August 2009
FAN2108 — TinyBuck™
3-24V Input, 8A, High-Efficiency, Integrated Synchronous
Buck Regulator
FAN2108 — TinyBuck™, 3-24V Input, 8A, High-Efficiency, Integrated Synchronous Buck Regulator
Features
Wide Input Voltage Range: 3V-24V
Wide Output Voltage Range: 0.8V to 80% V
IN
8A Output Current
Programmable Frequency Operation: 200KHz to
600KHz
Over 95% Peak Efficiency
Integrated Schottky Diode on Low-side MOSFET
Boosts Efficiency
Internal Bootstrap diode
Power-Good Signal
Pre-Bias Startup
Accepts Ceramic Capacitors on Output
External Compensation for Flexible Design
Input Under-Voltage Lockout
Programmable Current Limit
Under-Voltage, Over-Voltage, and Thermal
Shutdown Protections
Internal Soft-Start
5x6mm, 25-Pin, 3-Pad MLP Package
Description
The FAN2108 TinyBuck™ is a highly efficient, small
footprint, 8A, synchronous buck regulator.
The FAN2108 contains both synchronous MOSFETs
and a controller/driver with optimized interconnects in
one package, which enables designers to solve highcurrent requirements in a small area with minimal
external components.
External compensation, programmable switching
frequency, and current limit features allow design
optimization and flexibility.
The summing current mode modulator uses lossless
current sensing for current feedback and over-current
protection. Voltage feedforward helps operation over a
wide input voltage range.
Fairchild’s advanced BiCMOS power process,
combined with low-R
thermally efficient MLP package, provide the ability to
dissipate high power in a small package.
Output over-voltage, under-voltage, and thermal
shutdown protections help protect the device from
damage during fault conditions. FAN2108 prevents prebiased output discharge during startup in point-of-load
applications.
