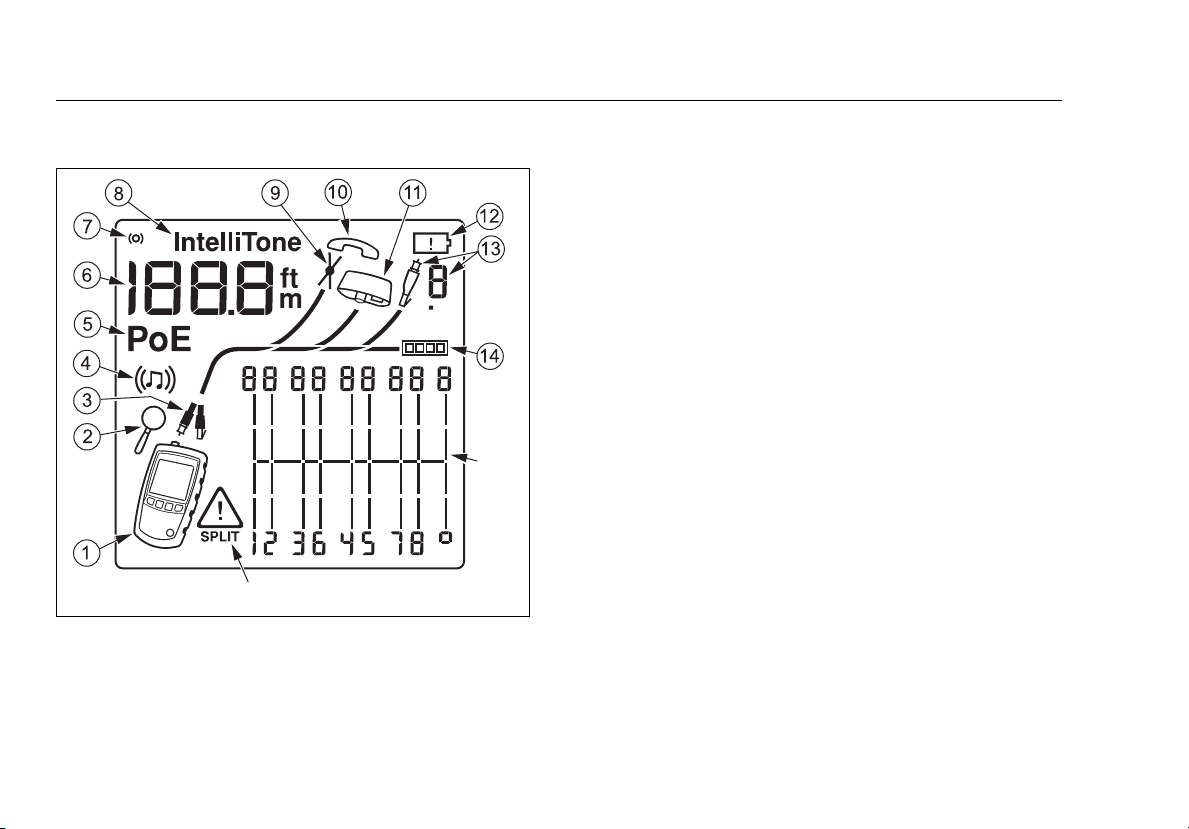
Figure 3. Display Features
O
egk02.eps
A
Tester icon
B
Detail screen indicator. See page 20.
C
Indicates which port is active, the RJ45 port (U) or the
coaxial port (T).
D
Tone mode indicator. See page 32.
E
Power over Ethernet mode indicator. See page 31.
F
Numeric display with feet/meters indicator.
G
Test activity indicator, which is animated when a test is
running.
H
IntelliTone appears when the toner is in IntelliTone
mode. See pages 32 and 36.
I
Indicates a short on the cable. See pages 13 and 30.
J
Telephone voltage indicator. See page 16.
K
Indicates a wiremap adapter is connected to the far
end of the cable.
L
Low battery indicator. See page 40.
M
Indicates an ID locator is connected to the far end of
the cable and shows the locator’s number.
N
Ethernet port indicator. See page 18.
8
Page 17

