Page 1

Chapter
Troubleshooting & Repair
6.1 Introduction
This chapter provides the most common problem encountered with the A985 notebook
computer and some troubleshooting means. Some of the common problems are:
• System BIOS Related Problems
LCD Display Problems
•
• System Power and Boot-Up Problems
External Interface Problems (Serial, Printer, CRT, USB, PS/2)
•
• Audio Problems
PCMCIA Problems
•
• Power Management Problems
Input Device Problems (Keyboard and Glidepad)
•
6.1.1 Helpful Starters
Here are a few helpful starters to begin with before troubleshooting the notebook:
Is there any external power source connected to the computer?
•
• Does the battery installed been fully charged?
Is the computer turn on and the POWER LED activated?
•
Are all cables connected properly and securely?
•
Are all needed device drivers been installed properly?
•
Is the Power Management function enabled under OS Setup? Press any key to wake
•
system up again.
6.2 System BIOS Related Problems
This section provides you with information on how the BIOS handles errors encountered
during POST (Power On Self Test) and translate them to beep codes and error messages.
Refer to this whenever you encounter error messages or beep codes generated by the
computer during startup.
6.2.1 POST Messages
The following is a summary of the Phoenix BIOS startup error messages that is displayed
on the notebook’s screen. These messages help you in understanding some of the
notebook’s problems that may be corrected by entering the BIOS SETUP program and
checking the original values.
FIC A985 Service Manual 6-1
PDF created with FinePrint pdfFactory trial version http://www.fineprint.com
Page 2
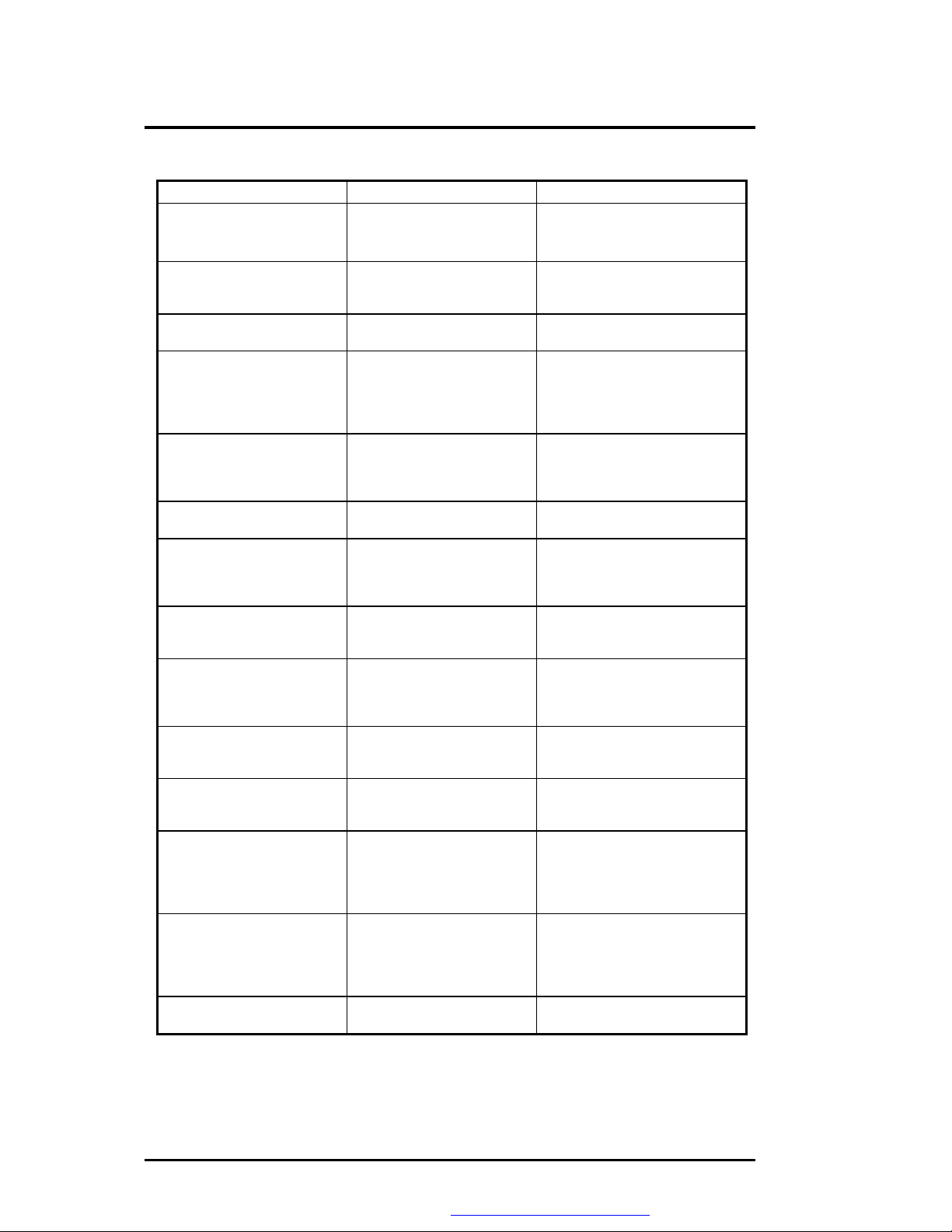
Troubleshooting and Repair
Table 6-1(a) POST Error Messages
Message Possible Cause Action
Diskette drive A failure The drive failed or is missing.
Floppy Disk Controller is
disabled.
Diskette read failure - press
F1 to retry boot, F2 for
SETUP utility
Display adapter failed,
using alternate
Gate A20 failure The keyboard controller is not
Fixed disk configuration
error
Fixed disk controller failure The fixed disk may be
Fixed disk read failurepress F1 to retry boot, F2
for SETUP utility
Pointer device failure The PS/2-style mouse failed. Try rebooting. If problem
No boot device available press F1 to retry boot, F2
for SETUP utility
No boot sector on fixed
disk – press F1 to retry
boot, F2 for SETUP utility
Not a boot diskette - press
F1 to retry boot, F2 for
SETUP utility
No timer tick interrupt The timer chip has failed. Check the system board, Turn
Shutdown failure Either the keyboard controller
Time of day not set - run
SETUP program
The diskette is either not
formatted or is defective.
The primary video adapter
failed.
accepting command,
specifically, the enable and
disable A20 command.
The specified configuration is
not supported or doesn't
match the actual hardware
installed.
defective.
The fixed disk may be
configured incorrectly or is
defective.
Either diskette drive A:, the
fixed disk, or both the
diskette and fixed disk are
defective.
The C: drive is not formatted
or is not bootable.
The diskette in drive A: is not
formatted as a bootable
diskette.
is not accepting the reset
command or the associated
reset logic has failed.
Real Time Clock not set. Run SETUP utility.
Check the drive to determine the
problem.
Enabled the FDD Controller.
Replace the diskette with a
bootable diskette and retry.
Check the primary video
adapter.
Check the keyboard controller
and system board. Turn the
power off, then back on again. If
the problem persists contact
qualified service personnel.
Correct the fixed disk
configuration.
Try rebooting. If that doesn't
work, replace the fixed disk.
Check the drive type selected in
SETUP. Try rebooting. If that
does not work, replace the fixed
disk.
