Page 1

VN-Matrix 300
User Guide
Matrix Systems
68-1995-01 Rev. A
12 10
Page 2

Safety Instructions • English
This symbol is intended to alert the user of important operating and maintenance (servicing) instructions in the literature provided with the equipment.
This symbol is intended to alert the user of the presence of uninsulated
dangerous voltage within the product’s enclosure that may present a risk of
electric shock.
Caution
Read Instructions • Read and understand all safety and operating instructions before using the equipment.
Retain Instructions • The safety instructions should be kept for future reference.
Follow Warnings • Follow all warnings and instructions marked on the equipment or in the user information.
Avoid Attachments • Do not use tools or attachments that are not recommended by the equipment
manufacturer because they may be hazardous.
Warning
Power sources • This equipment should be operated only from the power source indicated on the product. This
equipment is intended to be used with a main power system with a grounded (neutral) conductor. The third
(grounding) pin is a safety feature, do not attempt to bypass or disable it.
Power disconnection • To remove power from the equipment safely, remove all power cords from the rear of
the equipment, or the desktop power module (if detachable), or from the power source receptacle (wall plug).
Power cord protection • Power cords should be routed so that they are not likely to be stepped on or pinched
by items placed upon or against them.
Servicing • Refer all servicing to qualified service personnel. There are no user-serviceable parts inside. To prevent
the risk of shock, do not attempt to service this equipment yourself because opening or removing covers may
expose you to dangerous voltage or other hazards.
Slots and openings • If the equipment has slots or holes in the enclosure, these are provided to prevent
overheating of sensitive components inside. These openings must never be blocked by other objects.
Lithium battery • There is a danger of explosion if battery is incorrectly replaced. Replace it only with the
same or equivalent type recommended by the manufacturer. Dispose of used batteries according to the
manufacturer’s instructions.
Precautions/Safety Instructions
Consignes de Sécurité • Français
Ce symbole sert à avertir l’utilisateur que la documentation fournie avec le
matériel contient des instructions importantes concernant l’exploitation et la
maintenance (réparation).
Ce symbole sert à avertir l’utilisateur de la présence dans le boîtier
de l’appareil de tensions dangereuses non isolées posant des risques
d’électrocution.
Attention
Lire les instructions• Prendre connaissance de toutes les consignes de sécurité et d’exploitation avant
d’utiliser le matériel.
Conserver les instructions• Ranger les consignes de sécurité afin de pouvoir les consulter à l’avenir.
Respecter les avertissements • Observer tous les avertissements et consignes marqués sur le matériel ou
présentés dans la documentation utilisateur.
Eviter les pièces de fixation • Ne pas utiliser de pièces de fixation ni d’outils non recommandés par le
fabricant du matériel car cela risquerait de poser certains dangers.
Sicherheitsanleitungen • Deutsch
Dieses Symbol soll dem Benutzer in der im Lieferumfang enthaltenen
Dokumentation besonders wichtige Hinweise zur Bedienung und Wartung
(Instandhaltung) geben.
Dieses Symbol soll den Benutzer darauf aufmerksam machen, daß im Inneren
des Gehäuses dieses Produktes gefährliche Spannungen, die nicht isoliert sind
und die einen elektrischen Schock verursachen können, herrschen.
Achtung
Lesen der Anleitungen • Bevor Sie das Gerät zum ersten Mal verwenden, sollten Sie alle Sicherheits-und
Bedienungsanleitungen genau durchlesen und verstehen.
Aufbewahren der Anleitungen • Die Hinweise zur elektrischen Sicherheit des Produktes sollten Sie
aufbewahren, damit Sie im Bedarfsfall darauf zurückgreifen können.
Befolgen der Warnhinweise • Befolgen Sie alle Warnhinweise und Anleitungen auf dem Gerät oder in der
Benutzerdokumentation.
Keine Zusatzgeräte • Verwenden Sie keine Werkzeuge oder Zusatzgeräte, die nicht ausdrücklich vom
Hersteller empfohlen wurden, da diese eine Gefahrenquelle darstellen können.
Avertissement
Alimentations • Ne faire fonctionner ce matériel qu’avec la source d’alimentation indiquée sur l’appareil. Ce
matériel doit être utilisé avec une alimentation principale comportant un fil de terre (neutre). Le troisième
contact (de mise à la terre) constitue un dispositif de sécurité : n’essayez pas de la contourner ni de la
désactiver.
Déconnexion de l’alimentation• Pour mettre le matériel hors tension sans danger, déconnectez tous les
cordons d’alimentation de l’arrière de l’appareil ou du module d’alimentation de bureau (s’il est amovible) ou
encore de la prise secteur.
Protection du cordon d’alimentation • Acheminer les cordons d’alimentation de manière à ce que personne
ne risque de marcher dessus et à ce qu’ils ne soient pas écrasés ou pincés par des objets.
Réparation-maintenance • Faire exécuter toutes les interventions de réparation-maintenance par un
technicien qualifié. Aucun des éléments internes ne peut être réparé par l’utilisateur. Afin d’éviter tout danger
d’électrocution, l’utilisateur ne doit pas essayer de procéder lui-même à ces opérations car l’ouverture ou le
retrait des couvercles risquent de l’exposer à de hautes tensions et autres dangers.
Fentes et orifices • Si le boîtier de l’appareil comporte des fentes ou des orifices, ceux-ci servent à empêcher les
composants internes sensibles de surchauffer. Ces ouvertures ne doivent jamais être bloquées par des objets.
Lithium Batterie • Il a danger d’explosion s’ll y a remplacment incorrect de la batterie. Remplacer uniquement
avec une batterie du meme type ou d’un ype equivalent recommande par le constructeur. Mettre au reut les
batteries usagees conformement aux instructions du fabricant.
Vorsicht
Stromquellen • Dieses Gerät sollte nur über die auf dem Produkt angegebene Stromquelle betrieben werden.
Dieses Gerät wurde für eine Verwendung mit einer Hauptstromleitung mit einem geerdeten (neutralen) Leiter
konzipiert. Der dritte Kontakt ist für einen Erdanschluß, und stellt eine Sicherheitsfunktion dar. Diese sollte nicht
umgangen oder außer Betrieb gesetzt werden.
Stromunterbrechung • Um das Gerät auf sichere Weise vom Netz zu trennen, sollten Sie alle Netzkabel aus der
Rückseite des Gerätes, aus der externen Stomversorgung (falls dies möglich ist) oder aus der Wandsteckdose
ziehen.
Schutz des Netzkabels • Netzkabel sollten stets so verlegt werden, daß sie nicht im Weg liegen und niemand
darauf treten kann oder Objekte darauf- oder unmittelbar dagegengestellt werden können.
Wartung • Alle Wartungsmaßnahmen sollten nur von qualiziertem Servicepersonal durchgeführt werden.
Die internen Komponenten des Gerätes sind wartungsfrei. Zur Vermeidung eines elektrischen Schocks
versuchen Sie in keinem Fall, dieses Gerät selbst öffnen, da beim Entfernen der Abdeckungen die Gefahr eines
elektrischen Schlags und/oder andere Gefahren bestehen.
Schlitze und Öffnungen • Wenn das Gerät Schlitze oder Löcher im Gehäuse aufweist, dienen diese zur
Vermeidung einer Überhitzung der empndlichen Teile im Inneren. Diese Öffnungen dürfen niemals von
anderen Objekten blockiert werden.
Litium-Batterie • Explosionsgefahr, falls die Batterie nicht richtig ersetzt wird. Ersetzen Sie verbrauchte Batterien
nur durch den gleichen oder einen vergleichbaren Batterietyp, der auch vom Hersteller empfohlen wird.
Entsorgen Sie verbrauchte Batterien bitte gemäß den Herstelleranweisungen.
Instrucciones de seguridad • Español
Este símbolo se utiliza para advertir al usuario sobre instrucciones importantes de operación y mantenimiento (o cambio de partes) que se desean
destacar en el contenido de la documentación suministrada con los equipos.
Este símbolo se utiliza para advertir al usuario sobre la presencia de elementos con voltaje peligroso sin protección aislante, que puedan encontrarse
dentro de la caja o alojamiento del producto, y que puedan representar
riesgo de electrocución.
Precaucion
Leer las instrucciones • Leer y analizar todas las instrucciones de operación y seguridad, antes de usar el
equipo.
Conservar las instrucciones • Conservar las instrucciones de seguridad para futura consulta.
Obedecer las advertencias • Todas las advertencias e instrucciones marcadas en el equipo o en la
documentación del usuario, deben ser obedecidas.
Evitar el uso de accesorios • No usar herramientas o accesorios que no sean especificamente
recomendados por el fabricante, ya que podrian implicar riesgos.
安全须知 • 中文
这个符号提示用户该设备用户手册中有重要的操作和维护说明。
这个符号警告用户该设备机壳内有暴露的危险电压,有触电危险。
注意
阅读说明书 • 用户使 用该设备前必须阅读并理 解所有安全和 使用说明。
保存说明书 • 用户应保存安全说明 书以备将来使用。
遵守警告 • 用户应遵守产品和用户指南上的所有安 全和操作说明。
避免追加 • 不要使 用该产品厂商没有推荐的工具或追加设备,以避免危险。
Advertencia
Alimentación eléctrica • Este equipo debe conectarse únicamente a la fuente/tipo de alimentación eléctrica
indicada en el mismo. La alimentación eléctrica de este equipo debe provenir de un sistema de distribución
general con conductor neutro a tierra. La tercera pata (puesta a tierra) es una medida de seguridad, no
puentearia ni eliminaria.
Desconexión de alimentación eléctrica • Para desconectar con seguridad la acometida de alimentación
eléctrica al equipo, desenchufar todos los cables de alimentación en el panel trasero del equipo, o desenchufar
el módulo de alimentación (si fuera independiente), o desenchufar el cable del receptáculo de la pared.
Protección del cables de alimentación • Los cables de alimentación eléctrica se deben instalar en lugares
donde no sean pisados ni apretados por objetos que se puedan apoyar sobre ellos.
Reparaciones/mantenimiento • Solicitar siempre los servicios técnicos de personal calicado. En el interior no
hay partes a las que el usuario deba acceder. Para evitar riesgo de electrocución, no intentar personalmente la
reparación/mantenimiento de este equipo, ya que al abrir o extraer las tapas puede quedar expuesto a voltajes
peligrosos u otros riesgos.
Ranuras y aberturas • Si el equipo posee ranuras o orificios en su caja/alojamiento, es para evitar el
sobrecalientamiento de componentes internos sensibles. Estas aberturas nunca se deben obstruir con otros
objetos.
Batería de litio • Existe riesgo de explosión si esta batería se coloca en la posición incorrecta. Cambiar esta
batería únicamente con el mismo tipo (o su equivalente) recomendado por el fabricante. Desachar las baterías
usadas siguiendo las instrucciones del fabricante.
警告
电源 • 该设备只能使用产品上标明的电源。 设备必须使用有地线的供电系统供电。 第三条线(
地线)是安全设施,不能不用或跳过 。
拔掉电源 • 为安全 地从设备拔掉电源,请拔掉所有设备后或桌面电源的电源线,或任何接到市电
系统的电源 线。
电源线保护 • 妥善布线, 避免被踩踏,或重物挤压。
维护 • 所有维修必须由认证的维修人员进行。 设备内部没有用户可以更换的零件。为避免出现触
电危险不 要自己试图打开 设备盖子维修 该设备。
通风孔 • 有些设备机壳上有通风槽或孔,它们是用来防止机内敏感元件过热。 不要用任何 东西
挡住通风孔。
锂电池 • 不正确的更换电池会有爆炸的危险。必须使用与厂家推荐的相同或相近型号的电池。按
照生产厂的建议处 理废弃电 池。
ii
Page 3

Notational Conventions Used in this Guide
TIP: A tip provides a suggestion to make setting up or working with the device easier.
NOTE: A note draws attention to important information.
CAUTION: A caution warns of things or actions that might damage the equipment.
WARNING: A warning warns of things or actions that might cause injury, death, or
other severe consequences.
Copyright
© 2010 Extron Electronics. All rights reserved.
Trademarks
All trademarks mentioned in this guide are the properties of their respective owners.
iii
Page 4

iv
Page 5

Contents
Introduction ......................................................... 1
About the VN-Matrix 300 ..................................... 1
Functional Overview ............................................. 1
Signal Compatibility — Video ............................ 2
Signal Compatibility — Audio ........................... 2
Unit Setup and Configuration .............................2
System Control ...................................................... 3
Integrated Web Management System .............. 3
Additional Control Features .............................. 3
Network Requirements ...................................... 3
VN-Matrix 300 System Overview..........................4
Data Transport Methods .................................... 4
Front Panel Features ............................................. 8
Indicators ............................................................ 8
Test Button.......................................................... 9
Reset Button ....................................................... 9
Rear Panel Features ..............................................9
Digital Video Connectors ................................. 10
Power Supply Input .......................................... 10
Network Connectors ........................................ 10
Serial I/O Connectors ........................................ 10
Installation and Basic Setup
Procedures .......................................................... 11
Choosing a Suitable Location.............................11
Environmental Requirements ............................11
Orientation ....................................................... 11
Temperature ..................................................... 12
Ventilation ........................................................ 12
Humidity and Water ......................................... 12
Rack Mount Requirements ................................. 12
Mounting and Support .................................... 12
Ventilation ........................................................ 12
Power Supply .................................................... 12
Mains Power Connection (via PSU) .................... 13
Mains Power Cord (for PSU) ............................... 13
Power-up Procedure ....................................... 13
Fitting a Mains Plug ......................................... 14
External Supply Protection .............................. 14
Accessories...........................................................15
Supplied Accessories ........................................ 15
Optional Accessories ........................................ 15
Rack Mounting ................................................. 16
Basic Setup Procedure ........................................17
Configuring a VN-Matrix 300 System ............. 17
Network Communications Setup .................... 17
Network (NIC) Connections ................................ 20
Single Network Connection ............................. 20
Dual Network Connection ............................... 20
System Control Data ........................................ 20
Video and Audio Data ..................................... 21
Switched Network Configuration,
Example 1 ........................................................ 21
Switched Network Configuration,
Example 2 ........................................................ 22
Routed Network Configuration Example ....... 24
System Configuration .................................... 26
VN-Matrix 300 Web Interface ............................26
Start Up and Login Procedure............................27
Login Screen — User Accounts ........................ 27
Device List Page ..................................................28
Device Type ....................................................... 28
Device Mode ..................................................... 28
Device Page ......................................................... 29
Device Summary ............................................... 29
Licensed Features ............................................. 29
Device Setup ..................................................... 30
Create Source (Encoder) .................................. 30
Configuration ................................................... 30
Create Display (Decoder) ................................. 31
Configuration Page — Videoport (Encoder) .....32
Encoder Videoport Panel ................................. 32
Encoder Streams Panel ..................................... 33
Bandwidth Management Page — Videoport
(Encoder) ............................................................ 34
Bandwidth Management — Standard
Control ............................................................ 35
Advanced Control — Video Quality and
Bandwidth Management ................................ 36
Video Quality Management ............................ 37
Bandwidth Management ................................. 38
Streams Panel ................................................... 38
Configuration Page — Ancport (Encoder) ........39
ANC Panel ......................................................... 40
FEC Panel .......................................................... 40
Forward Error Correction ................................. 40
Streams Panel (ANC) ........................................ 42
Typical Application Bit Rates .......................... 44
Configuration Page — Videoport (Decoder) ....45
Decoder Videoport Panel ................................. 46
Decoder Streams Panel .................................... 46
Decoder
— Bit Rate and Stream Statistics ...... 48
VN-Matrix 300 • Contents v
Page 6
Device Page — Peripherals ................................. 49
Serial Port Control ............................................ 49
Pass-through Control Mode ............................ 49
Configuring a Serial Pass-through Group ....... 50
Firmware, Licensing Upgrades and
User Accounts .................................................... 52
Upgrading Device Firmware ..............................52
Uploading the Firmware File to the
VN-Matrix 300 Controller ............................... 53
Licensing ........................................................... 56
User Accounts ................................................... 57
Clock Management.............................................58
Controller Licensing ......................................... 58
Alarms and SNMP ............................................ 59
Overview — Alarms ............................................59
Alarms Page ........................................................60
Filter Settings .................................................... 60
Alarm Type ........................................................ 61
Alarm Source .................................................... 61
Alarm Severity .................................................. 61
Alarm Reporting ............................................... 61
Applying Alarm Filter Settings ........................ 61
Alarm List .......................................................... 61
Alarm Logs ..........................................................62
Alarm Type Description — Encoder ............... 63
Alarm Type Description — Decoder ............... 64
Alarm Type Description
Overview — SNMP .............................................65
Using SNMP — Password ................................. 65
SNMP Trap Version ........................................... 65
SNMP Community ............................................ 65
SNMP Trap Destinations .....................................65
— Controller ............ 64
Reference Information .................................. 66
Specifications ......................................................66
Hardware ............................................................68
Network Port 1: RJ45 ....................................... 68
Network Port 2: SFP ......................................... 69
RS-232 Serial I/O (COM1 and COM2) .............. 70
Extron® Warranty ............................................. 74
Contact Information ....................................... 74
VN-Matrix 300 • Contents vi
Page 7
Introduction
This section describes:
z About the VN-Matrix 300
z Functional Overview
z Setup and Configuration
z System Control
z Front Panel Features
z Rear Panel Features
About the VN-Matrix 300
The Extron® range of VN-Matrix™ 300 video encoders/decoders (VNC 300 codecs) distribute
digital SD and HDTV broadcast quality video across an IP network. The VN-Matrix 300
provides the bridge between digital video devices and IP-based networks. This user guide
describes the operation of a VN-Matrix 300 series device tted with v.4.5g rmware or later.
Video signals connected to a VN-Matrix 300 encoder are compressed into a TCP or RTP data
stream for transport across a local area or wide area network. At the far end of the network
another VN-Matrix 300 unit decodes the compressed stream back into the original video
signal format.
Ancillary (primarily audio data associated with the original video signal) is preserved in an
uncompressed form and is transported across the network alongside the video signal.
Functional Overview
The VNC 300 codec can be congured to operate in one of two modes, as an:
z Encoder — to encode a source and stream it across a network
z Decoder — to decode a VN-Matrix 300 data stream from a network
Therefore, any VN-Matrix 300 system will comprise at least two devices, one congured as
an encoder and the other as a decoder. Multiple encoders and decoders can co-exist on the
same network.
On a given network, any decoder can display the source provided by any encoder.
NOTE: The VN-Matrix 300 is also available as a decoder only device (VND 300). In this
case, details included here relating to the encoding of digital video signals are
not relevant.
VN-Matrix 300 • Introduction 1
Page 8
Signal Compatibility — Video
The VN-Matrix 300 is supplied in one of three options, based on the type of digital video
transport and video resolutions that it is intended to support.
Digital Video Transport
Model Number SMPTE424/425M SMPT292 SMPTE 259M
VN-Matrix 300 SD Not supported Not supported 525i/59.94 Hz; 625i/50 Hz;
VN-Matrix 300 HD Not supported 1080i @50/59.95/60 Hz
VN-Matrix 300 3G 1080p @50/59.94/60Hz;
10bit, 4:2:2, YCrCb
1080p @23.97/24/25/29.97/30 Hz
720p @ 23.97/24/25/29.97/30/50/59.94/60 Hz,
10bit, 4:2:2, YCrCb, YCrCb
Supported Video modes
10 bit, 4:2:2. YCrCb
The VN-Matrix 300 incorporates advanced image acquisition circuitry which can auto-detect
the format of the connected signal without the need for any additional setup. Input sources
are encoded and decoded at their native resolution and format.
Signal Compatibility — Audio
The VN-Matrix 300 range of codecs support the transport of embedded audio data as
described by the following SMPTE standards.
z SMPTE 299M: 24 bit digital audio
z SMPTE 272M-A: 20 bit digital audio
VNC 300 configured as an Encoder
The source signal is connected to the input BNC of the VNC 300. A reclocked loop through
connection is provided for an external local monitor. In addition, a second loop through is
available that includes an overlay function that may be used for identification purposes.
VNC 300 configured as a Decoder
The decoded video signal is available on the output BNC. The loop through connector is not
active.
NOTE: The input connector BNC on the decoder may be used to connect to a digital
studio genlock signal.
Unit Setup and Configuration
Low level communications setup of the VNC 300 or VND 300 is achieved using a serial data
link to the COM1 port. This interface provides for configuration of the network settings for
each unit and is undertaken during commissioning.
High level conguration is achieved via the network using the Integrated Web Management
System.
There is no need for the VN-Matrix 300 units to be congured for a specic source type. The
VNC 300 or VND 300 automatically identies the source format of the signal connected to
the encoder. The decoded image is presented in exactly the same format.
Conguration of the system specic parameters is made via the Integrated Web
Management provided by the controller.
VN-Matrix 300 • Introduction 2
Page 9

