Page 1

Chemical Compatibility of Elastomers and Metals
Te c h n i c a l
Introduction
This section explains the uses and compatibilities of elastomers
commonly used in Fisher® regulators. The following tables
provide the compatibility of the most common elastomers and
metals to a variety of chemicals and/or compounds.
The information contained herein is extracted from data we believe
to be reliable. However, because of variable service conditions over
which we have no control, we do not in any way make any warranty,
either express or implied, as to the properties of any materials or as to
the performance of any such materials in any particular application, and
we hereby expressly disclaim any responsibility for the accuracy of any
of the information set forth herein.
Refer to the applicable process gas service code or standard
to determine if a specic material found in the Process Gases
Application Guide is allowed to be used in that service.
Elastomers: Chemical Names and Uses
NBR - Nitrile Rubber, also called Buna-N, is a copolymer of
butadiene and acrylonitrile. Nitrile is recommended for: general
purpose sealing, petroleum oils and uids, water, silicone greases
and oils, di-ester based lubricants (such as MIL-L-7808), and
ethylene glycol based uids (Hydrolubes). It is not recommended
for: halogenated hydrocarbons, nitro hydrocarbons (such as
nitrobenzene and aniline), phosphate ester hydraulic uids
(Skydrol, Cellulube, Pydraul), ketones (MEK, acetone), strong
acids, ozone, and automotive brake uid. Its temperature range is
-60° to 225°F (-51° to 107°C), although this would involve more
than one compound and would depend upon the stress state of the
component in service.
EPDM, EPM - Ethylenepropylene rubber is an elastomer prepared
from ethylene and propylene monomers. EPM is a copolymer of
ethylene and propylene, while EPDM contains a small amount
of a third monomer (a diene) to aid in the curing process. EP is
recommended for: phosphate ester based hydraulic uids, steam to
400°F (204°C), water, silicone oils and greases, dilute acids, dilute
alkalis, ketones, alcohols, and automotive brake uids. It is not
recommended for: petroleum oils, and di-ester based lubricants.
Its temperature range is -60° to 500°F (-51° to 260°C) (The high
limit would make use of a special high temperature formulation
developed for geothermal applications).
FKM - This is a uoroelastomer of the polymethylene type having
substituent uoro and peruoroalkyl or peruoroalkoxy groups
on the polymer chain. Viton® and Fluorel® are the most common
trade names. FKM is recommended for: petroleum oils, di-ester
based lubricants, silicate ester based lubricants (such as MLO
8200, MLO 8515, OS-45), silicone uids and greases, halogenated
hydrocarbons, selected phosphate ester uids, and some acids. It
is not recommended for: ketones, Skydrol 500, amines (UDMH),
anhydrous ammonia, low molecular weight esters and ethers, and
hot hydrouoric and chlorosulfonic acids. Its temperature range is
-20° to 450°F (-29° to 232°C) (This extended range would require
special grades and would limit use on each end of the range.).
CR - This is chloroprene, commonly know as neoprene, which
is a homopolymer of chloroprene (chlorobutadiene). CR is
recommended for: refrigerants (Freons, ammonia), high aniline
point petroleum oils, mild acids, and silicate ester uids. It is
not recommended for: phosphate ester uids and ketones. Its
temperature range is -60° to 200°F (-51° to 93°C), although this
would involve more than one compound.
NR - This is natural rubber which is a natural polyisoprene,
primarily from the tree, Hevea Brasiliensis. The synthetics
have all but completely replaced natural rubber for seal use.
NR is recommended for automotive brake uid, and it is not
recommended for petroleum products. Its temperature range is
-80° to 180°F (-62° to 82°C).
FXM - This is a copolymer of tetrauoroethylene and propylene;
hence, it is sometimes called PTFE/P rubber. Common trade
names are Aas® (Asahi Glass Co., Ltd) and Fluoraz® (Greene,
Tweed & Co.). It is generally used where resistance to both
hydrocarbons and hot water are required. Its temperature range is
20° to 400°F (-7° to 204°C).
ECO - This is commonly called Hydrin® rubber, although that is a
trade name for a series of rubber materials by B.F. Goodrich. CO
is the designation for the homopolymer of epichlorohydrin, ECO is
the designation for a copolymer of ethylene oxide and chloromethyl
oxirane (epichlorohydrin copolymer), and ETER is the designation
for the terpolymer of epichlorohydrin, ethylene oxide, and an
unsaturated monomer. All the epichlorohydrin rubbers exhibit
better heat resistance than nitrile rubbers, but corrosion with
aluminum may limit applications. Normal temperature range is
(-40° to 250°F (-40° to 121°C), while maximum temperature ranges
are -40° to 275°F (-40° to 135°C) (for homopolymer CO) and
-65° to 275°F (-54° to 135°C) (for copolymer ECO and
terpolymer ETER).
FFKM - This is a peruoroelastomer generally better known as
Kalrez® (DuPont) and Chemraz® (Greene, Tweed). Peruoro
rubbers of the polymethylene type have all substituent groups on
the polymer chain of uoro, peruoroalkyl, or peruoroalkoxy
groups. The resulting polymer has superior chemical resistance
and heat temperature resistance. This elastomer is extremely
expensive and should be used only when all else fails. Its
temperature range is 0° to 480°F (-18° to 249°C). Some materials,
such as Kalrez® 1050LF is usable to 550°F (288°C) and
Kalrez® 4079 can be used to 600°F (316°C).
FVMQ - This is uorosilicone rubber which is an elastomer that
should be used for static seals because it has poor mechanical
properties. It has good low and high temperature resistance and
is reasonably resistant to oils and fuels because of its uorination.
Because of the cost, it only nds specialty use. Its temperature
range is -80° to 400°F (-62° to 204°C).
VMQ - This is the most general term for silicone rubber. Silicone
rubber can be designated MQ, PMQ, and PVMQ, where the Q
designates any rubber with silicon and oxygen in the polymer
chain, and M, P, and V represent methyl, phenyl, and vinyl
substituent groups on the polymer chain. This elastomer is used
only for static seals due to its poor mechanical properties. Its
temperature range is -175° to 600°F (-115° to 316°C) (Extended
temperature ranges require special compounds for high or
low temperatures).
659
Page 2
Chemical Compatibility of Elastomers and Metals
Te c h n i c a l
660
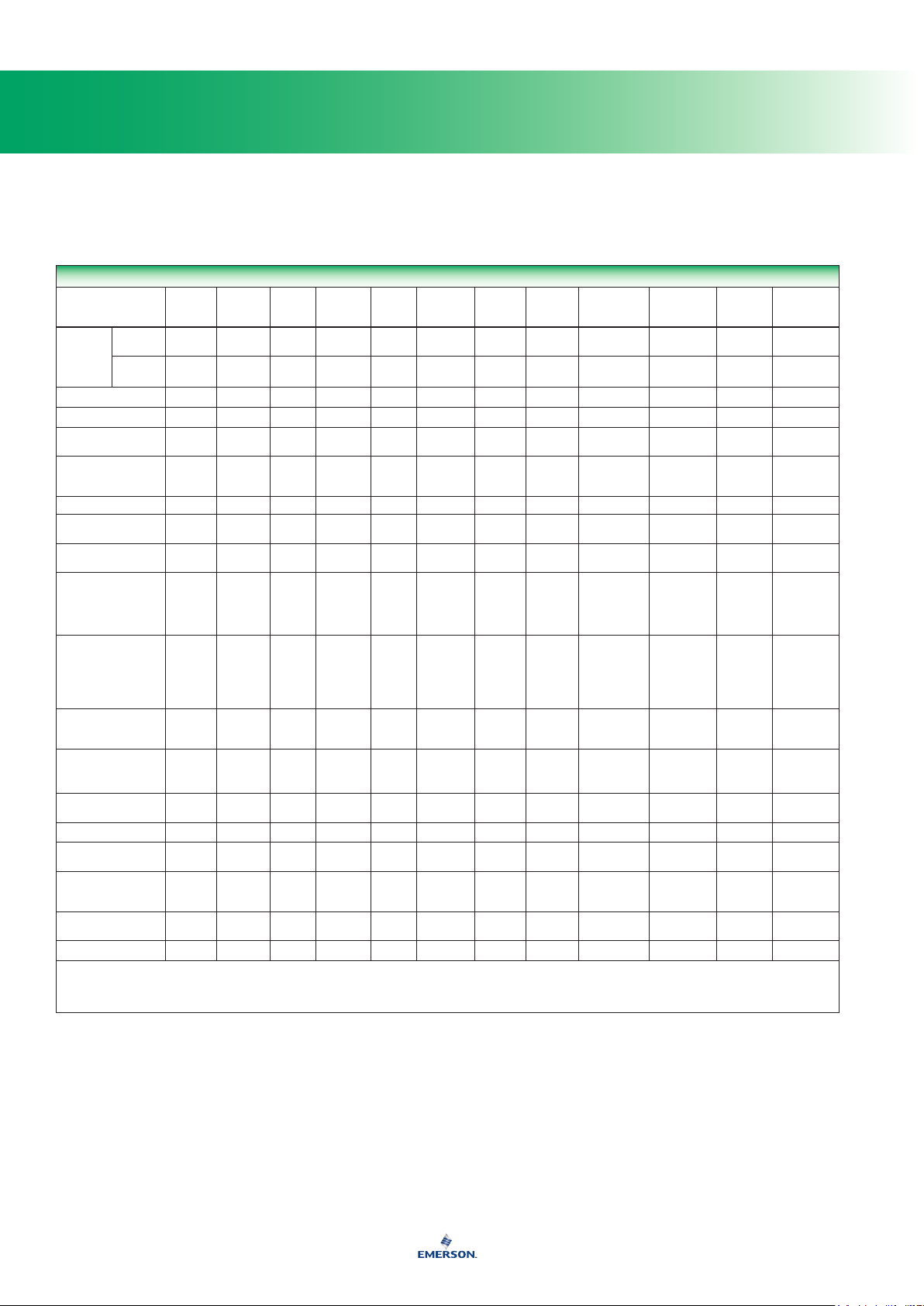
General Properties of Elastomers
PROPERTY
Tensile
Strength,
Psi (bar)
Abrasion Resistance Excellent Good Good Excellent Fair Poor Poor Excellent Very Good Excellent Good Good
Cracking Resistance
Solvent Resistance:
Aliphatic Hydrocarbon
Aromatic Hydrocarbon
Oxygenated Solvent
Halogenated Solvent
Low Aniline Mineral Oil
High Aniline Mineral
Synthetic Lubricants
Organic Phosphates
Gasoline Resistance:
Diluted (Under 10%)
Flexibility (Maximum)
Permeability to Gases Fair Fair Fair Very Good Very Good Good Fair Very Good Good Good Good Good
Diluted (Under 10%)
Elongation (Maximum) 700% 500% 500% 500% 700% 400% 300% 300% 425% 625% 200% 500%
1. Do not use with steam.
2. Do not use with ammonia.
3. Do not use with petroleum based uids. Use with ester based non-ammable hydraulic oils and low pressure steam applications to 300°F (149°C).
4. Except for nitric and sulfuric acid.
Pure Gum
Reinforced
Tear Resistance Excellent Poor-Fair Fair Good Good Fair Poor-Fair Excellent Good Excellent Fair Poor
Aging: Sunlight
Oxidation
Heat
(Maximum
Temperature)
Static (Shelf) Good Good Good Very Good Good Fair Good Good - - - - - - - - Good Good
Flex
Compression Set
Resistance
Oil Resistance:
Oil
Aromatic
Non-Aromatic
Acid Resistance:
Concentrated
Low Temperature
Water Resistance Good Very Good
Alkali Resistance:
Concentrated
Resilience Very Good Fair Fair Very Good Very Good Poor Good Good Good Fair Very Poor Very Good
NATURAL
RUBBER
(93°C)
Excellent Good Good Excellent Excellent Fair Fair Excellent - - - - Excellent Good - - - -
Very Poor
Very Poor
Very Poor
Very Poor
Very Poor
Very Poor
Very Poor
Very Poor
Very Poor
(4)
(-54°C)
BUNA-S
3000
(207)
4500
3000 (207)
(310)
Poor
Good
200°F
Good Good
Very Poor
Very Poor
Good
Very Poor
Very Poor
Very Poor
Very Poor
Very Poor
Very Poor
Very Poor
Good
Fair
-65°F
Good
(-46°C)
Fair
400
(28)
Poor
Fair
200°F
(93°C)
Good
Good
Poor
-50°F
Good
Fair
NITRILE
(NBR)
(41)
4000
(276)
Poor
250°F
(121°C)
Very
Good
Good
Poor
Very Poor
Excellent
Excellent
Very Poor
Good
Excellent
Good
Poor
-40°F
(-40°C)
Very
Good
Good
NEO-
PRENE
600
Excellent
Fair
(93°C)
Excellent Fair Poor Good Poor Poor Good Good Fair
Fair
Very Poor
Fair
Very Poor
Very Poor
(-40°C)
Fair
BUTYL THIOKOL®SILICONE HYPALON
(CR)
3500
(241)
3500
(241)
Good
200°F
Fair
Poor
Fair
Fair
Good
Poor
Good
Fair
Fair
-40°F
Fair Very Good Fair Fair Fair Excellent Fair Fair Very Good
Good
Good
3000
(207)
3000
(207)
Excellent
Good
200°F
(93°C)
Poor
Very Poor
Good
Poor
Very Poor
Very Poor
Poor
Good
Very Poor
Very Poor
Good
Fair
-40°F
(-40°C)
Very Good
Very Good
300
(21)
1500
(103)
Good
Good
140°F
(60°C)
Excellent
Good
Fair
Poor
Excellent
Excellent
Poor
Poor
Excellent
Excellent
Poor
Very Poor
-40°F
(-40°C)
Poor
Poor
200 to 450
(14 to 31)
1100
(76)
Good
Very Good
450°F
(232°C)
Poor
Very Poor
Poor
Very Poor
Poor
Good
Fair
Poor
Poor
Good
Fair
Poor
-100°F
(-73°C)
Fair
Poor
4000
(276)
4400
(303)
Excellent
Very Good
300°F
(149°C)
Fair
Poor
Poor
Very Poor
Fair
Good
Poor
Poor
Poor
Fair
Good
Good
-20°F
(-29°C)
Good
Good
FLUORO-
®
ELASTOMER
(FKM)
- - - - - - - -
2300
(159)
Excellent
Excellent
400°F
(204°C)
Excellent
Very Good
Good
- - - -
Excellent
Excellent
- - - Poor
Good
Very Good
Excellent
Very Good
-30°F
(-34°C)
Excellent
Very Good
(1,2)
POLY-
URETHANE
6500
(448)
Excellent
Excellent
200°F
(93°C)
Very Good
Fair
Poor
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
- - - Poor
Fair
Good
Fair
Poor
-40°F
(-40°C)
Fair
Poor
POLY-
(2)
(1)
ACRYLIC
100
(7)
1800
(124)
Excellent
Excellent Good
350°F
(177°C)
Good
Poor
Poor
Poor
Excellent
Excellent
Fair
Poor
Fair
Poor
Poor
Poor
-10°F
(-23°C)
Poor
Poor
ETHYLENE-
PROPYLENE
(EPDM)
- - - -
2500
(172)
350°F
(177°C)
Poor
Fair
- - - Poor
Poor
Poor
Poor
Very Good
Fair
Poor
Very Good
Good
-50°F
(-45°C)
Excellent
Good
( 3 )
Page 3
Chemical Compatibility of Elastomers and Metals
661
Te c h n i c a l
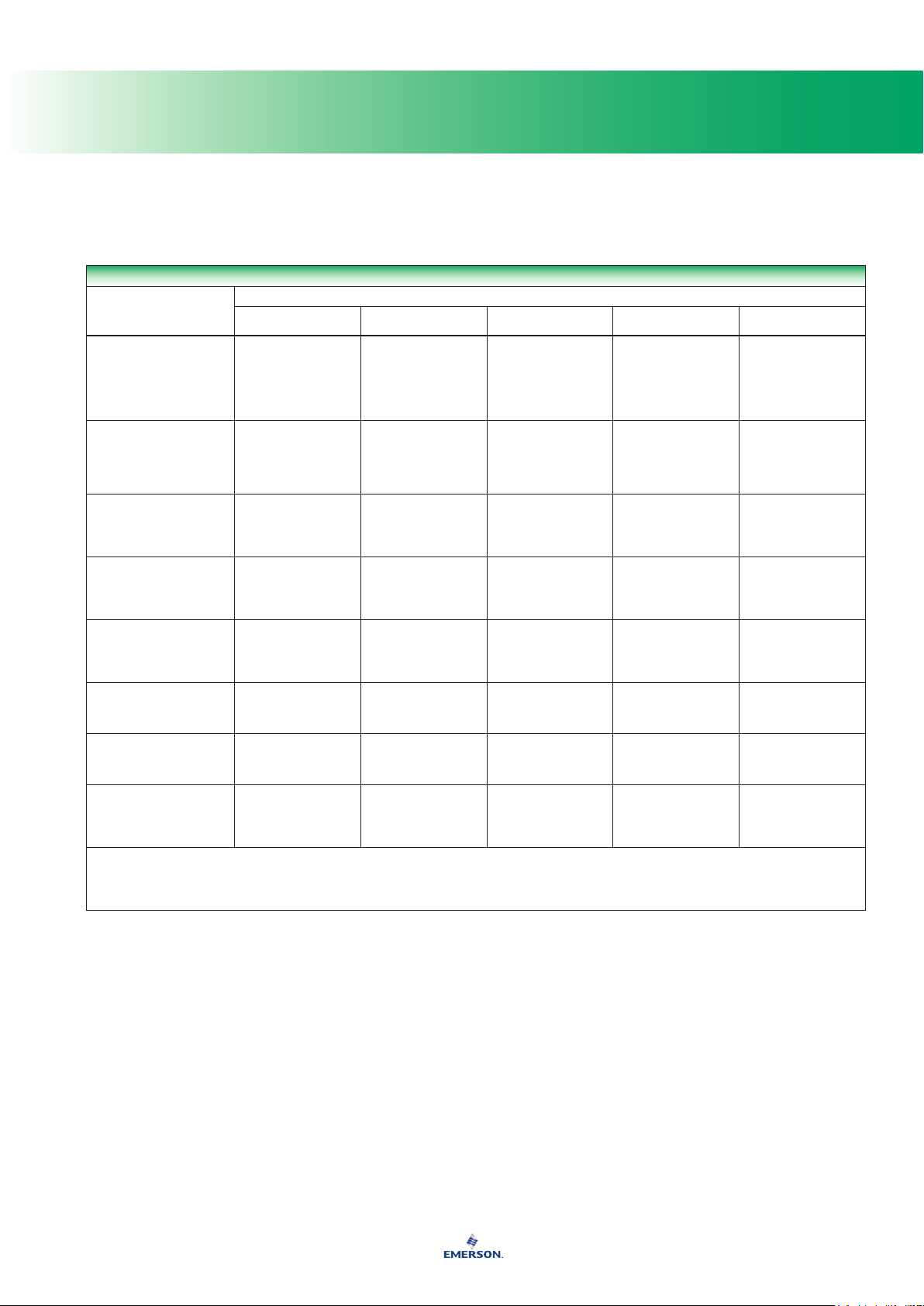
Fluid Compatibility of Elastomers
FLUID
Acetic Acid (30%)
Acetone
Air, Ambient
Air, Hot (200°F (93°C))
Alcohol (Ethyl)
Alcohol (Methyl)
Ammonia (Anhydrous) (Cold)
Ammonia (Gas, Hot)
Beer
Benzene
Brine (Calcium Chloride)
Butadiene Gas
Butane (Gas)
Butane (Liquid)
Carbon Tetrachloride
Chlorine (Dry)
Chlorine (Wet)
Coke Oven Gas
Ethyl Acetate
Ethylene Glycol
Freon 11
Freon 12
Freon 22
Freon 114
Gasoline (Automotive)
Hydrogen Gas
Hydrogen Sulde (Dry)
Hydrogen Sulde (Wet)
Jet Fuel (JP-4)
Methyl Ethyl Ketone (MEK)
MTBE
Natural Gas
Nitric Acid (50 to 100%)
Nitrogen
Oil (Fuel)
Propane
Sulfur Dioxide
Sulfuric Acid (up to 50%)
Sulfuric Acid (50 to 100%)
Water (Ambient)
Water (at 200°F (93°C))
1. Performance worsens with hot temperatures.
A - Recommended
B - Minor to moderate effect. Proceed with caution.
C - Unsatisfactory
N/A - Information not available
Neoprene (CR) Nitrile (NBR) Fluoroelastomer (FKM)
B
C
A
C
A
A
A
B
A
C
A
C
A
C
C
C
C
C
C
A
C
A
A
A
C
A
A
B
B
C
C
A
C
A
C
B
A
B
C
A
C
C
C
A
B
C
A
A
C
A
C
A
C
A
A
C
C
C
C
C
A
B
A
C
A
B
A
(1)
A
C
A
C
C
A
C
A
A
A
C
C
C
A
B
MATERIAL
C
C
A
A
C
C
C
C
A
B
B
B
A
A
A
A
B
A
C
A
A
B
C
B
A
A
C
C
A
C
C
A
B
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
B
Ethylenepropylene
(EPDM)
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
B
A
C
A
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
B
A
C
B
A
A
C
A
A
A
C
A
C
C
C
A
C
C
A
B
B
A
A
Peruoroelastomer
(FFKM)
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
Page 4
Chemical Compatibility of Elastomers and Metals
Te c h n i c a l
662
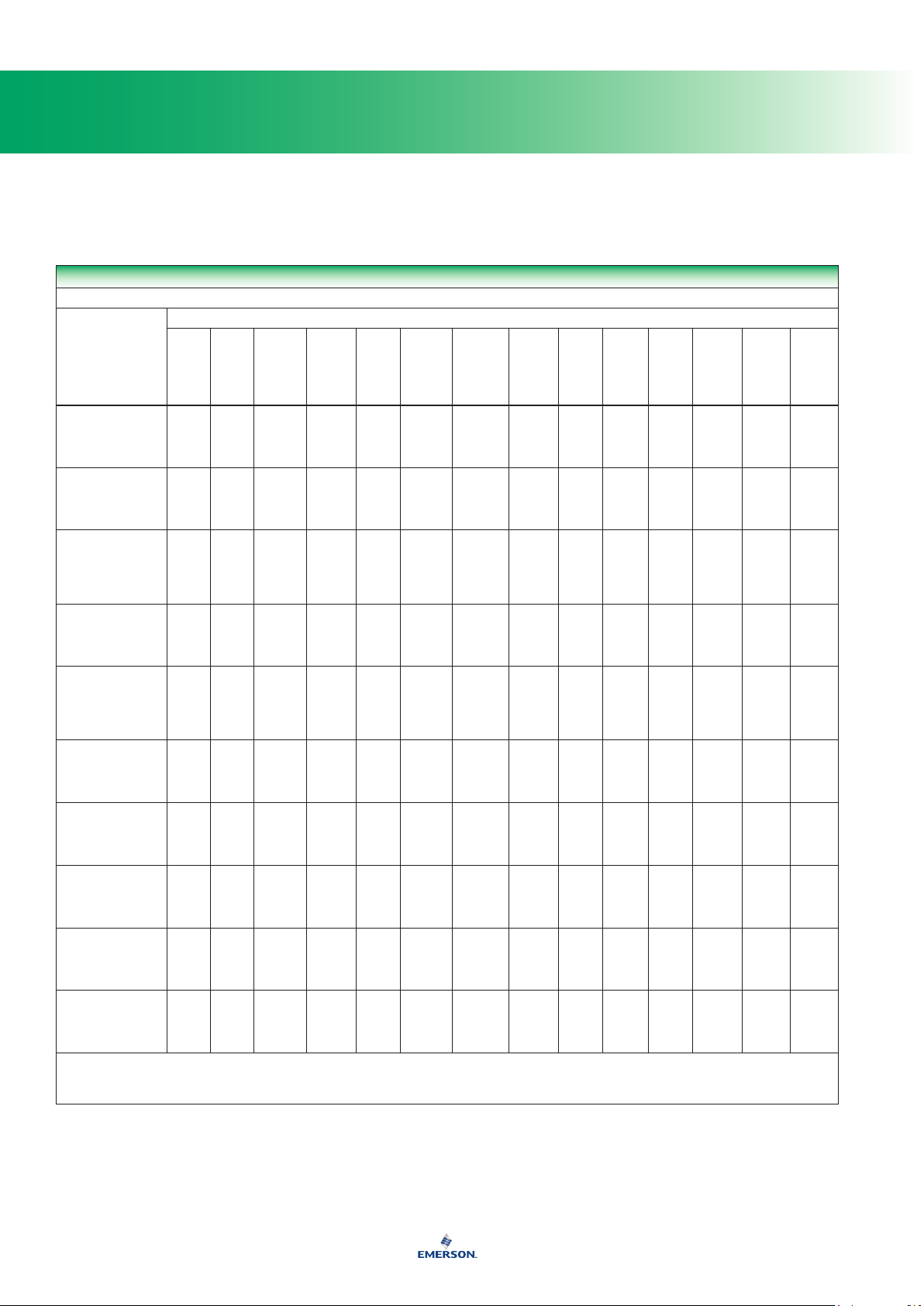
Compatibility of Metals
CORROSION INFORMATION
Material
Fluid
Acetaldehyde
Acetic Acid, Air Free
Acetic Acid, Aerated
Acetic Acid Vapors
Acetone
Acetylene
Alcohols
Aluminum Sulfate
Ammonia
Ammonium Chloride
Ammonium Nitrate
Ammonium Phosphate
(Mono Basic)
Ammonium Sulfate
Ammonium Sulte
Aniline
Asphalt
Beer
Benzene (Benzol)
Benzoic Acid
Boric Acid
Butane
Calcium Chloride
(Alkaline)
Calcium Hypochlorite
Carbolic Acid
Carbon Dioxide, Dry
Carbon Dioxide, Wet
Carbon Disulde
Carbon Tetrachloride
Carbonic Acid
Chlorine Gas, Dry
Chlorine Gas, Wet
Chlorine, Liquid
Chromic Acid
Citric Acid
Coke Oven Gas
Copper Sulfate
Cottonseed Oil
Creosote
Ethane
Ether
Ethyl Chloride
Ethylene
Ethylene Glycol
Ferric Chloride
Formaldehyde
Formic Acid
Freon, Wet
Freon, Dry
Furfural
Gasoline, Rene
A - Recommended
B - Minor to moderate effect. Proceed with caution.
C - Unsatisfactory
IL - Information lacking
Carbon
Steel
A
C
C
C
A
A
A
C
A
C
A
C
C
C
C
A
B
A
C
C
A
B
C
B
A
C
A
B
C
A
C
C
C
IL
A
C
A
A
A
B
C
A
A
C
B
IL
B
B
A
A
Cast
Iron
A
C
C
C
A
A
A
C
A
C
C
C
C
C
C
A
B
A
C
C
A
B
C
B
A
C
A
B
C
A
C
C
C
C
A
C
A
A
A
B
C
A
A
C
B
C
B
B
A
A
S302
or S304
Stainless
Steel
A
B
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
B
A
A
B
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
C
B
A
A
A
A
B
B
B
C
C
C
B
A
B
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
C
A
B
B
A
A
A
S316
Stainless
Steel
A
B
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
B
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
B
B
A
A
A
A
B
B
B
C
C
B
A
A
B
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
C
A
B
A
A
A
A
Bronze Monel
A
B
A
B
A
IL
A
B
C
B
C
B
B
C
C
A
B
A
A
A
A
C
B
A
A
B
C
A
B
B
C
B
C
A
B
B
A
C
A
A
A
A
A
C
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
B
A
B
A
A
A
B
A
B
C
B
A
C
B
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
B
A
A
A
B
A
A
A
C
C
A
B
B
C
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
C
A
A
A
A
A
A
®
Hastelloy
B
IL
A
A
IL
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
IL
A
A
A
A
IL
A
A
A
C
A
A
A
A
B
A
A
C
C
C
A
A
IL
A
A
A
A
A
A
IL
C
A
A
A
A
A
A
®
Hastelloy®
Titanium
Durimet®
C
20
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
B
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
IL
B
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
B
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
B
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
C
B
C
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
C
A
A
A
A
A
A
Cobalt-
Base
Alloy 6
IL
A
A
A
A
IL
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
IL
A
A
A
A
IL
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
IL
C
A
C
A
A
A
A
A
IL
A
A
A
A
IL
A
A
C
A
A
A
A
IL
IL
B
IL
IL
IL
IL
IL
B
B
B
B
IL
IL
A
A
A
B
A
B
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
S416
Stainless
Steel
A
C
C
C
A
A
A
C
A
C
C
B
C
B
C
A
B
A
A
B
A
C
C
IL
A
A
B
C
A
C
C
C
C
B
A
A
A
A
A
A
B
A
A
C
A
C
IL
IL
B
A
440C
Stainless
Steel
A
C
C
C
A
A
A
C
A
C
B
B
C
B
C
A
B
A
A
B
A
C
C
IL
A
A
B
A
A
C
C
C
C
B
A
A
A
A
A
A
B
A
A
C
A
C
IL
IL
B
A
17-4PH
Stainless
Steel
A
B
B
B
A
A
A
IL
IL
IL
IL
IL
IL
IL
IL
A
A
A
A
IL
A
IL
IL
IL
A
A
IL
IL
A
C
C
C
C
B
A
A
A
A
A
A
IL
A
A
IL
A
B
IL
IL
IL
A
- continued -
Page 5
Chemical Compatibility of Elastomers and Metals
663
Te c h n i c a l
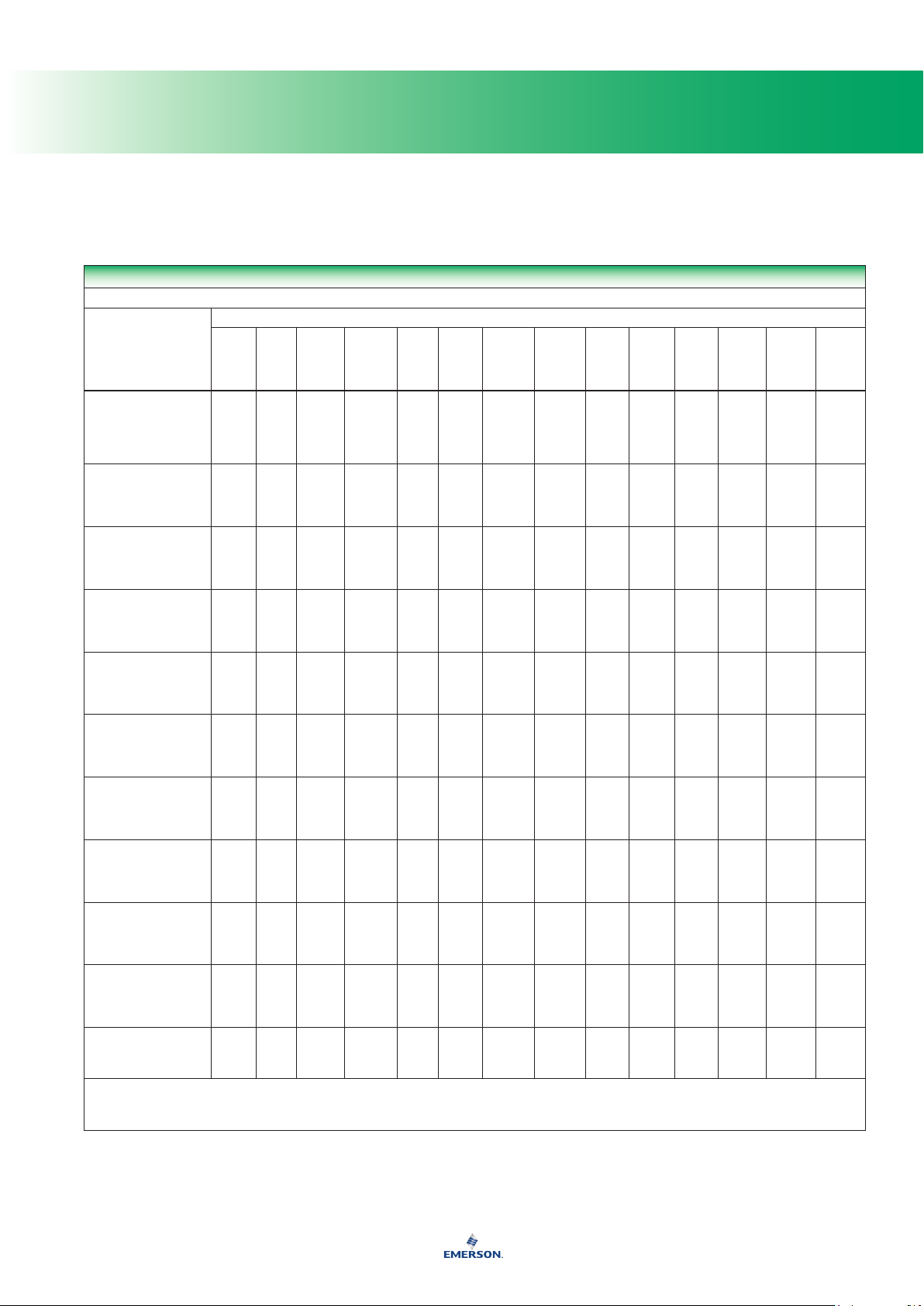
Compatibility of Metals (continued)
CORROSION INFORMATION
Material
Fluid
Carbon
Steel
Cast
Iron
S302
or S304
Stainless
Steel
S316
Stainless
Steel
Bronze Monel
Hastelloy
®
®
Hastelloy® CDurimet®
B
Titanium
20
Cobalt-
Base
Alloy 6
S416
Stainless
Steel
440C
Stainless
Steel
17-4PH
Stainless
Steel
Glucose
Hydrochloric Acid, Aerated
Hydrochloric Acid, Air free
Hydrouoric Acid, Aerated
Hydrouoric Acid, Air free
Hydrogen
Hydrogen Peroxide
Hydrogen Sude, Liquid
Magnesium Hydroxide
Mercury
Methanol
Methyl Ethyl Ketone
Milk
Natural Gas
Nitric Acid
Oleic Acid
Oxalic Acid
Oxygen
Petroleum Oils, Rened
Phosphoric Acid, Aerated
Phosphoric Acid, Air Free
Phosphoric Acid Vapors
Picric Acid
Potassium Chloride
Potassium Hydroxide
Propane
Rosin
Silver Nitrate
Sodium Acetate
Sodium Carbonate
Sodium Chloride
Sodium Chromate
Sodium Hydroxide
Sodium Hypochloride
Sodium Thiosulfate
Stannous Chloride
Stearic Acid
Sulfate Liquor (Black)
Sulfur
Sulfur Dioxide, Dry
Sulfur Trioxide, Dry
Sufuric Acid (Aerated)
Sufuric Acid (Air Free)
Sulfurous Acid
Tar
Trichloroethylene
Turpentine
Vinegar
Water, Boiler Feed
Water, Distilled
Water, Sea
Whiskey and Wines
Zinc Chloride
Zinc Sulfate
A - Recommended
B - Minor to moderate effect. Proceed with caution.
C - Unsatisfactory
IL - Information lacking
A
A
C
C
C
C
B
C
A
C
A
A
IL
A
C
C
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
C
C
A
A
C
C
C
C
C
C
A
A
A
A
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
B
B
B
B
A
A
B
B
C
C
A
A
A
A
C
C
A
A
A
A
C
C
C
C
B
B
A
C
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
C
C
C
C
C
C
A
A
B
B
B
B
C
C
B
C
A
A
B
B
C
C
C
C
C
C
A
C
C
C
C
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
B
A
A
A
A
B
A
A
A
A
A
A
B
A
B
A
A
C
A
C
A
A
A
A
A
C
C
B
A
B
A
A
A
A
B
A
C
A
A
C
C
B
B
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
B
A
B
A
A
A
A
B
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
B
A
A
C
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
C
C
B
A
A
A
A
A
A
B
A
C
A
B-C
A
A
B
C
A
A
A
C
B
A
A
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
A
A
A
C
A
C
C
B
A
C
B
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
C
C
B
A
B
B
A
A
A
A
C
C
C
B
C
C
C
C
B
B
B
A
A
A
A
A
C
C
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
C
A
B-C
C
C
C
B
B
B
C
A
C
A
A
A
A
A
C
C
B
B
B
C
A
A
A
B
A
A
A
A
B
C
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
B
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
C
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
C
A
A
A
A
A
B
B
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
B
B
A
A
A
B
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
B
A
A
A
A
A
A
IL
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
C
C
C
C
B
C
B
C
A
A
A
A
B
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
IL
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
B
A
A
A
A
A
B
A
B
A
B
A
IL
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
IL
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
B
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
B
A
B
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
IL
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
B
A
A
A
B
C
B
C
B
C
IL
C
A
A
IL
B
A
C
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
C
A
A
C
C
A
A
B
B
A
A
A
A
A
C
A
C
C
C
IL
B
IL
C
IL
B
A
A
A
A
B
B
A
A
A
B
A
B
A
A
A
B
IL
C
IL
B
IL
C
B
B
A
IL
A
A
A
B
A
B
B
C
B
C
B
C
A
A
B
A
C
B
B
C
C
C
B
A
C
C
C
C
A
B
C
A
A
B
A
C
A
C
A
B
A
A
C
C
C
B
C
B
A
A
B
A
B
B
A
B
C
B
C
B
IL
A
B
B
C
C
C
A
B
A
C
A
B
C
C
C
B
A
C
C
C
IL
A
IL
IL
IL
B
A
A
C
A
B
IL
IL
A
A
IL
IL
IL
IL
IL
IL
A
A
IL
A
A
B
A
A
IL
IL
IL
IL
IL
A
IL
IL
C
C
IL
A
IL
A
A
A
IL
A
IL
IL
IL
Page 6

Regulator Tips
664
Te c h n i c a l
1. All regulators should be installed and used in accordance with
federal, state, and local codes and regulations.
2. Adequate overpressure protection should be installed to protect
the regulator from overpressure. Adequate overpressure
protection should also be installed to protect all downstream
equipment in the event of regulator failure.
3. Downstream pressures signicantly higher than the regulator's
pressure setting may damage soft seats and
other internal parts.
4. If two or more available springs have published pressure
ranges that include the desired pressure setting, use the spring
with the lower range for better accuracy.
5. The recommended selection for orice diameters is the
smallest orice that will handle the ow.
6. Most regulators shown in this application guide are generally
suitable for temperatures to 180°F (82°C). With high
temperature uoroelastomers (if available), the regulators
can be used for temperatures to 300°F (149°C). Check
the temperature capabilities to determine materials and
temperature ranges available. Use stainless steel diaphragms
and seats for higher temperatures, such as steam service.
7. The full advertised range of a spring can be utilized without
sacricing performance or spring life.
8. Regulator body size should not be larger than the pipe size. In
many cases, the regulator body is one size smaller than the
pipe size.
9. Do not oversize regulators. Pick the smallest orice size or
regulator that will work. Keep in mind when sizing a station
that most restricted trims that do not reduce the main port size
do not help with improved low ow control.
10. Speed of regulator response, in order:
• Direct-operated
• Two-path pilot-operated
• Unloading pilot-operated
• Control valve
Note: Although direct-operated regulators give the fastest
response, all types provide quick response.
11. When a regulator appears unable to pass the published
ow rate, be sure to check the inlet pressure measured at
the regulator body inlet connection. Piping up to and away
from regulators can cause signicant owing pressure losses.
12. When adjusting setpoint, the regulator should be owing at
least ve percent of the normal operating ow.
13. Direct-operated regulators generally have faster response to
quick ow changes than pilot-operated regulators.
14. Droop is the reduction of outlet pressure experienced by
pressure-reducing regulators as the ow rate increases. It is
stated as a percent, in inches of water column (mbar) or in
pounds per square inch (bar) and indicates the difference
between the outlet pressure setting made at low ow rates
and the actual outlet pressure at the published maximum
ow rate. Droop is also called offset or proportional band.
15. Downstream pressure always changes to some extent when
inlet pressure changes.
16. Most soft-seated regulators will maintain the pressure within
reasonable limits down to zero ow. Therefore, a regulator
sized for a high ow rate will usually have a turndown ratio
sufcient to handle pilot-light loads during off cycles.
17. Do not undersize the monitor set. It is important to realize
that the monitor regulator, even though it is wide-open,
will require pressure drop for ow. Using two identical
regulators in a monitor set will yield approximately
70 percent of the capacity of a single regulator.
18. Diaphragms leak a small amount due to migration of gas
through the diaphragm material. To allow escape of this gas,
be sure casing vents (where provided) remain open.
19. Use control lines of equal or greater size than the control tap
on the regulator. If a long control line is required, make it
bigger. A rule of thumb is to use the next nominal pipe size
for every 20 feet (6,1 m) of control line. Small control
lines cause a delayed response of the regulator, leading
to increased chance of instability. 3/8-inch (9,5 mm) OD
tubing is the minimum recommended control line size.
20. For every 15 psid (1,0 bar d) pressure differential
across the regulator, expect approximately a one degree
drop in gas temperature due to the natural refrigeration
effect. Freezing is often a problem when the ambient
temperature is between 30° and 45°F (-1° and 7°C).
21. A disk with a cookie cut appearance probably means you had
an overpressure situation. Thus, investigate further.
22. When using relief valves, be sure to remember that the
reseat point is lower than the start-to-bubble point. To
avoid seepage, keep the relief valve setpoint far enough
above the regulator setpoint.
Page 7