persists, check the mouse, it's
cable and connector.
Try rebooting. If problem
persists, replace the diskette or
the fixed disk.
Format the C: drive and make it
bootable.
Replace the diskette with a
bootable diskette and try
rebooting.
the power off, then back on
again. If the problem persists,
contact qualified service
personnel.
Check the keyboard controller
and system board. Turn the
power off, then back on again. If
the problem persists, contact
qualified service personnel.
6-2 FIC A985 Service Manual
PDF created with FinePrint pdfFactory trial version http://www.fineprint.com
Page 3
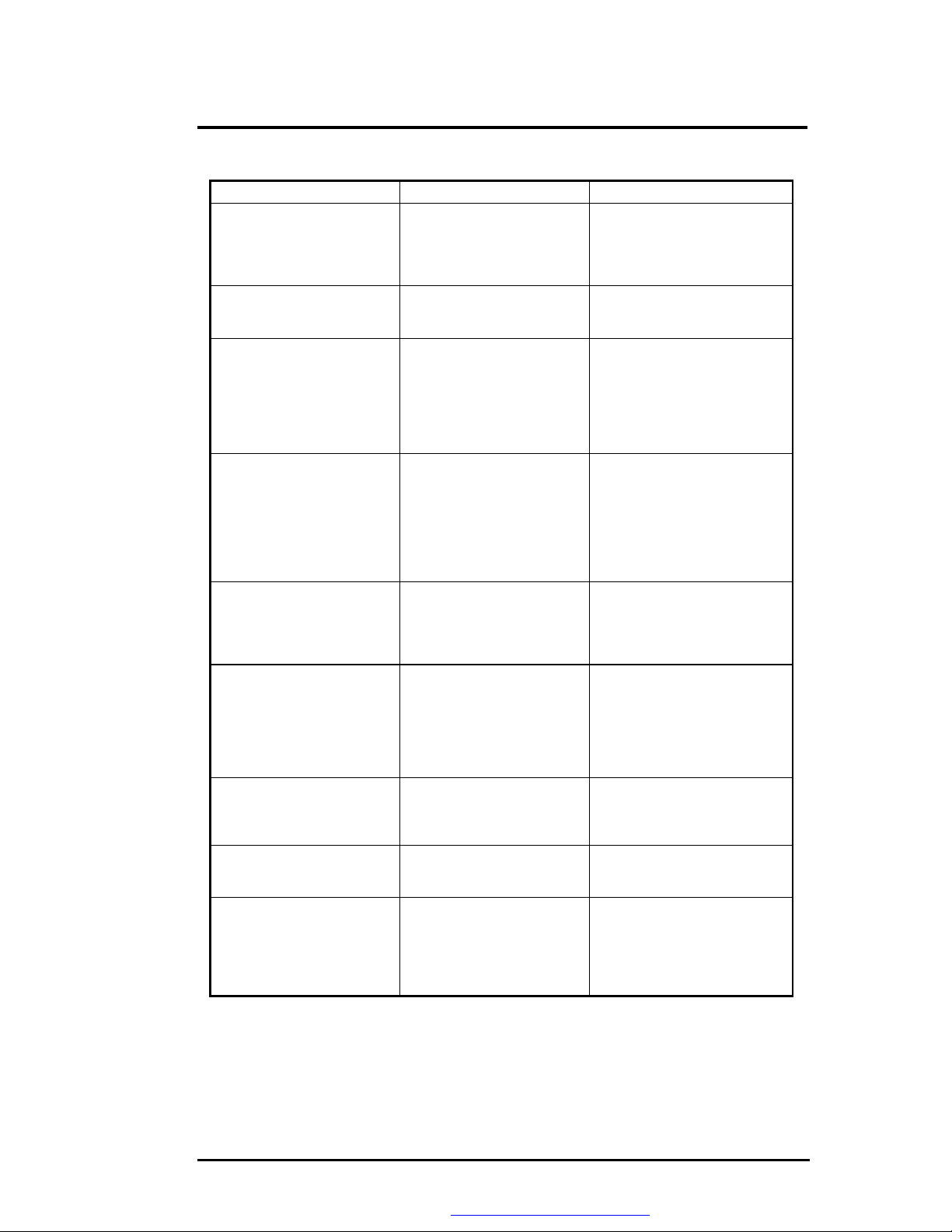
Troubleshooting and Repair
Table 6-1(b) POST Error Messages
Message Possible Cause Action
Timer 2 failure The timer chip has failed. Check the system board. Turn
F2 to enter ROM-based
SETUP
Invalid configuration
information - please run
SETUP
Keyboard clock line failure
Keyboard data line failure The keyboard controller
Keyboard stuck key failure
Memory failure at hex-
value, read hex-value,
expecting hex-value
Unexpected interrupt in
protected mode
Real time clock failure The RTC or battery failed. Run SETUP and turn the power
Invalid configuration
information must be changed.
Display adapter is configured
incorrectly.
Memory size is incorrect.
Wrong number of diskette
drives.
Other configuration errors.
The keyboard, the keyboard
cable connection, or the
keyboard controller is
defective.
firmware has failed.
A key is jammed. Locate the jammed key and fix
Circuitry associated with the
memory chips has failed.
Hardware interrupt or NMI
occurred while in protected
mode.
the power off, then back on
again. If the problem persists,
contact qualified service
personnel.
You must run SETUP utility and
correct configuration
information.
Run the SETUP utility.
Make sure the keyboard cable
and keyboard are connected
properly. Check the keyboard
controller and the system
board. Turn the power off, then
back on again. If the problem
persists, contact qualified
service personnel.
Check the keyboard controller
and system board. Turn the
power off, then back on again.
If the problem persists, contact
qualified service personnel.
it. Make sure the keyboard
cable and keyboard are
connected properly. Turn the
power off, then back on again.
If the problem persists, contact
qualified service personnel.
Turn the power off, then back
on again. If the problem
persists, contact qualified
service personnel.
Check the timer chip or the
interrupt controller on the
system board.
off and on. If the problem
persists, replace the RTC
battery. If the problem remains,
contact qualified service
personnel.
FIC A985 Service Manual 6-3
PDF created with FinePrint pdfFactory trial version http://www.fineprint.com
Page 4
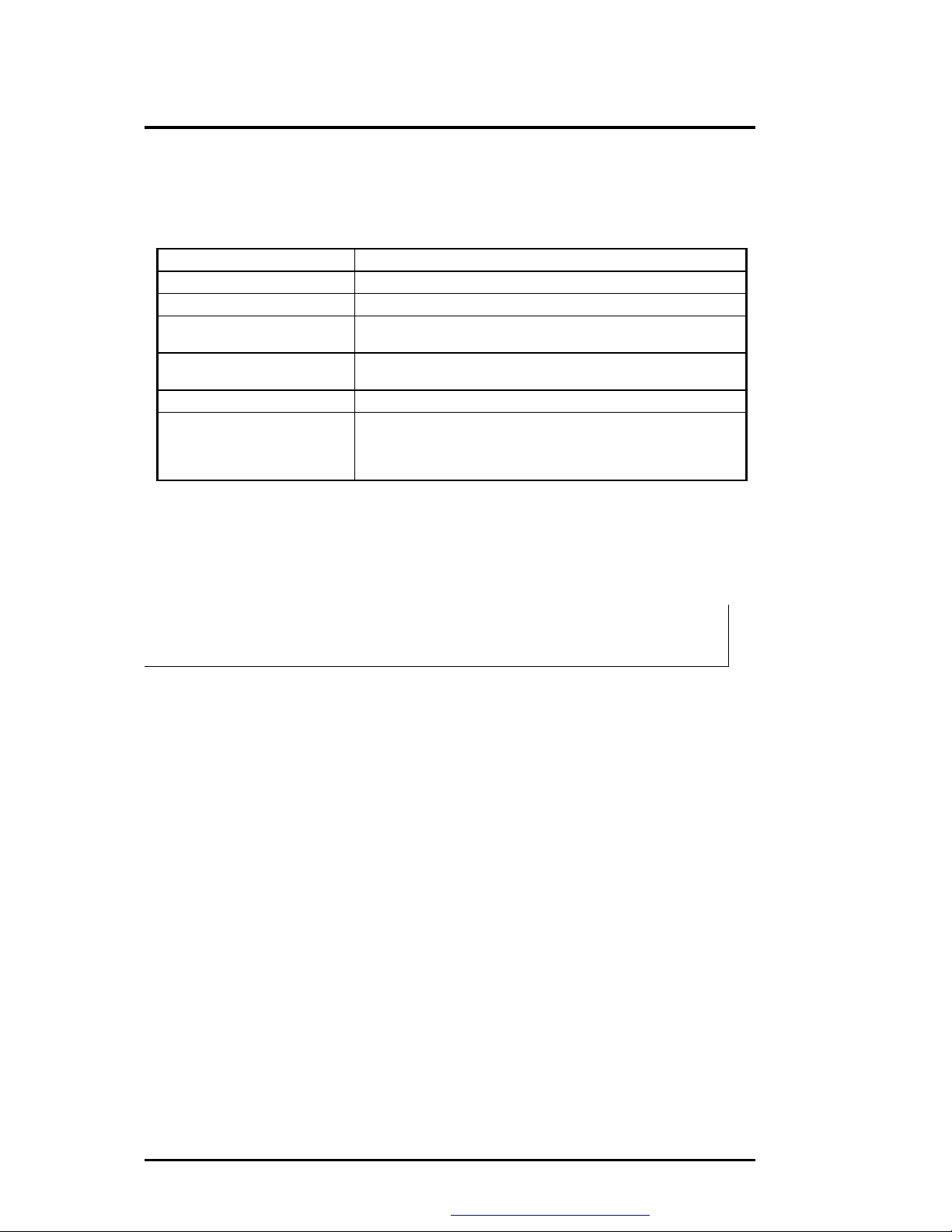
Troubleshooting and Repair
6.2.2 Informational Messages
This section lists the messages that provide information to the user but require no action.
Table 6-2 BIOS Informational Messages
Message Meaning
nnnK Base Memory The amount of base memory that tested successfully.
nnnK Extended The amount of extended memory that tested successfully.
Memory tests terminated by
keystroke
Press the F1 key to continue This message indicates that an error was found during POST.
Beginning memory test A user can stop the memory tests by pressing the spacebar.
Press the F1 key to
continue, F2 to run the
Setup utility
6.2.3 Beep Codes
Beep codes are used to identify a POST error that occurs when the screen is not available.
Once the screen is operating, diagnostic messages are reported to the screen. There are beep
codes for both fatal and non-fatal system board errors.
The message indicates that a user pressed the spacebar while
memory tests were running and stopped the memory tests.
Pressing the F1 key allows the system to attempt to reboot.
