
F™ A
D
P
E
R
ASTCOM
FASTCOM™: 422/2-PCI
1.5Mbaud Dual Channel RS-422/RS-485 Interface
for PCI Bus
Hardware Reference Manual
A
T
S
Manufactured by:
9011 E 37th St N
Wichita KS 67226-2006


9011 E. 37TH STREET N.
WICHITA, KANSAS 67226-2006
(316) 636-1131
FAX (316) 636-1163
http://www.commtech-fastcom.com/
COPYRIGHT (C) 1999, 2002, 2003
All rights reserved, including those to reproduce this document or parts thereof in
any form without permission in writing from Commtech, Inc.
FASTCOM and SMART14 are trademarks of Commtech, Inc.
IBM is a registered trademark of International Business Machines Corporation.
Microsoft is a registered trademark of Microsoft Corporation.
WINDOWS is a trademark of Microsoft Corporation.

REVISION NOTES
REVISION PAGE NUMBER CHANGES MADE
2.1 14 Changed warranty to 2 years
2.2 6 Added link to installation manual
2.3 12 Updated contact information
2.4 8,9 Updated Fastcom Serial Settings
2.5 13 Changed warranty period to lifetime

CONTENTS
“CE” CERTIFICATE .............................................................................................................. 1
INTRODUCTION
Description / Block Diagram
Specifications / Features
Board Layout
INSTALLATION
Installing the Hardware
Testing the Installation
FASTCOM SERIAL SETTINGS
DB9 PIN DESCRIPTION
RS-422/485
Termination Resistance
TECHNICAL SUPPORT
APPENDIX A
16C850 UART Technical Data
................................................................................................................... 5
..................................................................................................... 6
.................................................................................................... 10
......................................................................................................................... 11
..................................................................................................... 13
............................................................................................ 3
................................................................................................. 4
/ Software................................................................................... 6
............................................................................................ 8
................................................................................................. 12
...................................................................................... 14


1
EUROPEAN UNION DECLARATION OF CONFORMITY
Information Technology Equipment
The Company COMMTECH, INC. declares under its own and full responsibility that the product
" Fastcom: 422/2-PCI - Revision 1.0 "
on which is attached this Certificate is compliant to the "89/336/EEC" Directive, amended by 92/31/EEC and
93/88/EEC.
[ ] The product identified above complies with the requirements of the above EU Directive by meeting the
following standards:
• EN 50081-1 (1992) EMC Generic Emission Standard - Part 1, Residential, Commercial and Light Industry
- EN 55022 (1995), CISPR 22 (1993) Limits and Methods of Measurement of Radio Disturbance
Characteristics of Information Technology Equipment, 30 MHz - 1 GHz, Class B Limits
• EN 50082-1 (1992) EMC Generic Immunity Standard - Part 1, Residential, Commercial and Light Industry
- IEC 801-2 (1984), Method of Evaluating Susceptibility to Electrostatic Discharge, Level 4
- IEC 801-3 (1984), Radiated Electromagnetic field Requirements, Level 3
- IEC 801-4 (1988), Electrical Fast Transient/Burst Requirements, Level 2
Products listed on this declaration are exempt from the requirements of the 73/23/EEC directive due to the input
voltage specification as stated in Article 1 of the directive.
The technical documentation required to demonstrate that this product meets the requirements of the EMC Directive
has been compiled by the signatory below and is available for inspection by the relevant enforcement authorities.
In WICHITA, KS on December 31st of 1995
9011 E. 37th Street North
Wichita, KS 67226-2006
(316) 636-1131
Fax (316) 636-1163
Mr. Glen R. Alvis
Chief Engineer

