Page 1

DMP 128
Digital Matrix Processor
User Manual
Audio Products
Mixers and Processors
68-2036-01 Rev. A
12 12
Page 2
Safety Instructions
Safety Instructions • English
WARNING: This symbol, , when used on the product, is intended to
alert the user of the presence of uninsulated dangerous voltage within
the product’s enclosure that may present a risk of electric shock.
ATTENTION: This symbol, , when used on the product, is intended
to alert the user of important operating and maintenance (servicing)
instructions in the literature provided with the equipment.
For information on safety guidelines, regulatory compliances, EMI/EMF
compatibility, accessibility, and related topics, see the Extron Safety and
Regulatory Compliance Guide, part number 68-290-01, on the Extron
website, www.extron.com.
Instructions de sécurité • Français
AVERTISSEMENT: Ce pictogramme, , lorsqu’il est utilisé sur le
produit, signale à l’utilisateur la présence à l’intérieur du boîtier
du produit d’une tension électrique dangereuse susceptible de
provoquer un choc électrique.
ATTENTION: Ce pictogramme, , lorsqu’il est utilisé sur le produit,
signale à l’utilisateur des instructions d’utilisation ou de maintenance
importantes qui se trouvent dans la documentation fournie avec le
matériel.
Pour en savoir plus sur les règles de sécurité, la conformité à la
réglementation, la compatibilité EMI/EMF, l’accessibilité, et autres sujets
connexes, lisez les informations de sécurité et de conformité Extron,
réf. 68-290-01, sur le site Extron, www.extron.fr.
Sicherheitsanweisungen • Deutsch
WARNUNG: Dieses Symbol auf dem Produkt soll den Benutzer
darauf aufmerksam machen, dass im Inneren des Gehäuses dieses
Produktes gefährliche Spannungen herrschen, die nicht isoliert sind
und die einen elektrischen Schlag verursachen können.
VORSICHT: Dieses Symbol auf dem Produkt soll dem Benutzer in
der im Lieferumfang enthaltenen Dokumentation besonders wichtige
Hinweise zur Bedienung und Wartung (Instandhaltung) geben.
Chinese Simplified(简体中文)
警告: 产品上的这个标志意在警告用户该产品机壳内有暴露的危险
电 压 ,有 触 电 危 险 。
注意: 产品上的这个标志意在提示用户设备随附的用户手册中有
重要的操作和维护(维修)说明。
关于我们产品的安全指南、遵循的规范、
使用的特性等相关内容,敬请访问
安全规范指南,产品编号
68-290-01。
EMI/EMF 的兼容性、无障碍
Extron 网站 www.extron.com,参见 Extron
Chinese Traditional(繁體中文)
警告: 若產品上使用此符號,是為了提醒使用者,產品機殼內存在著
可能會導致觸電之風險的未絕緣危險電壓。
注意 若產品上使用此符號,是為了提醒使用者。
有關安全性指導方針、法規遵守、EMI/EMF 相容性、存取範圍和相關主題的詳細
資訊,請瀏覽 Extron 網站:www.extron.com,然後參閱《Extron 安全性與法
規遵守手冊》,準則編號 68-290-01。
Japanese
警告: この記 号 が製品上に表示されている場合は、筐体内に絶縁されて
いない高電圧が流れ、感電の危険があることを示しています。
注意: この 記号 が製品上に表示されている場合は、本機の取扱説明書に
記載されている重要な操 作と保守(整備 )の指示についてユーザーの
注意を喚起するものです。
安全上のご注意、法規厳守、EMI/EMF適合性、その他の関連項目に
つ い て は 、エク スト ロ ン の ウェ ブ サ イト www.extron.comより
『Extron Safety and Regulatory Compliance Guide 』 (P/N 68-290-01) をご覧くだ さ い 。
Weitere Informationen über die Sicherheitsrichtlinien, Produkthandhabung,
EMI/EMF-Kompatibilität, Zugänglichkeit und verwandte Themen finden Sie in
den Extron-Richtlinien für Sicherheit und Handhabung (Artikelnummer
68-290-01) auf der Extron-Website, www.extron.de.
Instrucciones de seguridad • Español
ADVERTENCIA: Este símbolo, , cuando se utiliza en el producto,
avisa al usuario de la presencia de voltaje peligroso sin aislar dentro
del producto, lo que puede representar un riesgo de descarga
eléctrica.
ATENCIÓN: Este símbolo, , cuando se utiliza en el producto, avisa
al usuario de la presencia de importantes instrucciones de uso
y mantenimiento recogidas en la documentación proporcionada
con el equipo.
Para obtener información sobre directrices de seguridad, cumplimiento
de normativas, compatibilidad electromagnética, accesibilidad y temas
relacionados, consulte la Guía de cumplimiento de normativas y seguridad
de Extron, referencia 68-290-01, en el sitio Web de Extron, www.extron.es.
Korean
경고: 이 기호 , 가 제품에 사용될 경우, 제품의 인클로저 내에 있는
접지되지 않은 위험한 전류로 인해 사용자가 감전될 위험이 있음을
경고합니다.
주의: 이 기호 , 가 제품에 사용될 경우, 장비와 함께 제공된 책자에 나와
있는 주요 운영 및 유지보수(정비) 지침을 경고합니다.
안전 가이드라인, 규제 준수, EMI/EMF 호환성, 접근성, 그리고 관련
항목에 대한 자세한 내용은 Extron 웹 사이트(www.extron.com)의
Extron 안전 및 규제 준수 안내서, 68-290-01 조항을 참조하십시오.
Page 3
FCC Class A Notice
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class A digital
device, pursuant to part15 of the FCC rules. The ClassA limits provide reasonable
protection against harmful interference when the equipment is operated in a commercial
environment. This equipment generates, uses, and can radiate radio frequency energy and,
if not installed and used in accordance with the instruction manual, may cause harmful
interference to radio communications. Operation of this equipment in a residential area is
likely to cause interference; the user must correct the interference at his own expense.
NOTE: This unit was tested with shielded I/O cables on the peripheral devices. Shielded
cables must be used to ensure compliance with FCC emissions limits.
For more information on safety guidelines, regulatory compliances,
EMI/EMF compatibility, accessibility, and related topics, see the “Extron Safety and
Regulatory Compliance Guide” on the Extron website.
Specifications Availability
Product specifications are available on the Extron website, www.extron.com.
Page 4
Conventions Used in this Guide
Notifications the following are used:
DANGER: A danger indicates a situation that will result in death or severe injury.
WARNING: A warning indicates a situation that has the potential to result in death or
severe injury.
CAUTION: A caution indicates a situation that may result in minor injury.
ATTENTION: Attention indicates a situation that may damage or destroy the product or
associated equipment.
NOTE: A note draws attention to important information.
TIP: A tip provides a suggestion to make working with the application easier.
Software Commands
Commands are written in the fonts shown here:
^AR Merge Scene,,Op1 scene 1,1 ^B 51 ^W^C
[01] R 0004 00300 00400 00800 00600 [02] 35 [17] [03]
E X! *X1&* X2)* X2#* X2! CE}
NOTE: For commands and examples of computer or device responses mentioned
in this guide, the character “0” is used for the number zero and “O” represents the
capital letter “o.”
Computer responses and directory paths that do not have variables are written in the font
shown here:
Reply from 208.132.180.48: bytes=32 times=2ms TTL=32
C:\Program Files\Extron
Variables are written in slanted form as shown here:
ping xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx —t
SOH R Data STX Command ETB ETX
Selectable items, such as menu names, menu options, buttons, tabs, and field names are
written in the font shown here:
From the File menu, select New.
Click the OK button.
Copyright
© 2012 Extron Electronics. All rights reserved.
Trademarks
All trademarks mentioned in this guide are the properties of their respective owners.
Page 5

Contents
Introduction .......................................................... 1
About This Manual .............................................. 1
About the DMP128 Digital Matrix Processor ...... 1
Features ............................................................. 1
DMP128 Application Diagram ............................ 4
Installation ............................................................. 5
Mounting the DMP128 ...................................... 5
DMP 128 Models ............................................... 5
Rear Panel Features and Cabling ........................ 6
USB Configuration Port (Front Panel) .............. 8
Hardware Operation ............................................ 9
DMP128 Operation............................................ 9
Front Panel Operation ....................................... 10
Rear Panel Operation ....................................... 11
Power Cycle ................................................. 11
Firmware Updates ........................................ 11
Reset Actuator and LED ............................... 12
Digital I/O Ports ............................................ 13
DMP Software ..................................................... 14
Software Control............................................... 14
Embedded Web Pages..................................... 15
Windows-based Program Control ..................... 15
Installing the DSP Configurator Program ....... 15
Installing the USB Driver ............................... 17
DSP Configurator Program Basics .................... 18
Starting the Program .................................... 18
Using the Program ........................................ 18
Navigation .................................................... 23
DSP Configurator Toolbar Menus .................. 23
Presets Drop-down ...................................... 27
Mode Buttons .............................................. 27
Audio Level, Mix-point, Processing Blocks,
and Signal Chains ............................................ 28
Level Control Blocks ..................................... 29
Processor Blocks.......................................... 29
Mic/Line Input Signal Chain Controls ................ 31
Gain Control (GAIN) ...................................... 31
Filter (FILT) .................................................... 32
Acoustic Echo Cancellation (AEC) ................ 42
AEC Dialog ................................................... 43
Setting Gain Structure for AEC ..................... 44
Advanced AEC Controls ............................... 45
Dynamics (DYN)............................................ 46
Delay (DLY) ................................................... 51
Ducking ....................................................... 52
Ducking Configuration Dialog ...................... 53
Ducker Tutorials ................................................ 55
Ducking and Priority Ducking ........................ 55
Automix (AM) .................................................... 56
Pre-mixer Gain (GAIN) .................................. 59
Line Output Channels ....................................... 60
Post-mixer Trim Control (TRIM) .................... 60
Loudness (LOUD) ......................................... 60
Delay Block (DLY) ........................................ 63
Filter Block (FILT) .......................................... 63
Dynamics Block (DYN) ................................. 63
Volume Control (VOL) .................................. 64
Virtual Bus Returns ........................................... 65
Virtual Bus Returns, A-D ................................... 65
Feedback Suppressor (FBS) ......................... 65
Filter (FILT) .................................................... 70
Dynamics (DYN)............................................ 70
Loudness (LOUD) ......................................... 70
Delay (DLY) ................................................... 70
Gain (GAIN) .................................................. 70
Virtual Bus Returns, E-H ................................... 70
Output Mix Matrix ............................................. 71
Mix-point GUI Behavior: ................................ 73
Mix-point Examples ...................................... 75
Virtual Send Bus Mix Matrix .............................. 78
Expansion Bus Mix Matrix ................................. 80
Multi-device Digital Audio I/O ........................ 81
Device Manager ............................................ 81
Group Masters ................................................. 82
Group Members ........................................... 82
Grouped Controls ......................................... 82
Configuring a Group Master .......................... 84
Deleting a Group Master ............................... 85
Viewing and Using a Group Master ............... 85
Add a Group ................................................. 85
Tools ............................................................. 86
Soft Limits .................................................... 87
DigitalI/OPorts ................................................ 88
Reinitialize Digital I/O ..................................... 89
Emulate Mode and Live Mode .......................... 89
Synchronizing: Pull from or
Push to the Device ...................................... 89
Selecting Live Mode and
Pushing or Pulling Data ................................ 90
vDMP128 • Contents
Page 6
Presets ............................................................. 93
Previewing/Recalling a Preset ....................... 94
Building a Preset ........................................... 94
Managing Presets in the GUI ........................ 96
Presets: Pull, Push, or Create Live ................ 96
Protected Configuration .................................... 97
Save Protected Configuration ....................... 97
Recall Protected Configuration...................... 97
Change PIN .................................................. 97
DSP Configurator Windows Menus .................. 98
Keyboard Navigation .................................... 98
Optimizing Audio Levels ................................. 101
About Setting Gain Structure ...................... 102
Setting Input Gain ....................................... 103
Setting a Nominal Output Level................... 103
Adjusting Trim ............................................. 104
Adjusting Pre-mixer Gain ............................ 104
Setting Output Gain Structure ..................... 104
Setting Mic/Line Input and Mix Levels ......... 105
Adjusting Trim ............................................. 105
Setting Volume Control
for the Amplifier Stage ............................... 105
Signal Path Building Blocks ............................ 106
Adding a Building Block .............................. 108
Organize Building Blocks ............................ 110
HTML Operation ............................................... 137
Download the Startup Page ............................ 137
Status Tab ...................................................... 139
System Status Page ................................... 139
Configuration Tab ........................................... 140
System Settings Page ................................ 140
Passwords Page......................................... 143
Firmware Upgrade Page ............................. 144
File Management Tab ..................................... 148
File Management Page ............................... 148
Special Characters ......................................... 148
Reference Information .................................... 149
Part Numbers and Accessories ...................... 149
Included Parts ............................................ 149
Accessories ................................................ 150
Firmware Loader ............................................ 151
DMP128 Hardware Reset Modes .................. 152
MountingtheDMP128 .................................. 153
Tabletop Use .............................................. 153
UL Rack Mounting Guidelines ..................... 153
Rack Mounting ........................................... 154
Table or Wall Mounting ................................ 154
SIS Programming and Control ...................... 113
Connection Options ........................................ 113
RS-232 Port ............................................... 114
USB Port (front panel) ................................. 114
Ethernet (LAN) Port ..................................... 114
Verbose Mode ............................................ 115
Host-to-device Communications .................... 116
DMP128-initiated Messages ...................... 116
Password Information ................................. 116
Using the Command/Response Tables ....... 116
Error Responses ......................................... 117
Simple Control Port Commands -
Telnet and Web-browser Accessible .......... 118
Command/Response Tables ........................... 119
Basic SIS Commands ................................. 119
DSP SIS Commands .................................. 124
Symbol Definitions ...................................... 125
Special Characters ..................................... 125
Setting Audio Levels ................................... 130
DMP128 • Contents vi
Page 7

Introduction
This section describes this manual and the DMP128, including:
• About This Manual
• About the DMP128 Digital Matrix Processor
• Features
About This Manual
This manual contains installation, configuration, and operating information for the
ExtronElectronicsDMP128ProDSP™ Digital Matrix Processor, software controlled digital
audio processor.
In this manual, the DMP128 may also be referred to as “the mixer” or “device.”
About the DMP128 Digital Matrix Processor
The Extron DMP 128 Digital Matrix Processor is a 12x8 audio mixer featuring
ExtronProDSP, automixing, and I/O expansion capabilities, and is available with
AEC - acoustic echo cancellation. The DMP 128 offers a configuration approach to DSP in
order to simplify mixing, routing, conferencing, and room optimization. Quick and intuitive
configuration using the DSP Configurator™ Software allows the DMP 128 to be installed in
very little time, with easy-to-learn adjustments that can be heard in real-time. A digital audio
expansion port allows two DMP 128 units to be linked together to expand input and output
signal management and routing capabilities. The DMP 128 is ideal for presentation and
conferencing applications in boardrooms, courtrooms, and conference centers that require
advanced matrix mixing with DSP.
The DMP128 has no front panel controls. All configuration is performed using the
ExtronDSPConfigurator™ program from a host computer via any of the communication
ports, RS-232, USB or Ethernet (high-speed ports recommended). Signal presence and clip
LEDs for the twelve input channels and eight output channels are on the front panel.
Features
• Two models with 12 mic/line inputs and 8 outputs:
• 12x8 ProDSP processor
• 12x8 ProDSP processor with AEC
• Inputs — Twelve balanced or unbalanced mic/line level on 3.5 mm, 3-pole and 6-pole
captive screw connectors
• Outputs — Eight balanced or unbalanced line level on 3.5 mm, 6-pole captive screw
connectors
• Eight channels of acoustic echo cancellation (AEC) — The DMP 128 C models
include eight independent channels of high performance AEC, as well as selectable
noise cancellation. Extron AEC features advanced algorithms that deliver fast echo
canceler convergence for optimal intelligibility in situations that challenge AEC
performance, including double-talk, and the use of wireless microphones at the near
end.
DMP128 • Introduction 1
Page 8

• Digital audio expansion port for linking two DMP 128 units — An expansion
port allows any two DMP 128 models to be linked together via a single shielded
CAT6 cable. This allows eight matrix mixes of the inputs, plus eight virtual paths to be
sent and received between units.
• Automixer with eight gate groups — The DMP 128 features an automixer with
advanced features for managing signal levels from multiple microphones. The
automixer includes a gating mode that automatically gates channels on or off, as well
as a gain sharing mode that maintains the overall system gain based on the number
of active mics.
• ProDSP™ audio signal processing — The DMP 128 features 32/64-bit floating
point audio DSP processing, which maintains very wide dynamic range and audio
signal transparency, to simplify management of gain staging while reducing the
possibility of DSP signal clipping.
• 48 volt phantom power — The DMP 128 is equipped with selectable 48 volt
phantom power for the first eight inputs, allowing the use of condenser microphones.
• Studio grade 24-bit/48 kHz analog-to-digital and digital-to-analog converters
— Professional converters fully preserve the integrity of the original audio signal.
• Fixed, low latency DSP processing — Input to output latency is low within
the DMP 128 and stays constant, regardless of the number of active channels or
processes. While latency increases marginally on channels with AEC enabled, overall
latency remains low. Fixed latency processing keeps audio in sync with video, and
prevents distractions to presenters or performers resulting from delayed live audio.
• DSP Configurator™ Software — A powerful yet user-friendly PC-based software
tool for managing all audio operations of the DMP 128. It enables complete setup
and configuration of digital audio processing tools on the ProDSP platform, as well as
routing and mixing.
• Intuitive Graphical User Environment — The DSP Configurator Software features
a Graphical User Environment that offers a clear view of all input and outputs, audio
processing blocks, routing, mix-points, and virtual routing in a single screen. This
allows a designer or installer to quickly view an audio configuration without having to
access multiple dialog boxes or menus.
• Device Manager enables configuration of multiple Extron DSP products
— Device Manager in the DSP Configurator Software enables easy configuration of
multiple Extron DSP products, including two linked DMP 128 processors, by toggling
between Graphical User Environments for each unit. Processors can be grouped into
folders for organizing as separate rooms or buildings. Settings for multiple Extron DSP
products in Device Manager can be saved to a single file.
• Flexible control options — The DMP 128 can be controlled using the DSP
Configurator Software and a PC connection to the Ethernet port, the RS-232 serial
port, or the USB 2.0 port on the front panel. The DMP 128 can also be controlled
through a control system with Extron SIS™ - Simple Instruction Set commands, and
by accessing the internal Web pages.
• Copy and paste for processing blocks — To help speed audio system design
and setup, parameter settings can be quickly copied between individual processing
blocks or identical groups of blocks within the Graphical User Environment, using
conventional cut-and-paste commands.
• Building Blocks processor settings — A collection of pre-designed processor
settings optimized for a specific type of input or output device, such as microphones
and Extron speakers, with preset levels, filters, dynamics, and more. Flexible Building
Blocks are available on each I/O strip and allow system designers to fully customize
and save their own Building Blocks, further streamlining audio system design and
integration.
DMP128 • Introduction 2
Page 9

• Live and Emulate operation modes with configuration file saving — Live
mode allows integrators to connect to the DMP 128 and make live parameter
adjustments while hearing or metering them in real-time. This avoids the need to
compile and upload a configuration file to the DSP. Emulation mode allows settings to
be configured offline, then uploaded to the DMP 128. The software also downloads
configuration files from the mixer for archiving. Settings for two DMP 128 processors
linked together can be saved to a single configuration file.
• 32 DSP Configurator presets — Using the DSP Configurator Software, any
parameters for DSP processing, levels, or audio routing can be saved as presets.
These settings can be saved for the entire system, or any selected group of inputs,
outputs, mix-points, and DSP blocks.
• 20 digital I/O ports for remote control or feedback — Twenty configurable digital
I/O ports are provided, so that the DMP 128 can be programmed to sense and then
respond to external triggers such as mic activation, muting, and recall of presets.
• Triple matrix design provides output, virtual, and expansion routing options—
Employs a triple matrix design that offers substantial flexibility in routing, mixing, and
processing audio input sources. An output matrix allows any of the twelve inputs to
be mixed to any or all eight outputs. If desired, any of the inputs can first be directed
into a virtual matrix, which routes the inputs to eight virtual buses, before being mixed
back into the output matrix. Virtual buses allow inputs to be processed together as
a group. When two DMP 128 processors are linked together via the expansion ports
over shielded CAT 6 cable, inputs and virtual buses of one unit can be routed to the
other processor through an expansion matrix, for additional processing or matrix
mixing into the outputs.
• Group masters — The DMP 128 provides the capability to consolidate gain or mute
control throughout the system. Gain or mute controls can be selected and added to a
group master, which can then be controlled by a single master fader or mute control.
Each group master can have up to 16 members, and up to 32 group masters can be
created.
• Soft limits provide optimal group master adjustment range — The group
master volume range can be limited using soft limits to maintain optimal minimum
and maximum levels when using external volume control. This prevents operators
from over or under-adjusting levels when using digital I/O or RS-232 control. The DSP
Configurator Software provides quick drag-and-drop adjustment of soft limits from the
Group Controls screen.
• SpeedNav™ keyboard navigation — SpeedNav enables user-friendly, keyboard-
based navigation of the DSP Configurator Software without the need for a mouse
or touchpad. Using keyboard navigation keys and shortcuts, the user can access
any input or output, mix-point, and all audio DSP tools. Using only the keyboard for
software access can help expedite audio system setup and optimization while on-site
using laptop PCs.
• Front panel input and output signal presence and clipping LEDs — The
DMP 128 provides LEDs on the front panel for each input and output, for real-time
monitoring of signal presence. A separate LED illuminates as a warning whenever
analog signal clipping is detected.
• Front panel USB configuration port — Enables easy configuration without having
to access the rear panel of the processor.
• Ethernet monitoring and control — Engineered to meet the needs of professional
AV environments, Ethernet control enables the DMP 128 to be proactively monitored
and managed over a LAN, WAN, or the Internet, using standard TCP/IP protocols.
• Rack-mountable — 1U, full rack width metal enclosure
DMP128 • Introduction 3
Page 10
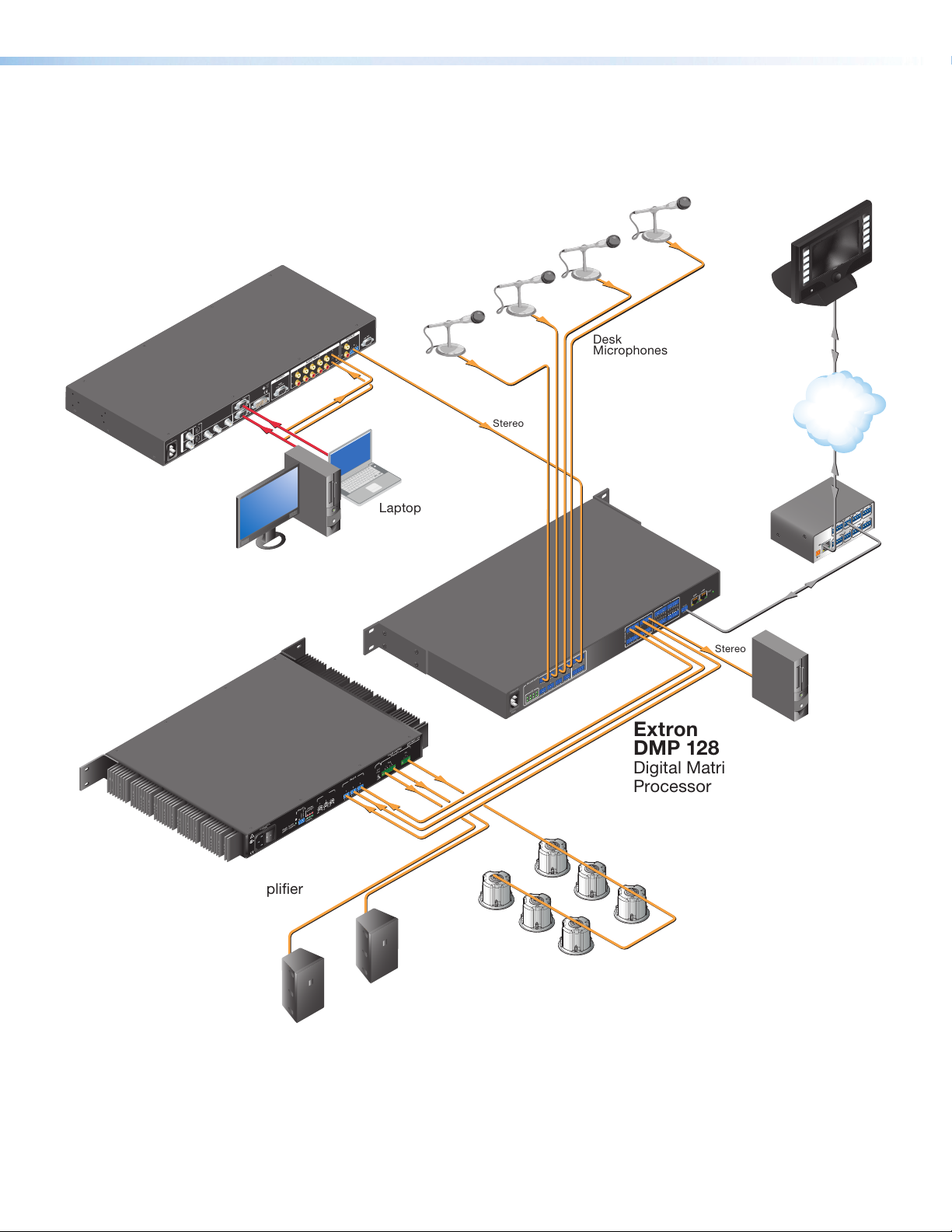
DMP128 Application Diagram
RS-232
OUTPUT
A
B
L
L R
6
R
8
4 5
7
3
AUDIO INPUT
2
1
L
OUTPUT
R
RGB
LISTED
1T23
U S
I.T.E.
Y, B-Y, R-Y
C
6
8
DVI
RGB
7
RGB
3
YC
R-Y
1
VID
5
B-Y
I
Y
N
VID
100-240V 50-60Hz
4
P
U
2
T
Extron
IN1508
Scaling Presentation
Switcher
PC
Laptop
Stereo
Desk
Microphones
ON
OFF
DISPLAY
MUTE
SCREEN
UP
SCREEN
DOWN
Extron
TLP 700TV
7" TouchLink
Tabletop
Touchpanel
Extron
IPL 250
IP Link Ethernet
Control
Processor
™
Ethernet
TCP/IP
Network
COM1
RT SC TS
TXRX
INPUT
3 4
2
LAN
1
POWER
12V
500mA
MAX
VCR
DVD
DOC
CAM
LAPTOP
PC
2
RELAY
1
2
IR
1
COM 2
RX
4
RELAY
TX
G S G
3
S
IR
4
3
COM 3
TXRX
G S G
S
LAN
RESET
EXP
DIGITAL I/O
RS-232
8 9 10
6 7
Tx Rx
5
1617 18 1920
4
15
14
1 2 3
3 4
13
12
11
1 2
8
7
O
U
T
P
5 6
U
T
9 10
4
3
11
2
8
1
7
6
MIC/LINE INPUTS
5
MIC
+48V
4
100-240V 0.6A
3
8
2
7
1
6
5
50/60 Hz
INPUTS
3
2
1
LEVEL
3
2
0
1
0
LIMITER/
0
REMOTE
PROTECT
TIMER DISABLE
STANDBY
SIGNAL
1.3A MAX
100-240V 50/60 Hz
GREEN - ACTIVE
AMBER - STANDBY
Listed
17TT
AUDIO/VIDEO
APPARATUS
XPA 2003C -70V
70V
3
CLASS 2 WIRING
OUTPUTS
4/8
HPF
1 2
CH 3
80 Hz
OFF
S
12
Extron
DMP 128
Digital Matrix
Processor
Stereo
Recording Device
RS-232
Extron
XPA 2003C 70V
Combo Power Amplier
Extron
SI 26CT
Two-Way Ceiling
Extron
Speakers
SI 28
Surface-Mount
Speakers
DMP128 • Introduction 4
Page 11