This message indicates that an error was found during POST.
Pressing the F1 key allows the system to attempt to boot. Press
F2 allows users to run the ROM-based SETUP utility to correct
configuration information.
i No beep code is generated if a test is aborted while in progress. However,
diagnostic cards can be installed in order to display the contents of the
diagnostic port 80h and identify the area of failure.
Explanation of test terms for beep code table
The following terms are used in the Test Performed column of the beep code table:
1. Pattern test - One or more particular patterns are written to a location then read back
from the same location. Examples of patterns used are 55h and AAh. If the value read
does not match the value written, the test is considered a failure.
2. Rolling ones test - Several patterns are constructed. These patterns represent a one rolling
through the given location. For example, to roll a one through three bits, the following
patterns would be constructed: 001, 010, 011, 100, 101, 110, and 111. The patterns are
written to the location and then read back, one by one. If the value read does not match
the value written, the test is considered a failure.
3. Rolling zeros test - Several patterns are constructed. These patterns represent a zero
rolling through the given location. For example, to roll a zero through three bits, the
following patterns would be constructed: 011, 001, and 000. The patterns are written to
the location and then read back, one by one. If the value read does not match the value
written, the test is considered a failure.
4. Checksum test - All of the values in a given range of locations are added together. The
range includes a location which when added to sum of the ranges, will produce a known
result, such as zero.
6-4 FIC A985 Service Manual
PDF created with FinePrint pdfFactory trial version http://www.fineprint.com
Page 5
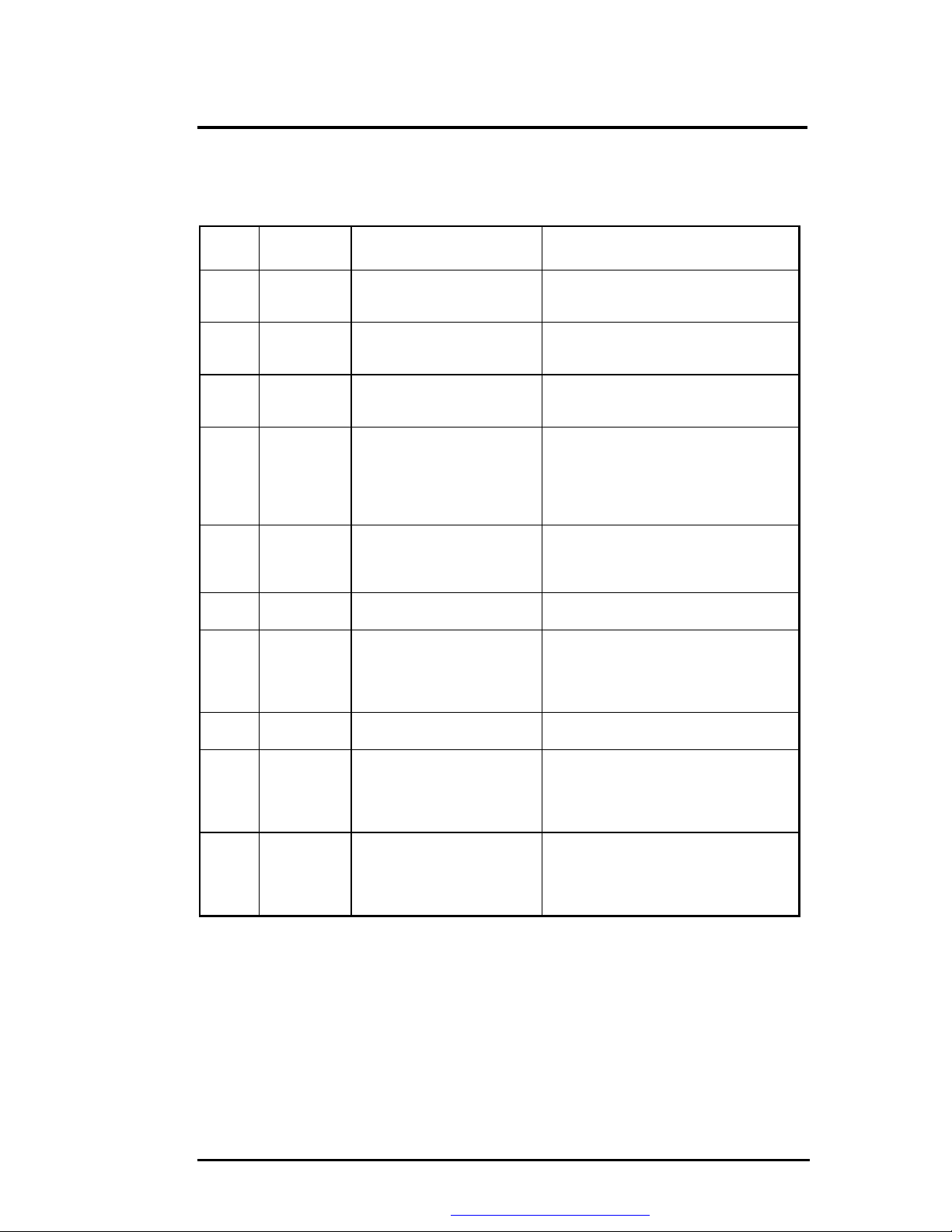
Troubleshooting and Repair
Beep codes for system board errors
Table 6-3 (a) BIOS Beep Codes
Beep
Code
none 01h CPU registers test in
1-1-3 02h CMOS write/read test in
1-1-4 03h ROM BIOS checksum test in
1-2-1 04h Programmable interval timer
1-2-2 05h DMA channel 0 address and
1-2-3 06h DMA page register write/read
1-3-1 08h RAM refresh verification test
none 09h First 64K RAM test in
1-3-3 0Ah First 64K RAM chip or data
1-4-2 0Dh Parity failure first 64K RAM At the completion of the rolling ones and
Diagnostic
Code
Description Test Performed
progress or failure
progress or failure.
progress or failure.
0 test in progress or failure.
count register test in progress
or failure.
test in progress of failure.
in progress or failure.
progress.
line failure, multi-bit.
Pattern test of most of the 16-bit CPU
registers. Failure will result in a system
halt.
Rolling ones test in the shutdown byte
(offset 0Eh) of the CMOS RAM. Failure
will result in a system halt.
The range of ROM that includes the
BIOS is checksummed. Failure will result
in a system halt.
Over a period of time, the current count
values in timer 0 are read and
accumulated by ORing them into the
values read so far. It is expected that
during the time period, all bits will be set.
Failure will result in a system halt.
Rolling ones and rolling zeros test of the
address and count registers of DMA
channel 0. Failure will result in a system
halt.
Pattern test of DMA page registers.
Failure will result in a system halt.
Over a period of time, the refresh bit (bit
4) in port 60h is read and tested. The
refresh bit should toggle from 0 to 1, then
1 to 0 within the time period. Failure will
result in system halt.
No specific test is performed - just
indicates that the test is beginning.
The first 64K of RAM is tested with a
rolling ones test and a pattern test. If any
of the pattern tests fail, then the BIOS