internal MOSFETs and a
DS(ON)
Applications
Servers
Point-of-Load Regulation
Related Application Notes
AN-8022 — TinyCalc™ Calculator
High-End Computing Systems
Graphics Cards
Battery-Powered Equipment
Set-Top Boxes
Ordering Information
Operating
Part Number
FAN2108MPX -10°C to 85°C Molded Leadless Package (MLP) 5x6mm Green Tape and Reel
FAN2108EMPX -40°C to 85°C Molded Leadless Package (MLP) 5x6mm Green Tape and Reel
For Fairchild’s definition of Eco Status, please vis it: http://www.fairchildsemi.com/company/green/rohs_green.html.
© 2008 Fairchild Semiconductor Corporation www.fairchildsemi.com
FAN2108 • Rev. 1.0.1
Temperature Range Package
Eco
Status
Packing
Method
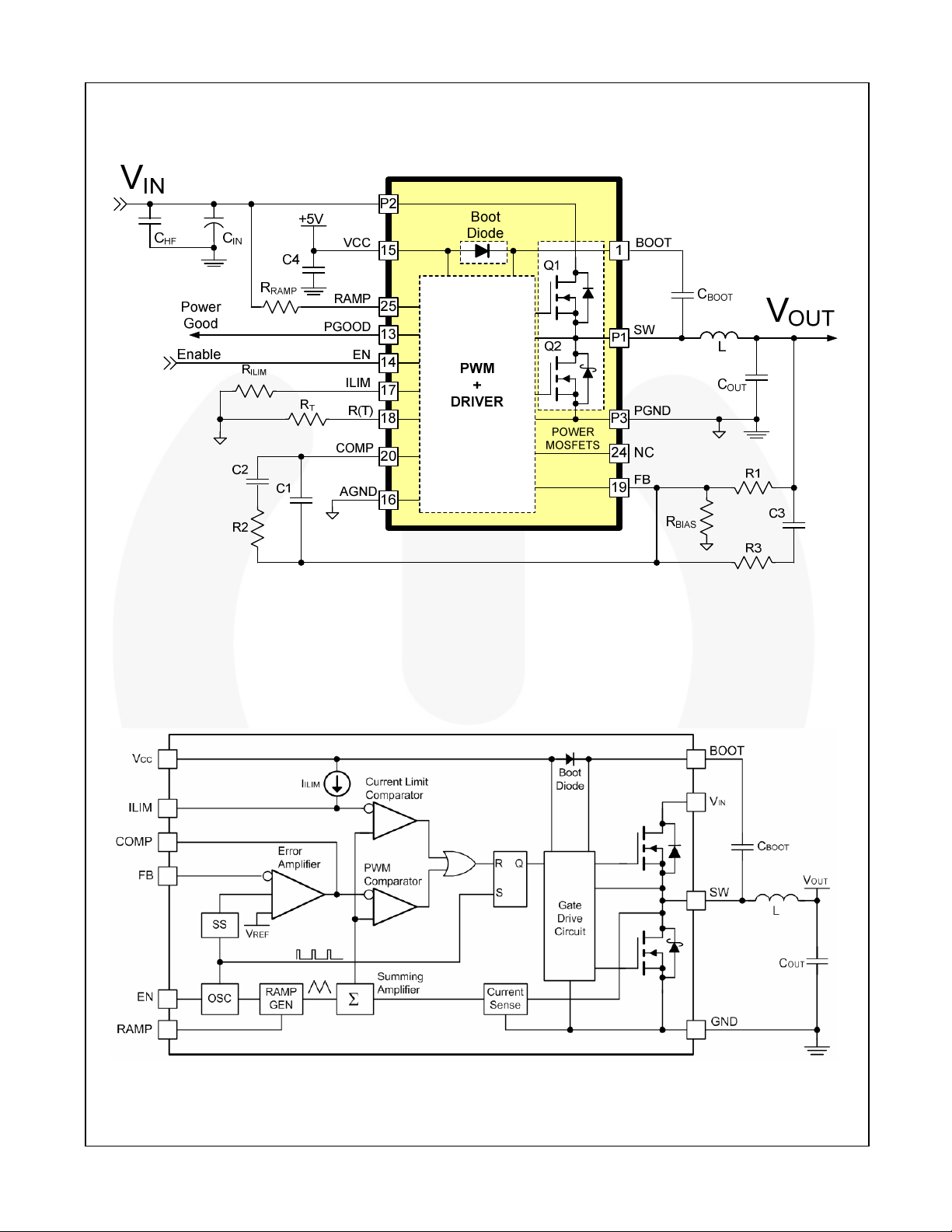
Typical Application
FAN2108 — TinyBuck™, 3-24V Input, 8A, High-Efficiency, Integrated Synchronous Buck Regulator
Block Diagram
Figure 1. Typical Application Diagram
Figure 2. Block Diagram
© 2008 Fairchild Semiconductor Corporation www.fairchildsemi.com
FAN2108 • Rev. 1.0.1 2
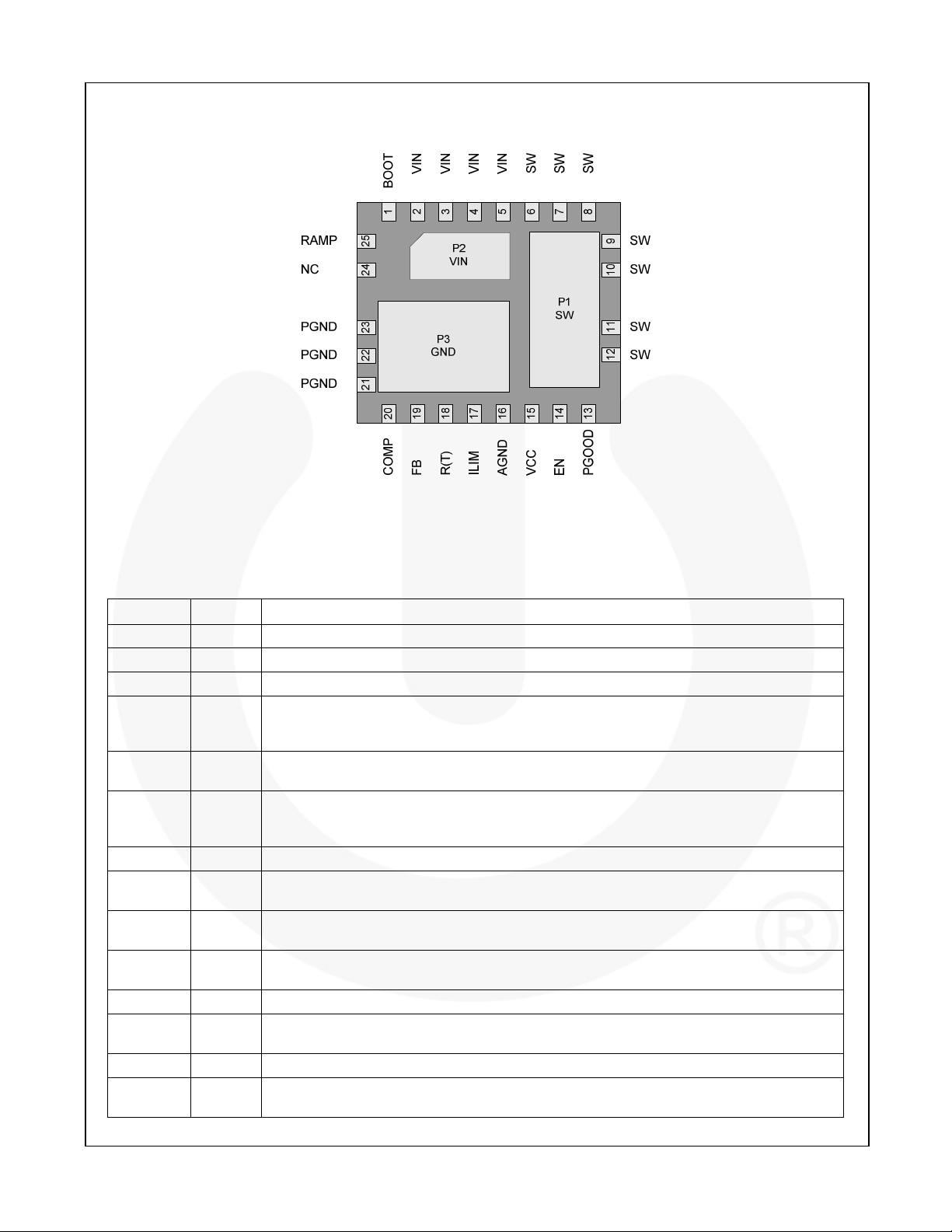
Pin Configuration
FAN2108 — TinyBuck™, 3-24V Input, 8A, High-Efficiency, Integrated Synchronous Buck Regulator
Figure 3. MLP 5x6mm Pin Configuration (Bottom View)
Pin Definitions
Pin # Name Description
P1, 6-12 SW
P2, 2-5 VIN
P3, 21-23 PGND
1 BOOT
13 PGOOD
14 EN
15 VCC
16 AGND
17 ILIM
18 R(T)
19 FB
20 COMP
24 NC
25 RAMP
Switching Node.
Power Input Voltage. Connect to the main input power source.
Power Ground. Power return and Q2 source.
High-Side Drive BOOT Voltage. Connect through capacitor (C
includes an internal synchronous bootstrap diode to recharge the capacitor on this pin to
V
when SW is LOW.
CC
Power-Good Flag. An open-drain output that pulls LOW when FB is outside a ±10% range
of the reference. PGOOD does not assert HIGH until the fault latch is enabled.
