
Quick Start Configuration for Ethernet
Routing Switch 4900 and 5900 Series
Release 7.5
NN47211-500
Issue 07.01
December 2017

©
2017, Extreme Networks, Inc.
All Rights Reserved.
Notice
While reasonable efforts have been made to ensure that the
information in this document is complete and accurate at the time of
printing, Extreme Networks, Inc. assumes no liability for any errors.
Extreme Networks, Inc. reserves the right to make changes and
corrections to the information in this document without the obligation
to notify any person or organization of such changes.
Documentation disclaimer
“Documentation” means information published in varying mediums
which may include product information, operating instructions and
performance specifications that are generally made available to users
of products. Documentation does not include marketing materials.
Extreme Networks shall not be responsible for any modifications,
additions, or deletions to the original published version of
Documentation unless such modifications, additions, or deletions
were performed by or on the express behalf of Extreme Networks.
End User agrees to indemnify and hold harmless Extreme Networks,
Extreme Networks’ agents, servants and employees against all
claims, lawsuits, demands and judgments arising out of, or in
connection with, subsequent modifications, additions or deletions to
this documentation, to the extent made by End User.
Link disclaimer
Extreme Networks is not responsible for the contents or reliability of
any linked websites referenced within this site or Documentation
provided by Extreme Networks. Extreme Networks is not responsible
for the accuracy of any information, statement or content provided on
these sites and does not necessarily endorse the products, services,
or information described or offered within them. Extreme Networks
does not guarantee that these links will work all the time and has no
control over the availability of the linked pages.
Warranty
Extreme Networks provides a limited warranty on Extreme Networks
hardware and software. Refer to your sales agreement to establish
the terms of the limited warranty. In addition, Extreme Networks’
standard warranty language, as well as information regarding support
for this product while under warranty is available to Extreme
Networks customers and other parties through the Extreme Networks
Support website:
http://www.extremenetworks.com/support under the
link ““Policies” or such successor site as designated by Extreme
Networks. Please note that if You acquired the product(s) from an
authorized Extreme Networks Channel Partner outside of the United
States and Canada, the warranty is provided to You by said Extreme
Networks Channel Partner and not by Extreme Networks.
“Hosted Service” means an Extreme Networks hosted service
subscription that You acquire from either Extreme Networks or an
authorized Extreme Networks Channel Partner (as applicable) and
which is described further in Hosted SAS or other service description
documentation regarding the applicable hosted service. If You
purchase a Hosted Service subscription, the foregoing limited
warranty may not apply but You may be entitled to support services
in connection with the Hosted Service as described further in your
service description documents for the applicable Hosted Service.
Contact Extreme Networks or Extreme Networks Channel Partner (as
applicable) for more information.
Hosted Service
THE FOLLOWING APPLIES ONLY IF YOU PURCHASE AN
EXTREME NETWORKS HOSTED SERVICE SUBSCRIPTION
FROM EXTREME NETWORKS OR AN EXTREME NETWORKS
CHANNEL PARTNER (AS APPLICABLE), THE TERMS OF USE
FOR HOSTED SERVICES ARE AVAILABLE ON THE EXTREME
NETWORKS WEBSITE,
https://extremeportal.force.com OR SUCH
SUCCESSOR SITE AS DESIGNATED BY EXTREME NETWORKS,
AND ARE APPLICABLE TO ANYONE WHO ACCESSES OR USES
THE HOSTED SERVICE. BY ACCESSING OR USING THE
HOSTED SERVICE, OR AUTHORIZING OTHERS TO DO SO, YOU,
ON BEHALF OF YOURSELF AND THE ENTITY FOR WHOM YOU
ARE DOING SO (HEREINAFTER REFERRED TO
INTERCHANGEABLY AS “YOU” AND “END USER”), AGREE TO
THE TERMS OF USE. IF YOU ARE ACCEPTING THE TERMS OF
USE ON BEHALF A COMPANY OR OTHER LEGAL ENTITY, YOU
REPRESENT THAT YOU HAVE THE AUTHORITY TO BIND SUCH
ENTITY TO THESE TERMS OF USE. IF YOU DO NOT HAVE SUCH
AUTHORITY, OR IF YOU DO NOT WISH TO ACCEPT THESE
TERMS OF USE, YOU MUST NOT ACCESS OR USE THE
HOSTED SERVICE OR AUTHORIZE ANYONE TO ACCESS OR
USE THE HOSTED SERVICE.
Licenses
THE SOFTWARE LICENSE TERMS AVAILABLE ON THE
EXTREME NETWORKS WEBSITE,
https://extremeportal.force.com
OR SUCH SUCCESSOR SITE AS DESIGNATED BY EXTREME
NETWORKS, ARE APPLICABLE TO ANYONE WHO
DOWNLOADS, USES AND/OR INSTALLS EXTREME NETWORKS
SOFTWARE, PURCHASED FROM EXTREME NETWORKS, INC.,
ANY EXTREME NETWORKS AFFILIATE, OR AN EXTREME
NETWORKS CHANNEL PARTNER (AS APPLICABLE) UNDER A
COMMERCIAL AGREEMENT WITH EXTREME NETWORKS OR
AN EXTREME NETWORKS CHANNEL PARTNER. UNLESS
OTHERWISE AGREED TO BY EXTREME NETWORKS IN
WRITING, EXTREME NETWORKS DOES NOT EXTEND THIS
LICENSE IF THE SOFTWARE WAS OBTAINED FROM ANYONE
OTHER THAN EXTREME NETWORKS, AN EXTREME
NETWORKS AFFILIATE OR AN EXTREME NETWORKS CHANNEL
PARTNER; EXTREME NETWORKS RESERVES THE RIGHT TO
TAKE LEGAL ACTION AGAINST YOU AND ANYONE ELSE USING
OR SELLING THE SOFTWARE WITHOUT A LICENSE. BY
INSTALLING, DOWNLOADING OR USING THE SOFTWARE, OR
AUTHORIZING OTHERS TO DO SO, YOU, ON BEHALF OF
YOURSELF AND THE ENTITY FOR WHOM YOU ARE
INSTALLING, DOWNLOADING OR USING THE SOFTWARE
(HEREINAFTER REFERRED TO INTERCHANGEABLY AS “YOU”
AND “END USER”), AGREE TO THESE TERMS AND CONDITIONS
AND CREATE A BINDING CONTRACT BETWEEN YOU AND
EXTREME NETWORKS, INC. OR THE APPLICABLE EXTREME
NETWORKS AFFILIATE (“EXTREME NETWORKS”).
Extreme Networks grants You a license within the scope of the
license types described below. Where the order documentation does
not expressly identify a license type, the applicable license will be a
Designated System License as set forth below in the Designated
System(s) License (DS) section as applicable. The applicable
number of licenses and units of capacity for which the license is
granted will be one (1), unless a different number of licenses or units
of capacity is specified in the documentation or other materials
available to You. “Software” means computer programs in object
code, provided by Extreme Networks or an Extreme Networks
Channel Partner, whether as stand-alone products, pre-installed on
hardware products, and any upgrades, updates, patches, bug fixes,
or modified versions thereto. “Designated Processor” means a single
stand-alone computing device. “Server” means a set of Designated
Processors that hosts (physically or virtually) a software application
to be accessed by multiple users. “Instance” means a single copy of
the Software executing at a particular time: (i) on one physical
machine; or (ii) on one deployed software virtual machine (“VM”) or
similar deployment.
License type(s)
Designated System(s) License (DS). End User may install and use
each copy or an Instance of the Software only: 1) on a number of
Designated Processors up to the number indicated in the order; or 2)
up to the number of Instances of the Software as indicated in the
order, Documentation, or as authorized by Extreme Networks in
writing. Extreme Networks may require the Designated Processor(s)
to be identified in the order by type, serial number, feature key,
Instance, location or other specific designation, or to be provided by
End User to Extreme Networks through electronic means established
by Extreme Networks specifically for this purpose.
Copyright
Except where expressly stated otherwise, no use should be made of
materials on this site, the Documentation, Software, Hosted Service,
or hardware provided by Extreme Networks. All content on this site,
the documentation, Hosted Service, and the product provided by
Extreme Networks including the selection, arrangement and design
of the content is owned either by Extreme Networks or its licensors
and is protected by copyright and other intellectual property laws
including the sui generis rights relating to the protection of databases.
You may not modify, copy, reproduce, republish, upload, post,
transmit or distribute in any way any content, in whole or in part,

including any code and software unless expressly authorized by
Extreme Networks. Unauthorized reproduction, transmission,
dissemination, storage, and or use without the express written
consent of Extreme Networks can be a criminal, as well as a civil
offense under the applicable law.
Virtualization
The following applies if the product is deployed on a virtual machine.
Each product has its own ordering code and license types. Note,
unless otherwise stated, that each Instance of a product must be
separately licensed and ordered. For example, if the end user
customer or Extreme Networks Channel Partner would like to install
two Instances of the same type of products, then two products of that
type must be ordered.
Third Party Components
“Third Party Components” mean certain software programs or
portions thereof included in the Software or Hosted Service may
contain software (including open source software) distributed under
third party agreements (“Third Party Components”), which contain
terms regarding the rights to use certain portions of the Software
(“Third Party Terms”). As required, information regarding distributed
Linux OS source code (for those products that have distributed Linux
OS source code) and identifying the copyright holders of the Third
Party Components and the Third Party Terms that apply is available
in the products, Documentation or on Extreme Networks’ website
at:http://www.extremenetworks.com/support/policies/software-
licensing or such successor site as designated by Extreme Networks.
The open source software license terms provided as Third Party
Terms are consistent with the license rights granted in these Software
License Terms, and may contain additional rights benefiting You,
such as modification and distribution of the open source software.
The Third Party Terms shall take precedence over these Software
License Terms, solely with respect to the applicable Third Party
Components to the extent that these Software License Terms impose
greater restrictions on You than the applicable Third Party Terms.
The following applies only if the H.264 (AVC) codec is distributed with
the product. THIS PRODUCT IS LICENSED UNDER THE AVC
PATENT PORTFOLIO LICENSE FOR THE PERSONAL USE OF A
CONSUMER OR OTHER USES IN WHICH IT DOES NOT RECEIVE
REMUNERATION TO (i) ENCODE VIDEO IN COMPLIANCE WITH
THE AVC STANDARD (“AVC VIDEO”) AND/OR (ii) DECODE AVC
VIDEO THAT WAS ENCODED BY A CONSUMER ENGAGED IN A
PERSONAL ACTIVITY AND/OR WAS OBTAINED FROM A VIDEO
PROVIDER LICENSED TO PROVIDE AVC VIDEO. NO LICENSE IS
GRANTED OR SHALL BE IMPLIED FOR ANY OTHER USE.
ADDITIONAL INFORMATION MAY BE OBTAINED FROM MPEG LA,
L.L.C. SEE
Service Provider
THE FOLLOWING APPLIES TO EXTREME NETWORKS CHANNEL
PARTNER’S HOSTING OF EXTREME NETWORKS PRODUCTS
OR SERVICES. THE PRODUCT OR HOSTED SERVICE MAY USE
THIRD PARTY COMPONENTS SUBJECT TO THIRD PARTY
TERMS AND REQUIRE A SERVICE PROVIDER TO BE
INDEPENDENTLY LICENSED DIRECTLY FROM THE THIRD
PARTY SUPPLIER. AN EXTREME NETWORKS CHANNEL
PARTNER’S HOSTING OF EXTREME NETWORKS PRODUCTS
MUST BE AUTHORIZED IN WRITING BY EXTREME NETWORKS
AND IF THOSE HOSTED PRODUCTS USE OR EMBED CERTAIN
THIRD PARTY SOFTWARE, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO
MICROSOFT SOFTWARE OR CODECS, THE EXTREME
NETWORKS CHANNEL PARTNER IS REQUIRED TO
INDEPENDENTLY OBTAIN ANY APPLICABLE LICENSE
AGREEMENTS, AT THE EXTREME NETWORKS CHANNEL
PARTNER’S EXPENSE, DIRECTLY FROM THE APPLICABLE
THIRD PARTY SUPPLIER.
WITH RESPECT TO CODECS, IF THE EXTREME NETWORKS
CHANNEL PARTNER IS HOSTING ANY PRODUCTS THAT USE
OR EMBED THE G.729 CODEC, H.264 CODEC, OR H.265
CODEC, THE EXTREME NETWORKS CHANNEL PARTNER
ACKNOWLEDGES AND AGREES THE EXTREME NETWORKS
CHANNEL PARTNER IS RESPONSIBLE FOR ANY AND ALL
RELATED FEES AND/OR ROYALTIES. THE G.729 CODEC IS
LICENSED BY SIPRO LAB TELECOM INC. SEE
WWW.SIPRO.COM/CONTACT.HTML. THE H.264 (AVC) CODEC IS
LICENSED UNDER THE AVC PATENT PORTFOLIO LICENSE FOR
HTTP://WWW.MPEGLA.COM.
THE PERSONAL USE OF A CONSUMER OR OTHER USES IN
WHICH IT DOES NOT RECEIVE REMUNERATION TO: (I) ENCODE
VIDEO IN COMPLIANCE WITH THE AVC STANDARD (“AVC
VIDEO”) AND/OR (II) DECODE AVC VIDEO THAT WAS ENCODED
BY A CONSUMER ENGAGED IN A PERSONAL ACTIVITY AND/OR
WAS OBTAINED FROM A VIDEO PROVIDER LICENSED TO
PROVIDE AVC VIDEO. NO LICENSE IS GRANTED OR SHALL BE
IMPLIED FOR ANY OTHER USE. ADDITIONAL INFORMATION
FOR H.264 (AVC) AND H.265 (HEVC) CODECS MAY BE
OBTAINED FROM MPEG LA, L.L.C. SEE
WWW.MPEGLA.COM.
Compliance with Laws
You acknowledge and agree that it is Your responsibility for
complying with any applicable laws and regulations, including, but not
limited to laws and regulations related to call recording, data privacy,
intellectual property, trade secret, fraud, and music performance
rights, in the country or territory where the Extreme Networks product
is used.
Preventing Toll Fraud
“Toll Fraud” is the unauthorized use of your telecommunications
system by an unauthorized party (for example, a person who is not a
corporate employee, agent, subcontractor, or is not working on your
company's behalf). Be aware that there can be a risk of Toll Fraud
associated with your system and that, if Toll Fraud occurs, it can
result in substantial additional charges for your telecommunications
services.
Security Vulnerabilities
Information about Extreme Networks’ security support policies can be
found in the Global Technical Assistance Center Knowledgebase at
https://gtacknowledge.extremenetworks.com/.
Downloading Documentation
For the most current versions of Documentation, see the Extreme
Networks Support website:
documentation.extremenetworks.com, or such successor site as
designated by Extreme Networks.
Contact Extreme Networks Support
See the Extreme Networks Support website:
www.extremenetworks.com/support for product or Hosted Service
notices and articles, or to report a problem with your Extreme
Networks product or Hosted Service. For a list of support telephone
numbers and contact addresses, go to the Extreme Networks
Support website:
(or such successor site as designated by Extreme Networks), scroll
to the bottom of the page, and select Contact Extreme Networks
Support.
Contact Avaya Support
See the Avaya Support website:
product or Hosted Service notices and articles, or to report a problem
with your Avaya product or Hosted Service. For a list of support
telephone numbers and contact addresses, go to the Avaya Support
website:
designated by Avaya), scroll to the bottom of the page, and select
Contact Avaya Support.
Trademarks
The trademarks, logos and service marks (“Marks”) displayed in this
site, the Documentation, Hosted Service(s), and product(s) provided
by Extreme Networks are the registered or unregistered Marks of
Extreme Networks, Inc., its affiliates, its licensors, its suppliers, or
other third parties. Users are not permitted to use such Marks without
prior written consent from Extreme Networks or such third party
which may own the Mark. Nothing contained in this site, the
Documentation, Hosted Service(s) and product(s) should be
construed as granting, by implication, estoppel, or otherwise, any
license or right in and to the Marks without the express written
permission of Extreme Networks or the applicable third party.
Extreme Networks is a registered trademark of Extreme Networks,
Inc.
All non-Extreme Networks trademarks are the property of their
respective owners. Linux® is the registered trademark of Linus
Torvalds in the U.S. and other countries.
http://www.extremenetworks.com/support/contact/
https://support.avaya.com (or such successor site as
http://
https://support.avaya.com for
HTTP://
http://

For additional information on Extreme Networks trademarks, please
see: http://www.extremenetworks.com/company/legal/