reports that multiple data bits failure.
Failure results in a system halt.
pattern tests of the first 64K, the BIOS
checks the parity error bits (bits 7 and 6)
of port 60h. Failure results in a system
halt.
FIC A985 Service Manual 6-5
PDF created with FinePrint pdfFactory trial version http://www.fineprint.com
Page 6
Troubleshooting and Repair
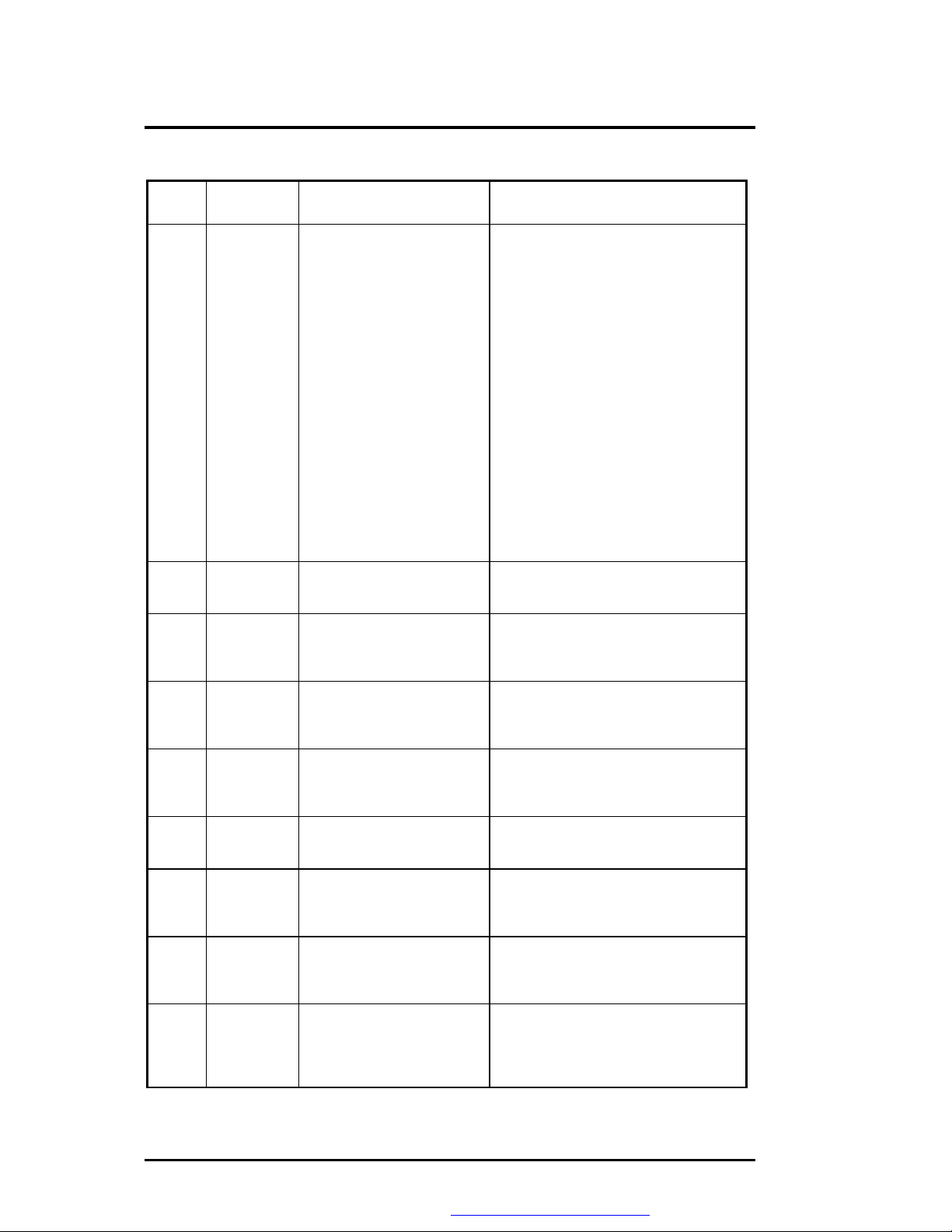
Table 6-3 (b) BIOS Beep Codes
Beep
Code
2-1-1
2-1-2
2-1-3
2-1-4
2-2-1
2-2-2
2-2-3
2-2-4
2-3-1
2-3-2
2-3-3
2-3-4
2-4-1
2-4-2
2-4-3
2-4-4
3-3-1 20h Slave DMA register test in
3-1-2 21h Master DMA register test in
3-1-3 22h Master interrupt mask register
3-1-4 23h Slave interrupt mask register
none 25h Interrupt vector loading in
3-2-4 27h Keyboard controller test in
None 28h CMOS RAM power failure
None 29h CMOS RAM configuration
Diagnostic
Code
10h-1Fh First 64K RAM chip or data
line failure on bit x
progress or failure.
progress or failure.
test in progress or failure.
test in progress or failure.
progress.
progress or failure.
and checksum calculation
test in progress.
validation for video in
progress.
Description Test Performed
The first 64K of RAM is tested with a
rolling ones test and a pattern test. If any
of the rolling ones tests fail, then the
BIOS reports the specific bit that failed.
To determine the bit number from the
diagnostic code, subtract 10h. For
example, if 12h is displayed at the
diagnostic port, bit 2 failed. Failure
results in a system halt.
Pattern test of channels 1 through 3 of
the slave controller (starting port address
= 02h). Failure results in a system halt.
Pattern test of channels 1 through 3 of
the master DMA controller (starting port
address = C4h). Failure results in a
system halt.
Rolling ones and zeros tests of the mask
register of the master programmable
interrupt controller (port 21h). Failure
results in a system halt.
Rolling ones and zeros tests of the mask
register of the master programmable
interrupt controller (port A1h). Failure
results in a system halt.
No specific test is performed - just
indicates that the Interrupt Vector table is
being initialized.
The self-test command (AAh) is issued to
the 8042 (keyboard controller) and the
results are monitored. Failure results in a
system halt.
The power-fail bit in CMOS RAM is
tested and the lower CMOS RAM area is
being checksummed. A failure does not
result in system halt.
No specific test is performed - just
indicates that the configuration specified
in CMOS for video is being matched
against the actual installation. A failure
does not result in a system halt.
6-6 FIC A985 Service Manual
PDF created with FinePrint pdfFactory trial version http://www.fineprint.com
Page 7
Troubleshooting and Repair
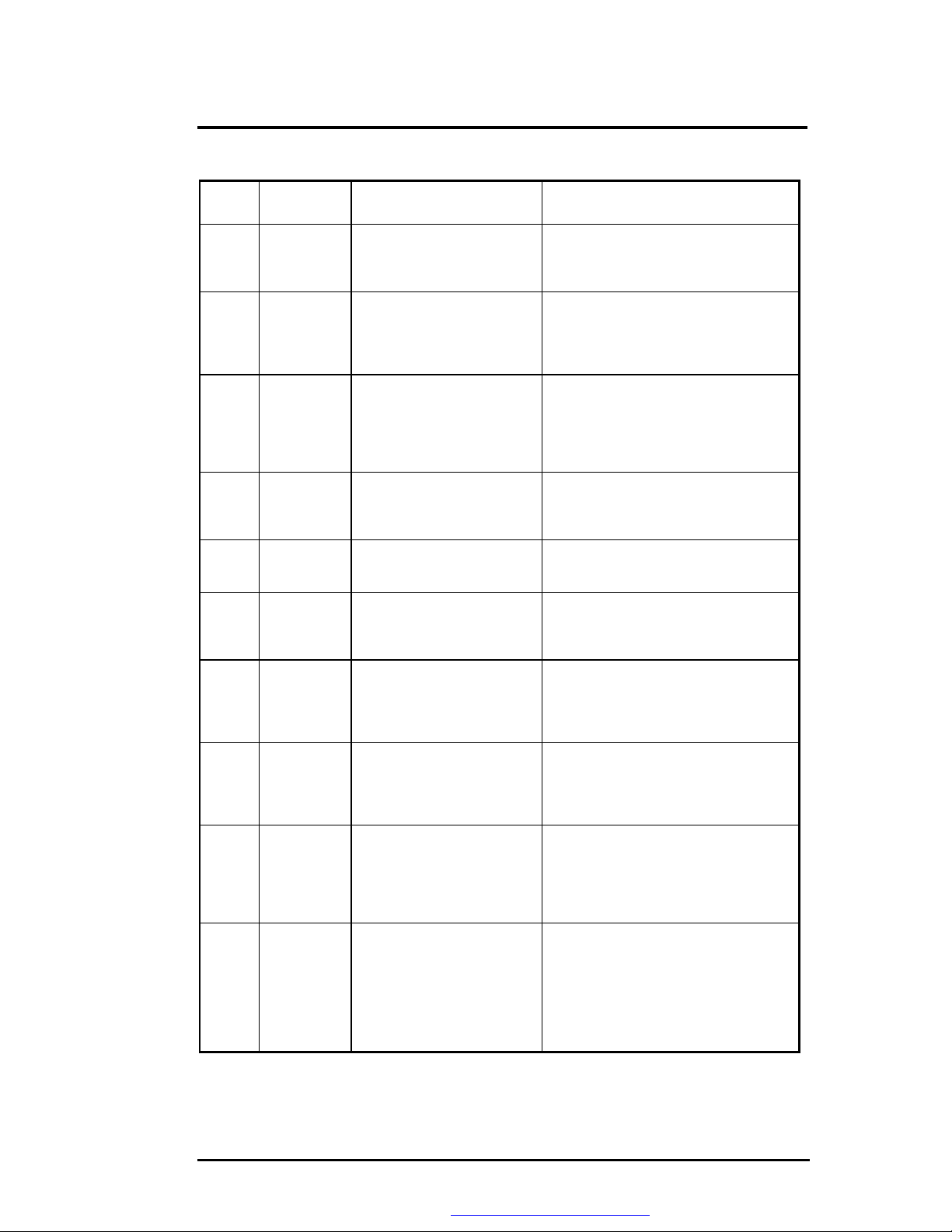
Table 6-3 (c) BIOS Beep Codes
Beep
Code
3-3-4 2Bh Screen memory test in
3-4-1 2Ch Screen initialization in
3-4-2 2Dh Screen retrace test in
None 2Eh Search for video ROM in
none 30h Screen running with video
none 31h Monochrome monitor
none 32h Color monitor (40-column)
none 33h Color monitor (80-column)
4-2-1 34h Timer-tick interrupt test in
4-2-2 35h Shutdown test in progress or
Diagnostic
Code
Description Test Performed
progress or failure.
progress.
progress or failure.
progress.
ROM.
operable.
operable.
operable.
progress or failure.
failure.
The video buffers (B0000h and B8000h)
are tested with a pattern test and a
rolling ones test. Failure will result in a
beep code but not a system halt.
Until the video installation is confirmed,
any calls to INT 10h Function 0 (set
mode) will be prefaced with the
diagnostic code. There is no expected
failure from this.
Over a period of time, the retrace bit
(bit0) in the appropriate CRT controller
status register (either port 3BAh or
3DAh) is read and tested. The retrace bit
should toggle from 0 to 1, then 1 to 0
within the time period.
