Page 1

User’s manual
FLIR T10xx series
Page 2

Page 3

Page 4
Important note
Before operating the device, you must read, understand, and follow all instructions, warnings, cautions, and legal disclaimers.
Důležitá poznámka
Před použitím zařízení si přečtěte veškeré pokyny, upozornění, varování a vyvázání se ze záruky, ujistěte se, že jim rozumíte, a řiďte se
jimi.
Vigtig meddelelse
Før du betjener enheden, skal du du læse, forstå og følge alle anvisninger, advarsler, sikkerhedsforanstaltninger og ansvarsfraskrivelser.
Wichtiger Hinweis
Bevor Sie das Gerät in Betrieb nehmen, lesen, verstehen und befolgen Sie unbedingt alle Anweisungen, Warnungen, Vorsichtshinweise
und Haftungsausschlüsse
Σημαντική σημείωση
Πριν από τη λειτουργία της συσκευής, πρέπει να διαβάσετε, να κατανοήσετε και να ακολουθήσετε όλες τις οδηγίες,
προειδοποιήσεις, προφυλάξεις και νομικές αποποιήσεις.
Nota importante
Antes de usar el dispositivo, debe leer, comprender y seguir toda la información sobre instrucciones, advertencias, precauciones y
renuncias de responsabilidad.
Tärkeä huomautus
Ennen laitteen käyttämistä on luettava ja ymmärrettävä kaikki ohjeet, vakavat varoitukset, varoitukset ja lakitiedotteet sekä noudatettava
niitä.
Remarque importante
Avant d'utiliser l'appareil, vous devez lire, comprendre et suivre l'ensemble des instructions, avertissements, mises en garde et clauses
légales de non-responsabilité.
Fontos megjegyzés
Az eszköz használata előtt figyelmesen olvassa el és tartsa be az összes utasítást, figyelmeztetést, óvintézkedést és jogi nyilatkozatot.
Nota importante
Prima di utilizzare il dispositivo, è importante leggere, capire e seguire tutte le istruzioni, avvertenze, precauzioni ed esclusioni di
responsabilità legali.
重要な注意
デバイスをご使用になる前に、あらゆる指示、警告、注意事項、および免責条項をお読み頂き、その内容を理解して従ってください。
중요한 참고 사항
장치를 작동하기 전에 반드시 다음의 사용 설명서와 경고, 주의사항, 법적 책임제한을 읽고 이해하며 따라야 합니다.
Viktig
Før du bruker enheten, må du lese, forstå og følge instruksjoner, advarsler og informasjon om ansvarsfraskrivelse.
Belangrijke opmerking
Zorg ervoor dat u, voordat u het apparaat gaat gebruiken, alle instructies, waarschuwingen en juridische informatie hebt doorgelezen en
begrepen, en dat u deze opvolgt en in acht neemt.
Ważna uwaga
Przed rozpoczęciem korzystania z urządzenia należy koniecznie zapoznać się z wszystkimi instrukcjami, ostrzeżeniami, przestrogami i
uwagami prawnymi. Należy zawsze postępować zgodnie z zaleceniami tam zawartymi.
Nota importante
Antes de utilizar o dispositivo, deverá proceder à leitura e compreensão de todos os avisos, precauções, instruções e isenções de
responsabilidade legal e assegurar-se do seu cumprimento.
Важное примечание
До того, как пользоваться устройством, вам необходимо прочитать и понять все предупреждения, предостережения и
юридические ограничения ответственности и следовать им.
Viktig information
Innan du använder enheten måste du läsa, förstå och följa alla anvisningar, varningar, försiktighetsåtgärder och ansvarsfriskrivningar.
Önemli not
Cihazı çalıştırmadan önce tüm talimatları, uyarıları, ikazları ve yasal açıklamaları okumalı, anlamalı ve bunlara uymalısınız.
重要注意事项
在操作设备之前,您必须阅读、理解并遵循所有说明、警告、注意事项和法律免责声明。
重要注意事項
操作裝置之前,您務必閱讀、了解並遵循所有說明、警告、注意事項與法律免責聲明。
Page 5

User’s manual
FLIR T10xx series
#T559954; r. AL/37426/37426; en-US
v
Page 6

Page 7

Table of contents
1 Disclaimers ........................................................................................ 1
1.1 Legal disclaimer .........................................................................1
1.2 Usage statistics .......................................................................... 1
1.3 Changes to registry ..................................................................... 1
1.4 U.S. Government Regulations........................................................ 2
1.5 Copyright ..................................................................................2
1.6 Quality assurance .......................................................................2
1.7 Patents.....................................................................................2
1.8 Third-party licenses..................................................................... 3
1.8.1 GNU Lesser General Public License (LGPL) ..........................3
1.8.2 Fonts (Source Han Sans)................................................... 3
1.8.3 Fonts (DejaVu) ................................................................3
2 Safety information ...............................................................................4
3 Notice to user .....................................................................................9
3.1 User-to-user forums .................................................................... 9
3.2 Calibration................................................................................. 9
3.3 Accuracy .................................................................................. 9
3.4 Disposal of electronic waste .......................................................... 9
3.5 Training ....................................................................................9
3.6 Documentation updates ............................................................... 9
3.7 Important note about this manual.................................................... 9
3.8 Note about authoritative versions.................................................. 10
4 Customer help .................................................................................. 11
4.1 General .................................................................................. 11
4.2 Submitting a question ................................................................ 11
4.3 Downloads .............................................................................. 12
5 Introduction...................................................................................... 13
5.1 General description ................................................................... 13
5.2 Key benefits............................................................................. 13
6 Quick start guide ............................................................................... 14
6.1 Procedure ............................................................................... 14
7 About FLIR Tools/Tools+..................................................................... 15
7.1 Introduction ............................................................................. 15
7.2 Workflow................................................................................. 16
7.2.1 General........................................................................ 16
7.2.2 Figure.......................................................................... 16
7.2.3 Explanation................................................................... 16
8 Using the high-speed interface (HSI) ................................................... 17
8.1 General .................................................................................. 17
8.2 System overview ...................................................................... 17
8.2.1 Figure.......................................................................... 17
8.2.2 Explanation................................................................... 17
8.3 Quick start guide ...................................................................... 18
8.4 HSI box indicator LED................................................................ 18
8.5 Digital I/O ................................................................................ 18
9 A note about ergonomics ................................................................... 19
9.1 General .................................................................................. 19
9.2 Figure .................................................................................... 19
#T559954; r. AL/37426/37426; en-US
vii
Page 8

Table of contents
10 Camera parts .................................................................................... 20
10.1 View from the right .................................................................... 20
10.1.1 Figure.......................................................................... 20
10.1.2 Explanation................................................................... 20
10.2 View from the left ...................................................................... 21
10.2.1 Figure.......................................................................... 21
10.2.2 Explanation................................................................... 21
10.3 View from the bottom ................................................................. 22
10.3.1 Figure.......................................................................... 22
10.3.2 Explanation................................................................... 22
10.4 View from the rear..................................................................... 23
10.4.1 Figure.......................................................................... 23
10.4.2 Explanation................................................................... 23
10.5 Neck strap attachment points ...................................................... 25
10.5.1 Figure.......................................................................... 25
10.6 Battery condition LED indicator .................................................... 25
10.6.1 Figure.......................................................................... 25
10.6.2 Explanation................................................................... 25
10.7 Power LED indicator .................................................................. 26
10.7.1 Figure.......................................................................... 26
10.7.2 Explanation................................................................... 26
10.8 Laser pointer ........................................................................... 26
10.8.1 Figure.......................................................................... 26
10.8.2 Laser warning label......................................................... 27
10.8.3 Laser rules and regulations .............................................. 27
11 Screen elements ............................................................................... 28
11.1 Figure .................................................................................... 28
11.2 Explanation ............................................................................. 28
11.3 Status icons and indicators ......................................................... 28
11.4 Image overlay information........................................................... 29
12 Navigating the menu system............................................................... 30
12.1 General .................................................................................. 30
12.2 Navigating using the joystick ....................................................... 30
13 Handling the camera .......................................................................... 31
13.1 Charging the battery.................................................................. 31
13.1.1 Using the power supply to charge the battery ....................... 31
13.1.2 Using the stand-alone battery charger to charge the
battery ......................................................................... 31
13.2 Turning on the camera ............................................................... 31
13.2.1 Procedure .................................................................... 31
13.3 Turning off the camera ............................................................... 31
13.3.1 Procedure .................................................................... 31
13.4 Adjusting the viewfinder’s dioptric correction (sharpness) .................. 32
13.4.1 Figure.......................................................................... 32
13.4.2 Procedure .................................................................... 32
13.5 Adjusting the angle of the lens ..................................................... 33
13.5.1 Figure.......................................................................... 33
13.6 Adjusting the infrared camera focus manually ................................. 33
13.6.1 Figure.......................................................................... 33
13.6.2 Procedure .................................................................... 33
#T559954; r. AL/37426/37426; en-US
viii
Page 9

Table of contents
13.7 Autofocusing the infrared camera ................................................. 34
13.7.1 General........................................................................ 34
13.7.2 Figure.......................................................................... 34
13.7.3 Procedure .................................................................... 34
13.8 Continuous autofocus ................................................................ 35
13.8.1 General........................................................................ 35
13.8.2 Procedure .................................................................... 35
13.9 Operating the laser pointer.......................................................... 35
13.9.1 Figure.......................................................................... 36
13.9.2 Procedure .................................................................... 36
13.10 Using the digital zoom function .................................................... 36
13.10.1 General........................................................................ 36
13.10.2 Figure.......................................................................... 37
13.10.3 Procedure .................................................................... 37
13.11 Assigning functions to the programmable buttons ............................ 37
13.11.1 General........................................................................ 37
13.11.2 Procedure .................................................................... 38
13.12 Using the camera lamp as a flash ................................................. 38
13.12.1 General........................................................................ 38
13.12.2 Procedure .................................................................... 38
13.13 Changing lenses....................................................................... 38
13.14 Using the close-up lens .............................................................. 42
13.14.1 General........................................................................ 42
13.14.2 Attaching the close-up lens .............................................. 42
13.14.3 Removing the close-up lens.............................................. 44
13.15 Calibrating the compass ............................................................. 46
13.15.1 Procedure .................................................................... 46
14 Saving and working with images ......................................................... 47
14.1 About image files ...................................................................... 47
14.1.1 General........................................................................ 47
14.1.2 File-naming convention ................................................... 47
14.1.3 Image capacity .............................................................. 47
14.1.4 About UltraMax.............................................................. 47
14.2 Saving an image ....................................................................... 47
14.2.1 General........................................................................ 47
14.2.2 Procedure .................................................................... 48
14.3 Previewing an image ................................................................. 48
14.3.1 General........................................................................ 48
14.3.2 Procedure .................................................................... 48
14.4 Opening a saved image.............................................................. 48
14.4.1 General........................................................................ 48
14.4.2 Procedure .................................................................... 48
14.5 Editing a saved image................................................................ 49
14.5.1 General........................................................................ 49
14.5.2 Procedure .................................................................... 49
14.5.3 Related topics ............................................................... 49
14.6 Creating a PDF report in the camera ............................................. 49
14.6.1 General........................................................................ 49
14.6.2 Naming convention......................................................... 50
14.6.3 Procedure .................................................................... 50
14.7 Deleting an image ..................................................................... 50
#T559954; r. AL/37426/37426; en-US
ix
Page 10

Table of contents
14.7.1 General........................................................................ 50
14.7.2 Procedure .................................................................... 50
14.8 Deleting multiple images ............................................................ 50
14.8.1 General........................................................................ 50
14.8.2 Procedure .................................................................... 50
14.9 Deleting all images.................................................................... 51
14.9.1 General........................................................................ 51
14.9.2 Procedure .................................................................... 51
14.10 Resetting the image counter........................................................ 51
14.10.1 General........................................................................ 51
14.10.2 Procedure .................................................................... 51
15 Achieving a good image ..................................................................... 53
15.1 General .................................................................................. 53
15.2 Adjusting the infrared camera focus .............................................. 53
15.3 Adjusting the infrared image ........................................................ 53
15.3.1 General........................................................................ 53
15.3.2 Example 1 .................................................................... 54
15.3.3 Example 2 .................................................................... 54
15.3.4 Manual adjustment in Level, Span mode ............................. 55
15.3.5 Manual adjustment in Level, Max, Min mode ........................ 55
15.4 Changing the temperature range .................................................. 55
15.4.1 General........................................................................ 55
15.4.2 Procedure .................................................................... 55
15.5 Changing the color palette .......................................................... 56
15.5.1 General........................................................................ 56
15.5.2 Procedure .................................................................... 57
15.6 Changing the object parameters .................................................. 57
15.7 Calibrating the camera ............................................................... 58
15.7.1 General........................................................................ 58
15.7.2 Manual calibration .......................................................... 58
15.8 Hiding all overlay ...................................................................... 58
15.8.1 General........................................................................ 58
15.8.2 Procedure .................................................................... 59
16 Working with image modes................................................................. 60
16.1 General .................................................................................. 60
16.2 Image examples ....................................................................... 60
16.3 Selecting the image mode .......................................................... 61
17 Working with measurement tools ........................................................ 62
17.1 General .................................................................................. 62
17.2 Adding/removing measurement tools ............................................ 62
17.3 Working with user presets........................................................... 62
17.3.1 General........................................................................ 62
17.3.2 Procedure .................................................................... 62
17.4 Resizing or moving a measurement tool......................................... 63
17.4.1 General........................................................................ 63
17.4.2 Procedure .................................................................... 63
17.5 Changing object parameters ....................................................... 64
17.5.1 General........................................................................ 64
17.5.2 Types of parameters ....................................................... 64
17.5.3 Recommended values..................................................... 65
#T559954; r. AL/37426/37426; en-US
x
Page 11

Table of contents
17.5.4 Procedure .................................................................... 65
17.5.5 Related topics ............................................................... 66
17.6 Displaying values in the result table and displaying a graph ................ 66
17.6.1 General........................................................................ 66
17.6.2 Procedure .................................................................... 67
17.7 Creating and setting up a difference calculation............................... 67
17.7.1 General........................................................................ 67
17.7.2 Procedure .................................................................... 67
17.8 Setting a measurement alarm ...................................................... 68
17.8.1 General........................................................................ 68
17.8.2 Types of alarm ............................................................... 68
17.8.3 Alarm signals ................................................................ 68
17.8.4 Procedure .................................................................... 69
18 Working with color alarms and isotherms ............................................. 71
18.1 Color alarms ............................................................................ 71
18.1.1 General........................................................................ 71
18.1.2 Image examples ............................................................ 71
18.2 Setting up above, below, and interval alarms................................... 72
18.3 Building isotherms .................................................................... 73
18.3.1 About the Condensation alarm .......................................... 73
18.3.2 About the Insulation alarm ................................................ 73
18.3.3 Setting up condensation and insulation alarms ..................... 73
19 Annotating images ............................................................................ 74
19.1 General .................................................................................. 74
19.2 Adding a note .......................................................................... 74
19.2.1 General........................................................................ 74
19.2.2 Procedure .................................................................... 74
19.3 Adding a table .......................................................................... 74
19.3.1 General........................................................................ 74
19.3.2 Procedure .................................................................... 75
19.4 Adding a voice annotation........................................................... 75
19.4.1 General........................................................................ 75
19.4.2 Procedure .................................................................... 76
19.5 Adding a sketch........................................................................ 76
19.5.1 General........................................................................ 76
19.5.2 Procedure .................................................................... 76
20 Programming the camera (time lapse) ................................................. 78
20.1 General .................................................................................. 78
20.2 Procedure ............................................................................... 78
21 Recording video clips ........................................................................ 79
21.1 General .................................................................................. 79
21.2 Procedure ............................................................................... 79
22 Screening alarm ................................................................................ 80
22.1 General .................................................................................. 80
22.2 Procedure ............................................................................... 80
23 Pairing Bluetooth devices................................................................... 81
23.1 General .................................................................................. 81
23.2 Procedure ............................................................................... 81
24 Configuring Wi-Fi .............................................................................. 82
24.1 General .................................................................................. 82
#T559954; r. AL/37426/37426; en-US
xi
Page 12