Contents
Chapter 1: Preface.................................................................................................................... 7
Purpose.................................................................................................................................. 7
Training.................................................................................................................................. 7
Providing Feedback to Us........................................................................................................ 7
Getting Help............................................................................................................................ 7
Extreme Networks Documentation............................................................................................ 8
Subscribing to service notifications........................................................................................... 9
Chapter 2: New in this document.......................................................................................... 10
Chapter 3: Fundamentals....................................................................................................... 11
System connection................................................................................................................ 11
System Logon....................................................................................................................... 12
Secure and nonsecure protocols............................................................................................ 13
Out-of-band management...................................................................................................... 14
New unit Quick Configuration................................................................................................. 16
Password encryption............................................................................................................. 16
Quick Start............................................................................................................................ 16
Enterprise Device Manager.................................................................................................... 17
Chapter 4: Connecting and configuring the switch............................................................. 21
Connecting a terminal to the switch......................................................................................... 21
Configuring the switch........................................................................................................... 22
Configuring Quick Start using CLI..................................................................................... 22
Configuring Quick Start using EDM................................................................................... 24
Configuring the terminal......................................................................................................... 25
Configuring BootP on the current instance of the switch or server.............................................. 26
Configuring diagnostics quick mode........................................................................................ 27
Setting user access limitations using CLI................................................................................. 27
Configuring multiple local read-write (RW) and read-only (RO) users accounts..................... 28
Enabling and disabling passwords.................................................................................... 29
Setting user access limitations using Enterprise Device Manager.............................................. 29
Configuring the console password using EDM................................................................... 30
Configuring the web and telnet password using EDM......................................................... 31
Configuring the CLI banner.................................................................................................... 32
Configuring system identification............................................................................................ 34
Enabling logging.................................................................................................................... 36
Configuring Simple Network Time Protocol.............................................................................. 36
Configuring real-time clock..................................................................................................... 37
Configuring local time zone.................................................................................................... 38
Configuring the clock............................................................................................................. 40
Configuring a static route....................................................................................................... 40
December 2017 Quick Start Configuration for ERS 4900 and 5900 Series 5

Contents
Enabling remote access......................................................................................................... 42
Using telnet to log on to the device......................................................................................... 42
Enabling the web server management interface....................................................................... 43
Accessing the switch through the web interface....................................................................... 43
Enabling or disabling Quick Configuration............................................................................... 44
Recording a Quick Configuration............................................................................................ 45
Configuring a VLAN using CLI................................................................................................ 46
Configuring VLAN using EDM................................................................................................ 49
Installing a license file............................................................................................................ 52
Saving the configuration......................................................................................................... 53
Storing the configuration files................................................................................................. 54
Chapter 5: Configuring management IP addresses using CLI........................................... 57
Configuring an in-band management IP address...................................................................... 57
Obtaining an in-band management IP address automatically.................................................... 59
Displaying in-band management information........................................................................... 59
Configuring an out-of-band management IPv4 address............................................................ 60
Displaying out-of-band management information...................................................................... 62
Configuring a management route............................................................................................ 63
Configuring an in-band management IPv6 address.................................................................. 64
Displaying in-band IPv6 management information.................................................................... 65
Configuring an out-of-band management IPv6 address............................................................ 66
Displaying out-of-band management IPV6 information............................................................. 69
Enabling or disabling the out-of-band management port........................................................... 71
Setting in-band management IP address parameters from the ip.cfg file on a USB device........... 71
Configuring a Domain Name Server........................................................................................ 74
Resolving domain names to IP addresses............................................................................... 74
Clearing the IP address ......................................................................................................... 75
Setting the in-band default IP gateway address........................................................................ 76
Deleting the in-band default IP gateway address...................................................................... 77
Chapter 6: Configuring management IP addresses using EDM......................................... 78
Configuring out-of-band management using EDM.................................................................... 78
Chapter 7: Verification............................................................................................................ 81
Pinging an IP device.............................................................................................................. 81
Verifying the software release................................................................................................. 81
Displaying local alarms.......................................................................................................... 82
December 2017 Quick Start Configuration for ERS 4900 and 5900 Series 6

Chapter 1: Preface
Purpose
This document provides basic instructions to install the hardware and perform basic configuration on
the following platforms:
• Extreme Networks Ethernet Routing Switch 4900 Series
• Extreme Networks Ethernet Routing Switch 5900 Series
Examples and network illustrations in this document may illustrate only one of the supported
platforms. Unless otherwise noted, the concept illustrated applies to all supported platforms.
Training
Ongoing product training is available. For more information or to register, you can access the Web
site at www.extremenetworks.com/education/.
Providing Feedback to Us
We are always striving to improve our documentation and help you work better, so we want to hear
from you! We welcome all feedback but especially want to know about:
• Content errors or confusing or conflicting information.
• Ideas for improvements to our documentation so you can find the information you need faster.
• Broken links or usability issues.
If you would like to provide feedback to the Extreme Networks Information Development team about
this document, please contact us using our short
directly at internalinfodev@extremenetworks.com
online feedback form. You can also email us
Getting Help
December 2017 Quick Start Configuration for ERS 4900 and 5900 Series 7

Preface
Product purchased from Extreme Networks
If you purchased your product from Extreme Networks, use the following support contact information
to get help.
If you require assistance, contact Extreme Networks using one of the following methods:
•
GTAC (Global Technical Assistance Center) for Immediate Support
- Phone: 1-800-998-2408 (toll-free in U.S. and Canada) or +1 408-579-2826. For the support
phone number in your country, visit: www.extremenetworks.com/support/contact
- Email:
or model number in the subject line.
• GTAC Knowledge – Get on-demand and tested resolutions from the GTAC Knowledgebase, or
create a help case if you need more guidance.
The Hub – A forum for Extreme customers to connect with one another, get questions
•
answered, share ideas and feedback, and get problems solved. This community is monitored
by Extreme Networks employees, but is not intended to replace specific guidance from GTAC.
Support Portal – Manage cases, downloads, service contracts, product licensing, and training
•
and certifications.
Before contacting Extreme Networks for technical support, have the following information ready:
• Your Extreme Networks service contract number and/or serial numbers for all involved Extreme
Networks products
• A description of the failure
• A description of any action(s) already taken to resolve the problem
• A description of your network environment (such as layout, cable type, other relevant
environmental information)
• Network load at the time of trouble (if known)
• The device history (for example, if you have returned the device before, or if this is a recurring
problem)
support@extremenetworks.com. To expedite your message, enter the product name
• Any related RMA (Return Material Authorization) numbers
Product purchased from Avaya
If you purchased your product from Avaya, use the following support contact information to get help.
Go to the Avaya Support website at
documentation, product notices, and knowledge articles. You can also search for release notes,
downloads, and resolutions to issues. Use the online service request system to create a service
request. Chat with live agents to get answers to questions, or request an agent to connect you to a
support team if an issue requires additional expertise.
http://support.avaya.com for the most up-to-date
Extreme Networks Documentation
To find Extreme Networks product guides, visit our documentation pages at:
December 2017 Quick Start Configuration for ERS 4900 and 5900 Series 8
Subscribing to service notifications
Current Product Documentation www.extremenetworks.com/documentation/
Archived Documentation (for previous
versions and legacy products)
Release Notes www.extremenetworks.com/support/release-notes
www.extremenetworks.com/support/documentationarchives/
Open Source Declarations
Some software files have been licensed under certain open source licenses. More information is
available at: www.extremenetworks.com/support/policies/software-licensing.
Subscribing to service notifications
Subscribe to receive an email notification for product and software release announcements,
Vulnerability Notices, and Service Notifications.
About this task
You can modify your product selections at any time.
Procedure
1. In an Internet browser, go to http://www.extremenetworks.com/support/service-notification-
form/ .
2. Type your first and last name.
3. Type the name of your company.
4. Type your email address.
5. Type your job title.
6. Select the industry in which your company operates.
7. Confirm your geographic information is correct.
8. Select the products for which you would like to receive notifications.
9. Click Submit.
December 2017 Quick Start Configuration for ERS 4900 and 5900 Series 9

Chapter 2: New in this document
There are no feature changes in this release.
December 2017 Quick Start Configuration for ERS 4900 and 5900 Series 10

Chapter 3: Fundamentals
Provisioning follows hardware installation.
The Quick Start Configuration for Ethernet Routing Switch 4900 and 5900 Series includes the
minimum, but essential, configuration steps to:
• Provide a default, starting point configuration
• Establish a management interface
• Establish basic security on the node
The shipment includes the following:
• An installation kit
• A foldout poster
For more information about hardware specifications and installation procedures, see Installing
Ethernet Routing Switch 5900 Series or Installing Ethernet Routing Switch 4900 Series.
For more information about how to configure security, see Configuring Security on Ethernet Routing
Switch 4900 and 5900 Series.
To download and print selected technical publications and release notes directly from the Internet,
go to https://extremeportal.force.com.
System connection
Use the console cable to connect the terminal to the switch console port. The console cable and
connector must match the console port on the switch (DB-9 or RJ-45, depending on your model).
The following are the default communication protocol settings for the console port:
• 9600 baud
• 8 data bits
• 1 stop bit
• No parity
• No flow control
• VT100 or VT100/ANSI Terminal Protocol
December 2017 Quick Start Configuration for ERS 4900 and 5900 Series 11
Fundamentals
To use the console port, you need the following equipment:
• A terminal or TeleTypewriter (TTY)-compatible terminal, or a portable computer with a serial
port and terminal-emulation software.
• An Underwriters Laboratories (UL)-listed straight-through or null modem RS-232 cable with a
female DB-9 connector for the console port on the switch. The other end of the cable must use
a connector appropriate to the serial port on your computer or terminal.
You must shield the cable that connects to the console port to comply with emissions regulations
and requirements.
System Logon
After the platform boot sequence is complete, a logon prompt appears. The following table shows
the default values for logon and password for console and Telnet sessions.
Note:
With enhanced secure mode enabled, the person in the role-based authentication level of
security administrator configures the login and password values for the other role-based
authentication levels. The security administrator initially logs on to the switch using the default
login as admin and the default password as password.
After the initial login, the switch prompts the security administrator to create a new security
administrator account and password. The default account named admin is removed and during
the first login, security administrator must change the password of the newly created account.
The administrator then configures default login and password for the other users based on the
role-based authentication levels of the user. For more information, see Configuring Security on
Ethernet Routing Switch 4900 and 5900 Series.
Note:
Enhanced secure mode is a boot mode operation. By default, enhanced secure mode is
disabled. The switch must be restarted after the feature is enabled or disabled in order to apply
the new setting.
Configurations are not transferable between operating modes with enhanced secure mode
enabled or enhanced secure mode disabled. The switch resets to default configuration when the
modes of operation are switched.
For more information about enhanced secure mode, see Configuring Security on Ethernet
Routing Switch 4900 and 5900 Series.
December 2017 Quick Start Configuration for ERS 4900 and 5900 Series 12
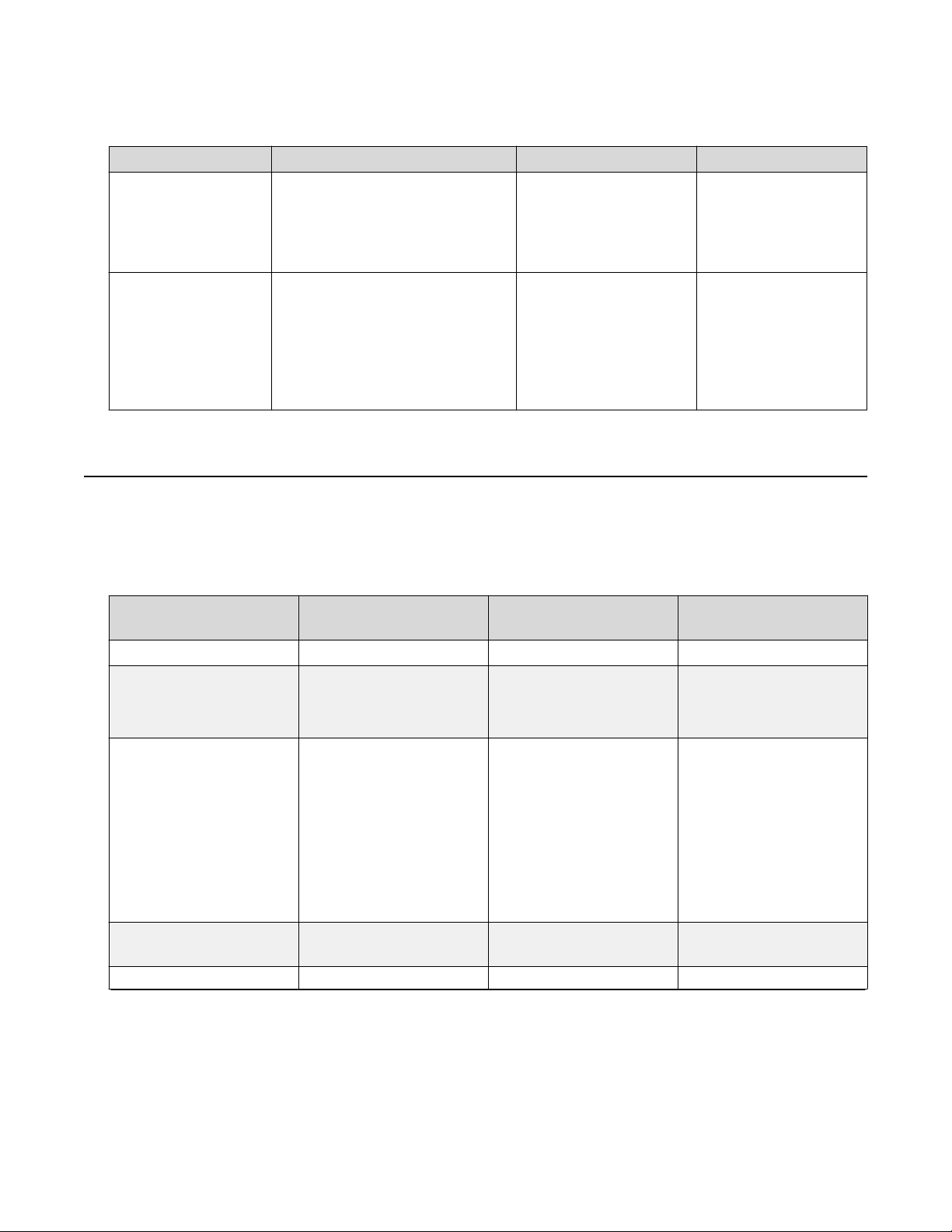
Secure and nonsecure protocols
Table 1: Access levels and default logon values
Access level Description Default Logon Default Password
Read-only Permits view-only configuration
and status information. Is
equivalent to Simple Network
Management Protocol (SNMP)
read-only community access.
Read/write View and change configuration
and status information across the
switch. You can change security
and password settings. This
access level is equivalent to
SNMP read/write community
access.
RO user
RW secure
Secure and nonsecure protocols
The following table describes the secure and nonsecure protocols that the switch supports.
Table 2: Secure and nonsecure protocols
Nonsecure protocols Default status Equivalent secure
protocols
FTP Disabled SCP Disabled
Telnet Enabled SSH v1, v2
You should use SSHv2
instead of SSHv1.
SNMPv1, SNMPv2 Enabled SNMPv3
You must load the
DES/AES image on the
platform to use SNMPv3.
For more information,
see Configuring Security
on Ethernet Routing
Switch 4900 and 5900
Series
Rlogin Disabled Secure SHell (SSH) v1,v2Disabled
HTTP Disabled HTTPS Enabled
Default status
Disabled
Disabled
Table continues…
December 2017 Quick Start Configuration for ERS 4900 and 5900 Series 13
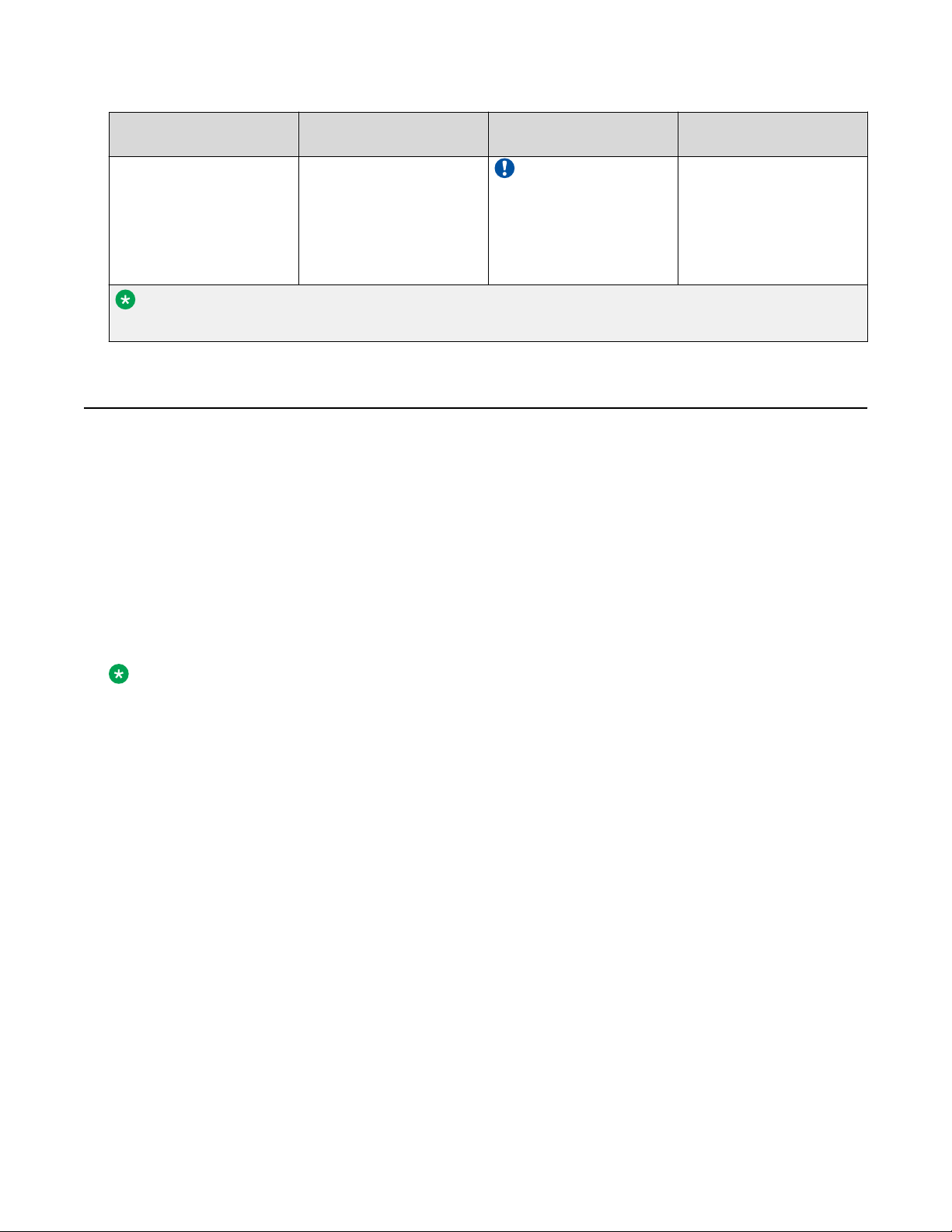
Fundamentals
Nonsecure protocols Default status Equivalent secure
protocols
Important:
You should take the
appropriate security
precautions within
the network if you
use HTTP.
Note:
On SSH, by default, HTTP is enabled and HTTPS is disabled.
Default status
Out-of-band management
Out-of-band management allows IPv4 or IPv6 switch or stack management using the dedicated outof-band management port. Out-of-band management supports Telnet, Secure Shell (SSH) protocol,
Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP), HTTP, or HTTPS, without requiring an in-band
management VLAN.
To configure out-of-band management, you assign an IP address to the RJ-45 Ethernet
management port for a switch or stack. You can configure a specific out-of-band management
default gateway, which takes precedence over the in-band default gateway. If you do not configure
an out-of-band management default gateway, the in-band default gateway is used for out-of-band
switch or stack management.
Note:
The out-of-band switch or stack management IP address must be different than the in-band IP
address and belong to a different subnet.
You can use the out-of-band management port to perform tasks such as downloading software
images and, when the SNMP server is enabled, access the Enterprise Device Manager (EDM)
interface for a switch or stack. To access EDM, you type the out-of-band management IP address in
the address bar of an Internet browser.
The out-of-band management port supports full auto negotiation, which enables management
stations to connect at any of the supported speeds or duplexes.
Stack mode
In stack mode, when you use the unit, switch, or stack parameters, the device assigns the IPv4 or
IPv6 address to the management stack. If a management stack IP address is in use, you can only
access the stack through the management port base unit. If the base unit goes down, the stack
management IP address becomes unreachable and the switch management IP address becomes
status up.
December 2017 Quick Start Configuration for ERS 4900 and 5900 Series 14