System Control
Integrated Web Management System
Additional Control Features
Network Requirements
The VN-Matrix 300 incorporates an integrated web management system (referred to in
this manual as the web interface). This allows any VN-Matrix 300 unit on a network to be
congured via a Windows®-based PC (on the same network), using a standard web browser
(such as Mozilla FireFox® or Internet Explorer®).
This interface provides for full control of the VN-Matrix 300 feature set.
One VN-Matrix 300 unit in the system is designated as a controller. This unit acts as a server
for the web interface and holds a record of the conguration for all VN-Matrix 300 devices
on the network. The controller manages the communications to all VN-Matrix 300 devices.
Any VN-Matrix 300 unit, whether it is congured as an encoder or decoder, can be used as a
controller.
Remote Control
RS-232 serial data can be routed between selected VN-Matrix 300 units using the COM2
port, for example to provide remote control of an external device.
The VN-Matrix 300 uses highly efcient compression algorithms to minimize the amount of
data needed to be transported across the network.
It is, however, crucial to the effective operation of VN-Matrix 300 that sufcient data
throughput can be achieved, especially where multiple sources are being encoded.
The efficiency of a network will be directly affected by the speed and configuration of each
element within its infrastructure, such as switchers and routers. The VN-Matrix 300 will
achieve optimum transmission results over a dedicated 1 Gbps network (Gigabit Ethernet).
VN-Matrix 300 • Introduction 3
Page 10
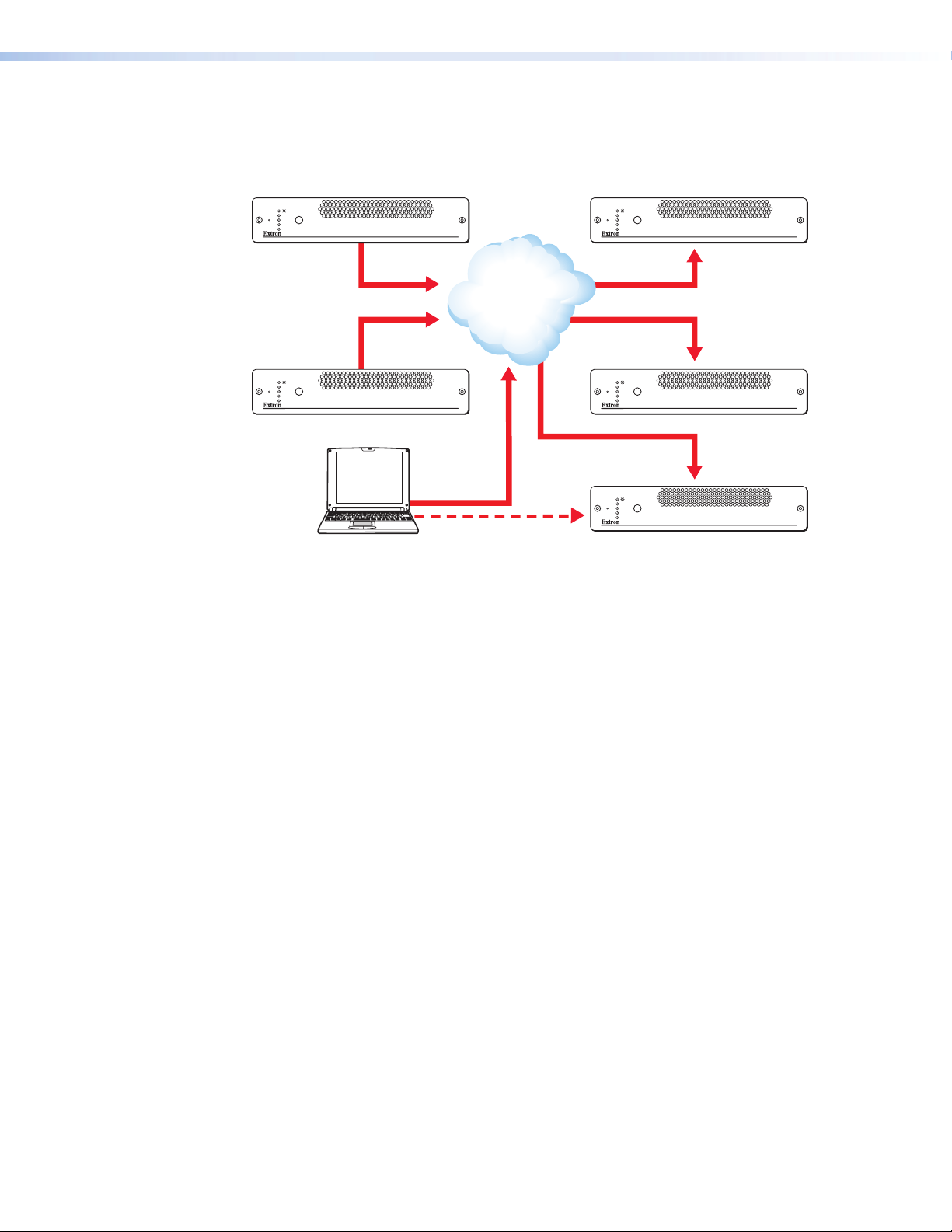
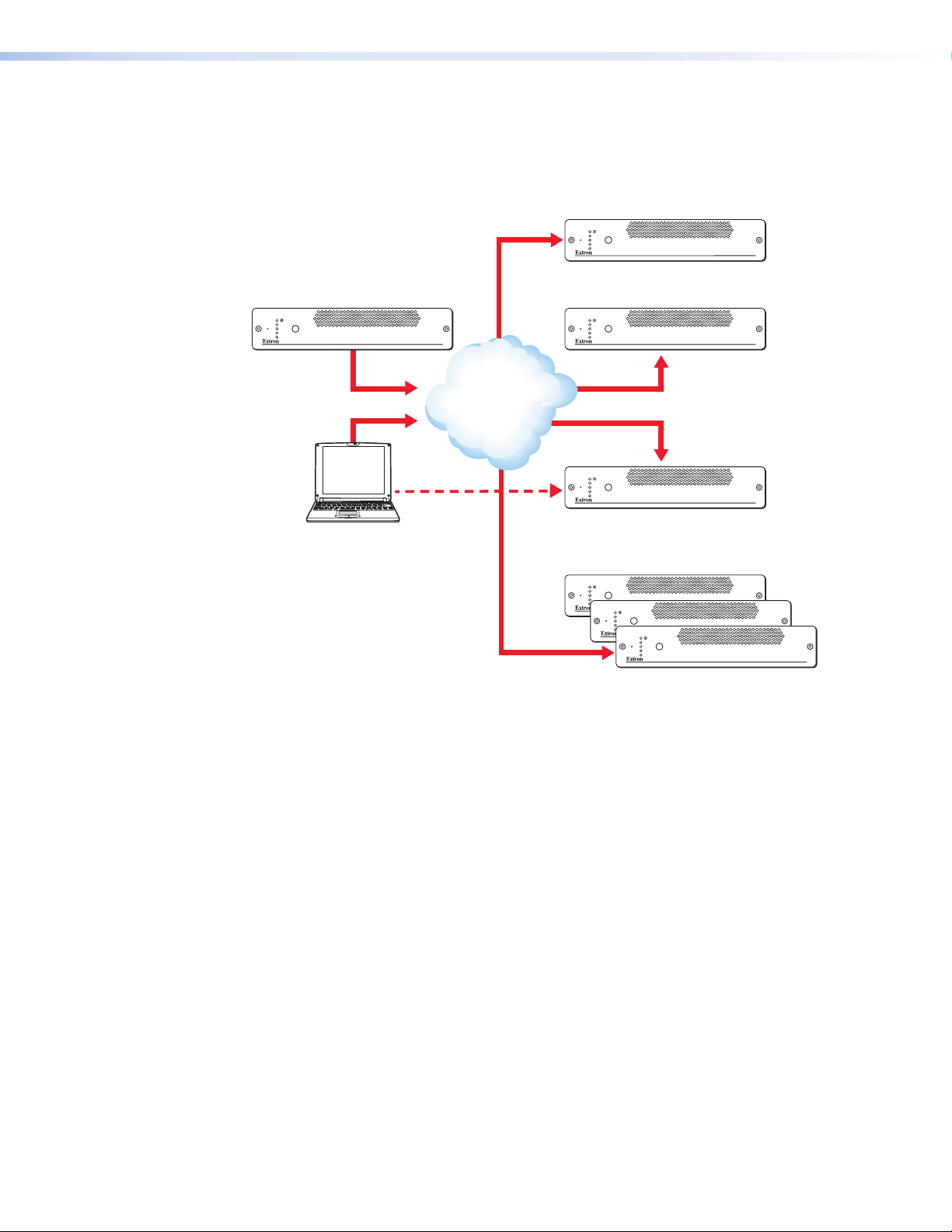
VN-Matrix 300 System Overview
IP Tx 1
IP Rx (a)
In this example either of the two encoder streams may be routed to any of the three decoder
units. The VN-Matrix 300 labelled IP Rx is the controller for the system.
LAN-1
LAN-2
STATUS
ALARM
TEST
VN-MATRIX 300 SERIES
SERIAL DIGITAL VIDEO OVER IP
LAN-1
LAN-2
STATUS
ALARM
TEST
VN-MATRIX 300 SERIES
SERIAL DIGITAL VIDEO OVER IP
Network
IP TX 2
LAN-1
LAN-2
TEST
STATUS
ALARM
VN-MATRIX 300 SERIES
SERIAL DIGITAL VIDEO OVER IP
System Control
Monitoring &
Control
Figure 1. VN-Matrix 300 In Use to Transmit (Encode) and Receive (Decode)
Configuration of each device, including which source is displayed on which display, can
be achieved by any PC on the same network, using the VN-Matrix 300 Integrated Web
Management System
IP Rx (b)
LAN-1
LAN-2
TEST
STATUS
ALARM
VN-MATRIX 300 SERIES
IP Rx (c)
LAN-1
LAN-2
TEST
STATUS
ALARM
VN-MATRIX 300 SERIES
Decoder Configured as Controller
SERIAL DIGITAL VIDEO OVER IP
SERIAL DIGITAL VIDEO OVER IP
Data Transport Methods
Source (video) data from a VN-Matrix 300 Encoder can be distributed to multiple displays/
decoders (one-to-many) or to a single display/decoder (point-to-point).
Video data is transported from the source (encoder) to the display (decoder) using one of
three methods:
z Multicast RTP
z Unicast RTP
z Unicast TCP
A description of each method, together with its advantages and disadvantages, can be
found on the following pages.
VN-Matrix 300 • Introduction 4
Page 11
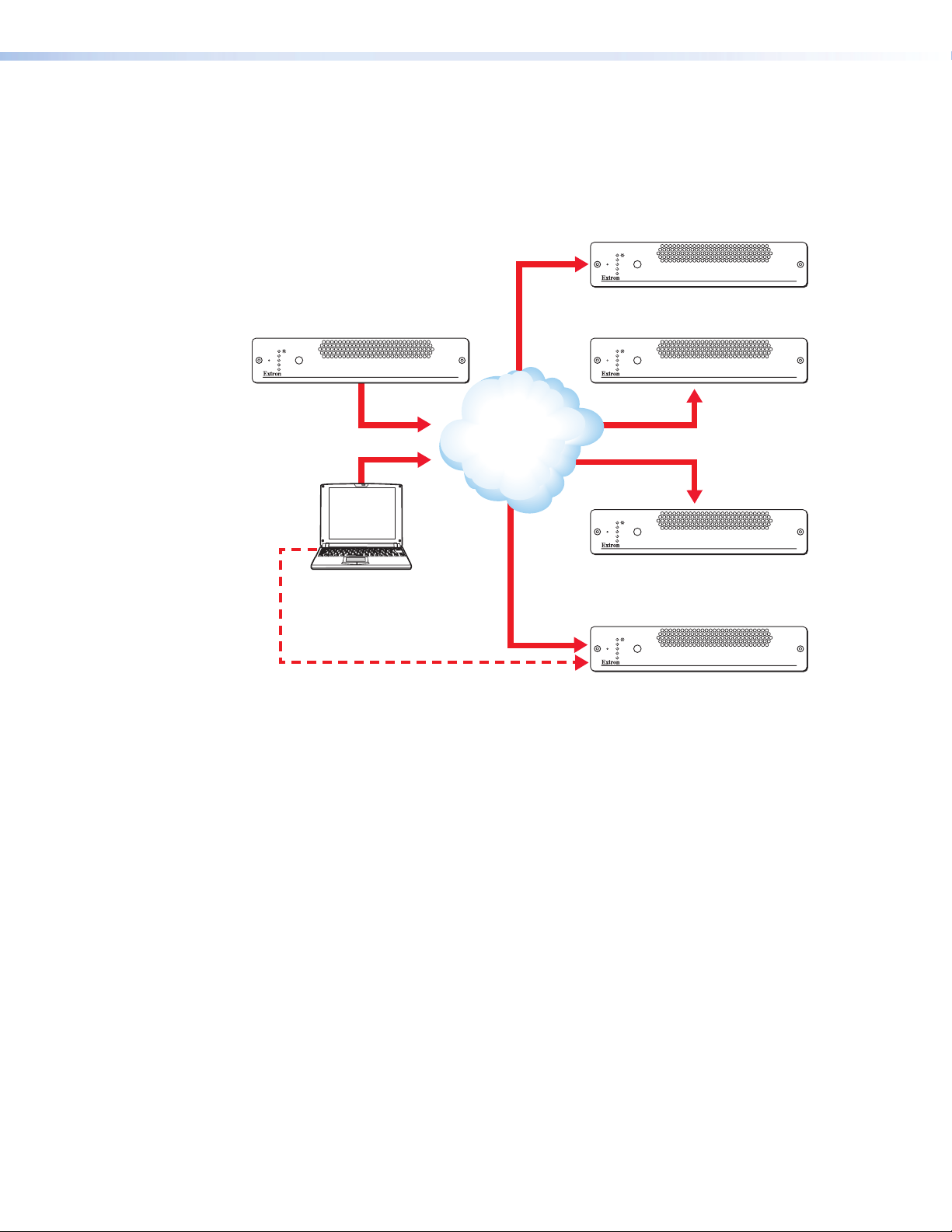
Multicast RTP
IP Rx (a)
This transport method uses a real-time variation of UDP (User Datagram Protocol), called
RTP (Real Time Protocol). Multicast RTP allows a source to be displayed on any number of
displays.
RTP
Program Data
LAN-1
LAN-2
TEST
STATUS
ALARM
VN-MATRIX 300 SERIES
SERIAL DIGITAL VIDEO OVER IP
IP Tx 1
LAN-1
LAN-2
STATUS
ALARM
TEST
VN-MATRIX 300 SERIES
SERIAL DIGITAL VIDEO OVER IP
RTP
Program Data
Network
IP Rx (b)
LAN-1
LAN-2
TEST
STATUS
ALARM
RTP
Program Data
RTP
Program Data
VN-MATRIX 300 SERIES
SERIAL DIGITAL VIDEO OVER IP
IP Rx (c)
Monitoring &
Control
System Control
LAN-1
LAN-2
TEST
STATUS
ALARM
VN-MATRIX 300 SERIES
SERIAL DIGITAL VIDEO OVER IP
IP Rx (d)
RTP
Program Data
LAN-1
LAN-2
TEST
STATUS
ALARM
LAN-1
LAN-2
TEST
STATUS
ALARM
LAN-1
LAN-2
TEST
STATUS
ALARM
VN-MATRIX 300 SERIES
SERIAL DIGITAL VIDEO OVER IP
VN-MATRIX 300 SERIES
SERIAL DIGITAL VIDEO OVER IP
VN-MATRIX 300 SERIES
SERIAL DIGITAL VIDEO OVER IP
IP Rx n-1
IP Rx n
Any number of decoders
Figure 2. Using Multicast RTP to Display a Source on Numerous Displays
The source encoder uses RTP to send data to a multicast group. RTP provides very low
latency which is important for video transport. The RTP protocol compensates for jitter and
any breaks in the sequence of data during the transfer over an IP network.
This is the recommended transport method for real time video and audio data over an
IP network. However, because RTP is a connection-less protocol, data delivery is not
guaranteed. Where data packets are lost (such as due to excessive network traffic) the
VN-Matrix 300 carefully manages the data stream to minimize any image disruption.
VN-Matrix 300 • Introduction 5
Page 12
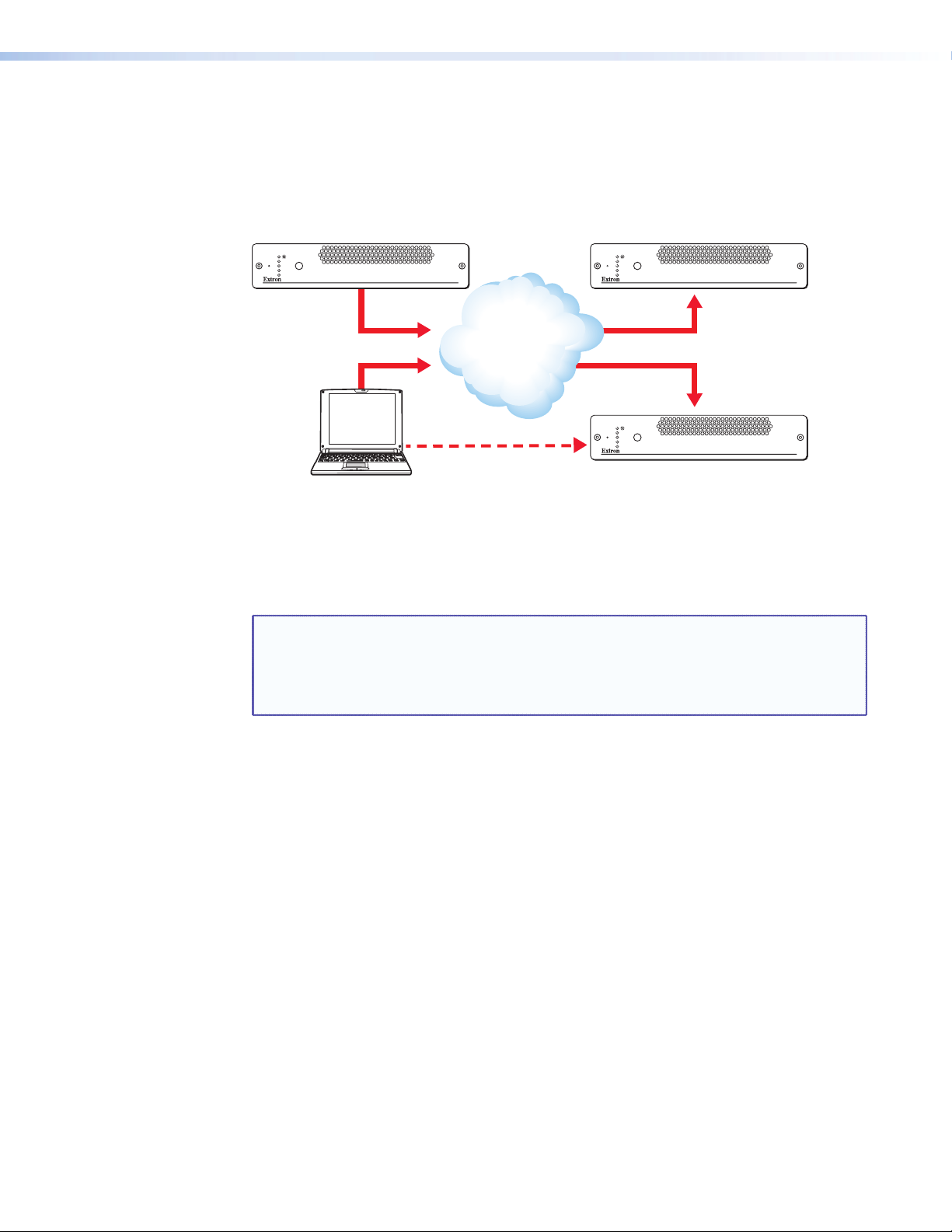
Unicast RTP
Like Multicast RTP, this method uses a real-time variation of UDP protocol, called RTP. This
method can be used where the network infrastructure does not support multicast traffic.
Typically this should be used as a point-to-point configuration (that is: single source to single
display) but it can also be used for up to four displays.
IP Rx (a)
LAN-1
LAN-2
TEST
STATUS
ALARM
VN-MATRIX 300 SERIES
SERIAL DIGITAL VIDEO OVER IP
Up to four decoders may be part of
the UNICAST RTP group.
RTP
Program Data
IP Tx 1
LAN-1
LAN-2
STATUS
ALARM
TEST
VN-MATRIX 300 SERIES
SERIAL DIGITAL VIDEO OVER IP
RTP
Program Data
Network
IP Rx (b)
LAN-1
LAN-2
TEST
STATUS
ALARM
RTP
Program Data
RTP
Program Data
VN-MATRIX 300 SERIES
SERIAL DIGITAL VIDEO OVER IP
IP Rx (c)
LAN-1
LAN-2
TEST
STATUS
ALARM
VN-MATRIX 300 SERIES
SERIAL DIGITAL VIDEO OVER IP
Monitoring &
Control
System Control
RTP
Program Data
IP Rx (d)
LAN-1
LAN-2
STATUS
ALARM
TEST
VN-MATRIX 300 SERIES
SERIAL DIGITAL VIDEO OVER IP
Figure 3. Using Unicast RTP Where the Network Infrastructure Does Not Support
Multicast Traffic
RTP provides very low latency which is important for video transport. The RTP protocol