Installation
This section describes the installation of the DMP128, including:
• Mounting the DMP128
• DMP 128 Models
• Rear Panel Features and Cabling
Mounting the DMP128
The 1U high, full rack width, 8.5 inch deep DMP128 Digital Matrix Processor can be:
• Set on a table,
• Mounted on a rack shelf,
• Mounted under a desk or tabletop.
For detailed mounting options and UL rack mounting guidelines, (see
“MountingtheDMP128” on page153).
DMP 128 Models
There are currently two models of the DMP128 available. Each model has a different
feature set for various applications.
DMP128 Model Matrix
The following feature matrix provides a breakdown of the various DMP128 model
variations. Where differences occur in operation, they are noted in the text.
Model Description
DMP128 DMP128
DMP128 C DMP128 with AEC
DMP128 • Installation 5
Page 12
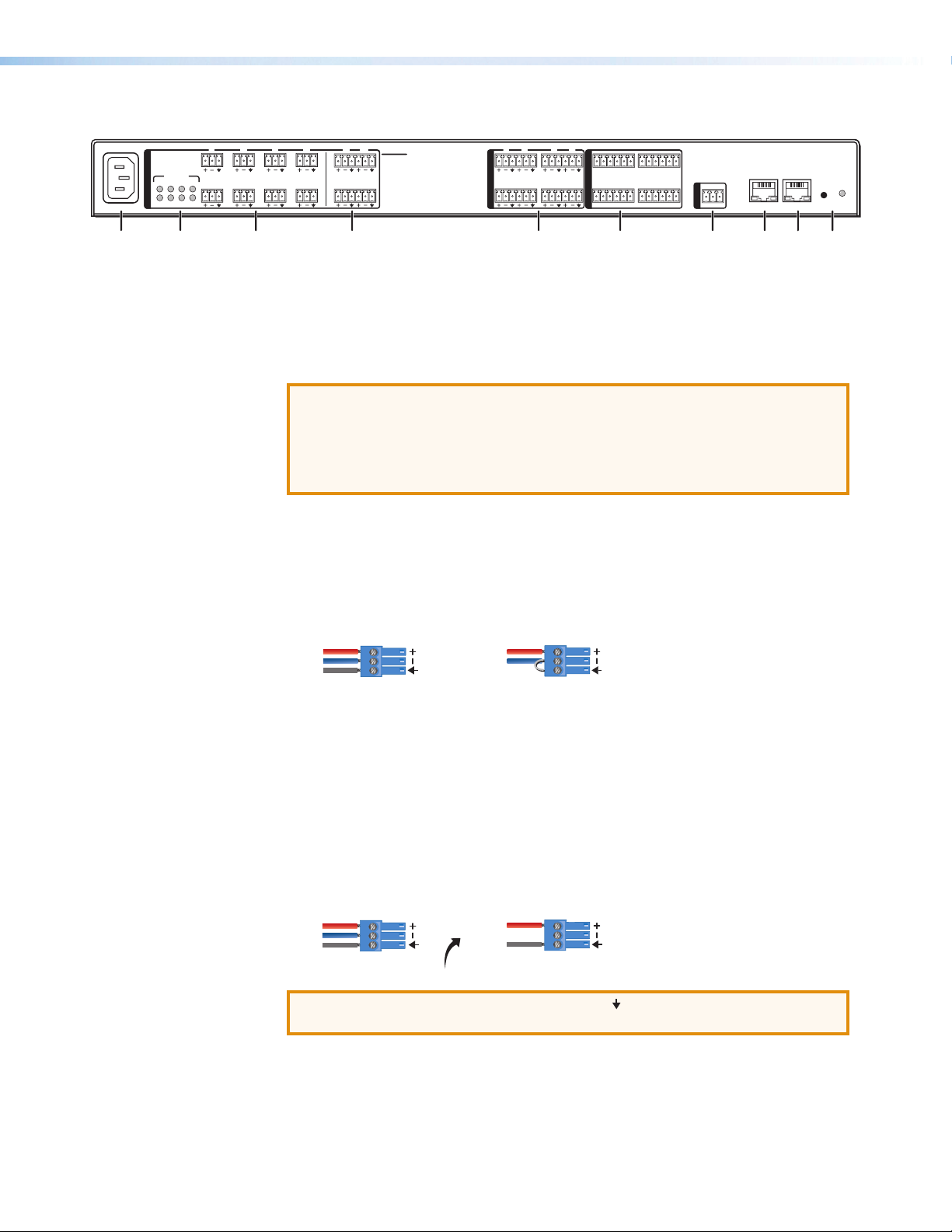
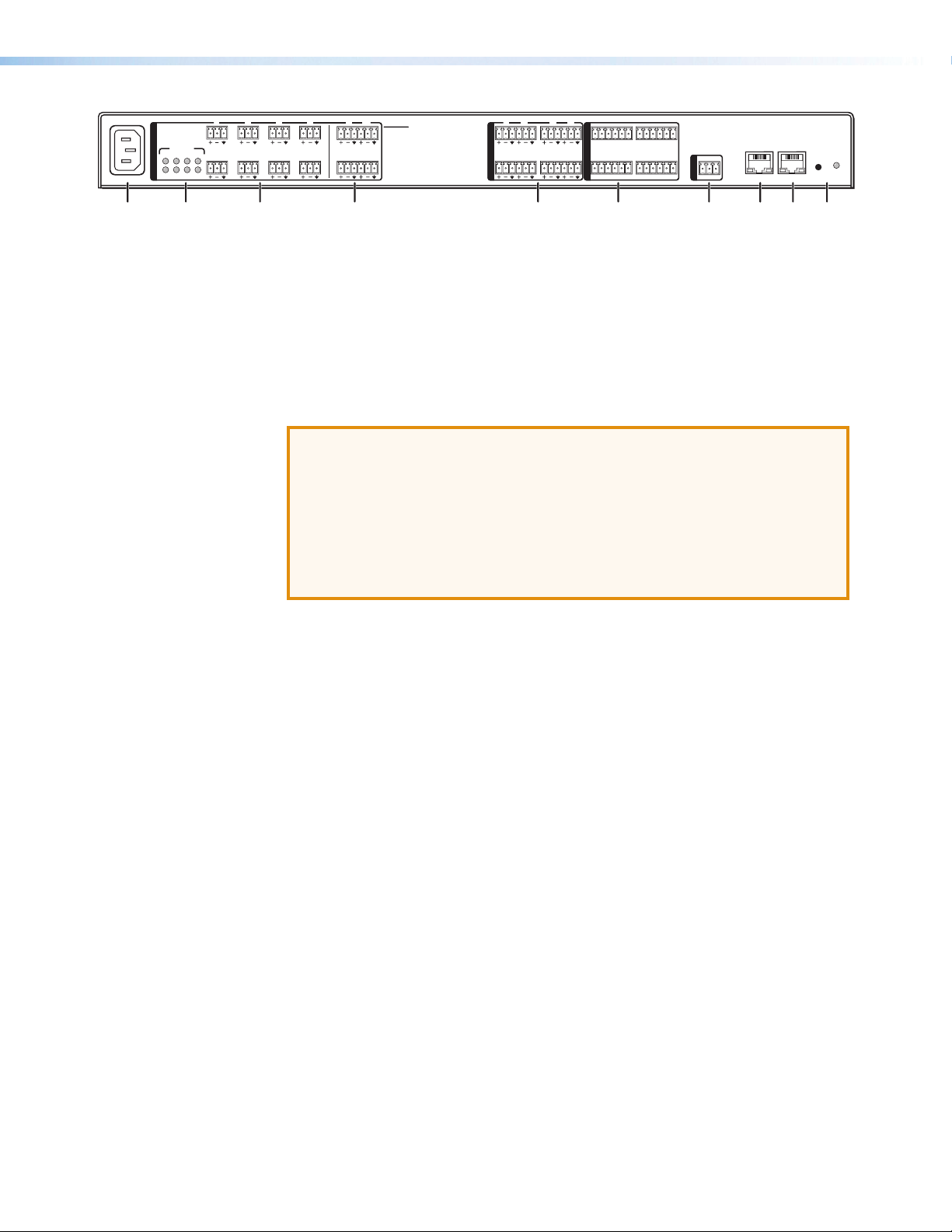
Rear Panel Features and Cabling
Audio Input Wiring
Audio Output Wiring
Audio Input Wiring
Unbalanced Input
Tip
Sleeve
Balanced Input
Tip
Sleeve
Ring
100-240V ~ 0.7A MAX
50/60 Hz
MIC +48V
1234
MIC/LINE INPUTS
5678
3
2
1
6
5
910
4 1
8
DMP 128
11 127
ab cd ef gh ji
Figure 1. DMP128 Rear Panel
234
56 78
OUTPUTS
12345G678910G
DIGITAL I/O
11 12 13 14 15 G1617181920G
RS-232
Tx Rx G
REMOTE
a Power connector — IEC power connector 100 - 240 VAC, 50 - 60 Hz
b Phantom Power indicators — Green LEDs light when +48V phantom power is
placed on the corresponding mic/line input. Phantom power voltage is not adjustable
and is only available to Micinputs 1-8.
ATTENTION:
• Condenser mics require phantom power. Dynamic mics do not require
power.
• Never set a dynamic mic to 48 V. Doing so may damage the mic. For
condenser mics, verify the mic will operate safely at 48 VDC.
c Mic/Line 1-8 input connectors — Eight 3-pole 3.5 mm captive screw connectors
accept balanced or unbalanced mono mic or line level signals. Mic/line inputs provide
gain settings to accommodate consumer (–10dBV) and professional (+ 4dBu)
operating line level sources, plus mic level sources. Up to eight mono mics or line
inputs, balanced and unbalanced in any combination may be connected to these
inputs. See the following diagram for wiring instructions.
RESET
LAN
EXP
Tip
Ring
Sleeve
Balanced Input
Tip
Sleeve
Unbalanced Input
Figure 2. Balanced or Unbalanced Mic and Line Input Wiring
d Mic/Line 9-12 input connectors — Four 6-pole 3.5 mm captive screw connectors
accept balanced or unbalanced mono mic or line level signals. Mic/line inputs provide
gain settings to accommodate consumer (–10dBV) and professional (+ 4dBu)
operating line level sources, plus mic level sources. Up to four mono mics or line
inputs (or two stereo line inputs), balanced and unbalanced in any combination may
be connected to these inputs.
e Mono output connectors — Four 6-pole 3.5 mm captive screw connectors provide
up to eight balanced or unbalanced connections for mono line level output signals.
Tip
Ring
Sleeve
Balanced Output
ATTENTION: Connect the sleeve to ground ( ). Connecting the sleeve only to
a negative(–) terminal will damage the audio output circuits.
Figure 3. Output Connector Wiring
Tip
NO Ground Here
Sleeve
Unbalanced Output
DMP128 • Installation 6
Page 13
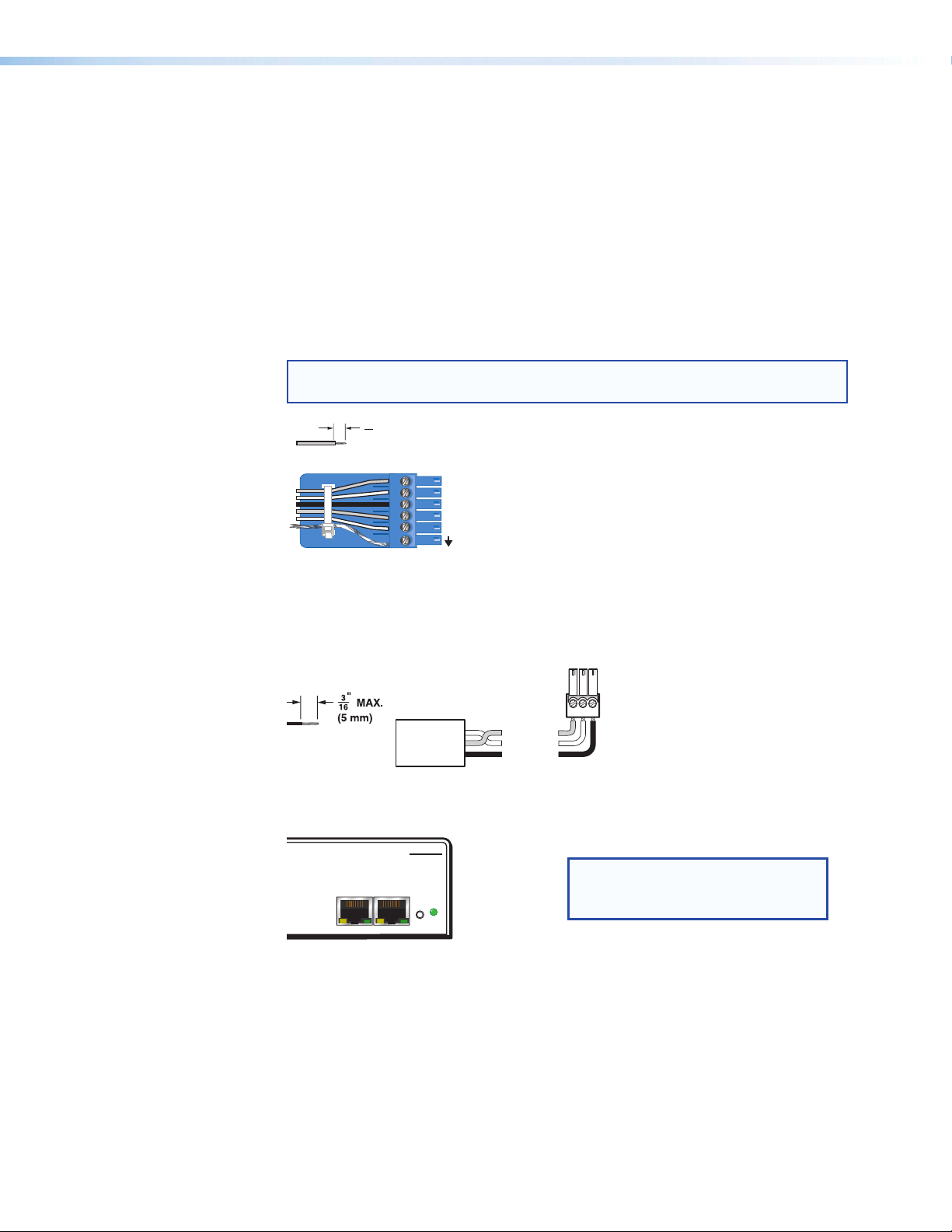
f Digital I/O output connectors — Four 6-pole 3.5 mm captive screw connectors
3 "
each provide five configurable digital input or output ports allowing connection of up
to twenty various devices such as motion detectors, alarms, lights, LEDs, buttons,
photo (light) sensors, temperature sensors, and other devices.
Digital I/O ports are used to monitor or drive TTL level digital signals. The inputs
can be configured to operate in one of two modes: digital input or digital output.
In OUTPUT mode, the device can source up to 250mA at +5 V. In INPUT mode,
voltages greater than 1 V indicate a logic ‘high’ signal while voltages less than 1 V
indicate a logic ‘low’.
All digital I/O ports are tied to a common ground (one common ground for each
6-pole connector), but can be individually configured to operate in one of two modes:
digital input or digital output
NOTE: These ports can be configured via the DSP Configurator (see
“DigitalI/OPorts” on page88).
(5 mm) MAX.
16
Do not tin the wires!
1
2
3
4
5
Figure 4. Digital I/O Wiring
g RS-232 connector — One 3-pole 3.5 mm captive screw connector, labeled RS-232,
for bi-directional RS-232 (±5V) serial control. Default baud rate is 38400. The RS-232
port is not intended to be used for configuring the DMP128.
G
RxTx
RS-232
Device
Do not tin
the wires!
Transmit (Tx)
Receive (Rx)
Ground ( )
G
Bidirectional
Transmit (Tx)
Receive (Rx)
Ground (G)
Figure 5. RS-232 Wiring
h EXP port connector — One RJ45 jack for one additional DMP128 connection.
DMP 128
Digital Matrix
Processor
LANEXP
RESET
NOTE: A one foot shielded CAT6
cable is provided for the EXP
connection.
Figure 6. EXP and LAN Connections
i LAN (RJ-45) connector — A standard RJ-45 jack (see above) accepts an RJ-45
plug for Ethernet connection.
• A yellow (ACT) LED indicates data activity on the connection.
• A green (Link) LED indicates the jack is connected properly to the network.
See “SIS Programming and Control” on page 113 for additional information
on Ethernet cabling.
DMP128 • Installation 7
Page 14

j Reset button and LED indicator — The reset button (see figure 6 on previous
page) is used to return the DMP128 to different tiers of default states and to place
the unit into an event recording mode for troubleshooting. The LED flashes to signify
the different tiers (see “DMP128 Hardware Reset Modes” on page152).
USB Configuration Port (Front Panel)
A front panel configuration port uses an Extron USB A Male to USB Mini B Male
Configuration Cable, 26-654-06 for connection to a PC computer via the USB port. For
USB driver installation details, see “Installing the USB Driver” on page 17 .
DMP128 • Installation 8
Page 15

