Fairchild FDC640P service manual
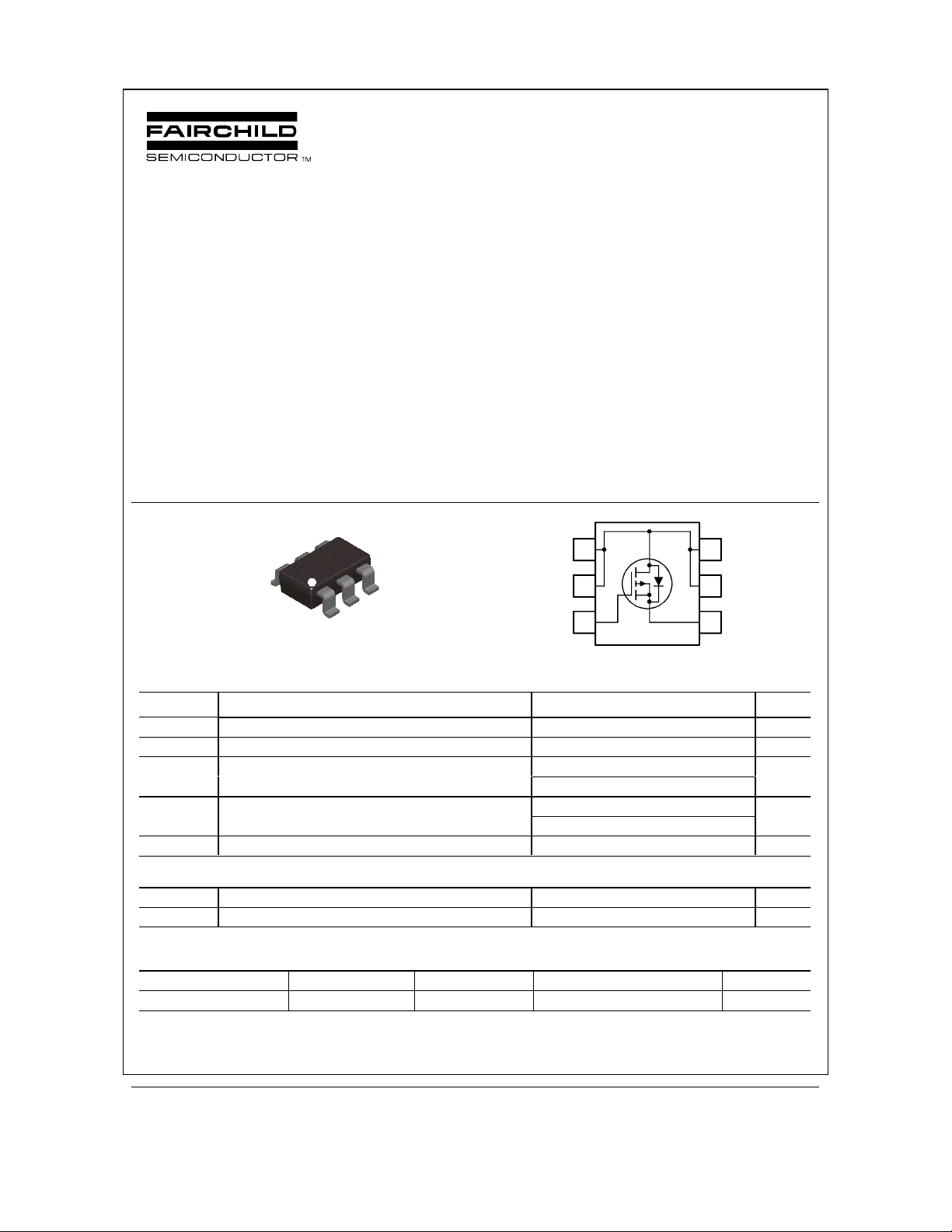
FDC640P
P-Channel 2.5V PowerTrench
Specified MOSFET
FDC640P
January 2001
General Description
This P-Channel 2.5V specified MOSFET uses a rugged
gate version of Fairchild’s advanced PowerTrench
process. It has been optimized for power management
applications with a wide range of gate drive voltage
(2.5V – 12V).
