Page 1
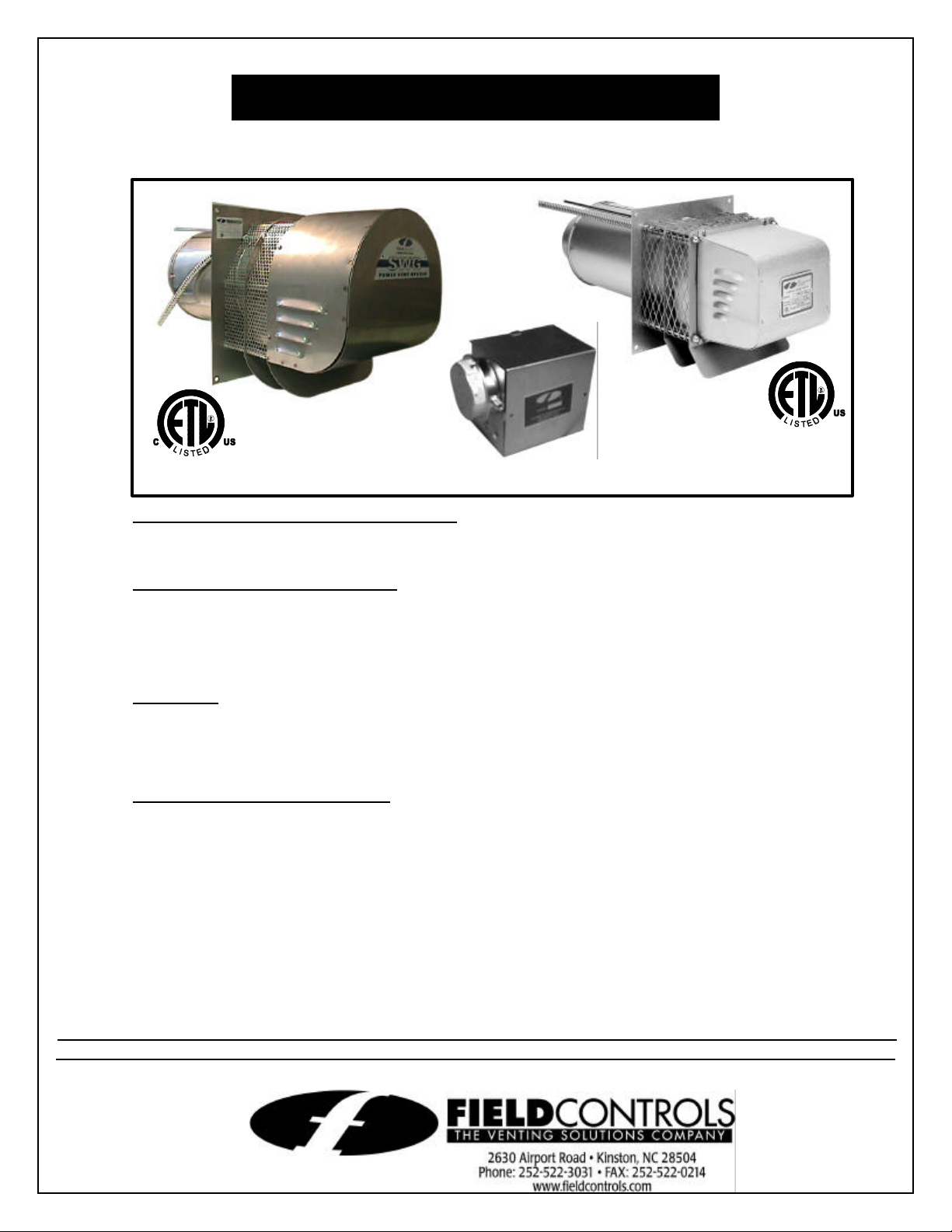
SIDEWALL POWER VENTER KIT
CK series control kit
Model: SWG, SWGII & SWG Stainless Series
*Patented
TYPICAL VENTING SYSTEM COMPONENTS
1 - SWG Series Power Venter
1 - CK Series Control Kit (sold separately)
sold separately
OPTIONAL SYSTEM COMPONENTS
SWG SERIES THROUGH-WALL EXTENSION KIT
For installation in wall thickness over 8 inches. Models PEK-4 through PEK-8 are available.
