Page 1

Chapter
Software Functional Overview
3.1 Overview
The M785 is an IBM PC/AT compatible Notebook PC which supports the Intel
uFCPGA Socket Pentium IV processor family. The following are the major features that
M785 supports.
§ Microsoft PC99 logo and WinXP logo approval.
§ 14.1" XGA / 15.1" XGA, SXGA+ panel support.
§ APM 1.2 compliance
§ Support ACPI 1.0B (or above).
§ Support PCI 2.2 (or above).
§ Support AGP 2.0.
§ Support USB 1.1, 2.0
§ Support SMBIOS 2.3.
§ Support 400/533 Mhz CPU front side bus.
3.2 Summary of the BIOS Specification
Below is the summary of the BIOS software specification:
Controller Chip Description
BIOS Feature
CPU
DRAM
Cache
Shadow
§ Microsoft PC99 logo and WinXP logo approval.
§ Support Boot Block / Crisis Rescue.
§ APM 1.2 Compliance
§ Support ACPI 1.0B (or above) Spec.
§ Support PCI 2.1 (or above) Spec.
§ Support SMBIOS 2.3 Spec
§ Support AGP 2.0 Spec.
§ Support, Windows 2000 and Windows XP.
§ Support flash function including both DOS and Windows
interface for new BIOS update.
§ Support 2 different keyboards on same BIOS.
§ Support boot from HDD and CDROM Drive.
Auto detect the CPU type and speed for the Intel Pentium 4
based system
Auto sizing and detection. Support PC-200/266 DDR SDRAM.
§ Level 2 SRAM auto sizing and detection
§ Always enable CPU L1 and L2 cache.
Always enable VGA and System BIOS shadow
FIC M785 Service Manual 3-1
PDF created with FinePrint pdfFactory Pro trial version http://www.pdffactory.com
Page 2
Software Functional Overview
Controller Chip Description
Display
Hard Disk
Multi Boot
Plug and Play
Smart Battery
Keyboard Controller
PCMCIA
Power Management
Support
§ System auto detects LCD or CRT presence on boot and lid
closed
§ Support Panning while LCD in a display resolution greater
than supported
§ Support Microsoft Direct 3D
§ Support AGP 4x BUS
§ Enhanced IDE spec.
§ Support auto IDE detection.
§ Support LBA mode for larger capacity HDD.
§ Support Ultra DMA 33/66/100.
§ Support Fast PIO mode 1-4 transfer.
§ Support 32 bit PIO transfer.
§ Support Multi-Sector transfer.
§ Support SMART monitoring.
Allow the user to select boot from HDD and CD-ROM
Support PnP Run Time Service and conflict-free allocation of
resource during POST
Support BIOS interface to pass battery information to the
application via SMBus.
Support Fn hot keys, two Windows hot keys, built-in Glide Pad
and external PS/2 mouse/keyboard
Compliant with PCMCIA 2.1 specification.
The power management is compliant with ACPI 1.0B
specification and supports the following power state:
§ S0 (Full-On) Mode
§ S3 (STR) Mode
§ S4 (STD) Mode
§ S5 (Soft-Off) Mode
3-2 FIC M785 Service Manual
PDF created with FinePrint pdfFactory Pro trial version http://www.pdffactory.com
Page 3
Software Functional Overview
3.3 Subsystem Software Functions
This section provides introduction on the software functions of the notebook subsystems and
BIOS related function.
3.3.1 Key Chipset Summary
Following are the main chipsets used in the notebook:
Controller Chip Vendor Description
Processor Intel DT Pentium 4 (2.0, 2.2, 2.4, 2.6GHz)
North Bridge SIS SIS M650 + SIS 302LV
South Bridge SIS SIS 962
Video Controller SIS Embedded in SIS M650
PCMCIA
Controller
Supper I/O
Controller
Audio Controller SIS Embedded in SIS 962
Audio Codec Realtek ALC201
Keyboard
Controller
PMU Controller Mitsubishi PMU08
ROM BIOS SST 49LF040A
IEEE 1394 SIS Embedded in SIS 962
On board LAN SIS Embedded in SIS 962
BlueTooth Not support
Modem MDC AC'97 S/W Modem
ENE CB1410
SMSC LPC47N267
ENE ENE KB3886
3.3.2 System Memory
The system memory consists of SDRAM memory on 64-bit bus and the module size options
are 128/256/512MB upward. The BIOS will automatically detect the amount of memory in
the system and configure CMOS accordingly during the POST (Power-On Self Test) process.
This must be done in a way that requires no user interaction.
Base SO-DIMM DRAM slot
(Bank 0 & 1)
NIL 128MB 128MB
NIL 256MB 256MB
NIL 512MB 512MB
128MB NIL 128MB
128MB 128MB 256MB
128MB 256MB 384MB
FIC M785 Service Manual 3-3
Base SO-DIMM DRAM slot
(Bank 2 & 3)
PDF created with FinePrint pdfFactory Pro trial version http://www.pdffactory.com
Total Size
Page 4
Software Functional Overview
128MB 512MB 640MB
256MB NIL 256MB
256MB 128MB 384MB
256MB 256MB 512MB
256MB 512MB 768MB
512MB NIL 512MB
512MB 128MB 640MB
512MB 256MB 768MB
512MB 512MB 1024MB
3.3.3 Video
The Video subsystem used External DDR memory of Video memory. The system will
support the true ZV port, the Microsoft Direct 3D assist, simultaneous display, monitor
sense for auto display on boot and VESA Super VGA function call.
3.3.4 Supported Video Mode
The following is the display modes supported by the SIS Mobility Video control in
LCD only, CRT only, and simultaneous mode. The VGA BIOS will allow mode sets of
resolutions greater than the panel size but only show as much mode display as will fit
on the panel.
• Supported Standard VGA Mode
The VGA BIOS supports the IBM VGA Standard 7-bit VGA modes numbers.
Mode Pixel Resolution
00h/01h 40*25 16 Text
02h/03h 80*25 16 Text
04h/05h 320*200 4 2-bit Planar
06h 640*200 2 1-bit Planar
07h 80*25 Mono Text
0Dh 320*200 16 4-bit Planar
0Eh 640*200 16 4-bit Planar
0Fh 640*350 Mono 1-bit Planar
Mode Pixel Resolution
10h 640*350 16 4-bit Planar
11h 640*480 2 2-bit Planar
12h 640*480 16 4-bit Planar
13h 320*200 256 8-bit Planar
Note: All Standard VGA Modes are limited to the standard VGA refresh rates.
Colors Memory
Colors Memory
3-4 FIC M785 Service Manual
PDF created with FinePrint pdfFactory Pro trial version http://www.pdffactory.com
Page 5
Software Functional Overview
• Supported extended video modes
CRT device will support all listed VESA mode; and other devices such as PANEL & TV may
be limited to the mode support due to their characteristics
CRT device will support all listed VESA mode; and other devices such as PANEL & TV
may be limited to the mode support due to their characteristics.
VESA
Mode
100h 640 x 400 8-bit Packed 70 2MB
101h 640 x 480 8-bit Packed 60, 72, 75, 85 2MB
102h 800 x 600 4-bit Planar 60, 72, 75, 85, 100 2MB
103h 800 x 600 8-bit Packed 60, 72, 75, 85, 100 2MB
104h 1024 x 768
105h 1024 x 768
106h 1280 x 1024
107h 1280 x 1024 8-bit Packed 43(I), 60, 75, 85
10Eh 320 x 200 16-bit Packed 70
10Fh 320 x 200 32-bit Unpacked 70
111h 640 x 480 16-bit Packed 60, 72, 75, 85
112h 640 x 480 32-bit Unpacked 60, 72, 75, 85
114h 800 x 600 16-bit Packed 60, 72, 75, 85, 100
115h 800 x 600 32-bit Unpacked 60, 72, 75, 85, 100
117h 1024 x 768 16-bit Packed 43(I), 60, 70, 75, 85,
118h 1028 x 768 32-bit Unpacked 43(I), 60, 70, 75, 85,
11Ah 1280 x 1024 16-bit Packed 43(I), 60, 75, 85
11Bh 1280 x 1024 32-bit Unpacked 43(I), 60, 75, 85
11Dh 640 x 400 16-bit Packed 70
11Eh 640 x 400 32-bit Packed 70
120h 1600 x 1200 8-bit Packed 48(I), 60, 75, 85
122h 1600 x 1200 16-bit Packed 48(I), 60, 75, 85
124h 1600 x 1200 32-bit Unpacked 48(I), 60, 75, 85
12Ah 640 x 480 24-bit Packed 60, 72, 75, 85
12Bh 800 x 600 24-bit Packed 60, 72, 75, 85, 100
Pixel
Resolution
Memory Model Refresh Rates In
(Hz)
4-bit Planar 43(I), 60, 70, 75, 85,
100
8-bit Packed 43(I), 60, 70, 75, 85,
100
4-bit Planar 43(I), 60, 75, 85
100
100
Minimm
Memory
2MB
2MB
2MB
2MB
2MB
2MB
2MB
2MB
2MB
2MB
2MB
4MB
4MB
8MB
2MB
2MB
2MB
4MB
8MB
2MB
2MB
FIC M785 Service Manual 3-5
PDF created with FinePrint pdfFactory Pro trial version http://www.pdffactory.com
Page 6
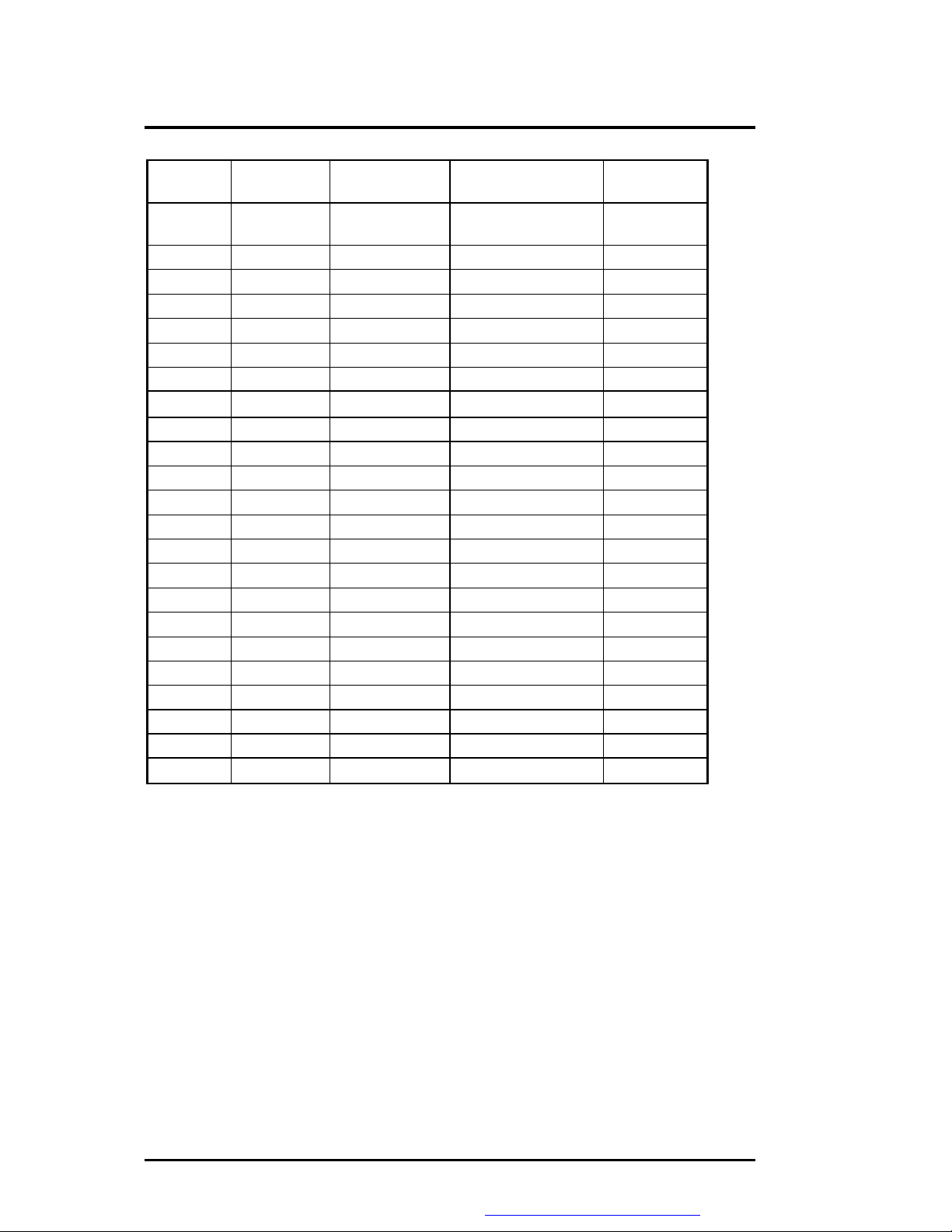
Software Functional Overview
VESA
Mode
12Ch 1024 x 768 24-bit Packed 43(I), 60, 70, 75, 85,
12Dh 1280 x 1024 24-bit Packed 43(I), 60, 75, 85
12Eh 320 x 200 8-bit Packed 70
131h 320 x 200 8-bit Packed 72
133h 320 x 200 16-bit Packed 72
134h 320 x 200 32-bit Packed 72
13Bh* 1400 x 1050 8-bit Packed 60, 75
13Ch* 1400 x 1050 16-bit Packed 60, 75
13Eh* 1400 x 1050 32-bitUnpacked 60, 75
141h 400 x 300 8-bit Packed 72
143h 400 x 300 16-bit Packed 72
144h 400 x 300 32-bitUnpacked 72
151h 512 x 384 8-bit Packed 70
153h 512 x 384 16-bit Packed 70
154h 512 x 384 32-bitUnpacked 70
171h 720 x 480 8-bit Packed 75
173h 720 x 480 16-bit Packed 75
174h 720 x 480 24-bit Packed 75
175h 720 x 480 32-bitUnpacked 75
176h 720 x 576 8-bit Packed 75
178h 720 x 576 16-bit Packed 75
179h 720 x 576 24-bit Packed 75
17Ah 720 x 576 32-bitUnpacked 75
Note: “*” The modes may not be available. Their availability should be determined by VESA
function calls.
Pixel
Resolution
Memory Model Refresh Rates In
(Hz)
100
Minimum
Memory
4MB
4MB
2MB
2MB
2MB
2MB
2MB
4MB
8MB
2MB
2MB
2MB
2MB
2MB
2MB
2MB
2MB
2MB
2MB
2MB
2MB
2MB
2MB
l Panel Type Initialization
The VGA BIOS will issue INT 15h function call during POST. This function call allows the
system BIOS to specify the panel type to the VGA BIOS. The system BIOS should get the
panel type from GPI pins before the VGA chip initialized, and pass this information to VGA
BIOS through INT 15 Function code.
− LCD Panel ID pin Definition:
3-6 FIC M785 Service Manual
PDF created with FinePrint pdfFactory Pro trial version http://www.pdffactory.com
Page 7
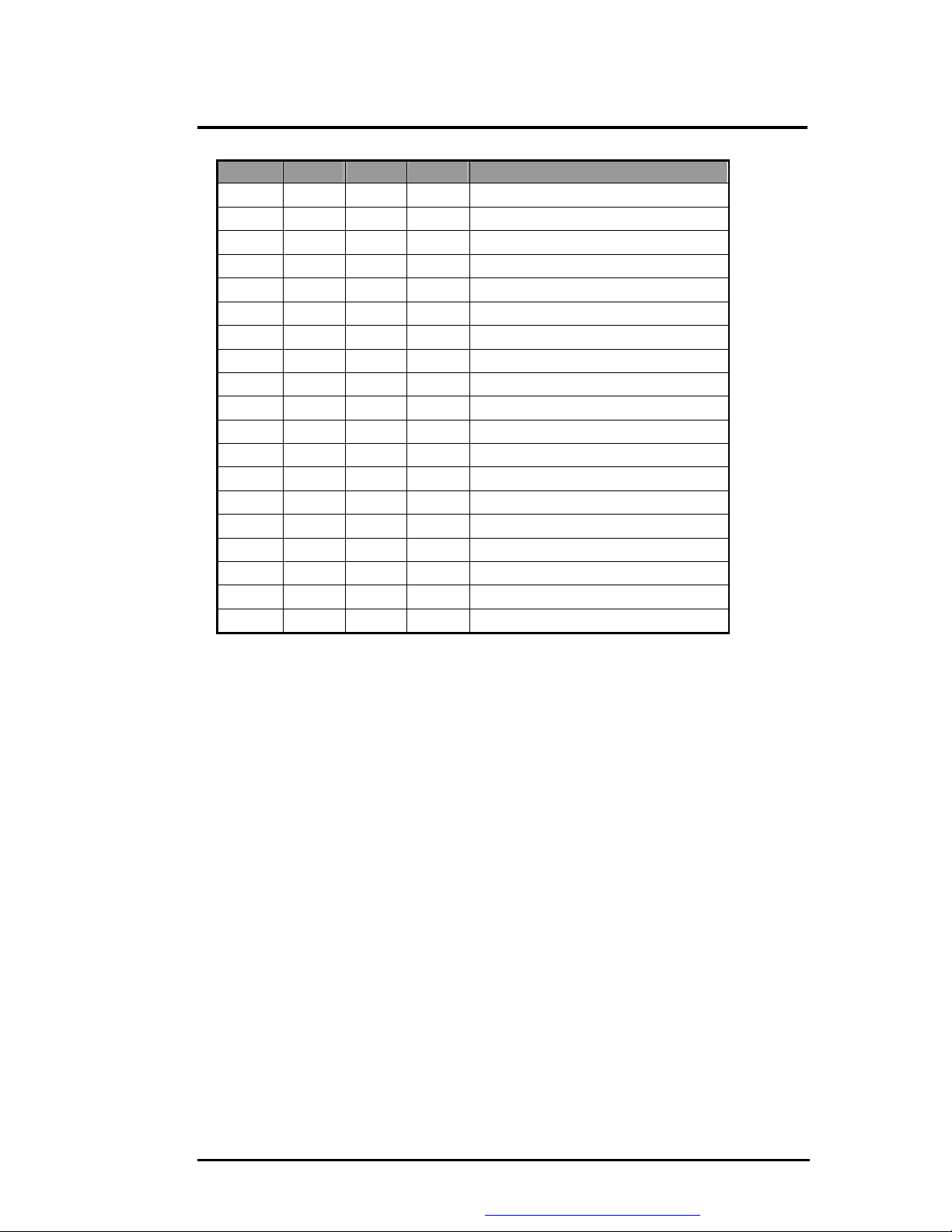
Software Functional Overview
GPI[45] GPI[46] GPI[10] GPI[22]
0 0 0 0
0 0 0 1
0 0 1 0
0 0 1 1
0 1 0 0
0 1 0 1
0 1 1 0
0 1 1 1
1 0 0 0
1 0 0 1
1 0 1 0
1 0 1 1
1 1 0 0 LTN141X8-L04 (Samsung)
1 1 0 1 B141XN04V2 (AU)
1 1 1 0
1 1 1 1 LTN150U1-L02 (Samsung)
LTN150P3-L04 (Samsung)
Panel Type
3.3.5 Enhanced IDE
The system BIOS must be ready to support 4 IDE devises on two controllers. The BIOS
