Page 1

SSP 7.1
7.1 Channel Surround Sound Processor
User Guide
Audio
68-1339-01 Rev. C
06 12
Page 2

Safety Instructions • English
This symbol is intended to alert the user of important operating and
maintenance (servicing) instructions in the literature provided with the
equipment.
This symbol is intended to alert the user of the presence of uninsulated
dangerous voltage within the product enclosure that may present a risk of
electric shock.
Caution
Read Instructions • Read and understand all safety and operating instructions before using the equipment.
Retain Instructions • The safety instructions should be kept for future reference.
Follow Warnings • Follow all warnings and instructions marked on the equipment or in the user information.
Avoid Attachments • Do not use tools or attachments that are not recommended by the equipment
manufacturer because they may be hazardous.
Warning
Power sources • This equipment should be operated only from the power source indicated on the product. This
equipment is intended to be used with a main power system with a grounded (neutral) conductor. The third
(grounding) pin is a safety feature, do not attempt to bypass or disable it.
Power disconnection • To remove power from the equipment safely, remove all power cords from the rear of the
equipment, or the desktop power module (if detachable), or from the power source receptacle (wall plug).
Power cord protection • Power cords should be routed so that they are not likely to be stepped on or pinched by
items placed upon or against them.
Servicing • Refer all servicing to qualified service personnel. There are no user-serviceable parts inside. To prevent
the risk of shock, do not attempt to service this equipment yourself because opening or removing covers may
expose you to dangerous voltage or other hazards.
Slots and openings • If the equipment has slots or holes in the enclosure, these are provided to prevent
overheating of sensitive components inside. These openings must never be blocked by other objects.
Lithium battery • There is a danger of explosion if battery is incorrectly replaced. Replace it only with the same or
equivalent type recommended by the manufacturer. Dispose of used batteries according to the instructions of
the manufacturer.
Consignes de Sécurité • Français
Ce symbole sert à avertir l’utilisateur que la documentation fournie avec le
matériel contient des instructions importantes concernant l’exploitation et la
maintenance (réparation).
Ce symbole sert à avertir l’utilisateur de la présence dans le boîtier
de l’appareil de tensions dangereuses non isolées posant des risques
d’électrocution.
Attention
Lire les instructions• Prendre connaissance de toutes les consignes de sécurité et d’exploitation avant d’utiliser
le matériel.
Conserver les instructions• Ranger les consignes de sécurité afin de pouvoir les consulter à l’avenir.
Respecter les avertissements • Observer tous les avertissements et consignes marqués sur le matériel ou
présentés dans la documentation utilisateur.
Eviter les pièces de fixation • Ne pas utiliser de pièces de fixation ni d’outils non recommandés par le fabricant
du matériel car cela risquerait de poser certains dangers.
Sicherheitsanleitungen • Deutsch
Dieses Symbol soll dem Benutzer in der im Lieferumfang enthaltenen
Dokumentation besonders wichtige Hinweise zur Bedienung und Wartung
(Instandhaltung) geben.
Dieses Symbol soll den Benutzer darauf aufmerksam machen, daß im Inneren
des Gehäuses dieses Produktes gefährliche Spannungen, die nicht isoliert sind
und die einen elektrischen Schock verursachen können, herrschen.
Achtung
Lesen der Anleitungen • Bevor Sie das Gerät zum ersten Mal verwenden, sollten Sie alle Sicherheits-und
Bedienungsanleitungen genau durchlesen und verstehen.
Aufbewahren der Anleitungen • Die Hinweise zur elektrischen Sicherheit des Produktes sollten Sie
aufbewahren, damit Sie im Bedarfsfall darauf zurückgreifen können.
Befolgen der Warnhinweise • Befolgen Sie alle Warnhinweise und Anleitungen auf dem Gerät oder in der
Benutzerdokumentation.
Keine Zusatzgeräte • Verwenden Sie keine Werkzeuge oder Zusatzgeräte, die nicht ausdrücklich vom Hersteller
empfohlen wurden, da diese eine Gefahrenquelle darstellen können.
Avertissement
Alimentations • Ne faire fonctionner ce matériel qu’avec la source d’alimentation indiquée sur l’appareil. Ce
matériel doit être utilisé avec une alimentation principale comportant un fil de terre (neutre). Le troisième
contact (de mise à la terre) constitue un dispositif de sécurité : n’essayez pas de la contourner ni de la
désactiver.
Déconnexion de l’alimentation• Pour mettre le matériel hors tension sans danger, déconnectez tous les cordons
d’alimentation de l’arrière de l’appareil ou du module d’alimentation de bureau (s’il est amovible) ou encore de
la prise secteur.
Protection du cordon d’alimentation • Acheminer les cordons d’alimentation de manière à ce que personne ne
risque de marcher dessus et à ce qu’ils ne soient pas écrasés ou pincés par des objets.
Réparation-maintenance • Faire exécuter toutes les interventions de réparation-maintenance par un technicien
qualifié. Aucun des éléments internes ne peut être réparé par l’utilisateur. Afin d’éviter tout danger
d’électrocution, l’utilisateur ne doit pas essayer de procéder lui-même à ces opérations car l’ouverture ou le
retrait des couvercles risquent de l’exposer à de hautes tensions et autres dangers.
Fentes et orifices • Si le boîtier de l’appareil comporte des fentes ou des orifices, ceux-ci servent à empêcher les
composants internes sensibles de surchauffer. Ces ouvertures ne doivent jamais être bloquées par des objets.
Lithium Batterie • Il a danger d’explosion s’il y a remplacment incorrect de la batterie. Remplacer uniquement
avec une batterie du meme type ou d’un type equivalent recommande par le constructeur. Mettre au reut les
batteries usagees conformement aux instructions du fabricant.
Vorsicht
Stromquellen • Dieses Gerät sollte nur über die auf dem Produkt angegebene Stromquelle betrieben werden.
Dieses Gerät wurde für eine Verwendung mit einer Hauptstromleitung mit einem geerdeten (neutralen) Leiter
konzipiert. Der dritte Kontakt ist für einen Erdanschluß, und stellt eine Sicherheitsfunktion dar. Diese sollte nicht
umgangen oder außer Betrieb gesetzt werden.
Stromunterbrechung • Um das Gerät auf sichere Weise vom Netz zu trennen, sollten Sie alle Netzkabel aus der
Rückseite des Gerätes, aus der externen Stomversorgung (falls dies möglich ist) oder aus der Wandsteckdose
ziehen.
Schutz des Netzkabels • Netzkabel sollten stets so verlegt werden, daß sie nicht im Weg liegen und niemand
darauf treten kann oder Objekte darauf- oder unmittelbar dagegengestellt werden können.
Wartung • Alle Wartungsmaßnahmen sollten nur von qualiziertem Servicepersonal durchgeführt werden. Die
internen Komponenten des Gerätes sind wartungsfrei. Zur Vermeidung eines elektrischen Schocks versuchen
Sie in keinem Fall, dieses Gerät selbst öffnen, da beim Entfernen der Abdeckungen die Gefahr eines
elektrischen Schlags und/oder andere Gefahren bestehen.
Schlitze und Öffnungen • Wenn das Gerät Schlitze oder Löcher im Gehäuse aufweist, dienen diese zur
Vermeidung einer Überhitzung der empndlichen Teile im Inneren. Diese Öffnungen dürfen niemals von
anderen Objekten blockiert werden.
Litium-Batterie • Explosionsgefahr, falls die Batterie nicht richtig ersetzt wird. Ersetzen Sie verbrauchte Batterien nur
durch den gleichen oder einen vergleichbaren Batterietyp, der auch vom Hersteller empfohlen wird. Entsorgen
Sie verbrauchte Batterien bitte gemäß den Herstelleranweisungen.
Instrucciones de seguridad • Español
Este símbolo se utiliza para advertir al usuario sobre instrucciones
importantes de operación y mantenimiento (o cambio de partes) que se
desean destacar en el contenido de la documentación suministrada con los
equipos.
Este símbolo se utiliza para advertir al usuario sobre la presencia de
elementos con voltaje peligroso sin protección aislante, que puedan
encontrarse dentro de la caja o alojamiento del producto, y que puedan
representar riesgo de electrocución.
Precaucion
Leer las instrucciones • Leer y analizar todas las instrucciones de operación y seguridad, antes de usar el
equipo.
Conservar las instrucciones • Conservar las instrucciones de seguridad para futura consulta.
Obedecer las advertencias • Todas las advertencias e instrucciones marcadas en el equipo o en la
documentación del usuario, deben ser obedecidas.
Evitar el uso de accesorios • No usar herramientas o accesorios que no sean especificamente recomendados
por el fabricante, ya que podrian implicar riesgos.
安全须知 • 中文
这个符号提示用户该设备用户手册中有重要的操作和维护说明。
这个符号警告用户该设备机壳内有暴露的危险电压,有触电危险。
注意
阅读说明书 • 用户使 用该设备前必须阅读并理 解所有安全和 使用说明。
保存说明书 • 用 户应保存安全说明书以备将来使用。
遵守警告 • 用户应遵守产品和用户指南上的所有安 全和操作说明。
避免追加 • 不要使 用该产品厂商没有推荐的工具或追加设备,以避免危险。
Advertencia
Alimentación eléctrica • Este equipo debe conectarse únicamente a la fuente/tipo de alimentación eléctrica
indicada en el mismo. La alimentación eléctrica de este equipo debe provenir de un sistema de distribución
general con conductor neutro a tierra. La tercera pata (puesta a tierra) es una medida de seguridad, no
puentearia ni eliminaria.
Desconexión de alimentación eléctrica • Para desconectar con seguridad la acometida de alimentación eléctrica
al equipo, desenchufar todos los cables de alimentación en el panel trasero del equipo, o desenchufar el
módulo de alimentación (si fuera independiente), o desenchufar el cable del receptáculo de la pared.
Protección del cables de alimentación • Los cables de alimentación eléctrica se deben instalar en lugares donde
no sean pisados ni apretados por objetos que se puedan apoyar sobre ellos.
Reparaciones/mantenimiento • Solicitar siempre los servicios técnicos de personal calicado. En el interior no
hay partes a las que el usuario deba acceder. Para evitar riesgo de electrocución, no intentar personalmente la
reparación/mantenimiento de este equipo, ya que al abrir o extraer las tapas puede quedar expuesto a voltajes
peligrosos u otros riesgos.
Ranuras y aberturas • Si el equipo posee ranuras o orificios en su caja/alojamiento, es para evitar el
sobrecalientamiento de componentes internos sensibles. Estas aberturas nunca se deben obstruir con otros
objetos.
Batería de litio • Existe riesgo de explosión si esta batería se coloca en la posición incorrecta. Cambiar esta batería
únicamente con el mismo tipo (o su equivalente) recomendado por el fabricante. Desachar las baterías usadas
siguiendo las instrucciones del fabricante.
警告
电源 • 该设备只能使用产品上标明的电源。 设备必须使用有地线的供电系统供电。 第三条线(
地线)是安全设施,不能不用或跳过 。
拔掉电源 • 为安全 地从设备拔掉电源,请拔掉所有设备后或桌面电源的电源线,或任何接到市电
系统的电源 线。
电源线保护 • 妥善布线, 避免被踩踏,或重物挤压。
维护 • 所有维修必须由认证的维修人员进行。 设备内部没有用户可以更换的零件。为避免出现触
电危险不 要自己试图打开设备盖子维修 该设备。
通风孔 • 有些设备机壳上有通风槽或孔,它们是用来防止机内敏感元件过 热。 不要用任何 东西
挡住通风孔。
锂电池 • 不正确的更换电池会有爆炸的危险。必须使 用与厂家推荐的相同或相近型号的电池。按
照生产厂的建议处理废弃电 池。
Page 3

FCC Class B Notice
Class B digital device, pursuant to part 15 of the FCC rules. These limits provide
reasonable protection against harmful interference in a residential installation. This
equipment generates, uses, and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed
and used in accordance with the instructions, may cause harmful interference to radio
communications. There is no guarantee that interference will not occur. If this equipment
does cause interference to radio or television reception, which can be determined by turning
the equipment off and on, you are encouraged to try to correct the interference by one or
more of the following measures:
z Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
z Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
z Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to which the
z Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
NOTES: • This unit was tested with shielded I/O cables on the peripheral devices.
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a
receiver is connected.
Shielded cables must be used to ensure compliance with FCC emissions limits.
• For more information on safety guidelines, regulatory compliances, EMI/EMF
compatibility, accessibility, and related topics, see the “Extron Safety and
Regulatory Compliance Guide” on the Extron website.
Copyright
© 2012 Extron Electronics. All rights reserved.
Trademarks
All trademarks mentioned in this manual are the properties of their respective owners.
Page 4
Conventions Used in this Guide
Notications the following are used:
DANGER: Danger indicates a situation that will result in death or severe
injury. For example:
DANGER: Severe Electric Shock. Disconnect power to this
furnishing before cleaning.
WARNING: A warning indicates a situation that has the potential to result in death or
severe injury. For example:
WARNING: May result in Electric Shock. Devices used in this furnishing
should be connected to a properly grounded outlet only (see Grounding
Instructions in the device manual).
CAUTION: A caution indications a situation that may result in minor injury.
ATTENTION: Attention indicates a situation that may damage or destroy the product
or associated equipment. For example:
ATTENTION: Potential Damage to Property. The opening in the table
should be cut only by licensed and bonded craftspeople. Exercise care to
prevent scarring or damaging the furniture.
NOTE: A note draws attention to important information.
TIP: A tip provides a suggestion to make working with the application easier.
Software Commands
Commands are written in the fonts shown here:
^AR Merge Scene,,Op1 scene 1,1 ^B 51 ^W^C
[01] R 0004 00300 00400 00800 00600 [02] 35 [17] [03]
E X! *X1&* X2)* X2#* X2! CE
NOTE: For commands and examples of computer or device responses mentioned
Computer responses and directory paths that do not have variables are written in the
font shown here:
Reply from 208.132.180.48: bytes=32 times=2ms TTL=32
C:\Program Files\Extron
Variables are written in slanted form as shown here:
ping xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx —t
SOH R Data STX Command ETB ETX
Selectable items, such as menu names, menu options, buttons, tabs, and field names are
written in the font shown here:
From the
Click the OK button.
}
in this guide, the character “0” is used for the number zero and “O”
represents the capital letter “o.”
File menu, select New.
Page 5
Contents
Introduction............................................................ 1
About the SSP 7.1............................................... 1
SSP 7.1 Features ................................................. 2
Features ................................................................... 4
Rear Panel Features ............................................. 4
Front Panel Features and Operation .................... 6
Source Format................................................. 6
Mode Override Selection ................................. 7
Input Selection ................................................ 9
Mute Output ................................................ 10
Complete System Reset ................................. 10
Volume Adjustment ...................................... 11
Analog Input Gain Adjustment ...................... 11
Front Panel Security Lockout
(Executive Mode) ......................................... 12
Setup ...................................................................... 13
Speaker Setup................................................... 13
Abbreviations ................................................ 14
Bass Management ............................................ 15
Speaker Size Settings .................................... 15
Speaker Delay Settings ...................................... 17
Test Signals ....................................................... 17
Output Channel Trim Settings ........................... 17
Listening Mode Settings .................................... 18
Dolby Pro Logic II or IIx Music ........................ 18
DTS Neo:6 Music or Cinema ......................... 18
Dynamic Range Compression Control ............... 19
Tone Controls ................................................... 20
Volume Output ................................................. 21
Equalization ...................................................... 21
Setup and Control Software ............................. 22
Installing the SSP 7.1 Setup and
Control Software ............................................. 22
Live and Emulate Modes ................................... 23
Running the SSP 7.1 Setup and
Control Software ............................................. 24
“Connect to device?” Dialog Box .................. 24
Main Tab ....................................................... 26
Speaker Setup Tab ........................................ 30
Speaker Configuration Tab ............................ 30
Speaker Delay Tab ......................................... 32
Testing & Output Trim Tab ............................. 36
Speaker Equalization Tab ............................... 41
Listening Mode Setup Tab ............................. 45
Preferences Tab ............................................. 45
Override Preferences Tab ............................... 48
Dolby, DTS and Mono Settings Tab ................ 49
Drop-down Menus ........................................ 51
SSP 7.1 Setup and Control Software Help File ... 55
Firmware Updates ............................................. 56
Specifications, Parts, and Accessories ............ 58
Specifications .................................................... 58
Included Parts ............................................... 60
Optional Accessories ..................................... 60
SSP 7.1 • Contents v
Page 6
Reference Material ............................................. 61
Source Formats ................................................. 61
Surround Channel Information ...................... 61
Dolby Digital Source Formats (
DTS Source Formats (DTS) ............................. 64
PCM Digital Source Format (PCM) ................. 65
2-Channel Source Format (2CH) .................... 65
Sampling Frequency ...................................... 65
Listening Mode Options and Usage ................... 66
Listening Mode Options ................................ 66
Listening Modes Usage ................................. 70
Listening Mode and Output Channels ........... 73
Source Formats and Listening Modes with
Different Speaker Setups .............................. 75
D) ............. 63
SIS Commands ..................................................... 78
Introduction to SIS ........................................... 78
Symbols Used in this Manual............................. 79
Error Messages ................................................. 84
Expected Unsolicited Responses ........................ 84
Command and Response Table for
SIS Commands ................................................ 85
Setting Speaker Delay Settings Using
SIS Commands ................................................ 94
Two Person Setup ......................................... 94
Setup with a Real Time Analyzer (RTA)
Calibration Tool ............................................ 95
Setting up Test Sources with SIS Commands.. 96
Mounting .............................................................. 97
Tabletop Placement ........................................... 97
Rack Mounting ................................................. 97
UL Guidelines for Rack Mounting .................. 97
Rack Mounting Procedure ............................. 98
Under-desk Mounting ....................................... 98
Glossary ................................................................. 99
Index .................................................................... 102
SSP 7.1 • Contents vi
Page 7
Introduction
This manual contains information on how to mount, install, and congure the Extron®
SSP 7.1 surround sound processor.
Unless otherwise specied, references in this manual to the SSP 7.1, “sound processor,” or
“surround sound processor” all refer to the SSP 7.1 unit.
About the SSP 7.1
The SSP 7.1 is a 7.1 channel surround sound processor with four digital inputs and one
analog input. A variety of selectable listening modes can be changed to match the source
format.
The unit can accept 2 channel analog signals, as well as digital pulse code modulation (PCM)
signals, and output them through various matrix decoding mode options for use in 5.1 to
7.1 system congurations.
The SSP 7.1 can decode and process licensed, branded digital source formats from
Dolby® Digital1 and DTS®2, in their originally encoded formats. These include:
z Dolby Digital 2/0
z Dolby Digital 2/0 Surround
z Dolby Digital 5.1
z Dolby Digital Surround EX
z DTS 2-channel
z DTS Digital Surround
z DTS 96/24
z DTS-ES
z DTS 96/24 ES Matrix 6.1
z DTS-ES Discrete 6.1
™2
®2
Matrix 6.1
™1
®2
1. Manufactured under license from Dolby Laboratories. Dolby, Pro Logic, and the double-D symbol are
trademarks of Dolby Laboratories.
2. Manufactured under license under U.S. patent numbers: 5,451,942; 5,956,674; 5,974,380; 5,978,762;
6,226,616; 6,487,535; 7,003,467; 7,212,872 and other U.S. and worldwide patents issued and pending. DTS,
DTS Digital Surround, ES, and Neo:6 are registered trademarks and the DTS logos, symbol and DTS 96/24 are
trademarks of DTS, Inc.
© 1996-2010 DTS, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
SSP 7.1 • Introduction 1
Page 8

SSP 7.1 Features
Advanced control and configuration — The SSP 7.1 Setup and Control Software provides
additional configuration options beyond those available through front panel control.
Emulate and Live modes for configuration — The control program can be used in
Emulate mode to create an SSP 7.1 conguration. The modications can be saved and
applied to the unit when a connection is established. In Live mode, the changes are made
directly to the unit.
Four digital audio inputs — The unit accepts four digital inputs through two optical
(TOSLINK®) digital inputs and two S/PDIF coaxial (RCA) digital inputs.
One analog input — The unit accepts one balanced/unbalanced analog input on a 5-pole
captive screw connector.
Configurable analog input — Input 5 accepts balanced or unbalanced stereo analog
inputs and can be configured to accept one or two balanced or unbalanced mono inputs
through a captive screw connector. The mono source can be left, right, or a mix summed of
the two.
Automatic surround sound format detection and decoding — The SSP 7.1
automatically detects the format of the incoming audio signal, and then applies the userdefined decoding so that signals are sent to the appropriate outputs.
Input source surround sound format indicator — The appropriate LED indicator
illuminates to indicate the incoming format of the selected input source, whether
Dolby Digital, DTS, PCM, or two-channel analog.
Dolby Digital and DTS playback — The unit is able to decode and process source format
from Dolby Digital and DTS, in their originally encoded formats.
Matrix decoding — The surround sound processor can decode stereo signals to produce
multichannel output.
Downmix multichannel source formats — Downmixing produces a mixed stereo
or mono channel with an additional option to redistribute the downmixed signal to all
channels.
Front panel audio level adjustment with LED level and analog clip indication —
Provides overall output volume adjustment for all outputs as well as adjustment of input
level for the analog input. Accompanying LEDs display input gain level, and a dedicated LED
indicator illuminates red when analog clipping has occurred.
Multiple listening modes — Not all listening modes are compatible with certain input
signals. The listening mode depends not only on the format of the source material but also
on the speaker configuration of the setting. Only those listening modes that are compatible
for a given input are available for that signal. The SSP 7.1 comes with factory default
listening modes that have been matched to the source format to take into account source
format and speaker configuration.
Listening mode override — Listening mode override customizes the listening mode to the
needs of the source format, speaker configuration, the venue, and the personal preferences
of the listener. Selections made through the front panel can be further rened by the SSP 7.1
Setup and Control Software.
This feature can be used to associate a specific listening mode with each input type, allowing
the user to switch quickly to the listening mode that suits each input type for a given room
configuration and the individual user preferences.
SSP 7.1 • Introduction 2
Page 9