O
Wiremap diagram. For opens, the number of segments
lit for the wire pair indicates the approximate distance
to the fault. The rightmost segments indicate the
shield. See pages 12 through 15.
P
The W Indicates a fault or high voltage on the cable.
SPLIT appears when the fault is a split pair. See page 15.
Auto Shutoff
The tester turns off after 10 minutes if no keys are pressed
and nothing changes at the tester’s connectors.
Note
Auto shutoff is disabled in toner and demonstration
modes.
Auto Shutoff
Changing the Length Units
1
Hold down Y and E while turning on the tester.
2
Press M to switch between meters and feet.
3
Turn the tester off then on to return to testing mode.
9
Page 18
MicroScanner2 Cable Verifier
Users Manual
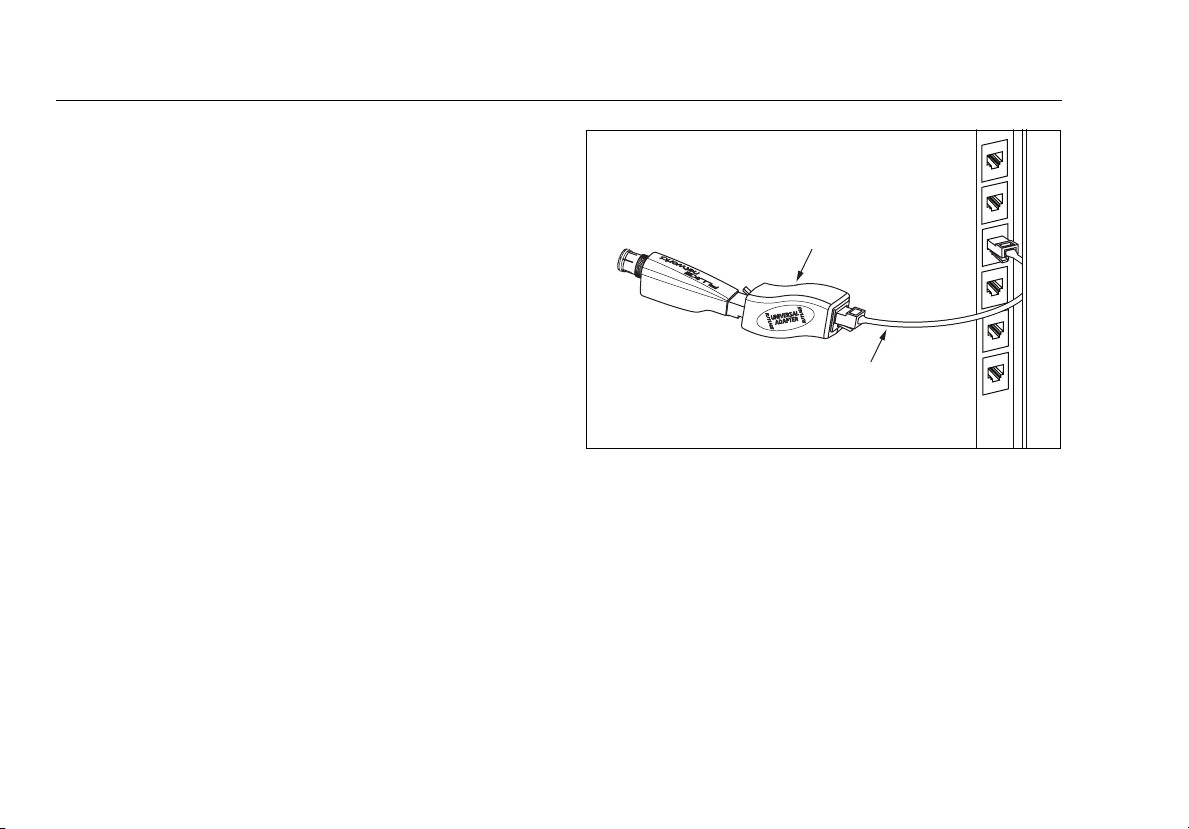
Using the Wiremap Adapter and Remote ID Locators
Terminating twisted pair cabling with the standard
wiremap adapter or optional remote ID locators lets the
tester detect all types of wiremap faults. Without this
termination, the tester cannot detect crossed wires or
crossed pairs. For a wire pair with one wire open,
termination is required to detect which wire is open.
Without termination, the tester shows both wires as open.
Using multiple remote ID locators helps you identify
connections at patch panels. The tester shows the number
of the locator connected to the far end of the cabling, as
shown on page 23.
To connect a remote ID locator to a modular (RJ) jack in a
confined area or to a 4-pin modular jack (RJ11), use the
optional universal adapter and a patch cord, as shown in
Figure 4.
Universal adapter
(8-pin and 4-pin)
Remote ID
locator
8-pin or 4-pin
modular patch
cord
egk15.eps
Figure 4. Connecting a Remote ID Locator in a Confined
Area or to an RJ11 Jack
10
Page 19