support Ultra DMA33/66/100 and also supports automatic configuration of drives using both
the LBA and CHS large drive remapping method. In addition to supporting standard drives
through an auto-configuration process that does NOT require user involvement or
confirmation. The system should automatically do this at POST time in a way that is
transparent to the user. If a drive is connected to the bus, the drive should be automatically
recognized, configured and available for use under MS-DOS 6.2x.
3.3.6 Audio
The audio subsystem will support the requirements identified by the AC’97 specification.
Both software and hardware will control the volume level for the internal audio subsystem. In
addition to the volume control, the user will be able to mute the sound to completely cut off
the volume using both software and hardware.
3.3.6 Super I/O
This controller contains 16550A or FIFO Enabled UART, ECP/Standard/Bi-directional
Parallel Port meeting the 1284 specification, and an Infrared port that supports IrDA Super IR
(4Mbps)
FIC M785 Service Manual 3-7
PDF created with FinePrint pdfFactory Pro trial version http://www.pdffactory.com
Page 8
Software Functional Overview
3.3.7 PCMCIA
The PCMCIA controller chip of the notebook provides the following features:
• Support for only single CardBus slot (two type II stacked)
• Individually accessed, dual-buffer implementation
• Support for 3.3v, 5v and 12v (flash programming) cards
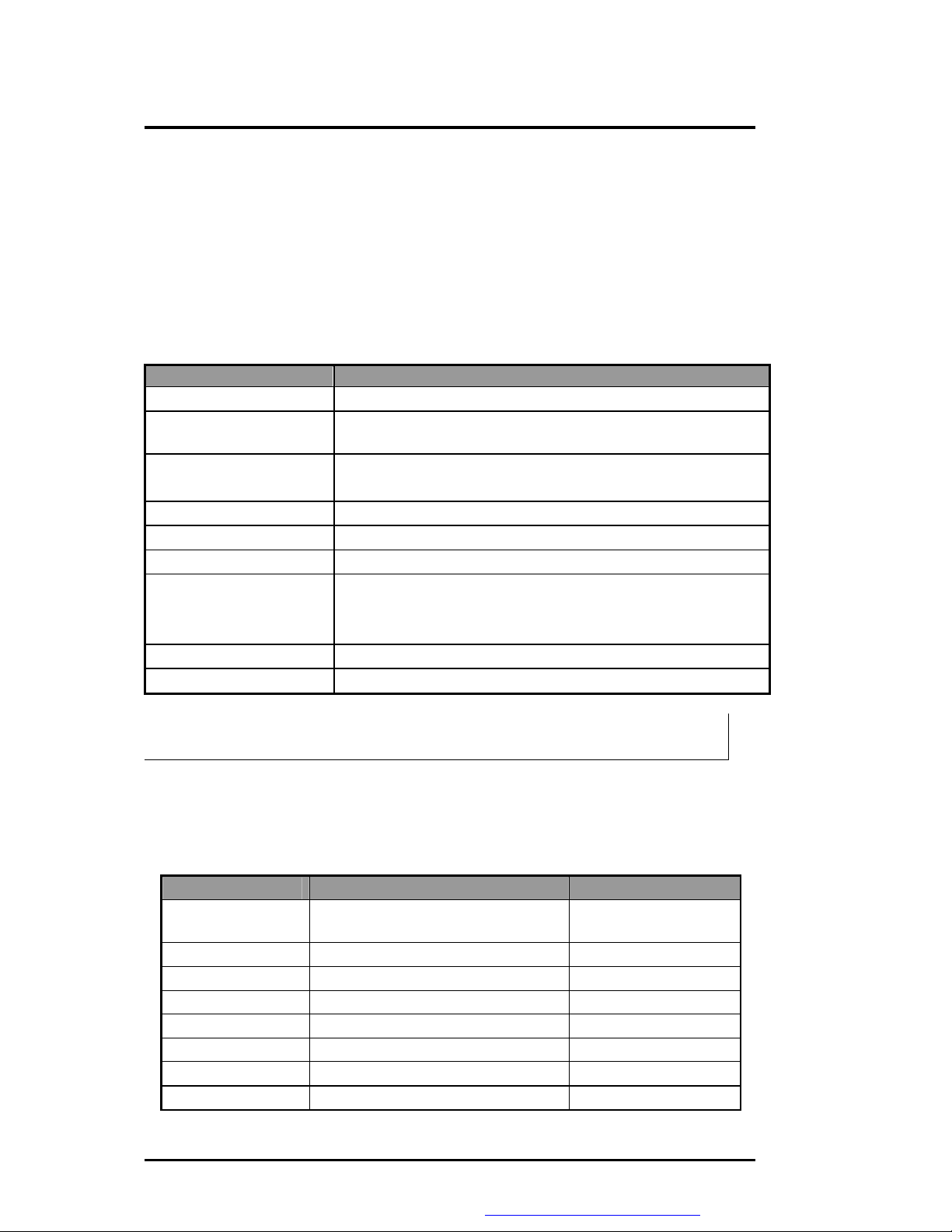
3.3.8 LED Indicator
The table below lists down the functions of the Status LED indicator:
Indicator Function Description
IDE accessing LEDŒ
FDD accessing LEDŒ
Battery Charging LED
CapsLock LEDŒ
ScrollLock LEDŒ
NumLock LEDŒ
Power Status LED
Mail LEDŒ
GPRS statusŒ
This LED will turn on while accessing the IDE Device.
This LED will turn on while accessing the FDD Device. (M785
No support)
Turn on (Amber) – Battery is under charging mode
Turn off – Battery full charged or no battery
This LED will turn on when the function of CapsLock is active.
This LED will turn on when the function of ScrollLock is active.
This LED will turn on when the function of NumLock is active.
Green – System is powered on.
Green Blinking- System is entered suspend mode.
Amber – Battery Low.
This LED will turn on while Mail was arrived.
None
i Π- There LEDs will be turned off during Suspend mode.
3.3.9 Hot Keys Definition
All Hot keys must be active at all times under all operation systems.
l Hot Keys by Internal Keyboard
Hot Key Function Handler
Fn + F3 Toggle Display
(LCD/CRT/LCD&CRT)
Fn + F4 System entered into standby mode BIOS Handler
Fn + F6 System Speaker On/Off BIOS Handler
Fn + F8 Brightness Increase Controlled by PMU08
Fn + F9 Brightness Decrease Controlled by PMU08
ScrLock Scroll Lock
Internet Button Internet Function Key Controlled by Driver
Mail Button Mail Function Key Controlled by Driver
3-8 FIC M785 Service Manual
BIOS Handler
PDF created with FinePrint pdfFactory Pro trial version http://www.pdffactory.com
Page 9
Software Functional Overview
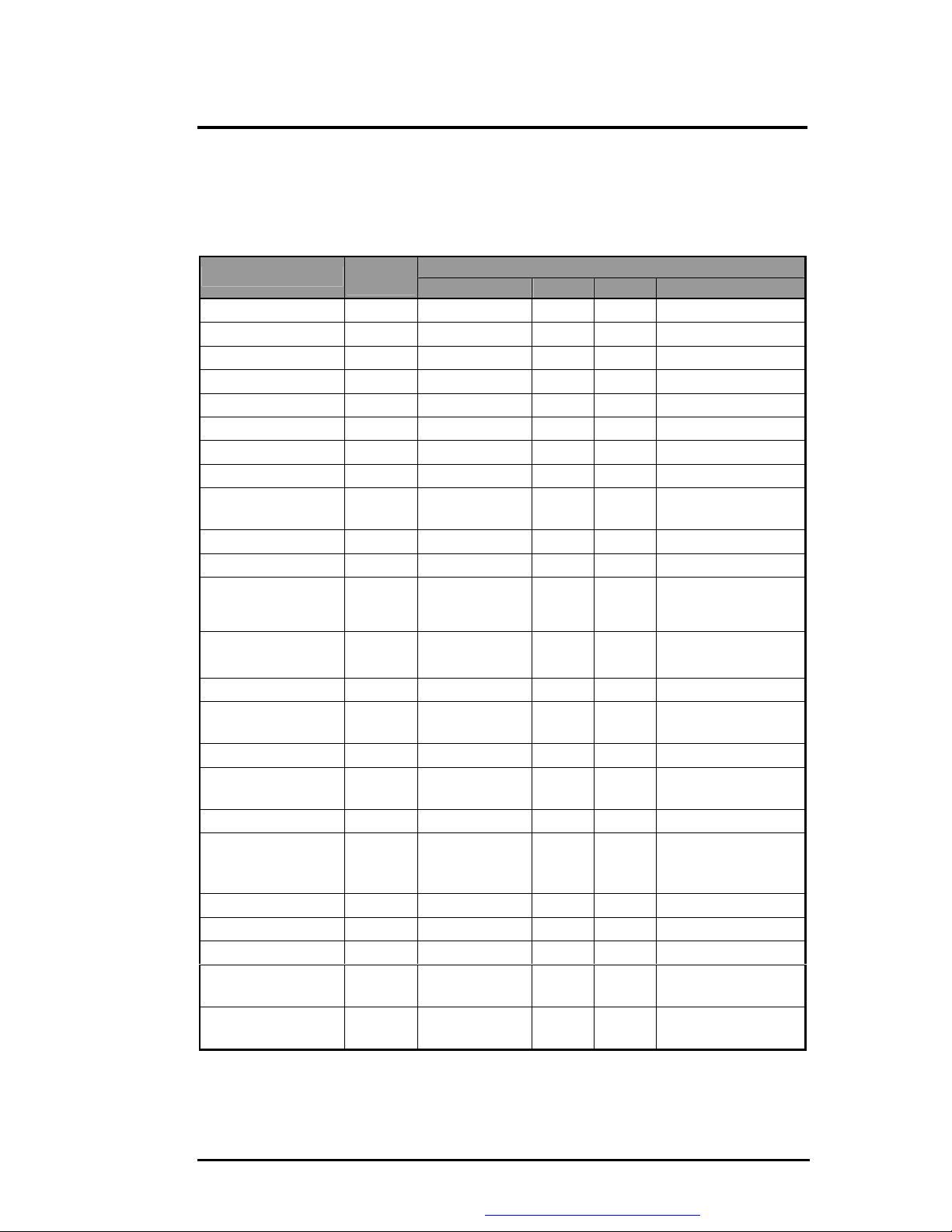
3.3.10 Plug & Play
The BIOS supports the Plug and Play Specification 1.0A. (Include ESCD) This section
describes the device management. The system board devices and its resources are as follows:
Device
DMA Controller
Interrupt Controller
System Timer
RTC
ISA Bus
System Speaker
System Board
PnP Mother Board
Keyboard
Controller
PMU08 Controller
Math Coprocessor
PS/2 Mouse
Video Controller
Serial Port
ECP, Parallel port
FDC
Dual IDE Controller
CardBus Controller
Audio chip
IEEE1394
Modem
LAN
SIR
USB Host
Controller
Connect
Type
Static
Static
Static
Static
Static
Static
Static
Static
Static
Static
Static
Enable /
Disable
Static
Static
Static
Dynamic
Dynamic
Static
Static
Dynamic
Dynamic
Dynamic
Dynamic
Enable /
Disable
Dynamic
Resources
I/O IRQ DMA Memory
00~0F, 81~8F
20~21, A0~A1 IRQ2
40~43 IRQ0
70~71 IRQ8
- DMA4
- -
- -
- -
- - - -
61 - - -
- - - E0000~FFFFF
80 - - -
60, 64 IRQ1
- -
68, 6C - - -
F0~FF IRQ13
- IRQ12
3B0~3BB,
IRQ5
- -
- -
- A0000~BFFFF,
3C0~3DF
3F8~3FF IRQ4
378~37F,
IRQ7 DMA1
- -
778~77F
3F0~3F5, 3F7 IRQ6 DMA2
170~177,
1F0~1F7, 3F6
3E0~3E1 IRQ11
220~22F,
IRQ14,
- -
15
- -
IRQ5 DMA3
300~301,
388~38B
IRQ11
3E8~3EF IRQ10
1080~10FF IRQ10
158~15F, 2F8-
IRQ3
- -
- -
- -
2FF
EF80~EF9F IRQ5
- -
-
C0000~CFFFF
-
-
-
FIC M785 Service Manual 3-9
PDF created with FinePrint pdfFactory Pro trial version http://www.pdffactory.com
Page 10
Software Functional Overview
• PCI Device
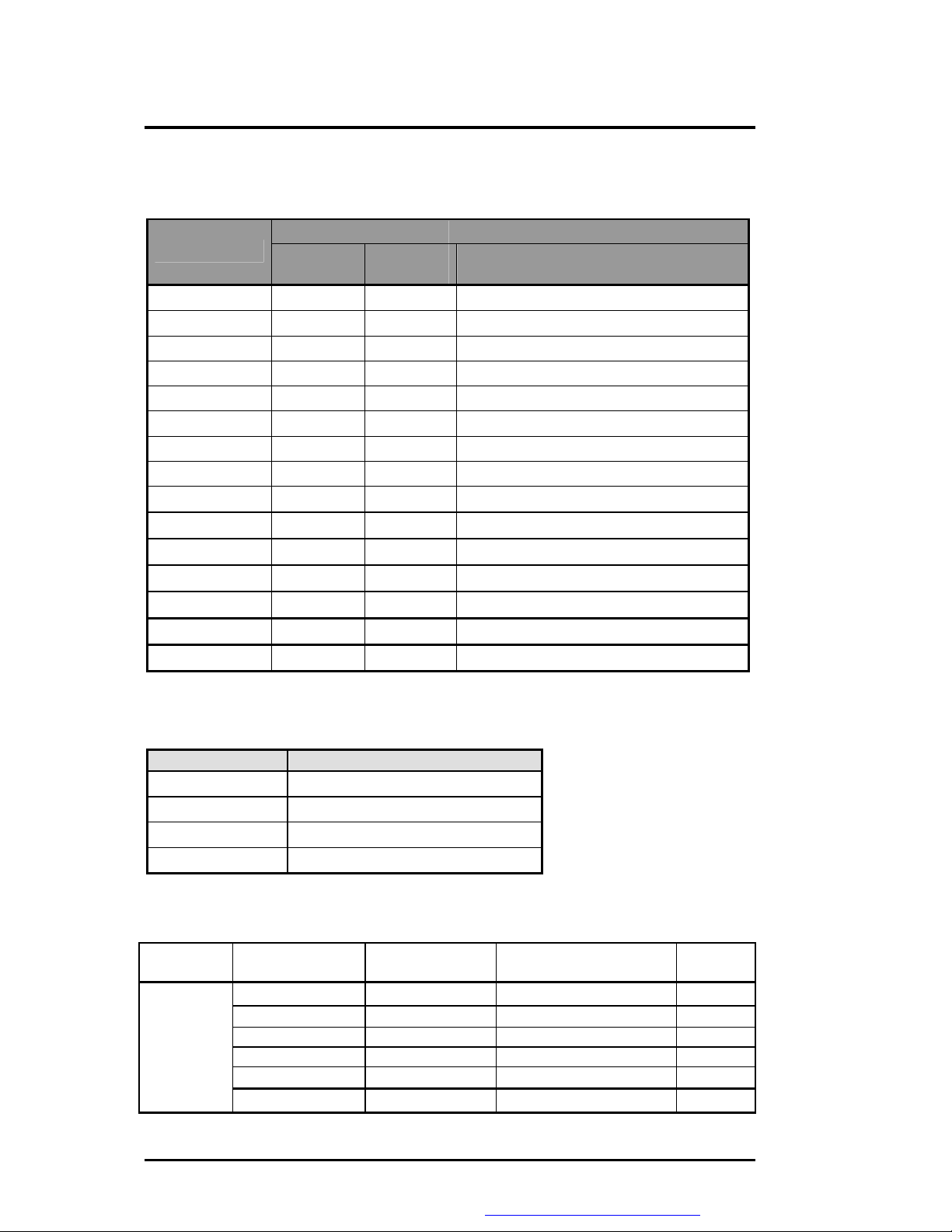
The table below summarizes the PCI IDSEL Pin Allocation:
PCI Device
IDSEL Pin
AD11 Device 00 Function 0 SISM650 - Host to PCI bridge
AD12 Device 01 Function 0 SIS962 – PCI to PCI bridge
AD13 Device 02 Function 0 SIS962 - PCI to ISA bridge
Function 2 SIS962 - ADSL (Not support)
Function 3 SIS962 - 1394
Function 4 SIS962 - PMU and SMBus interface
Function 5 SIS962 - IDE interface
Function 6 SIS962 - AC97 Modem interface
Function 7 SIS962 - AC97 Audio interface
AD14 Device 03 Function 0 SIS962 - USB0
Device
Number
Function
Number
Device Name
Function 1 SIS962 - USB1
Function 2 SIS962 - USB2
Function 3 SIS962 - USB3
AD15 Device 04 Function 0 SIS962 - LAN
AD23 Device 0C Function 0 ENE1410 - Card Bus Socket A
The table below summarizes the INT Pin Allocation:
INT Pin PCI Device
INTA
INTB
INTC
INTD
IDE/
1394/SMB
VGA (Embedded in SISM650)/Audio
USB (Embedded in SIS962)/LAN
The table below summarizes the PCI bus master Allocation:
Arbiter
Signal Agents
Function Use
(Master)
REQ00/GNT00 SIS962 LAN Controller
SIS 962
REQ20/GNT20 MDC MODEM Controller
REQ30/GNT30 SIS962 1394 controller
REQ40/GNT40 None None
REQ10/GNT10 CB1410 Card Bus Controller
3-10 FIC M785 Service Manual
PDF created with FinePrint pdfFactory Pro trial version http://www.pdffactory.com
Page 11
Software Functional Overview
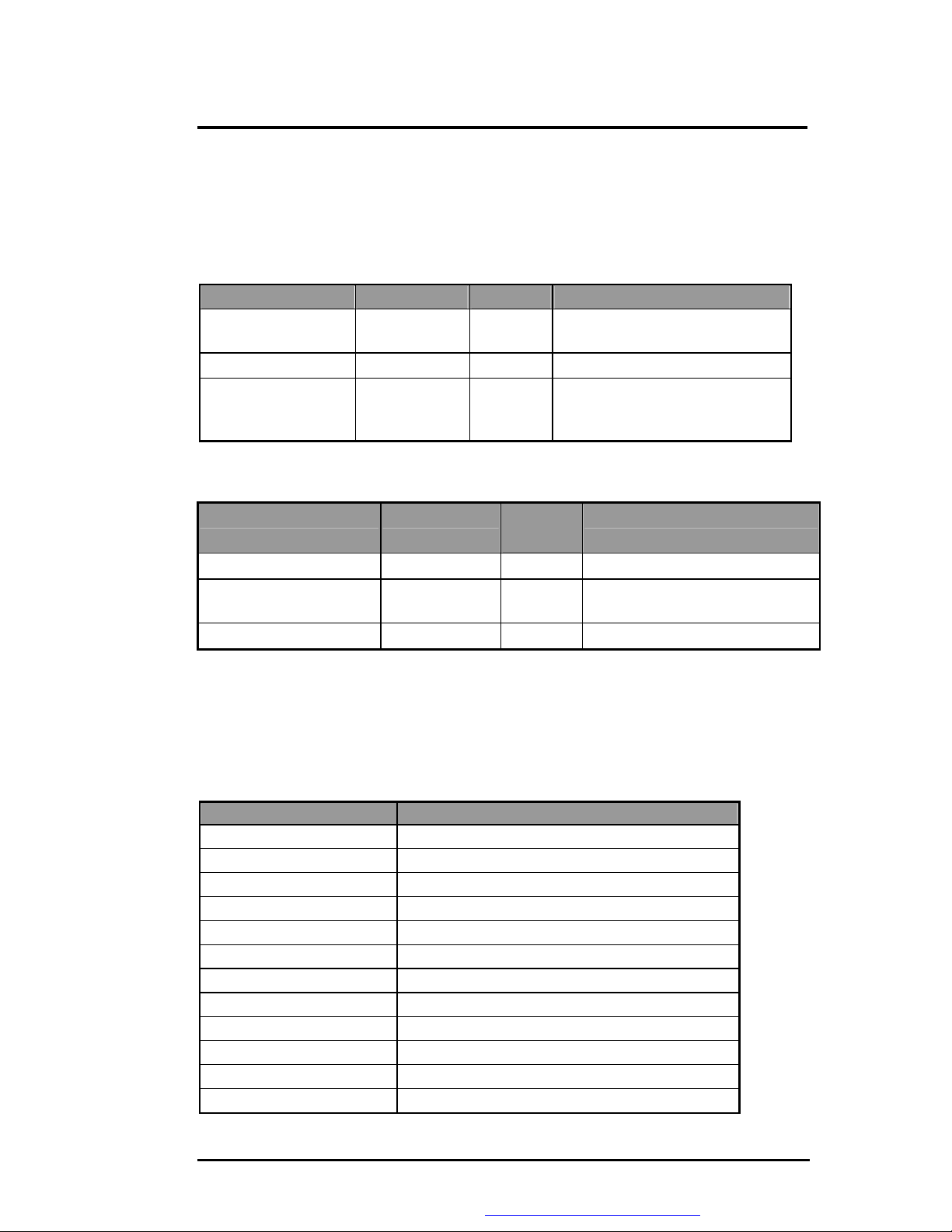
3.3.11 MBus Devices
The SMBus is a two-wire interface through which the system can communicate with powerrelated chips. The BIOS should initialize the SMBus devices during POST.
SIS961 SMBus Connection Devices
SMBus Device Master/Slave Address
SIS650 – Core Logic Both Host and
Slave
SO-DIMM Slave A0h Not Need
ICS952001, ICS93722
CLK Generator
PMU 08 SMBus Connection Devices
SMBus Device Host/Slave Address
PMU08 Master 10h Enable PS01 decode interface
MAX1617 (Thermal
sensor)
Battery (1st Battery) Slave A8h No Need
Slave D2h Program the desired clock
Slave 9Ch Program the desired temperature
02h Enable SMBus interface and
A7 ~ A1
BIOS Need to Initialization
SMBus interrupt
frequency (Pin23 output 24MHz,
Pin22 output 48MHz)
BIOS Need to Initialization
range
3.3.12 Resource Allocation
This section summarizes the resource allocation of the notebook computer.
l I/O Map
Hex Address Device
000 - 01F 8237-1
020 - 021 8259-1
022 SIS 962
040 - 05F 8254
060 - 064 Keyboard Controller
068 – 06C PMU08 Controller
070 - 07F RTC & NMI Mask
080 - 08F DMA Page Registers
092 System Control Port
0A0 - 0A1 8259-2
0B2 Advanced Power Management Control Port
0B3 Advanced Power Management Status Port
FIC M785 Service Manual 3-11
PDF created with FinePrint pdfFactory Pro trial version http://www.pdffactory.com
Page 12
Software Functional Overview
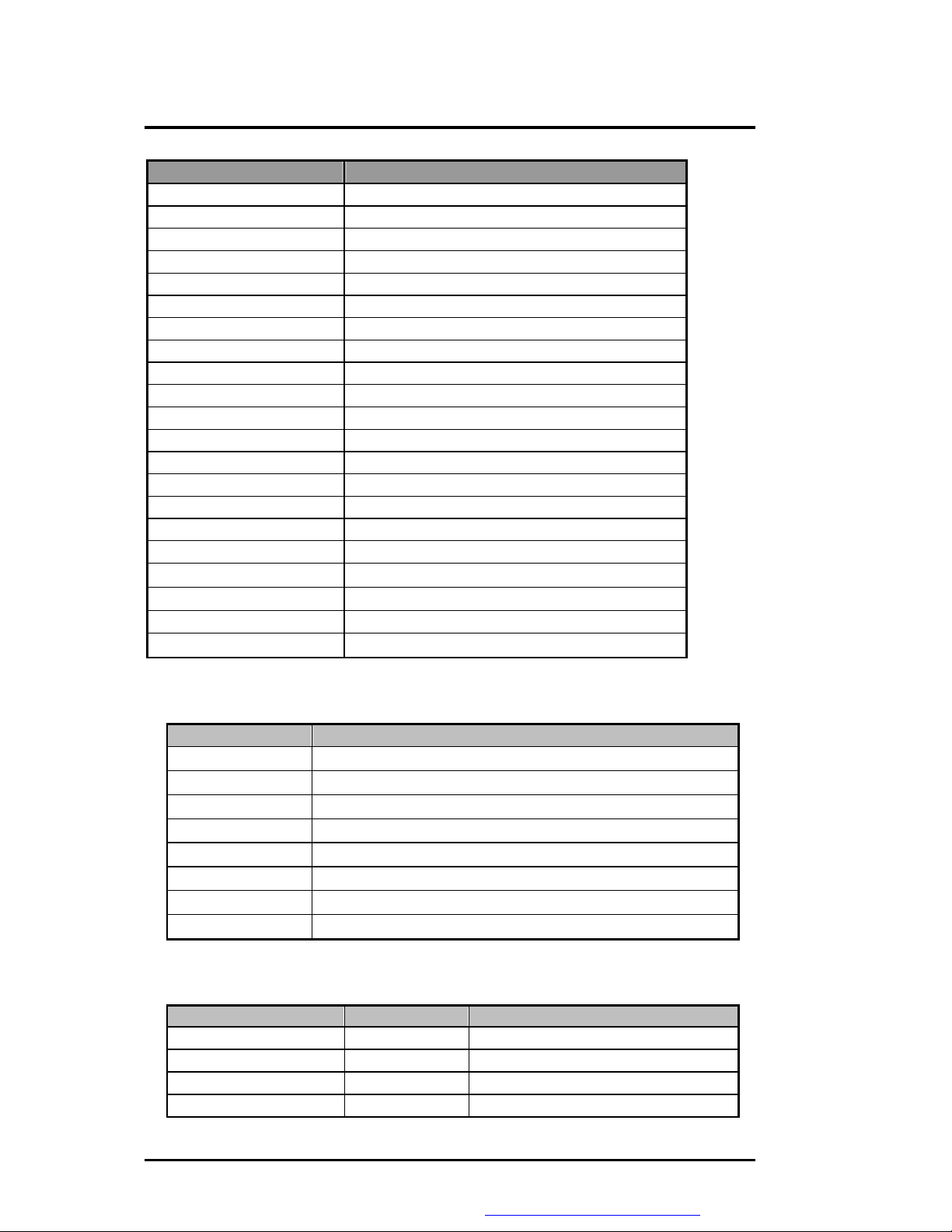
Hex Address Device
0C0 – 0DF 8237-2
0F0 – 0FF Math Coprocessor
170 – 177 Secondary IDE Controller
1F0 – 1F7 Primary IDE Controller
200 – 20F Game Port
220 – 22F Sound Blaster
279 PnP configuration – Address port
330 – 333 MIDI
370 – 371 Sound chip control port
378 – 37A Parallel Port
388 – 38B FM Synthesizer
398 – 399 Super I/O Chip
3B0 – 3DF Video Controller
3E0 – 3E1 PCMCIA Controller
3E8 – 3EF Fax/Modem
3F0 – 3F7 Floppy Disk Controller
3F8 – 3FF Serial Port 1
530 – 537 Microsoft Sound System
778 – 77B ECP port
A79 PnP configuration – Write data port
CF8 – CFC PCI BUS configuration register
l ISA DMA Map
DMA Channel Device
DMA 0
DMA 1
DMA 2
DMA 3
DMA 4
DMA 5
DMA 6
DMA 7
l Memory Map
Address Range Length Description
00000 ~ 9FBFFh
9FC00 ~ 9FFFFh
A0000 ~ BFFFFh
C0000 ~ CFFFFh
Unused
ECP
Floppy Disk
Audio
[Cascade]
Unused
Unused
Unused
640 KB System Memory
128 KB Video Memory
40 KB Video ROM
72 KB Unused
3-12 FIC M785 Service Manual
PDF created with FinePrint pdfFactory Pro trial version http://www.pdffactory.com
Page 13
Software Functional Overview
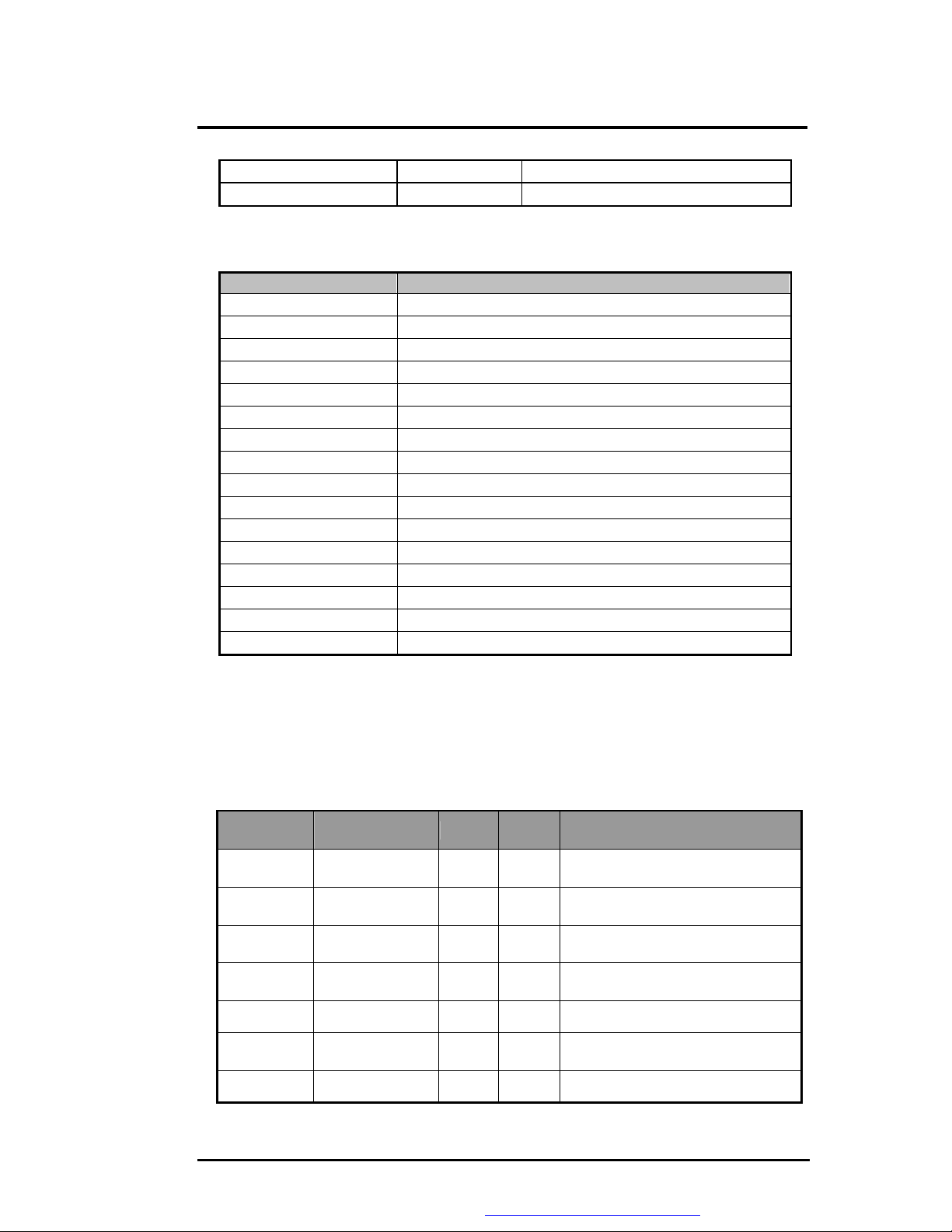
D0000 ~ DFFFFh
E0000 ~ FFFFFh
l IRQ Map
IRQ10
IRQ11
IRQ12
IRQ13
IRQ14
IRQ15
16 KB DMI information
128 KB System ROM BIOS
IRQ# Description
IRQ 0
IRQ 1
IRQ 2
IRQ 3
IRQ 4
IRQ 5
IRQ 6
IRQ 7
IRQ 8
IRQ 9
System Timer
Keyboard
[Cascade]
PHS (Serial)
Serial Port
Audio/VGA/USB
Floppy Disk Drive
Parallel Port
RTC Alarm
Reserved for PCMCIA card
LAN / Modem or Combo, (Card Bus), IEEE 1394
ACPI
PS/2 Mouse
FPU (FERR)
Hard Disk Drive
CD-ROM or DVD-ROM
3.4 GPIO Pin Assignment
The GPI and GPO pins connected to system devices. The BIOS can get device’s status and
control the device via the GPI and GPO pins.
• SiS650 GPI pin assignment
GPIO
Number
GPIO0 LPC_PME0 1 I 0 : LPC_PME0 Event Enable
GPIO1 PMUFLASH0 1 O 0 : Flash PMU08 firmware
GPIO2 MB_ID0 1 I 0 : Mother Board ID0 Select
GPIO3 Q_SMI0 1 I 0 : External K/B SMI0
GPIO4 N.C. -- -- -GPIO5
GPIO6 N.C. -- -- --
Signal Name Default I/O Notes
1 : normal operation
1 : normal operation
1 : normal operation
1 : normal operation
N.C --
FIC M785 Service Manual 3-13
PDF created with FinePrint pdfFactory Pro trial version http://www.pdffactory.com
Page 14