2
3
S
INTRODUCTION
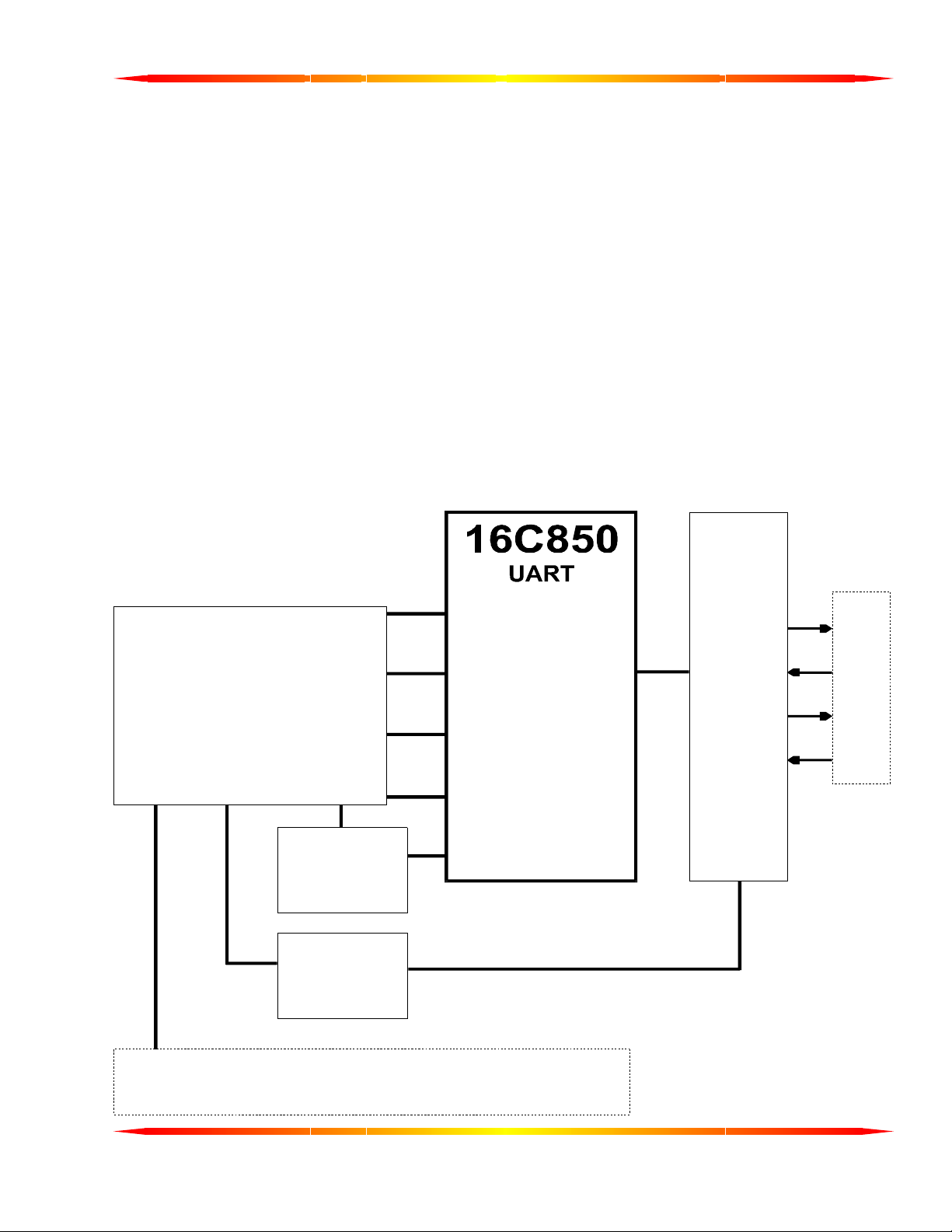
The Fastcom: 422/2-PCI adapter is the fastest, most advanced two-channel RS-422/485 adapter in the industry.
Primarily designed for commercial, industrial, and OEM applications, the Fastcom: 422/2-PCI features two
discrete RS-422/485 channels, complete with RTS and CTS hand-shaking signals for each channel.
The advanced universal asynchronous receiver and transmitter (UART) chips used on the Fastcom: 422/2-PCI
are fully register compatible with standard 16C550 UARTs, but provide extraordinary 128 byte FIFOs for
receive and transmit buffering. This buffering is extremely valuable when working with RS-422/485
communications within high-overhead operating systems such as Windows NT and Windows 98. The two
advanced UARTs on the Fastcom: 422/2-PCI are each capable of all standard baud rates plus a high-speed
mode capable of up to an amazing 1.5 Mbaud.
Software drivers for Windows 98/NT/2000/XP and Linux are supplied. Multiple Fastcom: 422/2-PCI adapters can
be installed in all operating systems.
The Fastcom RS-422-PCI family also includes the four-channel Fastcom: 422/4-PCI and the isolated ground
single-channel Fastcom: IG422/1-PCI. ISA bus versions are also available.
The following is the basic structure of the Fastcom: 422/2-PCI:
PCI
INTERFACE
CONTROLLER
CLOCK
CONTROL
REGISTER
422/485
CONTROL
REGISTER
CS
A0-A2
DATA
INTERRUPT
CLOCK
RS-422
RS-485
DB9
TX
RX
RTS
DRIVERS /
RECEIVERS
CTS
PCI BU