Table of contents
24.2 Setting up a wireless access point (most common use) ..................... 82
24.3 Connecting the camera to a WLAN (less common use) ..................... 82
25 Changing settings ............................................................................. 83
25.1 General .................................................................................. 83
25.1.1 Define user presets ........................................................ 83
25.1.2 Camera temperature range .............................................. 83
25.1.3 Save options & storage.................................................... 83
25.1.4 Programmable buttons .................................................... 84
25.1.5 Device settings .............................................................. 85
25.2 Procedure ............................................................................... 87
26 Technical data................................................................................... 88
26.1 Online field-of-view calculator ...................................................... 88
26.2 Note about technical data ........................................................... 88
26.3 Note about authoritative versions.................................................. 88
26.4 FLIR T1020 12° ........................................................................ 89
26.5 FLIR T1020 28° ........................................................................ 96
26.6 FLIR T1020 45° ...................................................................... 103
26.7 FLIR T1020 28° and 12° ........................................................... 110
26.8 FLIR T1020 28° and 45° ........................................................... 117
26.9 FLIR T1020 28°, 12°, and 45° .................................................... 124
26.10 FLIR T1030sc 12° ................................................................... 131
26.11 FLIR T1030sc 28° ................................................................... 138
26.12 FLIR T1030sc 45° ................................................................... 145
26.13 FLIR T1040 12° ...................................................................... 152
26.14 FLIR T1040 28° ...................................................................... 159
26.15 FLIR T1040 45° ...................................................................... 166
26.16 FLIR T1050sc 12° ................................................................... 173
26.17 FLIR T1050sc 28° ................................................................... 180
26.18 FLIR T1050sc 45° ................................................................... 187
26.19 IR lens, f=36 mm (28°) with case ................................................ 194
26.20 Close-up lens 3× (51 µm) with case ............................................ 196
26.21 IR lens f=21.2 mm (45°) with case .............................................. 197
26.22 IR lens f=83.4 mm (12°) with case .............................................. 199
26.23 FLIR T10xx SC kit ................................................................... 201
27 Mechanical drawings ....................................................................... 203
28 Digital I/O pin configuration .............................................................. 211
28.1 Pin configuration for the Digital I/O connector on the HSI box............ 211
29 Digital I/O connection diagram .......................................................... 212
30 CE Declaration of conformity ............................................................ 214
31 Cleaning the camera ........................................................................ 216
31.1 Camera housing, cables, and other items..................................... 216
31.1.1 Liquids....................................................................... 216
31.1.2 Equipment.................................................................. 216
31.1.3 Procedure .................................................................. 216
31.2 Infrared lens .......................................................................... 216
31.2.1 Liquids....................................................................... 216
31.2.2 Equipment.................................................................. 216
31.2.3 Procedure .................................................................. 216
31.3 Infrared detector ..................................................................... 217
31.3.1 General...................................................................... 217
#T559954; r. AL/37426/37426; en-US
xii
Page 13

Table of contents
31.3.2 Procedure .................................................................. 217
32 Application examples....................................................................... 218
32.1 Moisture & water damage ......................................................... 218
32.1.1 General...................................................................... 218
32.1.2 Figure........................................................................ 218
32.2 Faulty contact in socket............................................................ 218
32.2.1 General...................................................................... 218
32.2.2 Figure........................................................................ 219
32.3 Oxidized socket...................................................................... 219
32.3.1 General...................................................................... 219
32.3.2 Figure........................................................................ 219
32.4 Insulation deficiencies.............................................................. 220
32.4.1 General...................................................................... 220
32.4.2 Figure........................................................................ 220
32.5 Draft .................................................................................... 221
32.5.1 General...................................................................... 221
32.5.2 Figure........................................................................ 221
33 About FLIR Systems ........................................................................ 223
33.1 More than just an infrared camera .............................................. 224
33.2 Sharing our knowledge ............................................................ 224
33.3 Supporting our customers......................................................... 225
34 Glossary ........................................................................................ 226
35 Thermographic measurement techniques .......................................... 229
35.1 Introduction .......................................................................... 229
35.2 Emissivity.............................................................................. 229
35.2.1 Finding the emissivity of a sample.................................... 229
35.3 Reflected apparent temperature................................................. 233
35.4 Distance ............................................................................... 233
35.5 Relative humidity .................................................................... 233
35.6 Other parameters.................................................................... 233
36 History of infrared technology........................................................... 234
37 Theory of thermography................................................................... 237
37.1 Introduction ........................................................................... 237
37.2 The electromagnetic spectrum................................................... 237
37.3 Blackbody radiation................................................................. 237
37.3.1 Planck’s law ................................................................ 238
37.3.2 Wien’s displacement law................................................ 239
37.3.3 Stefan-Boltzmann's law ................................................. 240
37.3.4 Non-blackbody emitters ................................................. 241
37.4 Infrared semi-transparent materials............................................. 243
38 The measurement formula................................................................ 244
39 Emissivity tables ............................................................................. 248
39.1 References............................................................................ 248
39.2 Tables .................................................................................. 248
#T559954; r. AL/37426/37426; en-US
xiii
Page 14

Page 15

1
Disclaimers
1.1 Legal disclaimer
All products manufactured by FLIR Systems are warranted against defective materials
and workmanship for a period of one (1) year from the delivery date of the original purchase, provided such products have been under normal storage, use and service, and in
accordance with FLIR Systems instruction.
Uncooled handheld infrared cameras manufactured by FLIR Systems are warranted
against defective materials and workmanship for a period of two (2) years from the delivery
date of the original purchase, provided such products have been under normal storage,
use and service, and in accordance with FLIR Systems instruction, and provided that the
camera has been registered within 60 days of original purchase.
Detectors for uncooled handheld infrared cameras manufactured by FLIR Systems are
warranted against defective materials and workmanship for a period of ten (10) years from
the delivery date of the original purchase, provided such products have been under normal
storage, use and service, and in accordance with FLIR Systems instruction, and provided
that the camera has been registered within 60 days of original purchase.
Products which are not manufactured by FLIR Systems but included in systems delivered
by FLIR Systems to the original purchaser, carry the warranty, if any, of the particular supplier only. FLIR Systems has no responsibility whatsoever for such products.
The warranty extends only to the original purchaser and is not transferable. It is not applicable to any product which has been subjected to misuse, neglect, accident or abnormal
conditions of operation. Expendable parts are excluded from the warranty.
In the case of a defect in a product covered by this warranty the product must not be further used in order to prevent additional damage. The purchaser shall promptly report any
defect to FLIR Systems or this warranty will not apply.
FLIR Systems will, at its option, repair or replace any such defective product free of charge
if, upon inspection, it proves to be defective in material or workmanship and provided that
it is returned to FLIR Systems within the said one-year period.
FLIR Systems has no other obligation or liability for defects than those set forth above.
No other warranty is expressed or implied. FLIR Systems specifically disclaims the implied
warranties of merchantability and fitness for a particular purpose.
FLIR Systems shall not be liable for any direct, indirect, special, incidental or consequen-
tial loss or damage, whether based on contract, tort or any other legal theory.
This warranty shall be governed by Swedish law.
Any dispute, controversy or claim arising out of or in connection with this warranty, shall be
finally settled by arbitration in accordance with the Rules of the Arbitration Institute of the
Stockholm Chamber of Commerce. The place of arbitration shall be Stockholm. The language to be used in the arbitral proceedings shall be English.
1.2 Usage statistics
FLIR Systems reserves the right to gather anonymous usage statistics to help maintain
and improve the quality of our software and services.
1.3 Changes to registry
The registry entry HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Lsa
\LmCompatibilityLevel will be automatically changed to level 2 if the FLIR Camera Monitor
service detects a FLIR camera connected to the computer with a USB cable. The
#T559954; r. AL/37426/37426; en-US
1
Page 16

Disclaimers1
modification will only be executed if the camera device implements a remote network service that supports network logons.
1.4 U.S. Government Regulations
This product may be subject to U.S. Export Regulations. Please send any inquiries to exportquestions@flir.com.
1.5 Copyright
© 2016, FLIR Systems, Inc. All rights reserved worldwide. No parts of the software including source code may be reproduced, transmitted, transcribed or translated into any language or computer language in any form or by any means, electronic, magnetic, optical,
manual or otherwise, without the prior written permission of FLIR Systems.
The documentation must not, in whole or part, be copied, photocopied, reproduced, translated or transmitted to any electronic medium or machine readable form without prior consent, in writing, from FLIR Systems.
Names and marks appearing on the products herein are either registered trademarks or
trademarks of FLIR Systems and/or its subsidiaries. All other trademarks, trade names or
company names referenced herein are used for identification only and are the property of
their respective owners.
1.6 Quality assurance
The Quality Management System under which these products are developed and manufactured has been certified in accordance with the ISO 9001 standard.
FLIR Systems is committed to a policy of continuous development; therefore we reserve
the right to make changes and improvements on any of the products without prior notice.
1.7 Patents
One or several of the following patents and/or design patents may apply to the products
and/or features. Additional pending patents and/or pending design patents may also apply.
000279476-0001; 000439161; 000499579-0001; 000653423; 000726344; 000859020;
001106306-0001; 001707738; 001707746; 001707787; 001776519; 001954074;
002021543; 002058180; 002249953; 002531178; 0600574-8; 1144833; 1182246;
1182620; 1285345; 1299699; 1325808; 1336775; 1391114; 1402918; 1404291;
1411581; 1415075; 1421497; 1458284; 1678485; 1732314; 2106017; 2107799;
2381417; 3006596; 3006597; 466540; 483782; 484155; 4889913; 5177595; 60122153.2;
602004011681.5-08; 6707044; 68657; 7034300; 7110035; 7154093; 7157705; 7237946;
7312822; 7332716; 7336823; 7544944; 7667198; 7809258 B2; 7826736; 8,153,971;
8,823,803; 8,853,631; 8018649 B2; 8212210 B2; 8289372; 8354639 B2; 8384783;
8520970; 8565547; 8595689; 8599262; 8654239; 8680468; 8803093; D540838;
D549758; D579475; D584755; D599,392; D615,113; D664,580; D664,581; D665,004;
D665,440; D677298; D710,424 S; D718801; DI6702302-9; DI6903617-9; DI7002221-6;
DI7002891-5; DI7002892-3; DI7005799-0; DM/057692; DM/061609; EP 2115696 B1;
EP2315433; SE 0700240-5; US 8340414 B2; ZL 201330267619.5; ZL01823221.3;
ZL01823226.4; ZL02331553.9; ZL02331554.7; ZL200480034894.0; ZL200530120994.2;
ZL200610088759.5; ZL200630130114.4; ZL200730151141.4; ZL200730339504.7;
ZL200820105768.8; ZL200830128581.2; ZL200880105236.4; ZL200880105769.2;
ZL200930190061.9; ZL201030176127.1; ZL201030176130.3; ZL201030176157.2;
ZL201030595931.3; ZL201130442354.9; ZL201230471744.3; ZL201230620731.8.
#T559954; r. AL/37426/37426; en-US
2
Page 17

Disclaimers1
1.8 Third-party licenses
1.8.1 GNU Lesser General Public License (LGPL)
http://www.gnu.org/licenses/lgpl-2.1.en.html
(Retrieved May 27, 2015)
1.8.2 Fonts (Source Han Sans)
https://github.com/adobe-fonts/source-han-sans/blob/master/LICENSE.txt
(Retrieved May 27, 2015)
1.8.3 Fonts (DejaVu)
http://dejavu-fonts.org/wiki/License
(Retrieved May 27, 2015)
#T559954; r. AL/37426/37426; en-US
3
Page 18
2
Safety information
WARNING
Applicability: Class B digital devices.
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital device, pursuant
to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful
interference in a residential installation. This equipment generates, uses and can radiate radio frequency
energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with the instructions, may cause harmful interference
to radio communications. However, there is no guarantee that interference will not occur in a particular installation. If this equipment does cause harmful interference to radio or television reception, which can be
determined by turning the equipment off and on, the user is encouraged to try to correct the interference
by one or more of the following measures:
• Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
• Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
• Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to which the receiver is connected.
• Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
WARNING
Applicability: Digital devices subject to 15.19/RSS-247 issue 1.
NOTICE: This device complies with Part 15 of the FCC Rules and with RSS-247 issue 1 of Industry Cana-
da. Operation is subject to the following two conditions:
1. this device may not cause harmful interference, and
2. this device must accept any interference received, including interference that may cause undesired
operation.
WARNING
This device is granted pursuant to the Japanese Radio Law (電波法) and the Japanese Telecommunications Business Law (電気通信事業法). This device should not be modified (otherwise the granted designation number will become invalid)
WARNING
Applicability: Digital devices subject to 15.21.
NOTICE: Changes or modifications made to this equipment not expressly approved by FLIR Systems
may void the FCC authorization to operate this equipment.
WARNING
Applicability: Digital devices subject to 2.1091/2.1093/OET Bulletin 65.
Radiofrequency radiation exposure Information: The radiated output power of the device is below
the FCC/IC radio frequency exposure limits. Nevertheless, the device shall be used in such a manner that
the potential for human contact during normal operation is minimized.
WARNING
Applicability: Cameras with one or more laser pointers.
Do not look directly into the laser beam. The laser beam can cause eye irritation.
WARNING
Applicability: Cameras with one or more batteries.
Do not disassemble or do a modification to the battery. The battery contains safety and protection devices
which, if damage occurs, can cause the battery to become hot, or cause an explosion or an ignition.
#T559954; r. AL/37426/37426; en-US
4
Page 19
2
Safety information
WARNING
Applicability: Cameras with one or more batteries.
If there is a leak from the battery and you get the fluid in your eyes, do not rub your eyes. Flush well with
water and immediately get medical care. The battery fluid can cause injury to your eyes if you do not do
this.
WARNING
Applicability: Cameras with one or more batteries.
Do not continue to charge the battery if it does not become charged in the specified charging time. If you
continue to charge the battery, it can become hot and cause an explosion or ignition. Injury to persons
can occur.
WARNING
Applicability: Cameras with one or more batteries.
Only use the correct equipment to remove the electrical power from the battery. If you do not use the correct equipment, you can decrease the performance or the life cycle of the battery. If you do not use the
correct equipment, an incorrect flow of current to the battery can occur. This can cause the battery to become hot, or cause an explosion. Injury to persons can occur.
WARNING
Make sure that you read all applicable MSDS (Material Safety Data Sheets) and warning labels on containers before you use a liquid. The liquids can be dangerous. Injury to persons can occur.
CAUTION
Do not point the infrared camera (with or without the lens cover) at strong energy sources, for example,
devices that cause laser radiation, or the sun. This can have an unwanted effect on the accuracy of the
camera. It can also cause damage to the detector in the camera.
CAUTION
Do not use the camera in temperatures more than +50°C (+122°F), unless other information is specified
in the user documentation or technical data. High temperatures can cause damage to the camera.
CAUTION
Applicability: Cameras with one or more laser pointers.
To prevent damage, put the protective cap on the laser pointer when you do not operate the laser pointer.
Damage to the laser pointer can occur if you do not do this.
CAUTION
Applicability: Cameras with one or more batteries.
Do not attach the batteries directly to a car’s cigarette lighter socket, unless FLIR Systems supplies a specific adapter to connect the batteries to a cigarette lighter socket. Damage to the batteries can occur.
CAUTION
Applicability: Cameras with one or more batteries.
Do not connect the positive terminal and the negative terminal of the battery to each other with a metal
object (such as wire). Damage to the batteries can occur.
#T559954; r. AL/37426/37426; en-US
5
Page 20