Test signals for setup and calibration — The SSP 7.1 generates test signals, including
band-limited Dolby noise and full-bandwidth pink noise, to facilitate calibration of sound
pressure levels from all speakers, and to fine-tune the interaction of a speaker with the
acoustical environment. The SSP 7.1 also offers the option to use an external source for test
signals, which can then be directed to any speaker, or all speakers in sequence.
Speaker compensation delay — The signal to each output channel can be individually
delayed so that the sound from all speakers is synchronized when it reaches the listener.
Lip sync offset — This feature delays an audio signal so that it is resynchronized with a
video signal that has been delayed by video processing. The offset can be applied to each
input channel independently.
Equalization — Nine bands of parametric EQ are available to enhance tone, compensate
for differences in individual speaker output, and adjust frequency response for a given
acoustic environment.
SSP 7.1 • Introduction 3
Page 10
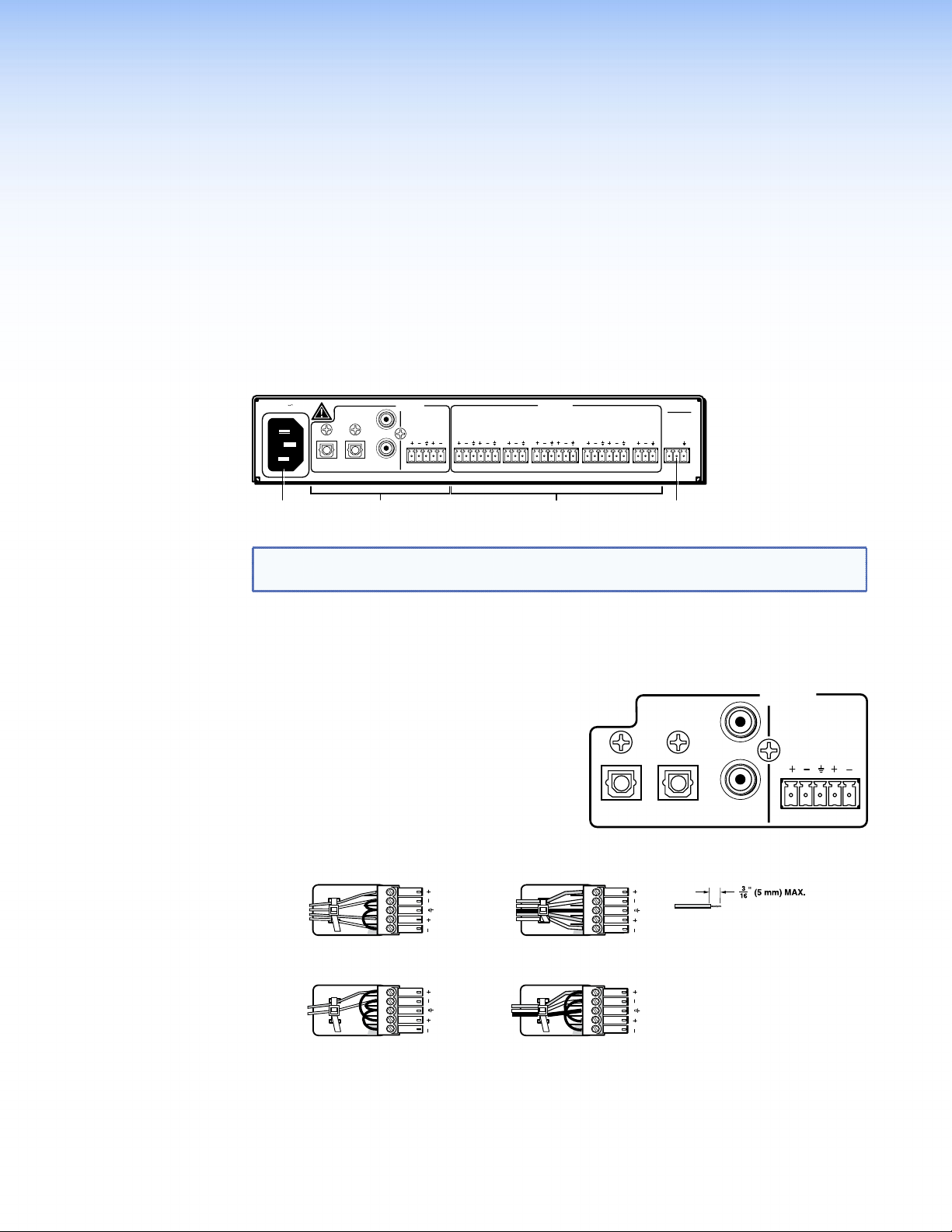
Features
bc
INPUTS
The next two sub-sections describe the features and operation of the SSP 7.1.
z Rear Panel Features
z Front Panel Features and Operation
Rear Panel Features
100-240V .5A
50/60Hz
a d
Figure 1. SSP 7.1 Rear Panel Features
NOTE: On earlier models of the SSP 7.1, the Surround Output Channels are labeled
DIGITAL
1
Side.
INPUTS
ANALOG
3
L
4
2
FRONT
5
L
R
R
CENTER
OUTPUTS
SURROUND
L
SSP 7.1
SUB
BACK
L
R
R
WOOFER
RS-232
Tx Rx
a AC power input — Use an IEC power cable to connect the processor to a
100 - 240 VAC, 50 - 60 Hz, power source.
b Audio inputs — The SSP 7.1 accepts four digital inputs and one analog input.
z Inputs 1 and 2 accept digital signals
through S/PDIF optical cables.
z Inputs 3 and 4 accept digital signals
through S/PDIF coaxial cables.
z Input 5 accepts a balanced or
unbalanced, stereo or mono, analog
input through a 5-pin captive screw
connector.
The following diagram shows the correct wiring for different analog input signals.
Tip
Sleeve
Tip
Sleeve
Unbalanced Stereo Input
Tip
Sleeve
Unbalanced Mono Input
LR
LR
Tip
Ring
Sleeves
Tip
Ring
Balanced Stereo Input
Tip
Ring
Sleeve
Balanced Mono Input
(high impedance)
Figure 2. Wiring for Analog Input (Input 5)
1
DIGITAL
2
LR
LR
3
4
Do not tin the wires!
ANALOG
5
L
R
SSP 7.1 • Features 4
Page 11
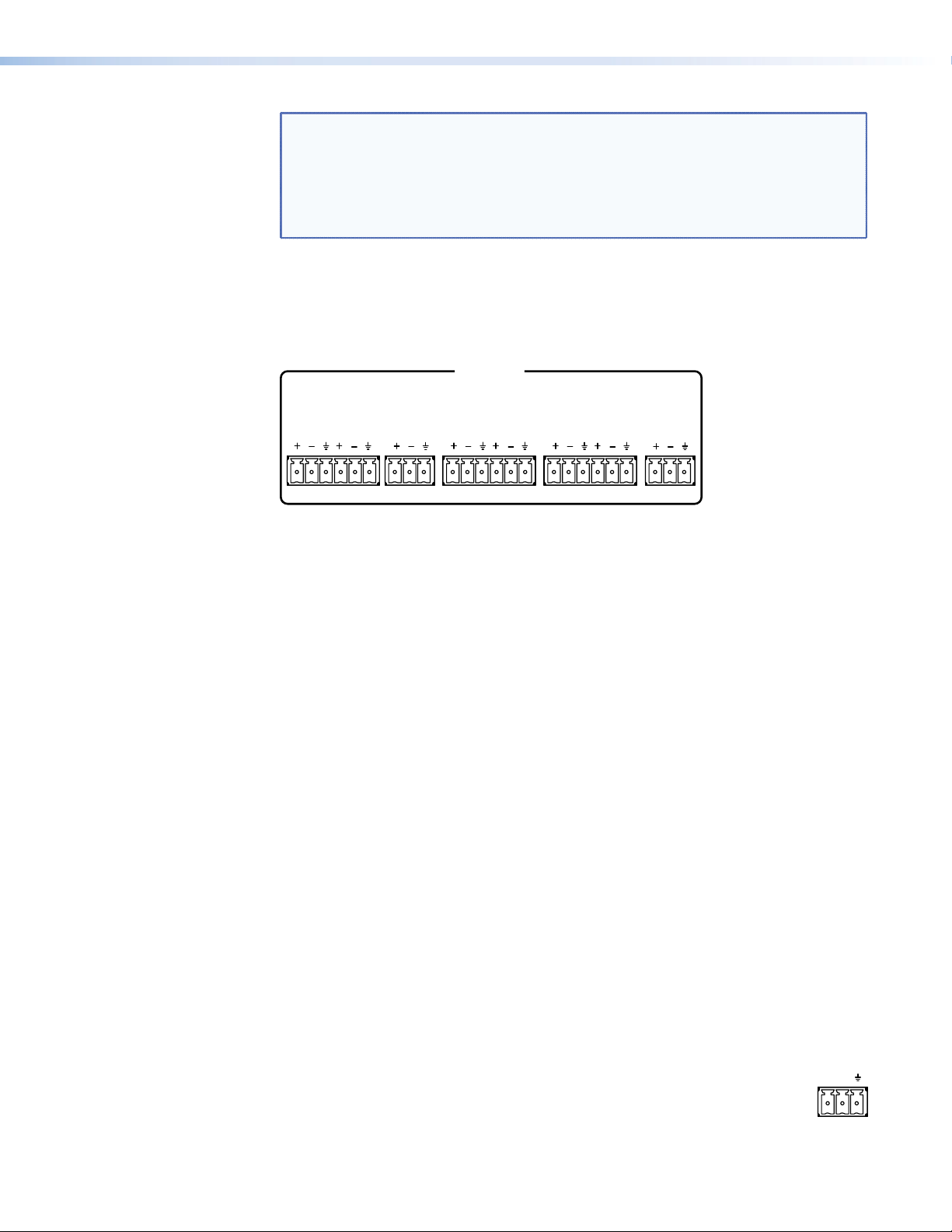
NOTES: • The length of the exposed wires in the stripping process is critical. The
OUTPUTS
RS-232
ideal length is 3/16 inches (5 mm). Any longer and the exposed wires may
touch, causing a short circuit between them. Any shorter and the wires
can be easily pulled out even if tightly fastened by the captive screws.
• Do not tin the wires. Tinned wire does not hold its shape and can become
loose over time.
For more information about input formats, see “Front Panel Features and
Operations” on page 6 and the “Source Formats” section on page 61.
c Audio outputs — Outputs are balanced or unbalanced line level analog signals that
feed into multichannel ampliers for congurations up to 7.1 surround sound. For more
information about Speaker Setup, see page 13.
FRONT
L
CENTER
R
SURROUND
L
R
BACK
L
R
SUB
WOOFER
Figure 3. Audio Outputs
Individual output settings are configured through the SSP 7.1 Setup and Control
Software (see page 30) or SIS commands (see page 86):
Mono — Output is through the center channel only but can be reconfigured to be
output through the left and right front channels. In the absence of a center channel,
mono is also output through the left and right front channels.
2-channel (stereo) — Only the front left and front right channels are used.
2.0 to 2.1 surround configurations — Audio is output through front left and front
right channels with (2.1) or without (2.0) a subwoofer.
3.0 to 3.1 surround configurations — Audio is output through front left, front right,
and center channels with (3.1) or without (3.0) a subwoofer.
4.0 to 5.1 surround configurations — Audio is output through a combination of front
left and right, left and right surround, center and subwoofer channels.
6.0 to 6.1 surround configurations — Adds a back channel to 5.0 or 5.1
configurations. The back left channel receives the sixth channel information and serves
as the center back speaker in this configuration.
7.0 to 7.1 surround configurations — Both the back left and right channels are
active. Listening modes designed for 6.1 channel outputs pass the same signal to both
the back left and right channels. Listening modes designed for 7.1 channel outputs pass
separate signals to each channel to produce a stereo back sound effect.
For more information about speaker configuration and output formats, see the
“Listening Mode Options and Usage” section on page 66.
d RS-232 port — The SSP 7.1 can be congured using the SSP 7.1 Setup and Control
Software or SIS commands, using this 3-pole captive screw connector (or the 2.5 mm
Tip Ring Sleeve (TRS) mini jack plug on the front panel).
For more information about the SSP 7.1 Setup and Control Software, see
page 22. For more information about SIS commands, see page 78.
SSP 7.1 • Features 5
Tx Rx
Page 12
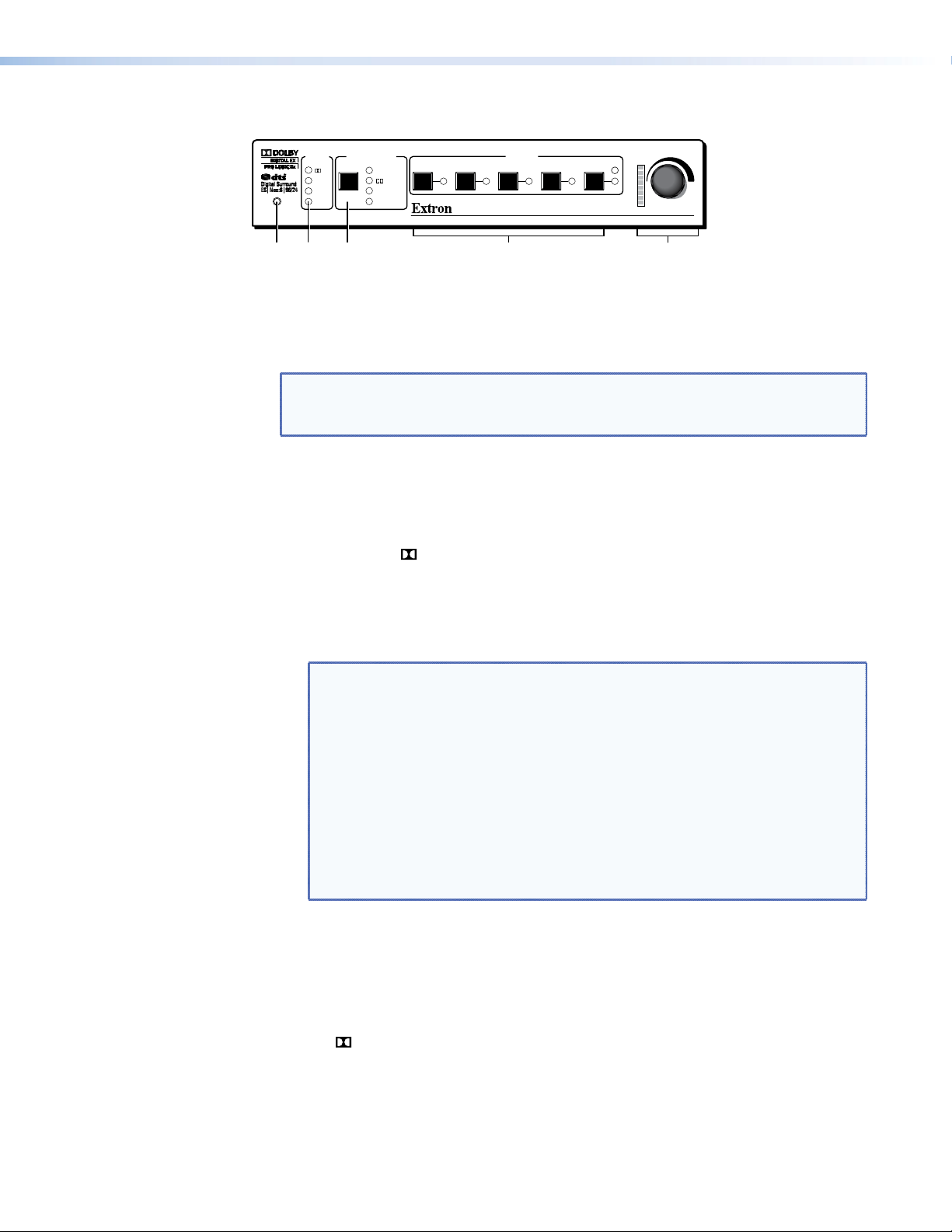
Front Panel Features and Operation
MODE OVERRIDE
CONFIG
SOURCE
DTS
PCM
2-CH
D
1 2 3 4 5
DOWNMIX
PL II/IIx
DTS NEO:6
TO ALL
INPUTS
VOLUME
CLIP
SURROUND SOUND PROCESSOR
SSP 7.1
f
g
i
Figure 4. SSP 7.1 Front Panel Features
e Configuration port — The SSP 7.1 can be congured using Extron Simple Instruction
Set™ (SIS™) commands through this 2.5 mm Tip Ring Sleeve (TRS) mini jack plug (or
through the 3-pole captive screw connector on the rear panel). For more information
about SIS commands, see page 78.
NOTE: Both the rear panel RS-232 port and the front panel configuration port can
be used at the same time. Neither has precedence. The SSP 7.1 responds to
commands in the order received.
Source Format
f Input source format indicator — The bank of four LEDs identify the format of the
audio input.
z Dolby Digital ( D): Dolby Digital 2/0, Dolby Digital 2/0 Surround, Dolby Digital 5.1,
or Dolby Digital Surround EX.
z DTS: DTS 2-Channel, DTS Digital Surround, DTS 96/24, DTS-ES Matrix 6.1,
DTS 96/24 ES Matrix 6.1, or DTS-ES Discrete 6.1.
z PCM: 2-channel uncompressed digital source format.
NOTES: • A digital signal that does not have a supported sampling rate or is
compressed PCM is considered an unrecognized signal and is muted.
• When a DVD player is paused during playback, the SSP 7.1 may or
may not continue to receive source format information from the
DVD player. Some players continue to send the same source format
information in a loop, allowing the SSP 7.1 to retain the previous
settings. Other DVD players completely disconnect the signal from the
SSP 7.1 (unlocked state), so that the active input blinks as if there is no
connection present. The remainder of DVD players change the source
output to PCM without an actual signal being sent (digital silence).
During digital silence, the PCM LED lights but the 2-CH source LED
does not.
z 2-Channel (2-CH):
z Any source coming through analog input 5.
z If a PCM digital signal is present on any of the digital inputs, both the PCM and
the 2-CH LEDs light.
z If a Dolby Digital 2/0 or Dolby Digital 2/0 Surround source is present, both the
D and the 2-CH LEDs light.
z If a DTS 2-Channel source format is present, both the DTS and 2-CH LEDs light.
To understand more about source formats, see page 61.
SSP 7.1 • Features 6
Page 13

Mode Override Selection
MODE OVERRIDE
g Mode Override selector — The SSP 7.1 has a wide range of listening modes,
although not all listening modes are compatible with every source format. The speaker
configuration of the system may further limit which listening mode is available for a
source format. Other factors, such as the room layout and listener preferences, may also
influence the listening mode selection.
The SSP 7.1 has default listening modes associated with each source format. The front
panel provides the user with a limited set of Mode Override settings. These can change
the listening mode that is associated with a specific combination of source format
and input. The override selections can be further defined using the SSP 7.1 Setup and
Control Software, or SIS commands.
The new, user-defined listening mode continues to be associated with that source
format until Mode Override is used, again, to associate a new listening mode with the
source format. To select a listening mode:
1. Use the push button to toggle through the available listening
modes. When no mode override is chosen, none of the LEDs
light, indicating that a user-defined listening mode is in use.
Otherwise, one of the four LEDs shows the current selection.
2. Release the button when the desired LED is lit to select that
listening mode. If a listening mode is not an available option
for the current input source, toggling the button skips that mode and goes to the next
available mode.
3. If required, further dene the selection using the SSP 7.1 Setup and Control Software
Listening Mode Setup Tab (page 45).
The mode override selections that are available through the front panel are:
z Downmix (DOWNMIX) — Downmixes any multichannel source format (digital
inputs only). It also downmixes a 2-channel source format, if the listening mode is
set to mono.
It is further defined from the Setup and Control Software (see page 48). Options
include:
z Stereo, output on left front and right front channels.
z Mono, output to center channel only or to left and right front channels equally.
z Dolby Pro Logic II/IIx ( PL II/IIx) — uses Dolby Pro Logic II or Dolby Pro Logic IIx
surround processing technology.
z Dolby Pro Logic II extends 2-channel sources to output 5.1 channels. It can be
further defined by control software as either Dolby Pro Logic II Movie (default)
or Dolby Pro Logic II Music.
z Dolby Pro Logic IIx extends 2-channel sources to output 6.0 to 7.1 channels
(depending on the speaker setup). It can be further defined by control software
as either Dolby Pro Logic IIx Movie or Dolby Pro Logic IIx Music.
z Dolby Pro Logic IIx also provides an extended surround option for multichannel
sources such as DTS Digital Surround or Dolby Digital 5.1.
z DTS Neo:6 (DTS NEO:6) — Uses DTS Neo:6 surround processing technology
to extend analog or 2-channel digital source formats (PCM, Dolby Digital 2/0,
Dolby Digital 2/0 Surround, DTS 2-Channel) to output up to 7.1 channels. It
is further defined by control software as either DTS Neo:6 Cinema (default) or
DTS Neo:6 Music.
DOWNMIX
PL II/IIx
DTS NEO:6
TO ALL
SSP 7.1 • Features 7
Page 14
z To All (TO ALL) — Distributes a mono or 2-channel source to all applicable
channels.
z Mono sources are sent to all available output channels, including center.
z 2-channel sources are sent to all stereo pairs only.
z Multichannel sources are downmixed and output to Mono to All or Stereo to
All, as defined by the user.
z Digital or analog stereo sources may be output to Mono to All or Stereo to All,
as defined by the user. If Mono to All is selected, the signal is downmixed to
mono before being output to all channels.
NOTE: If an analog mono source is on the left channel, Stereo to All listening
mode outputs only to the left channels of available stereo pairs. A right
channel analog mono source is output only to the right channels of
available stereo pairs.
When used in conjunction with the Input buttons, the Mode Override button is used to
mute all outputs (see page 10).
The Mode Override button is used to perform a complete system reset (see “Complete
System Reset” on page 10).
To learn more about listening modes, see “Listening Mode Options” on page 66. To
learn how listening modes depend on both source format and speaker configuration,
see “Source Formats and Listening Modes with Different Speaker Setups” on
page 75.
SSP 7.1 • Features 8
Page 15

Input Selection
INPUTS
1 2 3 4 5
CLIP
Figure 5. SSP 7.1 Input Selection Switches
h Input selections — Push one of the buttons to select between five possible audio
inputs. The LED next to the currently active input lights.
In conjunction with the Mode Override button, the input buttons are used to mute all
outputs (see page 10).
The input buttons are also used to enable or disable front panel security lockout
(executive mode). For more information, see page 12.
In conjunction with the volume adjust knob, the analog input (Input 5) is used to set
analog input gain level for the analog source (see page 11).
The SSP 7.1 accepts four digital inputs and one analog input (see Rear Panel Features
on page 4):
z Inputs 1 and 2 accept digital signals through S/PDIF optical cables. The optical
cable supports TOSLINK or TOSLINK-compatible optical connectors that conform to
IEC-958, S/PDIF standards.
z Inputs 3 and 4 accept digital signals through S/PDIF coaxial cables.
All four digital inputs accept 16-24 bits PCM audio at 32, 44.1, 48, 88.2, and 96 kHz
sample rates. They support Dolby Digital and DTS source formats.
NOTE: For digital inputs, if there is no valid clock signal at the input and no lock is
achieved, the LED associated with the source blinks twice per second.
z Input 5 accepts a balanced or unbalanced analog input through a 5-pin captive
screw connector. The unit can be configured to accept:
z A stereo signal
z A mono signal from the right channel
z A mono signal from the left channel
z A mixed sum of right and left channels
The input can also be selected using the SSP 7.1 Setup and Control Software (see Input
Source on page 26).
SSP 7.1 • Features 9
Page 16

Mute Output
When the mute state is enabled, all channels are muted simultaneously. To toggle between
mute and unmute:
1. Press and hold the active input button (the button next to the LED that is lit).
2. While still holding the active input button, press the Mode Override button.
When the mute state is enabled, the individual LEDs of the Volume Adjustment LED bar light
in sequence from the top down. This scrolling down pattern repeats while the mute state
persists.
All channels can also be muted using the SSP 7.1 Setup and Control Software (see Master
Volume and Mute on page 29).
NOTES: • Selecting another input button while the mute function is enabled, disables
the mute function.
• Adjusting the volume control encoder to change the volume (or the analog
input gain) settings while the mute function is enabled, disables the mute
function and increases (or decreases) the volume (or gain) from its previous
setting.
• If SIS commands have been used to mute a specific channel, muting and
unmuting all channels also unmutes the channel that was specifically muted. It
does not remain in its previously muted state.
Complete System Reset
The SSP 7.1 has three levels of System Reset.
Standard system reset — All parameters that can be adjusted by the control program are
reset to default.
Factory reset — In addition to resetting all the parameters of the standard system reset, the
baud rate for communicating with the computer is also reset.
Complete system reset — In addition to resetting all the parameters of the factory reset,
the firmware is reset to the factory-installed version.
The standard and factory resets are performed using SIS commands (see the System Reset
SIS commands on page 94).
To perform a complete system reset, hold the Mode Override button while shutting off and
restoring power.
SSP 7.1 • Features 10
Page 17
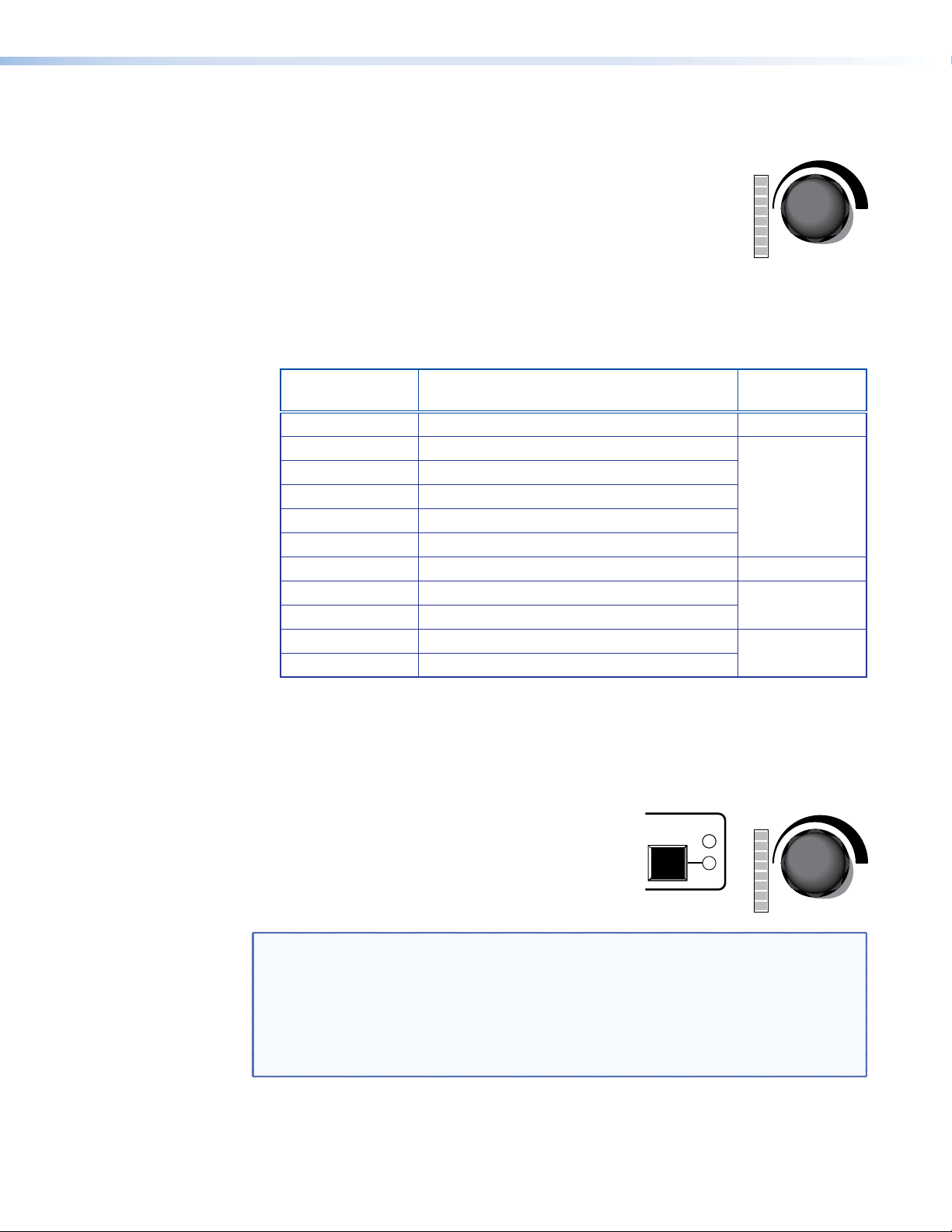
Volume Adjustment
VOLUME
VOLUME
i Volume adjust knob and LED bar or Analog input gain level
control and LED bar — Use the rotary encoder to adjust the output
volume from 0 (-100 dB) to 100 (0 dB). The default setting is 50
(-50 dB).
The degree to which the volume is incremented or decremented for
each step the encoder is turned, depends on the current volume
setting (see the last column in the table below).
As the volume increases or decreases, the LED bar lights to indicate the current volume
range, as shown in the table below. As the volume is increased or decreased within a
volume range, the top LED to be lit flashes once. If the knob is turned past maximum
volume, all 8 LEDs flash, for as long as the knob continues to be turned.
Volume steps for
each LED (dB)
>0 All LEDs blink if user tries to turn knob further
0 All 8 LEDs on
-4 to -1 All 8 LEDs on
-9 to -5 Bottom 7 LEDs on
-14 to -10 Bottom 6 LEDs on
-19 to -15 Bottom 5 LEDs on
-29 to -20 Bottom 4 LEDs on 2
-49 to -30 Bottom 3 LEDs on
-69 to -50 Bottom 2 LEDs on
-99 to -70 Bottom LED on
-100 All LEDs off
Table 1. Volume Level and Lighting of LED Bar
The volume can also be controlled using the SSP 7.1 Setup and Control Software
(see Master Volume and Mute on page 29).
LEDs lit Increment
(dB/knob step)
1
4
5
Analog Input Gain Adjustment
Alternatively, the rotary encoder controls the gain level
of the analog signal on input 5. Analog input gain is
adjustable from 0 dB (fully counterclockwise) to +24 dB
(fully clockwise).
To adjust input gain, press and hold the Input 5 button,
while turning the rotary encoder.
CLIP
5
NOTES: • If the gain level is too high, clipping may occur. When clipping occurs, the red
LED above the Input 5 button lights.
• When using Mono or Mono to All listening mode, the left and right signals
are summed (in the digital domain), which can cause a boost in level up to
6 dB. This type of clipping does not cause the clip indicator LED to light but
is audible. If using a mono mode, it is recommended that the input gain be
reduced by 9 dB below clipping to prevent clipping from occurring.
SSP 7.1 • Features 11
Page 18