Testing Twisted Pair Cabling
1
Turn on the tester.
If the tester is already on and in coaxial test mode (T),
press Y to switch to twisted pair test mode (U).
2
Connect the tester and wiremap adapter or ID locator to
the cabling as shown in Figures 5 through 17.
The test runs continuously until you change modes or turn
the tester off.
Notes
You can measure length without connecting a far
end adapter; however, an adapter is required for a
complete wiremap test.
PoE indicator appears, see page 31.
If the
Testing Twisted Pair Cabling
Patch panel
RJ45 patch
cords
Wall
outlet
Wiremap
adapter
egk03.eps
Figure 5. Connecting to Twisted Pair Network Cabling
11
Page 20

MicroScanner2 Cable Verifier
Users Manual
Twisted Pair Test Results
The following figures show typical test results for twisted
pair cabling.
Open on Twisted Pair Cabling
Figure 6 shows an open on wire 4.
Notes
If only one wire in a pair is open and a wiremap
adapter or remote ID locator is not connected, both
wires are shown as open.
The warning icon (
wires in a pair are open because open pairs are
normal for some cabling applications.
The three segments shown for the wire pair length indicate
the open is approximately 3/4 the distance to the end of the
cabling. The cable length is 75.4 m.
To see the distance to the open, use E or D to view the
individual result for the wire pair. See page 20.
W) does not appear if both
12
egk05.eps
Figure 6. Open on Twisted Pair Cabling
Page 21

Testing Twisted Pair Cabling
Short on Twisted Pair Cabling
Figure 7 shows a short between wires 5 and 6. The shorted
wires flash to indicate the fault. The cable length is 75.4 m.
Note
When there is a short, the far-end adapter and the
mapping of the unshorted wires are not shown.
“Short”
icon
ekg06.eps
Figure 7. Short on Twisted Pair Cabling
Crossed Wires
Figure 8 shows that wires 3 and 4 are crossed. The the pin
numbers flash to indicate the fault. Cable length is
53.9 m. The cable is shielded.
Detection of crossed wires requires a far-end adapter.
Shield
indicator
egk08.eps
Figure 8. Crossed Wires
13
Page 22

MicroScanner2 Cable Verifier
Users Manual
Crossed Pairs
Figure 9 shows that pairs 1,2 and 3,6 are crossed. The pin
numbers flash to indicate the fault. This crossed pair is likely
caused by mixing 568A and 568B cabling.
Detection of crossed pairs requires a far-end adapter.
egk09.eps
Figure 9. Crossed Pairs
14
Page 23

Split Pair
Figure 10 shows a split pair on 3,6 and 4,5. The split pair
flashes to indicate the fault. The cable length is 75.4 m.
In a split pair, continuity from end to end is correct, but is
made with wires from different pairs. Split pairs cause
excessive crosstalk that interferes with network operation.
Note
Cables with untwisted pairs, such as telephone
cords, typically show split pairs due to excessive
crosstalk.
Testing Twisted Pair Cabling
Split pair
icon
The split
pair flashes
Split pair wiring
egk10.eps
Figure 10. Split Pair
15
Page 24

MicroScanner2 Cable Verifier
Users Manual
Telephone Voltages Detected
Figure 11 shows that telephone voltage is detected on pair
4,5.
Length is not shown because the voltage interferes with
length measurements.
WWarningX
The tester is not intended to be connected to
active telephone inputs, systems, or equipment,
including ISDN devices. Prolonged exposure to
the voltages applied by these interfaces may
damage the tester.
Telephone
voltage icon
Positive
wire (tip)
Negative
wire (ring)
egk11.eps
Figure 11. Telephone Voltages Detected
16
Page 25

Bridge Tap Detected
Figure 12 shows a bridge tap detected at about 53.2 m.
Only the first bridge tap detected is reported. The distance
to a bridge tap is approximate because multiple reflections
from the bridge tap interfere with length measurements.
Note
Bridge taps more than 328 ft (100 m) from the tester
or taps less than 16 ft (5 m) long may not be
detected.
Testing Twisted Pair Cabling
egk12.eps
Figure 12. Bridge Tap Detected
17
Page 26

MicroScanner2 Cable Verifier
Users Manual
Ethernet Port Detected
The tester can detect active and inactive Ethernet ports, as
shown in Figure 13.
A
Ethernet port icon.
B
Port speed for an active 1000 megabit port. The speeds
are 10, 100, or 1000 megabits per second. The example
shows 1000 megabits per second. If the port supports
multiple speeds the number cycles through the speeds.
C
Cable length. Dashes are shown if the tester cannot
measure the length. This can occur if the port does not
produce reflections.
Length may fluctuate or be obviously too high if the
port’s impedance fluctuates or varies from the cable’s
impedance. When in doubt, disconnect the cable from
the port to get an accurate length measurement.
18
Page 27

