Page 1

Surveyor
User’s Guide
Page 2

Surveyor User’s Guide
Trademarks and Copyrights
Finisar, Surveyor, THGm, THGs, THGsE, THGnotebook, THGp, Century 12-Tap, 12-Tap, Century Tap,
Packet Blaster plug-in, Remote plug-in, Expert plug-in, Multi-QoS plug-in, and Century Tool Kit are trademarks of Finisar Corporation. Windows NT, Windows XP, Windows 2000, Microsoft Mail, and Excel are trademarks of Microsoft Corporation. Pentium is a trademark of Intel Corporation. Magic Packets is a trademark of
Advanced Micro Devices. Sniffer is a trademark of Network General, Inc. All other trademarks are those of
their respective companies.
Finisar Software License Agreement
This Software Program and accompanying written materials are proprietary products of Finisar, and are protected by copyright laws and international treaties. You must keep the Software Program in strict confidence
and treat it like any other copyrighted material. You may not copy the Software, documentation, or associated
written materials except as provided below.
License
Subject to the provisions of this License, Finisar hereby grants to Licensee, a non-exclusive, non-transferable
license to use the Software and all documentation and upgrades provided for said Software. The Software may
be loaded and executed on a single host computer. Title to the Software shall at all times remain with Finisar.
Licensee may not copy or sublicense such Software, documentation, or other written material, in whole or in
part, without prior written consent of Finisar, except for as provided below.
Term
This License shall become effective upon shipment or other transfer of the designated Software from Finisar
and shall remain in full force and effect in perpetuity, unless terminated pursuant to the provisions of this
License. This agreement can be terminated at any time by returning or destroying all copies of the Software
and related written materials and documentation and by notifying Finisar in writing of your termination of
the License.
If either party defaults in the performance of any of its obligations thereunder, and such default continues for
thirty (30) days after receipt of notice from the non-defaulting party, the non-defaulting party shall have the
right to terminate this License immediately by giving written notice. Upon termination of this License, Licensee shall, at Finisar’s request, either return to Finisar or destroy all copies of the licensed Software and documentation.
Restrictions
Licensee shall have the right to make one backup copy of the Software for use in the event the original Software is damaged. Such License does not convey any right, expressly or by implication, to manufacture, duplicate or otherwise copy or reproduce any of the Software or documentation. Licensee hereby agrees not to trace,
decompile or disassemble the Software, or use any other means to identify the source codes of the Software.
Finisar’s Software is commercial computer Software and, together with any related documentation, is subject
to the restrictions on US Government use, duplication or disclosure set forth in DOD FAR j2.2277013(c)(1)(II). Licensee agrees to mark any Software and related documentation that is to be directly or indirectly delivered to any branch or agency of the US Government with the legend set forth below in such manner that it can be readily and visually perceived:
ii
Page 3

Surveyor User’s Guide
Restricted Rights Legend
Use, duplication, or disclosure by the Government is subject to restrictions as set forth in subdivision
(c)(l)(lI) of the Rights in Technical Data and Computer Software clause at DOD FAR 52.227-7013
1389 Moffett Park Drive
Finisar
Sunnyvale CA 94089
Limited Software Warranty
A Finisar Limited Software Warranty is provided with each Software Product purchased through one of
Finisar’s authorized distribution channels. For a period of twelve (12) months from date of shipment, Finisar
warrants Software to conform with Finisar’s published specifications on date of shipment when properly operated in accordance with procedures described in documentation supplied by Finisar.
Defects in the Software will be reported to Finisar accompanied by supporting information reasonably
requested by Finisar to verify, diagnose and correct the defect. Finisar’s exclusive obligation with respect to
nonconforming Software Product shall be, at Finisar’s option, (a) to replace that copy of the Software with one
that conforms to the specifications, or, (b) to use diligent efforts to provide the customer with a correction or
workaround of the defect. Finisar is under no obligation to provide Software updates which contain additional
features and enhancements other than defect corrections.
Patent and Copyright Indemnification
Finisar shall have no liability to the Licensee if any patent or copyright infringement is based upon or arises
out of: (1) compliance with designs, plans or specifications furnished by or on behalf of the Licensee as to the
Products or services, (2) alterations of the Products or services by the Licensee, (3) failure of the Licensee to
use updated Products or services, including error corrections and updates, provided by Finisar for avoiding
infringement, (4) use of Products or services in a manner for which the same was neither designed nor contemplated, or (5) a patent or copyright in which the Licensee or affiliate or subsidiary of the Licensee has any
direct or indirect interest by license or otherwise.
Limitation of Liability
Finisar’s liability under or for breach of this license shall be limited to refund of the purchase price actually
paid by the Licensee to Finisar for the specific item causing the damage. In no event shall Finisar be liable for
costs of procurement of substitute goods, loss of profits, or for any special, consequential or incidental damages, however caused, whether for breach of warranty, breach of contract, repudiation of contract, negligence
or otherwise.
Forum
This License shall be interpreted in accordance with the laws of the State of California, and exclusive jurisdiction and venue shall lie in the state or federal courts of Santa Clara County, California.
Entirety
These terms and conditions represent the entire agreement between the parties relative to the license of the
Software and firmware incorporated in or provided with the designated equipment. Any modification hereto
must be embodied in a writing signed by both parties. No modification hereof shall be effected by either
party’s use of a purchase order, acknowledgment, or other form containing additional or different conditions.
iii
Page 4

Surveyor User’s Guide
About This Guide
This guide provides descriptions of the software components, features, and capabilities of
the Surveyor product, Release 5.0. It also contains detailed tutorials and examples that will
enable you to install, configure, and run the Surveyor software.
On-line Help System
We have included an extensive, on-line Help system with the Surveyor software. The on-line
Help system contains nearly all the tutorials and instructions contained in this guide plus
additional examples and tips to help you get the most from your Surveyor. Be sure to browse
on-line Help. From any location in the Surveyor program, and with just a few clicks of the
mouse, you will find that you can locate the answer to almost any question you might have.
Specific task information is included in the on-line Help system that is not included in this
manual.
Quick Start
Surveyor includes a Quick Start guide to get you up and running.
Contacting Customer Support
There are several ways to contact Finisar if you need support.
Customer Support Phone 1 408.400.1100
1 888.746.6484
Customer Support FAX 1 408.744.1778
Internet Address techsupport@Finisar.com
World-Wide Web http://www.Finisar.com/
Mailing Address Finisar
1389 Moffett Park Drive
Sunnyvale, CA 94089
iv
Page 5

Table of Contents
Chapter Page
1 Introduction ................................................................................... 1-1
Surveyor Functions ..................................................................................... 1-2
Analyzer Devices ........................................................................................ 1-4
Protocols Supported .................................................................................... 1-4
What's New in Release 5.0.......................................................................... 1-8
Capture to Disk and THGsE Analyzer Support ............................... 1-8
Disk Caching ...................................................................................... 1-8
Capture Management ........................................................................ 1-8
Expanded Multi-QoS Support ........................................................... 1-9
SMNP Extended Agent ...................................................................... 1-9
New and Enhanced Protocol Decodes ............................................... 1-9
2 Installation ..................................................................................... 2-1
System Requirements.................................................................................. 2-1
Upgrading Surveyor.................................................................................... 2-2
Installing Surveyor...................................................................................... 2-3
Installing Analyzer Hardware ..................................................................... 2-4
Installing Analyzer Hardware in a Desktop PC............................... 2-4
Installing Analyzer Hardware in a Notebook PC............................. 2-5
Installing More Than One Analyzer Card in a Notebook PC .......... 2-8
Compatibility Matrix................................................................................... 2-9
3 Getting Started .............................................................................. 3-1
The Surveyor System .................................................................................. 3-1
Launching Surveyor........................................................................... 3-1
Basic Navigation Tips................................................................................. 3-3
Buttons and Toolbars .................................................................................. 3-6
Surveyor Toolbar ................................................................................ 3-6
Module Toolbar (Summary View)...................................................... 3-6
v
Page 6

Surveyor
User’s Guide
Detail View Toolbar ............................................................................ 3-8
Data Views Toolbar ............................................................................ 3-10
Filter Design Toolbar.......................................................................... 3-13
Filter States Design Toolbar .............................................................. 3-13
Capture View Toolbar......................................................................... 3-15
File Formats ................................................................................................. 3-18
.HST Extension – Capture Files ....................................................... 3-18
.CAP Extension – Internal Capture Files.......................................... 3-18
.NAM Extension – Name Table Files ................................................ 3-18
.CFD Extension – Capture Filters ..................................................... 3-18
.DFD Extension – Display Filters...................................................... 3-18
.TSP Extension – Transmit Specifications ........................................ 3-18
Providing a Name Table to Surveyor .......................................................... 3-19
Establishing Links for THGm...................................................................... 3-20
4 Configuring Surveyor ................................................................... 4-1
Configuring the Interface............................................................................. 4-1
Customizing Views and Windows ...................................................... 4-1
Capture View Display Options........................................................... 4-2
Histogram Options.............................................................................. 4-4
Setting the Monitoring View for a Module ........................................ 4-5
Configuring Chart Views.................................................................... 4-6
Table Views ......................................................................................... 4-6
Module Settings (Properties) ....................................................................... 4-7
Buffer Size........................................................................................... 4-8
Packet Slice (Slicing Size) .................................................................. 4-8
Stop-and-Save Capture Buffer ........................................................... 4-9
Modes................................................................................................... 4-9
MAC Control Frame ........................................................................... 4-10
System Settings............................................................................................ 4-10
Configuring Ports to Scan .................................................................. 4-10
Configuring Remote Communications ............................................... 4-11
Protocol Color Coding ......................................................................... 4-12
Setting Update Timers ....................................................................... 4-12
Disk Options........................................................................................ 4-14
Configuring Counter Logging............................................................. 4-15
Configuring Alarms ..................................................................................... 4-15
Configuring a Multi-Port Tap or Switch...................................................... 4-16
Setting the Local COM Port for Taps and Switches ......................... 4-18
Connecting a Tap with THGs or THGsE........................................... 4-18
Settings for Analyzer Devices ..................................................................... 4-18
Resetting an Analyzer Device ............................................................ 4-18
Updating an Analyzer Device ............................................................ 4-19
vi
Page 7

Contents (continued)
Advanced Configuration.............................................................................. 4-20
surveyor.ini
Customizing Expert Diagnostic Information .................................... 4-20
Assigning Names to Protocols (Monitor) ........................................... 4-21
Assigning TCP or UDP Ports to Protocol Parsers............................. 4-26
File.......................................................................... 4-20
5 Resources and Modes .................................................................. 5-1
Resource Browser........................................................................................ 5-1
Remote Resources ....................................................................................... 5-2
Naming Remote IP Resources (Aliases) ............................................ 5-4
Resource Protection ............................................................................ 5-5
Modes .......................................................................................................... 5-6
Hardware Devices........................................................................................ 5-6
Synchronized Resources ..................................................................... 5-8
Hints and Tips for Resources....................................................................... 5-9
6 Views .............................................................................................. 6-1
Summary View ............................................................................................ 6-3
Detail View.................................................................................................. 6-4
Using Capture + Monitor Mode in Detail View ................................ 6-6
Capture View............................................................................................... 6-7
Capture View Window........................................................................ 6-7
Creating Filters from Capture View.................................................. 6-8
Exporting and Printing Decodes ........................................................ 6-8
Configuring the Capture View Display ............................................. 6-8
Using the Histogram Control....................................................................... 6-9
Histogram Color Coding ..................................................................... 6-10
Histogram Button Controls ................................................................ 6-14
Histogram Mouse Controls ................................................................ 6-15
Saving Portions of the Data ............................................................... 6-16
Resume Analysis................................................................................. 6-17
Packet Editor................................................................................................ 6-17
Data Views .................................................................................................. 6-18
Ring Statistics View (Token Ring Only)............................................ 6-18
MAC Statistics View (Rx)................................................................... 6-19
MAC Statistics View (Tx) ................................................................... 6-20
Frame Size Distribution View............................................................ 6-20
Protocol Distribution View ................................................................. 6-21
Utilization/Error View........................................................................ 6-23
Host Table View.................................................................................. 6-24
Network Layer Host Table View........................................................ 6-25
Application Layer Host Table View................................................... 6-27
Host Matrix View................................................................................ 6-28
vii
Page 8

Surveyor
User’s Guide
Network Layer Matrix View .............................................................. 6-30
Application Layer Matrix View .......................................................... 6-31
VLAN View.......................................................................................... 6-33
Address Mapping View....................................................................... 6-34
Packet Summary View ....................................................................... 6-35
Duplicate Address View (Expert plug-in only) .................................. 6-35
Expert View (Expert plug-in only) ..................................................... 6-36
Application Response Time View (Expert plug-in only) ................... 6-36
Multi-QoS View (Multi-QoS software only)....................................... 6-36
Hints and Tips for Using Views .................................................................. 6-37
7 Capture and Display Filters .......................................................... 7-1
Getting Started with the Filter Interface ...................................................... 7-1
Creating Filters with Filter Templates......................................................... 7-2
Creating and Applying a Conversation ............................................. 7-5
Creating and Applying a Port Number.............................................. 7-7
Selecting Filter Templates ................................................................. 7-7
Creating Custom Filter Templates .................................................... 7-8
Filter Creation.............................................................................................. 7-12
Creating Filter Template Combinations ........................................... 7-12
Filter Actions....................................................................................... 7-13
Counter Conditions for Filters ........................................................... 7-15
Frame Types........................................................................................ 7-16
Multi-State and Multi-Statement Filters ...................................................... 7-17
Filter Structure ................................................................................... 7-19
Filter States ........................................................................................ 7-20
Filter Statements ................................................................................ 7-21
Capture and Display Filter Differences ....................................................... 7-22
Activating Display Filters .................................................................. 7-22
Activating Capture Filters ................................................................. 7-22
Filter Examples............................................................................................ 7-23
Filter Example, Capture Conversation ............................................. 7-23
Filter Example, Template Combination ............................................ 7-25
Filter Example, Capture TCP Port Traffic........................................ 7-27
Filter Example, Advanced Filter ....................................................... 7-29
Rules of the Capture or Display Filter......................................................... 7-30
Hints and Tips for Using Filters .................................................................. 7-31
Filtering Tips Unique to THG-class Devices..................................... 7-32
8 Transmit Specification .................................................................. 8-1
Transmit Specifications ............................................................................... 8-1
Transmit Specification Dialog Box .................................................... 8-2
Repeating Frames ............................................................................... 8-5
viii
Page 9

Contents (continued)
Stream Modes ..................................................................................... 8-7
Bursts .................................................................................................. 8-7
Transmission Mode............................................................................. 8-8
Specifying Transmit Data............................................................................ 8-8
Packet Editor ...................................................................................... 8-8
Changing Fields Directly in the Dialog Box...................................... 8-9
Using Templates ................................................................................. 8-11
Creating Templates ............................................................................ 8-11
Transmitting Capture Files .......................................................................... 8-12
Transmit Specification Examples................................................................ 8-12
Transmit Specification Example, Bursts .......................................... 8-14
Hints and Tips for a Transmit Specification................................................ 8-15
9 Alarms ............................................................................................ 9-1
Current Module Alarms............................................................................... 9-2
Alarm Editor ................................................................................................ 9-4
Multi-QoS Alarms............................................................................... 9-5
Expert Alarms..................................................................................... 9-6
Using Alarms with Different Devices ................................................ 9-7
Thresholds and Alarms................................................................................ 9-8
Alarm Actions.............................................................................................. 9-9
Log File Settings ................................................................................. 9-10
E-Mail Settings ................................................................................... 9-10
Pager Settings.................................................................................... 9-11
SNMP Trap Settings .......................................................................... 9-11
Viewing the Alarm List and the Alarm Log................................................ 9-14
Hints and Tips for Alarms ........................................................................... 9-14
Alarm Examples .......................................................................................... 9-15
Alarm Example, Utilization ............................................................... 9-15
Alarm Example, MAC Errors............................................................. 9-16
Alarm Example, Frame Size .............................................................. 9-17
Alarm Example, VoIP Calls ............................................................... 9-18
Alarm Example, Expert and Application Response.......................... 9-19
10 Expert Features ............................................................................. 10-1
Expert System Views................................................................................... 10-2
Getting Started with Expert View ............................................................... 10-2
Expert Overview Details .................................................................... 10-4
Expert Layers............................................................................................... 10-6
Expert Symptoms, Analyses, and Network Entities.................................... 10-10
Symptoms............................................................................................ 10-10
Analyses .............................................................................................. 10-11
Entities ................................................................................................ 10-11
ix
Page 10

Surveyor
User’s Guide
Expert Diagnostic Messages........................................................................ 10-15
Working with the Expert System................................................................. 10-16
Configuring the Expert System ......................................................... 10-16
Module Settings for the Expert System............................................. 10-17
Setting Expert Alarms........................................................................ 10-17
Customizing Expert Diagnostic Information .................................... 10-17
Exporting Expert Data ....................................................................... 10-18
Printing Expert Data .......................................................................... 10-18
Working with Timestamps ................................................................. 10-18
Working with Analyzer Devices ......................................................... 10-19
Application Response Time......................................................................... 10-19
Application Layer ........................................................................................ 10-20
Excessive Mailslot Broadcasts ........................................................... 10-20
FTP Login Attempts ........................................................................... 10-21
Missed Browser Announcement......................................................... 10-22
NCP File Retransmission ................................................................... 10-23
NCP Read/Write Overlap ................................................................... 10-24
NCP Request Denied .......................................................................... 10-25
NCP Request Loop .............................................................................. 10-26
NCP Server Busy ................................................................................ 10-27
NCP Too Many File Retransmissions ................................................ 10-28
NCP Too Many Requests Denied ....................................................... 10-29
NCP Too Many Request Loops........................................................... 10-30
NFS Retransmissions ......................................................................... 10-31
No HTTP POST Response .................................................................. 10-32
No Server Response ............................................................................ 10-33
Slow HTTP GET Response ................................................................. 10-34
Slow HTTP POST Response............................................................... 10-35
Slow Server Connect ........................................................................... 10-36
Slow Server Response ......................................................................... 10-37
SMB Invalid Network Name .............................................................. 10-38
SMB Invalid Password ....................................................................... 10-39
Session Layer............................................................................................... 10-40
No WINS Response ............................................................................. 10-40
TNS Slow Server Connect .................................................................. 10-41
TNS Slow Server Response ................................................................ 10-42
Transport Layer............................................................................................ 10-43
Idle Too Long....................................................................................... 10-43
Non Responsive Station...................................................................... 10-44
TCP Checksum Errors........................................................................ 10-45
TCP Fast Retransmission .................................................................. 10-46
TCP Frozen Window ........................................................................... 10-47
TCP Long Ack ..................................................................................... 10-49
TCP Repeat Ack .................................................................................. 10-50
x
Page 11