Regulator Tips
665
Te c h n i c a l
23. Vents should be pointed down to help avoid the accumulation
of water condensation or other materials in the spring case.
24. Make control line connections in a straight run of pipe about
10 pipe diameters downstream of any area of turbulence,
such as elbows, pipe swages, or block valves.
25. When installing a working monitor station, get as much
volume between the two regulators as possible. This
will give the upstream regulator more room to control
intermediate pressure.
26. Cutting the supply pressure to a pilot-operated regulator
reduces the regulator gain or sensitivity and, thus, may
improve regulator stability. (This can only be used with two
path control.)
27. Regulators with high ows and large pressure drops generate
noise. Noise can wear parts which can cause failure and/or
inaccurate control. Keep regulator noise below 110 dBA.
28. Do not place control lines immediately downstream of rotary
or turbine meters.
29. Keep vents open. Do not use small diameter, long vent lines.
Use the rule of thumb of the next nominal pipe size every
10 feet (3,1 m) of vent line and 3 feet (0,9 m) of vent line
for every elbow in the line.
30. Fixed factor measurement (or PFM) requires the regulator
to maintain outlet pressure within ±1% of absolute pressure.
For example: Setpoint of 2 psig + 14.7 psia = 16.7 psia x
0.01 = ±0.167 psi. (Setpoint of 0,14 bar + 1,01 bar = 1,15 bar x
0,01 = ±0,0115 bar.)
31. Regulating Cg (coefcient of ow) can only be used for
calculating ow capacities on pilot-operated regulators.
Use capacity tables or ow charts for determining a direct-
operated regulator’s capacity.
32. Do not make the setpoints of the regulator/monitor too close
together. The monitor can try to take over if the setpoints are
too close, causing instability and reduction of capacity. Set
them at least one proportional band apart.
33. Consider a butt-weld end regulator where available to lower
costs and minimize ange leakages.
34. Do not use needle valves in control lines; use full-open
valves. Needle valves can cause instability.
35. Burying regulators is not recommended. However, if you
must, the vent should be protected from ground moisture
and plugging.
Page 8
666
Te c h n i c a l
Conversions, Equivalents, and Physical Data
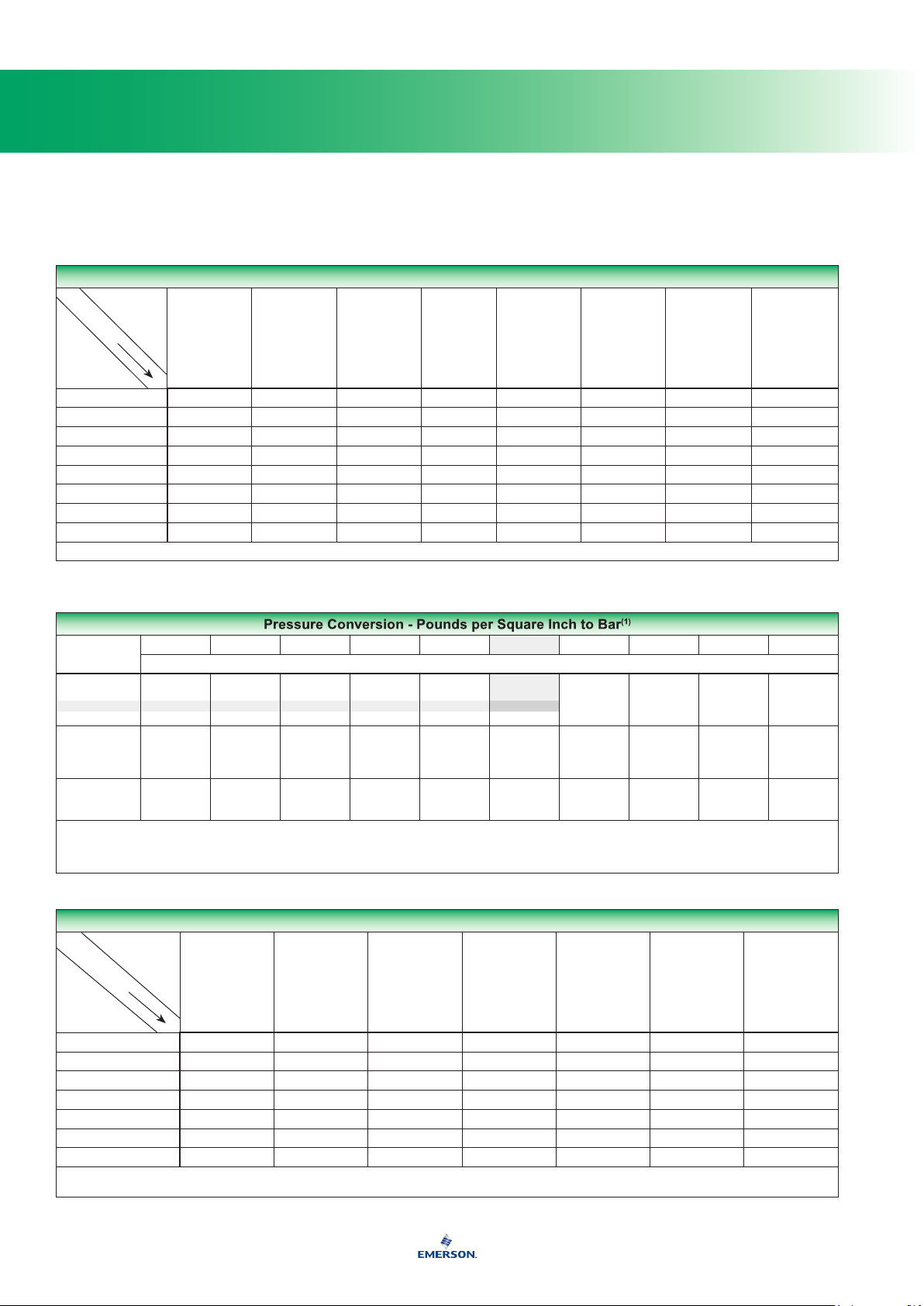
Pressure Equivalents
TO
OBTAIN
BY
MULTIPLY
NUMBER
OF
Kg per square cm 1 14.22 0.9678 0,98067 28.96 98,067 394.05 32.84
Pounds per square inch 0,07031 1 0.06804 0,06895 2.036 6,895 27.7 2.309
Atmosphere 1,0332 14.696 1 1,01325 29.92 101,325 407.14 33.93
Bar 1,01972 14.5038 0.98692 1 29.53 100 402.156 33.513
Inches of Mercury 0,03453 0.4912 0.03342 0,033864 1 3,3864 13.61 1.134
Kilopascals 0,0101972 0.145038 0.0098696 0,01 0.2953 1 4.02156 0.33513
Inches of Water 0,002538 0.0361 0.002456 0,00249 0.07349 0,249 1 0.0833
Feet of Water 0,3045 0.4332 0.02947 0,029839 0.8819 2,9839 12 1
1 ounce per square inch = 0.0625 pounds per square inch
KG PER
SQUARE
CENTIMETER
POUNDS PER
SQUARE INCH
ATMOSPHERE BAR
INCHES OF
MERCURY
KILOPASCALS
INCHES OF
WATER COLUMN
FEET OF
WATER COLUMN
0,414
1,103
1,793
2,482
3,172
3,861
4,551
5,240
5,929
6,619
7,308
(1)
0,482
1,172
1,862
2,551
3,241
3,930
4,619
5,309
5,998
6,688
7,377
0,552
1,241
1,931
2,620
3,309
3,999
4,688
5,378
6,067
6,757
7,446
0,621
1,310
1,999
2,689
3,378
4,068
4,758
5,447
6,136
6,826
7,515
Pressure Conversion - Pounds per Square Inch to Bar
POUNDS PER
SQUARE INCH
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
100
1. To convert to kilopascals, move decimal point two positions to the right; to convert to megapascals, move decimal point one position to the left.
*Note: Round off decimal points to provide no more than the desired degree of accuracy.
To use this table, see the shaded example.
25 psig (20 from the left column plus ve from the top row) = 1,724 bar
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
Bar
0,000
0,689
1,379
2,068
2,758
3,447
4,137
4,826
5,516
6,205
6,895
0,069
0,758
1,448
2,137
2,827
3,516
4,275
4,964
5,585
6,274
6,964
0,138
0,827
1,517
2,206
2,896
3,585
4,275
4,964
5,654
6,343
7,033
0,207
0,896
1,586
2,275
2,965
3,654
4,344
5,033
5,723
6,412
7,102
0,276
0,965
1,655
2,344
3,034
3,723
4,413
5,102
5,792
6,481
7,171
0,345
1,034
1,724*
2,413
3,103
3,792
4,482
5,171
5,861
6,550
7,239
Volume Equivalents
TO
OBTAIN
CUBIC
BY
MULTIPLY
NUMBER
OF
Cubic Decimeters (Liters) 1 61.0234 0.03531 1.05668 0.264178 0,220083 0.00629
Cubic Inches 0,01639 1 5.787 x 10
Cubic Feet 28,317 1728 1 29.9221 7.48055 6,22888 0.1781
U.S. Quart 0,94636 57.75 0.03342 1 0.25 0,2082 0.00595
U.S. Gallon 3,78543 231 0.13368 4 1 0,833 0.02381
Imperial Gallon 4,54374 277.274 0.16054 4.80128 1.20032 1 0.02877
U.S. Barrel (Petroleum) 158,98 9702 5.6146 168 42 34,973 1
1 cubic meter = 1,000,000 cubic centimeters
1 liter = 1000 milliliters = 1000 cubic centimeters
DECIMETERS
(LITERS)
CUBIC INCHES CUBIC FEET U.S. QUART U.S. GALLON IMPERIAL GALLON
-4
1.01732 0.004329 0,003606 0.000103
U.S. BARREL
(PETROLEUM)
Page 9
667
Te c h n i c a l
Conversions, Equivalents, and Physical Data
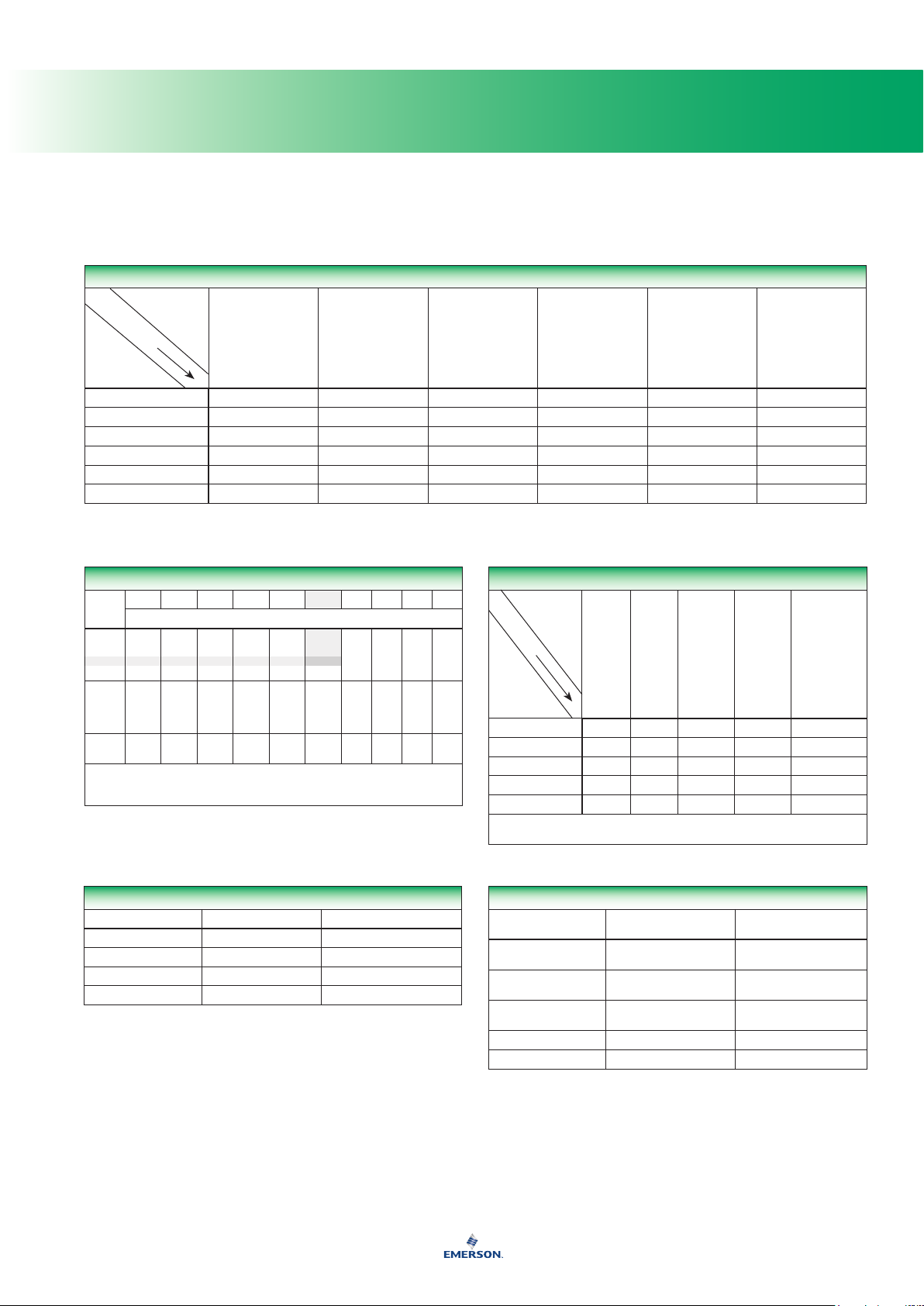
Volume Rate Equivalents
TO
OBTAIN
BY
MULTIPLY
NUMBER
OF
Liters per Minute 1 0,06 2.1189 60 0.264178 9.057
Cubic Meters per Hour 16,667 1 35.314 1000 4.403 151
Cubic Feet per Hour 0,4719 0,028317 1 28.317 0.1247 4.2746
Liters per Hour 0,016667 0,001 0.035314 1 0.004403 0.151
U.S. Gallons per Minute 3,785 0,2273 8.0208 227.3 1 34.28
U.S. Barrels per Day 0,1104 0,006624 0.23394 6.624 0.02917 1
LITERS
PER MINUTE
CUBIC METERS
PER HOUR
CUBIC FEET
PER HOUR
LITERS
PER HOUR
U.S. GALLONS
PER MINUTE
U.S. BARRELS
PER DAY
Mass Conversion - Pounds to Kilograms
POUNDS
1 pound = 0,4536 kilograms
*NOTE: To use this table, see the shaded example.
25 pounds (20 from the left column plus ve from the top row) = 11,34 kilograms
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
Kilograms
0
0,00
0,45
0,91
1,36
1,81
2,27
10
4,54
20
9,07
30
13,61
40
18,14
50
22,68
60
27,22
70
31,75
809036,29
40,82
4,99
9,53
14,06
18,60
23,13
27,67
32,21
36,74
41,28
5,44
9,98
14,52
19,05
23,59
28,12
32,66
37,20
41,73
5,90
10,43
14,97
19,50
24,04
28,58
33,11
37,65
42,18
6,35
10,89
15,42
19,96
24,49
29,03
33,57
38,10
42,64
6,80
11,34*
15,88
20,41
24,95
29,48
34,02
38,56
43,09
2,72
7,26
11,79
16,33
20,87
25,40
29,94
34,47
39,01
43,55
3,18
7,71
12,25
16,78
21,32
25,86
30,39
34,93
39,46
44,00
3,63
8,16
12,70
17,24
21,77
26,31
30,84
35,38
39,92
44,45
4,08
8,62
13,15
17,69
22,23
26,76
31,30
35,83
40,37
44,91
Temperature Conversion Formulas
TO CONVERT FROM TO SUBSTITUTE IN FORMULA
Degrees Celsius Degrees Fahrenheit (°C x 9/5) + 32
Degrees Celsius Kelvin (°C + 273.16)
Degrees Fahrenheit Degrees Celsius (°F - 32) x 5/9
Degrees Fahrenheit Degrees Rankine (°F + 459.69)
Area Equivalents
TO
OBTAIN
BY
MULTIPLY
NUMBER
OF
Square Meters 1 1549.99 10.7639 3.861 x 10
Square Inches 0,0006452 1 6.944 x 10-32.491 x 10
Square Feet 0,0929 144 1 3.587 x 10-89,29 x 10
Square Miles 2 589 999 - - - - 27,878,400 1 2,59
Square Kilometers 1 000 000 - - - - 10,763,867 0.3861 1
1 square meter = 10 000 square centimeters
1 square millimeter = 0,01 square centimeter = 0.00155 square inches
SQUARE
METERS
SQUARE
INCHES
SQUARE
FEET
SQUARE
MILES
SQUARE
KILOMETERS
-7
-10
6,452 x 10
1 x 10
Kinematic-Viscosity Conversion Formulas
VISCOSITY SCALE RANGE OF t, SEC
Saybolt Universal 32 < t < 100 t > 100
Saybolt Furol 25 < t < 40 t > 40
Redwood No. 1 34 < t < 100 t > 100
Redwood Admiralty - - - - 0.027t - 20/t
Engler - - - - 0.00147t - 3.74/t
KINEMATIC VISCOSITY,
STROKES
0.00226t - 1.95/t
0.00220t - 1.35/t
0.0224t - 1.84/t
0.0216t - 0.60/t
0.00226t - 1.79/t
0.00247t - 0.50/t
-6
-10
-8
Page 10
668
Te c h n i c a l
Conversions, Equivalents, and Physical Data
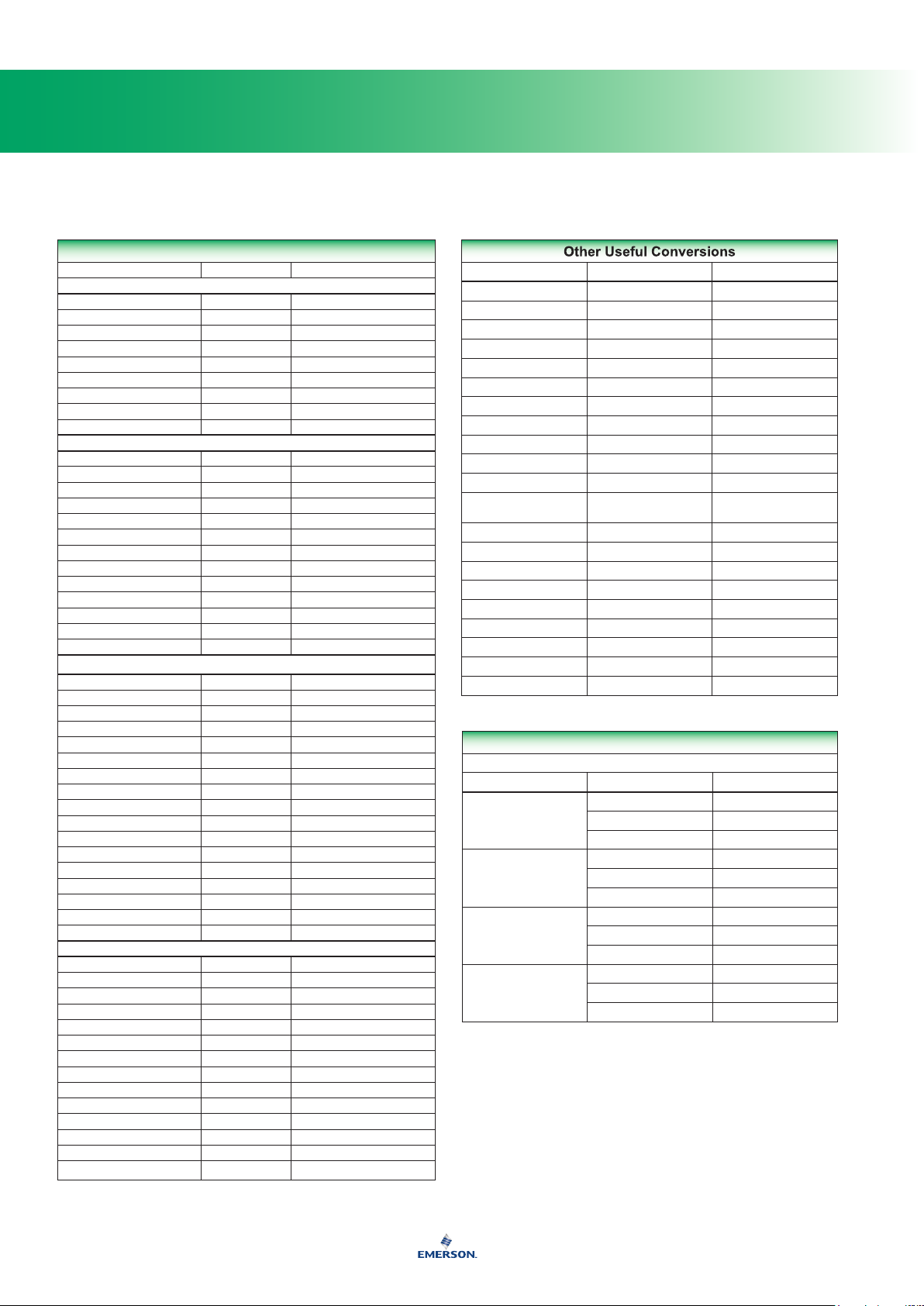
Conversion Units
MULTIPLY BY TO OBTAIN
Volume
Cubic centimeter 0.06103 Cubic inches
Cubic feet 7.4805 Gallons (US)
Cubic feet 28.316 Liters
Cubic feet 1728 Cubic inches
Gallons (US) 0.1337 Cubic feet
Gallons (US) 3.785 Liters
Gallons (US) 231 Cubic inches
Liters 1.057 Quarts (US)
Liters 2.113 Pints (US)
Miscellaneous
BTU 0.252 Calories
Decitherm 10,000 BTU
Kilogram 2.205 Pounds
Kilowatt Hour 3412 BTU
Ounces 28.35 Grams
Pounds 0.4536 Kilograms
Pounds 453.5924 Grams
Pounds 21,591 LPG BTU
Therm 100,000 BTU
API Bbls 42 Gallons (US)
Gallons of Propane 26.9 KWH
HP 746 KWH
HP (Steam) 42,418 BTU
Pressure
Grams per square centimeter 0.0142 Pounds per square inch
Inches of mercury 0.4912 Pounds per square inch
Inches of mercury 1.133 Feet of water
Inches of water 0.0361 Pounds per square inch
Inches of water 0.0735 Inches of mercury
Inches of water 0.5781 Ounces per square inch
Inches of water 5.204 Pounds per foot
kPa 100 Bar
Kilograms per square centimeter 14.22 Pounds per square inch
Kilograms per square meter 0.2048 Pounds per square foot
Pounds per square inch 0.06804 Atmospheres
Pounds per square inch 0.07031 Kilograms per square centimeter
Pounds per square inch 0.145 KPa
Pounds per square inch 2.036 Inches of mercury
Pounds per square inch 2.307 Feet of water
Pounds per square inch 14.5 Bar
Pounds per square inch 27.67 Inches of water
Length
Centimeters 0.3937 Inches
Feet 0.3048 Meters
Feet 30.48 Centimeters
Feet 304.8 Millimeters
Inches 2.540 Centimeters
Inches 25.40 Millimeters
Kilometer 0.6214 Miles
Meters 1.094 Yards
Meters 3.281 Feet
Meters 39.37 Inches
Miles (nautical) 1853 Meters
Miles (statute) 1609 Meters
Yards 0.9144 Meters
Yards 91.44 Centimeters
Other Useful Conversions
TO CONVERT FROM TO MULTIPLY BY
Cubic feet of methane BTU 1000 (approximate)
Cubic feet of water Pounds of water 62.4
Degrees Radians 0,01745
Gallons Pounds of water 8.336
Grams Ounces 0.0352
Horsepower (mechanical) Foot pounds per minute 33,000
Horsepower (electrical) Watts 746
Kg Pounds 2.205
Kg per cubic meter Pounds per cubic feet 0.06243
Kilowatts Horsepower 1.341
Pounds Kg 0,4536
Pounds of Air
(14.7 psia and 60°F)
Pounds per cubic feet Kg per cubic meter 16,0184
Pounds per hour (gas) SCFH 13.1 ÷ Specic Gravity
Pounds per hour (water) Gallons per minute 0.002
Pounds per second (gas) SCFH 46,160 ÷ Specic Gravity
Radians Degrees 57.3
SCFH Air SCFH Propane 0.81
SCFH Air SCFH Butane 0.71
SCFH Air SCFH 0.6 Natural Gas 1.29
SCFH Cubic meters per hour 0.028317
Cubic feet of air 13.1
Converting Volumes of Gas
CFH TO CFH OR CFM TO CFM
Multiply Flow of By To Obtain Flow of
0.707 Butane
Air
Butane
Natural Gas
Propane
1.290 Natural Gas
0.808 Propane
1.414 Air
1.826 Natural Gas
1.140 Propane
0.775 Air
0.547 Butane
0.625 Propane
1.237 Air
0.874 Butane
1.598 Natural Gas
Page 11
669
Te c h n i c a l
Conversions, Equivalents, and Physical Data
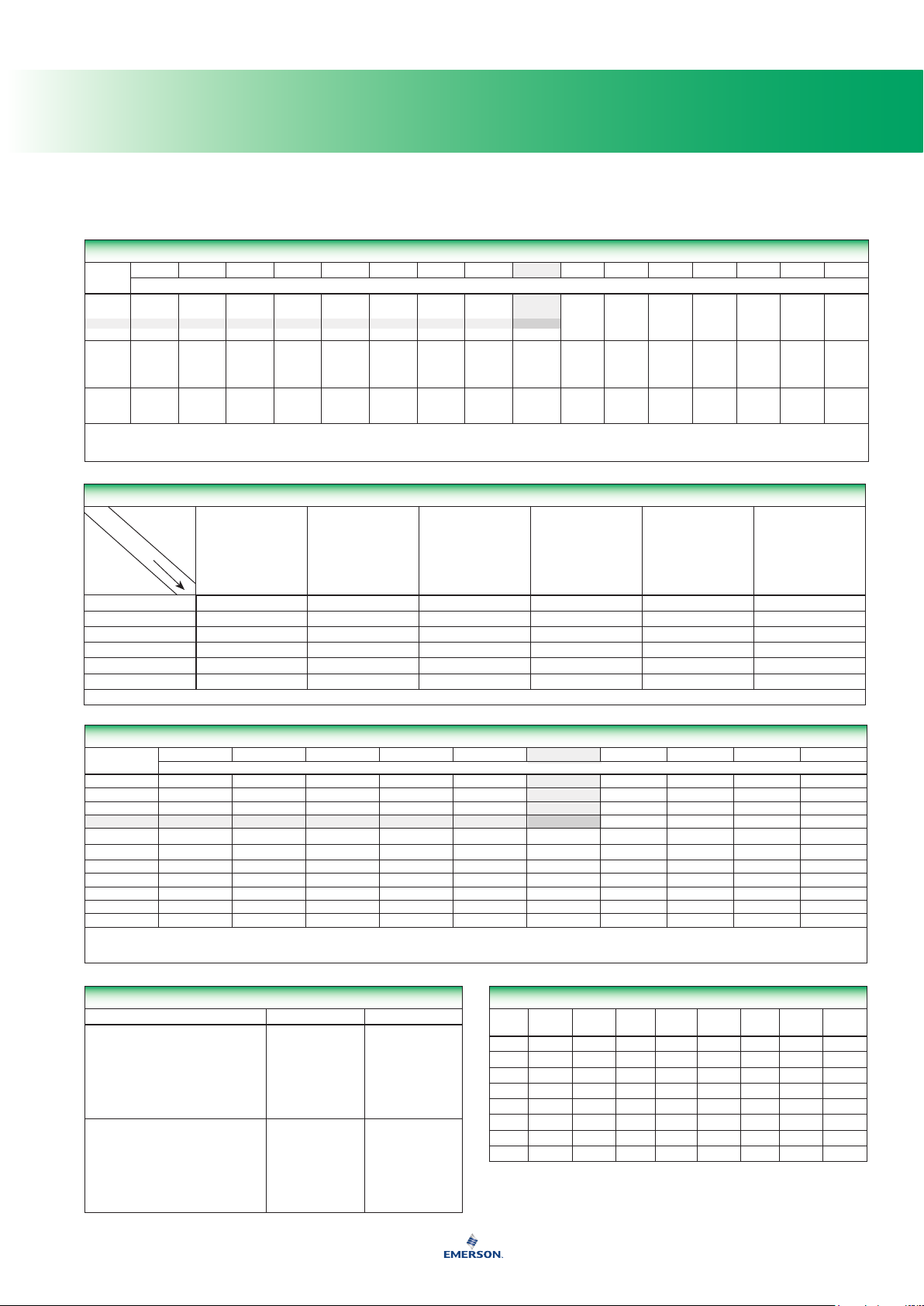
Fractional Inches to Millimeters
INCH
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
1-inch = 25,4 millimeters
NOTE: To use this table, see the shaded example.
2-1/2-inches (2 from the left column plus 1/2 from the top row) = 63,5 millimeters
MULTIPLY
NUMBER
OF
1 meter = 100 cm = 1000 mm = 0,001 km = 1,000,000 micrometers
0 1/16 1/8 3/16 1/4 5/16 3/8 7/16 1/2 9/16 5/8 11/16 3/4 13/16 7/8 15/16
0,0
25,4
50,8
76,2
101,6
127,0
152,4
177,8
203,2
228,6
254,0
1,6
27,0
52,4
77,8
103,2
128,6
154,0
179,4
204,8
230,2
255,6
3,2
28,6
54,0
79,4
104,8
130,2
155,6
181,0
206,4
231,8
257,2
4,8
30,2
55,6
81,0
106,4
131,8
157,2
182,6
208,0
233,4
258,8
6,4
31,8
57,2
82,6
108,0
133,4
158,8
184,2
209,6
235,0
260,4
7,9
33,3
58,7
84,1
109,5
134,9
160,3
185,7
211,1
236,5
261,9
9,5
34,9
60,3
85,7
111,1
136,5
161,9
187,3
212,7
238,1
263,5
11,1
36,5
61,9
87,3
112,7
138,1
163,5
188,9
214,3
239,7
265,1
mm
12,7
38,1
63,5
88,9
114,3
139,7
165,1
190,5
215,9
241,3
266,7
14,3
39,7
65,1
90,5
115,9
141,3
166,7
192,1
217,5
242,9
268,3
15,9
41,3
66,7
92,1
117,5
142,9
168,3
193,7
219,1
244,5
269,9
17,5
42,9
68,3
93,7
119,1
144,5
169,9
195,3
220,7
246,1
271,5
19,1
44,5
69,9
95,3
120,7
146,1
171,5
196,9
222,3
247,7
273,1
20,6
46,0
71,4
96,8
122,2
147,6
173,0
198,4
223,8
249,2
274,6
Length Equivalents
TO
OBTAIN
BY
Meters 1 39.37 3.2808 1000 0.0006214 0,001
Inches 0,0254 1 0.0833 25,4 0.00001578 0,0000254
Feet 0,3048 12 1 304,8 0.0001894 0,0003048
Millimeters 0,001 0.03937 0.0032808 1 0.0000006214 0,000001
Miles 1609,35 63,360 5,280 1 609 350 1 1,60935
Kilometers 1000 39,370 3280.83 1 000 000 0.62137 1
METERS INCHES FEET MILLIMETERS MILES KILOMETERS
22,2
47,6
73,0
98,4
123,8
149,2
174,6
200,0
225,4
250,8
276,2
23,8
49,2
74,6
100,0
125,4
150,8
176,2
201,6
227,0
252,4
277,8
Whole Inch-Millimeter Equivalents
INCH
0 0,00 25,4 50,8 76,2 101,6 127,0 152,4 177,8 203,2 228,6
10 254,0 279,4 304,8 330,2 355,6 381,0 406,4 431,8 457,2 482,6
20 508,0 533,4 558,8 584,2 609,6 635,0 660,4 685,8 711,2 736,6
30 762,0 787,4 812,8 838,2 863,6 889,0 914,4 939,8 965,2 990,6
40 1016,0 1041,4 1066,8 1092,2 1117,6 1143,0 1168,4 1193,8 1219,2 1244,6
50 1270,0 1295,4 1320,8 1346,2 1371,6 1397,0 1422,4 1447,8 1473,2 1498,6
60 1524,0 1549,4 1574,8 1600,2 1625,6 1651,0 1676,4 1701,8 1727,2 1752,6
70 1778,0 1803,4 1828,8 1854,2 1879,6 1905,0 1930,4 1955,8 1981,2 2006,6
80 2032,0 2057,4 2082,8 2108,2 2133,6 2159,0 2184,4 2209,8 2235,2 2260,6
90 2286,0 2311,4 2336,8 2362,2 2387,6 2413,0 2438,4 2463,8 2489,2 2514,6
100 2540,0 2565,4 2590,8 2616,2 2641,6 2667,0 2692,4 2717,8 2743,2 2768,6
Note: All values in this table are exact, based on the relation 1-inch = 25,4 mm.
To use this table, see the shaded example.
25-inches (20 from the left column plus ve from the top row) = 635 millimeters
MULTIPLICATION FACTOR PREFIX SYMBOL
1 000 000 000 000 000 000 = 10
1 000 000 000 000 000 = 10
0.000 000 000 000 001 = 10
0.000 000 000 000 000 001 = 10
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
Metric Prexes and Symbols
1 000 000 000 000 = 10
1 000 000 000 = 10
1 000 000 = 10
1 000 = 10
100 = 10
10 = 10
0.1 = 10
0.01 = 10
0.001 = 10
0.000 01 = 10
0.000 000 001 = 10
0.000 000 000 001 = 10
18
15
12
9
6
3
2
1
-1
-2
-3
-6
-9
-12
-15
-18
exa
peta
tera
giga
mega
kilo
hecto
deka
deci
centi
milli
micro
nano
pico
femto
atto
E
P
T
G
M
k
h
da
d
c
m
m
n
p
f
a
mm
Greek Alphabet
LOWER
CASE
GREEK
NAME
CAPS
Α α Alpha Ι ι Iota Ρ ρ Rho
Β β Beta Κ κ Kappa Σ σ Sigma
Γ γ Gamma Λ λ Lambda Τ τ Tau
Δ δ Delta Μ μ Mu Υ υ Upsilon
Ε ε Epsilon Ν ν Nu Φ φ Phi
Ζ ζ Zeta Ξ ξ Xi Χ χ Chi
Η η Eta Ο ο Omicron Ψ ψ Psi
Θ θ Theta Π π Pi Ω ω Omega
CAPS
LOWER
CASE
GREEK
NAME
CAPS
LOWER
CASE
GREEK
NAME
Page 12
670
Te c h n i c a l
Conversions, Equivalents, and Physical Data
Length Equivalents - Fractional and Decimal Inches to Millimeters
INCHES
Fractions Decimals Fractions Decimals Fractions Decimals Fractions Decimals
0.00394 0.1 0.23 5.842 1/2 0.50 12.7 0.77 19.558
0.00787 0.2 15/64 0.234375 5.9531 0.51 12.954 0.78 19.812
0.01 0.254 0.23622 6.0 0.51181 13.0 25/32 0.78125 19.8438
0.01181 0.3 0.24 6.096 33/64 0.515625 13.0969 0.78740 20.0
1/64 0.015625 0.3969 1/4 0.25 6.35 0.52 13.208 0.79 20.066
0.01575 0.4 0.26 6.604 0.53 13.462 51/64 0.796875 20.2406
0.01969 0.5 17/64 0.265625 6.7469 17/32 0.53125 13.4938 0.80 20.320
0.02 0.508 0.27 6.858 0.54 13.716 0.81 20.574
0.02362 0.6 0.27559 7.0 35/64 0.546875 13.8906 13/64 0.8125 20.6375
0.02756 0.7 0.28 7.112 0.55 13.970 0.82 20.828
0.03 0.762 9/32 0.28125 7.1438 0.55118 14.0 0.82677 21.0
1/32 0.03125 0.7938 0.29 7.366 0.56 14.224 53/64 0.828125 21.0344
0.0315 0.8 19/64 0.296875 7.5406 9/16 0.5625 14.2875 0.83 21.082
0.13543 0.9 0.30 7.62 0.57 14.478 0.84 21.336
0.03937 1.0 0.31 7.874 37/64 0.578125 14.6844 27/32 0.84375 21.4312
0.04 1.016 5/16 0.3125 7.9375 0.58 14.732 0.85 21.590
3/64 0.046875 1.1906 0.31496 8.0 0.59 14.986 55/64 0.859375 21.8281
0.05 1.27 0.32 8.128 0.5905 15.0 0.86 21.844
0.06 1.524 21/64 0.328125 8.3344 19/32 0.59375 15.0812 0.86614 22.0
1/16 0.0625 1.5875 0.33 8.382 0.60 15.24 0.87 22.098
0.07 1.778 0.34 8.636 39/64 0.609375 15.4781 7/8 0.875 22.225
5/64 0.078125 1.9844 11/32 0.34375 8.7312 0.61 15.494 0.88 22.352
0.07874 2.0 0.35 8.89 0.62 15.748 0.89 22.606
0.08 2.032 0.35433 9.0 5/8 0.625 15.875 57/64 0.890625 22.6219
0.09 2.286 23/64 0.359375 9.1281 0.62992 16.0 0.90 22.860
3/32 0.09375 2.3812 0.36 9.144 0.63 16.002 0.90551 23.0
0.1 2.54 0.37 9.398 0.64 16.256 29/32 0.90625 23.0188
7/64 0.109375 2.7781 3/8 0.375 9.525 41/64 0.640625 16.2719 0.91 23.114
0.11 2.794 0.38 9.652 0.65 16.510 0.92 23.368
0.11811 3.0 0.39 9.906 21/32 0.65625 16.6688 59/64 0.921875 23.1456
0.12 3.048 25/64 0.390625 9.9219 0.66 16.764 0.93 23.622
1/8 0.125 3.175 0.39370 10.0 0.66929 17.0 15/16 0.9375 23.8125
0.13 3.302 0.40 10.16 0.67 17.018 0.94 23.876
0.14 3.556 13/32 0.40625 10.3188 43/64 0.671875 17.0656 0.94488 24.0
9/64 0.140625 3.5719 0.41 10.414 0.68 17.272 0.95 24.130
0.15 3.810 0.42 10.668 11/16 0.6875 17.4625 61/64 0.953125 24.2094
5/32 0.15625 3.9688 27/64 0.421875 10.7156 0.69 17.526 0.96 24.384
0.15748 4.0 0.43 10.922 0.70 17.78 31/32 0.96875 24.6062
0.16 4.064 0.43307 11.0 45/64 0.703125 17.8594 0.97 24.638
0.17 4.318 7/16 0.4375 11.1125 0.70866 18.0 0.98 24.892
11/64 0.171875 4.3656 0.44 11.176 0.71 18.034 0.98425 25.0
0.18 4.572 0.45 11.430 23/32 0.71875 18.2562 63/64 0.984375 25.0031
3/16 0.1875 4.7625 29/64 0.453125 11.5094 0.72 18.288 0.99 25.146
0.19 4.826 0.46 11.684 0.73 18.542 1 1.00000 25.4000
0.19685 5.0 15/32 0.46875 11.9062 47/64 0.734375 18.6531
0.2 5.08 0.47 11.938 0.74 18.796
13/64 0.203125 5.1594 0.47244 12.0 0.74803 19.0
0.21 5.334 0.48 12.192 3/4 0.75 19.050
7/32 0.21875 5.5562 31/64 0.484375 12.3031 0.76 19.304
0.22 5.588 0.49 12.446 49/64 0.765625 19.4469
Note: Round off decimal points to provide no more than the desired degree of accuracy.
mm
INCHES
mm
INCHES
mm
INCHES
mm
Page 13
671
Te c h n i c a l
Conversions, Equivalents, and Physical Data
Temperature Conversions
TEMP. IN °C
°C
OR °F TO BE
CONVERTED
-273,16 -460 -796 -90,00 -130 -202.0 -17,8 0 32.0 21,1 70 158.0
-267,78 -450 -778 -84,44 -120 -184.0 -16,7 2 35.6 22,2 72 161.6
-262,22 -440 -760 -78,89 -110 -166.0 -15,6 4 39.2 23,3 74 165.2
-256,67 -430 -742 -73,33 -100 -148.0 -14,4 6 42.8 24,4 76 168.8
-251,11 -420 -724 -70,56 -95 -139.0 -13,3 8 46.4 25,6 78 172.4
-245,56 -410 -706 -67,78 -90 -130.0 -12,2 10 50.0 26,7 80 176.0
-240,00 -400 -688 -65,00 -85 -121.0 -11,1 12 53.6 27,8 82 179.6
-234,44 -390 -670 -62,22 -80 -112.0 -10,0 14 57.2 28,9 84 183.2
-228,89 -380 -652 -59,45 -75 -103.0 -8,89 16 60.8 30,0 86 186.8
-223,33 -370 -634 -56,67 -70 -94.0 -7,78 18 64.4 31,1 88 190.4
-217,78 -360 -616 -53,89 -65 -85 -6,67 20 68.0 32,2 90 194.0
-212,22 -350 -598 -51,11 -60 -76.0 -5,56 22 71.6 33,3 92 197.6
-206,67 -340 -580 -48,34 -55 -67.0 -4,44 24 75.2 34,4 94 201.2
-201,11 -330 -562 -45,56 -50 -58.0 -3,33 26 78.8 35,6 96 204.8
-195,56 -320 -544 -42,78 -45 -49.0 -2,22 28 82.4 36,7 98 208.4
°F °C
TEMP. IN °C
OR °F TO BE
CONVERTED
°F °C
TEMP. IN °C
OR °F TO BE
CONVERTED
°F °C
TEMP. IN °C
OR °F TO BE
CONVERTED
°F
-190,00 -310 -526 -40,00 -40 -40.0 -1,11 30 86.0 37,8 100 212.0
-184,44 -300 -508 -38,89 -38 -36.4 0 32 89.6 43,3 110 230.0
-178,89 -290 -490 -37,78 -36 -32.8 1,11 34 93.2 48,9 120 248.0
-173,33 -280 -472 -36,67 -34 -29.2 2,22 36 96.8 54,4 130 266.0
-169,53 -273 -459.4 -35,56 -32 -25.6 3,33 38 100.4 60,0 140 284.0
-168,89 -272 -457.6 -34,44 -30 -22.0 4,44 40 104.0 65,6 150 302.0
-167,78 -270 -454.0 -33,33 -28 -18.4 5,56 42 107.6 71,1 160 320.0
-162,22 -260 -436.0 -32,22 -26 -14.8 6,67 44 111.2 76,7 170 338.0
-156,67 -250 -418.0 -31,11 -24 -11.2 7,78 46 114.8 82,2 180 356.0
-151,11 -240 -400.0 -30,00 -22 -7.6 8,89 48 118.4 87,8 190 374.0
-145,56 -230 -382.0 -28,89 -20 -4.0 10,0 50 122.0 93,3 200 392.0
-140,00 -220 -364.0 -27,78 -18 -0.4 11,1 52 125.6 98,9 210 410.0
-134,44 -210 -356.0 -26,67 -16 3.2 12,2 54 129.2 104,4 220 428.0
-128,89 -200 -328.0 -25,56 -14 6.8 13,3 56 132.8 110,0 230 446.0
-123,33 -190 -310.0 -24,44 -12 10.4 14,4 58 136.4 115,6 240 464.0
-117,78 -180 -292.0 -23,33 -10 14.0 15,6 60 140.0 121,1 250 482.0
-112,22 -170 -274.0 -22,22 -8 17.6 16,7 62 143.6 126,7 260 500.0
-106,67 -160 -256.0 -21,11 -6 21.2 17,8 64 147.2 132,2 270 518.0
-101,11 -150 -238.0 -20,00 -4 24.8 18,9 66 150.8 137,8 280 536.0
-95,56 -140 -220.0 -18,89 -2 28.4 20,0 68 154.4 143,3 290 665.0
-continued-
Page 14
672
Te c h n i c a l
Conversions, Equivalents, and Physical Data
Temperature Conversions (continued)
°C
21,1 70 158.0 204,4 400 752.0 454,0 850 1562.0
22,2 72 161.6 210,0 410 770.0 460,0 860 1580.0
23,3 74 165.2 215,6 420 788.0 465,6 870 1598.0
24,4 76 168.8 221,1 430 806.0 471,1 880 1616.0
25,6 78 172.4 226,7 440 824.0 476,7 890 1634.0
26,7 80 176.0 232,2 450 842.0 482,2 900 1652.0
27,8 82 179.6 237,8 460 860.0 487,8 910 1670.0
28,9 84 183.2 243,3 470 878.0 493,3 920 1688.0
30,0 86 186.8 248,9 480 896.0 498,9 930 1706.0
31,1 88 190.4 254,4 490 914.0 504,4 940 1724.0
32,2 90 194.0 260,0 500 932.0 510,0 950 1742.0
33,3 92 197.6 265,6 510 950.0 515,6 960 1760.0
34,4 94 201.2 271,1 520 968.0 521,1 970 1778.0
35,6 96 204.8 276,7 530 986.0 526,7 980 1796.0
36,7 98 208.4 282,2 540 1004.0 532,2 990 1814.0
TEMP. IN °C
OR °F TO BE
CONVERTED
°F °C
TEMP. IN °C
OR °F TO BE
CONVERTED
°F °C
TEMP. IN °C
OR °F TO BE
CONVERTED
°F
37,8 100 212.0 287,8 550 1022.0 537,8 1000 1832.0
43,3 110 230.0 293,3 560 1040.0 543,3 1010 1850.0
48,9 120 248.0 298,9 570 1058.0 548,9 1020 1868.0
54,4 130 266.0 304,4 580 1076.0 554,4 1030 1886.0
60,0 140 284.0 310,0 590 1094.0 560,0 1040 1904.0
65,6 150 302.0 315,6 600 1112.0 565,6 1050 1922.0
71,1 160 320.0 321,1 610 1130.0 571,1 1060 1940.0
76,7 170 338.0 326,7 620 1148.0 576,7 1070 1958.0
82,2 180 356.0 332,2 630 1166.0 582,2 1080 1976.0
87,8 190 374.0 337,8 640 1184.0 587,8 1090 1994.0
93,3 200 392.0 343,3 650 1202.0 593,3 1100 2012.0
98,9 210 410.0 348,9 660 1220.0 598,9 1110 2030.0
104,4 220 428.0 354,4 670 1238.0 604,4 1120 2048.0
110,0 230 446.0 360,0 680 1256.0 610,0 1130 2066.0
115,6 240 464.0 365,6 690 1274.0 615,6 1140 2084.0
121,1 250 482.0 371,1 700 1292.0 621,1 1150 2102.0
126,7 260 500.0 376,7 710 1310.0 626,7 1160 2120.0
132,2 270 518.0 382,2 720 1328.0 632,2 1170 2138.0
137,8 280 536.0 287,8 730 1346.0 637,8 1180 2156.0
143,3 290 665.0 393,3 740 1364.0 643,3 1190 2174.0
-continued-
Page 15
673
Te c h n i c a l
Conversions, Equivalents, and Physical Data
Temperature Conversions (continued)
TEMP. IN °C
°C
OR °F TO BE
CONVERTED
148,9 300 572.0 315,6 600 1112.0 482,2 900 1652.0 648,9 1200 2192.0
154,4 310 590.0 321,1 610 1130.0 487,8 910 1670.0 654,4 1210 2210.0
160,0 320 608.0 326,7 620 1148.0 493,3 920 1688.0 660,0 1220 2228.0
165,6 330 626.0 332,2 630 1166.0 498,9 930 1706.0 665,6 1230 2246.0
171,1 340 644.0 337,8 640 1184.0 504,4 940 1724.0 671,1 1240 2264.0
176,7 350 662.0 343,3 650 1202.0 510,0 950 1742.0 676,7 1250 2282.0
182,2 360 680.0 348,9 660 1220.0 515,6 960 1760.0 682,2 1260 2300.0
187,8 370 698.0 354,4 670 1238.0 521,1 970 1778.0 687,8 1270 2318.0
189,9 380 716.0 360,0 680 1256.0 526,7 980 1796.0 693,3 1280 2336.0
193,3 390 734.0 365,6 690 1274.0 532,2 990 1814.0 698,9 1290 2354.0
204,4 400 752.0 371,1 700 1292.0 537,8 1000 1832.0 704,4 1300 2372.0
210,0 410 770.0 376,7 710 1310.0 543,3 1010 1850.0 710,0 1310 2390.0
215,6 420 788.0 382,2 720 1328.0 548,9 1020 1868.0 715,6 1320 2408.0
221,1 430 806.0 287,8 730 1346.0 554,4 1030 1886.0 721,1 1330 2426.0
226,7 440 824.0 393,3 740 1364.0 560,0 1040 1904.0 726,7 1340 2444.0
°F °C
TEMP. IN °C
OR °F TO BE
CONVERTED
°F °C
TEMP. IN °C
OR °F TO BE
CONVERTED
°F °C
TEMP. IN °C
OR °F TO BE
CONVERTED
°F
232,2 450 842.0 398,9 750 1382.0 565,6 1050 1922.0 732,2 1350 2462.0
237,8 460 860.0 404,4 760 1400.0 571,1 1060 1940.0 737,8 1360 2480.0
243,3 470 878.0 410,0 770 1418.0 576,7 1070 1958.0 743,3 1370 2498.0
248,9 480 896.0 415,6 780 1436.0 582,2 1080 1976.0 748,9 1380 2516.0
254,4 490 914.0 421,1 790 1454.0 587,8 1090 1994.0 754,4 1390 2534.0
260,0 500 932.0 426,7 800 1472.0 593,3 1100 2012.0 760,0 1400 2552.0
265,6 510 950.0 432,2 810 1490.0 598,9 1110 2030.0 765,6 1410 2570.0
271,1 520 968.0 437,8 820 1508.0 604,4 1120 2048.0 771,1 1420 2588.0
276,7 530 986.0 443,3 830 1526.0 610,0 1130 2066.0 776,7 1430 2606.0
282,2 540 1004.0 448,9 840 1544.0 615,6 1140 2084.0 782,2 1440 2624.0
287,8 550 1022.0 454,4 850 1562.0 621,1 1150 2102.0 787,0 1450 2642.0
293,3 560 1040.0 460,0 860 1580.0 626,7 1160 2120.0 793,3 1460 2660.0
298,9 570 1058.0 465,6 870 1598.0 632,2 1170 2138.0 798,9 1470 2678.0
304,4 580 1076.0 471,1 880 1616.0 637,8 1180 2156.0 804,4 1480 2696.0
310,0 590 1094.0 476,7 890 1634.0 643,3 1190 2174.0 810,0 1490 2714.0
Page 16
674
Te c h n i c a l
Conversions, Equivalents, and Physical Data
A.P.I. and Baumé Gravity Tables and Weight Factors
A.P.I.
Baumé
Specic
Gravity
Gravity
0 10.247 1.0760 8.962 0.1116 - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
1 9.223 1.0679 8.895 0.1124 31 30.78 0.9808 7.251 0.1379 61 60.46 0.7351 6.119 0.1634 81 80.25 0.6659 5.542 0.1804
2 8.198 1.0599 8.828 0.1133 32 31.77 0.8654 7.206 0.1388 62 61.45 0.7313 6.087 0.1643 82 81.24 0.6628 5.516 0.1813
3 7.173 1.0520 8.762 0.1141 33 32.76 0.8602 7.163 0.1396 63 62.44 0.7275 6.056 0.1651 83 82.23 0.6597 5.491 0.1821
4 6.148 1.0443 8.698 0.1150 34 33.75 0.8550 7.119 0.1405 64 63.43 0.7238 6.025 0.1660 84 83.22 0.6566 5.465 0.1830
5 5.124 1.0366 8.634 0.1158 35 34.73 0.8498 7.075 0.1413 65 64.42 0.7201 6.994 0.1668 85 84.20 0.6536 5.440 0.1838
6 4.099 1.0291 8.571 0.1167 36 35.72 0.8448 7.034 0.1422 66 65.41 0.7165 5.964 0.1677 86 85.19 0.6506 5.415 0.1847
7 3.074 1.0217 8.509 0.1175 37 36.71 0.8398 6.993 0.1430 67 66.40 0.7128 5.934 0.1685 87 86.18 0.6476 5.390 0.1855
8 2.049 1.0143 8.448 0.1184 38 37.70 0.8348 6.951 0.1439 68 67.39 0.7093 5.904 0.1694 88 87.17 0.6446 5.365 0.1864
9 1.025 1.0071 8.388 0.1192 39 38.69 0.8299 6.910 0.1447 69 68.37 0.7057 5.874 0.1702 89 88.16 0.6417 5.341 0.1872
10 10.00 1.0000 8.328 0.1201 40 39.68 0.8251 6.870 0.1456 70 69.36 0.7022 5.845 0.1711 90 89.15 0.6388 5.316 0.1881
Gravity
Lbs/U.S.
Gallons
U.S.
Gallons-
/Lb
A.P.I.
Gravity
Baumé
Gravity
Specic
Gravity
Lbs/U.S.
Gallons
U.S.
Gallons-
/Lb
A.P.I.
Gravity
Baumé
Gravity
Specic
Gravity
Lbs/U.S.
Gallons
U.S.
Gallons-
/Lb
A.P.I.
Gravity
Baumé
Gravity
Specic
Gravity
Lbs/U.S.
Gallons
U.S.
Gallons-
/Lb
11 10.99 0.9930 8.270 0.1209 41 40.67 0.8203 6.830 0.1464 71 70.35 0.6988 5.817 0.1719 91 90.14 0.6360 5.293 0.1889
12 11.98 0.9861 8.212 0.1218 42 41.66 0.8155 6.790 0.1473 72 71.34 0.6953 5.788 0.1728 92 91.13 0.6331 5.269 0.1898
13 12.97 0.9792 8.155 0.1226 43 42.65 0.8109 6.752 0.1481 73 72.33 0.6919 5.759 0.1736 93 92.12 0.6303 5.246 0.1906
14 13.96 0.9725 8.099 0.1235 44 43.64 0.8063 6.713 0.1490 74 73.32 0.6886 5.731 0.1745 94 93.11 0.6275 5.222 0.1915
15 14.95 0.9659 8.044 0.1243 45 44.63 0.8017 6.675 0.1498 75 74.31 0.6852 5.703 0.1753 95 94.10 0.6247 5.199 0.1924
16 15.94 0.9593 7.989 0.1252 46 45.62 0.7972 6.637 0.1507 76 75.30 0.6819 5.676 0.1762 96 95.09 0.6220 5.176 0.1932
17 16.93 0.9529 7.935 0.1260 47 50.61 0.7927 6.600 0.1515 77 76.29 0.6787 5.649 0.1770 97 96.08 0.6193 5.154 0.1940
18 17.92 0.9465 7.882 0.1269 48 50.60 0.7883 6.563 0.1524 78 77.28 0.6754 5.622 0.1779 98 97.07 0.6166 5.131 0.1949
19 18.90 0.9402 7.930 0.1277 49 50.59 0.7839 6.526 0.1532 79 78.27 0.6722 5.595 0.1787 99 98.06 0.6139 5.109 0.1957
20 19.89 0.9340 7.778 0.1286 50 50.58 0.7796 6.490 0.1541 80 79.26 0.6690 5.568 0.1796 100 99.05 0.6112 5.086 0.1966
The relation of degrees Baume or A.P.I. to Specic Gravity is expressed by these formulas:
21 20.88 0.9279 7.727 0.1294 51 50.57 0.7753 6.455 0.1549
22 21.87 0.9218 7.676 0.1303 52 51.55 0.7711 6.420 0.1558
23 22.86 0.9159 7.627 0.1311 53 52.54 0.7669 6.385 0.1566
24 23.85 0.9100 7.578 0.1320 54 53.53 0.7628 6.350 0.1575
25 24.84 0.9042 7.529 0.1328 55 54.52 0.7587 6.136 0.1583
26 25.83 0.8984 7.481 0.1337 56 55.51 0.7547 6.283 0.1592
27 26.82 0.8927 7.434 0.1345 57 56.50 0.7507 6.249 0.1600
28 27.81 0.8871 7.387 0.1354 58 57.49 0.7467 6.216 0.1609
29 28.80 0.8816 7.341 0.1362 59 58.48 0.7428 6.184 0.1617
30 29.79 0.8762 7.296 0.1371 60 59.47 0.7389 6.151 0.1626
For liquids lighter than water: For liquids heavier than water:
Degrees Baume = Degrees Baume =
Degrees A.P.I. =
G = Specic Gravity = ratio of weight of a given volume of oil at 60°F to the weight of the same
volume of water at 60°F.
The above tables are based on the weight of 1 gallon (U.S.) of oil with a volume of 231 cubic
inches at 60°F in air at 760 mm pressure and 50% relative humidity. Assumed weight of 1 gallon
of water at 60°F in air is 8.32828 pounds.
To determine the resulting gravity by mixing oils of different gravities:
D =
D = Density or Specic Gravity of mixture
m = Proportion of oil of d1 density
n = Proportion of oil of d2 density
d1 = Specic gravity of m oil
d2 = Specic gravity of n oil
140 140
- 130 G =
G 130 + Degrees Baume
141 141.5
- 131.5 G =
5 131.5 + Degrees A.P.I.
md1+md
2
m + n
145 145
145 - G =
5 145 – Degrees Baume
Page 17
675
Te c h n i c a l
Conversions, Equivalents, and Physical Data
Characteristics of the Elements
ELEMENT SYMBOL
Actinium
Aluminum
Americum
Antimony
(Stibium)
Argon
Arsenic
Astatine
Barium
Berkelium
Beryllium
Bismuth
Boron
Bromine
Cadmium
Calcium
Californium
Carbon
Cerium
Cesium
Chlorine
Chromium
Cobalt
Copper
Curium
Dysprosium
Einsteinium
Erbium
Europium
Fermium
Fluourine
Francium
Gadolinium
Gallium
Germanium
Gold
Hafnium
Helium
Holmium
Hydrogen
Indium
Iodine
Iridium
Iron
Krypton
Lanthanum
Lawrencium
Lead
Lithium
Lutetium
Magnesium
Manganese
Mendelevium
Mercury
Molybdenum
Neodymium
1. Mass number shown is that of stable isotope most common in nature. Mass numbers shown in parentheses designate the isotope with the longest half-life (slowest rate of
radioactive decay) for those elements having an unstable isotope.
2. Calculated
> Greater than
Ac
Am
Sb
Ar
As
Ba
Bk
Be
Br
Cd
Ca
Cf
Ce
Cs
Cr
Co
Cu
Cm
Dy
Es
Er
Eu
Fm
Gd
Ga
Ge
Au
Hf
He
Ho
Fe
Kr
La
Lw
Pb
Lu
Mg
Mn
Mv
Hg
Mo
Nd
Al
At
Bi
B
C
Cl
F
Fr
H
In
I
Ir
Li
ATOMIC
NUMBER
89
13
95
51
18
33
85
56
97
4
83
5
35
48
20
98
6
58
55
17
24
27
29
96
66
99
68
63
100
9
87
64
31
32
79
72
2
67
1
49
53
77
26
36
57
103
82
3
71
12
25
101
80
42
60
MASS
NUMBER
(227)
27
(243)
121
40
75
(210)
138
(247)
9
209
11
79
114
40
(249)
12
140
133
35
52
59
63
(248)
164
(254)
166
153
(252)
19
(223)
158
69
74
197
180
4
165
1
115
127
193
56
84
139
(257)
208
7
175
24
55
(256)
202
98
142
MELTING
(1)
POINT (°C)
sublimes at 615
1278±5
1150±50
-259.14
2620±10
BOILING
POINT (°C)
1600†
659.7
630.5
-189.2
sublimes at 615
850
271.3
2300
-7.2
320.9
842±8
>3550
804
28.5
-103±5
1890
1495
1083
-223 -188
29.78
958.5
1063
1700
-272
156.4
113.7
2454
1535
-156.6
826
327.43
186
651
1260
-38.87
840
1560±5
(2)
2000±10
184.35
1336±5
356.58
2057
1380
-185.7
1140
2970
2550
58.78
767±2
1240
4200
1400
670
-34.6
2480
2900
2336
1983
2700
2600
>3200
-268.9
-252.8
>4800
3000
-152.9
1620
1107
1900
4800
ELEMENT SYMBOL
Neon
Neptunium
Nickel
Niobium
Nitrogen
Nobelium
Osmium
Oxygen
Palladium
Phosphorus
Platinum
Plutonium
Polonium
Potassium
Praseodymium
Promethium
Protactinium
Radium
Radon
Rhenium
Rhodium
Rubidium
Ruthenium
Samarium
Scandium
Selenium
Silicon
Silver
Sodium
Strontium
Sulfur
Tantalum
Technetium
Tellurium
Terbium
Thallium
Thorium
Thulium
Tin
Titanium
Tungsten
(Wolfram)
Uranium
Vanadium
Xenon
Ytterbium
Yttrium
Zinc
Zirconium
Ne
Np
Nb
No
Os
Pd
Pu
Po
Pm
Pa
Ra
Rn
Re
Rh
Rb
Ru
Sm
Sc
Se
Ag
Na
Ta
Tc
Te
Tb
Th
Tm
Sn
Xe
Yb
Zn
ATOMIC
NUMBER
10
102
93
28
41
7
76
8
46
15
78
94
84
19
59
61
91
88
86
75
45
37
44
62
21
34
14
47
11
38
16
73
43
52
65
81
90
69
50
22
74
92
23
54
70
39
30
40
Ni
N
O
P
Pt
K
Pr
Si
Sr
S
Tl
Ti
W
U
V
Y
Zr
MASS
NUMBER
20
(237)
58
93
14
(253)
192
16
106
31
195
(242)
(209)
39
141
(145)
(231)
(226)
(222)
187
103
85
102
152
45
80
28
107
23
88
32
180
(99)
130
159
205
232
169
120
48
184
238
51
132
174
89
64
90
(1)
MELTING
POINT (°C)
-248.67
1455
2500±50
-209.86
2700
-218.4
1549.4
1773.5
53.3
940
700
-71
3167±60
1966±3
38.5
2450
>1300
1200
217
1420
960.8
97.5
800
2996±50
452
327±5
302
1845
231.89
1800
3370
c.1133
1710
-112
1800
1490
419.47
1857
BOILING
POINT (°C)
-245.9
2900
3700
-195.8
>5300
-182.86
2000
4300
760
1140
-61.8
>2500
700
2700
2400
688
2355
1950
880
1150
c.4100
1390
1457±10
4500
2270
>3000
5900
3000
-107.1
2500
907
>2900
Page 18