Out-of-band management
Only the base unit allows all commands for out-of-band management. if the base unit leaves the
stack, the stack IP addresses and priveleges transfer to the temporary base unit (TBU). You need a
link in the management port TBU for the IP address to be operational.
On the base unit, if you configure the IP stack address, the base unit is the only active IP address in
the stack. On the non-base units, the IP addresses you configure only become active and reachable
if they become stand alone.
Stand alone mode
In stand alone mode, you assign the IPv4 or IPv6 address only to the switch. You can configure IP
addresses on every switch in the stack.
On the non-base units, the IP addresses you configure only become active and reachable if they
become stand alone.
Considerations and limitations
The following considerations and limitations apply when you configure and use out-of-band
management:
• You must configure all out-of-band management IP addresses for a stack to the same subnet.
• You can configure only one out-of-band management default gateway for each stack.
• You cannot automatically obtain an out-of-band management IP address using BootP or
DHCP.
• With out-of-band management you can issue the ping command from the out-of-band
management port on a stack base unit only.
• With out-of-band management you can only download a software image, or load a
configuration file from the base unit in a stack.
• You can access a management stack from the out-of-band management port on the stack base
unit only.
• You can configure both an in-band and out-of-band management IP:
- The out-of-band management default gateway takes precedence over the in-band
management default gateway.
- In Layer 2 mode, once an out-of-band management default gateway is configured, the inband management address is reachable only through a directly attached subnet for the
management VLAN.
- In Layer 3 mode, you must configure a management route to maintain connectivity with the
management network when you use out-of-band management.
• The MAC address for the out-of-band management port is created using the switch MAC
address plus the management offset. The management offset value for the primary out-of-band
management port is 0x300 and the management offset value for the secondary out-of-band
management port is 0x301.
• The out-of-band management port speed is automatically negotiated, however, you can
change it manually.
• The out-of-band management port does not support generation or processing of Autotopology
packets when an out-of-band management IP is configured.
• RADIUS authentication is not supported for the out-of-band management IP.
December 2017 Quick Start Configuration for ERS 4900 and 5900 Series 15
Fundamentals
New unit Quick Configuration
You can use the new unit Quick Configuration feature to create a default configuration that applies
to any new unit joining the stack. Quick Configuration can configure the VLAN IDs, port speed,
PVID, tagging, and spanning tree groups for the new unit without resetting the stack.
Password encryption
The local passwords for the switch are stored in the configuration file.
Important:
For security reasons, you should configure the passwords to values other than the factory
defaults.
For more information about configuring passwords, see:
Using CLI and EDM on Ethernet Routing Switch 4900 and 5900 Series
Configuring Security on Ethernet Routing Switch 4900 and 5900 Series
Quick Start
You can use the install command in Command Line Interface (CLI) or the Quick Start menu in
Enterprise Device Manager (EDM) to configure the following:
• quick start VLAN
• in-band IP address and subnet mask
• default gateway
• management subnet mask, management IP address and management default gateway
• read-only and read-write community strings
• IPv6 in-band address and IPv6 default gateway
• management IPV6 address and management IPV6 default gateway
Note:
When you reset the switch to factory default, the setup utility does not start automatically. Use
the install command to start the setup utility. The default IP address of the switch is
192.168.1.1 if the switch does not get its IP address from another source.
December 2017 Quick Start Configuration for ERS 4900 and 5900 Series 16
Enterprise Device Manager
Enterprise Device Manager
Enterprise Device Manager (EDM) is an embedded graphical user interface (GUI) that you can use
to manage and monitor the platform through a standard web browser. EDM is embedded in the
switch software, and the switch operates as a web server, so you do not require additional client
software. For more information about EDM, see Using CLI and EDM on Ethernet Routing Switch
4900 and 5900 Series.
To manage the switch from a centralized location, using Configuration and Orchestration Manager
(COM) 2.0 and higher, you can use product-specific EDM plug-ins for COM include other features,
such as centralized syslog, trap viewer, troubleshooting and diagnostic tools.
For more information, or to purchase plug-ins, go to
https://extremeportal.force.com.
Enterprise Device Manager access
EDM has been tested with the following web browsers:
Browser Version
Microsoft Internet Explore, Windows 7 11.0.9600.18537
Mozilla Firefox, Windows 7 52.0
Google Chrome, Windows 7 57.0.2987.98
Microsoft Edge, Windows 10 20.10240.17146.0
To access EDM, open http://<deviceip>/login.html or https://<deviceip>/login.html.
Important:
You must enable the web server from CLI to enable HTTP access to EDM. If you want HTTP
access to the device, you must also disable the web server secure-only option. The web server
secure-only option is enabled by default and allows HTTPS access to the device. Take the
appropriate security precautions within the network if you use HTTP.
If you experience issues while connecting to EDM, check the proxy settings. Proxy settings can
affect EDM connectivity to the switch. Clear the browser cache, and do not use a proxy when
connecting to the device.
Default user name and password
The following table contains the default user name and password that you can use to log on to the
switch using EDM. For more information about changing the passwords, see Configuring Security
on Ethernet Routing Switch 4900 and 5900 Series.
December 2017 Quick Start Configuration for ERS 4900 and 5900 Series 17
Fundamentals
Table 3: EDM default user name and password
User Name Password
admin password
Important:
The default passwords and community strings are documented and well known. You should
change the default passwords and community strings immediately after you first log on. For
more information about changing user names and passwords, see Configuring Security on
Ethernet Routing Switch 4900 and 5900 Series.
The following table describes access levels and default logon values when Enhanced Secure Mode
is disabled.
Table 4: Access levels and default logon values for EDM
Access level Default logon Default password
Read-only RO user
Read/write RW secure
Device Physical View
When you access EDM, the first panel in the work area displays a switch summary view. The tab
behind the summary view is a real-time physical view of the front panel of the device or stack called
the Device Physical View.
Objects in the Device Physical View are:
• Stand-alone switch, called a unit
• Switch stack, called a chassis
• Port
From the Device Physical View, you can:
• Determine the hardware operating status
• Select a switch or a port to perform management tasks on specific objects or view fault,
configuration, and performance information for specific objects
Click to select an object. The system outlines the object in yellow to indicate that the object is
selected.
The conventions on the device view are similar to the actual switch appearance except that LEDs in
Device Physical View do not blink. The LEDs and the ports are color-coded to reflect hardware
status. Green indicates the port is up and running; red indicates that the port is disabled.
From the menu bar, you can click the Device Physical View tab to open the Device Physical View
any time during a session.
December 2017 Quick Start Configuration for ERS 4900 and 5900 Series 18

Figure 1: Device Physical View
EDM window
The EDM window contains the following parts:
1. Navigation tree—The navigation pane on the left side of the window that displays available
command folders in a tree format.
Enterprise Device Manager
2. Navigation tree toolbar—The area displays buttons for common functions.
3. Menu bar—The area at the top of the window that displays primary and secondary tabs that
you accessed during the session; the tabs remain available until you close them.
4. Toolbar—The area just below the menu bar that provides quick access to the most common
operational commands such as Apply, Refresh, and Help.
5. Work area—The main area on the right side of the window that displays the dialog boxes
where you view or configure switch parameters.
6. Auto Complete Search — The area between the navigation tree toolbar and the navigation
tree where you can type a partial or complete search string to find menus. When you type
the search string, the navigation tree changes to display only the entries associated with
your search. To return to the full navigation tree display, click the x beside the Auto Complete
Search dialog box.
December 2017 Quick Start Configuration for ERS 4900 and 5900 Series 19

Fundamentals
Figure 2: EDM window
December 2017 Quick Start Configuration for ERS 4900 and 5900 Series 20

Chapter 4: Connecting and configuring the
switch
This chapter describes how to connect a terminal to the switch and the required procedures for the
initial provisioning.
Connecting a terminal to the switch
This procedure describes the steps to connect a terminal to the console port on the switch.
Before you begin
To use the console port, you need the following equipment:
• Terminal with AC power cord and keyboard. Any terminal or a computer with an appropriate
terminal emulator can be used as the management station. See Installing Ethernet Routing
Switch 5900 Series or Installing Ethernet Routing Switch 4900 Series for a list of the terminal
emulation settings that must be used with any terminal emulation software used to connect to
the switch.
• Use the RJ-45 or DB-9 console cable to connect the switch console port to your management
terminal. See Installing Ethernet Routing Switch 5900 Series or Installing Ethernet Routing
Switch 4900 Series for console port pin-out information. You can use the pin-out information to
verify or create a console cable for use with your maintenance terminal.
Procedure
1. Connect one end of the serial cable to the connector on the terminal or on the computer.
2. Connect the other end of the serial cable to the console port on the switch.
3. Turn the terminal or computer on.
4. Set the terminal protocol on the terminal or terminal emulation program to VT100 or VT100/
ANSI.
5. Connect to the switch using the terminal or terminal emulation application. The switch
banner displays when you connect to the switch through the console port.
6. Press Ctrl+Y to obtain a CLI prompt.
The switch only supports the CLI. The old Bay Stack menu interface is not supported on this
product.
December 2017 Quick Start Configuration for ERS 4900 and 5900 Series 21

Connecting and configuring the switch
Configuring the switch
Use the procedures in this section to configure the switch using Quick Start.
Configuring Quick Start using CLI
The Install script consists of a series of prompts that are used to set up the minimum
configuration information.
You must enter the following information when prompted:
• Quick start VLAN
• IP address
• Subnet mask
• Default gateway
• Management subnet mask
• Management IP address
• Management default gateway
• Read-only community string
• Read-write community string
• Management IPV6 address
• Management IPV6 default gateway
Before you begin
• Connect to the switch using the terminal or terminal emulation application.
Procedure
1. Press
CTRL + Y to obtain a CLI prompt.
2. Enter enable
3. Enter install
The switch setup utility banner appears.
4. Enter the VLAN ID for the Quick Start at the following prompt:
Please provide the Quick Start VLAN <1–4094> [1]:
5. Enter the IP address at the following prompt:
Please provide the in-band IP Address[192.168.1.1]:
6. Enter the sub-net mask at the following prompt:
December 2017 Quick Start Configuration for ERS 4900 and 5900 Series 22

