Page 1

MGP 462
MGP 462D
Multi-Graphic Processor
68-840-01 Rev. C
08 06
Page 2

Precautions
Safety Instructions • English
This symbol is intended to alert the user of important operating and maintenance
(servicing) instructions in the literature provided with the equipment.
This symbol is intended to alert the user of the presence of uninsulated dangerous
voltage within the product's enclosure that may present a risk of electric shock.
Caution
Read Instructions • Read and understand all safety and operating instructions before using the
equipment.
Retain Instructions • The safety instructions should be kept for future reference.
Follow Warnings • Follow all warnings and instructions marked on the equipment or in the user
information.
Avoid Attachments • Do not use tools or attachments that are not recommended by the equipment
manufacturer because they may be hazardous.
Consignes de Sécurité • Français
Ce symbole sert à avertir l’utilisateur que la documentation fournie avec le matériel
contient des instructions importantes concernant l’exploitation et la maintenance
(réparation).
Ce symbole sert à avertir l’utilisateur de la présence dans le boîtier de l’appareil de
tensions dangereuses non isolées posant des risques d’électrocution.
Attention
Lire les instructions• Prendre connaissance de toutes les consignes de sécurité et d’exploitation avant
d’utiliser le matériel.
Conserver les instructions• Ranger les consignes de sécurité afin de pouvoir les consulter à l’avenir.
Respecter les avertissements • Observer tous les avertissements et consignes marqués sur le matériel ou
présentés dans la documentation utilisateur.
Eviter les pièces de fixation • Ne pas utiliser de pièces de fixation ni d’outils non recommandés par le
fabricant du matériel car cela risquerait de poser certains dangers.
Sicherheitsanleitungen • Deutsch
Dieses Symbol soll dem Benutzer in der im Lieferumfang enthaltenen
Dokumentation besonders wichtige Hinweise zur Bedienung und Wartung
(Instandhaltung) geben.
Dieses Symbol soll den Benutzer darauf aufmerksam machen, daß im Inneren des
Gehäuses dieses Produktes gefährliche Spannungen, die nicht isoliert sind und
die einen elektrischen Schock verursachen können, herrschen.
Achtung
Lesen der Anleitungen • Bevor Sie das Gerät zum ersten Mal verwenden, sollten Sie alle Sicherheits-
und Bedienungsanleitungen genau durchlesen und verstehen.
Aufbewahren der Anleitungen • Die Hinweise zur elektrischen Sicherheit des Produktes sollten Sie
aufbewahren, damit Sie im Bedarfsfall darauf zurückgreifen können.
Befolgen der Warnhinweise • Befolgen Sie alle Warnhinweise und Anleitungen auf dem Gerät oder in
der Benutzerdokumentation.
Keine Zusatzgeräte • Verwenden Sie keine Werkzeuge oder Zusatzgeräte, die nicht ausdrücklich vom
Hersteller empfohlen wurden, da diese eine Gefahrenquelle darstellen können.
Instrucciones de seguridad • Español
Este símbolo se utiliza para advertir al usuario sobre instrucciones importantes de
operación y mantenimiento (o cambio de partes) que se desean destacar en el
contenido de la documentación suministrada con los equipos.
Este símbolo se utiliza para advertir al usuario sobre la presencia de elementos con
voltaje peligroso sin protección aislante, que puedan encontrarse dentro de la caja
o alojamiento del producto, y que puedan representar riesgo de electrocución.
Precaucion
Leer las instrucciones • Leer y analizar todas las instrucciones de operación y seguridad, antes de usar
el equipo.
Conservar las instrucciones • Conservar las instrucciones de seguridad para futura consulta.
Obedecer las advertencias • Todas las advertencias e instrucciones marcadas en el equipo o en la
documentación del usuario, deben ser obedecidas.
Evitar el uso de accesorios • No usar herramientas o accesorios que no sean especificamente
recomendados por el fabricante, ya que podrian implicar riesgos.
•
ᅝܼ乏ⶹ
䖭Ͼヺোᦤ ⼎⫼᠋䆹䆒⫼᠋ ݠЁ
䖭Ͼヺো䄺⫼᠋䆹䆒ᴎݙ᳝
⊼ᛣ
䯙䇏䇈ᯢк•
ֱᄬ䇈ᯢк• 䑩ㅸⷕ⪙⫊₩嬵㕏ᶧḦ⡈⭇㚦Ề䑩ɿ
䙉ᅜ䄺 • 䑩ㅸⷕ徶⫉␂ ⏍䑩ㅸ㉈⊘ᵋ䗅ㆁ㙊⫊₩
䙓ܡ䗑ࡴ
•
Ё᭛
᳝䞡㽕ⱘ᪡㓈ᡸ䇈ᯢDŽ
䴆ⱘ䰽⬉ˈ᳝㾺⬉䰽
䑩ㅸỀ䑩嬦嫿 ⡈⼆枼敆嬼 䍇夤ㆁ㙊
ᵎ壂Ề䑩嬦␂⋃⒇㯢㙊㋩劑䗅₸ㅗ弾
⫊₩⏍Ề䑩嬵㕏ɿ
⏍㐎ẝ嬵㕏ɿ
⇡嫿⡈澤Ḧ忀₎⊲斪
ɿ
ɿ
Warning
Power sources • This equipment should be operated only from the power source indicated on the product.
This equipment is intended to be used with a main power system with a grounded (neutral)
conductor. The third (grounding) pin is a safety feature, do not attempt to bypass or disable it.
Power disconnection • To remove power from the equipment safely, remove all power cords from the rear
of the equipment, or the desktop power module (if detachable), or from the power source receptacle
(wall plug).
Power cord protection • Power cords should be routed so that they are not likely to be stepped on or
pinched by items placed upon or against them.
Servicing • Refer all servicing to qualified service personnel. There are no user-serviceable parts inside. To
prevent the risk of shock, do not attempt to service this equipment yourself because opening or
removing covers may expose you to dangerous voltage or other hazards.
Slots and openings • If the equipment has slots or holes in the enclosure, these are provided to prevent
overheating of sensitive components inside. These openings must never be blocked by other objects.
Lithium battery • There is a danger of explosion if battery is incorrectly replaced. Replace it only with the
same or equivalent type recommended by the manufacturer. Dispose of used batteries according to the
manufacturer's instructions.
Avertissement
Alimentations• Ne faire fonctionner ce matériel qu’avec la source d’alimentation indiquée sur l’appareil.
Ce matériel doit être utilisé avec une alimentation principale comportant un fil de terre (neutre). Le
troisième contact (de mise à la terre) constitue un dispositif de sécurité : n’essayez pas de la
contourner ni de la désactiver.
Déconnexion de l’alimentation• Pour mettre le matériel hors tension sans danger, déconnectez tous les
cordons d’alimentation de l’arrière de l’appareil ou du module d’alimentation de bureau (s’il est
amovible) ou encore de la prise secteur.
Protection du cordon d’alimentation • Acheminer les cordons d’alimentation de manière à ce que
personne ne risque de marcher dessus et à ce qu’ils ne soient pas écrasés ou pincés par des objets.
Réparation-maintenance • Faire exécuter toutes les interventions de réparation-maintenance par un
technicien qualifié. Aucun des éléments internes ne peut être réparé par l’utilisateur. Afin d’éviter tout
danger d’électrocution, l’utilisateur ne doit pas essayer de procéder lui-même à ces opérations car
l’ouverture ou le retrait des couvercles risquent de l’exposer à de hautes tensions et autres dangers.
Fentes et orifices • Si le boîtier de l’appareil comporte des fentes ou des orifices, ceux-ci servent à
empêcher les composants internes sensibles de surchauffer. Ces ouvertures ne doivent jamais être
bloquées par des objets.
Lithium Batterie • Il a danger d'explosion s'll y a remplacment incorrect de la batterie. Remplacer
uniquement avec une batterie du meme type ou d'un ype equivalent recommande par le constructeur.
Mettre au reut les batteries usagees conformement aux instructions du fabricant.
Vorsicht
Stromquellen • Dieses Gerät sollte nur über die auf dem Produkt angegebene Stromquelle betrieben
werden. Dieses Gerät wurde für eine Verwendung mit einer Hauptstromleitung mit einem geerdeten
(neutralen) Leiter konzipiert. Der dritte Kontakt ist für einen Erdanschluß, und stellt eine
Sicherheitsfunktion dar. Diese sollte nicht umgangen oder außer Betrieb gesetzt werden.
Stromunterbrechung • Um das Gerät auf sichere Weise vom Netz zu trennen, sollten Sie alle Netzkabel
aus der Rückseite des Gerätes, aus der externen Stomversorgung (falls dies möglich ist) oder aus der
Wandsteckdose ziehen.
Schutz des Netzkabels • Netzkabel sollten stets so verlegt werden, daß sie nicht im Weg liegen und
niemand darauf treten kann oder Objekte darauf- oder unmittelbar dagegengestellt werden können.
Wartung • Alle Wartungsmaßnahmen sollten nur von qualifiziertem Servicepersonal durchgeführt
werden. Die internen Komponenten des Gerätes sind wartungsfrei. Zur Vermeidung eines
elektrischen Schocks versuchen Sie in keinem Fall, dieses Gerät selbst öffnen, da beim Entfernen der
Abdeckungen die Gefahr eines elektrischen Schlags und/oder andere Gefahren bestehen.
Schlitze und Öffnungen • Wenn das Gerät Schlitze oder Löcher im Gehäuse aufweist, dienen diese zur
Vermeidung einer Überhitzung der empfindlichen Teile im Inneren. Diese Öffnungen dürfen niemals
von anderen Objekten blockiert werden.
Litium-Batterie • Explosionsgefahr, falls die Batterie nicht richtig ersetzt wird. Ersetzen Sie verbrauchte
Batterien nur durch den gleichen oder einen vergleichbaren Batterietyp, der auch vom Hersteller
empfohlen wird. Entsorgen Sie verbrauchte Batterien bitte gemäß den Herstelleranweisungen.
Advertencia
Alimentación eléctrica • Este equipo debe conectarse únicamente a la fuente/tipo de alimentación eléctrica
indicada en el mismo. La alimentación eléctrica de este equipo debe provenir de un sistema de
distribución general con conductor neutro a tierra. La tercera pata (puesta a tierra) es una medida de
seguridad, no puentearia ni eliminaria.
Desconexión de alimentación eléctrica • Para desconectar con seguridad la acometida de alimentación
eléctrica al equipo, desenchufar todos los cables de alimentación en el panel trasero del equipo, o
desenchufar el módulo de alimentación (si fuera independiente), o desenchufar el cable del
receptáculo de la pared.
Protección del cables de alimentación • Los cables de alimentación eléctrica se deben instalar en lugares
donde no sean pisados ni apretados por objetos que se puedan apoyar sobre ellos.
Reparaciones/mantenimiento • Solicitar siempre los servicios técnicos de personal calificado. En el interior
no hay partes a las que el usuario deba acceder. Para evitar riesgo de electrocución, no intentar
personalmente la reparación/mantenimiento de este equipo, ya que al abrir o extraer las tapas puede
quedar expuesto a voltajes peligrosos u otros riesgos.
Ranuras y aberturas • Si el equipo posee ranuras o orificios en su caja/alojamiento, es para evitar el
sobrecalientamiento de componentes internos sensibles. Estas aberturas nunca se deben obstruir con
otros objetos.
Batería de litio • Existe riesgo de explosión si esta batería se coloca en la posición incorrecta. Cambiar esta
batería únicamente con el mismo tipo (o su equivalente) recomendado por el fabricante. Desachar las
baterías usadas siguiendo las instrucciones del fabricante.
䄺
⬉⑤• 嬦嫿⡈⌫倾Ề䑩␂ᵋ㝈㕏䗅䑶㷑ɿ嫿 ⡈⼆枼
䩭ᵊ㚢一澠♱一澡㕰
• ᵻ⫊₩♱ḏ嫿⡈㈕㋊䑶㷑澤嬸㈕㋊ㆁ㙊嫿
ᢨᥝ⬉⑤
ㅗḼẖ㋦ⅱⵃ䑶䰼丠䗅
⫊₩嫿 㓾澤ᵎ倾ᵎ䑩ㅗ崴弈ɿ
䑶㷑一ɿ
⬉⑤㒓ֱᡸ• ⣦Ⓟⵄ一澤忀₎埬嵪嵐澤ㅗ愎䆪㉥⋌ɿ
㓈ᡸ• ㆁ㙊丵Ἧ⼆枼䑲嫥嬂䗅丵Ἧ⎙弜垍ɿ嫿⡈
ᵻ忀₎℻䋱大䑶⊲斪
䗮亢ᄨ• 㙊嫿⡈㙻⠴ᵋ㙊彛栏㤾ㅗ⪕澤⫄ḭ 㕰䑩㚦
ᵎ壂䑩Ḽẖᵝ壀㉢Ẑ彛
ᵎ壂儫ⴲ嬖☿㆔⹁嫿⡈䘗⪑丵Ἧ嬦嫿⡈ɿ
栏⪕ɿ
䫖⬉∴• ᵎ㪤䞯䗅㘵㊣䑶㮡ṛ㙊䅇㿹䗅⊲斪ɿ⼆枼Ề䑩
㉊䂨䑠⋃
䗅⸻嫯⡅䍇ⷠ⹄䑶㮡ɿ
Ề䑩㙊♱一䗅Ờ䑶䰼丠Ờ䑶ɿ
⡈⍏ㅗ㞍暣䑶㷑䗅䑶㷑一澤
怩㯢㙊䑩ㅸ⌰Ḧ㘵㊣䗅昷ḷɿ
敳㪣㙻㒐だ₄ḷ弈䀮ɿ
ᵏ⋃⫷㋩劑 䗅䘹⍍ㅗ 䘹弒⛌⌸䗅䑶㮡ɿ
Page 3
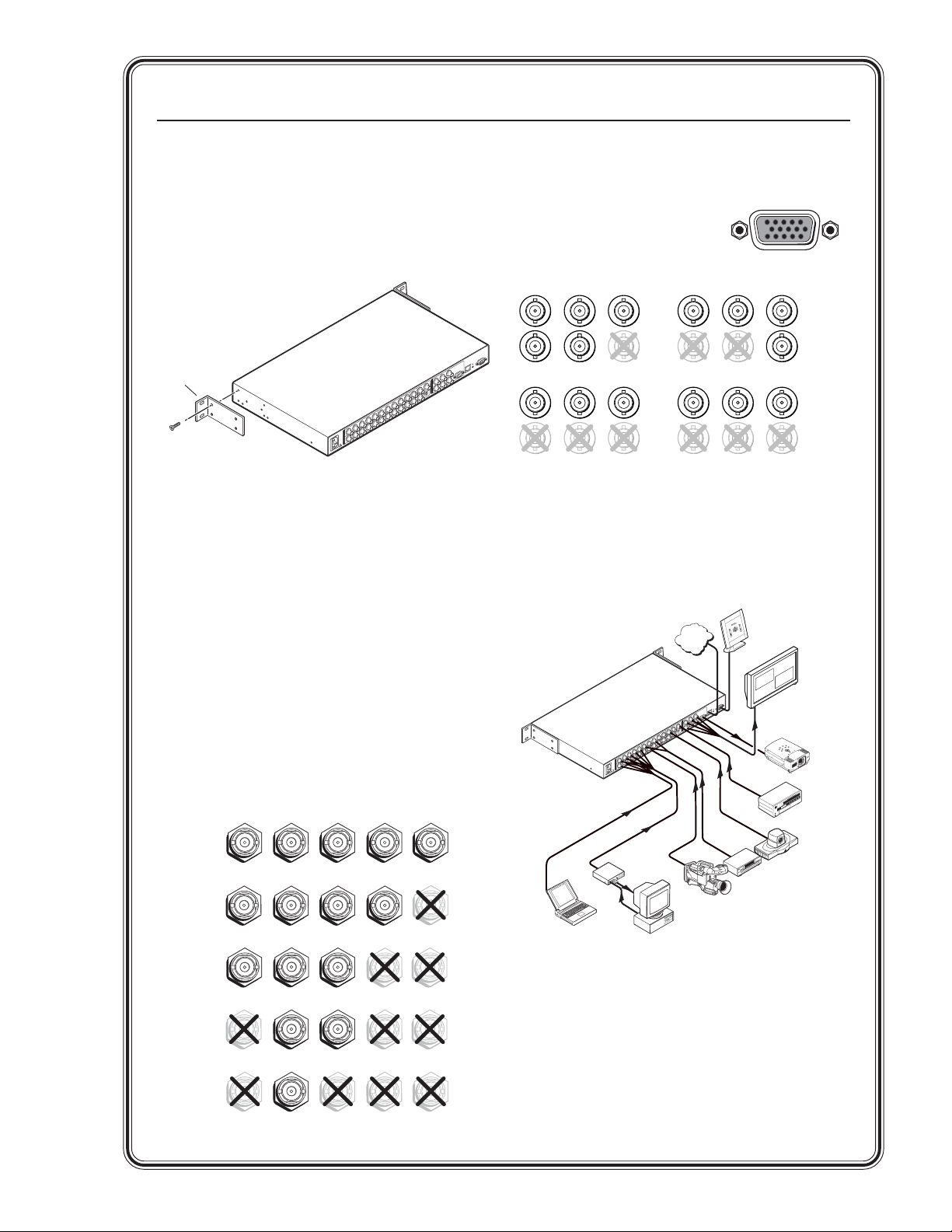
Quick Start — MGP 462, cont’d
Quick Start — MGP 462
Installation
Step 1
Install the four rubber feet on the bottom of the
MGP 462, or mount the unit using the supplied
rack mounting brackets.
Rack-mount
Bracket
/Y
G
ID
V
/
R
-Y
R
1
I
N
/Y
G
ID
V 0.3A
P
V
2
100-240
U
/
R
-Y
T
R
S
50/60 Hz
Rack mounting the MGP 462
Step 2
Turn off power to the input and output devices,
and remove the power cords from them.
Step 3
Attach the input devices to the MGP 462. The
inputs can accept the following signal types:
Inputs 1, 2, 3, 4 — RGB, component video,
S-video, or composite video
Inputs 3 and 4 — Component video, S-video, or
composite video
Input 5 — S-video or composite video
Input 6 — S-video (4-pin mini DIN connector),
composite video (VID BNC connector), or SDI
(MGP 462D model only)
RGBHV
Video
R/R-Y
RGBS or
RGBcvS
Video
R/R-Y
RGsB or
Component
Video
R/R-Y
S-Video
R/R-Y
Composite
Video
R/R-Y
Input connectors
G/Y
VID
G/Y
VID
G/Y
VID
G/Y
VID
G/Y
VID
B/C
B-Y
B/C
B-Y
B/C
B-Y
B/C
B-Y
B/C
B-Y
5 6
V
/
H
V
H
/C
B
-Y
B
/Y
G
V
ID
V
/
/
R
H
-Y
V
R
H
3
/C
V
B
-Y
B
/
/Y
H
G
V
H
ID
V
4
/C
B
/
R
-Y
B
-Y
R
V
/
H
V
H
/C
B
-Y
B
H/HV
H/HV
H/HV
H/HV
H/HV
Step 4
Attach an output device to the
RGBHV/YUV BNC connectors
(shown below) and/or to the
15-pin HD output connector
(shown at right).
RGBHV RGBS
R
/R-YG/Y
RS-232/422
RESET
LAN
/
B
Y
-Y
B
/
G
RGB/R-Y, B-Y,
Y
/
R
-Y
R
S
O
I
D
U
V
T
ID S
V
P
H
U
ID
V
T
/Y
S
C
Y
-Y
B
-Y
R
/C
HVS
R
/R-YG/Y
HVS
B
/B-Y
B
/B-Y
RGsB HDTV Component Video
BNC output connectors
RGB/R-Y, Y, B-Y
R
G
/R-Y
HVS
R
/R-Y
HVS
B
/Y
/B-Y
G
B
/Y
/B-Y
Step 5
Plug the MGP 462, input devices, and output
devices into a grounded AC source, and power
on the input and output devices.
TCP/IP
Network
B/
-Y
B-Y
B
,
-Y
/R
/
B
G
G
R
Y
R/
R-Y
O
SDI5
U
V S
T
VID
P
U
6
VID
T
/Y
S
V
YCH
H/
B-Y
HV
B/C
R-Y
B-Y
/C
G/Y
V
VID
R/
H/
R-Y
HV
3
V
B/C
B-Y
H/
G/Y
HV
VID
4
B/C
R/
B-Y
R-Y
G/Y
V
VID
R/
H/
R-Y
HV
1
B/C
I
B-Y
N
G/Y
P
VID
2
100-240V 0.3A
U
R/
T
R-Y
Extron
MGP 462
Multi-Graphic Processor
V
50/60 Hz
S
Extron
RGB 109xi
Interface
Video Camera
V
Laptop
PC
MGP 462 connection diagram
V
Step 6
Use the LCD menu screens and Adjust knobs to
configure the MGP 462 and adjust the picture
V
controls (see the following section, Configuring
and Adjusting the MGP 462). See chapter 2 for
installation instructions, chapter 3 for front panel
V
operation information, chapter 4 for control via
the RS-232/422 interface, and chapter 5 for
Ethernet control.
Control
System
2
2
/4
2
3
-2
S
R
T
E
S
E
R
N
A
L
Y
,
Plasma
Projector
Broadcast VTR
CODEC
DVD
QS-1MGP 462 • Quick Start
Page 4
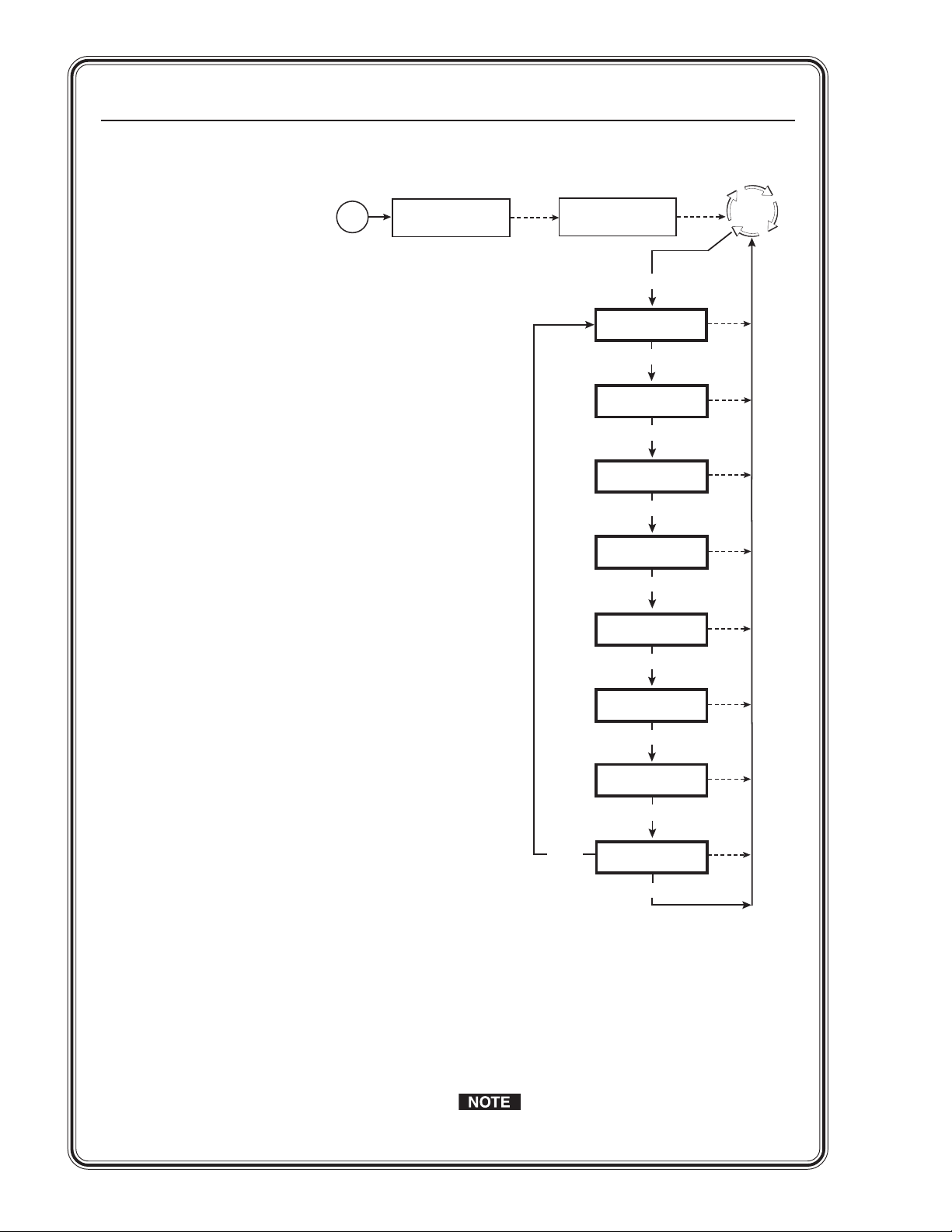
Quick Start — MGP 462, cont’d
Quick Start — MGP 462, cont’d
Getting Started
After you have installed and
connected the MGP 462, follow
these steps to configure and
adjust it to get it ready for use.
Configuring the MGP 462
Step 1
Use the Input Configuration menu to configure
each of the six inputs.
Step 2
Use the Output Configuration menu to configure
the output signal type and the output rate for the
desired resolution.
Step 3
From the Advanced Configuration menu, Test
Pattern submenu, select the Alternating Pixels
(Alt. Pixels) test pattern. Adjust your display’s
total pixel and phase settings for maximum
picture quality.
Power
on
MGP 462 V2.01
Extron
2 sec.
Multi-Graphic
Processor
MENU
Auto
Image
MENU
Input
Configuration
MENU
Output
Configuration
MENU
Window
Configuration
MENU
2 sec.
20 sec.
20 sec.
20 sec.
20 sec.
Default
Cycle
Step 4
From the Advanced Configuration menu, change
the test pattern to Crop, and adjust your
display’s positioning until all four sides of the
crop pattern are visible.
Adjusting the picture
controls
Step 5
Use the Window Configuration menu to select a
window border color for each window. This will
aid in window sizing and positioning.
Step 6
Select input 1 for both windows.
Step 7
Adjust windows 1 and 2 to full screen:
a. Press the Window 1 or the Window 2
button to select the window to adjust.
b. Press the Window/Image Position button
once, and turn the Adjust knobs until both
the H and V values = 0000.
Window Text
MENU
Configuration
MENU
Background
Capture
MENU
Advanced
Configuration
MENU
Exit Menu
Press Next
NEXT
20 sec.
20 sec.
20 sec.
60 sec.
Main Menu flow
c. Press the Window/Image Size button
once, and turn the Adjust knobs to the
right until they stop. The window size
setting displays the same resolution as the
output.
d. Repeat steps a through c for the
remaining window.
With both windows at full screen size,
you must mute window 2 in order to set
window 1, and vice versa.
MGP 462 • Quick StartQS-2
Page 5
Quick Start — MGP 462, cont’d
Step 8
For each input, size and position the image
within both window 1 and window 2.
a. Press one of the six input buttons in the
top row (for window 1) or the bottom row
(for window 2).
b. Press the window button that corresponds
with the input button that you pressed
(e.g., if you pressed the top input 3 button
in step 1, press the Window 1 button).
c. Press the Window/Image Size or the
Window/Image Position button twice.
The LCD window displays the number of
the input whose image you are sizing or
positioning.
d. Rotate the Adjust knobs until the H and V
values represent the image dimensions or
position coordinates you want for the
selected input.
e. Repeat steps c and d as needed to refine
the size and position adjustments for the
selected input.
f. Repeat steps a through e for the same
input in the other window.
g. Repeat steps a through f for each
remaining input.
Step 10
When finished adjusting the desired picture
controls, save your configuration as a window
preset:
a. Press the Preset Recall/Save button
and hold it for at least 2 seconds.
b. Use either Adjust knob to select the preset
number to which you want to save this
configuration.
c. Press the Enter button.
Step 11
You can now size and position windows for each
of your applications and save each one to any
one of the remaining 24 window preset locations
for easy recall of window settings.
You can also save presets using the MGP 462 Web
pages (see chapter 5) or the MGP 462 Windows
based configuration software (see Windows
Configuration Software in chapter 4 for instructions
on accessing the software and its online Help).
®
-based
®
-
Auto Image
Auto Image provides a quick way to size an
input to fit the current window size. To auto-size
an image, follow these steps:
a. Press the numbered button for the input
that you want to auto-size.
b. Press the Menu button once to select the
Auto Image menu.
c. Press the Next button to display the Auto
Image selection screen in the LCD window.
d. Turn either Adjust knob to select
window 1 or 2.
e. Press the Next button again to implement
your selection.
Step 9
Use the Input Configuration menu to make any
desired advanced adjustments, including
Horizontal and Vertical Start, Pixel Phase, Total
Pixel, Active Pixel, and Active Lines. See
chapter 3, Operation, for information on these
adjustments.
QS-3MGP 462 • Quick Start
Page 6