FOR MOST MULTIPLE HEATING EQUIPMENT SYSTEMS
One CK Series Control Kit for each appliance. Except for a 24V gas furnace or boiler and a
30mV water heater multiple venting system, use the CK-90 Series Control Kit.
CONTENTS
Available Control Kits.................................... 2 Maintenance.............................................8
Installation Instructions ................................. 2 General Inspection ...................................8
Wiring............................................................ 7 Repair Parts..............................................9
Air Flow Adjustments.................................... 7 System Information ................................11
GENERAL SYSTEM INFORMATION
Designed for operation with natural gas, LP gas and #2 fuel oil appliances.
1. The thermostat (wall thermostat or aquastat) calls for heat and energizes a relay which activates
the power venter. After the venter motor has come up to speed, the pressure switch closes. This
closes the circuit to the burner and allows the burner to fire.
2. For millivolt controlled water heaters using the CK-20 Series Control Kit, the gas valve pressure
switch activates the power venter at the same time as the burner fires.
3. After the heating requirement has been satisfied, the thermostat circuit will open and de-activate
the burner and power venter circuit.
4. For venting systems equipped with a post purge device, the power venter operates for a period
of time after the burner has shut off to purge remaining flue gases.
DO NOT DESTROY
THESE INSTRUCTIONS MUST REMAIN WITH EQUIPMENT
Page 2

CONTROL KITS
CK-20F/HWK: For operation with 30 or 750 millivolt gas-fired water heaters, gas-fired space heaters and gas-fired pool or
spa heaters with an internally mounted thermostat. Includes a fixed post purge.
CK-21: For operation with gas-fired instantaneous water heaters with a pressure tap port in the burner manifold.
CK-40F/41F: For operation with gas-fired furnaces, boilers, unit heaters and water heaters operating with a 24 VAC gas
valve. For systems not equipped with factory mounted spillage switches, use the CK-41F which includes
two GSK-3 spill switches. Includes a fixed post purge.
CK-43/43F: For draft induced 24 VAC gas valve systems. Includes a 4" MG-1 draft control and electronic post purge.
The CK-43F includes a fixed post purge.
CK-61: For operation with oil-fired systems. Has electronic post purge.
CK-62: For operation with oil-fired systems. Has thermally activated post purge.
CK-63: For operation with oil-fired systems. Has electronic post purge. For operating venter with or without burner
motor.
CK-81: For operation with 750 millivolt operated boilers, furnaces, water heaters, pool or spa heaters and gas-
fired fireplaces when operating with remote mounted thermostat. Operated off a 24 VAC thermostat. For
operation off of a 120 VAC thermostat or wall switch, use the CK-80.
CK-91/91F: For gas fired draft induced 24 VAC gas valve systems and a 30 millivolt operated water heater. Includes a
4" MG-1 draft control and an electronic post purge. The CK-91F includes a fixed post purge.
CK-92*/92F: For operation with gas -fired furnaces, boilers, unit heaters and water heaters operating with a 24 VAC gas
valve and a 30 millivolt operated water heater. Includes an electronic post purge. The CK-92F includes a
fixed post purge.
INSTALLATION SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS
CAUTION: This device must be installed by a qualified installer in accordance with the manufacturer's installation instructions.
Appliances should have a minimum of 75% combustion efficiency or have a maximum measured flue gas temperature of
550°F (Stainless steel units maximum temperature rating 650°F US/575°F CA) at the inlet of the power venter.
1. The power venting system must be installed by a qualified installer. "Qualified Installer" shall mean an individual who
has been properly trained or a licensed installer. The installer must write or imprint his name, phone number and date
of installation on the installation tag. The tag should be attached to the power venting system control kit box or power
venter unit. Recording burner and venting system initial operational information is strongly recommended as a guide
for service or burner tune-up. Enter this on the back page of this manual.
2. Safety inspection of a venting system should be performed before and after installing a power venting system on an
existing or new appliance. Procedures to follow are those recommended by the National Flue Gas Code
A.N.S.I.Z223.1, or refer to the General Installation Inspection section of this manual.
3. Plan the vent system layout before installation to avoid the possibility of accidental contact with concealed wiring or
plumbing inside walls.
4. Single wall vent pipe (refer to Diagram B) may be used to join an appliance to the venting system, but if proper
clearances cannot be maintained from combustible materials, Class B Vent Pipe should be used for gas appliances
and Class L Type Vent Pipe for oil appliances. Refer to national or local codes for guidelines.