2
Safety information
CAUTION
Applicability: Cameras with one or more batteries.
Do not get water or salt water on the battery, or permit the battery to become wet. Damage to the batteries
can occur.
CAUTION
Applicability: Cameras with one or more batteries.
Do not make holes in the battery with objects. Damage to the battery can occur.
CAUTION
Applicability: Cameras with one or more batteries.
Do not hit the battery with a hammer. Damage to the battery can occur.
CAUTION
Applicability: Cameras with one or more batteries.
Do not put your foot on the battery, hit it or cause shocks to it. Damage to the battery can occur.
CAUTION
Applicability: Cameras with one or more batteries.
Do not put the batteries in or near a fire, or into direct sunlight. When the battery becomes hot, the built-in
safety equipment becomes energized and can stop the battery charging procedure. If the battery becomes hot, damage can occur to the safety equipment and this can cause more heat, damage or ignition
of the battery.
CAUTION
Applicability: Cameras with one or more batteries.
Do not put the battery on a fire or increase the temperature of the battery with heat. Damage to the battery
and injury to persons can occur.
CAUTION
Applicability: Cameras with one or more batteries.
Do not put the battery on or near fires, stoves, or other high-temperature locations. Damage to the battery
and injury to persons can occur.
CAUTION
Applicability: Cameras with one or more batteries.
Do not solder directly onto the battery. Damage to the battery can occur.
CAUTION
Applicability: Cameras with one or more batteries.
Do not use the battery if, when you use, charge, or put the battery in storage, there is an unusual smell
from the battery, the battery feels hot, changes color, changes shape, or is in an unusual condition. Speak
with your sales office if one or more of these problems occurs. Damage to the battery and injury to persons can occur.
#T559954; r. AL/37426/37426; en-US
6
Page 21
2
Safety information
CAUTION
Applicability: Cameras with one or more batteries.
Only use a specified battery charger when you charge the battery. Damage to the battery can occur if you
do not do this.
CAUTION
Applicability: Cameras with one or more batteries.
Only use a specified battery for the camera. Damage to the camera and the battery can occur if you do
not do this.
CAUTION
Applicability: Cameras with one or more batteries.
The temperature range through which you can charge the battery is ±0°C to +45°C (+32°F to +113°F),
unless other information is specified in the user documentation or technical data. If you charge the battery
at temperatures out of this range, it can cause the battery to become hot or to break. It can also decrease
the performance or the life cycle of the battery.
CAUTION
Applicability: Cameras with one or more batteries.
The temperature range through which you can remove the electrical power from the battery is -15°C to
+50°C (+5°F to +122°F), unless other information is specified in the user documentation or technical data.
If you operate the battery out of this temperature range, it can decrease the performance or the life cycle
of the battery.
CAUTION
Applicability: Cameras with one or more batteries.
When the battery is worn, apply insulation to the terminals with adhesive tape or equivalent materials before you discard it. Damage to the battery and injury to persons can occur if you do not do this.
CAUTION
Applicability: Cameras with one or more batteries.
Remove any water or moisture on the battery before you install it. Damage to the battery can occur if you
do not do this.
CAUTION
Do not apply solvents or equivalent liquids to the camera, the cables, or other items. Damage to the battery and injury to persons can occur.
CAUTION
Be careful when you clean the infrared lens. The lens has an anti-reflective coating which is easily damaged. Damage to the infrared lens can occur.
CAUTION
Do not use too much force to clean the infrared lens. This can cause damage to the anti-reflective
coating.
#T559954; r. AL/37426/37426; en-US
7
Page 22

2
Safety information
NOTE
The encapsulation rating is only applicable when all the openings on the camera are sealed with their correct covers, hatches, or caps. This includes the compartments for data storage, batteries, and
connectors.
CAUTION
Applicability: Cameras with a viewfinder.
Make sure that the beams from the intensive energy sources do not go into the viewfinder. The beams
can cause damage to the camera. This includes the devices that emit laser radiation, or the sun.
#T559954; r. AL/37426/37426; en-US
8
Page 23

3
Notice to user
3.1 User-to-user forums
Exchange ideas, problems, and infrared solutions with fellow thermographers around the
world in our user-to-user forums. To go to the forums, visit:
http://www.infraredtraining.com/community/boards/
3.2 Calibration
We recommend that you send in the camera for calibration once a year. Contact your local
sales office for instructions on where to send the camera.
3.3 Accuracy
For very accurate results, we recommend that you wait 5 minutes after you have started
the camera before measuring a temperature.
3.4 Disposal of electronic waste
As with most electronic products, this equipment must be disposed of in an environmentally friendly way, and in accordance with existing regulations for electronic waste.
Please contact your FLIR Systems representative for more details.
3.5 Training
To read about infrared training, visit:
• http://www.infraredtraining.com
• http://www.irtraining.com
• http://www.irtraining.eu
3.6 Documentation updates
Our manuals are updated several times per year, and we also issue product-critical notifications of changes on a regular basis.
To access the latest manuals, translations of manuals, and notifications, go to the Download tab at:
http://support.flir.com
It only takes a few minutes to register online. In the download area you will also find the lat-
est releases of manuals for our other products, as well as manuals for our historical and
obsolete products.
3.7 Important note about this manual
FLIR Systems issues generic manuals that cover several cameras within a model line.
This means that this manual may contain descriptions and explanations that do not apply
to your particular camera model.
#T559954; r. AL/37426/37426; en-US
9
Page 24

Notice to user3
3.8 Note about authoritative versions
The authoritative version of this publication is English. In the event of divergences due to
translation errors, the English text has precedence.
Any late changes are first implemented in English.
#T559954; r. AL/37426/37426; en-US
10
Page 25
4
Customer help
4.1 General
For customer help, visit:
http://support.flir.com
4.2 Submitting a question
To submit a question to the customer help team, you must be a registered user. It only
takes a few minutes to register online. If you only want to search the knowledgebase for
existing questions and answers, you do not need to be a registered user.
When you want to submit a question, make sure that you have the following information to
hand:
• The camera model
• The camera serial number
• The communication protocol, or method, between the camera and your device (for example, HDMI, Ethernet, USB, or FireWire)
#T559954; r. AL/37426/37426; en-US
11
Page 26

4
Customer help
• Device type (PC/Mac/iPhone/iPad/Android device, etc.)
• Version of any programs from FLIR Systems
• Full name, publication number, and revision number of the manual
4.3 Downloads
On the customer help site you can also download the following, when applicable for the
product:
• Firmware updates for your infrared camera.
• Program updates for your PC/Mac software.
• Freeware and evaluation versions of PC/Mac software.
• User documentation for current, obsolete, and historical products.
• Mechanical drawings (in *.dxf and *.pdf format).
• Cad data models (in *.stp format).
• Application stories.
• Technical datasheets.
• Product catalogs.
#T559954; r. AL/37426/37426; en-US
12
Page 27
5
Introduction
5.1 General description
The FLIR T10xx series is designed for the expert requiring the highest performance and
the latest technology available. The camera series combines excellent ergonomics and
feature-rich flexibility with superior image quality of 1024 × 768 pixel infrared resolution.
High accuracy and sensitivity together with radiometric recording and streaming options
make the FLIR T10xx series well suited for advanced research and development.
5.2 Key benefits
• Tailor made for research and development: The FLIR T10xx series has high accuracy
and high sensitivity, to accurately measure the smallest temperature differences. With
real-time radiometric recording by the camera, it is possible to capture fast events on
the camera’s SD card for further analysis by the supplied analysis software.
• Flexible and feature rich: A wide variety of measuring and analysis functions makes the
camera flexible for your every need. Two programmable buttons provide easy access to
favorite functions.
• Highest performance with the latest technology: The FLIR T10xx series is equipped
with the innovative Multi Spectral Dynamic Imaging (MSX) feature, which produces an
image richer in detail than ever before. With its continuous autofocus, the FLIR T10xx
series is a fully automatic infrared camera.
#T559954; r. AL/37426/37426; en-US
13
Page 28

6
Quick start guide
6.1 Procedure
Follow this procedure:
1. Put a battery into the battery compartment.
2. Charge the battery for 4 hours before starting the camera for the first time.
3. Insert a memory card into the card slot.
4. Push the On/off button
5. Aim the camera toward the object of interest.
6. Adjust the focus.
Note It is very important to adjust the focus correctly. Incorrect focus adjustment affects how the image modes work. It also affects the temperature measurement.
7. Push the Save button fully down to save an image.
8. Go to http://support.flir.com/tools and download FLIR Tools.
9. Install FLIR Tools on your computer.
10. Start FLIR Tools.
11. Connect the camera to the computer using a USB cable.
12. Import the images into FLIR Tools.
13. Select one or more images.
14. Click Generate report.
15. Click Export to export the report as a PDF file.
16. Send the PDF report to your client.
to turn on the camera.
#T559954; r. AL/37426/37426; en-US
14
Page 29
7
About FLIR Tools/Tools+
7.1 Introduction
FLIR Tools is available as a free download at http://support.flir.com/tools. FLIR Tools+ provides extended functionality to the standard FLIR Tools software. A license card for FLIR
Tools+ is included with the FLIR T10xx camera.
FLIR Tools/Tools+ is a software suite specifically designed to provide an easy way to update your camera and create inspection reports.
Examples of what you can do in FLIR Tools/Tools+ include the following:
• Import images from your camera to your computer.
• Apply filters when searching for images.
• Lay out, move, and resize measurement tools on any infrared image.
• Group and ungroup files.
• Create panoramas by stitching several smaller images into a larger one.
• Create PDF imagesheets of any images of your choice.
• Add headers, footers, and logos to imagesheets.
• Create PDF/Microsoft Word reports for images of your choice.
• Add headers, footers, and logos to reports.
• Update your camera with the latest firmware.
For more information, refer to the User’s manual for FLIR Tools/Tools+.
#T559954; r. AL/37426/37426; en-US
15
Page 30

7
About FLIR Tools/Tools+
7.2 Workflow
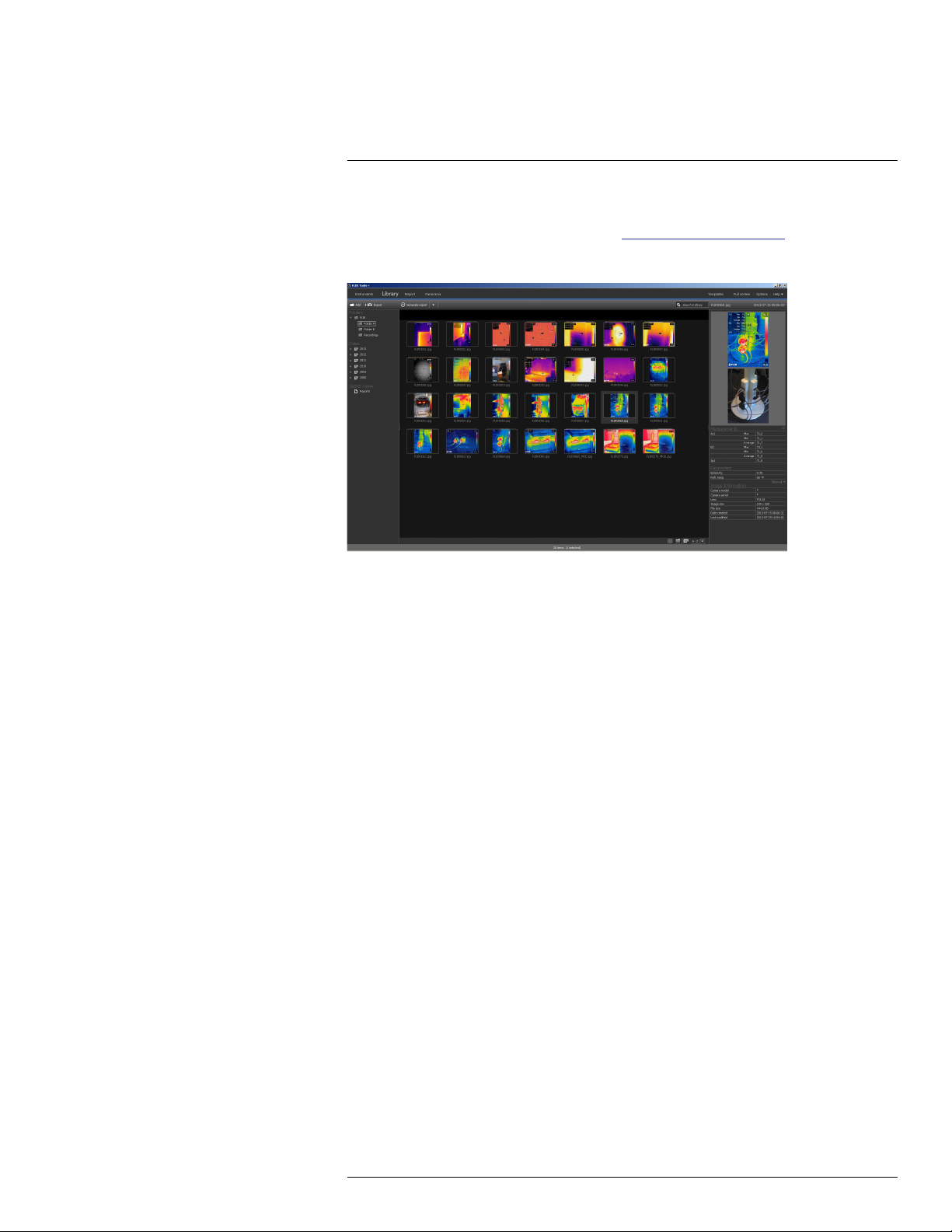
7.2.1 General
When you carry out an infrared inspection you follow a typical workflow. This section gives
an example of an infrared inspection workflow.
7.2.2 Figure
7.2.3 Explanation
1. Use your camera to take your infrared images and/or digital photos.
2. Connect your camera to a PC using a USB connector.
3. Import the images from the camera into FLIR Tools/Tools+.
4. Do one of the following:
• Create a PDF imagesheet in FLIR Tools.
• Create a PDF report in FLIR Tools.
• Create a non-radiometric Microsoft Word report in FLIR Tools+.
• Create a radiometric Microsoft Word report in FLIR Tools+.
5. Send the report to your client as an attachment to an e-mail.
#T559954; r. AL/37426/37426; en-US
16
Page 31

8
Using the high-speed interface (HSI)
8.1 General
The high-speed interface (HSI) is included in the FLIR T10xx SC kit. The high-speed interface enables streaming of live video from the FLIR T10xx camera to a PC running the FLIR
ResearchIR Max software. The high-speed interface is primarily intended for R&D usage
and development purposes. As an example, the camera can capture and stream very rapid processes, which cannot be perceived by the human eye, for later processing and analysis in the PC software. The streamed video is fully radiometric and uncompressed.
8.2 System overview
8.2.1 Figure
8.2.2 Explanation
1. PC running FLIR ResearchIR Max (a download card with a printed license key is in-
cluded with the HSI box).
2. USB 3 connection.
3. USB 3 cable connector.
4. Optional digital I/O connector.
5. HSI box
#T559954; r. AL/37426/37426; en-US
17
Page 32