The LED bar lights from the bottom up to indicate the current gain level. No LEDs lit indicates
no gain (0 dB, or unity gain); all the LEDs lit indicates maximum gain (24 dB). Each solidly lit
LED represents 3 dB. A slowly blinking LED indicates an additional 1 dB or a quickly blinking
LED indicates an additional 2 dB:
Number of LEDs lit
solidly
8 24 - 7 21 22 23
6 18 19 20
5 15 16 17
4 12 13 14
3 9 10 11
2 6 7 8
1 3 4 5
None No LEDs lit; 0 dB 1 2
Table 2. Gain level and lighting of LED bar
The analog input gain can also be controlled using the SSP 7.1 Setup and Control Software
(see Master Volume and Mute on page 29).
No Blinking Slow Blinking Fast Blinking
Gain (dB)
Front Panel Security Lockout (Executive Mode)
When the front panel is locked, the user cannot make any changes from the front panel
(except disabling the security lockout). If the user attempts to make changes with the
front panel locked out, all the input LEDs ash simultaneously. The lockout does not block
changes made using SIS commands or the SSP 7.1 Setup and Control Software. To lock out
the front panel:
1. Press and hold the active input button (the button next to the LED that is lit).
2. While holding the active input button, press and hold any other input button. All the
LEDs blink in ascending order (from 1 to 5) and then the active input button lights.
3. The front panel is unlocked in exactly the same way. All the LEDs blink in descending
order (5 rst and 1 last) and then the active input button lights.
This feature can also be set, using the SSP 7.1 Setup and Control Software (see Front Panel
on page 52).
SSP 7.1 • Features 12
Page 19
Setup
This section provides background information about arranging speakers in a room and about
some of the settings that can be adjusted by the SSP 7.1 Setup and Control Software. Extron
strongly recommends that the control software is used to make any configuration changes
to the SSP 7.1. (See “Setup and Control Software” on page 22).
z Speaker Setup
z Bass Management
z Speaker Delay Settings
z Test Signals
z Output Channel Trim Settings
z Listening Mode Settings
z Dynamic Range Compression Control
z Tone Controls
z Volume Output
z Equalization
Speaker Setup
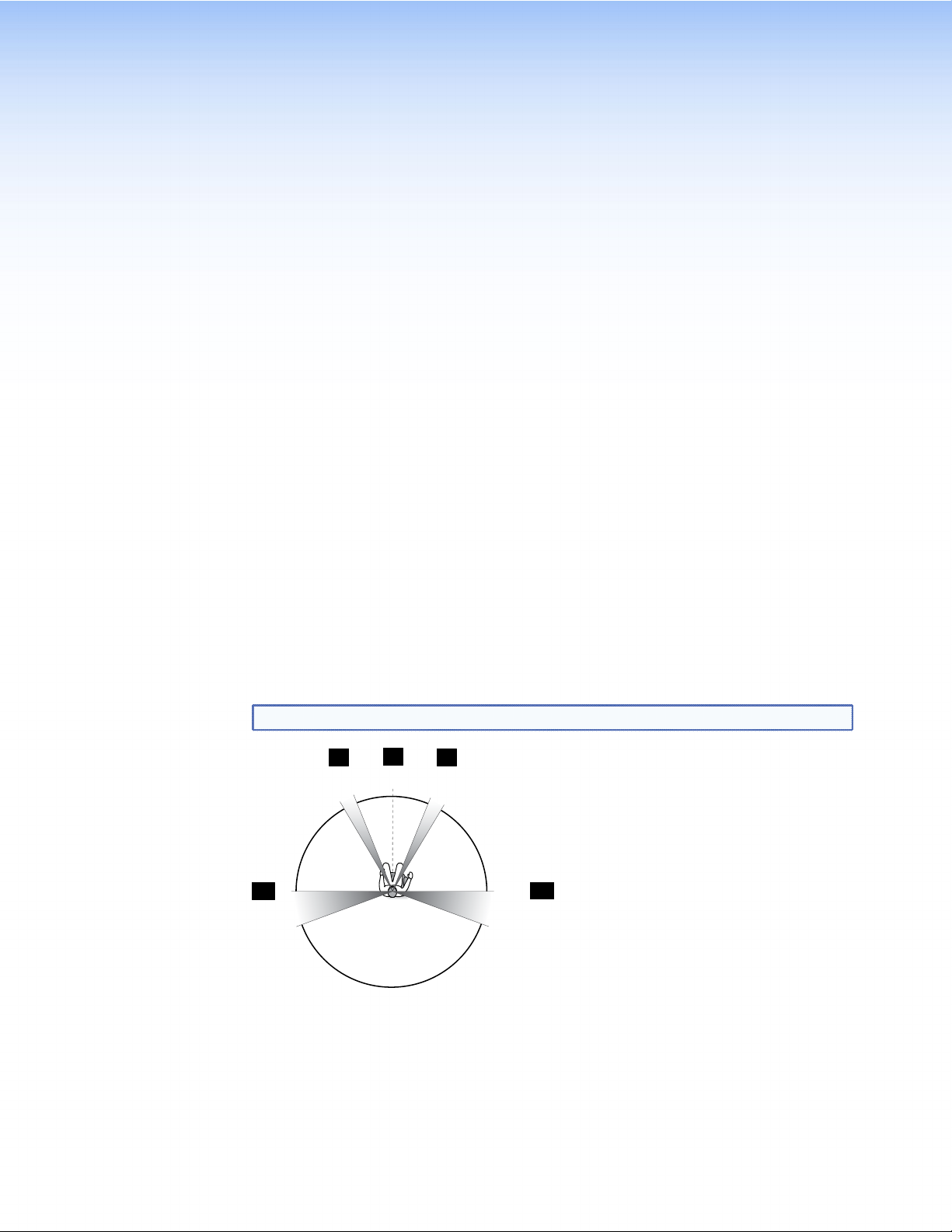
The following figures show the recommended speaker placement, relative to the listener, for
a five, six, or seven speaker system and for subwoofer placement.
NOTE: All speakers should be angled inwards so that they face towards the listener.
L
LS
Figure 6. Five Speaker Setup
C
0°
22°
R
30°
90°
110°
RS
For an explanation of speaker abbreviations, see page 14.
SSP 7.1 • Setup 13
Page 20
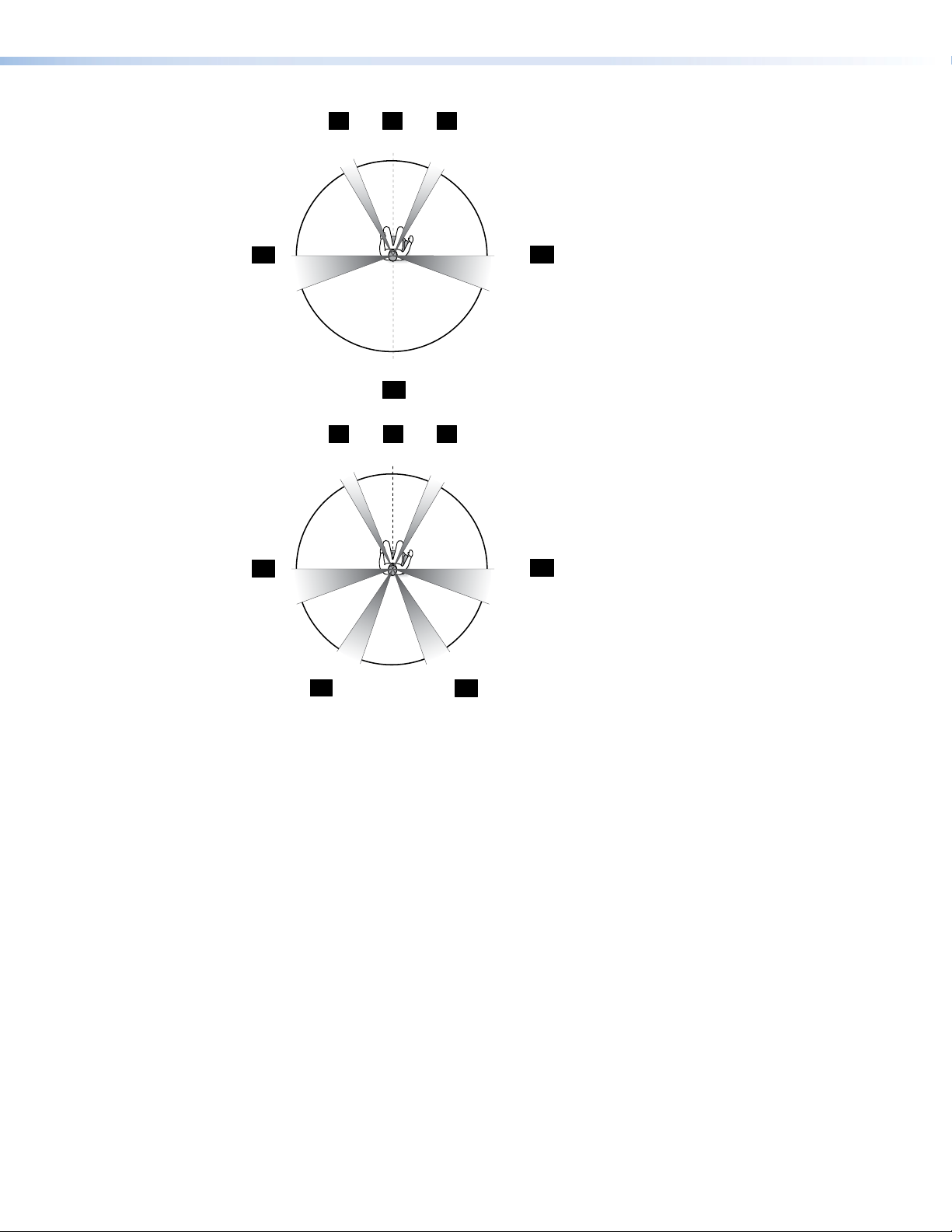
L
C
0°
22°
R
30°
LS
180°
90°
110°
RS
CB
Figure 7. Six Speaker Setup
LS
LB
L
C
0°
22°
150°
R
30°
135°
RB
90°
110°
RS
Figure 8. Seven Speaker Setup
Abbreviations
C = Center
CB = Center Back (Six Speaker Setup only)
L = Left
LB = Left Back (Seven Speaker Setup only)
LS = Left Surround
R = Right
RB = Right Back (Seven Speaker Setup only)
RS = Right Surround
SW = Subwoofer
SSP 7.1 • Setup 14
Page 21
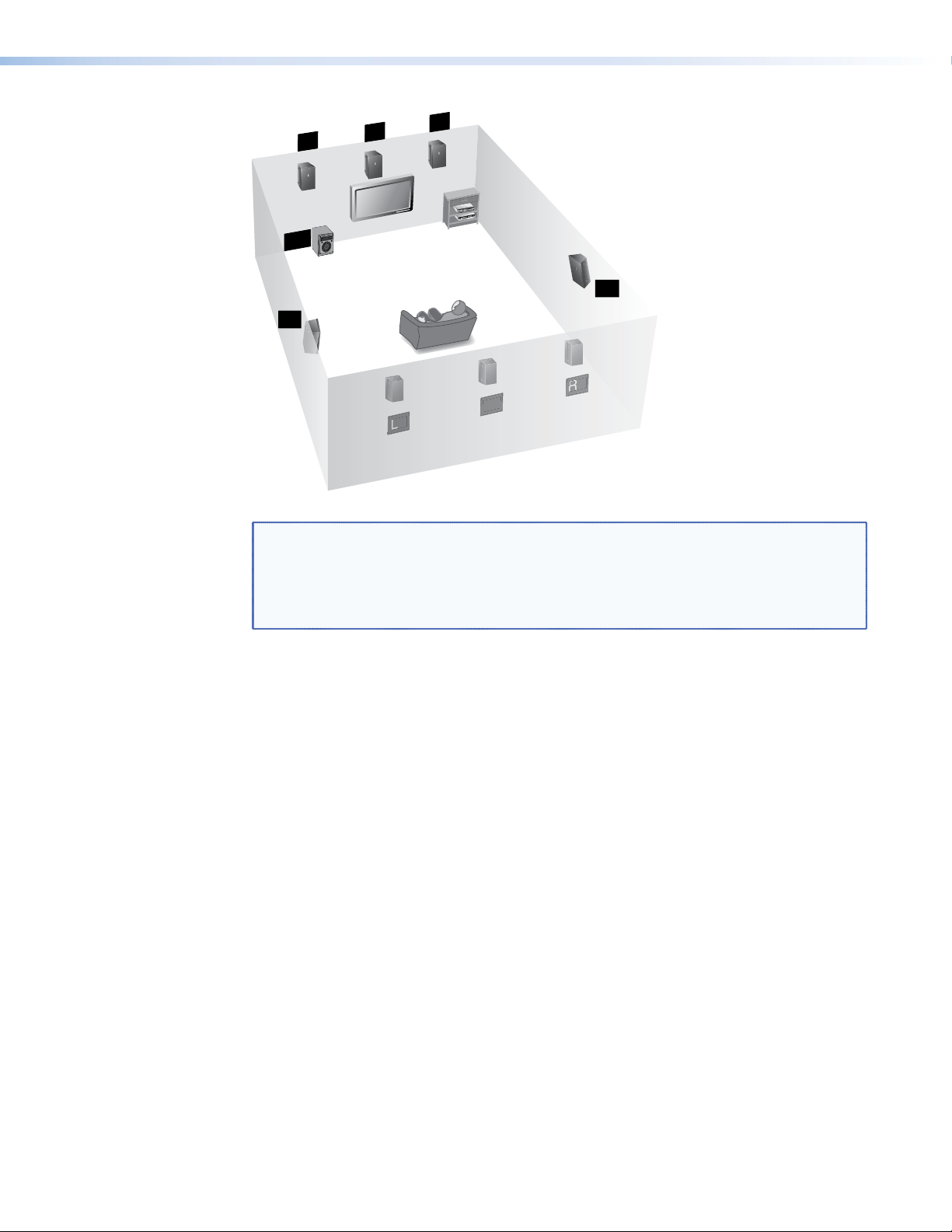
L
CB
C
R
DVD-RW/-R RECORDING
Cinema Progressive
Precision
SW
RS
LS
RB
CB
LB
Figure 9. Subwoofer Placement
NOTES: • To produce a good bass response from the subwoofer, it should be located at
the front of the room, somewhere between either corner and a point about
one third of the way along the front wall.
• The output channel used for the Left Back speaker (in 7.1 configurations) is
also used for the Center Back speaker (in 6.1 configurations).
Bass Management
Speaker Size Settings
Low frequency sound is usually better handled by the subwoofer. Bass management creates
the subwoofer channel by separating the low frequency information from the satellite
speakers at a user-dened crossover point. This is summed with the Low Frequency Effects
(LFE) information encoded in the source format. When no subwoofer is present, subwoofer
content is sent to speakers set to Large (excluding the center speaker).
This feature sets bass management on or off for a particular speaker, defining the frequency
range output by that speaker. These settings also enable or disable the subwoofer and set
the crossover frequency.
z Left and right front speakers and left and right surround speakers are set in pairs.
z The center speaker is set as an individual speaker.
z Back speaker(s) can be set as a single speaker or as a pair of speakers, depending on the
system configuration.
Small — Bass management is on for that speaker. The output to each speaker (other than
the subwoofer) is limited to frequencies above the crossover frequency. By default, center
and surround speakers are set to Small.
SSP 7.1 • Setup 15
Page 22

Large — Bass management is off for that speaker. The full range of audio frequencies from
the audio source is fed through the output of each individual channel. This may be set in the
absence of a subwoofer. By default, front speakers are set to large.
When there is no subwoofer, all speakers set to Large (except the center channel) receive the
summed audio from the filtered low frequency signals of speakers set to Small.
None — This mode prevents any signal from being sent to that output channel. It is not an
option for front speakers.
One Small Speaker, Two Small Speakers, One Large Speaker, Two Large Speakers, or
None (Surround back speakers only) — This mode determines whether the audio output
channels for the back speaker(s) are passed to the left back and right back (in 7.1 setups) or
to the center back (in 6.1 setups).
If either of the one speaker options are chosen, the highest possible number of outputs is
6.1 speakers. In this case, the output is directed to the left back channel output.
If either of the two speaker options are chosen, the SSP 7.1 is able to output up to 7.1
channels. Source formats with discrete or matrix mixed 6.1 encoded channels output the
surround back channel signal equally to the left and right back channels. Dolby Pro Logic
IIx and DTS Neo:6 listening mode options output a stereo signal to the left and right back
channels.
NOTE: If the surround speakers have been disabled, the back speaker options are also
disabled.
By default, the back speaker is set to None, which prevents a signal from being output on
the back channel(s).
Subwoofer — This option allows the subwoofer to be enabled or disabled. When the
subwoofer is enabled, the signal contains filtered low frequency signals from speakers set
to Small in addition to the LFE signal from the source format. If the subwoofer is absent or
disabled, the LFE signal is mixed with the bass information of all speakers in the system that
are set to Large, except the center speaker.
NOTES: • When the surround and back speakers are set to None, all multichannel input
signal formats are downmixed and output on all remaining channels.
• In addition, in the absence of a center channel, mono signals are output
equally between the front left and front right channels. Multichannel sources
are downmixed to all remaining channels, but Mono to All and Stereo to All
options are disabled. Choosing Mono listening mode first downmixes the
multichannel source and outputs it to the front left and right channels equally
as a dual mono signal.
Crossover Frequency — The crossover frequency sets the boundary below which
the low frequency signals from designated output channels are incorporated into bass
management. Low frequency signals are only taken from speakers that have been set to
Small (see ”Speaker Size Settings” on page 15). The bass management signal is passed
to the subwoofer (if present) or speakers that have been set to Large (except for the center
speakers) if a subwoofer is not present.
The crossover frequency can be adjusted within the range of 40 Hz to 250 Hz, with a default
setting of 100 Hz. Speakers set to Small (see “Speaker Size Settings” on page 15) play
only signals above the set frequency.
SSP 7.1 • Setup 16
Page 23

Speaker Delay Settings
There are two different signal delays that compensate for different needs.
Compensation delay — In a room where speakers are not equidistant from the listener,
sound from the closest speaker reaches the listener before sound from the farthest speaker.
This feature allows the user to enter the speaker distance value for each speaker output
channel. The application calculates the delay values for the closest speakers, up to 100.0 ms,
so that all audio arrives at a central location (the “sweet spot”) at the same time.
Lip sync offset — Video delays occur due to changes in programming from a source (TV,
Cable, Satellite, or DVD player) and also if the video signal has to be processed through
another device between the source and the display. The lip sync offset feature allows the
user to delay the audio sent to all output channels so that video and audio output are
synchronized.
Since each source may need a different level of compensation, the lip sync offset for each
input is independently adjustable from 0.0 to 100.0 ms. Apply lip sync offset to the audio
until what is heard matches up with what is seen on the display.
To congure these settings using the SSP 7.1 Setup and Control Software, see “Speaker
Delay Tab” on page 32.
Test Signals
Test signals are used during setup to calibrate the level for each channel and to ensure
proper connection between the individual output channels of the SSP 7.1 and the line
level input channels of an audio signal processor, a receiver with built in amplifier, or a
stand alone amplifier that powers the loudspeakers.
The three options for test signal source are pink noise, Dolby noise, and an external source.
By default, the test signal is switched off.
Pink Noise — Pink noise is a random signal, generated by the SSP 7.1, with all audio
frequencies present. It provides equal energy per octave to provide a flat response over all
frequencies. The main purpose of pink noise is to calibrate the interaction of a speaker with
its environment.
Dolby Noise — Dolby noise provides a bandpass-ltered noise, centered at 750 Hz with a
12 dB/octave roll off. This signal is also generated by the SSP 7.1 and is used to set speakers
to the same level when calibrating the room.
Active Input — This option requires an external test signal source, such as a signal
generator, played through the selected input source. Generally, this is a device with an
analog signal output, with the SSP 7.1 analog input used as the active input.
Signal generators are usually used to test specic decoding mode outputs. When the
External Source option is chosen, the speakers that receive the test signal can be specied.
To calibrate speaker output, use any of these test signals with the SSP 7.1 Setup and Control
Software, see Test Signals on page 36.
Output Channel Trim Settings
This control adjusts the output channel trim level for each output channel to match the
levels to the unique needs of any listening environment. The level can be adjusted within the
range from -24 dB to +12 dB. The default setting for each speaker is 0 dB. See Output Trim
on page 39 for more information.
SSP 7.1 • Setup 17
Page 24
Listening Mode Settings
The SSP 7.1 provides a range of settings that rene the sound distribution for each listening
mode, depending on the decoding mode that has been selected.
Dolby Pro Logic II or IIx Music
Dimension control — This feature alters the ratio of L+R to L-R for two-channel input
signals, which adjusts the sound field towards the front or towards the back. The available
settings are Front, Neutral, or Back. The default setting is Neutral.
Center width control — Pro Logic decoding produces a single center signal that comes
from the center speaker. If there is no center speaker, a “phantom” center image is
produced that is split between the right and left speakers.
If right, left, and center speakers are present, center width control allows variable adjustment
of the center image so that is heard only from the center speaker, only from the right and
left speakers, or from all three speakers in varying degrees.
There are up to eight different settings, with each corresponding to a specific calculation
angle (Φ). When the setting is 0, the sound comes from the center speaker, when the setting
is 7, the sound is from the L/R speakers. The default setting is 3.
Control Position Calculation Angle
(Φ)
0 0.0 0.0 Off
1 20.8 -0.6 -12.0
2 28.0 -1.1 -9.6
3 36.0 -1.8 -7.6
4 54.0 -4.6 -4.8
5 62.0 -6.6 -4.1
6 69.2 -9.0 -3.6
7 90.0 Off -3.0
NOTE: The level of the center speaker (C Level) is related to cosine Φ. The level of the
left and right speakers (L/R Level) is related to sine Φ.
Panorama control — This feature extends the center width control, so that all or part of
the center image can be heard from the surround speakers for a “wraparound” effect. The
feature may be On or Off. The default setting is Off.
C Level (dB) L/R Level (dB)
DTS Neo:6 Music or Cinema
Center image control — The center image control varies the amount of attenuation
applied to the left and right channel information of the input source that is used for creating
the output center channel effects. When it is set to 0, the mixed input signal information,
intended for use in creating the center output channel of the DTS Neo:6 listening modes, is
filtered back to the front left and right output channels. This creates the effect of spreading
the centralized audio signal across all three front output channels. When this control is
set to 10, the matrixed information intended for the center output channel effects is fully
attenuated, allowing the center channel to create a more centralized effect from the front
channels.
The default setting for DTS Neo6: Music is 3. The default for DTS Neo6: Cinema is 10.
SSP 7.1 • Setup 18
Page 25