5. Disconnect power supply before making wiring connections to prevent electrical shock and equipment damage.
6. This equipment is designed to overcome minor negative pressure conditions. To ensure extreme negative pressure
does not exist, follow the General Installation Inspection section of this manual.
7. Heating appliances equipped with draft hoods, such as boilers or furnaces, LP gas appliances and Natural gas
appliances SHOULD have a secondary spillage switch installed. On appliances without draft hoods, it is recommended
that a secondary safety switch such as a WMO-1, GSK, FTS, or TSP-1 be used. Gas-fired 30 millivolt power systems
MUST be equipped with a spillage switch.
8. Air flow adjustment MUST be made to ensure appliance efficiency. This should be done at the appliance exhaust
outlet with a velocity meter, draft gauge or by "match test procedure". A match test is in accordance with National Fuel
Gas Code A.N.S.I.Z223.1, Section 8.6.
9. On oil-fired and gas-fired heating appliances not equipped with a draft hood, a barometric draft control MUST be
installed to regulate proper air flow and fluctuations in the system's air flow during operation. Fluctuations may come
from wind loads on the outlet of the power venter, house de-pressurization during windy days and the different house
ventilation requirements between summer and winter operation. For gas appliances, use a Field Controls Type MG-1
Barometric Draft Control. For oil appliances use a Field Controls Type M or RC Barometric Draft Control. Gas-fired
draft induced systems should have a single-acting barometric draft control installed.
Page 2
Page 3

INSTALLATION OF SWG POWER VENTER (See Table 1)
Table 1
UNIT SIZING CHART
OIL GAS
MAX*
OIL GPH
BTU/HR.
INPUT
MAX**
IMPUT
MAXIMUM EQUIVALENT FEET OF VENT
PIPE
AT MAX BTU/HR
INPUT
AT 60% OF MAX
BTU/HR INPUT
VENTING WITH
VENT PIPE SIZE
MODEL
21 80 3”
N/A 70,000
50 100 4”
SWG-3
--- --- ---
1.10 170,000
--- 23 3”
35 100 4”
SWGII-4HD
SWG-4s
65 100 5”
1.85 290,000
16 44 4”
51 100 5”
SWGII-5
SWG-5s
95 100 6”
2.65 416,000
28 78 5’”
68 100 6”
SWGII-6
SWG-6s
100 100 7”
28 78 6”
3.60 566,000
61 100 7”
SWG-7
90 100 8”
26 72 7”
4.75 740,000
51 100 8”
SWG-8
70 100 9”