8
Using the high-speed interface (HSI)
6. High-speed LVDS connection.
7. High-speed interface cable connector.
8. FLIR T10xx camera, optionally with a close-up lens.
9. Object of study.
8.3 Quick start guide
Follow this procedure:
1. Go to http://support.flir.com/rir4 and download FLIR ResearchIR Max.
2. Install FLIR ResearchIR Max.
3. Start FLIR ResearchIR Max.
When asked for the license key, enter the license key that is printed on the FLIR ResearchIR Max download card. The card is included with the HSI box.
4. Connect the HSI box to the computer using the provided USB 3 cable.
5. Connect the camera to the HSI box using the integrated high-speed interface cable.
6. Start the camera. This displays a start-up dialog box in FLIR ResearchIR Max. If the
start-up dialog box is not displayed, go to View > Startup Dialog.
7. In the start-up dialog box, click the camera you want to connect to.
For more information about the installation and connection processes, see the FLIR ResearchIR Max manual.
8.4 HSI box indicator LED
Indicator LED status Explanation
The indicator LED displays a continuous blue light. The HSI box is operational, and video data is now
The indicator LED displays a flashing blue light,
with a period time of about 1 second.
The indicator LED displays a continuous blue light
with short interrupts.
continuously streamed to the computer.
The HSI box is connected to the computer, but the
link between the camera and the box is not up. Either the cable to the camera is not correctly connected or there is another error on the link.
Each interrupt in the continuos light indicates a bit
error in the video data stream.
8.5 Digital I/O
For information about the optional Digital I/O connection, see sections 28 Digital I/O pin
configuration, page 211 and 29 Digital I/O connection diagram, page 212.
#T559954; r. AL/37426/37426; en-US
18
Page 33

9
A note about ergonomics
9.1 General
To prevent strain-related injuries, it is important that you hold the camera ergonomically
correctly. This section gives advice and examples on how to hold the camera.
Note
• Always tilt the touch-screen LCD to suit your work position.
• When you hold the camera, make sure that you support the optics housing with your left
hand too. This decreases the strain on your right hand.
• Always use the supplied neck strap. See section 10.5 Neck strap attachment points,
page 25.
9.2 Figure
#T559954; r. AL/37426/37426; en-US
19
Page 34

10
Camera parts
10.1 View from the right
10.1.1 Figure
10.1.2 Explanation
1. Knob to change the dioptric correction for the viewfinder.
2. Hand strap.
3. Digital zoom button.
4. Save button (push fully down).
Note The infrared camera can be configured to autofocus when you push the Save
button half-way down. To enable the autofocus function of the Save button, select
(Settings) > Save options & storage > Save button half-press = Autofocus.
#T559954; r. AL/37426/37426; en-US
20
Page 35

10
Camera parts
10.2 View from the left
10.2.1 Figure
10.2.2 Explanation
1. Digital camera.
2. Camera lamp.
3. Laser pointer.
Note The laser pointer may not be enabled in all markets.
4. Infrared lens.
5. Camera lamp.
6. Digital camera.
7. Focusing ring.
8. Programmable button
.
9. Button to operate the laser pointer.
#T559954; r. AL/37426/37426; en-US
21
Page 36

10
Camera parts
10.3 View from the bottom
10.3.1 Figure
10.3.2 Explanation
1. Memory card.
2. LED indicator showing that the memory card is busy.
Note
• Do not eject the memory card when this LED is flashing.
• Do not connect the camera to a computer when this LED is flashing.
3. USB Micro B cable (to connect the camera to a computer).
4. HDMI cable (for digital video output).
5. Battery condition LED indicator.
6. Power supply cable (to power the camera and charge the battery).
7. High-speed interface cable.
8. Tripod mount.
9. Button to release the lens.
10. Latch to release the battery.
#T559954; r. AL/37426/37426; en-US
22
Page 37

10
Camera parts
10.4 View from the rear
10.4.1 Figure
10.4.2 Explanation
1. Sensor that adjusts the touch-screen LCD intensity automatically.
2.
button.
Function:
• Push to switch between touch-screen LCD mode and viewfinder mode.
3. Viewfinder.
4. Programmable button
.
5. Joystick with push-button functionality.
Function:
• Move the joystick left/right or up/down to navigate in menus, submenus, and dialog
boxes, and to change values in dialog boxes.
• Push the joystick to confirm changes and settings in menus and dialog boxes.
6. Back button
.
Function:
• Push to leave dialog boxes and to go back into the menu system.
7. Camera lamp button
.
Function:
• Push to turn on or off the camera lamp.
Note The camera lamp must be enabled. Select
(Settings) > Device settings
> Set up camera > Lamp & laser > Enable lamp & laser.
#T559954; r. AL/37426/37426; en-US
23
Page 38

10
Camera parts
8.
button.
Function:
• Push to switch between automatic and manual image adjustment mode.
9. Image archive button
.
Function:
• Push to open the image archive.
• Push and hold for more than 2 seconds to perform a manual calibration.
10. Touch-screen LCD.
11. Power indicator.
12. On/off button
.
Function:
• Push and release to turn on the camera.
• Push and hold for more than 0.5 second to turn off the camera.
#T559954; r. AL/37426/37426; en-US
24
Page 39

10
Camera parts
10.5 Neck strap attachment points
10.5.1 Figure
10.6 Battery condition LED indicator
10.6.1 Figure
10.6.2 Explanation
Type of signal Explanation
The green LED flashes twice per second. The battery is being charged.
The green LED glows continuously. The battery is fully charged.
#T559954; r. AL/37426/37426; en-US
25
Page 40

10
Camera parts
10.7 Power LED indicator
10.7.1 Figure
10.7.2 Explanation
Type of signal Explanation
The LED is off. The camera is off.
The LED is blue. The camera is on.
10.8 Laser pointer
10.8.1 Figure
Figure 10.1 This figure shows the difference in position between the laser pointer and the optical center of
the infrared lens.
WARNING
Do not look directly into the laser beam. The laser beam can cause eye irritation.
#T559954; r. AL/37426/37426; en-US
26
Page 41

10
Camera parts
Note
• The symbol
• The laser pointer is enabled by a setting. Select
is displayed on the screen when the laser pointer is on.
(Settings) > Device settings > Set
up camera > Lamp & laser > Enable lamp & laser.
Note The laser pointer may not be enabled in all markets.
10.8.2 Laser warning label
A laser warning label with the following information is attached to the camera:
10.8.3 Laser rules and regulations
Wavelength: 635 nm. Maximum output power: 1 mW.
This product complies with 21 CFR 1040.10 and 1040.11 except for deviations pursuant
to Laser Notice No. 50, dated June 24, 2007.
#T559954; r. AL/37426/37426; en-US
27
Page 42

11
Screen elements
11.1 Figure
11.2 Explanation
1. Programmable button P4.
2. Programmable button P3.
3. Digital zoom factor.
4. Result table.
5. Status icons.
6. Measurement tool (e.g., spotmeter).
7. Temperature scale.
8. Submenu.
9. Main menu.
10. Settings button.
11. Color button.
12. Measurement button.
13. Image mode button.
14. Measurement parameters button.
15. Recording mode button.
11.3 Status icons and indicators
Battery status indicator.
Memory card storage status indicator.
Manual adjustment mode is enabled.
The camera lamp is turned on.
#T559954; r. AL/37426/37426; en-US
The camera is connected to a device using USB.
Wi-Fi connectivity indicator.
Bluetooth connectivity indicator.
28
Page 43

11
Screen elements
A Bluetooth headset is connected.
The GPS indicator.
• Gray icon: GPS is enabled, but there is no satellite contact.
• White icon: GPS is enabled, with satellite
contact.
External infrared window compensation is enabled.
Compass indicator (part of the image overlay
information).
The laser pointer is turned on.
11.4 Image overlay information
The image information consists of items such as date, emissivity, and atmospheric temperature. All image information is saved in the image file and can be viewed in the image
archive. You can also choose to display selected items as image overlay information. All
image overlay information displayed on the live image will also be displayed on saved images. For more information, see sections 25.1.5 Device settings, page 85 and 15.8 Hiding
all overlay, page 58.
#T559954; r. AL/37426/37426; en-US
29
Page 44
12
Navigating the menu system
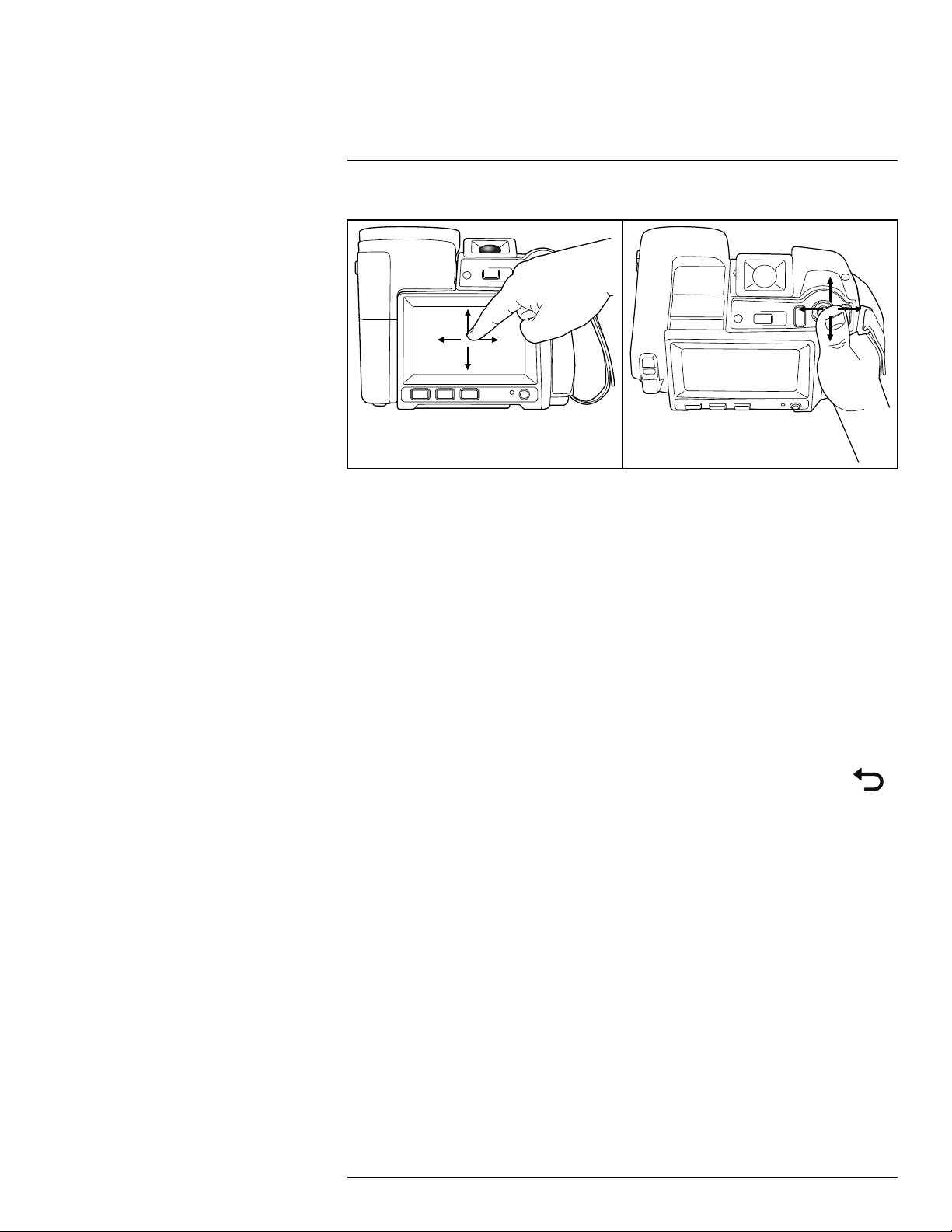
12.1 General
The figure above shows the two ways to navigate the menu system in the camera:
• Using the index finger or a stylus pen specially designed for capacitive touch usage to
navigate the menu system (left).
• Using the joystick to navigate the menu system (right) and the Back button.
You can also use a combination of the two.
In this manual, it is assumed that the joystick is used, but most tasks can also be carried
out using the index finger or a stylus pen.
12.2 Navigating using the joystick
You navigate the menu system by using the joystick and the Back button:
• To display the menu system, push the joystick.
• To navigate in menus, submenus, and dialog boxes, and to change values in dialog
boxes, move the joystick up/down or left/right.
• To confirm changes and settings in menus and dialog boxes, push the joystick.
• To leave dialog boxes and to go back in the menu system, push the Back button
.
#T559954; r. AL/37426/37426; en-US
30
Page 45

13
Handling the camera
13.1 Charging the battery
Note You must charge the battery for 4 hours before you start using the camera for the
first time.
13.1.1 Using the power supply to charge the battery
13.1.1.1 Procedure
Follow this procedure:
1. Connect the power supply cable plug to the power connector on the camera.
2. Connect the power supply mains-electricity plug to a mains socket.
3. It is good practice to disconnect the power supply cable plug when the green light of
the battery condition LED indicator is continuous.
13.1.2 Using the stand-alone battery charger to charge the battery
13.1.2.1 Explanation
Type of signal Explanation
The blue LED flashes. The battery is being charged.
The blue LED glows continuously. The battery is fully charged.
13.1.2.2 Procedure
Follow this procedure:
1. Put the battery in the battery charger.
2. Connect the power supply cable plug to the connector on the battery charger.
3. Connect the power supply mains-electricity plug to a mains socket.
4. It is good practice to disconnect the power supply cable plug when the blue LED on
the battery charger is glowing continuously.
13.2 Turning on the camera
13.2.1 Procedure
Follow this procedure:
1. To turn on the camera, push and release the On/off button
13.3 Turning off the camera
13.3.1 Procedure
Follow this procedure:
1. To turn off the camera, push and hold the On/off button
Note Do not remove the battery to turn off the camera.
.
for more than 0.5 second.
#T559954; r. AL/37426/37426; en-US
31
Page 46

Handling the camera13
13.4 Adjusting the viewfinder’s dioptric correction (sharpness)
13.4.1 Figure
CAUTION
Applicability: Cameras with a viewfinder.
Make sure that the beams from the intensive energy sources do not go into the viewfinder. The beams
can cause damage to the camera. This includes the devices that emit laser radiation, or the sun.
13.4.2 Procedure
Follow this procedure:
1. Push the
button to switch from touch-screen LCD mode to viewfinder mode.
2. To adjust the viewfinder’s dioptric correction, look through the viewfinder and rotate the
adjustment knob clockwise or counter-clockwise for the best sharpness.
Note
• Maximum dioptric correction: +2.
• Minimum dioptric correction: –2.
#T559954; r. AL/37426/37426; en-US
32
Page 47

Handling the camera13
13.5 Adjusting the angle of the lens
13.5.1 Figure
13.6 Adjusting the infrared camera focus manually
13.6.1 Figure
13.6.2 Procedure
Follow this procedure:
1. Do one of the following:
• For far focus, rotate the focus ring clockwise (looking at the touch-screen LCD side
of the camera).
• For near focus, rotate the focus ring counter-clockwise (looking at the touch-screen
LCD side of the camera).
#T559954; r. AL/37426/37426; en-US
33
Page 48

Handling the camera13
Note
• Do not touch the lens surface when you adjust the infrared camera focus manually. If
this happens, clean the lens according to the instructions in 31.2 Infrared lens, page
216.
• The focus ring can be rotated infinitely, but only a certain amount of rotation is needed
when focusing.
• The response of the focus mechanism is progressive, meaning that a faster rotation of
the focus ring gives a disproportional higher speed of focus change. This allows for
both fine adjustment with a relatively large (but slow) rotation and rapid change with a
smaller (but faster) rotation. Furthermore, for a very slow rotation, the lens moves in
very small, discrete steps (which you can hear), allowing for a controlled fine adjustment of the focus.
13.7 Autofocusing the infrared camera
13.7.1 General
The infrared camera can be configured to autofocus when you push the Save button halfway down.
13.7.2 Figure
13.7.3 Procedure
Follow this procedure:
1. To enable the autofocus function of the Save button, select
tions & storage > Save button half-press = Autofocus.
2. To autofocus, push the Save button half-way down.
(Settings) > Save op-
Note You can also assign the autofocus function to the programmable button
or .
For more information, see section 13.11 Assigning functions to the programmable buttons,
page 37..
#T559954; r. AL/37426/37426; en-US
34
Page 49