Please provide the in-band sub-net mask [255.255.255.0]:
7. Enter the default gateway IP address at the following prompt:
Please provide the Default Gateway [0.0.0.0]:
8. Enter the management sub-net mask at the following prompt:
Please provide the management sub-net mask[0.0.0.0]:
9. Enter the management IP address at the following prompt:
Please provide the management IP Address[0.0.0.0]:
10. Enter the management default gateway at the following prompt:
Please provide the management Default Gateway[0.0.0.0]:
11. Enter the read only community string at the following prompt:
Please provide the Read-Only Community String [**********]:
12. Enter the read write community string at the following prompt::
Please provide the Read-Write Community String [**********]:
Configuring the switch
13. Enter the in-band IPv6 address at the following prompt:
Please provide the in-band IPV6 Address/Prefix_length [ : :/0]:
14. Enter the in-band IPv6 default gateway at the following prompt:
Please provide the in-band IPV6 Default Gateway [ : :]:
15. Emter the management IPV6 address at the following prompt:
Please provide the management IPV6 Address/Prefix_length[::/0]:
16. Enter the management IPV6 default gateway at the following prompt:
Please provide the management IPV6 Default Gateway[::]:
Successful completion displays the following message: Basic switch parameters
have been configured and saved.
Example
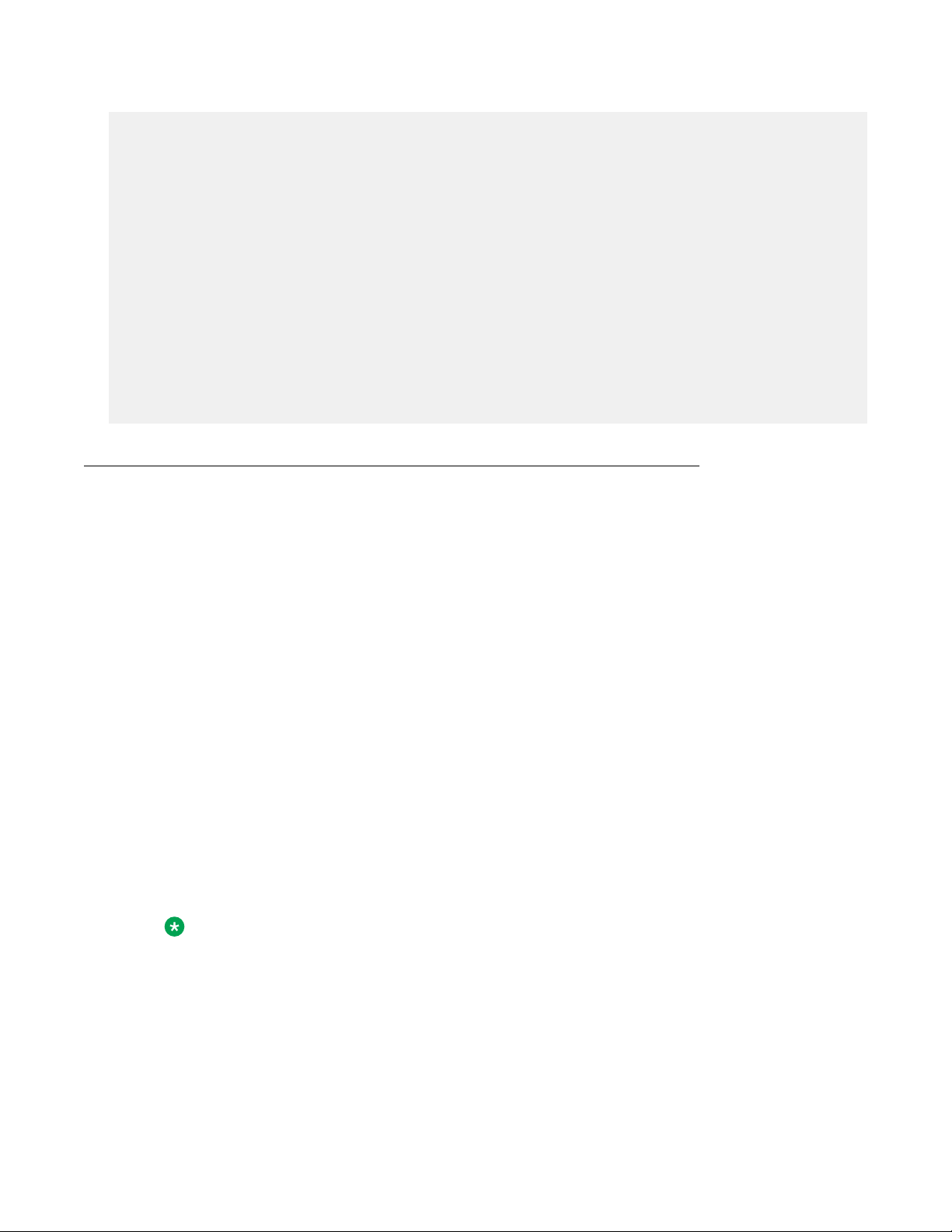
The following example displays sample output for the install command.
Switch>enable
Switch#install
###############################################################################
Welcome to the switch setup utility.
You will be requested to provide the switch basic connectivity settings.
After entering the requested info, the configuration will be applied and
stored into the switch NVRAM.
Once the basic connectivity settings are applied, additional configuration
can be done using the available management interfaces.
Use Ctrl+C to abort the configuration at any time.
###############################################################################
December 2017 Quick Start Configuration for ERS 4900 and 5900 Series 23
Connecting and configuring the switch
Please provide the Quick Start VLAN <1-4094> [1]:
Please provide the in-band IP Address[192.168.1.1]:
Please provide the in-band sub-net mask[255.255.255.0]:
Please provide the Default Gateway[0.0.0.0]:
Please provide the management sub-net mask[0.0.0.0]:
Please provide the management IP Address[0.0.0.0]:
Please provide the management Default Gateway[0.0.0.0]:
Please provide the Read-Only Community String[**********]:
Please provide the Read-Write Community String[**********]:
Please provide the in-band IPV6 Address/Prefix_length[::/0]:
Please provide the in-band IPV6 Default Gateway[::]:
Please provide the management IPV6 Address/Prefix_length[::/0]:
Please provide the management IPV6 Default Gateway[::]:
###############################################################################
Basic switch parameters have now been configured and saved.
###############################################################################
Switch#
Configuring Quick Start using EDM
Use the following procedure to configure the Quick Start setup mode using EDM.
About this task
You can use Quick Start to quickly setup a new switch or stack.
Procedure
1. From the navigation tree, double-click Administration.
2. In the Administration tree, click Quick Start.
3. In the work area, click the IP/Community/Vlan tab.
4. In the In-Band Switch IP Address field, type a switch or stack IP address.
5. In the In-Band Stack Subnet Mask field, type a subnet mask.
6. In the Default Gateway field, type a gateway IP address.
7. In the Read-Only Community String field, type a community string. Re-type the community
string in the verification field.
8. In the Read-Write Community String field, type a community string. Re-type the community
string in the verification field.
Note:
For security, enter different community strings for Read-Only and Read-Write.
9. In the Quick Start VLAN field, type a VLAN ID ranging from 1 to 4094.
10. On the toolbar, click Apply.
December 2017 Quick Start Configuration for ERS 4900 and 5900 Series 24
Configuring the terminal
Configuring the terminal
You can configure the switch terminal settings to suit your preferences for the terminal speed and
display.
About this task
Use the following procedure to configure terminal settings including the terminal connection speed,
and number of characters in the terminal display width and length.
Important:
After you modify the terminal configuration, the new settings are applied to the current active
session and to all future sessions (serial, telnet or SSH). Terminal configuration change does
not affect open concurrent sessions.
Procedure
1. Log on to CLI to enter User EXEC mode.
2. At the command prompt, enter the following command:
terminal {speed <19200 | 38400 | 9600> | length <0-132> | width
<1-132>}
3. To display the current serial port information, enter the following command:
show terminal
Example
Switch#show terminal
Terminal speed: 9600
Terminal width: 79
Terminal length: 23
Variable definitions
Use the definitions in the following table to use the terminal command.
Variable Definition
length Sets the length of the terminal display in lines. By
default, 23 lines are displayed.
DEFAULT: 23
Important:
If you set the terminal length to 0, the pagination
is disabled and the display scrolls continuously.
speed <19200 | 38400 | 9600> Sets the transmit and receive baud rates for the
terminal.
DEFAULT: 9600
Table continues…
December 2017 Quick Start Configuration for ERS 4900 and 5900 Series 25

Connecting and configuring the switch
Variable Definition
width Sets the width of the terminal display in characters.
By default, 79 characters are displayed.
DEFAULT: 79
Configuring BootP on the current instance of the switch or server
About this task
The default operational mode for BootP on the switch is BootP or DefaultIP. The switch requests an
IP address from BootP only if one is not already configured from the console terminal (or if the IP
address is the default IP address 192.168.1.1).
Procedure
1. Enter Global Configuration mode:
enable
configure terminal
2. At the command prompt, enter the following command:
ip bootp server {always | disable | last | default-ip}
Variable definitions
Use the definitions in the following table to use the ip bootp server command.
Variable Definition
always | disable | last | default-ip Specify when to use BootP:
• default-ip—Use BootP or the default IP
• last—Use BootP or the last known address
• disable—Never use BootP
• always—Always use BootP
By default, default-ip is selected.
December 2017 Quick Start Configuration for ERS 4900 and 5900 Series 26

Configuring diagnostics quick mode
Configuring diagnostics quick mode
The diagnostics quick mode flag enables you to choose the diagnostic test behavior during boot.
You can enable quick mode boot tests or all the diagnostic tests. The impact to boot time is 15 to 20
seconds when all diagnostic tests run during startup.
The diagnostic quick mode is disabled by default.
Procedure
1. Enter Global Configuration mode:
enable
configure terminal
2. To enable the diagnostics quick mode flag, enter the following command at the command
prompt:
diagnostics-quick-mode enable
3. To disable the diagnostics quick mode flag, enter either of the following commands at the
command prompt:
no diagnostics-quick-mode enable
OR
default diagnostics-quick-mode
4. To display the configuration, enter the following command at the command prompt:
show diagnostics-quick-mode
Example
Enable diagnostics quick mode:
Switch>enable
Switch#configure terminal
Switch(config)#diagnostics-quick-mode enable
Switch(config)#show diagnostics-quick-mode
2013-10-02 08:53:27 GMT+00:00
Diagnostics quick mode: Enabled
Setting user access limitations using CLI
The administrator can use CLI to limit user access by creating and maintaining passwords for web,
telnet, and console access. This is a two-step process that requires that you first create the
password and then enable it.
December 2017 Quick Start Configuration for ERS 4900 and 5900 Series 27

Connecting and configuring the switch
Configuring multiple local read-write (RW) and read-only (RO) users accounts
Use the following procedure to create, modify and delete local users.
Procedure
1. Enter Global Configuration mode:
enable
configure terminal
2. To create a user, enter the following command:
username add <username> role-name {RO|RW} [password]
3. To delete a user, enter the following command:
no username <username>
4. To enable a user, enter the following command:
username <username> enable
5. To disable a user, enter the following command:
no username <username> enable
6. To change the password for a specific user, enter the following command:
username <username> password
7. To change the password for the current user, enter the following command:
username password
8. To reset the settings for a user to default, enter the following command:
default username <username>
9. To enable or disable ssh access for a user enter the following command:
username <username> ssh-access [enable | disable]
10. To enable or disable telnet access for a user enter the following command:
username <username> telnet-access [enable | disable]
Variable Definitions
Variable Value
<username> Specifies the user name.
December 2017 Quick Start Configuration for ERS 4900 and 5900 Series 28

Setting user access limitations using Enterprise Device Manager
Enabling and disabling passwords
After you set the read-only and read-write passwords, you can individually enable or disable them
for the various switch-access methods.
About this task
Follow this procedure to enable or disable a password for a specific access method.
Procedure
1. Enter Global Configuration mode:
enable
configure terminal
2. Enter the following command:
cli password {telnet | serial} {none | local | radius | tacacs}
Variable definitions
Use the definitions in the following table to use the cli password command.
Variable Definition
{telnet | serial} Specify whether the password is enabled or disabled for telnet
or the console. Telnet and web access are connected so that
enabling or disabling passwords for one enables or disables
passwords for the other.
none | local | radius | tacacs Specify the password type to modify:
• none: disables the password.
• local: uses the locally defined password for serial console or
telnet access.
• radius: uses RADIUS authentication for serial console or
telnet access.
• tacacs: uses TACACS+ authentication, authorization and
accounting (AAA) services for serial console or telnet access.
Setting user access limitations using Enterprise Device
Manager
You can use Enterprise Device Manager (EDM) to limit user access by creating and maintaining
passwords for web, telnet, and console access.
December 2017 Quick Start Configuration for ERS 4900 and 5900 Series 29

Connecting and configuring the switch
Configuring the console password using EDM
About this task
Use this procedure to configure a password for serial console access to a stack or standalone
switch.
Procedure
1. From the navigation tree, double-click Security.
2. In the Security tree, double-click Web/Telnet/Console.
3. In the work area, click the Console Password tab.
4. Click the arrow on the Console Stack Password Type field.
5. Select a password type from the list.
6. Type the password for read-only access in the Read-Only Stack Password field.
7. Type the same password for read-only access in the Re-enter to verify field.
8. Type the password for read-write access in the Read-Write Stack Password field.
9. Type the same password for read-write access in the Re-enter to verify field.
10. On the toolbar, click Apply.
Variable definitions
Use the data in the following table to configure the console switch password.
Variable Value
Console Stack Password Type Specifies the type of password to use. Values
include:
• none—disables the password
• Local Password— uses the locally defined
password for serial console access.
• RADIUS Authentication— uses RADIUS
authentication for serial console access.
• TACACS Authentication— uses TACACS+
authentication, authorization, and accounting
(AAA) services authentication for console access.
Read-Only Stack Password Specifies the read-only password for stack or switch
access. The following are the requirements for the
password:
• The maximum length is 255 characters.
• Password must contain 10 characters. A minimum
of two uppercase characters, two lowercase
Table continues…
December 2017 Quick Start Configuration for ERS 4900 and 5900 Series 30

Setting user access limitations using Enterprise Device Manager
Variable Value
characters, two numbers, and two special
characters.
Read-Write Stack Password Specifies the read-write password for stack or switch
access. The following are the requirements for the
password:
• The maximum length is 255 characters.
• Password must contain 10 characters. A minimum
of two uppercase characters, two lowercase
characters, two numbers, and two special
characters.
Configuring the web and telnet password using EDM
About this task
Use the following procedure to configure a password for web and telnet access to a stack or
standalone switch.
Procedure
1. From the navigation tree, double-click Security.
2. In the Security tree, click Web/Telnet/Console.
3. In the work area, click the Web/Telnet tab.
4. Click the arrow on the Web/Telnet Switch Password Type field.
5. Select a password type from the list.
6. Type the password for read-only access in the Read-Only Stack Password field.
7. Type the same password for read-only access in the Re-enter to verify field.
8. Type the password for read-write access in the Read-Write Switch Password field.
9. Type the same password for read-write access in the Re-enter to verify field.
10. On the toolbar, click Apply.
Variable definitions
Variable Value
Web/Telnet Stack Password Type Specifies the type of the password to use. Values
include:
• none—disables the password
• Local Password— uses the locally defined
password for Web and Telnet access.
Table continues…
December 2017 Quick Start Configuration for ERS 4900 and 5900 Series 31

Connecting and configuring the switch
Variable Value
• RADIUS Authentication— uses RADIUS password
authentication for Web and Telnet access.
• TACACS Authentication— uses TACACS+
authentication, authorization, and accounting
(AAA) services authentication for Web and Telnet
access.
Read-Only Stack Password Specifies the read-only password for stack or switch
access. The following are the requirements for the
password:
• The maximum length is 255 characters.
• Password must contain 10 characters. A minimum
of two uppercase characters, two lowercase
characters, two numbers, and two special
characters.
Read-Write Switch Password Specifies the read-write password for stack or switch
access. The following are the requirements for the
password:
• The maximum length is 255 characters.
• Password must contain 10 characters. A minimum
of two uppercase characters, two lowercase
characters, two numbers, and two special
characters.
Configuring the CLI banner
You can configure the banner that is presented when a user logs on to the switch through CLI to a
user-defined value.
You can use the custom logon banner to display company information, such as company name and
contact information.
The banner cannot exceed 1539 bytes, or 19 rows by 80 columns plus line termination characters.
The banner control setting is saved to NVRAM, and both the banner file and control setting are
distributed to all units within a stack.
About this task
Follow this procedure to configure the CLI banner.
Procedure
1. Enter Global Configuration mode:
enable
configure terminal
December 2017 Quick Start Configuration for ERS 4900 and 5900 Series 32

2. Configure the switch to use a custom banner or use the default banner:
banner {custom | static}
3. Create a custom banner:
banner <line_number> "<LINE>"
4. Save the configuration:
save config
5. Display the banner information:
show banner
6. Log on again to verify the configuration.
7. (Optional) Disable the banner:
no banner
Example
The following is an example of CLI banner configuration:
Switch>enable
Switch#configure terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
Switch(config)#show banner
Current banner setting: STATIC
Switch(config)#banner custom
Switch(config)#banner 1 "My Company Name"
Switch(config)#banner 2 "123A My Address Avenue My Town CA 12345"
Switch(config)#banner 3 "Phone: (123) 555-5555 * Fax (123) 555-5555"
Switch(config)#banner 4 "http://www.mycompanywebsite.com"
Switch(config)#save config
Switch(config)#show banner
Current banner setting: CUSTOM
Switch(config)#end
Switch#exit
My Company Name
123A My Address Avenue My Town CA 12345
Phone: (123) 555-5555 * Fax (123) 555-5555
http://www.mycompanywebsite.com
Configuring the CLI banner
Enter Ctrl-Y to begin.
***************************************************************
*** Ethernet Routing Switch <Switch> ***
*** Extreme Networks, Inc. ***
*** Copyright (c) 2017, All Rights Reserved ***
*** ***
*** HW:R0D.7 FW:7.4.0.8 SW:v7.5.0.083 ***
***************************************************************
December 2017 Quick Start Configuration for ERS 4900 and 5900 Series 33

Connecting and configuring the switch
Variable definitions
Use the definitions in the following table to use the banner command.
Variable Definition
custom Disable the use of the default banner.
static Activate the use of the default banner.
<line_number> Banner line number you are configuring. The range
is 1 to 19
<LINE> Specify the characters in the line number.
Configuring system identification
About this task
You can configure system identification to specify the system name, contact person, and location of
the switch, and to add a trap receiver to the trap-receiver table.
Procedure
1. Enter Global Configuration mode:
enable
configure terminal
2. Enable the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) server:
snmp-server enable
3. Configure the read-only community name:
snmp-server community ro
Note:
Enter the community string twice.
If you ran the install script to set up the configuration information, the read-only
community name is already configured.
4. Configure the read-write community name:
snmp-server community rw
Note:
Enter the community string twice.
December 2017 Quick Start Configuration for ERS 4900 and 5900 Series 34