No specific test is performed by the
system BIOS - just indicates that the
BIOS is about to jump to the initialization
code in the video option ROM.
No specific test is performed - just
indicates that a video option ROM was
found and believed to be operating.
No specific test is performed - just
indicates that the BIOS believes a
monochrome monitor is installed and is
operating.
No specific test is performed - just
indicates that the BIOS believes a color
monitor is installed and is operating. The
mode has been set to 40-column as
selected by the user in CMOS RAM.
No specific test is performed - just
indicates that the BIOS believes a color
monitor is installed and is operating. The
mode has been set to 80-column as
selected by the user in CMOS RAM.
All interrupts expect the timer-tick
interrupt are masked off at the interrupt
controllers. If a timer-tick interrupt does
not occur during a specific time period,
an error message is displayed on the
screen. The system does not halt.
A return address is stored in 40:67h and
the processor is reset via the keyboard
controller. If a timer tick occurs during
this time period, an error message is
displayed on the screen. Other failures
are hard to detect. If possible, the BIOS
will continue with POST, skipping the
memory tests.
FIC A985 Service Manual 6-7
PDF created with FinePrint pdfFactory trial version http://www.fineprint.com
Page 8
Troubleshooting and Repair
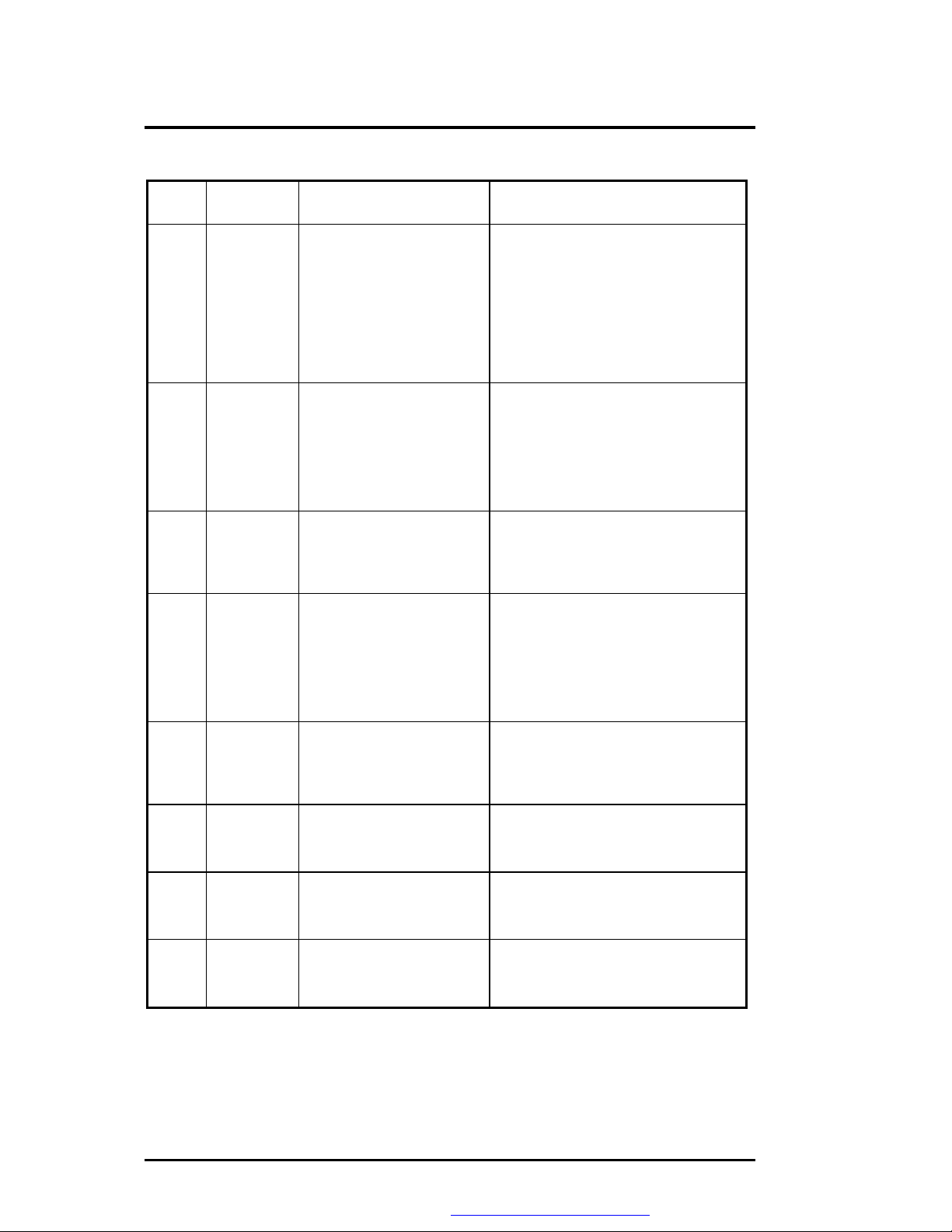
Table 6-3 (d) BIOS Beep Codes
Beep
Code
4-2-3 36h Gate A20 failure. To test extended memory, the processor
4-2-4 37h Unexpected interrupt in
4-3-1 38h RAM test of memory above
4-3-2 3Ah Programmable interval timer
4-3-4 3Bh Real-time clock test in
4-4-1 3Ch Serial port test in progress or
4-4-2 3Dh Parallel port test in progress
4-4-3 3Eh Math coprocessor test in
Diagnostic
Code
Description Test Performed
protected mode.
64K in progress or failure.
channel 2 test in progress or
failure.
progress or failure.
failure.
or failure.
progress or failure.
must be placed in protected mode and
the A20 line must be enabled. For the
memory tests, the BIOS generally uses
the keyboard controller to enable A20. If
the A20 line is not properly set during the
memory test, an error message is
displayed on the screen and the memory
test are suspended. The system does
not halt.
During the memory tests, the processor
is placed in protected mode. All
interrupts in the interrupt descriptor table
are initialized to point to special handler
that displays a message on the screen.
All hardware interrupt are disabled. The
system does not halt when an
unexpected interrupt occurs.
The memory above the first 64K is tested
with a rolling ones test and a pattern test.
All success and failure messages are
displayed on the screen and POST will
continue.
Over a period of time, the current count
values in timer 2 are read and
accumulated by ORing them into the
values read so far. It is expected that
during the time period, all bits will be set.
If an error is detected, an error message
will be displayed on the screen and
POST will continue.
Over a period of time, the Update-InProgress bit of Status Register A of the
real-time clock is read and tested. The bit
should toggle from 0 to 1 within the time
period.
Pattern test of one or more of the
installed serial ports. If a failure is
detected, an error message will be
displayed and POST will continue.
Rolling ones test is done to one or more
of the installed parallel ports. If a failure
is detected, an error message will be
displayed and POST will continue.
An integer load and store is performed
with the math coprocessor. If the values
do not match, an error message will be
displayed and POST will continue.
6-8 FIC A985 Service Manual
PDF created with FinePrint pdfFactory trial version http://www.fineprint.com
Page 9