Handling the camera13
13.8 Continuous autofocus
13.8.1 General
The infrared camera can be set up to perform continuous autofocusing.
Note
• In this mode, the digital camera is used, which means that continuous autofocus will
not work in darkness.
• When continuous autofocus is enabled, it is not possible to manually adjust the focus
by rotating the focus ring.
• To stop continuous autofocus (e.g., to stabilize the focus before saving an image), push
the Save button half-way down.
13.8.2 Procedure
Follow this procedure:
1. Push the joystick to display the menu system.
2. Use the joystick to go to
(Settings).
3. Push the joystick to display the Settings menu.
4. Select Device settings and push the joystick.
5. Select Continuous autofocus and push the joystick.
6. Select On and push the joystick.
Note You can also assign the function Continuous autofocus to one of the program-
mable buttons. Select
(Settings) > Programmable buttons.
13.9 Operating the laser pointer
WARNING
Do not look directly into the laser beam. The laser beam can cause eye irritation.
Note The laser pointer is enabled by a setting. Select (Settings) > Device settings >
Lamp & laser > Enable lamp & laser.
Note The laser pointer may not be enabled in all markets.
#T559954; r. AL/37426/37426; en-US
35
Page 50

Handling the camera13
13.9.1 Figure
13.9.2 Procedure
Follow this procedure:
1. To turn on the laser pointer, push and hold the laser button.
2. To turn off the laser pointer, release the laser button.
Note The symbol
is displayed on the screen when the laser pointer is on.
13.10 Using the digital zoom function
13.10.1 General
The current zoom factor is displayed in the upper left corner of the screen.
In preview/edit mode, it is possible to pan a zoomed image by touching the screen.
#T559954; r. AL/37426/37426; en-US
36
Page 51

Handling the camera13
13.10.2 Figure
13.10.3 Procedure
Follow this procedure:
1. To zoom, push the zoom button left or right.
13.11 Assigning functions to the programmable buttons
13.11.1 General
There are four programmable buttons: two hardware buttons, and two software buttons on
the screen.
#T559954; r. AL/37426/37426; en-US
37
Page 52

Handling the camera13
1. Programmable button
2. Programmable button
.
.
3. Programmable button P3.
4. Programmable button P4.
You can assign different functions to the programmable buttons. For a complete list of
functions, see section 25.1.4 Programmable buttons, page 84.
13.11.2 Procedure
Follow this procedure:
1. Push the joystick to display the menu system.
2. Use the joystick to go to
(Settings).
3. Push the joystick to display the Settings menu.
4. Select Programmable buttons and push the joystick.
5. Select one of the buttons and push the joystick:
• P Button: Hardware button
• P2 Button: Hardware button
.
.
• P3 Button (on screen): Software button P3 on the screen.
• P4 Button (on screen): Software button P4 on the screen.
6. Select one of the functions and push the joystick.
13.12 Using the camera lamp as a flash
13.12.1 General
The camera lamp can be used as a flash for the digital camera. When the flash function is
activated, the camera lamp will flash when an image is saved by pushing the Save button
fully down.
13.12.2 Procedure
Follow this procedure:
1. Push the joystick to display the menu system.
2. Use the joystick to go to
(Settings).
3. Push the joystick to display the Settings menu.
4. Select Device settings and push the joystick.
5. Select Lamp & laser and push the joystick.
6. Select Enable lamp & laser + Use lamp as flash and push the joystick.
Note You can also assign the function Switch camera flash On <> Off to one of the pro-
grammable buttons. Select
(Settings) > Programmable buttons.
13.13 Changing lenses Note Do not touch the lens surface when you change lenses. If this happens, clean the
lens according to the instructions in 31.2 Infrared lens, page 216.
#T559954; r. AL/37426/37426; en-US
38
Page 53

Handling the camera13
Follow this procedure:
1. Take a firm grip around the outermost part of the lens.
2. Push the release button and rotate the lens 45° counter-clockwise.
#T559954; r. AL/37426/37426; en-US
39
Page 54

Handling the camera13
3. Carefully pull out the lens from the lens bayonet mount.
4. The infrared detector is now fully exposed. Do not touch this surface. If you see dust
on the detector, follow the instructions in 31.3 Infrared detector, page 217.
#T559954; r. AL/37426/37426; en-US
40
Page 55

Handling the camera13
5. Note the index marks on the lens bayonet mount and on the lens.
6. Align the lens correctly to the bayonet mount. Carefully push the lens into position.
#T559954; r. AL/37426/37426; en-US
41
Page 56

Handling the camera13
7. Rotate the lens 45° clockwise. The lens makes a click when it locks in place.
13.14 Using the close-up lens
13.14.1 General
If you need to look at small objects very close up, you can attach the close-up lens to the
infrared lens.
When the close-up lens is attached, the digital camera and the infrared camera do not see
the same scene. This means that functions that are based on content captured by the digital camera cannot be used, e.g., continuous autofocus and some image modes.
When using the close-up lens, keep the following in mind. (For instructions, see section
13.14.2 Attaching the close-up lens, page 42.)
• For best performance, adjust the focus to infinity.
• The working distance for the close-up lens is 97 mm. (The working distance is the dis-
tance between the front of the lens and the closest surface of the object when the object is in sharp focus.)
• You must activate the global parameter External IR window compensation.
• Only use the Thermal image mode.
• Deactivate continuous autofocus.
• Do not use the laser pointer.
Note The close-up lens can only be used with the infrared lens f = 36 mm (28°).
13.14.2 Attaching the close-up lens
Note Do not touch the lens surfaces when you attach the close-up lens. If this happens,
clean the lens according to the instructions in 31.2 Infrared lens, page 216.
#T559954; r. AL/37426/37426; en-US
42
Page 57

Handling the camera13
Follow this procedure:
1. Before attaching the close-up lens, adjust the focus to infinity by doing the following:
1.1. Aim the camera toward a distant object (more than 40 m (130′) away).
1.2. Autofocus the camera (see section 13.7 Autofocusing the infrared camera,
page 34) or adjust the focus manually (see section 13.6 Adjusting the infrared
camera focus manually, page 33).
Note Once the focus is set to infinity, be careful when you continue with the procedure. Make sure you do not rotate the focusing ring by mistake.
2. Remove the outermost rubber protection from the infrared lens.
3. Align the close-up lens with the infrared lens. Carefully push the close-up lens into
position.
4. Turn the close-up lens clockwise until it stops.
#T559954; r. AL/37426/37426; en-US
43
Page 58

Handling the camera13
5. Activate the global parameter External IR window compensation by doing the
following:
5.1. Push the joystick to display the menu system.
5.2. Select
(Measurement parameters) and push the joystick. This displays a
submenu.
5.3. Select
(External IR window compensation) and push the joystick. This dis-
plays a dialog box.
5.4. In the dialog box, define the settings for the infrared window compensation:
• Turn compensation on/off: Select On.
• Temperature: Select the temperature of the close-up lens.
• Transmission: Select 0.89, which is a typical transmission value for the
close-up lens.
5.5. Push the Back button
5.6. The status icon
to go back in the menu system.
is now displayed.
6. Select the image mode Thermal by doing the following:
6.1. Push the joystick to display the menu system.
6.2. Select
6.3. Select
6.4. Push the Back button
7. Deactivate continuous autofocus by selecting
(Image mode) and push the joystick. This displays a submenu.
(Thermal) and push the joystick.
to go back in the menu system.
(Settings) > Device settings > Con-
tinuous autofocus = Off.
13.14.3 Removing the close-up lens
Note Do not touch the lens surfaces when you remove the close-up lens. If this happens,
clean the lens according to the instructions in 31.2 Infrared lens, page 216.
Follow this procedure:
1. Turn the close-up lens counter-clockwise until it separates from the infrared lens.
#T559954; r. AL/37426/37426; en-US
44
Page 59

Handling the camera13
2. Carefully pull out the close-up lens from the infrared lens.
3. Note the grooves on the infrared lens and their counterparts on the inside of the rubber
protection.
4. Align the rubber protection with the infrared lens.
#T559954; r. AL/37426/37426; en-US
45
Page 60

Handling the camera13
5. Push the rubber protection into position.
6. Deactivate the global parameter External IR window compensation by doing the
following:
6.1. Push the joystick to display the menu system.
6.2. Select
(Measurement parameters) and push the joystick. This displays a
submenu.
6.3. Select
(External IR window compensation) and push the joystick. This dis-
plays a dialog box.
6.4. In the dialog box, select Turn compensation on/off = Off.
6.5. Push the Back button
to go back in the menu system.
13.15 Calibrating the compass
It is recommended that the compass is calibrated every time you move the camera to a
new location.
13.15.1 Procedure
Follow this procedure:
1. Push the joystick to display the menu system.
2. Use the joystick to go to
(Settings).
3. Push the joystick to display the Settings menu.
4. Select Device settings and push the joystick.
5. Depending on the camera configuration, select Wireless & geolocation, Wireless, or
Geolocation and push the joystick.
6. Select Compass and push the joystick.
7. If the Compass check box is unchecked, push the joystick to enable the compass.
8. Select Calibrate compass and push the joystick. Follow the on-screen instructions.
Note You must rotate the camera slowly.
#T559954; r. AL/37426/37426; en-US
46
Page 61

14
Saving and working with images
14.1 About image files
14.1.1 General
The camera saves an image file, including all thermal and visual information. This means
that you can open an image file at a later time and, for example, select another image
mode, apply color alarms, and add measurement tools.
The image *.jpg file is fully radiometric and saved lossless, which enables full post-processing in image analysis and reporting software from FLIR Systems. There is also a regular *.jpg component (lossy) for convenient viewing in non-FLIR Systems software (e.g.,
Microsoft Explorer).
The camera can also be configured to save an extra visual image as a separate file. Select
(Settings) > Save options & storage > Photo as separate JPEG = On.
14.1.2 File-naming convention
The default naming convention for image files is FLIRxxxx.jpg, where xxxx is a unique
counter.
It is also possible to save images with a date prefix added to the file name. However, these
files may not automatically be detected by third-party applications. For more information,
see section the setting File naming format in section 25.1.3 Save options & storage, page
83.
14.1.3 Image capacity
The capacity of a 4 GB memory card is theoretically 1000 images (with no annotations).
14.1.4 About UltraMax
UltraMax is an image enhancement feature that increases the image resolution and lowers
the noise, making small objects easier to see and measure. An UltraMax image is twice as
wide and high as an ordinary image.
When an UltraMax image is captured by the camera, several ordinary images are saved
within the same file. Capturing all the images can take up to 1 second. To fully utilize UltraMax, the images need to be slightly different, which can be accomplished by a slight
movement of the camera. You should hold the camera firmly in your hands (do not put it
on a tripod), which will make these images vary just a little during the capture. Correct focus, a high-contrast scene, and a non-moving target are other conditions that help to
achieve a good-quality UltraMax image.
At present, only FLIR Tools/Tools+ and FLIR ResearchIR Max have the ability to process
UltraMax images. Other FLIR software will treat the image as a regular image.
To configure the camera for UltraMax, select
age resolution = UltraMax.
14.2 Saving an image
14.2.1 General
You can save images to the memory card.
(Settings) > Save options & storage > Im-
#T559954; r. AL/37426/37426; en-US
47
Page 62

14
Saving and working with images
14.2.2 Procedure
Follow this procedure:
1. To save an image, push the Save button fully down.
Note Depending on the settings in
(Settings) > Save options & storage, the following
may happen:
• A preview image is displayed before the image is saved.
• An annotation tool or the annotation menu is displayed when the image has been
saved.
14.3 Previewing an image
14.3.1 General
You can preview an image before you save it. This enables you to see if the image contains
the information you want before you save it. You can also adjust and edit the image.
Note The camera must be configured to display a preview image before saving. Select
(Settings) > Save options & storage > Preview image before saving = On.
14.3.2 Procedure
Follow this procedure:
1. To preview an image, push the Save button fully down. This displays the preview.
2. Manual image adjustment mode is now active, and the status icon
is displayed.
For image adjustment instructions, see section 15.3 Adjusting the infrared image, page
53.
3. To edit the image, push the joystick. This displays a context menu. For editing instructions, see section 14.5 Editing a saved image, page 49.
4. Do one of the following:
• To save the image, push the Save button fully down.
• To exit preview mode without saving, push the Back button
.
14.4 Opening a saved image
14.4.1 General
When you save an image, the image file is stored on the memory card. To display the image again, open it from the image archive.
14.4.2 Procedure
Follow this procedure:
1. Push the Image archive button
.
2. Move the joystick up/down or left/right to select the image you want to view.
3. Push the joystick. This displays the image at full size.
#T559954; r. AL/37426/37426; en-US
48
Page 63

14
Saving and working with images
4. Do one or more of the following:
• To switch between an infrared image and a visual image, move the joystick up/down.
• To view the previous/next image, move the joystick left/right.
• To edit the image, add annotations, display information, or delete the image, push
the joystick. This displays a context menu.
• To return to the image archive overview, push the Back button
.
14.5 Editing a saved image
14.5.1 General
You can edit a saved image. You can also edit an image in preview mode.
14.5.2 Procedure
Follow this procedure:
1. Open the image in the image archive.
2. Push the joystick and select
3. Manual image adjustment mode is now active, and the status icon
(Edit) from the menu.
is displayed.
For image adjustment instructions, see section 15.3 Adjusting the infrared image, page
53.
4. Push the joystick. This displays a context menu.
• Select
• Select
• Select
• Select
(Cancel) to exit edit mode.
(Measurement parameters) to change the global parameters.
(Image mode) to change the image mode.
(Measurement) to add a measurement tool.
• Select
• Select
(Color) to change the color palette or set a color alarm.
(Save) to save and exit edit mode.
14.5.3 Related topics
• 17.5 Changing object parameters, page 64.
• 16 Working with image modes, page 60.
• 17 Working with measurement tools, page 62.
• 15.5 Changing the color palette, page 56.
• 18 Working with color alarms and isotherms, page 71.
14.6 Creating a PDF report in the camera
14.6.1 General
You can create a PDF report and save it to the memory card. You can then transfer the
PDF report to a computer, iPhone, or iPad using FLIR Tools/Tools+, and send the report to
a customer.
#T559954; r. AL/37426/37426; en-US
49
Page 64

14
Saving and working with images
14.6.2 Naming convention
The naming convention for report files is REPORTxxxx.jpg, where xxxx is a unique
counter.
14.6.3 Procedure
Follow this procedure:
1. Push the Image archive button
.
2. Move the joystick up/down or left/right to select an image.
3. Push the joystick to display the image.
4. Push the joystick to display a context menu.
5. Select
(Information & reports) and push the joystick. This displays information
about the image.
6. Select Create report and push the joystick. The created report will be available in the
archive.
14.7 Deleting an image
14.7.1 General
You can delete an image file from the memory card.
Note Both images in the image file (thermal and visual) will be deleted.
14.7.2 Procedure
Follow this procedure:
1. Push the Image archive button
.
2. Move the joystick up/down or left/right to select the image you want to delete.
3. Push the joystick to display the image.
4. Push the joystick and select
(Delete) from the menu. This displays a dialog box.
5. Use the joystick to select Delete. Push the joystick to confirm.
14.8 Deleting multiple images
14.8.1 General
You can delete multiple image files from the memory card.
14.8.2 Procedure
Follow this procedure:
1. Push the Image archive button
.
2. Touch and hold one of the images you want to delete. This displays a context menu.
#T559954; r. AL/37426/37426; en-US
50
Page 65