Dynamic Range Compression Control
This control is available only with Dolby Digital and DTS source formats that have a Dynamic
Range Compression flag.
This control adjusts the gain applied to Dolby Digital or DTS listening modes to compress the
signal outputs during the decoding process. The three possible settings are None, Minimum,
and Maximum. The default setting is None.
Off — The signal is uncompressed and is played with the full original dynamic range.
Minimum — The audio is partially compressed. In this mode, the volume of the loudest
passages is reduced but quieter passages are kept at their original level. This level is
recommended for normal listening.
Maximum — The audio is fully compressed. This level is recommended for environments
where loud audio is not permitted.
NOTE: DTS source formats have only two states (On and Off) for dynamic range
compression. Therefore, Minimum and Maximum both apply the same dynamic
range compression.
SSP 7.1 • Setup 19
Page 26
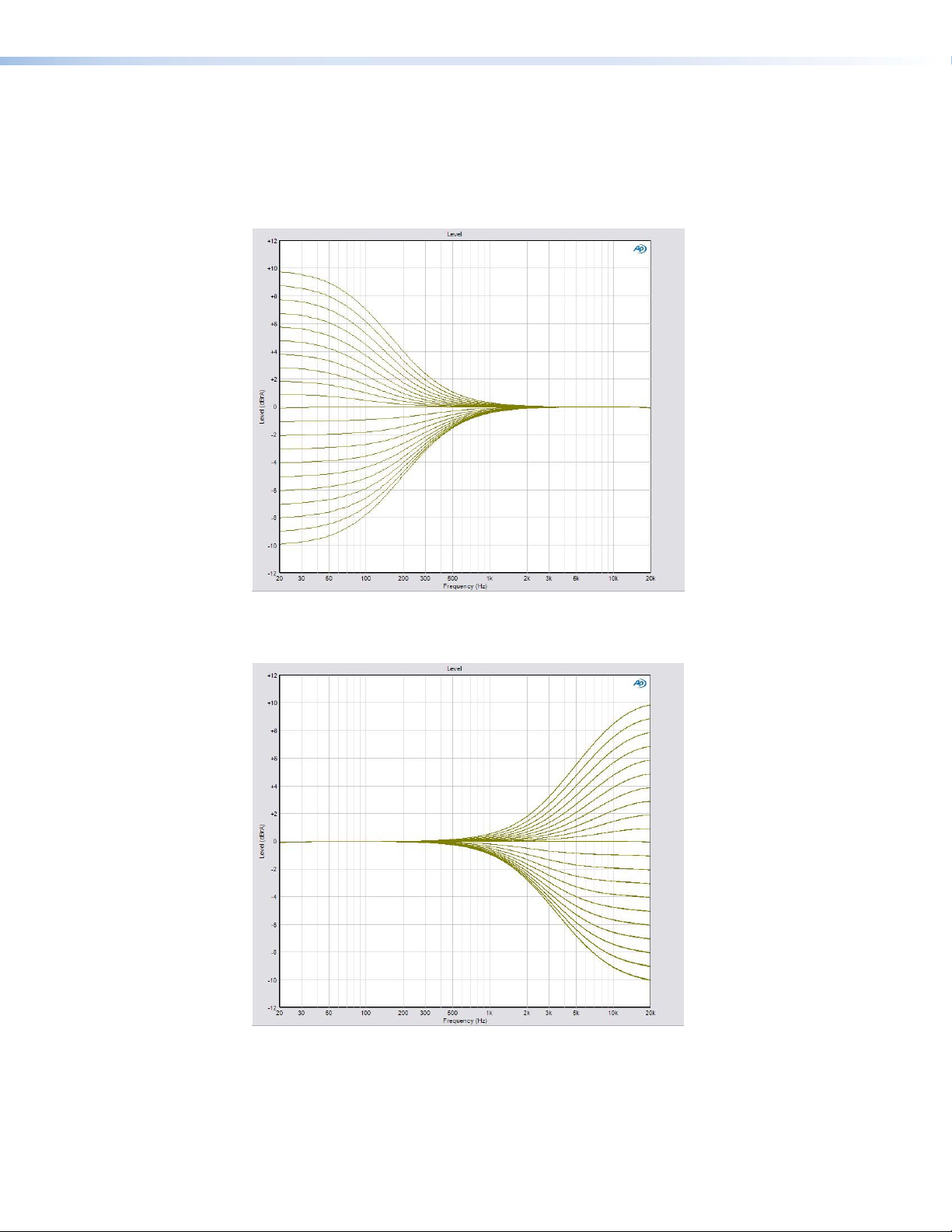
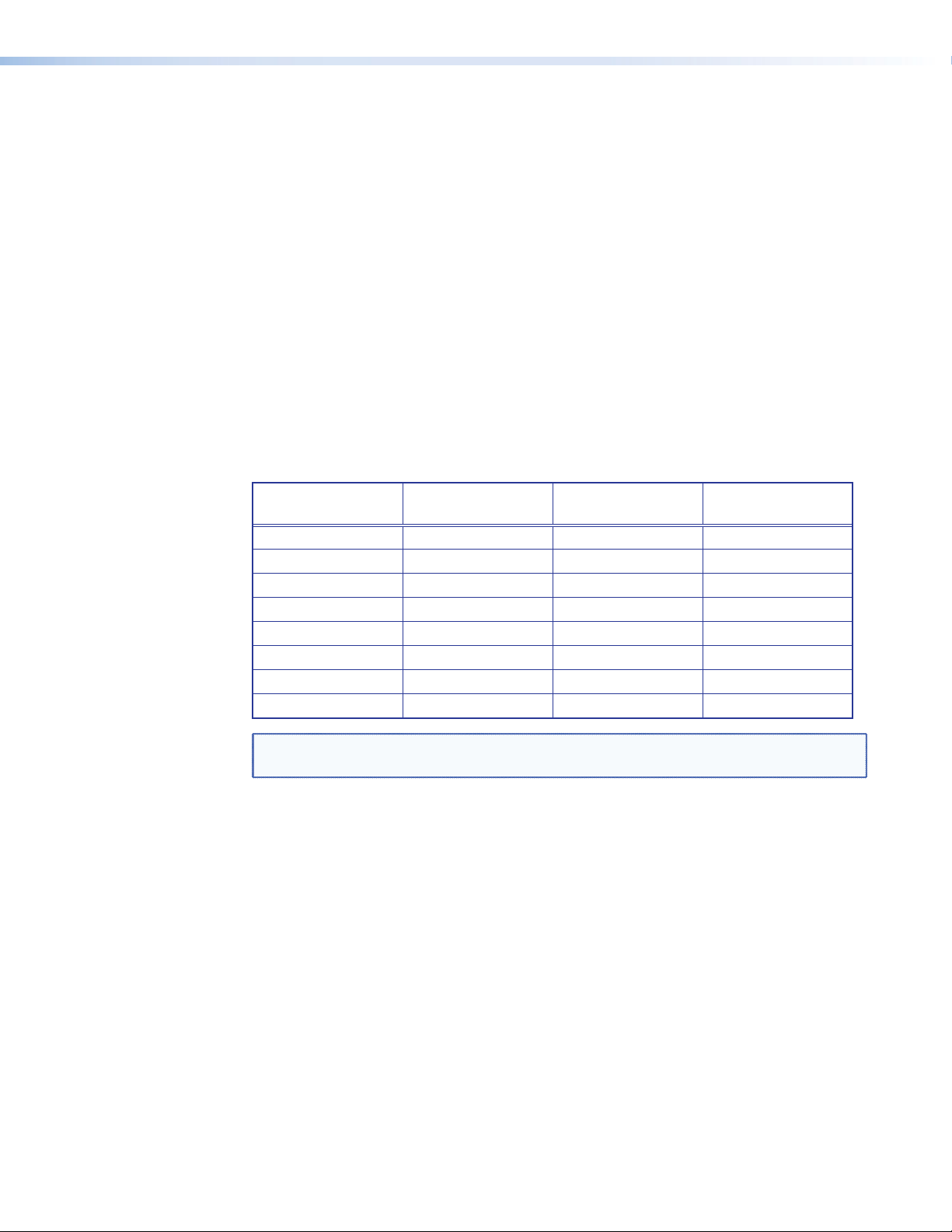
Tone Controls
These controls regulate the bass and treble settings for the system. To adjust the bass or
treble tone controls, see Tone Controls on page 27.
Bass — The bass control regulates the amount by which low frequency signals are boosted
or cut (see figure below). It is applied to outputs for all speakers, including the subwoofer.
Figure 10. Bass Range
Treble — The treble control regulates the amount by which high frequency signals for all
speakers, except the subwoofer, are boosted or cut (see figure below).
Figure 11. Treble Range
SSP 7.1 • Setup 20
Page 27

Volume Output
Equalization
This control sets the volume of the audio output through all channels, globally, to either
Variable (the default value) or Fixed.
Variable — When the Volume output is set to Variable, the volume can be attenuated using
the front panel knob, the SSP 7.1 Setup and Control Software, or SIS commands.
Fixed — The Fixed option sets the volume to the current attenuation level. Likewise, all the
Output Channel Trim levels (see Output Trim on page 39) are fixed at the values they had
immediately before the Volume Output was set to Fixed.
When Fixed is selected, the volume cannot be adjusted through the front panel knob, by the
SSP 7.1 Setup and Control Software, or by SIS commands.
Parametric equalization (or parametric “EQ”) allows the control of amplitude of each band,
center frequency (which can be shifted, widened, or narrowed) and bandwidth (which may
be labeled “Q” for Quality). Parametric equalization is used to improve the audio output in a
specific acoustic environment.
Resonance reduction — Reduces the level at specific frequencies that are too loud.
Speaker compensation — Compensates for peaks and dips in individual speaker output
response.
Tonal enhancement — Increases the level of frequencies within a broad or narrow range
that sound too quiet.
SSP 7.1 • Setup 21
Page 28

Setup and Control
Software
The SSP 7.1 Setup and Control Software provides an intuitive, easy to operate, graphical
user interface that allows the user to configure the audio system quickly and efficiently. It
provides more options than the front panel. As selections are made, only the options that
are available for the current conguration are displayed by the software. Extron strongly
recommends using the SSP 7.1 Setup and Control Software for all conguration.
The program comes on a disk, supplied with the unit. It can also be downloaded, free of
charge, from the Extron Web site (www.extron.com).
The following sections describe:
z Installing the SSP 7.1 Setup and Control Software
z Live and Emulate Modes
z Running the SSP 7.1 Setup and Control Software
z SSP 7.1 Setup and Control Software Help File
z Firmware Updates
Installing the SSP 7.1 Setup and Control Software
The minimum system requirements for installing the program on the computer are:
z Operating system — Microsoft
z CPU — Intel
z Hard disk space — At least 10 MB
z Memory — At least 64 MB of RAM
z Device connection — Serial COMM Port
Insert the disk provided into the CD or DVD ROM drive of the computer. If the setup
program does not start automatically, run Launch.exe from the CD or DVD ROM directory
in Windows My Computer. Select the Software tab, locate the SSP 7.1 Setup and Control
Software, and click Install. Follow the on-screen instructions to install the program.
Alternatively, go to the Extron Web site, click on the Download tab, and click on the
Software option in the left sidebar. Navigate to the SSP 7.1 Setup and Control Software
and click Download. Follow the on-screen instructions to install the program.
By default, the Installer program creates a C:\Program Files\Extron\SSP7.1 folder
to contain the SSP 7.1 Setup and Control Software. An icon may also be placed
on the Windows desktop.
NOTE: Updating the SSP 7.1 Setup and Control software may also require a more recent
®
Pentium® II processor with a 400 MHz clock speed or faster
version of the firmware to be installed (see Firmware Updates on page 56).
®
Windows® 2000 or higher
SSP 7.1 • Setup and Control Software 22
Page 29
If the new software detects an old version of the Firmware, a pop-up window informs the
user that the firmware should be updated and also prompts the user to save the existing
conguration for reloading onto the SSP 7.1 when the new rmware has been installed.
When the rmware has been updated, open the SSP 7.1 software in Emulate mode
(see below) and open the saved configuration. Click on the Live button and, when
the Synchronize with Device pop-up appears, select Push the data from this
configuration to device, overwriting any data currently in it. option.
Live and Emulate Modes
The SSP 7.1 Setup and Control Software offers a choice of Live or Emulate mode. In Live
mode, any changes made using the software directly affect the configuration of the sound
processor.
In Emulate mode, the computer is not connected to the sound processor and any
changes you make must be saved as an *.esp file. The file can be used later to update
the configuration of the sound processor when the computer is directly connected to the
SSP 7.1 in Live mode.
You may choose between Live and Emulate modes either when the program rst starts up
in the Connect to Device? dialog box (see page 24) or, when the main program window
is running, using the Live and Emulate buttons in the top right corner (see the figure at
right). You can also toggle between the two modes, by using the F5 and F6 keys or clicking
on Connect... (F5) or Disconnect (F6) under the Device menu (see page 52).
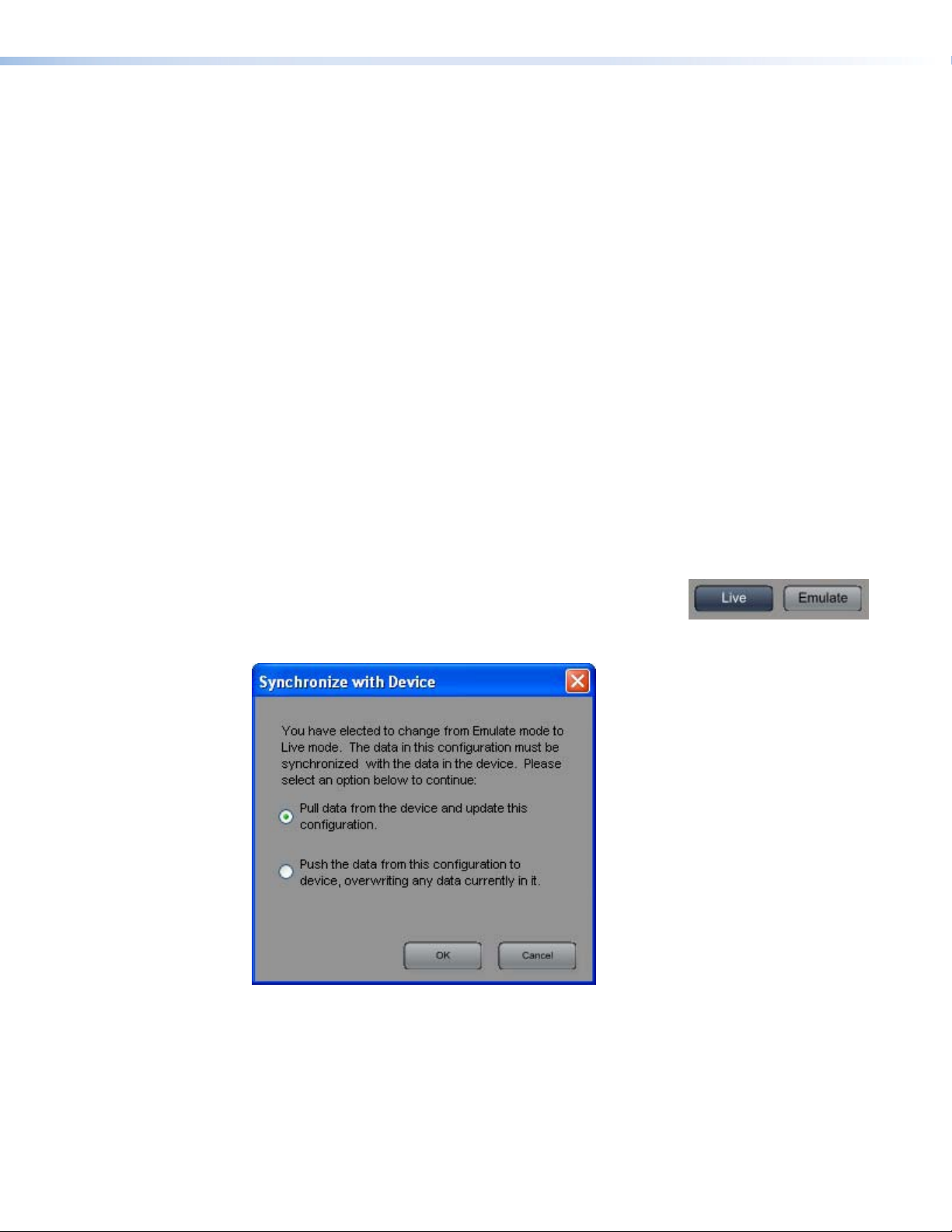
When you switch from Emulate to Live mode, you are prompted to synchronize the settings
in the SSP 7.1 Control and Setup Software with the current
conguration in the SSP 7.1 device. Select Push to overwrite the
configuration in the device with the software settings made in
Emulate mode, or select Pull to overwrite the software settings
with the configuration in the device.
Figure 12. Synchronize with Device Dialog Box
SSP 7.1 • Setup and Control Software 23
Page 30
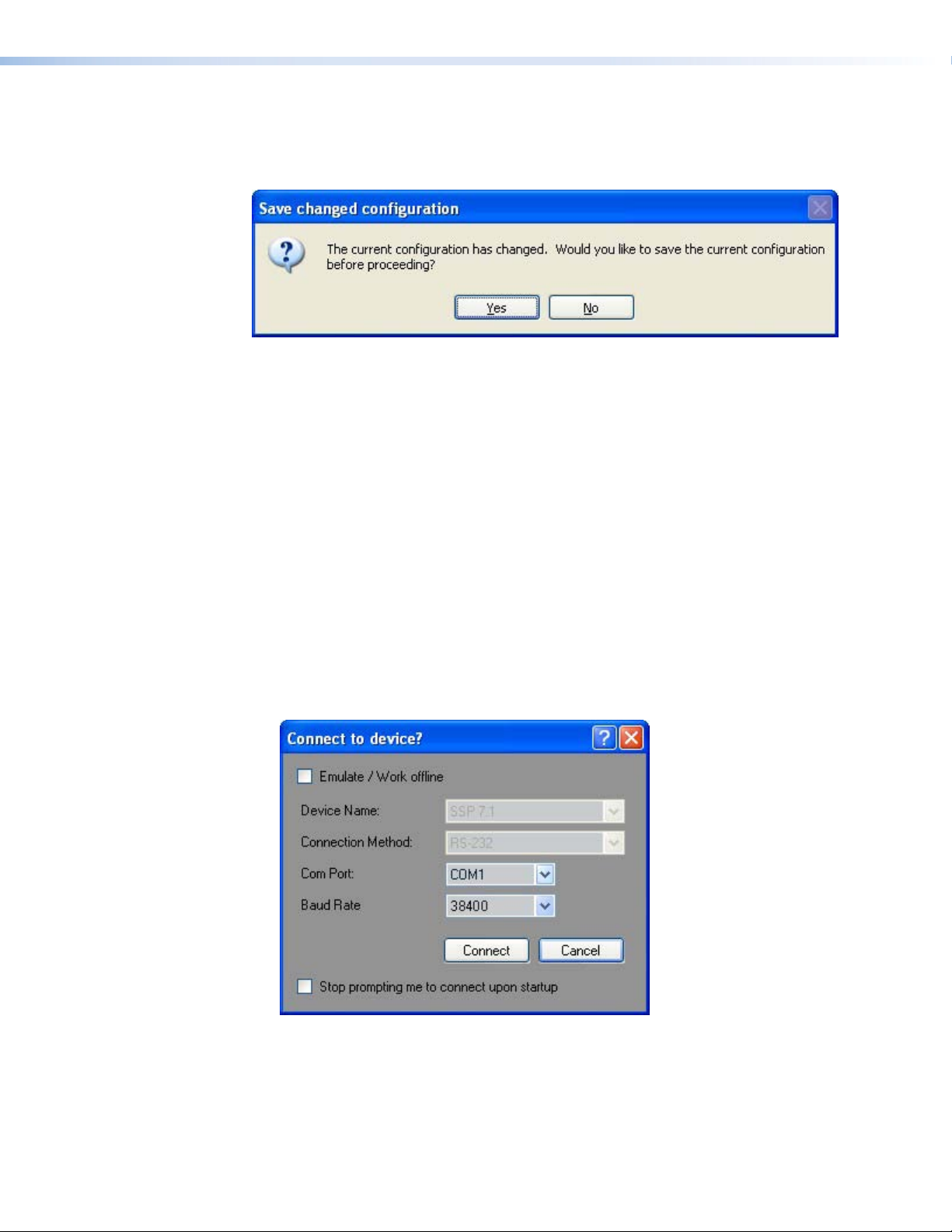
When the SSP 7.1 Control and Setup software is opened directly to Live mode, the current
conguration in the device is read from the SSP 7.1 unit, automatically overwriting the
settings in the software. When the program is closed, you are prompted to save any changes
that have been made during that session.
Figure 13. Save changed configuration Box
Running the SSP 7.1 Setup and Control Software
Connect to device? Dialog Box
The computer must be connected to the SSP 7.1 using either the RS-232 captive screw
connector on the rear panel or the Config port on the front panel.
To start the program, click on the desk-top icon or click on the Windows Start button and
select All Programs > Extron Electronics > SSP7.1 > SSP7.1. When the program
launches, the “Connect to device?” dialog box (shown below) opens.
To work ofine in Emulate mode, check the Emulate/Work offline box. To connect
directly to the SSP 7.1, leave the box unchecked. See the previous section, “Live and
Emulate Modes,” for a description of each mode.
If you choose to work directly with the SSP 7.1:
1. The Device name (SSP 7.1) and Connection Method (RS-232) are already entered and no
other selections are available for these fields.
2. Select the correct Com Port and Baud Rate (default 38400).
Figure 14. Connect to device? Dialog Box — Live Mode
SSP 7.1 • Setup and Control Software 24
Page 31

3. Click the Connect button (or Cancel to exit the program).
If you select Emulate, click on the Work Offline button (or Cancel to exit the
program).
Figure 15. Connect to device? Dialog Box — Emulate Mode
NOTE: When Emulate/Work Offline is selected, the Connect button is
replaced by a Work Offline button. Instead of establishing a connection
with the sound processor, the program allows you to create a configuration
that can be saved as a file and used to update the configuration of the
sound processor when the program is in Live mode.
When the program opens, you may still toggle between Live or Emulate modes by using
the buttons in the top right corner of the program window, as described in “Live and
Emulate Modes” on page 23.
If you check the “Stop prompting me to connect upon startup” box, the next time the
program opens, this dialog box is not shown and the program automatically opens in
Emulate mode. Click the Live button in the program window to switch to Live mode.
To re-enable this box, use the menu system to navigate to Options>Re-enable Dialogs
(see Re-enable Dialogs on page 53). This clears the check box in all dialog boxes and
all previously disabled pop-up messages occur regularly again.
SSP 7.1 • Setup and Control Software 25
Page 32

Main Tab
The program opens with the Main tab selected. Two other tabs are available: Speaker
Setup (page 30) and Listening Mode Setup (page 45). It is advisable to congure each tab
in the sequence they appear at the top of the screen. Full instructions on how to configure
each screen are available in the help file, which can be accessed under the Help menu
option or by pressing F1 from within the program.
Figure 16. Main Tab
The Main tab offers the options that are available on the SSP 7.1 front panel:
Input source — The five buttons allow the user to select between five possible audio
inputs: four digital inputs and one analog input. The currently selected input is shown in
blue; the other sources are shown in gray. Further information about the input sources is
available in the Source Formats section on page 61.
Figure 17. Main Tab — Input Selection
SSP 7.1 • Setup and Control Software 26
Page 33

Tone controls — Bass control adjusts the amount of low-frequency
boost or cut applied to the audio outputs for all speakers, including
the subwoofer. Treble control adjusts the amount of high-frequency
boost or cut applied to the audio outputs for all speakers, except the
subwoofer. Both controls are adjustable between -10 dB and +10 dB,
and the current value is shown in the text box. Adjust the value in any
of these ways.
z Grab and drag the slider bar to adjust tone in 1 dB increments.
z Click on one of the slider bars to make it active and use the up
and down arrows beside the text box to adjust the tone in 1 dB
increments.
z Click on one of the slider bars to make it active and use the up and down keys on the
keyboard to adjust the tone in 1 dB increments.
z Click in one of the text boxes and type a number between -10 and +10.
z Click on one of the slider bars to make it active and use the page up and page down
keys on the keyboard to adjust the tone in 5 dB increments.
Analog input gain — This control is only available when input 5 (analog) is selected. It is
locked and cannot be adjusted when inputs 1-4 are selected.
The Analog Input Gain control allows the gain to be adjusted between
0 dB and +24 dB. The current setting is displayed in the text box.
The gain can be changed in any of the following ways.
z Grab and drag the slider bar to adjust gain in 1 dB increments.
z Click on one of the slider bars to make it active and use the up
and down arrows beside the text box to adjust the gain in 1 dB
increments.
z Click on one of the slider bars to make it active and use the up and
down keys on the keyboard to adjust the gain in 1 dB increments.
z Click in the text box and type a number between 0 and +24 dB (do
not type the “+” or “dB”).
z Click on one of the slider bars to make it active and use the page
up and page down keys on the keyboard to adjust the gain in 5 dB
increments.
The red virtual LED lights when the input level is 0 dBFS or higher,
indicating that the input level is too high.
NOTE: If the gain level is turned too high, clipping may occur (depending on the input
volume). When clipping occurs, the red virtual LED next to the Input 5 button
lights.
Dynamic Range Compression (only with Dolby Digital and DTS source
formats that have a Dynamic Range Compression flag) — These
buttons allow a choice of Off, Minimum, and Maximum. The default setting
is Off. For more information about Dynamic Range Compression Control,
see page 19.
SSP 7.1 • Setup and Control Software 27
Page 34

Input and Output information bar — The Input and Output
information bar, on the right side of the screen, is visible in all tabs
and provides information about:
z The current input
z Selected input channel
z Source format
z Sampling frequency
z Encoded channels
z The current output
z Speaker configuration
z Listening mode
z Mode override selection
z Master volume
z Mute
NOTE: While the Master Volume value and Mute status can be adjusted using the slider
bar and button in this panel, the Input and Output status information in this
information bar is read only.
Input status — The Input box indicates which input channel is being used. Underneath are
three lines of information about the source format, the sampling frequency, and encoded
channels.
The box underneath highlights the active channels for the audio source in blue.
L = Left front
C = Center
R = Right front
LS = Left surround
RS = Right surround
S = Surround (only available with 3/1
or 2/1 sources): LS and RS carry a
mono surround signal.
SB = Surround back
LFE = Low Frequency Effect (primarily
used for subwoofer channel output)
Further information about the source
format configuration from the
SSP 7.1 front panel can be found
on page 6. To understand more about
Source Formats, see page 61.
SSP 7.1 • Setup and Control Software 28
Page 35

Output status — A text box indicates
the speaker configuration, the current
listening mode, and the mode override
status.
Underneath, a box shows the current
speaker configuration. Speakers that
are available are highlighted in blue and
speakers that are not available are not
shown.
Speakers that are set to large (see
Speaker Configuration on the next
page) are represented by large icons
and speakers that are set to small are
represented by small icons.
Speakers that are present but have been
muted are shown in red.
Master volume and mute — The
output status section of the screen also
contains the Master Volume adjustment
and the Mute button.
The master volume can be adjusted
between 0 (-100 dB) and 100 (0 dB). The current volume setting is displayed in the text box.
The volume can be changed in any of the following ways:
z Grab and drag the slider bar to adjust volume in 1 dB steps.
z Click on the slider bar to make it active and use the up and down arrows beside the text
box to adjust the volume in 1 dB steps.
z Click in the text box and type in a negative number in the box (corresponding to the
attenuation, in dB, from the maximum volume). Typing a positive number resets to
maximum volume (0 dB attenuation). Do not type the “dB.”
z Click on the slider bar to make it active and use the up and down keys on the keyboard
to adjust the volume in 1 dB steps.
z Click on the slider bar to make it active and use the page up and page down keys on
the keyboard to adjust the volume in 5 dB steps.
The Mute button mutes or unmutes all channel outputs.
NOTE: Moving the volume or the analog gain sliders, or switching inputs disables the
mute function and restores the volume settings.
SSP 7.1 • Setup and Control Software 29
Page 36

Speaker Setup Tab
After completing the Main tab, the next tab is Speaker Setup, which is the first tab to
allow system configuration that is not available from the front panel. The Speaker Setup
tab provides access to four second-level tabs (Speaker Configuration, Speaker Delay,
Testing & Output Trim, and Speaker Equalization).
Speaker Conguration Tab
Figure 18. Speaker Configuration Tab
Speaker size
Speaker size determines whether or not bass management applies to that speaker. For more
information about bass management and speaker size, see pages 15 and 16.
Speaker size settings — All the buttons in a single column offer mutually exclusive
choices. Only one selection can be made from each column. For example, front speaker size
must be set to either 2 Large or 2 Small. It cannot be set to both values or neither value.
Figure 19. Speaker Size Settings
SSP 7.1 • Setup and Control Software 30
Page 37

z Left and right front speakers and left and right surround speakers are set in pairs.
z The center speaker is set as an individual speaker.
z Back speaker(s) can be set as a single speaker or as a pair of speakers, depending on the
system configuration.
z The subwoofer can be set to Present or None.
Small — Bass management is on (see page 15).
Large — Bass management is off (see page 16).
None — No signal is sent to the output for that channel, effectively removing the speaker
from the current configuration. It is not an option for front speakers (see page 16).
One Small Speaker, Two Small Speakers, One Large Speaker, Two Large
Speakers, or None (Back speakers only) — These options determine whether the audio
output channels for the back speakers are output to the left back and right back (in 7.1
setups) or to the center back (in 6.1 setups). For more information, see page 16.
Subwoofer — This option allows the subwoofer to be enabled or disabled (see page 16).
Crossover — The crossover frequency sets the boundary below which the low frequency
signals from designated output channels are incorporated into bass management (see
page 16). The crossover frequency is adjustable using the drop-down
menu.
z From 40 - 80 Hz, increment and decrement in 5 Hz steps
z From 80 - 150 Hz, increment and decrement in 10 Hz steps
z From 150 - 250 Hz, increment and decrement in 25 Hz steps
Speaker configuration
The speaker configuration is displayed in a graphics box that is very similar to the graphics
box shown in the Input and Output information bar.
Only the speakers available in the current configuration are
displayed.
If the speakers are set to Large, they are represented by large
icons, as shown in the figure at right. If the speakers are set to
Small, they are represented by small icons.
If the speakers are set to None, they are not available in the
current configuration and are not displayed.
If the back speakers are set to 1 Large or 1 Small, the CB
speaker, but not the LB and RB speakers, are shown (6.1
setups). If the back speakers are set to 2 Large or 2 Small, the LB and RB speakers, but not
the CB speaker, are shown (7.1 setups).
Input and Output information bar
The Input and Output information bar is available from all GUI tabs and is described in detail
on pages 28 and 29.
SSP 7.1 • Setup and Control Software 31
Page 38