C
A
Testing Twisted Pair Cabling
C
A
B
Active Ethernet port Inactive Ethernet port
egk13.eps
Figure 13. Ethernet Port Detected
19
Page 28

MicroScanner2 Cable Verifier
Users Manual
Viewing Individual Results
To see individual results for each wire pair, use E or D; to
move among the screens.
In this mode, the tester continuously tests only the wire pair
you are viewing.
Figure 14 shows examples of these screens.
A
Short on pair 1,2 at 29.8 m.
Notes
On the individual results screens, shorts are shown
only when they are between wires in a pair.
When there is a short, the far-end adapter and the
mapping of the unshorted wires are not shown.
B
Pair 3,6 is 67.7 m long and is terminated with the
wiremap adapter.
C
Open on pair 4,5 at 48.1 m. The open could be on one
or both wires.
20
Page 29

Figure 14. Results Screens for Individual Wire Pairs
Testing Twisted Pair Cabling
egk14.eps
21
Page 30

MicroScanner2 Cable Verifier
Users Manual
Using Multiple Remote ID Locators
Using multiple remote ID locators helps you identify
multiple network connections at a patch panel, as shown in
Figure 15.
The display in Figure 15 shows that the tester is connected
to the cable terminated with remote ID locator number 3.
WCaution
Do not use multiple far end adapters in star or
bus topologies. Doing so causes incorrect
wiremap results.
22
Page 31

Patch panel
Testing Twisted Pair Cabling
Locator # 2
Locator # 3
Remote ID locators
connected to wall
outlets
Locator # 4
Locator # 5
Figure 15. Using Multiple Remote ID Locators
egk04.eps
23
Page 32

MicroScanner2 Cable Verifier
Users Manual
Connecting to Telephone Networks Wired in Star Topologies
Telephone cables wired in a star topology (Figure 16) are
connected together at a bridge tap at the distribution
center. The bridge tap connects each wire to all other wires
of the same number.
The tester detects bridge taps and measures the distance to
the bridge tap. To measure the length of each cable
connected to the bridge tap, connect the wiremap adapter
or remote ID locator to the bridge tap and the tester to the
wall outlet.
The tester cannot measure length past the bridge tap
because reflections from the bridge tap connections
interfere with measurements.
If you connect the tester to the bridge tap, the tester
measures the length only to the bridge tap, which is only
the patch cord length.
WCaution
Do not use multiple far end adapters in star or
bus topologies. Doing so causes incorrect
wiremap results.
24
Page 33

Distribution
center
Testing Twisted Pair Cabling
Common connection
to bridge tap
RJ11 patch
cord
Wiremap
adapter
Note: For a correct length reading, connect the
tester and wiremap adapter as shown. See
“Connecting to Star Topologies” for details.
Figure 16. Connecting to a Telephone Network Wired in a Star Topology
RJ11 patch
cord
Wall
outlets
egk16.eps
25
Page 34

MicroScanner2 Cable Verifier
Users Manual
Connecting to Telephone Networks Wired in Bus Topologies
Telephone cables wired in a bus topology (Figure 17)
connect the wall outlets in series. In this topology, you
measure the length from the last outlet to the wiremap
adapter.
If you connect to an outlet in the middle of the series, the
tester reports a bridge tap. The length reported is the
length to the outlet, which is the patch cord length. The
tester cannot measure length past the outlet because
reflections from the cables on either side interfere with
measurements.
If you are unsure which outlet is the last in the bus, do the
following:
1
Connect the wiremap adapter or ID locator to the
beginning of the bus at the distribution center.
2
Connect the tester to an outlet and run the twisted pair
cable test.
If the tester reports a bridge tap, move to another
outlet. The last outlet will not show a bridge tap, and
will show the length to the distribution center.
WCaution
Do not use multiple far end adapters in star or
bus topologies. Doing so causes incorrect
wiremap results.
26
Page 35

Distribution
center
Connection to bus
RJ11 patch
cord
Wiremap
adapter
Note: Locations of the tester and wiremap
adapter may be swapped.
Testing Twisted Pair Cabling
Wall
outlets
RJ11 patch
cord
Figure 17. Connecting to a Telephone Network Wired in a Bus Topology
egk17.eps
27
Page 36

MicroScanner2 Cable Verifier
Users Manual
Testing Coaxial Cabling
1
Turn on the tester; then press Y to switch to coaxial
test mode (T).
2
Connect the tester and wiremap adapter or ID locator to
the cabling as shown in Figure 18.
For cabling not terminated with an F-connector, use an
adapter or hybrid patch cord to connect to the cabling.
The test runs continuously until you change modes or turn
the tester off.
Connection to
service
Coaxial patch cords
Wall
outlet
Wiremap
adapter
egk19.eps
Figure 18. Connecting to Coaxial Cabling
28
Page 37