Quick Start — MGP 462, cont’d
Quick Start — MGP 462, cont’d
MGP 462 • Quick StartQS-4
Page 7

Table of Contents
Chapter 1 • Introduction ....................................................................................................... 1-1
About This Manual ............................................................................................................. 1-2
About the MGP 462/462D................................................................................................ 1-2
Features ................................................................................................................................... 1-2
Application Diagram ......................................................................................................... 1-3
Chapter 2 • Installation .......................................................................................................... 2-1
Mounting the MGP 462 .................................................................................................... 2-2
Tabletop use ....................................................................................................................... 2-2
Rack mounting ................................................................................................................... 2-2
Connecting the MGP 462................................................................................................. 2-3
Installing or Replacing Button Labels ...................................................................... 2-3
Cabling ..................................................................................................................................... 2-4
Input connectors ................................................................................................................ 2-5
LAN connector ................................................................................................................... 2-5
Configuring the LAN port .......................................................................................... 2-6
Reset button and LED ........................................................................................................ 2-6
Remote control connector ................................................................................................ 2-7
Output connectors ............................................................................................................. 2-7
Power connector ................................................................................................................ 2-7
Chapter 3 • Operation ............................................................................................................. 3-1
Front Panel Features ......................................................................................................... 3-2
Power-up and Default Cycle .......................................................................................... 3-3
Input Selection ..................................................................................................................... 3-3
Window Selection Buttons ............................................................................................ 3-4
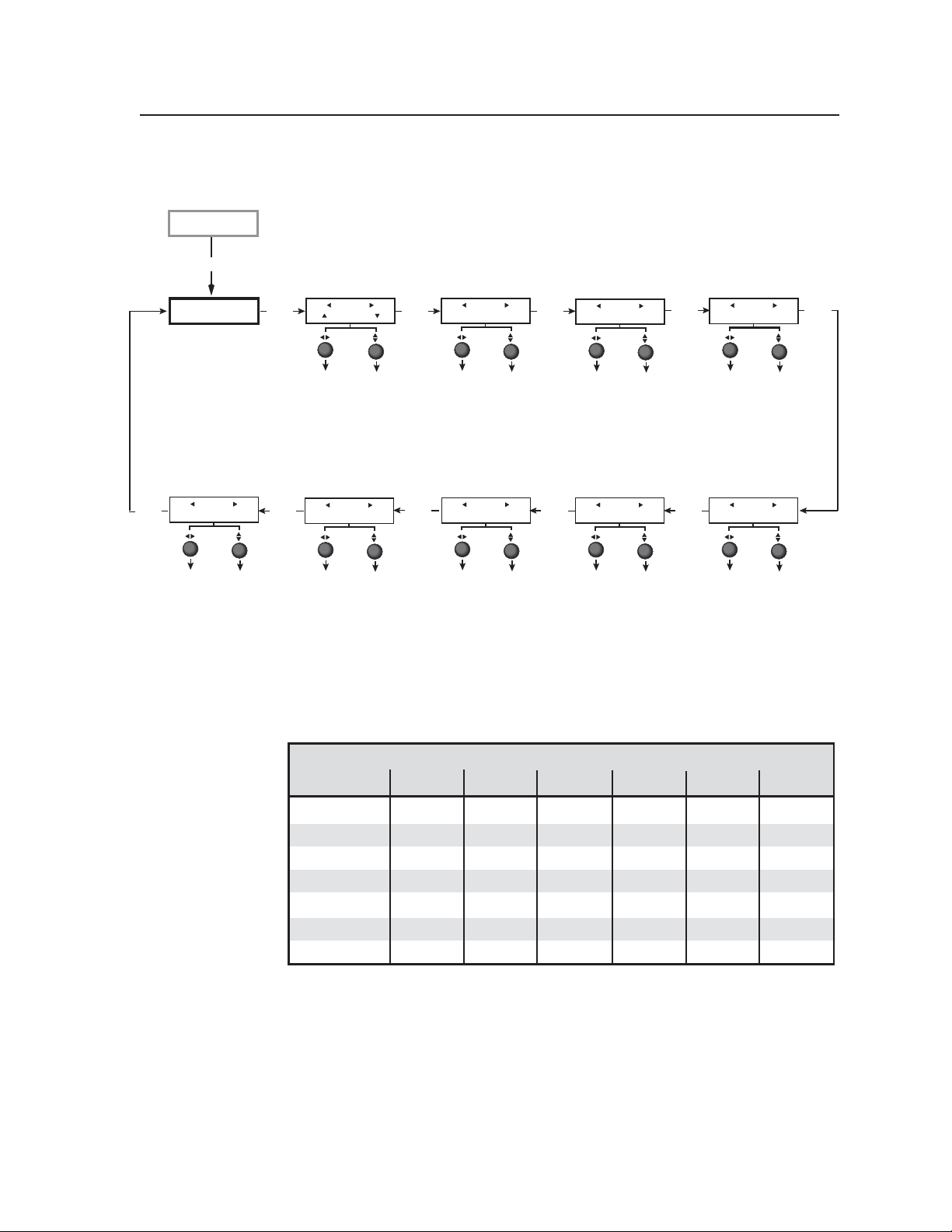
Menus, Configuration, and Adjustments ............................................................... 3-4
Menu system overview ...................................................................................................... 3-4
Using the menus ................................................................................................................ 3-4
Auto Image menu .............................................................................................................. 3-6
Input Configuration menu ................................................................................................ 3-6
Input configuration submenu adjustments ............................................................... 3-8
Output Configuration menu .............................................................................................3-9
Resolution and Refresh Rate submenu .................................................................... 3-10
Output Type submenu .............................................................................................. 3-11
Sync Polarity submenu ..............................................................................................3-11
Window Configuration menu .........................................................................................3-11
Window Priority submenu ........................................................................................ 3-11
Window 1 Border and Window 2 Border submenus .............................................. 3-12
Window Effect submenu .......................................................................................... 3-12
Available effects .................................................................................................. 3-12
Effect Duration submenu ......................................................................................... 3-13
MGP 462 • Table of Contents
i
Page 8

Table of Contents, cont’d
Window Text Configuration menu ................................................................................. 3-14
Window Text Position submenu............................................................................... 3-14
Window Text Size submenu ..................................................................................... 3-14
Windows 1 and 2 Text Color submenus ...................................................................3-14
Windows 1 and 2 Text Background submenus ........................................................ 3-15
Windows 1 and 2 Text Border submenus ................................................................ 3-15
Windows 1 and 2 Text Label screens ........................................................................ 3-15
Background Capture menu ............................................................................................. 3-16
Memory space for background files ........................................................................ 3-16
Saving a background to memory ............................................................................. 3-16
Recalling a background from memory .................................................................... 3-17
Advanced Configuration menu....................................................................................... 3-17
Background Color submenu .....................................................................................3-18
Blue Mode submenu .................................................................................................3-18
Test Pattern submenu ............................................................................................... 3-18
Serial Port Mode submenu ....................................................................................... 3-19
Internal Temperature screen .................................................................................... 3-19
Factory Default submenu ......................................................................................... 3-19
Picture Controls ................................................................................................................. 3-19
Adjusting the picture controls ........................................................................................ 3-20
Memory Presets ................................................................................................................. 3-21
Window presets ............................................................................................................... 3-21
Saving a window preset ........................................................................................... 3-21
Recalling a window preset ....................................................................................... 3-22
Default presets .......................................................................................................... 3-23
Input presets .................................................................................................................... 3-23
Additional Functions....................................................................................................... 3-24
Freeze mode ..................................................................................................................... 3-24
Front panel security lockout (executive mode) ..............................................................3-24
Resetting the unit ............................................................................................................ 3-24
Chapter 4 • Software Configuration and Control ................................................ 4-1
Setting Up RS-232 / RS-422 Communication .......................................................... 4-2
Using Simple Instruction Set (SIS™) Commands .................................................. 4-2
Host-to-MGP communications .......................................................................................... 4-2
MGP-initiated messages .................................................................................................... 4-2
Error responses ............................................................................................................ 4-3
Error response references ...........................................................................................4-3
Telnet and Web communications...................................................................................... 4-3
Symbol definitions ............................................................................................................. 4-5
Command/response table for SIS commands ................................................................... 4-8
Command/response table for IP control port commands .............................................. 4-18
Using the Windows®-based Control Software.................................................... 4-31
Installing the software .................................................................................................... 4-31
Starting the control program .......................................................................................... 4-33
Using the Button Label Generator ...........................................................................4-34
ii MGP 462 • Table of Contents
Page 9

Chapter 5 • Ethernet Configuration and Control ................................................. 5-1
Accessing the Web pages................................................................................................ 5-2
Viewing System Status .................................................................................................... 5-3
Using the Configuration Pages .................................................................................... 5-4
System Settings screen ....................................................................................................... 5-4
IP Settings fields .......................................................................................................... 5-4
Unit Name field ..................................................................................................... 5-4
DHCP radio buttons ............................................................................................... 5-4
IP Address field ...................................................................................................... 5-5
Gateway IP Address field ...................................................................................... 5-5
Subnet Mask field .................................................................................................. 5-5
MAC Address field ................................................................................................. 5-5
Setting the date and time .......................................................................................... 5-5
Scaler Settings screen ........................................................................................................ 5-6
Input configuration .................................................................................................... 5-7
Naming inputs ....................................................................................................... 5-7
Selecting the video signal type ............................................................................. 5-7
Output configuration ................................................................................................. 5-7
Window configuration ............................................................................................... 5-7
Parameters with separate menus for Window 1 and Window 2 ........................ 5-8
Advanced configuration .............................................................................................5-8
Background capture ................................................................................................... 5-8
Passwords screen ................................................................................................................ 5-9
Assigning a password ................................................................................................. 5-9
Clearing a password .................................................................................................... 5-9
Email Alerts screen ........................................................................................................... 5-10
Setting up SMTP authorization ................................................................................ 5-11
Firmware Upgrade screen ............................................................................................... 5-11
Determining the current firmware version ............................................................. 5-11
Downloading the firmware ...................................................................................... 5-12
Updating the firmware on the MGP 462 .................................................................5-12
Using the File Management Page ............................................................................. 5-14
Uploading files ................................................................................................................. 5-14
Adding a directory ........................................................................................................... 5-14
Other file management activities ................................................................................... 5-15
Using the Control Pages ................................................................................................ 5-15
User Control screen .......................................................................................................... 5-15
Select Window .......................................................................................................... 5-15
Input Selection .......................................................................................................... 5-15
Window Mute ........................................................................................................... 5-16
Executive Mode ......................................................................................................... 5-16
Freeze ........................................................................................................................ 5-16
Film Mode .................................................................................................................. 5-16
Picture Controls – Window ....................................................................................... 5-16
Picture Controls – Image ........................................................................................... 5-17
iiiMGP 462 • Table of Contents
Page 10

Table of Contents, cont’d
Window Presets screen ....................................................................................................5-18
Naming a window preset ......................................................................................... 5-19
Saving (creating) a window preset .......................................................................... 5-19
Recalling a window preset ....................................................................................... 5-19
Input Presets screen ......................................................................................................... 5-19
Saving (creating) an input preset ............................................................................. 5-20
Recalling an input preset .......................................................................................... 5-20
Chapter 6 • Special Application........................................................................................ 6-1
Connecting the MGP 462 to a Matrix Switcher ................................................... 6-2
Setting up the MGP to work with the switcher ............................................................... 6-3
Synchronizing the MGP 462 to the matrix switcher ........................................................ 6-4
Additional setup procedures if using a third party control system
without the MGP Sync tool ............................................................................................... 6-5
Appendix A • Specifications and Part Numbers ................................................... A-1
Specifications....................................................................................................................... A-2
Included Parts ...................................................................................................................... A-4
Accessories ............................................................................................................................ A-4
Appendix B • Installing the SDI Card ............................................................................B-1
Installing a Serial Digital Interface (SDI) Card..................................................... B-2
Appendix C • Firmware Update Guide......................................................................... C-1
Determining the Firmware Version...........................................................................C-2
Using the LCD display at power-on .................................................................................. C-2
Using a Web browser......................................................................................................... C-2
Using the Windows-based control software ....................................................................C-3
Downloading the Firmware ..........................................................................................C-4
Updating the Firmware.................................................................................................... C-4
Updating using the Web pages ........................................................................................ C-5
Updating using the Windows-based control software .................................................... C-6
All trademarks mentioned in this manual are the properties of their respective owners.
68-840-01 Rev C
08 06
iv MGP 462 • Table of Contents
Page 11
MGP 462 Multi-Graphic Processor
Chapter One
1
Introduction
About This Manual
About the MGP 462/462D
Features
Application Diagram
Page 12

Introduction, cont’d
Introduction
About This Manual
This manual discusses how to install, operate, and configure the Extron MGP 462
multi-graphic processor.
Throughout this manual, the terms “MGP,” “multi-graphic processor,” and
“processor” are used interchangeably to refer to the same product.
About the MGP 462/462D
The MGP 462 is a six-input, one-output RGB and video processor that can display
two video sources on a single screen in picture-in-picture or picture-by-picture
format. It provides switching among inputs, picture controls, and presets.
The MGP accepts RGB video, component video, S-video, and composite video
inputs. The MGP 462D is an MGP 462 with an SDI board installed so that input 6
can also accept SDI signals. (See appendix B, Installing the SDI Card, for information
on installing this board.)
Both versions can be controlled remotely via the RS-232/RS-422 interface using
Special Instruction Set (SIS
MGP 462’s embedded Web pages. The MGP 462 Windows
program can also be used to control the MGP via either the RS-232/422 or the
Ethernet connection.
™
) commands or via an Ethernet LAN using the
®
-based control software
Features
Inputs — The MGP 462 has six video inputs: fully configurable inputs 1 through 4
accept RGB, component, S-video, and composite video signals; input 5
accepts component video, S-video, and composite video; and input 6 accepts
S-video and composite video. The MGP 462D model also accepts SDI signals
on input 6.
Output — The MGP 462 has one scaled RGB or HD YUV output, available on both
a 15-pin HD connector and a set of five BNC connectors. This enables two
output devices to be connected to the MGP at the same time (both displaying
the same image).
Picture controls — Picture controls allow you to adjust size, position, brightness,
contrast, color, tint, detail, and zoom for each window.
Window and input presets — Window presets save sizing, positioning, and
priority information. Input presets save input signal type information and
picture control settings.
Window transition effects — Six types of window transition effects (22 different
effects altogether) seamlessly mute and unmute (close and open) the two
windows.
Freeze control — Freeze control freezes (locks) a window to the current image.
3:2 pulldown detection for NTSC video and 2:2 film detection for PAL video —
These advanced film mode processing features help maximize image detail
and sharpness for video sources that originated from film.
When film is converted to NTSC video, the film frame rate has to be matched
to the video frame rate in a process called 3:2 pulldown. Jaggies and other
image artifacts can result if conventional deinterlacing techniques are used
on film-source video. The MGP 462’s advanced film mode processing
recognizes signals that originated from film. The MGP then applies video
processing algorithms that optimize the conversion of video that was made
with the 3:2 pulldown process. This results in richly detailed images with
sharply defined lines.
MGP 462 • Introduction1-2
Page 13
A similar process, 2:2 film detection, is used for PAL film-source video.
Background image capture, save, and recall — Background Capture enables you to
capture and save the image currently on the output screen. You can then
recall the captured image and display it as a background later.
™
Auto Image
— Auto Image automatically sizes, centers, and optimizes the image
to the scaled output rate, filling the window.
Remote control — The MGP 462 can be operated remotely via the RS-232/422
interface using the Windows-based control software or SIS commands, or via
the Ethernet interface using the embedded Web pages.
Rack mounting — The 1U high and full rack wide metal enclosure can be rack
mounted using the included rack mounting brackets (part #70-077-03).
Front panel security lockout (executive mode) — Locks the front panel controls to
prevent accidental changes to the unit’s settings.
RGB and video scaling — All sources are scaled to a single output rate.
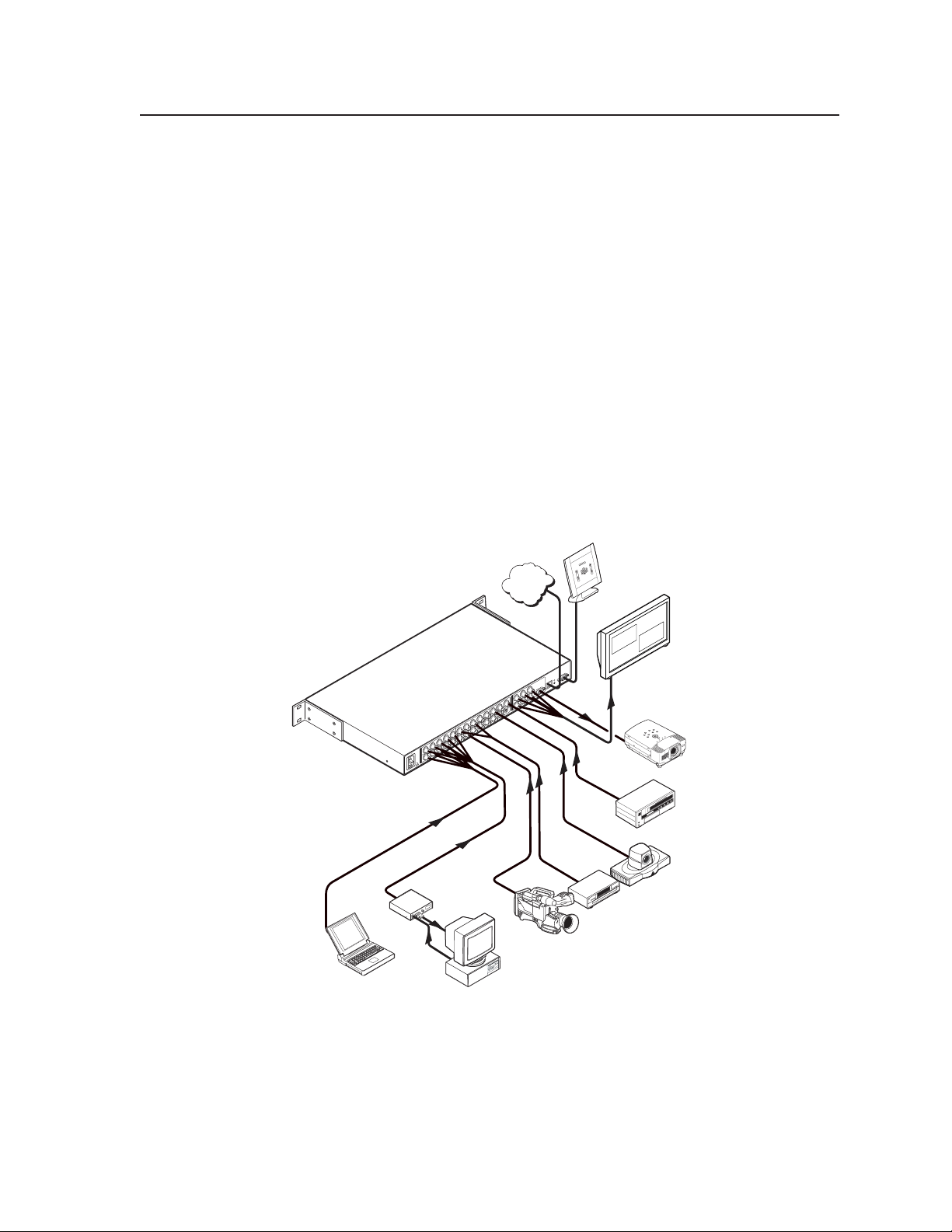
Application Diagram
The application diagram below gives an example of how devices may be connected
to the MGP 462.
1
I
N
P
2
100-240V 0.3A
U
T
Extron
S
50/60 Hz
MGP 462
Multi-Graphic Processor
Laptop
Connection diagram
R/
R-Y
3
V
H/
HV
4
B/C
R/
B-Y
R-Y
G/Y
V
VID
R/
H/
R-Y
HV
B/C
B-Y
G/Y
VID
R/
R-Y
Extron
RGB 109xi
Interface
B/C
B-Y
G/Y
VID
B/C
B-Y
G/Y
VID
SDI5
VID
6
VID
/Y
V
H/
B-Y
HV
R-Y
/C
V
H/
HV
PC
TCP/IP
Network
RS-232/422
RESET
LAN
B/
Y
B-Y
B-Y,
G/
RGB/R-Y,
Y
R/
R-Y
O
U
V S
T
P
U
T
S
YC H
Video Camera
Control
System
Plasma
Projector
Broadcast VTR
CODEC
DVD
1-3MGP 462 • Introduction
Page 14

Introduction, cont’d
MGP 462 • Introduction1-4
Page 15
MGP 462 Multi-Graphic Processor
Chapter Two
2
Installation
Mounting the MGP 462
Connecting the MGP 462
Installing or Replacing Button Labels
Cabling
Page 16
Installation, cont’d
Rack-mount
Bracket
50/60 Hz
100-240
V 0.3A
RGB/R-Y,
B-Y,
Y
LAN
RESET RS-232/422
2
1
R
/
R
-Y
R
/
R
-Y
G
/Y
V
ID
B
/C
B
-Y
H
/
H
V
V
G
/Y
V
ID
B
/C
B
-Y
H
/
H
V
V
4
3
R
/
R
-Y
R
/
R
-Y
R
/
R
-Y
G
/Y
V
ID
G
/
Y
B
/
B
-Y
B
/C
B
-Y
H
/
H
V
V
ID
/Y
V
V
ID
S
D
I5 6
G
/Y
V
ID
B
/C
B
-Y
H
/
H
V
R
-Y
/C
V
B
-Y
Y
C
H
V
S
I
N
P
U
T
S
O
U
T
P
U
T
S
Installation
Mounting the MGP 462
Tabletop use
Four self-adhesive rubber feet are included with the MGP 462. For tabletop use,
attach one foot to each corner of the bottom side of the unit and place the MGP in
the desired location.
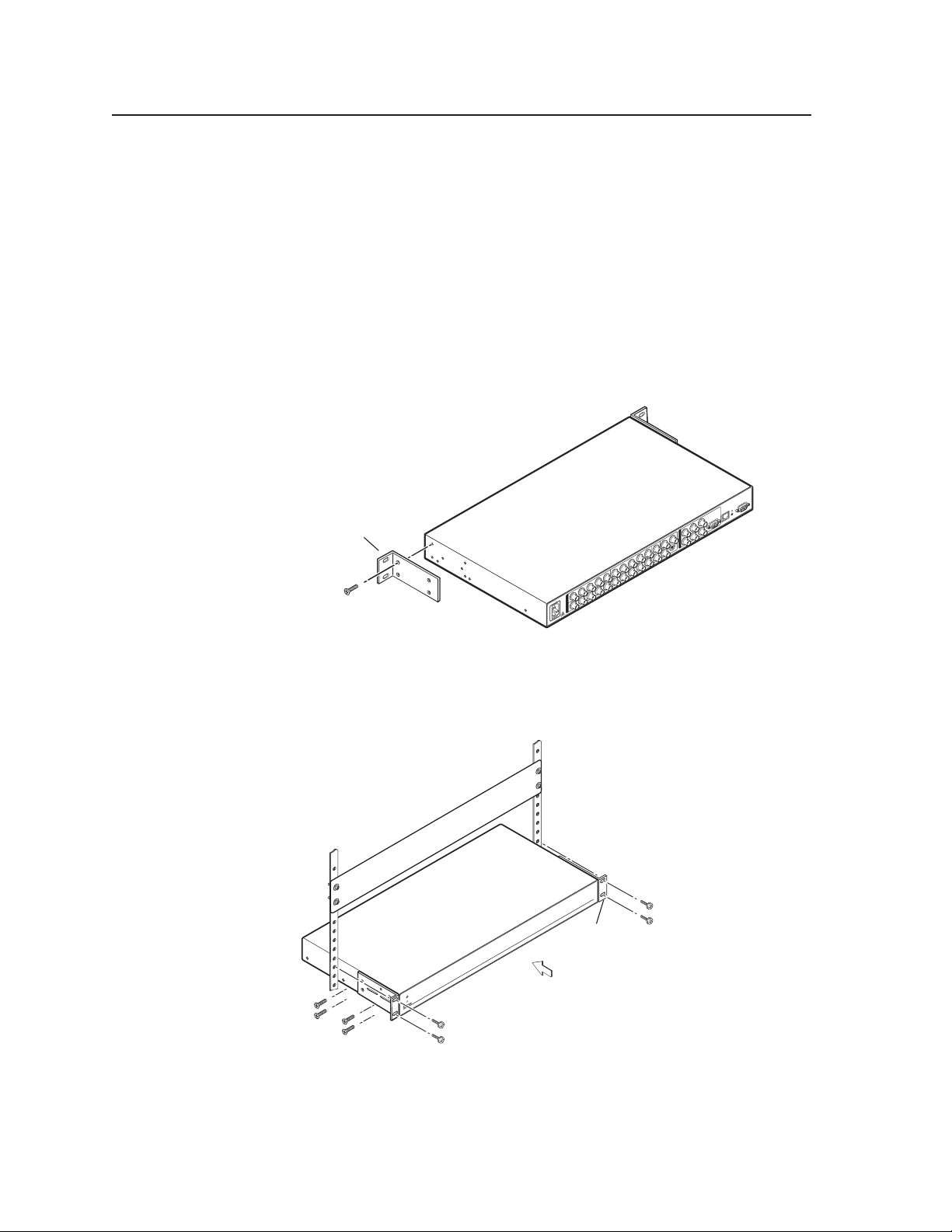
Rack mounting
The MGP can optionally be mounted in a rack with the supplied MBD 149 rack
mounting kit (part #70-077-03). Follow these steps:
1. Attach the mounting brackets to the unit using eight of the machine screws
supplied with the mounting kit.
Attaching the mounting brackets
2. Insert the unit into the rack and align the holes in the mounting brackets with
the holes in the rack. Use four of the supplied machine screws to attach the
brackets to the rack.
Rack Mount
Bracket
Rack mounting the MGP 462
MGP 462 • Installation2-2
Page 17