Contents (continued)
TCP Retransmissions ......................................................................... 10-51
TCP RST Packets................................................................................ 10-52
TCP SYN Attack ................................................................................. 10-53
TCP Window Exceeded....................................................................... 10-54
TCP Window Probe............................................................................. 10-55
TCP Zero Window ............................................................................... 10-56
Too Many Retransmissions ................................................................ 10-57
Network Layer............................................................................................. 10-58
Duplicate Network Address ............................................................... 10-58
HSRP Coup ......................................................................................... 10-59
HSRP Errors ....................................................................................... 10-60
HSRP Resign....................................................................................... 10-61
ICMP All Errors.................................................................................. 10-62
ICMP Bad IP Header.......................................................................... 10-63
ICMP Destination Host Access Denied ............................................. 10-64
ICMP Destination Host Unknown ..................................................... 10-65
ICMP Destination Network Access Denied....................................... 10-66
ICMP Destination Network Unknown .............................................. 10-67
ICMP Destination Unreachable......................................................... 10-68
ICMP Fragment Reassembly Time Exceeded................................... 10-70
ICMP Fragmentation Needed [D/F set] ............................................ 10-71
ICMP Host Redirect............................................................................ 10-72
ICMP Host Redirect for TOS ............................................................. 10-73
ICMP Host Unreachable .................................................................... 10-74
ICMP Host Unreachable for TOS ...................................................... 10-75
ICMP Inconsistent Subnet Mask ....................................................... 10-76
ICMP Network Redirect ..................................................................... 10-77
ICMP Network Redirect for TOS ....................................................... 10-78
ICMP Network Unreachable.............................................................. 10-79
ICMP Parameter Problem.................................................................. 10-80
ICMP Port Unreachable ..................................................................... 10-81
ICMP Protocol Unreachable............................................................... 10-82
ICMP Redirect .................................................................................... 10-83
ICMP Required IP Option Missing.................................................... 10-84
ICMP Source Quench ......................................................................... 10-85
ICMP Source Route Failed ................................................................. 10-86
ICMP Time Exceeded ......................................................................... 10-87
ICMP Time to Live Exceeded ............................................................. 10-88
Illegal Network Source Address ........................................................ 10-89
IP Checksum Errors ........................................................................... 10-90
IP Time to Live Expiring .................................................................... 10-91
ISL BPDU/CDP Packets..................................................................... 10-92
ISL Illegal VLAN ID........................................................................... 10-93
OSPF Broadcasts ................................................................................ 10-94
xi
Page 12

Surveyor
User’s Guide
RIP Broadcasts.................................................................................... 10-95
Router Storm....................................................................................... 10-96
Same Network Addresses................................................................... 10-97
SAP Broadcasts................................................................................... 10-98
Total Router Broadcasts ..................................................................... 10-99
Unstable MST ..................................................................................... 10-100
Zero Broadcast Address ...................................................................... 10-101
MAC Layer .................................................................................................. 10-102
Bad Frames ......................................................................................... 10-102
Broadcast/Multicast Storms ............................................................... 10-103
CRC Frame counter ............................................................................ 10-104
Excessive ARP..................................................................................... 10-105
Excessive BOOTP ............................................................................... 10-106
Excessive Broadcasts .......................................................................... 10-107
Excessive Collisions ............................................................................ 10-108
Excessive Multicasts........................................................................... 10-109
Fragment Frame ................................................................................. 10-110
Illegal MAC Source Address .............................................................. 10-111
Jabber Frame ...................................................................................... 10-112
Network Overload ............................................................................... 10-113
New MAC Stations ............................................................................. 10-114
Oversized Frame ................................................................................. 10-115
Overload Frame Rate ......................................................................... 10-116
Overload Utilization Percentage ........................................................ 10-117
Physical Errors ................................................................................... 10-118
Runt Frame ......................................................................................... 10-119
Same MAC Addresses......................................................................... 10-120
Total MAC Stations ............................................................................ 10-121
Hints and Tips for Expert Features .............................................................. 10-122
Summary of Expert Counters and Symptoms.............................................. 10-123
11 Multi-QoS ....................................................................................... 11-1
Protocols Supported by Multi-QoS..................................................... 11-2
Using Multi-QoS with Analyzer Hardware....................................... 11-2
Multi-QoS User Interface Overview............................................................ 11-3
Surveyor and RTCP Jitter Values ..................................................... 11-5
Configuring Multi-QoS................................................................................ 11-6
Multi-QoS Performance Optimization ............................................... 11-8
Call Filtering with Multi-QoS ............................................................ 11-8
All Calls Table............................................................................................. 11-9
Field Descriptions for All Calls Table................................................ 11-10
Call Range Graphs and Summaries ............................................................. 11-11
Call Jitter, Call RTCP Jitter, Call Setup Time ................................. 11-11
Dropped Packets, RTCP Dropped Packets ........................................ 11-13
xii
Page 13

Contents (continued)
Field Descriptions for Call Range Summaries.................................. 11-15
VQMon Metrics........................................................................................... 11-16
Utilization Graph ......................................................................................... 11-19
Field Descriptions for Call Details.............................................................. 11-20
Channel Table Details ................................................................................. 11-24
Filtering on Single Channels ............................................................. 11-29
Call Playback ...................................................................................... 11-29
Customizing Multi-QoS Table Displays ..................................................... 11-30
Customizing All Calls or Range Summary Tables............................ 11-30
Customizing Channel Tables ............................................................. 11-31
Exporting Multi-QoS Data .......................................................................... 11-32
Exporting All Multi-QoS Data to CSV Format ................................. 11-32
Exporting a Single Multi-QoS Table to CSV Format ....................... 11-33
12 Counters ........................................................................................ 12-1
Packet Counters ........................................................................................... 12-1
Custom Counters ......................................................................................... 12-2
Error Counters ............................................................................................. 12-2
Expert Counters ........................................................................................... 12-5
Multi-QoS Counters .................................................................................... 12-9
Counter Log File Overview......................................................................... 12-9
Log Directory Structure ..................................................................... 12-10
13 Utilities ........................................................................................... 13-1
Name Table Utility ...................................................................................... 13-2
Building a Name Table From the Network....................................... 13-4
NIS-to-Name Table Conversion Utility ...................................................... 13-5
Sniffer™ Translator Utility ......................................................................... 13-6
Internet Advisor™ Translator Utility.......................................................... 13-6
Get Version Information Utility .................................................................. 13-6
Convert Capture Files to Histogram Files ................................................... 13-7
Merge Histogram Files ................................................................................ 13-7
Extract Frames From a File Using a Filter .................................................. 13-8
Logging Utilities.......................................................................................... 13-8
Export Utilities ............................................................................................ 13-8
Exporting Packets............................................................................... 13-8
Exporting Tables to CSV Format or Graphs to a Bitmap ................ 13-9
Exporting to Optimal CSV Format.................................................... 13-9
Exporting Counter Log Files to Excel ............................................... 13-10
xiii
Page 14

Surveyor
User’s Guide
A Implementation Profile ................................................................. A-1
Buffers ......................................................................................................... A-1
How Resources Use Buffers........................................................................ A-1
Hardware Dependencies .............................................................................. A-3
About NDIS Mode....................................................................................... A-5
Captured Packets................................................................................ A-5
Capture Rate / Transmit Speed ......................................................... A-5
Counters .............................................................................................. A-5
Rx Counter Display............................................................................. A-5
Transmit Specification ....................................................................... A-5
NDIS Configuration Options....................................................................... A-6
Setting the Interface ........................................................................... A-6
Set Capture Buffer and Packet Slicing Size ...................................... A-6
B Pre-Defined Filter Templates ....................................................... B-1
Filter Templates ........................................................................................... B-1
C Keyboard Shortcuts ...................................................................... C-1
Function Keys.............................................................................................. C-1
Standard and Navigational Keys.................................................................. C-2
D Parser Names ................................................................................ D-1
Recognized Parser Names ........................................................................... D-1
Glossary
Index
xiv
Page 15

List of Figures
Figure Page
5-1. Remote Host Connections ............................................................................... 5-3
5-2. Host Properties Dialog Box for Establishing an Alias .................................... 5-4
6-1. Histogram Display and Button Controls ......................................................... 6-10
6-2. Histogram Display Showing Colors ................................................................ 6-12
6-3. Histogram Display, Large Capture Example .................................................. 6-13
6-4. Histogram Showing Mouse Control ................................................................ 6-16
6-5. MAC Statistics View (Capture) ...................................................................... 6-19
6-6. MAC Statistics View (Transmit) .................................................................... 6-20
7-1. Filter Design Window ..................................................................................... 7-4
7-2. Template Description Window Showing a Macro Filter ................................ 7-8
7-3. Example Filter Actions Dialog Box ................................................................ 7-14
7-4. Example Filter States Design Window ........................................................... 7-18
7-5. Filter Design Window, Conversation Example .............................................. 7-23
7-6. Filter Design Window, Template Combination Example ............................... 7-25
7-7. Filter Design Window, Capture TCP Port Example ....................................... 7-27
7-8. Advanced Filter, Filter States Design Window ............................................... 7-29
8-1. Transmit Specification Dialog Box ................................................................. 8-2
8-2. Transmit Specification Dialog Box, Packet Gaps ........................................... 8-13
8-3. Transmit Specification Dialog Box, Bursts .................................................... 8-14
9-1. Current Module Alarms .................................................................................. 9-2
9-2. Alarm Editor .................................................................................................... 9-3
9-3. Modify Alarms ................................................................................................ 9-3
9-4. E-Mail Settings for THGs ............................................................................... 9-11
9-5. SNMP Trap Settings for THGs ....................................................................... 9-12
9-6. Alarm Example, Utilization ............................................................................ 9-15
9-7. Alarm Example, MAC Errors ......................................................................... 9-16
9-8. Alarm Example, Frame Size ........................................................................... 9-17
9-9. Alarm Example, Call Jitter and Call Setup Time ............................................ 9-18
xv
Page 16

Surveyor
User’s Guide
9-10. Alarm Example, Expert and Application Response ........................................ 9-19
10-1. Expert Overview Example ............................................................................... 10-3
10-2. Expert Overview Detail Table Example .......................................................... 10-5
10-3. Expert Application Layer Example ................................................................. 10-7
10-4. Entities for the Transport Layer Example ........................................................ 10-12
10-5. Expert Diagnosis Example ............................................................................... 10-15
10-6. Expert Configuration Example ........................................................................ 10-16
11-1. Multi-QoS Interface Overview ........................................................................ 11-4
11-2. Multi-QoS Configuration ................................................................................. 11-6
11-3. Multi-QoS All Calls Table ............................................................................... 11-9
11-4. Multi-QoS Jitter Graph Example ..................................................................... 11-11
11-5. Multi-QoS Configuration, Call Jitter Ranges .................................................. 11-12
11-6. Multi-QoS Packets Dropped Graph Example .................................................. 11-13
11-7. Multi-QoS Configuration, Packets Dropped ................................................... 11-14
11-8. Multi-QoS R-factor Example ........................................................................... 11-17
11-9. Multi-QoS Configuration, R-factor Ranges ..................................................... 11-18
11-10. Multi-QoS Utilization Graph Example ............................................................ 11-19
11-11. Example Call Details Window (H.323) ........................................................... 11-20
11-12. Channel Table Example ................................................................................... 11-25
11-13. Multi-QoS View Options Example .................................................................. 11-30
11-14. Multi-QoS Channel Table View Options, SCCP Example ............................. 11-31
13-1. Example Name Table Dialog Box ................................................................... 13-3
xvi
Page 17

List of Tables
Table Page
1-1. Surveyor Functions ......................................................................................... 1-2
1-2. Surveyor Optional Software Modules and Their Functions ........................... 1-3
1-3. Finisar Analyzer Devices ................................................................................ 1-4
1-4. Protocols Supported in Surveyor .................................................................... 1-5
1-5. Supported Multi-Media Protocols................................................................... 1-7
2-1. System Requirements...................................................................................... 2-1
2-2. Supported Analyzer Cards and Network Adapter Cards ................................ 2-2
2-3. Hardware/Software Compatibility Matrix ...................................................... 2-9
3-1. Default Account Names, Passwords and Privileges ....................................... 3-2
4-1. Configurable Capture View Columns ............................................................. 4-3
4-2. Histogram Color Defaults ............................................................................... 4-4
4-3. Hardware Device Properties............................................................................ 4-7
4-4. Default Module Settings ................................................................................. 4-8
4-5. Remote Communications Tab Functions and Default Settings....................... 4-11
4-6. Remote Polling Timers.................................................................................... 4-13
4-7. Strip Chart Display Timers.............................................................................. 4-13
4-8. Default Display Timer Settings....................................................................... 4-13
4-9. History Log File Settings and Default Values................................................. 4-15
4-10. Alarm Actions ................................................................................................. 4-16
4-11. Default Names for Non-WKP TCP Ports ....................................................... 4-25
4-12. Default Names for Non-WKP UDP Ports....................................................... 4-25
5-1. Remote User Privileges................................................................................... 5-5
5-2. Surveyor Resource Modes .............................................................................. 5-6
5-3. Hardware Device Capabilities......................................................................... 5-7
6-1. Surveyor’s Primary Windows for Viewing Information................................. 6-1
6-2. Data Views Provided Within Summary, Detail and Capture View................. 6-2
6-3. Module Window Tabs Within Summary View ............................................... 6-3
6-4. Histogram Default Colors ............................................................................... 6-13
xvii
Page 18

Surveyor
User’s Guide
6-5. Packet Editor Buttons ..................................................................................... 6-17
6-6. Frame Size Distribution View, Frame Size Statistics ..................................... 6-21
6-7. Protocol Distribution View, Chart Buttons - Protocols................................... 6-22
6-8. Protocol Distribution View, Chart Buttons - Packets...................................... 6-22
6-9. Protocol Distribution View, Graph Type Buttons........................................... 6-23
6-10. Protocol Distribution View, Table Column Descriptions ............................... 6-23
6-11. Host Table View, Table Column Descriptions ................................................ 6-24
6-12. Network Layer Host Table View, Table Column Descriptions....................... 6-26
6-13. Application Layer Host Table View, Table Column Descriptions.................. 6-27
6-14. Host Matrix View, Table Column Descriptions.............................................. 6-29
6-15. Network Layer Matrix View, Table Column Descriptions ............................. 6-30
6-16. Application Layer Matrix View, Table Column Descriptions ........................ 6-32
6-17. VLAN View, Table Column Descriptions ...................................................... 6-34
6-18. Address Map View, Table Column Descriptions............................................ 6-34
6-19. Duplicate Address View, Table Column Descriptions.................................... 6-35
6-20. Application Response Time View, Column Descriptions............................... 6-36
7-1. Defining Conversations .................................................................................. 7-5
7-2. Defining Port Numbers................................................................................... 7-7
7-3. Operator Buttons for Template Combinations................................................ 7-13
7-4. Capture Filter Actions..................................................................................... 7-14
7-5. Display Filter Actions..................................................................................... 7-15
7-6. Capture Filter Global Values........................................................................... 7-16
7-7. Capture and Display Frame Types/Size .......................................................... 7-17
7-8. Logic Sequence for Capture and Display Filter Statements .......................... 7-21
8-1. Stream Function Buttons................................................................................. 8-4
8-2. Transmit Specification Control Buttons ......................................................... 8-5
8-3. Methods to Repeat Frames ............................................................................. 8-5
8-4. Stream Modes ................................................................................................. 8-7
8-5. Packet Editor Buttons ..................................................................................... 8-9
9-1. Alarm Editor ................................................................................................... 9-4
9-2. Expert Alarms, Listed by Protocol Layer....................................................... 9-6
9-3. Alarms and Hardware Devices ....................................................................... 9-7
9-4. Alarm Actions................................................................................................. 9-9
10-1. Expert Symptoms and Analyses by Layer...................................................... 10-9
10-2. Summary of Expert Features .......................................................................... 10-124
11-1. All Calls Table Field Descriptions.................................................................. 11-10
11-2. Defaults for Call Jitter and Call Setup Time Ranges (in milliseconds).......... 11-12
11-3. Defaults for Packets Dropped Ranges ............................................................ 11-14
11-4. Call Range Summary Field Descriptions........................................................ 11-15
11-5. Voice Quality, R-factors, and MOS Range ..................................................... 11-17
11-6. Ranges for R-factors ....................................................................................... 11-18
xviii
Page 19

Tables (continued)
11-7. SCCP Call Field Descriptions ........................................................................ 11-21
11-8. H.323 Call Field Descriptions ........................................................................ 11-22
11-9. SIP Call Field Descriptions ............................................................................ 11-23
11-10. UNKNOWN Call Field Descriptions ............................................................. 11-24
11-11. H.323, SIP, or UNKNOWN Channel Table Column Descriptions ................ 11-26
11-12. SCCP Channel Table Column Descriptions ................................................... 11-28
12-1. MAC Layer Counter Types ............................................................................ 12-1
12-2. Alphabetical List and Descriptions of Ethernet Error Counters..................... 12-2
12-3. Alphabetical List and Descriptions of Token Ring Error Counters................ 12-4
12-4. Alphabetical List and Descriptions of Expert Counters ................................. 12-5
12-5. Alphabetical List and Descriptions of Multi-QoS Counters .......................... 12-9
13-1. Ethernet and Fast Ethernet Network Management Utilities........................... 13-1
13-2. Sniffer Translator Utility, Tool Menu Options ............................................... 13-6
13-3. Internet Advisor Translator Utility, Tool Menu Options................................ 13-6
A-1. Buffer Types Used By Surveyor..................................................................... A-1
A-2. Resource Use of Buffers................................................................................. A-2
A-3. Hardware Real-Time Functions...................................................................... A-3
A-4. Hardware Transmit Functions ........................................................................ A-3
A-5. Hardware Capture Functions.......................................................................... A-4
A-6. Hardware Connectivity................................................................................... A-4
B-1. Surveyor Filter Templates, Ethernet EV2....................................................... B-2
B-2. Surveyor Filter Templates, IP and IPX over Ethernet EV2............................ B-3
B-3. Surveyor Filter Templates, TCP/IP over Ethernet EV2.................................. B-5
B-4. Surveyor Filter Templates, UDP/IP over Ethernet EV2................................. B-7
B-5. Surveyor Filter Templates, Ethernet LLC/Novell .......................................... B-9
B-6. Surveyor Filter Templates, Ethernet SNAP.................................................... B-10
B-7. Surveyor Filter Templates, Ethernet ISL........................................................ B-11
B-8. Standard Filter Templates, Token Ring .......................................................... B-14
C-1. Shortcut Keys from Summary and Detail View ............................................. C-1
C-2. Shortcut Keys from All Windows .................................................................. C-2
C-3. Shortcut Keys from Summary View............................................................... C-2
C-4. Shortcut Keys from Detail View..................................................................... C-2
C-5. Shortcut Keys from the Capture View Window............................................. C-2
C-6. Shortcut Keys from the Capture Filter Window............................................. C-3
D-1. Parser Names, DLC Suite............................................................................... D-1
D-2. Parser Names, Applications and Others ......................................................... D-1
D-3. Parser Names, Apple Talk Suite..................................................................... D-2
D-4. Parser Names, Banyan Suite........................................................................... D-2
D-5. Parser Names, Cisco Suite.............................................................................. D-3
D-6. Parser Names, DECnet Suite .......................................................................... D-3
D-7. Parser Names, Fujitsu Suite............................................................................ D-3
xix
Page 20