Troubleshooting and Repair
6.2.4 Run-time Error Messages
Table 6-4 BIOS Run-time Error Messages
Message Cause Action
I/O card parity interrupt at
address. Type (S)hut off NMI,
(R)eboot, other keys to continue
Memory parity interrupt at
address. Type (S)hut off NMI,
(R)eboot, other keys to continue
Unexpected HW interrupt
interrupt at address. Type
(R)eboot, other keys to continue
Unexpected SW interrupt
interrupt at address. Type
(R)eboot, other keys to continue
Unexpected type 02 interrupt at
xxxxh. Type (S)hut off NMI,
(R)eboot, other keys to continue
Memory on a peripheral card
has failed.
A memory chip(s) has failed. Check the memory on the
Hardware problem. Not
displayed if the expected
interrupt handler is not enabled.
Error(s) in the software
program. Not displayed if the
extended interrupt handler is not
enabled.
A parity error occurred, but the
source can not be determined.
Check the memory cards
installed in the system.
system board.
Check all hardware in the
system.
Turn the machine off and
then on again. If doesn’t
work, check the program.
Turn the power off and then
on again.
FIC A985 Service Manual 6-9
PDF created with FinePrint pdfFactory trial version http://www.fineprint.com
Page 10

Troubleshooting and Repair
6.3 Quick Troubleshooting
This section summarizes problems that may develop during system operation and lists
suggested corrective actions to isolate problem properly.
Table 6-5 (a) Quick Troubleshooting
Problem or Symptoms Corrective Actions
No power (Power LED not on) 1. Check that the AC adapter is plugged into the DC-IN
Power LED is on but no display
and system does not turn on
Display on the LCD is
unreadable
LCD screen does not show
display
Battery Power does not last or
does not read properly under
Win98 / Win Me
connector of the notebook. Also, that the AC adapter is
plugged into a properly grounded AC power outlet.
2. If using the battery as main power source, check if the
battery pack is of the right type, charged and is inserted
correctly.
3. Check the internal Battery board of the notebook if it is
inserted into the main board connector properly.
Otherwise, replace the Battery board.
1. Press power button for 4 seconds to reset hardware
settings. Check if Power LED turns off.
2. Check memory module if it is inserted properly. Try to
check also the module on the internal slot.
3. Reset CMOS RTC.
4. Replace memory module, CPU module, or Battery
board.
1. Adjust the brightness display controls.
2. Check if installed VGA driver is correct and resolution is
set according to LCD size and type.
3. Check if the LCD cables are inserted properly. Check
also connections inside the LCD panel.
4. Check LCD inverter board inside LCD panel if faulty.
5. Check the North Bridge chip on the main board if there is
any cold or loosed soldering.
6. Replace the main board.
1. Check the LED Status Bar if Power Saving mode is
activated. Press any key or press the power button to
resume operation and display.
2. Check if the display output is switched to the external
monitor.
3. Check if there is power.
4. Check if LCD cables are disconnected or loosed.
5. Replace LCD Inverter board found inside the LCD Panel.
1. Make sure that the power management options under
OS Setup are enabled and set properly.
2. Recharge the battery pack for at 3 least hours before
using again.
3. Discharge and recharge the battery twice (Battery LowLow Suspend Off) to allow more accurate reading of
battery meter under Windows 98 or Windows Me.
4. Replace the battery pack.
6-10 FIC A985 Service Manual
PDF created with FinePrint pdfFactory trial version http://www.fineprint.com
Page 11