Configuring system identification
If you ran the install script to set up the configuration information, the read-write
community name is already configured.
5. Configure the system name:
snmp-server name <text>
6. Configure the system contact:
snmp-server contact <text>
7. Configure the location:
snmp-server location <text>
8. Configure the SNMP host to add a trap receiver to the trap-receiver table:
snmp-server host <host-ip> <community-string>
Variable definitions
Use the definitions in the following table to use the snmp-server name command.
Table 5: snmp-server name command
Variable Definition
<text> Specify the SNMP system name value. Enter an
alphanumeric string of up to 255 characters.
Note:
On the console, the SNMP server name is
truncated. On the web interface, the full SNMP
server name appears.
Use the definitions in the following table to use the snmp-server contact command.
Table 6: snmp-server contact command
Variable Definition
<text> Specify the SNMP system contact value. Enter an
ASCII string of up to 255 characters.
Use the definitions in the following table to use the snmp-server location command.
Table 7: snmp-server location command
Variable Definition
<text> Specify the SNMP system location value. Enter an
alphanumeric string of up to 255 characters.
December 2017 Quick Start Configuration for ERS 4900 and 5900 Series 35

Connecting and configuring the switch
Use the definitions in the following table to use the snmp-server host command.
Table 8: snmp-server host command
Variable Definition
<host-ip> Specify an IPv4 or IPv6 address for a host intended
to be the trap destination.
<community-string> If you are using the proprietary method for SNMP,
enter a community string that works as a password
and permits access to the SNMP protocol.
Enabling logging
Use this procedure to enable the logging of system messages. For more information about logging,
see Logs Reference for Ethernet Routing Switch 2000, 3000, 4000, 5000, 5900 Series and Virtual
Services Platform 7000 Series.
Procedure
1. Enter Global Configuration mode:
enable
configure terminal
2. To enable system logging, enter the following command at the command prompt:
logging remote level informational
Configuring Simple Network Time Protocol
The Simple Network Time Protocol (SNTP) feature synchronizes the Universal Coordinated Time
(UTC) to an accuracy within 1 second. This feature adheres to the IEEE RFC 2030 (MIB is the
s5agent). With this feature, the system can obtain the time from any RFC 2030-compliant NTP/
SNTP server.
For more information on SNTP, see Configuring Systems on Ethernet Routing Switch 4900 and
5900 Series.
About this task
Use this procedure to configure the Network Time Protocol (NTP) servers for SNTP.
Procedure
1. Enter Global Configuration mode:
enable
December 2017 Quick Start Configuration for ERS 4900 and 5900 Series 36

configure terminal
2. Enter the following command to configure the SNTP server primary IP address:
sntp server primary address [<A.B.C.D> |
<primary_server_ipv6address>]
3. Enter the following command to configure the SNTP secondary server IP address:
sntp server secondary address [<A.B.C.D> |
<secondary_server_ipv6address>]
Note:
SNTP supports primary and secondary NTP servers. The system attempts to access the
secondary NTP server only if the primary NTP server is unresponsive.
4. Enter the following command to enable SNTP:
sntp enable
Variable definitions
Configuring real-time clock
Use the definitions in the following table to use the sntp server command.
Variable Definition
<A.B.C.D> Enter the IP address of the NTP server.
<primary_server_ipv6address> Enter the IPv6 address of the primary NTP server.
<secondary_server_ipv6address> Enter the IPv6 address of the secondary NTP server.
Configuring real-time clock
About this task
Configure the real-time clock (RTC) to provide the switch with time information. The RTC provides
the switch with time information in the instance that SNTP time is not available.
Procedure
1. Log on to CLI to enter User EXEC mode.
2. Enter Privileged EXEC mode:
enable
3. Enter the following command to configure RTC:
clock set {hh:mm:ss <1–31> [<1–31> {[MONTH <2005–2099>] [MONTH <1–
31> <2005–2099>]} [LINE]}
December 2017 Quick Start Configuration for ERS 4900 and 5900 Series 37

Connecting and configuring the switch
Variable definitions
Use the definitions in the following table to use the clock set command.
Variable Value
<LINE> Specify a string in the format of mmddyyyyhhmmss
that defines the current local time.
<hh:mm:ss> Specify the current local time in the hh:mm:ss
format.
<1–31> RTC date
<MONTH> RTC month
<2005–2099> RTC year
Configuring local time zone
Configure the time zone to use an internal system clock to maintain accurate time. The time zone
data does not include daylight saving time changes. You must configure daylight saving time.
About this task
Use this procedure to configure the local time zone.
Procedure
1. Enter Global Configuration mode:
enable
configure terminal
2. Enter the following command to enable SNTP:
sntp enable
3. Enter the following command to configure the time zone:
clock time-zone <zone> <hours> [minutes]
4. Enter the following command to configure daylight saving time:
clock summer-time zone date day month year hh:mm day month year
hh:mm [offset]
5. Save the changed configuration.
Example
Configuring the time zone
Switch>enable
December 2017 Quick Start Configuration for ERS 4900 and 5900 Series 38

Configuring local time zone
Switch#configure terminal
Switch(config)#clock time-zone PST -8
This command sets the time zone to UTP minus 8 hours and the time zone is displayed as "PST."
Configuring daylight saving time
Switch(config)#clock summer-time BST date 28 Mar 2013 2:00 30 Aug 2013
15:00 +60
This command sets the daylight saving time to begin at 02:00 on March 28, 2013 and end on
August 30, 2013 at 15:00. The change to daylight saving time moves the clock forward by 60
minutes and the time zone is displayed as "BST". These changes to and from daylight saving time
occur automatically.
Variable definitions
Use the definitions in the following table to use the clock time-zone command.
Table 9: clock time-zone command
Variable Definition
<zone> Time zone acronym to be displayed when showing system time (up to
4 characters).
<hours> Difference from UTC in hours. This can be any value between -12
and +12.
[minutes] Optional: This is the number of minutes difference from UTC. Minutes
can be any value between 0 and 59.
Use the definitions in the following table to use the clock summer-time zone command.
Table 10: clock summer-time zone command
Variable Definition
date Indicates that daylight saving time you set to start and end on the
specified days every year.
day Day to start daylight saving time.
month Month to start daylight saving time.
year Year to start daylight saving time.
hh:mm Hour and minute to start daylight saving time.
day Day to end daylight saving time.
month Month to end daylight saving time.
year Year to end daylight saving time.
hh:mm Hour and minute to end daylight saving time.
Table continues…
December 2017 Quick Start Configuration for ERS 4900 and 5900 Series 39

Connecting and configuring the switch
Variable Definition
offset Number of minutes to add during the summertime.
zone The time zone acronym to be displayed when daylight saving time is
in effect. If unspecified, the acronym defaults to the time zone
acronym that was configured when the time zone was configured.
Configuring the clock
In addition to SNTP time configuration, a clock provides the switch with time information. This clock
provides the switch information whent SNTP time is not available.
About this task
Use this procedure to configure the time source for the switch.
Procedure
1. Enter Global Configuration mode:
enable
configure terminal
2. Enter the following command:
clock source {ntp | sntp | rtc | sysUpTime }
Variable definitions
Use the definitions in the following table to use the clock source command.
Variable Definition
ntp Configure NTP as the time source.
sntp Configure SNTP as the time source.
rtc Specifies Real Time Clock (RTC) as the time source.
sysUpTime Configure System Up Time as the time source.
Configuring a static route
Create static routes to manually configure a path to destination IP address prefixes.
Procedure
1. Enter Global Configuration mode:
December 2017 Quick Start Configuration for ERS 4900 and 5900 Series 40

Configuring a static route
enable
configure terminal
2. Enter the following command to enable IP routing globally:
ip routing
3. Enter the following command to configure an IP address on a VLAN:
ip address <ip address> <mask> [<MAC-offset>]
4. Enter the following command to configure a static route:
ip route <destination ip> <mask> <next-hop> {<cost> | disable |
enable | weight <cost>}
5. Enter the following command to display all the static routes:
show ip route static [<dest-ip>] [-s <subnet> <mask>]
6. Save the configuration.
Variable definitions
Use the definitions in the following table to use the ip route command.
Variable Definition
<ipaddr> Specify the IP address to attach to the VLAN.
<mask> Specify the subnet mask to attach to the VLAN
<MAC-offset> Specify the value used to calculate the VLAN MAC
address, which is offset from the switch MAC
address. The valid range is 1 to 256. Specify the
value 1 for the Management VLAN only. If no MAC
offset is specified, the switch applies one
automatically.
<destination ip> Specify the destination IP address for the route being
added.
0.0.0.0 is considered the default route.
<mask> Specify the destination subnet mask for the route
being added.
<next-hop> Specify the next-hop IP address for the route being
added.
<cost> Specify the weight, or cost, of the route being added.
Range is 1 to 65535.
enable Enable the specified static route.
disable Disable the specified static route.
weight <cost> Change the weight, or cost, of an existing static
route. Range is 1 to 65535.
December 2017 Quick Start Configuration for ERS 4900 and 5900 Series 41

Connecting and configuring the switch
Enabling remote access
You can enable remote access for telnet, SSH (on SSH software images), SNMP, and webpage
access.
For more information, see Using CLI and EDM on Ethernet Routing Switch 4900 and 5900 Series
and Configuring Systems on Ethernet Routing Switch 4900 and 5900 Series.
About this task
Use the following procedure to enable and configure remote access to the management features of
the switch.
Procedure
1. Enter Global Configuration mode:
enable
configure terminal
2. To enable telnet remote access, enter the following command:
telnet-access enable
3. To enable SSH remote access, enter the following command:
ssh
4. To enable SNMP remote access, enter the following command:
snmp-server enable
5. To enable webpage remote access, enter the following command:
web-server enablte
Example
The following is an example of enabling telnet remote access:
Switch>enable
Switch#configure terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
Switch(config)#telnet-access enable
Switch(config)#
Using telnet to log on to the device
About this task
Use telnet to log on to the device and remotely manage the switch.
December 2017 Quick Start Configuration for ERS 4900 and 5900 Series 42

Enabling the web server management interface
Procedure
1. From a computer or terminal, start a telnet session:
telnet <IPv4_address>
where <IPv4_address> is the IP address of the switch. The stand-alone units use the default
IP address of 192.168.1.1 if the switch does not obtain its IP address from another source.
2. Enter the user ID and password when prompted.
Enabling the web server management interface
The web server must be enabled to access Enterprise Device manager (EDM). If you do not want
EDM to be accessible on the device, disable the web server. By default, the web server is enabled.
About this task
Use this procedure to enable the web server.
Procedure
1. Enter Global Configuration mode:
enable
configure terminal
2. At the command prompt, enter the following command:
web-server enable
Accessing the switch through the web interface
You can use EDM to configure and maintain your switch through a web-based graphical user
interface. You can monitor the switch through a web browser from anywhere on the network.
By default, you can access the web interface using Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure (HTTPS)
only.
For more information about configuring the web server to respond to HTTPS only or to both HTTPS
and Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) client browser requests, see Configuring Security on
Ethernet Routing Switch 4900 and 5900 Series.
By default, the web interface uses a 15 minute time-out period. If no activity occurs for 15 minutes,
the system logs off the switch web interface, and you must reenter the password information.
To configure inactivity time-out, see Configuring Security on Ethernet Routing Switch 4900 and 5900
Series.
December 2017 Quick Start Configuration for ERS 4900 and 5900 Series 43

Connecting and configuring the switch
Before you begin
• Ensure that the switch is running.
• Note the switch IP address.
• Ensure that the web server is enabled.
• Note the user name and password.
• Open one of the supported web browsers.
For more information about the supported browsers, see Using CLI and EDM on Ethernet
Routing Switch 4900 and 5900 Series.
About this task
Use this procedure to access the switch through a web browser.
Procedure
1. Start your web browser.
2. Type the switch IP address as the URL in the Web address field.
http://<IP Address>
OR
https://<IP Address>
3. Enter the user name.
4. Enter the password.
5. Click Log On.
Enabling or disabling Quick Configuration
Use the following commands to enable or disable Quick Configuration:
Before you begin
Quick Configuration requires a stack.
About this task
The new unit Quick Configuration can store a default configuration that applies to a new unit joining
the stack.
Procedure
1. Enter Global Configuration mode:
enable
configure terminal
2. To enable Quick Configuration, enter the following command:
December 2017 Quick Start Configuration for ERS 4900 and 5900 Series 44

Recording a Quick Configuration
quickconfig enable
3. To disable Quick Configuration, enter the following command:
no quickconfig enable
4. To default Quick Configuration, enter the following command:
default quickconfig
Next steps
Use the quickconfig start-recording command to record a default configuration that applies
to new units joining the stack.
Recording a Quick Configuration
Use this procedure to record a Quick Configuration:
Before you begin
Quick Configuration requires a stack.
Quick Configuration must be enabled.
About this task
You can use the new unit Quick Configuration feature to create a default configuration that applies
to any new unit joining the stack. You can record the default values for VLAN IDs, port speed,
duplex mode, PVID, tagging, and spanning tree groups for the new unit without the need to reset the
stack.
Procedure
1. Enter Privileged EXEC mode:
enable
2. At the command prompt, enter the following command:
quickconfig start-recording
3. Record your required Quick Configuration by entering one command on each line in CLI.
See the following example.
Important:
The first two commands must be enable and config term, otherwise the
configuration commands that follow do not apply.
Use $ as a wildcard for the slot. The unit number is not known when a new unit joins a
stack, so the wildcard can match any slot number.
To end the recording process enter a . on the last line in CLI.
December 2017 Quick Start Configuration for ERS 4900 and 5900 Series 45

Connecting and configuring the switch
Example
The following example records a Quick Configuration for VLAN and port configurations that applies
to a new unit joining a stack if Quick Configuration is enabled:
enable
config term
vlan port $/13-40 tag untagPvidonly
vlan create 10 name vlan_10 type port
vlan create 20 name vlan_20 type port
vlan members add 10 $/13-40
vlan members add 20 $/13-40
interface fast $/13-34
speed 100
end
.
Configuring a VLAN using CLI
Use this procedure to create a VLAN using CLI. Optionally, you can choose to assign the VLAN a
name or rename the VLAN.
For more information about configuring a VLAN and creating Private VLAN, see Configuring VLANs,
Spanning Tree, and MultiLink Trunking on Ethernet Routing Switch 4900 and 5900 Series.
Procedure
1. Enter Global Configuration mode:
enable
configure terminal
2. Enter the following command at the command prompt:
vlan create <VID_list> [name <LINE>] type { port { <1–8>|cist|
msti<1–7>] } | private-vlan {secondary (2–4094)[<1–8> | cist |
msti]}| protocol decEther2 | protocol-decOtherEther2 | protocolipEther2 | protocol-ipv6Ether2 | protocol ipx802.2 | protocolipx802.3 | protocol-ipxEther2 | protocol ipxSnap | protocol-Netbios
| protocol-RarpEther2 | protocol sna802.2 | protocol-snaEther2 |
protocol-vinesEther2 | protocol-xnsEther2 | protocol-Userdef {ether
<4096-65534> | llc <1-65534> | snap <1-65534>} | voice-vlan | spbmbvlan | spbm-switchedUni [<1-8>]} | [voice-vlan]
Note:
If you tag protocol VLAN client ports, the system cannot assign frames to the protocol
VLAN, regardless of the defined ethertype. Frames are not assigned to the protocol
VLAN because untagged packets are assigned to the VLAN identified by the port PVID.
December 2017 Quick Start Configuration for ERS 4900 and 5900 Series 46

Configuring a VLAN using CLI
Example
Creating a range of port-based VLANs:
Switch(config)#vlan create 100,107,109-113,115 type port
Creating a protocol-based VLAN:
Switch(config)#vlan create 200 type protocol-decEther2
Creating and naming a voice-VLAN:
Switch(config)#vlan create 300 name my_vlan type port voice-vlan
Renaming an existing VLAN:
Switch(config)#vlan name 300 my_vlan2
Creating a VLAN using a user-defined protocol and specifying the frame encapsulation
header type:
Switch(config)#vlan create 500 type protocol-userdef ether 6004
Creating an SPBM-BVLAN:
Switch(config)#vlan create 600 type spbm-bvlan
Creating an RSPAN VLAN:
Switch(config)#vlan create 700 type port remote-span
Displaying a range of VLANs:
Switch(config)#show vlan id 100,107,109-113,115,200,300,500,600,700
Id Name Type Protocol PID Active IVL/SVL Mgmt
---- -------------------- -------- ---------------- ------- ------ ------- ---100 VLAN #100 Port None 0x0000 Yes IVL No
Port Members: NONE
107 VLAN #107 Port None 0x0000 Yes IVL No
Port Members: NONE
109 VLAN #109 Port None 0x0000 Yes IVL No
Port Members: NONE
110 VLAN #110 Port None 0x0000 Yes IVL No
Port Members: NONE
111 VLAN #111 Port None 0x0000 Yes IVL No
Port Members: NONE
112 VLAN #112 Port None 0x0000 Yes IVL No
Port Members: NONE
113 VLAN #113 Port None 0x0000 Yes IVL No
Port Members: NONE
115 VLAN #115 Port None 0x0000 Yes IVL No
Port Members: NONE
200 VLAN #200 Protocol Declat Ether2 0x6004 Yes IVL No
Port Members: NONE
300 my_vlan2 Voice None 0x0000 Yes IVL No
Port Members: NONE
500 VLAN #500 Protocol Ether2 User-Def. 0x1774 Yes IVL No
Port Members: NONE
600 VLAN #600 B-VLAN None 0x0000 Yes IVL No
Port Members: NONE
700 VLAN #700 Port None 0x0000 Yes IVL No
Port Members: NONE
Total VLANs: 13
December 2017 Quick Start Configuration for ERS 4900 and 5900 Series 47