676
Te c h n i c a l
Conversions, Equivalents, and Physical Data
Recommended Standard Specications for Valve Materials Pressure-Containing Castings
1 Carbon Steel
ASTM A216 Grade WCC
Temperature Range = -20° to 800°F
Composition (Percent)
C 0.25 maximum
Mn 1.20 maximum
P 0.04 maximum
S 0.04 maximum
Si 0.60 maximum
2 Carbon Steel
ASTM A216 Grade WCB
Temperature Range = -20° to 1000°F
Composition (Percent)
C 0.30 maximum
Mn 1.00 maximum
P 0.05 maximum
S 0.06 maximum
Si 0.60 maximum
11 Type 304 Stainless Steel
ASTM A351 Grade CF-8
Temperature Range = -425° to 1500°F
Composition (Percent)
C 0.08 maximum
Mn 1.50 maximum
Si 2.00 maximum
S 0.04 maximum
P 0.04 maximum
Cr 18.00 to 21.00
Ni 8.00 to 11.00
12 Type 316 Stainless Steel
ASTM A351 Grade CF-8M
Temperature Range = -425° to 1500°F
Composition (Percent)
C 0.08 maximum
Mn 1.50 maximum
Si 2.00 maximum
P 0.04 maximum
S 0.04 maximum
Cr 18.00 to 21.00
Ni 9.00 to 12.00
Mo 2.00 to 3.00
3 Carbon Steel
ASTM A352 Grade LCC
Temperature Range = -50° to 650°F
Composition: same as ASTM A216
Grade WCC
5 Chrome Moly Steel
ASTM A217 Grade C5
Temperature Range = -20° to 1100°F
Composition (Percent)
C 0.20 maximum
Mn 0.40 to 0.70
P 0.05 maximum
S 0.06 maximum
Si 0.75 maximum
Cr 4.00 to 6.50
Mo 0.45 to 0.65
7 Chrome Moly Steel
ASTM A217 Grade WC6
Temperature Range = -20° to 1000°F
Composition (Percent)
C 0.20 maximum
Mn 0.50 to 0.80
P 0.05 maximum
S 0.06 maximum
Si 0.60 maximum
Cr 1.00 to 1.50
Mo 0.45 to 0.65
9 3.5% Nickel Steel
ASTM A352 Grade LC3
Temperature Range = -150° to 650°F
Composition (Percent)
C 0.15 maximum
Mn 0.50 to 0.80
P 0.05 maximum
S 0.05 maximum
Si 0.60 maximum
Ni 3.00 to 4.00
4 Carbon Steel
ASTM A352 Grade LCB
Temperature Range = -50° to 650°F
Composition: same as ASTM A216
Grade WCB
6 Carbon Moly Steel
ASTM A217 Grade WC1
Temperature Range = -20° to 850°F
Composition (Percent)
C 0.25
Mn 0.50 to 0.80
P 0.05 maximum
S 0.06 maximum
Si 0.60 maximum
Mo 0.45 to 0.65
8 Chrome Moly Steel
ASTM A217 Grade WC9
Temperature Range = -20° to 1050°F
Composition (Percent)
C 0.18 maximum
Mn 0.40 to 0.70
P 0.05 maximum
Si 0.60 maximum
Cr 2.00 to 2.75
Mo 0.90 to 1.20
10 Chrome Moly Steel
ASTM A217 Grade C12
Temperature Range = -20° to 1100°F
Composition (Percent)
C 0.20 maximum
Si 1.00 maximum
Mn 0.35 to 0.65
Cr 8.00 to 10.00
Mo 0.90 to 1.20
P 0.05 maximum
S 0.06 maximum
13 Cast Iron
ASTM A126 Class B
Temperature Range = -150° to 450°F
Composition (Percent)
P 0.75 maximum
S 0.12 maximum
15 Ductile Iron
ASTM A395 Type 60-45-15
Temperature Range = -20° to 650°F
Composition (Percent)
C 3.00 minimum
Si 2.75 maximum
P 0.80 maximum
17 Standard Valve Bronze
ASTM B62
Temperature Range = -325° to 450°F
Composition (Percent)
Cu 84.00 to 86.00
Sn 4.00 to 6.00
Pb 4.00 to 6.00
Zn 4.00 to 6.00
Ni 1.00 maximum
Fe 0.30 maximum
P 0.05 maximum
19 Manganese Bronze
ASTM B147 Alloy 8A
Temperature Range = -325° to 350°F
Composition (Percent)
Cu 55.00 to 60.00
Sn 1.00 maximum
Pb 0.40 maximum
Ni 0.50 maximum
Fe 0.40 to 2.00
Al 0.50 to 1.50
Mn 1.50 maximum
Zn Remainder
14 Cast Iron
ASTM A126 Class C
Temperature Range = -150° to 450°F
Composition (Percent)
P 0.75 maximum
S 0.12 maximum
16 Ductile Ni-Resist* Iron
ASTM A439 Type D-2B
Temperature Range = -20° to 750°F
Composition (Percent)
C 3.00 maximum
Si 1.50 to 3.00
Mn 0.70 to 1.25
P 0.08 maximum
Ni 18.00 to 22.00
Cr 2.75 to 4.00
18 Tin Bronze
ASTM B143 Alloy 1A
Temperature Range = -325° to 400°F
Composition (Percent)
Cu 86.00 to 89.00
Sn 9.00 to 11.00
Pb 0.30 maximum
Zn 1.00 to 3.00
Ni 1.00 maximum
Fe 0.15 maximum
P 0.05 maximum
20 Aluminum Bronze
ASTM B148 Alloy 9C
Temperature Range = -325° to 500°F
Composition (Percent)
Cu 83.00 minimum
Al 10.00 to 11.50
Fe 3.00 to 5.00
Mn 0.50
Ni 2.50 maximum
Minimum total named
elements = 99.5
- continued -
Page 19
677
Te c h n i c a l
Conversions, Equivalents, and Physical Data
Recommended Standard Specications for Valve Materials Pressure-Containing Castings (continued)
21 Mondel* Alloy 411
(Weldable Grade)
Temperature Range = -325° to 900°F
Composition (Percent)
Ni 60.00 minimum
Cu 26.00 to 33.00
C 0.30 maximum
Mn 1.50 maximum
Fe 3.50 maximum
S 0.015 maximum
Si 1.00 to 2.00
Nb 1.00 to 3.00
23 Nickel-Moly-Chrome Alloy “C”
ASTM A494 (Hastelloy® “C” †)
Temperature Range = -325° to 1000°F
Composition (Percent)
Cr 15.50 to 17.50
Fe 4.50 to 7.50
W 3.75 to 5.25
C 0.12 maximum
Si 1.00 maximum
Co 2.50 maximum
Mn 1.00 maximum
V 0.20 to 0.40
Mo 16.00 to 18.00
P 0.04
S 0.03
Ni Remainder
25 Aluminum Bar
ASTM B211 Alloy 20911-T3
Composition (Percent)
Si 0.40 maximum
Fe 0.70 maximum
Cu 5.00 to 6.00
Zn 0.30 maximum
Bi 0.20 to 0.60
Pb 0.20 to 0.60
Other Elements 0.15 maximum
Al Remainder
27 Naval Brass Bar
ASTM B21 Allow 464
Composition (Percent)
Cu 59.00 to 62.00
Sn 0.50 to 1.00
Pb 0.20 maximum
Zn Remainder
29 Carbon Steel Bar
ASTM A108 Grade 1018
Composition (Percent)
C 0.15 to 0.20
Mn 0.60 to 0.90
P 0.04 maximum
S 0.05 maximum
22 Nickel-Moly Alloy “B”
ASTM A494 (Hastelloy® “B” †)
Temperature Range = -325° to 700°F
Composition (Percent)
Cr 1.00 maximum
Fe 4.00 to 6.00
C 0.12 maximum
Si 1.00 maximum
Co 2.50 maximum
Mn 1.00 maximum
V 0.20 to 0.60
Mo 26.00 to 30.00
P 0.04 maximum
S 0.03 maximum
Ni Remainder
24 Cobalt-based Alloy No.6
Stellite † No. 6
Composition (Percent)
C 0.90 to 1.40
Mn 1.00
W 3.00 to 6.00
Ni 3.00
Cr 26.00 to 32.00
Mo 1.00
Fe 3.00
Se 0.40 to 2.00
Co Remainder
26 Yellow Brass Bar
ASTM B16 1/2 Hard
Composition (Percent)
Cu 60.00 to 63.00
Pb 2.50 to 3.70
Fe 0.35 maximum
Zn Remainder
28 Leaded Steel Bar
AISI 12L14
Composition (Percent)
C 0.15 maximum
Mn 0.80 to 1.20
P 0.04 to 0.09
S 0.25 to 0.35
Pb 0.15 to 0.35
30 AISI 4140 Chrome-Moly Steel
(Suitable for ASTM A193
Grade B7 bolt material)
Composition (Percent)
C 0.38 to 0.43
Mn 0.75 to 1.00
P 0.035 maximum
S 0.04 maximum
Si 0.20 to 0.35
Cr 0.80 to 1.10
Mo 0.15 to 0.25
Fe Remainder
31 Type 302 Stainless Steel
ASTM A276 Type 302
Composition (Percent)
C 0.15 maximum
Mn 2.00 maximum
P 0.045 maximum
S 0.030 maximum
Si 1.00 maximum
Cr 17.00 to 19.00
Ni 8.00 to 10.00
33 Type 316 Stainless Steel
ASTM A276 Type 316
Composition (Percent)
C 0.08 maximum
Mn 2.00 maximum
P 0.045 maximum
S 0.030 maximum
Si 1.00 maximum
Cr 16.00 to 18.00
Ni 10.00 to 14.00
Mo 2.00 to 3.00
35 Type 410 Stainless Steel
ASTM A276 Type 410
Composition (Percent)
C 0.15 maximum
Mn 1.00 maximum
P 0.040 maximum
S 0.030 maximum
Si 1.00 maximum
Cr 11.50 to 13.50
Al 0.10 to 0.30
37 Nickel-Copper Alloy Bar
Alloy K500 (K Monel®*)
Composition (Percent)
Ni 63.00 to 70.00
Fe 2.00 maximum
Mn 1.50 maximum
Si 1.00 maximum
C 0.25 maximum
S 0.01 maximum
Al 2.00 to 4.00
Ti 0.25 to 1.00
Cu Remainder
39 Nickel-Moly-Chrome Alloy “C” Bar
ASTM B336 (Hastelloy® “C” †)
Composition (Percent)
Cr 14.50 to 16.50
Fe 4.00 to 7.00
W 3.00 to 4.50
C 0.08 maximum
Si 1.00 maximum
Co 2.50 maximum
Mn 1.00 maximum
Va 0.35 maximum
Mo 15.00 to 17.00
P 0.04
S 0.03
Ni Remainder
32 Type 304 Stainless Steel
ASTM A276 Type 304
Composition (Percent)
C 0.08 maximum
Mn 2.00 maximum
P 0.045 maximum
S 0.030 maximum
Si 1.00 maximum
Cr 18.00 to 20.00
Ni 8.00 to 12.00
34 Type 316L Stainless Steel
ASTM A276 Type 316L
Composition (Percent)
C 0.03 maximum
Mn 2.00 maximum
P 0.045 maximum
S 0.030 maximum
Si 1.00 maximum
Cr 16.00 to 18.00
Ni 10.00 to 14.00
Mo 2.00 to 3.00
36 Type 17-4PH Stainless Steel
ASTM A461 Grade 630
Composition (Percent)
C 0.07 maximum
Mn 1.00 maximum
Si 1.00 maximum
P 0.04 maximum
S 0.03 maximum
Cr 15.50 to 17.50
Nb 0.05 to 0.45
Cu 3.00 to 5.00
Ni 3.00 to 5.00
Fe Remainder
38 Nickel-Moly Alloy “B” Bar
ASTM B335 (Hastelloy® “B” †)
Composition (Percent)
Cr 1.00 maximum
Fe 4.00 to 6.00
C 0.04 maximum
Si 1.00 maximum
Co 2.50 maximum
Mn 1.00 maximum
V 0.20 to 0.40
Mo 26.00 to 30.00
P 0.025 maximum
S 0.030 maximum
Ni Remainder
Page 20

678
Te c h n i c a l
Conversions, Equivalents, and Physical Data
Recommended Standard Specications for Valve Materials Pressure-Containing Castings
MATERIAL CODE
AND DESCRIPTION
1 Carbon Steel ASTM A 216 Grade WCC 70,000 40,000 22 35 30.4 137 to 187
2 Carbon Steel ASTM A 216 Grade WCB 70,000 36,000 22 35 27.9 137 to 187
3 Carbon Steel ASTM A 352 Grade LCC 70,000 40,000 22 35 29.9 137 to 187
4 Carbon Steel ASTM A 352 Grade LCB 65,000 35,000 24 35 27.9 137 to 187
5 Chrome Moly Steel ASTM A217 Grade C5 90,000 60,000 18 35 27.4 241 Maximum
6 Carbon Moly Steel ASTM A217 Grade WC1 65,000 35,000 24 35 29.9 215 Maximum
7 Chrome Moly Steel ASTM A217 Grade WC6 70,000 40,000 20 35 29.9 215 Maximum
8 Chrome Moly Steel ASTM A217 Grade WC9 70,000 40,000 20 35 29.9 241 Maximum
9 3.5% Nickel Steel ASTM A352 Grade LC3 65,000 40,000 24 35 27.9 137
10 Chrome Moly Steel ASTM A217 Grade C12 90,000 60,000 18 35 27.4 180 to 240
11 Type 304 Stainless Steel ASTM A351 Grade CF8 65,000 28,000 35 - - - - 28.0 140
12 Type 316 Stainless Steel ASTM A351 Grade CF8M 70,000 30,000 30 - - - - 28.3 156 to 170
13 Cast Iron ASTM A126 Class B 31,000 - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 160 to 220
14 Cast Iron ASTM A126 Class C 41,000 - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 160 to 220
15 Ductile Iron ASTM A395 Type 60-45-15 60,000 45,000 15 - - - - 23-26 143 to 207
16 Ductile Ni-Resist Iron
17 Standard Valve Bronze ASTM B62 30,000 14,000 20 17 13.5 55 to 65*
18 Tin Bronze ASTM B143 Alloy 1A 40,000 18,000 20 20 15 75 to 85*
19 Manganese Bronze ASTM B147 Alloy 8A 65,000 25,000 20 20 15.4 98*
20 Aluminum Bronze ASTM B148 Alloy 9C 75,000 30,000 12 minimum 12 17 150
21 Mondel Alloy 411 (Weldable Grade) 65,000 32,500 25 - - - - 23 120 to 170
22 Nickel-Moly Alloy “B” ASTM A494 (Hastelloy® “B”) 72,000 46,000 6 - - - - - - - - - - - -
23 Nickel-Moly-Chrome Alloy “C” ASTM A494 (Hastelloy® “C”) 72,000 46,000 4 - - - - - - - - - - - -
24 Cobalt-base Alloy No.6 Stellite No. 6 121,000 64,000 1 to 2 - - - - 30.4 - - - -
25 Aluminum Bar ASTM B211 Alloy 20911-T3 44,000 36,000 15 - - - - 10.2 95
26 Yellow Brass Bar ASTM B16-1/2 Hard 45,000 15,000 7 50 14 - - - -
27 Naval Brass Bar ASTM B21 Alloy 464 60,000 27,000 22 55 - - - - - - - -
28 Leaded Steel Bar AISI 12L14 79,000 71,000 16 52 - - - - 163
29 Carbon Steel Bar ASTM A108 Grade 1018 69,000 48,000 38 62 - - - - 143
30 AISI 4140 Chrome-Moly Steel
31 Type 302 Stainless Steel ASTM A276 Type 302 85,000 35,000 60 70 28 150
32 Type 304 Stainless Steel ASTM A276 Type 304 85,000 35,000 60 70 - - - - 149
33 Type 316 Stainless Steel ASTM A276 Type 316 80,000 30,000 60 70 28 149
34 Type 316L Stainless Steel ASTM A276 Type 316L 81,000 34,000 55 - - - - - - - - 146
35 Type 410 Stainless Steel ASTM A276 Type 410 75,000 40,000 35 70 29 155
36 Type 17-4PH Stainless Steel ASTM A461 Grade 630 135,000 105,000 16 50 29 275 to 345
37 Nickel-Copper Alloy Bar Alloy K500 (K Monel®) 100,000 70,000 35 - - - - 26 175 to 260
38 Nickel-Moly Alloy “B” Bar ASTM B335 (Hastelloy® “B”) 100,000 46,000 30 - - - - - - - - - - - -
39 Nickel-Moly Alloy “C” Bar ASTM B336 (Hastelloy® “C”) 100,000 46,000 20 - - - - - - - - - - - -
1. 500 kg load.
(1)
ASTM A439 Type D-2B 58,000 30,000 7 - - - - - - - - 148 to 211
(Suitable for ASTM A193 Grade B7
bolt material)
MINIMUM PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
Tensile
(Psi)
135,000 115,000 22 63 29.9 255
Yield
Point (Psi)
Elong.
in 2-inches
(%)
Reduction
of Area (%)
MODULUS OF
ELASTICITY AT
70°F (PSI x 106)
APPROXIMATE
HARDNESS
BRINELL
Page 21