Surveyor
User’s Guide
D-8. Parser Names, IBM Suite................................................................................ D-4
D-9. Parser Names, Internet Suite........................................................................... D-4
D-10. Parser Names, Internet Next Generation Suite ............................................... D-6
D-11. Parser Names, Netware Suite.......................................................................... D-6
D-12. Parser Names, PPP Suite ................................................................................ D-7
D-13. Parser Names, XNS Suite ............................................................................... D-7
D-14. Parser Names, H.323 Suite ............................................................................. D-8
D-15. Parser Names, ITU Codecs............................................................................. D-8
D-16. Parser Names, Cisco IP Telephony Suite........................................................ D-9
D-17. Parser Names, Other Multimedia.................................................................... D-9
D-18. Parser Names, Intel Suite................................................................................ D-9
D-19. Parser Names, VPN Suite ............................................................................... D-9
xx
Page 21

Chapter 1
1 Introduction
Finisar is the technology leader in providing LAN and SAN analysis tools. Finisar's
fully distributed, full-line-rate performance network analysis products monitor,
measure, analyze, and troubleshoot 10/100/1000 Ethernet and VoIP. These products
deliver unrivaled scalability, performance, accuracy and value to customers
worldwide. Finisar's Surveyor software is a Windows-based (2K, NT 4.x, XP)
software analyzer-plus-monitor application for 10/100/1000 Ethernet networks.
Surveyor provides users with the most robust, easy to use set of network analysis
and monitoring tools in a single package. Surveyor's features include full 7-layer
packet decode and analysis, real-time network statistics, advanced alarm setting and
actions, packet edit and slicing, multi-layer filtering, and automatic name table
updating. Optional software modules provide multi-layer expert analysis, traffic
generation, and the ability to monitor remote segments.
Finisar's Multi-QoS software plug-in monitors, measures, and analyzes QoS of
VoIP (Voice Over IP) calls. Multi-QoS includes Telchemy’s VQMon VoIP call
quality analysis engine. VQMon enables you to measure call quality from "ear-toear" using ITU standard passive test methods. This feature allows you to accurately
predict MOS scores and confirm SLA performance. Multi-QoS reports over 20 QoS
metrics (jitter, packet loss, delay, etc.) and provides Call and Channel table
summaries similar to Call Detail Records (CDRs) for standard and custom VoIP
protocols including H.323, SIP, and Cisco SSP and SCCP calls. Multi-QoS is one of
the first products to provide both network analysis and VoIP measurement and
verification for Cisco AVVID (Architecture for Voice, Video and Integrated Data).
Features include call playback of G.711 codec data.
Surveyor typically interfaces with one or more of Finisar's hardware analyzer tools.
Surveyor can simultaneously capture, monitor, and analyze multiple devices and
analyze captured data. Surveyor monitors local network segments, and the optional
Remote plug-in allows Finisar software to communicate with Finisar hardware and
access Finisar products on remote segments.
1-1
Page 22
Surveyor
User’s Guide
Surveyor's user interface provides both a comprehensive view of the network as
well as the ability to easily drill down to a specific network segment. Surveyor's
main window provides a single, user-defined view for each of the segments being
monitored. The user determines what information to view for each segment such as
network utilization, protocol distribution, host table, etc. In this same window, the
user can create alarms that monitor multiple segments simultaneously.
An optional Expert plug-in includes expert features for automatic and very detailed
problem diagnosis. Potential error conditions are automatically logged. Counters,
addresses, protocols, and diagnostic information related to the detected network
condition are displayed. You can also set alarms to be informed of any events
detected by the Expert system.
For test and development environments, an optional Packet Blaster plug-in software
provides advanced traffic generation and intelligent packet and file editing
capabilities.
Surveyor Functions
Surveyor provides tremendous flexibility in performing the tasks required to
monitor and troubleshoot your network. As your Surveyor expertise grows you will
find that the number of ways you can set up and apply the tool are virtually limitless.
1-2
The basic functions of Surveyor are described in Table 1-1. Table 1-2 on the next
page shows the additional functions available with the optional Surveyor software
modules, called plug-ins.
Table 1-1. Surveyor Functions
Function Description
Capture Capture data from a network and place it in system memory space (buffer)
on an analyzer device. Surveyor lets you create and save capture filters that
direct analyzer devices to capture only the information you want to view and
analyze.
Capture View Look at the data in a way that is useful for network analysis and troubleshoot-
ing. Surveyor lets you create and save viewing filters to display only the information you want to analyze. The data can be viewed in numerous ways and
from different perspectives. Display of the data can be either as graphical
charts or row-and-column tables.
Filter Surveyor lets you create and save capture/display filters to collect/display
only the information you want to view and analyze.
Save Move captured data from a capture buffer to a storage device on the Sur-
veyor host PC. Surveyor enables you to store captured data onto your hard
drive for later viewing, analysis, or transmission.
Page 23
Introduction
Surveyor Functions
Table 1-1. Surveyor Functions (continued)
Log Record counter information. Surveyor enables you to capture all byte, frame,
and error counter values compiled during the capture or transmission of data.
Monitor Real-time views for data seen on a network segment. The data can be
viewed in numerous ways and from different perspectives. Display of the
data can be either graphical charts or row-and-column tables.
Settings Alarms Alarms can be set to flag network conditions. Actions can be performed
when alarms are triggered.
Table 1-2. Surveyor Optional Software Modules and Their Functions
Function Description
1
Remote Functions
(Remote plug-in)
Transmit
(Packet Blaster
plug-in)
Expert Analysis
(Expert plug-in)
Voice/Video over
Ethernet Analysis
(Multi-QoS plug-in)
All data collection and data management functions described in Table 1-1
are available from other devices in a distributed network.
Send data to a network. Surveyor lets you see what happens to your network
under precisely controlled conditions. You can play back streams of captured
data or you can transmit edited data. You can edit a stream of captured data
by changing the sequence of the packets, deleting or adding (inserting) packets, creating bad packets, eliminating all packets of a certain type (protocol)
and so on. Surveyor also gives you complete control of when, how fast, how
long, and how often it transmits the data you want to send over the network.
Expert analysis starts with the automatic logging of possible problems.
Expert data views display counters, addresses, protocols, and diagnostic
information related to the detected network condition. Expert alarms can be
set to flag network error conditions. Actions can be performed when alarms
are triggered.
Decode VoIP and other synchronous protocols in an Ethernet environment
and present the data in tables.
detail records showing QoS statistics, addresses, and protocol conditions
related to conversations and channels within the H.323, SIP, or Cisco’s
SCCP protocol.
Multi-QoS data views display counters, call
1-3
Page 24
Surveyor
User’s Guide
Analyzer Devices
The full power of Surveyor is realized through optional hardware analyzer cards
available from Finisar. Analyzer cards from Finisar are installed in a PC, a notebook
PC, or in a separate analyzer device. The table below provides a brief summary of
the Finisar analyzer devices used by Surveyor:
Finisar Device Description
Table 1-3. Finisar Analyzer Devices
THGm (Ten/Hundred/
Gigabit module)
THGs Analyzer device accessed remotely by Surveyor. THGs contains two syn-
THGsE Analyzer device accessed remotely by Surveyor. THGsE contains two syn-
THGp Portable analyzer/PC device running Surveyor and other analyzer soft-
THGnotebook Portable undercarriage unit with one or two THGm analyzer cards
Portable Surveyor 10/
100 Ethernet Analyzer Card
PCI-bus hardware card that installs in a PC for analyzing 10/100 Ethernet
or Gigabit Ethernet networks.
chronized THGm modules for analysis of full-duplex 10, 100, or Gigabit
Ethernet traffic at full-line rate.
chronized THGm modules for analysis of full-duplex 10, 100, or Gigabit
Ethernet traffic at full-line rate. THGsE also contains a 80MB hard disk for
capture to disk.
ware. THGp contains one or more THGm modules for analysis of 10, 100,
or Gigabit Ethernet traffic at full-line rate.
designed to operate with a high-performance notebook computer. Connection to the notebook PC is via PCI bus expansion. Full line rate THGm analyzer cards are made available from a notebook PC.
CardBus analyzer/adapter card that installs in a notebook PC for analyzing
10/100 Ethernet networks.
See Chapter 5 for more detailed information on how Surveyor uses analyzer
devices.
Protocols Supported
Table 1-4 on the following page lists the network and application protocols that
Surveyor can decode. For a listing of protocol specifications and information, refer
to Appendix C.
Note that Finisar continually adds to the list of protocols it can decode. If you do not
see a protocol on this list that you need, visit the Finisar web site, www.Finisar.com,
or check with Customer Support for new additions.
1-4
Page 25
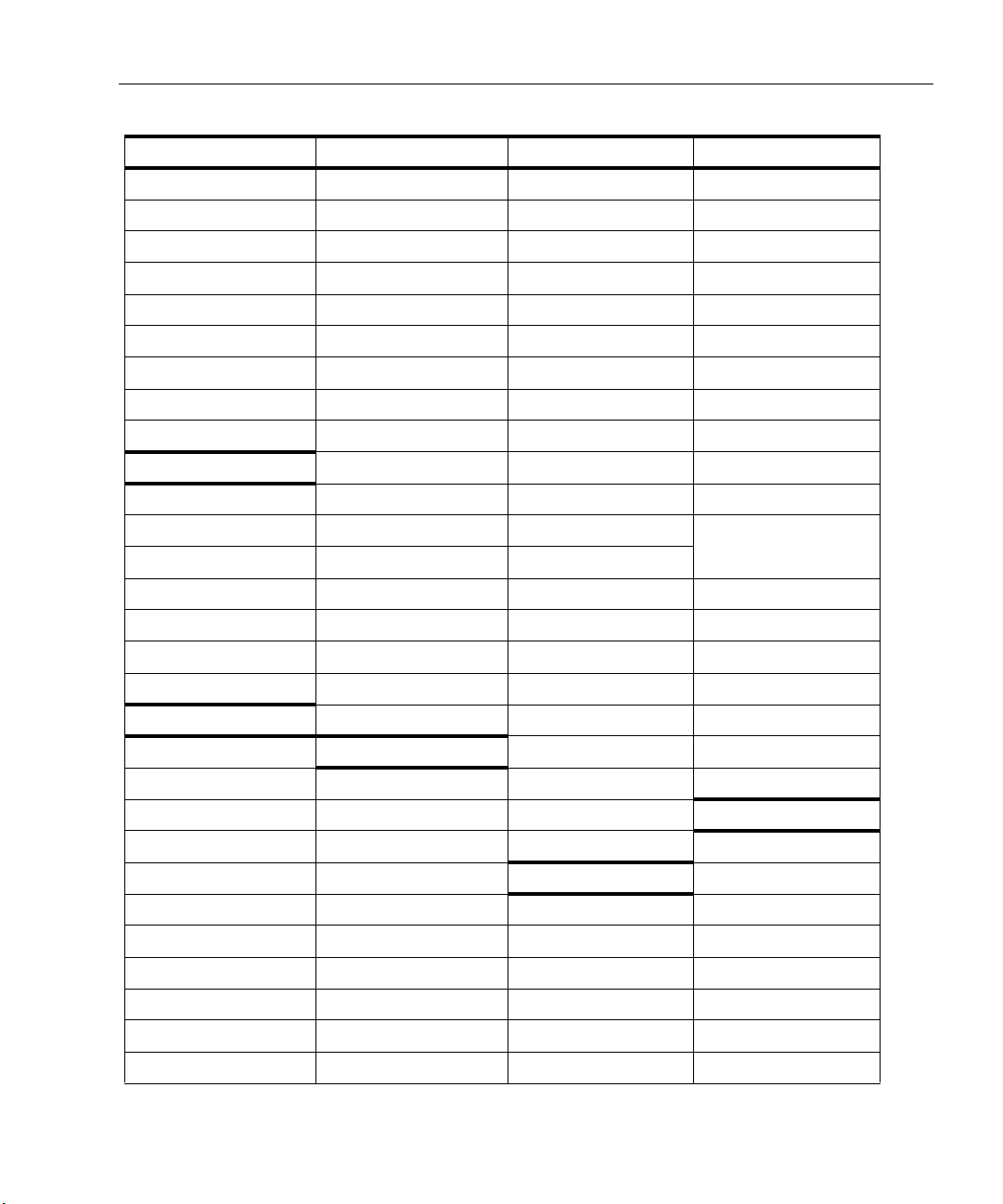
Table 1-4. Protocols Supported in Surveyor
Introduction
Protocols Supported
1
MAC Layer TCP/IP Suite TCP/IP Suite
IEEE 802.2 (LLC) ARP Ident RPC
IEEE 802.3 ASF-RMCP iFCP RTSP
Ethernet II BGP (Version 4) IGMP SGCP
IEEE 802.5 BOOTP IMAP SLP
Loopback CharGen IMSP IP SMTP
MAC Control Frame DHCP iSCSI SNMP (v1, v2, v3)
IEEE SNAP Discard LDAP TCP
IEEE 802.1X DNS MIME TELNET
Echo Mobil_IP (A11) TFTP
PPP Suite EGP MOUNT TPKT
PPPCHAP Finger NetBIOS UDP
PPPIPCP FTP NFS UNIX Remote Svcs
PPPIPX GGP NIS
PPPLCP Gopher NNTP VRRP
PPPNBFCP HTTP NTP WebNFS
PPP over Ethernet HTTPS OSPF WhoIs
ICMP PH XDR
(Cont.) TCP/IP Suite (Cont.)
(lpr, rcp, rexec, login, rsh)
Cisco Suite POP3 XDMCP
CDP IPX/SPX Suite PORT MAPPER Xwindows
DISL Diagnostic RARP
EIGRP Error RIP (Version 2) XNS
HSRP IPX Echo Protocol
IGRP IPX BCAST IP Multicast Error Protocol
ISL IPX EIGRP DVMRP IDP
RUDP IPX Ping MOSPF NetBOIS over SSP
SSP, SCCP IPX RIP, IPX WAN PIM-DM PEP
VTP NBCAST PIM-SM RIP
NCP RSVP SSP
NDS
1-5
Page 26
Surveyor
User’s Guide
Oracle Suite IPX/SPX Suite (cont.) LOA Banyan Vines Suite
TNS (TCP/IP only) NetBOIS LOA VARP
SQLNET NLSP VICP
AppleTalk Phase2 Packet Burst VIP
AARP SAP VIPC
ADSP Serialization Sybase Suite VRPC
AEP SPX TDS (TCP/IP only) VRTP
AFP SPX II VSPP
ASP Watchdog Fujitsu Suite
ATP DECnet Phase IV FNA
AURP CTERM LNDFC SNA Protocol Suite
DDP DAP 3270
DDP EIGRP DRP Applications FDC
LAP FOUND cc:Mail FID2
NBP LAT Lotus Notes FM
PAP L AVC F inisa r R SP NC
RTMP MOP XWIN XID
ZIP NICE SC
NSP
IPV6 IpSec VPN Bridge Protocols
DHCPng AH L2TP BDPU
ICMPng ESP LDP IEEE 802.1D
IDRPng ISAKMP PPPOEDS IEEE 802.1Q VLAN
IPng KERBEROS PPPOESS GARP (802.1p)
OSPFng RADIUS GMRP
RIPng SOCKS Microsoft GVRP
RSVPng SSH NMPI
TACACS SMB
TLS SMB+ (CIFS)
WebNFS
1-6
Page 27
Protocols Supported
IBM ISO Intel MPLS
NetBEUI CLNP MTP2 CR-LDP
NetBIOS CONP MTP3 RSVP-TE
ESIS RTSP
ISIS TCAP
ISO
Table 1-5. Supported Multi-Media Protocols
Multi-Media
ITU H.323 IETF Cisco Codec
ASN.1 H.248 / Megaco RUDP CellB
GK DISC MGCP SCCP G.711
H.225.0 RTCP SSP G.721
H.245 RTP G.722
H.323v4 RTSP G.723
Introduction
1
H.450.1 SGCP G.728
Q.921 SIP G.729
Q.931 H.261
RAS H.263
T.120 JPEG
T. 38 MPEG (v1, v2)
PCMU
PCMA
1-7
Page 28

Surveyor
User’s Guide
What's New in Release 5.0
A synopsis of what's new in Surveyor 5.0 is provided below.
Capture to Disk and THGsE Analyzer Support
Surveyor now supports streaming large amounts of data to disk. A new hardware
analyzer, named THGsE, has been developed to make streaming of capture data to
disk possible. The THGsE is the essentially the same hardware analyzer device as
the THGs, with the addition of an internal disk. With THGsE, up to 80GB of disk
space is available for capture.
Like THGs, the THGsE comes with two THGm analyzer cards that can capture
CAT5 Ethernet traffic at 10/100 Mbps or capture fiber optic Gigabit Ethernet at full
line rate. A 10/100 Mbps management port, a local serial port for configuration, plus
a serial port for connection to a single port tap or a multi-port switching tap are all
included. The THGsE can be controlled and configured from Surveyor similar to the
THGs; the device is seen as a remote analyzer that can be started and stopped from
Surveyor. Note that capture to disk at full line rate is not supported for 100Mbps or
Gigabit Ethernet speeds.
Disk Caching
Large capture segments, when opened, are now saved to a Cache location on the
local hard drive. This is a useful performance enhancement since capture segments
from a remote module are now handled locally. Capture segments no longer need to
be downloaded again when decoding, filtering, editing, or saving actions are taken.
You can set the cache size based on the availability of space on his local hard drive.
Capture Management
Several new features have been added to the Surveyor interface to support the
analysis of very large capture files:
• Histogram display to locate position and area of interest within a large capture
file
• Decode of captured data in manageable sections of approximately 10MB
• Ability to merge capture files
A master capture management file with extension .HST has been added to Surveyor.
When the .HST capture file is opened or when a capture buffer is opened, a
histogram will build and then the first segment of the capture will be decoded. All
new captures are saved in .HST format. A histogram file can have many capture
files (.CAP), each of which is a segment of the total capture data.
1-8
Page 29

Expanded Multi-QoS Support
The Multi-QoS software has been expanded to recognize a broader range of VoIP
calls.This includes call formats used by Avaya and Alcatel.
Multi-QoS now has the capabilities to build the call table without signaling
information. Such calls are listed with a protocol type of UNKNOWN. This can be
useful to see calls where signaling packets are unsupported or for probing end
points that do not see signaling packets.
SMNP Extended Agent
The SNMP agent for Surveyor has been expanded to include management fields
other than alarms. The new Surveyor agent implementation uses SNMPv2.
New and Enhanced Protocol Decodes
The following protocol decodes are new or enhanced in version 5.0 of Surveyor:
• ASF-RMCP, Alert Standard Format protocol
Introduction
What's New in Release 5.0
1
1-9
Page 30

Surveyor
User’s Guide
1-10
Page 31

System Requirements
The system requirements for installing and running the Surveyor software are
shown in the table below.
Table 2-1. System Requirements
Chapter 2
2 Installation
CPU
Operating System
Software
System Memory for
Opening Capture
Files*
Video Display
CDROM
Disk Space
Browser
*The amount of memory and processor speed required depends on the size of a
capture file opened for viewing/analysis. Surveyor contains a utility to break up
large capture files if you need to view large captures and have limited system
resources.
See the Readme file for the latest system requirements for Surveyor 5.0.
Pentium @ 233Mhz for 10/100 Ethernet applications
Pentium@ 1Ghz for Gigabit Ethernet applications
(see processing memory below for type of processor required)
Windows 2000, Windows NT 4.0 with Service Pack 3, 4, 5, and 6 plus
administrative privileges, or Windows XP.
Capture Buffer Size, Pentium Virtual
Local or Remote
16MB PII 64MB 64MB
32MB PII 128MB 500MB
64MB PIII 256MB 600MB
128MB PIII 512MB 700MB
256MB PIII 1000MB 1000MB
800x600 or higher resolution, 16-bit color
CDROM drive is required to install Surveyor software.
25MB of free disk space.
For THGs Web access, Internet Explorer version 5.5 or greater or
Netscape version 4.0 or greater.
Processor RAM Memory
2-1
Page 32