Speaker Delay Tab
After completing the Speaker Configuration tab, configure the Speaker Delay tab.
Figure 20. Speaker Delay Tab
These controls introduce a signal delay for each speaker that has not had its size value set to
None. The two main reasons to adjust the signal delay are:
z To compensate for unequal distances between the speakers and the listener, which
causes sound from different speakers to reach the listener at different times.
z To compensate for a lack of coordination between the audio and the accompanying
video signal.
Speaker distance
When speakers are arranged in a room, there is a central
location or “sweet spot” that offers the best listening point.
However, even in that central location, the speakers are not
necessarily all equidistant from the listener and the sound
from the closest speaker reaches the listener before the sound
from speakers that are further away.
Speaker distance settings delay the signals going to each
individual speaker (from 0 to 100 ms) so that the signals
from all the speakers are synchronized and reach the listener
simultaneously. The default setting for each speaker is 0 ms.
Speakers that are not available in the current conguration are not displayed. When the
back surround is set to one speaker, the right back speaker is unavailable and the left back
speaker is renamed center back.
SSP 7.1 • Setup and Control Software 32
Page 39

Extron recommends that the SSP 7.1 Setup and Control Software is used to set speaker
delays, using either of the following methods.
Two person setup
NOTE: Setting up speaker delays is easier with two people. If only one person is
available, the position of the ears of the listener must be marked precisely. A pile
of boxes could be used to ensure that the distances are consistently measured
to the correct height. Do not try to guess ear positions, as this introduces
measurement errors.
1. Pick an ideal central location where all speaker output signals converge.
2. Use a tape measure to measure the distance from each speaker to the convergence
location. Be sure to measure to the same spot from each speaker.
NOTE: Measurements from the speaker must be to the midrange driver in a
three-way speaker or from halfway between the tweeter and the woofer in
a two-way speaker. Measurements to the convergence locations must be at
ear height.
3. Click on the Feet (ft) or Meters (m) button to select the units and enter the
Speaker Distance values for each speaker (in feet or meters) in the boxes in the SSP 7.1
Setup and Control Software Speaker Delay tab. The up and down (
{) arrows increase
the distance in increments corresponding to steps of 0.1 ms (0.12 feet or 0.03 meters).
The software automatically selects the farthest speaker and calculates the delay time (in
milliseconds) for each speaker.
These values are shown in the Calculated Delay box. The current values are shown in
blue, changes (yet to be saved) are shown in orange.
Figure 21. Calculated Delay — Values Pending
SSP 7.1 • Setup and Control Software 33
Page 40

4. Click the Apply button to save the changes. The new values (previously in orange) are
shown in blue as the current values and there are no values displayed in orange.
To retain the original values, click Cancel instead of Apply.
Figure 22. Calculated Delay — Values Applied
NOTE: Users who wish to calculate the delay time for themselves should follow the full
procedure shown on page 94 in “Setting Speaker Delay Settings using SIS
Commands.”
Setup with a Real Time Analyzer (RTA) calibration tool
1. Choose an ideal central location on which all speaker output signals converge.
2. Place the microphone from the RTA at ear level in the convergence location.
3. Play the audio source. This can be an analog source, provided by the RTA.
4. Use the Test Signal Output buttons in the Testing & Output Trim Tab (see page 36) to
select which speakers are tested and the order in which the speakers are tested.
5. Use the RTA to measure the speaker distance (in ms) for each channel.
6. In the SSP 7.1 Setup and Control Software Speaker Delay tab, select the
milliseconds (ms) button and enter the values for each speaker (in ms) into the boxes.
The up and down (
{) arrows increase the distance in increments of 0.1 ms.
7. Repeat steps 4 to 6 until the speaker distance has been entered for all available
speakers.
NOTE: The maximum allowable distance for the furthest speaker is 100 ms.
8. Click the Apply button to save the changes. The new values (previously in orange, see
figure 21) are shown in blue as the current values and there are no values displayed in
orange (see figure 22).
To retain the original values, click Cancel instead of Apply.
SSP 7.1 • Specifications, Parts, and Accessories 34
Page 41

Lip Sync Offset
Lip sync offset compensates for a lack of
coordination between the audio and the
accompanying video signal. This frequently
occurs if the video signal has undergone
complex manipulation that can delay it
several milliseconds relative to the audio
signal.
Since some sources may require more
manipulation than others, the lip sync
offset is set for each source individually to
synchronize the audio for that source with
the corresponding video signal.
Enter the appropriate value in the lip sync
offset box. This delay is added to every
available speaker to resynchronize the video
and audio signals.
Input and Output information bar
The Input and Output information bar is available from all GUI tabs and is described in detail
on pages 28 and 29.
SSP 7.1 • Specifications, Parts, and Accessories 35
Page 42

Testing & Output Trim Tab
After the Speaker Delay tab, configure the Testing & Output Trim tab.
Figure 23. Testing & Output Trim Tab
Several factors can affect the sound level reaching the listener from different speakers. These
factors include the distance from the speaker to the listener, slight variations between the
output channels of a single amplier, and variations between the individual speakers. Use
the output trim to set the output level of each individual channel to compensate for all these
variations and ensure that the sound level reaching the listener is the same from all speakers.
This tab also provides a test signal utility.
Test signals
Test signals are used during setup to calibrate the level of each
channel and to ensure proper connection between the individual
output channels of the SSP 7.1 and the line level input channels
of an audio signal processor, a receiver with built in amplifier, or
a stand alone amplifier that powers the loudspeakers.
Selecting test signal source
There are four test signal options (see Test Signals on page 17):
Off, Dolby Noise, Pink Noise, or Active Input. They are
selected from the mutually exclusive Source Signal Type buttons.
By default, the test signal is Off. The Dolby Noise and Pink
Noise test signals are generated by the SSP 7.1.
NOTE: The Active Input selection is normally used with an analog source on input 5.
The output must be set to Mono to All.
SSP 7.1 • Setup and Control Software 36
Page 43

Set the external source to Mono to All using one of these methods.
Listening Mode Preferences Tab
1. Select the listening mode Preferences tab (see page 45).
2. Select the input channel that is providing the test signal source (1-5).
3. For whatever source format the test signal is using, select Mono to All.
4. Return to the Testing & Output Trim tab and click on Active Input.
Override Preferences Tab
1. Select the Override Preferences tab (see page 48) and select the input source.
2. For selectable mode To All choose the override Mono to All.
3. On the front panel of the SSP 7.1, use the Mode Override button to select To All.
Selecting speakers to be tested
The currently available speakers are displayed in a
graphics box. Speakers that are not available are
not displayed.
Click on the individual speaker to select or deselect
it from the list of speakers to be tested. Click on
All to select all speakers.
NOTE: If all speakers have been selected,
clicking All deselects all speakers.
SSP 7.1 • Setup and Control Software 37
Page 44

Speaker test sequence
5.1 Setup 6.1 Setup 7.1 Setup
To run an automatic test sequence
1. Select the Auto button. This sends a
two second test signal to each output
channel in the sequence shown in the
diagram at right. All other speakers
are muted. The test sequence cycles
through each speaker multiple times
until the test signal is switched off.
2. Click on Off in the Select Signal Type
area to switch off the test signal and
end the test sequence.
2 Sec
Left Front
channel
2 Sec
Center
channel
2 Sec
Right Front
channel
2 Sec
Right Surround
channel
2 Sec
2 Sec
2 Sec
Center Back
channel
Right Back
channel
2 Sec
Left Back
channel
To test the speakers manually:
1. Click Auto to deselect it.
2. Click the forward (>) or back (<) buttons to move forward or backward
3. Click Off in the Select Signal Type area to switch off the test signal and
Left Surround
Subwoofer
through the sequence shown in the diagram below.
end the test sequence.
channel
2 Sec
2 Sec
2 Sec
SSP 7.1 • Setup and Control Software 38
Page 45

Output Trim
The Output Trim sliders control the audio signal level for each individual channel output.
Only channels that are enabled in the current speaker conguration are available; the others
are displayed but cannot be adjusted. Output trim is adjustable from -24 dB to +12 dB. The
current value for each output channel is shown in the text box.
Figure 24. Output Trim
NOTE: The maximum output volume is tied to the output trim. When an output trim
value is higher than 0 dB, the highest possible output volume is reduced by that
amount. For example, if the highest output trim for any channel is set to +5 dB,
the maximum output volume is -5 dB.
Extron recommends using a Sound Pressure Level (SPL) meter to set the output trim for each
speaker:
1. Set up the SPL meter at the sweet spot in the room.
2. Send a test signal, generated as described in Test Signals on page 36, to each
individual speaker in turn. Extron recommends using the Dolby Noise signal and sending
the signals to the speakers manually.
NOTE: The test signal should have a sound level at least 20 - 30 dB above ambient
levels.
3. Measure and write down the sound pressure for each speaker.
4. To avoid decreasing the maximum output volume (see the note above), Extron
recommends that you use the speaker with the lowest SPL reading as the zero reference
point. Then attenuate all the other speakers by the required amount to balance all
speakers.
SSP 7.1 • Setup and Control Software 39
Page 46

In the example below, the SPL readings for five channels are given in column 2.
Channel 4 has the lowest reading and is used as the zero reference point. The difference
between each speaker and the zero reference is calculated in column 3. This is the
adjustment that must be made to the output trim for that channel.
Channel SPL Reading Output Trim Adjustment (dB)
1 75 -1
2 76 -2
3 79 -5
4 74 0
(zero reference channel)
5 77 -3
5. Use any of these methods to adjust the output trim for each speaker.
z Grab and drag the slider bar to adjust output trim in 1 dB increments.
z Click on one of the output trim slider controls to activate it and use the up and
down arrows beside the text box to adjust it in 1 dB increments.
z Click on one of the output trim slider controls to activate it and use the up and
down keys on the keyboard to adjust it in 1 dB increments.
z Click on one of the output trim slider controls to activate it and use the page up and
page down keys on the keyboard to adjust it in 5 dB increments.
z Highlight the value in the text box, type a number (omit the dB), and press Enter on
the keyboard.
The Reset button returns the output trim values for all speakers to the default value (0 dB).
Input and Output information bar
The Input and Output information bar is available from all GUI tabs and is described in detail
on pages 28 and 29.
SSP 7.1 • Setup and Control Software 40
Page 47

Speaker Equalization Tab
After the Testing & Output Trim tab, configure the Speaker Equalization tab.
Figure 25. Speaker Equalization Tab
The Speaker Equalization tab provides nine parametric EQs for each output channel.
The default frequency values correspond to a nine-band graphic equalizer, which provides a
starting point for refining the output signal from each speaker channel.
All the properties of the SSP 7.1 parametric EQs can be dened by the user.
Speaker selection
Select the speaker to be configured from the drop-down menu.
Figure 26. Speaker Selection Menu
EQ selection
Select the EQ to be adjusted (1-9) by pressing the desired numbered button and deactivating
the corresponding Bypass button. The numbered buttons are a mutually exclusive set (only
one button can be activated at a time). By default all EQs are bypassed.
Figure 27. EQ Band Selection Buttons
SSP 7.1 • Setup and Control Software 41
Page 48

When an EQ has been selected, it can be adjusted in the graphic box or the text boxes at the
bottom of the screen.
When the bypass is activated for an EQ, the values are saved for future use but do not act
on the signal path. When the bypass is deactivated, changes made to that EQ contribute to
the composite graph that is displayed. The graph shows how the activated EQs combine to
affect the signal path in the current setup.
Right click the EQ number to bring up a context sensitive menu (see gure 27). Select
Reset to return to default values for the currently selected EQ only, or select Reset All to
return to default values for all EQs for the selected speaker channel.
Adjust EQ graphically
When an EQ is selected (see “EQ selection” on page 41) the EQ Graph displays a composite
curve showing the individual EQ that is being congured with three parameter adjustment
handles. A vertical white line marks the position of the handle (frequency) currently being
adjusted.
Click and drag the EQ number (highlighted at the top of the graph) to adjust the horizontal
position of the handle. Click and drag the center handle up or down to adjust the boost or
cut level (in dB).
Click either of the outer handles to adjust the bandwidth, expressed as a Q value (frequency
divided by bandwidth). If either of these outer handles moves, the other outer handle moves
in the opposite direction to maintain a symmetry about the center handle.
NOTE: When values are altered in the graphics display, the numeric values in the
“Adjust EQ Numerically” section (see next page) are updated to reflect the
changes.
In the example below, the adjustment handles for EQ 3 are shown. The selected EQ is
highlighted at the top of the graph.
Figure 28. Graph for EQ Band 3
SSP 7.1 • Setup and Control Software 42
Page 49

In the graph below, EQs 1, 2, 3, and 4 have been adjusted. The effects of adjusting EQs 2, 3,
and 4 can be seen by the deviation from the horizontal line. The effect of adjusting EQ 1 is
not seen because the bypass button for that EQ is still activated and adjustments to EQ 1 are
not used to process the audio signal. The numbers of the EQs contributing to the graph (2,
3, and 4, but not 1) are shown in white against a blue background at the top of the graph.
Figure 29. Graph After Bands 2, 3, and 4 Have Been Adjusted
Adjust EQ numerically
These four fields control the parameters that can also be adjusted in the graph.
Figure 30. Menus for Adjusting EQ Numerically
EQ# — selects which EQ is adjusted.
Frequency — adjusts the frequency of the center handle on the graph.
Boost/Cut — adjusts the amount of amplification or attenuation applied to that particular
EQ.
Q — adjusts the bandwidth to which the boost or cut is applied. As the Q value increases,
the bandwidth becomes narrower.
NOTE: When values are altered in the Adjust EQ Numerically fields, the graphic display
is updated to reflect the changes.
SSP 7.1 • Setup and Control Software 43
Page 50

Test Signals
Use the Test Signals section of the screen
to select Pink Noise or the Active
Input signal as the sound source. Use
the sequence arrows to apply the test
signal to the appropriate output channel.
Input and Output information bar
The Input and Output information bar is available from all GUI tabs and is described in detail
on pages 28 and 29.
SSP 7.1 • Setup and Control Software 44
Page 51

Listening Mode Setup Tab
After completing the Speaker Setup tab, the final tab is Listening Mode Setup. This
tab provides access to three second-level tabs (Preferences, Override Preferences, and
Dolby, DTS, and Mono Settings).
For each combination of source format and speaker conguration, the SSP 7.1 has a default
listening mode. However, this cannot take into account the characteristics of the room or
the personal preferences of the listener. The Listening Mode Setup tab allows users
to customize their preferences for each input channel and for each combination of source
format and speaker configuration.
Preferences Tab
The Listening Mode Setup tab opens at the Preferences tab.
Figure 31. Preferences Tab
Input channel
Select the input channel to be configured from the drop-down
menu.
SSP 7.1 • Setup and Control Software 45
Page 52

Listening mode selection
Use the drop-down menus to select the preferred listening mode to be associated with each
source format. A full list of all options can be found in “Source Formats and Listening
Modes with Different Speaker Setups” on page 75.
The available selections are dynamically populated so that they represent only the values that
are available for the current speaker conguration. When input 5 is selected, the only Source
Format available is Analog (see figure 32 below). When a digital input is selected, a full
range of digital source formats is available (see figure 33 below).
Figure 32. Listening Mode Selection (Input 5)
Figure 33. Listening Mode Selection (Input 2)
The default listening mode for each source format is initially shown. The drop-down menu
offers all the listening modes that are available for each source format per each speaker
configuration.
Figure 34. Listening Mode Menu
NOTE: When a listening mode that sums the left and right channels is applied, clipping
is possible on the summed channels. Instances of this include applying Mono,
Mono to All, or PL II/IIx listening modes to a stereo source.
SSP 7.1 • Setup and Control Software 46
Page 53

No Mode Override
MODE OVERRIDE
MODE OVERRIDE
MODE OVERRIDE
MODE OVERRIDE
MODE OVERRIDE
selected
Downmix selected
Dolby PL II/IIx selected
DTS Neo:6 selected
The Selected Override text matches the current state of the front panel Mode Override LEDs.
DOWNMIX
PL II/IIx
DTS NEO:6
TO ALL
DOWNMIX
PL II/IIx
DTS NEO:6
TO ALL
DOWNMIX
PL II/IIx
DTS NEO:6
TO ALL
DOWNMIX
PL II/IIx
DTS NEO:6
TO ALL
To All selected
DOWNMIX
PL II/IIx
DTS NEO:6
TO ALL
Figure 35. Selected Override Matches Front Panel LEDs
When there is no source, the Selected Override box reads “No Override.“
Input and Output information bar
The Input and Output information bar is available from all GUI tabs and is described in detail
on pages 28 and 29.
SSP 7.1 • Setup and Control Software 47
Page 54

Override Preferences Tab
Listening mode override
After selecting the listening mode, click on the Override Preferences tab to adjust the
mode override options. These preferences are applied when the front panel override option
is engaged and allow further refinement of the front panel override. The available options
for each mode override group are listed under the appropriate drop-down menu.
Figure 36. Listening Mode — Override Preferences
The table below shows the Mode Override options that are available from the drop-down
menus for each selectable mode.
Selectable Mode Listening Mode Options
Downmix
PL II/IIx
DTS NEO:6
TO ALL
More information can be found in the Reference Material section about source formats
(page 61), listening modes (page 66), mode override (page 7), and listening modes
that are available for each source format (page 75).
Stereo (default)
Mono
Dolby Pro Logic II/IIx Movie (default)
Dolby Pro Logic II/IIx Music
DTS Neo:6 Cinema (default)
DTS Neo:6 Music
Stereo to All (default)
Mono to All
Input and Output information bar
The Input and Output information bar is available from all GUI tabs and is described in detail
on pages 28 and 29.
SSP 7.1 • Setup and Control Software 48
Page 55

Dolby, DTS and Mono Settings Tab
After configuring Override Preferences, click the Dolby, DTS and Mono Settings tab.
Figure 37. Dolby, DTS and Mono Settings Tab
This tab allows advanced adjustments to the settings for Dolby ProLogic II/IIx Music,
DTS Neo:6, and how mono signals are received and output by the SSP 7.1.
Dolby Pro Logic II/IIx Music Settings
The Dolby Pro Logic II/IIx Music listening mode is used for
listening to any stereo music recordings. More information
about this listening mode can be found on page 68
of the Reference material. These controls adjust global
settings for the listening mode, to tailor the sound to
individual listening tastes.
Dimension control
These buttons allow the user to choose Front,
Neutral, or Rear (the default is Neutral). See page
68 for more information about Dimension Control.
Panorama control
These buttons allow the user to switch the Panorama
settings On or Off (the default is Off). See page 68 for
more information about Panorama Control.
Center Width control
This sliding bar adjusts the Center Width control in the range 0-7. When the control is set
to 0, the sound comes from the front center speaker. At 7, the sound comes from the front
right and left speakers. The default setting is 3 (bold and underlined). See page 68 for more
information about Center Width control.
SSP 7.1 • Setup and Control Software 49
Page 56

DTS Neo:6 settings
Center Image Settings
These controls set the center image for DTS Neo:6 Cinema
and DTS Neo:6 Music listening modes. More information
about this listening mode is found on page 69.
The sliding bars adjust the center image control settings:
z DTS Neo:6 Cinema: 0 - 10 (the default is 10)
z DTS Neo:6 Music: 0 - 10 (the default is 3)
Setting the control to 0 creates the effect of spreading out
the audio signal across the front speakers. Setting the control
to 10 creates the effect of centralizing the audio signal.
See page 69 for more information about Center Image control.
Mono Settings
Two advanced configurations apply only to mono
sources or outputs.
Analog Source (applies to Input 5 only)
A mono signal may be input as left channel only,
right channel only, or the sum of left and right
channels (both channels input identical mono
signals). These controls allow the user to decide
whether the Left Only, Right Only, or L+R
(Sum) summed input becomes the source for
the mono decoding mode. The default is L + R (Sum).
Output Channel(s)
These buttons let the user select whether mono signals are output to the center channel
(Center Only) or a dual mono signal is sent to the right and left front channels (Front
L+R Only). The default is Center Only.
Input and Output information bar
The Input and Output information bar is available from all GUI tabs and is described in detail
on pages 28 and 29.
SSP 7.1 • Setup and Control Software 50
Page 57

Drop-down Menus
The menu bar at the top of the window provides additional
tools and options. The four top-level headings are File,
Device, Options, and Help (see figure at right).
File
The File menu options allow you to save changes made to the
conguration of the SSP 7.1, whether you are running the software
in Live or Emulate mode. The current conguration can be saved as
an *.esp file, which can be opened, further modified, saved, or saved
by a different name. The File menu has five options.
New — If the software is in Emulate mode, you can save the
configuration changes you have made to a new file by clicking on
New. This creates a new file with the default settings that can be
saved in any directory on your network.
Open — Opens an existing le. The current settings of the SSP 7.1 are replaced by the
values in the file being opened.
Save — If the le that is currently being modied in Emulate mode has already been named
and saved, this option saves any updates to the same file.
Save As — If the le that is currently being modied in Emulate mode has not been
named, this allows you to name the file, place it in any directory on your network, and save
it.
Exit — Clicking on Exit shuts down the program.
Changes to the conguration of the SSP 7.1 made in Live mode are saved as they are made.
Exiting the program after a Live mode session, leaves all changes from that session in effect.
To restore all values to factory defaults, select the Reset... option in the Device menu on the
following page.
SSP 7.1 • Setup and Control Software 51
Page 58

Device
The Device menu has eight options.
Connect... (F5) — In Emulate mode, the option
Connect... is available, allowing the user to switch to
Live mode and open a direct connection to the SSP 7.1
unit. You may also use the F5 keyboard button to
switch from Emulate to Live. The Connect... option is
not available in Live mode.
Disconnect (F6) — In Live mode, the option
Disconnect is available, allowing the user to close the
connection to the SSP 7.1 unit and switch to Emulate
mode. You may also use the F6 keyboard button to
switch from Live to Emulate. The Disconnect option is
not available in Emulate mode.
For more information about Live and Emulate modes, see page 23.
Set Baud Rate... — This opens the Device Settings dialog box, which allows the user to
change the baud rate of the connection between the computer and the SSP 7.1. Changing
the baud rate closes the connection between the computer and the SSP 7.1. The control
program then attempts to reconnect to the sound processor at the new baud rate.
Figure 38. Device Settings Dialog Box
Front Panel — When the Locked
option is selected, the front panel
cannot be used to perform any
functions from the front panel
(except unlocking the front panel); when the Unlocked option is selected, the functions can
again be controlled from the front panel.
Volume Output — The volume of the audio output through all channels can be set
globally using these sub-menu options to choose either Fixed or Variable (the default value).
The Fixed option sets the volume to
full output with no attenuation. The
volume cannot be adjusted through
the front panel knob or by using the
SSP 7.1 Setup and Control Software or SIS commands. All the Output Channel Trim Levels
(see page 39) are xed at the values they had immediately before the Volume Output was
set to Fixed.
The Variable option allows the volume to be attenuated through the front panel knob, the
SSP 7.1 Setup and Control Software, or by SIS commands.
SSP 7.1 • Setup and Control Software 52
Page 59

Reset Mode Overrides — This option removes any mode overrides that have been set
using the front panel Mode Override button.
Update Firmware... — Launches the Firmware Loader application. For information
about how to update the SSP 7.1 rmware, see “Firmware Updates“ on page 56.
NOTE: The Firmware Loader application must be installed on your PC for this option to
work.
Reset... — The Factory Reset option undoes any user changes and resets all values to the
factory defaults.
Options
The Options menu has two choices.
Show Trace Window — The Show
Trace Window command opens the
Trace Window (see gure at right).
This window displays all commands
and data sent from the computer to
the SSP 7.1 unit in the upper pane,
and all responses and data sent from
the SSP 7.1 unit to the computer in
the lower pane. These data are useful
to qualified service personnel for
some troubleshooting situations.
The Clear Data button clears data
from both panes.
The Close button, shuts down the
window. Data are still being sent
between the computer and the sound
processor and can still be viewed by
reopening the window.
Re-enable Dialogs — Certain
warning dialog boxes, such as the
one shown at right, have a check
box that stop them from being
shown again. If you discover that
it is helpful to receive the warning,
selecting Re-enable Dialogs
restores all the dialog boxes that had
been blocked.
SSP 7.1 • Setup and Control Software 53
Page 60

Help
The Help menu has four options.
About This Software — Click About This Software to open a flash screen with
information about the SSP 7.1, including the software version installed (Version x.x.x.xx)
and the rmware version installed (Firmware Version: x.xx.xxxx).
To close the screen, click on OK or the X in the top right corner.
Figure 39. About SSP 7.1 Screen
SSP 7.1 Help (F1) — Click the SSP 7.1 Help option or press the F1 key on the keyboard
while running the SSP 7.1 Setup and Control Software to open the help le. For more
information about the SSP 7.1 Setup and Control Software help file, see page 55.
Search Help — The Search Help option opens the help le with a search box, which
allows the user to find a specific topic in the file.
Go to Extron.com — Click Go to Extron.com to open your default web browser at the
Extron home page (www.extron.com).
SSP 7.1 • Setup and Control Software 54
Page 61

SSP 7.1 Setup and Control Software Help File
Information about the SSP 7.1 Setup and Control Software can also be found in the
associated help le. Click the SSP 7.1 Help option in the Help menu or press the F1 key
when the program is being used to open the help file.
Figure 40. SSP 7.1 Setup and Control Software Help File — Contents
Use the Table of Contents in the left panel to nd and navigate to a topic.
You can also click on the Search tab or select the Search Help option from the Help
menu of the control software. This opens the help file search tool.
Figure 41. SSP 7.1 Setup and Control Software Help File — Search
SSP 7.1 • Setup and Control Software 55
Page 62