4
SPECIFICATIONS:
UART 16C850
BAUD RANGE Any rate up to 1.5 Mbaud
BUFFERING Transmit - 128 bytes
Receive - 128 bytes
INTERFACE RS-422 / RS-485
TX, RX, RTS, CTS
BUS PCI
POWER
REQUIREMENTS: +5 600mA (Typical)
ADDRESS
REQUIREMENTS: PCI Controller 128 bytes
UARTs 16 bytes
Control Registers 4 bytes
INTERRUPT
REQUIREMENTS: 1 (per board)
FEATURES:
New high performance 16C850 UARTS
Standard
All baud rates up to 1.5 Mbaud
128 byte FIFOs for improved throughput
User programmable baud rate
“Switchless” design
Hardware control for 485 driver
“Echo cancel” available in 485 mode
Comprehensive Hardware and Software Documentation
Made in Wichita, Kansas, U.S.A.
on the Fastcom: 422/2-PCI, no extra charge

FASTCOM: 422/2-PCI
BOARD LAYOUT
CHANNEL 1
(DB9 CONNECTOR)
TRANSMIT/RECEIVE LEDs
CHANNEL 1
CHANNEL 2
CHANNEL 2
(DB9 CONNECTOR)
5
16C850
UARTs
PCI CONTROLLER
PACKING LIST
FASTCOM: 422/2-PCI CARD
FASTCOM CD
If an omission has been made, please call technical support for a replacement.

6
HARDWARE INSTALLATION
Important: Observe Electrostatic Discharge (ESD) precautions when handling the Fastcom: 422/2-PCI
board.
1. Unpack the Fastcom: 422/2-PCI. Keep the box and static bag for warranty repair returns
2. Select an open PCI slot in your PC.
3. After removing the blank bracket from your PC, install the Fastcom: 422/2-PCI in the PC by pressing it firmly
into the slot. Install the bracket screw to hold it firmly in place.
4. Re-install the cover on your PC.
.
SOFTWARE INSTALLATION
Select the link above to open the Installation Manual. Under Fastcom – Async-PCI series cards, select your
operating system and follow the instructions. When you are finished, select Fastcom: 422/2-PCI from the list at
the end of the Fastcom – Async-PCI series cards section to return to this manual.
TESTING THE INSTALLATION
To fully test the installation of your Fastcom: 422/2-PCI, you will need to build a "loop back plug". Materials
needed are a DB9 male plug, solder cup style, and two short pieces of 20 or 24 AWG stranded wire. This loop
back plug can be used to test any RS-422 port. Jumper the pins together on the DB9 as illustrated below:
4 TX+
5 TX8 RX+
9 RX-
TESTING YOUR FASTCOM ASYNC PCI PORT IN WINDOWS
These instructions assume that you have already installed the card and have followed the installation instructions.
The SERIALGT.EXE program (98, NT) or the Device Manager (2K, XP) should show the boards/ports that are
installed, and the COM numbers assigned to those ports.
1. Install the loopback plug on the port to test.
2. Find and run the TTY example program (simple terminal).
From the Start menu, choose Run, browse to and select D:\Fastcom_disks\AsyncPCI\tty\tty2.exe.
Click the Open button.
4
5
8
9