Testing Coaxial Cabling
Coaxial Results
Figure 19 shows a good coaxial cable 38.4 m long and
terminated with remote ID number 3.
Figure 19. Coaxial Results
egk20.eps
Open on Coaxial Cabling
Figure 20 shows an open 12.1 m from the tester.
egk21.eps
Figure 20. Open on Coaxial Cabling
29
Page 38

MicroScanner2 Cable Verifier
Users Manual
Short on Coaxial Cabling
Figure 21 shows a short 12.1 m from the tester.
Figure 21. Short on Coaxial Cabling
Unknown Termination on Coaxial Cabling
Figure 22 shows a cable connected to a device at the far
end, such as a television, CATV service, VCR, DVD player,
satellite dish, splitter, or antenna. Dashes shown for length
mean the tester cannot measure length because the device
does not produce reflections.
egk22.eps
egk23.eps
Figure 22. Unknown Termination on Coaxial Cabling
30
Page 39

Detecting Power Over Ethernet
The tester can detect PoE voltage from 802.3af sources.
Detecting Power Over Ethernet
To select PoE mode, press
display, as shown in Figure 23 (
In PoE mode, the tester solicits PoE power on pairs 1,2-3,6
and 4,5-7,8. The tester may activate a PoE source and will
not be damaged by PoE power.
If PoE power is detected,
pairs (B). The Poemay blink as the PoE source turns the
power on and off.
In twisted pair test mode, a flashing
means that PoE power may be available. To verify the
presence of a PoE source, switch the tester to PoE mode.
The tester will not detect PoE schemes that are not
compliant with the IEEE 802.3af standard, such as
®
Inline Power.
Cisco
M until PoE appears on the
A
).
Poeappears above the powered
PoE mode indicator
Note
egk30.eps
Figure 23. PoE Display
31
Page 40

MicroScanner2 Cable Verifier
Users Manual
Using the Toner
You can use the tester with an optional tone probe to
locate cables in bundles, at patch panels, or behind walls.
Use the tester’s IntelliTone
Networks IP100 or IP200 tone probe. The digital IntelliTone
signal is easier to detect at a distance than analog tones,
and its frequency and encoding eliminate cable
misidentification due to signal bleed and radiated or
ambient noise.
The tester’s analog tone mode is compatible with most tone
probes.
The analog tone mode features the SmartTone
for positive identification of cables in bundles.
™
mode with an optional Fluke
™
function
Toning in IntelliTone Mode (optional IntelliTone probe required)
Refer to Figures 24 and 25.
1
Connect the tester to the cable.
2
Press Y to select twisted pair (U) or coaxial (T) cable.
3
Press M until L, IntelliTone, and and a scrolling
pattern of 1s and 0s appear on the display (A, B, and
C in Figure 24).
4
To toggle between the two IntelliTone songs press E
then
D. The display shows the song number (D).
If you press
through the IntelliTone and analog songs.
5
Turn the probe’s rotary switch to M (locate).
6
Use the probe to find the general location of the tone at
a cable rack, patch panel, or behind a wall, as shown in
Figure 25. The SYNC LED lights up green when the
probe is receiving the IntelliTone signal.
The probe’s LEDs light up from 1 to 8 as the signal
strength increases. The higher the number, the stronger
the signal.
D or E repeatedly, the tester cycles
32
Page 41

Notes
If you cannot locate the IntelliTone signal on
2-conductor cables, the cable may be shorted. Use
the tester to check for shorts. See pages 11 and 13.
7
Turn the probe’s rotary switch to N (isolate).
8
Use the probe to isolate the tone source in the cable
bundle or at the patch panel. The SYNC LED lights up
green when the probe is receiving the IntelliTone signal.
The probe’s LEDs light up from 1 to 8 as the signal
strength increases. The higher the number, the stronger
the signal.
Using the Toner
egk07.eps
Figure 24. IntelliTone Toner Mode Display
33
Page 42

MicroScanner2 Cable Verifier
Users Manual
Wall
outlet
Locating Cables
Isolating Cables
Volume
control
34
egk24.eps
Figure 25. Using the Toner in IntelliTone Mode
Page 43

Analog Toner Mode (optional tone probe
A
required)
Refer to Figure 26.
1
Connect the tester to the cable.
Using the Toner
C
2
Press Y to select twisted pair or coaxial cable.
3
Press M until L appears on the display (A); then
press
D to enter analog toner mode. The display shows
a scrolling sinewave in analog toner mode (
4
To change songs, press D. The display shows the song
number (C). The analog toner has four songs.
If you press
through the analog and IntelliTone songs.
5
Use the probe to search for the cable.
D or E repeatedly, the tester cycles
B
B
).
egk25.eps
Figure 26. Analog Toner Mode Display
35
Page 44