Firmware Updates
NOTES: • Ensure that you are using the latest versions of the SSP 7.1 Setup and Control
Software and firmware. To update firmware, install the Extron Firmware Loader
on your PC. All three programs are available from the Extron Web site.
• To download software from the Extron Web site, click on the Download
tab and select either the Firmware or Software option in the left sidebar.
Navigate to the appropriate program and click Download. Follow the onscreen instructions to install the program.
Upgrade the SSP 7.1 rmware as follows:
1. Turn off or disconnect all audio inputs before updating the firmware.
ATTENTION: Updating the rmware while the unit is still accepting active audio
inputs may cause the firmware update to freeze.
2. Power on the SSP 7.1 and a computer.
3. Connect the computer to the SSP 7.1 through the rear panel RS-232 captive screw
connectors.
4. If necessary, install the Extron Firmware Loader utility. This is on the software disk
provided or can be downloaded from the Extron Web site (www.extron.com).
5. From the same site, download the
rmware for the SSP 7.1.
6. To download the firmware for the
SSP 7.1, click on the Download tab
at the top of the Extron home page
and then click Firmware in the
sidebar to the left.
7. Navigate to the firmware for the
SSP 7.1 and click on Download.
8. In the dialog box, click Save.
NOTE: Make a note of the folder where you save the firmware.
SSP 7.1 • Setup and Control Software 56
Page 63

9. Open the SSP 7.1 Setup and Control software and click on the Update Firmware
option in the Device menu. The Firmware Loader Add Device... dialog box opens.
Figure 42. Add Device... Dialog Box
10. Select SSP 7.1 from the device list, RS-232 as the connection method, select the
correct com port and baud rate (default rate is 38400) and click the Connect button.
The PC connects to the SSP 7.1.
When the connection is made, the name of the device appears, with a green check
mark, in the Connected Device box.
11. Click the Browse button and navigate to the folder where the firmware file was saved
(see step 8).
12. Click the Add button. The Add Device... box closes to reveal the main Firmware Loader
window.
Figure 43. Firmware Loader Main Window
13. Click on the Begin button.
14. When the transfer is complete, the Total Progress box reads 100% and the entry in the
Status column reads Complete.
SSP 7.1 • Setup and Control Software 57
Page 64

Specications,
Parts, and
Accessories
This section provides information about:
z Specifications
z Included Parts
z Optional Accessories
Specifications
Audio
Gain ...............................................
Unbalanced output: -6 dB; balanced output: 0 dB, when volume is set to 0 dB gain.
Frequency response ........................ 20 Hz to 20 kHz, ±0.2 dB
Subwoofer frequency response....... 4 Hz to 250 Hz, ±3 dB
THD + Noise ................................... <0.03% @ 1 kHz, at maximum output level
S/N ................................................. >100 dB, 20 Hz to 20 kHz, unweighted
Stereo channel separation .............. Analog input only: >90 dB @ 1 kHz
CMRR ............................................ Analog input only: >75 dB (typical) @ 1 kHz
Bass adjustment ............................. ±10 dB @ 90 Hz
Treble adjustment ........................... ±10 dB @ 7500 Hz
Volume control ............................... - 100 dB to 0 dB
Bass management crossover frequencies
40 Hz to 250 Hz
Audio input — analog
Number/signal type ........................ 1 analog stereo/mono, balanced/unbalanced
Listening modes ............................. Stereo, stereo to all, mono, mono to all, Dolby® Pro Logic
Movie/Music, Dolby Pro Logic IIx Movie/Music, DTS™ Neo:6 Cinema/Music
Connector ...................................... (1) 3.5 mm captive screw connector, 5 pole
Impedance ..................................... >10k ohms balanced/unbalanced, DC coupled
Nominal level ................................. +4 dBu (1.23 Vrms) balanced or -10 dBV (316 mVrms) unbalanced
Maximum level ............................... +21 dBu (balanced/unbalanced)
Input gain adjustment .................... 0 dB to +24 dB (default = 0 dB), adjustable via RS-232 or front panel
NOTE: 0 dBu = 0.775 Vrms, 0 dBV = 1 Vrms, 0 dBV ≈ 2 dBu
®,
Dolby Pro Logic II
SSP 7.1 • Specifications, Parts, and Accessories 58
Page 65

Audio input — digital
Number/signal type ........................ 4 S/PDIF (2 optical, 2 coaxial)
Source formats ............................... PCM, Dolby Digital 2/0, Dolby Digital 2/0 Surround, Dolby Digital 5.1,
Dolby Digital Surround EX, DTS 2-channel, DTS Digital Surround,
DTS-ES Matrix 6.1, DTS-ES Discrete 6.1, DTS 96/24, DTS 96/24 ES Matrix 6.1
Listening modes ............................. Stereo, stereo to all, mono, mono to all, Dolby Digital 5.1, Dolby Digital EX,
Dolby Pro Logic, Dolby Pro Logic II Movie/Music, Dolby Pro Logic IIx Movie/
Music, Dolby Digital Pro Logic IIx Movie/Music, DTS, DTS 96/24, DTS-ES Matrix,
DTS 96/24 ES Matrix, DTS-ES Discrete, DTS Neo:6 Cinema/Music, DTS + Dolby EX,
DTS 96/24 + Dolby EX, DTS + Dolby Pro Logic IIx Movie/Music, DTS 96/24 + Dolby
Pro Logic IIx Movie/Music
Connectors .................................... 2 TOSLINK
2 RCA jacks
Audio output
Number/signal type ........................
Connectors .................................... (3) 3.5 mm captive screw connectors, 6 pole
Impedance ..................................... 50 ohms unbalanced, 100 ohms balanced
Gain error ...................................... ±0.2 dB channel to channel
Maximum level (Hi-Z) ...................... >+21 dBu balanced or >+15 dBu unbalanced at 0.03% THD+N
Output level range per channel ...... -24 dB to + 12 dB
D/A conversion ............................... 24 bit, 96 kHz
Control/remote — audio processor
Serial host control port ................... 1 bidirectional RS-232 front panel 2.5 mm mini stereo jack
Baud rate and protocol ................... 9600, 19200, 38400 (default), 115200 baud (adjustable); 8 data bits, 1 stop bit,
Pin configurations .......................... Mini stereo jack: tip = Tx, ring = Rx, sleeve = GND
Program control ............................. Extron control/conguration program for Windows®
General
Power ............................................ 100 VAC to 240 VAC, 50-60 Hz, 12 watts, internal
Temperature/humidity .................... Storage: -40 to +158 °F (-40 to +70 °C) / 10% to 90%, noncondensing
Cooling .......................................... Convection, no vents
Mounting
Rack mount ............................. Yes, with optional 1U rack shelf
Furniture mount ...................... Yes, with optional under-desk mounting kit
Enclosure type ................................ Metal
Enclosure dimensions ..................... 1.7” H x 8.75” W x 6.0” D (1U high, half rack wide)
Product weight ............................... 1.3 lbs (0.6 kg)
Shipping weight ............................. 3 lbs (2 kg)
8 balanced/unbalanced, for left and right front, left and right sides, left and right back,
center, and subwoofer output
(2) 3.5 mm captive screw connectors, 3 pole
1 bidirectional RS-232 rear panel 3.5 mm captive screw connector, 3 pole
no parity
Captive screw connector: pin 1 = Tx, 2 = Rx, 3 = GND
Extron Simple Instruction Set™ (SIS™)
Operating: +32 to +122 °F (0 to +50 °C) / 10% to 90%, noncondensing
(4.3 cm H x 22.2 cm W x 15.2 cm D)
(Depth excludes connectors and knob.)
™
fiber optic connectors
SSP 7.1 • Specifications, Parts, and Accessories 59
Page 66

Vibration ........................................ ISTA 1A in carton (International Safe Transit Association)
Regulatory compliance
Safety ...................................... CE, c-UL, UL
EMI/EMC ................................. CE, C-tick, FCC Class B, ICES, VCCI
Environmental .......................... Complies with the appropriate requirements of RoHS and WEEE.
MTBF ............................................. 30,000 hours
Warranty ........................................ 3 years parts and labor
NOTES: • All nominal levels are at ±10%
• Specifications are subject to change without notice.
Included Parts
Description Part Number
(1) SSP 7.1 60-842-01
(4) Rubber feet (not attached)
(1) 5-pole, 3.5 mm captive screw plug
(9) 3-pole, 3.5 mm captive screw plug
Extron Control Software disk
Tweeker
(1) IEC power cable
SSP 7.1 Setup Guide
Optional Accessories
Description Part Number
RSU 129 (1U 9.5 inch deep rack shelf kit) 60-190-01
RSB 129 (1U 9.5 inch deep basic rack shelf) 60-604-01
RSU 126 (1U 6 inch deep rack shelf kit) 60-190-10
RSB 126 (1U 6 inch deep basic rack shelf) 60-604-10
MBU 125 (under desk mounting kit) 70-077-01
CSR 6 (5-pin captive screw to RCA female audio adapter) 26-575-01
SSP 7.1 • Specifications, Parts, and Accessories 60
Page 67

Reference
Material
This section provides information about Source Formats and Listening Mode Options
and Usage.
Source Formats
Surround Channel Information
Surround channel information is written in the following format:
A/B.C (For example 3/2.1)
A represents the number of front channels (maximum 3: front right, front left, and center).
If A is 1, the source format has a mono encoded signal for playback through the center
channel. If A is 2, the source format encodes two discrete channels for stereo playback
through the front right and front left channels. If A is 3, there is a discrete encoded signal for
all three front speakers.
B represents the number of surround channels (maximum 3: surround right, surround left,
and back). If B is 1, the source format has a mono encoded signal for playback as dual mono
through the surround right and surround left channels. If B is 2, the source format encodes
two discrete channels for stereo playback through the surround right and surround left
channels. If B is 3, there is a discrete encoded signal for all three speakers, including the back
speaker.
NOTE: There is no “4” option because, while the SSP 7.1 can output up to eight
full bandwidth channels, there are presently no source formats that can pass
digital bit stream audio information containing 7.1 discrete encoded channels
through S/PDIF connections, which is the connection type that the SSP 7.1
supports.
C represents the presence or absence of LFE (1 = present; 0 = none or absent). This is the
discrete bass information, normally designated for use with the subwoofer channel, but may
be mixed with other channels in the absence of a subwoofer.
SSP 7.1 • Reference Material 61
Page 68

Encoded Channels Minimum Required
Output Speaker
Configuration
1/0.0 or 2/0.0 2.0
1/0.1 or 2/0.1 2.1
2/1.0 5.0
2/1.1 5.1
2/2.0 5.0
2/2.1 5.1
2/3.0 6.0
2/3.1 6.1
3/0.0 3.0
3/0.1 3.1
3/1.0 5.0
3/1.1 5.1
3/2.0 5.0
3/2.1 5.1
3/3.0 6.0
3/3.1 6.1
NOTES: • The minimum allowable configuration of the SSP 7.1 is 2.0 because the left
and right front speakers are always on. In the absence of a center channel,
1/0.0 and 1/0.1 encoded channels are output equally to both front channels.
• 7.0, 7.0 (with no center channel), 7.1, and 7.1 (with no center channel) are
valid output speaker configurations. However, standard DVD audio sources
cannot be encoded as 2/4.0, 2/4.1, 3/4.0, or 3/4.1.
• Blu-Ray DVD players output audio from Blu-Ray DVDs, which can carry 7.1
or more discrete encoded channels. However, that audio can be transmitted
only via the HDMI output and can be processed only by an AV receiver
that supports HDMI connections. The Blu-Ray player should support S/PDIF
connections that output Dolby Digital and DTS multichannel source formats,
which are also embedded in the Blu-Ray DVD and can be used to feed into
the SSP 7.1 via a TOSLINK or coaxial connection.
SSP 7.1 • Reference Material 62
Page 69

Dolby Digital Source Formats ( D)
Inputs 1- 4 only
Dolby Digital 5.1
(3/2.1, 3/2, 3/1.1, 3/1, 3/0, 3/0.1, 2/2.1, 2/2, 2/1.1, 2/1, 2/0.1, 2/0, 1/0.1, or 1/0)
Dolby Digital is a flexible, discrete, digital technology for carrying audio. Dolby Digital is a
5.1-channel surround sound format and is the standard for DVD video.
Dolby Digital features up to five discrete channels (front center, front left, front right,
surround left, and surround right), which gives it the “5” designation. Each of the channels
is full frequency with respect to human hearing (20 Hz to 20k Hz). There is an additional
channel reserved for low frequency effects (LFE), which is usually reserved for the subwoofer
speaker(s) or other speakers capable of reproducing low frequencies (3 - 120 Hz). This gives
the “.1” designation, since the sixth channel is not full frequency.
Although referred to as 5.1, it includes a variety of combinations, including 1.0, 2.0, 2.1,
3.0, 3.1, 4.0, 4.1, 5.0, and 5.1.
Dolby Digital 2/0
(2/0)
Dolby Digital 2/0 is a specic stereo format encoded by Dolby Digital technology. Encoded
information is intended primarily for playback by the front left and front right speakers. TV
broadcasts or DVD movie commentaries often have audio tracks encoded using this format.
When the SSP 7.1 detects this source format, both the D and 2-CH LEDs are lit.
Dolby Digital 2/0 Surround
(2/0)
Dolby Digital 2/0 Surround is the consumer version of the original Dolby multichannel analog
film sound format. Left, center, right, and mono surround are matrix-encoded onto two
audio tracks. These two tracks can be decoded by Dolby Pro Logic to recreate the original
four-channel sound. This source format is typically used for digital television broadcast
signals and older, remastered, movies.
When the SSP 7.1 detects this source format, both the D and 2-CH LEDs are lit.
Dolby Digital Surround EX
(3/2.1)
Dolby Digital Surround EX is a commercial format that reproduces the center channel
information through speakers placed directly behind the listener.
The back surround information is matrix-encoded onto the right and left surround channels
of conventional Dolby 5.1 formats. If there is no back channel speaker, the information for
that channel is played through the right and left surround speakers.
SSP 7.1 • Reference Material 63
Page 70

DTS Source Formats (DTS)
Inputs 1- 4 only
DTS 2-Channel
(2/0)
DTS 2-Channel is a specific DTS encoded stereo format. Material encoded in this source
format is typically found in DTS-HD Blue Ray DVDs and is primarily intended for playback by
the left and right front speakers. When this source format is present, both the DTS and the
2-CH LEDs light.
DTS Digital Surround
(3/2.1, 3/2, 3/1.1, 3/1, 3/0, 3/0.1, 2/2.1, 2/2, 2/1.1, 2/1, 2/0.1, 2/0, 1/0.1, or 1/0)
DTS Digital Surround is a 5.1-channel surround sound format similar to Dolby Digital 5.1. As
with the Dolby format, there are five full frequency channels (front center, front left, front
right, surround left, and surround right) and an additional LFE channel.
DTS 96/24
(3/2.1, 3/2, 3/1.1, 3/1, 3/0, 3/0.1, 2/2.1, 2/2, 2/1.1, 2/1, 2/0.1, 2/0, 1/0.1 or 1/0)
DTS 96/24, provides high quality audio reproduction of music and movies from DVDs
encoded with DTS Digital Surround source format information. The 96 kHz sampling
frequency improves on the more typical 48 kHz. All DTS formats have 24 bit depth, which
allows more audio information to be stored compared with the normal 16 bit depth.
DTS-ES Matrix 6.1
(3/2.1)
DTS-ES Matrix 6.1 is a 5.1 channel format with the back surround channel matrix-encoded
into the right and left surround channels. This is achieved in much the same way as the front
center channel is matrix-encoded into the front left and right channels of the Dolby Pro Logic
format. The back surround channel is not discrete, so this is not a true 6.1 source format.
DTS 96/24 ES Matrix 6.1
(3/2.1)
This mode is similar to DTS-ES Matrix 6.1 but also has DTS 96/24 encoded.
DTS-ES Discrete 6.1
(3/3.1)
DTS-ES Discrete 6.1 has a back surround channel that is discretely encoded into the DTS
bitstream. This format gives better sound spatialization for complete sound localization and
sound pans (the movement of a sound source through the sound field). This format provides
a data flag to signal the decoder that the bitstream contains an extra channel.
Material encoded in the DTS-ES Discrete 6.1 format cannot carry DTS 96/24 information
because of bandwidth limitations as a result of the discretely encoded surround back
channel information.
When the SSP 7.1 detects DTS source material with the DTS 96/24 feature, the sampling
frequency of the signal is displayed by the SSP 7.1 Setup and Control Software. The SSP 7.1
Setup and Control Software also changes the text associated with the listening modes to
reflect that DTS 96/24 is being output.
SSP 7.1 • Reference Material 64
Page 71

PCM Digital Source Format (PCM)
Inputs 1-4 only
Two channel, uncompressed, digital signals are processed through any of the four digital
inputs. The sampling frequency of the digital signal is displayed by the SSP 7.1 Setup and
Control Software.
When the SSP 7.1 detects this source format, both the PCM and 2 CH LEDs are lit.
2-Channel Source Format (2CH)
Analog
Input 5 only
Any balanced or unbalanced stereo signal (or two balanced or unbalanced mono sources) is
accepted. This includes older VCR tape recordings that were labeled as having Dolby 2/0 Pro
Logic audio.
Digital
Inputs 1-4 only
When the SSP 7.1 detects any two channel digital signal (including PCM, Dolby Digital 2/0,
Dolby Digital 2/0 Surround, or DTS 2-Channel) the 2 CH LED is lit.
Sampling Frequency
The following table shows the most common sampling frequencies of digital inputs and the
uses with which they are most often associated.
Sampling
Frequency
(kHz)
32 Used for some cassette recordings, speech, and all other audio where
smaller files are desired, with only slight compromise on sound quality. In the
44.1 Audio CD, also commonly used with MPEG-1 audio (VCD, SVCD, MP3).
48 Digital sound used for mini DV, digital TV, DVD, DAT, films and professional
88.2 Sampling rates used by professional recording equipment when the
96 DVD-Audio, some LPCM DVD tracks, DTS 96/24, and DTS 96/24
past, used with products such as NICAMs.
Adopted from the PCM adaptor using PAL video tapes (294 lines by 3
samples by 50 frames per second).
audio.
destination is CD (multiple of 44.1k Hz).
ES Matrix 6.1 source formats always output this sampling frequency.
Use
SSP 7.1 • Reference Material 65
Page 72

Listening Mode Options and Usage
Listening Mode Options
Stereo
This mode plays a stereo source in its pure, unprocessed form. It is the default factory setting
for any analog signal and any PCM or Dolby Digital 2/0 source coming through the digital
inputs.
It can be used to downmix a multichannel source format into a mixed stereo output signal.
Mono
This mode plays mono source material or stereo that has been mixed to a mono form. It can
be used to downmix a multichannel source format into a single mixed mono output signal.
The audio can be output to the center channel only or to the front left and front right
channels as a dual mono signal.
Two advanced configurations apply only to mono sources and outputs.
Analog Source (applies to Input 5 only) — If two mono signals are input on input 5
(analog), the user can choose whether the source input for the mono decoding mode is
Left Only, Right Only, or L+R (Sum). The default option is L+R (Sum).
Output Channels — This adjustment lets the user select whether mono signals are output
to the center channel (Center Only) or a dual mono signal is sent to the right and left
front channels (Front L+R Only). The default option is Front L+R Only.
Stereo to All
This mode plays stereo or downmixed stereo sources to all stereo channel output pairs in the
system.
If the source is a single analog mono signal and the listening mode is set to Stereo to All, the
following conditions apply:
z If the mono source is set to left channel only, the audio is output only to available left
channels in the system.
z If the mono source is set to right channel only, the audio is output only to available right
channels in the system.
z If the mono source is set to L+R (Sum), the audio is distributed evenly as a dual mono
signal to all available stereo pairs.
Mono to All
This mode plays mono or downmixed mono sources to all channel outputs in the system.
The mono source (Left Only, Right Only, or L+R (Sum)) can be selected using the
SSP 7.1 Setup and Control Software or SIS commands.
Dolby Digital 5.1
This mode is used with Dolby Digital encoded source formats. It produces up to 5.1 discrete
channels (center, left and right front, left and right surround, and a low frequency effects
channel).
SSP 7.1 • Reference Material 66
Page 73

DTS
This mode is used with DTS Digital Surround encoded source formats. It also produces up
to 5.1 discrete channels (center, left and right front, left and right surround, and a low
frequency effects channel).
This is the default mode for DTS-ES Matrix 6.1 source formats when the system is set
up for 3.0 to 5.1. It can be used with this source format to play the audio without the
matrix-encoded back channel information.
DTS 96/24
This mode is used with DTS Digital Surround source formats that have been encoded using
DTS 96/24. It also produces up to 5.1 output channels with audio sampled at 96 kHz at
24 bit depth.
This is also the default listening mode for DTS 96/24 ES Matrix 6.1 source formats for
systems with a 3.0 to 5.1 speaker conguration or if the listener wants to play the audio
without the matrix-encoded back channel information.
DTS-ES Matrix
This mode decodes DTS-ES Matrix 6.1 source formats, for use in a 6.0 to 7.1 system. Upon
playback, the additional surround back channel signal is decoded from the surround left and
right channels.
The listening mode can also be used with DTS Digital Surround sources where a surround
back channel is created through matrix processing.
DTS 96/24 ES Matrix
This mode is similar to DTS 96/24 but is used with DTS-ES Matrix 6.1 source formats. It can
also be used to extend DTS 96/24 source formats from 5.1 to 6.1 by creating a surround
back channel using matrix processing.
DTS-ES Discrete
This mode decodes DTS-ES Discrete 6.1 source formats and reproduces all 6.1 channels,
including the center channel information that was recorded independently, using the Digital
Discrete system.
Dolby Digital EX
This listening mode decodes source material that was recorded using Dolby Digital
Surround EX technology. It uses matrix mixing to produce extended surround back channel
effects, which create 6.1 outputs from 5.1 source formats. When used with 6.1 source
formats, the original back channel information is replaced by a matrix mixed sixth channel.
NOTE: This mode is available only when the SSP 7.1 is set up for 6.1 or 7.1 outputs and
a multichannel Dolby Digital source format is available.
Dolby Pro Logic
This mode decodes source audio that is encoded in two-channel Dolby Surround to
provide four-channel playback (center, left, right and mono surrounds). Sources include
videocasettes, DVDs, and TV broadcasts.
Logic steering techniques extend the impact of the sound track over a wider listening area.
This listening mode creates a mono surround channel with a high frequency roll off above
7 kHz.
SSP 7.1 • Reference Material 67
Page 74

Dolby Pro Logic II/IIx Movie or Music
Dolby Pro Logic II builds on Dolby Pro Logic by breaking the mono surround channel into a
pair of stereo surround channels for playback in a 5.1 surround sound setup. This is achieved
by a matrix surround decoder.
Dolby Pro Logic II works only with two-channel source formats that are used in a 5.1
configuration. It is available as Dolby Pro Logic II Movie and Dolby Pro Logic II Music.
Dolby Pro Logic II Movie is used for VCRs, TV broadcasts, and all programs encoded in Dolby
Surround. Dolby Pro Logic II Music is used for any stereo music recordings.
Dolby Pro Logic IIx Movie and Music extend the Dolby Pro Logic II matrix decoding
technology to derive up to seven channels from two-channel or multichannel sources, which
provides additional outputs for surround back channel effects.
Both the Movie and Music modes produce up to seven full bandwidth matrixed channels.
Music mode has hard back effects (shared across all surround speakers) instead of just the
back speakers, which the Movie mode has.
Dolby Pro Logic II/IIx Music mode provides an additional set of commands to tailor the sound
to individual listening tastes.
Dimension control
This alters the ratio of L+R to L-R for two-channel input signals. This has the effect of
adjusting the sound field towards the front or towards the back, making the sound more or
less spacious.
Center Width control
Pro Logic decoding produces a single center signal that comes from the center speaker. If
there is no center speaker, a “phantom” center image is produced that is split between the
right and left speakers. Center Width control allows variable adjustment of the center image
so it is heard only from the center speaker, only from the right and left speakers, or from all
three speakers in varying degrees.
Panorama control
This extends the Center Width control, so that all or part of the center image can be heard
from the surround speakers for a “wraparound” effect.
Dolby Digital Pro Logic IIx Movie or Music
Both Dolby Digital Pro Logic IIx Movie mode and Dolby Digital Pro Logic IIx Music mode
build on the Dolby Pro Logic IIx matrix mixing technology to create two additional surround
back channels (right and left back) from the original Dolby Digital 5.1 channel information.
The Dolby Digital Pro Logic IIx Movie mode (applied to multichannel sources) uses the same
Dimension, Center Width, and Panorama controls that are available for Dolby Pro Logic IIx
Music mode (applied to stereo sources). For more information, see the section above.
NOTES: • This listening mode is only available when the SSP 7.1 is set up for 6.0 to 7.1
channel outputs and a multichannel Dolby Digital source format is present.
• Dolby Pro Logic IIx Movie and Dolby Digital EX are electronically equivalent
when the system is set up for 6.1.
SSP 7.1 • Reference Material 68
Page 75

DTS + Dolby Pro Logic IIx Movie or Music
This mode uses Dolby Pro Logic IIx matrix mixing effects to create up to two additional
surround back channel effects from the original 5.1 information of a DTS Digital Surround
source format. Both the Movie and Music modes produce up to seven full bandwidth
matrixed channels for right and left back surround.
NOTE: This listening mode is available only when the SSP 7.1 is set up for 6.0 to 7.1
channel outputs and a DTS Digital Surround source format is present.
DTS 96/24 + Dolby Pro Logic IIx Movie or Music
This mode is similar to DTS + Dolby Pro Logic IIx Movie or Music (see above), but is intended
for use with DTS 96/24 source formats.
DTS + Dolby EX
This mode uses Dolby Digital EX matrix mixing surround effects to create an additional
surround center back channel from the discrete 5.1 information of a DTS Digital Surround
source format to create up to 6.1 channel effects.
NOTE: This listening mode is available only when the SSP 7.1 is set up for 6.1 to 7.1
channel outputs and a DTS Digital Surround source format is present.
DTS 96/24 + Dolby EX
This mode is similar to DTS + Dolby EX (see above), but is intended for use with DTS 96/24
source formats.
DTS Neo:6 Cinema or Music
This mode produces up to seven separate full bandwidth matrix channels from a 2-channel
(stereo) audio input.
DTS Neo:6 Cinema assigns the in-phase component of the signal to the center channels and
the reversed-phase component to the left and right surround and center back or left and
right back channels.
With DTS Neo:6, the left and right front channels bypass the decoder and are played
directly with no loss of sound quality. The signal outputs from the center, right surround, left
surround (for 5.1), the center back (for 6.1), or left and right back (for 7.1) channels. In the
DTS Neo:6 Music or Cinema mode, there is one adjustable control:
Center Image control
The Center Image control varies the amount of attenuation applied to the left and right
channel information of the input source that is used for creating the output center channel
effects. When it is set to 0, the mixed input signal information, intended for use in creating
the center output channel of the DTS Neo:6 listening modes, is filtered back to the front
left and right output channels. This creates the effect of spreading the centralized audio
signal across all three front output channels. When this control is set to 10, the matrixed
information intended for the front left and front right output channel effects is fully
attenuated, allowing the center channel to create a more centralized effect from the front
channels.
SSP 7.1 • Reference Material 69
Page 76

