Fairchild Semiconductor 74F433SPC Datasheet
74F433
First-In First-Out (FIFO) Buffer Memory
74F433 First-In First-Out (FI F O) Buffer Memory
April 1988
Revised August 1999
General Description
The 74F433 is an expandable fall-throu gh type high-speed
First-In First-Out (FIFO) Buffer Memory that is optimized for
high-speed disk or tape controller and communication
buffer applications. It is organized as 64-words by 4-bits
and may be expanded to any number of words or any number of bits in multiples of four. Data may be entered or
extracted asynchronously in serial or parallel, allowing economical implementation of buffer memories.
The 74F433 has 3-S TATE outputs that provide added versatility, and is fully compatible with all TTL families.
Features
■ Serial or parallel input
■ Serial or parallel output
■ Expandable without additional logic
■ 3-STATE outputs
■ Fully compatible with all TTL families
■ Slim 24-pin package
■ 9423 replacement
Ordering Code:
Order Number Package Number Package Description
74F433SPC N24C 24-Lead Plastic Dual-In-Line Package (PDIP), JEDEC MS-100, 0.300 Wide
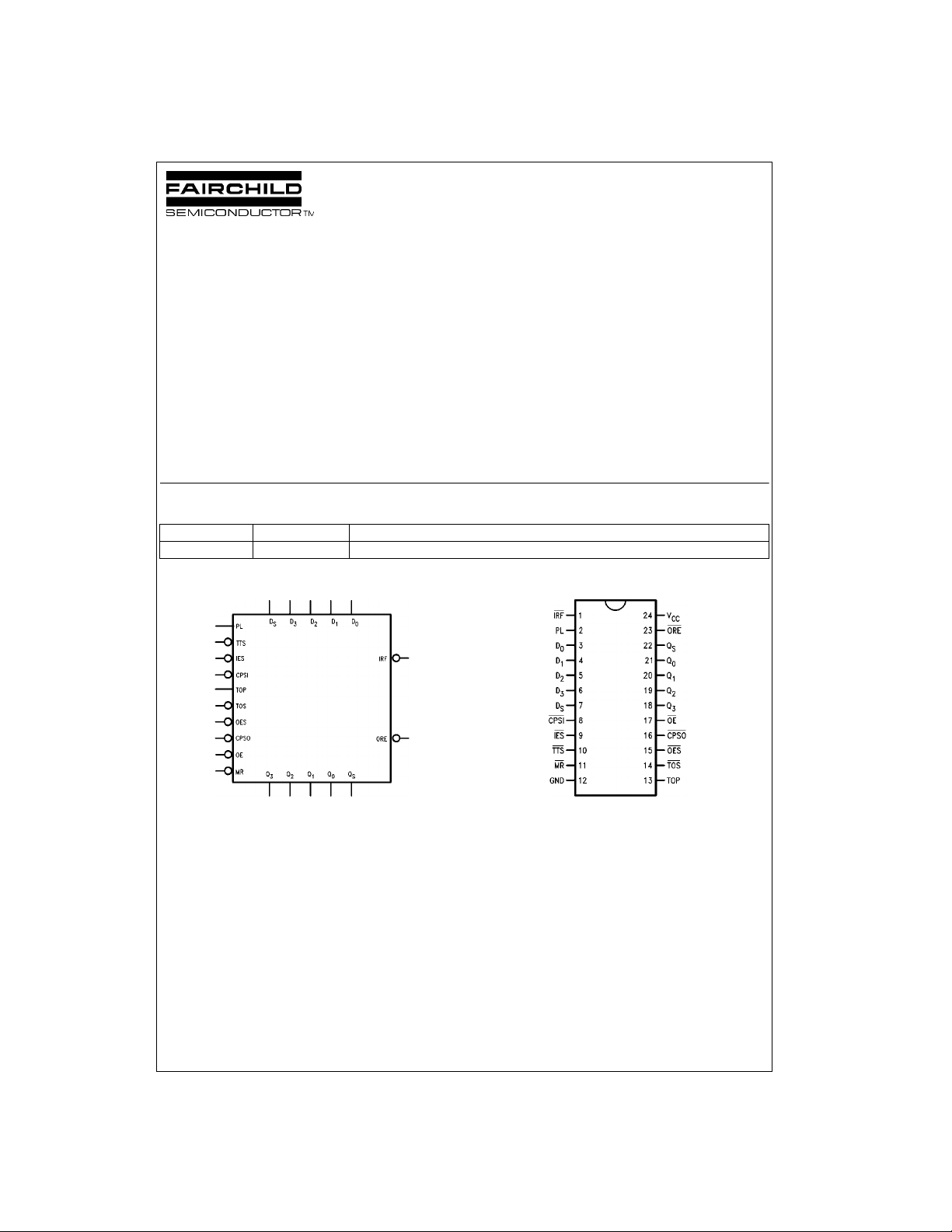
Logic Symbol Connection Diagram
© 1999 Fairchild Semiconductor Corporation DS009544 www.fairchildsemi.com
Unit Loading/Fan Out
74F433
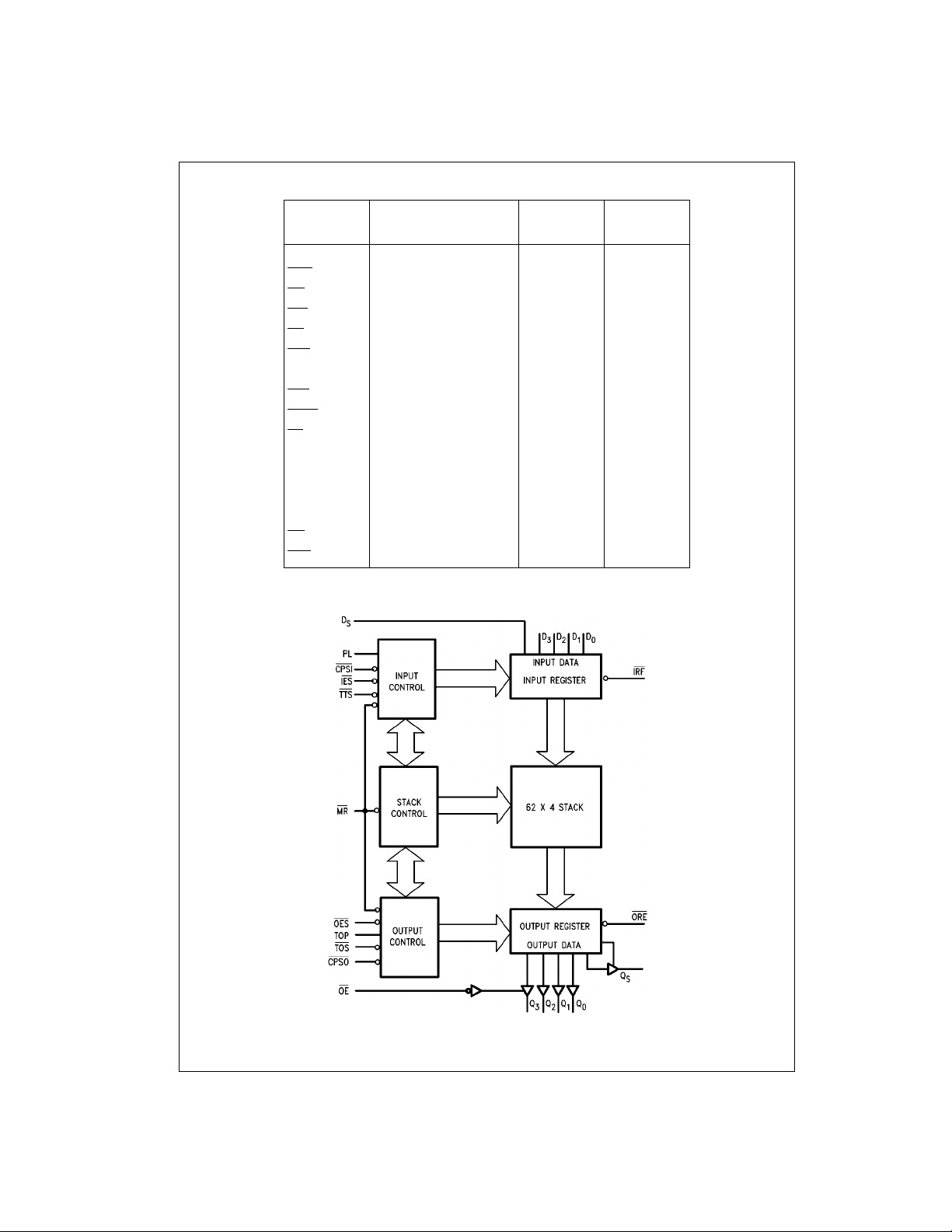
Block Diagram
Pin Names Description
PL Parallel Load Input 1.0/0.66 20 µA/400 µA
CPSI
IES
TTS
MR
OES
TOP Transfer Out Parallel 1.0/0.66 20 µA/400 µA
TOS
CPSO
OE
D
0–D3
D
S
Q
0–Q3
Q
S
IRF
ORE
Serial Input Clock 1.0/0.66 20 µA/400 µA
Serial Input Enable 1.0/0.66 20 µA/400 µA
Transfer to Stack Input 1.0/0.66 20 µA/400 µA
Master Reset 1.0/0.66 20 µA/400 µA
Serial Output Enable 1.0/0.66 20 µA/400 µA
Transfer Out Serial 1.0/0.66 20 µA/400 µA
Serial Output Clock 1.0/0.66 20 µA/400 µA
Output Enable 1.0/0.66 20 µA/400 µA
Parallel Data Inputs 1.0/0.66 20 µA/400 µA
Serial Data Input 1.0/0.66 20 µA/400 µA
Parallel Data Outputs 285/10 5.7 mA/16 mA
Serial Data Output 285/10 5.7 µA/16 mA
Input Register Full 20/5 400 µA/8 mA
Output Register Empty 20/5 400 µA/8 mA