Connecting and configuring the switch
Variable definitions
Use the definitions in the following table to use the vlan create command.
Variable Definition
<VID_list> Enter as an individual VLAN ID to create a single VLAN or enter
as a range of VLAN IDs to create multiple VLANs
simultaneously. A VLAN ID can range from 1 to 4094.
Note:
VLAN ID values 4001 through 4008 are reserved and
cannot be used.
name <line> Specify a unique alphanumeric name for an individual VLAN.
Note:
Do not enter a value for this parameter when you are
creating multiple VLANs simultaneously.
type Enter the type of VLAN to create:
• port—Port-based
• private-vlan
• protocol—Protocol-based (see the following list)
remote-span Specify as RSPAN VLAN.
protocol-decEther2 Specify a decEther2 protocol-based VLAN.
protocol-ipEther2 Specify an ipEther2 protocol-based VLAN.
protocol-decOtherEther2 Specifies a decOtherEther2 protocol-based VLAN.
protocol-ipv6Ether2 Specify an ipv6Ether2 protocol-based VLAN.
protocol-ipx802.2 Specify an ipx802.2 protocol-based VLAN.
protocol-ipx802.3 Specify an ipx802.3 protocol-based VLAN.
protocol-ipxEther2 Specify an ipxEther2 protocol-based VLAN.
protocol-ipxSnap Specify an ipxSnap protocol-based VLAN.
protocol-Netbios Specify a NetBIOS protocol-based VLAN.
protocol-RarpEther2 Specify a RarpEther2 protocol-based VLAN.
protocol-sna802.2 Specify an sna802.2 protocol-based VLAN.
protocol-snaEther2 Specify an snaEther2 protocol-based VLAN.
protocol-Userdef Specify a user-defined protocol-based VLAN.
Enter
• <4094–65534> {<1-8> | voice-vlan}—Ethernet II
user-defined VLAN with this Protocol ID, where <1-8> is
Spanning Tree Group ID
Table continues…
December 2017 Quick Start Configuration for ERS 4900 and 5900 Series 48

Configuring VLAN using EDM
Variable Definition
• ether <4096–65534> —Ethernet II user-defined VLAN
with this Protocol ID
• llc <1-65534> —LLC user-defined VLAN with this
Protocol ID
• snap <1-65534> —SNAP user-defined VLAN with this
Protocol ID
protocol-xnsEther2 Specify an xnsEther2 protocol-based VLAN.
protocol-vinesEther2 Specify a vinesEther2 protocol-based VLAN.
<1-8> Specify the Spanning Tree Group ID.
spbm-bvlan Specify as SPBM B-VLAN.
spbm-switchedUni Specify as SPBM switched UNI.
voice-vlan Specify as Voice VLAN.
Configuring VLAN using EDM
You can create a VLAN by IP subnet, port, protocol, or source MAC address using EDM.
You can assign an IP address to the VLAN. You can also assign a MAC-offset value that allows you
to manually change the default MAC address.
Before you begin
Ensure you follow the VLAN configuration rules for the switch. For more information about the VLAN
configuration rules and about configuring a VLAN, see Configuring VLANs, Spanning Tree, and
MultiLink Trunking on Ethernet Routing Switch 4900 and 5900 Series.
About this task
Use this procedure to create a VLAN and assign an IP address to a VLAN to enable routing on the
VLAN.
Procedure
1. In the navigation tree, expand the following folders: Configuration > VLAN.
2. Click VLANs.
3. On the Basic tab, click Insert.
4. In the Id field, enter an unused VLAN ID, or use the ID provided.
5. In the Name field, type the VLAN name, or use the name provided.
6. From the MstpInstance drop-down, select MSTP instance.
7. In the StgId field, specify the IDs to associate STG with the selected VLAN or VLANs.
8. In the Type box, select the type of VLAN you want to create.
December 2017 Quick Start Configuration for ERS 4900 and 5900 Series 49

Connecting and configuring the switch
9. Select VoiceEnabled to indicate whether a VLAN is voice VLAN.
10. Select RspanEnabled to indicate whether a VLAN is RSPAN enabled.
Field descriptions
Use the descriptions in the following table to create a VLAN using EDM.
Field Description
Id Specify the ID for the VLAN.
Name Specify an alphanumeric name for the VLAN. If you
do not type a name, the switch default name is
applied.
StgId Specify the Spanning Tree Group (STG) to associate
with the selected VLAN or VLANs. This is a readonly value.
Important:
This column is available only when the
Spanning Tree administration operating mode is
STG mode. When the operating mode is
Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol (MSTP) or
Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP), this
column is not available.
Type Indicate the type of VLAN. This is a read-only value.
Values include:
• byPort—VLAN by Port
• byProtocolId—VLAN by Protocol ID
• spbm-bvlan—Backbone VLAN for the Shortest
Path Bridging MAC (SPBM)
• spbm-switchedUni—To create one endpoint on one
Service Instance ID (I-SID) and another endpoint
on another I-SID.
SecondaryVlanId Specifies the VLAN ID for the Secondary VLAN.
Enter an unused VLAN ID.
VoiceEnabled Indicate whether VLAN is a voice VLAN (true) or not
(false).
SpbMcast Indicates whether IP Shortcut multicast routing is
enabled or disabled on the VLAN.
RspanEnabled Indicate whether VLAN is an RSPAN VLAN (true) or
not (false).
I-sid Indicates the VLAN I-SID ID.
Secondary I-sid Specifies the secondary VLAN I-SID ID.
Table continues…
December 2017 Quick Start Configuration for ERS 4900 and 5900 Series 50

Configuring VLAN using EDM
Field Description
PortMembers Specifies the ports that are members of the VLAN.
ActiveMembers Indicates the ports that are currently active in the
VLAN. Active ports include all static ports and any
dynamic ports where the VLAN policy was met. This
is a read-only value.
MstpInstance The MSTP instance associated with the VLAN.
Values include:
• none
• cist
• msti 1 to 7
Note:
This column is available only when the
Spanning Tree administration operating mode is
MSTP, when the operating mode is STG or
RSTP, this column is not available.
ProtocolId Indicate the protocol identifier for the VLAN. The
protocol ID is significant only when the VLAN type is
byProtocolId.
Values include:
• ip
• ipx802dot3
• ipx802dot2
• ipxSnap
• ipxEthernet2
• appleTalk
• decLat
• decOtherEther2
• sna802dot2
• snaEthernet2
• netBios
• xns
• vines
• ipv6
• usrDefined
• rarp
Table continues…
December 2017 Quick Start Configuration for ERS 4900 and 5900 Series 51

Connecting and configuring the switch
Field Description
UserDefinedPid Indicates the user defined protocol identifier for a
protocol based VLAN. This is a read-only value.
Encap Indicates the encapsulation type for user defined
protocol based VLANs only. This is a read-only
value. Values include:
• ethernet2
• llc
• snap
By default there is no value in this cell.
MacAddress Indicates the MAC address associated with the
VLAN. This is a read-only value.
Routing Specifies whether routing is enabled (true) or
disabled (false) for the VLAN.
Note:
If you change the name of an existing VLAN using the VLAN Basic tab, or using CLI, the new
name does not initially appear in EDM. To display the updated name, perform one of the
following actions:
• Refresh your browser to reload EDM
• Restart EDM (logout and login)
• Click Refresh in the VLAN Basic tab toolbar. If the old VLAN name appears in any other tabs,
click the Refresh toolbar button in those tabs also.
Use the data in the following table to use the Ports tab.
Name Description
PrivateVlanPortType Specifies the port type. If not specified, the port type
defaults to None.
• Isolated: An Isolated port can belong only to one
private VLAN
• Promiscuous: A Promiscuous port can belong to
many private VLANs.
• Trunk: A Trunk port can belong to many private
VLANs, is tagged, and can also belong to
nonprivate VLANs.
Installing a license file
Use this procedure to install a license file.
December 2017 Quick Start Configuration for ERS 4900 and 5900 Series 52

Saving the configuration
If the switch is reset to default, the license file must be reinstalled to reenable licensed features.
Resetting a switch to default removes the license file from its storage area in NVRAM. Store the
license file on a TFTP server accessible by the switch or stack before starting the installation
procedure. For switches equipped with a USB port, you can also use a USB mass storage device to
copy the license file to the switch.
About this task
Install a license file on the switch to enable licensed features.
Procedure
1. Enter Privileged EXEC mode:
enable
2. Enter the following command:
copy [tftp | usb] license <tftp_ip_address> filename
<license_file_name>
3. Restart the switch.
Example
Installing a license using USB in ERS 5900
1. Insert a USB mass storage device into a USB port on the front of the switch.
2. To copy a license from a USB mass storage device, use the following commands:
Switch>enable
Switch#copy usb license filename 5900.xml
The switch generates the following message:
License successfully downloaded.
Important:
You must restart the system to activate the license.
Saving the configuration
After you change the configuration, you must save the changes. Save the configuration to a file to
retain the configuration settings.
Note:
File Transfer Protocol (FTP) and TFTP support both IPv4 and IPv6 addresses, with no
difference in functionality or configuration.
Before you begin
Enable the Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP) on the switch.
December 2017 Quick Start Configuration for ERS 4900 and 5900 Series 53

Connecting and configuring the switch
About this task
Use this procedure to save the configuration.
Procedure
1. Enter Privileged EXEC mode:
enable
2. At the command prompt, enter the following command:
save config
Storing the configuration files
Before and after you upgrade your switch software, make copies of the configuration files. If an error
occurs, use backup configuration files to return to a previous state. You can store the files in binary
or ASCII format. Use the following procedure to store the configuration file in binary format. For
more information about storing the file in ASCII format, see Configuring Systems on Ethernet
Routing Switch 4900 and 5900 Series.
You should keep several copies of backup files.
Before you begin
If you use File Transfer Protocol (FTP) or Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP), ensure that you
enabled the FTP or TFTP server. FTP and TFTP support both IPv4 and IPv6 addresses, with no
difference in functionality or configuration.
About this task
Use this procedure to copy the saved configuration to a file in binary format.
Procedure
1. Enter Privileged EXEC mode:
enable
2. At the command prompt, enter the following command:
copy config usb {filename <filename> | unit <1-8>
Variable definitions
Use the definitions in the following table to use the copy config usb command.
Variable Definition
<filename> The name of the file to be retrieved.
Table continues…
December 2017 Quick Start Configuration for ERS 4900 and 5900 Series 54

Shutting down the switch
Variable Definition
<1-8> The unit number in which the USB device is inserted,
if the unit is a part of the stack.
Shutting down the switch
The switch administrator can use this feature to safely shut down the switch without interrupting a
process or corrupting the software image. After you issue the command, the configuration is saved,
auto-save functionality is temporarily disabled, and you are notified that it is safe to power off the
switch. If you cancel the shutdown, auto-save functionality returns to the state in which it was
previously functioning.
Important:
Any configurations or login performed on the switch after you initiate the shutdown command
are not saved to NVRAM and are lost after the reset.
About this task
Use this procedure to shut down the switch.
Procedure
1. Enter Privileged EXEC mode:
enable
2. At the command prompt, enter the following command:
shutdown [force][minutes-to-wait <1-60>] [cancel]
Variable definitions
Use the definitions in the following table to use the shutdown command.
Variable Definition
force Instruct the switch to skip the shutdown confirmation
prompt.
minutes-to-wait <1-60> Specify the number of minutes that pass before the
switch resets itself. The default wait time is 10
minutes.
cancel Cancel all scheduled switch shutdowns.
December 2017 Quick Start Configuration for ERS 4900 and 5900 Series 55

Connecting and configuring the switch
Reloading a remote switch after configuration
This procedure is intended to be used by system administrators to reload a remote switch when
configuration is complete. The configuration is not explicitly saved after the reload command is
issued. This means that any configuration changes must be explicitly saved before the switch
reloads
Use this procedure to disable auto-saving configuration changes and safeguard against a
configuration error when you perform dynamic configuration changes on a remote switch. If you
make an error while configuring a remote switch that results in the loss of connectivity (for example,
an error in the IP address or VLAN), the reload loads the last saved configuration to re-establish
connectivity.
This procedure temporarily disables auto-save functionality until the reload occurs. If you cancel the
reload, auto-save functionality returns to any previous setting.
Caution:
You must perform a timed reload command before making dynamic configuration changes to
safeguard against the loss of remote connectivity.
About this task
Use this procedure to reload a remote switch.
Procedure
1. Enter Privileged EXEC mode:
enable
2. At the command prompt, enter the following command:
reload [force] [minutes-to-wait] [cancel]
Variable definitions
Use the definitions in the following table to use the reload command.
Variable Definition
force Instruct the switch to skip the shutdown confirmation
prompt.
minutes-to-wait <1-60> Specify the number of minutes before the switch
resets itself. The default wait time is 10 minutes.
cancel Cancel all scheduled switch shutdowns.
December 2017 Quick Start Configuration for ERS 4900 and 5900 Series 56

Chapter 5: Configuring management IP
addresses using CLI
This chapter provides procedural information you can use to assign, clear, and view in-band and
out-of-band management IP addresses and gateway IP addresses.
Configuring an in-band management IP address
Use this procedure to configure the in-band management IPv4 address, subnet mask, and default
gateway for a switch or stack.
Important:
Changing or clearing the in-band management IP address or subnet mask disconnects any active IP
management connections.
About this task
You can dynamically change the in-band management IP address using Telnet, SSH, SNMP, HTTP,
and HTTPS.
Procedure
1. Enter Global Configuration mode:
enable
configure terminal
2. To assign or modify the in-band management IP address for a switch or stack, enter the
following at the command prompt:
ip address [switch | stack | unit <1–8>] <A.B.C.D> [netmask
<A.B.C.D>] [default-gateway <A.B.C.D>]
Note:
You configure the stack in-band management IP address on the stack base unit.
Important:
Only one management default gateway can operate for each unit or stack. The out-ofband management default gateway takes precedence over the in-band management
December 2017 Quick Start Configuration for ERS 4900 and 5900 Series 57

Configuring management IP addresses using CLI
default gateway. Once an out-of-band management default gateway is configured, the
in-band management address is reachable only through a directly attached subnet for
the management VLAN.
3. To clear the in-band management IP address and the default gateway, enter the following
commands at the command prompt:
no ip address [switch | stack | unit <1–8>]
no ip default-gateway
Example
Switch>enable
Switch#config terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
Switch(config)#ip address stack 192.0.2.13 netmask 255.255.255.0 default-gateway
192.0.2.20
Switch(config)#ip address switch 192.0.2.2
Switch(config)#ip address unit 2 192.0.2.3
Switch(config)#ip address unit 3 192.0.2.4
Variable definitions
The following table describes the parameters for the ip address command.
Variable
switch Specifies an in-band management IP address for an
stack Specifies an in-band management IP address for the
unit <1–8> Specifies an in-band management IP address for a
<A.B.C.D> Specifies an in-band management IPv4 address.
netmask <A.B.C.D> Specifies the subnet mask associated with the in-
default-gateway <A.B.C.D> Specifies the default gateway IP address.
Value
individual switch (standalone or stack unit).
stack.
specific stack unit. Values range from 1–8.
band management IP address for a standalone
switch or for a specific switch unit within a stack.
Note:
Although netmask appears as an optional
parameter with the ip address command,
you should change the netmask when you
dynamically change the in-band management
IP address for a switch or stack.
Note:
If you do not specify a parameter with the ip address command, the system automatically modifies the
stack IP address when in stack mode, and modifies the switch IP address when in standalone mode.
December 2017 Quick Start Configuration for ERS 4900 and 5900 Series 58