7
Click the OK button to run the program.
3. With the TTY program running, select Settings from the menu.
Select the COM port number that has the loopback plug on it.
Uncheck all of the flow control checkboxes (DTR/DSR, RTS/CTS, XON/XOFF).
Click OK.
From the TTY Main menu select Action, then Connect.
4. At this point you should get a blinking cursor in the upper left corner (under the menu bar).
5. You should be able to type on the keyboard and see the letters that you type on the screen. If you see what
you are typing, then your port is installed and operating properly.
If you do not get to the blinking cursor stage, but rather encounter a “Connection Failed” message box, some
possible causes are:
1. In NT, if multiple ports are opened (running more than one instance of TTY), the ports are using the same
IRQ, and the PermitShare registry entry is 0, the second port to be opened will fail. Use the registry
editor and expand HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE ->SYSTEM ->CurrentControlSet ->Services ->Serial,
change the PermitShare value from 0 to 1, reboot, and run the test again.
2. The interrupt that was selected by the plug-and-play bios is trying to be shared with another device that is
not configured to share the IRQ (either Device or Driver Exclusive IRQ setting). Try a different PCI slot or
disable the other offending device.
3. IRQ steering is enabled on Windows 98 and Windows is not assigning an IRQ to the Fastcom card. Try
disabling IRQ steering or varying the options in Control Panel ->System ->Device Manager ->System
Devices ->PCI Bus.
4. Multiple COMx assignments. In Windows NT, the driver setup assumes that there are not any ports
installed above COM4, and starts assigning the Fastcom ports at COM5. If there is already a COM5 (or
higher) in the system, it is likely that the Fastcom ports are being assigned to the same port name(s).
Run the SERIALGT.EXE program (D:\Fastcom_disks\AsyncPCI\nt\serialgt.exe for Windows NT,
D:\Fastcom_disks\AsyncPCI\95\serialgt.exe for Windows95) and re-assign the com port numbers to these
ports to be different than any other ports in the system.
If you get to the blinking cursor stage, but do not see what you type with the loopback installed, some possible
reasons are:
1. Incorrect/faulty loopback construction or a bad connection.
2. The port is setup to have RS-485 enabled and the “RX Echo Disable” checkbox is checked. If the RX
Echo Disable is checked you will be unable to run a simple loopback test, as the purpose of the echo
disable is to strip the characters that are sent/received at the same time. Uncheck the RX Echo disable,
reboot, and try the test again.
3. The RTS/CTS flow control is checked and there is not a RTS->CTS loopback or the CTS disabled
checkbox was unchecked. If you enable flow control, you must allow CTS to be active in order for the
driver to transmit data. Either disable flow control or wire the RTS->CTS (and possibly DTR->DSR) loops
and try the test again.
4. The loopback plug is not on the correct port/cable.

8
FASTCOM SERIAL SETTINGS
CLOCK/4
Clock divisors of 1 and 4 are available. Clearing the checkbox selects a divisor of 1 and setting the checkbox
selects a divisor of 4. It is best to leave this box unchecked.
Auto 485
When checked, OUT1 of the UART becomes a 485 driver control signal, enabling automatic tri-state control.
You must check 485 Enable and uncheck Enable Source for this to work.
RX Trigger
Determines the number of bytes that will be stored in the receive FIFO on the 16C850 before an interrupt is
triggered. Valid values are from 1 to 128 bytes. The optimal setting is 64 bytes. For 16C550 compatibility,
set to 8.
TX Trigger
Determines the number of bytes remaining in the transmit FIFO on the 16C850 before an interrupt is
triggered. Valid values are from 0 to 127 bytes. The optimal setting is 64 bytes. For 16C550 compatibility,
set to 0.
TX Write Size
Determines the number of bytes sent to the board at a time. Valid values are from 1 to 128. This number
plus the TX Trigger value should not exceed 128. The optimal value is 64. For 16C550 compatibility, set to
16 or 1.
CTS Disable
When checked, the CTS signal is forced active, ignoring the signal from the connector. When unchecked, the
CTS signal is read from the connector.
485 Enable
When checked, the 485 driver mechanism is enabled.
RX Echo Disable
When checked, the receive is disabled during transmit.
Enable Source
• When checked, the 485 driver control is RTS. This is compatible with older boards and software which
are not automatically controlled by hardware. Uncheck Auto 485.
• When unchecked, the 485 driver control is OUT1 on the UART. This is compatible with hardware control
of automatic 485 mode. Check Auto 485.
BaudTable (Win2K/XP)
This table represents the standard baud rates that the Fastcom card will currently support. If you wish to use
a non-standard baud, you may enter it into one of the boxes on the table and hit the tab key (do not hit enter,
hitting enter will exit the program). This will set the onboard clock generator to a frequency (see Input
Frequency below) that will divide down to the new baud rate. The rest of the table will also be updated to
reflect other bauds that can be used with the calculated clock frequency. If you wish to return to the standard
rates, you can set the top box to 115200 and hit tab and the rest of the bauds will be filled in.
Note: The baud rates that you set will not be available to standard Windows applications like HyperTerminal.
The new rates will be available to you in your code or in applications that allow user defined baud rates such
as TTY2, which can be found on the Fastcom disk (Fastcom_CD\Fastcom_disks\AsyncPCI\tty\tty2.exe).
THIS SETTING=THIS BITRATE (Baud Rate Substitution Table) (Win 98/NT)
Under THIS SETTING you will see the standard PC baud rates, from 115.2K to 300. If you wish to use a