compensates for jitter and any breaks in the sequence of data during the transfer over an IP
network.
However, because RTP is a connection-less protocol, data delivery is not guaranteed. Where
data packets are lost (for example: due to excessive network trafc) the VN-Matrix 300
carefully manages the data stream to minimize any image disruption.
VN-Matrix 300 • Introduction 6
Page 13
Unicast TCP
Each encoder is ‘paired’ to a decoder
This method transports data using standard TCP (Transport Control Protocol) and should only
ever be used for single point-to-point transfer of data.
with a point to point data link.
IP Tx 1 IP Rx (a)
LAN-1
LAN-2
STATUS
ALARM
TEST
VN-MATRIX 300 SERIES
SERIAL DIGITAL VIDEO OVER IP
TCP/IP
Program Data
LAN-1
LAN-2
TEST
STATUS
ALARM
TCP/IP
Program Data
VN-MATRIX 300 SERIES
SERIAL DIGITAL VIDEO OVER IP
Network
IP Rx (b)
System Controller
Monitoring &
Control
Figure 4. Using Unicast TCP as a Single Point-to-Point Transfer of Data
TCP is a connection-based protocol and, therefore, data is guaranteed to be delivered.
However, in the event of excessive network trafc, delivery may be delayed impacting
real-time performance.
LAN-1
LAN-2
STATUS
ALARM
TEST
VN-MATRIX 300 SERIES
SERIAL DIGITAL VIDEO OVER IP
NOTE: Multiple decoder connections are theoretically possible using this method but
NOT recommended. Each additional connection creates extra loading on the
encoder CPU which ultimately results in poor display performance. In addition,
multiple TCP streams carrying the same source data is an inefficient use of
network bandwidth.
VN-Matrix 300 • Introduction 7
Page 14
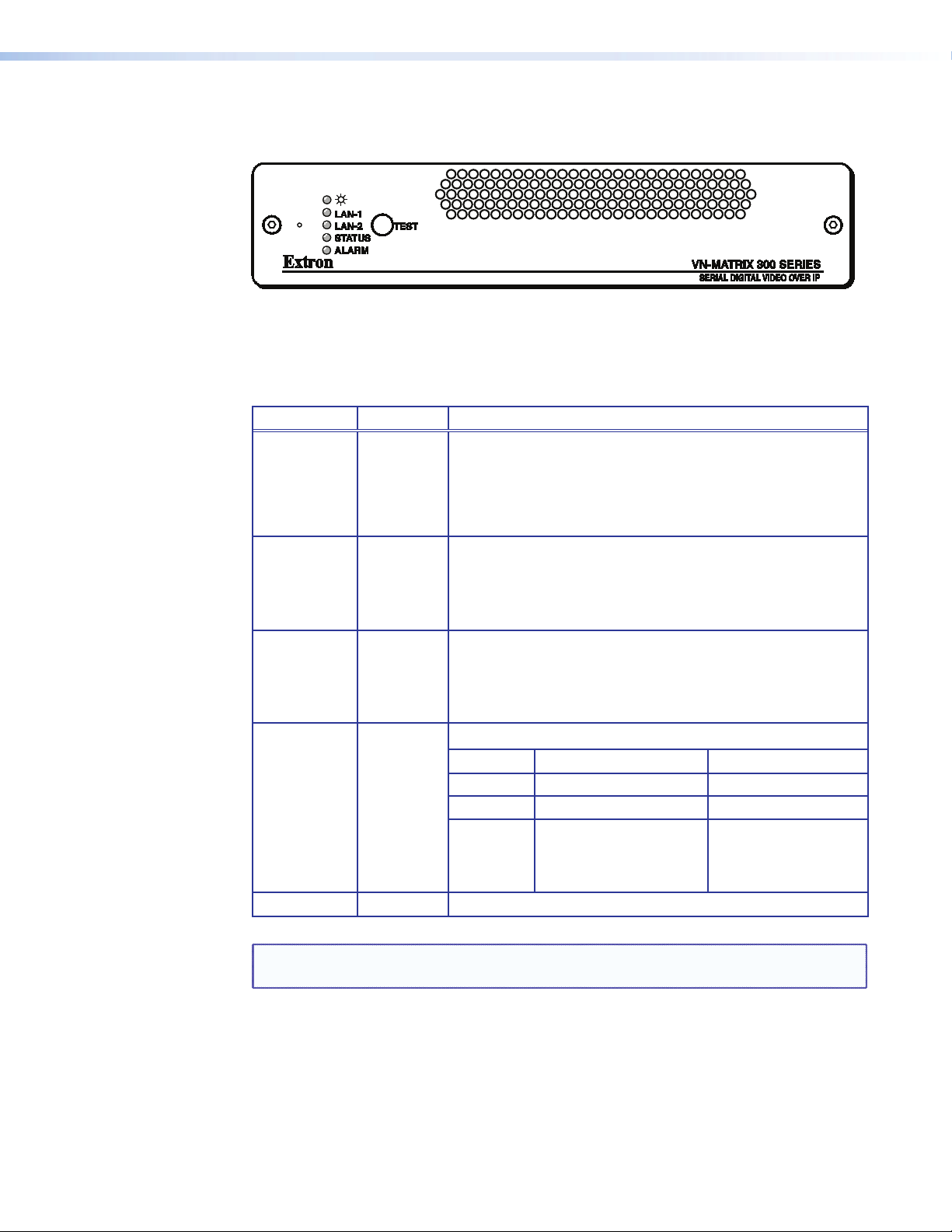
Front Panel Features
Indicators
Figure 5. VN-Matrix 300 Front Panel
The following indicators are visible on the front of the VN-Matrix 300:
Name Color Function
Power Green z Fully Lit – when the unit is receiving power from the 12V
supply input.
z Flashing – an over temperature condition has occurred
or there was a power overload/underload condition. Cycle
the power off/on to reset.
LAN 1 (RJ45) Orange Indicates the status of network port 1:
z Fully Lit or Flashing Intermittently – control or source
data is being transmitted or received by the port.
z Unlit – no data or no network connection detected.
LAN 2 (SFP) Orange
Indicates the status of network port 2:
z Fully Lit or Flashing Intermittently – control or source
data is being transmitted or received by the port.
z Unlit – no data or no network connection detected.
STATUS Green
Indicates the source status of the VN-Matrix 300:
Condition Encoder (source) Decoder (display)
Unlit No source input detected No source is received
Flashing Source being streamed Source being received
ALARM Red
Fully Lit Source present but not
being streamed (such as
unit currently disabled or
in standby mode)
Indicates that a critical alarm has occurred.
N/A
NOTE: During the VN-Matrix 300 boot up cycle (typically 20-30 seconds) the Network
and Status indicators may light or flash intermittently while the unit initializes.
VN-Matrix 300 • Introduction 8
Page 15
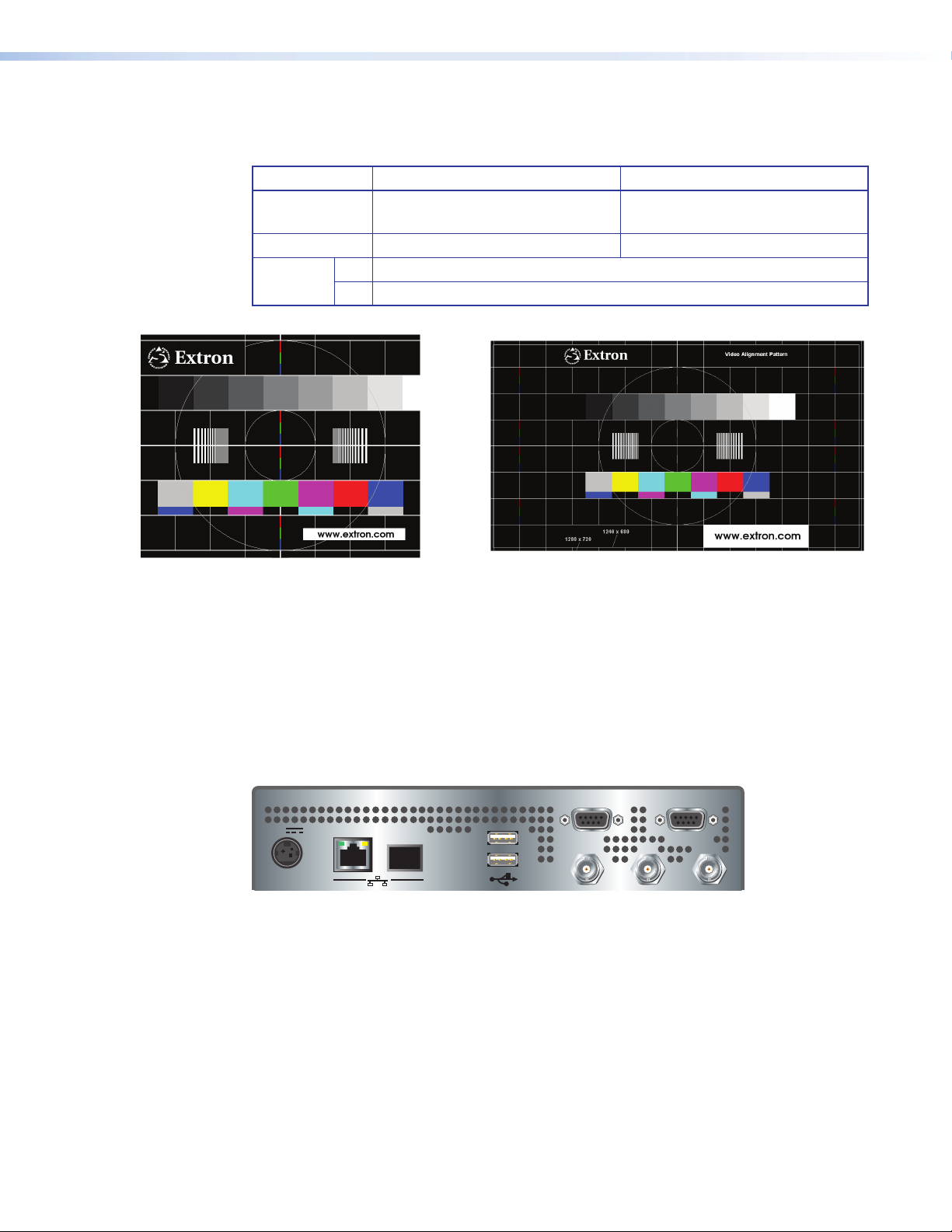
Test Button
The test button on the front panel provides the following functionality.
Encoder Decoder
Action Display the test pattern on the
SDI-OUT connector.
Active stream Suspended Not displayed
Output
format
HD 1280 x 720, progressive
SD 720 x 576 / 720 x 480, interlaced
Figure 6. Test Pattern: 720x480, 720x576 Figure 7. Test Pattern: 1280 x 720
Display the test pattern on the
SDI-OUT connector
Reset Button
Rear Panel Features
Each VN-Matrix 300 unit is tted with a concealed reset button. This can be used to reboot
the operating system, for example during firmware upgrade procedures.
To activate this button, insert the blade of a very small screwdriver (or similar tool) or
straightened paper clip into the hole on the front panel, on the left of the indicators.
12V DC
REG
6A MAX
COM 1
OUT IN LOOP
COM 2
Figure 8. VN-Matrix 300 Rear Panel
All connections to the VN-Matrix 300 are provided on the rear panel of the unit.
Full details of connector types, pin-outs and specifications can be found in the Technical Data
section.
VN-Matrix 300 • Introduction 9
Page 16
Digital Video Connectors
The VN-Matrix 300 provides 3 BNC connectors for the connection of digital video sources.
The function of the connectors may change dependant on the configuration of the unit
(encoder or decoder mode).
Mode SDI – IN SDI - OUT SDI - LOOP
Encoder
(IP TX)
Decoder
(IP RX)
Digital Video
input
Digital Genlock
input (optional)
Power Supply Input
The VN-Matrix 300 requires a 12V DC regulated power supply (rated at 5A) via this
connector.
A suitable mains-operated power supply unit (PSU) is provided.
Connector
This connector provides a loop
through of the original source
with a text overlay (optional)
for identification purposes.
Digital Video output.
z The video output will be
in the same format as the
originating source.
z When no video streams are
being decoded this output
can provide either a frozen
image of the last received
frame or a user definable
splash screen.
This connector provides a
simple re-clocked (buffered)
loop through connection of
the input source.
Not used
Network Connectors
These are used to connect the VN-Matrix 300 to an Ethernet network.
z Either port may be used for streaming images along with any associated audio and
ancillary data.
z It is not possible to stream data from both ports simultaneously.
z Either port may be used for control and monitoring purposes.
z It is possible to use one port for the streaming of image data and the other port for
control and monitoring purposes.
RJ45 – LAN 1 — Provides a 1000BASE-T connection.
SFP – LAN 2 — Provides for an (optional) 1000BASE-SX optical connection.
Serial I/O Connectors
COM1 and 2 are standard 9-pin D type connectors. These are used to establish a serial data
link between the VN-Matrix 300 and an external computer.
z COM1 is used for low level conguration of the VN-Matrix 300 unit via a serial link.
z COM2 is used for sending or receiving serial data across a network, for example for
control of external devices.
VN-Matrix 300 • Introduction 10
Page 17