Connecting the MGP 462
The MGP 462 processor can be connected to as many as six input devices
simultaneously, and two output devices (displaying the same image). Follow the
steps below to set up the MGP 462 hardware.
Disconnect power to the MGP, and turn off all other devices that will be
1
connected.
If the MGP 462 is to be mounted, see Mounting the MGP 462, earlier in this
2
chapter, for the mounting procedure.
Using the BNC input connectors, attach up to six video input devices to the
3
MGP rear panel.
S-video and composite video inputs cannot both be connected to input 6 at the
same time.
Connect one or two output devices to the RGBHV/YUV BNC output
4
connectors and/or to the 15-pin HD connector.
If the MGP 462 will be connected to a computer or to a host controller for
5
remote control, connect the host’s RS-232 cable to the processor’s 9-pin
RS-232/422 D-sub connector.
Connect an active LAN Ethernet cable to the RJ-45 port on the rear panel to
6
establish a link to the network.
Power up the input and output devices, then connect power to the processor.
7
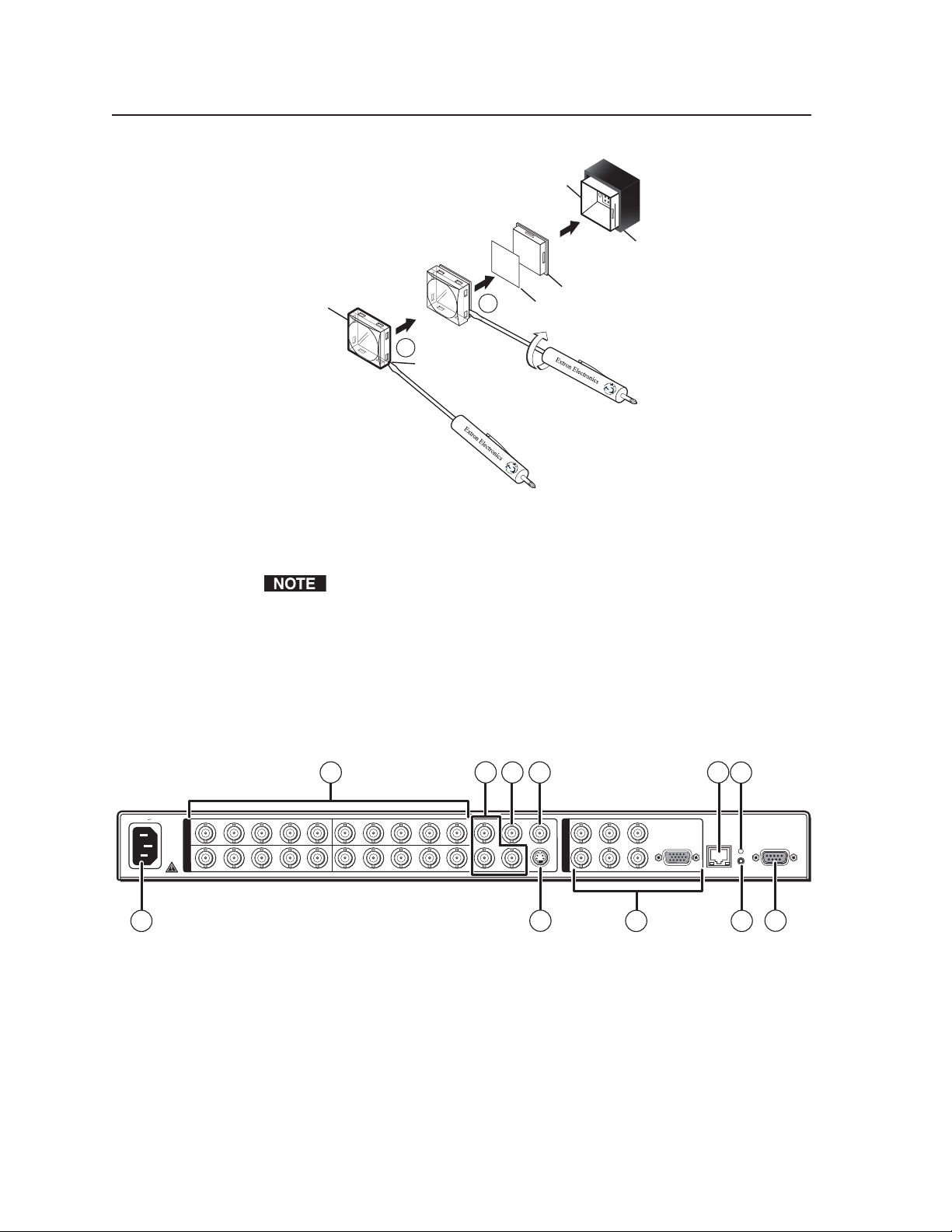
Installing or Replacing Button Labels
You may wish to customize your MGP’s buttons. The button caps are pre-labeled
for your convenience, but you can replace any of these labels with one of the
included button labels. You can also create custom labels using the Button-Label
Generator software (see Using the Button Label Generator in chapter 4, Software
Configuration and Control), or device such as the Brother P-Touch label maker. Cut
the labels so that they are square and ½ inch on each edge.
The button assembly consists of a clear lens cap, the button label, and a white
diffuser. (See the illustration on the next page.)
Follow these steps to replace button labels on your MGP:
1. Cut out the desired button label from the provided sheet, or make new labels
using the Button-Label Generator or other software and cut them out.
2. Remove the button assembly by inserting a small, flat-bladed screwdriver,
such as an Extron Tweeker, between the button’s base and the diffuser to
gently pry the button assembly off the button plunger.
3. Locate the small corner notch on the lens cap, and slide the screwdriver
between the lens cap and the diffuser. (See
page.)
4. Using a rotating motion of the screwdriver, carefully pry the two pieces apart.
(See
in the illustration on the next page.)
b
in the illustration on the next
a
2-3MGP 462 • Installation
Page 18
Installation, cont’d
Plunger
TEXT
Base
Diffuser
Button Label
Clear Lens
Separate the twopiece button at
the corner.
2
Notch
Pry the two
pieces apart.
1
Replacing a button label
5. Lift out the transparent square label that you want to replace. You may need
to use the small screwdriver to gently pry the label out.
Do not pry off the translucent diffuser that is behind the label.
6. Insert one of the new label you created in step 1 into the clear button cap,
align the white backing plate with the cap, and firmly snap it into place.
7. Gently, but firmly, press the reassembled button into place on the MGP front
panel.
8. Repeat steps 1 through 7 as needed to relabel other buttons.
Cabling
100-240V 0.3A
50/60 Hz
9
1
1
R/
G/Y
R-Y
I
N
P
U
2
T
S
R/
R-Y
B/C
VID
B-Y
G/Y
B/C
VID
B-Y
3
H/
V
R/
G/Y
HV
H/
HV
R-Y
4
V
R/
R-Y
B/C
VID
B-Y
G/Y
B/C
VID
B-Y
2
H/
V VID SDI 5 6
HV
H/
V B-Y YC H V S
HV
4
3
R/
VID
/Y
R-Y
/C
O
U
T
P
U
T
S
3
G/ Y B/
R-Y
B-Y
RGB/R-Y, Y, B-Y
8
5
6
LAN
RESET RS-232/422
6
7
MGP 462D rear panel (The MGP 462 is identical except that there is no SDI
connector [
d
].)
MGP 462 • Installation2-4
Page 19
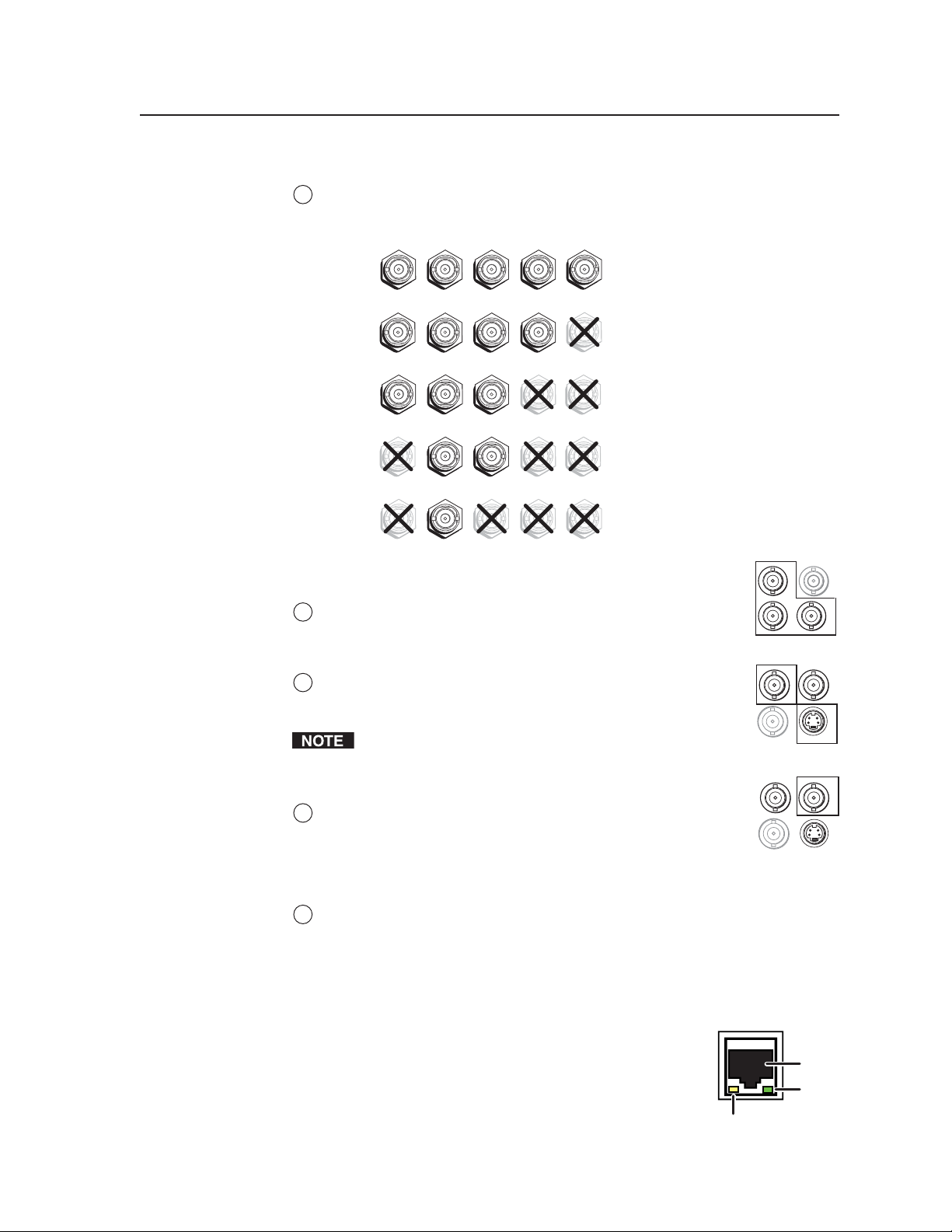
Input connectors
Inputs 1, 2, 3, and 4 — Plug RGB, component video, S-video, or composite
1
video sources into these BNC connectors as shown in the diagram below.
RGBHV
Video
RGBS or
RGBcvS
Video
RGsB or
Component
Video
S-Video
Composite
Video
Connector signal types for inputs 1 through 4
Input 5 — Plug a component video, S-video, or composite
2
video source into these BNC connectors.
R/R-Y
R/R-Y
R/R-Y
R/R-Y
R/R-Y
G/Y
VID
G/Y
VID
G/Y
VID
G/Y
VID
G/Y
VID
B/C
B-Y
B/C
B-Y
B/C
B-Y
B/C
B-Y
B/C
B-Y
H/HV
H/HV
H/HV
H/HV
H/HV
V
V
V
V
V
6
5
VID
VID
/Y
R-Y
B-Y
/C
Input 6 — Plug an S-video source into the 4-pin mini DIN
3
connector (in bottom row) or a composite video source into
the VID BNC connector (in top row).
SDI input — (MGP 462D only) Plug an SDI device into this
4
SDI BNC connector, as an alternative to input 6.
LAN connector
LAN connector — Plug an RJ-45 network cable into this connector to connect
5
the unit to a network (via a switch, hub, or router) or to a single computer.
Use a straight-through cable to connect to a network, or a crossover cable to
connect directly to a computer.
• For 10Base-T (10 Mbps) networks, use a Cat 3 or better cable.
• For 100 Base-T (max. 155 Mbps) networks, use a
See the illustration on the next page for information on
wiring the connector for these two types of cables..
Activity LED — This yellow LED blinks to indicate
Link LED — This green LED lights to indicate a good
Connecting S-video and composite video devices to input 6
simultaneously causes degraded output display quality.
Cat 5 cable.
network activity.
network connection.
LAN
Activity
LED
6
6
VID
B-Y
VID
SDI
YC
SDI
YC
B-Y
RJ-45
Por t
Link
LED
2-5MGP 462 • Installation
Page 20
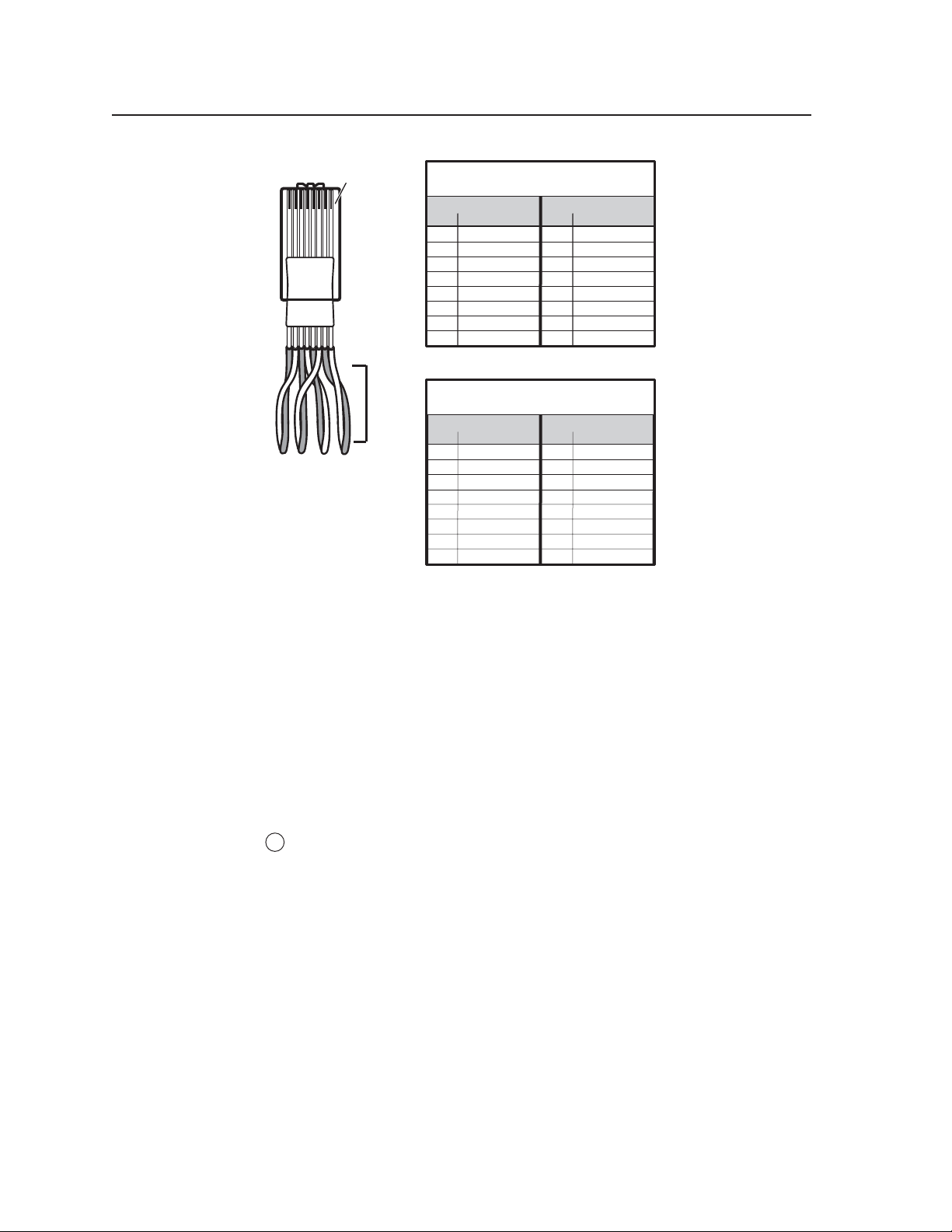
Installation, cont’d
Clip Down
12345678
1
23 45678
RJ-45
Connector
Straight-through Cable
(for connection to a switch, hub, or router)
End 1 End 2
Pin Wire Color Pin Wire Color
1 white-orange 1 white-orange
2 orange 2 orange
3 white-green 3 white-green
4 blue 4 blue
5 white-blue 5 white-blue
6 green 6 green
7 white-brown 7 white-brown
8 brown 8 brown
Crossover Cable
(for direct connection to a PC)
End 1 End 2
Pin Wire Color Pin Wire Color
1 white-orange 1 white-green
2 orange 2 green
3 white-green 3 white-orange
4 blue 4 blue
5 white-blue 5 white-blue
6 green 6 orange
7 white-brown 7 white-brown
8 brown 8 brown
1&2
3&6
4&5
Twi sted
Pairs
7&8
Pin assignments for LAN connector and cables
Configuring the LAN port
You also need to configure the LAN port before using it. This is done with SIS
commands. See Command/Response table for IP control port commands in chapter 4 for
information on these commands.
The LAN port defaults are:
Processor IP address: 192.168.254.254
Gateway IP address: 0.0.0.0
Subnet mask: 255.255.0.0
DHCP: off
Reset button and LED
Reset button and LED — Pressing this recessed button causes certain IP
6
functions and Ethernet connection settings to be reset to the factory defaults.
The green LED above the button blinks a varying number of times to indicate
which reset mode has been entered. See Resetting the unit in chapter 3,
Operations, for information on reset modes.
MGP 462 • Installation2-6
Page 21
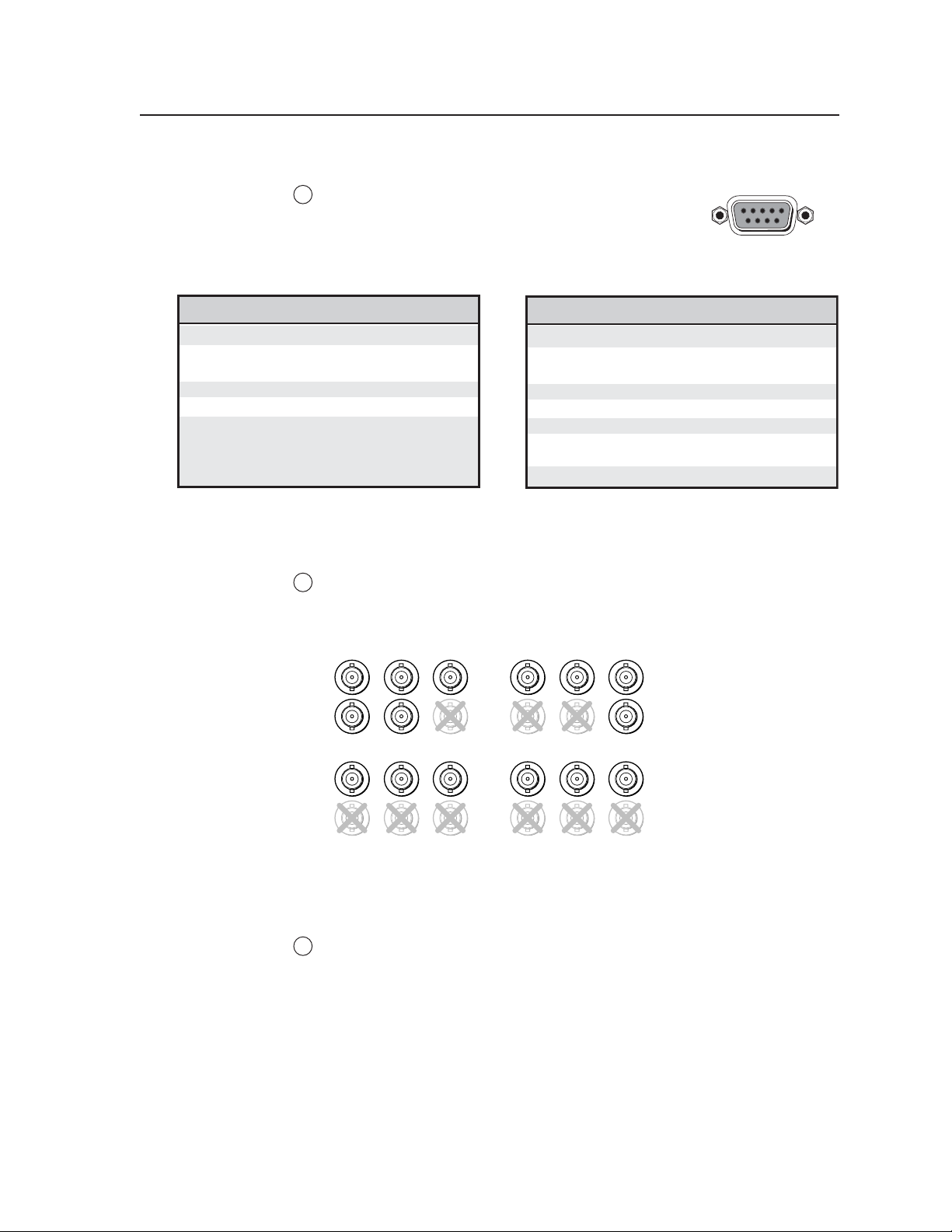
Remote control connector
RS-232/422 connector — Plug a computer or other
7
RS-232 or RS-422 host device into this female D-sub
connector. Wire the connector as shown in the tables
below. For more information on controlling the
MGP 462 remotely, see chapter 4, Software Configuration
and Control.
51
96
Pin RS-232 function Description
1 – No connection
2 Tx Transmit data
3 Rx Receive data
4 – No connection
5 Gnd Signal ground
6 – No connection
7 – No connection
8 – No connection
9 – No connection
Pin assignments for the RS-232/422 connector
Output connectors
Output connectors — Plug one or two output devices into the 5-BNC and/or
8
the 15-pin HD connector. (When two output devices are attached, they both
display the same picture.)
RGBHV RGBS
R
/R-Y
HVS
G
/Y
B
/B-Y
Pin RS-422 function Description
1 – No connection
2 Tx- Transmit ground
3 Rx- Receive ground
4 – No connection
5 Gnd Signal ground
6 – No connection
7 Rx+ Receive data
8 Tx+ Transmit data
9 – No connection
R
/R-Y
HVS
G
/Y
B
/B-Y
R
/R-Y
HVS
BNC output connectors
Power connector
AC power connector — Plug the power cord provided with the MGP 462 into
9
this connector to connect the MGP 462 to a 100–250 VAC, 50/60 Hz power
source.
G
/Y
RGsB HDTV Component Video
B
/B-Y
R
/R-Y
HVS
G
/Y
B
/B-Y
2-7MGP 462 • Installation
Page 22