679
Te c h n i c a l
Conversions, Equivalents, and Physical Data
Physical Constants of Hydrocarbons
CRITICAL CONSTANTS
Critical
Temperature
(5)
-116.63
(5)
(5)
206.01
305.65
274.98
369.10
321.13
435.83
420.13
440.29
495.00
503.78
513.48
477.23
475.95
505.85
496.44
564.22
530.44
519.46
610.68
499.35
570.27
(5)
(5)
(5)
324.37
311.86
292.55
376.93
(339)
(412)
552.22
605.55
651.24
651.02
(°F)
90.09
385.7
453.7
448.3
512.8
652.1
461.5
536.7
48.58
196.9
295.6
306
95.31
675.0
649.6
706.0
676.4
NO. COMPOUND FORMULA
1
Methane
2
Ethane
3
Propane
4
n-Butane
5
Isobutane
6
n-Pentane
7
Isopentane
8
Neopentane
9
n-Hexane
10
2-Methylpentane
11
3-Methylpentane
12
Neohexane
13
2,3-Dimethylbutane
14
n-Heptane
15
2-Methylhexane
16
3-Methylhexane
17
3-Ethylpentane
18
2,2-Dimethylpentane
19
2,4-Dimethylpentane
20
3,3-Dimethylpentane
21
Triptane
22
n-Octane
23
Disobutyl
24
Isooctane
25
n-Nonane
26
n-Decane
27
Cyclopentane
28
Methylcyclopentane
29
Cyclohexane
30
Methylcyclohexane
31
Ethylene
32
Propene
33
1-Butene
34
Cis-2-Butene
35
Trans-2-Butene
36
Isobutene
37
1-Pentene
38
1,2-Butadiene
39
1,3-Butadiene
40
Isoprene
41
Acetylene
42
Benzene
43
Toluene
44
Ethylbenzene
45
o-Xylene
46
m-Xylene
47
p-Xylene
48
Styrene
49
Isopropylbenzane
1. Calculated values.
2. ( ) - Estimated values.
3. Air saturated hydrocarbons.
4. Absolute values from weights in vacuum.
5. At saturation pressure (- - - -).
6. Sublimation point.
7. Saturation pressure at 60°F.
8. Apparent value for methane at 60°F.
9. Specic gravity, 119°F/60°F (sublimation point).
CH
C2H
C3H
C4H
C4H
C5H
C5H
C5H
C6H
C6H
C6H
C6H
C6H
C7H
C7H
C7H
C7H
C7H
C7H
C7H
C7H
C8H
C8H
C8H
C9H
C10H
C5H
C6H
C6H
C7H
C2H
C3H
C4H
C4H
C4H
C4H
C5H
C4H
C4H
C5H
C2H
C6H
C7H
C8H
C8H
C8H
C8H
C8H
C9H
4
6
8
10
10
12
12
12
14
14
14
14
14
16
16
16
16
16
16
16
16
18
18
18
20
22
10
12
12
14
4
6
8
8
8
8
10
6
6
8
2
6
8
10
10
10
10
8
12
MOLECULAR
WEIGHT
16.043
30.070
44.097
58.124
58.124
72.151
72.151
72.151
86.178
86.178
86.178
86.178
86.178
100.205
100.205
100.205
100.205
100.205
100.205
100.205
100.205
114.232
114.232
114.232
128.259
142.286
70.135
84.162
84.162
98.189
28.054
42.081
56.108
56.108
56.108
56.108
70.135
54.092
54.092
68.119
26.038
78.114
92.141
106.168
106.168
106.168
106.168
104.152
120.195
BOILING
POINT AT
14.696 PSIA
(°F)
-258.69
-127.48
-43.67
31.10
10.90
96.92
82.12
49.10
155.72
140.47
145.89
121.52
136.36
209.17
194.09
197.32
200.25
174.54
176.89
186.91
177.58
258.22
228.39
210.63
303.47
345.48
120.65
161.25
177.29
213.68
-154.62
-53.90
20.75
38.69
33.58
19.59
85.93
51.56
24.06
93.30
(6)
-119
176.17
231.13
277.16
291.97
282.41
281.05
293.29
306.34
VAPOR
PRESSURE AT
100°F (PSIA)
(2)
(5000)
(2)
(800)
190
51.6
72.2
15.570
20.44
35.9
4.956
6.767
6.098
9.856
7.404
1.620
2.271
2.130
2.012
3.492
3.292
2.773
3.374
0.537
1.101
1.708
0.179
0.0597
9.914
4.503
3.264
1.609
- - - -
226.4
63.05
45.54
49.80
63.40
19.115
(2)
(20)
(2)
(60)
16.672
- - - -
3.224
1.032
0.371
0.264
0.326
0.342
(2)
(0.24)
0.188
FREEZING
POINT AT
14.696 PSIA
(°F)
-296.46
-297.89
-305.84
-217.05
-255.29
-201.51
-255.83
2.17
-139.58
-244.63
- - - -
-147.72
-199.38
-131.05
-180.89
- - - -
-181.48
-190.86
-182.63
-210.01
-12.82
-70.18
-132.07
-161.27
-64.28
-21.36
-136.91
-224.44
43.77
-195.98
-272.45
-301.45
-301.63
-218.06
-157.96
-220.61
-265.39
-213.16
-164.02
-230.74
(5)
-114
41.96
-138.94
-138.91
-13.30
-54.12
55.86
-23.10
-140.82
SPECIFIC GRAVITY
AT 14.696 PSIA
Critical
Pressure
(psia)
667.8
707.8
616.3
550.7
529.1
488.6
490.4
464.0
436.9
436.6
453.1
446.8
453.5
396.8
396.5
408.1
419.3
402.2
396.9
427.2
428.4
360.6
360.6
372.4
332
304
653.8
548.9
591
503.5
729.8
669
583
610
595
580
(2)
(2)
590
(653)
628
(558.4)
890.4
710.4
595.9
523.5
541.4
513.6
509.2
580
465.4
(2)
(2)
(3, 4)
Liquid
60°F/60°F
0.3000
0.3564
0.5077
0.5844
0.5631
0.6310
0.6247
0.5967
0.6640
0.6579
0.6689
0.6540
0.6664
0.6882
0.6830
0.6917
0.7028
0.6782
0.6773
0.6976
0.6946
0.7068
0.6979
0.6962
0.7217
0.7342
0.7504
0.7536
0.7834
0.7740
- - - -
0.5220
0.6013
0.6271
0.6100
0.6004
(7)
0.645
(7)
0.658
0.6272
0.6861
(9)
0.615
0.8844
0.8718
0.8718
0.8848
0.8687
0.8657
0.9110
0.8663
(8)
(7)
(7)
(7)
(7)
(7)
(7)
(7)
(7)
(7)
(7)
(7)
,
Gas at 60°F
(Air = 1)
0.5539
1.0382
1.5225
2.0068
2.0068
2.4911
2.4911
2.4911
2.9753
2.9753
2.9753
2.9753
2.9753
3.4596
3.4596
3.4596
3.4596
3.4596
3.4596
3.4596
3.4596
3.9439
3.9439
3.9439
4.4282
4.9125
2.4215
2.9057
2.9057
3.3900
0.9686
1.4529
1.9372
1.9372
1.9372
1.9372
2.4215
1.8676
1.8676
2.3519
0.8990
2.6969
3.1812
3.6655
3.6655
3.6655
3.6655
3.5959
4.1498
(1)
Page 22
680
Te c h n i c a l
Conversions, Equivalents, and Physical Data
Physical Constants of Various Fluids
FLUID FORMULA
Acetic Acid HC2H3O
3
MOLECULAR
WEIGHT
60.06 245 - - - - - - - - - - - - 1.05 - - - -
BOILING POINT
(°F AT 14.696
PSIA)
Acetone C3H6O 58.08 133 - - - - 455 691 0.79 2.01
Air N2O
2
28.97 -317 - - - - -221 547 0.86
Alcohol, Ethyl C2H6O 46.07 173 2.3
Alcohol, Methyl CH4O 32.04 148 4.63
Ammonia NH
Ammonium
Chloride
Ammonium
Hydroxide
Ammonium
(1)
Sulfate
(1)
(1)
NH4Cl - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 1.07 - - - -
NH4OH - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 0.91 - - - -
(NH4)2SO
3
4
17.03 -28 114 270 1636 0.62 0.59
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 1.15 - - - -
Aniline C6H7N 93.12 365 - - - - 798 770 1.02 - - - -
Argon A 39.94 -302 - - - - -188 705 1.65 1.38
Bromine Br
Calcium
Chloride
(1)
CaCl
Carbon Dioxide CO
Carbon Disulde CS
2
2
2
2
159.84 138 - - - - 575 - - - - 2.93 5.52
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 1.23 - - - -
44.01 -109 839 88 1072 0.801
76.1 115 - - - - - - - - - - - - 1.29 2.63
Carbon Monoxide CO 28.01 -314 - - - - -220 507 0.80 0.97
Carbon
Tetrachloride
Chlorine Cl
Chromic Acid H2CrO
Citric Acid C6H8O
Copper Sulfate
(1)
CCl
CuSO
4
2
4
7
4
153.84 170 - - - - 542 661 1.59 5.31
70.91 -30 85 291 1119 1.42 2.45
118.03 - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 1.21 - - - -
192.12 - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 1.54 - - - -
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 1.17 - - - -
Ether (C2H5)2O 74.12 34 - - - - - - - - - - - - 0.74 2.55
Ferric Chloride
Fluorine F
(1)
FeCl
3
2
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 1.23 - - - -
38.00 -305 300 -200 809 1.11 1.31
Formaldehyde H2CO 30.03 -6 - - - - - - - - - - - - 0.82 1.08
Formic Acid HCO2H 46.03 214 - - - - - - - - - - - - 1.23 - - - -
Furfural C5H4O
Glycerine C3H8O
Glycol C2H6O
2
3
2
96.08 324 - - - - - - - - - - - - 1.16 - - - -
92.09 554 - - - - - - - - - - - - 1.26 - - - -
62.07 387 - - - - - - - - - - - - 1.11 - - - -
Helium He 4.003 -454 - - - - -450 33 0.18 0.14
Hydrochloric Acid HCl 36.47 -115 - - - - - - - - - - - - 1.64 - - - -
Hydrouoric Acid HF 20.01 66 0.9 446 - - - - 0.92 - - - -
Hydrogen H
Hydrogen
Chloride
2
HCl 36.47 -115 613 125 1198 0.86 1.26
2.016 -422 - - - - -400 188 0.07
Hydrogen Sulde H2S 34.07 -76 252 213 1307 0.79 1.17
Isopropyl Alcohol C3H8O 60.09 180 - - - - - - - - - - - - 0.78 2.08
Linseed Oil - - - - - - - - 538 - - - - - - - - - - - - 0.93 - - - -
1. Aqueous Solution - 25% by weight of compound.
2. Vapor pressure in psia at 100°F.
3. Density of liquid, gm/ml at normal boiling point.
VAPOR
PRESSURE
AT 70°F (PSIG)
(2)
(2)
CRITICAL
TEMPERATURE
(°F)
CRITICAL
PRESSURE
(PSIA)
SPECIFIC GRAVITY
Liquid 60°F/60°F Gas
‡
470 925 0.794 1.59
463 1174 0.796 1.11
(3)
(3)
1.0
1.52
0.07
Page 23
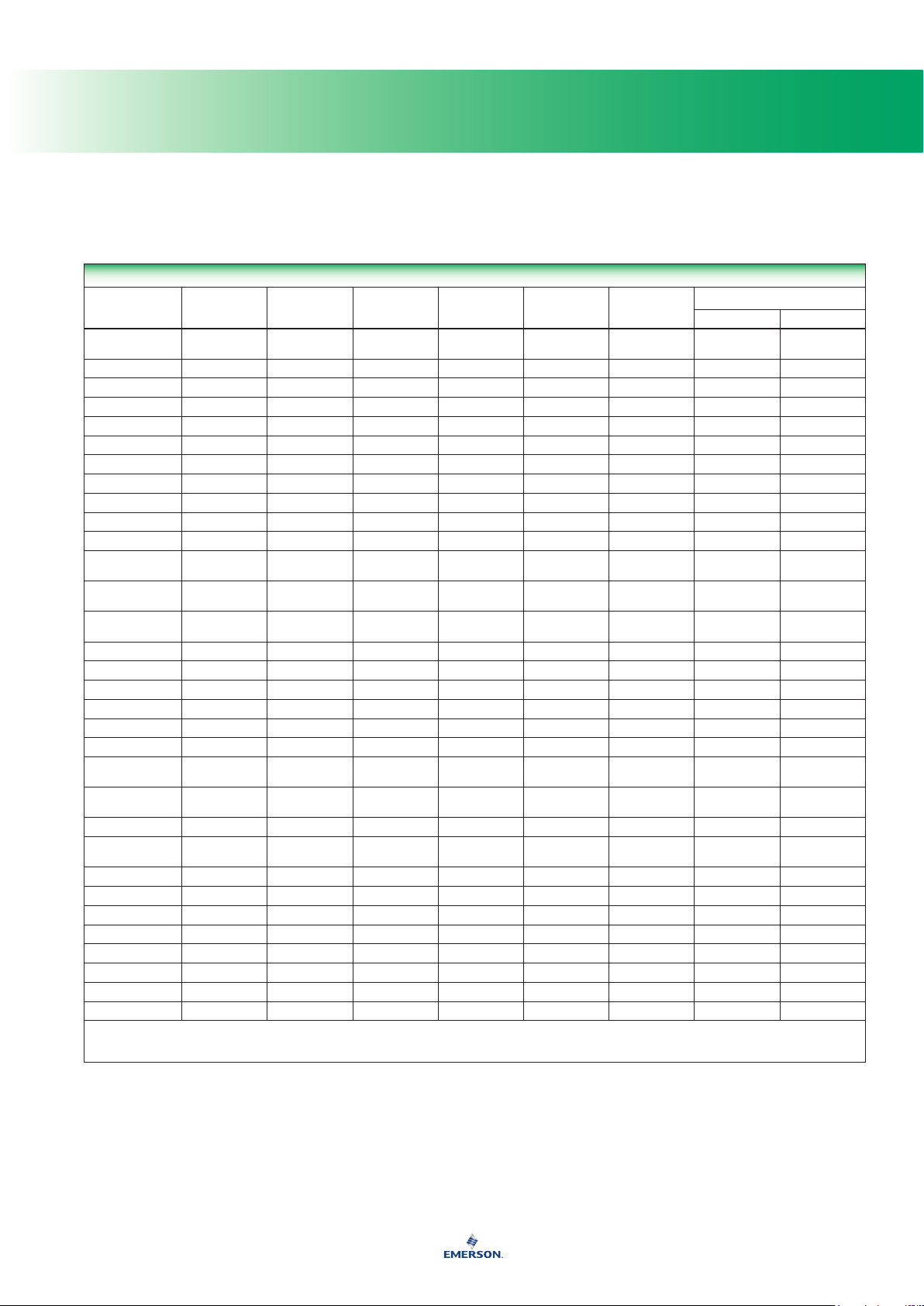
681
Te c h n i c a l
Conversions, Equivalents, and Physical Data
Physical Constants of Various Fluids (continued)
FLUID FORMULA
Magnesium
(1)
Chloride
MgCl
2
MOLECULAR
WEIGHT
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 1.22 - - - -
BOILING POINT
(°F AT 14.696
PSIA)
Mercury Hg 200.61 670 - - - - - - - - - - - - 13.6 6.93
Methyl Bromide CH3Br 94.95 38 13 376 - - - - 1.73 3.27
Methyl Chloride CH3Cl 50.49 -11 59 290 969 0.99 1.74
Naphthalene C10H
Nitric Acid HNO
Nitrogen N
8
3
2
128.16 424 - - - - - - - - - - - - 1.14 4.43
63.02 187 - - - - - - - - - - - - 1.5 - - - -
28.02 -320 - - - - -233 493 0.81
Oil, Vegetable - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 0.91 to 0.94 - - - -
Oxygen O
Phosgene COCl
Phosphoric Acid H3PO
Potassium
Carbonate
Potassium
Chloride
Potassium
Hydroxide
(1)
(1)
(1)
K2CO
KCl - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 1.16 - - - -
KOH - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 1.24 - - - -
2
2
4
3
32 -297 - - - - -181 737 1.14
98.92 47 10.7 360 823 1.39 3.42
98.00 415 - - - - - - - - - - - - 1.83 - - - -
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 1.24 - - - -
Refrigerant 11 CCl3F 137.38 75 13.4 388 635 - - - - 5.04
Refrigerant 12 CCl2F
Refrigerant 13 CClF
2
3
120.93 -22 70.2 234 597 - - - - 4.2
104.47 -115 458.7 84 561 - - - - - - - -
Refrigerant 21 CHCl2F 102.93 48 8.4 353 750 - - - - 3.82
Refrigerant 22 CHClF
Refrigerant 23 CHF
Sodium
(1)
Chloride
Sodium
(1)
Hydroxide
Sodium Sulfate
Sodium
Thiosulfate
(1)
(1)
NaCl - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 1.19 - - - -
NaOH - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 1.27 - - - -
Na2SO
Na2SO
2
3
4
3
86.48 -41 122.5 205 716 - - - - - - - -
70.02 -119 635 91 691 - - - - - - - -
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 1.24 - - - -
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 1.23 - - - -
Starch (C6H10O5)x - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 1.50 - - - -
Sugar Solutions
Sulfuric Acid H2SO
Sulfer Dioxide SO
(1)
C12H22O
11
4
2
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 1.10 - - - -
98.08 626 - - - - - - - - - - - - 1.83 - - - -
64.6 14 34.4 316 1145 1.39 2.21
Turpentine - - - - - - - - 320 - - - - - - - - - - - - 0.87 - - - -
Water H2O 18.016 212 0.9492
Zinc Chloride
Zinc Sulfate
1. Aqueous Solution - 25% by weight of compound.
2. Vapor pressure in psia at 100°F.
3. Density of liquid, gm/ml at normal boiling point.
(1)
(1)
ZnCl
ZnSO
2
4
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 1.24 - - - -
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 1.31 - - - -
VAPOR
PRESSURE
AT 70°F (PSIG)
(2)
CRITICAL
TEMPERATURE
(°F)
CRITICAL
PRESSURE
(PSIA)
SPECIFIC GRAVITY
Liquid 60°F/60°F Gas
(3)
(3)
706 3208 1.00 0.62
0.97
1.105
Page 24
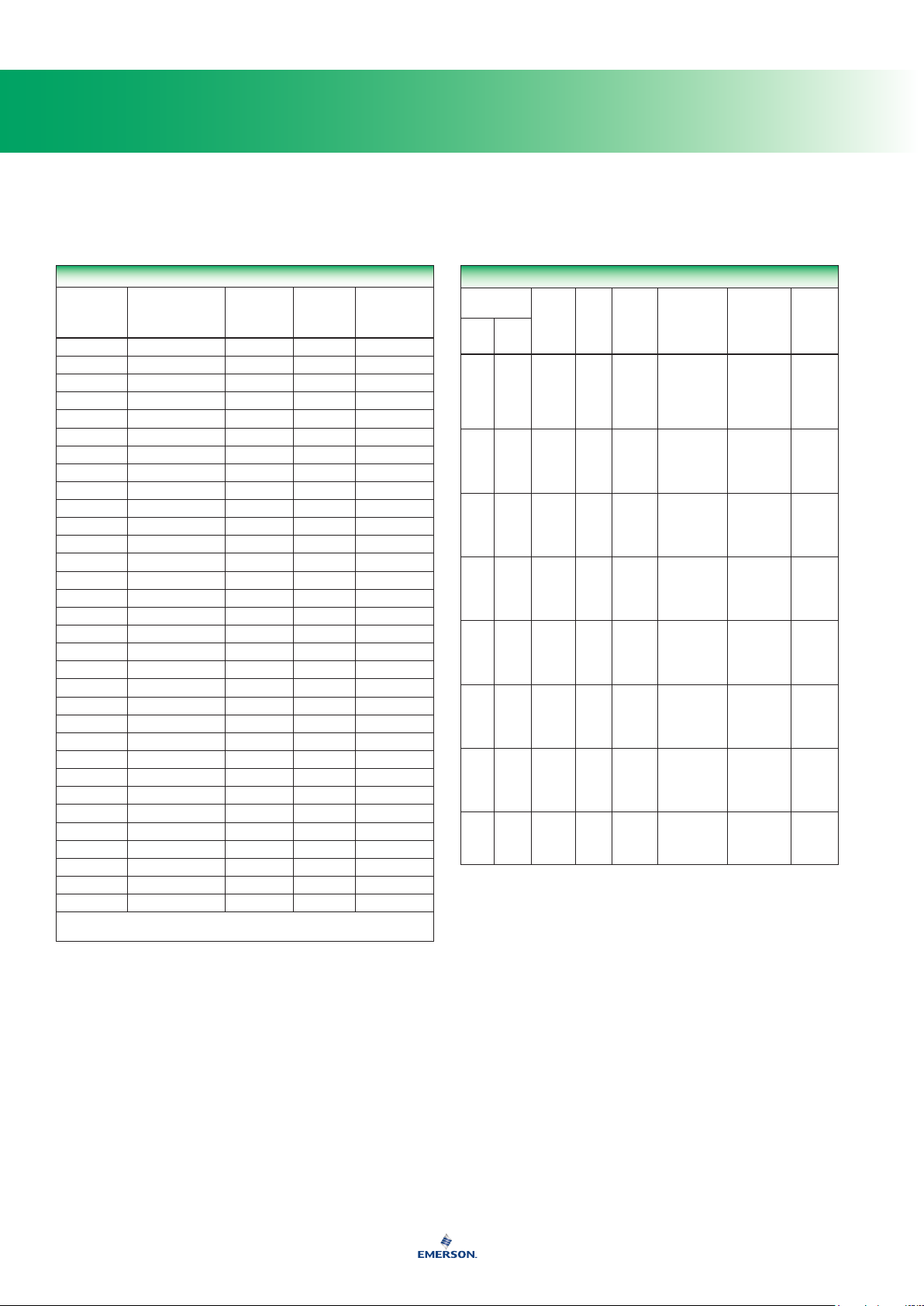
682
Te c h n i c a l
Conversions, Equivalents, and Physical Data
Properties of Water
TEMPERATURE
OF WATER (°F)
32 0.0885 8.345 1.0013 0.00199
40 0.1217 8.345 1.0013 0.00199
50 0.1781 8.340 1.0007 0.00199
60 0.2653 8.334 1.0000 0.00199
70 0.3631 8.325 0.9989 0.00200
80 0.5069 8.314 0.9976 0.00200
90 0.6982 8.303 0.9963 0.00200
100 0.9492 8.289 0.9946 0.00201
110 1.2748 8.267 0.9919 0.00201
120 1.6924 8.253 0.9901 0.00200
130 2.2225 8.227 0.9872 0.00202
140 2.8886 8.207 0.9848 0.00203
150 3.718 8.182 0.9818 0.00203
160 4.741 8.156 0.9786 0.00204
170 5.992 8.127 0.9752 0.00205
180 7.510 8.098 0.9717 0.00205
190 9.339 8.068 0.9681 0.00206
200 11.526 8.039 0.9646 0.00207
210 14.123 8.005 0.9605 0.00208
212 14.696 7.996 0.9594 0.00208
220 17.186 7.972 0.9566 0.00209
240 24.969 7.901 0.9480 0.00210
260 35.429 7.822 0.9386 0.00211
280 49.203 7.746 0.9294 0.00215
300 67.013 7.662 0.9194 0.00217
350 134.63 7.432 0.8918 0.00224
400 247.31 7.172 0.8606 0.00232
450 422.6 6.892 0.8270 0.00241
500 680.8 6.553 0.7863 0.00254
550 1045.2 6.132 0.7358 0.00271
600 1542.9 5.664 0.6796 0.00294
700 3093.7 3.623 0.4347 0.00460
1. Multiply ow in pounds per hour by the factor to get equivalent ow in gallons per
minute. Weight per gallon is based on 7.48 gallons per cubic foot.
SATURATION
PRESSURE (POUNDS
PER SQUARE INCH
ABSOLUTE)
WEIGHT
(POUNDS PER
GALLON)
SPECIFIC
GRAVITY
60°F/60°F
CONVERSION
FACTOR
LBS/HR TO GPM
Properties of Saturated Steam
ABSOLUTE
(1)
,
PRESSURE
Inches
PSIA
of Hg
0.20
0.25
0.30
0.35
0.40
0.45
0.50
0.60
0.70
0.80
0.90
1.0
1.2
1.4
1.6
1.8
2.0
2.2
2.4
2.6
2.8
3.0
3.5
4.0
4.5
5.0
10.18
5.5
11.20
6.0
12.22
6.5
13.23
7.0
14.25
7.5
15.27
8.0
16.29
8.5
17.31
9.0
18.32
9.5
19.34
10.0
20.36
11.0
22.40
12.0
24.43
13.0
26.47
14.0
28.50
0.41
0.51
0.61
0.71
0.81
0.92
1.02
1.22
1.43
1.63
1.83
2.04
2.44
2.85
3.26
3.66
4.07
4.48
4.89
5.29
5.70
6.11
7.13
8.14
9.16
VACUUM
(INCHES
OF HG)
29.51
29.41
29.31
29.21
29.11
29.00
28.90
28.70
28.49
28.29
28.09
27.88
27.48
27.07
26.66
26.26
25.85
25.44
25.03
24.63
24.22
23.81
22.79
21.78
20.76
19.74
18.72
17.70
16.69
15.67
14.65
13.63
12.61
11.60
10.58
9.56
7.52
5.49
3.45
1.42
TEMP.
(°F)
53.14
59.30
64.47
68.93
72.86
76.38
79.58
85.21
90.08
94.38
98.24
101.74
107.92
113.26
117.99
122.23
126.08
129.62
132.89
135.94
138.79
141.48
147.57
152.97
157.83
162.24
166.30
170.06
173.56
176.85
179.94
182.86
185.64
188.28
190.80
193.21
197.75
201.96
205.88
209.56
HEAT
OF THE
LIQUID
(BTU/LB.)
21.21
27.36
32.52
36.97
40.89
44.41
47.60
53.21
58.07
62.36
66.21
69.70
75.87
81.20
85.91
90.14
93.99
97.52
100.79
103.83
106.68
109.37
115.46
120.86
125.71
130.13
134.19
137.96
141.47
144.76
147.86
150.79
153.57
156.22
158.75
161.17
165.73
169.96
173.91
177.61
LATENT HEAT
OF
EVAPORATION
(BTU/LB.)
1063.8
1060.3
1057.4
1054.9
1052.7
1050.7
1048.8
1045.7
1042.9
1040.4
1038.3
1036.3
1032.7
1029.6
1026.9
1024.5
1022.2
1020.2
1018.3
1016.5
1014.8
1013.2
1009.6
1006.4
1003.6
1001.0
998.5
996.2
994.1
992.1
990.2
988.5
986.8
985.2
983.6
982.1
979.3
976.6
974.2
971.9
TOTAL HEAT
OF
STEAM HG
(BTU/LB.)
1085.0
1087.7
1090.0
1091.9
1093.6
1095.1
1096.4
1098.9
1101.0
1102.8
1104.5
1106.0
1108.6
1110.8
1112.8
1114.6
1116.2
1117.7
1119.1
1120.3
1121.5
1122.6
1125.1
1127.3
1129.3
1131.1
1132.7
1134.2
1135.6
1136.9
1138.1
1139.3
1140.4
1141.4
1142.3
1143.3
1145.0
1146.6
1148.1
1149.5
SPECIFIC
VOLUME
(CUBIC
FT./LB.)
1526.0
1235.3
1039.5
898.5
791.9
708.5
641.4
540.0
466.9
411.7
368.4
333.6
280.9
243.0
214.3
191.8
173.73
158.85
146.38
135.78
126.65
67.24
61.98
57.50
53.64
50.29
67.24
61.98
57.50
53.64
50.29
47.34
44.73
42.40
40.31
38.42
35.14
32.40
30.06
28.04
- continued -
Page 25
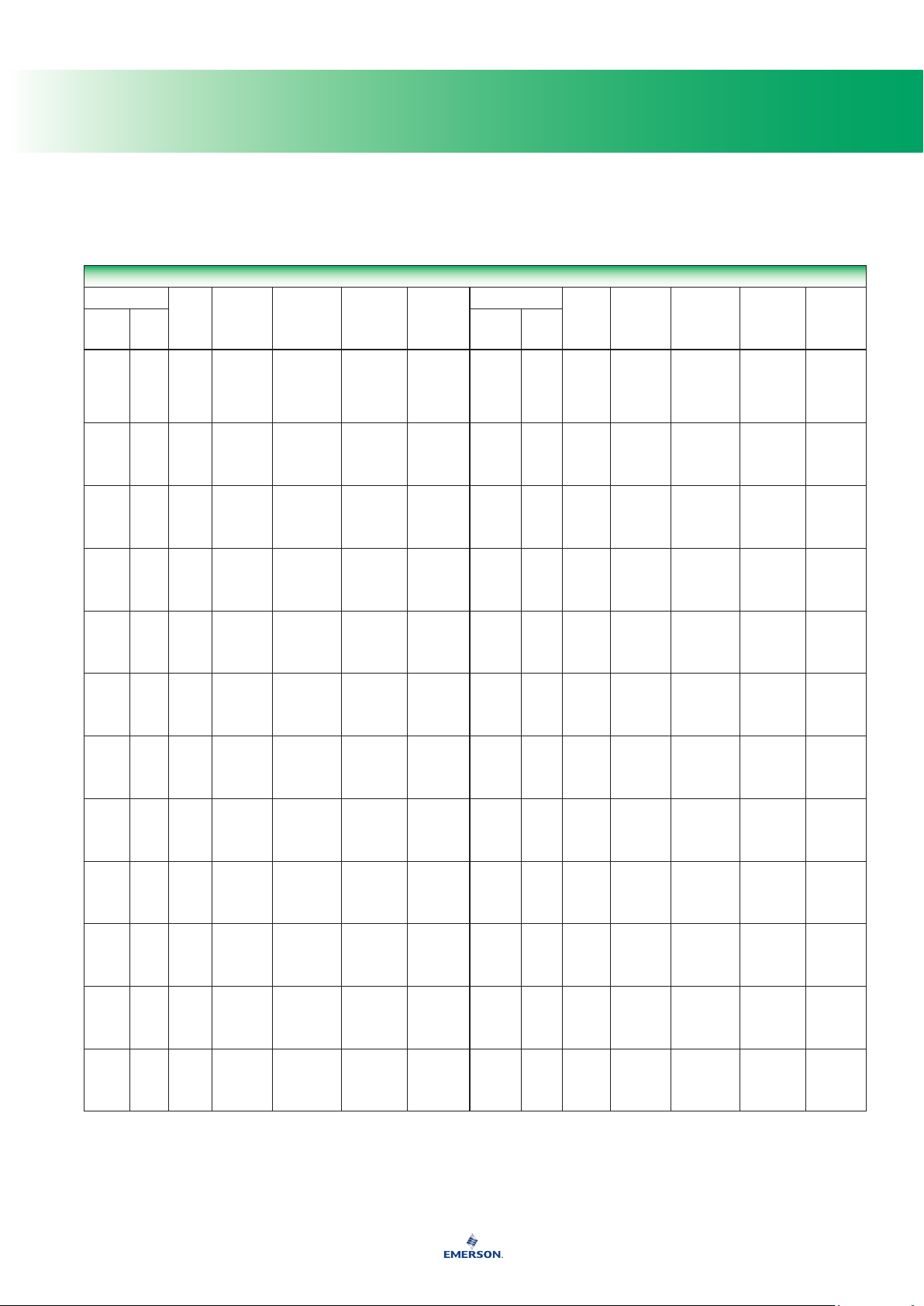
683
Te c h n i c a l
Conversions, Equivalents, and Physical Data
Properties of Saturated Steam (continued)
PRESSURE (PSI)
AbsoluteP’Gauge
14.696
15.0
16.0
17.0
18.0
19.0
20.0
21.0
22.0
23.0
24.0
25.0
26.0
27.0
28.0
29.0
30.0
31.0
32.0
33.0
34.0
35.0
36.0
37.0
38.0
39.0
40.0
41.0
42.0
43.0
44.0
45.0
46.0
47.0
48.0
49.0
50.0
51.0
52.0
53.0
54.0
55.0
56.0
57.0
58.0
59.0
60.0
61.0
62.0
63.0
64.0
65.0
66.0
67.0
68.0
69.0
70.0
71.0
72.0
73.0
74.0
0.0
0.3
1.3
2.3
3.3
4.3
5.3
6.3
7.3
8.3
9.3
10.3
11.3
12.3
13.3
14.3
15.3
16.3
17.3
18.3
19.3
20.3
21.3
22.3
23.3
24.3
25.3
26.3
27.3
28.3
29.3
30.3
31.3
32.3
33.3
34.3
35.3
36.3
37.3
38.3
39.3
40.3
41.3
42.3
43.3
44.3
45.3
46.3
47.3
48.3
49.3
50.3
51.3
52.3
53.3
54.3
55.3
56.3
57.3
58.3
59.3
P
TEMP.
(°F)
212.00
213.03
216.32
219.44
222.41
225.24
227.96
230.57
233.07
235.49
237.82
240.07
242.25
244.36
246.41
248.40
250.33
252.22
254.05
255.84
257.58
259.28
260.95
262.57
264.16
265.72
267.25
268.74
270.21
271.64
273.05
274.44
275.80
277.13
278.45
279.74
281.01
282.26
283.49
284.70
285.90
287.07
288.28
289.37
290.50
291.61
292.71
293.79
294.85
295.90
296.94
297.97
298.99
299.99
300.98
301.96
302.92
303.88
304.83
305.76
306.68
HEAT OF
THE LIQUID
(BTU/LB)
180.07
181.11
184.42
187.56
190.56
193.42
196.16
198.79
201.33
203.78
206.14
208.42
210.62
212.75
214.83
216.86
218.82
220.73
222.59
224.41
226.18
227.91
229.60
231.26
232.89
234.48
236.03
237.55
239.04
240.51
241.95
243.36
244.75
246.12
247.47
248.79
250.09
251.37
252.63
253.87
255.09
256.30
257.50
258.67
259.82
260.96
262.09
263.20
264.30
265.38
266.45
267.50
268.55
269.58
270.60
291.61
272.61
273.60
274.57
275.54
276.49
LATENT HEAT
OF
EVAPORATION
(BTU/LB)
970.3
969.7
967.6
965.5
963.6
961.9
960.1
958.4
956.8
955.2
953.7
952.1
950.7
949.3
947.9
946.5
945.3
944.0
942.8
941.6
940.3
939.2
938.0
936.9
935.8
934.7
933.7
932.6
931.6
930.6
929.6
928.6
927.7
926.7
925.8
924.9
924.0
923.0
922.2
921.3
920.5
919.6
918.8
917.9
917.1
916.3
915.5
914.7
913.9
913.1
912.3
911.6
910.8
910.1
909.4
908.7
907.9
907.2
906.5
905.8
905.1
TOTAL HEAT
OF STEAM H
(BTU/LB)
1150.4
1150.8
1152.0
1153.1
1154.2
1155.3
1156.3
1157.2
1158.1
1159.0
1159.8
1160.6
1161.3
1162.0
1162.7
1163.4
1164.1
1164.7
1165.4
1166.0
1166.5
1167.1
1167.6
1168.2
1168.7
1169.2
1169.7
1170.2
1170.7
1171.1
1171.6
1172.0
1172.4
1172.9
1173.3
1173.7
1174.1
1174.4
1174.8
1175.2
1175.6
1175.9
1176.3
1176.6
1176.9
1177.3
1177.6
1177.9
1178.2
1178.5
1178.8
1179.1
1179.4
1179.7
1180.0
1180.3
1180.6
1180.8
1181.1
1181.3
1181.6
SPECIFIC
VOLUME
g
(FT3/LB)
26.80
26.29
24.72
23.39
22.17
21.08
20.089
19.192
18.375
17.627
16.938
16.303
15.715
15.170
14.663
14.189
13.746
13.330
12.940
12.572
12.226
11.898
11.588
11.294
11.150
10.750
10.498
10.258
10.029
9.810
9.601
9.401
9.209
9.025
8.848
8.678
8.515
8.359
8.208
8.062
7.922
7.787
7.656
7.529
7.407
7.289
7.175
7.064
6.957
6.853
6.752
6.655
6.560
6.468
6.378
6.291
6.206
6.124
6.044
5.966
5.890
∇
PRESSURE (PSI)
AbsoluteP’Gauge
- - - -
75.0
76.0
77.0
78.0
79.0
80.0
81.0
82.0
83.0
84.0
85.0
86.0
87.0
88.0
89.0
90.0
91.0
92.0
93.0
94.0
95.0
96.0
97.0
98.0
99.0
100.0
101.0
102.0
103.0
104.0
105.0
106.0
107.0
108.0
109.0
110.0
111.0
112.0
113.0
114.0
115.0
116.0
117.0
118.0
119.0
120.0
121.0
122.0
123.0
124.0
125.0
126.0
127.0
128.0
129.0
130.0
131.0
132.0
133.0
134.0
P
- - - -
60.3
61.3
62.3
63.3
64.3
65.3
66.3
67.3
68.3
69.3
70.3
71.3
72.3
73.3
74.3
75.3
76.3
77.3
78.3
79.3
80.3
81.3
82.3
83.3
84.3
85.3
86.3
87.3
88.3
89.3
90.3
91.3
92.3
93.3
94.3
95.3
96.3
97.3
98.3
99.3
100.3
101.3
102.3
103.3
104.3
105.3
106.3
107.3
108.3
109.3
110.3
111.3
112.3
113.3
114.3
115.3
116.3
117.3
118.3
119.3
TEMP.
(°F)
- - - -
307.60
308.50
309.40
310.29
311.16
312.03
312.89
313.74
314.59
315.42
316.25
317.07
317.88
318.68
319.48
320.27
321.06
321.83
322.60
323.36
324.12
324.87
325.61
326.35
327.08
327.81
328.53
329.25
329.96
330.66
331.36
332.05
332.74
333.42
334.10
334.77
335.44
336.11
336.77
337.42
338.07
338.72
339.36
339.99
340.62
341.25
341.88
342.50
343.11
343.72
344.33
344.94
345.54
346.13
346.73
347.32
347.90
348.48
349.06
349.64
HEAT OF
THE LIQUID
(BTU/LB)
- - - -
277.43
278.37
279.30
280.21
281.12
282.02
282.91
283.79
284.66
285.53
286.39
287.24
288.08
288.91
289.74
290.56
291.38
292.18
292.98
293.78
294.56
295.34
296.12
296.89
297.65
298.40
299.15
299.90
300.64
301.37
302.10
302.82
303.54
304.26
304.97
305.66
306.37
307.06
307.75
308.43
309.11
309.79
310.46
311.12
311.78
312.44
313.10
313.75
314.40
315.04
315.68
316.31
316.94
317.57
318.19
318.81
319.43
320.04
320.65
321.25
LATENT HEAT
OF
EVAPORATION
(BTU/LB)
- - - -
904.5
903.7
903.1
902.4
901.7
901.1
900.4
899.7
899.1
898.5
897.8
897.2
896.5
895.9
895.3
894.7
894.1
893.5
892.9
892.3
891.7
891.1
890.5
889.9
889.4
888.8
888.2
887.6
887.1
886.5
886.0
885.4
884.9
884.3
883.7
883.2
882.6
882.1
881.6
881.1
880.6
880.0
879.5
879.0
878.4
877.9
877.4
876.9
876.4
875.9
875.4
874.9
874.4
873.9
873.4
872.9
872.5
872.0
871.5
871.0
TOTAL HEAT
OF STEAM H
(BTU/LB)
- - - -
1181.9
1182.1
1182.4
1182.6
1182.8
1183.1
1183.3
1183.5
1183.8
1184.0
1184.2
1184.4
1184.6
1184.8
1185.1
1185.3
1185.5
1185.7
1185.9
1186.1
1186.2
1186.4
1186.6
1186.8
1187.0
1187.2
1187.4
1187.5
1187.7
1187.9
1188.1
1188.2
1188.4
1188.6
1188.7
1188.9
1189.0
1189.2
1189.4
1189.5
1189.7
1189.8
1190.0
1190.1
1190.2
1190.4
1190.5
1190.7
1190.8
1190.9
1191.1
1191.2
1191.3
1191.5
1191.6
1191.7
1191.9
1192.0
1192.1
1192.2
SPECIFIC
VOLUME
g
∇
(FT3/LB)
- - - -
5.816
5.743
5.673
5.604
5.537
5.472
5.408
5.346
5.285
5.226
5.168
5.111
5.055
5.001
4.948
4.896
4.845
4.796
4.747
4.699
4.652
4.606
4.561
4.517
4.474
4.432
4.391
4.350
4.310
4.271
4.232
4.194
4.157
4.120
4.084
4.049
4.015
3.981
3.947
3.914
3.882
3.850
3.819
3.788
3.758
3.728
3.699
3.670
3.642
3.614
3.587
3.560
3.533
3.507
3.481
3.455
3.430
3.405
3.381
3.357
- continued -
Page 26

684
Te c h n i c a l
Conversions, Equivalents, and Physical Data
Properties of Saturated Steam (continued)
PRESSURE (PSI)
AbsoluteP’Gauge
135.0
136.0
137.0
138.0
139.0
140.0
141.0
142.0
143.0
144.0
145.0
146.0
147.0
148.0
149.0
150.0
152.0
154.0
156.0
158.0
160.0
162.0
164.0
166.0
168.0
170.0
172.0
174.0
176.0
178.0
180.0
182.0
184.0
186.0
188.0
190.0
192.0
194.0
196.0
198.0
200.0
205.0
210.0
215.0
220.0
225.0
230.0
235.0
240.0
245.0
250.0
255.0
260.0
265.0
270.0
275.0
280.0
285.0
290.0
295.0
300.0
320.0
340.0
360.0
380.0
P
120.3
121.3
122.3
123.3
124.3
125.3
126.3
127.3
128.3
129.3
130.3
131.3
132.3
133.3
134.3
135.3
137.3
139.3
141.3
143.3
145.3
147.3
149.3
151.3
153.3
155.3
157.3
159.3
161.3
163.3
165.3
167.3
169.3
171.3
173.3
175.3
177.3
179.3
181.3
183.3
185.3
190.3
195.3
200.3
205.3
210.3
215.3
220.3
225.3
230.3
235.3
240.3
245.3
250.3
255.3
260.3
265.3
270.3
275.3
280.3
285.3
305.3
325.3
345.3
365.3
TEMP.
(°F)
350.21
350.78
351.35
351.91
352.47
353.02
353.57
354.12
354.67
355.21
355.76
356.29
356.83
357.36
357.89
358.42
359.46
360.49
361.52
362.53
363.53
364.53
365.51
366.48
367.45
368.41
369.35
370.29
371.22
372.14
373.06
373.96
374.86
375.75
376.64
377.51
378.38
379.24
380.10
380.95
381.79
383.86
385.90
387.89
389.86
391.79
393.68
395.54
397.37
399.18
400.95
402.70
404.42
406.11
407.78
409.43
411.05
412.65
414.23
415.79
417.33
423.29
428.97
434.40
439.60
HEAT OF
THE LIQUID
(BTU/LB)
321.85
322.45
323.05
323.64
324.23
324.82
325.40
325.98
326.56
327.13
327.70
328.27
328.83
329.39
329.95
330.51
331.61
332.70
333.79
334.86
335.93
336.98
338.02
339.05
340.07
341.09
342.10
343.10
344.09
345.06
346.03
347.00
347.96
348.92
349.86
350.79
351.72
352.64
353.55
354.46
355.36
357.58
359.77
361.91
364.02
366.09
368.13
370.14
372.12
374.08
376.00
377.89
379.76
381.60
383.42
385.21
386.98
388.73
390.46
392.16
393.84
400.39
406.66
412.67
418.45
LATENT HEAT
OF
EVAPORATION
(BTU/LB)
870.6
870.1
869.6
869.1
868.7
868.2
867.7
867.2
866.7
866.3
865.8
865.3
864.9
864.5
864.0
863.6
862.7
851.8
860.9
860.0
859.2
858.3
857.5
856.6
855.7
854.9
854.1
853.3
852.4
851.6
850.8
850.0
849.2
848.4
847.6
846.8
846.1
845.3
844.5
843.7
843.0
841.0
839.2
837.4
835.6
833.8
832.0
830.3
828.5
826.8
825.1
823.4
821.8
820.1
818.5
816.9
815.3
813.7
812.1
810.5
809.0
803.0
797.1
797.4
785.8
TOTAL HEAT
OF STEAM H
(BTU/LB)
1192.4
1192.5
1192.6
1192.7
1192.9
1193.0
1193.1
1193.2
1193.3
1193.4
1193.5
1193.6
1193.8
1193.9
1194.0
1194.1
1194.3
1194.5
1194.7
1194.9
1195.1
1195.3
1195.5
1195.7
1195.8
1196.0
1196.2
1196.4
1196.5
1196.7
1196.9
1197.0
1197.2
1197.3
1197.5
1197.6
1197.8
1197.9
1198.1
1198.2
1198.4
1198.7
1199.0
1199.3
1199.6
1199.9
1200.1
1200.4
1200.6
1200.9
1201.1
1201.3
1201.5
1201.7
1201.9
1202.1
1202.3
1202.4
1202.6
1202.7
1202.8
1203.4
1203.7
1204.1
1204.3
SPECIFIC
g
VOLUME
(FT3/LB)
3.333
3.310
3.287
3.264
3.242
3.220
3.198
3.177
3.155
3.134
3.114
3.094
3.074
3.054
3.034
3.015
2.977
2.940
2.904
2.869
2.834
2.801
2.768
2.736
2.705
2.675
2.645
2.616
2.587
2.559
2.532
2.505
2.479
2.454
2.429
2.404
2.380
2.356
2.333
2.310
2.288
2.234
2.183
2.134
2.087
2.0422
1.9992
1.9579
1.9183
1.8803
1.8438
1.8086
1.7748
1.7422
1.7107
1.6804
1.6511
1.6228
1.5954
1.5689
1.5433
1.4485
1.3645
1.2895
1.2222
∇
PRESSURE (PSI)
AbsoluteP’Gauge
400.0
420.0
440.0
460.0
480.0
500.0
520.0
540.0
560.0
580.0
600.0
620.0
640.0
660.0
680.0
700.0
720.0
740.0
760.0
780.0
800.0
820.0
840.0
860.0
880.0
900.0
920.0
940.0
960.0
980.0
1000.0
1050.0
1100.0
1150.0
1200.0
1250.0
1300.0
1350.0
1400.0
1450.0
1500.0
1600.0
1700.0
1800.0
1900.0
2000.0
2100.0
2200.0
2300.0
2400.0
2500.0
2600.0
2700.0
2800.0
2900.0
3000.0
3100.0
3200.0
3206.2
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
P
385.3
405.3
425.3
445.3
465.3
485.3
505.3
525.3
545.3
565.3
585.3
605.3
625.3
645.3
665.3
685.3
705.3
725.3
745.3
765.3
785.3
805.3
825.3
845.3
865.3
885.3
905.3
925.3
945.3
965.3
985.3
1035.3
1085.3
1135.3
1185.3
1235.3
1285.3
1335.3
1385.3
1435.3
1485.3
1585.3
1685.3
1785.3
1885.3
1985.3
2085.3
2185.3
2285.3
2385.3
2485.3
2585.3
2685.3
2785.3
2885.3
2985.3
3085.3
3185.3
3191.5
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
TEMP.
(°F)
444.59
449.39
454.02
458.50
462.82
467.01
471.07
475.01
478.85
482.58
486.21
489.75
493.21
496.58
499.88
503.10
506.25
509.34
512.36
505.33
518.23
521.08
523.88
526.63
529.33
531.98
534.59
537.16
539.68
542.17
544.61
550.57
556.31
561.86
567.22
572.42
577.46
582.35
587.10
591.73
596.23
604.90
613.15
621.03
628.58
635.82
642.77
649.46
655.91
662.12
668.13
673.94
679.55
684.99
690.26
695.36
700.31
705.11
705.40
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
HEAT OF
THE LIQUID
(BTU/LB)
424.0
429.4
434.6
439.7
444.6
449.4
454.1
458.6
463.0
467.4
471.6
475.7
479.8
483.8
487.7
491.5
495.3
499.0
502.6
506.2
509.7
513.2
516.6
520.0
523.3
526.6
529.8
533.0
536.2
539.3
542.4
550.0
557.4
565.6
571.7
578.6
585.4
592.1
598.7
605.2
611.6
624.1
636.3
648.3
660.1
671.7
683.3
694.8
706.5
718.4
730.6
743.0
756.2
770.1
785.4
802.5
825.0
872.4
902.7
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
LATENT HEAT
OF
EVAPORATION
(BTU/LB)
780.5
775.2
770.0
764.9
759.9
755.0
750.1
745.4
740.8
736.1
731.6
727.2
722.7
718.3
714.0
709.7
705.4
701.2
697.1
692.9
688.9
684.8
680.8
676.8
672.8
668.8
664.9
661.0
657.1
653.3
649.4
639.9
630.4
621.0
611.7
602.4
593.2
584.0
574.7
565.5
556.3
538.0
519.6
501.1
482.4
463.4
444.1
424.4
403.9
382.7
360.5
337.2
312.1
284.7
253.6
217.8
168.1
62.0
0.0
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
TOTAL HEAT
OF STEAM H
(BTU/LB.)
1204.5
1204.6
1204.6
1204.6
1204.5
1204.4
1204.2
1204.0
1203.8
1203.5
1203.2
1202.9
1202.5
1202.1
1201.7
1201.2
1200.7
1200.2
1199.7
1199.1
1198.6
1198.0
1197.4
1196.8
1196.1
1195.4
1194.7
1194.0
1193.3
1192.6
1191.8
1189.9
1187.8
1185.6
1183.4
1181.0
1178.6
1176.1
1173.4
1170.7
1167.9
1162.1
1155.9
1149.4
1142.4
1135.1
1127.4
1119.2
1110.4
1101.1
1091.1
1080.2
1068.3
1054.8
1039.0
1020.3
993.1
934.4
902.7
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
SPECIFIC
VOLUME
g
∇
(CU. FT./LB.)
1.1613
1.1061
1.0556
1.0094
0.9670
0.9278
0.7815
0.8578
0.8265
0.7973
0.7698
0.7440
0.7198
0.6971
0.6757
0.6554
0.6362
0.6180
0.6007
0.5843
0.5687
0.5538
0.5396
0.5260
0.5130
0.5006
0.4886
0.4772
0.4663
0.4557
0.4456
0.4218
0.4001
0.3802
0.619
0.3450
0.3293
0.3148
0.3012
0.2884
0.2765
0.2548
0.2354
0.2179
0.2021
0.1878
0.1746
0.1625
0.1513
0.1407
0.1307
0.1213
0.1123
0.1035
0.0947
0.0858
0.0753
0.0580
0.0503
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
Page 27