Software Functional Overview
GPIO
Number
GPIO7 EC_SCI0 1 I 0 : PMU SCI Detect
GPIO8
GPIO9 N.C. -- -- -GPIO10 MB_ID1 1 I 0 : Mother Board ID1 Select
GPIO11 PM_SLP_S10 1 O 0 : When system into S1
GPIO12
GPIO13 N.C. -- -- -GPIO14 SPDMUX0 1
GPIO15 N.C. -- -- --
GPIO16 N.C. -- -- --
GPO17 N.C. -- -- -GPIO18 SPDMUX1 1 O SM BUS Select1
GPIO19
GPIO20 ICH_SMBDATA
Signal Name Default I/O Notes
1 : PMU SCI Not Detect
PM_RI0 1 I 0 : wakeup event input enable
1 : wakeup event input disable
1 : normal operation
1 : normal operation
STPCPU0 1 O 0 : Stop CPU Clock
1 : normal operation
O
SM BUS Select0
ICH_SMBCLK 1 O
1 I/O SM BUS Data
SM BUS Clock
3.4.1 PMU08 GPIO Signal Description
PIN Signal I/O
GPIOA0
GPIOA1
GPIOA2
GPIOA3
GPIOA4
GPIOA5
GPIOA6
GPIOA7
GPIOB0
GPIOB1
GPIOB2
GPIOB3
GPIOB4
LID# I LID Switch Low = LCD Close.
N.C. X
Mail LED# O Mail LED Low = Mail Arrival
QGSMI# I
PCMUTE# O Low = Mute PC speaker
PSTMSK# O
PCMRI# I CB1410 Low = Ring Signal from PCMCIA
RI1# I Serial Port Low = Ring Signal from Serial Port
N.C. X
N.C X
N.C. X
PDCOM# O MAX3243 Low = Power down RS232
N.C. X
Normal Runtime / Wake event
ENE
KB3886
Low = Keyboard SMI
Low = PCI Reset Mask, Hi = PCI
Reset Enable
3-14 FIC M785 Service Manual
PDF created with FinePrint pdfFactory Pro trial version http://www.pdffactory.com
Page 15