Surveyor
User’s Guide
Table 2-2. Supported Analyzer Cards and Network Adapter Cards
Network Analyzer
Cards
Network Adapters,
Network Adapter/
Analyzer Cards
Desktop PC:
THGm (Ten/Hundred/Gigabit module) analyzer card
THGm analyzer cards require an available PCI slot.
Analyzer cards require processing memory based on the capture buffer
memory available on the card.
Desktop PC: NDIS-compatible Ethernet adapter or NDIS-compatible 4/16
Token Ring adapter card.
• 10/100 Ethernet Adapters require an NDIS enhanced 16/32 bit driver
and must be in promiscuous mode.
• 4/16 Token Ring Adapters require an NDIS enhanced 16/32 bit driver.
Adapters accessible through NDIS drivers must be compatible with the NIC 2.0
standard. Not all Token Ring adapters are supported.
Notebook PC: Portable Surveyor 10/100 Ethernet Analyzer Card or
NDIS-compatible Ethernet adapter.
• Portable Surveyor 10/100 Ethernet Analyzer Cards require a CardBus
slot.
• 10/100 Ethernet Adapters require an NDIS enhanced 16/32 bit driver
and must be in promiscuous mode.
See the Readme file for the latest information on supported analyzers and adapters
for Surveyor 5.0.
Upgrading Surveyor
2-2
If you have a previous version of Surveyor, install version 5.0 into the same
directory as the previous version. Do not save older versions of the software on your
system.
The format of the .ini file has changed. If you have customized the .ini file in a
previous version, you will be required to re-enter your changes to the new .ini file
once the software is installed. Other user-generated files such as filters (.cfd),
capture files (.cap), and transmit specifications (.tsp) can be saved when you install
Surveyor in the same directory as the previous version.
Surveyor 5.0 has different table formats from previous versions. It is required that
you upgrade all PCs and remote analyzer devices to the latest software version.
Although remote communications may work without upgrading, you may see data
that is out of order or missing in Surveyor tables.
Page 33

Installing Surveyor
Begin by installing any local hardware analyzer cards and/or adapter cards.
Hardware analyzer cards are packaged separately from the Surveyor software.
Multiple cards may be installed in a single PC. If you need information on PC card
installation, see the following section in this chapter for hardware installation, setup, and connection instructions.
Perform the following steps to install the Surveyor software:
1. Place the Surveyor CDROM in your CDROM drive.
2. On most Windows systems an install screen will be displayed after a few
seconds. Select the install option. If this screen does not display automatically,
double-click the
drive. Double-click
3. Follow the installation program instructions to install the software. Enter your
serial number and software license key code when prompted. Approximately
20MB of free disk space is required to install the Surveyor software.
4. When you install over a previous version of Surveyor in the same directory,
you are given the option to save existing files to a different location. You may
want to save capture files, name tables, or filters you have created using a
previous version.
Installation
Installing Surveyor
My Computer icon on your desktop and select your CDROM
autorun.exe to bring up the install screen.
2
5. The installation software creates a program group called Finisar
Surveyor unless you choose to install in a different location. The program
group contains the icon for launching Surveyor software.
Connect any local analyzer cards or Ethernet adapters to the network. For THGm,
you may need to force the link. See the Launching Surveyor section in Chapter 3 for
instructions.
If you are going to use Surveyor to access remote resources, make sure the Surveyor
5.0 software is installed at the remote host and the remote resources are connected
to the network.
2-3
Page 34

Surveyor
User’s Guide
Installing Analyzer Hardware
The sections below provide installation information for the Finisar analyzer cards in
different hardware and software environments.
Installing Analyzer Hardware in a Desktop PC
Finisar offers an analyzer card that can be installed in a desktop PC. For PCI bus
expansion slots, Finisar offers the THGm analyzer card for 10/100/1000 Ethernets.
Finisar analyzer cards or other NDIS-compatible adapters can be installed in the
local PC before or after Surveyor software is installed. However, it is recommended
that you install local adapters or analyzer cards before you launch Surveyor software
for the first time.
Finisar analyzer cards install in a PC like any other card. The THGm analyzer card
can be installed as a Plug‘n’Play device for Windows 2000/XP. Refer to the
instructions below.
Installing the THGm, Windows NT
1. Power down your system.
2. Install the THGm card in your system. This requires opening the case of your
computer, inserting the card in an available PCI slot, and closing the case of
your computer. Refer to the THGm Hardware Installation Guide and your
computer’s documentation for instructions.
3. Secure the network connectors to the THGm, RJ-45 for 10/100Mbps Ethernet
or SC-type fiber optic for 1000Mbps Ethernet (optional – connection to the
network may be performed after card installation is complete).
4. Power up your system.
5. Insert the Surveyor CD in the CDROM drive and install Surveyor software. All
necessary Windows NT drivers for THGm are installed when Surveyor
software is installed.
6. When prompted, reboot your system.
7. To verify installation, open the Surveyor software. The THGm analyzer card
icon should appear under your local IP address.
Installing THGm, Windows 2000/XP
Use the procedures below for Windows 2000/XP. For Windows NT installation, see
the procedures above.
1. Power down your system.
2-4
Page 35

Installation
Installing Analyzer Hardware
2. Install the THGm card in your system. This requires opening the case of your
computer, inserting the card in an available PCI slot, and closing the case of
your computer. Refer to the THGm Hardware Installation Guide and your
computer’s documentation for instructions.
3. Secure the network connectors to the THGm, RJ-45 for 10/100Mbps Ethernet
or SC-type fiber optic for 1000Mbps Ethernet (optional – connection to the
network may be performed after card installation is complete).
4. Power up your system. Windows will detect the new card and display the
“New Hardware Found” message. Windows will then prompt for
configuration software with the
Next button to continue.
CAUTION
If the “New Hardware Found” window does not display, then the
hardware detection process was unable to find your adapter. The driver
can only be installed for Plug'n'Play adapters when the hardware can be
detected. Please consult your Windows manual for possible reasons for
this occurrence before contacting
Update Device Driver Wizard window. Click the
Finisar Technical Support.
5. Insert the Surveyor CD in the CDROM drive.
2
6. Use the
(
<CDROM-drive-letter>\drivers) on the Surveyor CDROM. The name of the
driver is
7. The
driver. Click the
Browse... button to find the Ethernet Driver directory
ww_w2000.inf.
Update Device Driver Wizard window will appear with the name of the
Finish button.
8. The Finisar driver will be copied to the hard drive. Windows will request the
Windows CDROM to install system files. Many of these system files can be
found directly on the hard drive in the
C:\windows\system and C:\windows
directory without using the CDROM.
9. Install Surveyor software and reboot your system.
10. To verify installation, open the Surveyor software. The THGm analyzer card
icon should appear under your local IP address.
Installing Analyzer Hardware in a Notebook PC
Finisar offers an Ethernet analyzer card that can be installed in a notebook PC, the
Portable Surveyor 10/100 Ethernet Analyzer Card (CardBus interface). Surveyor
software is used with at least one analyzer card from Finisar.
Please read the following before starting card installation:
2-5
Page 36

Surveyor
User’s Guide
• The Ethernet card uses a CardBus interface.
• Separate installation instructions are provided for Windows NT. Installation of
the Ethernet analyzer card in a notebook PC running Windows NT requires
CardWizard V5.00.10.
• Installation requires the Surveyor CDROM and may require the Windows
CDROM.
• It is recommended that Surveyor be installed into a dedicated notebook computer used exclusively for network analysis.
• Surveyor has limited support for 3rd party Token Ring cards. Please remove all
Token Ring network cards before using Surveyor unless you first contact Customer Support. Surveyor will work with 3rd party Ethernet cards.
• The Portable Surveyor 10/100 Ethernet Analyzer Card is a Plug 'n' Play analyzer card. Although they are hot swappable, it is advised that the initial installation of the analyzer cards be performed with the power off to avoid any device
conflicts.
Installing Portable Surveyor 10/100 Ethernet Analyzer Card, Windows NT
Use the procedures below for installing Finisar adapter cards in a notebook PC
running Windows NT.
2-6
1. Install CardWizard V5.00.10 software to your notebook computer. Follow the
installation instructions that come with the software. CardWizard is available
from SystemSoft Corporation. If you have other card installation software on
your system, you must uninstall this software before installing CardWizard.
2. Power down your system.
3. Insert the Portable Surveyor 10/100 Ethernet Analyzer Card into your system's
CardBus slot.
4. Secure the cable assembly to the Portable Surveyor 10/100 Ethernet Analyzer
Card and the RJ45 connector on the cable to the network (optional –
connection to the network may be performed after card installation is
complete).
5. Power up your system. Windows will detect the new card and display the
Wizard window. Click the OK button.
6. The
7. Form the
Network window displays. Click the Add button.
Select Network Adapter window, click the Have Disk... button. The
Insert Disk dialog box appears.
Page 37

8. Insert the Surveyor CD in the CDROM drive.
Installation
Installing Analyzer Hardware
2
9. Enter the path of the Ethernet Driver directory (
<CDROM-drive-letter>\drivers)
on the Surveyor CDROM and click OK.
10. The
11. In the
Select OEM Option window will appear. Select the “Finisar 10/100
Ethernet CardBus Adapter Plug & Play” driver. Click the
Settings window, all settings should remain as “CardWizard”. Click the
OK button to begin copying driver software to your hard disk.
OK button.
The system starts copying driver software. During the copy process, you
may receive a noncritical error message, “Cannot find file PSC1V1.hlp”.
Ignore to continue installation and complete copying driver software
Press
to your hard disk.
12. To verify that the analyzer card is properly installed, open the
the
Control Panel and expand the Network icon. If no error marks exist through
the
Network icon, the installation is complete. If an error exists, highlight the
problem adapter in the Network folder and press the
Remove button. Reboot
System folder in
the notebook computer and attempt the installation again. If the problem
persists, contact Technical Support.
13. Reboot your system.
Installing the Portable Surveyor 10/100 Ethernet Analyzer Card, Windows 2000/XP
The Portable Surveyor 10/100 Ethernet Analyzer Card is not recognized
automatically by Windows 2000 at this time. You must update the driver manually
for the card to function properly.
1. Power down your system.
2. Insert the Portable Surveyor 10/100 Ethernet Analyzer Card into your system's
CardBus slot.
3. Secure the cable assembly to the Portable Surveyor 10/100 Ethernet Analyzer
Card and the RJ45 connector on the cable to the network (optional –
connection to the network may be performed after card installation is
complete).
4. Power up your system. Windows 2000 will detect the new card and display the
“New Hardware Found” message. Windows 2000 will recognize the Portable
Surveyor 10/100 Ethernet Analyzer Card as a Racore card and use the Racore
device driver. You must update the device driver for the card to function
properly.
2-7
Page 38

Surveyor
User’s Guide
5. To update the device driver, click with the right mouse on My Network Places.
Select
Properties from the menu.
6. Double-click on
appear in the
7. Press
8. Press
Configure and then select the Device Driver tab.
Update Driver.... The Upgrade Device Driver Wizard displays. Click the
Next button to continue.
9. Select the
10. Click the
Have Disk... button. The Install from Disk window appears.
Local Area Connection. The Racore device driver should
Connect box.
Display a list of the known device.... radio button and then click Next.
11. Insert the Surveyor CD in the CDROM drive.
12. Use the
letter>\drivers) directory on the Surveyor CDROM and click OK.
13. The
Ethernet Analyzer Plug_Play” driver. Click the
14. Click the
display the
Browse... button to find the Ethernet Driver (<CDROM-drive-
Update Device Driver window will appear. Select the “Finisar 10/100
Next button.
Next button again when the next window appears. The system will
Digital Signature Not Found dialog box. Click Yes. (Note: You can
safely ignore the warning message. The message appears because Windows
2000 does not recognize the card properly at this time.)
15. The Finisar driver will be copied to the hard drive. Windows 2000/XP may
request the Windows CDROM to install system files. Many of these system
files can be found directly on the hard drive in the
C:\windows directory without using the CDROM.
C:\windows\system and
16. To verify that the analyzer card is properly installed, open the
the
Control Panel. Go to the Hardware tab in the System Properties window.
Select the
Device Manager. If no error marks exist through the Network icon, the
installation is complete. If an error exists, highlight the problem adapter and
press the
Remove button. Reboot the notebook computer and attempt the
installation again. If the problem persists, contact Technical Support.
17. Reboot your system.
Installing More Than One Analyzer Card in a Notebook PC
If you are installing two Portable Surveyor 10/100 Ethernet Analyzer Cards, install
one card, make sure it works within Surveyor, and then install the second card.
2-8
System folder in
Page 39

Compatibility Matrix
Table 2-3. Hardware/Software Compatibility Matrix
Installation
Compatibility Matrix
2
Desktop,
Win NT
Desktop,
Win 2000
Desktop,
Win XP
Notebook,
Win NT
Notebook,
Win 2000
Notebook,
Win XP
Finisar
THGm
Ye s - -- Yes
Ye s - -- Yes
Ye s - -- Yes
--- Yes Yes
--- Yes Yes
--- Yes Yes
Portable
Surveyor 10/
100 Ethernet
Analyzer Card
Ethernet,
NDIS
(3rd party)
2-9
Page 40

Surveyor
User’s Guide
2-10
Page 41

The Surveyor System
A complete Surveyor system consists of Surveyor software and at least one Finisar
distributed net QoS system, analyzer card, or NDIS-compatible Ethernet adapter.
Multiple devices can be installed in the local host PC.
With the Remote plug-in you have access to other PCs containing Finisar analyzer
cards, NDIS adapters, or other devices such as Finisar’s THGs or tap device. All
remote devices must be properly installed before they can be accessed by Surveyor.
Launching Surveyor
The base memory address is not required for portable analyzer cards or THGm cards
when you launch Surveyor.
Perform the following steps to set up your environment and launch the Surveyor
software:
Chapter 3
3 Getting Started
1. Launch the Surveyor program.
Double-click on the icon in the Surveyor group or other group where
you installed the Surveyor application.
2. The first time you launch Surveyor, you’ll be asked if you have any local
analyzer or tap devices.
If you do not have any local analyzer devices, do not check any boxes, click
and skip to step 3.
If you have THGm analyzer cards installed in your local system or switching
taps connected to your local system, select the appropriate box and click
Surveyor displays the
Use the
to access the analyzer cards you have installed on your system. Click the check
box opposite the module number that corresponds to base memory address of
Scanning Ports tab in the dialog box to tell Surveyor which ports to scan
System Settings dialog box.
OK.
OK,
3-1
Page 42

Surveyor
User’s Guide
each port on which you have installed a THGm analyzer card. Do not select
ports for other devices. Click
OK.
Use the
Local Ports for Switching Taps tab in the dialog box to tell Surveyor
which local COM port is attached to the tap device. Click the check box
opposite the correct port number.
You can change the ports to be scanned or the local port for a tap device at any
time. Select the
the
System Settings dialog box.
System Settings... option of the Configuration menu to display
3. With Remote plug-in, you are asked for an account name and password in the
Login dialog box.
Surveyor provides two default accounts,
guest and su. Table 3-1 shows the
password and privileges associated with these accounts. Choose an account,
complete the dialog box, and click
Table 3-1. Default Account Names, Passwords and Privileges
Default Account Name Password Privileges
guest public full
su manager super-user
OK.
Normally, you can use either account to access all remote resources. If a remote
resource will not permit access with either of these accounts, then get the user
name and password from the resource owner and establish an account on that
resource. To access a remote resource, you must have an account and password
set up on the remote system containing the resource or use the remote system’s
guest account.
3-2
You can also password-protect local resources. See the section called
“Protecting Local Resources” in the “Resources and Modes” chapter.
4. Surveyor starts (arms) your local devices automatically the first time you start
the software. For subsequent launches of Surveyor, local devices are not
started automatically.
From the Resource Browser, click on the button that corresponds to the analyzer
card or adapter that you want to control with the Surveyor software. The
resource can be local or remote. A monitor window appears for the analyzer
adapter you select.
Page 43

5. THGm analyzer cards have two interfaces, RJ45 for 10/100 copper wire and a
G-BIC for 1000 Mbps fiber optic. If you selected a THGm, you may need to
change the interface. From the
selects the bidirectional 10/100BASE-T port. The default is the
selects the G-BIC send/receive port pair.
6. If you selected a THGm for 10/100BASE-T, you may need to set the Interface
Mode. From the
Module menu, choose Interface Mode.
Auto Negotiate places the resource in auto-detection (10Mbps or 100Mbps)
mode. The interface mode can also force the module to only one speed.
7. If you selected a THGm for Gigabit Ethernet, you may need to disable auto
negotiation if you cannot establish a link. From the
Link and select the No Auto-Negotiation menu item. For more information on
auto negotiation, see “Establishing Links for THGm” on page 20 of this chapter.
Basic Navigation Tips
There are three main windows in Surveyor:
• Surveyor Main Window (Summary View)
Getting Started
Basic Navigation Tips
Module menu, choose Interface. On Board RJ45
G-BIC which
Module menu, choose Fiber
3
• Detail View Window
• Capture View Window
Summary View is used primarily for monitoring, as it shows a single view of many
different resources. It also contains the docking windows for selecting resources
(Resource Browser), setting alarms (Alarm Browser), and viewing system messages (Message window).
Refer to the Surveyor Quick Start Guide for pictures of the main windows used in
Surveyor.
Detail View is primarily for analyzing data from a single resource. You can look at
the data from Detail View in many different ways.
To display a resource in Detail View, click on (highlight) the resource icon in the
Resource Browser. Press the button to display Detail View for the resource.
Once you have data to analyze, stop the module and press from Detail View to
bring up Capture View. Capture View provides full decode of data in a capture
buffer. Capture View opens as a window within Detail View. Capture View has its
own toolbar so you can view captured data in many different ways.
3-3
Page 44

Surveyor
User’s Guide
You can also access Capture View from Summary View to view a Capture file.
From Summary View, click the button in the Surveyor toolbar. The contents of
the Capture file are displayed in the
Capture View window.
You’ll notice that many of the same functions can be performed from the different
windows. This design allows you to perform all the tasks you might expect to do
from any one of the major windows without having to switch to a different window.
Because of Surveyor’s flexibility, you can open many different windows and
subwindows within the program. To avoid confusion, close windows you are not
using.
Be sure to browse the Hints and Tips sections in the on-line Help system. There is a
“Hints and Tips” section for each major functional area within the product. Over
time, you’ll find the ways that you like to use the product. We encourage you to
contact us and let us know so we can include these tips in the help system and pass
these tips on to other customers and to user groups.
Here are some tips to help you use the Surveyor interface:
• Click on a resource in the Resource Browser to select that resource.
• Press the button to bring up Detail View for a resource. You can also bring
up Detail View by double-clicking with the left mouse button on the active
monitor view displayed within Summary View.
• Press the button from Detail View to bring up the
Capture Filter window.
Use this window to create/edit capture filters.
• Press the button from Detail View to bring up the
Display Filter window.
Use this window to create/edit display filters.
• Once a resource is stopped and you have captured data, press the button in
Detail View to bring up Capture View for analyzing packets and full protocol
decode.
• Press the button from Summary View to open a previously saved capture
file and bring up Capture View.
• Use the buttons in the Data Views toolbar to open many views of the same
resource within Detail View.
• Double-click on an analyzer device in the Resource Browser to create alarms
for that device.
3-4
Page 45