Installation and Basic Setup Procedures
This section describes basic installation and setup procedures, including:
z Choosing a Suitable Location
z Environmental Requirements
z Rack Mount Requirements
z Mains Power Connection
z Mains Power Cord
z Accessories
z Setup Procedure
z Network Connections
Choosing a Suitable Location
The VN-Matrix 300 is designed to be used either as a free-standing unit or to be mounted in
a 19-inch equipment rack using the optional kits available.
CAUTION: Whichever installation method you choose there are certain environmental
requirements, detailed on the following pages, which must be observed in
order to ensure safe and reliable operation.
Environmental Requirements
CAUTION: The criteria on this page must be observed for all installations of the
VN-Matrix 300, whether free-standing or rack-mounted.
Orientation
The VN-Matrix 300 is designed to be used free-standing on a stable, horizontal surface. It
can, however, be used in any orientation subject to the necessary ventilation requirements.
VN-Matrix 300 • Installation and Basic Setup Procedures 11
Page 18

Temperature
DO NOT install or operate the VN-Matrix 300 in an area where the ambient temperature
exceeds 35°C (95°F) or falls below 5°C (35°F).
Remember that, as with all electronic equipment, the VN-Matrix 300 and its associated PSU
also produces heat which may affect the ambient temperature.
After the VN-Matrix 300 has been in use for a period of time, the external casing may
become slightly warm to the touch. Ensure that any adjacent surfaces will not be affected by
the heat.
Ventilation
DO NOT obstruct the ventilation grills during use. The VN-Matrix 300 has an integral
forced-air cooling system. A fan draws air in through the grille in the front panel and expels
warmed air through the grilles in the back panel. The fan speed is controlled automatically
by an internal temperature sensor. The fan may, therefore, appear to run faster as the unit
warms up or if the ambient temperature is increased.
A self-resetting thermal cut-out will shutdown the VN-Matrix 300 if the temperature exceeds
design limits.
Humidity and Water
DO NOT install or operate the VN-Matrix 300 in an area in which the ambient relative
humidity exceeds 85% or in an area that is prone to condensation.
DO NOT install or operate the VN-Matrix 300 near water or in a location which may be
prone to water seepage — the VN-Matrix 300 is not waterproof.
Rack Mount Requirements
CAUTION: For rack-mounted installations, the following criteria must be observed.
Mounting and Support
Ventilation
Power Supply
ALWAYS use the special rack-mount kits (available separately) to secure the VN-Matrix 300.
Full details on using the kit are included with the kit. It will be necessary to remove the four
feet before rack mounting.
DO NOT stand other units directly on top of the VN-Matrix 300 when it is rack-mounted as
this will place excessive strain on the mounting brackets.
ALWAYS ensure that the rack enclosure is adequately ventilated. Sufcient airow must be
achieved (by convection or forced-air cooling) to satisfy the ventilation requirements of all
items of equipment installed within the rack.
No additional ventilation gap is required above or below the VN-Matrix 300 and adjacent
surfaces or equipment.
ALWAYS ensure that the mains power supply is of the correct voltage and frequency for all
equipment within the rack, and that it has a good ground/earth connection.
Where a power strip (mains distribution batten) is used (of either a hard-wired or plug and
socket type), always ensure that the current rating of both the power strip and the supply is
sufficient for all equipment within the rack.
VN-Matrix 300 • Installation and Basic Setup Procedures 12
Page 19
Mains Power Connection (via PSU)
The VN-Matrix 300 must be powered from a 12 Volt DC regulated supply. A suitable
mains-operated power supply unit (PSU) is provided. The mains connection details that
follow relate to the PSU.
CAUTION: Never connect the VN-Matrix 300 directly to the mains.
To ensure CE compliance ALWAYS use the PSU provided. If a backup or
replacement PSU is required, always use an Extron approved PSU.
Supply Requirements (for PSU)
CAUTION: ALWAYS observe the following instructions to ensure safe and reliable
operation of the PSU.
ALWAYS ensure that the mains supply voltage is single phase only and is within the
permitted range:
z 100 – 240 V AC (0.45 A Max.) 50 – 60 Hz.
NEVER connect the PSU to a DC supply.
DO NOT allow the mains power point to be overloaded. This is particularly important to
check when powering several items of equipment from a single power point (such as within
rack-mounted installations).
WARNINGS: This equipment must be grounded / earthed.
To avoid the possible risk of electric shock or product damage due to
condensation, ALWAYS allow the PSU to become acclimatized to ambient
temperature and humidity for at least thirty minutes BEFORE switching on.
This is particularly important when moving the unit from a cold to a warm
location.
Mains Power Cord (for PSU)
Power-up Procedure
The mains PSU is equipped with a 3-pin (male) type mains connector which requires a power
cord tted with a corresponding 3-pin IEC320 (female) connector.
The type of power cord that is supplied will be appropriate for use in your country:
WARNING: Do not allow anything to rest on the mains power cord.
You must always ensure that the VN-Matrix 300 is powered-up at the same time as the
source computer or slightly before.
VN-Matrix 300 • Installation and Basic Setup Procedures 13
Page 20
Fitting a Mains Plug
If you are fitting a plug to the unterminated power cord (or replacing an existing plug), you
must fit a plug that:
z Is rated for use with mains voltage
z Is equipped with a grounding pin/connection
z Complies with any applicable National or Local electrical regulations.
z Is tted with a correctly rated fuse (applicable to UK-style plugs only, see page 13)
WARNING: Never attempt to fit or use a plug without a ground or earth pin/
Wiring Details
The wires of both mains power cords (supplied with each VN-Matrix 300) are color-coded
as shown in the table below; be sure to connect your plug in accordance with the following
guidelines:
Connect the wire colored... to the plug terminal identified with...
Brown L or Live or Line
Blue N or Neutral
Green and Yellow E or E or Earth or Ground
connection.
(or colored red or brown)
(or colored blue or black)
(or colored green or green & yellow)
WARNING: If you are unsure of the connections, or if the markings in your plug do not
match those given above, CONSULT A QUALIFIED ELECTRICIAN.
NOTE: The PSU is double-insulated and does not require an earth/ground connection.
However, the earth cable of the mains lead must be connected in the plug.
External Supply Protection
CAUTION: The mains power cord supplied with this product is rated at 10A maximum
and must be protected from overload by an external fuse or circuit breaker.
Fused Plugs (UK-style)
If the power cord is tted with a UK-style BS1363 3-pin plug (that is, with provision for an
internal fuse), then it must be tted with a BS1362 ASTA approved 1 inch cartridge fuse.
This fuse must be rated at a maximum of 10A/250V. Since the current draw of the PSU is
less than 1A, a fuse of a lower rating not less that 3A/250V may be used.
WARNING: Never attempt to fit a fuse or circuit breaker of a higher maximum rating
than shown above.
VN-Matrix 300 • Installation and Basic Setup Procedures 14
Page 21
Accessories
Supplied Accessories
Unfused Plugs or Hard-wired
If the power cord is fitted with an unfused plug, or is hard-wired into a power strip (mains
distribution batten), then the power cord must be protected by an external fuse or circuit
breaker of a rating shown in the table below:
Supply Voltage 110V nominal 230V nominal
Maximum Fuse Rating 10A 10A
Minimum Fuse Rating 3A 3A
WARNING: Never attempt to fit a fuse or circuit breaker of a higher maximum rating
than shown above.
In addition to this User Guide, the VN-Matrix 300 is supplied with the following accessories.
Item Quantity Part Number
12 V Power Supply Unit (PSU) 1 70-761-01
RS-232 Serial cable 1 27-699-01LF
If any of these items is missing or damaged, please contact your Extron representative
immediately.
Optional Accessories
The following optional accessories are also available for use with the VN-Matrix 300 — these
must be ordered separately from your Extron dealer:
Item Description Part Number
VNM Dual Rack Mount Kit
(1U, Dual mounting)
VNM Quad Rack Mount Kit
(2U, Quad mounting)
VNM MBU A kit that allows a VN-Matrix 300 unit to be
VNM 12 PSDR A 12 way redundant power supply system,
Extron faceplate 60-1129-01
A kit that allows 2 VN-Matrix 300 units to
be installed in a 19 inch equipment rack. Full
instructions are included with the kit.
A kit that allows 4 VN-Matrix 300 units to be
installed, side by side, in a 19 inch equipment
rack. Full instructions are included with the
kit.
mounted to any convenient flat surface, such
as under a desk. Full instructions are included
with the kit.
for use when rack mounting multiple units.
60-1130-01
60-1131-01
60-1132-01
70-762-01
VN-Matrix 300 • Installation and Basic Setup Procedures 15
Page 22
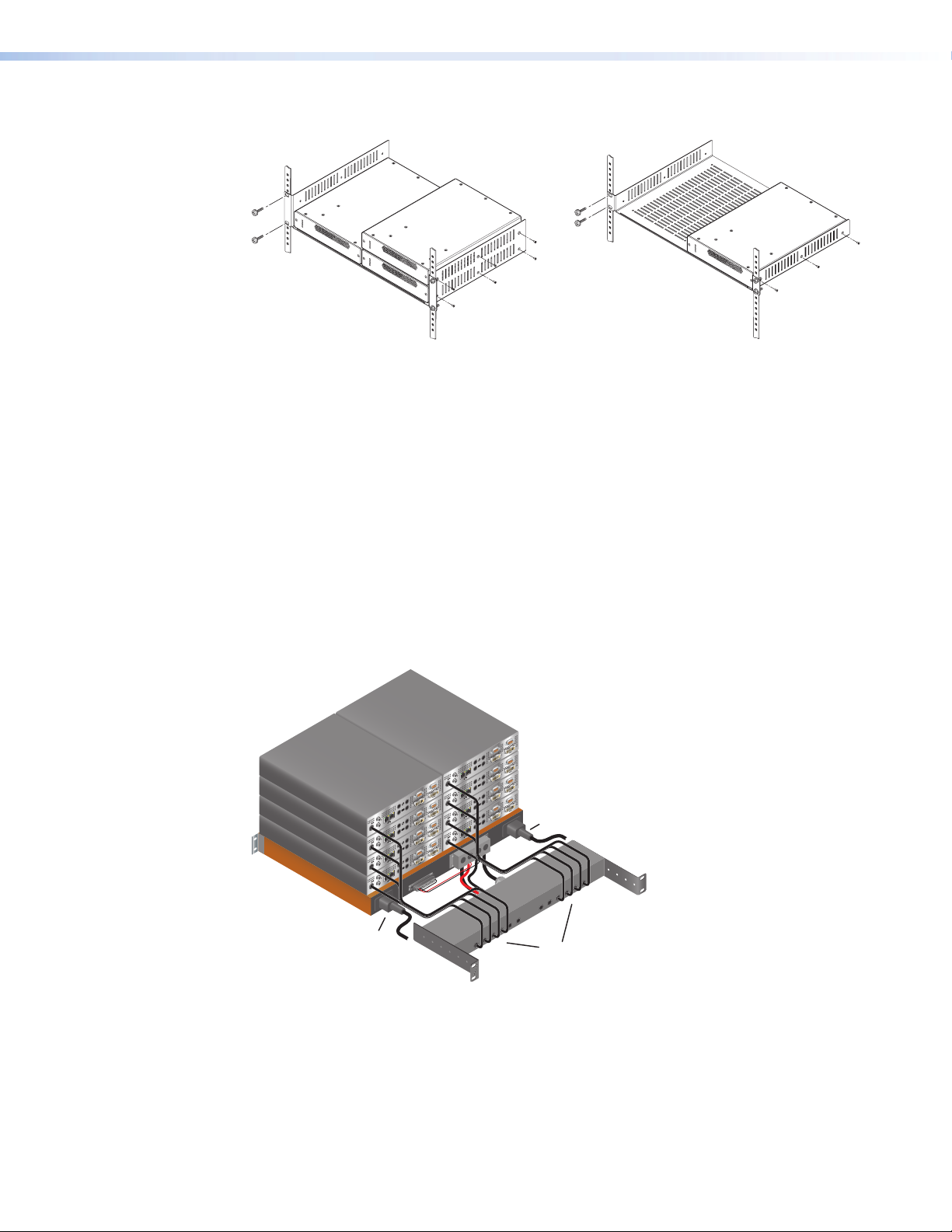
Rack Mounting
Figure 9. VNM Quad RMK – 2U High
for 4 VN-Matrix 300 Units
Figure 10. VNM Dual RMK – 1U High
for 2 VN-Matrix 300 Units
Full details of the VNM Dual RMK and VNM Quad RMK rack trays are available on request
from your Extron dealer.
Redundant PSU
A 12 way redundant power supply system (VNM12PSR) is available. This is designed to be
used for powering multiple VN-Matrix 300 units when they are rack mounted.
Power supply redundancy:
z 12 Units — with full redundancy
The redundant PSU is supplied in two parts:
z The power supply housing
z A cable breakout housing
Both are rack mounting. Full details are available on request.
IN
OUT
12V DC
REG
COM 2
DIGITAL
AUDIO
6A MAX I
IN
COM 1
DVI-I
OUT
IN
12V DC
REG
COM 2
DIGITAL
DVI-I
AUDIO
OUT
6A MAX I
IN
COM 1
PCPERIPH
DVI-I
OUT
IN
II
II
II
II
12V DC
REG
COM 2
DIGITAL
DVI-I
AUDIO
OUT
6A MAX I
IN
COM 1
PCPERIPH
DVI-I
OUT
IN
12V DC
REG
COM 2
DIGITAL
DVI-I
AUDIO
OUT
6A MAX I
COM 1
PC
DVI-I
PERIPH
IN
DVI-I
OUT
PC
PERIPH
VNM 12 PS
VNM 12 PSR
12V DC
REG
6A MAX I
12V DC
REG
6A MAX I
12V DC
REG
6A MAX I
12V DC
REG
6A MAX I
IN
OUT
DIGITAL
AUDIO
IN
OUT
DIGITAL
AUDIO
IN
OUT
DIGITAL
AUDIO
IN
OUT
DIGITAL
AUDIO
COM 2
COM 1
DVI-I
IN
COM 2
DVI-I
OUT
COM 1
PCPERIPH
DVI-I
IN
II
COM 2
DVI-I
OUT
VN Series
COM 1
PC
DVI-I
PERIPH
IN
DVI-I
OUT
COM 1
PCPERIPH
DVI-I
OUT
PCPERIPH
Encoder/Decoder
COM 2
DVI-I
IN
AC 1&2
II
II
II
AC 3&4
VNM 12 PSD
Figure 11. Rack Mounting
DC Power Cables
(8 Shown, 12 Max.)
VN-Matrix 300 • Installation and Basic Setup Procedures 16
Page 23
Basic Setup Procedure
Configuring a VN-Matrix 300 System
Setting up and connecting a VN-Matrix 300 system is best undertaken in three stages.
z Stage 1: Network Communications Setup
Configure the network settings for each device using a PC and serial data link, ensuring
that one device is configured as a controller.
z Stage 2: Connection
Connect each device to the network and connect its associated source or display
equipment.
z Stage 3: System Configuration
Using a PC connected to the same network, access the web interface (served by the
controller) and make a detailed configuration of each device.
CAUTION: Do not proceed with connecting or conguring the VN-Matrix 300 for
Network Communications Setup
an existing network until you are certain you know what you are doing
— incorrect connection or configuration may cause disruption to other
network users.
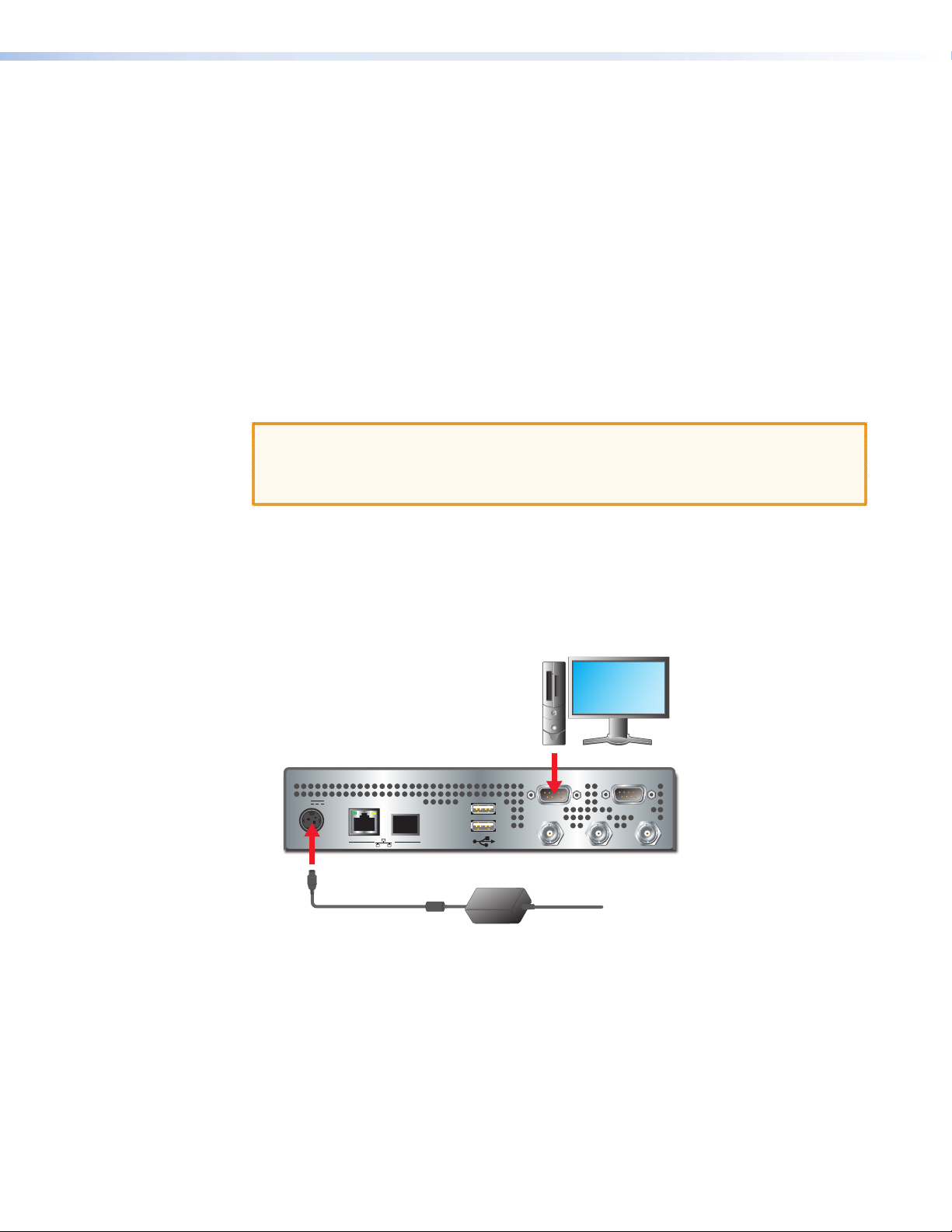
To establish a serial communications link
z Using a null modem type serial cable (supplied), connect the serial port of a PC to the
COM1 serial port on the VN-Matrix 300 to be congured:
VN 300
COM 1
12V DC
REG
6A MAX
Power Supply
OUTINLOOP
Figure 12. Connecting the Serial Port of a PC to the COM1 Serial Port on the
VN-Matrix 300
Configure PC
COM 2
VN-Matrix 300 • Installation and Basic Setup Procedures 17
Page 24
z On the PC run a terminal emulation program such as HyperTerminal, with the following
RJ-45 Network Port Optical Network Port
comms settings:
Baud rate: 115200
Data bits: 8
Parity: None
Stop bits: 1
Flow control: None
Low level configuration
z Connect the power to the VN-Matrix 300 (or, if already connected, cycle the power off
then on).
z The VN-Matrix 300 will commence sending setup/diagnostic data which should appear
in the HyperTerminal window. After a few seconds the diagnostic data will stop and you
will see a ashing cursor in the Hyperterminal window.
z Press the <Enter> key — the VN-Matrix 300 should respond with the following login
prompt:
VN Matrix(R) Maintenance Console: ver n.n
192.168.0.1 login:
NOTE: The login prompt will be preceded by the current IP Address of the unit.
z Type config and press the <Enter> key.
z When prompted for a password type config and press the <Enter> key.
z The following menu will then appear.
NOTE: The IP addresses here are for illustration and may not match those on your
unit.
Network Port 1 Network Port 2
============== ==============
0. Speed/Duplex: auto_10_100_1000 10. Speed/Duplex: fibre_fixed_1000F
1. Boot method: static [dhcp] 11. Boot method: static [dhcp]
2. address: 192.168.0.104 12. address: 192.168.1.2
3. netmask: 255.255.255.0 13. netmask: 255.255.255.0
4. gateway: 14. gateway:
5. broadcast: 15. broadcast: 192.168.1.255
6. mtu: 1500 16. mtu: 1500
7. controller ip: 192.168.0.101 17. ip forwarding: 0
8. controller port: 80 18. webserver port: 80
9. Exit
Please select an option:
VN-Matrix 300 • Installation and Basic Setup Procedures 18
Page 25