MicroScanner2 Cable Verifier
Users Manual
Using the SmartTone Function
Use the SmartTone™ function when you have trouble
locating a cable. This function changes the toner’s song
when you short a wire pair in the cable connected to the
tester. SmartTone works with the IntelliTone probe and
with analog probes.
Note
Use the SmartTone function only on dry pairs of
wires that are unterminated at both ends. Do not
use this function on powered wires.
1
Press Y to select twisted pair or coaxial cabling.
2
Press M until L appears on the display.
3
Press D to select the analog toner mode (IntelliTone
disappears from the display).
4
At the far end of the cabling, place the probe near the
ends of the cables.
5
Momentarily short a wire pair in a cable (twisted pair) or
short the conductor and shield in a cable (coaxial). If the
song changes when you release the short, you have
found the cable connected to the tester.
Using the IntelliTone Cable Map Function (optional IP200 probe required)
The tester’s IntelliTone function works with an optional
IP200 probe’s cable map function to verify wiring at the far
end of the cabling. The probe’s cable map function
identifies the most common wiring faults on twisted pair
cabling: shorts, opens, and crossed pairs.
1
Press Y to select twisted pair cabling (U).
2
Turn the probe’s rotary switch to CABLE MAP.
3
Connect the tester and probe to the cabling as shown in
Figure 27.
4
Press M until L appears on the display. IntelliTone
mode is indicated by IntelliTone and a scrolling pattern
of 1s and 0s on the display. See Figure 27.
5
The probe’s LEDs light in sequence to indicate the
cable’s wiring. See the probe’s documentation for
details.
36
Page 45

Using the IntelliTone Cable Map Function (optional IP200 probe required)
Note
Normally, the probe’s SYNC LED lights to indicate
reception of the IntelliTone signal. You may change
the LED’s function to indicate shield continuity. See
the probe’s documentation for details.
LEDs show the
wiremap. See
the ITK200
manual for
details.
egk26.eps
Figure 27. Using the Toner with the IP200 IntelliTone
Cable Map Function
37
Page 46

MicroScanner2 Cable Verifier
Users Manual
Calibrating Length Measurements
The tester uses an NVP value (nominal velocity of
propagation) and the signal delay through the cable to
calculate length. The tester’s default NVP values are usually
accurate enough to verify length; however, you can
increase the accuracy of length measurements by adjusting
the NVP to a specified or actual value.
The default NVP values are 70 % for twisted pair cable and
82 % for coaxial cable.
Note
NVP values can vary among cable types, lots, and
manufacturers. In most cases, these differences are
minor and may be disregarded.
Setting the NVP to a Specified Value
To enter the NVP value specified by the manufacturer:
1
Turn on the tester while holding down the Y and E
keys.
2
To set the NVP for the coaxial port (T), press Y.
3
Use E and D to set the NVP value.
4
To save the setting and exit NVP mode, turn the tester
off then on again.
Determining a Cable’s Actual NVP
You can determine a cable’s actual NVP by adjusting the
measured length to match a known length of cable.
To determine a cable’s NVP:
1
Turn on the tester while holding down the Y and E
keys.
2
To set the NVP for the coaxial port (T), press Y.
3
Connect a known length of the cable to be tested to the
tester’s twisted pair or coaxial connector.
38
Page 47

Maintenance
Notes
The cable must be at least 49 ft (15 m) long. If the
cable is too short, “---” appears for the length.
For the best accuracy, use a cable between 49 ft
(15 m) and 98 ft (30 m) long.
The cable must not be connected to anything.
4
To switch between meters and feet, press M.
5
Use E and D to change the NVP until the measured
length matches the actual length of the cable.
6
To save the setting and exit NVP mode, turn the tester
off then on again.
Maintenance
WWarningX
To avoid possible fire, electric shock, personal
injury, or damage to the tester:
•
Do not open the case. No user-serviceable parts
are inside.
•
Replacing electrical parts yourself will void the
tester’s warranty and might compromise its
safety features.
•
Use only specified replacement parts for userreplaceable items.
•
Use only Fluke Networks authorized service
centers.
39
Page 48