Getting Started
Basic Navigation Tips
• If you have the Expert plug-in, use the button in Detail View to bring up
the expert views.
• If you have the Multi-QoS plug-in, use the button in Detail View to bring
up the charts and tables for Voice over IP and Multimedia protocols.
• If you are running Packet Blaster plug-in, use the in Detail View to bring
Transmit Specification dialog box to create data streams for transmit.
up the
3
3-5
Page 46

Surveyor
User’s Guide
Buttons and Toolbars
Surveyor Toolbar
Open button
Opens a file, typically a capture file (.CAP). A dialog box displays
showing all files with extension.CAP in the current directory. From the
Summary Viewer, selecting a capture file to open will bring up Capture
View.
Save button
Saves the current contents of the capture buffer to a file. A dialog box
displays to select the file name and directory.
Print button
Prints the contents of the current view.
Name Table button
Brings up the
Name Table dialog box for editing the current name table,
saving a name table to a file, or loading a name table from a file.
Help button
Displays the help contents.
Module Toolbar (Summary View)
Start button
Starts a module. The module captures or transmits packets, depending
on whether the mode is set to transmit or capture. If green, the module
is not armed.
Stop button
Stops a module. The module ceases to capture packets or transmit
packets. If red, the module is armed.
3-6
Page 47

Getting Started
Buttons and Toolbars
Capture Mode button
Places the currently selected resource in capture mode. This button is
gray if the resource is currently active (started).
Monitor Mode button
Activates the monitor functions for the currently selected resource. If
the resource does not support monitoring functions, the resource is put
into capture mode. This button is gray if the resource is currently active
(started).
Cap+Disk Mode button
Places the currently selected resource in Cap+Disk mode. Captured
data is automatically saved to disk. This button is gray if the resource is
currently active (started).
Transmit Mode button
Places the currently selected resource in transmit mode.
(Packet Blaster plug-in only)
Detail View button
Brings up Detail View for the currently active resource.
3
Load Filter button
Brings up a dialog box to select a saved capture filter (.CFD
extension). If a capture filter is opened, that filter is applied to the
currently selected resource. This button is gray if the resource is
currently active (started).
Unload Filter button
If a filter is loaded for the currently selected module, pressing this
button will unload it. This button has no function if the currently
selected resource is in transmit or monitor only mode. This button is
gray if the resource is currently active (started).
Transmit button
Brings up a dialog box to select a saved transmit specification (.TSP
extension) or a capture file (.CAP extension) for transmit. This button
has no function if the currently selected resource is in capture or
monitor mode. This button is gray if the resource is currently active
(started). (Packet Blaster plug-in only)
3-7
Page 48

Surveyor
User’s Guide
Detail View Toolbar
Save button
Saves the current contents of the capture buffer to a file. A dialog box
displays, allowing you to select the file name and directory.
Print button
Prints the contents of the current view.
Start button
Starts a module. The module captures or transmits packets, depending
on the whether the mode is set to transmit or capture.
Stop button
Stops a module. The module ceases to capture packets or transmit
packets.
Capture Mode button
Places the currently selected resource in capture mode. This button is
gray if the resource is currently active (started).
3-8
Monitor Mode button
Activates the monitor functions for the currently selected resource. If
the resource does not support monitoring functions, the resource is put
into capture mode. This button is gray if the resource is currently active
(started).
Cap+Disk Mode button
Places the currently selected resource in Cap+Disk mode. Captured data
is automatically saved to disk. This button is gray if the resource is
currently active (started).
Transmit Mode button
Places the currently selected resource in transmit mode. This button is
gray if the resource is currently active (started).
Capture View button
Selects Capture View mode for viewing captured information. You can
see protocol decodes in this view. Capture View has its own toolbar to
allow you to select other view of captured information.
Page 49

Getting Started
Buttons and Toolbars
Capture Filter button
Display the
Capture Filter window. The window displays a previously
opened filter or the default filter.
Load Filter button
Brings up a dialog box to select a saved capture filter (.CFD
extension). If a capture filter is opened, that filter is applied to the
currently selected resource. This button is gray if the resource is
currently active (started).
Unload Filter button
If a filter is loaded for the currently selected module, pressing this
button will unload it.This button has no function if the currently
selected resource is in transmit or monitor only mode. This button is
gray if the resource is currently active (started).
Display Filter button
Display the
Display Filter window. The window displays a previously
opened filter or the default filter.
Unload Display Filter button
Unloads the current display filter. All frames in the current capture will
display.
3
Transmit Specification button
Brings up the
Transmit Specification dialog box to define/load a
transmit specification. (Packet Blaster plug-in only)
Transmit from Buffer button
Brings up a the dialog box to select a capture file and then load the
capture file to the module for transmission. (Packet Blaster plug-in
only)
Name Table button
Brings up the
Name Table dialog box for editing the current name table
or saving/loading a name table to/from a file.
Alarm List and Log button
Brings up a table showing all alarm groups assigned to this resource. It
lists alarm groups by name and identifies the type of alarm group.
Help button
Displays the help contents.
3-9
Page 50

Surveyor
User’s Guide
Data Views Toolbar
(Expert and Multi-QoS buttons)
Ring Statistics View button (Token Ring Only)
Brings up tables showing information about the rings and the ring
stations detected on the network. This button is available for Token
Ring adapters only.
MAC Statistics View button
Brings up MAC Statistics View for graphically viewing packet and
error counters. This view also contains module and capture buffer status
information. The view displays appropriate error counters depending on
the mode, capture or transmit.
Frame Size Distribution View button
Selects Frame Size Distribution View for viewing the distribution of
frame sizes.
3-10
Protocol Distribution View button
Selects Protocol Distribution View for viewing a chart of the
distribution of major protocols. Control buttons in this view allow you
to customize the way you view the protocol distribution.
Utilization/Error View button (Rx)
Brings up a strip chart that plots utilization and number of errors over
time. The table for this view contains packet counters and error counters
for receive.
Utilization/Error View button (Tx)
Brings up a strip chart that plots utilization and number of errors over
time. The table for this view contains packet counters and error counters
for transmit. (Packet Blaster plug-in only)
Page 51

Getting Started
Buttons and Toolbars
Host Table View button
Selects Host Table View for viewing information. You can see MAC
stations and their associated traffic in this view.
Network Layer Host Table View button
Selects Network Layer Host Table View for viewing information. You
can see network (IP/IPX) stations and their associated traffic in this
view.
Application Layer Host Table View button
Selects Application Layer Host Table View for viewing information.
You can see application stations and their associated traffic in this
view.
Host Matrix View button
Selects Host Matrix View for viewing information. You can see all
conversations between MAC stations in this view.
Network Layer Matrix View button
Selects Network Layer Matrix View for viewing information. You can
see all network layer conversations and their associated traffic in this
view.
3
Application Layer Matrix View button
Selects Application Layer Matrix View for viewing information. You
can see all application conversations and their associated traffic in this
view.
VLAN View button
Brings up VLAN view for viewing network traffic on virtual LANs.
Cisco’s ISL protocol is the only VLAN currently recognized.
Address Mapping View button
Brings up Address Mapping View for viewing associations between
MAC station names and addresses and network station names and
addresses.
3-11
Page 52

Surveyor
User’s Guide
Refresh button
Update the information in all open views.
Duplicate Address Button (Expert plug-in only)
Brings up a table showing all duplicate IP and IPX addresses. The
duplicate network and MAC addresses associated each duplicate are
displayed.
Expert View Button (Expert plug-in only)
Brings up a table showing all expert symptoms detected. There are two
views of the expert information. The Analysis tab shows all expert
symptoms detected. The Overview tab shows the total number of expert
symptoms detected in each expert category.
Application Response Time Button (Expert plug-in only)
Brings up a table showing the applications detected and their minimum,
maximum, and average response times. The number of connections for
each application is also displayed.
Multi-QoS (Multi-QoS plug-in only)
Brings up a table showing all VoIP calls. Multiple tables and views are
available within the Multi-QoS interface.
3-12
Page 53

Filter Design Toolbar
Create Filter button
Creates a new filter. The default window appears for the
window.
Open Filter button
Opens a filter. A dialog box displays to select the file. Capture filters
are designated with an extension of .CFD files and display filters with
an extension of .DFD.
Save Filter button
Saves the current contents of the filter to a file. A dialog box displays to
specify the file name and directory. Capture filters are saved as .CFD
files and display filters as .DFD files.
Load Filter button
Load the current filter to the currently active module.
Getting Started
Buttons and Toolbars
Filter Design
3
Disable Filter button
Disable the current filter. Subsequent starting of the module will
capture all packets (use default filter).
Filter Window Toggle button
Brings up the
window is used to create advanced filters with multi-state logic.
Help button
Displays a help topic on filters.
Filter States Design Toolbar
Create Filter button
Creates a new filter. The default filter appears in the
Design window.
Open Filter button
Opens a filter. A dialog box displays to select the file. Capture filters
Filter States Design window. The Filter States Design
Filter States
3-13
Page 54

Surveyor
User’s Guide
are designated with an extension of .CFD files and display filters with
an extension of .DFD.
Save Filter button
Saves the current contents of the
Filter States Design window to a file.
A dialog box displays to specify the file name and directory. Capture
filters are saved as .CFD files and display filters as .DFD files.
Load Filter button
Load the contents of the
Filter States Design window to the currently
active module.
Disable Filter button
Disable the current capture filter. For capture, subsequent starting of the
module will capture all packets (use default filter).
Filter Window Toggle button
Brings up the
Design window is used to edit the statement.
Filter Design window for the current statement. The Filter
Cut button
Cut the selected State or ELSE IF statement. The button does not work
if other types of statements are selected.
3-14
Add button
Adds a new level if an ELSE statement or ROOT statement is selected.
Adds a new ELSE IF statement if a State or an IF statement is selected.
Show/Hide Detail button
Shows or hides the details of the current filter. Details are the number of
filters used per state (maximum = 8) and the types of frames being
captured for each IF or ELSE IF statement.
Print button
Prints the current contents of the
Filter States Design window.
Help button
Displays a help topic on filters.
Page 55

Capture View Toolbar
Open File button
Opens a capture file (.CAP). A dialog box will display showing the
current directory with all files with extension .CAP.
Save File button
Saves the current contents of this view to a file.
Search Box
Use the box to specify an ASCII text string for which to search. Once
the string is entered, press the search button to the right of the search
box.
Getting Started
Buttons and Toolbars
3
Search button
Start search of the capture file contents for an ASCII text string.
Specify the string in the search box to the left. The first instance of the
string is found starting from the current position in the capture file.
Copy button
Copies the current contents of the
documents. A window displays with the text converted to ASCII
format. Use the window to select the text you want and copy it to the
clip board.
Print button
Print the currently selected line in the
Stop Load button
Capture files are loaded to Capture View as a background process.
Pressing this button stops the background process. Press the Resume
Load button to the right to resume the process.
Summary pane for pasting into other
Summary pane.
3-15
Page 56

Surveyor
User’s Guide
Resume Load button
Capture files are loaded to Capture View as a background process.
Pressing this button resumes the background process.
Go To Trigger button
Pressing this button moves you to the line in the capture file that was set
as the trigger position. If no trigger position is set, this button moves
you to the first captured frame.
Navigation buttons
Navigation buttons move you through the capture file. There are keys to
go to the beginning and the end of the file, page up, page down,
previous line, and next line.
Other buttons for views are the same as those in the
Data Views toolbar.
Frame Size Distribution View button
Selects Frame Size Distribution View for viewing the distribution of
frame sizes.
Protocol Distribution View button
Selects Protocol Distribution View for viewing a chart of the
distribution of major protocols. Control buttons in this view allow you
to customize the way you view the protocol distribution.
Host Table View button
Selects Host Table View for viewing captured information. You can see
MAC stations and their traffic in this view.
Network Layer Host Table View button
Selects Network Layer Host Table View for viewing captured
information. You can see network (IP/IPX) stations sorted according to
the traffic variable you select in this view.
Application Layer Host Table View button
Selects Application Layer Table Host View for viewing captured
information. You can see application stations sorted according to their
names in this view.
3-16
Page 57

Getting Started
Buttons and Toolbars
Host Matrix View button
Selects Host Matrix View for viewing captured information. You can
see all conversations between MAC stations in this view.
Network Layer Matrix View button
Selects Network Layer Matrix View for viewing captured information.
You can see all network conversations for IP and IPX traffic in this
view.
Application Layer Matrix View button
Selects Application Layer Matrix View for viewing captured
information. You can see all application conversations in this view.
VLAN View button
Brings up VLAN view for viewing network traffic on virtual LANs.
Cisco’s ISL protocol is the only VLAN recognized.
Address Mapping View button
Brings up Address Mapping View for viewing associations between
MAC station names and addresses and network station names and
addresses.
3
Duplicate Address Button (Expert plug-in only)
Brings up a table showing all duplicate IP and IPX addresses. The
duplicate network and MAC addresses associated each duplicate are
displayed.
Expert View Button (Expert plug-in only)
Brings up a table showing all expert symptoms detected. There are two
views of the expert information. The Analysis tab shows all expert
symptoms detected. The Overview tab shows the total number of
expert symptoms detected in each expert category.
Application Response Time Button (Expert plug-in only)
Brings up a table showing the applications detected and their minimum,
maximum, and average response times. The number of connections for
each application is also displayed.
Multi-QoS (Multi-QoS plug-in only)
Brings up a table showing all VoIP calls. Multiple tables and views are
available within the Multi-QoS interface.
3-17
Page 58

Surveyor
User’s Guide
File Formats
The following file formats are supported in Surveyor:
.HST Extension – Capture Files
File extension for capture data files. The .HST file contains formatting information
and a list of .CAP files that contain the actual capture data. All new captures made
by Surveyor are saved as .HST files.
The .HST file is a master capture management file that organizes large captures
(>10M) into multiple capture (.CAP) files. When the .HST capture file is opened or
when a capture buffer is opened, a histogram is displayed and the first segment of
the capture (.CAP file) is decoded. The histogram is used to navigate through the
multiple .CAP files as needed.
.CAP Extension – Internal Capture Files
File extension for capture data files used internally by Surveyor. Capture file format
is compliant with RFC 1761, referred to as "Snoop" format. However, capture files
include extensions that expand the information provided by snoop format. .CAP
files are not viewed directly in this version of Surveyor, but are internal files used
within .HST files. Older .CAP files opened in Surveyor are converted to the new
format and are then available as .HST files.
.NAM Extension – Name Table Files
Name table files contain equivalencies between symbolic names and hexadecimal
names. The name table file format is identical to .ini file format. The default
hosts.nam file contains names associated with well-known hexadecimal representations. For example, BROADCAST=C000FFFFFFFF.
.CFD Extension – Capture Filters
Capture filter files contain a set of instructions internal to Surveyor that tells the
software to save only a subset of the all the information on the network.
.DFD Extension – Display Filters
Display filters files contain a set of instructions internal to Surveyor that tells the
software to display only a subset of previously captured data. View filters are essentially the same as capture filters, except that they use capture files (.CAP files) as
input rather than data being captured from the network.
.TSP Extension – Transmit Specifications
Transmit specifications contain a set of instructions internal to Surveyor that will
generate packets. You can create transmit specifications and generate traffic if you
are running Packet Blaster plug-in.
3-18
Page 59

Providing a Name Table to Surveyor
A default name table file, hosts.nam, is included with the software. Surveyor
boots using this default name table. If you wish to change the start up default name
table, you must edit the surveyor.ini file by following these instructions:
1. Locate the surveyor.ini file in your Windows directory.
2. Open the surveyor.ini file with your text editor software.
Getting Started
Providing a Name Table to Surveyor
3
3. Search for this variable,
4. Delete the hosts.nam text on that line.
5. Replace text with your default name table file. It should have the .nam
extension.
6. Save the surveyor.ini file, exit your editor and start Surveyor application.
Address and symbolic name associations can be discovered by Surveyor. This table
can be saved as a file with the .nam extension and used as the default name table.
Refer to Chapter 13 for more information on the name table.
The default name table can always be changed to another
within the software. Click on the Name Table button and select
Open. Find the name table file you want and click OK.
NameTable=<install-directory>\hosts.nam.
Note
3-19
Page 60

Surveyor
User’s Guide
Establishing Links for THGm
The THGm is often connected to a device that cannot auto negotiate the connection,
such as when monitoring/analyzing a connection through a tap device. The device
will automatically go through a sequence of attempts to disable auto negotiation and
establish a link with a device that cannot auto negotiate. However, if a link cannot
be automatically established with a device, you can attempt to establish a link
manually by disabling auto negotiation mode. The
Module menu allows you to disable auto negotiation and alert the module to begin
listening for data. Make sure the
Auto negotiation enabled is the default value.
Module menu also has a Fiber Link → Link Status option which provides
The
information about a 1000 Mbps link. If the carrier wave is present, this option
returns a “link OK” message. If there is a problem with the link, a message screen
appears with diagnostic information that may help you troubleshoot the link.
The “link OK” message is returned if the device can sense the carrier wave on its
receive port. However, if a THGm has a proper physical connection to a device that
cannot auto negotiate the connection, this option will report that the link is OK even
though the devices do not recognize each other. The
use when connecting to devices such as taps where the problem is an auto
negotiation failure.
Fiber Link option from the
No Auto Negotiation item is selected from the menu.
Link Status option is of limited
3-20
Page 61

Configuring the Interface
In Surveyor, you can control the appearance of windows, the primary monitor view,
the appearance of tables and charts, and the colors of decode displays. The
following sections describe how to set up the interface to best meet your needs.
Customizing Views and Windows
The Surveyor graphical user interface is extremely flexible. It takes advantage of the
features of Windows to allow you to customize your interface.
Multiple windows can be opened within both Summary View and Detail View.
These sub-windows can be minimized, maximized, expanded, reduced, and tiled
within the area of the Summary or Detail View. You can open as many windows as
you have resources in Summary View. You can have all available views of a single
resource in Detail View. You can have one view per resource open within Summary
View.
Chapter 4
4 Configuring Surveyor
Docking Windows
Summary View opens when Surveyor is started. The
composed of Summary View area and three docking windows. The docking
windows are:
•Alarm Browser
• Resource Browser
•Message View
You can size the docking windows by moving (click the left mouse and hold) the
borders separating the windows. You can move the borders all the way to the edge
Summary View window, thus hiding the docking windows. You can also
of the
Summary View window is
4-1
Page 62