Troubleshooting and Repair
Table 6-5 (b) Quick Troubleshooting
Problem or Symptoms Corrective Actions
System halts during boot
sequence
I/O processing malfunctions 1. Check the connections of all internal devices.
Diskette drive does not work 1. Check if FDD option is DISABLED under BIOS Setup
Hard disk drive malfunction 1. Check if hard disk drive is set properly on BIOS
CD-ROM drive malfunction 1. Check if drive is set properly on BIOS Setup.
Memory malfunction 1. Check if the memory module is inserted properly. Try
External keyboard or PS/2
mouse doesn’t work
PCMCIA card does not work 1. Check if the PCMCIA card is inserted properly and all
1. Check condition of selected boot-load device (diskette
or hard disk) for bad boot track or incorrect OS files.
2. Try booting from a new bootable diskette and recopy
or repartition hard disk.
3. Check for any BIOS error messages on the display.
4. Replace main board.
2. Replace main board.
program.
2. Check if floppy drive cable is connected properly.
3. Check diskette type if correct and not faulty.
4. Replace diskette drive.
5. Replace main board.
SETUP.
2. Check cables and connections.
3. Check if disk drive is good. Replace the drive.
4. Replace the main board.
2. Check if device driver is installed properly. Do not use
other CD-ROM driver.
3. Check cables and connections.
4. Replace drive or main board.
to insert it also to the other slot.
2. Replace the memory module.
3. Replace the main board.
1. Check if keyboard or mouse is connected properly.
Check PS/2 Y-cable if it is being used. Power off
system first before plugging in the device.
2. Check PS/2 mouse driver if it is installed properly.
3. Replace the keyboard or mouse.
4. Replace the main board.
cables and connections are set.
2. Check the PCMCIA card driver installation for any IRQ
or IO address conflict. Try to disable the COM2 port
(SIR) inside the BIOS Setup menu to free up unused
IRQ.
3. If PC card is not detected, insert it to the other
PCMCIA slot. Otherwise, replace PC card.
4. Contact the PC card manufacturer for support.
5. Replace the main board.
FIC A985 Service Manual 6-11
PDF created with FinePrint pdfFactory trial version http://www.fineprint.com
Page 12