*Rating at 100 psi. Sizing based on appliance maximum input rate not actual firing rate. **Do not exceed maximum BTU/HR input rating or maximum oil
GPH input. For multiple venting system applications, add the input for each appliance. Category I gas-fired draft induced systems require an SWGII-4HD
or larger. Category III gas-fired draft induced systems require an SWGII-5 or larger.
Page 3
Page 4
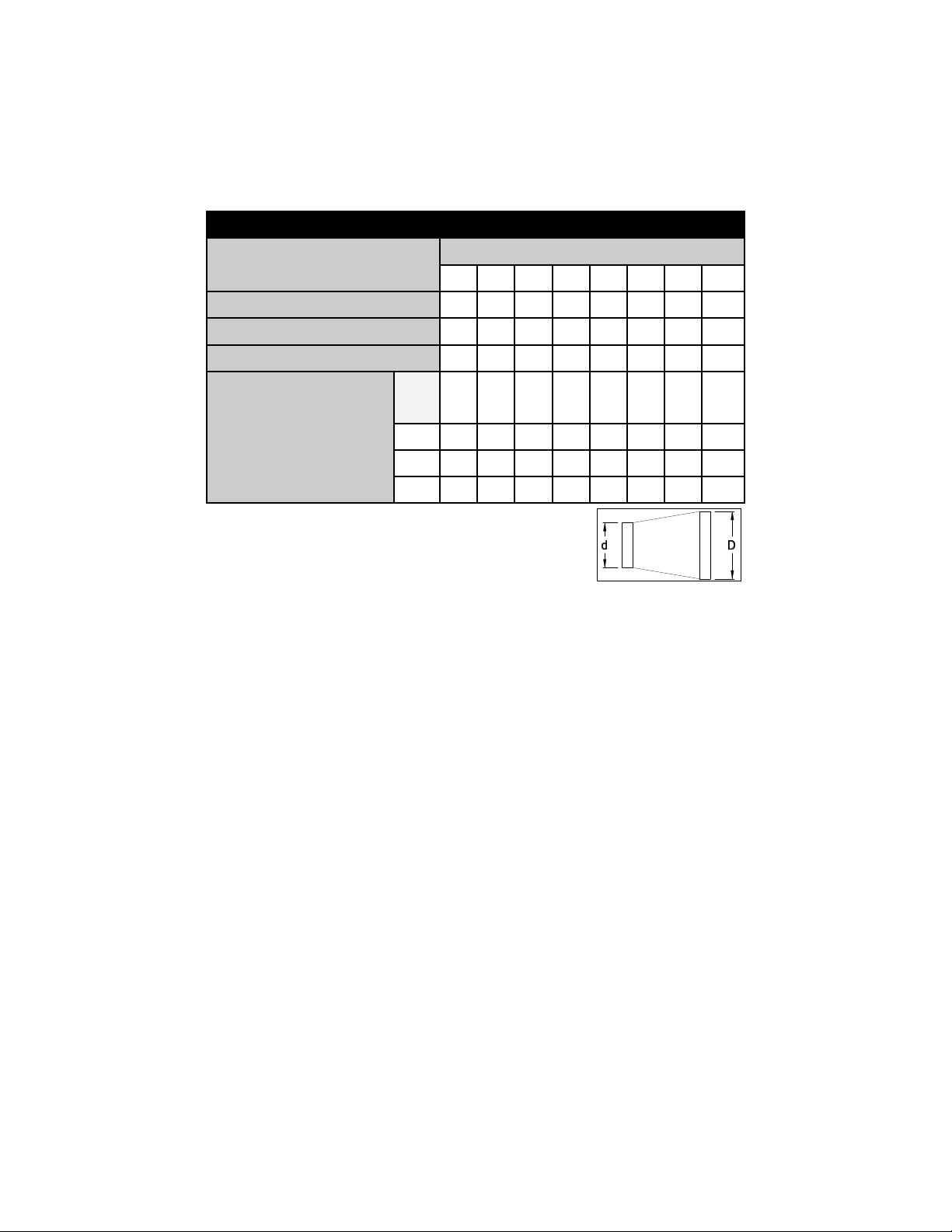
PROCEDURE FOR CALCULATING TOTAL EQUIVALENT PIPE LENGTH IN FEET
1. Calculate the total equivalent feet for each type of fitting used in the venting system from the chart below.
2. Calculate the total amount of feet for the straight lengths of vent pipe.
3. Add the equivalent feet for the fitting with the total amount of feet of straight lengths. This will approximate the total
equivalent feet of the vent system.
Table 2
EQUIVALENT LENGTH (FEET) OF VENT PIPE FOR VENT PIPE FITTING
VENT PIPE DIAMETER
VENT PIPE FITTINGS
TEE
90° ELBOW
45° ELBOW
d/D
3” 4” 5” 6” 7” 8” 9” 10”
19 25 31 38 44 50 56 63
5 7 9 11 12 14 16 18
3 4 4 5 6 7 8 9
SUDDEN REDUCER
OR INCREASER
FOR 3 *RATIOS (d/D)
1/4 8 11 14 17 19 22 25 28
1/2 5 7 8 10 12 13 15 17
3/4 2 3 3 4 4 5 6 6
*Reducer or increaser ratio (d/D) small diameter divided reducer
ratio is d/D = 4/8 = 1/2. To estimate the equivalent foot length for
the fitting, use the smaller pipe diameter for the equivalent length
figure. Example 4" to 8" reducer; the reducer ratio is 1/2 and the
smaller pipe diameter is 4". So, from the chart, the equivalent feet
would be 7 feet. (See Figure 1)
Figure 1
Example: System Pipe Size = 4"
Step 1 Two 4" 90° elbows @ 7 feet each = 14 ft.
Step 2 Ten 2 foot lengths of 4" pipe = 20 ft.
Step 3 Total equivalent feet = 14 ft. + 20 ft. = 34 ft.
INSTALLATION
CAUTION: Failure to install, maintain and/or operate the power venting system in accordance with manufacturer's
instructions will result in conditions which may produce bodily injury and/or property damage.
1. Remove power venter from box and inspect unit for damage. If the carton has been crushed or mutilated, check unit
very carefully for damage. Rotate blower wheel to insure that the motor and blower wheel rotate freely. DO NOT install
if any damage is apparent. Refer to unit sizing chart to check proper venting sizing.