MicroScanner2 Cable Verifier
Users Manual
Cleaning
Clean the display with glass cleaner and a soft, lint-free
cloth. Clean the case with a soft cloth dampened with
water or water and a mild soap.
WCaution
•
To avoid damaging the display or the case, do
not use solvents or abrasive cleansers.
Battery Life, Status, and Replacement
WWarningX
•
To avoid possible electric shock or personal
injury:
•
Turn off the tester and disconnect all test leads
before replacing the battery.
•
Use only the correct type of batteries, properly
installed in the case, to power the tester.
The batteries last for about 20 hours of typical use.
Replace the tester’s batteries when the low battery
indicator (
B) appears. See Figure 28.
You can use the following types of AA (IEC LR6) batteries in
the tester:
•
Alkaline
•
Lithium
•
Rechargeable nickel-metal hydride (NiMH)
•
Rechargeable nickel-cadmium batteries (NiCD)
egk28.eps
Figure 28. Replacing the Tester’s Batteries
40
Page 49

If Something Seems Wrong
Checking the Tester’s Version and Serial Number
Turn the tester on while holding down the E and D keys.
Use
E and D to scroll through the screens:
•
SOF: Software version
•
SN: Serial number
•
FAC: Factory test date
To exit this mode, turn the tester off.
Table 2. Troubleshooting the Tester
Symptom Action
The keypad does not respond. Press and hold I until the tester turns off; then turn the tester on again.
The tester will not turn on.
Length measurements are incorrect. Check the NVP value. See “Calibrating Length Measurements” on page 38.
Replace the batteries, verifying that they are installed correctly. See Figure 28
on page 40.
If Something Seems Wrong
If something seems wrong with the tester, refer to Table 2.
If Table 2 does not help you solve a problem with the tester,
contact Fluke Networks for additional help. If possible, have
the tester’s version and serial number.
For warranty information, refer to the warranty at the
beginning of this manual. If the warranty has lapsed,
contact Fluke Networks for repair prices.
41
Page 50

MicroScanner2 Cable Verifier
Users Manual
Options and Accessories
For the latest list of options and accessories visit the Fluke
Networks website at www.flukenetworks.com.
To order options and accessories (Table 3), contact Fluke
Networks.
Table 3. Options and Accessories
Option or Accessory Fluke Networks Model Number
Remote ID Locator Kit, numbers 2-7 MS2-IDK27
Wiremap adapter MS2-WM
Test lead, 8-pin modular plug (RJ45) to 8 alligator clips CLIP-SET
Coaxial Adapter Kit (F-connector barrel adapter, female-to-female BNC adapter,
CIQ-COAX
female-to-female RCA adapter)
Universal adapter, 8-pin/4-pin modular jack to 8-pin/4-pin modular jack CIQ-RJA
Carrying case for MicroScanner
Carrying pouch for MicroScanner
2
Professional kit MS2-CPK
2
tester MS2-POUCH
42
Page 51

Specifications
Specifications apply at 23 oC (73 oF), unless otherwise noted.
Environmental Specifications
Operating temperature 32 °F to 113 °F (0 oC to 45 oC)
o
Storage temperature -4 °F to +140 °F (-20
C to +60 oC)
Specifications
Operating relative humidity
(% RH without condensation)
Shock and Vibration
Safety EN 61010-1 2
Altitude 4000 m; Storage: 12000 m
EMC EN 61326-1
Certifications and compliance
90 % (50 °F to 95 °F; 10 oC to 35 oC)
75 % (95 °F to 113 °F; 35 oC to 45 oC)
Random, 2 g, 5 Hz-500 Hz (Class 2)
1 m drop test with and without wiremap adapter attached
nd
Edition
P Conforms to relevant European Union directives.
; Conforms to relevant Australian standards.
43
Page 52

MicroScanner2 Cable Verifier
Users Manual
General Specifications
Test connectors
Power
Dimensions and weight
(with batteries installed and
wiremap adapter attached
Display Monochrome LCD with backlight
Shielded 8-pin modular jack accepts 8-pin modular (RJ45) and 4-pin modular (RJ11) plugs.
F-connector for coaxial cable.
Battery type: 2 AA (NEDA 15A, IEC LR6) alkaline batteries
Battery life: 20 hours of typical use
Other compatible battery types: 2 AA photo lithium, NIMH, NICAD
3 in x 6.4” x 1.4 in (7.6 cm x 16.3 cm x 3.6 cm)
0.8 lb (0.36 kg)
Test Modes
Cable test
Tone Generates Intellitone™ and normal analog toning signals
PoE Solicits and detects the presence of 802.3af compatible PoE (Power over Ethernet) devices
Measures length, verifies wiremap, identifies remote ID locators, and detects Ethernet ports.
Displays results on one screen.
44
Page 53