Listening Modes Usage
Listening mode Number
Types of channels Media used
of signal
channels
Mono 1 z 1 discrete or 1 downmix
matrixed, full-bandwidth
channel (C)
Stereo 2 z 2 discrete or 2 downmix
matrixed, full-bandwidth
channel (L/R)
Mono to all Up to 7.1 z 1 discrete or 1 downmix
matrixed, full-bandwidth
channel (C)
z 2 to 6 matrixed,
z Analog signal
z CDs or DVDs downmixed to
1 channel
z Stereo music
z All DVDs downmixed to 2
channels
z Analog signal
z CDs or DVDs downmixed to
1 channel
full-bandwidth channels
(L/R, LS/RS, and CB or LB/
RB)
Stereo to all Up to 6.1 z 2 discrete or 2 downmix
matrixed, full-bandwidth
channels (L/R)
z 2 or 4 matrixed,
z Stereo music
z All DVDs downmixed to 2
channels
full-bandwidth channels
(LS/RS and/or LB/RB)
Dolby Pro Logic 4 z 2 discrete, full-bandwidth
channels (L/R)
z 1 matrixed, full-bandwidth
z Stereo and Dolby Surround
encoded VHS movies and
broadcast TV programs
channel (C)
z 1 matrixed,
Dolby Pro Logic II
5.1 z 2 discrete, full-bandwidth
Music or Movie
limited-bandwidth
channel (S)
channels (L/R)
z 3 matrixed, full-bandwidth
channels (C, LS/RS)
z 1 subwoofer channel via
z Stereo and Dolby Surround
encoded VHS movies and
broadcast TV programs
z Stereo music
z Video games
Dolby Pro Logic II bass
management
Dolby Digital 5.1 5.1 z 5 discrete, full-bandwidth
channels (L/R, C, LS/RS)
z 1 discrete LFE channel (LFE)
z All DVDs
z Some broadcast HDTV
z Some Direct Broadcast
Satellite (DBS)
DTS or DTS 96/24 5.1 z 5 discrete, full-bandwidth
channels (L/R, C, LS/RS)
z 1 discrete LFE channel (LFE)
z Some DVDs that are
encoded with DTS
z Some CDs that are encoded
with DTS
SSP 7.1 • Reference Material 70
Page 77

Listening mode Number
Types of channels Media used
of signal
channels
DTS Neo:6
Music or Cinema
Up to 7.1 z 2 discrete, full-bandwidth
channels (L/R)
z 3 to 5 matrixed,
full-bandwidth channels (C,
LS/RS, and CB, if 6.1, or
z Stereo VHS movies and
broadcast TV programs
z Stereo music
z Video games
LB/RB, if 7.1)
z 1 subwoofer channel
via DTS Neo:6 bass
management
Dolby Pro Logic IIx
Music
6.0 to 7.1 z 2 discrete, full-bandwidth
channels (L/R)
z 4 to 5 matrixed, full
bandwidth channels (C,
LS/RS, and CB or LB/RB)
z 1 subwoofer channel via
z Stereo and Dolby 2/0 Pro-
Logic encoded VHS movies
and broadcast TV programs
z Stereo music
z Video games
Dolby Pro Logic IIx bass
management
Dolby Pro Logic IIx
Movie
6.0 to 7.1 z 2 discrete, full-bandwidth
channels (L/R)
z 4 to 5 matrixed,
full-bandwidth channels (C,
LS/RS, and CB or LB/RB)
z 1 subwoofer channel via
z Stereo and Dolby Surround
encoded VHS movies and
broadcast TV programs
z Stereo music
z Video games
Dolby Pro Logic IIx bass
management
Dolby Digital EX
(for use with
Dolby Digital 5.1
or Dolby Digital
Surround EX)
DTS-ES Matrix or
DTS 96/24 ES Matrix
(For use with DTS
Digital Surround,
DTS 96/24, DTS ES
Matrix 6.1, or DTS
6.0 to 6.1 z 5 discrete, full-bandwidth
channels (L/R, C, LS/RS)
z 1 matrixed, full-bandwidth
channel (CB)
z 1 discrete LFE channel (LFE)
6.0 to 6.1 z 5 discrete, full-bandwidth
channels (L/R, C, LS/RS)
z 1 matrixed, full-bandwidth
channel (CB)
z 1 discrete LFE channel (LFE)
z Some DVDs that are
encoded with Dolby Digital
EX
z Dolby Digital 5.1 DVDs can
also be used with a Dolby
Digital EX decoder
z Some DVDs that are
encoded with DTS Digital
Surround, DTS 96/24,
DTS-ES Matrix 6.1, or DTS
96/24 ES Matrix 6.1
96/24 ES
Matrix 6.1 Source
Formats)
DTS-ES Discrete 6.0 to 6.1 z 6 discrete, full-bandwidth
channels (L/R, C, LS/RS, and
CB)
z 1 discrete LFE channel (LFE)
z Some DVDs that
are encoded with
DTS-ES Discrete 6.1
SSP 7.1 • Reference Material 71
Page 78

Listening mode Number
Types of channels Media used
of signal
channels
Dolby Digital Pro
Logic IIx Music
6.0 to 7.1 z Dependent on
configuration:
5 discrete, full-bandwidth
channels (L/R, C, LS/RS)
z 1 or 2 matrixed,
z All DVDs
z Some broadcast HDTV
z Some DBS
full-bandwidth channel (CB
or LB/RB)
z 1 discrete LFE channel (LFE)
Dolby Digital Pro
Logic IIx Movie
6.0 to 7.1 z Dependent on
configuration:
5 discrete, full-bandwidth
channels (L/R, C, LS/RS)
z 1 or 2 matrixed,
z All DVDs
z Some broadcast HDTV
z Some DBS
full-bandwidth channels
(CB or LB/RB)
z 1 discrete LFE channel (LFE)
DTS + Dolby EX or
DTS 96/24 + Dolby
EX
6.0 to 6.1 z 5 discrete, full-bandwidth
channels (L/R, C, LS/RS)
z 1 matrixed, full-bandwidth
channel (CB)
z 1 discrete LFE channel (LFE)
z Some DVDs that are
encoded with DTS Digital
Surround or DTS 96/24
z Uses Dolby Digital matrix
processing techniques
to produce Center Back
channel information
DTS + Dolby Pro
Logic IIx Music or
DTS 96/24 + Dolby
Pro Logic IIx Music
6.0 to 7.1 z Dependent on
configuration:
5 discrete, full-bandwidth
channels (L/R, C, LS/RS)
z 1 or 2 matrixed,
z Some DVDs that
are encoded with
DTS Digital Surround or
DTS 96/24
full-bandwidth channel (CB
or LB/RB)
z 1 discrete LFE channel (LFE)
DTS + Dolby Pro
Logic IIx Movie or
DTS 96/24 + Dolby
Pro Logic IIx Movie
6.0 to 7.1 z Dependent on
configuration:
5 discrete, full-bandwidth
channels (L/R, C, LS/RS)
z 1 or 2 matrixed,
z Some DVDs that
are encoded with
DTS Digital Surround or
DTS 96/24
full-bandwidth channels
(CB or LB/RB)
z 1 discrete LFE channel (LFE)
SSP 7.1 • Reference Material 72
Page 79

Listening Mode and Output Channels
Listening Mode Output Channels
L/R C LS/RS CB or
LB/RB
Mono -
(not
•
(used)
- - Yes, if LFE exists in the
used)
Stereo • - - - Yes, if LFE exists in the
Mono to All • • • CB or
LB/RB
Stereo to All • - • LB/RB Yes, if LFE exists in the
Dolby Pro Logic • • S - Yes, if L/R are set to Small
Dolby Pro Logic II Music or Movie • • • - Yes, if L/R are set to Small
Dolby Digital 5.1 • • • - Yes, if LFE exists in the
DTS or DTS 96/24 • • • - Yes, if LFE exists in the
DTS Neo:6 Music or Cinema • • • CB or
LB/RB
Dolby Pro Logic IIx Music or Movie • • • CB or
LB/RB
Dolby Digital EX • • • CB Yes, if LFE exists in the
DTS-ES Matrix or DTS 96/24 ES
• • • CB Yes, if LFE exists in the
Matrix
DTS-ES Discrete • • • CB Yes, if LFE exists in the
Dolby Digital Pro Logic IIx Music • • • CB or
LB/RB
Dolby Digital Pro Logic IIx Movie • • • CB or
LB/RB
DTS + Dolby EX or
• • • CB Yes, if LFE exists in the
DTS 96/24 + Dolby EX
Sub-woofer
source format or L/R are
set to Small
1
source format or L/R are
set to Small
Yes, if LFE exists in the
source format or L/R are
set to Small
source format or L/R are
set to Small
source format or L/R or
LS/RS are set to Small
source format or L/R or
LS/RS are set to Small
Yes, if L/R are set to Small
Yes, if L/R are set to Small
source format or L/R or
LS/RS are set to Small
source format or L/R or
LS/RS are set to Small
source format or L/R or
LS/RS are set to Small
Yes, if LFE exists in the
source format or L/R or
LS/RS are set to Small
Yes, if LFE exists in the
source format or L/R or
LS/RS are set to Small
source format or L/R or
LS/RS are set to Small
SSP 7.1 • Reference Material 73
Page 80

Listening Mode Output Channels
L/R C LS/RS CB or
Sub-woofer
LB/RB
DTS + Dolby Pro Logic IIx Music or
DTS 96/24 + Dolby Pro Logic IIx
Music
DTS + Dolby Pro Logic IIx Movie
or DTS 96/24 + Dolby Pro Logic IIx
Movie
• • • CB or
LB/RB
• • • CB or
LB/RB
Yes, if LFE exists in the
source format or L/R or
LS/RS are set to Small
Yes, if LFE exists in the
source format or L/R or
LS/RS are set to Small
NOTES: • shows which channels are used in each listening mode
- shows which channels are unused
S denotes that LS and RS receive the same signal
1
speakers can be set to Large, Small or None (see “Speaker Size Settings” on page 15).
CB denotes that surround back channel either outputs to LB only in 6.0 or 6.1 setups or to
LB and RB equally in 7.0 or 7.1 setups.
SSP 7.1 • Reference Material 74
Page 81

Source Formats and Listening Modes with Different Speaker Setups
NOTES: • Setups that have no surround or back channels, or center channel are classified as 2.0 to
2.1.
• Setups with no surround back channels are classified as 3.0 to 5.1.
• Setups with back channels are classified as 6.0 to 7.1, depending on whether one or
two surround back channels are present.
Source Format 2.0 or 2.1 3.0 to 5.1 6.0 to 7.1
Analog
(input 5 only)
PCM
(inputs 1-4 only)
Dolby Digital 2/0
(inputs 1-4 only)
Dolby Digital 2/0
Surround
(inputs 1-4 only)
Stereo (default)
Mono
Stereo (default)
Mono
Stereo (default)
Mono
Stereo (default)
Mono
Stereo (default)
Stereo to All
Mono
Mono to All
Dolby Pro Logic
Dolby Pro Logic II Movie
Dolby Pro Logic II Music
DTS Neo:6 Cinema
DTS Neo:6 Music
Stereo (default)
Stereo to All
Mono
Mono to All
Dolby Pro Logic
Dolby Pro Logic II Movie
Dolby Pro Logic II Music
DTS Neo:6 Cinema
DTS Neo:6 Music
Stereo (default)
Stereo to All
Mono
Mono to All
Dolby Pro Logic
Dolby Pro Logic II Movie
Dolby Pro Logic II Music
DTS Neo:6 Cinema
DTS Neo:6 Music
Stereo
Stereo to All
Mono
Mono to All
Dolby Pro Logic
Dolby Pro Logic II Movie
(default)
Dolby Pro Logic II Music
DTS Neo:6 Cinema
DTS Neo:6 Music
Stereo (default)
Stereo to All
Mono
Mono to All
Dolby Pro Logic
Dolby Pro Logic IIx Movie
Dolby Pro Logic IIx Music
DTS Neo:6 Cinema
DTS Neo:6 Music
Stereo (default)
Stereo to All
Mono
Mono to All
Dolby Pro Logic
Dolby Pro Logic IIx Movie
Dolby Pro Logic IIx Music
DTS Neo:6 Cinema
DTS Neo:6 Music
Stereo (default)
Stereo to All
Mono
Mono to All
Dolby Pro Logic
Dolby Pro Logic IIx Movie
Dolby Pro Logic IIx Music
DTS Neo:6 Cinema
DTS Neo:6 Music
Stereo
Stereo to All
Mono
Mono to All
Dolby Pro Logic
Dolby Pro Logic IIx Movie
(default)
Dolby Pro Logic IIx Music
DTS Neo:6 Cinema
DTS Neo:6 Music
SSP 7.1 • Reference Material 75
Page 82

Source Format 2.0 or 2.1 3.0 to 5.1 6.0 to 7.1
Dolby Digital 5.1
(inputs 1-4 only)
Stereo (default)
Mono
Stereo
Stereo to All
Mono
Mono to All
Dolby Digital 5.1 (default)
Stereo
Stereo to All
Mono
Mono to All
Dolby Digital 5.1 (default)
Dolby Digital EX
Dolby Digital Pro Logic IIx
Movie
Dolby Digital Pro Logic IIx
Music
Dolby Digital
Surround EX
(inputs 1-4 only)
Stereo (default)
Mono
Stereo
Stereo to All
Mono
Mono to All
Dolby Digital 5.1 (default)
Stereo
Stereo to All
Mono
Mono to All
Dolby Digital 5.1
Dolby Digital EX (default in
6.1)
Dolby Digital Pro Logic IIx
Movie (default in 7.1)
Dolby Digital Pro Logic IIx
Music
DTS 2-Channel
(inputs 1-4 only)
DTS 96/24
(inputs 1-4 only)
Stereo (default)
Mono
Stereo (default)
Mono
Stereo (default)
Stereo to All
Mono
Mono to All
Dolby Pro Logic
Dolby Pro Logic II Movie
Dolby Pro Logic II Music
DTS Neo:6 Cinema
DTS Neo:6 Music
Stereo
Stereo to All
Mono
Mono to All
DTS 96/24 (default)
Stereo (default)
Stereo to All
Mono
Mono to All
Dolby Pro Logic
Dolby Pro Logic IIx Movie
Dolby Pro Logic IIx Music
DTS Neo:6 Cinema
DTS Neo:6 Music
Stereo
Stereo to All
Mono
Mono to All
DTS 96/24 (default)
DTS 96/24 ES Matrix
DTS 96/24 + Dolby EX
DTS 96/24 + Dolby Pro
Logic IIx Movie
DTS 96/24 + Dolby Pro
Logic IIx Music
DTS Digital
Surround
(inputs 1-4 only)
Stereo (default)
Mono
Stereo
Stereo to All
Mono
Mono to All
DTS (default)
Stereo
Stereo to All
Mono
Mono to All
DTS (default)
DTS-ES Matrix
DTS + Dolby EX
DTS + Dolby Pro Logic IIx
Movie
DTS + Dolby Pro Logic IIx
Music
SSP 7.1 • Reference Material 76
Page 83

Source Format 2.0 or 2.1 3.0 to 5.1 6.0 to 7.1
DTS 96/24 ES
Matrix 6.1
(inputs 1-4 only)
Stereo (default)
Mono
Stereo
Stereo to All
Mono
Mono to All
DTS 96/24 (default)
Stereo
Stereo to All
Mono
Mono to All
DTS 96/24
DTS 96/24 ES Matrix
(default)
DTS-ES Matrix 6.1
(inputs 1-4 only)
Stereo (default)
Mono
Stereo
Stereo to All
Mono
Mono to All
DTS (default)
Stereo
Stereo to All
Mono
Mono to All
DTS
DTS-ES Matrix (default)
DTS-ES Discrete
6.1
(inputs 1-4 only)
Stereo (default)
Mono
Stereo
Stereo to All
Mono
Mono to All
DTS (default)
Stereo
Stereo to All
Mono
Mono to All
DTS-ES Discrete (default)
SSP 7.1 • Reference Material 77
Page 84

SIS Commands
This section provides information about the Extron Simple Instruction Set (SIS™) commands
that are used to congure the SSP 7.1 in the following sections:
z Introduction to SIS
z Symbols Used in this Manual
z Error Messages
z Expected Unsolicited Responses
z Command and Response Table for SIS Commands
z Setting Speaker Delay Settings using SIS Commands
z Setting up Test Sources with SIS Commands
Introduction to SIS
The SSP 7.1 accepts SIS commands from a host device such as a computer running the
HyperTerminal utility or other control system. The host device can be connected to the
3-pin captive screw connector on the rear panel or to the config port on the front panel.
To connect to the cong port, use the optional Extron 9-pin D female to 2.5 mm TRS
Configuration cable (part number 70-335-01).
The protocol is 38400 baud, 8 data bit, 1 stop bit, and no parity.
NOTES: • The wiring in the RS-232 cables crosses over so that the surround sound
processor Tx connects with the control device Rx and vice versa.
• Both the rear panel RS-232 port and the front panel configuration port can
be used at the same time. Neither has precedence. The SSP 7.1 responds to
commands in the order received.
SIS commands consist of a string (one or more characters per command eld). Unless
otherwise stated, upper and lower case characters may be used interchangeably. Commands
do not require any special characters to begin or end the command string. Each response
from the SSP 7.1 ends with a carriage return and a line feed (CR/LF =
end of the response character string.
When the SSP 7.1 is rst switched on, depending on the model, it sends the message:
(c) Copyright 2010, Extron Electronics, SSP 7.1, 60-842-01, V x.xx]
where 60-842-01 is the catalog part number and V x.xx is the firmware version number.
]), which signals the
SSP 7.1 • SIS Commands 78
Page 85

Symbols Used in this Manual
When programming in the eld, certain characters are most conveniently represented by
their hexadecimal rather than their ASCII values. The table below shows the hexadecimal
equivalent of each ASCII character:
ASCII to HEX Conversion Table
Space
Table 3. ASCII to HEX Conversion Table
] — carriage return with line feed
} — carriage return (no line feed)
• — space character
E — Escape key
The X/ values defined in this section are the variables used in the fields of the command
response table.
.
X! — Audio Inputs (1-5)
1 and 2 = Digital audio, optical input
3 and 4 = Digital audio, coaxial input
5 = Analog input
X@ — Audio Outputs (1-8)
1 = Left Front
2 = Center
3 = Right Front
4 = Left Surround
5 = Right Surround
6 = Left Back
7 = Right Back
8 = Subwoofer
X# — Status
0 = Off
1 = On
X$ — Volume Output Mode
0 = Fixed (volume no attenuation)
1 = Variable (default)
X% — Bass and treble adjustment range in dB -10 to +10 dB in 1 dB increments (default
0 dB)
SSP 7.1 • SIS Commands 79
Page 86

X^ — Volume Adjustment (0 - 100, default = 50 dB; corresponding to attenuation of -100
to 0 dB in 1 dB steps).
Max volume (no attenuation) = 0 dB; Min volume (full attenuation) = -100 dB
NOTE: The unit response to a command adjusting the volume always has three digits
and, if necessary, includes leading zeros. The command does not have to include
any leading zeros.
Example
Command: 50V (set the volume to 50 dB; no leading 0)
Response: Vol050] (volume set to 50 dB; with leading 0)
X& — Furthest speaker distance (in units of 0.01 seconds; default = 0)
NOTE: Furthest speaker distance is included for reference only; it is used only with the
SSP 7.1 Setup and Control Software (see Speaker Delay Tab on page 32).
X( — Input gain and attenuation readout (0 to +24 dB in 1 dB steps; default 0 dB)
X1) — Mono source
1 = Left
2 = Right
3 = Left + Right (default)
X1@ — Listening Mode (Matrix Decode Mode indicator on the front panel)
1 = Stereo
2 = Mono
3 = Stereo to All
4 = Mono to All
5 = Dolby Pro Logic
6 = Dolby Pro Logic II/IIx Movie
7 = Dolby Pro Logic II/IIx Music
8 = Dolby Digital 5.1
9 = Dolby Digital EX
10 = Dolby Digital Pro Logic IIx Movie
11 = Dolby Digital Pro Logic IIx Music
12 = DTS or DTS 96/24
13 = DTS ES Matrix or DTS 96/24 ES Matrix
14 = DTS ES Discrete
15 = DTS + Dolby EX or DTS 96/24 + Dolby EX
16 = DTS + Dolby Pro Logic IIx Movie or DTS 96/24 + Dolby Pro Logic IIx Movie
17 = DTS + Dolby Pro Logic IIx Music or DTS 96/24 + Dolby Pro Logic IIx Music
18 = DTS Neo:6 Cinema
19 = DTS Neo:6 Music
X1# — Status
0 = Not present or malfunction
1 = present or OK
X1$ — Internal temperature in °C
X1% — Speaker delay (default = 0 on all channels)
SSP 7.1 • SIS Commands 80
Page 87

X1^ — Speaker group size
0 = None (invalid for front speakers)
1 = Small
2 = Large
(defaults: Front = 2; Center = 1; Surround = 1)
X1& — Crossover Frequency 1 to 20 (default = step 11/100 Hz)
1 to 9 = 40 to 80 Hz in 5 Hz increments
9 to 16 = 80 to 150 Hz in 10 Hz increments
16 to 20 = 150 to 250 Hz in 25 Hz increments
X1( — Dolby Pro Logic IIx Music Center Width Control
(Range 0-7; default = 3)
X2) — DTS Neo:6 Music/Cinema Center Image (Range 0-10; default = 3 for DTS Neo:6
Music and 10 for DTS Neo:6 Cinema)
X2! — Version (x.xx)
X2@ — version and build number (x.xx.xxxx)
X2$ — Source Format (Source LED on front panel)
0 = Not Present
1 = Analog (2-CH)
2 = PCM (PCM and 2-CH)
3 = Dolby Digital 5.1 ( D)
4 = Dolby Digital 2/0 (when 2/0 encoding flag is detected) ( D and 2-CH)
5 = Dolby Digital 2/0 Surround (when 2/0 matrix encoding is detected) ( D
and 2-CH)
6 = Dolby Digital Surround EX (when EX encoding ag is detected) ( D)
7 = DTS Digital Surround or DTS 96/24 (DTS)
8 = DTS-ES Matrix 6.1 or DTS 96/24 ES Matrix 6.1 (When ES Matrix encoding
flag is detected) (DTS)
9 = DTS-ES Discrete 6.1 (When ES Discrete encoding ag is detected) (DTS)
10 = DTS 2-Channel (DTS and 2-CH)
X2% — Source Format Sampling Frequency
0 = None
1 = 32 kHz
2 = 44.1 kHz
3 = 48 kHz
4 = 88.2 kHz
5 = 96 kHz
X2^ — Source Format Encoded Channels
0 = None 9 = 3/0
1 = 1/0 10 = 3/0.1
2 = 1/0 .1 11 = 3/1
3 = 2/0 12 = 3/1.1
4 = 2/0.1 13 = 3/2
5 = 2/1 14 = 3/2.1
6 = 2/1.1 15 = 3/3
7 = 2/2 16 = 3/3.1
8 = 2/2.1
SSP 7.1 • SIS Commands 81
Page 88

X2& — Dolby Pro Logic II/IIx Music Dimension Control
0 = Neutral (default)
1 = Front
2 = Back
X2* — Lip Sync Offset 000 to 1000 in 0.1 ms increments (0 - 100 ms)
X3! — Speaker Groups
1 = Left and Right Front
2 = Center
3 = Left and Right Surround
X3@ — Surround Back Speaker Size
0 = None (default)
1 = 1 small speaker
2 = 2 small speakers
3 = 1 large speaker
4 = 2 large speakers
X3# — Output Channel Trim adjustment range in dB (-24 to +12 dB in 1 dB steps;
default 0 dB)
X3$ — Noise Test Source
0 = None (default)
1 = Dolby
2 = Pink noise
X3% — Dolby Pro Logic II/IIx Music Panorama
0 = Off (default)
1 = On
X3^ — Mono Output
1 = Center only (default)
2 = Front Left and Right only
X3& — Dynamic Range Compression
0 = Off (default)
1 = MIN
2 = MAX
X3* — Mode Override Group
0 = No Mode Override (no LEDs on)
1 = Multichannel Downmix (DOWNMIX)
2 = Dolby Pro Logic II/IIx ( PL II/IIx)
3 = DTS Neo:6 (DTS NEO:6)
4 = To All (TO ALL)
X3( — Mute Status
Eight digit representation with each position in the sequence representing a speaker. The
speakers are listed in the same order as in X@.
0 = unmuted
1 = muted
For example, Mut 00100001 means the right front speaker and subwoofer are muted and
all other speakers are unmuted.
SSP 7.1 • SIS Commands 82
Page 89

X4) — Active Channel Status
Eight digit representation with each position in the sequence representing a speaker. The
speakers are listed in the same order as in X@.
0 = no audio signal present on channel
1 = channel receiving audio signal
2 = channel receiving audio signal, but muted
For example, ActCh 11122001 means the first (left front), second (center), third (right
front), and eighth (subwoofer) channels are receiving an audio signal; the fourth (left
surround) and fth (right surround) are receiving a signal but it is muted; the sixth (left back)
and seventh (right back) are not receiving a signal.
X4! — Mode Override Group Listening Mode Options
1 = Stereo (DOWNMIX)
2 = Mono (DOWNMIX)
3 = Dolby Pro Logic II/IIx Movie ( PL II/IIx)
4 = Dolby Pro Logic II/IIx Music ( PL II/IIx)
5 = DTS Neo:6 Cinema (DTS NEO:6)
6 = DTS Neo:6 Music (DTS NEO:6)
7 = Stereo to All (TO ALL)
8 = Mono to All (TO ALL)
X4@ — Baud rate (bps)
0 = 9600
1 = 19200
2 = 38400 (default)
3 = 115200
X4# — DTS Neo:6 Center Image Control Mode
1 = Music
2 = Cinema
X4$ — Parametric EQ lter selection (1 to 9). Determines whether the corresponding
frequency range is bypassed or not. 1 is the lowest frequency range, 9 is the highest
frequency
X4% — Parametric EQ lter frequency. Default values:
62 Hz (lter 1)
125 Hz (lter 2)
250 Hz (lter 3)
500 Hz (lter 4)
1000 Hz (lter 5)
2000 Hz (lter 6)
4000 Hz (lter 7)
8000 Hz (lter 8)
16000 Hz (lter 9)
X4^ — Parametric EQ lter Trim adjustment range in dB (-24 to +24 dB in 1 dB steps;
default 0 dB).
X4& — Parametric EQ Q value, multiplied by 1000 (from 707 to 15000; default 2000).
SSP 7.1 • SIS Commands 83
Page 90