2. Location of the termination of the venting system should be installed in accordance with the National Fuel Gas Code
A.N.S.I.Z223.1, manufacturer's recommendations and/or local codes which are applicable. See requirements below or
refer to installation location, Diagram A, for typical locations.
a. The exit termination of mechanical draft systems shall not be less than 7' above grade when located adjacent to
public walkways.
b. A venting system shall terminate at least 3' above any forced air inlet located within 10'.
c. The venting system of other than a direct vent appliance shall terminate at least 4' below, 4' horizontally from or 1'
above any door, window or gravity air inlet into the building.
d. The vent termination of a direct vent appliance with an input of 50,000 BTU's per hour or less, shall be located at
least 9" from any opening through which vented gases could enter the building. With an input over 50,000 BTU's
per hour, a 12" termination clearance shall be required.
e. The vent termination point shall not be installed closer than 3' from an inside corner of an L-shaped structure.
f. The vent termination should not be mounted directly above, or within 3' horizontally from an oil tank vent or gas
meter.
g. The bottom of the vent terminal shall be located at least 12" above finished grade.
Page 4
Page 5

3. After determining the location of the venting system termination point (see
Diagram A
Diagram A), cut a square hole through the wall 1" larger than the outer pipe
diameter of the power venter. Mount the power venter through the wall, keeping
the outer pipe centered in the hole. (See Figure 3) Fasten the power venter to the
outside wall with appropriate fasteners. Seal the edges of the power venter base
plate to the wall with a high temperature silicone sealant. DO NOT enclose the
spaced plates on the power venter body. This will result in reduced cooling of the
power venter body. Wood or vinyl siding should be cut so that the unit mounts
directly on the wall board to provide a stable support. If the siding is greater than
1/2" thick use a spacer plate or board behind the power venter mounting plate.
(See Figure 2)
NOTE: If mounting the power venter though a combustible wall material and the flue
gas temperature is above 400°F at the power venter inlet, line the square hole with a
piece of corrosion resistant sheet metal or non-combustible material. The liner piece
should be the same width as the wall section. (See Figure 3) The power venter has a
maximum flue gas temperature of 550°F at the venter inlet. For installation in wall
thicknesses over 8 inches, use an SWG Series Though Wall Extension Kit, Model
PEK.
2. Remove the end pipe cover screws on the sides of the outside pipe and remove
end pipe cover. Then mount the backing plate over the outer pipe and route the
flexible conduit and pressure switch tube (if applicable) through the holes provided
in the backing plate. Fasten the backing plate to the inside wall with appropriate
fasteners. (See Figure 4) Re-install end pipe cover and screws.
Figure 2
Figure 3
Page 5
Figure 4
Page 6

Diagram B
CONNECTING POWER VENTER TO APPLIANCE
Venting system should be installed and supported in accordance with the National Flue Gas Code A.N.S.I.Z223.1, or in
accordance with any local codes. A vent pipe connector shall be supported for the design and weight of the material
employed, to maintain clearances, prevent physical damage and separation of joints. A vent pipe increaser or reducer may
be required for connecting the power venter to the vent system. If needed, place the reducer close to the power venter.
Smaller vent pipe sizes than a chimney-vented system may be used for the vent system.
If mounting venting system near combustible materials, refer to Diagram B for allowable installation clearances.
Clearances are based on an installation using single wall galvanized steel vent pipe. For metal thickness of galvanized
steel pipe connectors, refer to NFPA 211 or NFPA 54 Standards for guidelines. If manufactured double wall vent pipe is
required or used for the installation, clearance should be based on the vent pipes rated clearance. Always check local
code requirements for code restrictions.
Route the vent pipe from the appliance to the power venter using a minimum number of elbows as possible. The horizontal
section of the vent pipe should have a slight upward slope from the appliance to the power venter. For clearances to
combustible materials, multiple appliance venting and other installation requirements, refer to the National Fuel Gas Code
A.N.S.I.Z223.1, and/or any applicable local codes or appliance manufacturer's installation instructions.