14
Saving and working with images
3. Touch all the other images you want to delete.
4. Use the joystick to select (Delete) and push the joystick. This displays a dialog
box.
5. Use the joystick to select Delete. Push the joystick to confirm.
14.9 Deleting all images
14.9.1 General
You can delete all image files from the memory card.
Note This will delete all files (images, videos, and reports) from the memory card.
14.9.2 Procedure
Follow this procedure:
1. Push the joystick to display the menu system.
2. Use the joystick to go to
(Settings).
3. Push the joystick to display the Settings menu.
4. Select Save options & storage and push the joystick.
5. Select Delete all saved files... and push the joystick. This displays a dialog box where
you can choose to execute the delete action or to cancel.
6. To permanently delete all saved files, select Delete and push the joystick.
14.10 Resetting the image counter
14.10.1 General
You can reset the numbering of the image file names.
Note To prevent image files being overwritten, the new counter value will be based on
the highest existing file name number in the image archive.
14.10.2 Procedure
Follow this procedure:
1. Push the joystick to display the menu system.
#T559954; r. AL/37426/37426; en-US
51
Page 66

14
Saving and working with images
2. Use the joystick to go to
(Settings).
3. Push the joystick to display the Settings menu.
4. Select Device settings and push the joystick.
5. Select Reset options and push the joystick.
6. Select Reset image counter... and push the joystick. This displays a dialog box where
you can choose to execute the reset action or to cancel.
7. To reset the counter, select Reset and push the joystick.
#T559954; r. AL/37426/37426; en-US
52
Page 67

15
Achieving a good image
15.1 General
A good image depends on several different settings, although some settings affect the image more than others.
These are the settings you need to experiment with:
• Adjusting the infrared camera focus.
• Adjusting the infrared image, automatically or manually.
• Selecting a suitable temperature range.
• Selecting a suitable color palette.
• Changing the object parameters.
• Calibrating the camera.
The following sections explain how to change these settings.
In some situations, you may also want to hide the overlay graphics for a better view.
15.2 Adjusting the infrared camera focus
It is very important to adjust the focus correctly. Incorrect focus adjustment affects how the
image modes work. It also affects the temperature measurement.
You can adjust the focus manually by rotating the focus ring. For more information, see
section 13.6 Adjusting the infrared camera focus manually, page 33.
You can autofocus the infrared camera by the press of a button:
• The camera can be configured to autofocus when you push the Save button half-way
down. To enable the autofocus function of the Save button, select
options & storage > Save button half-press = Autofocus.
• You can assign the autofocus function to the programmable button
information, see section 13.11 Assigning functions to the programmable buttons, page
37.
The infrared camera can also be set up to perform continuous autofocusing. For more information, see section 13.8 Continuous autofocus, page 35.
15.3 Adjusting the infrared image
15.3.1 General
An infrared image can be adjusted automatically or manually.
In automatic mode, the camera continuously adjusts the level and span for the best image
presentation. The colors are distributed based on the thermal content of the image (histogram color distribution). The temperature scale to the right of the screen shows the upper
and lower temperatures of the current span.
In manual mode, you can adjust the temperature scale to values close to the temperature
of a specific object in the image. This will make it possible to detect anomalies and smaller
temperature differences in the part of the image of interest. In manual mode, the colors
are distributed evenly from the lowest to the highest temperature (linear color distribution).
This is indicated by lines on the temperature scale.
There are two different settings for the manual adjustment mode:
• Level, Span: With this setting, you can manually adjust the level and span.
• Level, Max, Min: With this setting, you can manually adjust the level. You can also
change the upper and lower temperatures individually.
(Settings) > Save
or . For more
#T559954; r. AL/37426/37426; en-US
53
Page 68

Achieving a good image15
Select the type of manual image adjustment mode under (Settings) > Device settings
> User interface options > Manual adjustment mode.
When manual image adjustment mode is active, the status icon
• In live mode, push the button
to switch between automatic and manual image adjust-
is displayed.
ment modes. You can also switch between the modes by touching the temperature
scale on the screen.
• In preview/edit mode, manual image adjustment mode is active.
Note You can also assign the function Auto adjust the manual temperature scale to one
of the programmable buttons, which allows you to perform an automatic adjustment of the
image while remaining in manual image adjustment mode. Select
(Settings) > Pro-
grammable buttons.
15.3.2 Example 1
Here are two infrared images of a building. In the left image, which is auto-adjusted, the
large temperature span between the clear sky and the heated building makes a correct
analysis difficult. You can analyze the building in more detail if you change the temperature
scale to values close to the temperature of the building.
Automatic Manual
15.3.3 Example 2
Here are two infrared images of an isolator in a power line. To make it easier to analyze
the temperature variations in the isolator, the temperature in the right image has been
changed to values close to the temperature of the isolator.
Automatic Manual
#T559954; r. AL/37426/37426; en-US
54
Page 69

Achieving a good image15
15.3.4 Manual adjustment in Level, Span mode
Note This procedure assumes that you have configured the camera for manual image
adjustments in Level, Span mode. Select Settings > Device settings > User interface op-
tions > Manual adjustment mode = Level, Span.
Follow this procedure:
1. In live mode, push the button
to enter manual adjustment mode.
2. Move the joystick up/down to increase/decrease the level.
3. Move the joystick left/right to increase/decrease the span.
4. (Optional step.) In preview/edit mode, push the button
to perform a one-shot auto-
adjust sequence.
15.3.5 Manual adjustment in Level, Max, Min mode
Note This procedure assumes that you have configured the camera for manual image
adjustments in Level, Max, Min mode. Select Settings > Device settings > User interface
options > Manual adjustment mode = Level, Max, Min.
Follow this procedure:
1. In live mode, push the button
to enter manual adjustment mode.
2. To simultaneously change the temperature scale minimum and maximum limits, move
the joystick up/down.
3. To change the minimum limit or the maximum limit, do the following:
• Move the joystick left/right to select (highlight) the maximum or minimum
temperature.
• Move the joystick up/down to change the value of the highlighted temperature.
4. (Optional step.) In preview/edit mode, push the button
to perform a one-shot auto-
adjust sequence.
15.4 Changing the temperature range
15.4.1 General
You must change the temperature range to suit the expected temperature of the object
you are inspecting.
15.4.2 Procedure
Follow this procedure:
1. Push the joystick to display the menu system.
2. Use the joystick to go to
(Settings).
3. Push the joystick to display the Settings menu.
4. Select Camera temperature range and push the joystick.
#T559954; r. AL/37426/37426; en-US
55
Page 70

Achieving a good image15
5. Select the appropriate temperature range and push the joystick.
Note You can also assign the function Switch temperature range to one of the program-
mable buttons. Select
(Settings) > Programmable buttons.
15.5 Changing the color palette
15.5.1 General
You can change the color palette that the camera uses to display different temperatures. A
different palette can make it easier to analyze an image.
Iron
Arctic
Rainbow
#T559954; r. AL/37426/37426; en-US
Rainbow high contrast
56
Page 71

Achieving a good image15
White hot
Lava
Black hot
15.5.2 Procedure
Follow this procedure:
1. Push the joystick to display the menu system.
2. Use the joystick to go to
(Color).
3. Push the joystick to display a submenu.
4. Use the joystick to select a different palette.
5. Push the joystick.
15.6 Changing the object parameters
For accurate measurements, you must set the object parameters:
• External IR window compensation.
• Object distance.
• Atmospheric temperature.
• Relative humidity.
• Reflected temperature.
• Emissivity.
You can set the object parameters globally. You can also change the Emissivity, Reflected
temperature, and Object distance parameters locally for a measurement tool.
For more information, see section 17.5 Changing object parameters, page 64.
#T559954; r. AL/37426/37426; en-US
57
Page 72

Achieving a good image15
15.7 Calibrating the camera
15.7.1 General
Calibration of the camera is performed as a non-uniformity correction (NUC). An NUC is
an image correction carried out by the camera software to compensate for different sensitivities of detector elements and other optical and geometrical disturbances
1
.
Calibration is needed whenever the output image becomes spatially noisy. The output can
become spatially noisy when the ambient temperature changes (such as from day to night
operation, and vice versa).
The calibration is carried out automatically when needed. It is also possible to perform a
calibration manually.
While the calibration is in progress, the text Calibrating... is displayed.
15.7.2 Manual calibration
You may, for example, want to perform a manual calibration just before you start recording
a video sequence.
15.7.2.1 Procedure
Follow this procedure:
1. To perform a manual calibration, push and hold down the Image archive button
for more than 2 seconds.
Note You can also assign the function Calibrate to one of the programmable buttons. Se-
lect
(Settings) > Programmable buttons .
15.8 Hiding all overlay
15.8.1 General
The camera overlay consists of overlay graphics and image overlay information. The overlay graphics include items such as measurement tool symbols, result tables, and status
icons. The image overlay information, which you activate on the Settings menu, provides
additional information such as the date, emissivity, and atmospheric temperature.
You can choose to hide all camera overlay by the press of a programmable button.
Image with camera overlay and image overlay
information.
1. Definition from the impending international adoption of DIN 54190-3 (Non-destructive testing – Thermographic
testing – Part 3: Terms and definitions).
#T559954; r. AL/37426/37426; en-US
Image with all overlay hidden.
58
Page 73

Achieving a good image15
15.8.2 Procedure
Follow this procedure:
1. Push the joystick to display the menu system.
2. Use the joystick to go to
(Settings).
3. Push the joystick to display the Settings menu.
4. Select Programmable buttons and push the joystick.
5. Select one of the buttons and push the joystick.
6. Select Hide image overlay graphics and push the joystick. You have now assigned this
function to the selected programmable button.
#T559954; r. AL/37426/37426; en-US
59
Page 74

16
Working with image modes
16.1 General
The camera captures both thermal and visual images at the same time. By your choice of
image mode, you select which type of image to display on the screen.
The camera supports the following image modes:
• Thermal MSX (Multi Spectral Dynamic Imaging): The camera displays infrared images
where the edges of the objects are enhanced with visual image details.
• Thermal: A full infrared image is displayed.
• Picture in picture: An infrared image frame is displayed on top of the visual image.
• Digital camera: The visual image captured by the digital camera is displayed.
Note
• These image modes only work correctly for calibrated lenses. The lens that ships with
the camera is factory calibrated. To have a new lens calibrated, you must send in the
camera and the lens to your local service department.
• All thermal and visual information is stored when an image is saved. This means that
you can edit the image later, in the image archive, in FLIR Tools/Tools+, or in FLIR ResearchIR Max, and select any of the image modes.
16.2 Image examples
This table explains the different types of image modes.
Image mode Image
Thermal
Thermal MSX
#T559954; r. AL/37426/37426; en-US
60
Page 75

Working with image modes16
Image mode Image
Picture in picture
Digital camera
16.3 Selecting the image mode
Follow this procedure:
1. Push the joystick to display the menu system.
2. Use the joystick to go to
(Image mode).
3. Push the joystick to display a submenu.
4. Use the joystick to go to one of the image modes:
•
(Thermal MSX)
•
(Thermal)
•
(Picture in picture)
•
(Digital camera)
Note If the *.csq video format is selected (Settings > Save options & storage > Video
compression ) and the recording mode Video is selected, it will only be possible to se-
lect the image mode Thermal.
5. Push the joystick confirm.
6. If Picture in picture mode is selected, you can at this point move and resize the infrared
image frame using the touch screen.
#T559954; r. AL/37426/37426; en-US
61
Page 76

17
Working with measurement tools
17.1 General
To measure a temperature, you can use one or more measurement tools, e.g., a spotmeter
or a box.
17.2 Adding/removing measurement tools
Follow this procedure:
1. Push the joystick to display the menu system.
2. Use the joystick to go to
3. Push the joystick to display a submenu.
• Select
• Select
• Select
• Select
• Select
models.)
• Select
models.)
4. Push the joystick. This displays the measurement tool or the group of preset tools on
the screen.
17.3 Working with user presets
17.3.1 General
A user preset is a measurement tool, or a group of measurement tools, with predefined
characteristics.
(No measurements) to remove all tools.
(Center spot) to add a center spot.
(Hot spot) to add a hot spot detection within a box area.
(Cold spot) to add a cold spot detection within a box area.
(User preset 1) to add user preset 1. (Not available in all camera
(User preset 2) to add user preset 2. (Not available in all camera
(Measurement).
17.3.2 Procedure
Follow this procedure:
1. Push the joystick to display the menu system.
#T559954; r. AL/37426/37426; en-US
62
Page 77

Working with measurement tools17
2. Use the joystick to go to
(Settings).
3. Push the joystick to display the Settings menu.
4. Select Define user presets and push the joystick.
5. Select Define preset 1 or Define preset 2 and push the joystick. This displays a context
menu.
6. Select
(Add measurement).
7. Push the joystick. This displays a submenu.
• Select
• Select
• Select
• Select
• Select
(Add spot) to add a spot.
(Add box) to add a box.
(Add circle) to add a circle.
(Add line) to add a line.
(Add delta) to set up a differential calculation.
8. Push the joystick. This displays the measurement tool on the screen.
9. Push the joystick. This displays a context menu, where you can select one or more of
the following actions (depending on the type of tool):
• Remove the tool.
• Resize, move, center, and rotate the tool.
• Display maximum, minimum, and average values.
• Set alarms.
• Set local parameters.
• When completed, select
10. When all measurement tools have been added, select
(Done).
(Save as preset).
17.4 Resizing or moving a measurement tool
17.4.1 General
You can resize and move a measurement tool.
17.4.2 Procedure
Note
• This procedure assumes that you have previously laid out a measurement tool or user
preset on the screen.
• You can also move and resize the measurement tool by touching the screen.
#T559954; r. AL/37426/37426; en-US
63
Page 78

Working with measurement tools17
Follow this procedure:
1. To select the measurement tool, touch the tool on the screen. The tool is now displayed with one or more handles.
Spot measurement tool:
Area measurement tool:
2. Push the joystick—or touch and hold the tool. This displays a context menu.
• Select
• Select
(Resize) to change the size of the tool.
(Move) to move the tool.
3. Move the joystick up/down and left/right to resize or move the tool.
4. When completed, push the joystick and select
(Done).
17.5 Changing object parameters
17.5.1 General
For accurate measurements, you must set the object parameters.
17.5.2 Types of parameters
The camera can use these object parameters:
• External IR window compensation, i.e., the temperature of any protective windows, ex-
ternal lenses (e.g., the close-up lens), etc., that are set up between the camera and the
object of interest. If no protective window, protective shield, or external lens is used, this
value is irrelevant and should be left inactive.
• Object distance, i.e., the distance between the camera and the object of interest.
• Atmospheric temperature, i.e., the temperature of the air between the camera and the
object of interest.
• Relative humidity, i.e., the relative humidity of the air between the camera and the ob-
ject of interest.
• Reflected temperature, which is used when compensating for the radiation from the
surroundings reflected by the object into the camera. This property of the object is
called “reflectivity”.
• Emissivity, i.e., how much radiation an object emits, compared with the radiation of a
theoretical reference object at the same temperature (called a “blackbody”). The opposite of emissivity is reflectivity. The emissivity determines how much of the radiation
originates from the object as opposed to being reflected by it.
Note There is an Emissivity mode setting, which you can use to enter the emissivity
by material instead of by value. Select
(Settings) > Device settings > User interface
options > Emissivity mode > Select from materials table.
Of the object parameters, Emissivity is the most important parameter to set correctly. If the
Emissivity is set to a low value, the Reflected temperature also becomes important. The
parameters Object distance, Atmospheric temperature, and Relative humidity are relevant
#T559954; r. AL/37426/37426; en-US
64
Page 79