U.L.
HIGH/LOW
Input I
Output I
IH/IIL
OH/IOL
www.fairchildsemi.com 2
Functional Description
As shown in the block diagram, the 74F433 co nsists of
three sections:
1. An Input Register with parallel and serial da ta inputs,
as well as control inputs and ou tputs for input handshaking and expansion.
2. A 4-bit-wide, 62-word -deep fall- throug h stack with se lfcontained control logic.
3. An Output Register with parallel and serial data outputs, as well as cont rol inputs and outputs fo r output
handshaking and expansion.
These three sections opera te asynchronously and are virtually independent of one another.
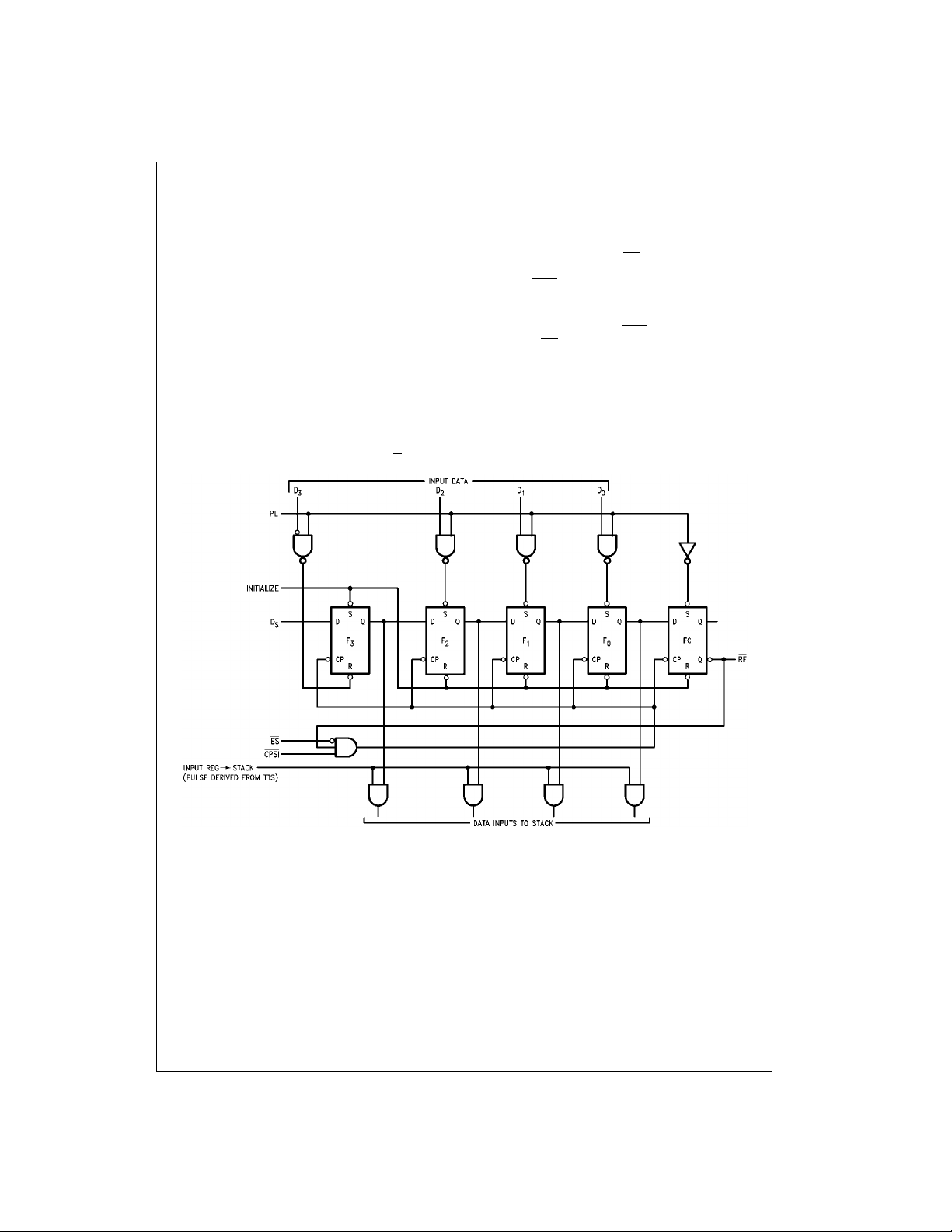
Input Register (Data Entry)
The Input Register can receive data in either bit-serial or 4bit parallel form. It stores t his data u ntil it is sent to the fallthrough stack, and also generates the necessary status
and control signals.
This 5-bit register (see Figure 1) is initialized by setting flip-
and resetting the other flip-flops. The Q-out put of
flop F
3
the last flip-flop (FC) is bro ught out as the Input Register
Full (IRF) signal. After initialization, this output is HIGH.
Parallel Entry—A HIGH on the Parallel Load (PL) input
loads the D
the FC flip-flop. Th i s f orces the IRF
inputs into the F0–F3 flip-flops and sets
0–D3
output LOW, indicating
that the input register is full. During parallel entry, the Serial
Input Clock (CPSI
Serial Entry—Data on the Serial Data (D
entered into the shift registe r (F
HIGH-to-LOW transition of the CPSI
Input Enable (IES
) input must be LOW.
) input is serially
S
, F2, F1, F0, FC) on each
3
input when the Serial
) signal is LOW. During serial e ntry, the
PL input should be LOW.
After the fourth clock transition, the four data bits are
located in flip-flops F
output LOW and intern ally inhibiting CPSI pulses
the IRF
. The FC flip-flop is set, forcing
0–F3
from affecting the register. Figure 2 illustrates the final positions in an 74F43 3 resulting from a 256-bit serial b it train
is the first bit, B
(B
0
the last).