Network Port Specific Options
Option Function Comment
0 and 10 Network port link
speed
z Option 0 allows the speed of the RJ45 network port to be
set manually.
z Option 10 reports the speed of the SFP port; this is xed at
1Gbs
1 and 11 Set STATIC or DHCP Entering 1 (11) will toggle this option. When DHCP is selected
items 2 (12) through 5 (15) are not accessible.
NOTE: It is necessary to assign a known IP
address for the controller. This address
must be entered manually into each
VN-Matrix 300 unit. Therefore it is
not always practical to use DHCP. It is
recommended to use a static IP address
scheme.
2 and 12 Set the local address of
the Network port
z Network port 1 is assigned to the RJ45 connector.
z Network port 2 is assigned the SFP connector.
z Standard ETHERNET IP addressing rules apply.
Do not use any leading zeroes in the IP address, for example
172.28.12.100 is valid, 172.028.012.100 is not valid.
3 and 13 Set the appropriate
subnet mask for the
network.
4 and 14 Set the IP address of
the default gateway.
z Standard ETHERNET subnet rules apply.
z Do not use leading zeroes in the subnet mask
z such as 255.255.10.0 is valid, 255.255.010.0 is not valid.
z Required for VN-Matrix 300 systems that include multiple
subnets.
The default gateway must be on the same subnet as the as
the port to which it is assigned.
z Only one default route is supported. Once a value is set
on either option, the other option is no longer available.
To clear a gateway address, select the option (4 or 14) and
enter return with no value set.
z Standard ETHERNET IP addressing rules apply.
Do not use any leading zeroes in the IP address for example
172.28.12.100 is valid, 172.028.012.100 is not valid.
5 and 15 Set the broadcast
Not required.
address.
6 and 16 Set the value of
the maximum
transmission unit, that
is, the number of bytes
(payload) in a frame.
z This value will affect the performance of the system. A large
value can cause packets to be fragmented (split) whilst
a small value may not make efficient use of the network
capacity.
z For ETHERNET this value is normally set to 1500. In certain
circumstance this value may need to be changed to better
match the network that is in use.
Unit Specific Options
7 Set the IP address of
the controller.
z Remember that one (and only one) VN-Matrix 300 must be
configured as a controller.
z The controller IP address must be set to the IP Address
(option 2 and 12) of either Network port on the unit
designated as the controller. This is port over which control
data is sent.
VN-Matrix 300 • Installation and Basic Setup Procedures 19
Page 26

Network Port Specific Options
Option Function Comment
Unit Specific Options
8 Set the number of the
port that is used for
communications with
the system controller.
18 Set the port number
that is used for
communication with
the server.
9 Reboot and activate
settings.
Network (NIC) Connections
All network connections are made at the rear panel of the VN-Matrix 300.
CAUTION: Do not proceed with connecting VN-Matrix 300 to an existing network until
it is correctly configured using the Low level configuration procedure.
Incorrect connection or configuration may cause disruption to other
network users.
By default this is set to 5432, this may be changed if required.
Note that all VN-Matrix 300 units MUST have the same port
number assigned.
By default this is set to 80, this may be changed if required.
Note that the browser in use must use the same port number.
Any changes made are only activated after a reboot of the
VN-Matrix 300 unit.
NOTE: Typing reboot at the hyperterminal
cursor will also reset the unit.
Typically, the VN-Matrix 300 will connect to convenient network point on an existing inhouse network. Use the correct cable type for your chosen network.
Single Network Connection
The VN-Matrix 300 may be congured to run on a single physical network port (1 or 2). In
this configuration all data (image, ancillary and control including monitoring) is transported
over a single physical link.
The VN-Matrix 300 may be used over both switched (single segment) and routed
(multi-segment) networks.
Dual Network Connection
If required, both network connections may be used. In this configuration image and ancillary
data is transported on one connection whilst the other network port is used for monitoring
and or management functions.
System Control Data
System control is managed by the VN-Matrix 300 that has been designated as the controller.
Any changes made in the interface are sent to the affected VN-Matrix 300 device from the
controller. The control information between the controller and any other VN-Matrix 300 unit
in the system is sent via the network that has been assigned to the controller.
VN-Matrix 300 • Installation and Basic Setup Procedures 20
Page 27

Video and Audio Data
NIC2:192.168.0.1
NIC1:172.28.0.1
NIC2:192.168.0.2
NIC1:172.28.0.2
Switch
Local NMS server
172.28.0.3
Browser
172.28.0.4
Unit 1
Unit 2
Controller
Browser (NIC2)
192.168.0.3
Switch
Browser address
192.168.0.1
Browser address
172.28.0.1
Video and audio data may be transported over either of the NICs on the VN-Matrix 300 unit
and are independent of the system control data.
NOTE: The browser is accessible via either network port on the unit that is configured
as the controller.
Switched Network Configuration, Example 1
NOTES: In this example, two VN-Matrix 300 units are congured to work across a
switched network.
• Unit 1 is congured as the controller, on IP address 172.28.0.1.
This unit serves the management interface (GUI).
• The browser (control) PC may be connected to either NIC.
System control data is always sent over the 172.28.x.x network
• Image data is congured to run over NIC 1 (the RJ45 connector).
This is defined in the management interface, described later.
Unit 1
Network Port 1 (RJ45) Network Port 2 (SFP)
0 Speed/Duplex:auto_10_100_1000 10 Speed/Duplex:Fiber_fixed_1000
1 Boot method: static [dhcp] 11 Boot method: static [dhcp]
2 Address: 172.28.0.1 12 Address: 192.168.0.1
3 Netmask: 255.255.0.0 13 Netmask: 255.255.255.0
4 Gateway: 14 Gateway:
5 Broadcast: 15 Broadcast:
6 Mtu: 1500 16 Mtu: 1500
7 Controller ip: 172.28.0.1
8 Controller port: 5432 18 Webserver port: 80
9 Exit
VN-Matrix 300 • Installation and Basic Setup Procedures 21
Page 28

Unit 2
NIC2:192.168.0.1
NIC1:172.28.0.1
NIC2:192.168.0.2
NIC1:172.28.0.2
Local NMS server
172.28.0.3
Browser (NIC2)
192.168.0.3
Unit 1
Unit 2
Controller
Switch
Switch
Browser (NIC1)
172.28.0.3
Local NMS server
172.28.0.3
Browser address
192.168.0.1
Browser address
172.28.0.1
Network Port 1 (RJ45) Network Port 2 (SFP)
0 Speed/Duplex:auto_10_100_1000 10 Speed/Duplex:Fiber_fixed_1000
1 Boot method: static [dhcp] 11 Boot method: static [dhcp]
2 Address: 172.28.0.2 12 Address: 192.168.0.2
3 Netmask: 255.255.0.0 13 Netmask: 255.255.255.0
4 Gateway: 14 Gateway:
5 Broadcast: 15 Broadcast:
6 Mtu: 1500 16 Mtu: 1500
7 Controller ip: 172.28.0.1
8 Controller port: 5432 18 Webserver port: 80
9 Exit
Switched Network Configuration, Example 2
NOTES: This example is the same as the first but the controller has now been assigned to
NIC 2 on unit 1.
• The browser interface is also available via NIC 1.
The controller interface is available on either NIC.
• Image data is configured to run over NIC 2 (the SFP connector).
System control data is now sent over the 192.168.0.x network.
• The controller IP address is now assigned in Option 17 under network port 2
in the configuration for both units.
Option 7 is no longer available under Network port 1.
VN-Matrix 300 • Installation and Basic Setup Procedures 22
Page 29

Unit 1
Network Port 1 (RJ45) Network Port 2 (SFP)
0 Speed/Duplex:auto_10_100_1000 10 Speed/Duplex:Fiber_fixed_1000
1 Boot method: static [dhcp] 11 Boot method: static [dhcp]
2 Address: 172.28.0.1 12 Address: 192.168.0.1
3 Netmask: 255.255.0.0 13 Netmask: 255.255.255.0
4 Gateway: 14 Gateway:
5 Broadcast: 15 Broadcast:
6 Mtu: 1500 16 Mtu: 1500
17 Controller ip: 192.168.0.1
8 Controller port: 5432 18 Webserver port: 80
9 Exit
Unit 2
Network Port 1 (RJ45) Network Port 2 (SFP)
0 Speed/Duplex:auto_10_100_1000 10 Speed/Duplex:Fiber_fixed_1000
1 Boot method: static dhcp] 11 Boot method: static [dhcp]
2 Address: 172.28.0.2 12 Address: 192.168.0.2
3 Netmask: 255.255.0.0 13 Netmask: 255.255.255.0
4 Gateway: 14 Gateway:
5 Broadcast: 15 Broadcast:
6 Mtu: 1500 16 Mtu: 1500
17 Controller ip: 192.168.0.1
8 Controller port: 5432 18 Webserver port: 80
9 Exit
VN-Matrix 300 • Installation and Basic Setup Procedures 23
Page 30

Routed Network Configuration Example
NIC2:192.168.0.1
NIC1:172.28.0.1
NIC2:192.168.1.1
NIC1:172.29.1.1
Local NMS server
172.28.0.3
Browser address
192.168.0.1
Unit 1
Unit 2
Controller
Switch
Switch
Switch
Switch
Browser (NIC1)
172.28.0.4
192.168.0.250 192.168.1.250
Browser (NIC1)
172.29.1.4
Local NMS server
172.29.1.3
Local SNMP
Browser (NIC2)
192.168.0.3
Browser address
172.28.0.1
NOTES: This is an example of a routed network configuration.
• Unit 1 is congured as the controller, on IP address 192.168.0.1.
The two VN-Matrix 300 units are connected across a WAN via an external
router.
• A gateway IP address is now set on NIC port 2 (option 14).
• Only 1 gateway may be assigned.
Image data is transported over NIC 2 (the SFP connector).
• The port used for image data transfer is set in the WEB interface, described
later.
Browser control is available on either NIC
• Enter the IP address of the appropriate NIC in the browser address bar.
A network management system connected via NIC 1 (RJ45).
• This provides isolation between image and SNMP traffic.
Unit 1
Network Port 1 (RJ45) Network Port 2 (SFP)
1 Boot method: static [dhcp] 11 Boot method: static [dhcp]
2 Address: 172.28.0.1 12 Address: 192.168.1.1
3 Netmask: 255.255.0.0 13 Netmask: 255.255.255.0
5 Broadcast: 15 Broadcast:
6 Mtu: 1500 16 Mtu: 1500
8 Controller port: 5432 18 Webserver port: 80
9 Exit
VN-Matrix 300 • Installation and Basic Setup Procedures 24
14 Gateway: 192.168.0.250
17 Controller ip: 192.168.0.1
Page 31

Unit 2
Network Port 1 (RJ45) Network Port 2 (SFP)
1 Boot method: static dhcp] 11 Boot method: static [dhcp]
2 Address: 172.29.1.1 12 Address: 192.168.1.1
3 Netmask: 255.255.0.0 13 Netmask: 255.255.255.0
14 Gateway: 192.168.1.250
5 Broadcast: 15 Broadcast:
6 Mtu: 1500 16 Mtu: 1500
17 Controller ip: 192.168.0.1
8 Controller port: 5432 18 Webserver port: 80
9 Exit
VN-Matrix 300 • Installation and Basic Setup Procedures 25
Page 32

System
Configuration
This section describes:
z VN-Matrix 300 Web Interface
z Start Up and Login Procedure
z Device List Page
z Device Page
z Configuration Page — Videoport (Encoder)
z Bandwidth Management Page — Videoport (Encoder)
z Configuration Page — Videoport (Decoder)
z Device Page Peripherals
VN-Matrix 300 Web Interface
Once all VN-Matrix 300 devices have been correctly set-up for and connected to a network,
any further system conguration is achieved via the VN-Matrix 300 web interface. This
comprises a number of pages which provide access to various system parameters.
The web interface is served up by the VN-Matrix 300 device that was designated as the
controller during the network set-up procedure. It can be viewed by any up-to-date web
browser, running on a PC that is connected to the same network as the VN-Matrix 300
devices.
Suitable browsers include (but are not necessarily limited to):
z Firefox/Mozilla (v1.3 and above)
Firefox is the recommended browser for use with the VN-Matrix 300 product family
z Internet Explorer (v6 and above)
NOTE: Whatever browser is used, it must be congured to accept cookies and be
JavaScript-enabled.
VN-Matrix 300 • System Conguration 26
Page 33

Start Up and Login Procedure
The IP address of the controller is entered into the address bar of the browser in the normal
way.
Figure 13. Entering the IP Address
In the example above, the IP address of the controller is 192.168.0.101.
NOTE: The IP address of the controller in your system will be different.
The login screen will be displayed in the browser (see gure 14).
Login Screen — User Accounts
VN-Matrix 300 has two user accounts:
z admin — which allows full read/write access to all setup parameters,
z public — which allows read only access to setup parameters.
Initially the password for both accounts is the same as the user name (that is, the account
name). It is recommended that these are changed once commissioning is complete.
For commissioning use the admin account and click LOGIN.
Figure 14. Login Screen
VN-Matrix 300 • System Conguration 27
Page 34

Device List Page
The Device List page will display. This page lists all of the VN-Matrix 300 codecs and
decoders that are present on the network.
Device Type
Three types of device may appear in the list
Device Mode
VN-Matrix 300 Devices are listed in one of three modes:
The mode for each device may be set as required.
Note that the VN-Matrix 300 is also supplied as a decoder only option. In this case the
source (encoder) mode is not available to be used.
z 3G-SDI — A codec that is licensed to operate at all resolutions up to and including the
3G-SDI standard.
z HDSDI — A codec that is licensed to operate at all resolutions up to and including the
HD-SDI standard.
z SDI — A codec that is licensed to operate at resolutions up to the SDI standard.
z As an Encoder
z Undened
z As a Decoder
Figure 15. Device Modes
NOTES: • Only devices that are configured to connect to the system controller will be
listed.
• The list may show more devices than you have in your system. This is because
the controller will maintain a list of devices that have been used in the past
and are not currently available. In this case, the IP address entry for that codec
will be blank.
VN-Matrix 300 • System Conguration 28
Page 35

Device Page
Select a device from the device list:
z Double click the mouse pointer on any of the entries for a device in the list (see
figure 15).
The Device page of the chosen unit will be displayed. The example below shows the
Device page for an encoder.
Figure 16. Device Page is Divided into Four Information Areas
Device Summary (a)
z Device Name — The name of the device may be changed to a User specic value. This
is the name of the device itself.
z Serial Number of the unit — For information only, required when upgrading the licence
on a device.
z IP address: port — This field shows two pieces of information:
z The IP address of the Media 1 ETHERNET interface.
z The port number that has been congured for send and receive of UDP control
information.
z By default these are 9001 (send), 5432 (receive).
z Link Status — The condition of the ETHERNET network link to the controller.
Licensed Features (b)
z This field provides a description of features that are enabled on the device.
z The licence management button provides access the License page where additional
features may be enabled.
VN-Matrix 300 • System Conguration 29
Page 36