Installation, cont’d
MGP 462 • Installation2-8
Page 23
MGP 462 Multi-Graphic Processor
Chapter Three
3
Operation
Front Panel Features
Power-up and Default Cycle
Input Selection
Window Selection Buttons
Menus, Configuration, and Adjustments
Picture Controls
Memory Presets
Additional Functions
Page 24
Operation, cont’d
Operation
The MGP 462 can be set up and operated by using:
• The front panel controls
• A computer, a touch screen panel, or any other device that can send and
receive serial communications through the RS-232/422 port. Settings can be
adjusted through the host computer using Extron’s Simple Instruction Set
(SIS
• A computer or other device using an Ethernet connection and IP protocol
(Telnet or a Web browser).
For details on setup and control via RS-232/422, see chapter 4; for Ethernet, see
chapter 5.
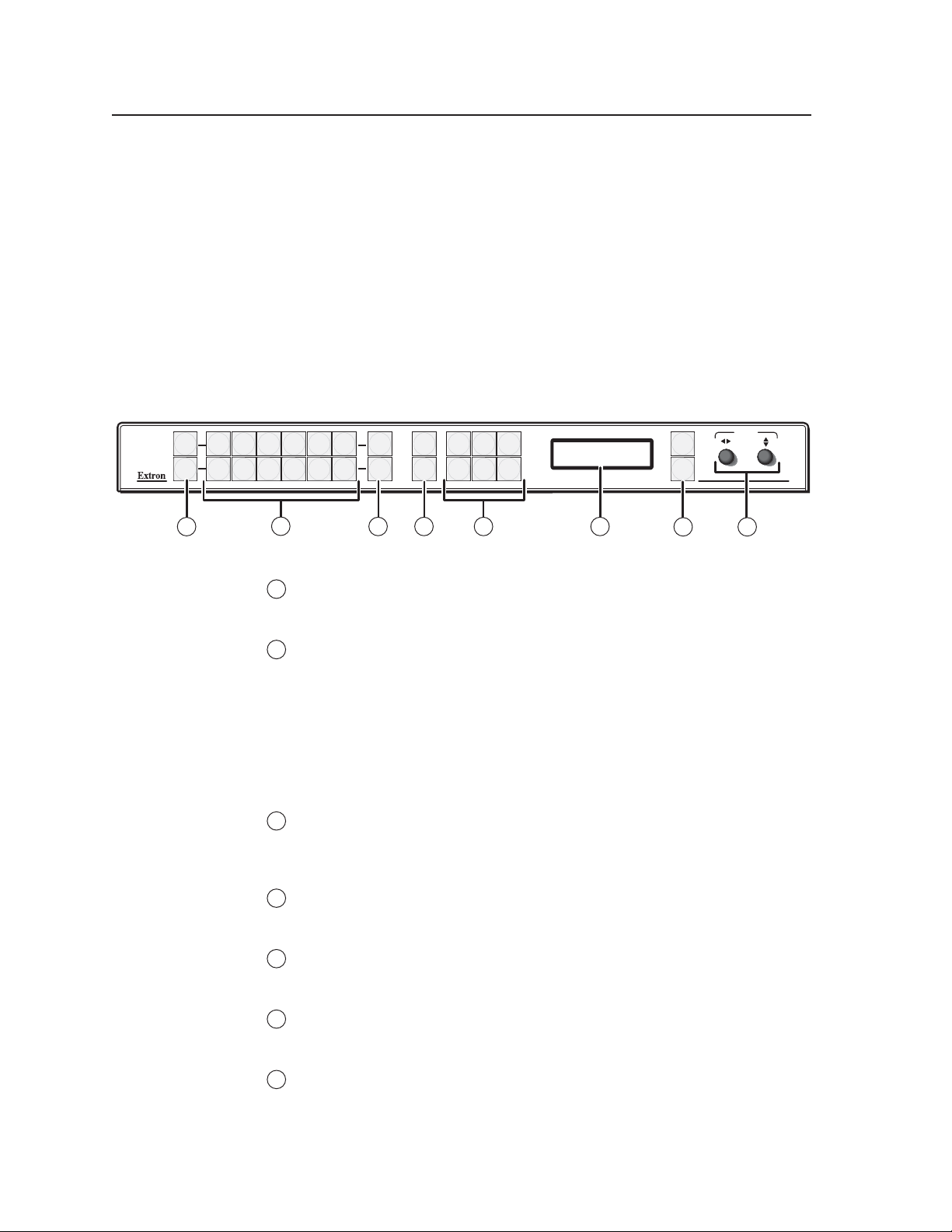
Front Panel Features
™
) or the Windows-based configuration software.
PRESET
WINDOW/
BRIGHT/
FREEZE
FREEZE
WINDOW
RECALL/
1
5
4
3
2
1
1
WINDOW
6
2
6
5
4
3
2
SAVE
ENTER
IMAGE
SIZE
WINDOW/
IMAGE
POSITION
CONT
COLOR/
TINT
DETAIL
WINDOW/
IMAGE
ZOOM
MENU
NEXT
1
2
3 4 6
5
7 8
ADJUST
MGP 462
MULTI-GRAPHIC PROCESSOR
MGP 462 front panel
Freeze buttons — Press these buttons to freeze window 1 (top button) or
1
window 2 (bottom button) to the current image. The Freeze buttons light
orange.
Input selection buttons — Press these buttons to select inputs for window 1
2
(top row) and window 2 (bottom row). Six pairs of buttons are provided.
When an input is selected, pressing the button again mutes the input. The
input’s signal turns off and the window closes. The Window Configuration
menu lets you select a window transition effect (e.g., dissolve, curtain, or
square wipe) with which the window will open or close (the default effect is
cut). See Window Configuration menu, later in this chapter, for more
information. The button flashes while the input remains muted. To unmute
the input, press its input button again.
Window selection buttons — Press these buttons to select a window to
3
adjust. (You do not need to press these buttons when freezing the windows
or selecting inputs.) While a window is selected, all picture controls are
associated with it.
Preset buttons — Press the Preset Recall/Save and Enter buttons to save or
4
recall window presets. See Window Presets, later in this chapter, for more
information.
Picture control buttons — Press these buttons to adjust image size, position,
5
brightness, contrast, color, tint, detail, and zoom. See Picture Controls, later in
this chapter, for further information.
LCD screen — This screen displays messages, menu information, and your
6
selections. See Menus, Configuration, and Adjustments, later in this chapter, for
more information.
Menu navigation buttons — Press Menu to access the MGP 462 menu system
7
and step through the menus. From each menu, press Next to step through its
submenus. See Menus, Configuration, and Adjustments, later in this chapter, for
more information.
MGP 462 • Operation3-2
Page 25
Adjust knobs — Turn these knobs to adjust picture controls and to scroll
8
through preset memory slots and submenu options. See Menus, Configuration,
and Adjustments, later in this chapter, for more information.
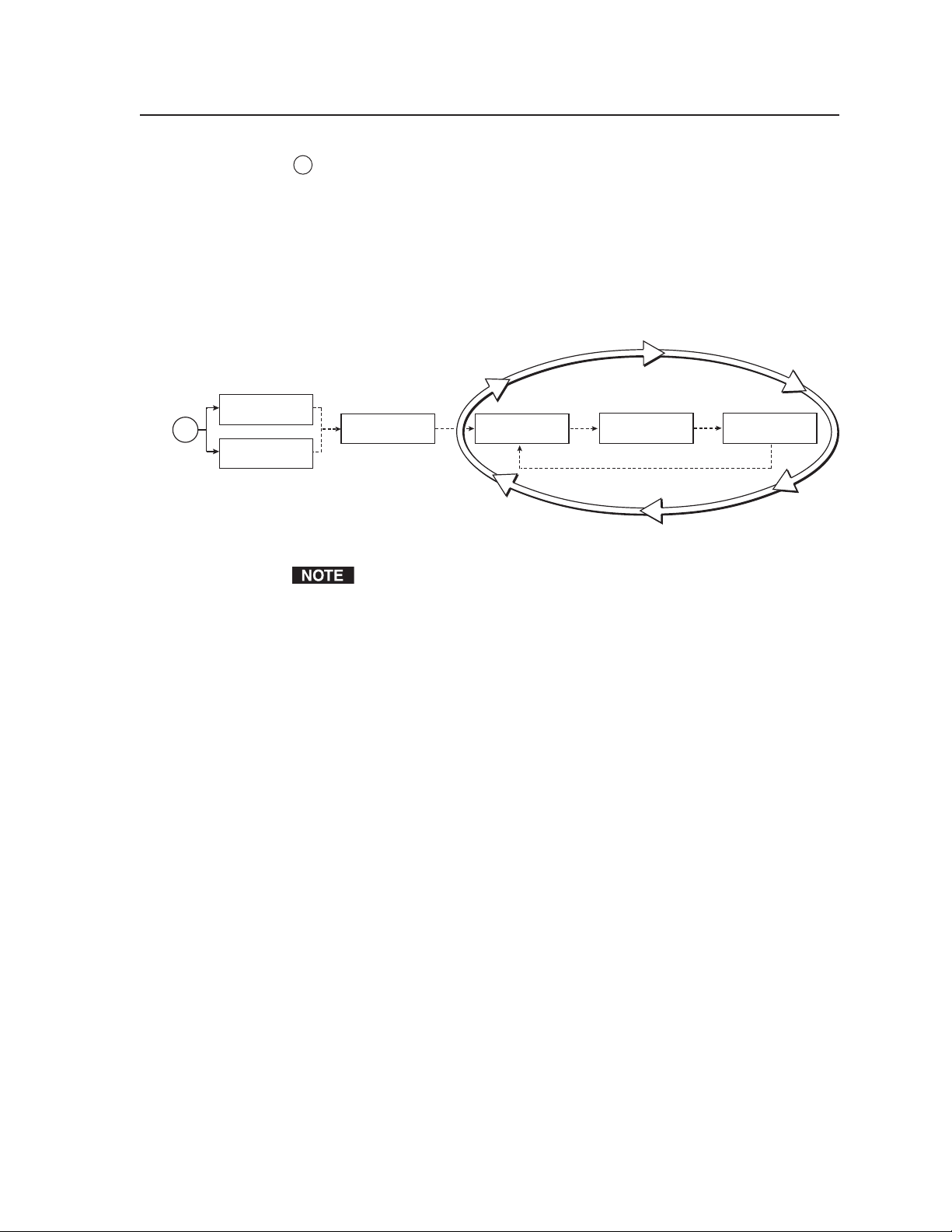
Power-up and Default Cycle
When you first plug the MGP 462 into a power source, the LCD screen displays a
series of initial messages, followed by the default cycle of screens. These screens
continue to display when the menu system is not in use. The following flow
diagram shows the order in which these screens appear.
Extron
Power
on
MGP 462D V2.01
MGP 462 V2.01
Extron
Default cycle
Multi-Graphic
Processor
2 sec.
From any menu or submenu, after 20 seconds of inactivity, the MGP 462
saves all adjustment settings and times out to the default screens.
2 sec.
Window 1
15.7 kHz 59.9 Hz
Default Cycle
2 sec.
Window 2
Freeze Enabled
2 sec.
Output Rate
1024 x 768 @ 60 Hz
2 sec.
Input Selection
The MGP 462 front panel contains two sets of six input buttons, which enable you
to select inputs for windows 1 and 2.
• To select an input, press the button containing the number of the input you
want to enable.
o To select the input for window 1, press an input button in the top row.
o To select the input for window 2, press an input button in the bottom
• To mute a selected input (turn off its signal and close the window), press its
button again. The button blinks continuously, indicating that the input is
muted.
When a window is muted or unmuted (opened or closed), the currently
selected transition effect (cut, wipe, or dissolve) is used to open or close the
window on the screen. See Window effects submenu in the Window
Configuration menu section, later in this chapter, for information on transition
effects.
To unmute the input, press its button again. The button’s backlight stops
flashing and returns to a steady light.
The button you pressed lights green.
row. The button you pressed lights red.
3-3MGP 462 • Operation
Page 26

Operation, cont’d
Window Selection Buttons
The MGP 462 front panel contains two Window buttons, located to the right of the
two input 6 buttons. Use these buttons with the picture control buttons to select
the window to be adjusted. When you select a picture control, it affects the selected
window. (Refer to Picture Controls, later in this chapter, for information on the
available controls.)
Select window 1 by pressing the top window button, which lights green. To select
window 2, press the window button on the bottom, which lights red.
To deselect a window, either press its button again, or press the other window
button.
Menus, Configuration, and Adjustments
The MGP 462’s menus enable you to configure the processor. The menu navigation
buttons, Menu and Next, are located immediately to the right of the LCD screen.
Press these buttons to cycle through the available menu and submenu options.
Menu system overview
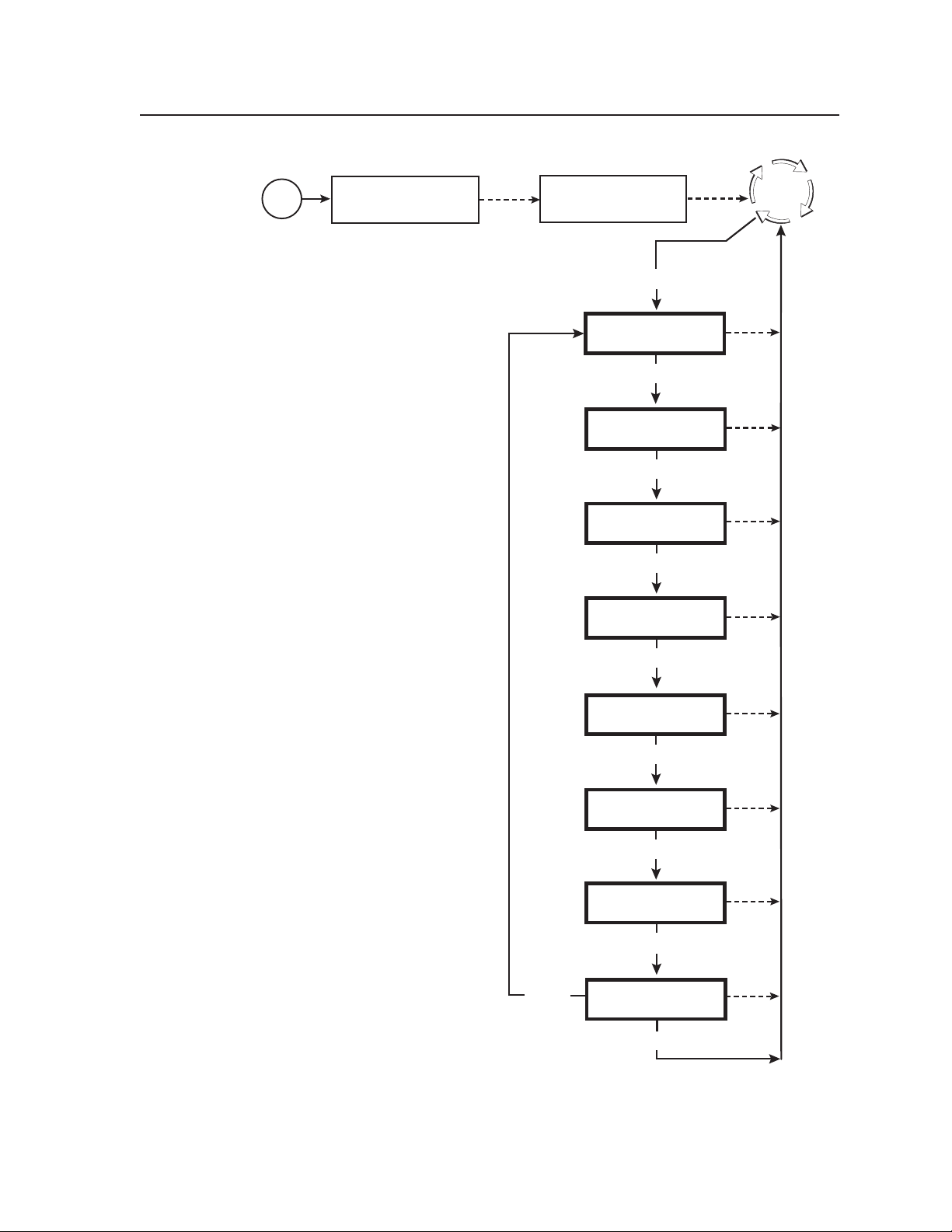
The MGP 462’s menu system consists of a main menu of eight options (menus).
Each of these menus has a set of submenus, which enable you to make desired
adjustments. (See the diagram on the next page.)
Using the menus
To use the menus to configure the system, follow these steps.
If you do not press a button or turn a knob for 20 seconds, the MGP 462 saves
any settings you have made, and the LCD screen reverts to the default cycle.
1. Main menu — To access the Main menu, press the Menu (top) button, located
to the right of the LCD screen. The first Main menu option (Auto Image) is
displayed on the screen.
2. Main menu options — By repeatedly pressing the Menu button, you display
additional menus. Press the Menu button repeatedly until the desired menu
is displayed.
3. Submenu options — When the Main menu item that you want to configure is
displayed on the LCD screen, press the Next button (below the Menu button)
to cycle through the displayed item’s submenu options.
4. Adjustments — The third level of menu selections consists of sub-options
that are selected by turning the horizontal (
When you have displayed the submenu option that you want to configure,
turn the knobs clockwise or counterclockwise to display each available
parameter for the selected option.
5. Implementation — To save and implement the adjustments you have
selected, do one of the following:
• Press Next to display another submenu option to adjust.
• Press Menu to return to the Main menu.
• Do nothing, and wait until the LCD screen returns to the default cycle.
Your adjustments remain in effect until you change them.
) and vertical ( ) Adjust knobs.
MGP 462 • Operation3-4
Page 27
Power
on
Extron
MGP 462 V2.01
2 sec.
Multi-Graphic
Processor
2 sec.
Default
Cycle
MENU
Auto
Image
20 sec.
MENU
Input
Configuration
20 sec.
MENU
Output
Configuration
20 sec.
MENU
Window
Configuration
20 sec.
Main menu flow
MENU
MENU
Window Text
Configuration
MENU
Background
Capture
MENU
Advanced
Configuration
MENU
Exit Menu
Press Next
NEXT
20 sec.
20 sec.
20 sec.
60 sec.
3-5MGP 462 • Operation
Page 28
Operation, cont’d
Auto Image menu
The Auto Image menu causes the MGP 462 to perform an automatic image
adjustment to the selected window. Auto Image measures where the active area
starts and stops, and adjusts input sampling accordingly.
When Auto Image is performed, the processor measures the sync frequencies of
the incoming video source and sets the active image area, total image area, and
sampling frequency according to a table stored on the MGP. If an unknown input
is connected to the MGP, the processor measures and estimates the resolution of
the incoming video. If the estimate proves not to be accurate, the Auto Image
function makes measurements to more accurately set up the input sampling.
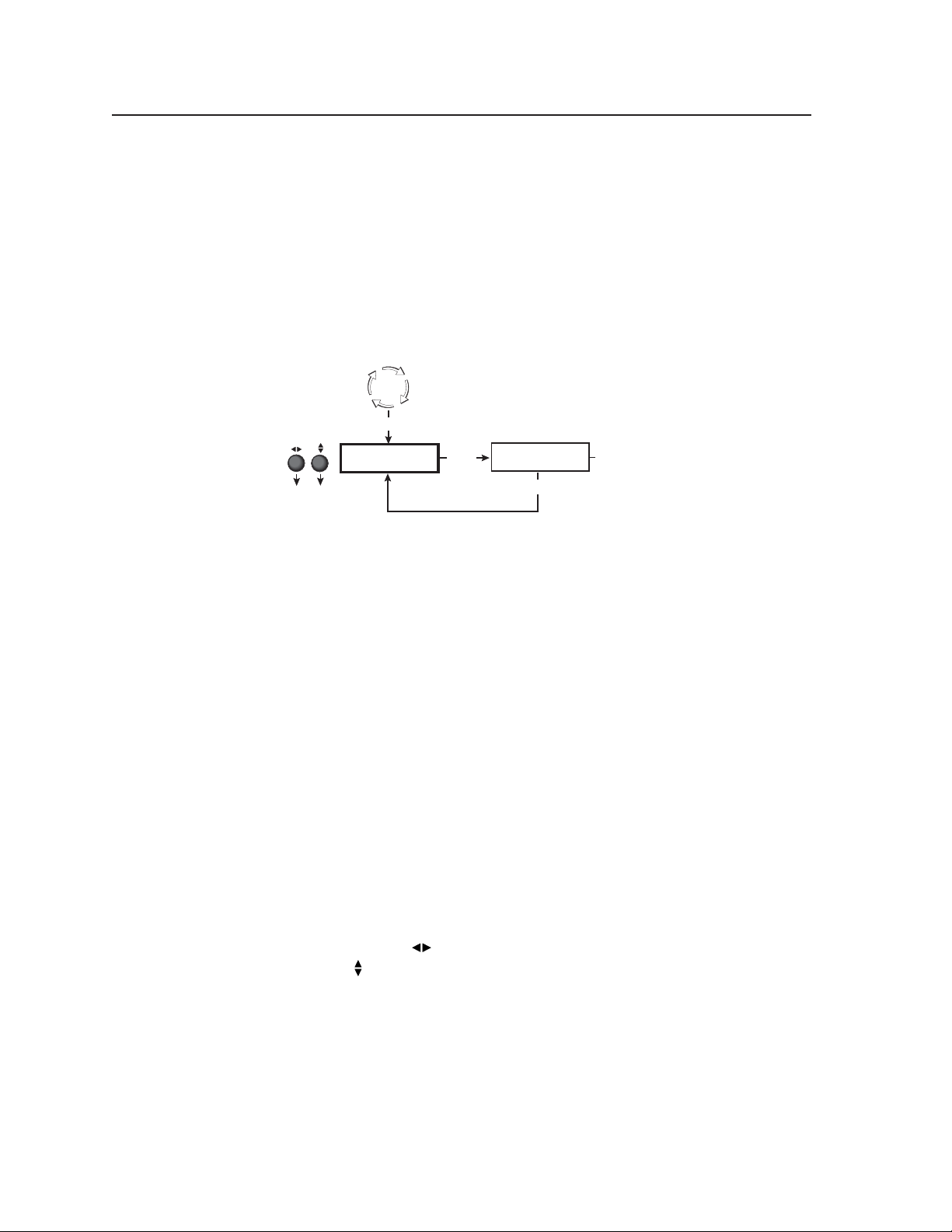
Use either Adjust knob
to adjust the submenu.
Auto Image menu flow
Default
Cycle
MENU
Auto
Image
NEXT
Auto Image
<NA> Win1 Win2
NEXT
Auto Image adjustment
Select the window on which
to perform an Auto Image adjustment.
Select NA to perform no adjustment.
To perform an Auto Image adjustment, do the following:
1. Press the Menu button once to display the Auto Image menu.
2. Press the Next button once to display the available option.
3. Rotate the horizontal ([) or vertical ({) Adjust knob to select the window for
which you want to perform Auto Image.
4. Press Next again to initiate the Auto Image adjustment.
5. If desired, repeat steps 3 and 4 to perform Auto Image in the other window.
6. When finished with Auto Image, do one of the following:
• Select NA and press Next.
Press the Menu button.
•
• Do nothing and wait for the menu to time out and return to the default
cycle.
Input Configuration menu
The Input Configuration menu allows you to select the type of video signal that
each of the six inputs will pass. You can also select the horizontal and vertical start
positions, pixel sampling phase for windows 1 and 2 (except for YUVi, S-video, and
composite video), total pixels, active pixels, and active lines for each input. Rotate
the horizontal Adjust ( ) knob to cycle through the six inputs, and the vertical
Adjust knob (
) to select settings.
MGP 462 • Operation3-6
Page 29
Auto
Image
MENU
The following diagram shows the submenus of the Input Configuration menu and
the adjustments that can be made from them.
NEXT
Input
Configuration
Input #1
Active Lns 1024
Input
• Input #1
• Input #2
• Input #3
• Input #4
• Input #5
• Input #6
Active Lines
Specify the height
in lines of the
active image area
to be sampled.
NEXT
NEXT
Input #1
RGB
Input
Input video type*
Select a signal format:
• Input #1
• Input #2
• RGB
• YUVp
• Input #3
• RGBcvS
• Input #4
• YUVi
• Input #5
• S-video
• Input #6
• Composite
Input #1
Active Pxl 1280
Input
• Input #1
• Input #2
• Input #3
• Input #4
• Input #5
• Input #6
• SDI (MGP 462D only)
* Video types available and default
settings vary with the input selected.
Active Pixels
Specify the width
in pixels of the
active image area
to be sampled.
NEXT
NEXT
Input #1
Film Mode ON
Input
• Input #1
• Input #2
• Input #3
• Input #4
• Input #5
• Input #6
Input #1
Total Pxl 1688
Input
• Input #1
• Input #2
• Input #3
• Input #4
• Input #5
• Input #6
NEXT
Film Mode
Turn Film Mode on
or off (for lowresolution devices).
NEXT
Total Pixels
Specify the width in
pixels of the total
image area to be
sampled.
Input #1
Vert Start 0128
Input
• Input #1
• Input #2
• Input #3
• Input #4
• Input #5
• Input #6
Input #1
Pxl Phase#2 16
Input
• Input #1
• Input #2
• Input #3
• Input #4
• Input #5
• Input #6
Vertical Start
Select a vertical
start line position
for the top edge of
the active video.
Pixel Phase 2
Adjust the pixel
sampling point for
window 2 for each
input.
Input Configuration menu flow
The following table lists the signal types available for each input.
NEXT
NEXT
Input #1
Horz Start 0128
Input
• Input #1
• Input #2
• Input #3
• Input #4
• Input #5
• Input #6
Input #1
Pxl Phase#1 16
Input
Input
• Input #1
• Input #1
• Input #2
• Input #2
• Input #3
• Input #3
• Input #4
• Input #4
• Input #5
• Input #5
• Input #6
• Input #6
NEXT
Horizontal Start
Select a horizontal
start pixel position
for the left edge of
the active video.
Pixel Phase 1
Adjust the pixel
sampling point for
window 1 for each
input.
Input video signal types
Signal Type Input 1 Input 2 Input 3 Input 4 Input 5 Input 6
RGB*** X* X* X* X*
YUVp XXXX
RGBcvS_ XXXX
YUVi XXXX X
S-video XXXX XX
Composite XXXX X*X*
SDI X**
* Default
** MGP 462D only
*** RGBHV, RGBS, and RGsB are accepted with this input setting.
3-7MGP 462 • Operation
Page 30
Operation, cont’d
Input configuration submenu adjustments
The table below shows which Adjust knob to use to make the selections and
adjustments that are accessed through the Input Configuration submenus.
Input Configuration submenu Horizontal knob adjustment Vertical knob adjustment
Video type
The following video signal types are
accepted:
RGB S-video
YUVp Composite video
YUVi SDI (MGP 462D only)
RGBcvS
Film mode
For low resolution inputs. The video
signal type for the input you are
configuring must be set to YUVi,
composite video, or S-video in order
to place the input in Film mode.
Vertical start position
Distance in lines from the top edge
of the input's total video display area
to the top edge of its active area
Horizontal start position
Distance in pixels from the left edge
of the input's total video display area
to the left edge of its active area
Pixel phase 1
The point at which pixels are
sampled for window 1. (The values
cannot be changed when the input is
YUVi, S-video, or composite video.)
Pixel phase 2
The point at which pixels are
sampled for window 2. (The values
cannot be changed when the input is
YUVi, S-video, or composite video.)
Select input #1-6. Select the desired video format for the
Select input #1-6.
Shows current Film mode status
for the displayed input:
ON, OFF, or na (not applicable).
Select input #1-6.
Shows the current vertical start
point for the displayed input.
Select input #1-6.
Shows the current horizontal
start point for the displayed
input.
Select input #1-6 for window 1. Increase or decrease the displayed value to
Select input #1-6 for window 2. Increase or decrease the displayed value to
displayed input.
Defaults:
Inputs 1-4 − RGB
Inputs 5 and 6 − Composite
Select ON or OFF to turn 3:2 or 2:2 pulldown
(Film mode) on and off for the selected input.
Increase or decrease the value indicating the
distance in lines from the top edge of the video
display's total area to the top edge of its active
area. The default is 128.
Increase or decrease the value indicating the
distance in pixels from the left edge of the
video display's total area to the left edge of its
active area. The default is 128.
move the pixel sampling point for window 1
in to an optimal sampling point that ensures
output clarity. The range of settings is 0-31;
the default is 16.
move the pixel sampling point for window 2
to an optimal sampling point that will ensure
output clarity. The range of settings is 0-31;
the default is 16.
Total pixels
Width in pixels of the total video
display area. (The values cannot be
changed when the input is YUVi,
S-video, or composite video.)
Active pixels
Width in pixels of the active video
area
A
ctive lines
Height in lines of the active video
area
MGP 462 • Operation3-8
Select input #1-64. Increase or decrease the width in pixels of the
Select input #1-6. Increase or decrease the width in pixels of the
Select input #1-6. Increase or decrease the height in lines of the
total video display area of the selected input.
The default is marked with an asterisk (*).
active video area of the selected input. The
default is marked with an asterisk (*).
active video area of the selected input. The
default is marked with an asterisk (*).
Page 31

Output Configuration menu
The Output Configuration menu allows you to set the output resolution, refresh
rate, output type, and sync polarity. The following flow diagram shows the
submenus of the Output Configuration menu, and the adjustments that can be
made from them.
The menus time out and return to the default cycle after 20 seconds of
inactivity. However, any selections you made with the Adjust knobs are saved
and remain in effect.
Input
Configuration
MENU
Output
Configuration
Resol 1024 x 768
NEXT
Refresh @60 Hz
Resolution Refresh rate
See the following table for available
combinations of resolutions and
refresh rates.
Default: 1024 x 768 @60 Hz
NEXT
Output configuration menu flow
Output Type
RGBHV
Video signal types
• RGBHV / RGBS (default)
• RGsB
• YUV Bi-Lvl (Current NTSC
standard)
• YUV TriLvl (Current HDTV
standard)
NEXT NEXT
Sync Polarity*
H Neg V Neg
Polarity combinations
• H Neg V Neg (default)
• H Neg V Pos
• H Pos V Neg
• H Pos V Pos
*Appears only when sync polarity is
applicable, based on other output settings.
3-9MGP 462 • Operation
Page 32

Operation, cont’d
Resolution and Refresh Rate submenu
Rotate the horizontal Adjust ([) knob while in this submenu to select from one of
the available resolutions. Rotate the vertical Adjust ({) knob while in this submenu
to select one of the available refresh rates. The available resolution and refresh
rates are listed in the following table.
Resolution
640 x 480 XXXX X X
800 x 600 XXXX X X
852 x 480 XXXX X
1024 x 768 XXXX
1024 x 852 XXXX
1024 x 1024 X X X
Available Scaler Output Resolutions and Rates
Refresh rates
50 Hz 60 Hz 72 Hz 96 Hz 100 Hz 120 Hz
1280 x 768 X
1280 x 1024 X X
1360 x 765 X
1365 x 768 X
1365 x 1024 X
1366 x 768 X
1400 x 1050 X X
1600 x 1200 X X
480p X
576p X
720p (HDTV) X X
1080i (HDTV) X X
1080p (HDTV) X X
MGP 462 • Operation3-10
Page 33

Rotate either Adjust knob
to adjust the submenus.
Output Type submenu
Rotate either the horizontal Adjust ( ) or the vertical Adjust ( ) knob to select the
output signal type required by the display device. Available signal types are
RGBHV, RGsB, YUV bi-level and YUV tri-level. The default is RGBHV.
Combined H and V Sync (S) is available on the “S” BNC connector when the
unit is set to RGBHV.
Sync Polarity submenu
The display device may require a particular combination of horizontal (H) and
vertical (V) sync signal polarities. Rotate either the horizontal Adjust (
vertical Adjust (
) knob to select the sync polarity. The options are H-V-, H+V-,
H-V+, H+V+, or na (appears when YUV Bi-lvl or YUV TriLvl is selected). The
default is H-V-.
This submenu appears only when sync polarity is applicable based on the other
selected output settings.
Window Configuration menu
The Window Configuration menu allows you to set window front/back priority,
add colored borders to the windows, select which window transition effect to use
when muting (closing) a window, and specify the duration of the selected effect.
Output
Configuration
MENU
Window
Configuration
NEXT
Window Priority
F 2 <1> B
NEXT
Window 1 Border
None
NEXT
Window 2 Border
None
NEXT
Window priority
• 1 2 (default)
• 2 1
Window 1 border color
• None (default) • Magenta
• Red • Cyan
• Green • Yellow
• Blue • Black
• White
Window 2 border color
• None (default) • Magenta
• Red • Cyan
• Green • Yellow
• Blue • Black
• White
Window Effect
Cut
NEXT
Effect Duration
0.5 second(s)
NEXT
) or the
Window effect
• Cut (Default) • Soft Wipe Curtain Out
• Dissolve • Hard Wipe Up
• Soft Wipe Up • Hard Wipe Down
• Soft Wipe Down • Hard Wipe Right
• Soft Wipe Right • Hard Wipe Left
• Soft Wipe Left • Hard Wipe Center In
• Soft Wipe Center In • Hard Wipe Center Out
Wipe Center Out • Hard Wipe Square In
• Soft
• Soft Wipe Square In • Hard Wipe Square Out
• Soft Wipe Square Out • Hard Wipe Curtain In
• Soft Wipe Curtain In • Hard Wipe Curtain Out
Effect duration (in seconds)
• 0.0 to 5.0 seconds
in 0.1 second increments
(default is 0.5)
Window Configuration menu flow
The menus time out and return to the default cycle after 20 seconds of
inactivity. However, any selections you made with the Adjust knobs are saved
and remain in effect.
Window Priority submenu
The Window Priority submenu allows you to set how the windows will overlap
one another. The submenu lists the two windows in order of their priority, from
left to right. Rotate the vertical Adjust (
) knob to switch the priority between
windows 1 and 2. (You do not use the horizontal Adjust knob with this submenu
on the MGP 462.)
3-11MGP 462 • Operation
Page 34