Software Functional Overview
PIN Signal I/O
GPIOB5
GPIOB6
GPIOB7
GPIOC0
GPIOC1
GPIOC2
GPIOC3
I : INPUT O : OUTPUT L-Lever : Low Lever
H-Lever : Hi Lever Function Pin Description :
N.C. X
PM_SLP_S
1#
I SIS962
PM_RI# O SIS962 Low = Wake Up Event (SMI or SCI)
N.C. X
N.C. X
CHGLED O Charge LED High = Turn ON Charge LED
N.C. X
Normal Runtime / Wake event
Low = POS, STR and STD suspend
state
A : A-D Converter Input Pin
3.4.2 M3886 GPIO Signal Description
Address Bit r/w Description Remark
0060h 7:0 r Read Data from Output Data Bus Buffer
0060h 7:0 w Write Data to into Input Data Bus Buffer
0064h 7:0 r Status
0064h 7:0 w Write Command into Input Data Bus
Buffer
Port Assign:
Port Pin Name In/Out Description
PORT 0 P07 : P00 OUT Key Scan Data Output
PORT 1 P17 : P10 OUT Key Scan Data Output
PORT 3 P37 : P30 IN Key Scan Data Input
PORT 2 P27 OUT SCROLL Lock LED
P26 OUT NUM Lock LED
P25 OUT CAPS Lock LED
P24 OUT BLEN1
P23 OUT Wireless_RFON
P22 OUT NC
P21 IN PULL DOWN 1K ohm
P20 OUT NC
PORT 4 P46 OUT NC
P45 OUT PULL UP 10Kohm
P44 OUT PULL UP 10Kohm
P43 OUT IRQ12
P42 OUT IRQ1
P41 OUT NC
P40 OUT KBCSMI0
FIC M785 Service Manual 3-15
PDF created with FinePrint pdfFactory Pro trial version http://www.pdffactory.com
Page 16