Device Setup (c)
The Device setup area allows a VN-Matrix 300 device to be congured as either an
encoder or as a decoder.
NOTE: The VN-Matrix 300 is available as a decoder (VND 300) only. In this case it is not
possible to configure the unit as an encoder.
Create Source (Encoder)
Select this option to create a source (ENCODER).
z Source will be shown adjacent to a change device type button.
z A videoport and ancport icon will be created in the Configuration window.
Figure 17. Source (Encoder) Configuration and Setup
Device Setup area provides access to the following controls and information.
The
z Mode:
z Enable — Normal operation; image transport is enabled.
z Disable — Image transport is disabled.
z Standby — Same as disable.
z Identify — When checked, causes the name of the device to be overlaid on the content
that is presented on the SDI-OUT connector on the rear panel.
z Data Interface — The selection defines which of the two network interfaces is to be
used for the data transport.
z Multicast TTL — This value sets the Time To Live (TTL) for multicast packets.
Configuration (d)
The Configuration area provides access to the device configuration pages.
z Click on an icon to access the configuration pages.
VN-Matrix 300 • System Conguration 30
Page 37

Create Display (Decoder)
Select this option to create a Display (Decoder).
z Display will be shown adjacent to a change device type button.
z A display icon will be created in the Configuration window.
Figure 18. Source (Decoder) Configuration and Setup
The Device Setup area provides access the following controls and information.
z Mode:
z Enable — Normal operation; image transport is enabled.
z Disable — Image transport is disabled; the local display will show a blank screen.
z Standby — Same as disable, the display will show a splash screen.
z Identify — When checked, causes the name of the device to be overlaid on the
decoded image output.
z Source Identify — When checked causes the name of the current source (stream) to be
overlaid on the decoded image output. This value is displayed in brackets immediately
after the device name.
z Data Interface — The selection defines which of the two network interfaces is to be
used for the data transport.
z Multicast TTL — This value sets the Time To Live (TTL) for multicast packets.
Configuration
z Provides access to the device configuration pages.
z Select an icon to access the configuration pages.
VN-Matrix 300 • System Conguration 31
Page 38

Configuration Page — Videoport (Encoder)
The encoder Configure page provides:
z Status information for the encoder
z Access to the Bandwidth Management page
z Stream statistics and multicast configuration
Figure 19. Configuration Page
Encoder Videoport Panel
The top panel of the videoport (Encoder) Configure page (see figure 19) provides the
following information:
z Name — This may be changed to a User specic value. This is the name that is applied
to the video port, that is, the name of the image stream. Note that this need not be the
same as the name applied to the physical unit itself.
z Input Mode — The VN-Matrix 300 codec supports a fully automatic detection of the
connected signal format. No manual configuration is required.
z Current Mode — This value reports the currently detected source type.
z Source Status — This value reports the status of the input connection.
z Unplugged — Indicates that either there is no source connected or no invalid video
is present.
z Active — Indicates that a valid video connection is present.
VN-Matrix 300 • System Conguration 32
Page 39

Encoder Streams Panel
The Streams panel of the Configure page for an encoder provides information on any
active streams that are configured on the encoder.
z Stream definition — Provides information on any active streams from the Encoder.
z Streams are provisioned at the display (decoder) device.
z Once a stream has been provisioned the details will appear in the listing.
RTP UNICAST Streams
When the multicast option is not selected, a decoder may connect using either:
z TCP/IP connection — Used for guaranteed delivery on point to point (single connection)
systems.
z RTP UNICAST connection — Streams are sent as RTP Unicast.
NOTE: In this mode, up to 4 simultaneous streams are supported. This is
Configuring a Multicast Connection
When the Multicast enable option (see figure 19) is selected, the user may configure a
multicast connection.
z The user is prompted to enter a Multicast group address in the range 224.nnn.nnn.nnn
to 239.nnn.nnn.nnn.
z Streams are sent as RTP Multicast.
z Note that the VN-Matrix 300 supports IGMP V2 for multicast working.
dependant on the total aggregated bit rate – which must not exceed
270 Mbs.
New export stream
This function is not supported.
VN-Matrix 300 • System Conguration 33
Page 40

Bandwidth Management Page — Videoport (Encoder)
Click the Bandwidth tab on the Configure page. The Bandwidth (see figure 20) page
opens.
Figure 20. Bandwidth Page
The Bandwidth page provides for the control of the spatial and temporal compression
settings for the encoded source.
The available controls are arranged as two main groups:
z Bandwidth Management (Standard control) — Provides a simple interface used to
congure a subset of the VN-Matrix 300 compression toolset.
z Advanced settings — Provides (advanced) control of the complete VN-Matrix 300
compression toolset. To hide this area, click the Standard button in the Bandwidth
Management control section.
NOTE: When hiding the Advanced control area section, default settings are applied
to some of the controls. These settings remain in force while the Standard
area controls are in use and will cancel any changes that were made
previously.
VN-Matrix 300 • System Conguration 34
Page 41

Bandwidth Management — Standard Control
Figure 21. Standard Control Area
The Standard control area provides a user with a quick configuration method for the
VN-Matrix 300 encoder.
Statistics for any active streams currently running from the encoder are provided in the
Streams information area.
Conguration for the encoder is made via 3 entries:
z Control Mode
z Image Quality
z Bit rate.
Control Mode
The Control Mode list is a set of 6 modes that are designed to manage the encoded image
data stream by applying different spatial and temporal compression schemes.
NOTE: These control modes are also accessible in the Advanced settings control
area
.
z None — In this mode the compression scheme maintains a constant image quality. The
bit rate will vary dependant on the content. Slowly moving or static image content will
have a lower bit rate than fast moving image sequences. There is no bit rate limiting in
this mode.
z Peak Flow — In this mode, the spatial image quality is held constant. However, a bit
rate limit is applied and maintained by controlling the frame update rate whenever this
limit is exceeded.
z PBR-F — This is a Peak bit rate mode. The spatial quality is held constant until the bit
rate limit is exceeded. At this point, additional spatial compression is applied to keep the
bit rate at the specified limit.
If the content is such that it is not possible to maintain the bit rate limit using only
spatial compression then a different control mode should be chosen or the bit rate limit
should be increased.
z PBR-F (FD) — This mode is as for PBR-F with the addition of dynamic frame rate
management if the spatial compression is insufficient to maintain the bit rate limit.
VN-Matrix 300 • System Conguration 35
Page 42

Image Quality
The Image Quality controls the spatial compression. A setting of 4 provides a visually lossless
image. A higher setting results in higher compression whilst a lower setting applies a lower
level of compression.
Changes made to this setting will result in a corresponding change in the bit rate for the
encoded stream.
Bit Rate
Enter a value up to a maximum of 300 Mbs to set the limit for the aggregate (total) bit rate
for all data.
z Image data
z Audio
z Ancillary
This control is not available when the Control mode is set to NONE.
Advanced Control — Video Quality and Bandwidth Management
Figure 22. Advanced Control Page
Click the Advanced button in the Bandwidth (simple) control area described in the previous
pages to access this sectopm.
The controls in this area provide access to the complete set of image quality and bit rate
tools for the VN-Matrix 300 encoder.
The controls are divided into to two main categories:
z Video Quality
z Bandwidth
Some of the controls that are available in the simple control interface described above are
also present in this area. Where controls are duplicated, the settings will track.
VN-Matrix 300 • System Conguration 36
Page 43

Video Quality Management
Spatial Compression settings
Figure 23. Spatial Compression Settings
The level of spatial compression is set using the Luminance and Chrominance control.
These controls are normally locked, with an optimal offset of 2 units between them.
A Luminance value of 0 provides the minimum spatial compression; a Luminance value of
10 provides the maximum spatial compression.
If required, the Chrominance compression may be set independently by unchecking the
Lock box.
A spatial compression setting of 4/6 will provide visually lossless compression for HD content.
NOTE: By default, the Luminance and Chrominance offset is set to 2 whenever the
simple (standard) management scheme is selected.
Temporal Compression settings
Temporal compression may be applied by selecting the Temporal check box.
By default, this option should always be selected.
Temporal compression causes data to be transferred only when a change occurs between frames.
Using the Threshold setting
The Threshold setting (see figure 23) modifies the detection point of the temporal
compression algorithm. A value of 0 results in all changes between frames being sent.
As the threshold value is increased, only changes above a certain level are sent, thus
reducing the bit rate. This control is used to compensate for image sources that have a level
of noise in them. In general, there is always a certain amount of noise in any source that
is produced by an analogue method. By applying a threshold this noise can effectively be
ignored by the PURE3 compression engine, resulting in a lower transmitted bit rate.
As a general rule, always set this to a 1 for a camera originated image.
When to use the Chroma setting
The Chroma setting adapts the temporal compression to take note of the chroma changes in
an image. When enabled, note that chroma thresholding will increase the bit rate.
This setting should be selected (on) for video sources.
Refresh Rate
Refresh rate controls how frequently the non-changing parts of the screen are updated
when temporal compression mode is enabled. This is useful when connecting new displays
to a Mb source and to fill in gaps in the data when using a lossy network transport such as
RTP. A value of 1 refreshes the screen in one second, a value of 0.1 refreshes the screen 10
times per second. A value of 0 disables the refresh.
VN-Matrix 300 • System Conguration 37
Page 44

Bandwidth Management
The Bandwidth management section provides a method to set a maximum bit rate for the
encoded stream. It duplicates the Control mode settings already described in the Standard
Control
Figure 24. Bandwidth Management Section
Control Mode: Manual Frame drop
In this mode, the spatial image quality is held constant. However, a bit rate limit is applied
and maintained by controlling the frame update rate whenever this limit is exceeded. The
frame rate is managed by setting a value for the Frame Drop Percentage. This is the
percentage of frames that are dropped whenever the bit rate limit is exceeded.
Control Mode: Shared Flow rate
This mode is the same as the Peak flow rate but the bit rate control is applied to the
aggregate value for all streams from the encoder, as would be the case if multiple
(maximum 4) Unicast streams are chosen as the data transport method.
area (already described above) but includes two additional modes of control.
Streams Panel
The streams panel provides statistics on all of the active connections running on the encoder.
Figure 25. Streams Panel Section
The bit rate figure that is reported here is the total for all streams, including video, ancillary
(audio) and FEC.
VN-Matrix 300 • System Conguration 38
Page 45

Configuration Page — Ancport (Encoder)
The AncPort configuration is accessed from the icon in the device, configuration page and
provides access to settings relating to the Ancillary data that is present in the video transport
connection. Primarily, this data relates to the embedded audio.
Figure 26. Configuration Page Icons
Figure 27. Configuration Page
The Name of the stream that is assigned to the ancillary data.
NOTE: That this may be different to that of the physical encoder unit itself.
VN-Matrix 300 • System Conguration 39
Page 46

ANC Panel
Provides for control and configuration of the ancillary data channels.
Selecting the Audio group
There are 16 audio channels present in the SDI/HDSDI/3G SDI video transport. These are
arranged in 4 groups each of 4 channels. The VN-Matrix 300 units can transport 1 group
(4 audio channels). The required audio group is selected here. The groups are presented as
channel pairs as described below.
z Channel pair 1: Group 1, channels 1&2
z Channel pair 2: Group 1, channels 3&4.
z Channel pair 3: Group 2, channels 1&2
z Channel pair 4: Group 2, channels 3&4.
z Channel pair 5: Group 3, channels 1&2
z Channel pair 6: Group 3, channels 3&4.
z Channel pair 7: Group 4, channels 1&2
z Channel pair 8: Group 4, channels 3&4.
The indicator to the right of the list showing each channel pair is green if that audio group is
present in the SDI source.
Selecting either of the check boxes associated with a group will automatically enable both of
the channel pairs in that group. It is not possible to select fewer than 2 channel pairs.
FEC Panel
Forward error correction may be applied to the ancillary data. This protects against packet
loss when the ancillary data is transported across a network.
Forward Error Correction
Forward error correction may be applied to the Ancillary data to protect against errors
caused by packet loss when the data is transported over a network. Forward Error Correction
(FEC) enables the decoder to recreate data that has been lost or corrupted without the need
for retransmission. The FEC data is sent separate from the image and ancillary data.
The level of FEC can be set to protect against different levels of data loss. This produces a
corresponding change in the amount of data that is transported and thus, the bit rate is
increased or decreased in proportion to the amount of FEC applied.
PRO-MPEG COP3
The error correction scheme employed on the VN-Matrix 300 product range is implemented
using the recommendations of PRO-MPEG COP3.
Row and Column FEC
The FEC may be applied as either column or column and row.
z Column FEC is used to protect against burst packet losses, providing that the burst of
packet losses are not in the same row. Column FEC is known as 1D (dimension) FEC, as
correction data is only calculated on one dimension.
z Row FEC is used to protect against the loss of a single packet. It is the simplest method
of protection and results in the lowest overhead in terms of bit rate and latency.
However, it is not able to handle consecutive (burst) burst packet loss.
VN-Matrix 300 • System Conguration 40
Page 47

By using both FEC methods together, 2 dimensional FEC, the combined effect can protect
against more loss permutations than either scheme used in isolation.
FEC works by adding additional data to the stream. Using this data it is possible for the
decoder to detect and reconstruct any lost packets.
P1 P2 P3 P4 FR1
P5 P6 P7
P9 P10 P11
P13 P14 P15
P17 P18 P19 P20 FR5
FC1 FC2 FC3 FC4
P8
P12
P16
FR2
FR3
FR4
The diagram to the left shows the FEC scheme
applied to a 4 (column) x 5 (row) structure. Note
that this adds 5 row FEC packets and 4 column FEC
packets to every 20 data packets. This scheme can
protect for burst packet losses up 5 packets long.
P1 P2 P3
P5 x P7
P9 P10 P11
P13 x x x FR4
P17 P18 P19
FC1 FC2 FC3 FC4
P4
P8
P12
P20
FR1 If packet 6 is lost or corrupted, this can be corrected
FR2
FR3
FR5
for using the FR2 FEC packet.
It is not possible to correct packets 14, 15, and 16
using the row FEC (FR4) as too much data is missing.
To correct these packets, the column FEC data is
used. Packets 15 and 16 may be corrected using FC3
and FC4 column FEC packets. To correct packet 14,
packet 6 must rst be corrected using the row FEC.
After this, the column FEC may be used to correct
packet 14.
Setting the FEC value
The values that are set in the FEC row and column drop down lists will depend on the quality
of the network link that is in use.
From the diagrams above it can be seen that the FEC data can add a large overhead to the
overall bit rate that is transported over the network. Therefore certain settings, whilst they
may provide a high level of reliability, will be inefficient. Settings that add little overhead may
not provide a sufcient level of protection on networks with a poor QoS.
The recommended setting is 5,5. This setting should be used as the starting point for the
error correction for the audio transport and provides rugged operation on uncorrected IP
networks.
NOTE: • FEC is ONLY applied to the ancillary data channel. It is NOT applied to the
video channel.
• FEC is only effective for RTP transports. It should not be used for TCP
transport.
Error injection rate
This setting should be left at 0. It used for test purposes only and is used to drop packets
articially in order to test the effectiveness of the FEC scheme.
VN-Matrix 300 • System Conguration 41
Page 48

Streams Panel (ANC)
The Streams panel of the Configure page for an encoder provides information on any
active streams (audio) that are configured on the encoder.
z Stream definition — Provides information on any active streams from the encoder.
z Streams are provisioned at the display (decoder) device.
z Once a stream has been provisioned the details will appear in the listing.
Configuring Audio as a Multicast Connection
When the Multicast enable option is selected, the user may configure a multicast
connection.
z The user is prompted to enter a multicast group address in the range 224.nnn.nnn.nnn
to 239.nnn.nnn.nnn.
z Streams are sent as RTP multicast.
z Note that the VN-Matrix 300 supports IGMP V2 for multicast working.
When this option is not selected
z Streams are sent as RTP unicast.
z Note that in this mode, up to 4 simultaneous streams are supported. This is dependant
on the total aggregated bit rate – which must not exceed 270 Mbs.
TIP: This setting DOES NOT track the same setting applied in the VideoPort page.
For most applications, this setting should be set to be the same as that for the
Videoport, but this is not mandatory.
Configuring FEC as a MULTICAST stream
Figure 28. Configuration Page Icons
VN-Matrix 300 • System Conguration 42
Page 49

The format of the FEC stream is set via the appropriate icon (either colefec or rowfec) in the
Configure dialog of the Device page.
Figure 29. Device Page, Configuration Dialog
z Multicast Enable — Allows the user to select the multicast option.
If selected:
z The user is prompted to enter a multicast group address in the range
224.nnn.nnn.nnn to 239.nnn.nnn.nnn.
z Streams are sent as RTP multicast.
z The VN-Matrix 300 supports IGMP V2 for multicast working.
When — this option is not selected:
z Streams are sent as RTP unicast.
NOTE: In this mode, up to 4 simultaneous streams are supported. This is dependant
on the total aggregated bit rate – which must not exceed 270Mbs.
TIP: This setting DOES NOT track the same setting applied in the VideoPort page.
For most applications, this setting should be set to be the same as that for the
Videoport, but this is not mandatory.
VN-Matrix 300 • System Conguration 43
Page 50

Typical Application Bit Rates
Typical bit rates — Video
Application z Broadcast Contribution
z Camera Panning
z Sports/Nature
z Lifestyle
Profile z High Detail
z High Motion
Control
PBR PBR with dynamic Frame
Mode
SDI
10 to 20 Mbps 3 to 10 Mbps 500 kbps to 3 Mbps
z Broadcast News Media
Gathering
z Static Camera Frame
z Interviews
z High Detail
z Low Motion
management
z Static Camera Frame
z Surveillance
z Telepresence
z Collaboration
z Video Phone
z Low Motion
z No Motion
Peak flow rate
(270 Mbs)
HD-SDI
50 to 90 Mbps 15 to 50 Mbps 2 to 15 Mbps
(1.5 Gbs)
Resolution
3G-SDI
100 to 180 Mbps 30 to 100 Mbps 4 to 30 Mbps
(3 Gbs)
Typical Bit rate (video)
Typical bit rates — Embedded Audio
The VN-Matrix 300 supports the transport of the Ancillary data that is embedded in the
video transport.
The ancillary data contains audio, timecode, closed caption and other user specific
information. The VN-Matrix 300 supports the transport of audio data only.
Audio overview:
z Available in blocks of 4 channels.
z Audio Bit rate
z For HD and 3G sources, the audio bit rate is approximately 4 Mbs for each channel
in the group. The total bit rate for each group is approximately 16 Mbs.
z For SD sources, the audio bit rate is approximately 2 Mbs for each channel in the
group. The total bit rate for each group is approximately 8 Mbs.
z Forward error correction may be applied to correct the network problem.
z FEC is required to correct for packet drops on the network.
z FEC is only added to Audio only
z Implements the recommendations dened of PRO-MPEG COP3
z FEC can add up to 50% bit rate overhead.
VN-Matrix 300 • System Conguration 44
Page 51