baud rate not shown, type the baud rate in the box next to 115200 (e.g., type 128K as 128000), and hit the
tab key. Do not hit enter. Hitting enter will exit the program. If the baud rate changes after you tab, move to
the next box down and try again. Continue moving down until the baud rate stays the way you want it. Now
note the standard PC baud rate to the left of the box you ended on. You will select this standard baud rate to
set up your com ports, and the baud rate you require will be substituted. If you receive an error message
stating that the maximum baud rate was exceeded, change the Clock Divisor to 1 and try again.
INPUT FREQUENCY
This is the calculated frequency required to generate the baud rate requested. When you click OK on the
Fastcom Serial Settings page, this frequency is sent to the clock generator and the new baud rates will be
available.
9

10
DB9 PIN DESCRIPTION
The FASTCOM: 422/2-PCI features two RS-422/RS-485 channels, which are accessed through two DB9
connectors on the board.
The following is a pin description of the DB9 connectors:
PIN NO. SIGNAL NAME DIRECTION
1 SIGNAL GROUND (GND) GROUND
2 READY TO SEND + (RTS+) OUTPUT
3 READY TO SEND – (RTS-) OUTPUT
4 TRANSMIT DATA + (TX+) OUTPUT
5 TRANSMIT DATA – (TX-) OUTPUT
6 CLEAR TO SEND – (CTS-) INPUT
7 CLEAR TO SEND + (CTS+) INPUT
8 RECEIVE DATA + (RX+) INPUT
9 RECEIVE DATA – (RX-) INPUT

11
RS-422/RS485
Most engineers have worked with RS-232 devices at least once in their career. If you have never worked with
RS-422 or RS-485 devices, you will be pleased to know that working with the FASTCOM: 422/2-PCI is not much
different from working with an RS-232 device.
The RS-422 standard was developed to correct some of the deficiencies of RS-232. In commercial and industrial
applications, RS-232 has some significant problems. First, the cable length between RS-232 devices must be
short (usually less than 50 feet at 9600 baud). Second, many RS-232 errors are the result of cables picking up
normal industrial electrical noises such as fluorescent lights, motors, transformers, and other EMF sources. Third,
RS-232 data rates are functionally limited to 19.2K Baud. On the other hand, the newer RS-422 standard makes
cable lengths up to 5000 feet possible and is highly immune to most industrial noises. Data rates are also
improved -- the FASTCOM: 422/2-PCI features data rates up to 1.5 Mbaud. These improvements were made
possible by differentially driving and receiving the data as opposed to the single ended method employed by the
RS-232 standard. With the RS-422 standard, the transmit signal (TX in RS-232) is a differential signal consisting
of TX+ and TX-; the receive signal (RX in RS-232) consists of RX+ and RX-.
Another draw back of RS-232 is that more than two devices cannot share a single cable. This is also true of
RS-422, and that's why the RS-485 standard was developed. RS-485 offers all of the benefits of RS-422 and
also allows multiple units (up to 32) to share the same “twisted pair” of wires (see
is often referred to as a "multi-drop" or "two-wire, half duplex" network. In order for an RS-485 system to work,
only one driver (transmitter) can occupy the network at a time. This means that each station on the network must
control the enabling/disabling of their drivers in order to avoid network conflicts. If two drivers engage the network
at the same time, data from both will be corrupted. In RS-485 mode, the receivers are always enabled.
For a more detailed description of RS-422 and RS-485, we recommend the following references:
LINEAR AND INTERFACE CIRCUITS APPLICATIONS
D.E. Pippenger and E. J. Tobaben. Published 1985 by Texas Instruments. ISBN-0-89512-185-9
Note: This book may be difficult to find in a bookstore. The best place to get it is directly from Texas
Instruments or from one their component dealers. Publication # SLYA002.
"Driver/Receiver Family Extends Data-Link Performance", ELECTRONIC PRODUCTS, January 15, 1985.
By Dale Pippenger and Joe Miller
, Volume 2: Line Circuits, Display Drivers. By
diagram on next page
). RS-485