Working with measurement tools17
for longer distances. The External IR window compensation must be activated if a protective window or external lens is used.
17.5.3 Recommended values
If you are unsure about the values, the following are recommended:
Object distance 1.0 m (3.3′)
Atmospheric temperature 20°C (69°F)
Relative humidity 50%
Reflected temperature 20°C (69°F)
Emissivity 0.95
17.5.4 Procedure
You can set the object parameters globally. You can also change the Emissivity, Reflected
temperature, and Object distance parameters locally for a measurement tool.
Local parameters are normally only effective for a fixed setup, where each measurement
tool is set to a specific object of interest. In a general handheld application, the global parameters are usually sufficient.
Note Of the object parameters, Emissivity and Reflected temperature are the two most
important to set correctly in the camera.
17.5.4.1 Setting global parameters
Follow this procedure:
1. Push the joystick to display the menu system.
2. Use the joystick to go to
(Measurement parameters).
3. Push the joystick to display a submenu. Use the joystick to select one or more of the
global object parameters:
•
(External IR window compensation)
•
(Object distance)
•
(Atmospheric temperature)
•
(Relative humidity)
•
(Reflected temperature)
•
(Emissivity)
4. Push the joystick to display a dialog box.
5. Use the joystick to change the parameter.
6. Push the joystick. This closes the dialog box.
17.5.4.2 Changing local parameters
You can change the local parameters for a measurement tool.
A P next to the measurement tool on the screen indicates that local parameters are acti-
vated for the tool.
#T559954; r. AL/37426/37426; en-US
65
Page 80

Working with measurement tools17
Follow this procedure:
1. To select the measurement tool, touch the tool on the screen. The tool is now displayed with one or more handles.
2. Push the joystick—or touch and hold the tool. This displays a context menu.
3. Use the joystick to go to
4. Push the joystick.
5. Push the joystick to activate the use of local parameters.
(Use local parameters).
(icon with gray indicator) is displayed.
(icon with blue indica-
tor) is displayed together with a submenu.
6. Use the joystick to select an object parameter.
7. Push the joystick to display a dialog box.
8. Use the joystick to change the parameter.
9. Push the joystick. This closes the dialog box.
17.5.5 Related topics
For in-depth information about parameters, and how to correctly set the emissivity and reflected apparent temperature, see section 35 Thermographic measurement techniques,
page 229.
17.6 Displaying values in the result table and displaying a graph
17.6.1 General
For the box, circle, and line tools, you can set the camera to display the maximum, minimum, and average values in the result table.
For the line tool, you can also display a graph.
#T559954; r. AL/37426/37426; en-US
66
Page 81

Working with measurement tools17
17.6.2 Procedure
Follow this procedure:
1. To select the measurement tool, touch the tool on the screen. The tool is now displayed with one or more handles.
2. Push the joystick—or touch and hold the tool. This displays a context menu.
3. Use the joystick to go to (depending on the tool)
, , or (Max/Min/Avg/Alarm)
or (Graph/Max/Min/Avg/Alarm).
4. Push the joystick. This displays a submenu.
• (Option available for the line tool.) Select
(Graph) and push the joystick to dis-
play a graph.
• Select
• Select
• Select
(Max) and push the joystick to display the maximum value.
(Min) and push the joystick to display the minimum value.
(Avg) and push the joystick to display the average value.
• (Optional step.) You can choose to show or hide the maximum and minimum
markers (the hot/cold spots). Select
(Max & min markers) and push the joystick
to toggle:
◦ When
◦ When
(icon with grey indicator) is displayed, the markers are hidden.
(icon with blue indicator) is displayed, the markers are shown.
5. When completed, move the joystick down to close the submenu.
6. Select
(Done) and push the joystick.
17.7 Creating and setting up a difference calculation
17.7.1 General
A difference calculation gives the difference between the values of two known measurement results.
17.7.2 Procedure
Note
• You can set up a difference calculation when defining user presets, or when editing an
image in the archive.
• This procedure assumes that you have previously laid out at least one measurement
tool on the screen.
#T559954; r. AL/37426/37426; en-US
67
Page 82

Working with measurement tools17
17.7.2.1 Procedure
Follow this procedure:
1. To set up a difference calculation, do the following:
• If you are defining user presets, select
(Add measurement) and then select
(Add delta).
• If you are editing an image in the archive, select
(Measurement) and then select
(Add delta).
2. Push the joystick. This displays a dialog box where you can select the measurement
tools that you want to use in the difference calculation. You can also select a fixed-temperature reference.
3. Push the joystick. The result of the difference calculation is now displayed on the
screen.
17.8 Setting a measurement alarm
17.8.1 General
You can make the camera trigger an alarm when certain measurement conditions are met.
17.8.2 Types of alarm
You can choose between the following alarm types:
• Above: Triggers an alarm when the temperature is above the preset alarm temperature.
• Below: Triggers an alarm when the temperature is below the preset alarm temperature.
17.8.3 Alarm signals
When an alarm is set, the symbol
is displayed in the result table.
When an alarm is triggered, the value in the result table is displayed in red (above alarm)
or blue (below alarm) and the symbol
#T559954; r. AL/37426/37426; en-US
(above alarm) or (below alarm) is blinking.
68
Page 83

Working with measurement tools17
You can also set an audible alarm (there will be a “beep” when the alarm is triggered).
17.8.4 Procedure
There are different procedures for setting up an alarm for a spot, box, circle, or line and for
a difference calculation.
17.8.4.1 Setting up an alarm for a spot
Follow this procedure:
1. To select the spot, touch the tool on the screen. The tool is now displayed with a frame.
2. Push the joystick—or touch and hold the tool. This displays a context menu.
3. Use the joystick to go to
(Set alarm on spot).
4. Push the joystick. This displays a dialog box where you can define the settings for the
alarm.
• Alarm condition: The condition that triggers the alarm. Applicable values are Above,
Below, or Off.
• Alarm limit: The temperature value that will be the critical condition when an alarm is
triggered or not.
• Alarm sound: Applicable values are Beep or No sound.
5. Push the joystick. This closes the dialog box.
17.8.4.2 Setting up an alarm for a box, circle, or line
Note This procedure assumes that you have previously set the camera to display at least
one value (maximum, minimum, or average) in the result table.
Follow this procedure:
1. To select the measurement tool, touch the tool on the screen. The tool is now displayed with one or more handles.
2. Push the joystick—or touch and hold the tool. This displays a context menu.
3. Use the joystick to go to (depending on tool)
, , or (Max/Min/Avg/Alarm) or
(Graph/Max/Min/Avg/Alarm).
4. Push the joystick. This displays a submenu.
5. Select
(Set alarm).
6. Push the joystick. This displays a dialog box where you can define the settings for the
alarm.
• Alarm condition: The condition that triggers the alarm. Applicable values are Above,
Below, or Off.
• Select measurement: Applicable settings are the values you have previously de-
fined (Max, Min, and/or Avg).
• Alarm limit: The temperature value that will be the critical condition when an alarm is
triggered or not.
• Alarm sound: Applicable values are Beep or No sound.
7. Push the joystick. This closes the dialog box.
17.8.4.3 Setting up an alarm for a difference calculation
Note
• You can set up an alarm for a difference calculation when defining user presets, or
when editing an image in the archive.
• This procedure assumes that you have previously set up a difference calculation.
#T559954; r. AL/37426/37426; en-US
69
Page 84

Working with measurement tools17
Follow this procedure:
1. To set up an alarm for a difference calculation, do the following:
• If you are defining user presets, select
(Add measurement). This displays a
submenu.
• If you are editing an image in the archive, select
(Measurement). This displays
a submenu.
2. Select
(Select). This displays a dialog box.
3. Select Delta. This displays a context menu.
4. Use the joystick to go to
(Set alarm on delta).
5. Push the joystick. This displays a dialog box where you can define the settings for the
alarm.
• Alarm condition: The condition that triggers the alarm. Applicable values are Above,
Below, or Off.
• Alarm limit: The temperature value that will be the critical condition when an alarm is
triggered or not.
• Alarm sound: Applicable values are Beep or No sound.
6. Push the joystick. This closes the dialog box.
#T559954; r. AL/37426/37426; en-US
70
Page 85

18
Working with color alarms and isotherms
18.1 Color alarms
18.1.1 General
By using color alarms (isotherms), anomalies can easily be discovered in an infrared image. The isotherm command applies a contrasting color to all pixels with a temperature
above, below, or between the set temperature levels. The camera also features isotherm
types that are specific to the building trade: condensation and insulation alarms.
You can make the camera trigger the following types of color alarms:
• Above alarm: This will apply a contrasting color to all pixels with a temperature above
the specified temperature level.
• Below alarm: This will apply a contrasting color to all pixels with a temperature below
the specified temperature level.
• Interval alarm: This will apply a contrasting color to all pixels with a temperature be-
tween two specified temperature levels.
• Condensation alarm: Triggers when the camera detects a surface where the relative hu-
midity exceeds a preset value.
• Insulation alarm: Triggers when there is an insulation deficiency in a wall.
18.1.2 Image examples
This table explains the different color alarms (isotherms).
Color alarm
Above alarm
Below alarm
Image
#T559954; r. AL/37426/37426; en-US
71
Page 86

Working with color alarms and isotherms18
Color alarm
Interval alarm
Condensation alarm
Insulation alarm
Image
18.2 Setting up above, below, and interval alarms
Follow this procedure:
1. Push the joystick to display the menu system.
2. Use the joystick to go to
(Color).
3. Push the joystick to display a submenu. Use the joystick to select the type of alarm:
•
(Above alarm)
•
(Below alarm)
•
(Interval alarm)
4. Push the joystick. The threshold temperature is displayed at the top of the screen.
#T559954; r. AL/37426/37426; en-US
72
Page 87

Working with color alarms and isotherms18
5. To change the threshold temperature, do the following:
• For the Interval alarm, move the joystick left/right to select the low/high-temperature
value.
• Move the joystick up/down to change the threshold temperature.
18.3 Building isotherms
Note The Condensation and Insulation alarms are not supported by all camera models.
18.3.1 About the Condensation alarm
To detect areas with potential moisture problems, you can use the Condensation alarm.
You can set the relative humidity above which the isotherm will colorize the image.
18.3.2 About the Insulation alarm
The Insulation alarm can detect areas where there may be an insulation deficiency in the
building. It will trigger when the insulation level (which is called the thermal index in the
camera) falls below a preset value of the energy leakage through a wall.
Different building codes recommend different values for the insulation level, but typical values are 60–80% for new buildings. Refer to your national building code for
recommendations.
18.3.3 Setting up condensation and insulation alarms
Follow this procedure:
1. Push the joystick to display the menu system.
2. Use the joystick to go to
(Color).
3. Push the joystick to display a submenu. Use the joystick to select the type of alarm:
•
(Condensation alarm)
•
(Insulation alarm)
4. Push the joystick. This displays a dialog box where you can define the settings for the
alarm.
For the Condensation alarm, the following parameters can be set:
• Atmospheric temperature: The current atmospheric temperature.
• Relative humidity: The current relative humidity.
• Relative humidity limit: The relative humidity level at which you want the alarm to be
triggered. A relative humidity of 100% means that water vapor condenses from the
air as liquid water (= dewpoint). A relative humidity of about 70% or above can
cause mold.
For the Insulation alarm, the following parameters can be set:
• Indoor temperature: The current indoor temperature.
• Outdoor temperature: The current outdoor temperature.
• Thermal index: The insulation level, an integer between 0 and 100.
5. Push the joystick. This closes the dialog box.
#T559954; r. AL/37426/37426; en-US
73
Page 88

19
Annotating images
19.1 General
You can save additional information with an infrared image by using annotations. Annotations make reporting and post-processing more efficient, by providing essential information about the image, e.g., conditions and information about where an image is taken.
Annotations are added to the image file, and can be viewed and edited in the image archive, and also when moving files from the camera to reporting software on the computer.
• You can set the camera to display annotation tools before an image is saved. Select
(Settings) > Save options & storage > Add annotation after saving.
• You can also add annotations to a saved image in the image archive.
Note This section describes the procedures for adding annotations to a saved image in
the image archive. Adding annotations when saving an image works in a similar way.
19.2 Adding a note
19.2.1 General
You can add a text note to the image file. Using this feature, you can annotate images by
entering free-form text.
19.2.2 Procedure
Follow this procedure:
1. Open the image in the image archive.
2. Push the joystick. This displays a context menu.
3. Select
4. Push the joystick. This displays a soft keyboard where you can enter the text you want
to save by touching the screen.
Note To select special characters, press and hold down the corresponding key on
the soft keyboard.
5. When completed, touch Done on the soft keyboard.
19.3 Adding a table
19.3.1 General
You can save a table with textual information to the image file. This feature is a very efficient way of recording information when you are inspecting a large number of similar
#T559954; r. AL/37426/37426; en-US
(Add note).
74
Page 89

Annotating images19
objects. The idea behind using a table with textual information is to avoid filling out forms
or inspection protocols manually.
The camera has a number of default table templates. You can also import your own table
templates from FLIR Tools/Tools+—refer to the FLIR Tools/Tools+ user’s manual. The templates are stored on the memory card.
19.3.2 Procedure
Follow this procedure:
1. Open the image in the image archive.
2. Push the joystick. This displays a context menu.
3. Select
4. Select
(Add table) and push the joystick.
(Add table contents) and push the joystick. This displays the default table
template that ships with the camera.
Note You can select another template by first selecting
(Select default template).
5. For each row in the table, do the following:
• Push the joystick. This displays the predefined values.
• Move the joystick up/down to select a predefined value. Push the joystick to confirm.
• Instead of selecting a predefined value, you can select the keyboard
and enter
other text by touching the screen.
6. When completed, select Save & Exit at the bottom of the table. Push the joystick to
confirm.
19.4 Adding a voice annotation
19.4.1 General
A voice annotation is an audio recording that is saved to the infrared image file. The recording can be played back in the camera, and in image analysis and reporting software
from FLIR Systems.
The voice annotation is recorded using a Bluetooth headset. For information on how to
pair a headset with the camera, see section 23 Pairing Bluetooth devices, page 81.
#T559954; r. AL/37426/37426; en-US
75
Page 90

Annotating images19
19.4.2 Procedure
Follow this procedure:
1. Open the image in the image archive.
2. Push the joystick. This displays a context menu.
3. Select
4. To start a recording, select
5. To stop the recording, select
6. To listen to the recording, select
7. To delete the recording, select
8. When completed, select
(Add voice annotation) and push the joystick.
(Record) and push the joystick.
(Stop) and push the joystick.
(Play) and push the joystick.
(Delete) and push the joystick.
(Done) and push the joystick.
19.5 Adding a sketch
19.5.1 General
You can add a freehand drawing to an image.
19.5.2 Procedure
Follow this procedure:
1. Open the image in the image archive.
2. Push the joystick. This displays a context menu.
3. Select
(Add sketch) and push the joystick.
4. You are now in sketch mode. Draw the sketch by touching the screen.
#T559954; r. AL/37426/37426; en-US
76
Page 91

Annotating images19
5. Push the joystick. This displays a context menu. Do one or more of the following:
• To change the color of the sketch tools, select
(Draw) and push the joystick. Se-
lect the color and push the joystick.
• To erase, select
(Eraser) and push the joystick. Erase parts of the sketch by
touching the screen.
• To add an arrow, circle, or cross, select
(Stamp sketch) and push the joystick.
Select the type of stamp and push the joystick. The stamp is displayed in the center
of the screen. You can move the stamp by using the joystick or by touching the
screen.
• To clear, select
• When the sketch is completed, select
(Clear all) and push the joystick.
(Save) and push the joystick.
#T559954; r. AL/37426/37426; en-US
77
Page 92