Operation, cont’d
Window 1 Border and Window 2 Border submenus
Use these submenus to select border colors for the two windows. Available options
are Red, Green, Blue, White, Magenta, Cyan, Yellow, and Black. You can also select
None (no border), which is the default setting.
Window Effect submenu
Use this submenu to select a transition effect for the MGP 462 to use when muting
and unmuting windows. To select a transition effect, follow these steps:
1. Press the Menu button repeatedly until Window Configuration is displayed
on the LCD screen.
2. Press the Next button repeatedly until Window Effect is displayed.
3. Rotate either the horizontal Adjust (
select a transition effect.
Available effects
Cut — A cut instantly mutes or unmutes the window. The effect duration does not
apply.
Dissolve — A dissolve causes the window to fade out.
Dissolve
Standard wipe (soft wipe or hard wipe) — A standard wipe causes the new
Center wipe — A center wipe causes the new window to appear to unroll over the
Dissolve
window to appear to unroll over the other one. The new window can roll
from the top, bottom, left, or right side of the window. A soft wipe has a
fuzzy leading edge; a hard wipe has a sharp edge.
other one in one of two ways:
) or the vertical Adjust knob ( ) to
• In from the top and bottom edges to the center of the window
• Out from the center to the top and bottom edges of the window
A center wipe can have a soft (fuzzy) leading edge or a hard (sharp) one.
MGP 462 • Operation3-12
Page 35

Square wipe — A square wipe causes the new window to appear to unroll over the
other one in one of two ways:
• In from the top, bottom, right, and left edges to the center of the
window
• Out from the center to the four edges of the window
This effect creates a square shaped transition.
A square wipe can have a soft (fuzzy) leading edge or a hard (sharp) one.
Curtain wipe — A curtain wipe causes the new window to appear to unroll over
the other one in one of two ways:
• In from the left and right edges to the center of the window
• Out from the center to the right and left edges of the window
A curtain wipe can have a soft (fuzzy) leading edge or a hard (sharp) one.
Effect Duration submenu
Use this submenu to set the amount of time it takes the MGP 462 to complete a
transition effect. Select from durations ranging from 0.0 to 5.0 seconds, in 0.1
second increments. (Duration is not available with the cut effect.)
To set an effect duration, follow these steps:
1. Press the Menu button until Window Configuration is displayed on the LCD
screen.
2. Press the Next button until Effect Duration is displayed.
3. Rotate either the horizontal Adjust (
select an effect duration.
) or the vertical Adjust ( ) knob to
3-13MGP 462 • Operation
Page 36

Operation, cont’d
Window Text Configuration menu
This menu enables you to add a text box, containing up to 16 characters, to each
window. The submenus allow you to enter the text for the label; select an on-screen
position where the text will appear; and specify colors for the text, the text box
background, and the border around the text.
Window
Configuration
MENU
Window Text
Configuration
Rotate ether Adjust knob
to adjust the submenus
(except for Text Label screens).
NEXT
Win Txt Position
None
NEXT
Window Text Size
Medium
NEXT
Win 1 Text Color
Black
NEXT
Win 2 Text Color
Black
NEXT
Win 1 Text Bkgnd
White
NEXT
Window text position
• None (Default) • Top Left
• Bottom Left • Top Center
• Bottom Center • Top Right
• Bottom Right
Window text size
• Small
• Medium (Default)
• Large
Window 1 text color
• Red • Magenta
• Green • Cyan
• Blue • Yellow
• White • Black (Default)
Window 2 text color
• Red • Magenta
• Green • Cyan
• Blue • Yellow
• White • Black (Default)
Window 1 text background
• Off • Magenta
• Red • Cyan
• Green • Yellow
• Blue • Black
• White (Default) • Translucent
Win 2 Text Bkgnd
White
NEXT
Win 1 Text Border
Black
NEXT
Win 2 Text Border
Black
NEXT
Win 1 Text Label
_ _ _ _ _ I
n p u t 1 _ _ _ _ _
NEXT
Win 2 Text Label
_ _ _ _ _ I
n p u t 1 _ _ _ _ _
Window 2 text background
• Off • Magenta
• Red • Cyan
• Green • Yellow
• Blue • Black
• White (Default) • Translucent
Window 1 text border
• Off • Magenta
• Red • Cyan
• Green • Yellow
• Blue • Black (Default)
• White • Translucent
Window 2 text border
• Off • Magenta
• Red • Cyan
• Green • Yellow
• Blue • Black (Default)
• White • Translucent
Move cursor
between
spaces.
Select
character.
Window Text Configuration menu flow
Window Text Position submenu
The Window Text Position submenu lets you place a text box at a specified location
on a window.
Rotate either the horizontal Adjust (
) or the vertical Adjust ( ) knob to select one
of the available text positions: Bottom Left, Bottom Center, Bottom Right, Top Left, Top
Center, or Top Right.
To turn off window text, select None (the default).
Window Text Size submenu
The Window Text Size submenu allows you to select the size of the text in the
window text box.
Rotate either the horizontal Adjust (
) or the vertical Adjust ( ) knob to select one
of the available text sizes: Small, Medium, or Large. The default is Medium.
Windows 1 and 2 Text Color submenus
The Windows 1 and 2 Text Color submenus let you select the color of the text
within the text box you place on window 1 or window 2.
Rotate either the horizontal Adjust (
) or the vertical Adjust ( ) knob to select one
of the available window text colors. Options are Red, Green, Blue, White, Magenta,
Cyan, Yellow, or Black. Black is the default.
MGP 462 • Operation3-14
Page 37

WIndows 1 and 2 Text Background submenus
The Windows 1 and 2 Text Background submenus let you select a background color
for the text box you place on window 1 or window 2.
Rotate either the horizontal Adjust (
of the available background colors. Options are Red, Green, Blue, White, Magenta,
Cyan, Yellow, Black, or Translucent. (Translucent provides a semitransparent
background for the text, through which the video behind the text box is faintly
visible.) The default is White.
) or the vertical Adjust ( ) knob to select one
WIndows 1 and 2 Text Border submenus
The Windows 1 and 2 Text Border submenus let you select a color for the border of
the text box you place on window 1 or window 2.
Rotate either the horizontal Adjust (
of the available border colors. Options are Red, Green, Blue, White, Magenta, Cyan,
Yellow, Black, or Translucent. (Translucent provides a semiopaque border through
which the window background can be seen.) The default is Black.
) or the vertical Adjust ( ) knob to select one
Windows 1 and 2 Text Label screens
The Windows 1 and 2 Text Label screens enable you to create text in a text box to
place on window 1 and/or window 2. The text is associated with the current input.
The Text Label screens provide 16 spaces in which you can enter characters.
The default LCD display for Text Label shows the word Input and the number of
the input that has been selected, preceded and followed by five dashes. (See the
example below.)
-----Input1-----
You can replace these characters with other characters by turning the Adjust knobs
as follows:
• Rotate the horizontal Adjust ( ) knob to move the cursor (which appears as
an underscore) to the space you want to change.
• Rotate the vertical Adjust ( ) knob to change the character displayed in the
selected space.
The following characters are available:
Symbols: : / – + " _
Numerals: 0 through 9
Letters: Lowercase a through z, uppercase A through Z
Spaces
To remove a character space from the text box, select
characters so that the blank character is at the end of the line.
(blank character).
, then reposition the
3-15MGP 462 • Operation
Page 38

Operation, cont’d
Background Capture menu
The Background Capture menu allows you to capture the image that is currently
displayed on the output screen and save it as a bitmap (.bmp) file with one of 16
designated image names. You can then recall the image and use it as a background.
Background Capture also can be done via Ethernet, using the MGP 462 Web pages.
See chapter 5, Ethernet Control, for further information.
Window Text
Configuration
MENU
Background
Capture
Use either Adjust knob
to adjust the submenus.
Background Capture menu flow
NEXT
Save Bkgd to Mem
<none>
NEXT
Recall Bkgd Mem
<none>
NEXT
If None is selected
NEXT
[Detail] = Confirm
<bkgNN.bmp>
Recalling
<bkgNN.bmp>
DETAIL
Saving Backgrnd
Please Wait 10%
Recalled
<bkgNN.bmp>
Save current image
as a background
Select a name for the
background file being
saved: bkg01.bmp
through bkg16.bmp
Recall a background
Image from memory
Select an image
file name to recall for
use as background:
bkg01.bmp through
bkg16.bmp
Memory space for background files
The MGP 462 has 16 MB of user storage space that can be used for saved
backgrounds and uploaded user Web pages. The number of images that you can
save depends on the size (in kB) of the image bitmap file and the resolution. The
following table shows the number of images you can store based on different
resolutions.
Resolution 640 x 480 800 x 600 1024 x 768 1280 x 1024 1400 x 1050 1600 x 1200
Image size (KB) 900.00 1406.25 2304.00 3804.00 4306.64 5625.00
Total images 16* 11 6 4 3 2
*16 is the maximum number of images that can be saved as backgrounds.
To calculate the size of a bitmap file for any image of any specified size, use this
formula:
file size (in kilobytes) = (horizontal x vertical x 3)
+ +
+ 54(file header ID)
+ +
Saving a background to memory
To save the current image to memory for use as a background, follow these steps:
1. Press Menu repeatedly until the Background Capture screen is displayed.
Press Next once to display the Save Background to Memory submenu screen.
2. Rotate either Adjust knob to select a background file name (bkg01.bmp
through bkg16.bmp) with which to save the image.
You can save the background image only under one of the file names on this
menu; you cannot make up a different name for it.
If you do not want to save the image, select None, then press Next. The Recall
Background submenu screen is displayed.
3. Press the Next button to save the image as a bitmap (.bmp) file. The LCD
screen displays the message “[Detail] = Confirm filename.bmp.”
The unit supports 24-bit bitmap files only. Their file names must have the
format Bkgnn.bmp.
MGP 462 • Operation3-16
Page 39

CAUTION
The image that you save overwrites any existing image file with the
same file name.
4. Press the Detail button (the top button located at the immediate left of the
LCD screen).
The LCD screen displays the message “Saving Background Please Wait,”
along with an incrementing number showing the percent of the file that has
been captured. The time the MGP takes to save an image varies depending
on the image file size. For example, a 102 by 768 pixel image takes about 90
seconds to save.
The unit does not respond to any commands while it is saving an image.
5. If you want to recall a background file for the output display, press Next
within 20 seconds. (After 20 seconds, the MGP 462 returns to the default
cycle.)
Recalling a background from memory
To recall an image from memory for use as a background:
1. Access the Recall Background from Memory submenu.
2. Rotate either Adjust knob to select one of background image files (bkg01.bmp
through bkg16.bmp) to use as the output background.
To perform no action, press the Menu button.
3. Press the Next button to recall the image. The LCD screen displays the
message “Recalling filename.bmp” while the image is being recalled, then
“Recalled filename.bmp” after the recall is complete.
Rotate either Adjust knob
to adjust the submenus.
Advanced Configuration menu
Use the Advanced Configuration menu to set the background color, turn Blue
Mode on and off, select test patterns, and select the serial communication mode.
You can also view the MGP’s internal temperature and reset the unit to its factory
defaults.
Background
Capture
MENU
Advanced
Configuration
NEXT
Background Color
None
NEXT
Blue Mode
Off
NEXT
Test Pattern
Off
NEXT
* These test pattern types vary depending on the
output rate selected.
Background color
• None (default) • Magenta
• Red • Cyan
• Green • Yellow
• Blue • Stored-Image
• White • User Defined
Blue Mode
• Off (default)
• On
Test pattern type
• Off (default)
• ColorBars
• X-Hatch
• 4 x 4 X-Hatch
• Grey Scale
• Crop
• Ramp
• Alt. Pixels
• Side-By-Side*
• 1.78 Aspect*
• 1.85 Aspect*
• 2.35 Aspect*
Serial Port Mode
<RS232> RS422
NEXT
Internal Temp.
120.20F 49C
NEXT
Factory Default
[DETAIL]
NEXT
Serial Communications Mode
• RS232 (default)
• RS422
Unit Internal Temperature
Current internal temperature
expressed in degrees Fahrenheit
and Celsius. Not adjustable.
DETAIL
Factory Reset
Please Wait !!!
Factory Default
Press the DETAIL button
to reset the unit to its
factory default settings.
When finished, the system
returns to the default cycle.
Advanced Configuration menu flow
3-17MGP 462 • Operation
Page 40

Operation, cont’d
Background Color submenu
Rotate either Adjust knob to select a background color for the output screen.
Options are None, Red, Green, Blue, White, Magenta, Cyan, Yellow, Stored-Image, and
User Defined.
• None, the default setting, produces a black background.
• Stored-Image is the saved background that was most recently recalled. When a
captured background is recalled, the Stored-Image option is automatically
selected. Select this option if you want to return to the recalled background
after having changed to a different background color.
• User Defined is the background color that you can set by using an SIS
command. See chapter 4, Software Configuration and Control, for the command
syntax.
Blue Mode submenu
Blue Mode causes only sync and blue video signals to be passed to the display.
This can aid in the setup of the MGP 462’s color and tint. While in the Blue Mode
submenu, rotate either Adjust knob to turn Blue Mode on and off.
Test Pattern submenu
Several test patterns are available via this submenu to adjust the display device for
color, convergence, focus, resolution, contrast, grayscale and aspect ratio. Use
either Adjust knob to select a test pattern. The available patterns are:
• Color Bars
• X-Hatch (16 by 12 crosshatch)
• 4 x 4 X-Hatch (4 by 4 crosshatch)
• Grayscale (Grey Scale)
• Crop
• Ramp
• Alt. Pixels (alternating pixels)
• Side-By-Side (4 by 3 or 16 by 9 side by side crop)
• 1.78 Aspect (film aspect ratio 1.78)
• 1.85 Aspect (film aspect ratio 1.85)
• 2.35 Aspect (film aspect ratio 2.35)
The default setting is “Off.” The side-by-side crop and aspect ratio patterns
available from the submenu vary depending on the aspect ratio of the output rate.
MGP 462 • Operation3-18
Page 41

Color Bars (8) Crosshatch 16x12 Crosshatch 4x4 Grayscale
4x3 4x3
Ramp Alt Pixels Crop 4x3 Side-by-side Crop
4x3 4x3
1.78 Aspect Ratio 1.85 Aspect Ratio 2.35 Aspect Ratio 16x9 Side-by-side Crop
Test patterns available for the MGP 462
Serial Port Mode submenu
Use the Serial Port Mode submenu to select either RS-232 or RS-422 for the MGP’s
serial communication standard. Turn either Adjust knob to move the brackets on
the LCD screen to RS232 or RS422.
Internal Temperature screen
The Internal Temp submenu displays the unit’s current internal temperature. The
MGP 462 displays the temperature in degrees Fahrenheit and Celsius. This is an
information-only screen; no adjustments can be made on it.
Factory Default submenu
This submenu lets you reset the MGP 462 to the default settings with which it was
delivered from the factory. Press the Detail button (the top button immediately to
the left of the LCD screen) to initiate the reset.
Picture Controls
The MGP 462 has six picture control buttons located on the front panel to the left of
the LCD screen. You can use these buttons to adjust size, position, brightness and
contrast, color and tint, detail, and magnification (zoom).
The table on the next page shows the buttons, their functions, and how to make
adjustments. (In the Display column, n stands for a single digit, 0 through 9.)
Picture controls are window-dependent. You set the values separately for each
window.
For Window/Image Size, Window/Image Position, and Window Image Zoom,
pressing the button repeatedly switches back and forth between window
settings and image settings.
3-19MGP 462 • Operation
Page 42

Operation, cont’d
Adjusting the picture controls
Make image adjustments to an input using the picture control buttons on the front
panel. When you select a picture control button, it lights with the same color (green
or red) as the selected buttons for the window and input that it will adjust. When
you select a control button, the window button for the most recently adjusted
window lights, indicating that it is being adjusted. The table on the next page
shows the picture control adjustments that can be made from the front panel.
Button Display Function Range Adjust Knob
Window/
Image
Size
Bright/
Cont
Detail
Window/
Image
Position
WINDOW n SIZE:
H=nnnn V=nnnn
(Press button twice.)
IMAGE # n SIZE:
H=n V=n
BRIT CONT
nnnn nnnn
DETAIL
nnnn
WINDOW n START:
H=±nnnn V=±nnnn
(Press button twice.)
IMAGE #n START:
H=±nnnn V=±nnnn
Enlarge or shrink
window 1 or 2.
Enlarge or shrink the
image within the
window.
Brightness: Increase or
decrease intensity of
video light on screen.
Contrast: Increase or
decrease range of image
light and dark values.
Adjust image sharpness.
Position window 1 or 2
on the screen in relation
to the screen's center.
Position image within
the window in relation
to the window center.
Min: 1/16 of the
output rate
Max: Output rate
Min: 1/16 of the
output rate
Max: 2 times the
output rate
Brightness: 000-127
Default: 064
Contrast: 000-127
Default: 064
000 - 127
Default: 064
Default: 0000 ± the
output rate
Default: 0000 ± the
output rate
For H (width):
horizontal
Adjust knob
For V (height):
vertical
Adjust knob
Bright:
horizontal
Adjust knob
Contrast:
vertical
Adjust knob
Either
For H:
horizontal
Adjust knob
For V:
vertical
Adjust knob
Color/
Tin t
Window/
Image
Zoom
MGP 462 • Operation3-20
COLOR TINT
nnnn nnnn
WINDOW n ZOOM:
H=nnnn V=nnnn
(Press button twice.)
IMAGE #n ZOOM:
H=nnnn V=nnnn
Color: Adjust color
intensity. (At lowest
adjustment, all colors are
shades of gray.)
Tint: Change the
appearance of colors.
Increase/decrease the
size of the image in the
selected window while
keeping the aspect ratio
constant.
Increase/decrease the
size of the image in the
selected window while
keeping the aspect ratio
constant.
Color: 000 - 127
Default: 064
Tint: 000 - 127
Default: 064
Min: 1/16 of the
output rate
Max: Output rate
Min: 1/16 of the
output rate
Max: 2 times the
output rate
Color:
horizontal
Adjust knob
Tint:
vertical
Adjust knob
For H:
horizontal
Adjust knob
For V:
vertical
Adjust knob
Page 43

To adjust the picture controls, follow these steps:
1. Press the Input button for the input that you want to adjust, if it is not
currently selected.
2. Press the Window 1 or 2 button to select the window you want to adjust.
3. Press the button for the desired picture control: Window/Image Size
(sizing), Bright/Cont (brightness and contrast), Detail (sharpness), Window/
Image Position (centering), Color/Tint (color and tint), or Window/Image
Zoom (magnification).
4. Rotate the horizontal Adjust (
a level from the available range.
5. Repeat steps 1 through 4 for each image adjustment to be made for the
selected input/window.
Memory Presets
Window presets
The MGP 462 allows up to 25 window presets that save information for both
windows. Use the Preset Save/Recall and Enter buttons on the front panel to save
and recall presets to and from their specified memory locations. Window presets
can also be saved, recalled, and named using SIS commands via an RS-232/422
interface or the product Web pages using an Ethernet connection (see chapter 4,
Software Configuration and Control, and chapter 5, Ethernet Configuration and Control,
for more information).
The following settings can be saved in a window preset:
Window border color Label text color
Window priority Label border color
Window transition effect Label background color
Transition effect duration Window background setting
Label text size Window size/position
Label location Window mute status
) and/or vertical Adjust ( ) knobs to select
The LCD screen may display “na,” indicating that an adjustment is not
available, in place of a number if that adjustment does not apply to the
input’s video format.
Saving a window preset
To save a window preset using the front panel buttons, follow these steps:
1. Set the parameters listed above as desired for windows 1 and 2.
2. Press and hold the Preset Recall/Save button for at least 2 seconds. The
LCD screen displays the following:
WINDOW
PRESET
Save to #01
3. Rotate either Adjust knob to select one of the 25 available window preset
locations in which to save the settings. (These location numbers are also the
preset numbers.)
3-21MGP 462 • Operation
Page 44

Operation, cont’d
4. Press the Enter button to save the current window setting in the preset
location number you selected. The LCD screen shows a message indicating
that the preset is being saved to the selected memory location, followed by a
message that the preset has been saved.
The following examples show a preset saved to location 1.
WINDOW
PRESET
Saving to #01
WINDOW
PRESET
#01 SAVED
If you want to exit this menu without saving any changes, repeatedly press
the Preset Recall/Save button until the following message appears on the
LCD screen, then press the Enter button to exit the Window Presets dialog.
Recalling a window preset
To recall a window preset using the front panel buttons:
1. Press and release the Preset Recall/Save button. The following message
WINDOW
[ENTER] TO EXIT
appears on the LCD screen:
WINDOW
Recall #01 woINP
PRESET
PRESET
2. If you do not want to recall the input whose number was displayed when the
preset was saved, proceed to step 3.
If you want to recall the input with the preset, press the Preset Recall/Save
button again. The following message appears:
3. Use either Adjust knob to select a window preset number to recall.
MGP 462 • Operation3-22
Recall #01 wINP
If you select this option, the inputs change to display the sources that were
displayed at the time the preset was saved, along with all input settings
specified by input presets. (See Input presets, on the next page.)
WINDOW
PRESET
Page 45

4. Press the Enter button to recall the preset you selected. The LCD screen
shows a message indicating that the preset was recalled. The following
example shows a message indicating that preset 1 was recalled.
If you want to exit this menu without recalling a preset, repeatedly press the
Preset Recall/Save button until you see the message Window Preset [Enter] to
Exit. Press the Enter button to exit the Window Presets dialog.
Default presets
The following figure shows the factory default preset window configurations.
These presets can be used for any output rate. If you overwrite them, you can
recover them by selecting Factory Defaults from the Advanced Configuration
menu. (See Advanced Configuration menu, earlier in this chapter.)
Preset #1
Window
2
Window
1
Preset #5
Window
2
Window
1
Preset #9
Background Area (solid color)
Window
1
Background Area (solid color)
Window
2
WINDOW
PRESET
#01 RECALLED
Preset #2
Window
Window
Window
Window1Window
2
1
Preset #6 Preset #7
Window
2
1
Preset #10
Preset #3
Window
1
Window
2
Preset #4
Window
2
Window
1
Preset #8
Window
Window
1
2
2
Window
2
Window
1
Factory default preset configurations
Input presets
The MGP 462 has 128 input preset locations, to which you can save signal type,
input configuration settings, picture control settings, and window text for any of
the inputs. These presets can be saved and recalled using the SIS commands via
the RS-232/422 connection or via Ethernet using the MGP 462 Web pages (see
chapters 4 and 5 for further information).
The following settings are contained in the input presets:
Input Type Horizontal Start Total Pixels
Input Name Vertical Start Active Pixels
Film Mode On/Off Pixel Phase Active Lines
Brightness Contrast Color
Tint Detail (sharpness) Image Size/Position*
*Image size and position are saved as percent of the window, so that the input
preset can be used for any size window.
3-23MGP 462 • Operation
Page 46

Operation, cont’d
Additional Functions
Freeze mode
The front panel Freeze buttons are the first buttons on the left. Press these buttons
to freeze the current image from the currently selected input in window 1 (top
button) and/or window 2 (bottom button). When the Freeze button for a window
is selected, it lights orange. You can also freeze the windows using the Windowsbased configuration software or SIS commands via the RS-232/422 connection.
If you switch inputs while a window is frozen, the freeze mode is cancelled and the
new input’s image appears in the window.
Front panel security lockout (executive mode)
To prevent access by unauthorized users or accidental changes to the MGP 462’s
settings, some of the front panel controls can be locked using executive mode.
When you place the MGP in executive mode via the front panel, the picture control
buttons and the menu selection buttons are locked. All other functions (input and
window selection, freezing, and preset saving and recalling remain accessible. The
RS-232/422 and Ethernet ports also remain unlocked.
You can enable or disable executive mode when the system is in the default cycle.
To turn executive mode on and off, press the Window/Image Size and the
Window/Image Position buttons simultaneously, and hold them for at least
2 seconds. The default is Disabled.
You can also enable and disable executive mode by using the SIS commands or the
Windows-based control software via the RS-232/422 interface (see chapter 4,
Software Configuration and Control, for more information).
If you place the MGP in executive mode by using SIS commands or the
Windows-based control software, you have an additional type of executive
mode available. In executive 2 mode, all the front panel controls are locked.
This mode is available only through SIS commands. See chapter 4, Software
Configuration and Control, for information on SIS commands, or the
control software’s Help program.
Resetting the unit
There are four reset modes (numbered 1, 3, 4, and 5 for the sake of comparison with
Extron IPL products) that you can access by pressing the Reset button on the rear
panel. The Reset button is recessed, so use a pointed stylus, ballpoint pen, or
Extron Tweeker to press it. See the table on the next page for a summary of the
reset modes.
CAUTION
The reset modes listed in the table close all open IP and Telnet connections and
close all sockets. Also, each mode is a separate function, not a continuation
from mode 1 to mode 5.
Review the reset modes carefully. Using the wrong reset mode may result
in unintended loss of flash memory programming, port reassignment, or
processor reboot.
MGP 462 • Operation3-24
Page 47

Reset Mode Comparison/Summary
Mode
Activation Result Purpose/Notes
1 Hold down the
3 Hold down the Reset
4 Hold down the Reset
5 Hold down the Reset
recessed Reset button
while applying power
to the unit.
button for about 3
seconds, until the Reset
LED blinks once. Then,
within 1 second, press
Reset again briefly (for
less than 1 second).
button for about 6
seconds, until the Reset
LED has blinked twice
(once at 3 seconds, once
at 6 seconds). Then,
within 1 second, pr
Reset briefly (for less
than 1 second).
button for about 9
seconds, until the Reset
LED has blinked three
times (once at 3
seconds, once at 6 sec.,
once at 9 seconds).
Then, within 1 second,
pr
ess Reset briefly (for
less than 1 second).
ess
Mode 1 causes the MGP 462 to revert to
the factory default firmware. Event
scripting does not start if the unit is
powered on in this mode. All user files
and settings (drivers, audio adjustments,
IP settings, etc.) are maintained.
Mode 3 turns events on or off. During
setting, the Reset LED flashes 2 times if
re
events are starting; 3 times if events are
stopping.
Mode 4 does the following:
• Enables ARP capability.
• Sets the IP address back to factory
default.
• Sets the subnet back to factory default.
• Sets the default gateway address back
to the factory default.
• Sets port mapping back to factory
default.
• Turns DHCP
• Turns all events off.
The Reset LED flashes 4 times in quick
succession during reset.
Mode 5 performs a complete reset to
factory defaults (except the firmware).
• Does everything mode 4 does.
• Resets everything that was set via the
Real Time Adjustments part of the
contr
and miscellaneous options.
• Resets all IP options.
• Removes/clears all files from the
processor.
The Reset LED flashes 4 times in quick
succession during the reset.
off.
ol program: all video settings
Use mode 1 to
remove a version of
firmware if
incompatibility
issues arise.
Events must be
turned on if you
want to change IP
settings or
scheduling.
Mode 4 enables you
to set IP address
information using
ARP and the MAC
address.
Mode 5 is useful if
you want to start
over with control
software
configuration and
uploading, and to
eplace events.
r
3-25MGP 462 • Operation
Page 48