ENABLE. Enables operation when pulled to logic HIGH or left open. Toggling EN resets the
regulator after a latched fault condition. This input has an internal pull-up when the IC is
functioning normally. When a latched fault occurs, EN is discharged by a current sink.
Input Bias Supply for IC. The IC’s logic and analog circuitry are powered from this pin.
Analog Ground. The signal ground for the IC. All internal control voltages are referred to
this pin. Tie this pin to the ground island/plane through the lowest impedance connection.
Current Limit. A resistor (R
limit trip threshold lower than the default setting.
Oscillator Frequency. A resistor (R
frequency.
Output Voltage Feedback. Connect through a resistor divider to the output voltage.
Compensation. Error amplifier output. Connect the external compensation network
between this pin and FB.
No Connect. This pin is not used.
Ramp Amplitude. A resistor (R
and provides voltage feedforward functionality.
) to SW. The IC
BOOT
) from this pin to AGND can be used to program the current-
ILIM
) from this pin to AGND sets the PWM switching
T
) connected from this pin to VIN sets the ramp amplitude
RAMP
© 2008 Fairchild Semiconductor Corporation www.fairchildsemi.com
FAN2108 • Rev. 1.0.1 3
FAN2108 — TinyBuck™, 3-24V Input, 8A, High-Efficiency, Integrated Synchronous Buck Regulator
Absolute Maximum Ratings
Stresses exceeding the absolute maximum ratings may damage the device. The device may not function or be
operable above the recommended operating conditions and stressing the parts to these levels is not recommended.
In addition, extended exposure to stresses above the recommended operating conditions may affect device
reliability. The absolute maximum ratings are stress ratings only.