12
5
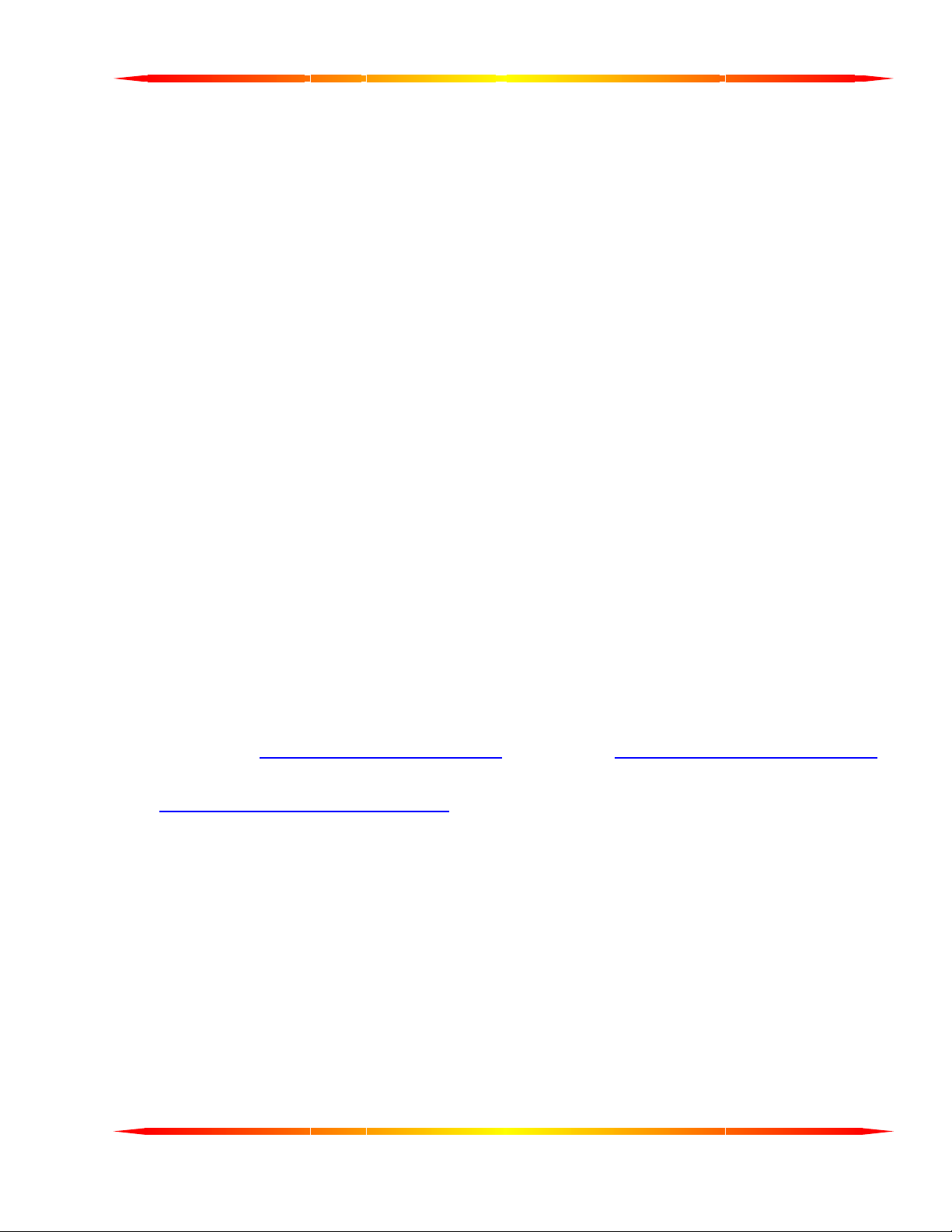
TERMINATION RESISTANCE
In both the RS-422 and the RS-485 mode, the receiver end of the cable between two stations must be terminated
with a resistor equal to the characteristic impedance of the wire. This is to prevent signal reflections in the wire
and to improve noise rejection. However, you do not need to add a terminator resistor to your cables when
you use the Fastcom: 422/2-PCI. The termination resistance is built in. We have installed a terminator
resistor for each receiver: between RX+ and RX- and between CTS+ and CTS- for each channel.
If you are using the Fastcom: 422/2-PCI in a multi-drop network, the termination resistor should be removed from
all units except the first and last (see the RS-485 illustration below). Call for technical support if you need to
modify the resistor. You may also order the Fastcom: 422/2-PCI without the termination resistor installed (it is
easier to add the resistor than to remove it). Observe the resistors in the following drawings and remember that
they are built into the Fastcom: 422/2-PCI (shown below):
Typical RS-422 Installation
TX
TX+
TX-
RX+
R2
RX-
RX
12
RX+
R1
RX-
R1 & R2 - Line Termination (100 ohms)
TX+
TX-
TXRX
Typical RS-485 Installation
RX+
RX-
TX+
TX-
RX+
RX-
TX+
TX-
RX
4
TX
RX
3
TX
TX
TX+
TX-
R1
R2
1
TX
RX+
RX-
TX+
TX-
RX
2
RX
RX+
RX-
R1 & R2 - Line Termination (100 ohms)
CHANNEL 1
RX
CTS
CHANNEL 2
RX
CTS
R12
R14
R13
R1
13
TECHNICAL SUPPORT
All products manufactured by Commtech are warranted against defective materials and workmanship for the
lifetime of the product. This warranty is available only to the original purchaser. Any product found to be
defective will, at the option of Commtech, be repaired or replaced with no charge for labor or parts not excluded
by the warranty. This warranty does not apply to any products that have been subjected to misuse, abuse, or