Error Messages
E01 — Invalid input channel number (too large)
E10 — Invalid command
E13 — Invalid value (too large)
E14 — Not valid for this configuration
NOTE: No Override (X3* = 0) in the EU command cannot be viewed or configured:
attempting to do so produces an E14 error message
Expected Unsolicited Responses
Some events trigger a response from the SSP 7.1 without an SIS command being entered:
Event Response
Audio Input
Audio Input Source Change
Volume Level
Input Listening Mode
Mode Override Selection
Analog Level Input Adjustment
Front Panel Lockout
Clip
DTS 96/24 if DTS Source Format
X!]
Aud
SrcFormat
X^]
Vol
X!*X2$*X1@]
SspL
X!*X2$*X3*]
SspQ
X(]
SspA
X#]
Exe
X#]
Sts3*
DTS9624•
X2$•SamplingX2%•EnChanX2^]
X#]
SSP 7.1 • SIS Commands 84
Page 91

Command and Response Table for SIS Commands
Command ASCII Command
(host to unit)
Serial Data Port Parameter Settings
Configure serial port
parameter
View serial port
parameter
Input Selection
Select audio input
View audio input
Select audio input
View audio input
Audio Mute
Mute all output channels
Unmute all output
channels
View mute all status
Mute specific channel
E X4@ CP} Ccp X4@] X4@ — Baud Rate (bps)
E CP} Ccp X4@]
X! $ Aud X!] X! — Audio Inputs (1-5)
$
X! ! All X!]
!
1Z
0Z
Z
X@ *1Z Amt X@ * X#]
Response
(unit to host)
X!]
Aud
X!]
All
X#]
Amt
X#]
Amt
X#]
Amt
Additional Description
0 = 9600
1 = 19200
2 = 38400 (default)
3 = 115200
1 and 2 = Digital audio, optical input
3 and 4 = Digital audio, coaxial input
5 = Analog input
Sets mute to On for all channels.
X# — Status
0 = Off (default)
1 = On
Sets mute to Off for all channels.
Reports mute status for all channels.
Set Mute to On for the selected output:
X@ — Audio Outputs (1-8)
1 = Left front
Unmute specific channel
View mute specific
channel status
NOTE: Audio Mute All and Unmute All are global settings. They take precedence over specifically muted channels.
If specific channels had been muted prior to enabling Mute All, they lose their previous channel mute
status — they are unmuted, along with all other channels, if the Unmute All command is issued.
X@ *0Z Amt X@ * X#]
X@ *Z Amt X@ * X#]
2 = Center
3 = Right front
4 = Left surround
5 = Right surround
6 = Left back
7 = Right back
8 = Subwoofer
Set Mute to Off for the selected output.
Shows the Mute Status of the selected
output.
SSP 7.1 • SIS Commands 85
Page 92

Command ASCII Command
(host to unit)
Speaker Configuration Information Request
View channel outputs
32I
activity
View mute channel
35I
Set Speaker Size Settings
Set speaker size
View specific speaker size
ESX3!*X1^SSP} SspS X3! * X1^]
ESX3!SSP} SspS X3! * X1^]
Surround Back Speaker Settings
Set surround back
E H0SSP} SspH X3@] X3@ — Surround Back Speaker Size
speakers to none
Set surround back
E H1SSP} SspH X3@]
speaker to one small
speaker
Set surround back
E H2SSP} SspH X3@]
speakers to two small
speakers
Set surround back
E H3SSP} SspH X3@]
speaker to one large
speaker
Set surround back
E H4SSP} SspH X3@]
speakers to two large
speakers
View surround back
E HSSP} SspH X3@]
speakers
Response
(unit to host)
ActCh
Mut
X4)]
X3(]
Additional Description
Shows activity of each channel.
Shows mute status of each channel.
Sets number of speakers in each group.
X3! — Speaker groups
1 = Left and Right Front
2 = Center
3 = Left and Right Surround Sound
X1^ — Speaker group size
0 = None (invalid for front speakers)
1 = Small
2 = Large
0 = None (default)
1 = 1 small speaker
2 = 2 small speakers
3 = 1 large speaker
4 = 2 large speakers
NOTE: X4) is an eight digit representation with each position in the sequence representing a speaker, listed in the same order as in X@.
0 = no audio signal present on channel
1 = channel receiving audio signal
2 = channel receiving audio signal, but muted
For example, ActCh 11122001 means the first (left front), second (center), third (right front), and eighth (subwoofer) channels are
receiving an audio signal; the fourth (left surround) and fifth (right surround) are receiving a signal but it is muted; the sixth (left back)
and seventh (right back) are not receiving a signal.
X3( is an eight digit representation with each position in the sequence representing a speaker, listed in the same order as in X@.
0 = unmuted
1 = muted
For example, Mut 00100001 means the right front speaker and subwoofer are muted and all other speakers are unmuted.
SSP 7.1 • SIS Commands 86
Page 93

Command ASCII Command
(host to unit)
Subwoofer Output
Set subwoofer off
Set subwoofer on
View subwoofer control
Output Channel Trim Settings
Set a specific output
channel trim
View a specific output
channel trim
Speaker Delay Settings
Set delay to a specific
speaker
E J0SSP} SspJ X#]
E J1SSP} SspJ X#]
E JSSP} SspJ X#]
EVX@*X3#SSP} SspVX@*X3#]
EVX@SSP} SspVX@*X3#]
EDX@*X1%SSP} SspD X@ * X1%]
Response
(unit to host)
Additional Description
Sets subwoofer to Off.
X# — Status
0 = Off
1 = On (default)
Sets subwoofer to On.
Shows subwoofer status.
Set gain for the selected output:
X@ — Audio Outputs (1-8)
1 = Left front
2 = Center
3 = Right front
4 = Left surround
5 = Right surround
6 = Left back
7 = Right back
8 = Subwoofer
X3# — Output gain and attenuation
readout in dB (-24 to +12; default = 0)
View the current gain setting for the
selected output.
Set speaker delay for the selected
output:
View delay to a specific
speaker
Farthest Speaker Distance
Set distance to the
farthest speaker
View distance to the
farthest speaker
Lip Sync Offset
Set lip sync offset per
input
View lip sync offset per
input
X1% — Speaker delay (in 0.1 ms units;
default = 0 on all channels):
EDX@SSP} SspD X@ * X1%]
E K X& SSP} SspK X&]
E KSSP} SspK X&]
View the current speaker delay for a
selected output
NOTE: This command is included
for reference: it is for use
with the SSP 7.1 Setup and
Control Software only.
EYX!*X2*SSP} SspY X! * X2*] Sets the lip sync offset (X2*) for the
specified input (X!)
EYX!SSP} SspY X! * X2*]
X2* — Lip Sync Offset 000 - 1000 in
0.1 ms increments (0 - 100 ms)
X! — Audio Inputs (1-5)
1 and 2 = Digital audio, optical input
3 and 4 = Digital audio, coaxial input
5 = Analog input
SSP 7.1 • SIS Commands 87
Page 94

Command ASCII Command
(host to unit)
Crossover Frequency Setting
Specify crossover
frequency
View crossover frequency
Volume Adjustment
Specify volume
The response to this command always has a three-digit number and, if necessary, includes leading 0s.
Example:
Increment volume
Decrement volume
View volume setting
Bass Adjustment
Specify bass level
E F X1& SSP} SspF X1&] X1& — Crossover frequency 1 - 20
E FSSP} SspF X1&]
X^ V Vol X^] X^ — Volume adjustment 0 (-100 dB) to
50V
+V
-V
V
E B X% SSP} SspB X%]
Response
(unit to host)
Vol050
Vol
Vol
Vol
]
X^]
X^]
X^]
Additional Description
(default = 11; equivalent to 100 Hz)
1-9 = 40-80 Hz in 5 Hz increments
9-16 = 80-150 Hz in 10 Hz increments
16-20 = 150-250 Hz in 25 Hz
increments
View low frequency filter status
100 (0 dB) in 1 dB steps:
Default = 50.
Max volume (no attenuation) = 100;
Min volume (full attenuation) = 0
Leading 0 for the response but not for
the command.
Increments volume in 1 dB steps.
Decrements volume in 1 dB steps.
View the current volume setting.
Sets the bass level.
View bass level setting
Treble Adjustment
Specify treble level
View treble level setting
Volume Output Mode
Set audio output mode to
variable
Set audio output mode
to fixed
View current audio
output mode status
Front Panel Lockout (Executive Mode)
Lock front panel
Unlock front panel
View current lockout
status
E BSSP} SspB X%]
E T X% SSP} SspT X%]
E TSSP} SspT X%]
E O1SSP} SspO X$]
E O0SSP} SspO X$]
E OSSP} SspO X$]
1X
0X
X
Exe
Exe
Exe
X#]
X#]
X#]
X% = -10 to +10 dB in 1 dB increments
(default = 0)
View the current bass level setting.
Sets the treble level.
X% = -10 to +10 dB in 1 dB increments
(default = 0)
View the current treble level setting.
Sets audio output mode to variable.
X$ — Audio output mode
0 = Fixed
1 = Variable (default)
View the current audio output mode
setting.
Locks front panel.
X# — Status: 0 = Off (default); 1 = On
Unlocks front panel
Displays current front panel lockout
status.
SSP 7.1 • SIS Commands 88
Page 95

Command ASCII Command
(host to unit)
Dolby Pro Logic II/IIx Music Dimension Control
Set dimension neutral
Set dimension front
Set dimension back
View dimension control
status
Dolby Pro Logic II/IIx Music Panorama Mode
Set panorama off
Set panorama on
View current panorama
status
Dolby Pro Logic II/IIx Music Center Width
Set center width
E Z0SSP} SspZ X2& ]
E Z1SSP} SspZ X2& ]
E Z2SSP} SspZ X2& ]
E ZSSP} SspZ X2& ]
E P0SSP} SspP X#]
E P1SSP} SspP X#]
E PSSP} SspP X#]
E C X1( SSP} SspC X1(]
Response
(unit to host)
Additional Description
Sets dimension control to neutral.
X2& — Dolby Pro Logic II/IIx Music
Dimension Control:
0 = Neutral (default)
1 = Front
2 = Back
Sets dimension control to front.
Sets dimension control to back.
Shows the current dimension control
status.
Sets panorama status off.
X# — Status
0 = Off (default)
1 = On
Sets panorama status on.
Shows the current panorama status.
Sets the center width.
View center width
DTS Neo:6 Center Image
Set center image for
music mode
Set center image for
cinema mode
View center image status
Dynamic Range Compression
Set dynamic range
compression to none
Set dynamic range
compression to min
Set dynamic range
compression to max
View dynamic range
compression status
E CSSP} SspC X1(]
E I1* X2) SSP} Ssp IX4# * X2)]
E I2* X2) SSP} Ssp IX4# * X2)]
E I X4# SSP} Ssp IX4# * X2)]
E R0SSP} SspR X3&]
E R1SSP} SspR X3&]
E R2SSP} SspR X3&]
E RSSP} SspR X3&]
X1( — Dolby Pro Logic IIx Music Center
Width Control; (Range 0-7; default = 3)
Displays the current center width status.
Sets the center image for music mode.
X2) — DTS Neo:6 Center Image Control
(Range 0-10;
default = 3 for Music Mode or 10 for
Cinema Mode)
X4# — DTS Neo:6 Center Image Control
Mode (1 = Music; 2 = Cinema)
Sets the center image for cinema mode.
Displays the current center image status.
Sets the dynamic range compression.
X3&— Dynamic Range Compression
0 = Off (default)
1 = Min
2 = Max
Displays the current dynamic range
compression status.
SSP 7.1 • SIS Commands 89
Page 96

Command ASCII Command
(host to unit)
Mono Output Mode
Set mono output to
E M1SSP} SspM X3^]
center channel only
Set mono output to l/r
E M2SSP} SspM X3^]
channels only
View current mono
E MSSP} SspM X3^]
source setting
Listening Mode
Set specific user listening
mode
View current listening
EL X!*X2$*X1@
SSP}
E LSSP} SspLX!*X2$*X1@]
mode status
View user listening mode
EXX!*X2$ SSP} SspXX!*X2$*X1@]
per input/source format
Mode Override Selection
Set mode override
EQX!*X2$*X3*
SSP}
View mode override for
EQX!*X2$SSP} SspQX!*X2$*X3*]
each input
Response
(unit to host)
SspLX!*X2$*X1@]
SspQX!*X2$*X3*]
Additional Description
Sets the mono output channel.
X3^ — Mono Output
1 = Center only
2 = Left + Right
Displays the current mono output
channel.
Sets the listening mode.
Displays the current listening mode
status.
Shows the current listening mode
associated with a source format and
input.
Sets the mode override.
Displays the current mode override
status.
NOTE: X! — Input (1-5): 1 and 2 = Digital audio, optical input; 3 and 4 = Digital audio, coaxial input; 5 = Analog input
X1@ — Listening Mode (Matrix Decode Mode indicator on the front panel): 1 = Stereo; 2 = Mono; 3 = Stereo to All; 4 = Mono to All;
5 = Dolby Pro Logic; 6 = Dolby Pro Logic II/IIx Movie; 7 = Dolby Pro Logic II/IIx Music; 8 = Dolby Digital 5.1; 9 = Dolby Digital EX;
10 = Dolby Digital Pro Logic IIx Movie; 11 = Dolby Digital Pro Logic IIx Music; 12 = DTS or DTS 96/24;
13 = DTS ES Matrix or DTS 96/24 ES Matrix; 14 = DTS ES Discrete; 15 = DTS + Dolby EX or DTS 96/24 + Dolby EX;
16 = DTS + Dolby Pro Logic IIx Movie or DTS 96/24 + Dolby Pro Logic IIx Movie;
17 = DTS + Dolby Pro Logic IIx Music or DTS 96/24 + Dolby Pro Logic IIx Music; 18 = DTS Neo:6 Cinema; 19 = DTS Neo:6 Music
X2$ — Source Format: 0 = Not Present ; 1 = Analog (2-CH); 2 = PCM (PCM and 2-CH); 3 = Dolby Digital 5.1 ( D);
4 = Dolby Digital 2/0 (when 2/0 encoding flag detected) ( D and 2-CH);
5 = Dolby Digital 2/0 Surround (when 2/0 matrix encoding detected) ( D and 2-CH);
6 = Dolby Digital Surround EX (when EX encoding ag detected) ( D);
7 = DTS Digital Surround or DTS 96/24 (DTS);
8 = DTS-ES Matrix 6.1 or DTS 96/24 ES Matrix 6.1 (when ES Matrix encoding ag detected) (DTS);
9 = DTS-ES Discrete 6.1 (when ES Discrete encoding ag detected) (DTS); 10 = DTS 2-Channel (DTS and 2-CH)
X3* — Mode Override Group: 0 = No Mode Override (no LEDs on); 1 = Multichannel Downmix (DOWNMIX);
2 = Dolby Pro Logic II/IIx ( PL II/IIx); 3 = DTS Neo:6 (DTS NEO:6); 4 = To All (TO ALL)
SSP 7.1 • SIS Commands 90
Page 97

Command ASCII Command
(host to unit)
Listening Mode Preference for each Mode Override Group
Set listening mode
preference for each mode
override group
View listening mode
preference for each mode
override group
Mono Source Setting (for Analog input #5 only)
Set mono source to left
channel
Set mono source to right
channel
Set mono source to left +
right channel
View current mono
source
Analog Input Gain Adjustment (for Analog Input #5 only)
Set analog input gain
level
View current analog input
gain level
Enable/Disable Parametric EQ Filter Bypass for each Output Channel
Enable bypass
Disable bypass
View current bypass
status
EUX!*X3**X4!
SSP}
EUX!*X3*SSP} SspUX!*X3**X4!]
E N1SSP} SspN X1)]
E N2SSP} SspN X1)]
E N3SSP} SspN X1)]
E NSSP} SspN X1)]
E A X( SSP} SspA X(]
E ASSP} SspA X(]
EEX@*X4$ *0SSE} SseE X@*X4$*X#] X# — Status
EEX@*X4$ *1SSE} SseE X@*X4$*X#]
EEX@*X4$ *SSE} SseE X@*X4$*X#]
Response
(unit to host)
SspUX!*X3**X4!]
Additional Description
Sets the listening mode preference for
each mode override group.
Displays the current listening mode
preference for each mode override
group.
Sets mono source:
X1) — Mono source
1 = Left
2 = Right
3 = Left + Right (default)
Shows the current mono source setting.
Sets the analog input gain level:
X( — Input gain
0 to +24 dB in 1 dB steps (default = 0)
Displays the current analog input gain
0 = Off (default)
1 = On
X4$ — Parametric EQ filter selection (1
to 9).
1 is the lowest frequency range
9 is the highest frequency
NOTE: X! Input (1-5): 1 and 2 = Digital audio, optical input; 3 and 4 = Digital audio, coaxial input; 5 = Analog input
X3* — Mode Override Group: 0 = No Mode Override (no LEDs on); 1 = Multichannel Downmix (DOWNMIX);
2 = Dolby Pro Logic II/IIx ( PL II/IIx); 3 = DTS Neo:6 (DTS NEO:6); 4 = To All (TO ALL)
X4! — Mode Override Group Listening Mode Options: 1 = Stereo (DOWNMIX); 2 = Mono (DOWNMIX);
3 = Dolby Pro Logic II/IIx Movie ( PL II/IIx); 4 = Dolby Pro Logic II/IIx Music ( PL II/IIx); 5 = DTS Neo:6 Cinema (DTS NEO:6);
6 = DTS Neo:6 Music (DTS NEO:6); 7 = Stereo to All (TO ALL); 8 = Mono to All (TO ALL))
SSP 7.1 • SIS Commands 91
Page 98

Command ASCII Command
(host to unit)
Response
(unit to host)
Parametric EQ Filter Frequency Setting for each Output Channel
Set frequency for each
filter and output channel
View frequency for each
EFX@*X4$*X4%
SseF X@*X4$*X4%]
SSE}
EFX@*X4$SSE} SseF X@*X4$*X4%]
filter and output channel
Parametric EQ Filter Gain Setting for each Output Channel
Set gain for each filter
and output channel
View gain for each filter
EGX@*X4$*X4^
SseGX@*X4$*X4^]
SSE}
EGX@*X4$SSE} SseGX@*X4$*X4^]
and output channel
Parametric EQ Filter Q Setting for each Output Channel
Set Q value for each filter
and output channel
View Q value for each
EQX@*X4$*X4&
SseQX@*X4$*X4&]
SSE}
EQX@*X4$SSE} SseQX@*X4$*X4&]
filter and output channel
Additional Description
Sets the frequency for each filter and
output channel.
Shows the current frequency for each
frequency and output channel.
Sets the gain for each filter and output
channel.
Shows the current gain for each filter
and output channel.
Sets the Q value for each filter and
output channel.
Shows the current Q value for each filter
and output channel.
NOTE: X@ — Audio Outputs (1-8): 1 = Left Front, 2 = Center, 3 = Right Front, 4 = Left Surround Side, 5 = Right Surround Side,
6 = Left Surround Back, 7 = Right Surround Back, 8 = Subwoofer
X4$ — Parametric EQ filter selection (1 to 9). Determines whether the corresponding frequency range is bypassed or not:
1 is the lowest frequency range, 9 is the highest frequency range
X4% — Parametric EQ filter frequency. Default values: 62 Hz (lter 1), 125 Hz (lter 2), 250 Hz (lter 3), 500 Hz (lter 4),
1000 Hz (filter 5), 2000 Hz (lter 6), 4000 Hz (lter 7), 8000 Hz (lter 8), 16000 Hz (lter 9)
X4^ — Parametric EQ Q value, multiplied by 1000 (from 707 to 15000; default 2000)
SSP 7.1 • SIS Commands 92
Page 99

Command ASCII Command
(host to unit)
Source Format Information Request
View source format
33I
information
Source Format Flag Detection
View if DTS 96/24
34I
encoded in DTS source
Test Signal Noise
Turn test signal off
Turn Dolby noise test
EX0TSTA} TstaXX3$] X3$ — Sets the test signal noise source:
EX1TSTA} TstaXX3$]
signal on
Turn pink noise test signal
EX2TSTA} TstaXX3$]
on
View test signal status
EXTSTA} TstaXX3$]
Information Request
Query firmware version
Query firmware version
Q
*Q
and build number
Request part number
Request general
N Pno60-842-01 SSP 7.1 part number: 60-842-01
I or 0I
information
Request model name
1I
Response
Additional Description
(unit to host)
SrcFormat
X2$•
SamplingX2%•
Displays the source format (X2$), source
format sampling frequency (X2%), and
source format encoded channels (X2^).
EnChanX2^]
DTS9624•
X#] X# — Status
0 = Off (default)
1 = On
0 = Off (default);
1 = Dolby;
2 = Pink
X2!] X2! — Version (x.xx)
Ver
X2@] X2@ — version and build number
Ver
(x.xx.xxxx)
X!•LModX1@
Aud
•VolX^•MutX#]
SSP 7.1
]
Displays the audio input number (X!),
listening mode (X1@), volume (X^), and
mute status (
X#).
Model name is SSP 7.1.
NOTE: X! — Audio Inputs (1-5): 1 and 2 = Digital audio, optical input, 3 and 4 = Digital audio, coaxial input, 5 = Analog input
X^ — Volume Adjustment 0 (-100 dB) to 100 (0 dB) in 1 dB steps, Default = 50: Max volume (no attenuation) = 100,
Min volume (full attenuation) = 0
X1@ — Listening Mode (Matrix Decode Mode indicator on the front panel): 1 = Stereo; 2 = Mono; 3 = Stereo to All; 4 = Mono to All;
5 = Dolby Pro Logic; 6 = Dolby Pro Logic II/IIx Movie; 7 = Dolby Pro Logic II/IIx Music; 8 = Dolby Digital 5.1; 9 = Dolby Digital EX;
10 = Dolby Digital Pro Logic IIx Movie; 11 = Dolby Digital Pro Logic IIx Music; 12 = DTS or DTS 96/24;
13 = DTS ES Matrix or DTS 96/24 ES Matrix; 14 = DTS ES Discrete; 15 = DTS + Dolby EX or DTS 96/24 + Dolby EX;
16 = DTS + Dolby Pro Logic IIx Movie or DTS 96/24 + Dolby Pro Logic IIx Movie;
17 = DTS + Dolby Pro Logic IIx Music or DTS 96/24 + Dolby Pro Logic IIx Music; 18 = DTS Neo:6 Cinema; 19 = DTS Neo:6 Music
X2$ — Source Format (Source LED on front panel): 0 = Not Present, 1 = Analog (2-CH), 2 = PCM (PCM and 2-CH),
3 = Dolby Digital 5.1 ( D), 4 = Dolby Digital 2/0 (when 2/0 encoding flag is detected) ( D and 2-CH),
5 = Dolby Digital 2/0 Surround (when 2/0 matrix encoding is detected) ( D and 2-CH),
6 = Dolby Digital Surround EX (when EX encoding ag is detected) ( D), 7 = DTS Digital Surround or DTS 96/24 (DTS)
8 = DTS-ES Matrix 6.1 or DTS 96/24 ES Matrix 6.1 (When ES Matrix encoding ag is detected) (DTS)
9 = DTS-ES Discrete 6.1 (When ES Discrete encoding ag is detected) (DTS), 10 = DTS 2-Channel (DTS and 2-CH)
X2% — Source Format Sampling Frequency: 0 = None, 1 = 32 kHz, 2 = 44.1 kHz, 3 = 48 kHz, 4 = 88.2 kHz, 5 = 96 kHz
X2^ — Source Format Encoded Channels: 0 = None, 1 = 1/0, 2 = 1/0.1, 3 = 2/0, 4 = 2/0.1, 5 = 2/1, 6 = 2/1.1, 7 = 2/2, 8 = 2/2.1,
9 = 3/0, 10 = 3/0.1, 11 = 3/1, 12 = 3/1.1, 13 = 3/2, 14 = 3/2.1, 15 = 3/3, 16 = 3/3.1
SSP 7.1 • SIS Commands 93
Page 100

Command ASCII Command
(host to unit)
System Reset
Master reset
Factory reset
Firmware Upload
Upload firmware
Status Commands
View internal temperature
(°C)
View clip status
EzXXX} Zpx]
EzQQQ} Zpq]
EUPLOAD} Go]
20S
3S
Response
(unit to host)
Up1]
Sts20*
Sts3*X#]
X1$] X1$ — Internal temperature in °C.
Additional Description
Resets all parameters to factory defaults.
Same as master reset but also resets
baud rate..
Upload begins.
Upload successful.
Displays Clip Status:
X# — Status: 0 = Off (default); 1 = On
Setting Speaker Delay Settings Using SIS Commands
NOTE: It is strongly recommended that, for ease and simplicity, these adjustments
are made with the SSP 7.1 Setup and Control Software (see page 22). If
this is not possible, the delay values can be calculated and entered, using SIS
commands.
To adjust Compensation Delays using SIS commands, follow these instructions.
Two Person Setup
NOTE: Setting up speaker delays is easier with two people. If only one person is
available, the position of the listener’s ears must be marked precisely using, for
1. Pick an ideal central location where all speaker output signals converge.
2. Use a tape measure to measure the distance from each speaker to the convergence
3. When the distances to every speaker have been measured accurately, select the speaker
4. Calculate the delay distance for each speaker, where:
example, a pile of boxes. Do not try to guess ear positions, as this introduces
measurement errors.
location. Be sure to measure to the same spot from each speaker.
NOTE: Measurements from the speaker should be to the midrange driver in a
three-way speaker or from halfway between the tweeter and the woofer in
a two-way speaker. Measurements to the convergence location should be at
ear height.
that is farthest from the convergence location and use that distance as a reference
value.
Delay Distance = Farthest Speaker Distance - Individual Speaker Distance
SSP 7.1 • SIS Commands 94
 Loading...
Loading...