INSTALLATION USING SINGLE WALL VENT PIPE (See Table 3)
Table 3
INSTALLATION CLEARANCE WITH SINGLE WALL VENT PIPE
DOUBLE PIPE SYSTEM SINGLE PIPE SYSTEM
Allowable inlet
temperature
SWG Stainless
Steel
Allowable inlet
temperature
SWG/SWGII
400°F or less 400°F or less
400°F to
650°F US/575°F CA
400°F to
650°F US/575°F CA
400°F to 550°F
400°F to 550°F
Clearance
(A)
1/2”
minimum
1”
minimum
1/2”
minimum
with sheet
metal liner
Allowable inlet
temperature
SWG Stainless
Steel
Allowable inlet
temperature
SWG/SWGII
400°F or less 400°F or less
400°F to
650°F US/575°F CA
400°F to
650°F US/575°F CA
400°F to 550°F
400°F to 550°F
Clearance
(B)
3”
minimum
4”
minimum
3”
minimum
with sheet
metal liner
Use a PEK series extension kit or follow installation method below for a double pipe system. To
install an outer pipe extension to the SWG power venter, the end pipe cover on the power venter
must be removed. Then, cut a 1-inch square notch into the vent pipe extension before attaching
the power venter. (See Figure 5) This allows clearance for the adjustment damper. Install the
needed pipe extensions and terminate the outer pipe extension with the end pipe cover (see
Diagram B). The table above shows minimum allowable clearances when using single or double
pipe systems. When the outer pipe is extended over the inner pipe, use the double pipe
guidelines when determining clearances. Figure 6 shows how the airflow pattern through an
Figure 5
SWG reduces the required clearances to combustibles. NOTE: Vent pipe joints should be
secured with at least (3) three sheet metal screws.
Page 6
Page 7

Figure 6
Figure 7
CLASS B AND CLASS L DOUBLE WALL VENT PIPE INSTALLATION
(Follow vent pipe manufacturer's listed or recommended clearances from combustible material)
1. Using a hand crimper or a like device, crimp the inner pipe of the SWG power venter approximately 1" long. (See
Figure 7)
2. Attach the vent pipe over the crimped end of the SWG power venter inner pipe.
3. Secure the vent pipe to the SWG power venter inner pipe with at least (3) three #8 sheet metal screws. Pre-drilling the
holes through both pipes will allow easier fastening.
WIRING
NOTE: Refer to appropriate control kit for proper installation instructions.
Wire the power venter motor and controls in accordance with the National Electric Code and applicable local codes. UNIT
MUST BE GROUNDED. Check ground circuit to make certain that the unit has been properly grounded. The wiring should
be protected by an over-current circuit device rated at 15 amperes. CAUTION MUST be taken to ensure that the wiring
does not come in contact with any heat source. All line voltage and safety control circuits, between the power venter and
the appliance, MUST be wired in accordance with the National Electrical Code for Class 1 wiring or equivalent.
AIR FLOW ADJUSTMENTS
In order to obtain proper system draft, the power venter has an airflow adjustment damper built in.
When used in a system with a barometric draft control, this damper should be used to make coarse
draft adjustments while the barometric should be used for finer adjustments. Loosen the locking
screw on the air flow adjustment damper on the outer pipe of the power venter. (See Figure 8) Adjust
the damper to the full open position. Follow appliance manufacturer's procedures for starting the
heating appliance. Then adjust the thermostat to call for "Heat". After the system has operated for
several minutes to stabilize flue gas temperatures, check for negative draft or up-draft at the heating
appliance outlet or air flow into the draft hood. Use a draft gauge, velocity meter or match test
procedure. Adjust the adjustment damper closed to obtain the minimum air flow required to maintain
draft. Then increase air flow slightly (10% over minimum air flow rate) to ensure proper venting. For
Figure 8
oil-fired or gas-fired power burners, adjust draft to proper over-fired draft.
If proper draft has been established, tighten the adjustment locking screw. For gas-fired systems, shut off thermostat and
check for residual heat spilling from draft hood. If this occurs, a post purge timer may be required. If so, use a Field
Controls PPC-5 Electronic Post Purge or a Control Kit which includes one. Before installing, refer to the General
Installation Inspection to check for negative pressure problems in the building. If sufficient combustion air for the burner is
not provided, a flow reversal during the off cycle could occur within the venting system. This may cause combustion
problems as well as condensation that could block the air pressure sensing tube. It may also contribute to premature
motor failure. Combustion, and/or make-up air, should be supplied from outside the structure and the air inlet should be on
the same wall as the power venter discharge. For example, tightly constructed homes and homes retro-fitted from electric
heated systems are more likely to experience combustion and/or make-up air problems. For further information consult
"The Field Report-Effects of insufficient combustion air on draft and heating systems". Refer to the appropriate control kit
installation instructions for pressure switch adjustment procedure and system checkout procedures before operating
continuously. NOTE: After proper venting has been established, it is recommended that a combustion test on gas and oil
units, a check for CO levels on gas units, and a smoke test on oil systems be performed to ensure maximum burner
efficiency. Oil burner air adjustments should be set at a zero to a trace smoke at the highest or recommended CO2%
setting set by heating equipment manufacturer.