255
74F433
FIGURE 1. Conceptual Input Section
3 www.fairchildsemi.com

74F433
FIGURE 2. Final Positions in an 74F433
Resulting from a 256-Bit Serial T rain
Fall-Through Stack—The outputs of flip-flops F
the stack. A LOW level on the Transfer to Stack (TTS
initiates a fall-through action; if the top location of the stack
is empty, data is loaded into the stack and the input register
is re-initialized. (Note that this initialization is delayed until
PL is LOW). Thus, automatic F IFO action is achieved by
connecting the IRF
An RS-type flip-flop (the initialization flip-flop) in the control
section records the f act that data has been transferred to
the stack. This prevents mul tiple entry of the same word
into the stack even though IRF
the initialization flip-flop is not cleared until PL goes LOW.
Once in the stack, data falls through automatically, pausing
only when it is necessary to wait for an empty next location.
In the 74F433, the master reset (MR
the stack control section and does not clear the data.
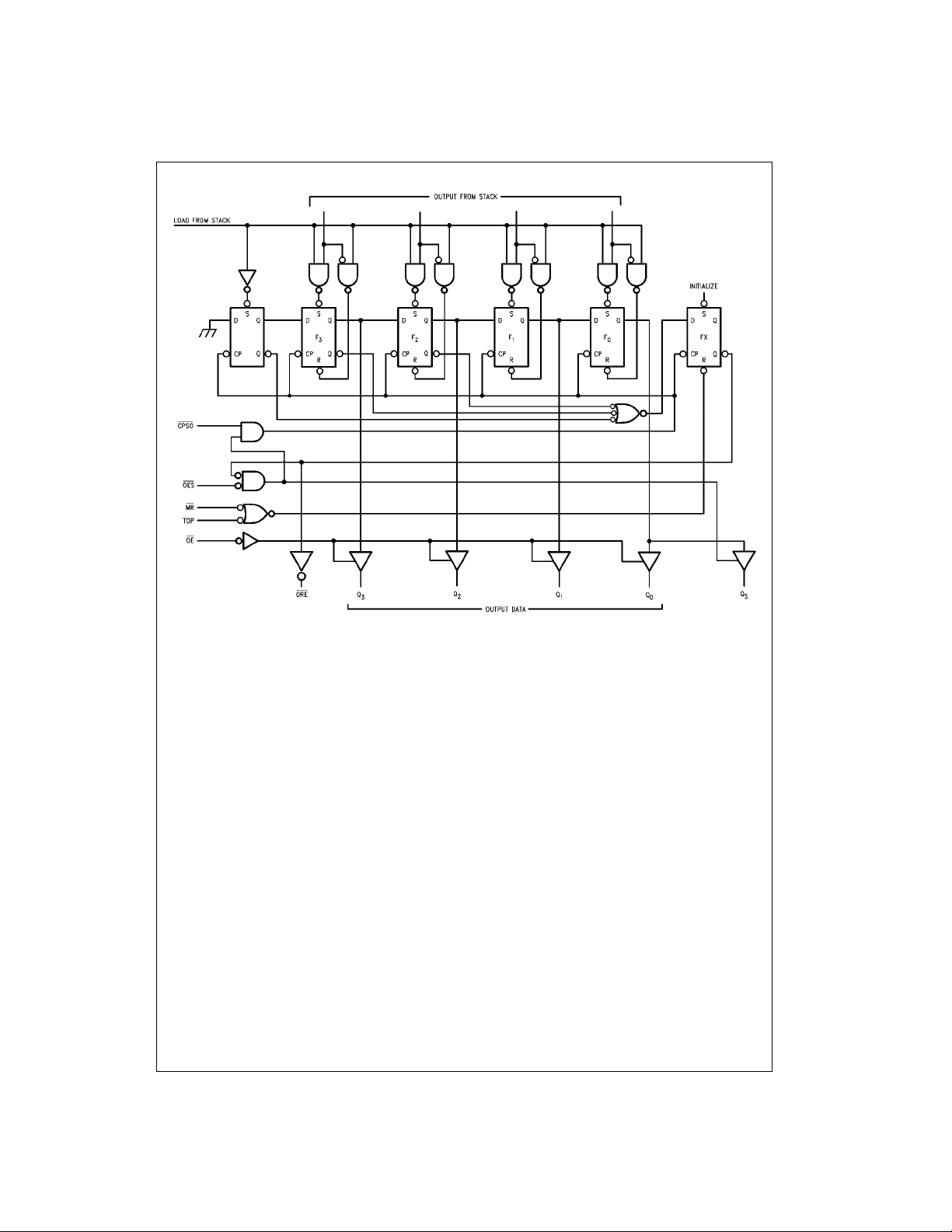
Output Register
The Output Register (see Figure 3) receives 4-bit data
words from the bottom stack location, stores them, and outputs data on a 3-STATE, 4-bit parallel data bus or on a 3 STATE serial data bus. The output secti on generates an d
receives the necessary status and control signals.