Hardware Operation
This section describes the hardware operation of the DMP128, including:
• DMP128 Operation
• Front Panel Operation
• Rear Panel Operation
DMP128 Operation
The DMP128 does not have physical controls for configuration or operation. Both are
accomplished using a PC running Windows XP or better and the DSPConfigurator
software (available on the included disc or at www.extron.com), an embedded web
page using Windows Internet Explorer, or the Extron Simple Instruction Set (SIS™) using
hyper-terminal, DataViewer, or a control system.
The DMP128 has several front and rear panel operational indicators and a rear panel
reset button for hardware resets outlined in the following pages.
DMP128 • Operation 9
Page 16
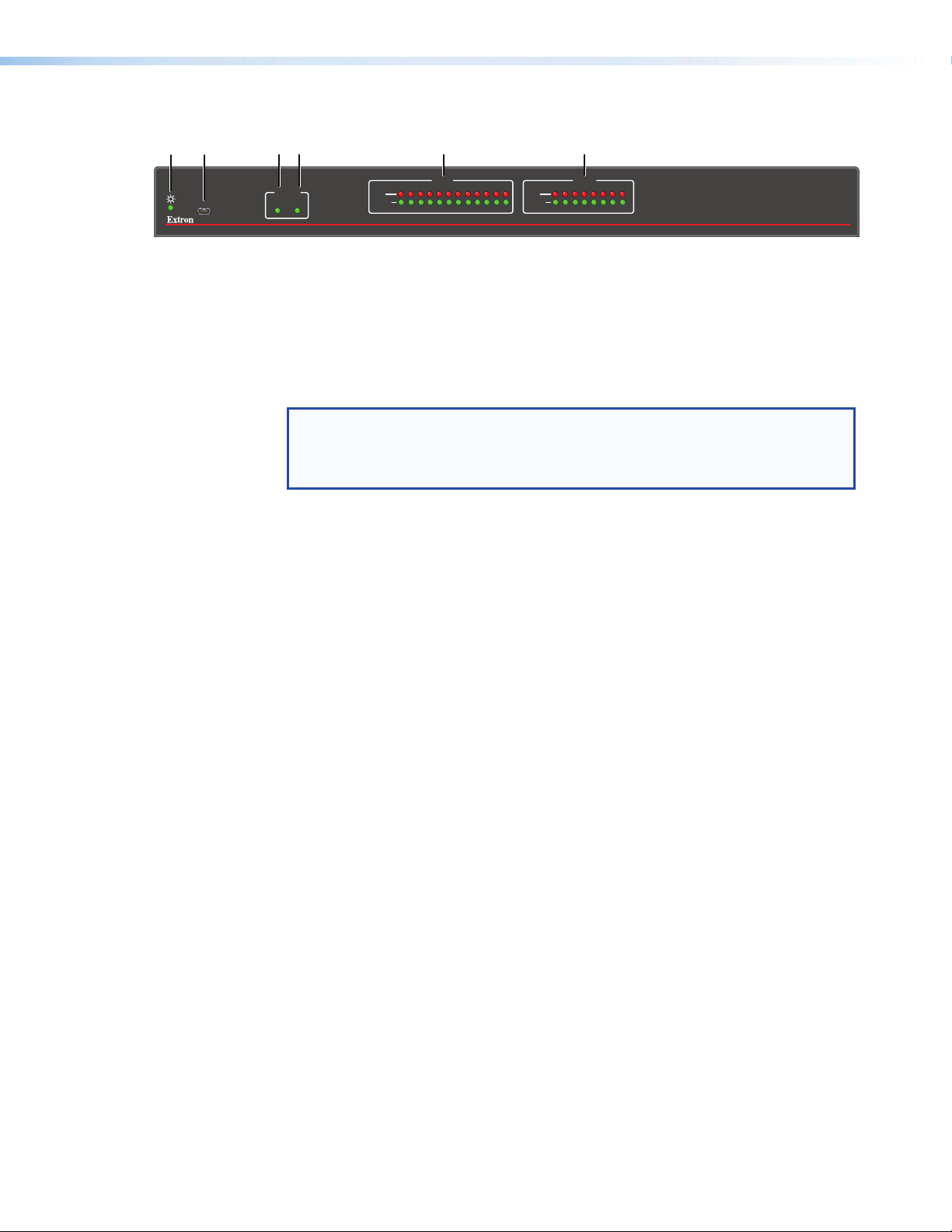
Front Panel Operation
bdea Ñ Ö
CONFIG
ACTIVITY
EXP LAN
INPUTS
12345678910 11 12
CLIP
SIGNAL
12345678
CLIP
SIGNAL
OUTPUTS
DMP 128
DIGITAL MATRIX PROCESSOR
Figure 7. DMP128 Front Panel
Power LED — The power indicator blinks during power-up and lights solid when the
a
DMP128 is operational.
USB configuration connector — The USB 2.0 port uses a mini type-B connector
b
to connect to a host computer for control. The DMP128 USB driver must be installed
prior to using the port (see “Installing the USB Driver” on page17).
NOTE: The DMP128 appears as a USB peripheral with bi-directional
communication. The USB connection can be used for software operation (see
“Windows-based Program Control” on page15), and SIS control (see
“SIS Programming and Control” on page113).
Activity Indicators — Two green LEDs labeled EXP (Ñ) for the expansion audio port
c
and LAN (Ö) for the standard Ethernet port
OFF — Unit is not connected to a second DMP 128.
Ñ
ON — Unit is connected to another DMP128 and is currently configured as the
primary unit.
BLINKING — Unit is connected to another DMP128 and is currently configured
as the secondary unit.
Ö Indicates activity on the corresponding rear panel Ethernet RJ-45 connections.
Input Indicators — Stacked red (signal clipping) and green (signal present) LEDs for
d
inputs 1 through 12 . Each stack represents one input channel.
The green signal LED varies in brightness corresponding to the real-time input signal
level. It begins to light at – 60dBFS increasing in steps to full intensity as the signal
level increases. When the signal reaches – 3dBFS or above, the red clipping LED
lights and remains lit as long as the signal remains above – 3dBFS. When it falls
below that level, the red LED remains lit for 200 milliseconds, after which the display
resumes real-time monitoring of the signal level.
Output Indicators — Stacked red (signal clipping) and green (signal present) LEDs
e
for outputs 1 through 8. Each LED stack represents one output channel.
The green signal LED varies in brightness corresponding to the output signal level. It
begins to light at – 60dBFS increasing to full intensity corresponding to signal level
increases. When the signal level reaches – 3dBFS or above, the red clipping LED
lights and remains lit as long as the signal remains above – 3dBFS. When it falls
below that level, the red LED remains lit for 200 milliseconds, after which the display
resumes real-time monitoring of the signal level.
DMP128 • Operation 10
Page 17
100-240V ~ 0.7A MAX
50/60 Hz
MIC +48V
1234
MIC/LINE INPUTS
5678
3
2
1
6
5
910
4 1
8
DMP 128
11 127
234
56 78
OUTPUTS
12345G678910G
DIGITAL I/O
11 12 13 14 15 G1617181920G
RS-232
Tx Rx G
REMOTE
ab cd ef gh ji
Figure 8. DMP128 Rear Panel
Rear Panel Operation
RESET
LAN
EXP
a c d e f g
See “Rear Panel Features and Cabling” on page 6 for details.
b Phantom Power indicators (MIC +48V) — These green LED indicators light when
+48 V phantom power is placed on the corresponding mic/line input. Phantom power
voltage is not adjustable and is available only on inputs 1 – 8.
ATTENTION:
• Condenser microphones require phantom power.
Dynamic microphones do not require power.
Never set an unbalanced dynamic microphone to +48V. Doing so may
damage the microphone.
• For condenser microphones, verify it will safely operate at +48 VDC.
• When a line level source is connected, be certain the +48V phantom
power is off (cleared).
h EXP — The EXP connector has a green LED to indicate proper connection to an
active expansion network and a yellow LED that blinks to indicate data activity.
i LAN — The LAN connector has a green LED to indicate proper connection to an
active LAN and a yellow LED that blinks to indicate data activity.
j Reset and Power/Reset LED — The reset actuator initiates system resets (see
“Reset Actuator and LED” on page12) . The green LED indicator adjacent to the
reset button duplicates the front panel LED operation.
Power Cycle
Current mixing and audio processor settings (the current state of the device) are saved in
nonvolatile memory. When the unit is powered off, all settings are retained. When the unit
is powered back on, it recalls settings from the nonvolatile memory. If a configuration was
in process during the power down, the saved mix, audio level, and audio DSP processor
settings become active.
On power up the unit performs a self-test. The front power indicator LED flashes during
the test, then lights solid when the unit is available for operation or programming.
Firmware Updates
The firmware of the DMP128 can be updated through an Ethernet, USB, or RS-232
connection. The user can obtain new firmware from the Extron website, or from an
Extron Applications Engineer via e-mail. After obtaining the new firmware, upload it to
the unit via the served web pages (see “HTML Operation” on page137), using the
Firmware Loader launched from the DSPConfigurator program (see “DMP Software”
on page14), or using the Extron standalone Firmware Loader software application
available on the included disc or at www.extron.com.
DMP128 • Operation 11
Page 18
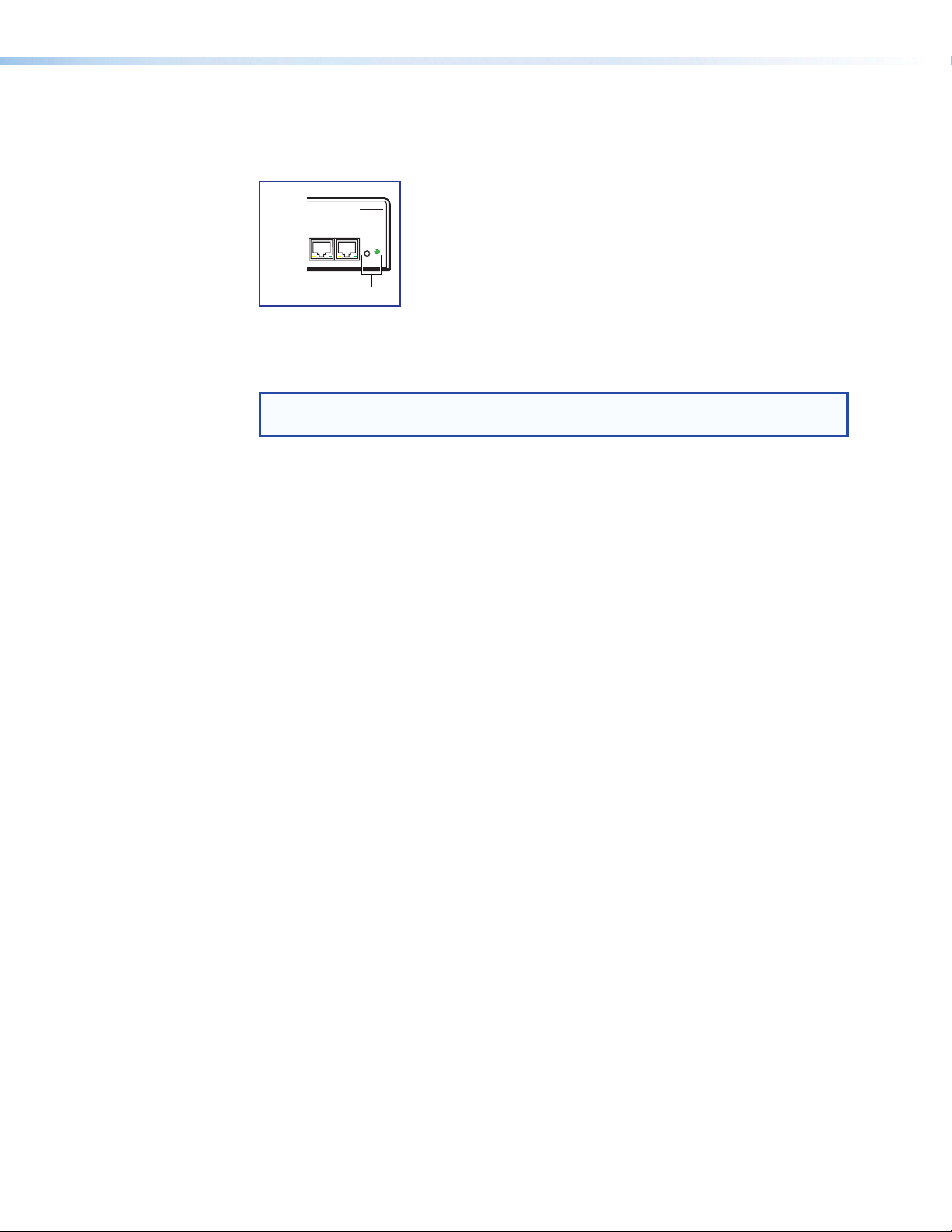
Reset Actuator and LED
j
A recessed button on the rear panel initiates several reset modes. The rear panel LED
blinks to indicate the reset mode.
Rear Panel
DMP 128
Digital Matrix
Processor
EXP
RS-232
TxRx
Figure 9. Reset Button and LED
Hardware Reset Modes:
NOTE: The reset modes listed below will close all open IP and Telnet connections,
and close all sockets.
With power on, when the reset button is held down, every three seconds the rear panel
LED will pulse (blink). At the first blink Mode 3 is available, at the second blink Mode 4 is
available and the third blink indicates Mode 5 is available. The reset modes have separate
and distinct functions outlined below (see “DMP128 Hardware Reset Modes” on
page152).
MODE 1 — Firmware reset: Disconnect power to the DMP128. Press and hold the
reset button while applying power to return the firmware to the version shipped with the
unit from the factory. Event scripting will not start when powered on in this mode. This
allows recovering a unit with incorrect or corrupt firmware.
All user files and settings are maintained. Some user web pages may not work correctly if
returning the unit to an earlier firmware release.
MODE 3 — Events reset: With power on, press and hold the reset button until the reset
LED blinks once (~3 seconds). Release the reset button, then within one(1) second press
it again to toggle events On or Off, depending on the current state.
If the event logging is currently stopped, following the momentary (<1 sec.) press, the
reset LED will flash twice indicating events logging has begun.
If any events are currently running, following the momentary (<1sec.) press, the reset LED
will flash three times indicating the events logging has stopped.
Each flash will last for 0.25 seconds. If the second momentary press does not occur
within 1 second, Mode 3 is exited.
MODE 4 — IP Address reset: With power on, press and hold the reset button about
6seconds until the reset LED blinks twice. Release the reset button, then within 1
second, press it again to reset the IP settings.
Mode 4 will:
• Enable ARP program capability
• Set IP back to factory default IP address (192.168.254.254)
• Set Subnet back to factory default (255.255.0.0)
• Set Gateway back to factory default (0.0.0.0)
• Set Digital I/O Port mapping back to factory default
• Turn DHCP off
• Turn events off
If a second momentary press does not occur within 1 second, the reset will be ignored.
LAN
RESET
DMP128 • Operation 12
Page 19

MODE 5 — Factory default reset: With power on, press and hold the reset button
until the reset LED blinks 3 times (~9 seconds). Release then momentarily (<1 second)
press the reset button to return the DMP128 to factory default conditions. If the second
momentary press does not occur within 1 second, the reset is exited.
The default (reset) state of the device is:
• All mix-points are set to 0dB gain and muted
• Input 1 is routed to Output 1
• Input 2 is routed to Output 2
• Input 3 is routed to Output 3
• Input 4 is routed to Output 4
• Input 5 is routed to Output 5
• Input 6 is routed to Output 6
• Input 7 is routed to Output 7
• Input 8 is routed to Output 8
• All outputs active (unmuted, 100% volume)
• No inserted or active DSP processing
• All audio inputs are set to 0dB gain and muted
• All preset and group master memory is clear (empty)
Digital I/O Ports
The four 6-pole 3.5 mm captive screw connector Digital I/O ports provide twenty
configurable digital input or output ports designed to connect to various devices such
as motion detectors, alarms, lights, LEDs, buttons, photo (light) sensors, temperature
sensors, relays (requiring ≥30 mA), and others.
All digital I/O ports are tied to a common ground (one common ground for each 6-pole
connector), but can be individually configured to operate in one of two modes: digital
input or digital output. Digital I/O port triggers are not limited to a specific unit and can
trigger events across a DMP128 system.
The ports are configured via DSPConfigurator. Each port can be configured to monitor
or drive TTL level digital signals. The ports consist of five I/Os with the sixth pin used as a
ground providing five ports total. The DSP Configurator software provides selection of a
script from a list, to be loaded to the DMP128. The scripts provide pre-configured sets of
functions.
From the main structure menu, select Tools > Configure Digital IO to access the
scripts (see “DigitalI/OPorts” on page88).
DMP128 • Operation 13
Page 20

DMP Software
This section describes the control software for the DMP128, including:
• Software Control
• Embedded Web Pages
• Windows-based Program Control
• DSP Configurator Program Basics
• DigitalI/OPorts
• Emulate Mode and Live Mode
• DSP Configurator Windows Menus
• Optimizing Audio Levels
• Signal Path Building Blocks
Software Control
The DMP128 can be controlled using the DSPConfigurator software, using SIS
commands through hyper terminal or DataViewer, or using embedded WebPages.
The DMP128 has the following connection options:
• RS-232 — One single stack 3-pole, 3.5 mm captive screw connector is used for
bi-directional RS-232 (± 5 V) serial control.
See “Rear Panel Features and Cabling” on page 6, for additional details on
connecting the RS-232 port.
• LAN — 10 Mbps, 100 Mbps, halfduplex, full duplex connections are supported. Two
LEDs indicate connection and activity status. The device has the following default
Ethernet configurations:
IP Address: 192.168.254.254 Default Gateway: 0.0.0.0
Subnet Mask: 255.255.0.0 DHCP: OFF
See “Rear Panel Features and Cabling” on page 6, and “Connection
Options” on page 113 for additional details on connecting the LAN.
• USB 2.0 — A Mini B-type USB connector located on the front panel (duplicated
on the rear panel) provides high-speed USB 2.0 connectivity to a host computer,
backward compatible to 1.0.
DMP128 • Software Control 14
Page 21

Embedded Web Pages
The embedded web pages, accessible via LAN using a web browser, include the following
information, available in a tabbed interface.
• System Status — The opening web page, displaying a report of system status
parameters.
• Configuration — this tab contains the following left menu items.
• System Settings. Contains IP address and date/time settings.
• Passwords. Enter/re-enter admin and user password fields to set up password
protected access.
• Firmware Upgrades. Browse/upload firmware to the device.
• File Management — Delete or upload files
• See “HTML Operation” on page 137 for further details.
Windows-based Program Control
The DSP Configurator Control Program is compatible with Windows XP, WindowsVista,
and Windows7, and provides remote control of the input gain/attenuation, output volume
output adjustment, and other features.
DSP Configurator can control the DMP128 via any of the three control ports, RS-232,
USB, or LAN.
Updates to this program can be downloaded from the Extron Web site at
www.extron.com.
Installing the DSP Configurator Program
The program is contained on the Extron Software Products disk.
Install the software as follows:
1. Insert the disk into the drive
2. Click the Software tab or software icon.
NOTE: If the DVD setup program does not start automatically, run Launch.exe
from the DVD ROM directory using Windows My Computer.
DMP128 • Software Control 15
Page 22
Figure 10. DVD Software Menu
3. Scroll to the DSP Configurator program and click on Install to its right.
Figure 11. DVD Control Software Menu
4. Follow the on-screen instructions. By default, the installation creates a
C:\Program Files\Extron\DSP_Configurator folder for the DSPConfigurator
program.
5. When the DSP Configurator installation is complete, the USB Installer starts
automatically (see figure 12 on page 17 ). It is recommended to install the USB drivers
whether they are used immediately or not.
DMP128 • Software Control 16
Page 23
Installing the USB Driver
When the USB installer begins, follow these instructions.
Figure 12. USB Installer Splash Screen
1. After the DMP Configurator program installation is complete, click
Figure 13. USB Installation
Next to proceed.
DMP128 • Software Control 17
Page 24
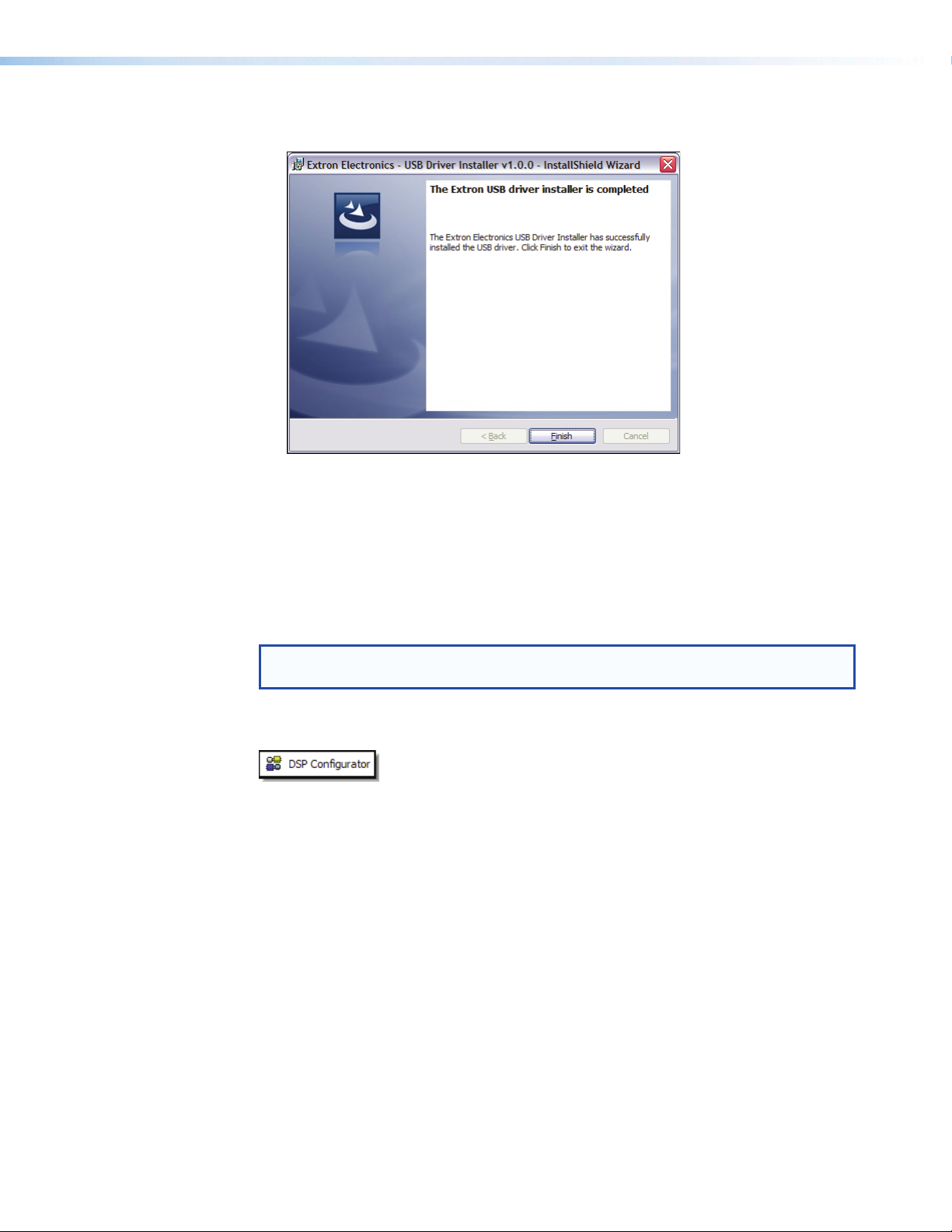
2. The USB driver installer is launched. When the installer has completed the installation
of the USB drivers, the following screen appears:
Figure 14. Successful USB Driver Installation
3. Click Finish.
USB driver installation is complete.
DSP Configurator Program Basics
Starting the program
NOTE: Extron recommends connection via the Ethernet LAN port for running the
DSPConfigurator program.
To run the DSP Configurator Program, click
Using the program
Start > Programs > Extron Electronics > DSP Configurator > DSP Configurator.
The DSP Configurator program starts in Emulate mode (see figure 15, next page). Also
see “Emulate Mode and Live Mode” on page 89.
In the DSP Configurator Emulate mode, audio parameters may be selected, then
transferred to the DMP128 by switching to Live mode (while connected to a DMP128).
Audio settings can also be tailored while connected to the DMP128 which allows
real-time auditioning of the audio output as adjustments are made
(see “Emulate Mode and Live Mode” on page89).
The main screen contains controls for the input and output channels, virtual sends and
returns, expansion sends and returns, and other information used in the operation of the
DMP128. There is too much information contained on the main screen to enable viewing
of the entire mix board at one time so several methods are provided to scroll through the
GUI.
DMP128 • Software Control 18
Page 25