Typical Bit Rates (HD and 3G Sources) — Audio
The total bit rate for each group is approximately 16 Mbs.
1 group
(4 channels)
Audio Bit rate 16 Mbs 32 Mbs 48 Mbs 64 Mbs
FEC overhead
(Example @ 40%)
Total audio + FEC 22 Mbs 44 Mbs 66 Mbs 88 Mbs
6 Mbs 12 Mbs 18 Mbs 24 Mbs
2 group
(8 Channels)
3 group
(12 channels)
4 group
(16 Channels)
VN-Matrix 300 — Maximum bit rate
The maximum supported bit rate is 300Mbs.
z This is the total combined bit rate for video and audio data.
z The VN-Matrix 300 GUI provides an indication of the total transport bit rate as
adjustments are made to compression and FEC.
Maximum bit rate example
Application z Broadcast Contribution
z Camera Panning
z Sports/Nature
z Lifestyle
Resolution
SD 10-20 Mbs 22 Mbs 42 Mbs
HD 50 to 90 Mbps 112 Mbs
3G 100 to 180 Mbps 202 Mbs
Video Bit rate Audio bit rate
(1 Group +
FEC @40%)
Total
(max)
Configuration Page — Videoport (Decoder)
The decoder Configuration page provides:
z Status information for the decoder
z Stream selection
z Bit rate monitoring.
Figure 30. Videoport Page
VN-Matrix 300 • System Conguration 45
Page 52

Decoder Videoport Panel
The top panel of the videoport (decoder) configuration page provides access to the following
features:
z Name — This may be changed to a user specific value. This is the name that is
displayed in the device list page.
z Nodata splash — Enables the display of a splash screen when the display device
detects a break in the input data stream. When this control is disabled the last decoded
frame is displayed.
z Active format — This value reports the currently selected output mode. The reported
mode will be the same as the source type. If no source is available then a the splash
screen resolution is reported.
Decoder Streams Panel
The lower panel provides for stream selection and bit rate monitoring.
Figure 31. Decoder Streams Panel
Decoder — Source stream selection
Figure 32. Active Source Stream
The active source (streams) that are available may be viewed in a drop down list under the
Source heading in the lower panel.
The available streams are listed by their device name (these may be user defined by renaming
the appropriate encoder device).
The type of connection that is to be established between an encoder and decoder is defined
by picking the stream type from this drop down list.
Stream Type —_tcp
A unicast TCP stream, used for guaranteed delivery point to point connections.
Stream Type — rtp unicast
A unicast UDP stream, used for best effort point to point connections. This type of
connection is replaced by the _rtp(m) type if a multicast stream has been configured at the
corresponding encoder.
VN-Matrix 300 • System Conguration 46
Page 53

Stream Type —_rtp MULTICAST
A multicast UDP stream, used for best effort point to multi point delivery. Note that
this stream type is only available when a multicast stream has been configured at the
corresponding encoder.
Decoder — Enabling audio streams
Transport of the audio content (the audio stream) associated with the selected video stream
may be enabled by selecting the Audio check box under the Audio heading.
Use the update button to apply the setting.
The selected audio stream will be listed adjacent to the audio heading in the bandwidth list.
Figure 33. Audio Stream in Bandwidth List
Decoder — Enabling FEC for audio streams
Forward error correction (FEC) for the selected audio stream may be enabled by selecting the
FEC check box under the FEC heading.
Select the the update button to apply the setting.
The associated FEC stream will be listed adjacent to the colfec and rowfec headings in the
bandwidth list.
Figure 34. FEC Stream
NOTES: • FEC data is only sent from an encoder when it is enabled for processing by a
decoder.
• FEC data is only sent for the audio stream.
VN-Matrix 300 • System Conguration 47
Page 54

Decoder — Bit Rate and Stream Statistics
The bit rate and statistics for each of the stream types (video, audio and FEC) may be
monitored.
NOTE: The bit rate statistic reported here applies to whichever stream type is being
monitored. This is different to the bit rate statistics reported by the encoder,
which is for the total of all stream types.
Select the stream that is to be monitored by selecting the appropriate entry in the
bandwidth list.
The following example is specic to the video data. Note that the scheme for audio and FEC
data is the same.
Bandwidth page — stream statistics
Figure 35. Stream Statistics on Bandwidth Page
z Source — Reports the currently select stream.
z rtp destination — Reports the IP destination address and port for the current stream.
When connecting using RTP this will be either a multicast group address or, for RTP
unicast, the IP address of the decoder. When connecting using TCP, this eld will be
empty.
z rtp source — Reports the multicast group address that reception statistics will be
reported to. In RTP unicast and TCP modes this reports the IP address of the encoder.
z Playback Delay — This defines the playback delay. The playback delay is the sum of
the transit time in the network and the time spent in the input buffer of the decoder.
This setting may me modified by the user.
z Setting the Playback Delay too small results in the playback image jumping as
network loading changes.
z Setting the Playback Delay too large increases the image latency and may result
in internal buffer overflow on high bandwidth data streams. This causes a jumpy
screen update and screen flashing.
The Playback Delay setting should be set to a value between 0.1 and 0.2 seconds.
VN-Matrix 300 • System Conguration 48
Page 55

Bit rate and network statistics for the current stream are reported in a tabular form.
z The total column contains counts for the history of the stream.
z The window1 and window2 columns contain counts over user programmable
intervals.
z Megabits/sec — The bit rate received from the current data source.
NOTE: The reported bit rate is for the video stream only. Statistics are available
for Audio and FEC on page 45.
z Packets/sec — The number of data packets per second received from the source.
z Dropped packets — The number of data packets dropped during the associated
interval time. This will always be 0 for TCP streams.
Dropped packets will be counted when using RTP streams on busy networks.
z Interval time — The time over which the previous counts are averaged.
The total column assumes an interval time of infinity. The remaining two times are user
programmable in seconds.
Device Page — Peripherals
Serial Port Control
Bi-directional serial communications (RS-232) can be achieved between any VN-Matrix 300
units on a network.
Serial data is sent independently of the other streams on the network and it is not necessary
to have a direct encoder to decoder relationship.
Pass-through Control Mode
In this mode, serial data is passed from one VN-Matrix 300 device to another. Data ow
is fully bi-directional and is independent of whether the VN-Matrix 300 is an encoder or
decoder. Thus control of external equipment is supported.
Figure 36. Pass-through Control
A single VN-Matrix 300 device is designated the server. One or more VN-Matrix 300 devices
are then configured as clients.
VN-Matrix 300 • System Conguration 49
Page 56

Data input to the server is sent to all clients simultaneously. Data received at a client is sent
to the server. Simultaneous data transfers are processed on a first in first out basis.
Any number of pass-through groups may exist on the same network.
Communication may only take place between a client and a server; it is not possible to
communicate from client to client.
Configuring a Serial Pass-through Group
Server Mode
Decide which device is to be the server.
1. On the Device page, select the peripherals tab.
2. On the Peripherals page, set the mode (a) to server.
3. Configure the other settings (b) (baud rate, data bits, stop bits, parity, and handshake)
as required.
4. Click the Save All tab.
Figure 37. Serial Pass-through Group — Server Mode
VN-Matrix 300 • System Conguration 50
Page 57

Client Mode
From the Devicepage, Peripherals tab of each device in the client group, configure the client
devices.
1. On the Device page, click on the device you want to configure as a client.
2. Select the Peripherals tab.
3. Set the mode a to client.
This reveals the destination listbox.
4. In the destination b listbox, select passthrough for the appropriate server.
5. Change the other settings
required.
6. Click Save All tab.
Figure 38. Serial Pass-through Group — Client Mode
c (baud rate, data bits, stop bits, parity, and handshake) as
VN-Matrix 300 • System Conguration 51
Page 58

Firmware, Licensing Upgrades and User Accounts
This section describes upgrading device firmware and clock management.
Upgrading Device Firmware
From time to time Extron may issue rmware upgrades for VN-Matrix 300 in order to make
new functionality available. Details of the latest firmware release will be published on our
website, www.extron.com.
Upgrades are supplied in a single le, named in the format upgrade_verx.x.tar where
verx.x is the version number. Before you start you will need to copy the upgrade le on to
the computer that you use to access the VN-Matrix 300 controller.
The update process is split into the following stages:
Stage Function Summary Performed On
Upload Copy the upgrade file from the control
PC to a temporary storage area on the
VN-Matrix 300 Controller
Prepare Unpack and copy the new rmware (from
the controller) into the VN-Matrix 300
alternate flash memory.
Activate Reboot the VN-Matrix 300 to start using
the new firmware. This is a temporary
mode that allows you to test the new
firmware. If you encounter any problems
you can back out of this mode and return
to the previous firmware version.
Commit Reboot the VN-Matrix 300 to start using
the new firmware permanently.
All stages of the upgrade process are carried out using the web interface. It is recommended
that all VN-Matrix 300 units in the same system are upgraded to the same rmware version
to ensure full compatibility.
The VN-Matrix 300 controller
only
Each VN-Matrix 300 device
including the controller
Each VN-Matrix 300 device
including the controller
Each VN-Matrix 300 device
including the controller
VN-Matrix 300 • Firmware, License Upgrades, and User Accounts 52
Page 59

NOTES: z Performing the Activate function on the controller will cause the device
to reboot and as a result the upgrade file (in the temporary storage are) will
be erased. It is recommended, therefore, that you PREPARE all devices
first, after which the upgrade file will no longer be needed. Then perform the
Activate function on each device, commencing with the controller.
• The Activate function must be performed on the controller device first, such
that the new firmware is in control of upgrading the remaining devices.
• When performing Activate or Commit on the controller, the device will
reboot.
• This will cause temporary loss of the web interface, since this is provided by
the controller.
• Wait for 30 seconds to allow the device time to reboot, then refresh the
browser.
Uploading the Firmware File to the VN-Matrix 300 Controller
z Login to the web interface.
z From the Device List page, click on the VN-Matrix 300 device that you wish to upgrade.
z From the Device page, click the Upgrade tab. The Upgrade page will appear:
Figure 39. Upgrade Page
z Upload — Browse to the le that you wish to upload to the VN-Matrix 300 device. This
file is loaded to a temporary area of memory on the controller. The Controller can hold a
maximum of two upgrade files. If another is loaded then the oldest file is deleted.
z Select Firmware Version — Select the upgrade version to be used. Usually this is the
version that you uploaded in the step above.
z Committed Version — This is the current version that is loaded and running on the
VN-Matrix 300 device.
z Upgrade Version — This is the version that you are upgrading to.
z Device Upgrade Status — This reports the status of the upgrade process. One of
seven possible messages (states) will be reported.
VN-Matrix 300 • Firmware, License Upgrades, and User Accounts 53
Page 60

Device Upgrade status messages
Device Upgrade
Description Action
Status
Wait This is the normal state when the unit
is running with the current version of
firmware.
z Browse to and load a new
version of firmware. The new
file is held in the controller.
z Select the firmware version for
the upgrade.
z Select the foward button to
move to the Prepare state.
Prepare This state is reported when an upgrade
file has been selected and is being
Wait until the Upgrade status box
reports READYTOACTIVATE.
uploaded to the unit. During this time,
the upgrade file is copied to a separate
(alternate) area of FLASH MEMORY
ready to be used by the VN-Matrix 300
that is to be upgraded.
Ready To Activate During this state, the device has
loaded the new rmware to FLASH
MEMORY and is ready to run the
firmware.
z Select the foward button to
activate the new firmware and
move to the Ready To Commit
state.
z Select the reverse button to
abandon the upgrade via the
BACKOUT state.
Ready To Commit During this state, the device is running
the new firmware. The old firmware is
still available to be used if the upgrade
is unsuitable.
z Select the forward button
to permanently store the new
version of firmware and move
to the Committing state.
z Select the reverse button to
abandon the upgrade via the
Ready To Activate state.
Committing At this point, the new firmware
version is being written the main
FLASH MEMORY. The original
The new code has been committed
when the status returns to the
Wait state.
firmware is overwritten and is no
longer available for use.
Backout The firmware version that is held in
the main flash area is being written to
Select the Reverse button to
abandon the upgrade.
the alternate flash memory area.
Device restarting The controller has temporarily lost
contact with the device while the
device is restarting.
To install the new firmware into a VN-Matrix 300 unit
NOTE: You must upgrade the VN-Matrix 300 controller rst. Please note, however,
that once you go past the ReadyToActivate stage the unit will reboot and the
upgrade file will be erased from the controller. It is recommended, therefore,
that you get ALL devices to the ReadyToCommit stage before completing
the controller upgrade, otherwise you will need to upload the file again (see
page 53.
1. Click the
filename directly into the field provided.
Browse button to navigate to the required upgrade file, or type the path and
VN-Matrix 300 • Firmware, License Upgrades, and User Accounts 54
Page 61

2. Click the Upload button to begin uploading the le to the VN-Matrix 300 controller.
This may take a few minutes.
Once the file is uploaded, you can begin installing it into each unit , starting with the
controller unit.
1. From the Device List page, click on the VN-Matrix 300 unit that you want to
upgrade.
2. From the Device page click the Upgrade tab. The Upgrade page will appear.
3. Click the Select Firmware Version listbox and choose the new firmware file you
want to install. Usually there will only be one le listed.
The remainder of the installation procedure is achieved using the forward and (if necessary)
reverse buttons, to move the installation between the various stages. The current stage/
status is indicated by the Device Upgrade Status field.
The process allows you to temporarily install and test the new firmware and, if everything is
OK, you can then permanently install (commit) the new rmware. Up until the last stage it is
possible to return to the existing firmware version.
Figure 40. Temporarily, Testing, and Permanently Installing New Software
1. Click the forward button. The Device Upgrade Status field will show PREPARE and
percentage progress. This stage may last a few minutes.
TIP: The chosen rmware version is conrmed in the Upgrade Version eld.
2. When
READY TO ACTIVATE appears, click the forward button again.
3. The unit will then reboot.
Once rebooted the Device Upgrade Status field will show READY TO COMMIT and
the VN-Matrix 300 will be using the new rmware. Test for correct operation.
4. If everything is working correctly, click forward again to permanently install the new
firmware.
The Device Upgrade Status field shows Committing and percentage progress. This
stage may last a few minutes.
If you experience any problems, click reverse to return to the previous stage.
5. When the Device Upgrade Status eld returns to WAIT the unit is ready for use.
VN-Matrix 300 • Firmware, License Upgrades, and User Accounts 55
Page 62

Licensing
Each VN-Matrix 300 unit is supplied with a feature set that is dened by a license key and a
structure. This is not intended to be changed as part of normal operation and this section is
provided for information only.
Figure 41. License Page
License structure
The licensed features are represented in the by the structure. The characters used in the
structure and their meaning are outlined below.
NOTES: • This information is provided for interest only; it is not essential for a user to be
familiar with this.
• As the range of licensed features increases, additional characters will be added
that may not appear in the list presented here.
Character String Representing
V Number of supported video (encoder) channels
D Number of supported display (decoder) channels
N Enables ancillary channel support.
mA Internal use – not user option
mH Internal use – not user option
oS Internal use – not user option
oD Internal use – not user option
S Supported video transports (SDI, HDSDI, 3GSDI)
U Number of supported audio (ancillary) channels
VN-Matrix 300 • Firmware, License Upgrades, and User Accounts 56
Page 63

User Accounts
Changing User Login Passwords
From the Device List page click the Accounts tab.
Figure 42. Accounts Page
The VN-Matrix 300 has three user accounts:
z Administrator — which allows full read/write access to all setup parameters,
z Public Account — which allows read only access to setup parameters.
z Recorder GUI Account — which allows full read and write access to all setup
parameters for the VN-Matrix recorder.
NOTE: The VN-Matrix Recorder features are not covered in this user guide.
Enter the Current Password for the user account you want to change.
Then enter the new password in both the
New Password and Confirm fields.
NOTE: The password can include letters, numbers and the underscore character,
and is case-sensitive.
z Click the Update Password button to save the change. The new password will be
required the next time you login.
VN-Matrix 300 • Firmware, License Upgrades, and User Accounts 57
Page 64

Clock Management
Figure 43. Accounts Page
The system clock is generated by the unit that is acting as the controller. All units in the
system receive their time stamps from the system controller.
The clock for all VN Matrix 300 series units is set in production and may be changed to
reflect the local time by entering the new time in the format shown below and clicking the
Change Time button.
Figure 44. Clock Management
Controller Licensing
The system controller is able to be licensed to add or remove features. Currently the license
is entered in production and users should not attempt modify this in any way, otherwise the
unit may become unstable.
VN-Matrix 300 • Firmware, License Upgrades, and User Accounts 58
Page 65

Alarms and SNMP
This section provide the following:
z Overview — Alarms
z Alarms Page
z Overview — SNMP
z SNMP Trap Destinations
Overview — Alarms
The VN-Matrix 300 is congured to generate alarms for range of error conditions. A list of
these error conditions and their meanings are presented on the following pages.
Alarms can be monitored at a number of locations throughout the WEB GUI:
z Alarms page
In the list immediately below the Filter Settings box. This details the alarm
conditions that are currently active on the system.
z Alarm Logs page
In the list immediately below the Filter Settings box. This provides a historical log of
when an alarm condition was raised and cleared.
z Device list page (see figure 15)
Where a Trafc light symbol in the Status Column is used to represent the status of a
device.
z In the top right hand corner of each page in the GUI.
Where the device status and system status is displayed.
In addition the red LED located on the front panel of the VN-Matrix 300 illuminates
whenever a critical alarm is triggered.
Alarm conditions, once triggered, will be remain active until the error that caused it has
cleared and then for a further 5 seconds.
VN-Matrix 300 • Alarms and SNMP 59
Page 66

Alarms Page
Filter Settings
Figure 45. The Alarms screen enables a user to define and monitor system alarms.
Figure 46. Filter Settings Section
The Filter Settings section allows the default settings for each alarm type to be modified.
a Alarm Type — Select the particular alarm that is to have its default setting changed.
b Alarm Source — Select the device on which the alarm is to changed.
c Alarm Severity — Set the alarm severity. Each alarm condition has a default severity
which may be overwritten using the filter controls. Note that the default setting is listed
in this drop down independently of any changes that have been made to the alarm
severity.
d Alarm Reporting — Set the alarm to be either reporting or not reporting. Each alarm
condition has a default reporting setting. Note that the default setting is listed in this
drop down independently of any changes that have been made to the alarm reporting.
VN-Matrix 300 • Alarms and SNMP 60
Page 67