Software Functional Overview
Port Pin Name In/Out Description
PORT 5 P57 OUT NC
P56 OUT NC
P55 IN GPRS_PWRENA
P54 IN GPRS_VDDPD
P50 OUT ISA ADDRESS (SA2)
PORT 6 P61 IN KBSEL2
P60 IN KBSEL1
P62 IN GPRS_ON/OFF
P63 IN LOGSEL
P64 OUT PASS0
P65 IN NC
P66 OUT BT_FETON1
P67 OUT BT_SENSE0
PORT 7 P70 I/O PS2 DATA
P73 I/O PS2 CLOCK
P72 I/O EXTERNAL KB DATA
P75 I/O EXTERNAL KB CLOCK
P74 I/O EXTERNAL MOUSE CLOCK
P71 I/O EXTERNAL MOUSE DATA
P76 I/O SMDAT_KBC
P77 I/O SMCLK_KBC
i I : INPUT O : OUTPUT
3-16 FIC M785 Service Manual
PDF created with FinePrint pdfFactory Pro trial version http://www.pdffactory.com
Page 17

Software Functional Overview
3.5 Power Management
This section provides the Power Management software function of the notebook.
3.5.1 General Requirements
The BIOS meet the following general Power Management requirements:
• Compliant with ACPI 1.0B / ACPI 2.0 Specification
• Support for Suspend-to-RAM and Suspend-to-Disk mode
• Support for Resume on External Modem Ring while in S3 Mode
• Support for Resume on Internal Modem Ring while in S3 / S4 Mode
• Support for LAN Remote Power while in S3 / S4 Mode
• Power Management must not substantially affect or degrade system performance
• Power Management must be OS independent
• Support resume on Time/Date
• Support Wireless LAN wake up
• Support Internet / Mail button wake up
3.5.2 System Power Plane
The system components are grouped as the following parties to let the system to control the
On/Off of power under different power management modes.
The power plane is divided as following:
Power Group Power Control Pin Controlled Devices
+B Nil IMM, (9V~20V)
+3VA Nil SIS962 (RTC I/F), Internal Modem Ring, PMU08
+12V PWRON PCMCIA Card, AC97 Codec
+5V PWRON PCMCIA Slot 5V
+3V PWRON VGA, PCMCIA, PCMCIA Slot 3V, DRAM,
Twister(DRAM I/F), ENE KB3886, MAX3243
+5VS SUSB# FLASH ROM, HDD, CD-ROM, USB, Internal K/B,
Glide Pad, External P/S2 Mouse, Audio AMP, Fan
+3VS SUSB# SIS962 (ISA I/F Power), Clock Generator & Buffer
(W137)
+RTCVCCS
Nil SIS962 (RTC)
3.5.3 Power Management Mode
l Full On Mode
The system state where no devices are power managed and the system can respond to
applications with maximum performance.
l Doze mode
The CPU clock is slow down and all other devices are full-on.
FIC M785 Service Manual 3-17
PDF created with FinePrint pdfFactory Pro trial version http://www.pdffactory.com
Page 18

Software Functional Overview
l Stand by mode
A suspend state where all motherboard components are still powered-on except for the
system clock generator device. The PCI and CPU buses are driven to the inactive idle state.
The system memory is powered and refreshed by the memory bridge, and the graphics frame
buffer is powered and refreshed by the graphic chip. The system provides a 32Khz clock
(SUSCLK) in this suspend mode to support refresh of these memory subsystems. Only an
enabled “resume event” can bring the system out of the stand by state. The SIS 961 also
provides a resume timer that allows the system to resume after a programmed time has
elapsed.
l Suspend to RAM mode (STR)
A suspend state where all motherboard components are powered-off. The CPU/L2 and
PCI busses are powered off. All devices connected to the CPU/L2 and PCI busses must either
be powered-off or isolate their bus interfaces. The system memory is powered and refreshed
by the memory bridge, and the graphics frame buffer is powered and refreshed by the
graphics chip. The system provides a 32 kHz clock (SUSCLK) in this suspend mode to
support refresh of these memory subsystems. Only an enabled “resume event” can bring the
platform out of the suspend to RAM (STR) state.
l Suspend to Disk mode (STD)
A suspend state where the context of the entire system is saved to disk, all motherboard
components are powered-off, and all clocks are stopped. Any enabled “resume event”, such as
PowerBTN or RTC, can bring the platform out of the suspend to disk (STD) state.
l Soft off mode (SOFF)
The This is the same as suspend to disk except the context of memory is not saved. The system
will resume from Soft Off as if a hard reset had occurred.
l Mechanical off mode
All power except the RTC has been removed from the system.
3-18 FIC M785 Service Manual
PDF created with FinePrint pdfFactory Pro trial version http://www.pdffactory.com
Page 19

Software Functional Overview
3.5.4 Power Management Mode Transition Flow
S1
Sleeping
G2 (S5) -
Soft Off
ACPI
Boot
(SCI_EN=1)
SLP_TYPx=S5
and
SLP_EN
or
PWRBTN_OR
Wake
Event
G0 (S0) -
Working
S4BIOS_REQ
to
SMI_CMD
OEM S4 BIOS
Handler
SLP_TYPx=S1
and
SLP_EN
SLP_TYPx=S2
and
SLP_EN
SLP_TYPx=S3
and
SLP_EN
SLP_TYPx=S4
and
SLP_EN
S2
Sleeping
G1
S3
Sleeping
S4
Sleeping
SLP_TYPx=S4
and
SLP_EN
FIC M785 Service Manual 3-19
PDF created with FinePrint pdfFactory Pro trial version http://www.pdffactory.com
Page 20

Software Functional Overview
3.5.5 Power Management Mode Transition Event
The following table summarizes the entry events and wake-up events of each power
Power State Entry Event Wake up Event
S1 OSPM control
Lid Close
S4 OSPM control,
STD hot key pressed
Lid Close
Battery Low – Low
S5 Power Button
Execute Windows shutdown
command
Power Button
Ring Indicator
Battery Low - Low
RTC Alarm
LAN Wake Up
Power Button
RTC Alarm
Power Button
RTC Alarm
3.5.6 Lid Switch
The function of Lid Switch is depends on the ACPI aware OS
3.5.7 Power button and suspend button
The function of Lid Switch is depends on the ACPI aware OS.
3.5.8 Device Power management
l Power state of local devices table
PowerState
Component
CPU Stop
L2 CACHE ON Power Down Power Off Power Off
SISM650 ON Stop Clock Power Off (except
SIS962 ON ON Power Off (except
DRAM ON Self Refresh Self Refresh Power Off
Clock Synthesizer ON Low Power Power Off Power Off
CDROM ON Power Down Power Off Power Off
HDD ON Power Down Power Off Power Off
FDD (M785 None) ON Power Down Power Off Power Off
KBC ON ON Power Down Power Off
Doze
Grant
Stand By STR STD/SOff
Stop Clock Power Off Power Off
Power Off
Vcc)
Power Off (except
SUSVcc, RTCVcc )
SUSVcc, RTCVcc)
3-20 FIC M785 Service Manual
PDF created with FinePrint pdfFactory Pro trial version http://www.pdffactory.com
Page 21

Software Functional Overview
PMU08 ON ON Power Down Power Down
VGA/VRAM ON Power Down Power Down Power Off
PCMCIA ON Power Down Power Down Power Off
Super I/O ON Power Down Power Off Power Off
AUDIO ON Power Down Power Off Power Off
Audio AMP ON Power Down Power Off Power Off
LCD Backlight ON Power Off Power Off Power Off
Serial Port ON Power Down Power Down Power Off
IR Module ON Power Down Power Off Power Off
LAN ON Power Down Power Down Power Down
Internal Modem ON Power Down Power Down Power Down
l Device PM control during Stand By mode
Device
CPU Hardware Controlled by SUS_STAT1# pin
L2 CACHE Hardware Controlled by BIOS
SISM650 Hardware Controlled by SUS_STAT1# pin
SIS962 Working
DRAM Hardware Self Refresh
Clock Synthesizer Hardware Controlled by SUSA# pin
CDROM Software CDROM support power down command
HDD Software HDD support power down command
FDD (M785 Not
support)
KBC Working
VGA/VRAM Software Controlled by SISM650
PCMCIA Software Controlled by Driver enter Dx status
Super I/O Software Controlled by SIS962
AUDIO Software Controlled by SIS962
Audio AMP Software Controlled by BIOS
LCD Backlight Hardware Controlled by VGA chip
Serial Port Software Controlled by PMU08 GPIO[B3] pin
IR Module Software IR module support power down command
LAN Software LAN support power down command
Internal Modem Software Modem support power down command
Power
Controlled by
Software FDD support power down command
Description
FIC M785 Service Manual 3-21
PDF created with FinePrint pdfFactory Pro trial version http://www.pdffactory.com
Page 22

Software Functional Overview
l Device PM control during STR mode
Device
CPU Hardware Controlled by SUSB# pin
L2 CACHE Hardware Power off
SIS962 Hardware Controlled by SUSB# pin
DRAM Software Self Refresh
Clock Synthesizer Hardware Controlled by SUSB# pin
CDROM Hardware Power off
HDD Hardware Power off
FDD (M785 Not
support)
KBC Software Controlled by ENE KB3886 power down
PMU08 Sofeware Controlled by PMU08 power down command
VGA/VRAM Software Controlled by SISM650
PCMCIA Software Controlled by SUSB# pin
Super I/O Hardware Controlled by SIS962
AUDIO Hardware Controlled by SIS962
Audio AMP Hardware Controlled by BIOS
LCD Backlight Hardware Power off
Serial Port Software Controlled by PMU08 GPIO[B3] pin
IR Module Hardware Controlled by SUSB# pin
LAN Hardware Controlled by Driver enter Dx status
Internal Modem Hardware Controlled by Driver enter Dx ststus
Power Down
Controlled by
Hardware Power off
command
Description
3-22 FIC M785 Service Manual
PDF created with FinePrint pdfFactory Pro trial version http://www.pdffactory.com
Page 23

Software Functional Overview
3.6.1 Expanding Event Through the Embedded Controller
The following figure shows the relationships between the devices that are wired to the
embedded controller, the embedded controller queries, and ACPI general
FIC M785 Service Manual 3-23
PDF created with FinePrint pdfFactory Pro trial version http://www.pdffactory.com
Page 24

Software Functional Overview
l SCI Source and Query Event from M38867
PMU08 Input Event GPE Event Handler
ADPIN# AC Plug In/Out GPI1 AML Handler
BAT0# Battery Plug In/Out GPI1 AML Handler
GPIOA0 LID Event RI AML Handler
GPIOA3 Keyboard SMI RI AML Handler
GPIOA6 PCMCIA Ring In RI AML Handler
GPIOA7 COM Port Ring In RI AML Handler
THRM Thermal Event GPI1 AML Handler
The system will issue a beep to inform user while the following SCI alerted:
§ AC (AC status change) update battery information.
§ BAT ( Battery status change) update battery information.
§ Lid (Lid close/open event) update Lid position status.
§ RI10 COM Port Ring Event
§ PCMRI10 PCMCIA Ring Event
§ THRM0 (Thermal event) update thermal level information
l Control Method Battery Subsystem
EC should support all the battery information to ACPI-OS
− Designed Battery capacity
− Designed Voltage
− Designed Low battery capacity
− Designed Low – Low battery capacity
− Latest Full charged capacity
− Present Remaining capacity
− Present drain rate
− Present voltage
− Present Battery Status
ACPI BIOS should support an independent device object in the name space, and
implement the following methods.
3-24 FIC M785 Service Manual
PDF created with FinePrint pdfFactory Pro trial version http://www.pdffactory.com
Page 25

Software Functional Overview
3.6.2 Thermal Control
There are three primary cooling policies that the OS use to control the thermal state of
the hardware.
Cooling Policy
Action cooling Fan On Always On
Action cooling Fan High On
Fan High Off
Passive cooling Throttling CPU On
Throttling CPU Off
Critical trip point System Shutdown
ACPI allows OS to be proactive in its system cooling policies. With OS in control of the
operating environment, cooling decisions can be made based on application load on the CPU
and the thermal heuristics of the system. Graceful shutdown of OS at critical heat levels
becomes possible as well. The following sections describe the thermal objects available to OS
to control platform temperature. ACPI expects all temperatures to be given in tenths of Kelvin.
The ACPI thermal design is based around regions called thermal zones. Generally, the entire
PC is one large thermal zone, but an OEM can partition the system into several thermal zones
if necessary.
l Active, Passive, and Critical Policies
There are three primary cooling policies that the OS uses to control the thermal state of the
hardware. The policies are Active, Passive and Critical:
− Passive cooling: The OS reduces the power consumption of the system to reduce the
thermal output of the machine by slowing the processor clock. The _PSV control
method is used to declare the temperature to start passive cooling.
− Active cooling: The OS takes a direct action such as turning on a fan. The _ACx
control methods declare the temperatures to start different active cooling levels.
− Critical trip point: This is the threshold temperature at which the OS performs an
orderly, but critical, shut down of the system. The _CRT object declares the critical
temperature at which the OS must perform a critical shutdown.
Action
Temperature Setting
Over 55oC
Below 50oC
Over 70oC
Below 60oC
Over 80oC
When a thermal zone appears, the OS runs control methods to retrieve the three temperature
points at which it executes the cooling policy. When the OS receives a thermal SCI it will run
the _TMP control method, which returns the current temperature of the thermal zone. The OS
checks the current temperature against the thermal event temperatures. If _TMP is greater
than or equal to _ACx then the OS will turn on the associated active cooling device(s). If
_TMP is greater than or equal to _PSV then the OS will perform CPU throttling. Finally if
_TMP is greater than or equal to _CRT then the OS will shutdown the system.
An optimally designed system that uses several SCI events can notify the OS of thermal
increase or decrease by raising an interrupt every several degrees. This enables the OS to
FIC M785 Service Manual 3-25
PDF created with FinePrint pdfFactory Pro trial version http://www.pdffactory.com
Page 26