accident or as a result of service or modification by anyone other than Commtech. In no case shall Commtech
liability exceed the original product purchase price.
If any Commtech product is damaged such that it cannot be repaired, you can return it to Commtech for
replacement under our Non-Repairable Replacement policy, regardless of the cause of damage. Commtech will
replace the unit at 60% of the then-current list price.
Commtech provides extensive technical support and application suggestions. Most of the problems that occur
with the FASTCOM: 422/2-PCI can be corrected by double-checking the switch positions, your cables and your
program. We recommend that you build the loop back plug that is described in the Programming section of this
manual. With that plug, you can quickly isolate the problem to the board, cables, or software.
If you still have unresolved questions, use the following procedure to get technical support:
1. Call our Technical Support Staff at (316) 636-1131. They are on duty from 9:00 AM to 5:00 PM Central
Time.
If you purchased your board from Kontron America, please call their 7-24 technical support line at 1-800-
480-0044.
2. Ask for technical support for the FASTCOM: 422/2-PCI. Be ready to describe the problem, your computer
system, your application, and your software.
3. If necessary, our staff will give you an RMA number (Return Material Authorization). Use this number on
the mailing label and in all references to your board. Put the board back in its static bag and in its box.
Ship the board back to us as directed.
4. If you prefer, you may FAX a description of the problem to us at (316) 636-1163, or we can be reached on
the Internet at “http://www.commtech-fastcom.com
Kontron America can be reached by telephone at (800) 480-0044 or on the web at
“http://www.kontron.com/support/index.cfm
”.
” or by email at "techsupport@commtech-fastcom.com".

14
APPENDIX A
16C850
UART DATA
 Loading...
Loading...