DSP Configurator - DMP 128 C
c
a
d
e
b
Figure 15. DMP128 Navigation Aids
a Minimize buttons — Click once to toggle the view of a selected section from minimum
to maximum. For example, the Inputs section is maximized with all processor blocks and
mix-points shown. Clicking once on the minimize button would then shrink the view to its
minimum screen area allowing items below to fill the screen.
b Maximize buttons — Click once to toggle the view of a selected section from maximum
to minimum. For example, the Virtual Returns section is minimized with all processor
blocks and mix-points hidden. Clicking once on the maximize button would then expand
the view to its maximum screen area.
c Toolbar — All tools and functions not available on the main screen are found here.
d Scroll Bar — When the sections are maximized such that the screen area takes up more
space than can be displayed at one time, items are pushed down or up and no longer
appear. Use the scroll bar to bring those items back into view.
e Hide Channels — Right-click the channel number to hide a channel that has no device
connected and will not be used in the current configuration.
NOTE: Hidden channels can be shown again using the tools menu and
selecting View>Show All Channels then unchecking the hidden channels.
DMP128 • Software Control 19
Page 26
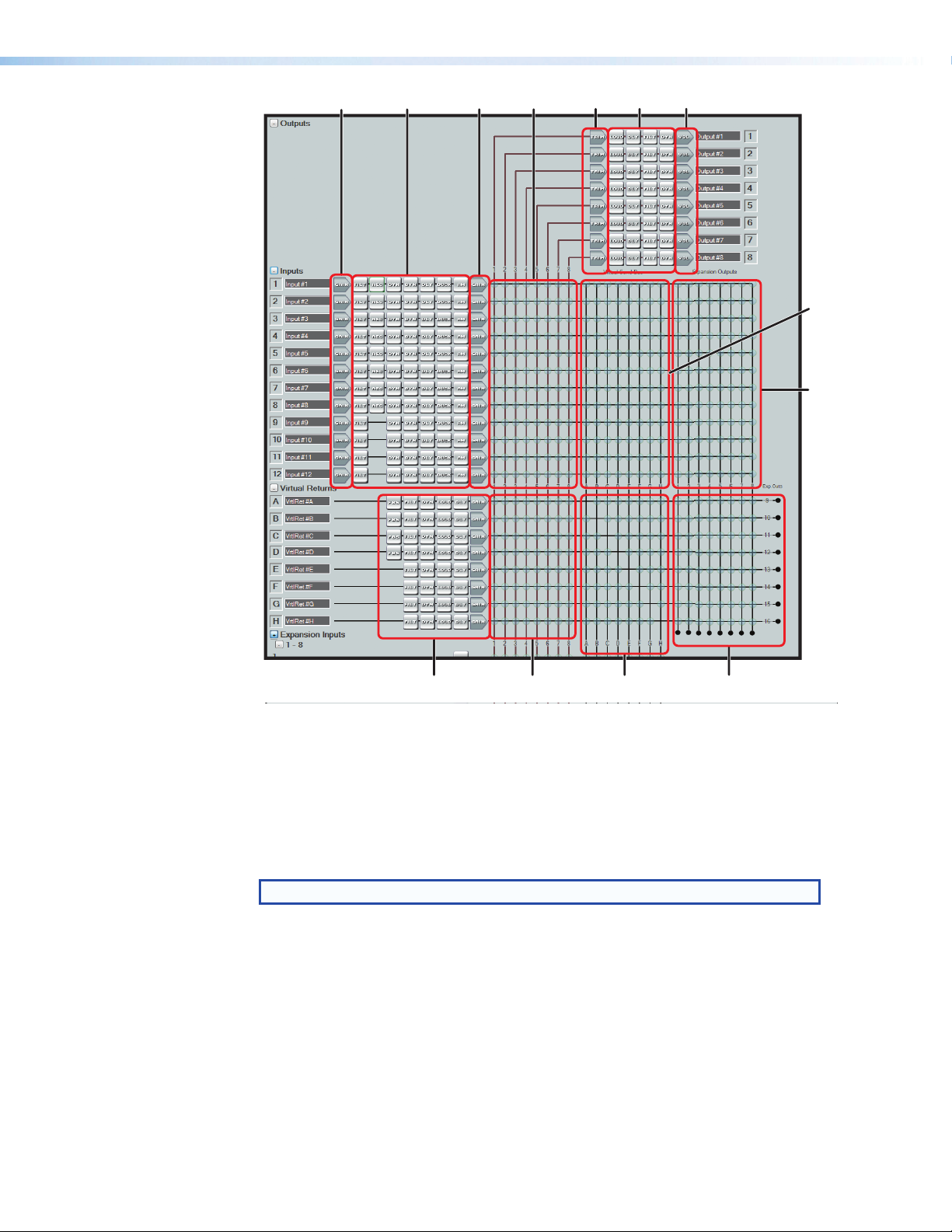
a
bcdfge
l
m
hi
Figure 16. DMP128 DSP Configurator Main Screen
The DSP Configurator program screen consists of an input and virtual return signal
processor chain, the mix-points, and an output signal processing chain. The main screen
consumes too much display area to show all mixers and processor chains at a single time
so there are max/min buttons to collapse each view and a scroll bar on the right side of
the menu to move up and down the screen.
The main mixer is separated into segments as shown in figure 16.
NOTE: The expansion bus returns mix-points are not shown in this view.
jk
a Input gain control h Virtual returns signal processor channel
b Input signal processor channel i Virtual returns to output mix-points
c Input pre-mixer gain j Virtual returns to virtual sends mix-points
d Inputs to Outputs mix-points k Virtual returns to EXP sends mix-points
e Output trim control (post-mixer trim) l Virtual send bus to virtual returns mix-points
f Output signal processor channel m Inputs to expansion sends mix-points
g Output volume control
DMP128 • Software Control 20
Page 27
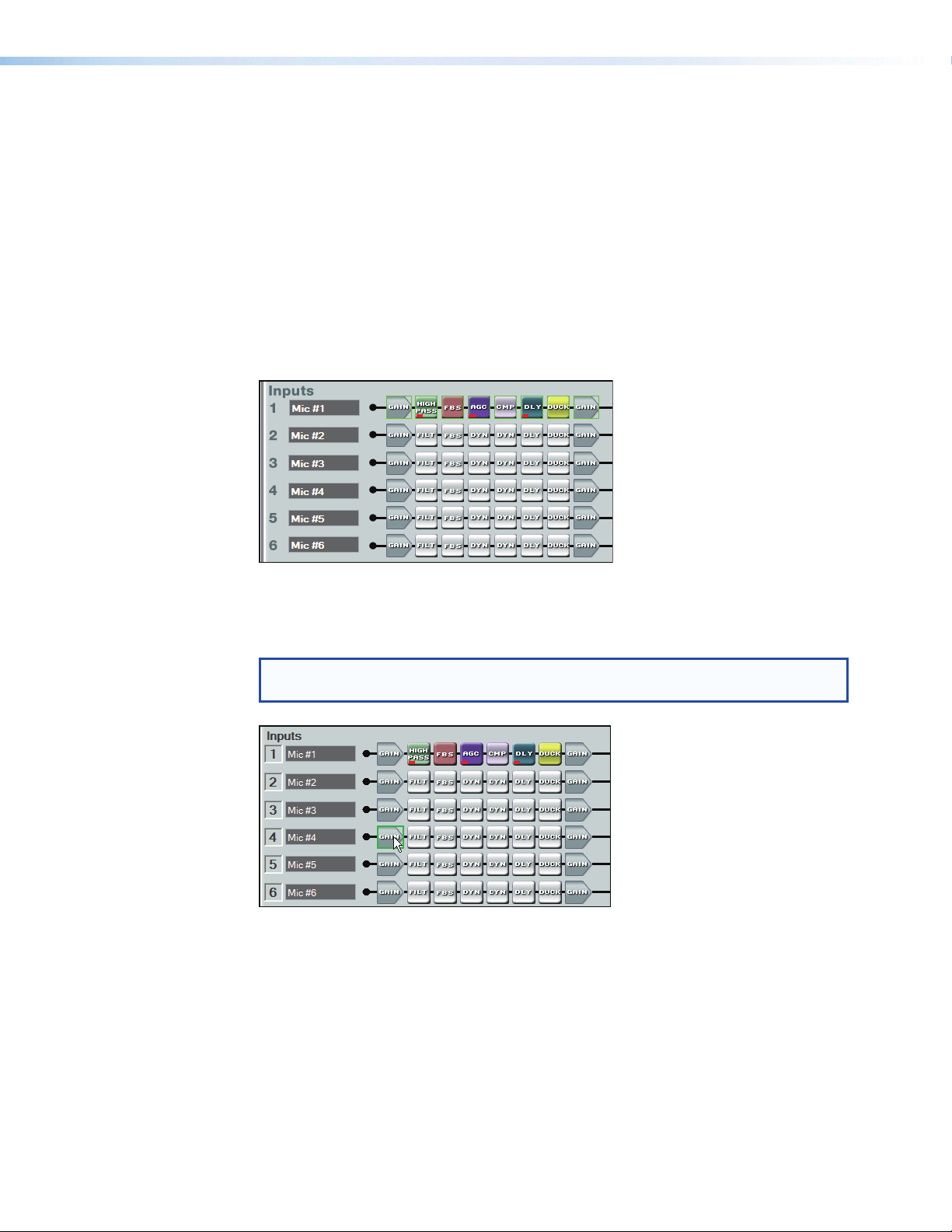
Cut, Copy, or Paste Functions
The user may cut, copy, or paste a GUI processor. These actions can be performed from
a context menu accessed by a right-click of the GUI element, using the Edit menu, or
using the standard Windows keystrokes: <Ctrl+X> = cut; <Ctrl+C> = copy; <Ctrl+V> =
paste.
Multiple GUI elements may be acted upon but the blocks copied must be compatible
with the desired paste blocks. A highlighted group of elements can be cut or copied to
a clipboard. The clipboard contents may then be pasted, but will only succeed if there is
an exact one-to-one relationship between the clipboard contents and the block or blocks
pasted to.
In the following example, the Mic #1 input signal path is copied to Mic #5. First the mouse
is clicked and dragged across the entire signal path. The selected blocks are highlighted
in green. Press <Ctrl+C>, or use the Edit > Copy menu selection to copy the blocks.
As shown below, the starting point for the paste, (the upper/leftmost element), must first
be focused by left-clicking the mouse on it. Note the green focus outline that appears on
the Mic #4 Gain block. The clipboard elements are pasted using the context menu Paste
command, the Edit menu Paste command, or <Ctrl+V>.
NOTE: A cut and copy of elements may be pasted to multiple locations. To copy the
clipboard to an additional location, click on the leftmost block and paste again.
DMP128 • Software Control 21
Page 28
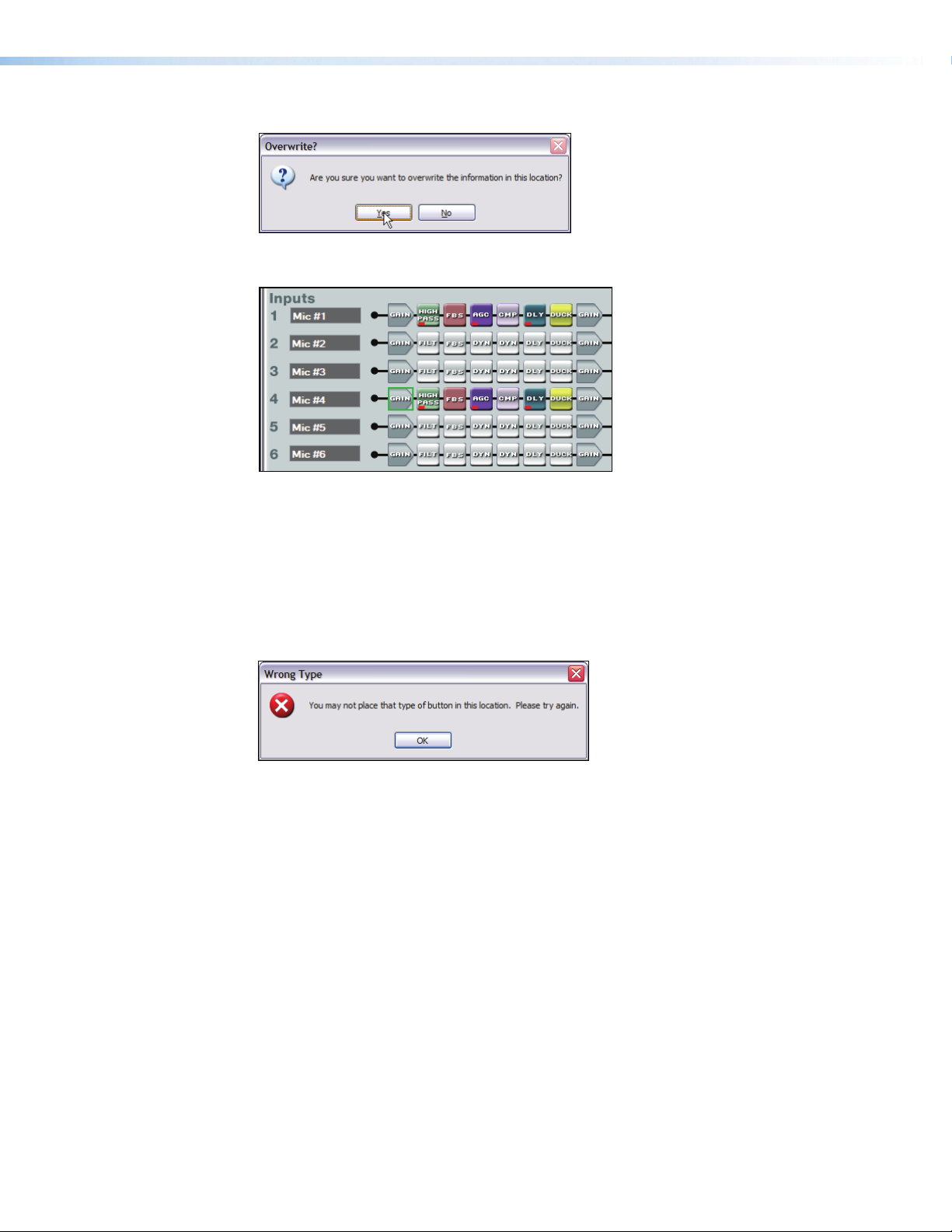
The program warns that all settings in the section being pasted to will be overwritten:
Upon clicking Yes, the entire Mic #4 input path is now identical to the Mic #1 input path
including signal levels, parameters settings, and mute/bypass selections.
Any single processor block may be copied, then pasted to a similar processor block in
the same or different input, virtual or output signal path. Mix-point gains can be copied
from one to another. Input gain, pre-mixer gain, post-mixer trim, and output volume
can only be copied to like gains. For example, an input gain can be copied to any other
input gain, but cannot be copied to a pre-mixer gain, post-mixer trim, or output volume.
Mix-point settings can be freely copied between mix-points. The user is always asked
whether they want to overwrite the existing information. If an attempt is made to copy a
processor block setting to an incompatible block, the user is advised the action cannot be
completed.
DMP128 • Software Control 22
Page 29
Navigation
There are two methods of navigation around the GUI:
• Keyboard • Mouse
One element in the GUI will always retain focus. When a new DSP Configurator file is
opened, the upper left element (Output #1 Trim) will be focused by default.
Keyboard Navigation
All GUI elements including mix-points have the ability to receive focus using the tab
and arrow keys or using the arrow keys following a single left-click (see “Keyboard
Navigation” on page98).
Mouse Navigation
Left-click — A single left click brings focus to a processor block, as well as other GUI
elements such as tabs, sliders, check boxes. Other left-click actions follow the Windows
standard.
Right-click — A single right click brings up a context menu specific to the processor
block right-clicked. Other right-click actions follow the Windows standard.
Double-click — A double-click will open a dialog box from either the focused or
unfocused state of a GUI element.
DSP Configurator Toolbar Menus
The DSP Configurator contains the following menu bar, arranged horizontally below the
title bar:
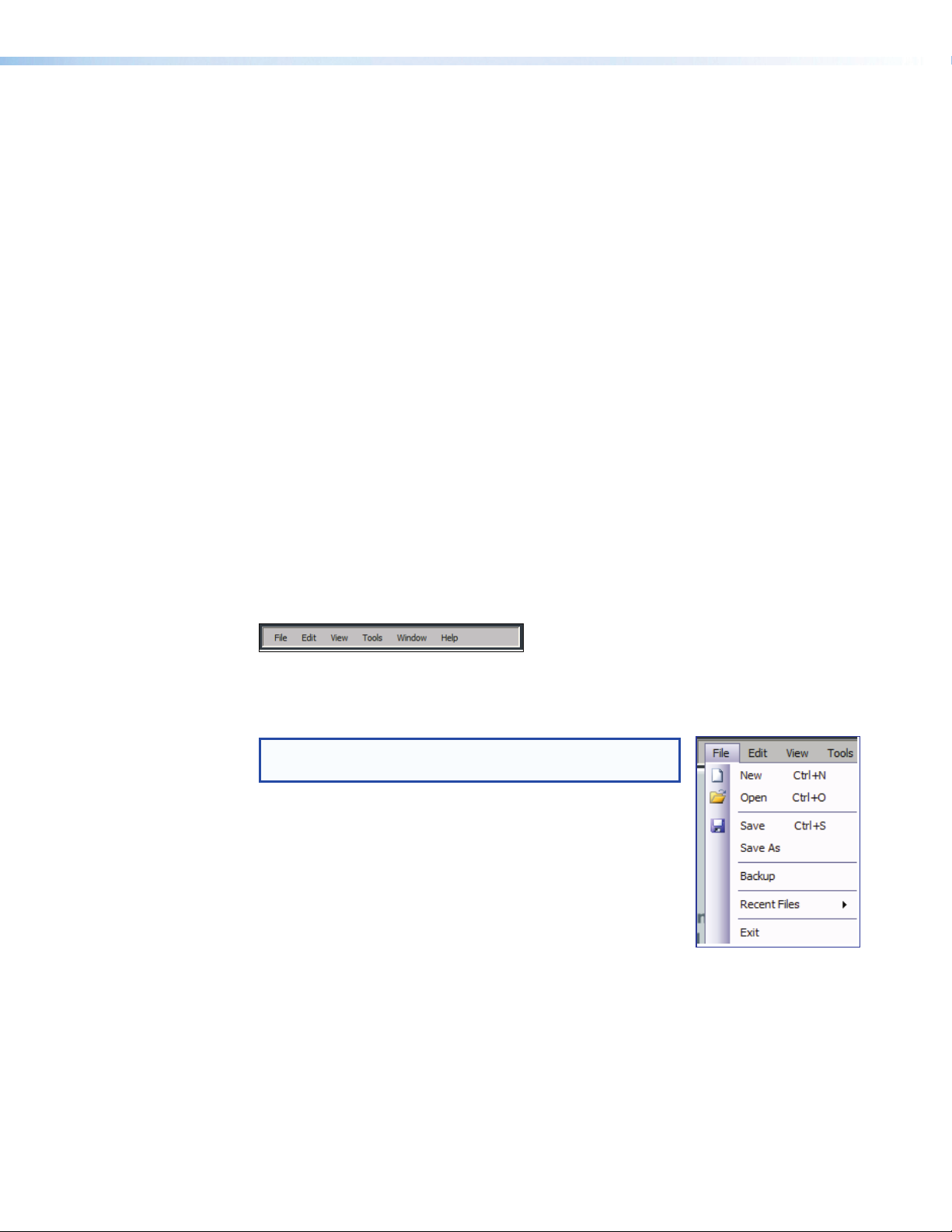
• File • Edit • View • Tools • Window • Help
File
NOTE: New, Open, and Recent Files are unavailable in
Live mode.
• New — Discards the current DSP configuration (after
prompting to save any changes) and opens a blank
configuration file.
• Open — Loads and activates a previously saved DSP
configuration file.
• Save — Saves all changes to the current DSP configuration
file under the current file name. If the file has not previously
been saved, prompts for a file name.
• Save As — Saves all changes to the current DSP configuration file under a new file
name.
• Backup — Transfers all partial presets plus the current configuration to a DSP
configuration file within the DSP Configurator program.
• Recent Files — Opens a list of recently opened or saved DSP configuration files.
• Exit — Closes the DSP Configurator Program.
DMP128 • Software Control 23
Page 30
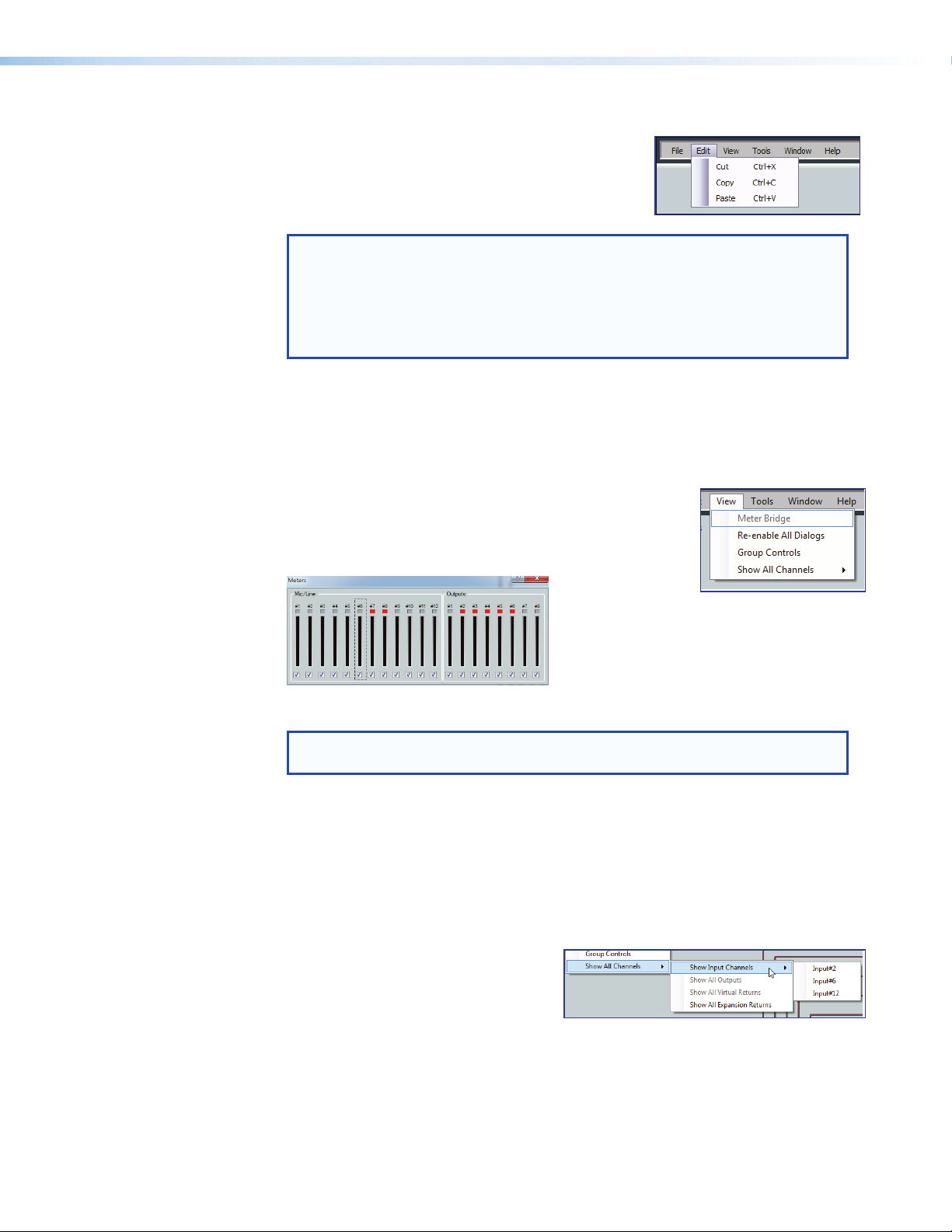
Edit
• Cut — Removes all parameters of a selected
processor block or set of selected blocks to the
clipboard. If not followed by a Paste command to a
different block, the parameters are restored.
NOTE: Processor blocks are not removed from the processor stream after a
Cut and a subsequent Paste operation. Only the parameters are moved.
Processor blocks and their parameters can be pasted only into another
block of the same type. For example, the input 1 filter block and all of its
parameters can be copied to the input 2 filter block but not to the input 1
delay block.
• Copy — Copies all of the parameters of a selected processor block, gain block, or
set of selected blocks to the clipboard.
• Paste — Inserts processor blocks and their parameters from the clipboard into the
DSP Configurator program at the location selected.
View
• Meter Bridge — Opens a Meters dialog box with real-time
meters that monitor signal levels at each input and output.
Figure 17. Meter Bridge
NOTE: Meter Bridge is available in Live mode only while connected via the
LAN port.
• Re-enable all dialogs — Re-enables all dialog boxes, the pop-ups that allow
changes to block parameters.
• Group Controls — Opens the Group Controls dialog box (see “Group Masters” on
page82).
• Show All Channels — Enables channels previously hidden from the main menu to
be viewed. The selection provides an option to either show all hidden channels for
that selection, or by moving to the right, an individual channel can be selected leaving
the others hidden.
DMP128 • Software Control 24
Page 31