Software Functional Overview
anticipate _ACx, PSV, or _CRT events and incorporate heuristics to better manage the
systems temperature.The operating system can request that the hardware change the priority
of active cooling vs passive cooling.
l Dynamically Changing Cooling Temperatures
An OEM can reset _ACx and _PSV and notify the OS to reevaluate the control methods to
retrieve the new temperature settings. The following three causes are the primary uses for this
thermal notification:
− When a user changes from one cooling mode to the other.
− When a swappable bay device is inserted or removed. A swappable bay is a slot that
can accommodate several different devices that have identical form factors, such as a
CD-ROM drive, disk drive, and so on. Many mobile PCs have this concept already in
place.
− When the temperature reaches an _ACx or the _PSV policy settings
In each situation, the OEM-provided AML code must execute a Notify ( thermal_zone, 0x80)
statement to request the OS to re-evaluate each policy temperature by running the _PSV and
_ACx control methods.
n Resetting Cooling Temperatures from the User Interface
When the user employs the UI to change from one cooling mode to the other, the
following occurs:
1. The OS notifies the hardware of the new cooling mode by running the Set
Cooling Policy (_SCP) control method.
2. When the hardware receives the notification, it can set a new temperature
for both cooling policies and notify the OS that the thermal zone policy
temperatures have changed.
3. The OS re-evaluates _PSV and _ACx.
n Resetting Cooling Temperatures to Adjust to Bay Device
Insertion or Removal
The hardware can adjust the thermal zone temperature to accommodate the
maximum operating temperature of a bay device as necessary. For example,
1. Hardware detects that a device was inserted into or removed from the bay
and resets the _PSV and/or _ACx and then notifies the OS of the thermal
and device insertion events.
2. The OS reenumerates the devices and reevaluates _PSV and _ACx.
n Resetting Cooling Temperatures to Implement Hysteresis
An OEM can build hysteresis into platform thermal design by dynamically
resetting cooling temperatures. For example,
3-26 FIC M785 Service Manual
PDF created with FinePrint pdfFactory Pro trial version http://www.pdffactory.com
Page 27

_AC1
_PSV
_CRT
_AC0
Software Functional Overview
1. When the heat increases to the temperature designated by _ACx, the OS
will turn on the associated active cooling device and the hardware will
reset the ACx value to a lower temperature.
2. The hardware will then run the Notify command and the OS will
reevaluate the new temperatures. Because of the lower _ACx value now,
the fan will be turned off at a lower temperature than when turned on.
3. When the temperature hits the lower _ACx value, the OS will turn off the
fan and reevaluate the control methods when notified.
3.6.3 Hardware Thermal Events
An ACPI-compatible OS expects the hardware to generate a thermal event notification
through the use of the SCI. When the OS receives the SCI event, it will run the _TMP control
method to evaluate the current temperature. Then the OS will compare the value to the
cooling policy temperatures. If the temperature has crossed over one of the three policy
thresholds, then the OS will actively or passively cool (or stop cooling) the system, or
shutdown the system entirely.
This is an SCI and you
can define how ever
many as necessary
Both the number of SCI events to be implemented and the granularity of the temperature
separation between each SCI event is OEM-specific. However, it is important to note that
since the OS can use heuristic knowledge to help cool the system, the more events the OS
receives the better understanding it will have of the system thermal characteristic.
3.6.4 Active Cooling Strength
The Active cooling methods (_Acx) in conjunction with active cooling lists (_ALx), allows an
OEM to use a device that offers varying degrees of cooling capability or multiple cooling
devices. The _ACx method designates the temperature at which the Active cooling is enabled
or disabled (depending upon the direction in which the temperature is changing). The _ALx
method evaluates to a list of devices that actively cool the zone. For example:
• If a standard single-speed fan is the Active cooling device, then the policy is
represented by the temperature to which _AC0 evaluates, and the fan is listed in
_AL0.
90
85
80
75
60
55
50
45
40
35
30
25
20
15
10
5
Method
SCI Event
FIC M785 Service Manual 3-27
PDF created with FinePrint pdfFactory Pro trial version http://www.pdffactory.com
Page 28

Software Functional Overview
• If the zone uses two independently-controlled single-speed fans to regulate the
temperature, then _AC0 will evaluate to the maximum cooling temperature using two
fans, and _AC1 will evaluate to the standard cooling temperature using one fan.
• If a zone has a single fan with a low speed and a high speed, the _AC0 will evaluate
to the temperature associated with running the fan at high-speed, and _AC1 will
evaluate to the temperature associated with running the fan at low speed. _AL0 and
_AL1 will both point to different device objects associated with the same physical fan,
but control the fan at different speeds.
3.6.5 Passive Cooling Equation
Unlike the case for _ACx, during passive cooling the OS takes the initiative to actively
monitor the temperature in order to cool the platform. On an ACPI-compatible platform that
properly implements CPU throttling, the temperature transitions will be similar to the
following figure.
100%
T
n - 1
∆
P
CPU Performance
Temperature
T
t
_TSP (Sampling period)
T
n
Time
50%
For the OS to assess the optimum CPU performance change required to bring the temperature
down, the following equation must be incorporated into the OS.
∆P [%] = _TC1 * ( Tn - Tn-1 ) + _TC2 * (Tn - Tt)
where
Tn = current temperature
Tt = target temperature (_PSV)
The two coefficients _TC1 and _TC2 and the sampling period _TSP are hardware-dependent
constants the OEM must supply to the OS (for more information, see section 12.3). The
object _TSP contains a time interval that the OS uses to poll the hardware to sample the
temperature. Whenever _TSP time has elapsed, the OS will run _TMP to sample the current
temperature (shown as Tn in the above equation). Then the OS will use the sampled
temperature and _PSV (which is the target temperature Tt) to evaluate the equation for ∆P.
The granularity of ∆P is determined by the CPU duty width of the system. A detailed
explanation of this thermal feedback equation is beyond the scope of this specification.
3-28 FIC M785 Service Manual
PDF created with FinePrint pdfFactory Pro trial version http://www.pdffactory.com
Page 29

Software Functional Overview
3.6.6 Critical Shutdown
When the heat reaches the temperature indicated by _CRT, the OS must immediately
shutdown the system. The system must disable the power either after the temperature reaches
some hardware-determined level above _CRT or after a predetermined time has passed.
Before disabling power, platform designers should incorporate some time that allows the OS
to run its critical shutdown operation. There is no requirement for a minimum shutdown
operation window that commences immediately after the temperature reaches _CRT. This is
because
− Heat might rise rapidly in some systems and slower on others, depending on casing
design and environmental factors.
− Shutdown can take several minutes on a server and only a few short seconds on a
hand-held device.
Because of this indistinct discrepancy and the fact that a critical heat situation is a remarkably
rare occurrence, ACPI does not specify a target window for a safe shutdown. It is entirely up
to the OEM to build in a safe buffer that it sees fit for the target platform.
3.6.7 Other Implementation of Thermal Controllable
Devices
The ACPI thermal event model is flexible enough to accommodate control of almost any
system device capable of controlling heat. For example, if a mobile PC requires the battery
charger to reduce the charging rate in order to reduce heat it can be seamlessly implemented
as an ACPI cooling device. Associating the charger as an active cooling device and reporting
to the OS target temperatures that will enable or disable the power resource to the device do
this. Figure as following illustrates the implementation. Because the example does not create
noise, this will be an implementation of silence mode.
90
85
80
75
60
55
50
45
40
35
30
25
20
15
10
5
_CRT
_AC0
_PSV
_AC1
Fan on/off
Throttle CPU
Reduce charge
rate
FIC M785 Service Manual 3-29
PDF created with FinePrint pdfFactory Pro trial version http://www.pdffactory.com
Page 30

Software Functional Overview
3.6.8 Thermal Control Methods
Control methods and objects related to thermal management are listed in the table below.
Object Description
_ACx Returns Active trip point in tenths Kelvin
_ALx List of pointers to active cooling device objects
_CRT Returns critical trip point in tenths Kelvin
_PSL List of pointers to passive cooling device objects
_PSV Returns Passive trip point in tenths Kelvin
_SCP Sets user cooling policy (Active or Passive)
_TC1 Thermal constant for Passive cooling
_TC2 Thermal constant for Passive cooling
_TMP Returns current temperature in tenths Kelvin
_TSP Thermal sampling period for Passive cooling in tenths of seconds
l _Acx
This control method returns the temperature at which the OS must start or stop Active cooling,
where x is a value between 0 and 9 that designates multiple active cooling levels of the
thermal zone. If the Active cooling device has one cooling level (that is, n”) then that cooling
level is named _AC0. If the cooling device has two levels of capability, such as a high fan
speed and a low fan speed, then they are named _AC0 and _AC1 respectively. The smaller
the value of x, the greater the cooling strength _ACx represents. In the above example, _AC0
represents the greater level of cooling (the faster fan speed) and _AC1 represents the lesser
level of cooling (the slower fan speed). For every ACx method, there must be a matching ALx
method.
Arguments: None.
Result Code: Temperature in tenths Kelvin
The result code is an integer value that describes up to 0.1 precisions in Kelvin. For example,
300.0K are represented by the integer 3000.
l _ALx
This object evaluates to a list of Active cooling devices to be turned on when the associated
_ACx trip point is exceeded. For example, these devices could be fans.
l _CRT
This control method returns the critical temperature at which the OS must shutdown the
system.
Arguments: None.
Result Code: Temperature in tenths Kelvin
The result is an integer value that describes up to 0.1 precisions in Kelvin. For example,
3-30 FIC M785 Service Manual
PDF created with FinePrint pdfFactory Pro trial version http://www.pdffactory.com
Page 31

Software Functional Overview
300.0K are represented by the integer 3000.
l _PSL
This object evaluates to a list of processor objects to be used for Passive cooling.
l _PSV
This control method returns the temperature at which the OS must activate CPU throttling.
Arguments: None.
Result Code: Temperature in tenths Kelvin.
The result code is an integer value that describes up to 0.1 precision in Kelvin. For example,
300.0 Kelvin is represented by 3000.
l _SCP
This control method notifies the hardware of the current user cooling mode setting. The
hardware can use this as a trigger to reassign _ACx and _PSV temperatures. The operating
system will automatically evaluate _ACx and _PSV objects after executing _SCP.
Arguments: 0 - Active; 1 - Passive
Result Code: None.
l _TC1
This is a thermal object that evaluates to the constant _ TC1 for use in the Passive cooling
formula:
∆Performance [%]= _TC2 * ( Tn - Tn-1 ) + _TC1 * (Tn. - Tt)
l _TC2
This is a thermal object that evaluates to the constant _TC2 for use in the Passive cooling
formula:
∆Performance [%]= _TC2 * ( Tn - Tn-1 ) + _TC1 *.(Tn. - Tt)
l _TMP
This control method returns the thermal zone current operating temperature in Kelvin.
Argument: None.
Result Code: Temperature in tenths Kelvin.
The result is an integer value that describes up to 0.1 precision in Kelvin. For example,
300.0K is represented by the integer 3000.
l _TSP
This is an object that evaluates to a thermal sampling period used by the OS to implement the
Passive cooling equation. This value, along with _TC1 and _TC2, will enable the OS to
provide the proper hysteresis required by the system to accomplish an effective passive
cooling policy. The granularity of the sampling period is 0.1second. For example, if the
sampling period is 30.0 seconds, then _TSP needs to report 300; if the sampling period is 0.5
seconds, then it will report 5. The OS can normalize the sampling over a longer period if
necessary.
FIC M785 Service Manual 3-31
PDF created with FinePrint pdfFactory Pro trial version http://www.pdffactory.com
Page 32

Software Functional Overview
3.6.9 AC Adapters and Power Source Objects
The Power Source objects describe the power source used to run the system.
Object Description
_PSR Returns present power source device
_PCL List of pointers to powered devices.
l _PSR
Returns the current power source devices. Used for the AC adapter and is located under the
AC adapter object in name space. Used to determine if system is running off the AC adapter.
Arguments: None
Results code: 0x00000000 = Off-line; 0x00000001 = On-line
l _PCL
This object evaluates to a list of pointers, each pointing to a device or a bus powered by the
power source device. Pointing a bus means that all devices under the bus is powered by it
power source device.
3.7 Battery Management
This notebook supports only Li-Ion Battery Pack. There is only one battery pack activating at
one time. The special designed Bridge Battery module can backup the system under Suspend
To RAM mode for a short period of time.
3.7.1 Battery Sub-system
§ The charger will stop charge the battery when the following condition is detected.
- The temperature of the system is too high
- The remaining capacity is 95% and more.
Note that the battery life is depend on different configuration running. E.g. with
CD-ROM battery life is shorter, document keyin only battery life is longer, PMU
disable battery life is short, PMU enable battery life is longer.
- Battery reading methodology is through PMU08 SMBus.
-
3.7.2 Battery Low Warning
When the battery voltage is approaching to the Low level, the PMU08 will generate
a battery low SMI. The system will do the following action.
1) The Power Indicator will become blinking.
2) The system will issue a Warning beep.
3.7.3 Battery Low
When the battery voltage is approaching to the Low-Low level, the PMU08 will
generate a battery low-low SMI. The system will do the following action.
1) The Power Indicator will keep on Blinking.
2) The system will enter Suspend To Disk mode even the power management is disabled.
The function of power-on or Resume will be inhibited until the battery Low – Low
condition is removed.
3-32 FIC M785 Service Manual
PDF created with FinePrint pdfFactory Pro trial version http://www.pdffactory.com
Page 33