Operation, cont’d
MGP 462 • Operation3-26
Page 49

MGP 462 Multi-Graphic Processor
Chapter Four
4
Software Configuration
and Control
Setting Up RS-232/RS-422 Communication
Using Simple Instruction Set (SIS
Using the Windows
Using the Button Label Generator
®
-based Control Software
™
) Commands
Page 50

Software Configuration and Control
Setting up RS-232/RS-422 Communication
The MGP 462’s RS-232/422 port is used to connect the MGP to a host or external
controlling device, such as a computer or control system, which can generate the
proper command codes and recognize the processor’s responses.
The cable used to connect the RS-232/422 port to a computer or control system
may need to be modified by removing pins or cutting wires. If unneeded pins
are connected, the processor may cease to function. See chapter 2,
Installation, for more information on wiring the
connectors.
The RS-232/422 connector on the rear panel is a 9-pin D female
connector (see the illustration at right) with the following pin
assignments.
51
96
Female
Pin RS-232 function Description
1 – No connection
2 Tx Tra nsmit data
3 Rx Receive data
4 – No connection
5 Gnd Signal ground
6 – No connection
7 – No connection
8 – No connection
9 – No connection
Pin RS-422 function Description
1 – No connection
2 Tx- Transmit ground
3 Rx- Receive ground
4 – No connection
5 Gnd Signal ground
6 – No connection
7 Rx+ Receive data
8 Tx+ Tr ansmit data
9 – No connection
Connector pin assignments
There are several programs that enable you to connect the MGP 462 to a computer
or control device via the RS-232/422 interface, and to enter commands.
HyperTerminal for Windows is one such program that is commonly used on PCs.
For any program that you use, set up communication using the following protocol:
Baud rate: 9600
Data bits: 8
Parity: None
Stop Bits: 1
Flow Control: None
Using Simple Instruction Set (SIS™) commands
Host-to-MGP communications
The MGP 462 accepts SIS (Simple Instruction Set) commands through the
RS-232/422 port. SIS commands consist of one or more characters per command
field. They do not require any special characters to begin or end the command
character sequence. Each response to an SIS command ends with a carriage return
and a line feed (CR/LF = ), which signals the end of the response character
string. A string is one or more characters.
MGP-initiated messages
When a local event such as a front panel selection or an adjustment takes place, the
MGP 462 responds by sending a message to the host. No response is required
from the host. Examples of MGP-initiated messages are listed below (underlined).
(C) Copyright 2006, Extron Electronics, MGP462, Vx.xx
The MGP 462 sends the copyright message when it is first powered on. Vx.xx is
the firmware version number.
MGP 462 • Software Configuration and Control4-2
Page 51

Out nn In nn (where Out nn is the window number, and In nn is the input
number).
The MGP 462 sends this response when an input is switched.
Error responses
When the MGP 462 receives a valid SIS command, it executes the command and
sends a response to the host device. If the MGP is unable to execute the command
because the command is invalid or contains invalid parameters, it returns an error
response to the host. The error response codes are:
E01 — Invalid input channel number (too large)
E09 — Invalid function number (too large)
E10 — Invalid command
E11 — Invalid preset number
E12 — Invalid output number (applies for addressing windows)
E13 — Invalid value (out of range)
E14 — Invalid command for this configuration
E17 — Invalid command for signal type
E24 — Privilege violation
E26 — Maximum number of users connected has been exceeded
E27 — Invalid event number
E28 — Bad filename/File not found
Error response references
The following superscripted numbers are used within the command descriptions
on the following pages to identify commands that may respond as shown:
14
= Commands that give an E14 (not valid for this configuration) response if the
unit’s current configuration doesn’t support that command
24
= Commands that give an E24 (privilege violation) response if you are not
logged in at the administrator level.
27
= Commands that may yield an E27 (invalid event number) response.
28
= Commands that may give an E28 (file not found) response.
Telnet and Web communications
The MGP 462 can also be controlled via an IP connection using either Telnet
(port 23) or a Web browser (port 80). The ASCII and URL commands listed in the
tables later in this chapter perform the same functions, but they are encoded
differently to accommodate the requirements of each port (Telnet or browser).
The ASCII to hexadecimal (hex) conversion table on the next page is for use with
the command/response tables for the IP control port commands, which begin on
page 4-18.
4-3MGP 462 • Software Configuration and Control
Page 52

Software Configuration and Control, cont’d
ASCII to HEX Conversion Table
•
ASCII to hexadecimal character conversion table
The command/response tables list valid ASCII (for Telnet) command codes, the
corresponding URL encoded (for Web browsers) command codes, the MGP’s
responses to the host, and a description of the command’s function or results from
executing the command.
• Upper- and lowercase characters may be used interchangeably in the
command field unless otherwise specified.
• Commands may be sent back-to-back without spaces; for example, 2*2!2*0B.
• Numbers can be entered as 1, 2, or 3 digits; for example, 8V = 08V = 008V.
• There are a few differences in how to enter the commands depending on
whether you are using Telnet or a Web browser.
• For control via a Web browser, all nonalphanumeric characters must be
represented as the hexadecimal equivalent, %xx, where xx represents the
two-character hex byte. For example, a comma (,) would be represented as
%2C.
• When using these commands through a Web browser, the URL reference is
used to shorten the examples. “URL” refers to the full URL of the control
interface and Web page reference, including all path information; for
example, http://192.168.100.10/myform.htm.
• Some characters differ depending on the method you use to send the
commands:
Telnet Web browser
Escape (hex 1B) W [must not be encoded]
Carriage return (hex 0D) Pipe character (
With Telnet you can use either the “Escape” commands or the “W”
commands, and either the carriage return or the pipe character. With the Web
browser, you are required to use the “W” commands and the pipe character.
) [must not be encoded]
|
In either method, the data string (shown in braces as {data} in the
Command/response table) is directed to the specified port, and must be
encoded if it is nonalphanumeric.
MGP 462 • Software Configuration and Control4-4
Page 53

Symbol definitions
• = Space
= Carriage return with line feed
= Carriage return with no line feed
Esc
= Escape
24, 27, 28
= Superscripts indicate the error message
displayed if the command is entered
incorrectly or with invalid parameters. See
Error responses, earlier in this chapter.
= Pipe (vertical bar) character
|
= Specific port number (01-99)
X1
= Command data section
X2
For Web encoding only:
Data is directed to the specified port and must be
encoded if it is nonalphanumeric. Because data can
include either command terminator, it must be
encoded as follows when used within the data
section:
Space (Hex 20) must be encoded as %20 (Hex:25
32 30)
Plus sign (Hex 2B) must be encoded as %2B (hex
25 32 42).
= Greenwich Mean Time (GMT) offset value (-12:00 to
X3
X5
X11
X12
X13
X14
X15
X17
X
X19
18
14:00) in hours and minutes (hh:mm)
= On/Off
0 = off/disable
1 = on/enable
= Version number (listed to two decimal places)
= Name that you give the unit. This name is a text
string of up to 24 characters drawn from the
alphabet (A-Z), digits (0-9), and the minus
sign/hyphen (-). The first character must be an
alpha character. The last character must not be
a minus. No blank or space characters are
permitted, and no distinction is made between
upper- and lowercase.
= Local date and time format
Set format (MM/DD/YY-HH:MM:SS);
e.g., 06/21/02-10:54:00
Read format (day of week, date month year
(HH:MM:SS), e.g., Thu, 20 Feb 2003 18:19:33
= IP address (xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx); leading zeros in
each of 4 fields are optional in setting values,
and are suppressed in returned values.
= Mail domain name (e.g., Extron.com)
= Time in tens of milliseconds to wait for characters
coming into a serial port before terminating
the connection (min = 0, max = 32767, and
default = 10 = 100 ms). The response is
returned with leading zeros. In RS-232
commands,
Commands using both
have either both values equaling zero or both
values set to nonzero.
= Hardware (MAC) address (xx-xx-xx-xx-xx-xx)
= Subnet mask (xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx). Leading zeros are
optional in setting values in each of four fields,
and are suppressed in returned values.
X17
and
X
20
are optional.
and
X17
= Time in tens of milliseconds to wait between
X
20
characters coming into a serial port before
terminating the connection (min = 0,
max = 32767, and default = 2 = 20 ms). The
response is returned with leading zeros. In
X
and
X17
20
are
and
RS-232/422 commands,
X17
optional. Commands using both
must have both values either equal zero
X
20
or both set to nonzero.
X21
= Parameter to set either the Length of the
message to receive or a Delimiter value.
L = byte count (min = 0, max = 32767,
and default = 0L [0 byte count).
D = decimal value for the ASCII
character (min = 0, max = 00255,
and default = 00000L).
Value is placed prior to parameter; for
example, 3 byte length = 3L, and the ASCII
0A delimiter is 10D. This parameter is case
sensitive; you must use uppercase D and L.
The response is returned with leading zeros.
(
is an optional parameter.)
X21
= Verbose response mode
X22
0 = clear/none
1 = verbose mode
2 = tagged responses for queries
3 = verbose mode and tagged responses for
queries
Default = 0 for Telnet connections; 1 for
RS-232/422 control
X23
= Priority status for receiving timeouts.
0 = use Send data string command
parameters.
1 = use Configure receive timeout
command parameters.
Default = 0.
= Baud rate: 300, 600, 1200, 1800, 2400, 3600, 4800,
X25
7200, 9600, 14400, 19200, 28800, 38400, 57600,
or 115200
= Parity (only the first letter is needed):
X26
Odd
Even
None
Mark
Space
= Data bits: 7, 8
X27
= Stop bits: 1, 2
X28
= Port type
X29
0 = RS-232
1 = RS-422
X30
= Flow control (only the first letter is needed):
Hardware
Software
must
X
20
X31
None (the default)
= Data pacing (specified in milliseconds between
bytes): 0000 - 1000.
= Password (12 characters = maximum length; no
X33
special characters are allowed.)
A user password cannot be assigned if no
administrator password exists; the E14 error code
is returned. If the administrator password is
cleared, the user password is also removed.
4-5MGP 462 • Software Configuration and Control
Page 54

Software Configuration and Control, cont’d
= Daylight savings time (used in the northern
X34
hemisphere [USA] and parts of Europe and
Brazil)
0 = off/ignore
1 = on
= Event number, range = 0 - 99
X35
= Event buffer
X36
0 = receive
1 = user
2 = NVRAM
= Event buffer offset (range = 0 to
X37
MaxBufferSize)
= Event data size
X38
b = bit
B = byte (8 bits)
S = short (16 bits)
L = long (32 bits)
This parameter is case sensitive.
= Event data to write
X39
= Number of bytes to read
X44
= E-mail event number (1 - 64)
X45
= E-mail recipient’s address
X46
= Name of e-mail file to be sent
X47
First line of the file is the subject.
The rest is the body of the e-mail.
= Default name: a combination of the model-name
X49
and the last 3 character pairs of the unit’s
MAC address (e.g., MGP-462-00-02-3D)
= (Ethernet only) Number of seconds before
X51
timeout on IP connections (min = 1,
max = 6500, and default = 30 = 300 seconds).
If no data is received during the timeout
period, the Ethernet connection is closed.
Each step is 10 seconds. When the unit is
connected via RS-232/422, only the global
timeout commands apply; anything else
returns an E13 error code. The response is
returned with leading zeros.
= Connection’s security level
X52
0 = not logged in
1 = user
2 = administrator
= ASCII digit(s) representing the numeric value of
X54
the data element read from the event buffer
(leading zeros are suppressed)
= Input 1 - 6
X55
= On/off
X56
0 = off
1 = on
= Window
X57
0 = both windows (available only for Freeze
and window muting)
1 = window 1
2 = window 2
= Input video format
X58
1 = RGB
2 = YUVp
3 = RGBcVs
4 = YUVi
5 = S-video
6 = Composite
7 = SDI
= Test pattern
X59
0 = off
1 = color bars
2 = crosshatch
3 = 4 x 4 crosshatch
4 = grayscale
5 = crop
6 = ramp
7 = Alternating pixels
8 = side-by-side crop
9 = 4 x 3/16 x 9 film aspect ratio 1.78
10 = 4 x 3/16 x 9 film aspect ratio 1.85
11 = 4 x 3/16 x 9 film aspect ratio 2.35
= Window text position
X60
0 = none
1= bottom left
2 = bottom center
3 = bottom right
4 = top left
5 = top center
6 = top right
= Window text, 16 characters maximum (Can
X61
use ASCII characters 32 - 126.)
= Picture adjustment range
X62
(0 - 127; default = 64)
= Scaler resolution
X63
1 = 640 x 480
2 = 800 x 600
3 = 852 x 480
4 = 1024 x 768
5 = 1024 x 852
6 = 1024 x 1024
7 = 1280 x 768
8 = 1280 x 1024
9 = 1360 x 765
10 = 1365 x 768
11 = 1366 x 768
12 = 1365 x 1024
13 = 1400 x 1050
14 = 1600 x 1200
15 = 480p
16 = 576p
17 = 720p
18 = 1080i
19 = 1080p
= Detected input signal standard
X64
0 = none
1 = NTSC
2 = PAL
4 = SECAM
– = not applicable (occurs when input
is set for RGB or YUV)
= Sharpness (detail) level (0 - 127)
X65
MGP 462 • Software Configuration and Control4-6
Page 55

= Window transition effect type
X67
1 = cut
2 = dissolve
3 = soft wipe up
4 = soft wipe down
5 = soft wipe right
6 = soft wipe left
7 = soft wipe center in
8 = soft wipe center out
9 = soft wipe square in
10 = soft wipe square out
11 = soft wipe curtain in
12 = soft wipe curtain out
13 = hard wipe up
14 = hard wipe down
15 = hard wipe right
16 = hard wipe left
17 = hard wipe center in
18 = hard wipe center out
19 = hard wipe square in
20 = hard wipe square out
21 = hard wipe curtain in
22 = hard wipe curtain out
= Blanking adjustment range (0 - 255 lines)
X68
= Window preset (1 - 25)
X69
= Input preset (1 - 128)
X70
X72
= Scaler refresh rate
1 = 50 Hz
2 = 60 Hz
3 = 72 Hz
4 = 96 Hz
5 = 100 Hz
6 = 120 Hz
X73
= Pixel phase (0-31)
X74
= Advanced picture settings range
(±128 auto-sensed value)
X75
= Window dissolve speed; 0 to 5 seconds in
0.1 second increments (01 = 0.1 second;
50 = 5.0 seconds)
X76
= Internal temperature in degrees Fahrenheit
= Background image number (01 - 16)
X77
Images must be named in the format
Bkgnn.bmp. nn = 01 - 16).
Images must be 24-bit bitmaps. Other
formats are not supported.
= Image/Window shift value (zero location
X78
is 2048, and limits are ± the output
resolution)
= Window size. Windows can be 1/16 the
X79
size of the output active area.
Maximum value is the active output
area.
= Image size. Image can be 1/16 the size of
X80
the input active area. Maximum value
is double the active output area for
200% zoom.
= E-mail account user name. Maximum
X81
length is 31 characters.
= E-mail account password. Maximum
X82
length is 31 characters. The MGP
responds with four asterisks (****) if a
password exists. If no password has
been set, the response is a blank field.
4-7MGP 462 • Software Configuration and Control
Page 56

Software Configuration and Control, cont’d
X57
X67
X57
.
.
X55
.
X58
to window
X55
to format
X55
Set input source
X55
In
X57
Set input
X58
Typ
View the video type of input
X55
X58
using a
X57
using a selected
X57
selected transition effect.
transition effect.
Blk1 Mute (blank) window
Blk0 Unmute (display) window
View the window muting status.
X57
X57
X56
.
entered.
displayed in front of window #1.
Set the priority of the windows to the order
X57
Display the priority of the windows.
•
X57
X57
•
X57
Select window transition effect
X67
View the current window transition effect.
X67
.
X75
.
in window
X62
Select color value
Select the next higher color value.
Select the next lower color value.
X62
X62
Col
X57
X62
Col
Col
Show the current color setting.
X57
X57
X57
Set the transition effect duration to
X75
View the transition effect duration time.
X75
! Out
X57
*
X55
(host to processor) (processor to host)
\
X58
*
\
X55
X55
* 1B
* 0B
B
X57
X57
X57
~ Pri
X57
*
X57
C
* 4# Eff
X67
* 5# Dur
X75
X62
*
+C
-C
C
X57
X57
X57
X57
Example: ~ 2 1 Window #2 has priority and will be
Command/response table for SIS commands
Command ASCII Command Response Additional description
Input selection
Set input to window
Input video type
Set input video type
Window muting/unmuting
View video type
Mute window
Unmute window
Window priority
View muting status
Set priority
View priority ~
Window transition effect
Select effect
Window effect duration
View effect 4#
Select speed
Color
Set color to a specific value
Decrement color value
View color setting
View speed 5#
Increment color value
MGP 462 • Software Configuration and Control4-8
Page 57

X57
X62
X57
X62
X62
X57
X57
X57
X62
X57
.
X57
X57
X62
X57
X57
X62
X57
X62
X57
X62
X62
X57
X57
X57
X62
X57
X57
X62
X57
X62
X57
X62
X57
X62
X62
X57
X57
X57
X62
X57
X57
X62
X57
X62
X57
X65
X57
X65
X65
X57
X57
X57
X65
X57
X57
X65
X57
X65
X57
X78
X57
X78
X57
X78
X57
X57
X78
X57
X57
X57
X78
X57
X57
X78
X57
.
.
.
.
.
.
to
in window
Select tint value
Select next higher tint value in window
Select next lower tint value in window
Tin
Tin
Tin
in window
Show the current tint setting.
Select contrast value
Select the next higher contrast value .
Con
Con
in window
Select the next lower contrast value.
Show the current contrast setting.
Con
Select brightness value
Select the next higher brightness value.
Select the next lower brightness value.
Show the current brightness setting.
Brt
Brt
Brt
in window
Set the detail level to
Det
right.
left.
.
Select the next higher detail level.
Select the next lower detail level.
Show the current detail level setting.
Det
Det
Set horizontal center of window
Shift window
Shift window
Show the current horizontal centering setting
for window
Whp
Whp
Whp
H
T
*
+ T
- T
T
^
*
+ ^
- ^
^
Y
*
+ Y
- Y
Y
D
*
+ D
- D
D
*
+ H
- H
H
(host to processor) (processor to host)
Command/response table for SIS commands (continued)
Command ASCII Command Response Additional description
Tint
Set tint to a specific value
Increment tint value
Decrement tint value
Contrast
View tint setting
Set contrast to a specific value
Increment contrast value
Decrement contrast value
Brightness
View contrast setting
Set brightness to a specific value
Increment brightness value
Decrement brightness value
Detail filter
View brightness setting
Set detail level
Increment detail level
Decrement detail level
Horizontal shift (window)
View detail value
Set horizontal shift to a specific value 1 *
Shift window right 1 *
Shift window left 1 *
View horizontal shift setting 1 *
4-9MGP 462 • Software Configuration and Control
Page 58

Software Configuration and Control, cont’d
X57
X78
X57
X78
X57
X78
X57
X57
X78
X57
X57
X57
X78
X57
X57
X62
X57
X57
X78
X57
X78
X78
X57
X57
X78
X57
X57
X57
X78
X57
X57
X78
X57
X57
X78
X57
X78
X57
X78
X57
X57
X78
X57
X57
X57
X78
X57
X57
X78
X57
X57
X79
X57
X79
X57
X79
X57
X57
X79
X57
X57
X57
X79
X57
X57
X79
X57
.
right.
left.
.
up.
down.
.
to
.
up.
down.
.
to
Set the horizontal centering of the image in
window
Shift the image in window
Shift the image in window
Show the current horizontal centering setting
Ihp
Ihp
for the image in window
Ihp
Shift window
Shift window
Show the current vertical centering setting
for window
Set the vertical centering of window to
Wvp
Wvp
Wvp
.
wider.
narrower.
to
.
Set the vertical centering of the image in
window
Shift the image in window
Shift the image in window
Show the current vertical centering setting
Ivp
Ivp
for the image in window
Ivp
Set the horizontal sizing of window
Make window
Make window
Whs
Whs
Whs
.
Show the current horizontal size setting for
window
H
*
+ H
- H
H
/
*
+ /
- /
/
/
*
+ /
- /
/
:
*
+ :
- :
:
(host to processor) (processor to host)
Horizontal shift (image)
Set horizontal shift to a specific value 2 *
Shift image right 2 *
Shift image left 2 *
View horizontal shift setting 2 *
Vertical shift (window)
Set vertical shift to a specific value 1 *
Shift window up 1 *
Shift window down 1 *
View vertical shift setting 1 *
Vertical shift (image)
Set vertical shift to a specific value 2 *
Shift image up 2 *
Shift image down 2 *
View vertical shift setting 2 *
Horizontal size (window)
Set horizontal size to a specific value 1 *
Increase horizontal size setting 1 *
Decrease horizontal size setting 1 *
Command/response table for SIS commands (continued)
Command ASCII Command Response Additional description
View horizontal size setting 1 *
MGP 462 • Software Configuration and Control4-10
Page 59

X57
.
X79
to
.
.
X57
X57
wider.
narrower.
X57
X57
taller.
shorter.
X57
X57
.
taller.
shorter.
X57
X57
.
X57
.
X80
to
window
X57
X57
.
X80
to
image in window
X57
.
X57
in window
.
.
X57
X57
window
window
Make window
Make window
X79
X79
Set the vertical sizing of window
X79
Wvs
Wvs
Show the current vertical size setting for
X57
X57
X79
; Wvs
X79
*
+ ;
- ;
;
X57
X57
X57
X57
(host to processor) (processor to host)
Set the horizontal sizing of image in window
Make the image in window
X80
Ihs
X57
:
X80
*
X57
Make the image in window
X80
X80
Ihs
Ihs
Show the current horizontal size setting for
X57
X57
X80
+ :
- :
:
X57
X57
X57
Set the vertical sizing of image in window
Make the image in window
Make the image in window
X80
X80
X80
Ivs
Ivs
Ivs
Show current vertical size setting for image
X57
X57
X57
X80
;
X80
*
+ ;
- ;
;
X57
X57
X57
X57
Set the size and position of window
X79
View the size and position of window
*
X79
X79
*
*
X79
X78
*
*
X78
X78
,
*
X57
X78
,
X57
XY Wxy
X79
*
X79
*
X78
*
X78
,
XY
X57
X57
Esc
Esc
Set the size and position of the image in
X79
View the size and position of the image in
*
X79
X79
*
*
X79
X78
*
*
X78
X78
*
,
X78
X57
,
X57
IY Ixy
X79
*
X79
*
X78
*
X78
,
IY
X57
X57
Esc
Esc
Vertical size (window)
Set vertical size to a specific value 1 *
Decrease vertical size setting 1 *
View vertical size setting 1 *
Command/response table for SIS commands (continued)
Command ASCII Command Response Additional description
Increase vertical size setting 1 *
Horizontal size (image)
Set horizontal size to a specific value 2 *
Increase horizontal size setting 2 *
Decrease horizontal size setting 2 *
View horizontal size setting 2 *
Vertical size (image)
Set vertical size to a specific value 2 *
The variables must be entered in the following order: window number, horizontal position, vertical position, horizontal size, vertical size.
Window size and position
Increase vertical size setting 2 *
Decrease vertical size setting 2 *
View vertical size setting 2 *
Set window size and position
View window size and position
Image size and position
Set image size and position
The variables must be entered in the following order: window number, horizontal position, vertical position, horizontal size, vertical size.
View image size and position
4-11MGP 462 • Software Configuration and Control
Page 60

Software Configuration and Control, cont’d
X69
X57
while
X57
while
X57
X57
without input
with input
X69
X69
the
X69
.
.
X57
to preset
X57
to window
X70
for
X61
keeping the aspect ratio constant.
keeping the aspect ratio constant.
Wzm Increase the size of window
Wzm Decrease the size of window
X57
X57
while keeping the aspect ratio constant.
Izm Increase the size of the image in window
Izm Decrease the size of the image in window
X57
X57
.
X69
while keeping the aspect ratio constant.
settings.
settings.
at location
Give the window preset at location
Recall window preset
Recall window preset
X69
Save the current window settings as a preset
X69
X69
X61
,
X69
.
X61
name
X70
location
Recall input preset
Save input settings in window
X70
X70
View the name of window preset
X61
.
.
X55
.
X55
input
Create a text label containing name
X61
,
X55
View the contents of the name label for input
X61
+ {
- {
X57
X57
+ {
X57
- {
X57
. Rpr 1 *
X69
. Rpr 2 *
X69
, Spr 2 *
X69
(host to processor) (processor to host)
Zoom mode (window)
Command/response table for SIS commands (continued)
Command ASCII Command Response Additional description
Zoom in 1 *
Zoom mode (image)
Zoom out 1 *
Zoom in 2 *
Zoom out 2 *
Window presets
Recall preset without input 1 *
Recall preset with input 2 *
Save window preset 2 *
NP Nmp
X61
,
NP
X69
X69
Esc
Esc
Window preset naming (Not viewable from unit LCD screen. Viewable through Web page and SIS commands.)
Write window name preset
Read window name preset
. Rpr 3 *
X70
*
X57
Input presets
Recall input preset 3 *
, Spr 3 *
X70
*
X57
Save input preset 3 *
NI Nmi
X61
,
NI
X55
X55
Esc
Esc
Input naming
Write input name
Read input name
MGP 462 • Software Configuration and Control4-12
Page 61

.
X68
to
X55
.
X57
.
X68
to
X55
X68
.
.
X68
X68
the window displaying input
after
before
window displaying input
Set the vertical location of first active pixel in
Select the next higher vertical start position
Select the next lower vertical start position
X68
X68
*
X55
X68
*
*
X55
X55
Show the current vertical start setting for the
X68
pixel for input
Set the horizontal location of the first active
Select the next higher horizontal start
X68
X68
*
*
X55
X55
.
.
.
X68
X55
.
X73
to
X57
.
X73
.
position after
before
input
Set the pixel phase value for the input in
Select the next lower horizontal start position
X68
*
X55
Show the current horizontal start setting for
X68
X73
*
X55
Phs
X57
X73
window
Select the next higher pixel phase value after
X73
*
X55
Phs
X57
before
Select the next lower pixel phase value
X73
*
X55
Phs
X57
.
X74
to
X55
.
X57
.
.
X74
input in window
Set the total pixels value for input
Select the next higher total pixels value after
X74
X74
*
*
X55
Show the current pixel phase setting for the
X73
X55
X74
Select the next lower total pixels value before
X74
*
X55
( Vst
X68
+ ( Vst
- ( Vst
(
X55
X55
(host to processor) (processor to host)
Command/response table for SIS commands (continued)
Vertical start
Command ASCII Command Response Additional description
Set vertical start to a specific value *
Increment vertical start value
X55
Decrement vertical start value
View vertical start setting
) Hst
X68
*
+ ) Hst
- ) Hst
X55
X55
X55
Horizontal start
Set horizontal start to a specific value
Decrement horizontal start value
Increment horizontal start value
U
)
X55
View horizontal start setting
X73
*
+ U
X57
X57
Pixel phase (Available only for RGB and YUVp input signals)
Set pixel phase to a specific value
Increment pixel phase value
* 11# Tpx
X74
- U
U
X57
X57
Decrement pixel phase value
View pixel phase setting
*
X55
Total pixels (Available only for RGB and YUVp input signals)
Set total pixels to a specific value
+ 11# Tpx
- 11# Tpx
X55
X55
Decrement total pixels value
Increment total pixels value
4-13MGP 462 • Software Configuration and Control
Page 62