Tools
The Tools menu contains the following items and sub-menu:
• Presets — Provides three options:
• Mark All Items — Mark (select) all parts of the current
configuration (excluding presets), including processors and
mix-points to save as a partial preset.
• Save Preset — Save the currently marked processors, and
mix-points as a partial preset.
• Clear Marked Items — Unmark (deselect) all parts of the
current configuration (excluding presets), including processors
and mix-points.
• Protected Configuration — Live mode only. Allows a user
(typically the installer) to save and recall a protected configuration.
The protected configuration is useful to establish the parameters and values (with the
exception of the device IP address) in a known state, either as a troubleshooting tool or as
a baseline configuration. The protected configuration, once saved in the device, is always
present and cannot be overwritten without entering a user-defined Personal Identification
Number (PIN) password. The protected configuration is restored without a PIN.
NOTE: The default PIN is 0000.
• Save — Save the current configuration (excluding presets), including processors and
mixes as a password protected configuration. The DSPConfigurator program prompts for
a PIN to save.
• Recall — Recall the protected configuration.
• Change PIN — Change the PIN associated with the protected configuration.
• Configure Digital I/O — Opens a utility to configure digital I/O ports. The DMP128 provides
twenty digital I/O ports that may be used to trigger external events from DMP128 actions, or
for external events to trigger DMP actions (see “DigitalI/OPorts” on page88).
• Connect to / Disconnect from Device (depending on Emulate or Live mode) —
Performs the same functions as the Mode Emulate and Mode Live buttons.
• Device Manager — Opens the Device Manager dialog box. If a device is connected, displays
the details (model, MAC address, IP address). In addition, a device can be added or removed,
or a selected device cloned, and new folders can be added to an existing device.
• Issue RESET Command — Initializes and clears the following: mix-points, presets,
processor blocks, and gain blocks. This reset is identical to the E ZXXX} SIS command (see
“SIS Programming and Control” on page113).
• Save Changes to Device (live mode only) — Saves configuration changes in the DMP128
to non-volatile memory. This is advised if you are about to power off the device.
• Firmware Loader — Calls the Firmware Loader program, which allows updating the firmware
without taking the DMP128 out of service (see “Firmware Loader” on page151).
• Organize Building Blocks — Allows organization of listed building blocks. You can
also import and export the building blocks file to use your set of building blocks on other
computers or sets from other computers on yours (see “Signal Path Building Blocks” on
page106).
• Configure Groups — Opens the configure groups dialog box (see “Group Masters” on
page82).
• Device Settings (live mode only) — Opens a dialog box that provides a means to change
the IPaddress, set administrator and user passwords, change the device name, change the
date and time, and to select the serial port baud rate.
DMP128 • Software Control 25
Page 32

• Options — Opens a tabbed dialog box that allows customization
>
of the DSPConfigurator appearance and operation.
• Colors — Tailor the appearance of the various graphs and
dialog boxes. Appearance uses a selected color scheme
for the complimentary and graph colors. Complimentary
Colors allows custom selection of colors used with the
various graphs and dialog boxes. Graph colors change the
row colors containing the information and descriptions of the
graphs seen in the processor blocks.
• Preferences — The startup splash screen contains options
for selection of the devices to connect to, or to “Always ask”
on startup. That selection can be changed using Default
Device.
• If Show Meters is set to True, Dynamic Block Meters may
be used to tailor the appearance of the dynamics
meters to use the full meter to show input and gain
reduction, or to show the level based on the output
and gain reduction.
• Processor Defaults, Reset All Defaults —
Returns the DMP128 processor and level control
blocks to factory default settings. Each processor,
and gain/volume/trim block also has an individual
default reset.
• Processor Defaults, Defaults — Individually selects the
default parameters for the various processor, trim, and gain
blocks.
Each row item contains default settings customized for the
processor, filter, trim, or gain block it represents.
Gain and volume blocks can be initially muted, while filter
and dynamics processor blocks can be initially bypassed.
NOTE: The bypass function is labeled “Enable”.
• To view the individual processor defaults, press the
button to the left of the
processor, trim, gain or meter device.
DMP128 • Software Control 26
Page 33

• Expansion Bus — Active only
when a second DMP128 is
connected. Provides a means to
select control of either the primary
or secondary device.
Window Menu
• Cascade — Rearranges all open DSP Configurator program
screens, including dialog boxes, in a cascading array.
• Close All Windows — Closes all open dialog boxes.
• Individual Windows — Lists all open dialog boxes. Clicking on the name brings the
associated dialog box to the front of the desktop.
Help Selection
The Help menu contains the following elements:
• Contents — opens the Help file at the Contents tab.
• Search — opens the Help file at the Search tab.
• About... — displays the name of the application, the current version number, and
copyright information.
NOTE: Help can be activated via the F1 key from any main screen or dialog
(which accesses context sensitive Help).
presets Drop-down
Displays a list of up to 32 presets. Select a preset from the list to
display it and either activate it (Recall), abort the selection without
either recalling or deleting it (Cancel), or delete it (Delete).
NOTE: An asterisk in the drop-down list indicates a partial preset exists only in
the DMP128 and has not been downloaded to the DSPConfigurator.
Mode Buttons
Provides selection between Live mode and Emulate mode (see
“Emulate Mode and Live Mode” on page89).
Backup
When in Live mode (connected to a DMP128), if presets exist in the DMP128 that are
not present in the DSPConfigurator program (indicated by an asterisk next to the preset
name), the function halts and prompts the user to run a backup.
Backup (File > Backup) transfers all partial presets plus the current configuration from
the DMP128 to a DSP configuration (.edc) file within the DSP Configurator program and
then displays a prompt to save the file to the hard drive. Backup is unavailable when the
DSPConfigurator program is in Emulate mode.
DMP128 • Software Control 27
Page 34

a
bcdfge
l
m
hi
Figure 18. Control Blocks and Processor Chains
jk
Audio level, Mix-point, processing Blocks, and Signal Chains
As outlined in red above, all control blocks on the main DSP control screen have one of
three main functions in the overall signal chain:
• Level control (gain/trim/volume),
• Mix-point (signal routing),
• Signal processing (filter/AEC/feedback/dynamics/delay/duck/loudness/automix).
The signal chain varies depending on whether it is in the input, output, virtual bus, or
EXP bus stage. Each of the three types of signal processing channels; Input (a/b/c),
Output(e/f/g), and Virtual (h) shown in figure 18 above, consist of a series of two basic
types of control blocks specific to that chain: level control (gain a/c, trim e, and volume
controlg), and signal processors (frequency filters, feedback suppression, dynamics,
delay, ducking, AEC, AM, and loudness). Both types of control blocks are always present
in the chains. Gain controls default to unmuted and processor blocks are bypassed upon
insertion.
The EXP returns bus has only an AM processing block.
Gain, trim and volume blocks can be muted and processor blocks (after being inserted)
can be bypassed for signal comparison. Mutes and bypasses are shown by a red
indicator in the lower left of the block.
Figure 19. Input Gain Control Muted, Dynamics Processor (AGC) Bypassed
DMP128 • Software Control 28
Page 35

Level Control Blocks
Double-click the
To access a gain, trim or volume control to view a setting, make a change, or observe a
live audio meter (input gain and output volume blocks only), double-click the gain block
icon (see figure 20). This action opens a dialog box that contains the fader for that control.
Double-click a gain,
trim, or volume control.
A dialog box opens,
containing the full
fader control.
NOTE: In Emulate mode
(the startup mode),
the meter is not operational.
Figure 20. Accessing a Typical Gain Control Dialog Box
Level controls always have a fader control for setting the signal level and a digital
indication of its current setting. They can also have switches or indicators required for their
specific function.
processor Blocks
Each processor block represents a menu of one or more processors that can be inserted
into the audio stream. For blocks that provide more than one processor, only one can be
selected. Each block can be inserted by a double-click or right-click>Insert then
selecting the desired processor (see figure 21). Once a block is inserted, the selected
processor is displayed in the block and the block changes color. Processor blocks default
to bypassed. Bypass is different from mute since the processor will pass an unprocessed
signal when in bypass mode. To have them default to “not bypassed” see “Tools” on
page 86.
processor block.
Click the desired
-orRight-click the
processor block.
processor.
Click insert.
The selected processor is displayed in the
block.
To change processor variables, double-click the
block again to open the processor dialog box.
Click to select the
desired processor.
Figure 21. Selecting a Processor Block
DMP128 • Software Control 29
Page 36

Once a processor is inserted, to view associated parameters that define the selected
processor (such as a frequency curve) or to remove the bypass, double-click on the
processor block. This action opens a new dialog box that contains parameters for the
process (see figure22).
Figure 22. Sample Processor Dialog Box
• The
Set Defaults button discards all custom settings and
reloads the default parameters.
• The Bypass button temporarily suspends the processing without
removing the processor block. Red indicates the processor is bypassed.
By default, each processor block is bypassed when inserted (the Bypass button in the
processor dialog box is red). This can be changed for each processor block type (see
Tools > Options and the specific defaults for the processor types).
NOTE: Figure 22 is a sample of one type of dialog box. Contents and appearance
of each dialog box are unique to the processor type.
The block can be removed from the signal chain by selecting it with a single mouse click
and depressing the keyboard <Delete> key or by right-clicking and selecting Delete.
Detailed explanations of each signal chain with their processor blocks along with mix-point
operation follow in the next section.
DMP128 • Software Control 30
Page 37

Mic/Line Input Signal Chain Controls
The input signal processor chain allows adjustments to program or microphone audio
material before input to the main mixer.
Gain Control (GAIN)
The gain control provides a single long-throw fader with a range of
–18dB to +80dB, adjustable in 1dB increments with the fader or
in 0.1dB increments using direct entry in the level setting readout
below the fader. The peak reading meter holds the peak level for
one second, displaying it numerically in the box below the meter.
The default setting is unity gain (0.0dB).
The Phantom Power checkbox, accessible in the dialog box, toggles
the +48 VDC phantom power on and off. Phantom power is typically
used to power a condenser microphone.
The Mute button, accessible in the dialog box, silences the mic/line
input.
The Polarity button, accessible in the dialog box, allows the
polarity of wires connected to the audio connectors (+/tip and –/ring)
to be flipped to correct for miswired connectors.
DMP128 • Software Control 31
Page 38

Filter (FILT)
Each filter block allows a total of five filters. The first filter is inserted from a processor
list that appears when the block is double-clicked or via a context list when the block is
right-clicked.
Figure 23. Insert Filter Menu
Once inserted, double-click the processor block to change parameters of the filter. After
the first filter is inserted, up to four additional filters may be added to the filter block using
the dialog box. Select the desired filters from the following list using the drop-down boxes:
• High pass filter — A high pass filter passes a band of frequencies extending from a
specified cutoff frequency (greater than zero) up toward the high end of the frequency
spectrum. All frequencies above the specified cutoff frequency are allowed to pass,
while all frequencies below are attenuated.
The default cutoff is 100 Hz.
• Low pass filter — A low pass filter passes a band of frequencies extending from a
specified cutoff frequency (less than infinite) towards the lower end of the frequency
spectrum. All frequencies below the specified frequency are allowed to pass, while all
frequencies above are attenuated.
The default cutoff is 10 kHz.
• Bass and treble filters — Also known as shelving or tone controls, the separate
bass and treble filters provide the ability to cut or boost gain linearly above or below a
specific frequency, with the end-band shape giving the visual appearance of a shelf.
The bass default frequency is 100 Hz and the treble default is 8 kHz.
• Parametric equalizer filter — The parametric filter is a frequency equalizer that
offers control of all parameters, including amplitude (the amount of gain/boost or
gain reduction/cut applied), center frequency (frequency), and range of affected
frequencies (Q) around the center frequency.
DMP128 • Software Control 32
Page 39

Figure 24. Filter Block Dialog Box
Additional filters are inserted by opening the filter block dialog box, then selecting a filter
type from the drop-down filter selection list. All filter parameters are modified via the Filter
block dialog box. Each filter loads with all applicable default parameters displayed to the
right of each drop-down filter selection list.
DMP128 • Software Control 33
Page 40

Figure 25. Filter Dialog Box, Filters Added
Within the dialog box, a filter is focused when a filter type is inserted, or is focused by
clicking the filter number to the left of the filter selection drop-down list. Note how box3 in
figure 25 is highlighted in yellow, indicating it is the filter in focus. The results of the filter in
focus (independent of other filters) will show in the graph as a dotted line the same color
as its filter row when bypassed. When active (not bypassed), the line is solid.
When multiple filters are enabled, the graph indicates the focused filter result (independent
of other filters) in the color of the filter row in the type/parameters table. The composite
response, the combined effect of all filters not bypassed, is always displayed in red.
DMP128 • Software Control 34
Page 41

Figure 26. Filter Dialog Box, Filter Not Bypassed
Above the graph, each filter has a "handle" (circled in red above) placed directly
above the cutoff or center frequency whose number corresponds to the filter number
(outlined in red). Clicking a handle or clicking the table row brings focus to that filter.
<Click+hold+dragging> the handle horizontally changes the cutoff or center frequency to
a new position on the x axis.
The table below shows each filter type with default parameter settings. The table
immediately following shows the possible range for each parameter.
Type Frequency Parameter 1 Parameter 2
High Pass 100 Hz Slope: 6dB N/A
Low Pass 10000 Hz Slope: 6dB N/A
Bass 100 Hz Boost/Cut: 0.0dB Slope: 6dB
Treble 8000 Hz Boost/Cut: 0.0dB Slope: 6dB
Parametric 1000 Hz Boost/Cut: 0.0dB Q: 1.0
Filter Parameter Settings Range
Frequency 20 Hz to 20 kHz
Boost/Cut -24.0dB to +24.0dB
Q (Parametric EQ only) 0.707 to 15.000
Slope (HP & LP filters only) 1st Order (6dB) and 2nd Order (12dB)
DMP128 • Software Control 35
Page 42

High Pass
The high pass filter allows all frequencies below the specified frequency to pass
unattenuated. All frequencies above the specified cutoff frequency are allowed to pass,
while all frequencies below are attenuated.
The default cutoff is 100 Hz.
Figure 27. High Pass Filter Response Curve
All frequencies lower than the specified frequency, 100 Hz, are attenuated leaving the
upper frequency response flat. Also note at the specified frequency (100 Hz) the signal is
about 3dB down, typical operation for high pass filters.
DMP128 • Software Control 36
Page 43

Low Pass
The low pass filter is the opposite of the High Pass filter. All frequencies above the
specified frequency are attenuated allowing lower frequencies to pass.
The default cutoff is 10 kHz.
Figure 28. Low Pass Filter Response Curve
Here, the frequencies higher than the specified frequency, 10 kHz, are attenuated leaving
the lower frequency response flat.
DMP128 • Software Control 37
Page 44

Bass and Treble Shelving
Bass and treble shelving may be added to the filter. Also known as shelving or tone
controls, the separate bass and treble filters provide the ability to cut or boost gain
linearly above or below a selected frequency, with the end-band shape giving the visual
appearance of a shelf.
If only a bass or only a treble filter is required, either bypass the unneeded control or set it
to “Unused” in the selection box.
The bass default frequency is 100 Hz and the treble default is 8 kHz.
NOTE: Selecting "Bass & Treble Filters" inserts two separate filters.
Figure 29. Bass and Treble Shelving
The corner frequency of the controls may be selected to 0.1 Hz accuracy. Two slopes,
6 and 12dB/octave are available along with the ability to boost or cut the signal up to
24dB.
DMP128 • Software Control 38
Page 45

Parametric (Equalizer)
The parametric filter is a frequency equalizer that offers control of all parameters, including
amplitude (the amount of gain/boost or gain reduction/cut applied), center frequency
(frequency), and range of affected frequencies (Q) around the center frequency.
Up to five parametric filters can be placed in the filter box at one time. Each may be set
to a different frequency creating a five band parametric equalizer. The control will boost or
cut the center frequency, and by changing the Q value, the range of affected frequencies
can be widened or narrowed around the center frequency. In general, a higher Q value
results in a narrower affected bandwidth.
To demonstrate how Q affects the filter, the following filter block (see figure 30) containing
five parametric filters centered at different frequencies but with the same Q of 1.0. The
filter in focus (c) has a center frequency of 1000 Hz boosting that frequency +12dB over
a Q of 1.0. Note the markers on either side of the peak frequency are at about 300Hz on
the left and 3000 Hz on the right, a bandwidth of about 2700 Hz.
Figure 30. Parametric Filter at 1000 Hz, Q: 1.000
DMP128 • Software Control 39
Page 46

By increasing the Q to 10.000, the center frequency remains the same. The markers show
the bandwidth of the filter narrowed to between 900Hz and 1200Hz, or about 300Hz
(see figure 31). Parametric filters can be used to notch out a very narrow, or very wide
range of frequencies using the Q.
Figure 31. Parametric Filter at 1000 Hz, Q: 10.000
The above dialog box shows the frequency curve for a single active filter. To add its effect
to the overall frequency response, remove the bypass on the other filters.
DMP128 • Software Control 40
Page 47

The overall frequency response is now shown as a solid red line with the filter in focus
(located in row 3 below) shown in the color of its table row.
Figure 32. All Parametric Filters Active
The parametric filter allows frequency selection accurate to 0.1 Hz and either 6 or 12dB
of slope. The 3dB down point will remain constant regardless of the slope setting. Only
the steepness of the frequency attenuation curve will change.
DMP128 • Software Control 41
Page 48

Acoustic Echo Cancellation (AEC)
The DMP128 C models provide one acoustic echo canceller processor for each of the
first eight mic/line inputs. A single reference can be selected for each AEC from a list of
the eight line outputs and virtual paths. The selected reference signal is compared to the
AEC input signal and the difference in gain is a decibel measurement reported via a meter
as an echo return loss (ERL).
About AEC
Echo occurs when audio from a talker in the far end is received and amplified into the
near end listener’s room, with that sound then being picked up by microphones in the
near end acoustic space and sent back to the far end. The amount of signal sent back
to the far end talker can be substantial, and with the added transmission delay, the result
is an echo effect that will seriously compromise communication in a teleconference or
videoconference.
The Acoustic Echo Cancellation processor removes the potential echo signal at the near
end mic channel by comparing it to the received signal from the far end, designated as
the “reference,” and then creating an adaptive filter to cancel the potential echo before it is
sent back to the far end.
AEC Setup
Successful operation of the AEC processing block is a function of proper gain structure
and selection of the AEC reference (see “Optimizing Audio Levels” on page101). This
section provides an overview of the two elements.
Proper gain structure involves the relationship between the signal at the selected reference
and the signal at the mic input, within the context of proper levels for the reference and
mic inputs independently. The mic input gain setting will naturally be optimized for the
voice level of the talker in that room; therefore the amount of signal from the far end that is
picked up by the mic is dependent on how much that far end signal is being amplified in
the near end room and the distance from the mic to the speakers.
The reference signal is the signal received from the far end, which will ultimately be sent to
a sound reinforcement system within the near end room. The output of the video codec
might be connected to any of inputs 9 – 12.
In the AEC dialog, a reference can be chosen from any channel in one of three signal
chains:
• Input Channels
• Virtual Return Channels
• Output Channels
Extron recommends using an input channel as the reference. An output channel or a
virtual channel may also be used as a reference; however, doing so adds a little more
delay to the signal being referenced.
Using an output or virtual channel reference allows for the combining of input channels
to a single reference, for instance, in a conferencing setup where both a telephone and
a video codec may be used in different instances. In this case, both the telephone and
video codec input channels can be routed to an output or virtual return, with that output
or virtual return then chosen as the reference.
DMP128 • Software Control 42
Page 49

When using an output channel as a reference, the reference point is post volume control;
therefore, changes to the listening volume in the room will affect the AEC gain structure
(see “AEC Dialog” on page43). If you have an output channel on the DMP128 that
is not being used, you can isolate the reference channel from the channel being used for
volume control by routing reference signals to the unused output channel.
Alternately, if you do want the reference signal to track with changes in listening volume,
yet want more control over the actual reference level:
a. Route the far end signal to both the amplifier output and the virtual (unused)
output.
b. Create a group master control that contains the amplifier output and virtual
output. Set soft limits for the group master control, as desired.
c. Set optimal level for the amplified output. Set optimal level for virtual output.
Relative levels between both settings will be maintained by using the group
master control.
AEC Configuration
To insert and configure an AEC processor:
1. Insert an AEC processor on the desired input channel using one of the following
methods:
• Double-click the AEC (filter) block in the DSP Configurator workspace.
• Right-click the AEC block to open the context menu and select Insert AEC.
• Click the AEC block to select it (or use the arrow keys to navigate to the AEC
block) and press the <Enter> key on your keyboard.
2. Double-click the AEC processor to open it. Open the Select Reference drop-down list
and select a reference.
3. Click the Bypass button to disengage bypass. The AEC processor is now operational.
AEC Dialog
The AEC dialog contains a number of meters and indicator LEDs
that are essential for setting up gain structure and monitoring activity.
The AEC reference must be selected from a list, otherwise the
echo canceller will not work. Noise Cancellation, part of the AEC
processor, is selected and adjusted here. A detailed description of
the AEC dialog components is included below.
Activity LEDs
• Far – lights when activity is detected from the remote site.
• Near – lights when activity is detected from the local site.
• Update – lights when the SEC is updating, i.e., converging or
reconverging.
DMP128 • Software Control 43
Page 50

Meters
• ERL – the ratio in dB between the signal at the reference and the signal at the AEC
channel input. When ERL is a positive number, the signal level at the AEC channel
input is lower than the signal at the selected reference (0 to +15dB is desirable).
• ERLE – the amount in dB of potential echo signal that the AEC algorithm, not
including NLP processing, is cancelling.
• TER – the sum of ERL + ERLE, in dB.
Select Reference
Select the AEC reference from a drop-down list, populated with
the following:
• Output channels (1 – 8)
• Input channels (1 – 12)
• Virtual Return channels (A – H)
Noise Cancellation
Noise cancellation can be switched on or off from the AEC dialog.
The noise canceller detects steady state noise, such as HVAC or
other continuous system noise, and effectively remove it without
causing audible artifacts.
Noise cancellation is engaged or disengaged using a checkbox.
When the box is checked, noise cancellation is engaged, or
switched on. When cleared, noise cancellation is disengaged, or
switched off. The default setting is noise cancellation switched on
and set to 15dB of noise attenuation.
Up to 20dB of noise cancellation is available, in 0.1dB
increments.
Setting Gain Structure for AEC
(see “Optimizing Audio Levels” on page101).
DMP128 • Software Control 44
Page 51