Parameter Conditions Min. Max. Unit
VIN to PGND 28 V
VCC to AGND AGND=PGND 6 V
BOOT to PGND 35 V
BOOT to SW -0.3 6.0 V
SW to PGND
All other pins -0.3 VCC+0.3 V
ESD
Continuous -0.5 24.0 V
Transient (t < 20ns, f <
Human Body Model, JEDEC JESD22-A114 2
600KHz) -5 30 V
kV
Charged Device Model, JEDEC JESD22-C101 2.5
Recommended Operating Conditions
The Recommended Operating Conditions table defines the conditions for actual device operation. Recommended
operating conditions are specified to ensure optimal performance to the datasheet specifications. Fairchild does not
recommend exceeding them or designing to absolute maximum ratings.
Symbol Parameter Conditions Min. Typ. Max. Unit
VCC Bias Voltage VCC to AGND 4.5 5.0 5.5 V
VIN Supply Voltage VIN to PGND 3 24 V
TA Ambient Temperature
FAN2108MPX -10 +85 °C
FAN2108EMPX -40 +85 °C
TJ Junction Temperature +125 °C
f Switching Frequency 600 kHz
Thermal Information
Symbol Parameter Min. Typ. Max. Unit
T
Storage Temperature -65 +150 °C
STG
TL Lead Soldering Temperature, 10 Seconds +300 °C
TVP Vapor Phase, 60 Seconds +215 °C
TI Infrared, 15 Seconds +220 °C
P1 (Q2) 4 °C/W
θJC
θ
J-PCB
PD Power Dissipation, TA=25°C
Thermal Resistance: Junction-to-Case
Thermal Resistance: Junction-to-Mounting Surface
(1)
2.8 W
Note:
1. Typical thermal resistance when mounted on a four-layer, two-ounce PCB, as shown in Figure 24. Actual results
are dependent on mounting method and surface related to the design.
P2 (Q1) 7 °C/W
P3 4 °C/W
(1)
35 °C/W
© 2008 Fairchild Semiconductor Corporation www.fairchildsemi.com
FAN2108 • Rev. 1.0.1 4
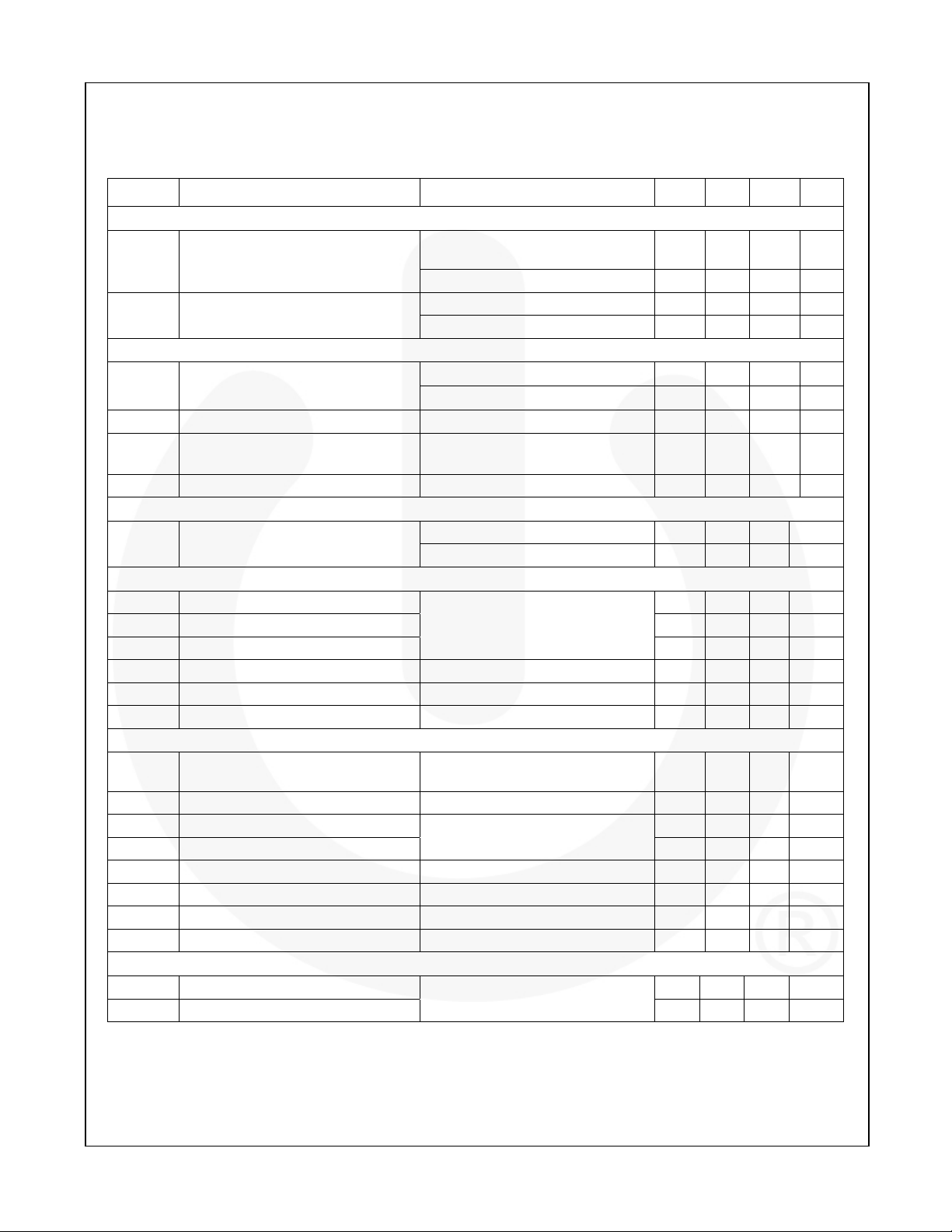
Electrical Specifications
Electrical specifications are the result of using the circuit shown in Figure 1 unless otherwise noted.
Symbol Parameter Conditions Min. Typ. Max. Unit