Troubleshooting and Repair
Table 6-5 (c) Quick Troubleshooting
Problem or Symptoms Corrective Actions
Glide pad does not work 1. Check if PS/2 mouse driver is properly installed. Remove
Serial device does not work 1. Check if Serial Port is set to ENABLED under BIOS
Parallel device does not work 1. Check if Printer is set to ENABLED under BIOS Setup
USB Port does not work 1. Check if USB port option under BIOS Setup is
Audio components does not work 1. Check external connections if OK and volume mixer is
any external PS/2 mouse.
2. Check the glide pad cable inside the system if it is
inserted properly.
3. Replace the glide pad module.
4. Check the keyboard controller chip for any cold or loosed
soldering.
5. Replace the main board.
Setup program (Advanced menu).
2. Check if serial device is connected properly.
3. If using serial mouse, check if internal glide pad is
disabled under BIOS Setup. On Windows 98 or Me,
check if it detects the serial mouse in System Device
Manager under the Control Panel.
4. Check if mouse driver is installed properly.
5. Replace serial device.
6. Check the South Bridge chip on the main board for any
cold or loosed soldering.
7. Replace the main board.
program (Advanced menu).
2. Check if all connections are properly set.
3. Check if external device is turned on.
4. Check if Printer Mode is set properly.
5. Check the South Bridge chip on the main board for any
cold or loosed soldering.
6. Replace the main board.
ENABLED.
2. Check if USB device connection is OK. Unplug and replug the device.
3. Check if the USB port driver and the USB device driver
are installed.
4. Replace USB device or contact USB device
manufacturer for support.
5. Replace main board.
set properly.
2. Check audio source (CD, tape, etc.) if faulty.
3. Check if audio driver is installed.
4. Check internal connections for speaker and microphone
if not working.
5. Check audio board, cables and connections.
6. Replace main board
6-12 FIC A985 Service Manual
PDF created with FinePrint pdfFactory trial version http://www.fineprint.com
Page 13

Troubleshooting and Repair
6.4 Component-Level Troubleshooting
This section provides an easy to follow flowcharts for performing component-level
troubleshooting on the A985 notebook.
6.4.1 General Overview
The component-level troubleshooting is broken down as follows:
Starting Check Figure 6-1
Memory Interface Check Figure 6-2
CRT Interface Check Figure 6-3
HDD Interface Check Figure 6-4
Internal Keyboard Interface Check Figure 6-5
Glide Pad Interface Check Figure 6-6
CD-ROM Interface Check Figure 6-7
Serial Port Interface Check Figure 6-8
External Keyboard Interface Check Figure 6-9
PS/2 Mouse Interface Check Figure 6-10
Printer Port Interface Check Figure 6-11
Audio Port Interface Check Figure 6-12
PCMCIA Interface Check Figure 6-13
USB Port Interface Check Figure 6-14
LCD Panel Interface Check Figure 6-15
TV-OUT Interface Check Figure 6-16
LED Indicator Function Check Figure 6-17
Cover Switch Function Check Figure 6-18
Mini-PCI Modem, LAN, or Combo Device Check Figure 6-19
FIR Interface Check Figure 6-20
IEEE1394 Interface Check Figure 6-21
Troubleshooting Item Figure
FIC A985 Service Manual 6-13
PDF created with FinePrint pdfFactory trial version http://www.fineprint.com
Page 14

Troubleshooting and Repair
6.4.2 Starting Check
Figure 6-1 Starting Check
6.4.3 Memory Interface Check
Figure 6-2 Memory Interface Check
6-14 FIC A985 Service Manual
PDF created with FinePrint pdfFactory trial version http://www.fineprint.com
Page 15

Troubleshooting and Repair
6.4.4 CRT Interface Check
Figure 6-3 CRT Interface Check
6.4.5 HDD Interface Check
Figure 6-4 HDD Interface Check
FIC A985 Service Manual 6-15
PDF created with FinePrint pdfFactory trial version http://www.fineprint.com
Page 16

Troubleshooting and Repair
6.4.6 Internal Keyboard Check
Figure 6-5 Internal Keyboard Check
6.4.7 Glidepad Interface Check
Figure 6-6 Glidepad Interface Check
6-16 FIC A985 Service Manual
PDF created with FinePrint pdfFactory trial version http://www.fineprint.com
Page 17

Troubleshooting and Repair
6.4.8 CD-ROM Interface Check
Figure 6-7 CD-ROM Interface Check
6.4.9 Serial Port Interface Check
Figure 6-8 Serial Port Interface Check
FIC A985 Service Manual 6-17
PDF created with FinePrint pdfFactory trial version http://www.fineprint.com
Page 18

Troubleshooting and Repair
6.4.10 External Keyboard Check
Figure 6-9 Internal Keyboard Check
6.4.11 PS/2 Mouse Interface Check
Figure 6-10 PS/2 Mouse Inteface Check
6-18 FIC A985 Service Manual
PDF created with FinePrint pdfFactory trial version http://www.fineprint.com
Page 19

Troubleshooting and Repair
6.4.12 Printer Port Interface Check
Figure 6-11 Printer Port Interface Check
6.4.13 Audio Port Interface Check
Figure 6-12 Audio Port Interface Check
FIC A985 Service Manual 6-19
PDF created with FinePrint pdfFactory trial version http://www.fineprint.com
Page 20

Troubleshooting and Repair
6.4.14 PCMCIA Interface Check
Figure 6-13 PCMCIA Interface Check
6.4.15 USB Port Interface Check
Figure 6-14 USB Port Interface Check
6-20 FIC A985 Service Manual
PDF created with FinePrint pdfFactory trial version http://www.fineprint.com
Page 21

Troubleshooting and Repair
6.4.16 LCD Panel Interface Check
Figure 6-15 LCD Panel Interface Check
6.4.17 TV-Out Interface Check
Figure 6-16 TV-Out Interface Check
FIC A985 Service Manual 6-21
PDF created with FinePrint pdfFactory trial version http://www.fineprint.com
Page 22

Troubleshooting and Repair
6.4.18 LED Indicator Function Check
Figure 6-17 LED Indicator Function Check
6-22 FIC A985 Service Manual
PDF created with FinePrint pdfFactory trial version http://www.fineprint.com
Page 23

Troubleshooting and Repair
6.4.19 Cover Switch Function Check
Figure 6-18 Cover Switch Function Check
6.4.20 Mini-PCI Modem , LAN, or Combo Device Check
Figure 6-19 Mini-PCI Modem, LAN, or Combo Device Check
FIC A985 Service Manual 6-23
PDF created with FinePrint pdfFactory trial version http://www.fineprint.com
Page 24

Troubleshooting and Repair
6.4.21 FIR Interface Check
Figure 6-20 FIR Interface Check
6.4.22 IEEE1394 Interface Check
Figure 6-21 IEEE1394 Interface Check
6-24 FIC A985 Service Manual
PDF created with FinePrint pdfFactory trial version http://www.fineprint.com
 Loading...
Loading...