Page 7
Page 8

GENERAL INSTALLATION INSPECTION
Recommended procedures for safety inspection of an appliance in accordance with the National Fuel Gas Code
A.N.S.I.Z223.1. The following procedure will help evaluate the venting system. It is intended as a guide to aid in
determining that the venting system is properly installed and is in a safe condition for continuous use. This procedure
should be recognized as a generalized procedure which cannot anticipate all situations. Accordingly, in some cases,
deviation from this procedure may be necessary to determine safe operation of the equipment. If it is determined that a
condition exists which could result in unsafe operation, the appliance should be shut off and the owner advised of the
unsafe condition. Corrections must be made before the appliance is put into continuous operation. The following steps
should be followed in making a safety inspection.
1. Visually inspect the venting system for proper size and determine that there is no flue gas spillage, blockage,
restriction, leakage, corrosion or other deficiency which could cause an unsafe operation.
2. Insofar as practical, close all building doors, fireplace dampers, windows and all doors in area in which the appliance is
located. Turn on clothes dryers, any exhaust fans, such as range hoods and bathroom exhausters so they operate at
maximum speed. Do not operate a summer exhaust fan. If, after completing Steps 3 through 7 it is believed sufficient
combustion air is not available, refer to the National Flue Gas Code A.N.S.I.Z223.1, or any applicable local codes for
guidance.
3. Place in operation the appliance being inspected. Follow the lighting instructions and adjust thermostat so appliance
will operate continuously.
4. Determine that the pilot or burner is operating properly and that the main burner ignition operates satisfactorily, by
interrupting and re-establishing the electrical power of the appliance in any convenient manner. Test the pilot or burner
safety device to determine if it is operating properly by extinguishing the pilot or disconnecting the flame safety circuit
and pressure switch sensing tube from the pressure switch.
5. Visually determine that the main burner is burning properly; i.e., no floating, lifting or flashbacks. When performing
smoke test on oil-fired systems, the burner should operate at a zero to a trace smoke. This can indicate reduced
available combustion air to burner.
6. If appliances are equipped with high and low flame control or flame modulation, check for proper main burner
operation at low flame.
7. Test for spillage at draft hood or barometric draft control opening and burnr inlet air location after 5 minutes of main
burner operation. Use a draft gauge, flame of a match or candle, smoke from a cigarette, cigar or pipe. If spillage
occurs, adequate air is not available. Shut off heating appliance thermostat and check for spillage around the draft
hood, barometric draft control or burner inlet air location after power venter has stopped operation. If a flow reversal is
noticed, house de-pressurization is occurring and make up air is required. For oil-fired systems, this may be noticed by
oil fume smell after post purge cycle.
8. Turn on all fuel burning appliances within the same room so that they will operate at their maximum input. Then repeat
Steps 5 through 7.
9. Return doors, windows, exhaust fans, fireplace dampers and any other fuel-burning appliances to their previous
condition of use.
MAINTENANCE
1. Motor: Inspect the motor once a year - motor should rotate freely. To prolong the life of the motor, it must be
lubricated with six drops of SWG Superlube, Part # 46226200, annually.
2. Wheel: Inspect the power venter wheel annually to clear any soot, ash or coating which inhibits either rotation or air
flow. Remove all foreign materials before operating.
3. Vent System: Inspect all vent connections annually for looseness, for evidence of corrosion and for flue gas leakage.
Replace, seal or tighten pipe connections if necessary. Check the power venter choke plate to insure it is secured in
place. Check the barometric draft control, if installed, to insure the gate swings freely.
4. System Safety Devices: With the heating system operating, disconnect the pressure sensing tube from the pressure
switch on the CK Kit. This will stop the burner operation. Re-connecting the tube will relight the burner. For 30 millivolt
operating systems, disconnect one lead of the spill switch circuit from the thermocouple junction block. This will shut
off the pilot and the burner. Re-connection will allow relighting the pilot.