Software Configuration and Control, cont’d
.
X74
to
X55
.
.
X74
X55
.
X55
Show the current total pixels setting for input
X74
.
X74
before
input
Set active pixels value for input
Select the next higher active pixels value after
Select the next lower active pixels value
X74
X74
*
X55
X74
*
*
X55
X55
Show the current active pixels setting for
X74
X74
to
X55
Set the active lines value for input
X74
*
X55
.
and
X63
.
X72
.
X59
.
X55
Select the next higher active lines value.
Select the next lower active lines value.
X74
X74
*
*
X55
X55
Show the current active lines setting for input
X74
Show the current output resolution and scan
rate settings.
the scan rate to
Set the scaler output resolution to
X72
X72
*
*
X63
X63
Select test pattern
X59
Show the current test pattern setting.
X59
Frz1 Freeze the video image.
Frz0 Unfreeze the video image.
Show the freeze status.
X57
X57
X56
* 12# Apx
* 11#
X55
(host to processor) (processor to host)
Total pixels, continued
Command/response table for SIS commands (continued)
Command ASCII Command Response Additional description
View total pixels setting
X74
*
+ 12# Apx
- 12# Apx
* 12#
X55
X55
X55
X55
Active pixels
Set active pixels to a specific value
Decrement active pixels value
Increment active pixels value
View active pixels setting
* 13# Aln
X74
*
+ 13# Aln
- 13# Aln
* 13#
X55
X55
X55
X55
Active lines
Set active lines to a specific value
Decrement active lines value
View active lines setting
Increment active lines value
MGP 462 • Software Configuration and Control4-14
= Rte
X72
*
X63
Scaler output resolution and scan rate
Set the output resolution and scan rate
View the output settings = Rte
J Tst
X59
Test Pattern
Select test pattern
View test pattern J
* 1F
X57
Freeze
Enable
* 0F
F
X57
X57
Disable
View status
Page 63

:
X!
adjustments only.
Lock all front panel controls including input
buttons; allow RS-232/422 control only.
Unlock all front panel controls.
0 = H-/V- (default)
1 = H-/V+
2 = H+/V-
3 = H+/V+
:
X!
1 = RGBHV (Default)
2 = RGsB
3 = YUV bi-level
4 = YUV tri-level
is:
X!
0 = off (default)
1 = on
is:
is:
X!
X!
.
.
X!
X!
.
X60
1 = small
2 = medium
3 = large
(host to processor) (processor to host)
Set output polarity
X!
Show executive mode status.
X56
View the current output polarity setting.
X!
* 1# Pol
X!
Set output sync format
X!
* 2# Syn
X!
Turn Blue mode on/off.
X!
View current output sync format setting.
X!
* 3# Blu
X!
Set location of text box to
Set the size of the label text to
X!
X60
View the current text position
View the current Blue Screen mode.
X!
X60
* 6# Tlc
* 10# Tsz
X!
X60
View the current text size setting.
X!
Executive mode
Enable executive mode 1X Exe1 Lock front panel control; allow RS-232/422
Command/response table for SIS commands (continued)
Command ASCII Command Response Additional description
Enable executive mode 2 2X Exe2
Special functions
View executive mode status X
Output polarity
Disable 0X Exe0
Output sync format
View polarity setting 1#
Blue screen
View sync format setting 2#
Text position
View Blue mode setting 3#
View text position setting 6#
Text size
View text size setting 10#
4-15MGP 462 • Software Configuration and Control
Page 64

Software Configuration and Control, cont’d
X57
is:
X!
.
X!
to
0 = off
1 = Red
2 = Green
Set the color of the text border in window
X!
Txb
X57
3 = Blue
4 = White
5 = Magenta
6 = Cyan
7 = Yellow
8 = Black
.:
X!
to
X57
9 = Translucent
1 = Red
2 = Green
3 = Blue
4 = White
5 = Magenta
6 = Cyan
Set the color of the text in window
X!
Txc
View the current text border color.
X!
X57
.
X57
:
X!
to
X57
in window
7 = Yellow
8 = Black
0 = off
Change the background color of the text label
X!
Tbc
View current text color in window
X!
X57
1 = Red
2 = Green
3 = Blue
4 = White
5 = Magenta
6 = Cyan
7 = Yellow
8 = Black
.
X57
label in window
9 = Translucent
View the current background color of the text
X!
* 14#
X!
*
X57
(host to processor) (processor to host)
Command/response table for SIS commands (continued)
Command ASCII Command Response Additional description
Special functions, continued
Text border color
* 16#
X!
* 14#
*
X57
X57
Text color
View text border color setting
MGP 462 • Software Configuration and Control4-16
* 17#
X!
* 16#
*
X57
X57
Text background color
View text color setting
* 17#
X57
View text background color setting
Page 65

:
X77
X!
to
X57
.
X57
to
:
X!
from memory to display.
X77
0 = none (default)
1 = red
2 = green
Set the border color for window
X!
Brd
X57
* 9#
X!
*
X57
(host to processor) (processor to host)
3 = blue
4 = white
5 = magenta
6 = cyan
7 = yellow
8 = black
memory.
Save current background image
Recall image
X77
X77
View current border color for window
X!
* 15# Ims
* 9#
X57
X77
View the currently displayed background
X77
* 15# Imr
X77
image number.
0 = none (default)
1 = red
2 = green
3 = blue
4 = white
5 = magenta
6 = cyan
7 = yellow
8 = background image
9 = user-defined color
Set the display background color to
X!
View the current background color setting.
X!
* 8# Bkg
X!
Special functions, continued
Command/response table for SIS commands (continued)
Command ASCII Command Response Additional description
Window border color
Background image
View window border color setting
Save background image 1 *
Recall background image 2 *
Background color
View current image number 15#
Background color
View background color setting 8#
4-17MGP 462 • Software Configuration and Control
Page 66

Software Configuration and Control, cont’d
X!
X!
X!
X!
X!
X!
X!
X!
X!
X!
X55
X55
X55
X55
X55
X57
X57
X57
Esc
X1
X17
X
20
X21
X2
X1
X17
X
20
X21
|
X2
X1
X17
X
20
X21
X2
X2
Esc
|
X17
X
20
X21
X17
X
20
= 0-255 level scale.
.
user-defined colors.
Show the red, green, and blue levels for the
respectively.
defined colors are 50, 100, and 150,
The red, green, and blue levels for the user-
user-defined color.
Set the red, green, and blue values for the
Disable Film mode.
2:2 pull-down.)
Enable Film mode. (Auto-senses for 3:2 or
Perform Auto Image adjustment on window
*
*
* 22# Ubk
*
*
(host to processor) (host to processor) (processor to host)
*
*
Flm1
(on) View the current Film mode setting.
(off) or 1
Flm0
Response from command
RS
Response from command
<data>
%2A
%2A
%2A
* 1 * 18#
* 0 * 18#
W
RS
*
* 18# 0
* 55# Aut
*
, be sure to convert nonalphanumeric characters to hex numbers.
<data>•
are not specified, the default values are used.
W05%2A4%2A7%2A3L RS
and
*
05*4*7*3L RS
sequence is optional. If
*
Example: 50 * 100 * 150 * 22# Ubk 50 * 100 * 150
Command ASCII (Telnet) URL Encoded (Web) Response Additional description
Command/response table for IP control port commands
Set user-defined color levels
Background color, continued
MGP 462 • Software Configuration and Control4-18
View user-defined color levels 22# Ubk
Disable Film mode
Enable Film mode
Film mode
Bi-directional serial data port
Run Auto Image
Auto Image
View Film mode status
= time in tens of milliseconds that the MGP will wait until receipt of the first response character before terminating the command
= port number (01-99).
Send data string
= time in tens of ms that the MGP will wait between characters being received via a serial port before terminating the current command or receive operation
Byte count # can be from 0 to 32767, default = 0. The ASCII decimal # can be from 0 to 00255, default = the byte count. A 3-byte length = 3L.
# = byte count (for L) or a single ASCII character expressed in decimal form (for D).
D =
L =
(default = 2 = 20 ms, max. = 32767).
(default = 10 = 100 ms, max. = 32767).
= command data section. For Web encoding for
The response includes leading zeros.
A delimiter of ASCII 0A = 10D.
Delimiter value
Length of the message to be received.
= #L or #D. The letter parameter is case sensitive (requires capital D or capital L).
Example:
*
The *
Page 67

)
X27
X29
X23
X21
),
X28
X26
), parity (
X25
), and stop bits (
.
X27
X1
Set baud rate (
data bits (
for port
:
X1
for port
X29
0 = RS-232
1 = RS-422
:
X30
and data pacing
. For
X1
X30
for port
X31
rate
H = hardware
S = software
N = none (default)
.
X1
to wait for
X1
= number of milliseconds
X31
between bytes. Range is 0000-1000;
default is 0 ms.
= waiting time in tens of ms
X17
first response character before
timing out.
X1
= priority status for port
= waiting time in tens of ms
20
X23
X
until receipt of the first response
character.
receiving timeouts.
0 = Use Send data string command
parameters (default).
between characters.
1 = Use Configure receive timeout
command parameters.
Response includes leading zeros.
X28
,
X27
,
X26
,
X25
|
CP
• Ccp
X28
X1
Cpn
%2A
X27
%2A
X26
%2A
X25
%2A
X1
W
CP
X28
,
X27
,
X26
,
X25
*
X1
Esc
(host to processor) (host to processor) (processor to host)
Set flow control
Show the serial port parameters.
Select port type
X28
,
,
• Cty
X26
X1
,
X25
Cpn
X31
,
X30
• Cfl
X1
X29
Cpn
|
CF
X31
|
CP
X1
CP W
X1
Esc
|
%2A CY
X1
CY W
X29
*
X1
Esc
|
CY
X1
CP W
X1
Esc
%2C
X30
%2A
X1
CF W
X31
,
X30
*
X1
Esc
Set the time for port
X21
,
X23
,
20
X
,
X2
X17
|
Show flow control rates for port
CE
X21
%2A
X23
%2A
20
X
• Cce
X1
Cpn
X31
,
X30
%2A
X17
|
Cf
%2A
X1
X1
CE
W
X21
*
X23
*
20
X
*
X17
CF W
*
X1
X1
Esc
Esc
,
,
20
X
,
X17
|
CE
X1
CE W
X1
Esc
24
24
24
24
Command/response table for IP control port commands (continued)
Command ASCII (Telnet) URL Encoded (Web) Response Additional description
Bi-directional serial data port, continued
Configure serial port parameters
View serial port parameters
Configure mode
Configure flow control
View mode
View flow control
Configure receive timeout
View receive timeout
4-19MGP 462 • Software Configuration and Control
Page 68

Software Configuration and Control, cont’d
X11
X11
) to two
X11
= number of seconds (in tens of
X51
seconds) before timeout on IP
connections.
version number (
decimal places. Gives the number
of the currently running version
of the user-updatable firmware.
Show bootstrap, factory-installed,
and updated firmware versions.
(See 2Q, 3Q, and 4Q, below.)
replaceable, but you may need this
information for
troubleshooting.
X51
Pti 0 *
X51
|
TC
X51
TC W 0 %2A
X51
0 *
(host to processor) (host to processor) (processor to host)
Esc
0TC W 0TC
Esc
Pti1 *
TC
|
TC W 1%2A
1 *
Esc
X51
|
X51
X51
X51
|
1TC W 1TC
Esc
Show the processor’s firmware
X11
The bootstrap firmware is not user-
With tagged response – verbose modes 2 and 3:
Ver01*
With tagged response – verbose modes 2 and 3:
X11
Ver00 * Sum of responses from 2Q-3Q-4Q
With tagged response – verbose modes 2 and 3:
Ver02 *
An asterisk (*) after the version number indicates which version is currently running. A caret (^) indicates bad checksum/invalid load. Question marks (?.??) indicate
version not loaded.
Command/response table for IP control port commands (continued)
Command ASCII (Telnet) URL Encoded (Web) Response Additional description
Ethernet data port
Set current connection port timeout
Set global IP port timeout
View global IP port timeout
View current connection port timeout
Firmware version requests
Query firmware version Q or 1Q Q or 1Q
Query verbose version information 0Q 0Q Sum of responses from 2Q-3Q-4Q
Example: 1Q 1Q 1.01
Query bootstrap version 2Q 2Q
Example: 2Q 2Q 0.06
MGP 462 • Software Configuration and Control4-20
Page 69

X11
In this example, the factory
X11
Factory-installed firmware is not
user-replaceable. This firmware
was installed at the factory; it is
the version the processor reverts
to after a mode 1 reset (see
chapter 3).
firmware version is 1.00, also
known as the kernel version 1.07,
for the MGP 462, dated
16 January, 2003.
which version of the firmware,
if any, was uploaded into the
processor after it left the
factory.
In this example, the factory
firmware version is 1.01, a.k.a.
kernel version 1.22, for MGP 462,
dated 17 January, 2005.
MGP 462 is 60-623-01.
MGP 462D (SDI) is 60-623-02.
(plus web ver.-desc-UL date/time)
X11
(host to processor) (host to processor) (processor to host)
(plus Web version–description–UL date/time)
Use this command to find out
With tagged response – verbose modes 2 and 3:
Ver03 *
X11
(plus Web version–description–UL date/time)
With tagged response – verbose modes 2 and 3:
Ver04 *
With tagged response – verbose modes 2 and 3:
Pno 60-623-01 or Pno 60-623-02
Example: 3Q 3Q 1.00(1.07-MGP462 Series -Wed, 16 Jan 2003 03:28:10 GMT)
Firmware version requests, continued
Command/response table for IP control port commands (continued)
Command ASCII (Telnet) URL Encoded (Web) Response Additional description
Query factory firmware version 3Q 3Q
Query updated firmware version 4Q 4Q
Example: 4Q 4Q 1.01 * (1.22-MGP462 Series -Mon, 17 Jan 2005 17:03:46 GMT)
Information requests
Request processor part number N N 60-XXX-XX Show processor part number.
4-21MGP 462 • Software Configuration and Control
Page 70

Software Configuration and Control, cont’d
X57
X55
X58
X64
X56
X76
X76
Esc
X35
X36
X37
X38
X35
X36
X37
X38
|
X54
X54
Esc
X35
X36
X37
X39
X38
X35
X36
X37
X39
X38
|
X35
X39
X35
X36
X37
X39
X38
,
,
operations.
total available memory for system
Show processor model name.
Inf01 * MGP 462 or INF01 * MGP 462D
With tagged response – verbose modes 2 and 3:
Show amount of memory used and
Inf02 * Multi-Graphic Processor
With tagged response – verbose modes 2 and 3:
memory.
and total available user
Show amount of user memoryused
Inf03 * n Bytes used out of n KBytes
With tagged response – verbose modes 2 and 3:
standard, and blanking status.
Show input number, video type, signal
• Blk
• Std
• Typ
Inf04 * n Bytes used out of n KBytes
Fahrenheit.
Show internal temperature in degrees
Sts20 *
With tagged response – Verbose modes 2 and 3:
.
to buffer
. Include data
.
size
offset by
event number
section of a memory buffer for
Read the contents of a specific
Write event
,
Ewr
E
E
,
,
,
,
,
(host to processor) (host to processor) (processor to host)
Request model name 1I 1I MGP 462
Information requests, continued
Command ASCII (Telnet) URL Encoded (Web) Response Additional description
Command/response table for IP control port commands (continued)
Request model description 2I 2I Multi-Graphic Processor Show type of unit.
Request system memory usage 3I 3I # Bytes Used out of #KBytes
* I/i Chn
Request user memory usage 4I 4I # Bytes used out of #Kbytes
Request general information
View internal temperature 20S
E
,
,
,
27
Read event buffer memory
Event Control
,
W
E
,
,
,
,
24 27
Write event to memory buffer
,
W
MGP 462 • Software Configuration and Control4-22
Page 71

, buffer
X39
X46
X35
bytes.
X44
,
X37
.
X37
from event
X39
, offset by
X36
, offset by
X36
{string} Show string from event
|
FE
X44
,
X37
,
X36
,
X35
(host to processor) (host to processor)
W
FE
X44
,
X37
,
X36
,
X35
Esc
27
24 27
FE
X37
,
X36
,
X35
,
X39
Esc
|
FE
X37
,
X36
,
X35
, %2A
X39
W
, buffer
X35
Write data string
,
X35
Ewr
Ego Initiate all programmed events.
Est Stop all programmed events.
#####
With tagged response – verbose modes 2 and 3:
Enm#####
|
|
|
1AE W1AE
0AE W0AE
AE WAE
Esc
Esc
Esc
= e-mail event number (1-64)
= e-mail recipient’s address
= name of e-mail file to besent
X45
X46
X47
(first line of the file = subject;
the rest = body of the e-mail).
X47
,
to jdoe@extron.com.
|
,
X45
Ipr
lpr5,jdoe@extron.com, 7.eml For e-mail event 5, send file 7.eml
|
CR
X47
,
X46
,
X45
W5%2Cjdoe%40extron%2Exom%2C 7%2Eem1 CR
CR W
X47
,
X46
,
X45
Esc
5, jdoe@extron.com, 7.eml CR
Esc
X47
,
X46
|
CR
X45
CR W
X45
Esc
X45
Eml
|
SM
X45
SM W
X45
Esc
24
24 27
24 27
Example:
Command/response table for IP control port commands (continued)
Command ASCII (Telnet) URL Encoded (Web) Response Additional description
Event control, continued
Read string from event buffer memory
Write string to event buffer memory
Stop events
Read number of events running
Start events
E-mail
Configure e-mail events
Send e-mail (event)
Read e-mail events
4-23MGP 462 • Software Configuration and Control
Page 72

Software Configuration and Control, cont’d
Esc
X14
X15
X81
X82
X14
X15
X81
X82
|
X14
X15
X81
X82
X81
X82
Esc
|
X14
X15
X81
X82
Esc
|
Esc
X12
X12
|
X12
X12
Esc
|
X49
X49
Esc
|
X12
X12
X49
Esc
X13
X13
|
X13
X13
). The
These parameters are
= E-mail account password.
= E-mail account user name.
optional.
Maximum length is 31 characters.
Maximum length is 31 characters.
,
,
,
CM
Ipm •
%2C
%2C
%2C
is its factory default
is local date and time format.
Example: 11/18/03-10:54:00
HH:MM:SS.
The set format is MM/DD/YY-
name.
name.
must be a letter, the last character
minus sign). The first character
alphanumeric characters (and the
name consists of up to 24
one of your choosing (
Change the processor’s name to
is the name the processor was
and the last three pairs of the hex
combination of the model name
shipped with: MPG462-##-##-##, a
Case does not matter.
cannot be a minus sign (hyphen).
is the processor’s current unit
address (e.g., MGP462-00-02-3d).
numbers in the processor’s MAC
,
,
,
Response from command
Ipn •
CN
Ipn •
Ipt •
CT
W
CM
,
,
,
(host to processor) (host to processor) (processor to host)
24
Command ASCII (Telnet) URL Encoded (Web) Response Additional description
Command/response table for IP control port commands (continued)
Set mail server IP, unit domain name
Mail server setup commands
Read mail server IP, unit domain name
MGP 462 • Software Configuration and Control4-24
W CM
WUB
W
CN
CM
UB
Read response from last URL cmd
Web browser specific commands
24
Set unit name
IP setup commands
W%20CN
WCN
W
CT
• CN
24
Set unit name to factory default
CN
Read unit name
24
Set time/date
Page 73

) for the
X3
DD month year HH:MM:SS.
Example: Tue, 18 Nov 2003
The Read format is day of week,
X13
|
18:19:33
Set the Greenwich Mean Time
X3
Ipz
|
CZ
X3
GMT) offset value (
processor’s location. GMT offset
(-12.00 to +14.00) represents the
time difference in hours and
minutes (± hh:mm relative to
Greenwich, England. The plus
sign and leading zero are
is the Daylight Savings time
X34
of day. Daylight Savings Time
(DST) is a 1-hour offset that is
observed in the USA and parts of
optional. Example: 5:30 = +05:30
Europe and Brazil.
X34
X3
Ipx
|
CX
|
X34
WCZ
For example, California uses
GMT -8:00 from April to October
and -7:00 GMT from November
to March. DST should be turned
off in Hawaii, American Samoa,
Guam, Puerto Rico, the U.S. Virgin
Islands, the eastern time zone part
of Indiana, and Arizona
(excluding the Navajo Nation).
0 = off/ignore
1 = on
X34
= IP address (xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx).
= 0 (off) or 1 (on).
X14
X5
Leading zeros in each of the four
fields are optional in setting
values.
X14
X5
Idh1
Idh0
Idh
Ipi •
|
|
|
|
|
CI
X14
CZ W
24
X3
Esc
Set GMT offset
CT WCT
Esc
(host to processor) (host to processor) (processor to host)
IP setup commands, continued
Command/response table for IP control port commands (continued)
Command ASCII (Telnet) URL Encoded (Web) Response Additional description
Read time/date
CX W
X34
Esc
24
Set daylight savings time
Read GMT offset CZ
CX WCX
1DH W1DH
0DH W0DH
DH WDH
CI W
Esc
Esc
24
Set DHCP on
Read daylight savings time
X14
Esc
24
24
Set DHCP off
View DHCP mode
Set IP address
4-25MGP 462 • Software Configuration and Control
Page 74

Software Configuration and Control, cont’d
is 4-12
X33
= hardware media access
18
X
fields are suppressed in returned.
values.
control (MAC) address
(xx-xx-xx-xx-xx-xx).
Leading zeros in each of the four
X14
|
18
X
|
= subnet mask
X19
(xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx). Syntax is the
same as for IP addresses. Leading
zeros are optional in setting
X19
values.
= IP address
X14
(xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx).
Leading zeros are optional.
X14
Leading zeros are suppressed.
Ips •
|
CS
X19
X19
Ipg •
|
CG
|
X14
password. (
alphanumeric characters.) The
password is case sensitive.
Special characters (spaces or
symbols) are not allowed.
Set the administrator access
X33
X14
Ipa •
|
CA
|
X33
(administrator and user).
Set the user password.
X33
Ipa • Clear/remove all passwords
|
X33
Ipu •
|
CU
|
X33
is 4-12 alphanumeric
X33
(
characters.) The password is
case sensitive. Special
characters (spaces or symbols)are
not allowed.
CS W
CI WCI
Esc
(host to processor) (host to processor) (processor to host)
24
IP setup commands, continued
Command/response table for IP control port commands (continued)
Command ASCII (Telnet) URL Encoded (Web) Response Additional description
Read IP address
CH WCH
Esc
Read hardware address (MAC)
X19
Esc
24
Set subnet mask
CG W
X14
CS WCS
Esc
Esc
24
Set gateway IP address
Read subnet mask
CG WCG
Esc
Read gateway IP address
CA W
X33
Esc
24
Set administrator password
• CA W%20CA
Esc
24
Clear administrator password
MGP 462 • Software Configuration and Control4-26
CU W
X33
CA WCA
Esc
Esc
24
A user password cannot be assigned if an administrator password does not exist. Entering a password when the MGP462 has not been configure yields an E14
14
response from the processor. If the administrator password is cleared (removed), the user password is also removed.
A user password cannot be assigned if an administrator password does not exist.
Set user password
Read administrator password
Page 75

:
X22
:
X52
mode. For
0 = off (disabled)
1 = on (enabled)
2 = tagged responses for queries
3 = verbose mode and tagged
responses for queries
0 = anonymous
1–10 = extended security levels
1 through 10
11 = User
12 = Administrator
Enable or disable the Verbose
X33
X22
Ipu • This clears the user password only.
For
X52
X22
X52
Pmt {port#}
Pmt 00023
Pmt 00000
{port#}
With tagged response – verbose modes 2 and 3:
Pvl
Pmh {port#}
Pmh 00080
Pmh 00000
{port#}
Pmd {port#}
|
|
CV
|
X22
CV W
X22
• CU W%20CU
CU WCU
Esc
Esc
(host to processor) (host to processor) (processor to host)
Esc
24
24
24
|
|
CV WCV
CK WCK
Esc
Esc
The MGP can send out unsolicited information (such as notice of a volume or input change or a change in some other setting). That is called verbose (wordy) relationship
between the processor and a connected device. For a direct RS-232/422 connection, the processor is set for Verbose mode by default. When the MGP 462 is
connected via Ethernet, Verbose mode is disabled by default in order to reduce the amount of communication traffic on the network. If you want to use the Verbose
mode with a processor connected via Ethernet, this mode must be set to On each time you reconnect to the processor.
|
|
|
{port#}MT W{port#}MT
23MT W23MT
0MT W0MT
Esc
Esc
Esc
24
24
24
|
|
MT WMT
{port#}MH W{port#}MH
Esc
Esc
24
24
|
|
80MH W80MH
0MH W0MH
Esc
Esc
24
|
|
MH WMH
{port#}MD W{port#}MD
Esc
Esc
24
24
IP setup commands, continued
Clear user password
Set Verbose mode
Command/response table for IP control port commands (continued)
Command ASCII (Telnet) URL Encoded (Web) Response Additional description
Read user password
Read connection’s security level
Read Verbose mode
Remapping port designations
Set Telnet port map
Reset Telnet port map
Disable Telnet port map
Read Telnet port map
Set Web port map
Reset Web port map
Disable Web port map
Read Web port map
Set Direct Access port map
4-27MGP 462 • Software Configuration and Control
Page 76

Software Configuration and Control, cont’d
Pmd 02001
Pmd 00000
{port#}
|
|
|
2001MD W2001MD
0MD W0MD
MD WMD
Esc
Esc
(host to processor) (host to processor) (processor to host)
Esc
24
24
24
(See below.)
|
Unit Web responses: HTML Sample Code
var connections = new Array ();
connections [1] = ‘Client IP1, timedate 1, uptime 1’;
connections [2] = ‘Client IP2, timedate 2, uptime 2’;
connections [3] = ‘Client IP3, timedate 3, uptime 3’;
...
connections [n] = ‘Client IPn, timedate n, uptime n’;
connections [n + 1] = ‘total clients, connections available’;
CC WCC
Esc
Remote client IP address: port number, time/date when connection was made, total connection time
Remote client IP address: port number, time/date when connection was made, total connection time
...
Unit Telnet text responses:
Remote client IP address: port number, time/date when connection was made, total connection time
Total clients • connections available
Command/response table for IP control port commands (continued)
Command ASCII (Telnet) URL Encoded (Web) Response Additional description
Remapping port designations, continued
Reset Direct Access port map
Disable Direct Access port map
Read Direct Access port map
Listing connections
Get connection listing
MGP 462 • Software Configuration and Control4-28
Page 77

MGP 462. Each line of the
response lists a differs t file name
and its corresponding file size.
The last line of the response
indicates how much available file
space remains.
{port#}
(See below.) Retrieve a list of files stored in the
|
|
MD WMD
DF WDF
Esc
(host to processor) (host to processor) (processor to host)
Esc
var file - new Array ():
file [1] = ‘filename 1, date 1, filesize 1’;
file [2] = ‘filename 2, date 2, filesize 2’;
file [3] = ‘filename 3, date 3, filesize 3’;
file [n] = ‘filename n, date n, filesize n’;
file [n + 1] = ‘space remaining, Bytes left’
Unit Telnet text responses: Unit Web responses:
filename x • date/time * length
filename x • date/time * length
filename x • date/time * length
filename x • date/time * length
... ...
space_remaining • Bytes left
{Responds with raw unprocessed data in file.}
Upl
|
|
{Raw unprocessed data in file up to filesize}
+ UF filesize, filename
Esc
filename SF 1B filename 52 46 0D {Responds with raw unprocessed data in file + 1 byte checksum.}
Esc
Example: http://192.168.254.254/mypage.html?cmd=WSF
File commands
Read Direct Access port map
Command/response table for IP control port commands (continued)
Command ASCII (Telnet) URL Encoded (Web) Response Additional description
Get listing
Stream files via port 80
Load file to user flash memory Use POST on port 80 followed by the delimited data to be written to the flash file memory.
Retrieve file from user flash memory Send a page GET on port 80 followed by: WSF
Stream files via Telnet or RS-232
Load file to user flash memory
Retrieve file from user flash memory
4-29MGP 462 • Software Configuration and Control
Page 78