685
Te c h n i c a l
Conversions, Equivalents, and Physical Data
Properties of Saturated Steam (Metric)
TEMPERATURE, °K PRESSURE, BAR
150 6.30 to 11 1.073 to 3 9.55 + 9 - 539.6 2273 - 2.187 16.54
160
170
180
190
200
210
220
230
240
250
255
260
265
270
273.15
273.15
275
280
285
290
295
300
305
310
315
320
325
330
335
340
345
350
355
360
365
370
373.15
375
380
385
390
400
410
420
430
440
450
460
470
480
490
500
510
520
530
540
550
560
570
580
590
600
610
620
625
630
635
640
645
647.31
7.72 to 10
7.29 to 9
5.38 to 8
3.23 to 7
1.62 to 6
7.01 to 6
2.65 to 5
8.91 to 5
3.72 to 4
7.59 to 4
1.23 to 3
1.96 to 3
3.06 to 3
4.69 to 3
6.11 to 3
0.00611
0.00697
0.00990
0.01387
0.01917
0.02617
0.03531
0.04712
0.06221
0.08132
0.01053
0.01351
0.01719
0.02167
0.02713
0.3372
0.4163
0.5100
0.6209
0.7514
0.9040
1.0133
1.0815
1.2869
1.5233
1.794
2.455
3.302
4.370
5.699
7.333
9.319
11.71
14.55
17.90
21.83
26.40
31.66
37.70
44.58
52.38
61.19
71.08
82.16
94.51
108.3
123.5
137.3
159.1
169.1
179.1
190.9
202.7
215.2
221.2
VOLUME, m3/kg ENTHALPY, kJ/kg ENTROPY, kJ/(kg x °K)
Condensed Vapor Condensed Vapor Condensed Vapor
1.074 to 3
1.076 to 3
1.077 to 3
1.078 to 3
1.079 to 3
1.081 to 3
1.082 to 3
1.084 to 3
1.085 to 3
1.087 to 3
1.087 to 3
1.088 to 3
1.089 to 3
1.090 to 3
1.091 to 3
1.000 to 3
1.000 to 3
1.000 to 3
1.000 to 3
1.001 to 3
1.002 to 3
1.003 to 3
1.005 to 3
1.007 to 3
1.009 to 3
1.011 to 3
1.013 to 3
1.016 to 3
1.018 to 3
1.021 to 3
1.024 to 3
1.027 to 3
1.030 to 3
1.034 to 3
1.038 to 3
1.041 to 3
1.044 to 3
1.045 to 3
1.049 to 3
1.053 to 3
1.058 to 3
1.067 to 3
1.077 to 3
1.088 to 3
1.099 to 3
1.110 to 3
1.123 to 3
1.137 to 3
1.152 to 3
1.167 to 3
1.184 to 3
1.203 to 3
1.222 to 3
1.244 to 3
1.268 to 3
1.294 to 3
1.323 to 3
1.355 to 3
1.392 to 3
1.433 to 3
1.482 to 3
1.541 to 3
1.612 to 3
1.705 to 3
1.778 to 3
1.856 to 3
1.935 to 3
2.075 to 3
2.351 to 3
3.170 to 3
9.62 + 8
1.08 + 8
1.55 + 7
2.72 + 6
5.69 + 5
1.39 + 5
3.83 + 4
1.18 + 4
4.07 + 3
1.52 + 3
956.4
612.2
400.4
265.4
206.3
206.3
181.7
130.4
99.4
69.7
51.94
39.13
27.90
22.93
17.82
13.98
11.06
8.82
7.09
5.74
4.683
3.846
3.180
2.645
2.212
1.861
1.679
1.574
1.337
1.142
0.980
0.731
0.553
0.425
0.331
0.261
0.208
0.167
0.136
0.111
0.0922
0.0776
0.0631
0.0525
0.0445
0.0375
0.0317
0.0269
0.0228
0.0193
0.0163
0.0137
0.0115
0.0094
0.0085
0.0075
0.0066
0.0057
0.0045
0.0032
- 525.7
- 511.7
- 497.8
- 483.8
- 467.5
- 451.2
- 435.0
- 416.3
- 400.1
- 318.5
- 369.8
- 360.5
- 351.2
- 339.6
- 333.5
0.00
7.80
28.8
49.8
70.7
91.6
112.5
133.4
154.3
175.2
196.1
217.0
237.9
258.8
279.8
300.7
321.7
342.7
363.7
384.7
405.8
419.1
426.8
448.0
469.2
490.4
532.9
575.6
618.6
661.8
705.3
749.2
793.5
838.2
883.4
929.1
975.6
1023
1071
1119
1170
1220
1273
1328
1384
1443
1506
1573
1647
1697
1734
1783
1841
1931
2107
2291
2310
2328
2347
2366
2384
2403
2421
2440
2459
2468
2477
2486
2496
2502
2502
2505
2514
2523
2532
2541
2550
2559
2568
2577
2586
2595
2604
2613
2622
2630
2639
2647
2655
2663
2671
2676
2679
2687
2694
2702
2716
2729
2742
2753
2764
2773
2782
2789
2795
2799
2801
2802
2801
2798
2792
2784
2772
2757
2737
2717
2682
2641
2588
2555
2515
2466
2401
2292
2107
- 2.106
- 2.026
- 1.947
- 1.868
- 1.789
- 1.711
- 1.633
- 1.555
- 1.478
- 1.400
- 1.361
- 1.323
- 1.281
- 1.296
- 1.221
0.000
0.028
0.104
0.178
0.251
0.323
0.393
0.462
0.530
0.597
0.649
0.727
0.791
0.854
0.916
0.977
1.038
1.097
1.156
1.214
1.271
1.307
1.328
1.384
1.439
1.494
1.605
1.708
1.810
1.911
2.011
2.109
2.205
2.301
2.395
2.479
2.581
2.673
2.765
2.856
2.948
3.039
3.132
3.225
3.321
3.419
3.520
3.627
3.741
3.805
3.875
3.950
4.037
4.223
4.443
15.49
14.57
13.76
16.03
12.38
11.79
11.20
10.79
10.35
9.954
9.768
9.590
9.461
9.255
9.158
9.158
9.109
8.890
8.857
8.740
8.627
8.520
8.417
8.318
8.224
8.151
8.046
7.962
7.881
7.804
7.729
7.657
7.588
7.521
7.456
7.394
7.356
7.333
7.275
7.210
7.163
7.058
6.959
6.865
6.775
6.689
6.607
6.528
6.451
6.377
6.312
6.233
6.163
6.093
6.023
5.953
5.882
5.808
5.733
5.654
5.569
5.480
5.318
5.259
5.191
5.115
5.025
4.912
4.732
4.443
Page 28

686
Te c h n i c a l
Conversions, Equivalents, and Physical Data
Properties of Superheated Steam
PRESSURE (PSI)
Absolute P’Gauge
14.696 0.0 212.00
20.0 5.3 227.96
30.0 15.3 250.33
40.0 25.3 267.25
50.0 35.3 281.01
60.0 45.3 292.71
70.0 55.3 302.92
80.0 65.3 312.03
90.0 75.3 320.27
100.0 85.3 327.81
120.0 105.3 341.25
140.0 125.3 353.02
160.0 145.3 363.53
180.0 165.3 373.06
200.0 185.3 381.79
220.0 205.3 389.86
240.0 225.3 397.37
260.0 245.3
280.0 265.3 411.05
300.0 285.3 417.33
320.0 305.3 423.29
340.0 325.3 428.97
360.0 345.3 343.40
∇ = specic volume, cubic feet per pound
hg = total heat of steam, BTU per pound
SAT.
TEMP.
(°F)
P
∇
hg
1221.1
∇
hg
1220.3
∇
16.072
hg
1218.6
∇
12.001
h
1216.9
g
∇
hg
1215.2
∇
hg
1213.4
∇
hg
1211.5
∇
hg
1209.7
∇
hg
1207.7
∇
hg
1205.7
∇
hg
1201.6
∇
hg
1197.3
∇
hg
∇
hg
∇
hg
∇
hg
∇
hg
∇
404.42
hg
∇
hg
∇
hg
∇
hg
∇
hg
∇
hg
360° 400° 440° 480° 500° 600° 700° 800° 900° 1000° 1200°
33.03
24.21
9.557
7.927
6.762
5.888
5.208
4.663
3.844
3.258
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
34.68
1239.9
25.43
1239.2
16.897
1237.9
12.628
1236.5
10.065
1235.1
8.357
1233.6
7.136
1232.1
6.220
1230.7
5.508
1229.1
4.937
1227.6
4.081
1224.4
3.468
1221.1
3.008
1217.6
2.649
1214.0
2.361
1210.3
2.125
1206.5
1.9276
1202.5
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
36.32
1258.8
26.65
1258.2
17.714
1257.0
13.247
1255.9
10.567
1254.7
8.779
1253.5
7.502
1252.3
6.544
1251.1
5.799
1249.8
5.202
1248.6
4.307
1246.0
3.667
1243.3
3.187
1240.6
2.813
1237.8
2.513
1234.9
2.267
1231.9
2.062
1228.8
1.8882
1225.7
1.7388
1222.4
1.6090
1219.1
1.4950
1215.6
1.3941
1212.1
1.3041
1208.4
37.96
1277.6
27.86
1277.1
18.528
1276.2
13.962
1275.2
11.062
1274.2
9.196
1273.2
7.863
1272.2
6.862
1271.1
6.084
1270.1
5.462
1269.0
4.527
1266.9
3.860
1264.7
3.359
1262.4
2.969
1260.2
2.656
1257.8
2.400
1255.4
2.187
1253.0
2.006
1250.5
1.8512
1247.9
1.7165
1245.3
1.5985
1242.6
1.4941
1239.9
1.4012
1237.1
TOTAL TEMPERATURE — °F
38.78
1287.1
28.46
1286.6
18.933
1285.7
14.168
1284.8
11.309
1283.9
9.403
1283.0
8.041
1282.0
7.020
1281.1
6.225
1280.1
5.589
1279.1
4.636
1277.2
3.954
1275.2
3.443
1273.1
3.044
1271.0
2.726
1268.9
2.465
1266.7
2.247
1264.5
2.063
1262.3
1.9047
1260.0
1.7675
1257.6
1.6472
1255.2
1.5410
1252.8
1.4464
1250.3
42.86
1334.8
31.47
1334.4
20.95
1333.8
15.688
1333.1
12.532
1332.5
10.427
1331.8
8.924
1331.1
7.797
1330.5
6.920
1329.8
6.218
1329.1
5.165
1327.7
4.413
1326.4
3.849
1325.0
3.411
1323.5
3.060
1322.1
2.772
1320.7
2.533
1319.2
2.330
1317.7
2.156
1316.2
2.005
1314.7
1.8734
1313.2
1.7569
1311.6
1.6533
1310.1
46.94
1383.2
34.47
1382.9
22.96
1382.4
17.198
1381.9
13.744
1381.4
11.441
1380.9
9.796
1380.4
8.562
1379.9
7.603
1379.4
6.835
1378.9
5.683
1377.8
4.861
1376.8
4.244
1375.7
3.964
1374.7
3.380
1373.6
3.066
1372.6
2.804
1371.5
2.582
1370.4
2.392
1369.4
2.227
1368.3
2.083
1367.2
1.9562
1366.1
1.8431
1365.0
51.00
1432.3
37.46
1432.1
24.96
1431.17
18.702
1431.3
14.950
1430.9
12.449
1430.5
10.662
1430.1
9.322
1429.7
8.279
1429.3
7.446
1428.9
6.195
1428.1
5.301
1427.2
4.631
1426.4
4.110
1425.6
3.693
1424.8
3.352
1424.0
3.068
1432.2
2.827
1422.3
2.621
1421.5
2.442
1420.6
2.285
1419.8
2.147
1419.0
2.025
1418.1
55.07
1482.3
40.45
1482.1
26.95
1481.8
20.20
1481.4
16.152
1481.1
13.452
1480.8
11.524
1480.5
10.077
1480.1
8.952
1479.8
8.052
1479.5
6.702
1478.8
5.738
1478.2
5.015
1477.5
4.452
1476.8
4.002
1476.2
3.634
1475.5
3.327
1474.8
3.067
1474.2
2.845
1473.5
2.652
1472.8
2.483
1472.1
2.334
1471.5
2.202
1470.8
59.13
1533.1
43.44
1533.0
28.95
1532.7
21.70
1532.4
17.352
1532.1
14.454
1531.9
12.383
1531.6
10.830
1531.3
9.623
1531.0
8.656
1530.8
7.207
1530.2
6.172
1529.7
5.396
1529.1
4.792
1528.6
4.309
1528.0
3.913
1527.5
3.584
1526.9
3.305
1526.3
3.066
1525.8
2.859
1525.2
2.678
1524.7
2.518
1524.1
2.376
1523.5
67.25
1637.5
49.41
1637.4
32.93
1637.2
24.69
1637.0
19.747
1636.8
16.451
1636.6
14.097
1636.3
12.332
1636.2
10.959
1635.9
9.860
1635.7
8.212
1635.3
7.035
1634.9
6.152
1634.5
5.466
1634.1
4.917
1633.7
4.467
1633.3
4.093
1632.9
3.776
1632.5
3.504
1632.1
3.269
1631.7
3.063
1631.3
2.881
1630.9
2.719
1630.5
- continued -
Page 29

687
Te c h n i c a l
Conversions, Equivalents, and Physical Data
Properties of Superheated Steam (continued)
PRESSURE
(PSI)
Absolute P’Gauge
380.0 365.3 439.60
400.0 385.3 444.59
420.0 405.3 449.39
440.0 425.3 454.02
460.0 445.3 458.5
480.0 465.3 462.82
500.0 485.3 467.01
520.0 505.3 471.07
540.0 525.3 475.01
560.0 545.3 478.85
580.0 565.3 482.58
600.0 585.3 486.21
620.0 605.0 489.75
640.0 625.3 493.21
660.0 645.3 496.58
680.0 665.3 499.88
700.0 685.3 503.10
750. 735.3 510.86
800.0 785.3 518.23
850.0 835.3 525.26
90.0 885.3 531.98
950.0 935.3 538.42
1000.0 985.3 544.61
∇ = specic volume, cubic feet per pound
hg = total heat of steam, BTU per pound
SAT.
TEMP.
°F
P
∇
hg
∇
hg
∇
hg
∇
hg
∇
hg
∇
hg
∇
hg
∇
hg
∇
hg
∇
hg
∇
hg
∇
hg
∇
hg
∇
hg
∇
hg
∇
hg
∇
hg
∇
hg
∇
hg
∇
hg
∇
hg
∇
hg
∇
hg
500° 540° 600° 640° 660° 700° 740° 800° 900° 1000° 1200°
1.3616
1247.7
1.2851
1245.1
1.2158
1242.5
1.1526
1239.8
1.0948
1237.0
1.0417
1234.2
0.9927
1231.3
0.9473
1228.3
0.9052
1225.3
0.8659
1222.2
0.8291
1219.0
0.7947
1215.7
0.7624
1212.4
0.7319
1209.0
0.7032
1205.4
0.6759
1201.8
- - -
- - -
- - -
- - -
- - -
- - -
- - -
- - -
- - -
- - -
- - -
- - -
- - -
- - -
1.4444
1273.1
1.3652
1271.0
1.2935
1268.9
1.2282
1266.7
1.1685
1264.5
1.1138
1262.3
1.0633
1260.0
1.0166
1257.7
0.9733
1255.4
0.9330
1253.0
0.8954
1250.5
0.8602
1248.1
0.8272
1245.5
0.7963
1243.0
0.7670
1240.4
0.7395
1237.7
0.7134
1235.0
0.6540
1227.9
0.6015
1220.5
0.5546
1212.7
0.5124
1204.4
0.4740
1195.5
- - -
- -
1.5605
1308.5
1.4770
1306.9
1.4014
1305.3
1.3327
1303.6
1.2698
1302.0
1.2122
1300.3
1.1591
1298.6
1.1101
1296.9
1.0646
1295.2
1.0224
1293.4
0.9830
1291.7
0.9463
1289.9
0.9118
1288.1
0.8795
1296.2
0.8491
1284.4
0.8205
1282.5
0.7934
1280.6
0.7319
1275.7
0.6779
1270.7
0.6301
1265.5
0.5873
1260.1
0.5489
1254.6
0.5140
1248.8
1.6345
1331.0
1.5480
1329.6
1.4697
1328.3
1.3984
1326.9
1.3334
1325.4
1.2737
1324.0
1.2188
1322.6
1.1681
1321.1
1.1211
1319.7
1.0775
1318.2
1.0368
1316.7
0.9988
1315.2
0.9633
1313.7
0.9299
1312.2
0.8985
1310.6
0.8690
1309.1
0.8411
1307.5
0.7778
1303.5
0.7223
1299.4
0.6732
1295.2
0.6294
1290.9
0.5901
1286.4
0.5546
1281.9
TOTAL TEMPERATURE — °F
1.6707
1342.0
1.5827
1340.8
1.5030
1339.5
1.4306
1338.2
1.3644
1336.9
1.3038
1335.6
1.2478
1334.2
1.1962
1332.9
1.1485
1331.5
1.1041
1330.2
1.0627
1328.8
1.0241
1327.4
0.9880
1326.0
0.9541
1324.6
0.9222
1323.2
0.8922
1321.7
0.8639
1320.3
0.7996
1316.6
0.7433
1312.9
0.6934
1309.0
0.6491
1305.1
0.6092
1301.1
0.5733
1297.0
1.7419
1363.8
1.6508
1362.7
1.5684
1361.6
1.4934
1360.4
1.4250
1359.3
1.3622
1358.2
1.3044
1357.0
1.2511
1355.8
1.2017
1354.6
1.1558
1353.5
1.1331
1352.3
1.0732
1351.1
1.0358
1349.9
1.0008
1348.6
0.9679
1347.4
0.9369
1346.2
0.9077
1345.0
0.8414
1341.8
0.7833
1338.6
0.7320
1335.4
0.6863
1332.1
0.6453
1328.7
0.6084
1325.3
1.8118
1385.3
1.7177
1384.3
1.6324
1383.3
1.5549
1382.3
1.4842
1381.3
1.4193
1380.3
1.3596
1379.3
1.3045
1378.2
1.2535
1377.2
1.2060
1376.1
1.1619
1375.1
1.1207
1374.0
1.0821
1373.0
1.0459
1371.9
1.0119
1370.8
0.9800
1369.8
0.9498
1368.7
0.8813
1366.0
0.8215
1363.2
0.7685
1360.4
0.7215
1357.5
0.6793
1354.7
0.6413
1351.7
1.9149
1417.3
1.8161
1416.4
1.7267
1415.5
1.6454
1414.7
1.5711
1413.8
1.5031
1412.9
1.4405
1412.1
1.3826
1411.2
1.3291
1410.3
1.2794
1409.4
1.2331
1408.6
1.1899
1407.7
1.1494
1406.8
1.1115
1405.9
1.0759
1405.0
1.0424
1404.1
1.0108
1403.2
0.9391
1400.9
0.8763
1398.6
0.8209
1396.3
0.7716
1393.9
0.7275
1391.6
0.6878
1389.2
2.083
1470.1
1.9767
1469.4
1.8802
1468.7
1.7925
1468.1
1.7124
1467.4
1.6390
1466.7
1.5715
1466.0
1.5091
1465.3
1.4514
1464.6
1.3978
1463.9
1.3479
1463.2
1.3013
1462.5
1.2577
1461.8
1.2168
1461.1
1.1784
1460.4
1.1423
1459.7
1.1082
1459.0
1.0310
1457.2
0.9633
1455.4
0.9037
1453.6
0.8506
1451.8
0.8031
1450.0
0.7604
1448.2
2.249
1523.0
2.134
1522.4
2.031
1521.9
1.9368
1521.3
1.8508
1520.7
1.7720
1520.2
1.6996
1519.6
1.636
1519.0
1.5707
1518.5
1.5132
1517.9
1.4596
1517.3
1.4096
1516.7
1.3628
1516.2
1.3190
1515.6
1.2778
1515.0
1.2390
1514.5
1.2024
1513.9
1.1196
1512.4
1.0470
1511.0
0.9830
1509.5
0.9262
1508.1
0.8753
1506.6
0.8294
1505.1
2.575
1630.0
2.445
1629.6
2.327
1629.2
2.220
1628.8
2.122
1628.4
2.033
1628.0
1.9504
1627.6
1.8743
1627.2
1.8039
1626.8
1.7385
1626.4
1.6776
1626.0
1.6208
1625.5
1.5676
1625.1
1.5178
1624.7
1.4709
1624.3
1.4269
1623.9
1.3853
1623.5
1.2912
1622.4
1.2088
1621.4
1.1360
1620.4
1.0714
1619.3
1.0136
1618.3
0.9615
1617.3
- continued -
Page 30

688
Te c h n i c a l
Conversions, Equivalents, and Physical Data
Properties of Superheated Steam (continued)
PRESSURE
(PSI)
Absolute
1200.0 1185.3 567.22
1300.0 1285.3 577.46
1400.0 1385.3 587.10
1500.0 1485.3 596.23
1600.0 1585.3 604.90
1700.0 1685.3 613.15
1800.0 1785.3 621.03
1900.0 1885.3 628.58
2000.0 1985.3 635.82
2100.0 2085.3 642.77
2200.0 2185.3 649.46
2300.0 2285.3 655.91
2400.0 2385.3 662.12
2500.0 2485.3 668.13
2600.0 2585.3 673.94
2700.0 2685.3 679.55
2800.0 2785.3 684.99
2900.0 2885.3 690.26
3000.0 2985.3 695.36
3100.0 3085.3 700.31
3200.0 3185.3 705.11
3206.2 3191.5 705.40
∇ = specic volume, cubic feet per pound
hg = total heat of steam, BTU per pound
Gauge 660° 700° 740° 760° 780° 800° 860° 900° 1000° 1100° 1200°
P’
1100.0 1085.3 556.31
SAT.
TEMP.
°F
∇
hg
∇
hg
∇
hg
∇
hg
∇
hg
∇
hg
∇
hg
∇
hg
∇
hg
∇
hg
∇
hg
∇
hg
∇
hg
∇
hg
∇
hg
∇
hg
∇
hg
∇
hg
∇
hg
∇
hg
∇
hg
∇
hg
∇
hg
0.5110
1288.5
0.4586
1279.6
0.4139
1270.2
0.3753
1260.3
0.3413
1249.8
0.3112
1238.7
0.2842
1226.8
0.2597
1214.0
0.2371
1200.2
0.2161
1184.9
0.1962
1167.7
0.1768
1147.8
0.1575
1123.8
- - - -
- - - -
- - -
- - -
- - - -
- - - -
- - -
- - -
- - - -
- - - -
- - -
- - -
- - - -
- - - -
- - -
- - -
- - - -
- - - -
- - -
- - -
0.5445
1318.3
0.4909
1311.0
0.4454
1303.4
0.4062
1295.5
0.3719
1287.2
0.3417
1278.7
0.3148
1269.7
0.2907
1260.3
0.2688
1250.4
0.2489
1240.0
0.2306
1229.0
0.2135
1217.4
0.1978
1204.9
0.1828
1191.5
0.1686
1176.8
0.1549
1160.6
0.1415
1142.5
0.1281
1121.4
0.1143
1095.9
0.0984
1060.7
- - - -
- - - -
- - -
- - -
- - -
- - -
0.5755
1345.8
0.5206
1339.6
0.4739
1333.3
0.4338
1326.7
0.3989
1320.0
0.3682
1313.0
0.3410
1305.8
0.3166
1298.4
0.2947
1290.6
0.2748
1282.6
0.2567
1274.3
0.2400
1265.7
0.2247
1256.7
0.2105
1247.3
0.1973
1207.6
0.1849
1227.3
0.1732
1216.5
0.1622
1205.1
0.1517
1193.0
0.1416
1180.1
0.1320
1166.2
0.1226
1151.1
0.1220
1150.2
0.5904
1358.9
0.5347
1353.2
0.4874
1347.3
0.4468
1341.3
0.4114
1335.2
0.3804
1328.8
0.3529
1322.3
0.3284
1315.5
0.3063
1308.6
0.2863
1301.4
0.2682
1294.0
0.2514
1286.3
0.2362
1278.4
0.2221
1270.2
0.2090
1261.8
0.1967
1252.9
0.1853
1243.8
0.1745
1234.2
0.1644
1224.3
0.1548
1213.8
0.1456
1202.9
0.1369
1191.4
0.1363
1190.6
TOTAL TEMPERATURE — °F (t)
0.6049
1371.7
0.5484
1366.4
0.5004
1361.0
0.4593
1355.4
0.4235
1349.7
0.3921
1343.9
0.3643
1337.9
0.3395
1331.8
0.3171
1325.4
0.2972
1319.0
0.2789
1312.3
0.2621
1305.4
0.2468
1298.4
0.2327
1291.1
0.2196
1283.6
0.2074
1275.8
0.1960
1267.9
0.1854
1259.6
0.1754
1251.1
0.1660
1242.2
0.1571
1233.0
0.1486
1223.5
0.1480
1222.9
0.6191
1384.3
0.5617
1379.3
0.5131
1374.3
0.4714
1369.1
0.4352
1363.8
0.4034
1358.4
0.3753
1352.9
0.3502
1347.2
0.3277
1341.5
0.3074
1335.5
0.2890
1329.5
0.2721
1323.3
0.2567
1316.9
0.2425
1310.3
0.2294
1303.6
0.2172
1296.8
0.2059
1289.7
0.1953
1282.4
0.1853
1274.9
0.1760
1267.2
0.1672
1259.3
0.1589
1251.1
0.1583
1250.5
0.6601
1420.8
0.6003
1416.7
0.5496
1412.5
0.5061
1408.2
0.4684
1403.9
0.4353
1399.5
0.4061
1395.0
0.3801
1390.4
0.3568
1385.8
0.3358
1381.2
0.3167
1376.4
0.2994
1371.5
0.2835
1366.6
0.2689
1361.6
0.2555
1356.5
0.2431
1351.4
0.2315
1346.1
0.2208
1340.8
0.2108
1335.3
0.2014
1329.7
0.1926
1324.1
0.1843
1318.3
0.1838
1317.9
0.6866
1444.5
0.6250
1440.7
0.5728
1437.0
0.5281
1433.1
0.4893
1429.3
0.4553
1425.3
0.4253
1421.4
0.3986
1417.4
0.3747
1413.3
0.3532
1409.2
0.3337
1405.0
0.3159
1400.8
0.2997
1396.5
0.2848
1392.2
0.2710
1387.8
0.2584
1383.4
0.2466
1378.9
0.2356
1374.3
0.2254
1369.7
0.2159
1365.0
0.2070
1360.3
0.1986
1355.5
0.1981
1355.2
0.7503
1502.2
0.6843
1499.2
0.6284
1496.2
0.5805
1493.2
0.5390
1490.1
0.5027
1487.0
0.4706
1484.0
0.4421
1480.8
0.4165
1477.7
0.3935
1474.5
0.3727
1471.4
0.3538
1468.2
0.3365
1464.9
0.3207
1461.7
0.3061
1458.4
0.2926
1455.1
0.2801
1451.8
0.2685
1448.5
0.2577
1445.1
0.2476
1441.8
0.2382
1438.4
0.2293
1434.9
0.2288
1434.7
0.8117
1558.8
0.7412
1556.4
0.6816
1553.9
0.6305
1551.4
0.5862
1548.9
0.5474
1546.4
0.5132
1543.8
0.4828
1541.3
0.4556
1538.8
0.4311
1536.2
0.4089
1533.6
0.3887
1531.1
0.3703
1528.5
0.3534
1525.9
0.3379
1523.2
0.3236
1520.6
0.3103
1518.0
0.2979
1515.4
0.2864
1512.7
0.2757
1510.0
0.2657
1507.4
0.2563
1504.7
0.2557
1504.5
0.8716
1615.2
0.7967
1613.1
0.7333
1611.0
0.6789
1608.9
0.6318
1606.8
0.5906
1604.6
0.5542
1602.5
0.5218
1600.4
0.4929
1598.2
0.4668
1596.1
0.4433
1593.9
0.4218
1591.8
0.4023
1589.6
0.3843
1587.4
0.3678
1585.3
0.3526
1583.1
0.3385
1580.9
0.3254
1578.7
0.3132
1576.5
0.3018
1574.3
0.2911
1572.1
0.2811
1569.9
0.2806
1569.8
Page 31

689
Te c h n i c a l
Conversions, Equivalents, and Physical Data
Determine Velocity of Steam in Pipes:
Velocity (ft/s) =
Where: A = Nominal pipe section area =
d = Diameter
(25) (A)
(V)
π (d)
4
2
V = Specic volume from steam tables in ft3/lb (m3/kg)
Note: Specic volume changes with steam pressure and
temperature. Make sure to calculate velocities of inlet and outlet
Recommended Steam Pipe Line Velocities
STEAM CONDITION
0 to 15 psig (0 to 1,0 bar),
Dry and saturated
15 psig (1,0 bar),
Dry and saturated and up
200 psig (13,8 bar),
Superheated and up
VELOCITY, FEET/SECOND
(METERS/SECOND)
piping of the regulator.
Typical Condensation Rates In Insulated Steam Pipes
PRESSURE,
PSIG (bar)
1 (0,069) 0.02 (0,009) 0.03 (0,014) 0.03 (0,014) 0.04 (0,018) 0.05 (0,023) 0.06 (0,027)
5 (0,34) 0.03 (0,014) 0.03 (0,014) 0.04 (0,018) 0.04 (0,018) 0.05 (0,023) 0.06 (0,027)
10 (0,69) 0.03 (0,014) 0.03 (0,014) 0.04 (0,018) 0.04 (0,018) 0.05 (0,023) 0.07 (0,032)
25 (1,7) 0.03 (0,014) 0.04 (0,018) 0.05 (0,023) 0.05 (0,023) 0.06 (0,027) 0.08 (0,036)
50 (3,4) 0.04 (0,018) 0.04 (0,018) 0.05 (0,023) 0.06 (0,027) 0.09 (0,041) 0.11 (0,05)
75 (5,2) 0.04 (0,018) 0.05 (0,023) 0.06 (0,027) 0.07 (0,032) 0.11 (0,05) 0.14 (0,064)
100 (6,9) 0.05 (0,023) 0.05 (0,023) 0.07 (0,032) 0.08 (0,036) 0.12 (0,054) 0.15 (0,068)
125 (8,6) 0.05 (0,023) 0.06 (0,027) 0.07 (0,032) 0.08 (0,036) 0.13 (0,059) 0.16 (0,073)
150 (10,3) 0.06 (0,027) 0.06 (0,027) 0.08 (0,036) 0.09 (0,041) 0.14 (0,064) 0.17 (0,077)
200 (13,8) 0.06 (0,027) 0.07 (0,032) 0.08 (0,036) 0.09 (0,041) 0.15 (0,068) 0.19 (0,086)
3/4 1 1-1/2 2 3 4
RATES IN POUNDS/HOUR (KG/HOUR) PER FOOT OF PIPE WITH 2-INCHES OF INSULATION
Pipe Diameter in Inches
100 (30,5)
175 (53,3)
250 (76,2)
Typical Condensation Rates In Steam Pipes Without Insulation
PRESSURE,
PSIG (bar)
1 (0,069) 0.11 (0,05) 0.15 (0,068) 0.21 (0,095) 0.25 (0,113) 0.38 (0,172) 0.46 (0,209)
5 (0,34) 0.14 (0,064) 0.16 (0,073) 0.22 (0,1) 0.26 (0,118) 0.41 (0,186) 0.50 (0,227)
10 (0,69) 0.15 (0,068) 0.18 (0,082) 0.24 (0,109) 0.29 (0,132) 0.44 (0,2) 0.53 (0,24)
25 (1,7) 0.17 (0,077) 0.22 (0,1) 0.31 (0,141) 0.36 (0,163) 0.53 (0,24) 0.65 (0,295)
50 (3,4) 0.22 (0,1) 0.27 (0,122) 0.39 (0,177) 0.46 (0,209) 0.66 (0,299) 0.83 (0,376)
75 (5,2) 0.26 (0,118) 0.31 (0,141) 0.45 (0,204) 0.54 (0,245) 0.77 (0,349) 1.04 (0,472)
100 (6,9) 0.29 (0,132) 0.35 (0,159) 0.50 (0,227) 0.61 (0,277) 0.86 (0,39) 1.11 (0,503)
125 (8,6) 0.32 (0,145) 0.39 (0,177) 0.55 (0,249) 0.68 (0,308) 0.94 (0,426) 1.23 (0,558)
150 (10,3) 0.35 (0,159) 0.42 (0,191) 0.60 (0,272) 0.74 (0,336) 1.03 (0,467) 1.33 (0,603)
200 (13,8) 0.40 (0,181) 0.49 (0,222) 0.69 (0,313) 0.81 (0,367) 1.19 (0,54) 1.50 (0,68)
3/4 1 1-1/2 2 3 4
RATES IN POUNDS/HOUR (KG/HOUR) PER FOOT OF BARE PIPE AT 72°F (22°C) AMBIENT AIR
Pipe Diameter in Inches
Page 32