Software Functional Overview
3.7.4 AC Adapter
When plug in the AC adapter, the system will do the following action:
- The charger will charge the Main Battery, if remaining capacity is not full.
- The Battery Charging Indicator will turn on if the battery is in changing mode.
3.8 PMU08
The embedded controller PMU08 acts as a supplement for power management control. It
supports a lot of functions via SMBus interface.
3.8.1 The System EC RAM With PMU08
Embedded Controller Command Set
The EC I/F command set allows the OS to communicate with the PMU08.
For detail information refer to ACPI 1.0B specification.
EC I/F
Command
Read Embedded
Controller
(RD_EC)
Write Embedded
Controller
(WR_EC)
Embedded
Controller
(BE_EC)
Burst Disable
Embedded
Controller
(BD_EC)
Embedded
Controller
(QR_EC)
Command
Byte
Encoding
0x80
0x81
0x82
0x83 #1 EC_SC W Command byte
0x84
Byte
#1 EC_SC W Command byte
#2 EC_DA
#3 EC_DA
#1 EC_SC W Command byte
#2 EC_DA
#3 EC_DA
#1 EC_SC W Command byte
#2 EC_DA
#1 EC_SC W Command byte
#2 EC_DA
Register
TA
TA
TA
TA
TA
TA
R
/
W
W Address byte to
R Read data to host Interrupt on
W Address byte to
W Data to write Interrupt on
R Burst
R Query value to
Description Interrupt
Interrupt on
Header
read
Header
write
Header
acknowledge byte
Header
Header
host
IBF=0
No Interrupt
OBF=1
Interrupt on
IBF=0
Interrupt on
IBF=0
IBF=0
No Interrupt Burst Enable
Interrupt on
OBF=1
Interrupt on
IBF=0
No Interrupt Query
Interrupt on
OBF=1
3.8.2 PMU08 EC RAM List
The micro controller PMU08 acts as a supplement for power management control. It supports
the following functions via SMBus Command ( 0x80 , 0xC0 )
FIC M785 Service Manual 3-33
PDF created with FinePrint pdfFactory Pro trial version http://www.pdffactory.com
Page 34

Software Functional Overview
Function Address
0Ah
0Ch
0Eh
1st Battery
[ _BIF ]
Register Bit Number
Name
00h
Power unit R(/W)
*3
02h
Design
*3
capacity
Last Full
04h
Charge
*3
Capacity
06h
Battery
*3
Technology
08h
Design
*3
Voltage
Design
capacity of
*3
Warning
Design
capacity of
*3
Low
Battery
capacity
*3
Granularity 1
Battery
10h
capacity
*3
Granularity 2
12h
Model
*3
number
14h
Serial
*3
Number
16h
Battery type R(/W)
*3
18h
OEM
*3
Information
R/W
R(/W)
R(/W)
R(/W)
R(/W)
R(/W)
R(/W)
R(/W)
R(/W)
R(/W)
R(/W)
R(/W)
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
DATA[15:0] *1 - 0xffff
DATA[15:0] *1 - 0xffff
DATA[15:0] *1 - 0xffff
DATA[15:0] *1 - 0xffff
DATA[15:0] *1 - 0xffff
DATA[15:0] *1 - 0xffff
DATA[15:0] *1 - 0xffff
DATA[15:0] *1 - 0xffff
DATA[15:0] *1 - 0xffff
DATA[15:0] *1 - 0xffff 0x0000 [Not support]
DATA[15:0] *1 - 0xffff 0x0000 [Not support]
DATA[15:8]
*1
All bits are 0
DATA
[15:8]
*1
All bits
are 0
CELL_TYP
[7:0]
Vender[7:0] - 0xffff
Logic Default Description
E
- 0xffff
0x0000: mWh [Fixed value]
0xffff: Unknown
0x0000-0xfffe(mWh)
0xffff: Unknown
0x0000-0xfffe(mWh)
0xffff: Unknown
0x0000 : Primary
0x0001: Secondary [Fixed value]
0xffff: Unknown.
0x0000-0xfffe(mV)
0xffff: Unknown
0x0000-0xfffe(mWh)
0xffff: Unknown
0x0000-0xfffe(mWh)
0xffff: Unknown
0x0000-0xfffe(mWh)
0xffff: Unknown
0x0000-0xfffe(mWh)
0xffff: Unknown
CELL_TYPE [3:0] This code
depends on battery data format. In the
future, this code may be added.
0x00: NiMH
0x01: Li-ion
0x10: Non-rechargeable battery
(Reserved)
Vender [7:0] This code depends on
battery data format.
And the following name should be
described in the ASL with the same
character code.
In the future, these codes will be
added.
0: “MoliEnergy”
1: “Panasonic”
2: (SANYO does not agree the vender
name display)
3: “TBCL” (Toshiba)
4: “Sony”
*1: The register type is word.
*3: This register is not cleared if the system is in S4-S5 state.
R(/W): This is the read only register, but the written data will be able to read back till PMU updates the data
periodically, or PMU detects the status change.
3-34 FIC M785 Service Manual
PDF created with FinePrint pdfFactory Pro trial version http://www.pdffactory.com
Page 35

R I T C H G D C H G
0x00 :DATA size is 2 byte. (PMU06)
Software Functional Overview
Function Address
1Ah
1st Battery
[ _BST ]
1st Battery
[ _BTP ]
2nd
Battery
[ _BIF ]
2nd
Battery
[ _BST ]
2nd
Battery
[ _BTP ]
1st Battery
[_BIF]
1st Battery
[_BST]
1st Battery
[_BTP]
Battery
[_BIF]
2nd
Battery
[_BST]
2nd
Battery
[_BTP]
1Ch
1Eh
20h
22h
24h
3Ch
3Eh
44h
46h *2 *2 *2 *2 *2 *2
48h
49h
4Ah
4Bh
4Ch
4Dh
4Eh
4Fh
50h
51h
6Bh
*1: The register type is word.
*2: Same as 1st Battery CMBatt Data
*3: This register is not cleared if the system is in S4-S5 state.
R(/W): This is the read only register, but the written data will be able to read back till PMU updates the data
Register Bit Number
Name
Battery State R(/W)
*3
Battery
*3
Present rate
Battery
Remaining
*3
Capacity
Battery
present
*3
Voltage
Battery Trip
Point
to
*3
to
*3
Battery data
Size
Design
capacity
Last Full
Charge
Capacity
Battery
Remaining
Capacity
Battery Trip
Point
Design
capacity
Last Full
Charge
Capacity
Battery
Remaing
Capacity
Battery Trip
Point
to
Reserved R/W Don’t care - -
*3
periodically, or PMU detects the status change.
R/W
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
DATA[15:3] *1
All bits are 0
R(/W)
R(/W)
R(/W)
R/W DATA[15:0] *1 - 0x0000
*2 *2 *2 *2 *2 *2
*2 *2 *2 *2 *2 *2
R(/W)
R(/W)
R(/W)
R(/W)
R(/W)
R(/W)
R/(/W) DATA[23:16] *1 *7 - 0xff
R(/W)
R(/W)
DATA[15:0] *1 - 0xffff
DATA[15:0] *1 - 0xffff
DATA[15:0] *1 - 0xffff
DATA[7:0] - -
DATA[23:16] *1 *7 - 0xff
DATA[23:16] *1 *7 - 0xff
DATA[23:16] *1 *7 - 0xff
DATA[23:16] *1 *7 - 0x00
DATA[23:16] *1 *7 - 0xff
DATA[23:16] *1 *7 - 0xff
DATA[23:16] *1 *7 0x00
C
Logic Default Description
- -
DCHG=1:
CHG =1 :
CRIT =1 :
0x0000-0xfffe(mW)
0xffff: Unknown
0x0000-0xfffe(mWh)
0xffff: Unknown
0x0000-0xfffe(mV)
0xffff: Unknown
0x0000 :Clear the trip point
0x0001-0xffff(mWh)
0x01 : DATA size is 3byte.(PMU06A)
*8
PMU06A use this data with 02/03h.
*7 *8
PMU06A use this data with 04/05h.
*7 *8
PMU06A use this data with 1E/1Fh.
*7 *8
PMU06A use this data with 22/23h.
*7 *8
PMU06A use this data with 26/27h.
*7 *8 2nd
PMU06A use this data with 28/29h.
*7 *8
PMU06A use this data with 42/43h.
*7 *8
PMU06A use this data with 46/47h.
*7 *8
The battery is
discharged
The battery is
charged
The battery is
critical (Empty)
FIC M785 Service Manual 3-35
PDF created with FinePrint pdfFactory Pro trial version http://www.pdffactory.com
Page 36

O N E A L R M R E S
E S
E S
R T
The SMBus address
) protection
Software Functional Overview
Function Address
6Ch
PMU
Access
SMBus
Reserved
6Dh
6Eh
6Fh PMU_DATA R/W DATA [7:0] - -
70h
71h
72h SMB_ADDR R/W
73h SMB_CMD R/W COMMAND - 74h
93h
94h SMB_BCNT R/W RES[7:5] BCNT[4:0] - -
95h
96h
97h
98h SMB_CNRL R/W RES[7:1]
99h
9Fh
*7: When this register is checked by polling, the interval time is necessary more than 500usec.
R(/W): This is the read only register, but the written data will be able to read back till PMU updates the data
Register Bit Number
Name
PMU_LOW_
ADR
PMU_HIG_
ADR
CHECK_
SUM
SMB_PTCL R/W PROTOCOL[7:0] - -
*7
SMB_STS R/W
*7
SMB_DATA
to
[0-31]
SMB_
ALARM_
ADDR
AMB_
to
ALARM_
DATA[0-1]
to
Reserved R/W Don't care - -
periodically, or PMU detects the status change.
R/W
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
R/W DATA [7:0] - -
R/W DATA [15:8] - -
R/W DATA [7:0] - -
D
R/W DATA - -
R(/W)
R(/W)
ADDRESS[6:0]
STATUS
[4:0]
ADDRESS
[6:0]
DATA - -
R
R
P
Logic Default Description
These registers are available when
PMU slave mode or charger mode is
selected.
For detail information, refer to PMU
slave communication section in this
document
- -
- -
- -
0x00
For detail information, refer to ACPI
1.0 specification
[ 13.9 SMBus Host controller
Interface via Embedded controller]
These registers are not available when
PMU slave mode or charger mode is
selected.
The PMU06 has access protect
function for the EEPROM in the
battery, to cancel the protection, set
the access protect cancel bit.
For detail, refer to SMBus section
PRT =1 :
(A8-AE
is cancelled.
3-36 FIC M785 Service Manual
PDF created with FinePrint pdfFactory Pro trial version http://www.pdffactory.com
Page 37

O N
B T P E M P L O W W A R E R R D C H G C H G C O N
E S
0
To clear the notified event flag
without unexpected event loss, clear
For this operation, this register has
(STS_X) AND (Written
T P 2 S M B A L R T G P I O R E S B A T 2 B A T 1 A D P
H
H
E R R L O W H I G H
To clear the notified event flag
without unexpected event loss, clear
For this operation, this register has
(STS_X) AND (Written
Function Address
A0h
*3
A1h
*3
A2h
*3
A3h
*3
A4h
*3
A5h
*3
A6h
*3
A7h
Status
A8h
*5
A9h
*5
AAh
*5
ABh
*5
ACh
*5
ADh
*5
AEh
*5
AFh
*5
Software Functional Overview
Register Bit Number
Name
ADP_STS R(/W)
BAT1_STS
(1st Battery)
BAT2_STS
(2nd Battery)
Reserved R/W Don’t care - -
BAT1_CAP R(/W)
BAT2_CAP R(/W)
Reserved R/W Don’t care - -
SMB_Alert_
ADDR
GPIO-A_
EVT_STS
GPIO-B_
EVT_STS
GPIO-C_
EVT_STS
RUN_
EVT_STS
WAKE_
EVT_STS
RUN_
EVT_STS_2
WAKE
EVT_STS_2
THERMAL_
EVT_STS
R/W
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
RES[7:1]
R(/W)
R(/W)
BCAP - -
BCAP - -
R/W ADDRESS[6:0]
R/W STS_A [7:0] 0x00
R/W 0 STS_B [6:0] 0x00
R/W 0 0 0 0 0
R/W 0x00
B
R/W
R/W Reserved [7:1]
R/W Reserved [7:1]
R/W Reserved [7:3]
STS
_C
[1:0]
Logic
C
R
Read
0:No
event
1:EVT
detection
Write
0:Clear
event
1:Ignore
Read
0:No
event
1:EVT
detection
Write
0:Clear
event
1:Ignore
T
T
De-
Description
fault
- - CON = 1 : AC adapter is connected
- -
- -
- 0x00
BTP =1:
EMP =1:
LOW =1:
WAR=1:
ERR =1:
DCHG=1:
CHG=1:
CON=1:
0x00-0x64 = 0-100(%)
0x7F = Unknown
0x80 = Not installed
SMBAlert output device address
The alert response function is
available when this register is cleared
(0x00) only.
When the several devices assert the
alert signal at the same time, the least
address is stored to this register. And
when this register is cleared , next
alert address is stored to this register.
the corresponding bit flag only.
special writing manner as follows.
STS_X ß
0x00
data)
BTP2 =1:
SMB =1 :
ALRT=1 :
GPIO =1 :
BATn=1 :
ADP =1 :
TH =1 :
HIGH=1 :
0x00
LOW =1 :
ERR =1 :
0x00
the corresponding bit flag only.
0x00
special writing manner as follows.
STS_X ß
0x00
data)
Battery trip point is
detected.
Battery is empty.
Battery is Low battery
Battery is warning state.
Battery is Warning state.
Battery is Error state.
Battery is discharged.
Battery is charged.
Battery is connected.
BTP2 event is detected
SMBus event is detected.
SMBAlert is detected.
GPIO event is detected.
Battery event is detected.
Battery event is detected.
Thermal event is
detected
High alarm point is
detected.
Low alarm point is
detected.
Polling communication
failure with retry.
*3: This register is not cleared if the system is in S4-S5 state.
*5: After writing to this register, Set the “00h” to the BURST_FLG_CLR register.
FIC M785 Service Manual 3-37
PDF created with FinePrint pdfFactory Pro trial version http://www.pdffactory.com
Page 38