Parallel Extraction—W he n the FI FO is e m pt y a ft e r a LO W
pulse is applied to the MR input, the Output Register Empty
) output is LOW. After data has been en ter ed in to th e
(ORE
FIFO and has fallen through to the bottom stack location, it
is transferred into the outp ut register, if the Transfer Out
Parallel (TOP) input is HIGH. A s a r esult of the da ta tran s-
output to the TTS inpu t.
and TTS may still be LOW;
) input only initializes
0–F3
feed
) input
fer, ORE
goes HIGH, indicating valid data on the dat a outputs (provided that the 3-STATE buffer is enabled). The
TOP input can then be used to clock out the next word.
When TOP goes LOW, ORE
that the output data has been extracted; however, the data
itself remains on the output bus until a HIG H level on TOP
permits the transfer of t he next word (if availa ble) into the
output register. During para llel data extraction, the s erial
output clock (CPSO
Serial (TOS
ation or connected to the appropriate ORE
expanded operation (refer to the “Expansion” section).
The TOP signal is not edge-triggered. Therefore , if TOP
goes HIGH before data is available from the stack but data
becomes available before TOP again go es LOW, that data
is transferred into the output register. However, internal
control circuitry prevents the same data from being transferred twice. If TOP goes HIGH and returns to LOW before
data is available f rom the stack, O RE
cating that there is no valid data at the outputs.
Serial Extraction—Wh en the FIFO is empty a fter a LOW
is applied to the MR input, the ORE
data has been entered into the FIFO and has fallen through
to the bottom stack location, it is transferred into the output
register, if the TOS
result of the data transfer, ORE
valid data is in the register.
The 3-STATE Serial Data Output (Q
enabled and puts th e first data bit on the output b us. Data
is serially shifted out on the HIGH-to-LOW transition of
. To prevent false shifting, CPSO should be LOW
CPSO
when the new word is being loaded into the output register.
The fourth transit ion em pties the s hift reg ister, forces O RE
LOW, and disables the serial output, QS. For serial opera-
tion, the ORE
ing a new word from the stack as soon as the previous one
has been shifted out.
Expansion
Vertical Expansion—The 74F433 may be vertically
expanded, without external components, to store more
words. The interconnections necessary to form a 190-word
by 4-bit FIFO are shown in F igure 4. Using th e same te chnique, any FIFO of (63n+1)-wo rds by 4-bits ca n be confi gured, where n is the number of devices. Note that
expansion does not sacrifice any of the 74F433 flexibility
for serial/parallel input and output.
) line should be LO W. The T ra n sf er Ou t
) line should be gr ounde d for s ingle -slice oper-
input is LOW and TOP is HIG H. As a
output may be tied to the TOS input, request-
also goes LOW, indicating
line for
remains LOW, indi-
output is LOW. After
goes HIGH, indicating t hat
) is automatically
S
www.fairchildsemi.com 4
74F433
FIGURE 3. Conceptual Output Section
5 www.fairchildsemi.com
 Loading...
Loading...