Advanced AEC Controls
Click on the open/collapse icon at the bottom of the AEC dialog to reveal the advanced
AEC controls.
Advanced control functionality is as follows:
Non-linear Processing (NLP) Controls
• Enable NLP — this box is selected by default. NLP
is necessary for the removal of echo.
• NLP Presets — click a button to load a set of
values to the three NLP parameters; Max NLP
Reduction, Attack Time, and Release Time.
• Soft
• Normal
• Aggressive
The default parameters (shown at right) match the
Normal preset.
• Max NLP Reduction – the maximum possible reduction in echo artifacts that
can be applied. The range is 0.0 to 80.0dB in 0.1 dB increments.
Default is 50.0dB.
• Attack Time – the speed in which NLP is applied. The range is 0.0 to
100.0msec in 0.1 msec increments.
Default is 6.0msec.
• Release Time – the speed in which NLP is released. The range is 1.0 to
3000.0msec in 0.1 msec increments.
Default is 150.0msec.
Additional Controls
• Double Talk Echo Reduction – sets the amount of echo reduction applied
during double-talk. The range is 0.0 to 20.0dB in 0.1 dB increments.
Default is 15.0dB.
• Comfort Noise – sets a comfort noise level in dB to eliminate states of complete
silence, which may be perceived as a failed connection. The range is 0.0 to
40.0dB in 0.1 dB increments.
Default is 0.0dB which turns comfort noise off.
DMP128 • Software Control 45
Page 52

Dynamics (DYN)
A dynamics processor alters the dynamic
range, the difference between the loudest
to the quietest portions, of an audio signal.
Each input channel provides two dynamics
processor blocks that, when inserted, provide
one of four types; AGC, Compressor, Limiter,
or a Noise Gate processor.
Once a processor has been inserted, individual
processor parameters can be changed in the
dialog box, accessed by double-clicking the
processor block. For comparison, the block
can be bypassed by clicking a Bypass button.
All parameters are displayed in a text box and have a resolution to 0.1 increments.
Parameters can be set by direct entry in the text box to replace existing text, then
pressing Enter, tabbing, or clicking to another area. Threshold, gain/attenuation, target,
and ratio parameters have adjustment points on the graph display. Use the mouse to
click + drag the graph point to the desired destination or value. All time values have a
horizontal slider allowing adjustment in 1 ms increments by either a click + drag of the
slider handle, or focusing on the slider, then using left or right arrow keys (Page Up and
Page Down keys adjust in increments of 10 ms).
The table below lists each dynamics processor type, parameters, and factory default
settings for the processor.
Parameter AGC Compressor Limiter Gate
Threshold -40.0dB -30.0dB -10.0dB -65.0dB
Max Gain 12.0dB
Target -10.0dB
Window 12.0dB
Attack Time 500.0 ms 5.0 ms 2.0 ms 1.0 ms
Release Time 1500.0 ms 100.0 ms 50.0 ms 1000.0 ms
Ratio 2.0 :1 20.0 :1
Hold Time 0.0 ms 100.0 ms 50.0 ms 300.0 ms
Max. Attenuation 25.0dB
Soft Knee Off Off
Details of the individual dynamics blocks follow.
DMP128 • Software Control 46
Page 53

AGC (Automatic Gain Control)
AGC adjusts the gain level of a signal based upon the input strength to achieve a more
consistent volume. Below the set threshold, the signal is not affected. Above the threshold,
weaker signals are boosted up to the maximum gain setting to reach a user-defined target
level. As the signal level approaches the target level it receives less gain or no gain at all. Once
the signal level reaches the target level all gain is removed.
Threshold — is the input level where maximum gain
will be applied (after the attack time is exceeded).
On the graph at right follow the red input level from
the lower left to -40dB where the first red circle is.
Signal levels less than -40dB remain at their original
levels. All signal levels at or exceeding -40dB will
have up to 12dB of gain applied (Maximum Gain).
The threshold level can be adjusted from -80.0 to
0.0dB in 0.1dB increments.
Default is -40.0dB.
Maximum Gain — is the highest amplification
applied to a signal exceeding the threshold and up
to the lower limit of the window (see below).
Maximum Gain can be set from 0.0dB to +60dB in
0.1dB increments.
Default is 12.0dB.
Target — is the desired average signal level of the
output when AGC is applied. AGC can vary the gain
according to the input signal level, specified target
level and maximum gain. As the signal approaches
the target level of –10dB, gain is reduced until at
–10dB, gain is no longer applied.
The target level can be adjusted from -40dB to
0.0dB in 0.1dB increments.
Default is –10.0dB.
Window — indicated by the two yellow lines, is a specified range above and below the
target level. Below the lower line maximum gain is always applied to the signal. When the
signal reaches the window, gain control begins scaling in a linear fashion to achieve smoother
results as the signal reaches the target level.
The window range can be set in 0.1dB increments from 0.0dB to 20.0dB.
The default threshold is – 40dB. The default target level is – 10.0dB. The default gain and
window are 12.0dB.
Attack Time — adjusts the time delay for AGC to engage after the input signal level reaches
or exceeds the threshold level.
Attack time can be adjusted from 0.0 to 3000.0 ms in 0.1ms increments.
Default is 500.0 ms.
Hold Time — adjusts how long AGC continues to boost the signal after the input signal drops
below the threshold and before release time begins.
Hold time can be adjusted from 0.0 to 3000.0ms in 0.1 ms increments.
Default is 0.0 ms.
Release Time — adjusts the time it takes to return the signal to normal (unprocessed) levels
after the signal no longer exceeds the threshold level setting. Release time begins only after
hold time is reached.
Release time can be adjusted from 10.0 to 10000.0 ms in 0.1ms increments.
Default is 1500.0 ms.
DMP128 • Software Control 47
Page 54

Compressor
The compressor regulates signal level by reducing, or compressing, the dynamic range
of the input signal above a specified threshold. The input level to output level ratio
determines the reduction in the dynamic range beyond the threshold setting. For example,
with a ratio setting of 2:1, for every 2dB of input above the threshold, the compressor
outputs 1dB.
Compression is commonly used to contain mic levels within an acceptable range for
maximum vocal clarity. A compressor can also make softer sounds louder in one of two
ways. The dynamic range can be reduced by compressing the signal above the threshold
while raising the post-compressor gain/trim (referred to as "make-up gain"). Alternately,
the input signal can be increased while the compression ratio above the threshold is
increased correspondingly to prevent clipping. Both techniques have the effect of making
louder portions of a signal softer while at the same time increasing softer signals to raise
them further above the noise floor.
Compression can also be used to protect a system or a signal chain from overload similar
to a limiter.
The default threshold is -30dB and default ratio is 2.0:1.
Threshold — is the input signal level above
which compression begins (subject to attack
time) and below which compression stops
(subject to hold and release time).
The threshold level can be adjusted from
-80.0 to 0.0dB in 0.1dB increments.
Default is -30.0dB.
Ratio — is the input signal level reduction
when compression is engaged.
Ratio can be adjusted from 1.0 to 100.0 in
0.1 increments.
Default is 2.0:1.
Attack Time — adjusts the time delay for
compression to engage after the input signal
level reaches or exceeds the threshold level.
Attack time can be adjusted from 0.0 to
200.0 ms in 0.1ms increments.
Default is 5.0 ms.
Hold Time — adjusts how long compression
continues after the input signal drops below
the threshold and before release time begins.
Hold time can be adjusted from 0.0 to
500.0ms in 0.1 ms increments.
Default is 100.0 ms.
Release Time — adjusts the time it takes to return the signal to normal (unprocessed)
levels after the signal no longer exceeds the threshold level setting. Release time begins
only after hold time is reached.
Release time can be adjusted from 10 to 1000.0 ms in 0.1 ms increments.
Default is 100.0 ms.
Soft Knee — Select the Soft Knee checkbox to smooth and soften the transition from
uncompressed to compressed output levels. There are no adjustments.
DMP128 • Software Control 48
Page 55

Limiter
The limiter restricts the input signal level by compressing its dynamic range above a
specified threshold. The limiter is most commonly used to prevent clipping, protecting a
system against component or speaker damage. While the limiter is closely related to the
compressor, it applies a much higher compression ratio of ∞:1 above the threshold. The
ratio is fixed and cannot be changed.
Threshold — is the input signal level above
which limiting begins (subject to attack time)
and below which compression stops (subject
to hold and release time).
Threshold level can be adjusted from – 80.0
to 0.0dB in 0.1dB increments.
Default is –10.0dB.
Attack Time — adjusts the time delay for
limiting to engage after the input signal level
reaches or exceeds the threshold level.
Attack time can be adjusted from 0.0 to
200.0 ms in 0.1ms increments.
Default is 2.0 ms.
Hold Time — adjusts how long limiting
continues after the input signal drops below
the threshold and before release time begins.
Hold time can be adjusted from 0.0 to
500.0ms in 0.1 ms increments.
Default is 50.0 ms.
Release Time — adjusts the time it takes
to return the signal to normal (unprocessed)
levels after the signal no longer exceeds the
threshold level setting. Release time begins
only after hold time is reached.
Release time can be adjusted from 10 to
1000.0 ms in 0.1 ms increments.
Default is 50.0 ms.
Soft Knee — Select the Soft Knee checkbox to smooth and soften the transition from
uncompressed to compressed output levels. There are no adjustments.
DMP128 • Software Control 49
Page 56

Noise Gate
The noise gate allows an input signal to pass only when it exceeds a specified threshold
level. Above the threshold level, the signal passes unprocessed; below the threshold the
signal is attenuated at the rate set by the ratio adjustment. The typical setting of the noise
gate threshold is just above the noise level of the environment or source equipment. That
allows signals that are above the noise to pass, and attenuates the noise when there is no
signal eliminating background noise.
Threshold — is the input signal level below
which attenuation (gating) begins (subject to
attack time) and above which gating stops
(subject to hold and release time).
The threshold level can be adjusted from
-80.0 to 0.0dB in 0.1dB increments.
Default is -65.0dB.
Max Attenuation — is the maximum
attenuation of the signal when it drops below
the threshold.
Maximum attenuation can be adjusted from
0.0 to 80.0dB in 0.1dB increments.
Default is 25.0dB.
Ratio — is the input signal level reduction
when gating is engaged.
The ratio can be adjusted from 1.0 to 100.0
in 0.1 increments.
Default is 20.0:1.
Attack Time — adjusts the time delay for
gating to engage after the input signal level
drops below the threshold level.
Attack time can be adjusted from 0.0 to
200.0 ms in 0.1ms increments.
Default is 1.0 ms.
Hold Time — adjusts how long gating continues after the input signal drops below
the threshold. If the signal is still below the threshold when hold time ends, release time
begins.
Hold time can be adjusted from 0.0 to 500.0ms in 0.1 ms increments.
Default is 300.0 ms.
Release Time — adjusts the time it takes to return the signal to normal (unprocessed)
levels after the signal is no longer below the threshold level setting. Release time begins
only after hold time is reached.
Release time can be adjusted from 10 to 1000.0 ms in 0.1 ms increments.
Default is 1000.0 ms.
DMP128 • Software Control 50
Page 57

Delay (DLY)
The delay processor block, when inserted, provides a means to delay the audio signal.
Audio Delay is used to sync audio to video or to time-align speakers that are placed at
different distances from the listener. The DMP128 can set delay by either of two criteria:
time or distance (feet or meters).
The default unit setting is time with a range of 0.0ms to 200.0 ms adjustable in 0.1 ms
steps. Default is 100.0 ms.
Settings are controlled with a vertical slider and indicated with a value readout field. The
value can be changed by clicking within the readout field, changing the number, then
either pressing Enter, tabbing, or clicking away from the field.
Figure 33. Delay Dialog
Slider adjustments made in feet or meters correspond incrementally to the distance
required to make 1 ms, or 5 ms adjustments (detailed in the table below). If more precision
is required, enter time in 0.1 ms increments into the readout field.
Method Time Feet Meters
Click + drag 1 ms ~1.1 feet ~0.3 m
Focus + arrow 1 ms ~1.1 feet ~0.3 m
Focus + Page Up/Down 5 ms ~5.6 feet ~1.7 m
When distance (feet or meters) is chosen, the conditions (temperature) field becomes
available and can be set either by degrees Fahrenheit or Celsius. When entering a
distance, time delay compensation is automatically modified based on differences in the
speed of sound due to air temperature.
Default is 70° Fahrenheit.
NOTE: When using distance (feet or meters), set a temperature value first, then set
the distance.
DMP128 • Software Control 51
Page 58

Ducking
Ducking provides a means to duck, or lower, the level of one or
more input signals when a specified source must take precedence.
The ducking processor block, when inserted, provides a means
to duck one or more mics and program material (ducking targets) when the processor
detects a signal from the ducking source. Ducking lasts for the duration of the interrupting
signal (ducking source) determined by the threshold setting (plus hold and release time)
and restores the original levels of the ducked inputs once the other signal has ceased.
NOTE: Ducking is not functional when an input chain includes active automixing. If
the input to output mix-point is orange, indicating it includes automixing, ducking
will not function for that input. To enable ducking either delete the automix
processor in the signal chain or uncheck “includes automixing” at the mixpoint.
Ducking is useful when:
• Program material needs to be
attenuated in order to more clearly
hear a narrator voice.
• One microphone, such as one
used by a master of ceremonies,
needs to have priority over other
mics, program material, or both.
• A paging mic needs to attenuate all
other signals.
All ducking processor blocks are
controlled via a common dialog box
that opens when any of the ducking
blocks are selected. All empty ducking
processor blocks have no ducking
source or target settings by default.
When the first ducking source is
inserted (shown at right), no ducking
targets are selected.
NOTE: Signal reduction is not cumulative. Ducking will only reduce an input by the
amount set in the by (dB): text box even if it is being ducked by another ducking
source (see “Ducking and Priority Ducking” on page55).
DMP128 • Software Control 52
Page 59

Ducking Configuration Dialog
Ducking is configured in a dialog box which opens when an active ducking processor block is
double-clicked.
a
Current source indicator
Shows the input selected as the ducking
source. Ducker settings affect the input channel
shown here. When a ducker dialog is opened
for a channel, the current source defaults to
that channel. The current source can also be
selected via the priority readout/source selector
(see below).
b
Enable mic/line source checkbox
When checked, ducking is enabled for the
current source and the ducker processor block
is lit. When cleared, ducking is disabled for the
current source and the ducker processor block
is unlit.
c
Duck Targets:
Shows all potential input targets. Only inputs that
are checked will be ducked. The current source
is not available as a target (a source cannot duck
itself). If the current source has been designated
as a target of another input channel, that input
channel is not available (a target cannot be the
source).
a
b
c
f
e
d
d
by: (Target gain reduction amount)
Individual attenuation settings for each duck
target indB. The default is 20.0dB. If additional
attenuation of a target is required, increase this
value.
The attenuation range is 80.0 to 0.0dB in 0.1dB increments.
e
priority
Displays the hierarchy of ducking source to duck targets. Priority levels are displayed in tree
fashion. Input channels that are targets being ducked by a source are shown as indented
below the source. Any input channel displayed in the tree is an active link. Click an input
channel to select that channel as the current source. The current source indicator (a) reflects
the selected input channel.
f
Settings:
Used to configure the parameter settings for the ducker source. When a ducker block is
copied, these settings are transferred.
Threshold — Sets the input signal level, indB, the ducking source must exceed before
ducking begins. If ducking does not occur quickly enough to avoid loss of speech or program
material from the ducking source, decrease this setting. If ducking occurs too soon, allowing
background noise to trigger ducking, increase the setting.
The range is -60 to 0dB in 1dB increments. Default is -30dB.
DMP128 • Software Control 53
Page 60

Attack Time — Adjusts the time to duck the targets once the threshold is exceeded.
The range is 0 to 3000 milliseconds in 1 millisecond increments. Default is 1millisecond.
Hold Time — Determines the time, in milliseconds, after a ducking source signal drops
below the threshold before ducking ceases.
The range is 0 to 10000milliseconds in 1 millisecond increments. Default is
1000milliseconds (1second).
Release — Determines how long, in milliseconds, after the ducking source level is below
the threshold and the hold time is met, the ducking targets take to restore signal levels.
The range is 10 to 10000 milliseconds in 1 millisecond increments. Default is
1000milliseconds (1second).
priority
In some cases, multiple levels of ducking may be required enabling an input source to
take precedence over all but one other input.
In this example, Inputs 2-6 are set to duck when Input #1 has a signal above the ducking
threshold. Input#2 is set to duck inputs 5-6. Since Input #1 has previously been set to
duck Input #2, Input #1 is disabled (grayed out) to prevent contradictory priorities.
Figure 34. Ducker Configuration, Input Priority
Notice the priority tree on the right. The inputs are arranged by their priority status. Input
#1 has all other ducked inputs under it, therefore if a signal is detected, it will trigger Inputs
2-6 to duck. If Input #2 detects a signal and there is no signal on Input #1, Input#2 will
trigger inputs 5-6 to duck. However if the Input#1 signal exceeds the threshold, it will
then duck all inputs including Input #2.
NOTE: Ducking attenuation is not additive. When an input target is ducked,
regardless of how far down the priority line it is, the maximum attenuation is that
set for the individual input and virtual send in the “by:” column near the center of
the dialog box.
See “Ducker Tutorials” on page 55 for additional information.
DMP128 • Software Control 54
Page 61

Ducker Tutorials
Ducking and Priority Ducking
The examples below are based on different input configurations. Insert a ducker from a
ducker processor block using one of the following methods:
Double-click the block,
then click “Ducker”
Right-click the box to open context
-or-
menu, then click “Insert Ducker”
Once inserted, double-click on the ducker block to open the ducker configuration dialog
box. The Enable Mic/Line Source box will be checked.
The first inserted mic will duck all selected targets.
To set a ducking source:
1. Insert a ducking processor to input #1.
2. Open the ducker configuration box and select the
desired duck targets. In this example inputs #2-6
are the ducking targets.
Any signal on input #1 that exceeds the ducking
threshold will now duck inputs2-6.
The ducking processor also provides a means to have
an additional input duck other targets using the Priority
feature. The second input ducks its selected duck
targets, and can also be ducked by the first ducking
source.
To set an additional ducking source:
1. Insert a ducking processor on the additional ducking source.
In this example input #2 will be the second ducking source, with input#1, as shown
above, as the first source.
NOTE: Since it was previously selected as a
ducking target, Input#1 will not be available
as a target of Input #2.
2. Open the ducking dialog box for the input and select
the desired duck targets. In this example inputs #5
and #6 are the ducking targets of input #2.
Any signal on input #2 that exceeds the
ducking threshold will now duck inputs 5-6. The
ducking targets may be changed at any time by
double-clicking the input #2 ducking processor block.
Since input #2 is a target of input #1, if a signal on
input #1 exceeds the ducking threshold, inputs 2-6
will still be ducked regardless of whether the signal on
input #2 exceeds its ducking threshold.
NOTE: No input will be ducked more than the
amount set in the “by(dB):” box.
DMP128 • Software Control 55
Page 62

Automix (AM)
An automixer manages multiple microphone sources, gating or varying input gain
automatically. When properly set, the automixer system will improve use and performance
when multiple mics are in use. The two basic types of automixer include gated and
gain-sharing.
A gated automixer attenuates an input channel when the signal level drops below a userdefined threshold. DSP Configurator allows the user to divide these auto mixers into
gating groups. Each gating group is effectively a separate automixer.
A gain sharing automixer sets a maximum room gain and splits this among all open mics,
based on their input levels. While a gain sharing mixer will typically have less delay in
reacting to a speaker, gated automixers will normally produce a better noise floor.
The DMP 128 allows the user to choose between a gating automixer and a gain sharing
automixer. When the number of open mics (NOM) is set to zero, the automixer is
gain-sharing. When a NOM value is provided, the automixer is gated.
The DMP128 uses an automix dialog box to configure the parameters of each channel
and select an AM group.
Automix parameters:
• AM Group (Assignment) —
Assigns the channel to a gating
group.
Selections are 1 – 8. Default is None.
• Show AM Group Details —
Accesses a popup dialog box that
details all current groups and the
input assignments to each (see the
following section).
• Last Mic Mode On/Off — prevents
all mics from gating off at the same
time, ensuring there is always one
active mic channel. There are four
possible states:
• If not enabled on any mic input, all mics will gate off.
• If enabled on all mics, the last active mic will remain on.
• If enabled on one mic:
• The enabled mic will remain active if it is active when all other mics gate off,
or
• If the enabled mic is not active, it will gate on when all other mics gate off.
• If enabled on some but not all mics, then:
• If enabled on the last active mic, this mic will remain active, or
• If not enabled on the last active mic, then the first enabled mic in the group
will gate on.
• Chairman Mode On/Off — one mic or multiple mics may be set to Chairman under
the Gating Priority list. When a chairman mic is gated on, all non-chairman mics are
gated off to the Off Reduction level.
• Current NOM — Displays the selection of the maximum number of mics that may be
gated open at any time, per gating group. The setting can be changed using the AM
Groups dialog box. Current NOM range is 1 – 12.
Gating Threshold
Indicator
Channel Level
(RMS)
Channel Level
Readout
DMP128 • Software Control 56
Page 63

• Gate Threshold — The signal level below which the mic channel gates off and above
which it gates on.
Range is –60.0dB to 0.0dB.
Default is –50.0dB.
• Off Reduction — The channel attenuation when a mic channel gates off.
Range is 0.0dB to 100.0dB attenuation (0 to –100 dB).
Default: 60.0dB.
• Attack Time — Sets the time at which gain is applied after a channel gates on.
Range is 0.0msec to 3000.0msec in 0.1 msec increments.
Default: 10.0msec.
• Hold Time — The time that a mic remains active after the signal drops below a
user-defined threshold.
Range is 0.0msec to 10000.0msec in 0.1msec increments.
Default: 400.0msec.
• Release Time — The time it takes to ramp the signal level to the Off Reduction
value when the mic channel gates off.
Range is 10.0msec to 10000.0msec in 0.1 msec increments.
Default is 100.0msec.
• Gate Status Indicator and meter — The meter provides real-time sampling of the
selected AM channel with a digital readout of the current level the meter. The indicator
lights when the channel is shut off.
To insert an automix block into a channel:
1. Insert an AM processing block in the desired channel.
Either:
a. Right-click the AM block and select Insert
Automixer,
b. Double-click the AM block and select Automixer.
2. Double-click the inserted AM block to open it (see “Automix parameters:” on
page56).
The AM block defaults to Bypass. Click the Bypass button to toggle the AM block to
active.
DMP128 • Software Control 57
Page 64

Automix Groups
Assigning individual automix channels to groups allows you to see and adjust all channels
assigned to the group on one page. The automix group dialog provides details of all
grouped and ungrouped inputs including the automix settings of each channel or mic.
This allows viewing of all channels in the selected group at a glance to provide a overview
of the group. Individual settings can be changed without leaving the groups dialog. You
can also select all “Ungrouped items” and see the channels currently unassigned to a
group.
Figure 35. Automix Groups Dialog
To Configure an Automix Group:
A channel must first have an active automix block before it can be included in an automix
group.
1. Insert an AM processing block in the desired channel. Either
a. Right-click the AM block and select Insert Automixer.
b. Double-click the AM block and select Automixer.
2. Double-click the inserted AM block to open it.
3. Select the group number from a range of 1 – 8.
4. Set the parameters for the channel.
5. Repeat steps 1 – 3 for all channels in the automix group.
6. Open any AM block and click Select AM Group Details to open the automix
group configuration page.
7. Set NOM for the selected group.
8. Test the system and make adjustments as needed.
Adjustments can be made to individual automix channels using the rows by opening
each individually, or globally to all channels using the AM group details page. Observe
Gate Status indicators to verify that channels gate on properly.
The AM Group Details dialog provides details of all grouped and ungrouped inputs
including the automix settings of each channel or mic. This allows viewing of all channels
in the selected group at a glance to provide an overview of the group. Individual settings
can be changed without leaving the groups dialog.
DMP128 • Software Control 58
Page 65