690
Te c h n i c a l
Conversions, Equivalents, and Physical Data
Flow of Water Through Schedule 40 Steel Pipes
DISCHARGE PRESSURE DROP PER 100 FEET AND VELOCITY IN SCHEDULE 40 PIPE FOR WATER AT 60°F
Gallons
Minute
Cubic
Velocity
Pressure
Velocity
Pressure
Velocity
Pressure
Velocity
Pressure
Velocity
Pressure
Velocity
Pressure
Velocity
Pressure
per
Ft. per
Second
0.2 0.000446 1.13 1.86 0.616 0.359
0.3 0.000668 1.69 4.22 0.924 0.903 0.504 0.159 0.317 0.061
0.4 0.000891 2.26 6.98 1.23 1.61 0.672 0.345 0.422 0.086
0.5 0.00111 2.82 10.5 1.54 2.39 0.840 0.539 0.528 0.167 0.301 0.033
0.6 0.00134 3.39 14.7 1.85 3.29 1.01 0.751 0.633 0.240 0.361 0.041
0.8 0.00178 4.52 25.0 2.46 5.44 1.34 1.25 0.844 0.408 0.481 0.102
1 0.00223 5.65 37.2 3.08 8.28 1.68 1.85 1.06 0.600 0.602 0.155 0.371 0.048 1-1/4-Inch
3 0.00668 9.25 64.1 5.04 13.9 3.17 4.33 1.81 1.09 1.114 0.336 0.644 0.090 0.473 0.043
4 0.00891 12.33 111.2 6.72 23.9 4.22 7.42 2.41 1.83 1.49 0.565 0.858 0.150 0.630 0.071
5 0.01114 2-Inch 8.40 36.7 5.28 11.2 3.01 2.75 1.86 0.835 1.073 0.223 0.788 0.104
6 0.01337 0.574 0.044
8 0.01782 0.765 0.073 13.44 91.1 8.45 27.7 4.81 6.60 2.97 1.99 1.72 0.518 1.26 0.241
10 0.02228 0.956 0.108 0.670 0.046
15 0.03342 1.43 0.224 1.01 0.094
20 0.04456 1.91 3.375 1.34 0.158 0.868 0.056 12.03 37.8 7.43 10.9 4.29 2.78 3.16 1.28
25 0.05570 2.39 0.561 1.68 0.234 1.09 0.083 0.812 0.041
30 0.06684 2.87 0.786 2.01 0.327 1.30 0.114 0.974 0.056 11.14 23.8 6.44 5.92 4.73 2.72
35 0.07798 3.35 1.05 2.35 0.436 1.52 0.151 1.14 0.071 0.882 0.041 12.99 32.2 7.51 7.90 5.52 3.64
40 0.08912 3.83 1.35 2.68 0.556 1.74 0.192 1.30 0.095 1.01 0.052 14.85 41.5 8.59 10.24 6.30 4.65
45 0.1003 4.30 1.67 3.02 0.668 1.95 0.239 1.46 0.117 1.13 0.064 9.67 12.80 7.09 5.85
50 0.1114 4.78 2.03 3.35 0.839 2.17 0.288 1.62 0.142 1.26 0.076
60 0.1337 5.74 2.87 4.02 1.18 2.60 0.46 1.95 0.204 1.51 0.107 12.89 22.2 9.47 10.21
70 0.1560 6.70 3.84 4.69 1.59 3.04 0.540 2.27 0.261 1.76 0.143 1.12 0.047
80 0.1782 7.65 4.97 5.36 2.03 3.47 0.687 2.60 0.334 2.02 0.180 1.28 0.060 12.62 17.59
90 0.2005 8.60 6.20 6.03 2.53 3.91 0.861 2.92 0.416 2.27 0.224 1.44 0.074 14.20 22.0
100 0.2228 9.56 7.59 6.70 3.09 4.34 1.05 3.25 0.509 2.52 0.272 1.60 0.090 1.11 0.036 15.778 26.9
125 0.2785 11.97 11.76 8.38 4.71 5.43 1.61 4.06 0.769 3.15 0.415 2.01 0.135 1.39 0.055 19.72 41.4
150 0.3342 14.36 16.70 10.05 6.69 6.51 2.24 4.87 1.08 3.78 0.580 2.41 0.190 1.67 0.077
175 0.3899 16.75 22.3 11.73 8.97 7.60 3.00 5.68 1.44 4.41 0.774 2.81 0.253 1.94 0.102
200 0.4456 19.14 28.8 13.42 11.68 8.68 3.87 6.49 1.85 5.04 0.985 3.21 0.323 2.22 0.130
225 0.5013 - - - - - - - - 15.09 14.63 9.77 4.83 7.30 2.32 5.67 1.23 3.61 0.401 2.50 0.162 1.44 0.043
250 0.557 - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 10.85 5.93 8.12 2.84 6.30 1.46 4.01 0.495 2.78 0.195 1.60 0.051
275 0.6127 - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 11.94 7.14 8.93 3.40 6.93 1.79 4.41 0.583 3.05 0.234 1.76 0.061
300 0.6684 - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 13.00 8.36 9.74 4.02 7.56 2.11 4.81 0.683 3.33 0.275 1.92 0.072
325 0.7241 - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 14.12 9.89 10.53 4.09 8.19 2.47 5.21 0.797 3.61 0.320 2.08 0.083
350 0.7798 - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 11.36 5.51 8.82 2.84 5.62 0.919 3.89 0.367 2.24 0.095
375 0.8355 - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 12.17 6.18 9.45 3.25 6.02 10.5 4.16 0.416 2.40 0.108
400 0.8912 - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 12.98 7.03 10.08 3.68 6.42 1.19 4.44 0.471 2.56 0.121
425 0.9469 - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 13.80 7.89 10.71 4.12 6.82 1.33 4.72 0.529 2.73 0.136
450 1.003 10-Inch - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 14.61 8.80 11.34 4.60 7.22 1.48 5.00 0.590 2.89 0.151
475 1.059 1.93 0.054 - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 11.97 5.12 7.62 1.64 5.27 0.653 3.04 0.166
500 1.114 2.03 0.059 - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 12.60 5.65 8.02 1.81 5.55 0.720 3.21 0.182
550 1.225 2.24 0.071 - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 13.85 6.79 8.82 2.17 6.11 0.861 3.53 0.219
600 1.337 2.44 0.083 - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 15.12 8.04 9.63 2.55 6.66 1.02 3.85 0.258
650 1.448 2.64 0.097 - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 10.43 2.98 7.22 1.18 4.17 0.301
(Ft. per
Second)
Drop
(Ft. per
(PSI)
Second)
1/8-Inch 1/4-Inch
2-1/2-Inch
Drop
(PSI)
(Ft. per
Second)
Drop
(Ft. per
(PSI)
Second)
3/8-Inch 1/2-Inch
10.08 51.9 6.33 15.8 3.61 3.84 2.23 1.17 1.29 0.309 0.943 0.145
3-Inch
Drop
(Ft. per
(PSI)
Second)
10.56 42.4 6.02 9.99 3.71 2.99 2.15 0.774 1.58 0.361
3-1/2-Inch
Drop
(Ft. per
(PSI)
Second)
3/4-Inch
9.03 21.6 5.57 6.36 3.22 1.63 2.37 0.755
4-Inch
Drop
(Ft. per
(PSI)
Second)
1-inch
9.28 16.7 5.37 4.22 3.94 1.93
5-Inch
10.74 15.66 7.88 7.15
6-Inch
Drop
(PSI)
Velocity
(Ft. per
Second)
1-1/2-Inch2 0.00446 11.29 134.4 6.16 30.1 3.36 6.58 2.11 2.10 1.20 0.526 0.743 0.164 0.429 0.044
11.05 13.71
8-Inch
Pressure
Drop
(PSI)
- continued -
Page 33
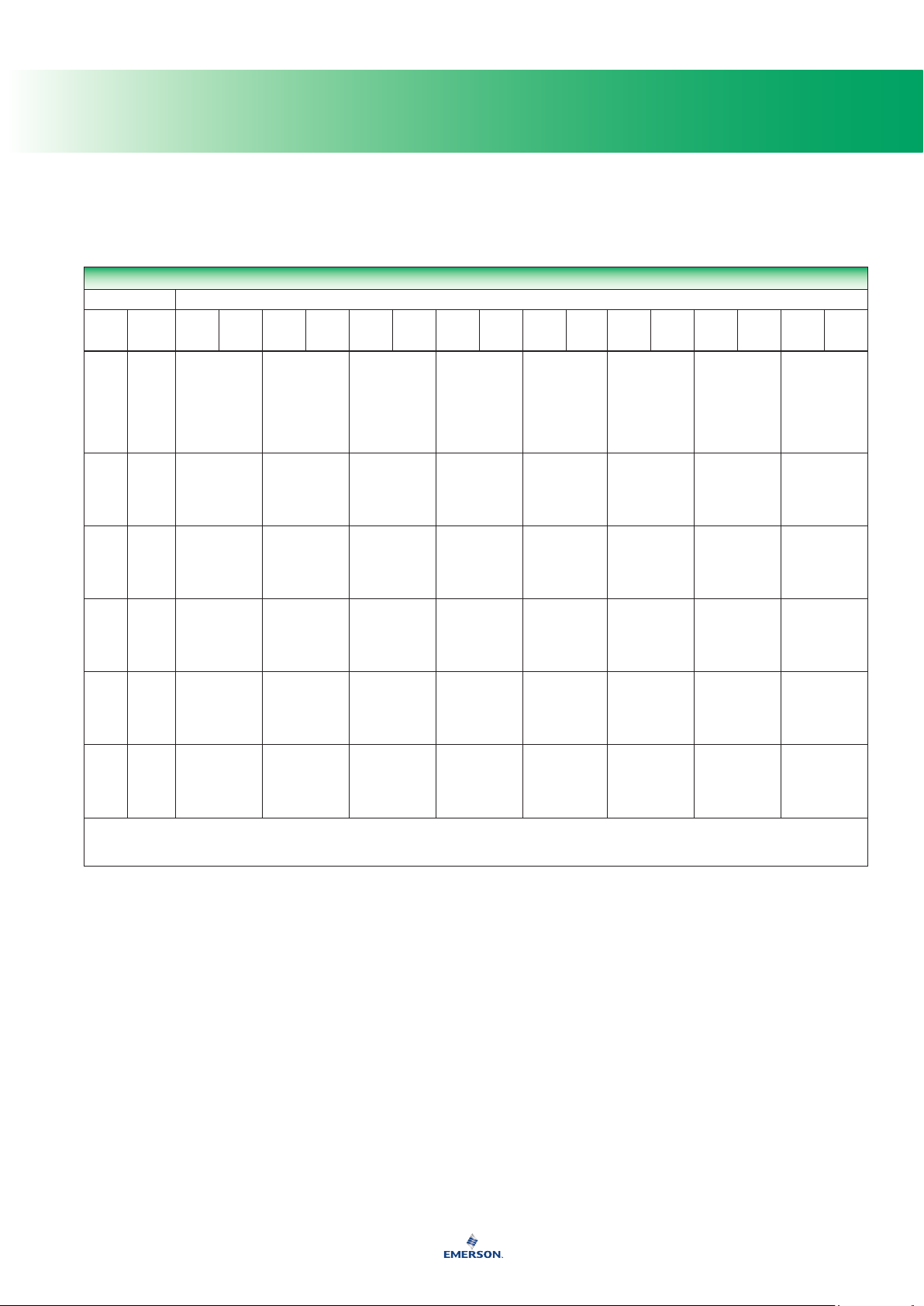
691
Te c h n i c a l
Conversions, Equivalents, and Physical Data
Flow of Water Through Schedule 40 Steel Pipes (continued)
DISCHARGE PRESSURE DROP PER 100 FEET AND VELOCITY IN SCHEDULE 40 PIPE FOR WATER AT 60°F
Gallons
Minute
10,000 22.28 - - - - - - - - 28.66 7.46 23.71 4.61 18.15 2.34 14.34 1.28 11.54 0.739 7.98 0.294 - - - - - - - -
12,000 26.74 - - - - - - - - 34.40 10.7 28.45 6.59 21.79 3.33 17.21 1.83 13.85 1.06 9.58 0.416 - - - - - - - -
14,000 31.19 - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 33.19 8.89 25.42 4.49 20.08 2.45 16.16 1.43 11.17 0.562 - - - - - - - -
16,000 35.65 - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 29.05 5.83 22.95 3.18 18.47 1.85 12.77 0.723 - - - - - - - -
18,000 40.10 - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 32.68 7.31 25.82 4.03 20.77 2.32 14.36 0.907 - - - - - - - -
20,000 44.56 - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 36.31 9.03 28.69 4.93 23.08 2.86 15.96 1.12 - - - - - - - -
For pipe lengths other than 100 feet, the pressure drop is proportional to the length. Thus, for 50 feet of pipe, the pressure drop is approximately one half the value given in the table or 300 feet,
three times the given value, etc.
Velocity is a function of the cross sectional ow area; thus, it is constant for a given ow rate and is independent of pipe length.
Extracted from Technical Paper No. 410, Flow of Fluids, with permission of Crane Co.
Cubic
Velocity
Pressure
Velocity
Pressure
Velocity
Pressure
Velocity
Pressure
Velocity
Pressure
Velocity
Pressure
Velocity
Pressure
Velocity
per
Ft. per
Second
700 1.560 2.85 0.112 2.01 0.047 - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 11.23 3.43 7.78 1.35 4.49 0.343
750 1.671 3.05 0.127 2.15 0.054 - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 12.03 3.92 8.33 1.55 4.81 0.392
800 1.782 3.25 0.143 2.29 0.061 - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 12.83 4.43 8.88 1.75 5.13 0.443
850 1.894 3.46 0.160 2.44 0.068 2.02 0.042 - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 13.64 5.00 9.44 1.96 5.45 0.497
900 2.005 3.66 0.179 2.58 0.075 2.13 0.047 - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 14.44 5.58 9.99 2.18 5.77 0.554
950 2.117 3.86 0.198 2.72 0.083 2.25 0.052 - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 15.24 6.21 10.55 2.42 6.09 0.613
1000 2.228 4.07 0.218 2.87 0.091 2.37 0.057
1100 2.451 4.48 0.260 3.15 0.110 2.61 0.068 - - - - - - - - 17.65 8.23 12.22 3.22 7.05 0.807
1200 2.674 4.88 0.306 3.44 0.128 2.85 0.800 2.18 0.042 - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 13.33 3.81 7.70 0.948
1300 2.896 5.29 0.355 3.73 0.150 3.08 0.093 2.36 0.048 - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 14.43 4.45 8.33 1.11
1400 3.119 5.70 0.409 4.01 0.171 3.32 0.107 2.54 0.055 - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 15.55 5.13 8.98 1.28
1500 3.342 6.10 0.466 4.30 0.195 3.56 0.122 2.72 0.063
1600 3.565 6.51 0.527 4.59 0.219 3.79 0.138 2.90 0.071 17.77 6.61 10.26 1.65
1800 4.010 7.32 0.663 5.16 0.276 4.27 0.172 3.27 0.088 2.58 0.050 19.99 8.37 11.54 2.08
2000 4.456 8.14 0.808 5.73 0.339 4.74 0.209 3.63 0.107 2.87 0.060 22.21 10.3 12.82 2.55
2500 5.570 10.17 1.24 7.17 0.515 5.93 0.321 4.54 0.163 3.59 0.091 16.03 3.94
3000 6.684 12.20 1.76 8.60 0.731 7.11 0.451 5.45 0.232 4.30 0.129 3.46 0.075
3500 7.798 14.24 2.38 10.03 0.982 8.30 0.607 6.35 0.312 5.02 0.173 4.04 0.101 22.44 7.56
4000 8.912 16.27 3.08 11.47 1.27 9.48 0.787 7.26 0.401 5.74 0.222 4.62 0.129 3.19 0.052 25.65 9.80
4500 10.03 18.31 3.87 12.90 1.60 10.67 0.990 8.17 0.503 6.46 0.280 5.20 0.162 3.59 0.065 28.87 12.2
5000 11.14 20.35 7.71 14.33 1.95 11.85 1.21 9.08 0.617 7.17 0.340 5.77 0.199 3.99 0.079 - - - - - - - -
6000 13.37 24.41 6.74 17.20 2.77 14.23 1.71 10.89 0.877 8.61 0.483 6.93 0.280 4.79 0.111 - - - - - - - -
7000 15.60 28.49 9.11 20.07 3.74 16.60 2.31 12.71 1.18 10.04 0.652 8.08 0.376 5.59 0.150 - - - - - - - -
8000 17.82 - - - - - - - - 22.93 4.84 18.96 2.99 14.52 1.51 11.47 0.839 9.23 0.488 6.38 0.192 - - - - - - - -
9000 20.05 - - - - - - - - 25.79 6.09 21.34 3.76 16.34 1.90 12.91 1.05 10.39 0.608 7.18 0.242 - - - - - - - -
(Ft. per
Second)
Drop
(Ft. per
(PSI)
Second)
10-Inch 12-Inch
Drop
(PSI)
(Ft. per
Second)
14-Inch
Drop
(PSI)
(Ft. per
Second)
16-Inch
Drop
(PSI)
(Ft. per
Second)
Drop
(Ft. per
(PSI)
Second)
- - - - - - - - 16.04 6.84 11.10 2.68 6.41 0.675
18-Inch
Drop
(Ft. per
(PSI)
Second)
5-Inch 6-Inch 8-Inch
20-Inch
Drop
(PSI)
16.66 5.85 9.62 1.46
24-Inch
Pressure
(Ft. per
Second)
19.24 5.59
Drop
(PSI)
Page 34

692
Te c h n i c a l
Conversions, Equivalents, and Physical Data
Flow of Air Through Schedule 40 Steel Pipes
FREE AIR
Q
Cubic Feet per
Minute at 60°F
and 14.7 psia
100 12.82 0.029 3-Inch 33.2 7.69 2.21 0.534 0.247 0.070
125 16.02 0.044 - - - - 11.9 3.39 0.825 0.380 0.107
150 19.22 0.062 0.021 - - - - 17.0 4.87 1.17 0.537 0.151
175 22.43 0.083 0.028 3-1/2-Inch - - - - 23.1 6.60 1.58 0.727 0.205
200 25.63 0.107 0.036 - - - - 30.0 8.54 2.05 0.937 0.264
225 28.84 0.134 0.045 0.022
250 32.04 0.164 0.055 0.027 - - - - 13.3 3.18 1.45 0.404
275 35.24 0.191 0.066 0.032 - - - - 16.0 3.83 1.75 0.484
300 38.45 0.232 0.078 0.037 - - - - 19.0 4.56 2.07 0.573
325 41.65 0.270 0.090 0.043 - - - - 22.3 5.32 2.42 0.673
350 44.87 0.313 0.104 0.050 - - - - 25.8 6.17 2.80 0.776
375 48.06 0.356 0.119 0.057 0.030 - - - - 29.6 7.05 3.20 0.887
400 51.26 0.402 0.134 0.064 0.034 - - - - 33.6 8.02 3.64 1.00
425 54.47 0.452 0.151 0.072 0.038 - - - - 37.9 9.01 4.09 1.13
450 57.67 0.507 0.168 0.081 0.042 - - - - - - - - 10.2 4.59 1.26
475 60.88 0.562 0.187 0.089 0.047 - - - - 11.3 5.09 1.40
500 64.08 0.623 0.206 0.099 0.052 - - - - 12.5 5.61 1.55
550 70.49 0.749 0.248 0.118 0.062 - - - - 15.1 6.79 1.87
600 76.90 0.887 0.293 0.139 0.073 5-Inch - - - - 18.0 8.04 2.21
650 83.30 1.04 0.342 0.163 0.086 - - - - 21.1 9.43 2.60
700 89.71 1.19 0.395 0.188 0.099 0.032 24.3 10.9 3.00
750 96.12 1.36 0.451 0.214 0.113 0.036 27.9 12.6 3.44
800 102.5 1.55 0.513 0.244 0.127 0.041 31.8 14.2 3.90
850 108.9 1.74 0.576 0.274 0.144 0.046 6-Inch 35.9 16.0 4.40
900 115.3 1.95 0.642 0.305 0.160 0.051 40.2 18.0 4.91
950 121.8 2.18 0.715 0.340 0.178 0.057 0.023 - - - - 20.0 5.47
1,000 128.2 2.40 0.788 0.375 0.197 0.063 0.025 - - - - 22.1 6.06
1,100 141.0 2.89 0.948 0.451 0.236 0.075 0.030 - - - - 26.7 7.29
1,200 153.8 3.44 1.13 0.533 0.279 0.089 0.035 - - - - 31.8 8.63
1,300 166.6 4.01 1.32 0.626 0.327 0.103 0.041 - - - - 37.3 10.1
COMPRESSED
’M
1 0.128 0.361 0.083 0.018
2 0.256 1.31 0.285 0.064 0.020
3 0.384 3.06 0.605 0.133 0.042
4 0.513 4.83 1.04 0.226 0.071
5 0.641 7.45 1.58 0.343 0.106 0.027
6 0.769 10.6 2.23 0.408 0.148 0.037
8 1.025 18.6 3.89 0.848 0.255 0.062 0.019
10 0.282 28.7 5.96 1.26 0.356 0.094 0.029
15 1.922 - - - - 13.0 2.73 0.834 0.201 0.062
20 2.563 - - - - 22.8 4.76 1.43 0.345 0.102 0.026
25 3.204 - - - - 35.6 7.34 2.21 0.526 0.156 0.039 0.019
30 3.845 - - - - - - - - 10.5 3.15 0.748 0.219 0.055 0.026
35 4.486 - - - - - - - - 14.2 4.24 1.00 0.293 0.073 0.035
40 5.126 - - - - - - - - 18.4 5.49 1.30 0.379 0.095 0.044
45 5.767 - - - - - - - - 23.1 6.90 1.62 0.474 0.116 0.055
50 6.408
60 7.690 40.7 12.2 2.85 0.819 0.200 0.094 0.027
70 8.971 - - - - 16.5 3.83 1.10 0.270 0.126 0.036
80 10.25 0.019 - - - - 21.4 4.96 1.43 0.350 0.162 0.046
90 11.53 0.023 - - - - 27.0 6.25 1.80 0.437 0.203 0.058
AIR
Cubic Feet per
Minute at 60°F
and 100 psig
1/8-Inch 1/4-Inch 3/8-Inch 1/2-Inch 3/4-Inch 1-Inch 1-1/4-Inch 1-1/2-Inch 2-Inch
2-1/2-Inch
PRESSURE DROP OF AIR IN POUNDS PER SQUARE INCH
PER 100 FEET OF SCHEDULE 40 PIPE FOR AIR AT 100 POUNDS
PER SQUARE INCH GAUGE PRESSURE AND 60°F TEMPERATURE
28.5 8.49 1.99 0.578 0.149 0.067 0.019
37.9 10.8 2.59 1.19 0.331
4-Inch
- continued -
Page 35

693
Te c h n i c a l
Conversions, Equivalents, and Physical Data
Flow of Air Through Schedule 40 Steel Pipes (continued)
FREE AIR
Q
Cubic Feet per
Minute at 60°F
and 14.7 psia
1,400 179.4 4.65 1.52 0.718 0.377 0.119 0.047 11.8
1,500 192.2 5.31 1.74 0.824 0.431 0.136 0.054 13.5
1,600 205.1 6.04 1.97 0.932 0.490 0.154 0.061 15.3
1,800 230.7 7.65 2.50 1.18 0.616 0.193 0.075 19.3
2,000 256.3 9.44 3.06 1.45 0.757 0.237 0.094 0.023 23.9
2,500 320.4 14.7 4.76 2.25 1.17 0.366 0.143 0.035 37.3
3,000 384.5 21.1 6.82 3.20 1.67 0.524 0.204 0.051 0.016
3,500 448.6 28.8 9.23 4.33 2.26 0.709 0.276 0.068 0.022
4,000 512.6 37.6 12.1 5.66 2.94 0.919 0.358 0.088 0.028 12-Inch
4,500 576.7 47.6 15.3 7.16 3.69 1.16 0.450 0.111 0.035
5,000 640.8 - - - - 18.8 8.85 4.56 1.42 0.552 0.136 0.043 0.018
6,000 769.0 - - - - 27.1 12.7 6.57 2.03 0.794 0.195 0.061 0.025
7,000 897.1 - - - - 36.9 17.2 8.94 2.76 1.07 0.262 0.082 0.034
8,000 1025 - - - - - - - - 22.5 11.7 3.59 1.39 0.339 0.107 0.044
9,000 1153 - - - - - - - - 28.5 14.9 4.54 1.76 0.427 0.134 0.055
10,000 1282 - - - - - - - - 35.2 18.4 5.60 2.16 0.526 0.164 0.067
11,000 1410 - - - - - - - - - - - - 22.2 6.78 2.62 0.633 0.197 0.081
12,000 1538 - - - - - - - - - - - - 26.4 8.07 3.09 0.753 0.234 0.096
13,000 1666 - - - - - - - - - - - - 31.0 9.47 3.63 0.884 0.273 0.112
14,000 1794 - - - - - - - - - - - - 36.0 11.0 4.21 1.02 0.316 0.129
15,000 1922 - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 12.6 4.84 1.17 0.364 0.148
16,000 2051 - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 14.3 5.50 1.33 0.411 0.167
18,000 2307 - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 18.2 6.96 1.68 0.520 0.213
20,000 2563 - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 22.4 8.60 2.01 0.642 0.260
22,000 2820 - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 27.1 10.4 2.50 0.771 0.314
24,000 3076 - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 32.3 12.4 2.97 0.918 0.371
26,000 3332 - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 37.9 14.5 3.49 1.12 0.435
28,000 3588 - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 16.9 4.04 1.25 0.505
30,000 3845 - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 19.3 4.64 1.42 0.520
Extracted from Technical Paper No. 410, Flow of Fluids, with permission of Crane Co.
’M
COMPRESSED
AIR
Cubic Feet per
Minute at 60°F
and 100 psig
2-1/2-Inch 3-Inch 3-1/2-Inch 4-Inch 5-Inch 6-Inch 8-Inch 10-Inch 12-Inch
PRESSURE DROP OF AIR IN POUNDS PER SQUARE INCH
PER 100 FEET OF SCHEDULE 40 PIPE FOR AIR AT 100 POUNDS
PER SQUARE INCH GAUGE PRESSURE AND 60°F TEMPERATURE
Page 36

694
Te c h n i c a l
Conversions, Equivalents, and Physical Data
Average Properties of Propane
Formula C3H
Boiling Point, °F (°C) -44 (-42)
Specic Gravity of Gas (Air = 1.00) 1.53
Pounds per Gallon of Liquid at 60°F (16°C) 4.24
BTU per Gallon of Gas at 60°F (16°C) 91,547
BTU per Pound of Gas 21,591
BTU per Cubic Foot of Gas at 60°F (16°) 2516
Cubic Feet of Vapor at 60°F (16°C) per Gallon of Liquid at 60°F (16°C) 36.39
Cubic Feet of Vapor at 60°F (16°C) per Pound of Liquid at 60°F (16°) 8.547
Latent Heat of Vaporization at Boiling Point, BTU per Gallon 785.0
Combustion Data
Cubic Feet of Air Required to Burn 1 Cubic Foot of Gas 23.86
Flash Point, °F (°C) -156 (-104)
Ignition Temperature in Air, °F (°C)
Maximum Flame Temperature in Air, °F (°C) 3595 (1979)
Limits of Inammability, Percentage of Gas in Air Mixture
at Lower Limit 2.4%
at Upper Limit 9.6%
Octane Number (ISO Octane = 100) Over 100
8
920 to 1020
(493 to 549)
Standard Domestic Propane Tank Specications
CAPACITY DIAMETER LENGTH TANK WEIGHT
Gallons (Liters) Inches (mm) Inches (mm) Pounds (kg)
120 (454) 24 (610) 68 (1727) 288 (131)
150 (568) 24 (610) 84 (2134) 352 (160)
200 (757) 30 (762) 79 (2007) 463 (210)
250 (946) 30 (762) 94 (2387) 542 (246)
325 (1230) 30 (762) 119 (3023) 672 (305)
500 (1893) 37 (940) 119 (3023) 1062 (482)
1000 (3785) 41 (1041) 192 (4877) 1983 (900)
Approximate Vaporization Capacities of Propane Tanks
BTU PER HOUR WITH 40% LIQUID IN DOMESTIC TANK SYSTEMS
Tank Size Water Capacity
120 235,008 417,792
150 290,304 516,096
200 341,280 606,720
250 406,080 721,920
325 514,100 937,900
500 634,032 1,127,168
1000 1,088,472 1,978,051
Prevailing Air Temperature
20°F (-7°C) 60°F (16°)
Orice Capacities for Propane
ORIFICE OR
DRILL SIZE
0.008 519 51 36531
0.009 656 50 39842
0.010 812 49 43361
0.011 981 48 46983
0.012 1169 47 50088
80 1480 46 53296
79 1708 45 54641
78 2080 44 60229
77 2629 43 64369
76 3249 42 71095
75 3581 41 74924
74 4119 40 78029
73 4678 39 80513
72 5081 38 83721
71 5495 37 87860
70 6375 36 92207
69 6934 35 98312
68 7813 34 100175
67 8320 33 103797
66 8848 32 109385
65 9955 31 117043
64 10535 30 134119
63 11125 29 150366
62 11735 28 160301
61 12367 27 168580
60 13008 26 175617
59 13660 25 181619
58 14333 24 187828
57 15026 23 192796
56 17572 22 200350
55 21939 21 205525
54 24630 20 210699
53 28769 19 223945
52 32805 18 233466
BTU per cubic foot = 2516
Specic Gravity = 1.52
Pressure at orice, inches of water column = 11
Orice Coefcient = 0.9
ORIFICE
CAPACITY BTU
PER HOUR,
11-INCHES W.C.
ORIFICE OR
DRILL SIZE
ORIFICE CAPACITY
BTU PER HOUR,
11-INCHES W.C
Page 37
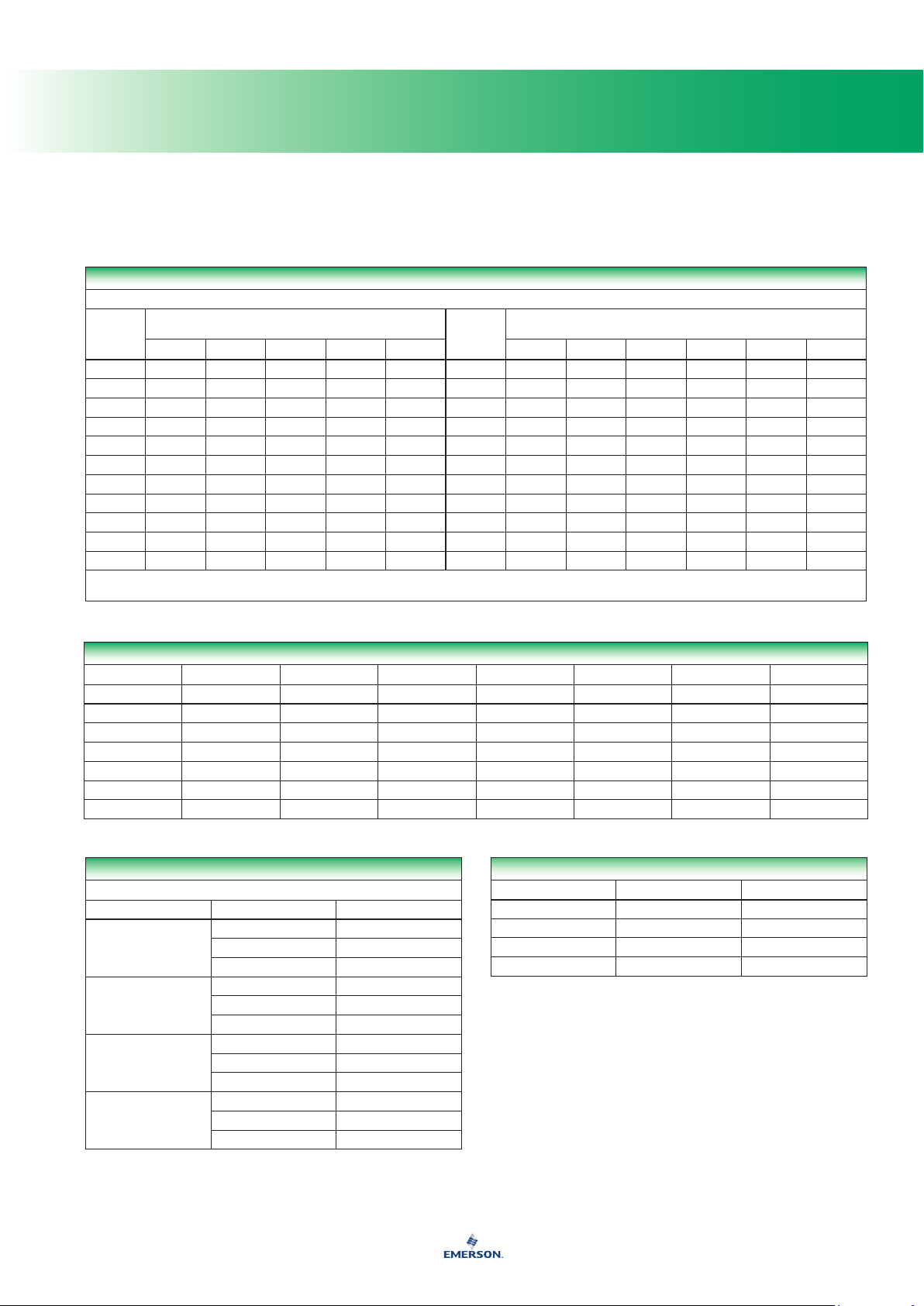
695
Te c h n i c a l
Conversions, Equivalents, and Physical Data
Pipe and Tubing Sizing
PROPANE PIPE AND TUBING SIZING BETWEEN SINGLE OR SECOND STAGE LOW PRESSURE REGULATORS AND APPLIANCES
Pipe or
Tubing
Length, Feet
To convert to capacities in cubic feet per hour, divide by 2.5
Note: Maximum undiluted propane capacities listed are based on 11-inches w.c. setting and a 0.5-inch w.c. pressure drop - Capacities in 1,000 BTU per hour.
3/8 (0.315) 1/2 (0.430) 5.8 (0.545) 3/4 (0.666) 7/8 (0.785) 1/2 (0.622) 3.4 (0.824) 1 (1.049) 1-1/4 (1.380) 1-1/2 (1.610) 2 (2.067)
10 49 110 206 348 536 10 291 608 1146 2353 3525 6789
20 34 76 151 239 368 20 200 418 788 1617 2423 4666
30 27 61 114 192 296 30 161 336 632 1299 1946 3747
40 23 52 97 164 253 40 137 282 541 1111 1665 3207
50 20 46 86 146 224 50 122 557 480 985 1476 2842
60 19 42 78 132 203 60 110 231 435 892 1337 2575
70 17 39 72 121 187 80 94 198 372 764 1144 2204
80 16 36 67 113 174 100 84 175 330 677 1014 1954
90 15 34 63 106 163 125 74 155 292 600 899 1731
100 14 32 59 100 154 150 67 141 265 544 815 1569
150 11 26 48 80
Outside Diameter (Inside Diameter), Type L
Copper Tubing Size,
Pipe or
Tubing
Length, Feet
Outside Diameter (Inside Diameter), Schedule 40
Nominal Pipe Size,
Vapor Pressures of Propane
TEMPERATURE PRESSURE TEMPERATURE PRESSURE TEMPERATURE PRESSURE TEMPERATURE PRESSURE
°F (°C) Psig (Bar) °F (°C) Psig (Bar) °F (°C) Psig (Bar) °F (°C) Psig (Bar)
130 (54) 257 (18) 70 (21) 109 (8) 20 (-7) 40 (2,8) -20 (-29) 10 (0,69)
120 (49) 225 (16) 65 (18) 100 (6,9) 10 (-12) 31 (2) -25 (-32) 8 (0,55)
110 (43) 197 (14) 60 (16) 92 (6) 0 (-17) 23 (2) -30 (-34) 5 (0,34)
100 (38) 172 (12) 50 (10) 77 (5) -5 (-21) 20 (1,4) -35 (-37) 3 (0,21)
90 (32) 149 (10) 40 (4) 63 (4) -10 (-23) 16 (1) -40 (-40) 1 (0,069)
80 (27) 128 (9) 30 (-1) 51 (4) -15 (-26) 13 (1) -44 (-42) 0 (0)
Converting Volumes of Gas
CFH TO CFH OR CFM TO CFM
Multiply Flow of By To Obtain Flow of
0.707 Butane
Air
Butane
Natural Gas
Propane
1.290 Natural Gas
0.808 Propane
1.414 Air
1.826 Natural Gas
1.140 Propane
0.775 Air
0.547 Butane
0.625 Propane
1.237 Air
0.874 Butane
1.598 Natural Gas
COMMON FUELS PER GALLON PER POUND
Propane 91,547 21,591
Butane 102,032 21,221
Gasoline 110,250 20,930
Fuel Oil 134,425 16,960
BTU Comparisons
Page 38
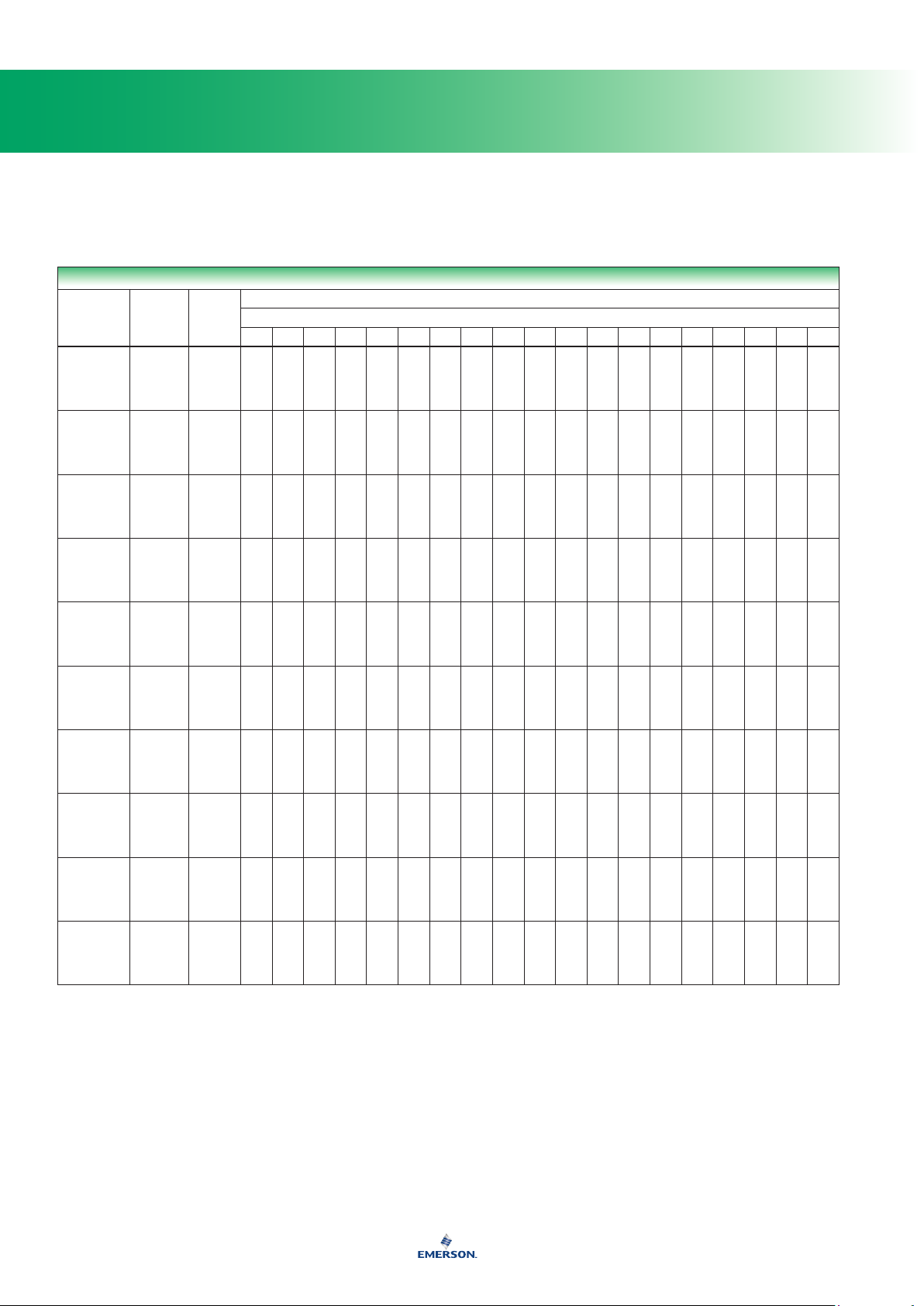
696
Te c h n i c a l
Conversions, Equivalents, and Physical Data
Capacities of Spuds and Orices
DRILL
DESIGNATION
80
79
1/64”
78
77
76
75
74
73
72
71
70
69
68
1/32”
67
66
65
64
63
62
61
60
59
58
57
56
3/64”
55
54
53
1/16”
52
51
50
49
48
5/64”
47
46
45
44
43
42
3/32”
41
40
39
38
37
DIAMETER,
INCHES
0.0135
0.0145
0.0156
0.0160
0.0180
0.0200
0.0210
0.0225
0.0240
0.0250
0.0260
0.0280
0.0292
0.0310
0.0313
0.0320
0.0330
0.0350
0.0360
0.0370
0.0380
0.0390
0.0400
0.0410
0.0420
0.0430
0.0465
0.0469
0.0520
0.0550
0.0595
0.0625
0.0635
0.0670
0.0700
0.0730
0.0760
0.0781
0.0785
0.0810
0.0820
0.0860
0.0890
0.0935
0.0937
0.0960
0.0980
0.0995
0.1015
0.1040
AREA,
SQUARE
INCHES
0.000143
0.000163
0.000191
0.000201
0.000234
0.000314
0.000346
0.000398
0.000452
0.000491
0.000531
0.000616
0.000670
0.000735
0.000765
0.000804
0.000855
0.000962
0.001018
0.001075
0.001134
0.001195
0.001257
0.001320
0.001385
0.001452
0.001698
0.00173
0.00212
0.00238
0.00278
0.00307
0.00317
0.00353
0.00385
0.00419
0.00454
0.00479
0.00484
0.00515
0.00528
0.00582
0.00622
0.00687
0.00690
0.00724
0.00754
0.00778
0.00809
0.00849
1.61
1.85
2.14
2.26
2.85
3.53
3.89
4.47
5.08
5.52
5.97
6.92
7.53
8.48
8.59
9.03
9.60
10.8
11.5
12.1
12.8
13.5
14.2
14.9
15.6
16.3
19.1
19.5
23.8
26.8
31.1
34.5
35.6
39.7
43.3
47.1
51.0
53.8
54.4
57.9
59.3
65.3
69.9
77.2
77.5
81.3
84.7
87.4
90.9
95.4
CAPACITIES IN CFH OF 0.6 GRAVITY HIGH PRESSURE NATURAL GAS AND AN ORIFICE COEFFICIENT OF 1.0
Upstream Pressure, Psi Gauge
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 12 14 16 18 20 25 30 40 50
2.26
2.76
3.17
3.52
3.84
4.13
4.40
4.65
4.88
2.61
3.02
3.18
4.02
4.97
5.48
7.08
7.16
7.78
8.41
9.75
10.6
12.0
12.2
12.8
13.6
15.3
16.2
17.1
18.0
19.0
19.9
20.9
22.0
23.0
26.9
27.4
33.6
37.7
44.0
48.6
50.2
55.9
61.0
66.4
71.9
75.9
76.6
81.6
83.6
92.1
98.5
109
110
115
120
124
128
135
3.18
3.68
3.88
4.90
6.05
6.67
7.67
8.71
9.46
10.3
11.9
13.0
14.6
14.8
15.5
16.5
18.6
19.7
20.8
21.9
23.1
24.3
25.5
26.7
28.0
32.8
33.4
40.9
45.9
53.6
59.2
61.1
68.0
74.2
80.8
87.5
92.3
93.3
99.2
102
113
120
133
133
140
146
150
156
164
3.65
4.23
4.45
5.62
6.95
7.65
8.80
10.0
10.9
11.8
13.7
14.9
16.7
17.0
17.8
18.9
21.3
22.6
23.8
25.1
26.5
27.8
29.2
30.7
32.1
37.6
38.3
46.9
52.7
61.5
67.9
70.1
78.1
85.2
92.7
101
106
107
114
117
129
138
152
153
161
167
172
179
188
4.06
4.70
4.94
6.25
7.72
8.51
9.78
11.2
12.1
13.1
15.2
16.5
18.6
18.8
19.8
21.1
23.7
25.1
26.5
27.9
29.4
30.9
32.5
34.1
35.7
41.8
42.6
52.1
58.5
68.4
75.5
78.0
86.8
94.7
103
112
118
119
127
130
143
153
169
170
178
186
192
199
209
4.43
5.13
5.40
6.82
8.43
9.29
10.7
12.2
13.2
14.3
16.6
18.0
20.3
20.6
21.6
23.0
25.9
27.4
28.9
30.5
32.1
33.8
35.5
37.2
39.0
45.6
46.5
57.0
63.9
74.7
82.5
85.1
94.8
104
113
122
129
130
139
141
157
167
185
186
195
203
209
218
228
4.77
5.52
5.81
7.34
9.07
10.0
11.5
13.1
14.2
15.4
17.8
19.4
21.9
22.1
23.3
24.7
27.8
29.4
31.1
32.8
34.6
36.4
38.2
40.0
42.0
49.1
50.0
61.3
68.8
80.3
88.8
91.6
102
112
121
132
134
140
149
153
169
180
199
200
210
218
225
234
246
5.07
5.87
6.18
7.81
9.65
10.7
12.4
13.9
15.1
16.4
19.0
20.0
23.2
23.5
24.7
26.3
29.6
31.3
33.1
34.9
36.8
38.7
40.6
42.6
44.7
52.2
53.2
65.2
73.2
85.4
94.4
97.4
109
119
129
140
148
149
159
163
179
192
212
212
223
232
239
249
261
5.36
6.20
6.53
8.25
10.2
12.3
13.0
14.7
16.0
17.3
20.0
21.8
24.5
24.9
26.1
27.6
31.3
33.1
34.9
36.8
38.8
40.8
42.9
45.0
47.2
55.1
56.2
68.8
77.3
90.3
99.7
103
115
125
136
148
156
158
168
172
189
202
223
224
235
245
253
263
276
5.63
6.51
6.85
8.66
10.8
11.8
13.6
15.4
16.8
18.1
21.0
22.9
25.8
26.1
27.4
29.2
32.8
34.7
36.7
38.7
40.8
42.9
45.0
41.2
49.5
57.9
59.0
72.3
81.1
94.7
105
108
121
132
143
155
164
165
176
180
199
212
234
235
247
257
265
276
290
5.31
6.12
7.09
7.46
9.42
11.7
12.9
14.8
16.8
18.3
19.7
22.9
24.9
28.0
28.4
29.9
31.8
35.7
37.8
39.9
42.1
44.4
46.7
49.0
51.4
53.9
63.0
64.2
78.7
88.3
104
114
118
131
143
156
169
178
180
191
196
216
231
255
256
269
280
289
300
315
5.65
6.52
7.55
7.95
10.1
12.5
13.7
15.8
17.9
19.4
21.0
24.4
26.5
29.9
30.3
31.8
33.8
38.1
40.3
42.5
44.8
47.3
49.7
52.2
54.8
57.4
67.1
68.4
83.8
94.1
110
122
126
140
153
166
180
190
192
204
209
230
246
272
273
287
298
308
320
336
6.05
6.98
8.08
8.50
10.8
13.3
14.7
16.9
19.1
20.8
22.5
26.1
28.4
32.0
32.4
34.0
36.2
40.7
42.4
45.5
48.0
50.6
53.2
55.8
58.6
61.4
71.8
73.2
89.6
101
118
130
134
150
163
178
192
203
205
218
224
246
263
291
292
306
319
329
342
359
6.44
7.43
8.61
9.05
11.5
14.2
15.6
18.0
20.4
22.1
23.9
27.8
30.2
34.0
34.5
36.2
38.5
43.4
45.9
48.4
51.1
53.8
56.6
59.5
62.4
65.4
76.5
77.9
95.5
108
126
139
143
159
174
189
205
216
218
232
238
262
280
310
311
326
340
351
365
383
6.84
7.89
9.13
9.61
12.2
15.0
16.6
19.1
21.6
23.5
25.4
29.5
32.1
36.1
36.6
38.5
40.9
46.0
48.7
51.4
54.2
57.1
60.1
63.1
66.2
69.4
81.2
82.7
102
114
133
147
152
169
184
201
217
229
232
246
253
278
298
329
350
346
361
372
387
406
7.82
9.02
10.5
11.0
13.9
17.2
19.0
21.8
24.7
26.9
29.1
33.8
36.7
41.3
41.9
44.0
46.8
52.6
55.7
58.8
62.0
65.4
68.7
72.2
75.7
79.4
92.8
94.6
116
132
152
168
174
193
211
229
249
262
265
282
289
319
340
376
378
396
413
426
443
464
8.80
10.2
11.8
12.4
15.7
19.4
21.3
24.5
27.6
30.3
32.7
38.0
41.3
46.5
47.1
49.5
52.7
59.2
62.7
66.2
69.8
73.6
77.4
81.3
85.3
89.4
105
107
131
147
172
189
196
218
237
258
280
295
298
317
325
359
383
423
425
446
464
479
498
523
10.8
12.5
14.4
15.2
19.2
23.7
26.1
30.0
34.1
37.0
40.0
46.4
50.5
56.9
57.7
60.6
64.4
72.5
76.7
81.0
85.4
90.0
94.7
99.5
105
110
128
131
160
180
210
232
239
266
290
316
342
361
365
388
398
439
469
518
520
546
568
585
610
640
12.8
14.7
17.1
17.9
22.7
28.0
30.9
35.5
40.3
43.8
47.3
54.9
59.7
67.3
68.2
71.7
76.2
85.7
90.7
95.8
101
107
112
118
124
130
152
155
189
212
248
274
283
315
343
374
405
427
432
459
471
519
555
612
615
645
672
693
721
757
- continued -
Page 39