20
Programming the camera (time lapse)
20.1 General
You can program the camera to save images periodically (time lapse).
20.2 Procedure
Follow this procedure:
1. Push the joystick to display the menu system.
2. Use the joystick to go to
3. Push the joystick. This displays a submenu.
4. Select
5. Push the joystick. This displays a dialog box, where you can set the save conditions:
• Save interval: Use the joystick to set the time interval between each saved image.
• Total number of images: Periodic saving will stop when the set number of images
have been saved.
6. Push the joystick. This closes the dialog box. The time interval is displayed at the top
of the screen.
7. To manually start or stop periodic saving, briefly push and release the Save button.
(Time lapse).
(Recording mode).
#T559954; r. AL/37426/37426; en-US
78
Page 93

21
Recording video clips
21.1 General
You can record and save video clips to the memory card.
Note The camera can be configured to save video in *.mpg or *.csq format. Select
(Settings) > Save options & storage > Video compression.
• Mpeg (*.mpg): Mpeg recordings cannot be edited after the file has been saved.
• Radiometric storage (*csq): A *.csq file supports full radiometry but is only supported
by FLIR Systems software. The file does not include any visual image information. With
this setting, only Thermal image mode is supported when recording video. If any other
image mode is active when Video recording mode is selected, the camera will autoswitch to Thermal image mode.
21.2 Procedure
Follow this procedure:
1. Push the joystick to display the menu system.
2. Use the joystick to go to
3. Push the joystick. This displays a submenu.
4. Select
5. Do the following:
• To start a recording, push and release the Save button. A counter at the top of the
screen displays the duration of the recording.
• To stop a recording, push and release the Save button.
6. The recording is automatically saved to the image archive, where you can play or delete it.
(Video) and push the joystick.
(Recording mode).
#T559954; r. AL/37426/37426; en-US
79
Page 94

22
Screening alarm
22.1 General
The screening alarm can be used, for example, at airports to detect passengers with elevated body temperatures, which may indicate the presence of a fever.
The screening alarm can also be used to detect temperature anomalies in a series of inspected objects in a similar/fixed setup.
Activating the screening alarm will turn on a measurement box and screening data in the
result table.
The sampled average temperature.
The alarm temperature.
The measured temperature.
The alarm will trigger when the measurement box measures a temperature higher than the
alarm temperature. The alarm temperature is, in turn, the sum of a specified allowed deviation and a sampled average value.
22.2 Procedure
Follow this procedure:
1. Enable the screening mode by selecting
face options > Screening mode = On.
2. Push the joystick to display the menu system.
3. Use the joystick to go to
4. Push the joystick. This displays a submenu.
5. Select
6. Push the joystick. This displays a dialog box where you can define the settings for the
alarm.
• Allowed deviation: The allowed deviation from the sampled average.
• Alarm sound: Applicable values are Beep or No sound.
7. Push the joystick. This closes the dialog box.
8. Aim the camera toward a point of interest. The object should be within the frame of the
measurement box.
9. Push and hold the programmable button
10. Push the programmable button
11. Aim the camera toward more points of interest. Sample 10 times to build up a sample
base by pushing the programmable button
The alarm is now set up and ready to use. Occasionally record a few samples if the
alarm is used for a long time or if the conditions change.
Note
• The algorithm has a memory of the last 10 samples. It discriminates between the high-
est and lowest values, and calculates an average of the remaining values.
• Do not modify the measurement setup or activate another alarm because this will deac-
tivate the screening alarm.
(Screening).
(Recording mode).
to sample.
(Settings) > Device settings > User inter-
to reset the sampled average.
.
#T559954; r. AL/37426/37426; en-US
80
Page 95

23
Pairing Bluetooth devices
23.1 General
Before you can use a Bluetooth device with the camera, you need to pair the devices.
23.2 Procedure
Follow this procedure:
1. Push the joystick to display the menu system.
2. Use the joystick to go to
3. Push the joystick to display the Settings menu.
4. Select Device settings and push the joystick.
5. Depending on the camera configuration, select Wireless & geolocation, Wireless, or
Geolocation and push the joystick.
6. Select Bluetooth and push the joystick.
7. If the Bluetooth check box is unchecked, push the joystick to activate Bluetooth.
Note You also need to ensure that the external Bluetooth device is in visible mode.
8. Select Available devices and push the joystick.
9. Wait until a list of available devices is displayed. This will take about 15 seconds.
10. When a Bluetooth device is found, select the device to add it, and begin the pairing
procedure. The device is then ready to be used.
Note
• Only Bluetooth-enabled headsets will appear in the list of available devices.
• You can add several devices.
• You can remove a device by selecting the device and then selecting Unpair device.
• After adding a Bluetooth-enabled headset, it is ready to be used for adding voice
annotations.
(Settings).
#T559954; r. AL/37426/37426; en-US
81
Page 96

24
Configuring Wi-Fi
24.1 General
Depending on your camera configuration, you can connect the camera to a wireless local
area network (WLAN) using Wi-Fi, or let the camera provide Wi-Fi access to other devices.
You can connect the camera in two different ways:
• Most common use: Setting up the camera as a wireless access point. This method is
primarily used with other devices, e.g., an iPhone or iPad.
• Less common use: Connecting the camera to a wireless local area network (WLAN).
24.2 Setting up a wireless access point (most common use)
Follow this procedure:
1. Push the joystick to display the menu system.
2. Use the joystick to go to
3. Push the joystick to display the Settings menu.
4. Select Device settings and push the joystick.
5. Depending on the camera configuration, select Wireless & geolocation, Wireless, or
Geolocation and push the joystick.
6. Select Wi-Fi and push the joystick.
7. Select Share and push the joystick.
8. (Optional step.) To display and change the parameters, select Share settings and push
the joystick.
• To change the SSID, select Network name (SSID) and push the joystick.
• To change the WPA2 password, select Password and push the joystick.
Note These parameters are set for your camera’s network. They will be used by the
external device to connect that device to the network.
24.3 Connecting the camera to a WLAN (less common use)
Follow this procedure:
1. Push the joystick to display the menu system.
2. Use the joystick to go to
3. Push the joystick to display the Settings menu.
4. Select Device settings and push the joystick.
5. Depending on the camera configuration, select Wireless & geolocation, Wireless, or
Geolocation and push the joystick.
6. Select Wi-Fi and push the joystick.
7. Select Connect to network and push the joystick.
8. To display a list of the available networks, select Networks and push the joystick.
9. Select one of the available networks.
Password-protected networks are indicated with a padlock icon, and for these you will
need to enter a password the first time you connect to the network. After that the camera will connect automatically to the network. To disable the automatic connection, select Forget network.
Note Some networks do not broadcast their existence. They appear in the list as Unti-
tled. To connect to such a network, you will be prompted to enter additional parameters.
(Settings).
(Settings).
#T559954; r. AL/37426/37426; en-US
82
Page 97

25
Changing settings
25.1 General
You can change a variety of settings in the camera. You do this on the Settings menu.
The Settings menu includes the following:
• Define user presets.
• Camera temperature range.
• Save options & storage.
• Programmable buttons.
• Device settings.
25.1.1 Define user presets
A user preset is a measurement tool, or a group of measurement tools, with predefined
characteristics. For more information, see section 17.3 Working with user presets, page
62.
• Define preset 1: This setting defines user preset 1.
• Define preset 2: This setting defines user preset 2.
25.1.2 Camera temperature range
For accurate temperature measurements, you must change the Camera temperature
range setting to suit the expected temperature of the object you are inspecting.
Available temperature range options are dependent on the camera model. The unit (℃ or
℉) depends on the temperature unit setting, see section 25.1.5 Device settings, page 85.
25.1.3 Save options & storage
• Save button half-press: This setting defines the function of the Save button. Available
options are:
◦ Autofocus: Pushing the Save button half-way down will autofocus the infrared
camera.
◦ None: Pushing the Save button half-way down will have no effect. With this setting,
you may want to assign the autofocus function to one of the programmable buttons.
• Preview image before saving: This setting defines if a preview image will be displayed
before the image is saved.
• Add annotation after saving: This setting defines if an annotation tool will be displayed
when the image has been saved. Available options are:
◦ Save: No annotation tool will be displayed.
◦ Save & add note: The note annotation tool will be displayed.
#T559954; r. AL/37426/37426; en-US
83
Page 98

25
Changing settings
◦ Save & add table: The table annotation tool will be displayed. This setting also allows
you to define the type of table. Available options are the default table templates. You
can also create your own table in FLIR Tools/Tools+ and upload it to the camera.
◦ Save & add voice annotation: The voice annotation tool will be displayed.
◦ Save & add sketch: The sketch annotation tool will be displayed.
◦ Save & add any annotation: The annotation tool menu will be displayed.
• Image resolution: This setting defines the resolution of the images captured by the camera. Available options are Normal and Ultramax. For more information, see section
14.1.4 About UltraMax, page 47.
• Video compression: This setting defines the storage format for video clips. Available
options are:
◦ Mpeg (*.mpeg): MPEG recordings cannot be edited after the file has been saved.
◦ Radiometric storage (*.csq): A CSQ file supports full radiometry but is only sup-
ported by FLIR Systems software. The file does not include any visual image information. With this setting, only Thermal image mode is supported when recording
video.
• Photo as separate JPEG: A visual image is always saved in the same JPEG file as the
thermal image. Enabling this setting saves an extra visual image as a separate JPEG
file.
• File naming format: This setting defines the naming format for new image/video files.
The setting has no impact on already saved files in the archive. Available options are:
◦ DCF: DCF (Design rule for Camera File system) is a standard that specifies the nam-
ing method of image files (and much more). With this setting, the name of a saved
image/video file will be FLIRxxxx, where xxxx is a unique counter. Example:
FLIR0001.
◦ Date prefix: A prefix will be added to the file name, including the date and the text
“IR_” for images and “MOV_” for videos. Examples: IR_2015-04-22_0002 and
MOV_2015-04-22_0003. The date format will follow the Date & time format setting,
see section 25.1.5 Device settings, page 85.
Note With the Date prefix setting, the files may not automatically be detected by
third-party applications.
• Delete all saved files...: This displays a dialog box where you can choose to permanently delete all the saved files (images, videos, and reports) from the memory card or
to cancel the delete action.
25.1.4 Programmable buttons
There are four programmable buttons. For more information, see section 13.11 Assigning
functions to the programmable buttons, page 37.
• P Button: This setting assigns a function to the hardware button
• P2 Button: This setting assigns a function to the hardware button
.
.
• P3 Button (on screen): This setting assigns a function to the software button P3 on the
screen.
• P4 Button (on screen): This setting assigns a function to the software button P4 on the
screen.
Available options for all programmable buttons:
• No action: This is the default setting. Nothing will happen when you push/press the
button.
#T559954; r. AL/37426/37426; en-US
84
Page 99

25
Changing settings
• Hide image overlay graphics: Hide all overlay graphics and image overlay information.
For more information, see section 15.8 Hiding all overlay, page 58.
• Calibrate: Perform a manual calibration of the camera. For more information, see section 15.7 Calibrating the camera, page 58.
• Auto-adjust the manual temperature scale: Perform an automatic adjustment of the image while remaining in manual image adjustment mode.
• Switch Thermal <> Digital camera: Switch between the image modes Thermal and Digi-
tal camera. For more information, see section 16 Working with image modes, page 60.
• Switch Thermal <> Thermal MSX: Switch between the image modes Thermal and Ther-
mal MSX. For more information, see section 16 Working with image modes, page 60.
• Switch 1x zoom <> Max zoom: Switch between the digital zoom factor of 1× and maximum zoom.
• Switch camera flash On <> Off: Switch between the activated/deactivated camera flash
function. For more information, see section 13.12 Using the camera lamp as a flash,
page 38.
Note The flash function will not be activated if the setting Lamp & laser is set to the
option Disable all. For more information, see section 25.1.5 Device settings, page 85.
• Switch single shot <> Video: Switch between the recording modes Single shot and
Video.
• Switch between two latest palettes: Switch between the two last-used color palettes.
For more information, see section 15.5 Changing the color palette, page 56.
• Switch temperature range: Cycle through the camera temperature ranges. For more information, see section 25.1.2 Camera temperature range, page 83.
Additional options for the hardware buttons
and :
• Autofocus.
• Continuous autofocus.
• Switch screen rotation On <> Off.
• Save.
• Save + Prompt for note.
• Save + Prompt for table.
• Save + Prompt for voice annotation.
• Save + Prompt for sketch.
• Save + Select annotation from menu.
• Preview.
• Preview + Prompt for note.
• Preview + Prompt for table.
• Preview + Prompt for voice annotation.
• Preview + Prompt for sketch.
• Preview + Select annotation from menu.
25.1.5 Device settings
• Language, time & units: This submenu includes settings for a number of regional
parameters:
◦ Language.
◦ Temperature unit.
◦ Distance unit.
◦ Time zone
◦ Date & time.
◦ Date & time format.
• Continuous autofocus: This setting is used to enable/disable continuous autofocus.
• Display settings: This submenu includes the following settings:
#T559954; r. AL/37426/37426; en-US
85
Page 100

25
Changing settings
◦ Screen rotation: This setting defines if the orientation of the overlay graphics will
change according to how you hold the camera.
◦ Image overlay information: This setting specifies what image information the camera
will display as an overlay on the image. For more information, see section 11.4 Im-
age overlay information, page 29. You can select to display the following information:
– Compass.
– Date & time.
– Emissivity.
– Reflected temperature.
– Distance.
– Relative humidity.
– Atmospheric temperature.
Note This setting only specifies what information to overlay on the image. All image information is always saved to the image file and is available in the image
archive.
◦ Screen brightness: This setting defines the brightness of the screen. Available op-
tions are Low, Medium, High, and Auto.
◦ Viewfinder brightness: This setting defines the brightness of the viewfinder. Available
options are Low, Medium, and High.
◦ HDMI: (Applicable when an HDMI cable is connected to the camera.) This setting
defines the resolution of the digital video output. The setting can be used to select
display of the image only, or display of the image and the entire overlay graphics.
• Wireless & geolocation, Wireless, or Geolocation (depending on the camera configuration): This submenu includes the following settings:
◦ Wi-Fi: This setting defines Wi-Fi networks. For more information, see section 24
Configuring Wi-Fi, page 82.
◦ Bluetooth: This setting defines Bluetooth connectivity. For more information, see
section 23 Pairing Bluetooth devices, page 81.
◦ GPS: This setting is used to enable/disable the GPS.
◦ Compass: This setting is used to enable/disable the compass and to calibrate the
compass. For more information, see section 13.15 Calibrating the compass, page
46.
• Lamp & laser: This submenu includes the following settings:
◦ Enable lamp & laser: This setting is used to enable the camera lamp and the laser
pointer.
◦ Enable lamp & laser + Use lamp as flash: This setting is used to activate the flash
function. When the flash function is activated, the camera lamp will flash when an image is saved.
◦ Disable all: This setting is used to disable the camera lamp, laser pointer, and flash
function.
• Auto power off: This setting defines how soon the camera is automatically turned off.
Available choices are Off, 5 min, and 20 min.
• User interface options: This submenu includes the following settings:
◦ Manual adjustment mode: This setting specifies the type of manual image adjust-
ment mode. Available options are Level, Max, Min and Level, Span. For more information, see section 15.3 Adjusting the infrared image, page 53.
◦ Emissivity mode: This setting specifies how the object parameter emissivity will be
entered. Available options are Select values and Select from materials table. For
more information, see section 17.5 Changing object parameters, page 64.
◦ Screening mode: This setting is used to enable/disable screening mode. For more
information, see section 22 Screening alarm, page 80.
#T559954; r. AL/37426/37426; en-US
86
 Loading...
Loading...