Page 8
Page 9

REPLACEMENT PARTS
Should the motor or blower wheel need replacing, the following replacement items are available. The Repair Motor
Assembly contains the Motor and Blower Wheel factory assemble to a mounting bracket.
PART NUMBERS
MODEL REPAIR MOTOR ASSEMBLY BLOWER WHEEL
SWG-3 46196601 46131800
SWG/SWGII-4HD
46234800 46310400
SWG-4s
SWG/SWGII-5
46234900 46213800
SWG-5s
SWG/SWGII-6
46235000 46385800
SWG-6s
SWG-7 46152401 46154700
SWG-8 46460101 46154800
SWG Repair
Motor Assembly
SWGII Repair
Motor Assembly
Blower
Wheel
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION OF THE SWG SERIES POWER VENTER MOTOR ASSEMBLY
REMOVAL
1. Remove the screws securing the motor enclosure cover. (See Figure 9)
2. Remove the screws securing the motor assembly. Rotate the motor assembly
counter-clockwise and slide the assembly into the center. Then pull the motor
assembly out of the unit. (See Figure 10)
3. Clean off any build-up inside the blower wheel housing and the blower wheel.
CAUTION: Avoid applying excess pressure on the blower wheel when cleaning off
any build-up of material. This will cause an imbalance of the blower wheel which
will result in excessive vibration and premature motor failure.
4. If replacing the motor assembly with a new assembly, disconnect the conduit from
the old motor and cut the wires close to the motor. The new motor assembly will
have an electrical box and connector for the conduit.
Figure 9
Figure 10
Page 9
Page 10

INSTALLATION
1. Insert the blower wheel through the hole in the front plate of the power venter
housing. (See Figure 11)
2. Using two nails or awls, align the two center holes of the motor mount bracket and
cover plate. Locate the motor assembly into position by sliding the assembly over
the mounting holes in the front plate. Use the nails or awls to hold the assembly in
position. Secure motor assembly into position at the four corners, then secure
center two holes. (See Figure 12)
3. Re-attach the flexible conduit and wires to the motor and secure the cover on the
electrical box.
4. Seal the top edge of the motor mount bracket against the front plate with a high
temperature silicone sealant.
5. Install motor cover with side louvers pointing down.
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION OF THE SWGII SERIES POWER VENTER
MOTOR ASSEMBLY
REMOVAL
Figure 11
1. Remove the motor enclosure cover by loosening the four screws. (See Figure 9)
2. Open the electrical box on the motor and disconnect the conduit and wires from
the motor. (See Figure 13)
3. Remove the four nuts securing the motor assembly, and pull the motor assembly
straight off of the unit. (See Figure 14)
4. Clean off any build-up inside the blower wheel housing and the blower wheel.
CAUTION: Avoid applying excess pressure on the blower wheel when cleaning off
any build-up of material. This will cause an imbalance of the blower wheel which will
result in excessive vibration and premature motor failure.
INSTALLATION
1. Align the holes in the circular cover plate with the holes in the motor mount bracket on
the motor assembly. (See Figure 14)
2. Slide the motor assembly onto the protruding threaded studs on the power venter
body with the exhaust chute pointing downward, and replace the four nuts securely
to the threaded studs. (See Figure 14)
3. Re-attach the flexible conduit and wires to the motor and secure the cover on the
electrical box.
4. Install the motor cover with the side louvers pointing downward.
Figure 12
Figure 13
Figure 14
Page 10
Page 11

INITIAL BURNER AND VENTING SYSTEM OPERATIONAL INFORMATION
List the following for each operating appliance on the sidewall venting system, as a guide for tune-up or service information
annually.
DATE:
FOR GAS FIRED EQUIPMENT
Heating Appliance BTU/HR Input
Gas Valve Operation Pressure
Vent System Draft Above Draft Hood or
Before Barometric Draft Control
CO2 Measurement
CO Measurement
Equipment Outlet Flue Gas Temperature
FOR OIL FIRED EQUIPMENT
Oil Burner Nozzle Size
Oil Burner Operating Pressure
Pump Operating Vacuum Pressure
Smoke Number
Over-fire Draft
Equipment Outlet Flue Gas Temperature
CO2 Measurement
Page 11
Page 12

Page 12
P/N 46139100 Rev J 05/01
 Loading...
Loading...