697
Te c h n i c a l
Conversions, Equivalents, and Physical Data
Capacities of Spuds and Orices (continued)
DRILL
DESIGNATION
36
7/64”
35
34
33
32
31
1/8”
30
29
28
9/64”
27
26
25
24
23
5/32”
22
21
20
19
18
11/64”
17
16
15
14
13
3/16”
12
11
10
9
8
7
13/64”
6
5
4
3
7/32”
2
1
A
15/64”
B
C
D
E=1/4”
F
G
17/64”
H
DIAMETER,
INCHES
0.1065
0.1094
0.1100
0.1110
0.1130
0.1160
0.1200
0.1250
0.1285
0.1360
0.1405
0.1406
0.1440
0.1470
0.1495
0.1520
0.1540
0.1562
0.1570
0.1590
0.1610
0.1660
0.1695
0.1719
0.1730
0.1770
0.1800
0.1820
0.1850
0.1875
0.1890
0.1910
0.1930
0.1960
0.1990
0.2010
0.2031
0.2040
0.2055
0.2090
0.2130
0.2187
0.2210
0.2280
0.2340
0.2344
0.2380
0.2420
0.2460
0.2500
0.2570
0.2610
0.2656
0.2660
AREA,
SQUARE
INCHES
0.00891
0.00940
0.00950
0.00968
0.01003
0.01057
0.01131
0.01227
0.01296
0.01433
0.01549
0.01553
0.01629
0.01697
0.01755
0.01815
0.01863
0.01917
0.01936
0.01986
0.02036
0.02164
0.02256
0.02320
0.02351
0.02461
0.02345
0.02602
0.02688
0.02761
0.02806
0.02865
0.02940
0.03017
0.03110
0.03173
0.03241
0.03269
0.03317
0.03431
0.03563
0.03758
0.03836
0.04083
0.04301
0.04314
0.04449
0.04600
0.04733
0.04909
0.05187
0.05350
0.05542
0.05557
CAPACITIES IN CFH OF 0.6 GRAVITY HIGH PRESSURE NATURAL GAS AND AN ORIFICE COEFFICIENT OF 1.0
Upstream Pressure, Psi Gauge
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 12 14 16 18 20 25 30 40 50
100
141
172
197
219
240
258
274
290
304
106
107
109
113
119
127
138
146
164
174
175
183
191
197
204
210
216
218
223
229
243
254
261
264
277
286
293
302
310
315
322
331
339
350
357
364
367
373
386
400
422
431
459
483
485
500
517
534
552
583
601
623
624
149
151
154
159
168
179
195
206
230
246
246
258
269
278
288
295
304
307
315
323
343
358
368
373
390
403
412
426
437
445
454
466
478
493
503
513
518
525
543
564
595
608
647
681
683
705
725
733
777
821
847
878
880
182
183
187
194
204
218
237
250
280
299
300
314
327
339
350
359
370
373
383
393
417
435
447
453
475
491
502
518
532
541
552
567
582
600
612
625
630
639
661
687
724
739
787
829
831
857
916
975
946
1000
1040
1070
1070
208
210
214
222
234
250
272
287
322
343
344
361
376
388
402
412
424
428
440
451
479
499
513
520
545
563
576
595
611
621
634
650
667
688
702
717
723
734
739
788
831
849
903
951
954
984
1020
1060
1090
1150
1190
1230
1230
231
234
238
247
260
278
302
319
357
381
382
401
417
432
446
458
472
476
488
501
532
555
571
578
605
626
640
661
679
690
704
723
742
765
780
797
804
816
844
876
924
943
1010
1060
1060
1100
1130
1170
1210
1280
1320
1370
1370
253
255
260
270
284
304
330
348
390
416
417
438
456
472
490
501
515
520
534
547
581
606
623
632
661
684
699
722
742
754
770
790
810
835
852
870
878
891
921
959
1010
1030
1100
1160
1160
1200
1240
1280
1320
1400
1440
1490
1500
272
275
280
290
306
327
355
375
420
448
449
471
491
507
525
539
554
560
574
589
625
652
671
680
711
736
752
777
798
811
828
850
872
899
917
937
945
959
991
1030
1090
1110
1180
1250
1250
1290
1330
1370
1420
1500
1550
1610
1610
289
292
298
309
325
348
377
399
447
476
478
501
522
540
558
573
589
595
611
626
665
694
713
723
756
782
800
826
849
862
881
904
927
956
975
996
1010
1020
1060
1100
1160
1180
1260
1330
1330
1370
1420
1460
1510
1600
1650
1710
1710
305
309
315
326
343
367
399
421
472
503
504
529
551
570
589
605
623
629
645
661
703
733
753
763
799
826
845
873
896
911
930
955
980
1010
1030
1060
1070
1080
1120
1160
1220
1250
1330
1400
1400
1450
1500
1550
1600
1690
1740
1810
1810
321
324
330
342
360
386
418
442
495
528
529
555
579
598
619
635
653
660
677
694
738
769
790
801
839
868
887
916
941
956
976
1010
1030
1060
1090
1110
1120
1130
1170
1220
1280
1310
1400
1470
1470
1520
1570
1620
1680
1770
1830
1890
1900
331
349
353
359
372
392
420
456
481
539
575
576
605
630
651
674
691
711
713
737
756
803
837
861
872
913
944
965
997
1030
1050
1070
1090
1120
1160
1180
1210
1220
1230
1280
1330
1400
1430
1520
1600
1600
1650
1710
1770
1830
1930
1990
2060
2070
352
372
376
383
396
418
447
485
512
575
612
614
644
671
694
718
737
758
765
785
805
855
892
917
929
973
1010
1030
1060
1100
1110
1140
1170
1200
1230
1260
1290
1300
1320
1360
1410
1490
1520
1620
1700
1710
1760
1820
1880
1940
2050
2120
2190
2200
377
398
402
410
424
447
478
519
548
615
655
657
689
718
742
768
788
811
819
840
861
915
954
981
994
1040
1080
1100
1140
1170
1190
1220
1250
1270
1320
1350
1370
1390
1410
1450
1510
1590
1630
1730
1820
1830
1880
1950
2010
2080
2200
2270
2350
2350
402
424
428
436
452
476
510
553
584
655
698
700
734
764
790
818
839
863
872
894
917
975
1020
1050
1060
1110
1150
1180
1210
1250
1270
1290
1330
1360
1400
1430
1460
1480
1500
1550
1610
1700
1730
1840
1940
1950
2010
2080
2140
2210
2340
2410
2500
2510
426
487
514
520
530
549
578
619
671
709
795
847
849
891
928
960
992
1020
1050
1060
1090
1120
1190
1240
1270
1290
1350
1400
1430
1470
1510
1540
1570
1610
1650
1700
1740
1780
1790
1820
1880
1950
2060
2100
2240
2360
2360
2440
2520
2600
2690
2840
2930
3030
3040
549
579
585
596
618
651
696
756
798
893
954
956
1010
1050
1080
1120
1150
1180
1200
1230
1260
1340
1390
1430
1450
1520
1570
1610
1660
1700
1730
1770
1810
1860
1920
1960
2000
2020
2050
2120
2200
2320
2370
2520
2650
2660
2740
2840
2930
3030
3200
3300
3410
3420
449
454
463
480
505
541
587
620
695
740
742
779
811
839
867
890
916
925
949
973
1040
1080
1110
1130
1180
1220
1250
1290
1320
1340
1370
1410
1450
1490
1520
1550
1570
1590
1640
1710
1800
1840
1950
2060
2070
2130
2200
2280
2350
2480
2560
2650
2660
671
708
716
729
756
796
852
924
976
1100
1170
1170
1230
1280
1330
1370
1410
1450
1460
1500
1540
1630
1700
1750
1770
1860
1920
1960
2030
2080
2120
2160
2220
2280
2350
2390
2450
2470
2500
2590
2690
2830
2890
3080
3240
3250
3350
3470
3580
3700
3910
4030
4180
4190
794
838
847
863
894
942
1010
1100
1160
1300
1380
1390
1460
1520
1570
1620
1660
1710
1730
1770
1820
1930
2010
2070
2100
2200
2270
2320
2400
2460
2500
2560
2620
2690
2770
2830
2890
2920
2960
2770
2830
2890
2920
2960
3060
3180
3350
3420
3640
4380
4620
4770
4940
4950
- continued -
Page 40

698
Te c h n i c a l
Conversions, Equivalents, and Physical Data
Capacities of Spuds and Orices (continued)
DRILL
DESIGNATION
I
J
K
9/32”
L
M
19/64”
N
5/16”
O
P
21/64”
Q
R
11/32”
S
T
23/64”
U
3/8”
V
W
25/64”
X
Y
13/32”
Z
27/64”
7/16”
29/64”
15/32”
31/64”
1/2”
33/64”
17/32”
35/64”
9/16”
37/64”
19/32”
39/64”
5/8”
41/64”
21/32”
43/64”
11/16”
23/32”
3/4”
25/32”
13/16”
27/32”
7/8”
29/32”
15/16”
31/32”
1.0”
DIAMETER,
INCHES
0.2720
0.2770
0.2810
0.2812
0.2900
0.2930
0.2969
0.3020
0.3125
0.3160
0.3230
0.3281
0.3320
0.3390
0.3437
0.3480
0.3580
0.3594
0.3680
0.3750
0.3770
0.3860
0.3960
0.3970
0.4040
0.4062
0.4130
0.4219
0.4375
0.4531
0.4687
0.4844
0.5000
0.5156
0.5313
0.5469
0.5625
0.5781
0.5938
0.6094
0.6250
0.6406
0.6562
0.6719
0.6875
0.7188
0.7500
0.7812
0.8125
0.8438
0.8750
0.9062
0.9375
0.9688
1.0000
AREA,
SQUARE
INCHES
0.005811
0.006026
0.006102
0.006113
0.006605
0.006835
0.006922
0.007163
0.007670
0.007843
0.008194
0.008456
0.008657
0.009026
0.009281
0.09511
0.1006
0.1014
0.1065
0.1105
0.1116
0.1170
0.1198
0.1238
0.1282
0.1295
0.1340
0.1398
0.1503
0.1613
0.1726
0.1843
0.1964
0.2088
0.2217
0.2349
0.2485
0.2625
0.2769
0.2917
0.3068
0.3223
0.3382
0.3545
0.3712
0.4057
0.4418
0.4794
0.5185
0.5591
0.6013
0.6450
0.6903
0.7371
0.7854
653
677
697
698
742
768
778
805
862
881
920
950
972
1020
1050
1070
1130
1140
1200
1240
1260
1320
1350
1390
1440
1460
1510
1570
1690
1820
1940
2070
2210
2350
2490
2640
2790
2950
3110
3280
3450
3620
3800
3980
4170
4560
4960
5390
5830
6280
6760
7250
7750
8280
8820
CAPACITIES IN CFH OF 0.6 GRAVITY HIGH PRESSURE NATURAL GAS AND AN ORIFICE COEFFICIENT OF 1.0
Upstream Pressure, Psi Gauge
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 12 14 16 18 20 25 30 40 50
916
1120
1290
1430
1560
1680
1790
1890
1980
957
983
984
1050
1090
1100
1140
1220
1250
1300
1340
1370
1430
1470
1510
1600
1610
1690
1750
1770
1860
1900
1960
2030
2060
2130
2220
2380
2560
2740
3280
3110
3310
3510
3720
3940
4160
4390
4620
4860
5110
5360
5620
5880
6430
7000
7590
8210
8850
9520
10 200
10 900
11 700
12 400
1170
1200
1200
1280
1320
1340
1380
1480
1520
1580
1630
1670
1740
1790
1840
1940
1960
2050
2130
2150
2260
2310
2390
2470
2500
2590
2700
2900
3110
3330
3550
3790
4030
4280
4530
4770
5060
5340
5620
5910
6210
6520
6830
7150
7820
8510
9240
9990
10 800
11 600
12 400
13 300
14 200
15 100
1340
1380
1380
1460
1520
1530
1590
1700
1740
1820
1870
1920
2000
2060
2110
2230
2250
2360
2450
2470
2590
2650
2740
2840
2870
2970
3100
3330
3570
3820
4080
4350
4620
4910
5200
5500
5810
6130
6450
6790
7130
7480
7840
8210
8970
9770
10 600
11 500
12 400
13 300
14 300
15 300
16 300
17 400
1490
1530
1530
1630
1680
1710
1760
1890
1930
2020
2080
2130
2220
2290
2340
2480
2500
2620
2720
2750
2900
2950
3050
3150
3190
3300
3440
3700
4000
4250
4530
4830
5140
5450
5780
6110
6450
6810
7170
7540
7920
8320
8720
9130
9970
10 900
11 800
12 800
13 800
14 800
15 900
17 000
18 200
19 300
1620
1670
1670
1780
1840
1860
1930
2060
2110
2200
2270
2330
2430
2500
2530
2710
2730
2860
2970
3000
3200
3220
3330
3450
3480
3600
3760
4040
4230
4640
4950
5280
5610
5960
6310
6680
7050
7440
7830
8240
8660
9080
9520
9970
10 900
11 900
12 900
14 000
15 000
16 200
17 400
18 600
19 800
21 100
1750
1800
1800
1910
1980
2000
2070
2220
2270
2370
2450
2500
2607
2690
2750
2910
2930
3080
3200
3230
3380
3460
3580
3710
3750
3870
4040
4350
4660
4990
5330
5680
6040
6410
6790
7180
7590
8000
8430
8870
9310
9770
10 300
10 600
11 800
12 800
13 900
15 000
16 200
17 400
18 700
20 000
21 300
22 700
1860
1910
1910
2030
2100
2130
2210
2360
2410
2520
2600
2660
2780
2860
2930
3100
3120
3270
3400
3430
3600
3680
3810
3940
3990
4130
4300
4620
5000
5310
5670
6340
6420
6820
7220
7640
8070
8510
8970
9430
9910
10 400
10 900
11 500
12 500
13 600
14 800
16 000
17 200
18 500
19 000
21 200
22 700
24 200
1960
2020
2020
2150
2220
2250
2330
2490
2550
2660
2750
2810
2930
3020
3090
3270
3300
3460
3590
3630
3800
3890
4020
4160
4210
4350
4540
4880
5140
5610
5990
6380
6780
7200
7630
8070
8520
8990
9470
9960
10 500
11 000
11 500
12 100
13 200
14 400
15 600
16 900
18 200
19 600
21 000
22 400
24 000
25 500
2060
2120
2120
2250
2330
2360
2440
2620
2660
2800
2890
2950
3080
3170
3240
3430
3460
3630
3770
3810
3990
4090
4220
4370
4420
4570
4770
5120
5500
5880
6280
6690
7120
7560
8010
8470
8950
9440
9940
10 500
11 000
11 600
12 100
12 700
13 900
15 100
16 400
17 700
19 100
20 500
22 000
23 600
25 100
26 800
2160
2240
2300
2310
2450
2540
2570
2660
2850
2910
3040
3140
3210
3350
3450
3530
3740
3770
3950
4100
4140
4340
4450
4600
4760
4810
4970
5190
5580
5990
6410
6840
7290
7750
8230
8720
9220
9740
10 300
10 900
11 400
12 000
12 600
13 200
13 800
15 100
16 400
17 800
19 300
20 800
22 300
24 000
25 600
27 400
29 200
2300
2390
2450
2460
2610
2710
2740
2830
3030
3100
3240
3350
3420
3570
3670
3760
4000
4010
4210
4370
4410
4630
4740
4900
5070
5120
5300
5530
5940
6380
6820
7280
7760
8250
8760
9290
9820
10 370
10 940
11 600
12 200
12 800
13 400
14 000
14 700
16 100
17 500
19 000
20 500
22 100
23 800
25 500
27 500
29 200
31 100
2460
2550
2630
2630
2800
2890
2930
3030
3250
3320
3470
3580
3660
3820
3930
4020
4260
4290
4500
4670
4720
5000
5100
5240
5420
5480
5670
5910
6360
6820
7300
7790
8310
8490
9370
9930
10 500
11 100
11 700
12 400
12 700
13 700
14 300
15 000
15 700
17 200
18 700
20 300
22 000
23 700
25 500
26 400
29 200
31 200
33 200
2620
2720
2800
2800
2980
3080
3120
3230
3460
3540
3690
3810
3900
4070
4180
4290
4530
4570
4790
4980
5030
5270
5400
5580
5780
5840
6040
6300
6770
7270
7770
8300
8850
9400
9980
10 600
11 200
11 900
12 500
13 200
13 900
14 600
15 300
16 000
16 800
18 300
19 900
21 600
23 400
25 200
27 100
29 100
31 100
33 200
35 400
2780
2880
2970
2970
3160
3270
3310
3430
3670
3750
3920
4040
4140
4320
4440
4550
4810
4850
5050
5280
5340
5590
5730
5920
6130
6200
6400
6680
7200
7700
8300
8800
9400
10 000
10 600
11 300
11 900
12 600
13 300
14 000
14 700
15 400
16 200
17 000
17 800
19 400
21 200
22 900
24 800
26 700
28 800
30 900
33 000
35 300
37 600
3180
3300
3390
3400
3610
3740
3790
3920
4200
4290
4480
4630
4740
4940
5080
5200
5500
5550
5820
6040
6100
6350
6550
6770
7010
7090
7330
7650
8220
8820
9440
10 100
10 800
11 500
12 200
12 900
13 600
14 400
15 200
16 000
16 800
17 700
18 500
19 400
20 300
22 200
24 200
26 200
28 400
30 600
32 900
35 300
37 800
40 300
43 000
3580
3710
3820
3830
4070
4210
4260
4410
4720
4830
5050
5210
5330
5560
5720
5860
6200
6240
6550
6800
6870
7200
7380
7620
7890
7980
8250
8610
9250
9930
10 700
11 400
12 100
12 900
13 700
14 500
15 300
16 200
17 100
18 000
18 900
19 900
20 900
21 900
22 900
25 000
27 200
29 500
32 000
34 400
37 000
39 700
42 500
45 400
48 400
4380
4540
4680
4680
4980
5150
5220
5400
5780
5910
6180
6370
6520
6800
6990
7170
7580
7640
8020
8330
8410
8820
9030
9330
9660
9760
10 100
10 600
11 400
12 200
13 000
13 900
14 800
15 800
16 700
17 700
18 800
19 800
20 900
22 000
23 100
24 300
25 500
26 700
28 000
30 600
33 300
36 100
39 100
42 100
45 300
48 600
52 000
55 600
59 200
5180
5370
5530
5540
5890
6090
6170
6390
6840
6990
7300
7540
7720
8040
8270
8480
8970
9040
9480
9850
9950
10 400
10 700
11 100
11 500
11 600
12 000
12 500
13 400
14 400
15 400
16 400
17 500
18 600
19 800
21 000
22 000
23 400
24 700
26 000
27 400
28 800
30 200
31 600
33 100
36 200
39 400
42 800
46 200
49 800
53 600
57 500
61 500
65 700
70 000
Page 41

699
Te c h n i c a l
Conversions, Equivalents, and Physical Data
SILICONE FLUID 200 CS
SILICONE FLUID 1000 CS
MIL-T-5624 (JP-4)
MIL-C-7024 TYPE II
JET A
ETHYLENE GLYCOL WATER MIXTURE 50/50
D IESEL FUEL
MIL-T-5624 (JP-5)
AND KEROSENE
JET A
H 0
2
BENZENE
ETHYLENE OXIDE
AUTOMOBILE GASOLINE AVG
MIL-T-5624 (JP-5)
AND KEROSENE
MIL-H-6083
MIL-H-5606
SKYDROL 500 B-4 AND LD-4
MIL-H-5606
MIL-L-23699
MIL-H-6083
MIL-L-7808
AND MIL-H-83282
MIL-L-7808 AND MIL-H-83282
SKYDROL 7000
MIL-L-6081 (1010)
# 4 FUEL OIL
# 4 FUEL OIL
DIESEL FUEL
ETHYLENE GLYCOL 100%
SAE 30
SAE 20
SAE 10
MIL-L-23699
SKYDROL 7000
SAE 40
10,000
Viscosities of Typical Fluids vs. Temperature
TEMPERATURE °F
KINEMATIC VISCOSITY - CENTISTOKES
5,000
2,000
1,000
500
200
100
50
20
10.0
8.0
6.0
4.0
3.0
2.0
1.5
1.0
0.9
0.8
0.7
0.6
350300250200150100806040200-20-40-60
SAE 90
SAE 90
SAE 140
SAE 140
SILICONE FLUID 500 CS
MIL-L-6081 (1010)
MIL-G-5572 AVIATION GASOLINE
ALCOHOL AND ACETONE
MIL-L-6082 (1100), SAE 50, AND BUNKER-C
Page 42

700
Te c h n i c a l
Conversions, Equivalents, and Physical Data
JET A
ALCOHOL AND ACETONE
H 0
2
H 0
2
MIL-G-5572 AVIATION GASOLINE
AUTOMOBILE GASOLINE AVG
ETHYLENE GLYCOL WATER MIXTURE 50/50
SKYDROL 500 B-4
SILICONE FLUIDS
#4 FUEL OIL
AND BUNKER-C
MIL-H-5606
AND MIL-H-83282
MIL-L-6081 (1010)
AND MIL-H-6083
MIL-T-5624 (JP-5)
MIL-C-7024 TYPE 11
MIL-T-5624 (JP-4)
MIL-L7808
MIL-L-23699
KEROSENE
MIL-L-6082 (1100), SAE 50, 90 AND 140 AVG
,
DIESEL FUELS, BENZENE AND SAE 10 THRU 40 AVG
SILICONE FLUIDS
SKYDROL 7000
SKYDROL LD-4
ETHYLENE GLYCOL 100%
1.20
1.15
1.05
1.05
1.00
0.95
0.90
0.85
0.80
0.75
0.70
0.65
0.60
0.55
0.50
TEMPERATURE °F
SPECIFIC GRAVITY
(WITH RESPECT TO H
2
O @ 60°F)
180100806040200-20-40-60 160140 280200120 260240 300220
Specific Gravity of Typical Fluids vs. Temperature
MIL-L7808
ETHYLENE OXIDE
Page 43

701
Te c h n i c a l
Conversions, Equivalents, and Physical Data
1.5:1 2:1 3:1 4:1
Effect of Inlet Swage On Critical
Flow C
g
Requirements
Valve Cg/Valve Inlet Area
Swaged C
g
/Linear-Size C
g
1
0 100
0.95
0.9
0.85
0.8
0.75
200 300 400 500 900 800700 600
Page 44

702
Te c h n i c a l
Conversions, Equivalents, and Physical Data
Seat Leakage Classications (In Accordance with ANSI/FCI 70-3-2004)
LEAKAGE CLASS
DESIGNATION
DESCRIPTION
MAXIMUM LEAKAGE
ALLOWABLE
I
II
III
IV
VI
VII
A modication of any Class II, III or IV regulator where the design intent is the
same as the basic class, but by agreement between user and supplier, no test
This class establishes the maximum permissible leakage generally associated with
commercial double-seat regulators with metal-to-metal seats.
This class establishes the maximum permissible leakage generally associated with
This class establishes the maximum permissible leakage generally associated with
Class II, but with a higher degree of seat and seal tightness.
commercial unbalanced single-seat regulators with metal-to-metal seats.
This class establishes the maximum permissible seat leakage generally
associated with resilient seating regulators either balanced or unbalanced with
This class establishes the maximum permissible seat leakage generally
associated with Class VI, but with test performed at the maximum operating
is required.
O-rings or similar gapless seals.
differential pressure.
- - - -
0.5% of maximum Cv
0.1% of maximum Cv
0.01% of maximum Cv
Leakage per following table as expressed in ml per minute
Leakage per following table as expressed in ml per minute
versus seat diameter.
versus seat diameter.
Nominal Port Diameter and Leak Rate
NOMINAL PORT DIAMETER LEAK RATE
Millimeters (Inches) Standard ml per Minute
(2)
<25 (<1)
38 (1.5)
51 (2)
64 (2.5)
76 (3)
102 (4)
152 (6)
203 (8)
250 (10)
300 (12)
350 (14)
400 (16)
1. Bubbles per minute as tabulated are an easily measured suggested alternative based on a suitable calibrated measuring device in this case a 0.24 inch (6 mm) O.D. x 0.04 inch (1 mm)
wall tube submerged in water to a depth of from 0.12 to 0.24 inch (3 to 6 mm). The tube end shall be cut square and smooth with no chamfers or burrs and the tube axis shall be
perpendicular to the surface of the water. Other apparatus may be constructed and the number of bubbles per minute may differ from those shown as long as they correctly indicate the
ow in ml per minute.
2. If valve seat diameter differs by more than 0.08 inch (2 mm) from one of the valves listed, the leakage rate may be obtained by interpolation assuming that the leakage rate varies as the
square of the seat diameter.
3. Standard millimeters based on 60 °F (16 °C) and 14.73 psia (1,016 bar a).
0,15
0,30
0,45
0,60
0,90
1,70
4,00
6,75
11,1
16,0
21,6
28,4
(3)
Bubbles per
(1)
Minute
(2)
1
2
3
4
6
11
27
45
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
Page 45

703
Te c h n i c a l
Conversions, Equivalents, and Physical Data
Flange, Valve Size, and Pressure-Temperature
Rating Designations
Sizes of ASME anges are designated as NPS (for “nominal
pipe size”). The nominal size is based on inches, but the units are
not required in the designation. For example: NPS 2 is the size.
Pressure ratings are designated by class. For example, CL150 is
the rating. ASME designations replace ANSI designations.
Sizes of EN and ISO anges are designated with DN (for “nominal
diameter”). The nominal diameter is based on millimeters, but
the units are not included in the designation. For example: DN 50
is the size. Pressure ratings are designated by PN (for “nominal
pressure”). For example PN 40 is the pressure rating. EN and ISO
designations replace DIN designations through PN 100.
ASME B16.5 anges will mate with EN 1759 anges but not with
EN 1092 anges (formerly DIN anges). ASME B16.5 anges
will mate with most ISO 7005 anges.
Common size designations in wide use are shown in the table below.
A summary of ange terminology is shown in the table below, and
equivalency of anges is shown in the table on the following page.
Pipe Thread Standards
There are three pipe thread standards that are accepted globally:
• NPT, ASME B1.20.1: General-purpose pipe threads (inches).
• G Series, ISO 228-1: Pipe threads for use where pressure-tight
joints are not made on the threads. The internal and external
threads are not tapered but are parallel or straight.
• R Series, ISO 7/1: Pipe threads for use where pressure-tight
joints are made on the threads. The internal thread is parallel
(straight) or tapered; external is always tapered.
Notes
Japanese (JIS) valves and anges are designated according to
JIS standards.
European Norm ange types, such as at-face and raised-face
are designated Type A, Type B, Type C. These types do not
correspond to the DIN 2526 Form A, Form D, etc., designations.
Common Size Designations
NPS 1/2 3/4 1 1-1/2 2 2-1/2 3 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 24
DN 15 20 25 40 50 65 80 100 150 200 250 300 350 400 450 500 600
Summary of Flange Terminology
ASME EUROPEAN NORM EXAMPLE OF PRINTED PRESENTATION
Pressure Rating CLASS PN CL300 or CL300, PN 40
Size NPS DN NPS 2, DN 50
Pipe Threads (Internal or
External)
NPT NPT, G (Straight), R (Tapered) G 1/4, 1/4 NPT, 1/4 NPT Internal (or External)
Page 46

704
Te c h n i c a l
Conversions, Equivalents, and Physical Data
Equivalency Table
ISO ASME DIN EUROPEAN NORM LIMITATIONS
ASME and European
Norm Only
European Norm Only - - - - EN 1092 Through PN 100
DIN Only - - - - DIN
ISO and ASME Only ISO 7005 Class Flanges ASME B16.5 - - - -
1. DIN is no longer used except for pressure ratings above PN 100.
2. DIN standards 2628, 2629, 2638, 2548, 2549, 2550, and 2551.
- - - - Class Flanges ASME B16.5 - - - - EN 1759-1
(2)
- - - - Above PN 100
Species ASTM materials but also permits
European materials per EN 1092-1.
(1)
(1)
A few sizes are compatible to previous
DIN standards. An older version contained
ange designations that do not appear in the
current standard.
Standard Pressure-Temperature Ratings for ASME CL150 Valve Bodies
SERVICE
TEMPERATURE,
°F (°C)
-20 to 100 (-29 to 38)
200 (93)
300 (149)
400 (204)
500 (260)
600 (316)
650 (343)
700 (371)
1. Table information is extracted from the Valve-Flanged, Threaded, and Welding End, ASME Standard B16.34-2004. These tables must be used in accordance with the ASME standard.
LCB LCC/WCC WCB CF8 or 304 CF8M/CF3M
265 (18,3)
255 (17,6)
230 (15,9)
200 (13,8)
170 (11,7)
140 (9,7)
125 (8,6)
110 (7,6)
290 (20,0)
260 (17,9)
230 (15,9)
200 (13,8)
170 (11,7)
140 (9,7)
125 (8,6)
110 (7,6)
WORKING PRESSURE, PSIG (bar)
285 (19,7)
260 (17,9)
230 (15,9)
200 (13,8)
170 (11,7)
140 (9,7)
125 (8,6)
110 (7,6)
275 (19,0)
230 (15,9)
205 (14,1)
190 (13,1)
170 (11,7)
140 (9,7)
125 (8,6)
110 (7,6)
Standard Pressure-Temperature Ratings for ASME CL300 Valve Bodies
SERVICE
TEMPERATURE,
°F (°C)
-20 to 100 (-29 to 38)
200 (93)
300 (149)
400 (204)
500 (260)
600 (316)
650 (343)
700 (371)
1. Table information is extracted from the Valve-Flanged, Threaded, and Welding End, ASME Standard B16.34-2004. These tables must be used in accordance with the ASME standard.
LCB LCC/WCC WCB CF8 or 304 CF8M/CF3M
695 (47,9)
660 (45,5)
640 (44,1)
615 (42,4)
585 (40,3)
550 (37,9)
535 (36,8)
510 (35,2)
750 (51,7)
750 (51,7)
730 (50,3)
705 (48,6)
665 (45,9)
605 (41,7)
590 (40,7)
555 (38,3)
WORKING PRESSURE, PSIG (bar)
740 (51,0)
680 (46,9)
655 (45,2)
635 (43,8)
605 (41,7)
570 (39.3)
550 (38,0)
530 (36,5)
720 (49,6)
600 (41,4)
540 (37,2)
495 (34,1)
465 (32,1)
440 (30.3)
430 (29,6)
420 (29,0)
(1)
275 (19,0)
235 (16,2)
215 (14,8)
195 (13,4)
170 (11,7)
140 (9,7)
125 (8,6)
110 (7,6)
(1)
720 (49,6)
620 (42,7)
560 (38,6)
515 (35,5)
480 (33,1)
450 (31,0)
440 (30,3)
435 (30,0)
Page 47

705
Te c h n i c a l
Conversions, Equivalents, and Physical Data
34,5
232
27,6
22,0
17,2
13,8
12,1
8,6
5,0
0
0
0
50
100
150
200
250
300
350
400
450
500
550
-20
100
TEMPERATURE, °F
TEMPERATURE, °C
PRESSURE RATING-PSI-LIQUID, GAS, STEAM
PRESSURE RATING-BAR
ASME CLASS
125 RATINGS
SATURATED
STEAM
ASME CLASS 250 RATINGS
Pressure/Temperature Ratings for ASTM A126 Cast Iron Valves
20817815010065
300
-29
200 300
353 406 450
Standard Pressure-Temperature Ratings for ASME CL600 Valve Bodies
SERVICE
TEMPERATURE,
°F (°C)
-20 to 100 (-29 to 38)
200 (93)
300 (149)
400 (204)
500 (260)
600 (316)
650 (343)
700 (371)
1. Table information is extracted from the Valve-Flanged, Threaded, and Welding End, ASME Standard B16.34-2004. These tables must be used in accordance with the ASME standard.
LCB LCC/WCC WCB CF8 or 304 CF8M/CF3M
1395 (96,2)
1320 (91,0)
1275 (87,9)
1230 (84,8)
1175 (81,0)
1105 (76,2)
1065 (73,4)
1025 (70,7)
1500 (103)
1500 (103)
1455 (100)
1405 (97,0)
1330 (91,7)
1210 (83,4)
1175 (81,0)
1110 (76,5)
WORKING PRESSURE, PSIG (bar)
1480 (102)
1360 (93,7)
1310 (90,3)
1265 (87,2)
1205 (83,1)
1135 (78,3)
1100 (75,8)
1060 (73,1)
1440 (99,3)
1200 (82,7)
1075 (74,1)
995 (68,6)
930 (64,1)
885 (61,0)
865 (59,6)
845 (58,3)
(1)
1440 (99,3)
1240 (85,5)
1120 (77,2)
1025 (70,7)
955 (65,8)
900 (62,1)
885 (61,0)
870 (60,0)
CLASS B (1”-12”)
CLASS A (1”-12”)
CLASS B (14”-24”)
CLASS B (1”-12”)
CLASS A (1”-12”)
CLASS B (14”-24”)
Page 48

706
Te c h n i c a l
Conversions, Equivalents, and Physical Data
Diameter of Bolt Circles
NOMINAL
PIPE SIZE,
INCHES
1
1-1/4
1-1/2
2
2-1/2
3
4
5
6
8
10
12
14
16
18
20
24
30
36
42
48
1. Sizes 1 through 12-inches also apply to ASME Class 150 bronze anges.
2. Sizes 1 through 8-inches also apply to ASME Class 300 bronze anges.
ASMECL125 (CAST IRON)
OR CL150
(1)
(STEEL)
3.12
3.50
3.88
4.75
5.50
6.00
7.50
8.50
39.50
11.75
14.25
17.00
18.75
21.25
22.75
25.00
29.50
36.00
42.75
49.50
56.00
ASME CL250
(CAST IRON) OR
CL300
(2)
(STEEL)
3.50
3.88
4.50
5.00
5.88
6.62
7.88
9.25
10.62
13.00
15.25
17.75
20.25
22.50
24.75
27.00
32.00
39.25
46.00
52.75
60.75
ASME
CL600
3.50
3.88
4.50
5.00
5.88
6.62
8.50
10.50
11.50
13.75
17.00
19.25
20.75
23.75
25.75
28.50
33.00
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
ASME
CL900
4.00
4.38
4.88
6.50
7.50
7.50
9.25
11.00
12.50
15.50
18.50
21.00
22.00
24.25
27.00
29.50
35.50
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
ASME
CL1500
4.00
4.38
4.88
6.50
7.50
8.00
9.50
11.50
12.50
15.50
19.00
22.50
25.00
27.75
30.50
32.75
39.00
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
ASME
CL2500
4.25
5.12
5.75
6.75
7.75
9.00
10.75
12.75
14.50
17.25
21.75
24.38
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
ASME Face-To-Face Dimensions for Flanged Regulators
BODY SIZE,
INCHES
1
1-1/4
1-1/2
2
2-1/2
3
4
6
8
10
12
16
FF—Flat-faced, RF—Raised-faced, and RTJ—Ring Type Joint
CL125 FF (Cast Iron)
CL150 RF (Steel),
Inches (mm)
7.25 (184)
7.88 (200)
8.75 (222)
10.00 (254)
10.88 (276)
11.75 (298)
13.88 (353)
17.75 (451)
21.38 (543)
26.50 (673)
29.00 (737)
40.00 (1016)
ASME CLASS AND END CONNECTIONS (INCH DIMENSIONS ARE IN ACCORDANCE WITH ISA S4.01.1-1997)
CL250 RF (Cast Iron)
CL300 RF (Steel),
Inches (mm)
41.62 (1057)
7.75 (197)
8.38 (213)
9.25 (235)
10.50 (267)
11.50 (292)
12.50 (317)
14.50 (368)
18.62 (473)
22.38 (568)
27.88 (708)
30.50 (775)
CL150 RJT (Steel),
Inches (mm)
7.75 (197)
8.38 (213)
9.25 (235)
10.50 (267)
11.38 (289)
12.25 (311)
14.38 (365)
18.25 (464)
21.88 (556)
27.00 (686)
29.50 (749)
40.50 (1029)
CL300 RJT (Steel),
Inches (mm)
8.25 (210)
8.88 (226)
9.75 (248)
11.12 (282)
12.12 (308)
13.12 (333)
15.12 (384)
19.25 (489)
23.00 (584)
28.50 (724)
31.12 (790)
42.25 (1073)
CL600 RF (Steel),
Inches (mm)
8.25 (210)
9.00 (229)
9.88 (251)
11.25 (286)
12.25 (311)
13.25 (337)
15.50 (394)
20.00 (508)
24.00 (610)
29.62 (752)
32.25 (819)
43.62 (1108)
CL600 RJT (Steel),
Inches (mm)
8.25 (210)
9.00 (229)
9.88 (251)
11.38 (289)
12.38 (314)
13.38 (340)
15.62 (397)
20.12 (511)
24.12 (613)
29.75 (756)
32.38 (822)
43.75 (1111)
Page 49