Applications
• Battery management
• Load switch
• Battery protection
Features
• –4.5 A, –20 V R
• Rugged gate rating (±12V)
• Fast switching speed
• High performance trench technology for extremely
low R
DS(ON)
= 0.053 Ω @ VGS = –4.5 V
DS(ON)
R
= 0.080 Ω @ VGS = –2.5 V
DS(ON)
S
D
D
1
2
6
5
G
SuperSOT -6
TM
D
D
Absolute Maximum Ratings T
=25oC unless otherwise noted
A
3
4
Symbol Parameter Ratings Units
V
DSS
V
GSS
I
D
D
TJ, T
STG
Drain-Source Voltage –20 V
Gate-Source Voltage
Drain Current – Continuous (Note 1a) –4.5 A
– Pulsed –20
Maximum Power Dissipation (Note 1a) 1.6 WP
(Note 1b)
Operating and Storage Junction Temperature Range –55 to +150
±12
0.8
V
°C
Thermal Characteristics
R
θJA
R
θJC
Thermal Resistance, Junction-to-Ambient (Note 1a) 78
Thermal Resistance, Junction-to-Case (Note 1) 30
Package Marking and Ordering Information
Device Marking Device Reel Size Tape width Quantity
.640 FDC640P 7’’ 8mm 3000 units
2001 Fairchild Semiconductor International
°C/W
°C/W
FDC640P Rev E(W)
FDC640P
Electrical Characteristics T
= 25°C unless otherwise noted
A
Symbol Parameter Test Conditions Min Typ Max Units
Off Characteristics
BV
DSS
∆BVDSS
∆T
I
DSS
I
GSSF
I
GSSR
Drain–Source Breakdown Voltage
Breakdown Voltage Temperature
Coefficient
J
V
= 0 V, ID = –250 µA
GS
I
= –250 µA, Referenced to 25°C
D
–20 V
–14
Zero Gate Voltage Drain Current VDS = –16 V, VGS = 0 V –1
Gate–Body Leakage, Forward VGS = 12 V, VDS = 0 V 100 nA
Gate–Body Leakage, Reverse VGS = –12 V, VDS = 0 V –100 nA
mV/°C
On Characteristics (Note 2)
V
GS(th)
∆VGS(th)
∆T
R
DS(on)
I
D(on)
g
FS
Gate Threshold Voltage
Gate Threshold Voltage
Temperature Coefficient
J
Static Drain–Source
On–Resistance
V
= VGS, ID = –250 µA
DS
I
= –250 µA, Referenced to 25°C
D
VGS = –4.5 V, ID = –4.5 A
= –2.5 V, ID = –3.6 A
V
GS
= –4.5 V, ID = –4.5A,TJ=125°C
V
GS
–0.6 –1.0 –1.5 V
3
0.039
0.062
0.053
On–State Drain Current VGS = –4.5 V, VDS = –5 V –20 A
Forward Transconductance VDS = –5 V, ID = –4.5 A 16 S
mV/°C
0.053
0.080
0.077
Dynamic Characteristics
C
iss
C
oss
C
rss
Input Capacitance 890 pF
Output Capacitance 244 pF
Reverse Transfer Capacitance
= –10 V, V
V
DS
f = 1.0 MHz
GS
= 0 V,
123 pF
Switching Characteristics (Note 2)
t
t
t
t
Q
Q
Q
d(on)
r
d(off)
f
g
gs
gd
Turn–On Delay Time 12 22 ns
Turn–On Rise Time 9 18 ns
= –10 V, ID = –1 A,
V
DD
= –4.5 V, R
V
GS
GEN
= 6 Ω
Turn–Off Delay Time 24 38 ns
Turn–Off Fall Time
Total Gate Charge 9 13 nC
Gate–Source Charge 2 nC
V
= –10 V, ID = –4.5 A,
DS
= –4.5 V
V
GS
Gate–Drain Charge
13 23 ns
3nC
Drain–Source Diode Characteristics and Maximum Ratings
I
S
V
SD
Notes:
1. R
θJA
pins. R
a. 78°C/W when mounted on a 1in
b. 156°C/W when mounted on a minimum pad.
2. Pulse Test: Pulse Width ≤ 300 µs, Duty Cycle ≤ 2.0%
Maximum Continuous Drain–Source Diode Forward Current –1.3 A
Drain–Source Diode Forward
VGS = 0 V, IS = –1.3 A (Note 2) –0.7 –1.2 V
Voltage
is the sum of the junction-to-case and case-to-ambient resistance where the case thermal reference is defined as the solder mounting surface of the drain
is guaranteed by design while R
θJC
2
pad of 2oz copper on FR-4 board.
is determined by the user's board design.
θCA
µA
Ω
FDC640P Rev E(W)
 Loading...
Loading...