Power Supplies
SW=Open, FB=0.7V, VCC=5V,
f
=600KHz
ICC VCC Current
V
VCC UVLO Threshold
UVLO
SW
Shutdown: EN=0, V
=5V 7 10 µA
CC
Rising VCC 4.1 4.3 4.5 V
Hysteresis 300 mV
Oscillator
f Frequency
tON Minimum On-Time
V
Ramp Amplitude, peak-to–peak
RAMP
t
Minimum Off-Time
OFF
(2)
(2)
50 65 ns
100 150 ns
RT=50KΩ
R
=24KΩ
T
16VIN, 1.8V
R
=200KΩ
RAMP
, RT=30KΩ,
OUT
Reference
VFB
Reference Voltage (see Figure 4 for
Temperature Coefficient)
FAN2108MPX, 25°C 794 800 806 mV
FAN2108EMPX, 25°C 795 800 805 mV
Error Amplifier
G DC Gain
BW Gain Bandwidth Product
V
Output Voltage
COMP
I
Output Current, Sourcing VCC=5V, V
SINK
I
Output Current, Sinking VCC=5V, V
SOURCE
I
FB Bias Current VFB=0.8V, 25°C -850 -650 -450 nA
BIAS
(2)
80 85 dB
(2)
12 15 MHz
V
=5V
CC
=2.2V 1.5 2.2 mA
COMP
=1.2V 0.8 1.2 mA
COMP
Protection and Shutdown
Open at 25°C (see Circuit
R
I
Current Limit
LIM
I
I
ILIM
T
Over-Temperature Shutdown +155 °C
TSD
T
HYS
V
OVP
V
UVLO
V
Fault Discharge Threshold Measured at FB Pin 250 mV
FLT
V
FLT_HYS
Current -11 -10 -9 µA
LIM
Over-Temperature Hysteresis
Over-Voltage Threshold Two Consecutive Clock Cycles 110 115 121 %V
Under-Voltage Shutdown 16 Consecutive Clock Cycles 68 73 78 %V
Fault Discharge Hysteresis Measured at FB Pin (VFB ~500mV) 250 mV
ILIM
Description)
Internal IC Temperature
Soft-Start
tSS V
tEN Fault Enable/SSOK (T1.0)
to Regulation (T0.8) 5.3 ms
OUT
Frequency=600KHz
Note:
2. Specifications guaranteed by design and characterization; not production tested.
8 12 mA
255 300 345 KHz
540 600 660 KHz
0.53 V
0.4 3.2 V
12 15 18 A
+30 °C
OUT
OUT
6.7 ms
FAN2108 — TinyBuck™, 3-24V Input, 8A, High-Efficiency, Integrated Synchronous Buck Regulator
© 2008 Fairchild Semiconductor Corporation www.fairchildsemi.com
FAN2108 • Rev. 1.0.1 5
 Loading...
Loading...