707
Te c h n i c a l
Conversions, Equivalents, and Physical Data
Wear and Galling Resistance Chart of Material Combinations
MATERIAL
304 Stainless Steel
316 Stainless Steel
Bronze
®
Inconel
®
Monel
Hastelloy® C
Nickel
Alloy 20
Type 416 Hard
Type 440 Hard
17-4PH
(1)
ENC
Cr Plate
Al Bronze
1. Electroless Nickel Coating S - Satisfactory
F - Fair P - Poor
304 STAINLESS
STEEL
P
P
F
P
P
F
P
P
F
F
F
F
F
F
316 STAINLESS
STEEL
P
P
F
P
P
F
P
P
F
F
F
F
F
F
BRONZE INCONEL
F
F
S
S
S
S
S
S
F
F
F
F
F
F
P
P
S
P
P
F
P
F
F
F
F
F
F
S
- continued -
®
MONEL
®
P
P
S
P
P
F
F
F
F
F
F
F
F
S
HASTELLOY® C NICKEL
F
F
S
F
F
F
F
F
F
F
F
F
S
S
P
P
S
F
F
F
P
P
F
F
F
F
S
S
Wear and Galling Resistance Chart of Material Combinations (continued)
MATERIAL ALLOY 20 TYPE 416 HARD TYPE 440 HARD 17-4PH ENC
304 Stainless Steel
316 Stainless Steel
Bronze
®
Inconel
®
Monel
Hastelloy® C
Nickel
Alloy 20
Type 416 Hard
Type 440 Hard
17-4PH
(1)
ENC
Cr Plate
Al Bronze
1. Electroless Nickel Coating S - Satisfactory
F - Fair P - Poor
P
P
S
F
F
F
P
P
F
F
F
F
S
S
F
F
F
F
F
F
F
F
F
S
F
S
S
S
F
F
F
F
F
F
F
F
F
F
S
S
S
S
F
F
F
F
F
F
F
F
F
S
P
S
S
S
(1)
F
F
F
F
F
F
F
F
S
S
S
P
S
S
Cr PLATE Al BRONZE
F
F
F
F
F
S
F
F
S
S
S
S
P
S
F
F
F
S
S
S
S
S
S
S
S
S
S
P
Equivalent Lengths of Pipe Fittings and Valves
TYPE OF FITTING
OR VALVE
Standard tee with entry or
discharge through side
Standard elbow or run
of tee reduced 1/2
Medium sweep elbow or
(1)
run
of tee reduced 1/4
Long sweep elbow or
(1)
run
of standard tee
or buttery valve
45° elbow 0.8 1.0 1.2 1.6 2.0 2.5 3.0 3.7 5.0 7.5 10 12 15 17 20 22 24 30 37
Close return bend 3.7 5.1 6.2 8.5 10 13 15 19 24 37 49 62 75 86 100 110 125 150 185
Globe valve, wide-open 0.6 22 27 40 43 45 65 82 120 170 240 290 340 400 440 500 550 680 850
Angle valve, wide-open 8.2 11 14 18 21 28 33 42 56 85 112 145 165 190 220 250 280 340 420
Swing check valve,
wide-open
Gate valve, wide-open, or
slight bushing reduction
1. A uid is said to ow through the run of a tee when the ow is straight through the tee with no change of direction.
2. A tee is said to be reduced 1/4 if the internal area of the smaller connecting pipe is 25% less than the internal area of the larger connecting pipe.
1/2 3/4 1 1-1/4 1-1/2 2 2-1/2 3 4 6 8 10 12 14 O.D. 16 O.D. 18 O.D. 20 O.D. 24 O.D. 30 O.D.
3.4 4.5 5.5 7.5 9.0 12 14 17 22 33 43 55 65 78 85 105 115 135 170
(1)
1.7 2.2 2.7 3.7 4.3 5.5 6.5 8 12 16 20 26 31 36 42 47 52 64 80
(2)
1.3 1.8 2.3 3.0 3.7 4.6 5.4 6.8 9.0 14 18 22 26 30 35 40 43 55 67
(2)
1 1.3 1.7 2.3 2.7 3.5 4.2 5.3 7 11 14 17 20 23 26 31 34 41 52
4.0 5.2 6.6 9.0 11 14 16 19 26 39 52 66 78 92 106 120 130 145 160
0.4 0.5 0.6 0.8 0.9 1.2 1.3 1.7 2.3 3.5 4.5 5.7 6.7 8.0 9.0 11 12 14 17
LENGTHS IN FEET OF STANDARD PIPE
Nominal Pipe Size in Inches
Page 50

708
Te c h n i c a l
Conversions, Equivalents, and Physical Data
Pipe Data: Carbon and Allow Steel—Stainless Steel
NOMINAL
PIPE SIZE
(INCHES)
1/8 0.405
1/4 0.540
3/8 0.675
1/2 0.840
3/4 1.050
1-1/4 1.660
1-1/2 1.900
Identication, wall thickness and weights are extracted from ASME B36.10 and B39.19.
The notations STD, XS, and XXS indicate Standard, Extra Strong, and Double Extra Strong pipe, respectively.
Transverse internal area values listed in “square feet” also represent volume in cubic feet per foot of pipe length.
OUTSIDE
DIAMETER
(INCHES)
1 1.315
2 2.375
Iron Pipe
IDENTIFICATION
Steel
Size
- - - STD
- - - STD
- - - STD
- - - -
- - - STD
- - - XXS
- - - -
- - - STD
- - - XXS
- - - -
- - - STD
- - - XXS
- - - -
- - - STD
- - - XXS
- - - -
- - - STD
- - - XXS
- - - -
- - - STD
- - - XXS
Schedule
XS 80 80S 0.095 0.215 0.0925 0.0365 0.00025 0.31 0.016
XS 80 80S 0.119 0.302 0.1574 0.0716 0.00050 0.54 0.031
XS 80 80S 0.126 0.423 0.2173 0.1405 0.00098 0.74 0.061
XS
XS
XS
XS
XS
XS
No.
- - - 40
- - - 40
- - - 40
- - - -
- - - 40
80
160
- - - -
- - - -
- - - 40
80
160
- - - -
- - - -
- - - 40
80
160
- - - -
- - - -
- - - 40
80
160
- - - -
- - - -
- - - 40
80
160
- - - -
- - - -
- - - 40
80
160
- - - -
Stainless Steel
Schedule No.
10S
40S
10S
40S
10S
40S
5S
10S
40S
80S
- - - -
- - - -
5S
10S
40S
80S
- - - -
- - - -
5S
10S
40S
80S
- - - -
- - - -
5S
10S
40S
80S
- - - -
- - - -
5S
10S
40S
80S
- - - -
- - - -
5S
10S
40S
80S
- - - -
- - - -
WALL
THICKNESS (t)
(INCHES)
0.049
0.068
0.065
0.088
0.065
0.091
0.065
0.083
0.109
0.147
0.187
0.294
0.065
0.083
0.113
0.154
0.219
0.308
0.065
0.109
0.133
0.065
0.250
0.358
0.065
0.109
0.140
0.191
0.250
0.382
0.065
0.109
0.145
0.200
0.281
0.400
0.065
0.109
0.154
0.218
0.344
0.436
INSIDE
DIAMETER (d)
(INCHES)
0.307
0.269
0.410
0.364
0.545
0.493
0.710
0.674
0.622
0.546
0.466
0.252
0.920
0.884
0.824
0.742
0.612
0.434
1.185
1.097
1.049
0.957
0.815
0.599
1.530
1.442
1.380
1.278
1.160
0.896
1.770
1.682
1.610
1.500
1.338
1.100
2.245
2.157
2.067
1.939
1.687
1.503
AREA OF
METAL
(SQUARE
INCHES)
0.0548
0.0720
0.0970
0.1250
0.1246
0.1670
0.1583
0.1974
0.2503
0.3200
0.3836
0.5043
0.2011
0.2521
0.3326
0.4335
0.5698
0.7180
0.2553
0.4130
0.4939
0.6388
0.8365
1.0760
0.3257
0.4717
0.6685
0.8815
1.1070
1.534
0.3747
0.6133
0.7995
1.068
1.429
1.885
0.4717
0.7760
1.075
1.477
2.190
2.656
TRANSVERSE INTERNAL
AREA
(a)
(Square
Inches)
0.0740
0.0568
0.1320
0.1041
0.2333
0.1910
0.3959
0.3568
0.3040
0.2340
0.1706
0.050
0.6648
0.6138
0.5330
0.4330
0.2961
0.148
1.1029
0.9452
0.8640
0.7190
0.5217
0.282
1.839
1.633
1.495
1.283
1.057
0.630
2.461
2.222
2.036
1.767
1.406
0.950
3.958
3.654
3.355
2.953
2.241
1.774
(A)
(Square
Feet)
0.00051
0.00040
0.00091
0.00072
0.00162
0.00133
0.00275
0.00248
0.00211
0.00163
0.00118
0.00035
0.00462
0.00426
0.00371
0.00300
0.00206
0.00103
0.00766
0.00656
0.00600
0.00499
0.00362
0.00196
0.01277
0.01134
0.01040
0.00891
0.00734
0.00438
0.01709
0.01543
0.01414
0.01225
0.00976
0.00660
0.02749
0.02538
0.02330
0.02050
0.01556
0.01232
WEIGHT
PIPE
(POUNDS
PER FOOT)
0.19
0.24
0.33
0.42
0.42
0.57
0.54
0.67
0.85
1.09
1.31
1.71
0.69
0.86
1.13
1.47
1.94
2.44
0.87
1.40
1.68
2.17
2.84
3.66
1.11
1.81
2.27
3.00
3.76
5.21
1.28
2.09
2.72
3.63
4.86
6.41
1.61
2.64
3.65
5.02
7.46
9.03
WEIGHT
WATER
(POUNDS
PER FOOT
OF PIPE)
0.032
0.025
0.057
0.045
0.101
0.083
0.172
0.155
0.132
0.102
0.074
0.022
0.288
0.266
0.231
0.188
0.128
0.064
0.478
0.409
0.375
0.312
0.230
0.122
0.797
0.708
0.649
0.555
0.458
0.273
1.066
0.963
0.882
0.765
0.608
0.42
1.72
1.58
1.45
1.28
0.97
0.77
- continued -
Page 51
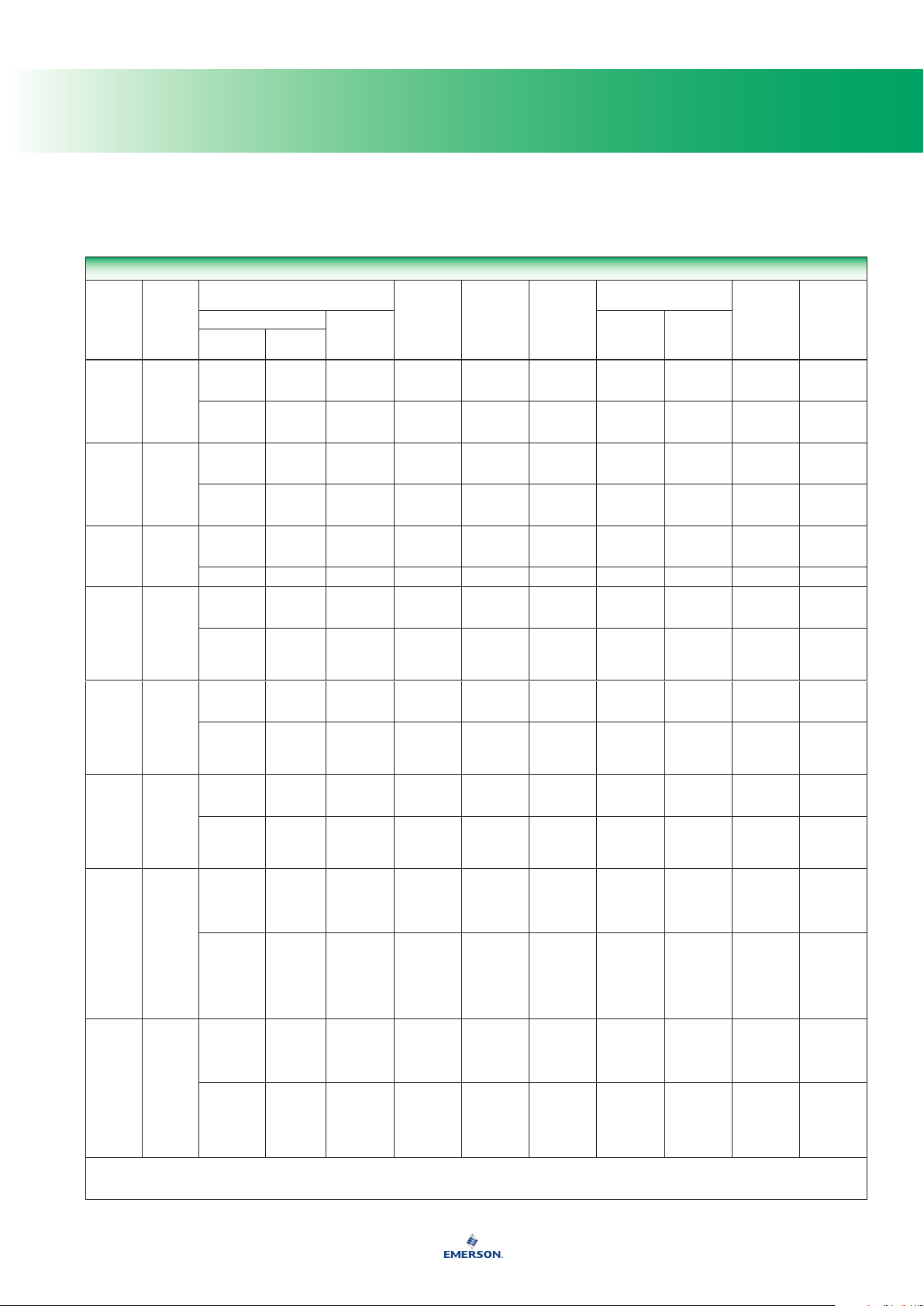
709
Te c h n i c a l
Conversions, Equivalents, and Physical Data
Pipe Data: Carbon and Allow Steel—Stainless Steel (continued)
NOMINAL
PIPE SIZE
(INCHES)
2-1/2 2.875
3-1/2 4.000
Identication, wall thickness and weights are extracted from ASME B36.10 and B39.19.
The notations STD, XS, and XXS indicate Standard, Extra Strong, and Double Extra Strong pipe, respectively.
Transverse internal area values listed in “square feet” also represent volume in cubic feet per foot of pipe length.
OUTSIDE
DIAMETER
(INCHES)
3 3.500
4 4.500
5 5.563
6 6.625
9 8.625
10 10.750
Iron Pipe
IDENTIFICATION
Steel
Size
- - - -
- - - STD
XS
- - - XXS
- - - -
- - - STD
XS
- - - XXS
- - - -
- - - STD
XS 80 80S 0.318 3.364 3.678 8.888 0.06170 12.50 3.84
- - - -
- - - STD
XS
- - - -
- - - XXS
- - - -
- - - STD
XS
- - - -
- - - XXS
- - - -
- - - STD
XS
- - - -
- - - XXS
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
- - - STD
- - - XS
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
XXS
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
STD
XS
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
XXS
- - - -
Schedule
No.
- - - -
- - - 40
80
160
- - - -
- - - -
- - - 40
80
160
- - - -
- - - -
- - - 40
- - - -
- - - 40
80
120
160
- - - -
- - - -
- - - 40
80
120
160
- - - -
- - - -
- - - 40
80
120
160
- - - -
- - - -
- - - 20
30
40
60
80
100
120
140
- - - -
160
- - - -
- - - 20
30
40
60
80
100
120
140
160
Stainless
Steel
Schedule No.
5S
10S
40S
80S
- - - -
- - - -
5S
10S
40S
80S
- - - -
- - - -
5S
10S
40S
5S
10S
40S
80S
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
5S
10S
40S
80S
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
5S
10S
40S
80S
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
5S
10S
- - - -
- - - 40S
- - - 80S
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
5S
10S
- - - -
- - - 40S
80S
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
WALL
THICKNESS (t)
(INCHES)
0.083
0.120
0.203
0.279
0.375
0.552
0.083
0.120
0.216
0.300
0.438
0.600
0.083
0.120
0.226
0.083
0.120
0.237
0.337
0.438
0.531
0.674
0.109
0.134
0.258
0.375
0.500
0.625
0.750
0.109
0.134
0.280
0.432
0.562
0.719
0.864
0.109
0.148
0.250
0.277
0.322
0.406
0.500
0.594
0.719
0.812
0.875
0.906
0.134
0.165
0.250
0.307
0.365
0.500
0.594
0.719
0.844
1.000
1.125
INSIDE
DIAMETER (d)
(INCHES)
2.709
2.635
2.469
2.323
2.125
1.771
3.334
3.260
3.068
2.900
2.624
2.300
3.834
3.760
3.548
4.334
4.260
4.026
3.826
3.624
3.438
3.152
5.345
5.295
5.047
4.813
4.563
4.313
4.063
6.407
6.357
6.065
5.761
5.501
5.187
4.897
8.407
8.329
8.125
8.071
7.981
7.813
7.625
7.437
7.187
7.001
6.875
6.813
10.482
10.420
10.250
10.136
10.020
9.750
9.562
9.312
9.062
8.750
8.500
AREA OF
METAL
(SQUARE
INCHES)
0.7280
1.039
1.704
2.254
2.945
4.028
0.8910
1.274
2.228
3.016
4.205
5.466
1.021
1.463
2.680
1.152
1.651
3.174
4.407
5.595
6.621
8.101
1.868
2.285
4.300
6.112
7.953
9.696
11.340
2.231
2.733
5.581
8.405
10.70
13.32
15.64
2.916
3.941
6.57
7.26
8.40
10.48
12.76
14.96
17.84
19.93
21.30
21.97
4.36
5.49
8.24
10.07
11.90
16.10
18.92
22.63
26.24
30.63
34.02
TRANSVERSE INTERNAL
(a)
(Square
Inches)
5.764
5.453
4.788
4.238
3.546
2.464
8.730
8.347
7.393
6.605
5.408
4.155
11.545
11.104
9.886
14.75
14.25
12.73
11.50
10.31
9.28
7.80
22.44
22.02
20.01
18.19
16.35
14.61
12.97
32.24
31.74
28.89
26.07
23.77
21.15
18.84
55.51
54.48
51.85
51.16
50.03
47.94
45.66
43.46
40.59
38.50
37.12
36.46
86.29
85.28
82.52
80.69
78.86
74.66
71.84
68.13
64.53
60.13
56.75
AREA
(A)
(Square
Feet)
0.04002
0.03787
0.03322
0.02942
0.02463
0.01710
0.06063
0.05796
0.05130
0.04587
0.03755
0.02885
0.08017
0.07711
0.06870
0.10245
0.09898
0.08840
0.07986
0.0716
0.0645
0.0542
0.1558
0.1529
0.1390
0.1263
0.1136
0.1015
0.0901
0.2239
0.2204
0.2006
0.1810
0.1650
0.1469
0.1308
0.3855
0.3784
0.3601
0.3553
0.3474
0.3329
0.3171
0.3018
0.2819
0.2673
0.2578
0.2532
0.5992
0.5922
0.5731
0.5603
0.5475
0.5185
0.4989
0.4732
0.4481
0.4176
0.3941
WEIGHT PIPE
(POUNDS
PER FOOT)
2.48
3.53
5.79
7.66
10.01
13.69
3.03
4.33
7.58
10.25
14.32
18.58
3.48
4.97
9.11
3.92
5.61
10.79
14.98
19.00
22.51
27.54
6.36
7.77
14.62
20.78
27.04
32.96
38.55
7.60
9.29
18.97
28.57
36.39
45.35
53.16
9.93
13.40
22.36
24.70
28.55
35.64
43.39
50.95
60.71
67.76
72.42
74.69
15.19
18.65
28.04
34.24
40.48
54.74
64.43
77.03
89.29
104.13
115.64
WEIGHT
WATER
(POUNDS
PER FOOT
OF PIPE)
2.50
2.36
2.07
1.87
1.54
1.07
3.78
3.62
3.20
2.86
2.35
1.80
5.00
4.81
4.29
6.39
6.18
5.50
4.98
4.47
4.02
3.38
9.72
9.54
8.67
7.88
7.09
6.33
5.61
13.97
13.75
12.51
11.29
10.30
9.16
8.16
24.06
23.61
22.47
22.17
21.70
20.77
19.78
18.83
17.59
16.68
16.10
15.80
37.39
36.95
35.76
34.96
34.20
32.35
31.13
29.53
27.96
26.06
24.59
Page 52

710
Te c h n i c a l
Conversions, Equivalents, and Physical Data
American Pipe Flange Dimensions
ASME CLASS FLANGE DIAMETER - INCHES, PER ASME B16.1, B16.5, AND B16.24
Nominal
Pipe Size
1. Sizes 1 through 12-inch also apply to ASME Class 150 bronze anges.
2. Sizes 1 through 8-inch also apply to ASME Class 300 bronze anges.
1
1-1/4
1-1/2
2
2-1/2
3
4
5
6
8
10
12
14
16
18
20
24
30
36
42
48
125 (Cast Iron)
or 150 (Steel)
4.25
4.62
5.00
6.00
7.00
7.50
9.00
10.00
11.00
13.50
16.00
19.00
21.00
23.50
25.00
27.50
32.00
38.75
46.00
53.00
59.50
250 (Cast Iron)
(1)
or 300 (Steel)
4.88
5.25
6.12
6.50
7.50
8.25
10.00
11.00
12.50
15.00
17.50
20.50
23.00
25.50
28.00
30.50
36.00
43.00
50.00
57.00
65.00
600 900 1500 2500
(2)
4.88
5.88
5.25
6.25
6.12
7.00
6.50
8.50
7.50
9.62
8.25
9.50
11.50
13.75
15.00
18.50
21.50
24.00
25.25
27.75
31.00
33.75
41.00
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
10.50
12.25
14.75
15.50
19.00
23.00
26.50
29.50
32.50
36.00
38.75
46.00
10.75
13.00
14.00
16.50
20.00
22.00
23.75
27.00
29.25
32.00
37.00
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
5.88
6.25
7.00
8.50
9.62
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
6.25
7.25
8.00
9.25
10.50
12.00
14.00
16.50
19.00
21.75
26.50
30.00
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
American Pipe Flange Dimensions
ASME CLASS, NUMBER OF STUD BOLTS AND HOLE DIAMETER IN INCHES,
Nominal
Pipe Size
1
1-1/4
1-1/2
2
2-1/2
3
4
5
6
8
10
12
14
16
18
20
24
30
36
42
48
1. Sizes 1 through 12-inch also apply to ASME Class 150 bronze anges.
2. Sizes 1 through 8-inch also apply to ASME Class 300 bronze anges.
PER ASME B16.1, B16.5, AND B16.24
125 (Cast
Iron) or 150
(Steel)
No. Ø No. Ø No. Ø No. Ø No. Ø No. Ø
4
4
4
4
4
4
8
8
8
8
12
12
12
16
16
20
20
28
32
36
44
(1)
0.50
0.50
0.50
0.62
0.62
0.62
0.62
0.75
0.75
0.75
0.88
0.88
1.00
1.00
1.12
1.12
1.25
1.25
1.50
1.50
1.50
250 (Cast
Iron) or 300
(2)
(Steel)
4
0.62
4
0.62
4
0.75
8
0.62
8
0.75
8
0.75
8
0.75
8
0.75
12
0.75
12
0.88
16
1.00
16
1.12
20
1.12
20
1.25
24
1.25
24
1.25
24
1.50
28
1.75
32
2.00
36
2.00
40
2.00
600 900 1500 2500
4
0.62
4
0.88
4
4
4
8
8
8
8
8
12
12
12
16
16
16
16
16
16
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
0.88
0.88
1.00
0.88
1.00
1.12
1.25
1.50
1.38
1.62
1.88
2.00
2.25
2.50
2.75
3.00
3.50
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
12
12
16
20
20
20
20
24
24
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
4
0.62
4
4
0.75
8
0.62
8
0.75
8
0.75
8
0.75
8
1.00
1.00
1.12
1.25
1.25
1.38
1.50
1.62
1.62
1.88
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
4
8
8
8
8
8
12
12
16
20
20
20
20
20
20
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
0.88
1.00
0.88
1.00
0.88
0.12
1.25
1.12
1.38
1.38
1.38
1.50
1.62
1.88
2.00
2.50
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
4
4
4
8
8
8
8
8
8
12
12
12
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
0.88
1.00
1.12
1.00
1.12
1.25
1.50
1.75
2.00
2.00
2.50
2.75
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
- - - -
EN 1092-1 Cast Steel Flange Standard-PN 16
(Nominal Pressure 16 bar)
NOMINAL
BORE,
mm
10
15
20
25
32
40
50
65
80
100
125
150
175
200
250
300
350
400
500
600
700
800
900
1000
1200
1400
1600
1800
2000
2200
PIPE
THICKNESS,
mm
6
6
6,5
7
7
7,5
8
8
8,5
9,5
10
11
12
12
14
15
16
18
21
23
24
26
27
29
32
34
36
39
41
43
FLANGE, mm BOLTING, mm
Outside
Diameter
90
95
105
115
140
150
165
185
200
220
250
285
315
340
405
460
520
580
715
840
910
1025
1125
1255
1485
1685
1930
2130
2345
2555
Thickness
16
16
18
18
18
18
20
18
20
20
22
22
24
24
26
28
30
32
36
40
42
42
44
46
52
58
64
68
70
74
Bolt Circle
Diameter
60
65
75
85
100
110
125
145
160
180
210
240
270
295
355
410
470
525
650
770
840
950
1050
1170
1390
1590
1820
2020
2230
2440
Number of
Bolts
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
8
8
8
8
8
12
12
12
16
16
20
20
24
24
28
28
32
36
40
44
48
52
Thread
M12
M12
M12
M12
M16
M16
M16
M16
M16
M16
M16
M20
M20
M20
M24
M24
M24
M27
M30
M33
M33
M36
M36
M39
M45
M45
M52
M52
M56
M56
Bolt Hole
Diameter
14
14
14
14
18
18
18
18
18
18
18
23
23
23
27
27
27
30
33
36
36
39
39
42
48
48
56
56
62
62
EN 1092-1 Cast Steel Flange Standard-PN 25
(Nominal Pressure 25 bar)
NOMINAL
BORE,
mm
10
15
20
25
32
40
50
65
80
100
125
150
175
200
250
300
350
400
500
600
700
800
900
1000
1200
1400
1600
1800
2000
PIPE
THICKNESS,
mm
6
6
6,5
7
7
7,5
8
8,5
9
10
11
12
12
12
14
15
16
18
21
23
24
26
27
29
32
34
37
40
43
FLANGE, mm BOLTING, mm
Outside
Diameter
90
95
105
115
140
150
165
185
200
235
270
300
330
360
425
485
555
620
730
845
960
1085
1185
1320
1530
1755
1975
2195
2425
Thickness
16
16
18
18
18
18
20
22
24
24
26
28
28
30
32
34
38
40
44
46
50
54
58
62
70
76
84
90
96
Bolt Circle
Diameter
60
65
75
85
100
110
125
145
160
190
220
250
280
310
370
430
490
550
660
770
875
990
1090
1210
1420
1640
1860
2070
2300
Number of
Bolts
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
8
8
8
8
8
12
12
12
16
16
16
20
20
24
24
28
28
32
36
40
44
48
Thread
M12
M12
M12
M12
M16
M16
M16
M16
M16
M20
M24
M24
M24
M24
M27
M27
M30
M33
M33
M36
M39
M45
M45
M52
M52
M56
M56
M64
M64
Bolt Hole
Diameter
14
14
14
14
18
18
18
18
18
23
27
27
27
27
30
30
33
36
36
39
42
48
48
56
56
62
62
70
70
Page 53
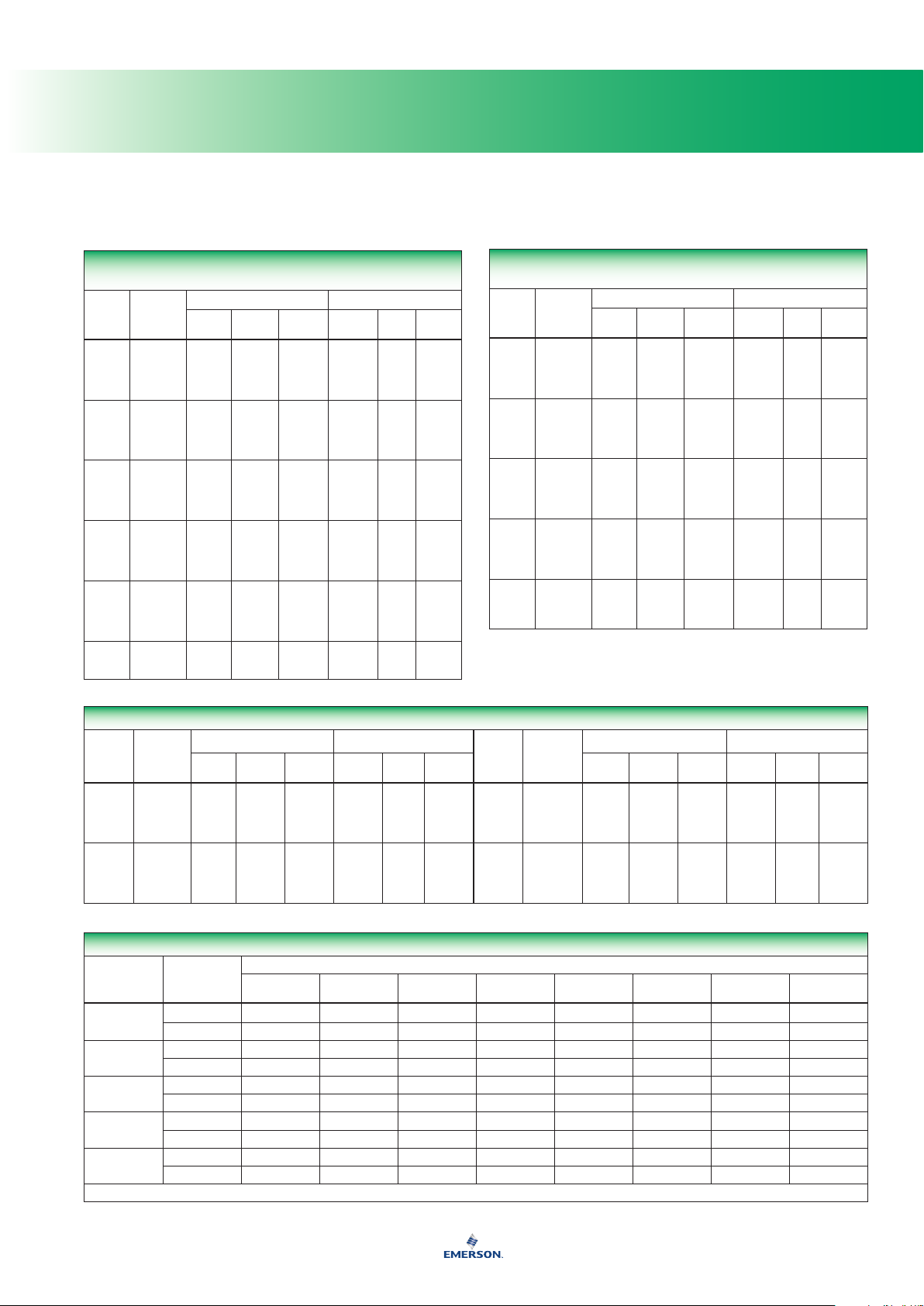
711
Te c h n i c a l
Conversions, Equivalents, and Physical Data
EN 1092-1 Cast Steel Flange Standard–PN 40
(Nominal Pressure 40 Bar)
NOMINAL
BORE,
mm
10
15
20
25
32
40
50
65
80
100
125
150
175
200
250
300
350
400
450
500
600
700
800
900
1000
1200
1400
1600
PIPE
THICKNESS,
mm
6
6
6,5
7
7
7,5
8
8,5
9
10
11
12
13
14
16
17
19
21
21
21
24
27
30
33
36
42
47
54
FLANGE, mm BOLTING, mm
Outside
Diameter
90
95
105
115
140
150
165
185
200
235
270
300
350
375
450
515
580
660
685
755
890
995
1140
1250
1360
1575
1795
2025
Thickness
16
16
18
18
18
18
20
22
24
24
26
28
32
34
38
42
46
50
50
52
60
64
72
76
80
88
98
108
Bolt Circle
Diameter
60
65
75
85
100
110
125
145
160
190
220
250
295
320
385
450
510
585
610
670
795
900
1030
1140
1250
1460
1680
1900
Number of
Bolts
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
8
8
8
8
8
12
12
12
16
16
16
20
20
20
24
24
28
28
32
36
40
Thread
M12
M12
M12
M12
M16
M16
M16
M16
M16
M20
M24
M24
M27
M27
M30
M30
M33
M36
M36
M39
M45
M45
M52
M52
M52
M56
M56
M64
Bolt Hole
Diameter
14
14
14
14
18
18
18
18
18
23
27
27
30
30
33
33
36
39
39
42
48
48
56
56
56
62
62
70
EN 1092-1 Cast Steel Flange Standard–PN 63
(Nominal Pressure 63 Bar)
NOMINAL
BORE,
mm
10
15
25
32
40
50
65
80
100
125
150
175
200
250
300
350
400
500
600
700
800
900
1000
1200
PIPE
THICKNESS,
mm
10
10
10
12
10
10
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
19
21
23
26
31
35
40
45
50
55
64
FLANGE, mm BOLTING, mm
Outside
Diameter
100
105
140
155
170
180
205
215
250
295
345
375
415
470
530
600
670
800
930
1045
1165
1285
1415
1665
Thickness
20
20
24
24
28
26
26
28
30
34
36
40
42
46
52
56
60
68
76
84
92
98
108
126
Bolt Circle
Diameter
70
75
100
110
125
135
160
170
200
240
280
310
345
400
460
525
585
705
820
935
1050
1170
1290
1530
Number of
Bolts
4
4
4
4
4
4
8
8
8
8
8
12
12
12
16
16
16
20
20
24
24
28
28
32
Thread
M12
M12
M16
M20
M20
M20
M20
M20
M24
M27
M30
M30
M33
M33
M33
M36
M39
M45
M52
M52
M56
M56
M64
M72X6
Bolt Hole
Diameter
14
14
18
23
22
22
22
22
26
30
33
33
36
36
36
39
42
48
56
56
62
62
70
78
EN 1092-1 Cast Steel Flange Standard—PN 100 (Nominal Pressure 100 Bar)
NOMINAL
BORE,
mm
10
15
25
32
40
50
65
80
100
125
PIPE
THICKNESS,
mm
10
10
10
12
10
10
11
12
14
16
FLANGE, mm BOLTING, mm
Outside
Diameter
100
105
140
155
170
195
220
230
265
315
Thickness
20
20
24
24
28
30
34
36
40
40
Bolt Circle
Diameter
70
75
100
110
125
145
170
180
210
250
Number
of Bolts
NOMINAL
BORE,
Bolt Hole
Thread
Diameter
4
M12
4
M12
4
M16
4
M20
4
M20
4
M24
8
M24
8
M24
8
M27
8
M30
14
14
18
23
22
26
26
26
30
33
mm
150
175
200
250
300
350
400
500
600
700
THICKNESS,
EN 1092-1 Pressure/Temperature Ratings for Cast Steel Flanges
PN
16
25
40
63
100
1. These ratings apply only for ange types 05, 11, 12, 13, and 21 having nominal sizes up and including DN 600.
MATERIAL
GROUP
1C1 232 (16,0) 226 (15,6) 219 (15,1) 209 (14,4) 194 (13,4) 186 (12,8) 180 (12,4) 157 (10,8)
1C2 218 (15,0) 218 (15,0) 218 (15,0) 225 (15,5) 216 (14,9) 206 (14,2) 199 (13,7) 157 (10,8)
1C1 363 (25,0) 354 (24,4) 344 (23,7) 326 (22,5) 303 (20,9) 290 (20,0) 281 (19,4) 245 (16,9)
1C2 363 (25,0) 363 (25,0) 363 (25,0) 363 (25,0) 338 (23,3) 322 (22,2) 310 (21,4) 245 (16,9)
1C1 580 (40,0) 567 (39,1) 550 (37,9) 522 (36,0) 486 (33,5) 463 (31,9) 451 (31,1) 392 (27,0)
1C2 580 (40,0) 580 (40,0) 580 (40,0) 580 (40,0) 540 (37,2) 516 (35,6) 496 (34,2) 392 (27,0)
1C1 914 (63,0) 892 (61,5) 864 (59,6) 824 (56,8) 764 (52,7) 730 (50,3) 711 (49,0) 616 (42,5)
1C2 914 (63,0) 914 (63,0) 914 (63,0) 914 (63,0) 851 (58,7) 812 (56,0) 780 (53,8) 616 (42,5)
1C1 1450 (100) 1417 (97,7) 1374 (94,7) 1307 (90,1) 1252 (86,3) 1157 (79,8) 1128 (77,8) 979 (67,5)
1C2 1450 (100) 1450 (100) 1450 (100) 1450 (100) 1350 (93,1) 1289 (88,9) 1239 (85,4) 979 (67,5)
14 to 212°F
(-10 to 100°C)
302°F
(150°C)
MAXIMUM ALLOWABLE PRESSURE, PSIG (bar)
392°F
(200°C)
482°F
(250°C)
PIPE
mm
18
20
21
25
29
32
36
44
51
59
Outside
Diameter
1145
572°F
(300°C)
FLANGE, mm BOLTING, mm
355
385
430
505
585
655
715
870
990
Thickness
44
48
52
60
68
74
78
94
104
120
(1)
662°F
(350°C)
Bolt Circle
Diameter
290
320
360
430
500
560
620
760
875
1020
Number
of Bolts
12
12
12
12
16
16
16
20
20
24
707°F
(375°C)
Thread
M30
M30
M33
M36
M39
M45
M45
M52
M56
M64
Bolt Hole
Diameter
752°F
(400°C)
33
33
36
39
42
48
48
56
62
70
Page 54
Te c h n i c a l
Conversions, Equivalents, and Physical Data
Drill Sizes for Pipe Taps
NOMINAL PIPE
SIZE, (INCHES)
1/8 11/32 1-1/2 1-23/32
1/4 7/16 2 2-3/16
3/8 19/32 2-1/2 2-9/16
1/2 23/32 3 3-3/16
3/4 15/16 4 4-3/16
1 1-5/32 5 5-5/16
1-1/4 1-1/2 6 6-5/16
DESIGNATION DIAMETER (IN.) AREA (SQ. IN.) DESIGNATION DIAMETER (IN.) AREA (SQ. IN.) DESIGNATION DIAMETER (IN.) AREA (SQ. IN.)
1/2
31/64
15/32
29/64
7/16
27/64
Z
13/32
Y
Z
25/64
W
V
3/8
U
23/64
T
S
11/32
R
Q
21/64
P
O
5/16
N
19/64
M
L
9/32
K
J
I
H
17/64
G
F
E 1/4
D
C
B
15/64
A
1
2
7/32 0.2188 0.03758 41 0.0960 0.00724 - - - - - - - - - - - -
Note: Designations are in fractions of an inch, in standard twist drill letters, or in standard twist drill numbers, the latter being the same as steel wire gauge numbers.
0.5000
0.4844
0.4688
0.4531
0.4375
0.4219
0.413
0.4063
0.404
0.397
0.3906
0.386
0.377
0.375
0.368
0.3594
0.358
0.348
0.3438
0.339
0.332
0.3281
0.323
0.316
0.3125
0.302
0.2969
0.295
0.29
0.2813
0.281
0.277
0.272
0.266
0.2656
0.261
0.257
0.2500
0.246
0.242
0.238
0.2344
0.234
0.228
0.221
0.1963
0.1843
0.1726
0.1613
0.1503
0.1398
0.1340
0.1296
0.1282
0.1238
0.1198
0.1170
0.1116
0.1104
0.1064
0.1014
0.1006
0.09511
0.09281
0.09026
0.08657
0.08456
0.08194
0.07843
0.07670
0.07163
0.06922
0.06835
0.06605
0.06213
0.06202
0.06026
0.05811
0.05557
0.05542
0.05350
0.05187
0.04909
0.04753
0.04600
0.04449
0.04314
0.04301
0.04083
0.03836
TAP DRILL SIZE,
(INCHES)
Standard Twist Drill Sizes
3
4
5
6
13/64
7
8
9
10
11
12
3/16
13
14
15
16
17
11/64
18
19
20
21
22
5/32
23
24
25
26
27
9/64
28
29
30
1/8
31
32
33
34
35
7/64
36
37
38
39
40
0.213
0.209
0.2055
0.204
0.2031
0.201
0.199
0.196
0.1935
0.191
0.189
0.1875
0.185
0.182
0.1800
0.1770
0.1730
0.1719
0.1695
0.1660
0.1610
0.1590
0.1570
0.1563
0.1540
0.1520
0.1495
0.1470
0.1440
0.1406
0.1405
0.1360
0.1285
0.1250
0.1200
0.1160
0.1130
0.1110
0.1100
0.1094
0.1065
0.1040
0.1015
0.0995
0.0980
NOMINAL PIPE
SIZE, (INCHES)
0.03563
0.03431
0.03317
0.03269
0.03241
0.03173
0.03110
0.03017
0.02940
0.02865
0.02806
0.02861
0.02688
0.02602
0.02554
0.02461
0.02351
0.02320
0.02256
0.02164
0.02036
0.01986
0.01936
0.01917
0.01863
0.01815
0.01755
0.01697
0.01629
0.01553
0.01549
0.01453
0.01296
0.01227
0.01131
0.01057
0.01003
0.00968
0.00950
0.00940
0.00891
0.00849
0.00809
0.00778
0.00754
3/32
42
43
44
45
46
47
5/64
48
49
50
51
52
1/16
53
54
55
3/64
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
1/32
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
1/64
79
80
TAP DRILL SIZE,
(INCHES)
0.0938
0.0935
0.0890
0.0860
0.0820
0.0810
0.0785
0.0781
0.0760
0.0730
0.0700
0.0670
0.0635
0.0625
0.0595
0.0550
0.0520
0.0473
0.0465
0.0430
0.0420
0.0410
0.0400
0.039
0.038
0.037
0.036
0.035
0.033
0.032
0.0313
0.031
0.0292
0.028
0.026
0.025
0.024
0.0225
0.021
0.020
0.018
0.016
0.0156
0.0145
0.0135
0.00690
0.00687
0.00622
0.00581
0.00528
0.00515
0.00484
0.00479
0.00454
0.00419
0.00385
0.00353
0.00317
0.00307
0.00278
0.00238
0.00212
0.00173
0.001698
0.001452
0.001385
0.001320
0.001257
0.001195
0.001134
0.001075
0.001018
0.000962
0.000855
0.000804
0.000765
0.000755
0.000670
0.000616
0.000531
0.000491
0.000452
0.000398
0.000346
0.000314
0.000254
0.000201
0.000191
0.000165
0.000143
712
 Loading...
Loading...