7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
B T P 2 S M B A L R T
D P
B T P E M P L O W W A R E R R C A P C / D C O N
1: Rising
1: Rising
Function Address
B0h
B1h
B2h
B3h
B4h
B5h
B6h
Event/
GPIO
Control
B7h
B8h
B9h
BAh
BBh
BCh
BDh
BEh
BFh
*4: Should be 0.
Software Functional Overview
Register Bit Number
Name
EC_RUN_
ENB
EC_WAKE_
ENB
BATT_RUN_
ENB
BATT_WAKE
_ENB
GPIO-A_
IO_CONF
GPIO-A_
DATA
GPIO-A_
RUN_ENB
GPIO-A_
EVT_POL
GPIO-A_
WAKE_ENB
GPIO-B_
IO_CONF
GPIO-B_
DATA
GPIO-B_
RUN_ENB
GPIO-B_
EVT_POL
GPIO-B_
WAKE_ENB
GPIO-C_
DATA
GPIO-C_
RUN_ENB
R/W
R/W
R/W
R/W
R/W
R/W
R/W
R/W RUN_ENB_A [7:0]
R/W
R/W WAKE_ENB_A [7:0]
R/W 1 CONF_B [6:0]
R/W 0 DATA_B [6:0] -
R/W 0 RUN_ENB_B [6:0]
R/W 0
R/W 0 WAKE_ENB_B [6:0]
R/W
R/W 0 0 0 0 0 0
CONF_A [7:0]
DATA_A [7:0] -
POL_A [7:0]
POL_B [6:0]
RES [7 :4]
*4
RES[4:1]
DATA_C
[3:0]
RUN_
ENB_
C
[1:0]
0:
Disable
1:
A
Enable
0:
Disable
1:
Enable
0:
Disable
1:
Enable
0:
Disable
1:
Enable
0: Input
1:
Output
0:
Disable
1:
Enable
0:
Falling
edge
edge
0:
Disable
1:
Enable
0: Input
1:
Output
0:
Disable
1:
Enable
0:
Falling
edge
edge
0:
Disable
1:
Enable
0:
Disable
1:
Enable
Logic
De-
Description
fault
0x00
BTP2:
SMB :
ALRT:
ADP:
0x00
BTP:
EMP:
0x00
LOW:
WAR:
ERR:
CAP:
0x00
C/D:
CON:
0x00
0x00
0x00
0x00
0x80
For detail information, refer to GPIO
section in this document.
0x00
0x00
0x00
0x00
BTP2 event
SMBus event.
SMBAlert event.
Adapter event.
Battery trip point
Empty.
Low battery
Warning
Error
Capacity learning
Charge/Discharge
Battery presence
3-38 FIC M785 Service Manual
PDF created with FinePrint pdfFactory Pro trial version http://www.pdffactory.com
Page 39

Software Functional Overview
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
0
E_
_C
W A K E S C I
R E S
*4 Q _ R U N
W A K E _ O U T S U S _ X
n and SCI_EVT
=1: SCI is output when the
and OBF=0. SCI_EVT shows
reflected to RUN_EVT_STS
=1: Runtime event status is
=0: Runtime and Wakeup is
=1: Runtime and Wakeup is
(GPIO B6 is used as SUS_A
H
Function Address
C0h
C1h
C2h EVT_CONT R/W
Event/
GPIO
Control
C3h
C4h
C5h
To
C7h
C8h
*6
C9h
*6
CAh
*6
CBh D/A_CONT R/W
CCh WAKE_DIS R/W
*4: Should be 0.
*6: This register’s response time is 150usec max.
Register Bit Number
Name
GPIO-C_
EVT_POL
GPIO-C_
WAKE_ENB
EC_RUN_
ENB_2
EC_WAKE_
ENB_2
Reserved R/W
GPI_AD0 R AD0_DATA [7:0] - -
GPI_AD1 R AD1_DATA [7:0] - -
Reserved R/W
R/W
R/W 0 0 0 0 0
R/W 0 0 0 0 0 0
RES
[7:6]
R/W
R/W
Logic
0:
Falling
POL_
edge
C
1:
[1:0]
Rising
edge
WAK
0:
Disable
ENB
1:
Enable
[1:0]
0x00
0:
Disable
1:
Enable
Reserved [7:1]
Don’t care
Don’t care - -
DATA [7:0] - 0xff
DATA [7:0] - 0x00
T
0:
Disable
1:
Enable
- -
De-
Description
fault
0x00
0x00
WAKE
=0: Wake# output is “Level”.
=1: Wake# output is “Pulse”.
SCI
=0: SCI is always output by
event detectio
shows the query data is
stored. And next SCI is not
output until SCI_EVT is
cleared.
command set is not executed
the output SCI is for event
Q_RU
notification.
N
=0: Runtime event ststus is
register.
reflected to Query data.
WAKE
=0: Wake event output is
_OUT
always enable.( in S0-S3)
=1: Wake event output is
enable when SUS_X=L.
SUS_X
selected by SUS_B.
(GPIO B6 is enable)
selected by SUS_A.
input.)
0x00
TH: Thermal event
0x00
For detail information, refer to GPIO
section in this document.
0x00-0xfe: D/A converter output data
0xff : Battery capacity(%) output
0x00 : WAKE# output enable
0x01 : WAKE# output disable
FIC M785 Service Manual 3-39
PDF created with FinePrint pdfFactory Pro trial version http://www.pdffactory.com
Page 40

7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
C H
R D Y #
C H G 2 C H G 1
C H G 2 D C H G 1
Function Address
Software Functional Overview
Register Bit Number
Name
R/W
Logic
De-
fault
Description
BAT_CHG_
D0h
CONT
BAT_DCH_
D1h
PRI
BAT_DCH_
D2h
CONT
BAT_WAR_
Battery
control
D3h
ABS
BAT_LOW_
D5h
ABS
BAT_WAR_
D7h
REL
BAT_LOW_
D8h
REL
D9h
FULL_DATA R/W
*3
CC_CUR_
Dah
DATA
DBh
To
BTP2 R/W
DCh
DDh
To
Reserved R/W
DFh
*3: This register is not cleared if the system is in S4-S5 state.
R(/W): This is the read only register, but the written data will be able to read back till PMU updates the data
periodically, or PMU detects the status change.
R/W RES[7:5]
R/W RES[7:3]
R/W
R/W
R/W
R/W
R/W
R DATA [7:0] - 0x00
G
_
RES
[3:2]
PAT
[2:0]
D
RES[7:2]
DATA[15:0] *1 -
DATA[15:0] *1 -
DATA [7:0] - 0x10
DATA [7:0] - 0x06
DATA [7:0] - 0xbe
DATA [15:0] -
Don't care - -
- -
- 0x00
0: Not
discharge
1:
Discharge
CHG_RDY# =0 : Charge ready
CHGn =1 : The nth battery is
charged
Battery discharge priority
0 : 2 1
1 : 1 2
2 : 2 1
3 : 2 1
4 : 1 2
5 : 1 2
6 : Same as 0
7 : Simultaneously discharge (Read
only :This data can be set using
PMU register)
The discharge battery can be
selected one of the batteries can be
discharged.
Absolute capacity battery Warning
0x000
detection point
0
0x0000-0xffff (mWh)
Absolute capacity battery Low
0x000
detection point
0
0x0000-0xffff (mWh)
Relative capacity battery Warning
detection point
00-C8h (0-100% step 0.5%)
Relative capacity battery Low
detection point
00-C8h (0-100% step 0.5%)
Full charge cancel point
00-C8h (0-100% step 0.5%)
Battery charging current setting
0x01-0xff (0.02-5.10A step 0.02A)
0x00 Depends on the battery
This register is “read only”, to
change the value, use the register in
PMU registers area.
0x0000: Clear the trip point
0x0001-0xffff : (mWh)
0x000
When all of the battery’s capacities
0
lesser than this setting value, the
BTP2 is detected if event is enabled.
3-40 FIC M785 Service Manual
PDF created with FinePrint pdfFactory Pro trial version http://www.pdffactory.com
Page 41

7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
C _ R E G
B A Y _ L E D P O W _ L E D
EC_REG =1:
PMU does not initialize EC
PMU indicates the Battery
S _ S T S
E S
is value, the
If the received data LE this value, the
After writing to the register addressed
Function Address
Software Functional Overview
Register Bit Number
Name
R/W
Logic
De-
fault
Description
E
E0h PMU_CONT R/W
PMU
control
ACPI_ACC_
E1h
ENB
E2h OFF_TIME R/W
POLLING_
E3h
ADDRESS
HIGH_
E4h
ALARM
LOW_
E5h
ALARM
POLLING_
E6h
Thermal
Sensor
Polling
PMU
control
R(/W): This is the read only register, but the written data will be able to read back till PMU updates the data
INTERVAL
POLLING_
E7h
DATA
HARDWARE_
E8h
SHUT_DOWN
POLLING_
E9h
COMMAND
RETRY_
EAh
COUNT
EBh
To
Reserved R/W
EFh
BURST_FLG_
F0h
CLR
F1h
To
Reserved R/W
FFh
periodically, or PMU detects the status change.
R/W
R/W Slave Address [6:0]
R/W
R/W
R/W
R(/W)
R/W
R/W
R/W
R/W
RES[7:3]
RES [7:1]
DATA [7:0] - 0x64
DATA [7:0]
DATA [7:0]
DATA [7:0] 0x00
DATA [7:0]
DATA [7:0]
DATA [7:0] 0x00
DATA [7:0] 0x10
Don't care
DATA [7:0] - -
Don't care
- 0x00
O
- 0x00
R
0x00
Signed
value
Signed
value
Signed
value
Signed
value
BAY_LED
=1:
POW_LED
=1:
OS_STS = 1:
= 0:
Power switch over ride function timer
01h-FFh (0.1-25.5esc step 0.1sec)
00h : Reserved
Address: 0x00-0x7F
The polling slave address setting
If this address is 00, the Polling is
disabled.
If the received data GE th
0x00
event will be detected.
0x00
event will be detected.
0x00 :Polling disable
0x01 – 0xFF [x 250ms] (250ms to
63.75sec)
This register shows data at latest
0x00
polling.
If the thermal sensor read value GE
0x7D
this value, the PMU automatically off
the power.
Polling command (data register)
address.
0x00 - 0xFF: Retry count value (0-
255)
A8h-AFh,
Set the 00h to this register.
register when system
power is off.
discharge status to the
LED_BAY#n, when the
battery is installed.
The Power LED blink
ACPI mode
Legacy mode
FIC M785 Service Manual 3-41
PDF created with FinePrint pdfFactory Pro trial version http://www.pdffactory.com
Page 42

Software Functional Overview
3.9 Miscellaneous
3.9.1 Power Button
The system may have different action upon pressing the Power Button when the system is in
the different state.
System Power State Action for Pressing Power Button
Full-on Power Off
Stand by Power Off
STR Resume from STR
STD Resume from STD
SOff/MOff Power On
3.9.2 Security
The user may enter up to 8 standard text characters for a password. The password includes
two levels. The higher priority is the Supervisor Password. The lower priority is the User
Password. The Supervisor Password can access all the system resource, while the User
Password may not access the floppy disk when it is protected by Supervisor Password. Also,
the User Password may not access the floppy disk when the Supervisor Password protects it.
When the security function is enabled, the system will request the user to enter password
during the following situation:
• Power On → The system will prompt the user to enter the password before booting
the OS. If the user key in the wrong password for 3 times, then the system will halt.
• Resume → The system will prompt the user to enter password while resuming from
STR or STD mode. If the user keys in the wrong password for 3 times, the system
will not resume and should return to Suspend mode.
• Entering CMOS Setup → The system will prompt the user to enter the password
before entering the CMOS Setup. If the user keys in the wrong password for 3 times,
then the system will halt.
3.10 CMOS Setup Utility
The Setup utility is used to configure the system. The Setup contains the information
regarding the hardware for boot purpose. The changed settings will take effect after the
system rebooted. Refer to Chapter 1 on running BIOS Setup Program for more detailed
information.
3.11 Definitions of Terms
10Base-T (Ethernet) - A networking standard that supports data transfer rates up to
10Mbps (10 megabits per second).
100Base-T (Fast Ethernet) - A relatively new networking standard that supports data
transfer rates up to 100Mbps.
ACPI - Advanced Configuration and Power Management Interface, a power
management specification developed by Intel, Microsoft, and Toshiba.
CardBus - The 32-bit version of the PCMCIA PC Card standard. In addition to
3-42 FIC M785 Service Manual
PDF created with FinePrint pdfFactory Pro trial version http://www.pdffactory.com
Page 43

Software Functional Overview
supporting a wider bus (32 bits instead of 16 bits), CardBus also supports bus mastering
and operation speeds up to 33MHz.
Clock Throttling – South bridge function that allows the CPU clock to be stopped
and started at a known duty cycle using the STPCLK# pin to enter and exit Stop Grant
mode. Clock throttling is used for power saving, thermal management, and reducing the
processing speed.
DIMM (SODIMM) - Dual In-line Memory Module, a small circuit board that holds
memory chips. A Single In-line Memory Module (SIMM) has a 32-bit path to the
memory chips whereas a DIMM has 64-bit path. Because the Pentium processor
requires a 64-bit path to memory, you need to install SIMMs two at a time. With
DIMMs, you can install one DIMM at a time. SODIMM is Small Outline Dual In-line
Memory Module used in notebook computers.
DMI - Desktop Management Interface, an API to enable software to collect
information about a computer environment about a computer environment. For example,
using DMI a program can determine what hardware and expansion boards are installed
on a computer.
GPI - General Purpose Input.
GPO - General Purpose Output.
Lid Switch - A switch that indicates the notebook LCD Panel has been closed and it
can be turned off.
MPEG-2 - Moving Picture Experts Group, a working group of ISO. The term also
refers to the family of digital video compression standards developed by the group.
There are two major MPEG standards : MPEG-1 and MPEG-2. The most common
implementations of the MPEG-1 standard provide a video resolution 352x240 at 30
frames per second(fps). A newer standard, MPEG-2, offers resolution of 720x480 and
1280x720 at 60 fps, with full CD-quality audio.
North Bridge - The CPU to PCI interface, also contains the memory and cache
controllers.
South Bridge - The PCI to ISA interface, also contains many legacy devices.
SMM - System Management Mode, Mode of operation while an SMI is active.
SMI - System Management Interrupt, non-maskable interrupt that causes the system
to enter SMM. SMM functions include power management, USB legacy keyboard
control, security, hot keys, and thermal monitoring.
SMB - System Management Bus, that is used for managing smart batteries, reading
SDRAM configuration information, and other miscel1aneous system function.
TBD -To Be Discussed. The mentioned specification is not final that should be
discussed with related engineers.
Ultra DMA-33 - A protocol developed by Quantum Corporation and Intel that
supports burst mode data transfer rates of 33.3 MBps.
USB - A new external bus standard that supports data transfer rates of 12 MBps. A
single USB port can be used to connect up to 127 peripheral devices, such as mice,
modems, and keyboards. USB also supports Plug-and-Play installation and hot plugging.
FIC M785 Service Manual 3-43
PDF created with FinePrint pdfFactory Pro trial version http://www.pdffactory.com
 Loading...
Loading...