Surveyor
User’s Guide
completely close a docking window. If you close a docking window, use the options
from the
View menu to get the window back.
You can extract any docking window from the
stand-alone window. If you turn off docking using the right mouse functions, the
window will not dock again when it is moved back over the
allowing you to cascade windows. You can also “float” a docking window within
the main window. In effect, you can create your own customized view of all the
windows available within the
Docking windows are a standard Windows feature. Refer to the Windows
documentation for a complete description of docking windows. It is suggested that
you do not undock windows.
Capture View Display Options
When using Capture View, you can control the display of data for packet decoding.
You can view the time as absolute, as a delta, as elapsed, or any combination of the
three. You can show/hide most fields in the decode display. You can also show/hide
protocol information about packets and set the starting point for elapsed time
Use the top part of the dialog box to select the columns you want to display in
Capture View. Not all columns can display on the screen without having to scroll;
limiting the number of columns can make it easier to see the exact information you
want. Specific display fields include Absolute Time, Delta Time, Elapsed Time,
Frame Size, Status, Network Address, Cumulative Byte Count and Throughput. See
Table 4-1 for a description of these fields.
Summary View window and make it a
Summary View window,
Summary View window.
4-2
Page 63

Configuring Surveyor
Configuring the Interface
Table 4-1. Configurable Capture View Columns
Capture View Column Description
Abs Time The absolute time of arrival for each packet taken from the system
clock when the capture was performed.
format: hh:mm:ss.mmm.uuu.nnn where ss=seconds,
mmm=milliseconds, uuu=microseconds, nnn=nanoseconds
Delta Time The time between each packet (interpacket gap).
format: s.mmm.uuu.nnn where s=seconds, mmm=milliseconds,
uuu=microseconds, nnn=nanoseconds
Elapsed Time The time stamp of each packet measured from a relative starting
point. The starting point may be either the module arm time or the
arrival time of a specific packet. See below for information on setting
the elapsed time starting point.
Size The frame size of the packet in bytes.
Status The Status field indicates if the frame has errors. For good frames, the
Status field is blank.
Display Network Address The destination and source IP address.
4
Cumulative Byte/
Throughput
Use the middle portion of the dialog box to set up the display of the Summary
column. The
give a very limited synopsis of protocol activity or provide complete details about
the protocols used in the packet. Check the
view detail about all the protocols used in the packet. Leaving the
Protocol Summary
you want to display protocol summary details, set the protocols you want to display
from the pull-down menu. For example, if you want to display only the Transport
layer and below, select Transport Layer. If you are not displaying protocol
summary details, the protocol layer you select in the pull-down menu will not affect
the display of the
Select the
symptom information in the
and have expert symptom information will display in reverse video in Capture
View.
The Cumulative Byte Count is a sum of all bytes received to this point
in time in a capture file. The Throughput is calculated by dividing the
cumulative bytes by the elapsed time. The elapsed time is the difference is always measured between the module arm time and the time
stamp of the current packet in the capture file.
Summary column will always display. However, this field can just
Display Detail Protocol Summary box to
Display Detail
box unselected gives a synopsis of all protocols in the packet. If
Summary.
Display Expert Symptoms check box if you wish to include expert
Summary field. Packets that trigger an expert symptom
4-3
Page 64

Surveyor
User’s Guide
Use the bottom portion of the dialog box to set the point from which Surveyor will
measure time when calculating and displaying the elapsed time stamp of each
packet. Set “time-zero” for capture in the
the
Display Options dialog box. The default option is Module Arm Time, which
starts time zero at the time the module is started. Select
and set the frame ID number in the box to start time zero when a particular frame
arrives. Setting this field only effects the display of the
protocol decode.
Histogram Options
Histogram options set the color, zoom factor, and the download size for the
hsitogram.
Setting Histogram Colors
You can change the default colors for the histogram display. To set new colors,
select the
Colors tab from the Configuration Æ Capture View Options Æ Histogram…
menu. Press the graphic element you want to change and select a new color. The
table below shows the graphic elements of the histogram display and the default
colors for each.
Elapsed Time Set Mark Option portion of
Frame ID nnn's Arrival Time
Elapsed Time field in the
Table 4-2. Histogram Color Defaults
4-4
Graphic Element Description Default Color
Line Color Color of the line graph showing frames/time in the histo-
gram.
Back Color Background color for the histogram. Sections that are
not currently part of any other category are shown in this
color.
Current Section
Color
Past Section Color Color of sections that are not active but are available in
Error/Lost Section
Color
Removed Section
Color
Incomplete Section
Color
Color of the currently active section. Decodes for the
active section appear in the Summary area.
the cache. Looking at these sections does not require
another download from the device.
Color of sections that are lost or not available for display. Red
Color of sections that were downloaded during this session, but have been removed from the cache. Review of
these sections requires another download from the
device.
Color of sections that are not a full 10MB of data, other
than the first section. This is typically the last section in a
large capture that does not ean on a 10MB boundary.
Red
Black
Magenta
Green
Yellow
Blue
Page 65

Configuring Surveyor
Configuring the Interface
Table 4-2. Histogram Color Defaults (continued)
Graphic Element Description Default Color
Zoom Cursor Color Color of the zoom cursor. White
4
Zoom Window Color Color of the area in the lower histogram that is currently
being display in the upper histogram.
Setting Histogram Zoom Factor
Set the Zoom Factor changes the number of data points that remain in the upper
zoom window when pressing the zoom button. The range for the Zoom Factor is
between 80 and 99, with a default of 80. Increasing the value for the Zoom Factor
will narrow and widen the number of data points in the upper histogram more
slowly. For the Zoom In function with the Zoom Factor set to 80, 80% of the previous data will main in the view, with 10% of the data on each end eliminated from
the view. When the Zoom Factor set to 98%, only 1% of the data on each end is
eliminated from the view.
Zoom in and out using the Zoom In and Zoom Out buttons or the menu items
from the
Histogram menu.
Setting the Histogram Download Size
This control sets the number of 10MB sections that will be downloaded from the
capture source each time a request is made for new capture data. The download size
can be set between 1 and 50 10MB increments. The default is 6 or 60MB of data.
Set this value high if you need to load and view large sections of data at one time. A
greater download size will increase the time it takes to perform each download.
Surveyor also has a setting for local disk cache size which will also affect the
performance of downloads.
Grey
Setting the Monitoring View for a Module
One monitoring view is available for each module in Summary View. The first tab
in the Summary View for a module displays the view selected.
1. In Summary View, choose
2. Choose
Monitor View Preferences.
3. Click the radio button in the
Module from the Configuration menu.
Monitor View Preferences tab for the view you
want. Only one view is allowed.
4. Click the
OK button.
4-5
Page 66

Surveyor
User’s Guide
Configuring Chart Views
Protocol distribution view and frame size distribution view can be customized using
buttons within the chart. The type of information in some chart views can be
customized using the procedures below.
Charts graph the “top ten” stations or conversations based on a byte count. The
count is the absolute percentage of the number of bytes out for stations, or the
absolute number of bytes passed between stations for conversations. The count
therefore provides a view of the stations or conversations with the most traffic,
which is what users typically want to view. You can, however, create a “top ten”
chart for any field that Surveyor supports. You can also reverse the sort order to
create a “bottom ten” chart for any field that Surveyor supports.
1. In Detail View, make sure the view you want to customize is the currently
active window.
2. Choose
3. The data view appears as a table. Click on the column you want to use to create
4. Choose
Table Views
The type of information in some table views can be customized. You can add or
subtract columns from the table.
1. In Detail View, make sure the view you want to customize is the currently
2. Choose
3. Click the radio button for each column you want to display in the table.
4. Click the
View options are not available for all tables.
Tab le from the tab at the bottom of the view.
a “top ten” list. Note that the information in the table sorts in descending order
for the column you selected. If the column you want is not there, see
“Customizing Table Views” for information on how to insert a column into the
table.
Chart from the tab at the bottom of the view to return to chart view.
active window. The Table view must be displayed.
View Options… from the Monitor Views or Capture Views menu. If the
View Options… selection is gray, no customization can be performed for this
table.
OK button.
4-6
Page 67

Module Settings (Properties)
Module settings configure options for the capture, monitor, and transmit functions
of devices. To configure modules, select
menu. Tabs appear that apply to the currently active device type; a tab will only
appear if this option can be set for the current device type. Hardware devices can
have properties set according to Table 4-3 below:
Table 4-3. Hardware Device Properties
Configuring Surveyor
Module Settings (Properties)
Module Settings... from the Configuration
4
Hardware
Device
THGm
THGs
THGsE
THGp
Portable
Surveyor 10/
100 Ethernet
Analyzer Card
NDIS
#
This option affects the display of tables for local devices only for 10/100 networks.
Set
Buffer
Size
Packet
Slice
Stop-andSave
Capture
Modes:
Expert
Mode
Modes:
NonWKP
NO YES YES YES YES
Modes:
M-QoS
Only
#
MAC
Control
Frame
YES YES
NO YES NO YES NO YES YES
NO YES NO YES NO YES YES
NO YES YES YES NO YES YES
YES YES YES YES YES
YES YES YES YES YES
#
#
YES
YES
#
#
NO
NO
4-7
Page 68

Surveyor
User’s Guide
Module settings are described in the subsections below. Default values for Module
Settings are shown in Table 4-4:
Table 4-4. Default Module Settings
Module Setting Default Values
Buffer Size 512K
Packet Slicing Size, Capture Full packet length
Packet Slicing Size, Monitor Full packet length (for THGm), 128 bytes (for standard NDIS
modules)
Enable Full Buffer Auto Save Not selected
Expert Symptoms All symptoms enabled except TCP checksum errors
Modes: Expert Analysis Mode Selected (Expert plug-in only)
Modes: Non-WKP Mode Not selected
Modes: Multi-QoS Only Not selected (Multi-QoS plug-in only)
Expert Threshold Each threshold has its own default value
MAC Control Frame Selected for THGm, not supported by others
Buffer Size
Portable Surveyor 10/100 Ethernet Analyzer Card and NDIS cards require that a
capture buffer size be set. The buffer size is the amount of system memory that will
be used to save captured data. Buffer sizes can be set between 64KB and 16MB.
THGm modules have a hardware buffer and do not require system memory for
captured data. The default buffer size is 512KB.
Packet Slice (Slicing Size)
All devices support packet slicing. Packet slicing means that a subset of the entire
packet is saved in the capture buffer. You can save the first 32 bytes (Mac layer), the
first 64 bytes (Network layer), the first 112 or 128 bytes (Application layer), or the
full length of the packet.
Packet slicing can be set separately for monitor and capture except for THGm. For
monitor, packet slicing can improve performance when monitoring the entire packet
contents is not required. For capture, packet slicing can save space in the capture
buffer for more packets when analysis of the entire contents of each packet is not
required.
4-8
Page 69

For THGm modules, the default is no packet slicing (full packet length). For
THGm, the slicing size must be 64 bytes or greater and packet slicing of 128 bytes
is not supported for 1Gbps Ethernet.
For Portable Surveyor 10/100 Ethernet Analyzer Cards, and NDIS cards, the default
setting is no packet slicing for capture, 128-byte packet slice for monitor. For NDIS
modules, you cannot have both monitor and capture set to full packet size.
Stop-and-Save Capture Buffer
Only local devices support a stop-and-save-to-disk function for the capture buffer.
Check the
Enable Full Buffer Auto Save box to enable the save-to-disk feature.
When using the save-to-disk feature, capture is stopped when the buffer is full and
the contents are written to disk. Capture is restarted as soon as the data is written to
the file. When the capture buffer fills again, the new contents are appended to the
file. If you start a new capture, the file is overwritten. If capture is stopped before
the capture buffer contents are full, the buffer contents are not automatically written
to disk; you must manually save the capture buffer to disk.
Modes
Select the
Modes tab from the Configuration → Module → Settings... to set the
modes for a module.
Configuring Surveyor
Module Settings (Properties)
4
Expert Analysis Mode
Expert Views and Alarms can be disabled. When disabled, no Expert Views or
Alarms will display in Surveyor software.
Uncheck the
Enable Expert Analysis Mode box to disable Expert Views and Alarms.
The default is to enable Expert Analysis. If you do not have the Expert plug-in, you
cannot enable Expert Analysis Mode.
Non-Well-Known-Ports Mode
Non-well-known port (non-WKP) numbers in tables can be enabled or disabled for
each module when monitoring with local devices. When disabled, most port numbers above 1023 display as TCP Other or UDP Other with no port number provided.
It is recommended that you leave this feature disabled unless you are looking for
specific port numbers greater than 1023, since non-WKP numbers can quickly fill
Application Layer Tables. Surveyor always displays the port number if the number
is less than or equal to 1023. Surveyor also displays some ports above 1023 since
applications associated with them are widely accepted.
Check the
Monitor TCP/UDP non-well-known-ports individually box to enable the
display of all non-WKP numbers. The default is to not display these port numbers.
With the option enabled all TCP packets with non-WKP numbers (TCP or UDP)
4-9
Page 70

Surveyor
User’s Guide
will be listed in the Application Tables as in the following example: UDP nonWKP:4620
This feature only affects the tables or charts that display TCP/UDP port numbers.
The display is affected for monitor views only of local modules. If you want
to display port numbers and name the ports in the display for remote devices, see
“Assigning Names to Protocols (Monitor)” on page 21 of this chapter. Also refer to
this section for more information on non-WKP numbers.
Monitor M-QoS Only Mode
By restricting monitor mode to multimedia tables only, you can improve the rate at
which Surveyor is able to view multimedia protocols without dropping packets. The
monitor Multi-QoS only mode is disabled by default; all view tables are built in
monitor mode.
Check the
Monitor M-QoS Only box to limit monitor mode to building Multi-QoS
tables only. All monitor table buttons are grayed out with the exception of MAC statistics.
This mode can be applied to any local analyzer device. For remote devices, Monitor
M-QoS Only mode can only be set for THGm/THGs/THGp devices.
MAC Control Frame
For Gigabit Ethernet a MAC Control Frame is sent to ensure that sending devices do
not overflow receive buffers. For THGm devices, you can select to capture these
frames or ignore them. The default is to capture MAC Control Frames. This setting
applies only to THGm devices.
System Settings
System settings establish general timing, file, and port information for the Surveyor
system.
Configuring Ports to Scan
Surveyor must search the ports on the local system to find an analyzer device
installed in the local system. Sometimes this creates a problem with certain devices
already on the system. Use this function to restrict the ports which are scanned. The
dialog box for configuring ports to scan comes up on Surveyor start-up. The ports to
scan are typically configured at start-up, but can be changed from Surveyor at any
time.
4-10
You can use Surveyor to set the ports on the PC to scan at any time. To set up or
change port scanning, do the following
1. Choose
Ports
System Settings… from the Configuration menu. Select the Scanning
tab.
Page 71

Configuring Surveyor
System Settings
2. A dialog box appears showing the ports within the local system. Check the box
of only those ports you want Surveyor to scan for an analyzer card.
4
3. Click the
OK button.
Configuring Remote Communications
The remote server protocol (RSP) is used to control the interface for connecting
with remote systems. You configure the options that effect connection time outs,
encryption of control packets, and auto-discovery of resources.
To configure remote communications, select
Configuration menu. Select the Remote Communications tab.
Table 4-5. Remote Communications Tab Functions and Default Settings
Tab Selection Description
Encrypt RSP Packets check box Select encryption if there is a need for security in the network
when transferring packets between the remote resource and
the local system.
The default setting is Not Selected.
No Autodiscovery check box Select this box to prevent auto-discovery of remote resources.
If selected, you will only be able to access remote resources by
manual discovery of resources using the Connect option from
the Host menu. This box can be selected when working with
only local resources to eliminate viewing all resources in the
Resource Browser. The auto-discovery of resources may take
some time, especially in a large network.
The default setting is Not Selected
RSP Time Out value Specifies, in seconds, how long the protocol waits before drop-
ping a connection when the remote resource is not responding.
The value must be between 1 and 30 seconds.
The default setting is 10 seconds.
System Settings… from the
4-11
Page 72

Surveyor
User’s Guide
Protocol Color Coding
Surveyor provides a real-time protocol decode called Packet Summary View and
protocol decodes in Capture View. To use these displays more effectively, you may
want to set the colors used for packet display. For example, you might want to display all transport layer packets in red and all others in black if you are looking only
for protocol decode information in the transport layer.
To set up or change color coding for protocol decode, do the following:
1. Choose
Color Coding tab.
System Settings… from the Configuration menu. Select the Protocol
2. Click on a protocol layer.
3. Using the color buttons, set the foreground and background color display for
the selected protocol.
4. Repeat as required for other protocol layers.
5. Make sure that the
6. Click the
Use the
Set Default button to reset the default to the colors currently displayed.
OK button.
Default All button to return all color settings to their default values. Use the
Setting Update Timers
Timers control how often counters, tables, and displays are updated. There are two
types of timers, display timers and polling timers. Remote polling timers control
how often data is updated from remote systems. Display timers control how often
displays of data are updated in the Surveyor software. All timer values are in
seconds.
For local devices, the MAC Layer counters are updated every second, and other
charts and tables for local devices are updated every 10 seconds.
Use Color Coding box is checked.
4-12
To configure the timers, select
Select the
Timers tab. The timers are listed and described in Table 4-6, Table 4-7,
and Table 4-8.
System Settings… from the Configuration menu.
Page 73

Configuring Surveyor
System Settings
4
:
Polling Timers Description
MAC Layer Counters Sets the interval for polling devices for MAC layer counters.
Protocol Distribution Sets the interval for polling devices for the protocol distribution information.
Host Table Sets the interval for polling devices for MAC layer host table information.
Matrix Views Sets the interval for polling devices for information on MAC, network, and
Expert Data Sets the interval for polling devices for expert data.
Remote Name Table Sets the polling interval for refreshing the local copy of the name table for
Display Timers Description
Strip Chart Display
Timer, Local
Strip Chart Display
Timer, Remote
Table 4-6. Remote Polling Timers
application layer conversations.
a remote resource.
Table 4-7. Strip Chart Display Timers
Sets the time between refreshing counters in strip charts for resources in
the local PC. This display timer is available for strip charts only.
Sets the time between refreshing counters in strip charts for resources in
remote hosts. This display timer is available for strip charts only.
The values for polling timers must be between 1 and 214783647 seconds. The
values for the display timers must be between 1 and 214783647 seconds. The
strip chart display timers must be in multiples of the MAC Layer Counter timer.
The default settings, in seconds, are shown in Table 4-8:
Table 4-8. Default Display Timer Settings
Display Timer Default Value
MAC Layer Counters 3
Protocol Distribution 5
Host Table Views 7
Matrix Views 10
Expert Data View 15
Remote Name Table 300
Strip Chart, Local 1
Strip Chart, Remote 3
4-13
Page 74