Obtaining an in-band management IP address automatically
Obtaining an in-band management IP address
automatically
Use this procedure to automatically obtain an in-band management IP address, subnet mask and
default gateway on the switch or stack.
About this task
When you use DHCP, the switch or stack can also obtain up to three DNS server IP addresses.
Procedure
1. Enter Global Configuration mode:
enable
configure terminal
2. At the command prompt, enter the following command:
ip address source {bootp-always | bootp-last-address | bootp-whenneeded | configured-address | dhcp-always | dhcp-last-address |
dhcp-when-needed}
Variable definitions
The following table describes the parameters for the ip address source command.
Variable
bootp-always Always use the BootP server.
bootp-last-address Use the last BootP server.
bootp-when-needed Use the BootP server when needed.
configured-address Use the manually configured IP configuration.
dhcp-always Always use the DHCP server.
dhcp-last-address Use the last DHCP server.
dhcp-when-needed Use DHCP client when needed.
Value
DEFAULT: bootp-when-needed
Displaying in-band management information
Use this procedure to display the stack and switch in-band management IP addresses, BootP/
DHCP mode, stack address, switch address, subnet mask, and the in-band default-gateway IP
address.
December 2017 Quick Start Configuration for ERS 4900 and 5900 Series 59

Configuring management IP addresses using CLI
About this task
This command displays the parameters for what is configured, what is in use, and the last BootP/
DHCP. If you do not enter any parameters, this command displays all IP-related configuration
information.
Procedure
1. Log on to CLI to enter User EXEC mode.
2. At the command prompt, enter the following command:
show ip [address] [address source] [bootp] [default-gateway]
Configuring an out-of-band management IPv4 address
Use this procedure to configure the out-of-band management IPv4 address, subnet mask, and
default gateway for a switch or stack.
Before you begin
You must connect the RJ-45 cable for link-up to the out-of-band management port on the rear panel.
About this task
When you physically connect the Ethernet RJ-45 out-of-band management port for a standalone
switch or stack to your network, and assign an IPv4 address and subnet to the port, you can use
out-of-band management to access the switch or stack using Telnet, SSH, SNMP, HTTP, and
HTTPS.
Note:
The out-of-band management IP address must be different than the switch or stack in-band
management IP address and must belong to a different subnet.
Procedure
1. Enter Global Configuration mode:
enable
configure terminal
2. To assign or modify an out-of-band management IP address for a switch or stack, enter the
following command at the command prompt:
ip mgmt {[address [switch | stack | unit <1–8>] <A.B.C.D>
[<subnet_mask>]] | [netmask <A.B.C.D>] | [default-gateway
<A.B.C.D>] }
Note:
You must configure the stack out-of-band management IP address on the base unit.
December 2017 Quick Start Configuration for ERS 4900 and 5900 Series 60

Configuring an out-of-band management IPv4 address
Important:
Only one management default gateway can operate for each unit or stack. The out-ofband management default gateway takes precedence over the in-band management
default gateway. Once an out-of-band management default gateway is configured, the
in-band management address is reachable only through a directly attached subnet for
the management VLAN.
3. To clear the out-of-band management IP address for a switch or stack, enter the following
command at the command prompt:
no ip mgmt address [switch | stack]
4. To clear the out-of-band management default gateway, enter the following command at the
command prompt:
no ip mgmt default-gateway
Example
Switch>enable
Switch#config terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
Switch(config)#ip mgmt address stack 192.0.2.2 netmask 255.255.255.0
Switch(config)#ip mgmt address switch 192.0.2.3 netmask 255.255.255.0
Switch(config)#ip mgmt default-gateway 192.0.2.4
Variable definitions
The following table describes the parameters for the ip mgmt address command.
Variable
switch Specifies an out-of-band management IP address for
stack Specifies an out-of-band management IP address for
unit <1–8> Specifies an out-of-band management IP address for
<A.B.C.D> Specifies an out-of-band management IPv4 address.
<subnet_mask> Specifies the management subnet mask.
netmask <A.B.C.D> Specifies the subnet mask associated with the out-
Value
an individual switch (standalone or stack unit).
the stack.
a specific stack unit. Values range from 1 to 8.
Note:
The unit parameter is available only in a stack
environment.
DEFAULT: 0.0.0.0
DEFAULT: 0.0.0.0
of-band management IP address.
Table continues…
December 2017 Quick Start Configuration for ERS 4900 and 5900 Series 61

Configuring management IP addresses using CLI
Variable Value
DEFAULT: 0.0.0.0
Note:
Although netmask appears as an optional
parameter with the ip mgmt address
command, you should change the netmask
when you dynamically change the out-of-band
management IP address for a switch or stack.
default-gateway <A.B.C.D> Specifies the management default gateway. Only
specify an out-of-band default gateway if you are not
routing the management IP.
Important:
The out-of-band management IP addresses for all stack units must belong to the same subnet.
Displaying out-of-band management information
Use this procedure to display IPv4 address out-of-band management configuration information for a
switch or stack.
Procedure
1. Log on to CLI to enter User EXEC mode.
2. At the command prompt, enter the following command:
show ip mgmt [switch | all | route]
3. To display the management port link status, enter the following command:
show mgmt-port status
Example
Switch>show ip mgmt all
Unit Ip Address Netmask Gateway Link / Speed Status
----- --------------- --------------- --------------- ------------- --------Stack 192.0.2.2 255.255.255.0 192.0.2.10 Up 1000F Enabled
1 192.0.2.3 255.255.255.0 192.0.2.10 Up 1000F Enabled
2 192.0.2.4 255.255.255.0 192.0.2.10 Up 1000F Enabled
Note:
In a stack environment, the base unit is identified as Stack in the Unit column.
Variable definitions
The following table describes the parameters for the show ip mgmt command.
December 2017 Quick Start Configuration for ERS 4900 and 5900 Series 62

Configuring a management route
Variable Value
all Displays out-of-band management configuration
information for all units within a stack.
route Displays management VLAN information.
Note:
If you do not enter a variable with the show ip mgmt command, out-of-band management
configuration information for the local switch is displayed.
Configuring a management route
Use this procedure to configure a management route. In Layer 3 mode, If you configure
management routes you can access both the out-of-band and in-band management addresses.
Procedure
1. Enter Global Configuration mode:
enable
configure terminal
2. To assign an IP management route, enter the following command at the command prompt:
ip mgmt route <destination-IP> <destination-netmask> <destinationgateway>
3. To clear an IP management route, enter the following command at the command prompt:
no ip mgmt route <destination-IP> <destination-netmask>
<destination-gateway>
Variable definitions
The following table describes the parameters for the ip mgmt route command.
Variable
<destination-IP> Specifies the destination IPv4 address.
<destination-netmask> Specifies the destination IPv4 subnet mask.
<destination-gateway> Specifies the destination IPv4 gateway.
Value
December 2017 Quick Start Configuration for ERS 4900 and 5900 Series 63

Configuring management IP addresses using CLI
Configuring an in-band management IPv6 address
Use this procedure to configure the in-band management IPv6 address for a switch or stack.
Important:
Changing or clearing the in-band management IPv6 address disconnects any active IP
management connections.
About this task
You can dynamically change the in-band management IPv6 address using Telnet, SSH, SNMP,
HTTP, and HTTPS.
Procedure
1. Enter Global Configuration mode:
enable
configure terminal
2. To assign or modify the in-band management IPv6 address for a switch or stack, enter the
following at the command prompt:
ipv6 address [switch | stack | unit <1–8>] <WORD>
Note:
You configure the stack in-band management IPv6 address on the stack base unit.
Important:
Only one management default gateway can operate for each unit or stack. The out-ofband management default gateway takes precedence over the in-band management
default gateway. Once an out-of-band management default gateway is configured, the
in-band management address is reachable only through a directly attached subnet for
the management VLAN.
3. To assign the default gateway, enter the following at the command prompt:
ipv6 default-gateway <WORD>
4. To clear the in-band management IPv6 address and the default gateway, enter the following
commands at the command prompt:
no ipv6 address [switch | stack | unit <1–8>]
no ipv6 defaul-gateway
Example
Switch>enable
Switch#config terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
Switch(config)#ipv6 address stack 2001:DB8::/32
Switch(config)#ipv6 default gateway 2001:db8:1::/32
Switch(config)#ipv6 address switch 2001:db8:2::/32
December 2017 Quick Start Configuration for ERS 4900 and 5900 Series 64

Displaying in-band IPv6 management information
Switch(config)#ipv6 address unit 2 2001:db8:3::/32
Switch(config)#ipv6 address unit 3 2001:db8:4::/32
Variable definitions
The following table describes the parameters for the ip address command.
Variable Value
switch Specifies an in-band management IPv6 address for
an individual switch (standalone or stack unit).
stack Specifies an in-band management IPv6 address for
the stack.
unit <1–8> Specifies an in-band management IPv6 address for
a specific stack unit. Values range from 1–8.
<WORD> Specifies an in-band management IPv6 address.
default-gateway <WORD> Specifies the default gateway IPv6 address.
Note:
If you do not specify a parameter with the ipv6 address command, the system automatically modifies the
stack IPv6 address when in stack mode, and modifies the switch IPv6 address when in standalone mode.
Displaying in-band IPv6 management information
Use this procedure to display the stack and switch in-band management IPv6 addresses, and the inband default-gateway IPv6 address.
Procedure
1. Log on to CLI to enter User EXEC mode.
2. To display the configured in-bank management IPv6 address, enter the following at the
command prompt:
show ipv6 address [stack][switch][unit <1–8>]
3. To display IPv6 default-gateway information, enter the following at the command prompt:
show ipv6 default-gateway
Example
Switch>show ipv6 address
Switch Address: 2001:db8:2::/32
Stack Address: 2001:db8:3::/32
Switch>show ipv6 default-gateway
December 2017 Quick Start Configuration for ERS 4900 and 5900 Series 65

Configuring management IP addresses using CLI
Default Gateway: 2001:db8:4::/32
Status: NotActive
Note:
The status of the default gateway is active when the IPv6 address configured is reachable.
Configuring an out-of-band management IPv6 address
Use this procedure to configure the out-of-band management IPv6 address and default gateway for
a switch or stack.
About this task
When you physically connect the Ethernet RJ-45 out-of-band management port for a standalone
switch or stack to your network, and assign an IPv6 address and subnet to the port, you can use
out-of-band management to access the switch or stack using Telnet, SSH, SNMP, HTTP, and
HTTPS.
Note:
In Layer 3 mode, both interfaces of the switch are reachable if the routes are configured. If you
are initiating the connection from the switch interfaces (serial, Telnet, SSH), the out-of-band
management route takes precedence. For example, if you execute a traceroute to a distant
host, the out-of-band route is chosen.
Note:
The out-of-band management IP address must be different than the switch or stack in-band
management IP address and must belong to a different subnet.
Procedure
1. Enter Global Configuration mode:
enable
configure terminal
2. To activate the IPv6 interface on the switch, enter the following command at the command
prompt:
ipv6 mgmt interface
3. To configure a stand alone switch out-of-band management IPv6 address, enter the following
command at the command prompt:
ipv6 mgmt address <WORD>
4. To assign or modify an out-of-band management IPv6 address for a switch, stack or unit,
enter the following command at the command prompt:
ipv6 mgmt address [switch | stack | unit <1–8>] <WORD>
December 2017 Quick Start Configuration for ERS 4900 and 5900 Series 66

Configuring an out-of-band management IPv6 address
Note:
You must configure the stack out-of-band management IPv6 address on the base unit.
Important:
Only one management default gateway can operate for each unit or stack. The out-ofband management default gateway takes precedence over the in-band management
default gateway. Once an out-of-band management default gateway is configured, the
in-band management address is reachable only through a directly attached subnet for
the management VLAN.
5. To configure the default-gateway, enter the following command at the command prompt:
ipv6 mgmt default—gateway <WORD>
6. To configure a static route for the management port, enter the following command at the
command prompt:
ipv6 route <WORD> mgmt
ipv6 route <WORD> mgmt [cost <1–65535> | enable | preference <1–
255>]
7. To display the IPv6 address out-of-band management configuration, enter the following
commands at the command prompt:
show ipv6 mgmt address [switch | stack | unit <1–8>]
show ipv6 mgmt default—gateway
show ipv6 mgmt interface
8. (Optional) To configure the default out-of-band management IPv6 address, enter the
following command at the command prompt:
default ipv6 mgmt address [switch | stack | unit <1–8>]
9. (Optional) To configure the default out-of-band IPv6 management default gateway, enter the
following command at the command prompt:
default ipv6 mgmt default-gateway
10. (Optional) To configure the default IPv6 interface process-redirect on the switch, enter the
following command at the command prompt:
default ipv6 mgmt interface [ process-redirect ]
11. (Optional) To clear the out-of-band management IPv6 address, enter the following
command at the command prompt:
no ipv6 mgmt address [switch | stack | unit <1–8>]
12. (Optional) To clear the out-of-band IPv6 management default gateway, enter the following
command at the command prompt:
no ipv6 mgmt default-gateway
December 2017 Quick Start Configuration for ERS 4900 and 5900 Series 67

Configuring management IP addresses using CLI
Example
Switch>enable
Switch#config terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
Switch(config)#ipv6 mgmt address stack 2001:db8:1::/32
% IPV6 Oob management interface does not exist
Switch(config)#ipv6 mgmt interface
Switch(config)#ipv6 mgmt address stack 2001:db8:1::/32
Switch(config)#show ipv6 mgmt interface
2013-08-06 17:28:49 GMT+02:00 UTC time: 2013-08-06 15:28:49
===============================================================================
Interface Information
===============================================================================
IFINDX VLAN-ID MTU PHYSICAL ADMIN OPER RCHBLE RETRAN TYPE
ADDRESS STATE STATE TIME TIME
------------------------------------------------------------------------------55001 1 1500 00:19:e1:55:07:00 enabled up 30000 1000 ETHER
===============================================================================
Address Information
===============================================================================
INTF IPV6 TYPE ORIGIN STATUS INDEX ADDRESS
------------------------------------------------------------------------------55001 2001:db8:1::/32 UNICAST MANUAL PREFERRED
55001 fe80::219:e1ff:fe55:700 UNICAST LINKLAYER PREFERRED
1 out of 1 Total Num of Interface Entries displayed.
2 out of 8 Total Num of Address Entries displayed.
Variable definitions
The following table describes the parameters for the ipv6 mgmt address command.
Variable
<WORD> Specifies an out-of-band management IPv6 address
switch Specifies an out-of-band management IP address for
stack Specifies an out-of-band management IP address for
unit <1–8> Specifies an out-of-band management IP address for
Value
or IPv6 address and prefix length.
DEFAULT for IPv6: 0::0/0
an individual switch (standalone or stack unit).
the stack.
DEFAULT: 0:0:0:0:0:0:0:0
a specific stack unit. Values range from 1 to 8.
Note:
The unit parameter is available only in a stack
environment.
Important:
The out-of-band management IP addresses for all stack units must belong to the same subnet.
December 2017 Quick Start Configuration for ERS 4900 and 5900 Series 68

Displaying out-of-band management IPV6 information
The following table describes the parameters for the ipv6 mgmt command.
Variable Value
default-gateway <WORD> Specifies the management default gateway. Only
specify an out-of-band default gateway if you do not
route the management IP.
WORD specifies an IPv6 address.
Only one management default gateway can operate
for each unit or stack. The out-of-band management
default gateway takes precedence over the in-band
management default gateway. After you configure an
out-of-band management default gateway, the inband management address is reachable only
through a directly attached subnet for the
management VLAN.
DEFAULT for IPv6: 0:0:0:0:0:0:0:0
interface Specifies the management default interface.
The following table describes the parameters for the ipv6 route command.
Variable Value
<WORD> mgmt Specifies a static route for the management port.
WORD specifies an IPv6 address route.
cost <1-65535> Specifies the cost.
enable Specifies if the IPv6 static route is enabled.
preference <1-255> Specifies the preference.
The following table describes the parameters for the show ipv6 mgmt command.
Variable
address unit <1–8> Indicates information about the management IPv6
default-gateway Indicates information about the management default
interface Indicates all of the IPv6 addresses.
Value
address from every unit in the stack.
gateway.
Displaying out-of-band management IPV6 information
Procedure
1. Log on to CLI to enter User EXEC mode.
2. To display all addresses for IPv6 interfaces, enter the following command at the command
prompt:
December 2017 Quick Start Configuration for ERS 4900 and 5900 Series 69