Configuring an Automix Channel
Before configuring automix, it is recommended that proper gain staging is set for the input
mics. This will ensure that adequate signal is provided for automix to work properly.
An automix block should be inserted for each microphone, and the mic assigned
to a group (see “Automix Groups Dialog” above). Setting a reasonable NOM for the
microphone group will increase intelligibility by limiting the number of open mics that are
allowed to gate on at once. A NOM of three is recommended.
In events where a small number of talkers may need priority over other talkers (such as a
presenter at a lectern) Chairman Mode can be enabled on the priority input channel.
Last Mic Mode may be used to minimize the frequency of gate changes. This helps to
prevent rapid switching of input mics by, ensuring that a talker is not gated off when their
speech is paused.
After the automixer is configured, be certain to set the appropriate mix-points to include
automixing.
Pre-mixer Gain (GAIN)
The post-input processing gain control (also called the
pre-mixer gain) provides gain or attenuation post-processing
gain block. It includes a mono long-throw fader with a –100.0
to +12.0dB gain range, and a current tlevel setting readout
below the fader. Fader adjustments are in 1dB increments,
while adjustments can be entered manually to 0.1dB
resolution.
Default is unmuted at unity (0.0dB) gain.
Selecting the fader handle with the mouse or clicking within
the fader area brings focus to the fader. The input signal level
can be adjusted using any of the following methods:
• Direct adjustment. Select and hold the fader handle, then
drag it to desired level in 1.0dB steps.
• Select or tab to the fader handle, then use the up/down
arrow to set the desired level in 1dB steps.
Page Up/Page Down increases/decreases level in 5dB
steps.
• Click in or tab to the level readout field. Type a new value, then press <Enter> or
<Tab> to another area.
Fader Handle
Input
Signal Level
Readout
DMP128 • Software Control 59
Page 66

Line Output Channels
Post-mixer Trim Control (TRIM)
Loudness (LOUD)
There are eight mono Line Output channels. Controls and processing blocks, identical for
each output channel, are described in the following sections.
The post-mixer trim control provides a fader for fine adjustment of the
program material prior to the output signal chain. The trim control has
a range of –12dB to +12dB in 0.1dB increments.
Default is unmuted at unity (0.0dB) gain.
The loudness processor block, when inserted, applies
a filter compensation curve to the signal in an inverse
relationship to the output volume control setting; the
higher the output volume setting, the less compensation is
applied
(see “Calibrating Loudness” on page61).
The loudness processor compensates for changes in human perception to varying volume
levels by applying a filter compensation curve to the signal in an inverse relationship to
the gain control setting. The higher the gain setting, the less loudness compensation is
applied. Generally, as volume is lowered, perception of certain frequencies is progressively
diminished, returning to a more flat response as volume is increased. Loudness will boost
those diminished frequencies to the highest degree at low volume levels, decreasing the
boost as volume increases.
Bypass must be disengaged for the loudness processor to function. The bypass button
is red when engaged (loudness control defeated), and gray when disengaged (loudness
control active).
DMP128 • Software Control 60
Page 67

When bypassed, the graph displays the current filter curve as a dotted line. When bypass
is disengaged, the current filter curve is displayed as a solid line.
Figure 36. Loudness Dialog Dialog box
The Loudness dialog box contains the following elements:
1. Graph — displays the compensation curve being applied to the signal. These curves
are read-only, and are not adjustable from the graph.
2. Compensation Adjustment slider — from a center zero-point, the user can slide to
the left for less loudness compensation (filter curve is reduced), or to the right for more
(filter curve is increased). The slider position is translated into adB value, displayed in
the compensation readout box contained in the Advanced Calibration section. The
slider has a 48dB (±24dB) range.
3. Advanced Calibration — The calibration box provides a value that corresponds
to the position of the compensation adjustment slider. The SPL box displays the
summed value of the slider and the preceding trim control.
Calibrating Loudness
The user may fine-tune the amount of loudness compensation using the compensation
adjustment slider and adjusting “by ear,” or by measuring SPL levels in a particular room,
then using the slider to adjust the loudness filter relative to the SPL of the room and
system gain structure.
Before calibrating loudness, set up the system gain structure (see “Optimizing Audio
Levels” on page101). A pre-recorded track of pink noise or pink noise from a signal
generator is preferable for this purpose. Program material may also be used (using familiar
material is recommended).
If using a signal generator set it to output –10dBu, then set the input gain of the
DSPConfigurator so the input meter reads –20dBFS. If using a recorded source the pink
noise should be recorded at –20dBFS and the player output level setting control set to
maximum, or 0dB of attenuation. For program material, set the input level to meter at
approximately –15dBFS, with peaks safely below 0dBFS.
DMP128 • Software Control 61
Page 68

Unmute the mix-point from the pink noise source to the output connected to the room
amplifier being calibrated. With the basic gain structure previously set up, loudness can be
calibrated using an SPL meter or by ear. (Loudness can also be set using an SPL meter,
then fine-tuned by ear.)
To calibrate loudness, use a sound pressure level meter set to “C” weighting:
1. Set the Loudness processor to Bypass (Bypass button red).
2. Place the meter in an average (but somewhat prominent) listening location.
3. Generate pink noise, or start the program material playback.
4. Measure the SPL in the room.
5. In the loudness dialog, adjust the slider until the value in the “SPL” readout box
matches the reading on the SPL meter.
NOTE: Theoretically, calibration can be performed with the output channel volume
and post-mixer gain level set to any comfortable listening level. But a relatively
loud volume (well above the ambient noise in the room) that can be easily
measured is preferred.
Loudness is now calibrated. Disengage Bypass to hear the compensation.
Alternate method to calibrate loudness:
1. Set up the procedure using steps 1 – 3 of the previous procedure.
2. Set the compensation adjustment slider to its default center position.
3. Set the output channel volume fader to 0dB (100% volume).
4. Adjust the amplifier until the SPL meter reads 90dB.
Loudness is now calibrated. This method works if 90dB is an acceptable amplifier/
volume limit for the room.
Setting Loudness “By Ear”
When setting loudness by ear, it is essential the system gain structure be set up first. Sit in
an average (but somewhat prominent) listening location.
1. Set the loudness processor to Bypass.
2. Set the output volume fader in the DSPConfigurator to a relatively quiet listening level.
Filter compensation from the loudness processor is most prominent at low listening
levels. Use familiar program material set to the levels described earlier.
3. The Calibrate slider should be set to 0, the center point. Disengage the loudness
Bypass. The result will be a moderate enhancement to the program material, with
more accentuated bass frequencies (below 500Hz), and more brightness in the
high frequencies that carry harmonic content (above 7kHz). Engage and disengage
the Bypass switch in order to “A/B” the difference between loudness off and on,
respectively.
4. To experiment with less loudness compensation, move the loudness compensation
slider to the left (less). For more loudness compensation, move the slider to the right
(more).
5. Any adjustment made to the loudness compensation slider will carry through to all
listening levels. Set the output volume fader in the DSP Configurator to a relatively
loud listening level.
6. Engage and disengage the Bypass switch in order to “A/B” the difference between
loudness off and on. At a loud listening level, the difference should be minimal or
barely perceivable.
DMP128 • Software Control 62
Page 69

Delay Block (DLY)
The delay processor block, when inserted, provides
a means to delay the audio signal to compensate for
loudspeaker placement in situations where speakers
delivering the same signal are much farther away than
others. The delay processor block is identical to the delay processor available on the
input and described in (see “Delay (DLY)” on page51). Typically the near speakers
would be delayed so that audio delivery time matches the speakers further away.
Filter Block (FILT)
The filter processor block, when first inserted, provides one of four
filter selections: High Pass, Low Pass, Bass & Treble filters and
Parametric EQ. Up to nine filters can be added to each filter block.
The output filter block is identical to the input filter processor block
except that up to nine filters total can be selected (see “Filter
(FILT)” on page32).
NOTE: Selecting the Bass & Treble Filter inserts two separate filters.
Dynamics Block (DYN)
A dynamics processor block, when inserted,
provides one of four dynamics processors:
AGC, Compressor, Limiter, and Noise Gate.
The available processors are identical to the
processors available on the input dynamics
processor block and described in (see
“Dynamics (DYN)” on page46).
DMP128 • Software Control 63
Page 70

Volume Control (VOL)
Each output channel volume block provides a mono long-throw
fader with a range of 0 to 100dB of attenuation, and a volume
setting readout (indB) below the fader. Volume level is adjustable
with the slider or by entering the desired level directly into the
volume setting readout in 0.1dB increments.
Clicking the fader handle or clicking within the fader area brings
focus to the fader. The input signal level can be adjusted using any
of the following methods:
• Direct adjustment. Click and hold the fader handle, then drag it
to desired level in 1.0dB steps.
• Click or tab to the fader handle, then use the up/down arrow
to desired level in 1dB steps. Page Up/Page Down increases/
decreases level in 5dB steps.
• Click in or tab to the level readout field. Type a new value, then
press <Enter> or <Tab> to another area.
Output polarity switching is also provided with a button that toggles
polarity.
The default setting is unmuted, at 0dB attenuation. A peak meter displays the real-time
audio level from – 60 to 0dBFS.
The OK button accepts settings and closes the dialog with a single click, while the Cancel
button ignores changes and closes the dialog.
The output volume control provides level control for each output. The output control is a
trim control adjustable from –100.0to 0dB. The default setting is unity gain (0.0dB).
The Polarity button, accessible in the dialog box, allows the polarity of the wires
connected to the audio connectors (+/tip and -/ring) to be flipped in order to easily correct
for miswired connectors.
The Mute button, accessible in the dialog box, allows the post-meter audio output to be
silenced. When the audio output is muted, the mute button lights red, and red indicators
in the block turn on.
If the output has been grouped with other inputs or outputs, the group number will be
indicated on the right side of this button (see “Line Output Channels” on page60).
DMP128 • Software Control 64
Page 71

Virtual Bus Returns
Virtual Bus Returns, A-D
Feedback Suppressor (FBS)
There are eight mono virtual bus return inputs, fed by the virtual bus sends. Channel
controls and processing blocks described in the sub-sections that follow are identical for
each virtual bus return channel.
The eight returns are divided into two similar paths. Channels A-D contain a feedback
suppression processing block in each channel. Channels E-H are identical to A-D except
there are no feedback processing blocks.
The virtual bus is used when additional processing of an input signal is required. It is also
useful to apply identical filtering, dynamics processing, loudness compensation, or signal
gain/attenuation to multiple inputs.
The Feedback Suppressor (FBS) is used when there is indication of feedback during
live operation. Dynamic filters automatically detect feedback on a live mic channel, and
engage a set of up to five fixed and 15 dynamic filters to counteract the frequency peaks
at the detected feedback frequency. Up to 15 separate filters may be employed at any
time. The 15 filters act in a FIFO, or first in, first out rotation. If all 15 filters are employed,
when an additional feedback frequency is detected it will overwrite the first detected
feedback frequency and so on.
To avoid a new feedback frequency overwriting a previously detected one, up to five of the
dynamic feedback frequencies can be placed into fixed filters. Once written into the fixed
filters, the feedback frequency can only be overwritten by the user manually writing a new
frequency to the filter.
The FBS dialog box has three tabs; Settings, Dynamic Filters and Fixed Filters.
Global settings and view options are controlled from the settings tab. Dynamic to fixed
filter allocations are handled from the dynamic filters tab. Filter parameters can be
modified from the Fixed Filters tab.
DMP128 • Software Control 65
Page 72

The FBS dialog box provides the following global buttons:
• Clear All — clears all dynamic filter settings.
• Lock — locks the dynamic filters to current settings, preventing automatic updates.
This temporary mode is useful while testing the system, or during the time when
dynamic filters are being converted to fixed filters. When the FBS dialog box is closed,
lock mode is automatically disengaged.
• Bypass FBS — turns off feedback detection when engaged (button is red). Only the
dynamic filters are bypassed. Fixed filters remain active.
• Set Defaults — Click once to return the FBS to default settings.
Figure 37. Feedback Suppressor
DMP128 • Software Control 66
Page 73

FBS Settings Tab
The settings tab enables selection of the feedback suppressor parameters.
• For Composite View show: — the graph view is set by one of three radio buttons:
• Only Dynamic FBS Filters
• Only Fixed FBS Filters
• Dynamic & Fixed FBS Filters (default)
• Mode: Q — adjusts the notch filter Q used by dynamic filters. Similar to Q on the
parametric equalizers, Q changes the bandwidth of the filter. The default setting can
be modified in Tools > Options. The range is from 5 to 65. Larger values provide
less change to the audio frequency response while lower values may provide greater
feedback suppression but with more possible impact to the tonal response of the
source audio.
Suggested values for specific applications are:
Q Value Application
7 Voice with considerable feedback potential
30 Voice with less feedback potential
65 Music with minimal feedback potential
• Attack Time — sets the time at which dynamic filters are generated after feedback
detection. A longer attack time (greater than 200 ms) reduces the chance that music
or audio content will trigger the dynamic filters to respond. A shorter attack time (less
than 2 ms) reduces the time between when feedback is detected and suppressed.
• Hold Time — expressed in hours:minutes:seconds up to 9 hours. Hold time sets
the time a dynamic filter setting persists before the filter is cleared. When hold time is
disabled (checkbox cleared) dynamic filters persist indefinitely unless cleared manually
or the device is power cycled.
Figure 38. FBS Settings Tab
DMP128 • Software Control 67
Page 74

FBS Dynamic Filters Tab
This tab contains the fifteen dynamic filters, with a scroll bar to display filters hidden due to
the dialog box size.
Dynamic filters are notch filters that are cut only, providing attenuation up to 30dB at the
specified Q. The default Q is set in the Tools > Options menu, but can be changed on
the settings tab prior to engaging the FBS dynamic filters. Changing the Q setting after
dynamic filters have been generated will clear all dynamic filters.
Figure 39. FBS Dynamic Filters Tab
Frequency and cut values are read only. Dynamic filters are in auto-detect mode when the
FBS block is active (when Bypass FBS is off). If testing reaches a point where no further
changes are desired, the lock button may be engaged. The lock mode of operation is
temporary, and is intended to be used during setup of the FBS. When the FBS dialog box
is closed, lock mode is automatically disengaged.
If there are specific dynamic filters the operator wants to assure are not overwritten, press
the Move to Fixed button to write the designated filter settings to the first available filter in
the Fixed Filter tab.
NOTE: When a dynamic filter setting is moved to the fixed filter, it will automatically
clear that frequency from the dynamic filter.
The Clear button will remove a detected frequency from the corresponding dynamic filter.
A cleared filter reverts to auto-detect mode unless Lock mode is engaged.
DMP128 • Software Control 68
Page 75

FBS Fixed Filters Tab
Fixed filters are notch filters with an adjustable center frequency and Q, and up to 30dB
of cut. The fixed filters are typically set by converting dynamic filters to fixed, however
adjustments to filter parameters can be manually made from the Fixed Filters tab.
Fixed Filters are inactive and the filter type is set to “Unused” by default.
Figure 40. FBS Fixed Filters Tab
No filter parameters are displayed when the filter type is set to Unused. As a filter is
moved to the fixed filter tab from a dynamic filter, the filter becomes active and displays
Notch as the filter type. The parameters copied from the dynamic filter are displayed in
the same line. Once a fixed filter is active, settings can be modified or adjusted if needed.
Fixed filters can also be individually bypassed by clicking the Bypass button.
FBS Settings Ranges and Fixed Filter Defaults
FBS Parameter Settings Range Default Setting
Frequency 20 Hz to 20 kHz N/A
Q 5.000 to 65.000 30.000
Attack Time 0.0 ms to 1000.0 ms 10.0 ms
Filter Hold Time 0 seconds to 9 hours 00:00:00; Disabled
Fixed Filter Parameter Settings Range Default Setting
Frequency 20 Hz to 20 kHz 1000.0 Hz
Q 1.000 to 65.000 30.000
Cut Up to 30dB cut 0.0dB
DMP128 • Software Control 69
Page 76

Filter (FILT)
Filter function and interface is identical to the mic/line input channel Filter block except
that only three filters are provided (see “Filter (FILT)” on page32).
Dynamics (DYN)
There is one dynamics processor block available on each virtual path. Dynamics function
and interface is identical to the mic/line input channel Dynamics block,
(see “Dynamics (DYN)” on page46).
Loudness (LOUD)
There is one loudness processor available on each virtual path. The loudness function and
interface is identical to the Output channel Loudness block (see “Loudness (LOUD)” on
page60).
Bypass must be disengaged for the loudness processor to function. The bypass button
is red when engaged (loudness control defeated), and gray when disengaged (loudness
control active).
Delay (DLY)
Audio Delay is used to sync audio to video or to time-align speakers that are placed at
different distances from the listener. The Delay function and interface is identical to the
input channel delay block (see “Delay (DLY)” on page51).
Gain (GAIN)
Virtual Bus Returns, E-H
Each virtual input channel gain block provides a mono long-throw fader with a –100.0
to +12.0dB gain range, and a level setting readout below the fader. Fader behavior is
identical to the Pre-mix-point gain block, described in the mic/line input section
(see “Pre-mixer Gain (GAIN)” on page59). Fader adjustments are in 1dB
increments, while adjustments can be entered manually to 0.1dB resolution.
Default is unmuted at unity (0.0dB) gain.
There are four additional mono virtual bus return inputs, also fed by the virtual bus sends.
Virtual Bus Returns E-H are identical to A-D except there are no feedback processors.
As with the virtual bus returns A-D, these returns are used when additional processing of
an input signal is required. It is also useful to apply identical filtering, dynamics processing,
loudness compensation, or signal gain/attenuation to multiple inputs.
DMP128 • Software Control 70
Page 77

Output Mix Matrix
The DSP architecture contains an output mix matrix that connects all inputs to the line
outputs, a virtual send mix matrix that connects all inputs to the virtual bus sends, and
an expansion (EXP) output mix matrix that connects the mic/line inputs and virtual bus
returns to the expansion bus sends (see figure 41 on the next page).
The DSP Configurator GUI provides control of the output mix matrix, used to set mix
levels from the post processing inputs and post processing virtual returns, to each line
output bus. The mix-point GUI behavior is shown in the table on page 73.
Each mic/line input and virtual bus return is connected to a mix-point for each of the eight
line outputs. In general, mix levels are set relative to each other, achieving a desired blend
of input signals at an optimal output level, close to, but not exceeding 0dBFS at the line
output Volume block level meter (while accounting for processing that may occur in the
line output signal chain).
NOTE: Although the virtual bus send and return lines, A-H, are shown as end points
in the GUI, they are connected A-A, B-B, C-C, D-D, E-E, F-F, G-G and H-H.
Those connections cannot be changed.
DMP128 • Software Control 71
Page 78

Outputs
Output
Virtual Send
Expansion Bus
Mix Matrix
Mix Matrix
Mix Matrix
Inputs
Virtual Returns
Expansion Inputs
1 - 8
1 2
3 4 5 6 7
1 2
1 2
3 4 5 6 7 8
3 4 5 6 7 8
Virtual Send BusExpansion Outputs
A B
8
C D E
F G
C D E
F G
A B
H
H
3 4 5 6 7
1 2
8
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
Expansion Outputs
9
9 - 16
Figure 41. Overview of DSP128 Mix-matrix
DMP128 • Software Control 72
Page 79

Mix-point GUI Behavior:
Mix-point color — There are three colors of mix-points:
• Teal indicates standard processing (default),
• Orange indicates the signal chain also includes an auto-mix channel
and,
• Green indicates that all signal processing has been bypassed.
No mix information — a faint circle (teal, green, or orange) on the
mix-point indicates it is muted (contains no mix information).
Mix information — a solid circle indicates the mix-point contains mix
information (the mix-point is unmuted).
Mouse-over — the cursor changes to a hand when a mouse-over occurs
at a mix-point whether the mix-point contains mix information or not.
Single-click — a single click brings focus to (selects) the mix-point,
indicated by a dark green outline around the circle.
Double-click — opens the mix-point dialog box. The focus outline turns
light green to indicate the open dialog box. If the mix-point is muted, the
mix-point circle is gray and the Mute button in the dialog box will be red. If
unmuted, the bubble is teal and the mute button in the dialog box is normal
(typically gray for most color schemes).
Multiple open dialog boxes — When multiple mix-point dialog boxes
are open, the mix-point for the most recently opened dialog box receives
the light green focus circle, while previously opened dialog boxes relinquish
their focus. Focus can be returned by either clicking on a previously
opened dialog box, or by double-clicking on a mix-point.
DMP128 • Software Control 73
Page 80

Clicking a mix-point brings focus to that mix-point. A circle appears around the teal
mix-point which remains transparent. Double-clicking a mix-point opens a configuration
dialog box with the following components:
• Mono Fader — Sets the signal level from the
selected input to the output bus. Gain range is -35dB
to +25dB. Fader behavior is identical to the input
channel gain block described in the mic/line input
section with the exception that course adjustment
(Page Up/Down) increases/decreases in 5dB
increments.
• Mute — Mutes and unmutes the signal to the output
bus. The mix-point ball is transparent when muted
(Mute button red) and solid when unmuted.
• No Input Processing — When checked, bypasses all
processing for the preceding gain string. This allows a
direct comparison of sound between the unprocessed
signal and fully processed. The mix-point turns green
when unmuted and transparent green when muted.
Default is cleared.
• Include Automixing — When checked, includes
the automix channel input. Default is cleared, muting
the automix channel input. The mix-point turns solid
orange when unmuted and transparent orange when
muted.
• OK/Cancel — click OK to accept changes and close the box. Cancel ignores
changes and closes the dialog box.
The title above the fader reflects the input and output channel names for the mix-point.
The example on the left is the Input #1 to Output #1 mix-point set to 0.0dB.
The input level text below the mute button indicates the input level setting for the input
gain control of the selected input signal path, in this example 6db.
Only when the mix-point is unmuted does the circle become solid.
NOTE: The No Input Processing and Include Auto-mixing buttons are
mutually exclusive. You cannot select both. If you are including an automix
channel in the signal path, when you select No Input Processing, Include
Auto-mixing
will clear and not turn back on even when No Input Processing
is unselected. If you want to continue to have an automixing channel in the signal
path, it must be selected again.
DMP128 • Software Control 74
Page 81

Mix-point Examples
In order to better understand how the mix-points work, the following diagrams provide
examples of mixes.
NOTE: To simplify the diagrams not all input and output lines are shown.
Figure 42. Input 1 to Output 1
In the first example (see figure 42) input audio from Mic/Line Input 1 is processed and
arrives at the output matrix mix-point. A double-click on the mix-point opens the dialog
box. When the mix-point is unmuted on Input 1 of the output mix-point, the mix junction
turns teal with a light green circle to indicate the open mix-point dialog box is the focus,
and the signal is routed to Output1.
The mix level can be adjusted using the slider or by direct input of a value between –35.0
and 25.0dB into the dialog box below the slider.
DMP128 • Software Control 75
Page 82

Figure 43. All Inputs to Output 1
In the next example (see figure 43), input audio from all twelve mic/line inputs are
processed individually and arrive at the output mix-point. When the individual mix-point
mute buttons are released, the output mix-point junctions turn teal, and the signals
are routed to Output 1. Since all the signals are now on output signal line 1, open the
individual mix-point dialog boxes to adjust signal levels for the desired balance. Open the
output trim, processing, or volume to change the signal levels or effects for the mixed
signals coming from the mix-points.
In this manner any single input, or any number of inputs can be routed to any single
output or any number of outputs.
DMP128 • Software Control 76
Page 83

Figure 44. Input 1 to All Outputs
In the example in figure 44 above, Input 1 has been routed to all eight outputs by
unmuting the mix-point for mic/line Input 1 for each output (1 – 8) bus. The example in
figure 44 also shows mix-point four with input processing bypassed (green) and mix-point
eight with active automix.
DMP128 • Software Control 77
Page 84