Surveyor
User’s Guide
Disk Options
Surveyor supports saving and examining very large capture files. Two disk options
are available to support large captures,
Location. Choose System Settings… from the Configuration menu and select the
Disk Options tab to set either option.
Cache File Location
To support viewing very large captures (greater than 10MB), you can specify the
size and location of a disk cache in the
large captures, the entire capture typically resides on a remote analyzer device disk,
such as in a THGsE. When using Surveyor to view capture contents, the entire
capture is not downloaded at once to your local disk; only the parts you access are
transferred. However, Surveyor retains the information you have downloaded in a
local disk cache, providing faster retrieval of recently downloaded information. You
specify the location and size of the cache based on the capacity and configuration of
your local system. For example, if your disk drive D: has a capacity of 100GB and
your drive C: has a 4GB capacity loaded with operating systems and applications,
you could set up a 50GB cache directory on disk drive D:.
Cache File Location and Disk Capture
Cache File Location area. When decoding
Use the
Browse button to specify a location for the cache directory and use the slider
to specify its maximum size. Surveyor will not allow you to specify a size greater
than the available free space on your disk drive. The minimum cache size is 40MB.
The cache directory is cleared of files containing information related to a capture
when you close the capture or exit the Surveyor application.
Disk Capture Location
To support local disk captures, you can specify the size limit and location in the
Capture Location area. Note that this governs the size of large captures created on
your local disk but does not affect the size of captures stored on remote analyzer
devices. This setting affects only large captures made from THGm cards within
your local system. Specify the location of the capture directory based on the
capacity and configuration of your local system.
Use the Browse button to specify a location for the capture directory and use the
slider to specify its maximum size. Surveyor will not allow you to specify a size
greater than the available free space on your disk drive and the minimum size is
40MB. Surveyor uses this directory for all captures made with local cards when
using
Cap+Disk mode. This is not, however, "permanent" storage of the capture
information. Capture information you want to save must be stored in a file using the
Save option. The capture directory is cleared of files containing information related
to this capture when you close Surveyor.
Disk
4-14
Page 75

Configuring Counter Logging
Counter log files contain snapshots of Surveyor counter information. All MAC
layer statistics can be recorded in the log file.
Configuring Surveyor
Configuring Alarms
4
To configure counter logging, select
Log File Settings… from the Configuration
menu.
To enable counter logging, check the
capturing counter information in the
(line entries) in the log file in the
setting
Log File Maximum Rows to 4,000 and Time Interval to 5 will record the
Enable Logging field. Set the time interval for
Time Interval field. Set the number of rows
Log File Maximum Rows field. For example,
counter information 4,000 times, once every 5 seconds.
Keep the
Keep History Log box selected to create history files of counter
information. The history file is written when all lines in the log file are full. When a
history file is created, the module log file is erased and new counter information is
recorded starting with the first line of the file. History files are named by date and
time. The format for the name of history files is:
mmddhhmm.ss
mm(month) dd(day) hh(hour) mm(minute) ss(second)
The minimum time between creation of unique history files is one second. If you
disable the creation of history files and the log file for the module is full, a new log
entry causes the module log file to be erased. No history of counters is saved.
The default settings are shown in Table 4-9 below:
Table 4-9. History Log File Settings and Default Values
Log Setting Default Value
Enable Logging Not selected
Time Interval 5 seconds
Log File Maximum Rows 4,000
Keep History Log Selected
Configuring Alarms
Alarms can be configured to generate events such as e-mail messages, pages, or
logging messages to a log file. E-mail recipients, pager recipients, and log file
names are global parameters that you set. All alarms are automatically sent to one
set of e-mail addresses and one log file.
The alarm E-mail feature works only with Microsoft Mail Exchange.
4-15
Page 76

Surveyor
User’s Guide
Using E-mail with Surveyor is turned off by default. If you want to use this feature,
you must reset a parameter in the Surveyor.ini file. Set Enable MAPI=1 to
enable the e-mail alarms feature through Microsoft Mail Exchange.
To configure alarm actions, select
select either
.
Alarm Action Setting Description
E-mail Settings The set of e-mail addresses that will receive mail if an alarm triggers
Pager Settings The pager number that will receive a page if an alarm triggers an
Log File Settings The name of the log file that will have an entry if an alarm triggers
E-Mail Settings, Pager Settings, or Log File Settings from the submenu.
Table 4-10. Alarm Actions
an event with the alarm action set to e-mail. When you click on the
Add Recipients button in the menu you can set up e-mail
addresses using Microsoft Mail’s address book.
event with the alarm action set to pager. The other settings for the
pager depend on the type of pager. For pager settings, you must set
the delay to at least 3 seconds.
an event with the alarm action set to log.
Alarms from the Configuration menu and then
Configuring a Multi-Port Tap or Switch
A multi-port tap or switch can be attached to the local system or be available as a
remote resource on the network. Typically a tap or switch will be used in the wiring
closet with a remote analyzer device and accessed as a remote resource. However,
taps and switches can be attached to the local system and accessed through a COM
port on the PC. See “Setting the COM Port for Taps and Switches” for information
on configuring these devices to talk to a local PC.
4-16
Taps or switches are devices that work in conjunction with a Finisar analyzer to
monitor multiple network segments. When connected properly, its icon will be
visible in the resource browser. The port of the tap or switch currently being
monitored will show under the resource. If you cannot see the tap or switch icon,
refer to the analyzer or tap hardware documentation for more information on
connecting these devices to the network.
Although the taps and switches show as a resource to the Surveyor software, they do
not directly perform monitoring and other analysis functions. They act as switching
devices for analyzers, so one device can be used to view many different LAN
segments, one-at-a-time.
Page 77

Configuring Surveyor
Configuring a Multi-Port Tap or Switch
The Surveyor software can be used to control which LAN segment is selected by
the tap or switch. To set the LAN segment:
1. In the resource browser, click on the local or remote resource connected to the
switch. The current port being monitored will display under the tap or switch
resource. The example below shows a switch with the LAN Segment
connected to port 5 selected.
2. Double-click on the tap or switch icon in the resource browser.
4
3. A list box appears showing the port-pairs on the tap or switch. You must know
which LAN segments are connected to the port-pairs on the tap or switch. Use
the radio buttons to select the LAN segment you wish to monitor. Only one
LAN segment can be selected.
4-17
Page 78

Surveyor
User’s Guide
4. Use the Bypass check boxes to set any network segments that you want to
restrict from being used with the analyzer. Any segment with the
Bypass box
checked cannot be set as the LAN segment.
5. Click the
OK button.
Information about the exact type of switch or tap is shown at the bottom of the
dialog box.
Setting the Local COM Port for Taps and Switches
The tap or switch can be controlled from a PC running Surveyor software. The tap
or switch can be directly connected to a COM port on the PC and controlled as a
local resource from Surveyor. In this configuration, the COM port used to connect
the tap or switch to the PC must be configured in Surveyor software.
To configure the COM port for a local connection to a tap or switch, do the
following:
1. Select
2. Select the
System Settings… from the Configuration menu.
Local COM Port for Tap Device tab to set the port for a Finisar multi-
port tap or switch. Select the
Local COM Port for Switch Device tab to set the
port for a switch.
3. Set the COM port value to the COM port (COM1 through COM4) where the tap
or switch is connected to the PC. Only one port can be selected.
The tap or switch is connected to the PC using a standard 9-pin serial cable. Only
one tap or switch device can be connected to the PC.
Connecting a Tap with THGs or THGsE
Surveyor has an option that allows the THGs/THGsE device to scan for attached
taps without resetting the device. Select
force the analyzer to scan for any newly attached tap devices. This option is only
available from the host menu when the host is a THGs or THGsE.
Settings for Analyzer Devices
You can use Surveyor to control analyzer hardware devices such as THGs or
THGsE. You must have “super-user” privileges to reset or update these devices.
Resetting an Analyzer Device
A remote analyzer device can be reset using Surveyor software. To reset a device do
the following:
1. Login to Surveyor with “super-user” privileges.
4-18
Re-Scan for Tap from the Host menu to
Page 79

Configuring Surveyor
Settings for Analyzer Devices
2. Click on the icon for the remote analyzer device in the Resource Browser.
4
3. Choose
4. Click the
5. Check the
Properties from the Host menu.
Reset Host/Image Upgrade button.
Warm Boot radio button under Reset Options. Leave all other fields
blank or unmarked.
6. Click the
OK button.
When you reset a remote analyzer device, you will lose the connection. Use the
Connect option from the Remote menu to reconnect.
Updating an Analyzer Device
You can update the software or change address information for a Finisar analyzer
device from Surveyor.
Before you can reset the device with a new image, you must place the new image on
a server that runs TFTP protocol.
Download the new software from the support web site,
http://www.finisar.com. Go to the software updates section of the Web
site to find the new analyzer image. Place the software on the server that runs the
TFTP protocol.
Before you can update the analyzer address information automatically, you must
have a server that contains the new address information and runs the BOOTP protocol.
Use the following procedure to update the analyzer image software.
1. Login to the remote analyzer device with “super-user” privileges.
2. Click on the icon for the analyzer device in the Resource Browser.
3. Choose
Properties from the Host menu.
4. Set the new IP Address, IP Gateway Address, and Subnet Mask for the
analyzer. If no address update is needed, or you are updating the address from
a BOOTP server, skip this step.
5. Click the
6. Check the
Reset Host/Image Upgrade button.
Enable BOOTP box if you are updating addresses from a BOOTP
server.
7. Check the
Image Upgrade (TFTP) box if you are updating addresses from a
TFTP server.
4-19
Page 80

Surveyor
User’s Guide
8. Enter the IP address of a server that runs BOOTP and/or TFTP protocols in the
IP Boot Server field.
9. If you are updating the image, set the path name to the software image file in
Boot Image Filename field.
the
10. Check the
11. Click the
You must use the
from the network. The
Warm Boot radio button under Reset Options.
OK button.
Warm Boot option to load the new image
Cold Boot option will not update the
image.
When you reset the device, you will lose the connection. Use the
from the
Remote menu to reconnect.
When a device is restarted, the new software image is written to non-volatile memory and becomes the new executable image.
Though not a part of the update procedure, you can use the
the device to run its self-tests. These tests will verify that the unit is operating properly.
Advanced Configuration
surveyor.ini File
Surveyor uses configuration settings from a .ini file called
surveyor.ini. If you want to run the product with different configurations, you
can save different sets of configuration information in different .ini files. Sur-
veyor always looks for the file named surveyor.ini in the directory where Surveyor is installed and will use that file for its configuration. If no surveyor.ini
file is found in the directory, Surveyor will build another surveyor.ini file
based on the factory default configuration settings.
!
Caution
Connect option
Cold Boot option to force
Different sets of configuration information can be especially useful for display timers and update timers. The first eight parameters of the surveyor.ini file are the
configuration values for the various display timers.
For information on other surveyor.ini settings, contact Customer Support. It is
not recommended that you alter the surveyor.ini file directly.
Customizing Expert Diagnostic Information
The EXPERTMSG.INI file contains Surveyor’s diagnostic information. Surveyor
always looks for the file named EXPERTMSG.INI in the Surveyor installation
4-20
Page 81

directory and will use that file for its diagnostic information. If no EXPERTMSG.INI file is found in the directory, Surveyor will not provide diagnostic infor-
mation.
You can change the diagnostic information if you want. Changing the diagnostic
information may be a useful way to customize Surveyor for your environment. For
example, if you have a known problem area to check when certain conditions occur
you can include this information directly in the diagnostic information.
Assigning Names to Protocols (Monitor)
Surveyor assigns names to protocols that have been detected, providing users with
an easy way to view what protocols have been discovered on the network. In most
cases, protocol names are well known; they are defined by the protocol’s creator, or
defined by a standards organization. However, you may want explicit information
about a protocol that does not have a well known name or is counted in Surveyor
monitor screens as a “TCP OTHER” or “UDP OTHER” protocol.
Surveyor includes a MONITOR.INI file to assign names to protocols. Entries in
the MONITOR.INI file allow you to:
• Rename the protocols that are currently being detected. For protocols that use
TCP or UDP as their transport protocol, the protocol can be assigned a name to
override it’s default name.
Configuring Surveyor
Advanced Configuration
4
• Extend the list of protocols that are monitored by Surveyor. You can extend the
monitoring of protocols that use TCP or UDP as their transport protocol.
See the section on How Surveyor Assigns Protocol Names to learn how Surveyor
names protocols by default. Understanding how Surveyor assigns names to protocols by default is important for understanding how protocol names can be altered
and how protocols can be added using MONITOR.INI.
The assigning of protocol names does not effect protocol decodes. See Assigning
TCP or UDP Ports to Protocol Parsers for information on assigning protocol parsers
to specific ports.
The MONITOR.INI file is located in your Surveyor installation directory. Examples of usage are included in the file.
Settings in the MONITOR.INI file will override any other configuration settings
you have made for the display of protocols.
MONITOR.INI Format
MONITOR.INI contains two sections, TCP and UPD. Each section may have zero
or more entries beginning with the keyword “mapping”. Each “mapping” entry is
followed by an equal sign and three variables:
mapping= <port num>,<short name>,<long name>
4-21
Page 82

Surveyor
User’s Guide
<port num> is a two-byte value that appears in a port fields of a
TCP or UPD packet header. It identifies the protocol,
by port number, to be included as a discrete protocol
in Surveyor’s monitor views.
<short name> is an alpha numeric string that is be between 1 and 12
characters This string is used as the name for the
protocol in Surveyor’s monitor tables.
<long name> is an alpha numeric string that should be between 1
and 50 characters. This string is used as the name of
the protocol where Surveyor displays a long name.
The structure of the MONITOR.INI file is:
[TCP]
mapping=<port num>,<short name>,<long name>
.. .
.. .
mapping=<port num>,<short name>,<long name>
[UDP]
mapping=<port num>,<short name>,<long name>
.. .
.. .
mapping=<port num>,<short name>,<long name>
MONITOR.INI Examples
Example 1
Assume that you wish to rename TCP port 80 from HTTP to WWW for World
Wide Web. The following entry would be made to the MONITOR.INI file in the
TCP section:
[TCP]
mapping=80,WWW,World Wide Web
4-22
Page 83

Configuring Surveyor
Advanced Configuration
Example 2
Assume that a company is using a proprietary protocol named “Company X Protocol” that uses UPD port 921. By default this protocol would appear with the generic
name “UDP WKP 921” in the monitor tables. Making the following entry to the
MONITOR.INI file UDP section would give the protocol a name with more meaning:
[UDP]
mapping=921,CXP,Company X Protocol
Example 3
X Windows could use non-WKP TCP ports in the range 6000 to 6063. However, by
default, Surveyor reports X Windows network traffic with a single entry in the Protocol Distribution table.
For example, if 100 X Windows packets detected on port 6000 and 200 were
detected on port 6029, the Protocol Distribution table would report that 300 hundred
XWIN packets were detected. If the network manager wanted the Protocol Distribution table to report the number of packet seen on each of the 64 X Window ports,
the MONITOR.INI would need the following 64 entries:
[TCP]
mapping=6000,XWIN6000,X Windows on port 6000
mapping=6001,XWIN6001,X Windows on port 6001
.. .
.. .
mapping=6063, XWIN6063,X Windows on port 6063
4
Example 4
Assume that a company installed an audio/video application on its network named
Video Audio Network Communicator. Assume that the application uses TCP port
2900. By default, packets on this port are attributed to the “TCP OTHERS” entry in
the Protocol Distribution table along with other TCP non-WKP packets. To count
and display the TCP port 2900 reported individually, the following entry needs to
be made to the MONITOR.INI file:
[TCP]
mapping=2900,VIDEO,Video Audio Network Communicator
4-23
Page 84

Surveyor
User’s Guide
How Surveyor Assigns Protocol Names
Surveyor explicitly monitors a predefined set of protocols/applications that use TCP
or UDP as their transport layer. However, some of the TCP or UCP ports monitored
are not given a well-known name. Also, some TCP and UDP ports are not explicitly
monitored, and information about these remaining protocols are collected as though
they were a single entity, one for TCP and one for UDP.
Surveyor monitors two port ranges, which are called Well Known Ports (WKP) and
non-Well Known Ports (non-WKP). In summary, there are four different ways TCP/
UDP ports are assigned names by Surveyor. They are:
• WKP that have an assigned, default name (i.e. HTTP, DNS, FTP, …)
• WKP that use a generic name (i.e. TCP WKP 29, UDP PORT 64, …)
• Non-WKP that have been assigned a specific default name (i.e. NFS, LOTUS
NOTES, RADIUS, …)
• Non-WKP that have not been assigned a name (TCP OTHER or UDP OTHER)
By changing the MONITOR.INI file, you can change names of generic names of
WKPs and assign names to non-WKPs that are not assigned names by default.
Monitoring Well-Known Ports
Surveyor monitors all protocols that fall in the WKP (Well Known Port) range,
ports with a value between 0 and 1023. If Surveyor detects a TCP or UDP with a
port in the WKP range, information will be maintained on that port (total bytes, total
packet, conversation, etc.).
4-24
Some of the ports have been assigned a name that is typically associated with the
port value. For example, TCP port 80 is assigned the name HTTP. This name is used
to represent that port when information about the port is displayed in the monitor
tables of Surveyor.
Other WKPs are not assigned a default name. If these ports are detected, their name
takes the generic form: “TCP WKP <port num>” or “UDP WKP: <port num>”
where <port num> is the WKP value. For example, the TCP port 29 is not assigned
a default name so if this port is detected the name used to represent the port would
be: “TCP WKP 29”.
Page 85

Monitoring Non Well-Known Ports
Surveyor also collects information about a subset of ports that fall outside of the
WKP range, port numbers greater than 1023. These ports are called non-WKP.
Some of these ports are monitored by Surveyor since applications associated with
them are widely accepted. The non-WKP ports that Surveyor monitors and their
associated port values are listed in Table 4-11 and Table 4-12.
Table 4-11. Default Names for Non-WKP TCP Ports
Name TCP port values
LOTUS NOTES 1352
TNS (Sybase) 1521
RSP 1704
TDS (Oracle) 2048
NFS 2049
CC:MAIL 3264
XWIN 6000-6063
Configuring Surveyor
Advanced Configuration
4
Table 4-12. Default Names for Non-WKP UDP Ports
Name UDP Port Value
RADIUS 1645
RSP 1704
RADIUS 1812
HSRP 1985
NFS 2049
RTP 5004
RTCP 5005
Surveyor treats all other non-WKP as a single entity given a single generic name.
The name for TCP non-WKP ports is “TCP OTHER”. The name for UDP nonWKP ports is “UDP OTHER”. For example, if 900 occurrences of the TCP port
11964 was detected and 200 occurrences of the TCP port 10564, there would be a
single name to identify these 1100 occurrences of the TCP non-WKPs called “TCP
OTHER”.
4-25
Page 86

Surveyor
User’s Guide
Assigning TCP or UDP Ports to Protocol Parsers
Use the ANALYSIS.INI file to assign any built-in Surveyor parser to a TCP or
UDP port. This is useful when a network is running a protocol/application over a
TCP or UDP port that is not using the default port. The assignment of a proper
parser allows Surveyor to properly decode and analyze the packets associated with
the TCP or UDP port.
The assigning of parsers does not effect how the information is displayed in monitor
views. See “Assigning Protocol Names” for information on assigning names for
monitor views.
The ANALYSIS.INI file is located in your Surveyor installation directory. Examples of usage are included in the file.
ANALYSIS.INI Format
The ANALYSIS.INI file has two sections, TCP and UDP. A section contains one
or more entries with the following format:
mapping=<port num>,<ip addr>,<parser name>,<name>
<port num> is any valid 2 byte value that represents a TCP or
UDP port value. It identifies the protocol, by port
number, to be parsed in Surveyor’s decode views.
4-26
<ip addr> is a valid IP address in dotted decimal notation. This
field can have an asterisk (*) to represent all IP
addresses.
<parser name> is the name of a valid Surveyor built-in parser. See
Parser Names for a list of parsers.
<name> is a name that will used to identify the mapping.
Example 1
Assume that the network administrator configured Oracle’s TNS protocol to use
TCP port 1029. This port value is different from the default value for TNS, which is
1521. The entry in the ANALYSIS.INI would be:
[TCP]
mapping=1029,*,TNS,Oracle TNS
“Oracle TNS” is the string that will be used in Surveyor’s displays to identify this
decode.
Example 2
Assume that the network administrator configured Sybase’s TDS protocol to use
TCP port 11964. This value is different from the value for TDS which is 2048. Fur-
Page 87

thermore suppose the network administrator only wants to decode TCP port 11964
when associated with IP address 192.168.1.98. The entry in the ANALYSIS.INI
file would be:
[TCP]
mapping=11964,192.168.1.98,TDS,Sybase TDS
Example 3
Assume that two real-time applications have been installed on a network that both
use RTP (Real-Time Transport Protocol). Assume that one of the applications uses
UDP port 10564 and the other uses 11964. Both of the UDP ports differ from the
default port of 5004. The entries in the ANALYSIS.INI file would be:
[UDP]
mapping=10564,*,RTP,RTP APPLICATION 1
mapping=11964,*,RTP,RTP APPLICATION 2
Parser Names
The tables in Appendix D contain the Parser Names that are built into Surveyor.
Each parser is responsible for decoding a specific protocol. Parser Names are as
similar as possible to protocol names. Parser Names must be entered exactly as
shown in the tables to correctly reference the built-in parser.
Configuring Surveyor
Advanced Configuration
4
4-27
Page 88