Configuring management IP addresses using CLI
show ipv6 address interfaces
3. To display IPv6 management addresses, enter the following command at the command
prompt:
show ipv6 mgmt address [unit <1–8>]
4. To display IPv6 management default-gateway information, enter the following command at
the command prompt:
show ipv6 mgmt default-gateway
5. To display IPv6 management interface information, enter the following command at the
command prompt:
show ipv6 mgmt interface
6. To display the neighbor table for the IPv6 management port, enter the following command at
the command prompt:
show ipv6 neighbor interface mgmt
7. To display the routing table for the IPv6 management port, enter the following command at
the command prompt:
show ipv6 route mgmt
Example
Switch(config)#show ipv6 mgmt address
2013-08-06 17:32:00 GMT+02:00 UTC time: 2013-08-06 15:32:00
Mgmt Switch Address: ::/0
Mgmt Stack Address: 2001:db8:1::/32
Switch(config)#show ipv6 neighbor interface mgmt
2013-08-06 17:32:45 GMT+02:00 UTC time: 2013-08-06 15:32:45
===============================================================================
Neighbor Information
===============================================================================
NET ADDRESS/ PHYS TYPE STATE LAST
PHYSICAL ADDRESS INTF UPD
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------2001:db8:3::/32/ O-1 LOCAL REACHABLE 0
00:19:e1:55:07:00
2001:db8:4::/32/ O-1 DYNAMIC REACHABLE 17061
00:19:e1:4d:7c:9c
2001:db8:5::/32/ O-1 LOCAL REACHABLE 16847
00:19:e1:55:07:00
fe80::219:e1ff:fe55:700/ O-1 LOCAL REACHABLE 16847
00:19:e1:55:07:00
4 out of 13 Total Num of Neighbor Entries displayed.
December 2017 Quick Start Configuration for ERS 4900 and 5900 Series 70

Enabling or disabling the out-of-band management port
Enabling or disabling the out-of-band management port
Use this procedure to administratively enable or disable the Ethernet RJ-45 out-of-band
management port.
Procedure
1. Enter Global Configuration mode:
enable
configure terminal
2. To disable the out-of-band management port, enter the following command at the command
prompt:
ip mgmt shutdown [all | unit <1–8>]
3. To enable the out-of-band management port, enter the following command at the command
prompt:
no ip mgmt shutdown [all | unit <1–8>]
Result
After you use the no ip mgmt shutdown [all | unit <1–8>] command to enable an out-ofband management port, there is a delay of approximately 90 seconds before the port is reachable.
Variable definitions
The following table describes the parameters for the ip mgmt shutdown and no ip mgmt
shutdown commands.
Variable
all Specifies to enable or disable the management port
unit <1–8> Specifies a specific switch unit within a stack for
Value
of all units in a stack.
which to enable or disable the out-of-band
management port.
Setting in-band management IP address parameters from the ip.cfg file on a USB device
If the switch does not obtain an in-band management IP address through BootP, you can load the IP
address and optionally new switch software and configuration from the USB memory device using
the ip.cfg file.
December 2017 Quick Start Configuration for ERS 4900 and 5900 Series 71

Configuring management IP addresses using CLI
Note:
The file name, ip.cfg is case-insensitive.
If a properly formatted file exists on a USB port, the switch uses that ip.cfg as the first option,
rather than the last. You can specify one or more of the optional parameters in the ip.cfg file. All
of the parameters are optional.
The following table describes the ip.cfg file parameters:
Parameter Description
IP <A.B.C.D> | <WORD> Specifies the IP address for the switch. A.B.C.D is
IPv4 address, WORD is IPv6 address.
Mask <xx.xx.xx.xx> Specifies the IPv4 network mask. Example:
255.255.255.0
Gateway <A.B.C.D> | <WORD> Specifies the default gateway. A.B.C.D is IPv4
address, WORD is IPv6 address.
SNMPread <string> Specifies the SNMP read community string.
Example: public
SNMPwrite <string> Specifies the SNMP write community string.
Example: private
VLAN <number> Specifies the management VLAN-ID. Example:
VLAN 1
USBdiag <string> Specifies the filename of the diagnostic image to
load from the USB. Example: vsp7000/
vsp7000_10.0.1.10.bin
USBascii <string> Specifies the filename of the ASCII config file to load
from the USB. Example: customer1.cfg
USBagent <string> Specifies the filename of the agent image to load
from the USB and specifies IPs for next boot.
Example: vsp7000/vsp7000_10.0.1.0.img
NEXTIP, NEXTMask, and NEXTGateway Specifies IP addresses, nework mask, and gateway
to be used once the switch is booted.
Note:
If you download an ASCII file or diag/image with an ip.cfg file, the specific ASCII file or diag/
image must be present on the USB device.
The ip.cfg file loads information from the ASCII configuration file in order of precedence. For
example, the stack IP becomes 192.0.2.2 no matter what IP address is in the ip.txt file if you
have an ip.cfg file with the following commands:
USBascii ip.txt IP 192.0.2.2
Mask 255.255.255.0
Gateway 192.0.2.20
December 2017 Quick Start Configuration for ERS 4900 and 5900 Series 72

Setting in-band management IP address parameters from the ip.cfg file on a USB device
The stack IP will be the IP address defined in the ip.txt file if you have an ip.cfg file with the
following commands:
IP 192.0.2.2
Mask 255.255.255.0
Gateway 192.0.2.20
USBascii ip.txt
Note:
The ip.cfg file runs only on a base or standalone unit. The file cannot be more than 4096
bytes or contain more than 200 lines.
The following figure shows an example of an ip.cfg file.
#Any lines starting with a # are comments
#IP <xx.xx.xx.xx> specifies the IP address for the switch
IP 192.0.2.2
#Mask <xx.xx.xx.xx> specifies the network mask MASK 255.255.255.0
#Gateway <xx.xx.xx.xx> specifed the default gateway Gateway 192.0.2.20 public
#SNMPwrite <string> specifed the SNMP write community string SNMPwrite private
#VLAN <number> specified the manamgent VLAN-ID VLAN 1
#USBdiag <string> speicifes the filename of the diagnostic image to load (noreset)
USBdiag ers5900/5900_74008_diags.bin
#USBagent <string> specifes the filname of the agent image to load (noreset)
USBageent ers5900/5900_740009s.img
#USBascii <string> specifies the filename of the ASCII config file to load
USBascii customer1.cfg
#NEXTIP <xx.xx.xx.xx> specifies the IP address for the switch NEXTIP 192.0.2.2
#NEXTMask <xx.xx.xx.xx> specifies the network mask NEXTMASK 255.255.255.0
#NEXTGateway <xx.xx.xx.xx> specifies the default gateway NEXTGateway 192.0.2.20
If the ip.cfg file specifies an image or agent code, the switch loads the software, even if the same
version is already installed on the switch. Ensuring that the appropriate software is always upgraded
on the units is the correct operation of ip.cfg.
Use the factory default command to reset the switch to the factory default after you insert the USB
memory device in the USB port. The USB memory device must contain the properly formatted
ip.cfg file in the root directory.
Note:
The system does not display a message to indicate the ip.cfg file progress, you need to
connect to the switch after 3 minutes of booting to verify the ip.cfg operation. You can
typically confirm the successful download of ip.cfg by using the CLI show ip command. If
the USB ip.cfg file download succeeded, all parameters read from the file show are present
in the switch and part of the runtime configuration.
December 2017 Quick Start Configuration for ERS 4900 and 5900 Series 73

Configuring management IP addresses using CLI
Configuring a Domain Name Server
Use this procedure to set the default DNS domain name for the switch.
Note:
This default domain name is appended to all DNS queries or commands that do not already
contain a DNS domain name.
Procedure
1. Enter Global Configuration mode:
enable
configure terminal
2. At the command prompt, enter the following command:
ip domain-name <DNS_domain name>
Variable definitions
The following table describes the parameters for the ip domain-name command.
Variable
<DNS_domain_name> Specify the default domain name to be used.
Value
The default form of this command is default ip
domain-name.
The no form of this command is no ip domain-name.
Resolving domain names to IP addresses
Use this procedure to set the domain name servers the switch uses to resolve a domain name to an
IP address.
About this task
A switch can have up to three domain name servers specified for this purpose.
Note:
To enter all three server addresses you must enter the command three times, each with a
different server address.
Procedure
1. Enter Global Configuration mode:
December 2017 Quick Start Configuration for ERS 4900 and 5900 Series 74

Clearing the IP address
enable
configure terminal
2. At the command prompt, enter the following command:
ip name-server [<ipv6_address> | <ip_address_1>]
ip name-server [<ipv6_address> | <ip_address_2>]
ip name-server [<ipv6_address> | <ip_address_3>]
Variable definitions
The following table describes the parameters for the ip name-server command.
Note:
The IPv6 parameter is valid only for switches that support IPv6.
Variable Value
ipv6_address The IPv6 address of the domain name server used
by the switch.
ip_address_1 The IP address of the domain name server used by
the switch.
ip_address_2 Optional. The IP address of a domain name server to
add to the list of servers used by the switch.
ip_address_3 Optional. The IP address of a domain name server to
add to the list of servers used by the switch.
no ip name-server [<ipv6_address> |
<ip_address_1>]
no ip name-server [<ipv6_address> |
<ip_address_2>]
The no form of this command removes domain name
servers from the list of servers used by the switch to
resolve domain names to an IP address.
no ip name-server [<ipv6_address> |
<ip_address_3>]
Clearing the IP address
Use this procedure to clear the IPv4 address and subnet mask or IPv6 address for a switch or a
stack.
Note:
When the IP address or subnet mask is changed, connectivity to Telnet can be lost. Any new
Telnet connection can be disabled and is required to connect to the serial console port to
configure a new IP address.
December 2017 Quick Start Configuration for ERS 4900 and 5900 Series 75

Configuring management IP addresses using CLI
About this task
This command sets the IP address and subnet mask for a stack, switch, or unit to all zeros (0).
Procedure
1. Enter Global Configuration mode:
enable
configure terminal
2. At the command prompt, enter the following command for IPv4 addresses:
no ip address {stack | switch | unit <1–8>}
OR
for IPv6 addresses, enter the following command:
no ipv6 address {stack | switch | unit <1–8>}
Setting the in-band default IP gateway address
Use this procedure to set the default IP gateway address for a switch or a stack.
Note:
When the IP gateway is changed, connectivity to Telnet can be lost.
Important:
Only one management default gateway can operate for each unit or stack. The out-of-band
management default gateway takes precedence over the in-band management default gateway.
When an out-of-band management default gateway is configured, the in-band management
address is reachable only through a directly attached subnet for the management VLAN.
Procedure
1. Enter Global Configuration mode:
enable
configure terminal
2. To configure the IPv4 address of the default gateway, enter the following command at the
command prompt:
ip default-gateway <A.B.C.D>
December 2017 Quick Start Configuration for ERS 4900 and 5900 Series 76

Deleting the in-band default IP gateway address
Deleting the in-band default IP gateway address
Use this procedure to delete the default IP gateway address.
Note:
When the IP gateway is changed, connectivity to Telnet can be lost.
Procedure
1. Enter Global Configuration mode:
enable
configure terminal
2. At the command prompt, enter the following command:
no ip default-gateway
OR
no ipv6 default-gateway
December 2017 Quick Start Configuration for ERS 4900 and 5900 Series 77

Chapter 6: Configuring management IP
addresses using EDM
This chapter provides procedural information you can use to assign, clear, and view in-band and
out-of-band management IP addresses and gateway IP addresses.
Configuring out-of-band management using EDM
Use this procedure to configure the out-of-band management IP address, subnet mask, and default
gateway.
About this task
When you physically connect Ethernet RJ-45 management port for standalone switch or stack to
your network and assign an IP address to the port, you can use the management port to access the
switch or stack using Telnet, SSH, SNMP, HTTP, and HTTPS.
Note:
The out-of-band management IP address must be different than the switch or stack in-band
management IP address.
Procedure
1. From the navigation pane, double-click Edit.
2. In the Edit tree, click Chassis.
3. In the Chassis tree, click Switch/Stack.
4. In the Switch/Stack work area, click the Management IP tab.
5. To configure out-of-band management parameters for a switch, double-click table cells as
required.
6. On the toolbar, click Apply.
7. On the toolbar, you can click Refresh to verify the out-of-band management configuration.
December 2017 Quick Start Configuration for ERS 4900 and 5900 Series 78

Configuring out-of-band management using EDM
Variable definitions
Variable Value
Unit Indicates a stack switch unit, for which to configure
an out-of-band management IP address. Values
range from 1 to 8.
For a stack environment, a Unit value of 1 specifies
the base unit.
For a standalone switch, the Unit value is 1.
IpMgmtAddress Specifies an out-of-band management IP address for
the selected switch.
DEFAULT for IPv4: 0.0.0.0
IpMgmtNetMask Specifies the subnet mask associated with the out-
of-band management IP address.
DEFAULT for IPv4: 0.0.0.0
IpMgmtGateway Specifies the IP address for the out-of-band
management default gateway.
DEFAULT for IPv4: 0.0.0.0
DEFAULT for IPv6: 0:0:0:0:0:0
Important:
If you configure an out-of-band default gateway,
the device disables the in-band default gateway.
The out-of-band management default gateway
takes precedence over the in-band
management default gateway.
Ipv6MgmtAddress Specifies an out-of-band management IP address for
the selected switch.
Specifies the IPv6 address associated with the
physical dedicated out-of-band management port of
a component. For a stackable system in stack mode,
this IPv6 address always applies to the individual
units in the stack.
DEFAULT for IPv6: 0::0/0
Ipv6MgmtNetMask Specifies the subnet mask associated with the out-
of-bank management IP address.
Specifies the IPv6 address associated with the
physical dedicated out-of-band management port of
a component. For a stackable system in stack mode,
this netmask always applies to the individual units in
the stack.
Table continues…
December 2017 Quick Start Configuration for ERS 4900 and 5900 Series 79

Configuring management IP addresses using EDM
Variable Value
DEFAULT for IPv6: 0::0/0
IpMgmtShutdown Specifies whether to enable or disable the
management port for the unit. A value of true
disables the port.
DEFAULT: false
December 2017 Quick Start Configuration for ERS 4900 and 5900 Series 80

Chapter 7: Verification
This chapter contains information about how to verify that your provisioning procedures result in a
functional switch.
Pinging an IP device
You can ping a device to test the connection between a switch and another network device. After
you ping a device, the switch sends an Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) packet to the
target device. If the device receives the packet, it sends a ping reply. After the switch receives the
reply, a message appears that indicates traffic can reach the specified IP address. If the switch does
not receive a reply, the message indicates the address does not respond.
About this task
Use this procedure to ping a device.
Procedure
1. Log on to CLI to enter User EXEC mode.
2. At the command prompt, enter the following command:
ping <IP_address>
where <IP_address> is an IPv4 or IPv6 address.
Verifying the software release
About this task
Use this procedure to display the currently-loaded and operational software load
Procedure
1. Log on to CLI to enter User EXEC mode.
2. At the command prompt, enter the following command:
show boot [diag | image [primary | secondary]]
December 2017 Quick Start Configuration for ERS 4900 and 5900 Series 81

Verification
Example
The following displays the output from the show boot command.
Switch#show boot
Unit Agent Image Secondary Image Active Image Diag Image Active Diag
----- ----------- --------------- ------------ ---------- ----------1 7.0.0.066 7.0.0.042 7.0.0.066 0.0.0.2c 0.0.0.2c
* - Unit requires reboot for new Active Image to be made operational.
# - Unit requires reboot for new Diag to be made operational.
Switch#show boot diag
Unit Diag Image Active Diag
----- ---------- ----------1 0.0.0.2c 0.0.0.2c
# - Unit requires reboot for new Diag to be made operational.
Switch#show boot image
Unit Agent Image Secondary Image Active Image
----- ----------- --------------- -----------1 7.0.0.066 7.0.0.042 7.0.0.066
* - Unit requires reboot for new Active Image to be made operational.
Switch#show boot image primary
Unit Agent Image Active Image
----- ----------- -----------1 7.0.0.163 7.0.0.163
* - Unit requires reboot for new Active Image to be made operational.
Variable definitions
Use the definitions in the following table to use the show boot command.
Variable Definition
diag Displays only information for the agent load.
image [primary |
secondary]
Displays information about the image load. Options are:
• primary—display primary image software version.
• secondary—display secondary image software version.
Important:
When the currently loaded and operational software status is displayed for a stack, the unit
number is replaced by the word All.
Displaying local alarms
You can view local alarms to monitor alarm conditions.
Local alarms are raised and cleared by applications running on the switch. Local alarms are an
automatic mechanism run by the system and do not require any additional user configuration. The
December 2017 Quick Start Configuration for ERS 4900 and 5900 Series 82

Displaying local alarms
raising and clearing of local alarms also creates a log entry for each event. Check alarms
occasionally to ensure no alarms require additional operator attention.
About this task
Use this procedure to display local alarms.
Procedure
1. Enter Global Configuration mode:
enable
configure terminal
2. At the command prompt, enter the following command :
show rmon alarm
December 2017 Quick Start Configuration for ERS 4900 and 5900 Series 83
 Loading...
Loading...