Software Configuration and Control, cont’d
ZQQQ command resets all
settings, adjustments, the IP
address, and subnet mask to the
factory default values. The IP
address is reset to 192.168.254.254,
and the subnet mask is set to
255.255.0.0. (This command is
identical to Reset mode 5).
address.
Dir•{path}/{directory}/
|
W {path}/{directory}/CJ
{path}/{directory}/CJ
Esc
(host to processor) (host to processor) (processor to host)
A directory does not actually exist until a file has been copied into the path.
Dir•/
Dir•{path}/{directory}/
|
|
/ CJ W%2FCJ
..CJ W%2E%2ECJ
Esc
Esc
{path}/{directory}/
|
CJ WCJ
Esc
Del • {filename}
Ddl
|
|
{filename} EF W {filename} EF
/EF W/EF
24, 28
Esc
Esc
24, 28
24, 28
Ddl
|
//EF W//EF
Esc
Zpf
|
ZFFF WZFFF
24
Esc
24
Zpx No IP-related settings are reset.
Zpq Reset all settings/memories. The
|
|
ZXXX WZXXX
ZQQQ WZQQQ
Esc
Esc
Zpy All settings are reset except the IP
|
ZY WZY
Esc
Command/response table for IP control port commands (continued)
Command ASCII (Telnet) URL Encoded (Web) Response Additional description
Directory commands
Change/create directory
Move up one directory
Move back to root directory
View current directory
File erase commands
Erase user-supplied Web page/file
Erase current directory and its files
Erase current directory and subdirectories
Reset (ZAP)/Erase commands
Erase flash memory
Reset all device settings to factory default
Absolute system reset
MGP 462 • Software Configuration and Control4-30
Absolute reset retaining IP address
Page 79

Using the Windows®-based Control Software
The MGP 462 Windows-based control software program provides a convenient
way to configure the inputs, output, windows, and images in each window. It also
lets you save and recall input and window presets, and perform nearly all the other
functions that can be accomplished via the front panel controls, the SIS commands,
or the MGP 462 Web pages.
Using the software, you can do the following types of tasks to configure your MGP:
Input configuration — Specify a name; video signal type; size in pixels of the
active video area; horizontal/vertical start points of the total video display
area; and the windows 1 and 2 pixel sampling points (pixel phase) for each of
the 6 inputs.
Output configuration — Set output resolution, refresh rate, sync polarity, and
signal type (RGBHV, RGBS, RGsB, or YUV bi-level and tri-level); select a test
pattern; and enable/disable blue mode in order to set video color and tint
levels.
Picture controls — Position and size the four windows and the images within the
windows, zoom in or out on the images/windows, and make fine
adjustments to contrast, brightness, color, tint, and detail.
Presets — Create, save, and recall window and input presets.
Window configuration — Set window priority; border color; text label colors, size,
and location; and transition effects for each window of the display.
Background capture — Capture the entire display on the output screen and save it
as a bitmap, to be recalled and used as a window background when needed.
Installing the software
The MGP 462 control software is provided on a CD that is delivered with your
MGP 462 unit. To use the software that is on the CD, you must install the program
on your computer. Follow these steps:
1. Insert the CD ROM into your CD drive. The disk should start automatically.
If it does not, double-click LAUNCH.EXE on the CD to start it.
2. On the Software Installation screen (shown on the next page), click the
MGP 462 Control Software link (outlined in red in the illustration).
4-31MGP 462 • Software Configuration and Control
Page 80

Software Configuration and Control, cont’d
Link to the installation software on the MGP 462 CD
3. On the File Download window that appears, click Run to begin installing the
program.
File Download window
If you want to save the installation file (MGP462Setupv2_n.exe) to your
desktop, click Save. On the Save As window, save the setup file to the desired
location on your PC. When you are ready to install the software, double-click
on the MGP462setupv2_n.exe icon.
4. A Security prompt appears. Click Run on this window to continue with the
installation.
5. Follow the instructions on the InstallShield Wizard screens to complete the
program installation.
By default the installation creates a folder called “MGP462” in the following
location on the PC:
c: \Program Files\Extron\MGP462
If there is no Extron folder in your Program Files folder, the installation program
creates it as well.
MGP 462 • Software Configuration and Control4-32
Page 81

Starting the control program
Most items in the MGP 462 configuration program can also be configured via the
front panel, described in chapter 3. Refer to that chapter for details on features and
settings. The MGP 462 software Help program provides information on settings
and on how to use the configuration program itself.
1. To run the MGP 462 configuration program, do either of the following:
• Double-click on the MGP462.exe icon, located on your computer at:
c: \Program Files\Extron\MGP462
• Access the program from the Start menu on your computer:
a. Click Start on your computer screen.
b. Select All Programs from the Start menu.
c. From the All Programs menu, select Extron Electronics.
d. From the Extron Electronics menu, select MGP 462.
e. Select MGP 462 Control Program. The Communication Type
Selection window appears.
2. On the Communication Type Selection window, select the tab for the
communication method you want to use between your computer and the
MGP 462.
• Select TCP/IP if you are using the LAN port.
• Select RS232 if you are using the RS-232/422 serial port.
Comm Port Selection window with TCP/IP and RS232 tabs
3. On the selected tab, enter the information required for the type of
communication you chose.
• TCP/IP: Enter your MGP’s IP address, Telnet port (the default is 23), and
a password if desired.
• RS-232/422: Select your PC’s communication port from the Port menu,
and the baud rate from the Speed menu. All other parameters are preset.
4. Click OK. After a few seconds, the MGP 462 main window opens.
4-33MGP 462 • Software Configuration and Control
Page 82

Software Configuration and Control, cont’d
MGP 462 window
5. For information on configuring the MGP 462 using the Windows-based
software, refer to the program’s Help. To access the Help file, select Contents
from the Help pull-down menu, or press the F1 key.
Using the Button Label Generator
The Button Label Generator software creates labels that you can place inside the
translucent covers of the input and output push buttons. You can create labels with
names, alphanumeric characters, icons, and even colored bitmaps for easy and
intuitive input and output selection. See Installing or Replacing Button Labels in
chapter 2 for procedures for removing and replacing the translucent covers.
The program is contained on the same CD-ROM as the MGP Windows-based
control software, and is installed automatically when you install the control
software.
By default, the Windows installation goes in the C:\ProgramFiles\Extron\
ButtonLabelGenerator directory. The Button Label Generator icon is placed in the
“Extron Electronics” group or folder.
1. To run the Button Label Generator program, double-click on
the Button Label Generator icon (shown at right) in the Extron
Electronics group or folder. The Button-Label Generator
window appears (see the figure on the next page).
2. From the Systems pull-down menu, select a system button configuration.
The MGP 462 selections most closely matches the button configuration of the
MGP. However, you can select any option from this menu. You can also
select Customize Button Layouts, which opens a blank worksheet on which
you can place your own buttons in the desired configuration.
MGP 462 • Software Configuration and Control4-34
Page 83

3. Click on the button representation that you want to edit. A red box surrounds
the selected button.
Button Label Generator window for the MGP 462
4. Edit the selected button by using any of the tools provided on the Button
Label Generator window. Some of the edits you can make are:
• Enter text in the text field on the button representation.
• Select the font, size, and color of the text from the drop-down menus on
the tool bar.
• Select an icon from the Button Picture Palette and drag it to the desired
button.
• Place a bitmap image from your computer on a selected button.
• To remove all the text or the image from a button label, click Clear
Button. To remove the text and images from all the button labels, click
Clear All Buttons.
To access the Button Label Generator Help program, select Use Help from the
Help menu.
5. When finished creating the labels, print them out by selecting Print from the
File pull-down menu in the upper-left corner of the Button Label Generator
Window.
To save the button label set as a .xml file on your computer, select Save As
from the File menu and give the label file a name.
4-35MGP 462 • Software Configuration and Control
Page 84

Software Configuration and Control, cont’d
MGP 462 • Software Configuration and Control4-36
Page 85

MGP 462 Multi-Graphic Processor
Chapter Five
5
Ethernet Configuration and Control
Accessing the Web Pages
Viewing System Status
Using the Configuration Pages
Using the File Management Page
Using the Control Pages
Page 86

Ethernet Configuration and Control
The MGP 462 can be controlled and configured using HTML Web pages accessed
over a network or from a local PC connected to the MGP 462’s LAN port. The
MGP 462 has factory-installed HTML Web pages that allow you to select and
configure inputs, adjust picture controls, configure windows, save and recall
presets, and perform other processor functions. Access these HTML pages using a
Web browser such as Microsoft’s Internet Explorer.
Administrators have access to all of the Web pages and are able to make
changes to settings. Users can access the pages on the System Status and
Control tabs only.
Accessing the Web Pages
To access the MGP 462’s HTML Web pages:
1. Start your Web browser program.
2. Enter the MGP 462’s IP address in the browser’s Address field.
If your local system administrators have not changed the value, use the
factory-specified default, 192.168.254.254, in this field.
3. If you want the browser to display a page other than the default page (such as
a custom page that you have created and uploaded), enter a slash (/) and the
name of the custom page file to open.
The browser’s Address field should display the address in the following format:
xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx/{optional_file_name.html}
The following characters are invalid in file names:
? ~ @ = ‘ [ ] { } < > ’ “ ; : | \ and space.
4. Press the Enter key. If the MGP 462’s HTML pages are not password
protected, the browser displays a start page as described in step 5.
If the MGP 462’s HTML page is password protected, the browser displays the
Enter Network Password page.
Example of an Enter Network Password window
a. Enter the administrator or user password in the Password field.
A User Name entry is not required.
b. If desired, select the check box to have the system input your password
the next time you enter your MGP 462’s IP address.
c. Click the OK button.
MGP 462 • Ethernet Configuration and Control5-2
Page 87

5. If in step 4 you entered the filename for a custom HTML page, the
browser displays that page. If not, the browser displays the System
Status page, which is the MGP 462’s default start page. You can select the
tabs at the top of this screen to display additional screens that enable you
to configure and control the MGP 462.
Viewing System Status
The System Status Web page on the Status tab provides information on your
MGP 462’s current settings. Changes to these settings can be made via the
Configuration Web pages, SIS programming, the Windows-based control software,
or the MGP 462 front panel. Personnel who have user access can view this page but
cannot access the Configuration pages; they see only the Status tab. The following
figure shows a typical MGP 462 System Status web page.
System Status screen
On password-protected connections, there are two levels of protection:
administrator and user. Administrators have full access to all the MGP’s
functions. Users can only view all the settings except passwords.
• Ethernet connection to the MGP, either entering SIS commands or using the
Windows-based Control Program (see chapter 4, Software Configuration and
Control) is password protected.
• Connection via the RS-232/RS-422 port is not password protected.
5-3MGP 462 • Ethernet Configuration and Control
Page 88

Ethernet Configuration and Control, cont’d
Using the Configuration Pages
There are five Configuration Web pages, which only administrators can access.
They are listed in the sidebar menu at the left of the Configuration screen. The
following sections describe the changes you can make from these screens.
System Settings screen
The System Settings screen is divided into two sections, in which you can set date
and time parameters, and change the IP information for the MGP 462. In each
section, click Submit to enter your changes. Clicking the Cancel button in either
section restores the previous settings, if the new values have not been submitted.
System Settings screen
IP Settings fields
The IP Settings fields provide a location for viewing and editing settings unique to
the Ethernet interface. After editing all desired settings in the IP Settings section,
click the Submit button at the bottom of this section.
Unit Name field
The Unit Name field contains the name used as the “from” information when the
MGP e-mails notification of its failed or repaired status. You can change this name
field to any valid name, up to 24 alphanumeric characters.
The following characters are invalid in the unit name:
+ ~ , @ = ‘ [ ] { } < > ’ “ ; : | \ and ?.
DHCP radio buttons
The DHCP On radio button directs the MGP to ignore any entered IP addresses
and to obtain its IP address from a Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP)
server (if the network is DHCP capable).
The DHCP Off radio button turns DHCP off. Contact your local system
administrator to find out this control’s setting.
MGP 462 • Ethernet Configuration and Control5-4
Page 89

IP Address field
The IP Address field contains the IP address of the connected MGP. This value is
encoded in the processor’s flash memory.
Valid IP addresses consist of four 1-, 2-, or 3-digit numeric subfields separated by
dots (periods). Each field can be numbered from 000 through 255. Leading zeros,
up to 3 digits total per field, are optional. Values of 256 and above are invalid.
The factory-installed default address is 192.168.254.254, but if this conflicts with
other equipment at your installation, you can change the IP address to any valid
value.
IP address changes can cause conflicts with other equipment. Only local
system administrators should change IP addresses.
Gateway IP Address field
The Gateway IP Address field identifies the address of the gateway to the mail
server to be used if the MGP and the mail server are not on the same subnet.
The gateway IP address has the same validity rules as the system IP address.
Subnet Mask field
A subnet is a
IP addresses in common. The Subnet Mask field is used to determine whether the
MGP is on the same subnet as the mail server when your unit is part of a subnet.
The subnet mask can be obtained from your system administrator.
MAC Address field
The Media Access Control (MAC) Address is hard coded in the MGP and cannot
be changed.
subset of a network — a set of IP devices that have portions of their
Setting the date and time
The Date/Time Settings fields provide a location for viewing and setting the date
and time functions. Change the date and time settings as follows:
1. In the desired Date/Time Settings field, click the desired variable’s drop box.
The adjustable variables are month, day, year, hours, minutes, AM/PM, and
(time) zone. A drop-down scroll box appears.
2. Click and drag the slider or click the scroll up button or scroll down button
until the desired variable is visible.
3. Click on the desired variable.
If setting the time, set the local time. The Zone variable allows you to then
enter the offset from Greenwich Mean Time (GMT).
The Zone field identifies the standard time zone that has been selected and
displays the amount of time, in hours and minutes, that the local time varies
from the GMT international time reference.
4. Repeat steps 1 through 3 for other variables that need to be changed.
5. Select the appropriate Daylight Saving radio button. To turn off daylight
savings time, select Off.
When daylight savings time is enabled, the MGP updates its internal clock
between Standard Time and Daylight Savings Time in the spring and fall on
the date that the time change occurs in the United States of America and parts
of Europe and Brazil. When daylight savings time is turned off, the MGP
does not adjust its time reference.
6. Click the Submit button at the bottom of the Date/Time Settings section to
implement your selections.
5-5MGP 462 • Ethernet Configuration and Control
Page 90

Ethernet Configuration and Control, cont’d
Scaler Settings screen
On the Scaler Settings screen, you can specify many configuration settings for the
six inputs, the output, and windows 1 and 2. You can also make changes to the
screen background, select a test pattern, enable and disable Blue mode, and select
between RS-232 and RS-422 for the serial port mode.
Scaler Settings screen
MGP 462 • Ethernet Configuration and Control5-6
Page 91

Input configuration
The Input Configuration section of the Scaler Settings screen lets you name and
select the video signal type for each of the six available inputs.
Naming inputs
You can assign names to the six inputs using the input name text boxes located
beneath each input number. Initially, a default name is displayed in each box:
- - - - - InputN - - - - -
Select the text in the box and delete it, then enter a name of up to 16 characters for
the input. The following characters are available:
Symbols: : / – _ + "
Numerals: 0 through 9
Letters: Lowercase a through z, uppercase A through Z
Spaces
Selecting the video signal type
Under each input name box is a menu from which you can select the video signal
type for the input.
RGB, YUVp, and RGBcvS are available on inputs 1 through 4 only. YUVi is
available on inputs 1 through 5. S-video and composite video are available on all
six inputs. SDI is available only on the MGP 462D and only on input 6.
Output configuration
In the Output Configuration section of the Scaler Settings screen, you can select
output parameters from four pull-down menus.
Resolution — Select the resolution at which the image will be displayed on the
output screen.
Refresh rate — Select the rate in Hz at which the output screen will be refreshed.
Output Sync Format — Select the output signal type required by the display
device. Available formats are RGBHV, RGsB, YUV bi-level, and YUV tri-level.
Output polarity — Select the combination of horizontal and vertical
synchronization signal polarities.
Window configuration
The menus and radio buttons in this section enable you to specify various
parameters for windows 1 and 2.
Window Priority — Select which window is displayed in front, overlapping or
covering the other window.
Window Effect — Select a transition effect that will be used when windows are
muted (closed) or unmuted (opened). Refer to Available effects, in the Window
Configuration menu section of chapter 3 for a description of the available transition
effects.
Dissolve Speed — Select the amount of time that the MGP 462 will take to
complete a transition (displaying the transition effect on the output screen) when
muting a window.
Text Location — Select the area on the screen in which a text label will be displayed
on both windows. The default is None, which specifies that no text label will be
displayed.
Text Size — Select one of three possible sizes for the text label on both windows.
5-7MGP 462 • Ethernet Configuration and Control
Page 92

Ethernet Configuration and Control, cont’d
Parameters with separate menus for Window 1 and Window 2
Text Border Color — Select a color for the border surrounding the text label in the
window. The default is Black.
Text Color — Select a color for the text displayed in the window. The default is
Black.
Text Background Color — Select a color for the text label background. The default
is White.
• Off specifies that there is no special background for the text label; only the
window background (specified from the Advanced Configuration menu; see
the next section) is behind the text.
• Translucent specifies that the window background shows through the text
background with a cloudy effect.
Window Border Color — Select a color for the border around the entire window
display. The default is Off, which specifies that there is no window border.
Advanced Configuration
This section contains menus and radio buttons that allow you to select additional
system parameters.
Background Color — Select a color for the background of the output screen display
on both windows.
Test Patterns — Select a test pattern to be displayed on the output.
Blue Screen Mode — Turn Blue mode off or on. Blue mode causes only the sync
and blue video signals to be passed to the display, which aids in the setup of the
display color and tint.
Serial Port Mode — Select RS-232 or RS-422 control.
Background Capture
The pull-down menus let you save an image, or to recall an image that has been
saved and use it as the background for the two windows.
The MGP 462 supports 24-bit bitmap files only. Their file names must have
the format Bkgnn.bmp. See Background Capture menu in chapter 3 for
information on calculating the size of an image.
Save Background Image — From this menu, select a number to assign to the image
you want to save.
Recall Background Image — From this menu, select the number that was assigned
to the image that you want to use for the background behind the windows.
MGP 462 • Ethernet Configuration and Control5-8
Page 93

Passwords screen
The Passwords screen lets you assign an administrator and/or user password to
control access to the MGP 462 Web pages.
An administrator password must be in place before a user password can be
assigned.
Passwords must contain 4 to 12 alphanumeric characters. Symbols and spaces
are not allowed, and the passwords are case sensitive.
Passwords screen
Assigning a password
To assign passwords, follow these steps:
1. Enter the new administrator password in the Administrator Password field.
2. In the Re-enter Admin Password field, enter the same password again to
confirm it.
3. If you want to assign a user password, enter it in the User Password field.
You cannot assign a user password unless an administrator password has been
assigned.
4. Enter the same user password in the Re-enter the User Password field.
5. Click the Submit button to set the password(s).
Clearing a password
To remove an assigned password, follow these steps:
1. In the Administrator Password or User Password field, clear any text, then
enter a single space.
2. Repeat step 1 in the Re-enter Admin Password or the Re-enter User Password
field.
3. Click the Submit button.
5-9MGP 462 • Ethernet Configuration and Control
Page 94

Ethernet Configuration and Control, cont’d
Email Alerts screen
The Email Alerts screen enables you to set up the MGP 462 to automatically send
e-mail alert messages when settings are changed on the unit. You may enter up to
64 e-mail addresses to alert recipients that an event has occurred.
You can also specify that SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol) authorization is
required for the MGP to accept incoming e-mail. This prevents unwanted e-mail
from taking up space in the MGP’s mail system.
Email Alerts screen (top portion)
To set up the system to send e-mail alerts when settings are changed, follow these
steps:
1. On the sidebar menu on the Configuration tab, click Email Alerts.
2. On the Email Alerts screen, click the Edit button located to the right of the
Mail IP Address and Domain Name fields. The button changes to Save.
3. Enter your MGP 462’s IP address and your domain name in the appropriate
fields. (This information is available from your network administrator.)
4. Click the Save button.
To set up e-mail addresses for notification, do the following for each recipient of
e-mail alerts:
1. Click the Edit button at the end of the address row. The Edit button changes
to Save.
2. Enter the e-mail address of the recipient, and the file name on your computer
(.eml extension) that contains the message.
3. Click the Save button to save the changes. The Save button changes back to
Edit.
MGP 462 • Ethernet Configuration and Control5-10
Page 95

Setting up SMTP authorization
To set the MGP to require SMTP authorization before accepting any e-mail, follow
these steps:
1. To enable the SMTP authorization fields, click the Edit button at the right of
the Mail IP Address field. The Edit button changes to Save.
2. Select the SMTP Authorization Required check box, located below the
Domain Name field. This enables the User Name and Password fields below
the check box.
3. In the User Name and Password fields, enter a user name and a password
that senders must enter in order for the MGP to accept their e-mail messages.
For the User name, you can use any combination of letters, numerals, spaces,
and symbols except the comma (,) and the single and double quotation marks
(‘ and “). For the password, you can use all characters except the comma. The
user name and password can each be from 1 to 30 characters.
You must specify both a user name and a password.
4.
Click the Save button next to the Mail IP Address field to save your user name
and password.
To remove SMTP authorization, click Edit, deselect the SMTP Authorization
Required check box, then click Save.
Firmware Upgrade screen
The Firmware Upgrade screen enables you to install a new version of firmware to
your MGP 462. You can download the latest firmware version from the Extron Web
site to your PC. Appendix C provides more details on firmware updating.
Determining the current firmware version
There are four methods you can use to find out what firmware version is currently
installed on your MGP 462:
• Using the LCD screen: Watch the LCD window as you connect the MGP 462
to a power source. The first piece of information displayed on the screen is
the firmware version (along with the product name).
• Using the System Status Web page: Select the Status tab on the MGP Web
page to display the System Status screen. The firmware version is the fourth
line in the System Description section (shown below).
System Status screen showing firmware version
5-11MGP 462 • Ethernet Configuration and Control
Page 96

Ethernet Configuration and Control, cont’d
• Select About... from the Help menu on the Windows-based control software
screen. See Using the Windows-based Control Software in chapter 4 for more
information.
• Enter the appropriate SIS command. See Using Simple Instruction Set (SIS)
Commands in chapter for for the command syntax.
Downloading the firmware
To obtain the latest version of MGP 462 firmware, follow these steps:
1. Visit the Extron Web site (www.extron.com) and go to the MGP 462 page.
2. Click Downloads.
3. On the Downloads page, click the Firmware link, listed under Software and
Firmware.
4. On the Download Center page, fill in the required information, then click the
Download_MGP462_FW2x01.exe button. A File Download – Security
Warning window is displayed.
5. Click Save. A Save As window opens.
6. Browse to the folder where you want to save your firmware file, and click
Save. The firmware installation file is placed on your computer drive.
7. When ready to install the new firmware, locate the downloaded file (called
MGP462_FW2x01.exe), and double-click on it to open it.
8. Follow the instructions on the screens to install the new firmware on your
computer. A Release Notes file, giving information on what has changed in
the new firmware version, and a set of instructions for updating the
firmware are also loaded to your computer.
Updating the firmware on the MGP 462
After you have installed the new firmware on your computer, you must upload it
to the MGP 462. Follow these steps to update the firmware using the Web pages.
1. On the MGP 462’s Configuration Web page, select Firmware Upgrade from
the sidebar menu to display the Firmware Upgrade screen.
2. Click Browse to open the Choose File window, and locate the firmware file
on your PC or server. The file extension must be .S19.
MGP 462 • Ethernet Configuration and Control5-12
Page 97

Choose file window
CAUTION
3.
Open the firmware file. Its name appears in the field below the Current
Firmware Version on the Firmware Upgrade screen.
Firmware Upgrade screen
4. Click the Upload button on the Firmware Update screen to start the firmware
update process. While the firmware is being uploaded, the Upload button
changes to Uploading...; and the LCD window on the MGP displays first
Firmware Upload Please Wait!!!, then Firmware Reboot Please Wait!!!
When the uploading process is complete, the Uploading... button on the screen
changes back to Upload, and the default cycle is displayed on the LCD screen.
Uploading a file with an extension other than .S19 may cause the unit to
stop functioning.
While the firmware is uploading and rebooting, do not press any front panel
buttons or make any selections on the Web pages.
5-13MGP 462 • Ethernet Configuration and Control
Page 98

Ethernet Configuration and Control, cont’d
Using the File Management Page
The File Management page lets you upload files to the MGP 462 from your PC or
network, and to delete files from the unit. You can also upload personalized Web
pages via this screen. To access the File Management page, select the File
Management tab on the MGP 462 Web site.
You can use this function to load background images from your computer or the
internet to display on the output screen. All background image files must be 24-bit
bitmaps. Their file names must have the format bkgnn.bmp.
File Management screen
Uploading files
Files to be uploaded to the MGP 462 must contain only valid alphanumeric
characters and underscores. No spaces or special characters (symbols) are allowed.
To upload files from the server, follow these steps:
1. Click the Browse button to the right of the file name field.
2. Browse to locate the file that you want to upload, and open it. The file’s name
and directory path are displayed in the file name field on the File
Management screen.
3. Click the Upload File button. The selected file name appears in the Files
column on the File Management screen. (Files are listed separately under
headings of their extensions.)
Adding a directory
To add a directory or folder to the MGP 462’s file system, follow these steps:
1. Enter the directory name in the Dir: field, following the slash (/).
2. Click the Add Dir button.
3. With the directory name displayed, perform the Uploading files procedure
described in the previous section to add a file to the directory. The directory
name appears at the top of the Files column, preceded by a slash.
To add more files to the directory, click the directory name to open it, then use the
Uploading files procedure. To exit the directory, click (root).
MGP 462 • Ethernet Configuration and Control5-14
Page 99

Other file management activities
You can also perform the following tasks on the File Management screen:
Opening a file — Click on the name of the file in the Files column.
Deleting a file — Click the Delete button at the right end of the line that contains
the file you want to remove.
Deleting all files — Click the Delete All button.
Selecting a file — From the Select menu, select a file name, or select All to select all
uploaded files.
Using the Control Pages
The pages that you can access through the Control tab enable you to set and
manage window and input presets, and to control other window-related functions.
User Control screen
The User Control screen allows you to manage MGP 462 functions relating to the
windows.
User Control screen, top section
Select Window
Use the Window 1, Window 2, and Both buttons to specify the window(s) to which
the following selections on this screen will apply. The Both selection can be used
only when you are selecting inputs, muting the windows, or freezing/unfreezing
the windows’ video.
Input Selection
Click one of the six Input Selection buttons to switch to that input for the selected
window. The corresponding input button lights on the MGP 462 front panel.
5-15MGP 462 • Ethernet Configuration and Control
Page 100

Ethernet Configuration and Control, cont’d
Window Mute
Select the Enable or Disable radio button in the Window Mute field to mute/
unmute the selected window. The corresponding Input button(s) on the front panel
blink continuously when the window is muted.
Executive Mode
Select the Enable radio button in the Executive Mode field to lock all front panel
controls except Input Selection, Freeze, and Window Preset. (The
RS-232/422 and Ethernet ports remain accessible.)
Freeze
Select the Enable radio button in the Freeze field to freeze the image in the selected
window. The front panel Freeze button(s) for the selected window(s) light when
Freeze is enabled.
Film Mode
Select the Enable radio button in the Film Mode field to have the MGP 462 detect
whether 3:2 or 2:2 pull-down is needed to deinterlace the input video. The input
you selected at the top of the screen must be set to YUVi, Composite, or S-video.
(See Using the Configuration Pages, Scaler Settings screen section for information on
selecting video signal types.)
User Control screen, bottom half
Picture Controls – Window
The Picture Controls section contains + and – buttons, which you can click to
increase or decrease parameter values for the selected window. If a text field is
provided, you can also enter the value in it.
You can make the following adjustments:
Horizontal Shift — Move the selected window to the right or left on the screen.
The value in the text box is the distance in pixels of the window’s left edge
from the left edge of the display. The range is determined by the output size;
the default is 2048 plus or minus the output rate.
MGP 462 • Ethernet Configuration and Control5-16
 Loading...
Loading...