Surveyor
User’s Guide
4-28
Page 89

Surveyor can gather statistical information and view network data from a variety of
hardware sources. The types of information you receive from a resource depends on
the hardware.
Surveyor’s auto-discovery feature automatically scans the network for available
resources, or you can enter the IP address of any host you can reach through a TCP/
IP connection. Surveyor remembers the name of the most recent connection made
so you can quickly reconnect to the host.
Resource Browser
The Resource Browser is a single window through which you can access all local
and remote resources available in the network. The Resource Browser window
works much the same as Microsoft Windows Explorer, allowing you to see hosts
and their associated resources in a hierarchical relationship. “Branches” can be
expanded or collapsed via point and click, so you can quickly customize your view
of available resources.
Chapter 5
5 Resources and Modes
Remote systems containing resources are listed by IP address unless there is a
Surveyor name table on the system. If an entry exists in the name table for the IP
address of a resource, the symbolic name in the name table is used to represent the
resource. Resources within remote systems are listed by module type and module
number. The module number is assigned by the software from the base address of
the module, which is set by jumpers during hardware installation. For NDIS
modules, the modules are numbered by the order in which they are discovered
within the local or remote host. It is possible to have two different modules with the
same name if they are within different hosts.
The Resource Browser opens as a docking window when Surveyor is started and
can be moved to its own window outside the main window.
5-1
Page 90

Surveyor
User’s Guide
Double-click on a resource to display a default view of the resource in Summary
View. If a remote resource is protected, you are asked for a user name and
password. Drag and drop resources onto alarms in the Alarm Browser to activate an
alarm for a resource.
Local resources are those within the local PC running Surveyor.
Remote Resources
Remote resources are all resources that can be reached through a TCP/IP
connection. When running Surveyor from the PC, you have complete access and
privileges to any resource in the PC. You can access remote resources and establish
accounts for your local resources if you are using Remote plug-in software available
from Finisar. Both the local and the remote resource require Remote plug-in
software for remote access to function.
Access to remote resources are controlled from the PC that contains the resource.
For example, if your PC contains two THGm modules, accounts, privileges, and
passwords for the modules are established at your PC. Remote users must have
access to a valid account to use the THGm modules in your PC.
A remote resource can be located in any host which can be accessed via a TCP/IP
connection. You’ll need to know the IP address of the remote host to log in to the
remote resource. If the remote resource can be auto-discovered by Surveyor, the IP
address or the name associated with the IP address of the host will display in the
Resource Browser. Typically, resources on the same LAN segment can be autodiscovered.
5-2
See Figure 5-1 for a diagram of how local and remote resources are accessed by
Surveyor.
Page 91

Resources and Modes
Remote Resources
Local
LAN
Segment
Local Host
Surveyor
Software
Surveyor
Software
Storage
Device
5
Data
Stream
Local Monitor/
Transmit/Capture
Finisar Analyzer Card
NDIS,
CMM or CMM2
or NDIS Adapter
Board
Remote Host
Surveyor
Software
Surveyor
Software
Network
Remote Monitor/
Transmit/Capture
TCP/IP
TCP/IP Connection
Connection (LAN,
(LAN, modem, etc.)
modem, etc.)
TCP/IP Connection
(LAN, modem, etc.)
NDIS network adapter,
Finisar Analyzer Card
CMM or CMM2
or NDIS Adapter
Board
Remote
LAN
Segment
Data
Stream
Figure 5-1. Remote Host Connections
5-3
Page 92

Surveyor
User’s Guide
Naming Remote IP Resources (Aliases)
The Resource Browser initially displays all nodes on a subnet using the IP Address.
Users can assign an alias (user defined name) to a node for easy identification. For
example, you can assign a name like “Chicago Node One” to the node. In addition,
you can add a descriptive comment for any node.
There are two methods for bringing up the
Host Properties dialog box to create an
alias:
• Single-click with the mouse on the node. Select
This brings up the complete
Host Properties dialog box.
Properties from the Host menu.
• Right-click with the mouse on a top-level node (IP Address/Alias Name) and
select the
Properties dialog box for setting the alias.
Within the
comment. An example of the
Properties... option from the popup menu. This brings up the Host
Host Properties dialog box, set the alias name and any optional
Host Properties dialog box is shown below. Additional
fields may be available in this dialog box depending on the type of node.
5-4
Figure 5-2. Host Properties Dialog Box for Establishing an Alias
All characters are allowed in alias names except $, #, <, and @.
When an alias is established, Surveyor window title bars change to reflect the new
alias name instead of the IP Address. For example, “//192.1.68.2/THGmModule(1)”
might display as “//Chicago Node One/THGmModule(1)”.
Page 93

Hovering the mouse over a top-level node which has an alias displays the name
with the IP Address in parenthesis along with the optional comment. For example,
“Chicago Node One (192.1.68.2). This is Mount Prospect node”.
Resource Protection
You are in control of local resources within a PC. Use the functions on the
menu to add and delete users for a resource, change passwords and protections, or
view the users currently logged in. There is a guest account for users with no
account. The guest user can be given all privileges to effectively disable resource
protection.
Note that there is no password protection for starting Surveyor on the local system.
If you can start Surveyor from a system, you automatically have complete access to
all local resources (called super-user privileges).
To access a remote resource, you must have an account and password set up on the
remote system containing the resource or use the guest account.
Privileges for remote users can be set to those described in Table 5-1 below:
Table 5-1. Remote User Privileges
Privilege Description
Resources and Modes
Remote Resources
Host
5
Monitor Only Allows a remote user to use the local device to monitor network activ-
ity only. You can access real-time monitor views on an armed (started)
module, but cannot start/stop a module or define/load a filter.
Capture/Monitor Allows a remote user to use the local device to monitor activity or cap-
ture network data. You can perform all Monitor Only functions, capture
data, and perform full seven-layer decode on the packets. You can
start/stop a module, define/load a filter, and edit the contents of packets.
Full Allows a remote user to use the local device to monitor activity, cap-
ture network data, or transmit network data. You can perform all Capture/Monitor functions plus all traffic generation capabilities available
through Surveyor.
Super User Allows a remote user the ability to transmit, capture, or monitor, plus
set up, delete, and change accounts for the local PC. You have Full
access plus the ability to configure a deployed THGs, change the
access table, and unlock any locked module. Be careful when granting
super-user privileges to remote users. This gives remote users complete control of your local resource.
5-5
Page 94

Surveyor
User’s Guide
Modes
Modes are applied to resources. Each resource can be in a different mode. The
modes available with Surveyor depend on the underlying hardware resource as
shown in Table 5-2 below:
Table 5-2. Surveyor Resource Modes
Mode Description Resource Type
Monitor Provides real-time views and decodes
of packets received by a device.
Capture Allows packets received by a device to
be stored in a buffer for analysis.
Capture + Monitor Provides both real-time monitoring
views and the ability to store packets for
later analysis.
Cap + Disk Allows packets received by a device to
be stored in a buffer for analysis and on
hard disk.
Transmit Allows the transmission of packets from
a device. You must have the Packet
Blaster plug-in from Finisar to use
Transmit mode.
Capture + Transmit Allows simultaneous capture and trans-
mit from the same module.
Multi-QoS Only Monitor-only mode that provides only
the Multi-QoS real-time views. The
Multi-QoS only mode is set using the
Settings option from the Module
menu.
Hardware Devices
All
All
Viewed/captured packets
for THGm are identical.
All, used primarily for
THGsE devices.
All
(Not recommended for
NDIS or Portable Analyzer
Cards)
All
All
5-6
The monitor and capture functions look at the same bit stream being received by a
device. The difference between monitor and capture modes is how the bit stream is
stored, viewed, and displayed by Surveyor. Because each device has different
capabilities for storing and viewing the bit stream, you must understand the
capabilities of the device you are using to completely understand what is possible in
each mode.
The capabilities of each hardware device supported by Surveyor are described in
Table 5-3. See Appendix A for more information on the implementation of
Surveyor and a summary of all differences between hardware devices.
Page 95

Resources and Modes
Hardware Devices
5
.
Device Hardware Device Capabilities
THGm (Ten/Hundred/Thousand
module)
THGs or THGsE The THGs is a protocol analysis tool that contains its own processor and two
THGnotebook The THGnotebook is a portable PC analyzer system consisting of a Note-
Table 5-3. Hardware Device Capabilities
THGm is Finisar’s premier analyzer card for 10/100/1000 Ethernet networks.
THGm supports all counters in Surveyor and supports all capture functions at
full line rate. TheTHGm also supports monitor and transmit functions. Special
views are supported for viewing the capture buffer when the device is
stopped. For THGm, you do not have to stop the device to load/unload filters.
The default mode for THGm is Capture + Monitor. THGm cards do not support Capture + Transmit mode.
THGm modules. The THGm modules in THGs support all counters in Surveyor. THGm supports all capture and transmit functions at full line rate.
The THGm modules are synchronized so you can analyze a full-duplex network segment from a single view. When viewing a THGs resource in the
Resource Browser, you will see three “devices”: one for the first THGm card,
one for the second THGm card, and one for the two cards synchronized as a
set. The default mode for modules in THGs is Capture + Monitor. THGm
cards in THGs do not support Capture + Transmit mode.
book PC running analyzer software and a portable undercarriage containing
two THGm cards. The THGm modules in THGnotebook support all features
and functions in Surveyor. THGm supports all capture functions at full line
rate and has a monitoring capability. When two THGm modules are
present, they are synchronized so you can analyze a full-duplex network segment from a single view. When viewing THGnotebook resources in the
Resource Browser, you will see three “devices” for each pair of synchronized
THGm cards in the device: one for the first THGm card, one for the second
THGm card, and one for the two cards synchronized as a set. The default
mode for modules in THGnotebook is Capture + Monitor. THGm cards in
THGnotebook do not support Capture + Transmit mode.
THGp The THGp is a portable PC system (Dolch PC) that contains up to four
THGm modules. The THGm modules in THGp support all features and functions in Surveyor. THGm supports all capture functions at full line rate and
has a monitoring capability. When two THGm modules are present, they
are synchronized so you can analyze a full-duplex network segment from a
single view. When viewing THGp resources in the Resource Browser, you
will see three “devices” for each pair of synchronized THGm cards in the
device: one for the first THGm card, one for the second THGm card, and one
for the two cards synchronized as a set. The default mode for modules in
THGp is Capture + Monitor. THGm cards in THGp do not support Capture +
Transmit mode.
5-7
Page 96

Surveyor
User’s Guide
Table 5-3. Hardware Device Capabilities (continued)
Portable Surveyor 10/100
Ethernet Analyzer
Card
NDIS Surveyor NDIS supports up to four adapters. The first adapter found during
Portable Surveyor 10/100 Ethernet Analyzer Card is an adapter/analyzer
card for 10/100 Ethernet networks in a notebook PC environment. Portable
Surveyor 10/100 Ethernet Analyzer Card adapters can be used to capture,
transmit, or monitor. When using an Portable Surveyor 10/100 Ethernet Analyzer Card adapter, all counters are supported. The default mode for Portable
Surveyor 10/100 Ethernet Analyzer Card adapters is Capture + Monitor; the
Capture+Transmit mode is not supported. All Surveyor real-time functions
are available.
The effective rates at which an Portable Surveyor 10/100 Ethernet Analyzer
Card adapter can capture and monitor is limited because these functions are
performed in software rather than hardware. Use Portable Surveyor 10/100
Ethernet Analyzer Card adapters in Monitor only or Capture only mode to
improve performance. Capture rates can approach full-line rate for 10 Mbps
networks if other PC functions are limited.
system initialization is seen by Surveyor software as module #1, the second
as module #2, and so on.
Standard Ethernet or Token Ring adapters can be used to capture, transmit,
or monitor, but have severe performance constraints. The effective rate at
which an NDIS module can capture or monitor is limited because it must perform these functions in software rather than hardware. An NDIS adapter is
often used in Monitor only mode to improve performance, since NDIS adapters cannot capture at full line rate. When using an NDIS adapter, check the
Information tab to see information about what counters are supported. Each
manufacturer supports a different set of counters. The default mode for NDIS
adapters is Capture + Monitor.
Multi-port Taps Taps are fault-tolerant wiring devices that provide connections for analyzer
Switches Switches are wiring devices that provide connections for analyzer devices.
Synchronized Resources
Synchronized resources are multiple hardware devices (two THGm) that have been
connected so that they use the same clock timer. Synchronized devices display in
the Resource Browser as a unique resource. For example, if the two THGm modules
in a full-duplex THGs are synchronized, then the Resource Browser shows three
resources available within the THGs; the first THGm, the second THGm, and the
synchronized configuration of both THGm modules together. Synchronized
5-8
devices. A Finisar multi-port tap shows as a “resource” to the Surveyor software, but is only used to select a LAN segment for monitoring and LAN analysis functions.
The switch shows as a “resource” to the Surveyor software, but is only used
to select a LAN segment for monitoring and LAN analysis functions. 4, 6, or
8-port Datacom Switches for 10/100 or Gigabit Ethernet are supported.
Page 97

resources are recognized by the synchronized resource icon in the Resource
Browser.
Synchronizing resources allows single actions to start a resource pair. All statistics
and all data about stations and conversations will appear as one resource to
Surveyor. This enables you to perform all capture or monitoring functions on a fullduplex network segment. Synchronized resources can also monitor two half-duplex
segments. Resources cannot transmit frames when they are synchronized.
Two THGm modules within the same PC can be synchronized. This requires a
special cable between the two cards to synchronize their clocks. Call customer
support for information on how to synchronize and use two analyzer cards with a
PC.
Synchronized modules within an analyzer device are typically used with a Finisar
multi-port or single-port tap to provide a connection to full-duplex network
segment(s). Multi-port taps provide a convenient, software-controlled means to
switch between segments. Contact customer support for more information on
Finisar tap products.
Hints and Tips for Resources
Resources and Modes
Hints and Tips for Resources
5
The following are a collection of hints and tips you may find useful when using
resources or the Resource Browser:
• When launching Surveyor, be sure to enter the password on the log-in screen so
you can see remote devices. If you fail to enter a password, Surveyor will not
allow you to see remote analyzer resources in your network.
• To connect to a remote host, choose
Connect... from the Remote menu and enter
the host IP address, user name, and password.
• To set up or change accounts, choose
• To see remote users logged on to your local resources, choose
from the
•Use the
Host menu.
Refresh button in dialog boxes to update the list of user accounts cur-
Access Privileges... from the Host menu.
Current Users...
rently established. Remote users with super-user privileges may have created a
new account since the dialog box was initially displayed.
• To prevent others from using a local resource, use
Lock from the Module menu.
• Monitor mode can be set in addition to capture if the resource supports monitoring functions. If the resource does not support monitoring functions, the
Monitor
button is disabled.
5-9
Page 98

Surveyor
User’s Guide
• Use synchronized THGm modules for full-duplex capture.
• For options to be displayed under the
Host menu, you must select the local host
name in the Resource Browser. Selecting a resource within the local host makes
the options in the
•Use the
Properties… option from the Host menu to find out information about
Host menu unavailable.
the host. Information includes host type, IP address, and the Surveyor software
version. The host name must be highlighted in the Resource Browser to get a
description.
• If you suspect that a remote resource is not responding, go to Summary View
and look at the Resource Browser. If the host for the remote resource is not
there, the connection has been lost with the remote host and the resource is not
available. Red Xs appearing over a host in the Resource Browser indicate that
the host is disconnected.
• To see which capture filter or transmit specification is associated with a particular resource, choose Active TSP and Capture Filter from the Module menu.
• Use aliases to more easily identify remote devices. Use the right mouse to select
a host. Select
•Use the
when connecting to a remote host (
Properties and enter an alias for the host.
Resume Analysis on host with the following histogram file... option
F5 key) to save time analyzing the histo-
gram. If the connection is dropped and then reestablished you retain the sections
of data you have already downloaded via the histogram.
5-10
Page 99

Chapter 6
6 Views
There are numerous ways to view data from Surveyor. This section describes the
primary windows you use to view data, and the actual data views you can see within
each window.
The primary windows for viewing information are shown in Table 6-1.
Table 6-1. Surveyor’s Primary Windows for Viewing Information
Primary GUI Window Description
Summary View From Summary View you can see one view of many different
resources. Viewing options include configurable charts and tables.
Detail View From Detail View you can see many different views simultaneously of
a single resource.
Capture View From Capture View you can see many different views of previously
captured data. Although the data is “static”, the presentation of the
data is the same as for viewing real-time data.
The data views that can be seen within each primary window are described
independently. Although you may be viewing data for different purposes from each
primary view, the way the information is presented in a data view is virtually
identical no matter which primary view you are using.
Table 6-2 shows which data views are supported from each primary window.
6-1
Page 100

Surveyor
User’s Guide
Table 6-2. Data Views Provided Within Summary, Detail and Capture View
Metric Summary View
(Single View)
MAC Statistics Y Y N
Utilization/Errors Strip Chart Y Y N
Frame Distribution Y Y Y
Protocol Distribution Y Y Y
Host Table YYY
Network Layer Host Table Y Y Y
Application Layer Host Table Y Y Y
Host Matrix YYY
Network Layer Matrix Y Y Y
Application Layer Matrix Y Y Y
VLANs Y Y Y
Address Mapping Y Y Y
Duplicate Address
(Expert plug-in only)
Expert (Expert plug-in only) Y Y Y
Application Response Time
(Expert plug-in only)
YYY
YYY
Detail View
(Multiple Views)
C a p t u r e V i e w
(Static Data)
6-2
Ring Statistics (Token Ring only) Y Y Y
Capture View (protocol decode) N Y Y
Multi-QoS Views
(Multi-QoS plug-in only)
Y = Data View Supported
N = Data View Not Supported
NYY
This chapter contains information on data views with the exception of Expert Views
and Multi-QoS Views. Refer to the Expert chapter for complete information on the
Multi-QoS Views. Refer to the Multi-QoS chapter for complete information on the
Multi-QoS views.
 Loading...
Loading...