Performance Specifications
Specifications
Cable types tested
Twisted pair: UTP, FTP, SSTP
Coaxial: 75 Ω, 50 Ω, 93 Ω
Length test
Range: 460 m (1500 ft)
Resolution: 0.3 m (1 ft)
Typical accuracy: ± 4% or 0.6 m (2 ft) whichever is greater. NVP uncertainty is an additional
error.
Calibration: User-settable NVP for twisted pair and coax. Can determine actual NVP with
known length of cable.
Wiremap test
Detects single-wire faults, shorts, miswires, split pairs, and up to seven far-end adapter IDs.
The wiremap is drawn with proportional length to visually indicate the approximate location
of faults.
Port detection Detects the advertised speed of 802.3 Ethernet ports.
Tone generator
Supports toning and cable mapping with a Fluke Networks digital IntelliTone
Generates four tones compatible with typical analog probes.
SmartTone
™
feature gives positive identification of cables in bundles when using an
IntelliTone or an analog probe.
™
probe.
45
Page 54

MicroScanner2 Cable Verifier
Users Manual
Regulatory Information
This equipment generates, uses, and can radiate radio
frequency energy, and, if not installed and used in
accordance with the manual, may cause interference to
radio communications. It has been tested and found to
comply with the limits for a Class A digital device pursuant
to Part 15, Subpart J of the FCC rules, which are designed to
provide reasonable protection against such interference
when operated in a commercial environment. Operation of
the equipment in a residential area is likely to cause
interference, in which case the user, at his own expense, will
be required to take whatever measures may be required to
correct the interference.
46
Page 55

Appendix A: Diagnosing Wiremap Faults
Appendix A lists the typical causes of wiremap failures.
Open
•
Wires connected to wrong pins at connector or
punchdown blocks
•
Faulty connections
•
Damaged connector
•
Damaged cable
•
Wrong pairs selected in setup
•
Wrong application for cable
Split Pair
Wires connected to wrong pins at connector or punchdown
block.
Reversed Pairs
Wires connected to wrong pins at connector or punchdown
block.
Crossed Pairs
•
Wires connected to wrong pins at connector or
punchdown block.
•
Mix of 568A and 568B wiring standards (12 and 36
crossed).
•
Crossover cables used where not needed (12 and 36
crossed).
47
Page 56

MicroScanner2 Cable Verifier
Users Manual
Short
•
Damaged connector
•
Damaged cable
•
Conductive material stuck between pins at connector.
•
Improper connector termination
•
Wrong application for cable
48
Page 57

Index
Symbols
"?" on coaxial screen, 30
–A–
accessories
optional, 42
standard, 3
analog toner, 35
auto shutoff, 9
–B–
batteries, 40
bridge tap, 17
bus topology, 26
–C–
cable map function, 36
cable tests
coaxial cabling, 28
twisted pair, 11
cleaning, 40
coaxial
connections, 28
open, 29, 30
short, 30
unknown termination, 30
connections
coaxial, 28
twisted pair, 11
connectors, 7
crossed pairs, 14
crossed wires, 13
customer support
contacting Fluke Networks, 2
problem with the tester, 41
49
Page 58

MicroScanner2 Cable Verifier
Users Manual
–E–
Ethernet port detected, 18
–F–
Fluke Networks, 2
–H–
help
contacting Fluke Networks, 2
problem with the tester, 41
high voltage, 4, 16
–I–
IntelliTone mode
cable map function, 36
toner, 32
ISDN, 4, 16
–K–
keys, 7
–L–
length calibration, 38
–M–
maintenance, 39
–N–
NVP, 38
–O–
open
coaxial, 29, 30
twisted pair, 12
options, 42
–P–
PoE (Power over Ethernet), 31
problems (with the tester), 41
–R–
registration, 2
remote ID locator, 10, 22
replacement parts, 42
RJ11 jack, 10
50
Page 59

Index
–S–
safety information, 4, 39
serial number, 41
service, 41
short
coaxial, 30
twisted pair, 13
SmartTone function, 35, 36
specifications, 43
split pair, 15
star topology, 24, 27
–T–
telephone cord (split pair), 15
telephone voltages, 4, 16
testing
coaxial cabling, 28
twisted pair cabling, 11
toner, 32
analog mode, 35
IntelliTone mode, 32
SmartTone function, 35, 36
troubleshooting
cabling faults, 47
the tester, 41
twisted pair
bridge tap, 17
connections
bus topology, 26
network cabling, 11
star topology, 24, 27
crossed pairs, 14
crossed wires, 13
individual results, 20
open, 12
PoE detection, 18
short, 13
split pair, 15
telephone voltages, 16
–U–
universal adapter, 10
–V–
version information, 41
voltage detection, 4, 16
51
Page 60

MicroScanner2 Cable Verifier
Users Manual
–W–
wiremap adapter, 10
52
 Loading...
Loading...