Virtual Send Bus Mix Matrix
The DSP architecture contains a virtual send bus mix matrix that connects the
mic/lineinputs and virtual bus return signals to the virtual bus sends. There is an additional
mix matrix to route EXP input signals to the virtual bus sends.
The DSPConfigurator GUI provides control of the virtual bus mix matrix, used to set levels
from input signals to the virtual bus sends. Each of the twelve mic/line and eight virtual
return inputs are connected to a mix-point for virtual bus A-H (and the EXP inputs). Each
mix-point is muted and set to 0.0dB (unity gain) by default. In general, mix levels are set
relative to each other, achieving a desired blend of input signals at an optimal level close
to, but not exceeding 0dBFS at the output volume level meter.
The secondary mix matrix contains a section (see figure 45 below) that allows virtual bus
returns to be routed back to the virtual bus matrix to allow further processing using an
additional virtual bus processing block. To prevent feedback loops, a virtual channel is
prevented from being routed back to itself by eliminating the mix-point that would allow
that to occur.
In situations requiring extra processing, the virtual bus return output is routed back to the
virtual bus mix matrix, virtual bus send, which then routes the signal back to a processing
signal chain other than the one it was routed from.
Virtual Send
Bus Mix Matrix
Virtual Send Bus Mix-points
(from Mic/Line Inputs)
Virtual Send Bus Mix-points
(from Virtual Bus Returns)
EXP Inputs to Virtual Bus
Sends
Figure 45. Virtual Bus Mix Matrix (EXP inputs 9-16 not shown)
DMP128 • Software Control 78
Page 85

In the example in figure 46 below, Input 1 is sent to the virtual bus send by muting all eight
signals on the Input1 output mix-points. The virtual bus now serves as additional signal
processing for the input. The signal routes from virtual send A and through virtual busA
signal chain before being sent to the virtual bus return mix-point and Output 1.
This configuration is useful when more than one input requires identical processing.
For example if all inputs were normalized but required a uniform gain to bring them up
to adequate output levels, rather than changing each pre-mix gain control by a similar
amount, all twelve inputs could be routed to a virtual bus (in this case virtual bus A). Then,
using the virtual bus A return gain control, a single adjustment can be used to apply the
same gain to all twelve inputs before sending the signal to the desired output line.
In other cases, if multiple mic inputs are being mixed with program material, only the
program material might require loudness contouring. So the mics could be routed directly
to the output but the program material input could be routed to the virtual bus return
where loudness contouring could be applied. The program material could then be routed
to the same output as the mics.
Figure 46. Input 1 to Virtual Bus A
DMP128 • Software Control 79
Page 86

Expansion Bus Mix Matrix
The DSP architecture contains a third mix matrix that supports connection and control
of a second DMP128 using the included shielded Cat 6 cable. The bus connects the
mic/line inputs, virtual sends, and virtual returns to the expansion bus sends and returns.
The DSP Configurator GUI provides all necessary control of the mix matrix.
Expansion Outputs
Mix Matrix
Inputs to
EXP Sends
(Outputs)
Virtual Returns
to
EXP Sends
(9-16 only)
Exp Inputs
to
Outputs
EXP Inputs
to
Virtual Sends
Figure 47. Expansion Bus Mix Matrix (EXP bus outlines 9-16 not shown)
DMP128 • Software Control 80
Page 87

Multi-device Digital Audio I/O
abcd
Extron EXP Bus
A digital audio connection to an external DMP128 is supported through the rear panel
EXP port using the expansion bus mix matrix. The expansion bus mix matrix can route
any or all of the mic/line inputs and virtual returns to the expansion outs (1-8) with eight
additional channels (expansion outs 9-16) directly connected to the virtual bus returns.
The expansion outputs use an Extron proprietary protocol to exchange audio channels
with another device using the same Extron protocol.
Multi-channel audio on the 16-channel expansion out bus may be processed and used by
the connected DMP128 then returned to the sixteen (16) input expansion bus return.
The expansion bus may also be used for AEC reference. Expansion inputs can include
automix processing, and be included in a gating group.
Only one device can be shown in the DSP Configurator screen at any time. There are two
ways to configure the two devices; switch between the two using the device manager
described above, or open a second DSP Configurator dialog box and connect it to the
second device.
Device Manager
When two DMP128 devices are connected using the EXP bus, the tools menu is used to
configure the connection.
By default, the DMP128 is configured as the primary device. One of the two connected
DMP128 devices must be set as a “secondary unit”. To change the active device in the
DSP Configurator dialog box to secondary, use the >Tools>Expansion Bus menu and
select primary or secondary. A checkmark appears beside the active device.
From the menu bar, select Tools>Device Manager to open the device manager dialog
shown in figure 48.
Figure 48. Device Manager Dialog
The icons function as follows:
a Add Device – Brings up the initial DSP Configurator dialog box that allows the
selection of the model number of the secondary device.
b Clone Device – Provides the option to duplicate the primary device configuration to
the connected secondary device.
c Delete Device – Deletes the highlighted device
d Expand or Collapse Device – If the device connection tree is collapsed, allows it to
be expanded. If the device tree is collapsed, expands it.
The icons for the devices will be grayed out if the device is offline.
DMP128 • Software Control 81
Page 88

Group Masters
Group Members
There are 32 Group Masters that can each be configured to simultaneously control up
to 16 group members. Group masters are configured in the DSP Configurator program
and are saved in the device. Working in emulate mode, group masters can be saved in a
configuration file and pushed to the device upon connection.
A group master can either be a gain control or a mute control. Only one control type
can be selected as group members for control by a group master. For example, a group
master can be configured to control post-matrix gain levels, but not post-matrix gains plus
input gain block. A group member can, however, be controlled by multiple group masters.
It is recommended this feature be used cautiously, as “overlapping” membership can
quickly become unmanageable.
Group master gain controls can send specific values, such as those sent by a fader
control. Group master gain can also be set by increment/decrement. For information on
using increment/decrement controls within the DSP Configurator software
(see “Tools” on page86).
Once a group has been created, the group members — the individual controls that
comprise the group update to indicate they are now part of a group. group members can
still be controlled individually, allowing for relative levels between group members to be
fine-tuned. Group Member levels can also be set by a preset recall.
Grouped Controls
Grouping is convenient when multiple controls require muting at the same time or when
multiple signal levels need to be increased or decreased simultaneously. For example, in a
system with several audio outputs dedicated to a single room, the operator may want all
outputs to change at the same rate and at the same time. The Output 1 through 4 volume
controls can be grouped into a master that controls the volume throughout the room.
For further flexibility, individual volume controls in the group can be set for an output level
based on its use. When the group fader is moved, all four output control faders move in
tandem while retaining their levels relative to each other.
Grouped faders move together at relative levels to the top or bottom of their travel (see
figure 49, next page). If one fader reaches the limit of its travel first, it retains that position
while the other faders continue to travel. When the grouped faders travel in the reverse
direction, the fader that was at its limit reverts to its position relative to the other faders.
NOTE: If a block was previously muted when the group mute is activated, that block
remains muted when the group mute is released.
TIP: When including a control in multiple groups, do so with care. Overlapping group
membership can quickly become unmanageable. Use presets to set individual
faders to known levels.
DMP128 • Software Control 82
Page 89

Figure 49. Sample Fader Group Master and Associated Gain Controls
Mute controls within the blocks can also be grouped (see figure 50).
Figure 50. Sample Mute Group Master and Muted Outputs
DMP128 • Software Control 83
Page 90

Configuring a Group Master
Configure a group as follows:
1. Click Tools > Configure Groups (see figure 49 on previous page) to open the
Configure Groups dialog box.
or click View > Group Controls and then click the Add a Group menu selection.
2. In the Select Group drop-down box, click a group to select it (see figure 51). The
list defaults to the first empty group. Select an empty group if necessary, or select an
existing group to overwrite.
Figure 51. Configure Groups Add Group Dialog Box
NOTE: <empty> groups have no group members assigned. Numbered groups
(such as <Group #1>) have controls assigned that may be overwritten if selected.
3. In the Select Control Type section, expand the tree for the type of control, Gain
or Mute, then select the desired control type. When a selection is made in the Select
Control Types section, the Available Group Members section populates with all
possible members for the selected control type.
NOTE: Potential group members in step 4 that are already assigned to a
different group are displayed in blue.
4. In the Available Group Members section, make appropriate selections by clicking
the checkbox(es). When a + sign exists, click to expand the tree and select individual
controls. Up to 16 group members may be added.
5. Click the Apply button to create or configure the group.
6. Repeat steps 2 through 5 to create or configure up to 32 groups.
7. Click the Close button to exit the configure groups dialog box.
DMP128 • Software Control 84
Page 91

Deleting a Group Master
To delete a group:
1. Click Tools > Configure Groups (see figure 52, below) to open the configure groups
dialog box
or click View > Group Controls and then click Add a Group.
2. In the Select Group drop-down box, click a numbered group (such as "Group #1")
to select it.
3. Click the Delete Current Group button in the lower left area.
4. Click Yes in the Confirm Deletion dialog box.
Viewing and Using a Group Master
Click View > Group Controls to open the group controls dialog box (see figure 52). The
group controls dialog contains two menu items:
• Add a Group allows you to add additional groups.
• Tools enable you to perform various functions from the group controls dialog box.
In addition, once groups are created a single mute button or a group fader plus the
current setting readout and any soft limits that have been set are visible.
Figure 52. Group Controls Dialog Box
The group fader controls function as follows:
• Slide a group fader up and down to adjust all gain controls in the group.
• Click and drag a soft limit (
NOTE: Soft limits cannot be dragged beyond the current setting of the group
fader.
) to set the ceiling and floor for the group.
Add a Group
To launch the configure groups dialog box from group controls, click Add a Group. When
a new group is added and the Add New Group dialog is closed, the group controls dialog
box refreshes to display the added control.
NOTE: If a block is muted, that block remains muted when the group mute is
released.
DMP128 • Software Control 85
Page 92

Tools
The Tools menu (see right) contains these selections:
• Clear All Groups — clears all
group members and group master
parameters. Soft limits are also
cleared.
• Increment/Decrement Simulator
— allows the user to test increment/
decrement values (see below for
more information)
• Refresh All Group Data — Updates
group members and group master parameters.
• Group Details Report — generates a report, listing all group masters and membership
(see next page for more details).
Increment/Decrement Simulator
The Increment/Decrement Simulator provides a control for increment and decrement, with the
ability to set increment and decrement values. This control is temporary, since this value is not
remembered in the device.
To use the Increment/Decrement Simulator:
1. Select Tools > Increment/Decrement Simulator from the Tools menu.
2. Select the group to be controlled from the Select Group drop-down list. The following
dialog box appears:
Figure 53. Increment/Decrement Simulator Dialog Box
NOTE: The Number of Group Members: readout indicates the number of
controls to be affected.
3. Enter an increment value and a decrement value. The default value is 1.
NOTE: The size of the increment can be changed by typing a value in the
Increment Value or Decrement Value field. Values can be as large as the
maximum range of the control or as fine as 0.1dB. For groups controlling
mute, 1 is the only valid value.
4. Click the Increment and Decrement buttons as needed. The group master control
increases or decreases by the set value to the top or bottom of its soft limit range.
NOTE: When set, soft limits cannot be exceeded.
DMP128 • Software Control 86
Page 93

Group Details Report
Select Tools > Group Details Report to create a Microsoft Word file that details all
created groups (see figure 54).
GROUP DETAILS REPORT
Group #1
Processor Type: Output Volume
Current Mute status: Unmuted
Current Group Members:
Main Amp (Output#1) Left Channel
Stage Mixer (Output#2) Right Channel
House Video (Output#3) Left Channel
Prgm Record (Output#4) Right Channel
Group #2
Processor Type: Pre-mixer Trim
Current Gain value: 2 dB
Current Group Members:
Mic #1 (Input#1)
Mic #2 (Input#2)
Mic #3 (Input#3)
Mic #4 (Input#4)
Mic #5 (Input#5)
Mic #6 (Input#6)
Figure 54. Sample Group Details Report
Soft Limits
Each gain type control provides upper and lower soft limits that can be used to limit the
range of the group master control. Soft limits ( ), shown at left, prevent group controls
from exceeding an upper limit or going below a lower limit. They are easily adjustable and
provide the ability to set a ceiling and floor for the group. When a group master is created,
the soft limits default to the hard limits (maximum and minimum) of that group of controls.
Soft Limits can be defined using the mouse by clicking on, then dragging the soft limit
icon. The resolution is 0.1dB.
For more precise setting use the keyboard as follows:
Click within the group master fader to bring focus, then use the following key
combinations:
To move the upper limit:
•
<Shift + Up/down arrow> key moves in 0.1dB increments.
• <Shift + Page Up/ Page Down> key moves in 10dB increments.
• <Shift + Home> moves limit to upper default. Shift + End moves limit to the current
fader position.
To move the lower limit:
• <Ctrl + Up/down arrow> key moves in 0.1dB increments.
• <Ctrl + Page Up/ Page Down> key moves in 10dB increments.
• <Ctrl + Home> moves limit to the current fader position. <Ctrl + End> moves limit
to lower default.
DMP128 • Software Control 87
Page 94

DigitalI/OPorts
The DMP128 provides twenty (20) digital I/O ports that may be used to trigger external
events from DMP128 actions, or for external events to trigger DMP128 actions. The
DSPConfigurator software provides pre-configured scripts with a fixed set of common
trigger/event combinations. When selected, the script is compiled and placed onto the
File Management system of the device. For more advanced or custom scripts, contact an
Extron Electronics Applications Engineer.
When no scripts are active, the digital I/O ports default to DI (digital input) and inactive
(‘Logic Hi’ ≈ +5VDC). The DI detects a Logic Hi as +5 VDC and LogicLow (active) as less
than +1 VDC.
A DO (digital output) sends a Logic Lo as less than +1 VDC and a Logic Hi as +5VDC.
For every script that involves a DO, two versions are available to provide either a
Logic Hi or a Logic Lo response to any action. The alternate script is designated as
“ReverseDO.”
To build a script and place it into the DMP128 File Management system:
1. From the tools menu, click
Configuration.
Configure Digital I/O, then select Build Digital I/O
2. This brings up a dialog that allows selection from a list of pre-configured scripts.
3. Select a script from the Select a Digital I/O Configuration section. The
eventdescription section describes the script and how the Digital I/O ports act while
the script is running. Highlight the desired script, then click OK.
4. A dialog box appears, verifying the file has been successfully uploaded to the device.
NOTE: When performing this procedure in Emulate mode, the connection
dialog will appear between step 3 and step 4. The DSP Configurator will
connect and then disconnect during the procedure, returning to Emulate
mode when completed.
DMP128 • Software Control 88
Page 95

Reinitialize Digital I/O
Should the script stop running for any reason, go to Tools > Configure Digital I/O,
then select Reinitialize Digital I/O. This option is only available in live mode.
To remove a digital I/O script from the DMP128:
Only one digital I/O configuration can be active at a time. If the I/O activity needs to be
modified, remove the current configuration by:
1. From the Tools menu, click Configure Digital I/O, then select Remove Digital
I/O Configuration from the Device and press OK.
2. If the DSP Configurator is connected to a device, the I/O configuration will be
removed. If it is not connected, a connection dialog box will appear.
3. Make certain the connection information is correct, then press OK. The I/O
configuration script will be removed and a confirmation dialog box will appear.
Emulate Mode and Live Mode
The DSP Configurator program has two operational modes, Live and Emulate. In live
mode, the program has established a connection and is synced with the DMP128.
Changes affect the device in real-time and changes in the current state of the device
are reflected in the DSP Configurator. In contrast, emulate mode allows the user to
work offline, creating or editing configurations that do not immediately affect DMP128
operation.
The DSP Configurator program always starts in Emulate mode. In emulate mode, all
functions of the DSP Configurator program are available without connecting to the
DMP128. The user can build a configuration from the blank screen, or open an existing
file that contains the last configuration displayed plus saved presets. Settings and
adjustments are saved to a configuration file on the PC. When the saved file is opened
in the DSPConfigurator program, the program restores all settings as the current
configuration (emulated if in Emulate mode or live if in Live mode).
Live mode can be entered at any time after program launch, either with a blank
configuration, after creating a configuration, or after loading a previously saved
configuration file.
In emulate mode, the current state is titled Current Emulation. In live mode, the current
state is titled, Current State.
Synchronizing: Pull from or Push to the Device
When switching to live mode, either:
• Pull data from the device and update the DSP Configurator program configuration.
This option downloads device settings from the DMP128 and synchronizes it with the
DSP Configurator program overwriting the current DSPConfigurator settings, or
• Push data from the DSPConfigurator program to the device, overwriting settings in
the DMP128.
Live mode can also be used to tailor audio settings in real time while listening to the audio
output.
DMP128 • Software Control 89
Page 96

Selecting Live Mode and Pushing or Pulling Data
To switch from Emulate to Live mode:
1. Select the desired connection to the DMP128 and make the proper connections.
NOTE: Extron recommends connection via the Ethernet LAN port when using
DSPConfigurator.
2. Click the Mode Live button (see b in figure 55). The communication type
selection dialog box appears.
2
3
4a
or
4b
4c
3
5a
5b
5c
or
3
Extron USB device
6a
6b
Figure 55. Selecting Live Mode
3. Click either:
• TCP/IP (for connection via the LAN port (preferred) — proceed to step 4,
• RS-232 (for connection via either of the rear panel RS-232 ports — proceed to
step 5,
• USB (for connection via the front panel configuration port — proceed to step6.
4. If TCP/IP was selected in step 3:
a. Observe the IP address field in the IP connection dialog box. The field displays
the last IP address entered.
• If the IP Address field is correct, proceed to step 4b.
• If the address is not correct, either click in the IP Address field and enter
the IP address or click on the button ( ) to open a drop-down list and select
from among recently used addresses. Proceed to step 4b.
NOTE: If the local system administrators have not changed the value,
the factory-specified default, 192.168.254.254, is the correct value
for this field.
b. If the device is password protected, click in the Password field and enter the
appropriate administrator password.
c. Click OK.
The Synchronize with Device dialog box (see figure 56 on page 92) appears. Proceed
to step 7.
DMP128 • Software Control 90
Page 97

5. If RS-232 was selected in step 3:
a. Click the Com Port drop-down menu and select the port that is connected to the
rear panel RS-232 port.
b. Check the baud rate displayed in the port selection dialog box. If the baud rate
does not match the device’s rate, click the Baud Rate drop-down menu and
select the desired baud rate. The default is 38400.
c. Click OK.
The Synchronize with Device dialog box (figure 56 on next page) appears. Proceed to
step 7.
6. If USB was selected in step3:
a. Click the USB Device drop-down menu and select DMP 128 (or Extron USB
device, if DMP128 is not available),
b. Click OK.
The Synchronize with Device dialog box (see figure 56 on next page) appears.
Proceed to step 7.
DMP128 • Software Control 91
Page 98

7a
9
-or-
7b
8
8d
9
7. Click either the:
a. Pull radio button to configure
the DSP Configurator program
to match the device — proceed
to step9
-or-
8a
8b
b. Push radio button to configure
the device to match the
DSPConfigurator program —
proceed to step8
8c
8d
8. To push all of the DSP Configurator
gain and processor block
adjustments (configuration), and all
presets to the DMP128, proceed to
step9.
To tailor the push (push only the
configuration, only the presets,
8e
or the configuration and selected
presets), click the Advanced button
and proceed to step 8a.
a. Select the Custom radio button.
b. Select the desired
checkbox(es); Push
Configuration
8f
and/or Push Presets. If Push
Configuration is the only box
checked, click OK and proceed
to step9.
10
Figure 56. Selecting Live Mode (Continued)
NOTE: Push Configuration includes all mix-point, gain and
processor block settings. It does not include partial presets.
c. If Push Presets was clicked in step 8b, click All to select all presets or
Selected to choose specific presets.
• If Selected was clicked, click OK and proceed to step 8d.
• If All was clicked (equivalent to a standard push), click OK and proceed to
step 9.
d. If Selected was clicked in step 8c, the Synchronize with Device dialog box (7b)
reappears. Click OK. The presets dialog box appears.
DMP128 • Software Control 92
Page 99

e. Select the desired partial presets to push by clicking the appropriate
checkbox(es).
f. Click OK. — Proceed to step 10.
9. Click OK. The DSP Configurator program is connected live to the device and the
processors, and presets are pushed or pulled as selected, completing the selection of
Live mode.
10. If changes were made to the DSP parameters (including mix-point, gain or processor
blocks) since the last file save, the DSP Configurator prompts to save the file. Click
Yes or No.
If a password was required and not entered or if an incorrect password wasentered, the
program prompts for the password.
The configuration and/or presets will be uploaded to the DMP128.
presets
Presets are used to recall a group of frequently used settings. Presets created by the DSP
Configurator may contain all elements (gain blocks, processor blocks, and mix-points) or
a portion of the elements available within the program. In Emulate mode, up to 32 partial
presets can be created, then uploaded as a set and stored to the device and/or stored to
disk as a configuration file. In Live mode, presets can be created one at a time from the
current state. They can then be saved to a chosen preset number in the device, with the
option to name/rename or save to disk.
When recalled, a preset will only overwrite elements contained in the preset. Presets are
useful when settings for a particular room or only certain elements of a configuration need
to be changed regularly.
Presets may be created in Live or Emulate modes. In Emulate mode, the presets are
created, saved to a file, then pushed to the DMP128 when connecting in Live mode.
When a pull data synchronization method is performed, preset data remains in the
DMP128, with only the list of preset names pulled from the device. Presets in this state
are marked with an asterisk until that preset is recalled (which pulls the preset data from
the device), or until a backup is performed (see “Backup” on page27). Presets pulled
from the device cannot be saved to disk until they have been recalled, at which time the
preset data is pulled into the DSP Configurator. Presets with no asterisk can be saved to
disk.
Saved presets can be recalled via the DSP Configurator, or a control system sending an
SIS preset recall command. Presets may also be saved and recalled via the embedded
web page. Presets saved via the web page contain input gain, output volume, and the
output mix-point settings.
DMP128 • Software Control 93
Page 100

Previewing/Recalling a Preset
A preset can be previewed in either Live or Emulate mode by selecting the preset from the
preset drop-down list.
The program indicates a view-only preset configuration by displaying each preset element
with a translucent green mask over the block.
Figure 57. Preset Preview
Behavior for previewing and applying presets is as follows:
• Live Mode – After selecting a preset, the DSP Configurator displays the preset
elements that will be affected by a preset recall with a translucent mask over the
element, and leaves all other DSP Configurator elements unaltered. Elements without
a translucent mask represent elements in the current state that will be unaffected
by a preset recall. Real-time changes to the current state will not be reflected in the
GUI while previewing a preset, and the user cannot alter GUI elements. To apply the
preset, the user clicks Recall. The preset reverts to “Current State.”
• Emulate Mode – After selecting a preset from the list, the DSP Configurator displays
the elements that will be affected by a preset recall with a green translucent mask,
leaving all other elements (which represent the current emulation) unaltered. The user
clicks Recall to apply the viewed preset to the current emulation. The preset number
reverts to “Current Emulation.”
Building a Preset
Only elements of the preset that are highlighted (given focus) will be saved as a preset.
Ctrl + A will highlight all elements within the DSP Configurator.
To build a preset highlight the desired DSP Configurator elements (gain/processor blocks,
mix-points) using standard Windows keyboard and mouse actions as follows:
1. <Left click> on the desired block to select a single block,
2. <Ctrl + left click> to select multiple blocks that are not adjacent,
3. <Shift/hold + click> on the first block and click on the last block in either a vertical
column or horizontal row to select multiple blocks, and
4. Click and drag a selection rectangle to select multiple adjacent blocks in either the
vertical or horizontal direction.
5. Go to Tools > Presets and select Mark All Items or press <Ctrl + A>. This will
mark all elements within the DSP Configurator, which will save a “full” preset,
6. To save the selection see “Save Preset” on the next page.
DMP128 • Software Control 94
 Loading...
Loading...