Alarm Type
This drop down lists the available alarm error conditions for all units. Alarm error conditions
are divided into two broad categories
z Alarm errors that occur on an Encoder
z Alarm errors that occur on a Decoder
In addition there is one alarm error that only occurs on the device that is configured as the
system controller.
Alarm Source
Alarm lters may be set for either a single, specic unit or for all VN-Matrix 300 devices in
the system.
Alarm Severity
Alarms may be set to one of three severities.
Alarm Severity Description
Critical
Warning When triggered, a warning alarm will result in the trafc light indicator
None
When triggered, a critical alarm illuminates the red LED on the front
panel of the affected unit. In addition, the normally open contacts of the
relay accessed via the COMM 2 connector will be closed.
The traffic light indicator for the device (Device list) will be shown in red.
for the device (device list) showing in amber.
A setting of None effectively filters the alarm condition. The alarm will
still appear in the alarms list but it will not affect any colored indicators.
Alarm Reporting
An alarm condition may be either reporting or not-reporting.
A reporting condition will cause an SNMP trap to be sent to an SNMP client whenever that
alarm condition is triggered.
Applying Alarm Filter Settings
z Changes made to the filter settings may be applied by clicking Apply filter change
button.
z Changes made will be lost after a power down unless the Save all tab is clicked to
make these changes permanent.
Alarm List
The Alarm list provides information on all alarm events that are currently active. The list is
refreshed each time the Alarms tab is selected.
Alarm events that are listed may be sorted by Type, Raise time, and Severity.
Position the mouse pointer over the required sorting heading (Type, Raise time, or Severity)
and left click to change the list order. The list will be refreshed each time the sorting criteria
is applied.
Figure 47. Alarm List Events
VN-Matrix 300 • Alarms and SNMP 61
Page 68

Alarm Logs
A historical list of the last 200 alarm events is provided in the Alarm Logs page.
Figure 48. Alarm Log Page Showing Error Conditions
The log provides data on when an alarm error condition was raised and cleared. Each event
is paired in the log so a raise and clear event is listed together.
The log holds a historical record of the last 200 alarm events. When more that 200 events
occur the oldest event is deleted from the log.
Alarm events that are listed in the log may be sorted by Type, Raise time and Severity.
Position the mouse pointer over the required sorting heading (Type, Raise time, or Severity)
and left click to change the list order. The list will be refreshed each time the sorting criteria
is applied.
VN-Matrix 300 • Alarms and SNMP 62
Page 69

Alarm Type Description — Encoder
Alarm Type Description Action Default Settings
No source No source present at the input. Check input
connections; is there
an output on the loop
through connector?
Bad source syncs Source is present, unrecognized
due to bad sync measurement.
No SDI source lock Source is present, unable to lock Critical, reporting
Unsupported SDI Mode Source is present, mode not
supported
Unsupported Mode Not applicable to VN-Matrix 300 N/A
Bad Source Not applicable to VN-Matrix 300 N/A
Analogue Phasing error Not applicable to VN-Matrix 300 N/A
Encoder Alarm
Hardware encoding
error
Unsupported audio
source
Data rate overload The compressed data rate is too
Network overload The network is dropping too
The hardware is unable to
encode the input signal.
Not applicable to VN-Matrix 300 N/A
Increase the
high.
many packets.
compression or
reduce the required
bit rate
Critical, reporting
Critical, reporting
Critical, reporting
Critical, reporting
Critical, reporting
Warning,
reporting
VN-Matrix 300 • Alarms and SNMP 63
Page 70

Alarm Type Description — Decoder
Alarm Type Description Action Default Settings
No decoder video data Indicates that there is a valid
connection, no video data present.
Usually accompanied by no source
data stream message in the WEB
interface.
No decoder mode No matching decoder mode for the
incoming stream.
No source report Unable to detect the format of the
received data stream.
Recovered audio Not applicable to VN-Matrix 300 N/A
No decoder audio data Not applicable to VN-Matrix 300 N/A
Bad audio at decoder Not applicable to VN-Matrix 300 N/A
Bad audio PLL Not applicable to VN-Matrix 300 N/A
Video network packets
dropped
Decoder buffer overflow The incoming data rate is high;
Decoder Alarm
Excessive network packet loss has
occurred.
reduce the pipeline delay.
Decoder buffer
underflow
The incoming data rate is too low;
increase the pipeline delay
Bad video PLL The decoder cannot synchronize to
the video data.
No decoder ANC data The decoder is not receiving any
embedded audio (ancillary) data.
Missing ANC at decoder The Decoder is receiving poor
quality ANC data
Recovered ANC Error correction has recovered
corrupted / missing ANC.
Warning, reporting
Warning, reporting
Warning, reporting
Warning, reporting
Warning, reporting
Warning, reporting
Warning, reporting
Warning, reporting
Warning, reporting
Warning, reporting
Alarm Type Description — Controller
Alarm Type Description Action Default Settings
Bad device The Controller is unable
to contact the specified
device. The device is not
Alarm
available or has failed.
Controller
Check the device in question
Critical, reporting
z Is power applied?
z Is the network cable / connection
present?
z Has the unit been removed?
VN-Matrix 300 • Alarms and SNMP 64
Page 71

Overview — SNMP
The VN-Matrix 300 system has the ability to report alarm events via an SNMP trap, providing
simple integration with Network management systems (NMS).
When communicating using SNMP the VN-Matrix 300 complies with the requirements of
SNMP v3.
When generating SNMP traps the VN-Matrix 300 complies with the requirements of SNMPv1
and SNMPv2C.
Using SNMP — Password
The SNMP password is the same as the administrator password. By default this is set to
admin.
It is necessary to enter the administrator password in the accounts a page before SNMP can
be used. This process must be carried out for each of the following circumstances:
z When rst using the system
z After a firmware upgrade to the system
A password for SNMPv3 is required to be 8 characters long.
z If the administrator password is less than 8 characters in length then the remaining
z If the administrator password is longer than 8 characters then the value is
characters are packed as follows:
admin becomes adminadm
concatenated:
concatenate becomes concaten
SNMP Trap Version
The VN-Matrix 300 supports both version 1 and version 2 SNMP traps (SNMPv1 and
SNMPv2c).
SNMP Community
The SNMP Community value acts as a password. It is used to authenticate messages
between the VN-Matrix 300 system and the NMS. By default the Community string is set to
public. The Community string must match that in use by the NMS; if not then it may not be
possible to manage the VN-Matrix 300 device.
SNMP Trap Destinations
The Filter Settings dialogue in the Alarm Logs page is used to add and remove destination
IP addresses for NMS servers.
Figure 49. Filter Settings Dialog Box
The IP address of the NMS should be entered in the Create Trap Destination box.
Multiple destinations may be added.
VN-Matrix 300 • Alarms and SNMP 65
Page 72

Reference Information
This sections covers specifications and hardware information.
Specifications
Video
Signal type ..................................... SDI, HD-SDI, 3G-SDI digital video
Resolution ...................................... 8 or 10 bits, automatic
Data rates ...................................... 270 Mbps, 1.485 Gbps, 2.970 Gbps.
Operation standards ....................... SMPTE 259M, SMPTE 296M, SMPTE 424M
Auto data rate lock ........................ Ye s
Video input and loop through — encoder
Number/signal type ........................ 1 digital component video with loop through
Connectors .................................... 2 female BNC: 1 for input, 1 for loop through
Nominal level ................................. 0.8 Vp-p
Impedance ..................................... 75 ohms
Data rates ...................................... 19 Mbps to 2.97 Gbps
Vertical frequency ........................... 23.97 Hz to 60 Hz, depending on signal format
Resolution range ............................ 525i, 625i, 720p, 1080i, 1080p, 1080psf
Video processing — decoder
Compression .................................. PURE3™ Codec
Frame rate delay ............................. 35 ms (70 ms encoding/decoding end-to-end)
Bit rate ........................................... 6 Mbps to 250 Mbps
Bit and frame rate control .............. Selectable
Frame rate ...................................... Up to 60 fps @ 1080p
Video output — decoder
Number/signal type ........................ 1 digital component video
10 bit, 4:2:2, with auto-detection
10 bit, 4:2:2, with auto-detection
NOTE: Output signal format follows the input format at the encoder.
Connectors .................................... 1 female BNC
Nominal level ................................. 0.8 Vp-p
Impedance ..................................... 75 ohms
Vertical frequency ........................... 23.97 Hz to 60 Hz, depending on signal format
Resolutions ..................................... 525i, 625i, 720p, 1080i, 1080p, 1080psf
Sync — genlock — decoder
External sync (genlock) ................... 0.8 Vp-p (digital component video)
Genlock connector ......................... 1 female BNC
VN-Matrix 300 • Technical Data 66
Page 73

Output impedance ......................... 75 ohms
Vertical frequency ........................... 23.97 Hz to 60 Hz, depending on signal format
Audio input and output
Number/signal type ........................ 4 groups of 4 channels, embedded with video signal
Source formats ............................... SMPTE 299M, SMPTE 272M
Connectors .................................... 1 female BNC (shared with video input)
Audio processing
Compression .................................. None
Standards ....................................... SMPTE 299M, SMPTE 272M-A
Sampling rates ............................... 20 or 24 bit digital audio
48 kHz (synchronous), 32 - 48 kHz (asynchronous)
Control/remote — local host — codecs, decoders
Serial control port ........................... (1) RS-232, male 9-pin D connector
Baud rate and protocol ................... 115200 baud, 8 data bits, 1 stop bit, no parity, no ow control
Serial control pin configurations ..... 1 = DCD, 2 = Rx, 3 = Tx, 4 = DTR, 5 = GND, 6 = DSR, 7 = RTS, 8 = CTS, 9 = ring
USB control ports ........................... 2 female USB, non-operational
Ethernet control port ...................... 1 female RJ-45
1 female SPF IP module
Ethernet data rate .......................... 10/100/1000Base-T, half/full duplex with autodetect
Ethernet protocol ........................... ICMP (ping), IP, TCP, RTP, RTCP, UDP, DHCP, HTTP, SMTP, Telnet
System control ............................... VN-Matrix Enterprise Controller, VN-Matrix Enterprise Retundant Controller
VN-Matrix Web server
Program control ............................. Extron control/conguration software (VNM Viewer, VNM Virtual Switch) for Windows®
Extron Command Line Interface (CLI)
Microsoft® Internet Explorer® and other Web browsers, Telnet
Network transport
Ethernet data rate .......................... 10/100/1000Base-T, half/full duplex with autodetect
Ethernet protocol
Streaming ................................ RTP, RTCP
Transport ................................. TCP, UDP (unicast or multicast)
All supported ........................... ICMP (ping), IP, TCP, RTP, RTCP, UDP, DHCP, HTTP, SNMP V3, Telnet
Video input/output ......................... PURE3™ Codec compression
Audio input/output ........................ Pass-through
General
External power supply .................... 100 VAC to 240 VAC, 50-60 Hz, external; to 12 VDC, 5 A max.
Power consumption ....................... 30 watts nominal, 60 watts max.
Temperature/humidity .................... Storage: -40 to +158 °F (-40 to +70 °C) / 10% to 90%, noncondensing
Operating: +41 to +95 °F (5 to +35 °C) / 10% to 85%, noncondensing
Cooling .......................................... Fan, vents front to back
Mounting
Rack mount ............................. Yes
Enclosure type ................................ Metal
Enclosure ....................................... 1.75" H* x 8.5" W x 12.2" D (1U high, half rack wide)
(4.4 cm H* x 21.5 cm W x 30.9 cm D)
*Height with feet is 2.1" (5.3 cm).
(Depth includes connectors.)
Product weight ............................... 2.8 lbs (1.3 kg) each
Shipping weight ............................. 8 lbs (4 kg)
VN-Matrix 300 • Technical Data 67
Page 74

Regulatory compliance
Safety ...................................... CE, UL
EMI/EMC ................................. CE, EN60950-1
Warranty ........................................ 3 years parts and labor
NOTE: All nominal levels are at ±10%.
NOTE: Specifications are subject to change without notice.
Hardware
Network Port 1: RJ45
Function: Port I is used for network connectivity and supports
10/100/1000BASE-T (Gigabit Ethernet) copper
connections.
Connector type: Shielded RJ-45 Socket.
Pin-out details:
Data TX/RX
indicator
Network Status
indicator
Pin Function Pin Function
1 TX_D1+ (TX+) 5 BI_D3–
2 TX_D1– (TX–) 6 RX_D2– (RX–)
3 RX_D2+ (RX+) 7 BI_D4+
4 BI_D3+ 8 BI_D4–
Mating connector: Shielded RJ-45 Plug.
Recommended cable: CAT 5E or CAT 6 Shielded twisted pair (STP).
Maximum cable length: 100 meters (330 feet).
Comms standard: 10/100/1000BASE-T (Gigabit Ethernet)
Ethernet (MAC) address: Each address is unique and in the format 0:E0:AA:10:
xx:yy
where:
yy is in the range 00 – FF,
xx is in the range 00 – FF
For example: Port I: 00:E0:AA:10:00:18
IP address: Factory-set default is:
Port I: 192.168.0.1
User-denable via the serial interface.
VN-Matrix 300 • Technical Data 68
Page 75

Network Port 2: SFP
Function: Port 2 is used for network connectivity and supports
10/100/1000BASE-LX (Gigabit Ethernet) optical and
10/100/1000BASE-TX (Gigabit Ethernet) copper
connections.
Connector type: SFP (mini-GBIC) GIGABIT slot for copper or Optical SFP
compatible transceivers.
Optical SFP compatible
transceivers:
Optical wavelength: 850nm
Recommended cable: Ethernet 1000base-SX
Maximum transfer
distance:
Compliant Standard: IEEE802.3
Ethernet (MAC) address: Each address is unique and in the format 0:E0:AA:10:xx:yy
IP address: Factory-set default is:
Dell / Finisar FTLF8519P2BNL Transceiver module
550meters
where:
yy is in the range 00 – FF
xx is in the range 00 – FF
For example: Port II: 00:E0:AA:10:10:18
Port II: 192.168.1.12
User-denable via the serial interface.
VN-Matrix 300 • Technical Data 69
Page 76

RS-232 Serial I/O (COM1 and COM2)
Function: COM1 – used for low level setup or system recovery.
COM2 – used for cross-network serial communications and
alarm relay.
Connector type: 9-pin D-type (male)
Pin-out details:
COM 1 connector pin out
View into chassis plug
Connector Shell = Screen
Pin Function Pin Function
1 DCD 6 DSR
2 RX (data in) 7 RTS
3 TX (data out) 8 CTS
4 DTR 9 RING
5 Ground
COM 2 connector pin out
Pin Function Pin Function
1 DCD 6 DSR
2 RX (data in) 7 RTS
3 TX (data out) 8 Alarm Relay NC
4 Alarm Relay COM 9 Alarm Relay NO
Mating connector: 9-pin D-type (female) with metal cover
Recommended cable: 6-core plus overall screen (low capacitance),
Maximum cable length: 2.95 meters (9.5 feet).
Comms standard: RS-232
COM1 default setting: Baud: 115200
COM2 setting:
The default settings are able
to be modified to suit user
requirements for control of
external equipment.
5 Ground
0.22 mm2 min. per core.
Bits: 8
Parity: None
Stop Bits: 1
Flow Control: None
Baud: 115200
Bits: 8
Parity: None
Stop Bits: 1
Flow Control: None
VN-Matrix 300 • Technical Data 70
Page 77

Extron® Warranty
Extron Electronics warrants this product against defects in materials and workmanship for a period of three years
from the date of purchase. In the event of malfunction during the warranty period attributable directly to faulty
workmanship and/or materials, Extron Electronics will, at its option, repair or replace said products or components,
to whatever extent it shall deem necessary to restore said product to proper operating condition, provided that it is
returned within the warranty period, with proof of purchase and description of malfunction to:
USA, Canada, South America,
and Central America:
Extron Electronics
1001 East Ball Road
Anaheim, CA 92805
U.S.A.
Europe, Africa, and the Middle
East:
Extron Europe
Hanzeboulevard 10
3825 PH Amersfoort
The Netherlands
Asia:
Extron Asia
135 Joo Seng Road, #04-01
PM Industrial Bldg.
Singapore 368363
Japan:
Extron Electronics, Japan
Kyodo Building, 16 Ichibancho
Chiyoda-ku, Tokyo 102-0082
Japan
China:
Extron China
686 Ronghua Road
Songjiang District
Shanghai 201611
China
Middle East:
Extron Middle East
Dubai Airport Free Zone
F12, PO Box 293666
United Arab Emirates, Dubai
Singapore
This Limited Warranty does not apply if the fault has been caused by misuse, improper handling care, electrical or
mechanical abuse, abnormal operating conditions, or if modifications were made to the product that were not
authorized by Extron.
NOTE: If a product is defective, please call Extron and ask for an Application Engineer to receive an RA (Return
Authorization) number. This will begin the repair process.
USA: (714) 491-1500 Europe: 31.33.453.4040
Asia: 65.6383.4400 Japan: 81.3.3511.7655
Units must be returned insured, with shipping charges prepaid. If not insured, you assume the risk of loss or damage
during shipment. Returned units must include the serial number and a description of the problem, as well as the
name of the person to contact in case there are any questions.
Extron Electronics makes no further warranties either expressed or implied with respect to the product and its quality,
performance, merchantability, or tness for any particular use. In no event will Extron Electronics be liable for direct,
indirect, or consequential damages resulting from any defect in this product even if Extron Electronics has been
advised of such damage.
Please note that laws vary from state to state and country to country, and that some provisions of this warranty may
not apply to you.
Extron USA - West
Headquarters
+800.633.9876
Inside USA/Canada Only
+1.714.491.1500
+1.714.491.1517 FAX
Extron USA - East
+800.633.9876
Inside USA/Canada Only
+1.919.863.1794
+1.919.863.1797 FAX
Extron Europe
+800.3987.6673
Inside Europe Only
+31.33.453.4040
+31.33.453.4050 FAX
Extron Asia
+800.7339.8766
Inside Asia Only
+65.6383.4400
+65.6383.4664 FAX
Extron Japan
+81.3.3511.7655
+81.3.3511.7656 FAX
Extron China
+400.883.1568
Inside China Only
+86.21.3760.1568
+86.21.3760.1566 FAX
Extron Middle East
+971.4.2991800
+971.4.2991880 FAX
© 2010 Extron Electronics All rights reserved. www.extron.com
 Loading...
Loading...