Extreme Networks Summit WM100, Summit WM1000, Summit WM200, Summit WM2000 Getting Started Manual

Summit WM Getting Started Guide
Extreme Networks, Inc.
3585 Monroe Street
Santa Clara, California 95051
(888) 257-3000
(408) 579-2800
http://www.extremenetworks.com
Published: March 2007
Part number: 120385-00 Rev 01

[copyright ©] Alpine, Alpine 3804, Alpine 3802, Altitude, BlackDiamond, BlackDiamond 6808, BlackDiamond 6816,
EPICenter, Ethernet Everywhere, Extreme Ethernet Everywhere, Extreme Networks, Extreme Turbodrive, Extreme Velocity,
ExtremeWare, ExtremeWorks, ExtremeXOS, GlobalPx Content Director, the Go Purple Extreme Solution Partners Logo,
Sentriant, ServiceWatch, Summit, Summit24, Summit48, Summit1i, Summit4, Summit5i, Summit7i, Summit 48i, SummitRPS,
SummitGbX, Triumph, vMAN, the Extreme Networks logo, the Alpine logo, the BlackDiamond logo, the Summit logos, the
Extreme Turbodrive logo, and the Color Purple, among others, are trademarks or registered trademarks of Extreme Networks,
Inc. or its subsidiaries in the United States and other countries. Other names and marks may be the property of their respective
owners.
© 2007 Extreme Networks, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Specifications are subject to change without notice.
Merit is a registered trademark of Merit Network, Inc. Solaris and Java are trademarks of Sun Microsystems, Inc. in the U.S.
and other countries. Avaya is a trademark of Avaya, Inc.
All other registered trademarks, trademarks and service marks are property of their respective owners.
The ExtremeXOS operating system is based, in part, on the Linux operating system. The machine-readable copy of the
corresponding source code is available for the cost of distribution. Please direct requests to Extreme Networks for more
information at the following address:
Legal Department
3585 Monroe Street
Santa Clara CA 95051
Summit WM Getting Started Guide

bkTOC.fm
120385-00 Rev 01, March 2007
Summit WM, Getting Started Guide 3
For internal use only Contents
Contents 0
1 About this guide . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
1.1 Who should use this guide. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
1.2 What is in this guide. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
1.3 Formatting conventions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
1.4 Document feedback. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
2 Summit WM-Series WLAN Switch Software Solution . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
2.1 Conceptual model . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
2.1.1 Summit WM Switch. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
2.1.1.1 Web-based centralized management of Altitude APs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
2.1.1.2 Virtualized user segmentation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
2.1.1.3 Summit Switch WM100: 32 WM-ADsAuthentication and encryption. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
2.1.1.4 Intrusion detection. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
2.1.1.5 Automatic assignment of IP addresse s to th e clien t devices. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
2.1.1.6 Web authentication . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
2.1.2 Altitude AP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
2.1.3 Summit WM-Series WLAN Solution topology and network elements. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
2.1.4 Discovery mechanism in Summit WM-Series WLAN Solution . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
2.1.4.1 Discovery mechanism between Altitude AP and Summit WM Switch. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
2.1.4.2 Discovery mechanism between mobility manager and mobility agents . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
2.1.5 DHCP usage scenarios in Summit WM-Series WLAN Solution . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
2.1.5.1 DHCP for Altitude APs. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
2.1.5.2 DHCP for WM-AD . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
2.1.5.3 DHCP relay for WM-AD. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
2.1.5.4 DHCP for traffic bridged locally at Altitude AP. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
2.2 Summit WM Switch’s physical description. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
2.2.1 Summit Switch WM2000 front panel. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
2.2.1.1 LED states and Seven Segment Display (SSD) codes. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
2.2.2 Summit Switch WM2000 back panel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
2.2.3 Summit Switch WM1000 front panel. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
2.2.4 Summit Switch WM1000 back panel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
2.2.5 Summit Switch WM100 front panel. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
2.2.6 Summit Switch WM100 back panel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
2.3 Collecting information for installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
3 Summit WM-Series WLAN Switch configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
3.1 Accessing the Summit WM-Series WLAN Switch for the first time . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
3.2 Connecting the Summit WM Switch to the enterprise network . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
3.3 Changing the administrator password . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
3.4 Configuring the network time . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
3.4.1 Configuring the network time using the system’s time . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
3.4.2 Configuring the network time using the NTP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
3.5 Generating a software license key. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
3.5.1 Retrieving a lost license key . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
3.6 Applying a license key . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
4 Physical ports configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
4.1 Physical data ports overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49

Contents For internal use only
120385-00 Rev 01, March 2007
4 Summit WM, Getting Started Guide
bkTOC.fm
4.2 Configuring data ports . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
5 Routing configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
5.1 Configuring static routing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
5.1.1 Viewing the forwarding table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
5.2 Configuring the OSPF routing. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
5.2.1 Enabling OSPF globally on the Summit WM Switch . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56
5.2.2 Defining the global OSPF parameters. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
5.2.2.1 Confirming the ports are set for OSPF. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58
6 Configuring DHCP, DNS and IAS services . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
6.1 DHCP service configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
6.1.1 Configuring DHCP in Windows 2003 Server. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
6.1.2 Configuring DHCP in Red Hat Linux Server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
6.2 IAS service configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 67
6.2.1 Installing IAS on Windows 2003 Server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
6.2.2 Enabling IAS to authenticate users in active directory . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
6.2.3 Configuring IAS properties . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
6.2.4 Configuring Summit WM Switch as IAS client. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
6.2.5 Configuring Remote Access Policies. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 72
6.3 DNS service configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 76
6.3.1 Configuring DNS for internet access . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 77
6.3.2 Configuring DNS for Altitude APs discovery . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 78
7 Altitude AP’s configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 81
7.1 Altitude AP overview. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 81
7.2 Configuring the Altitude APs for the first time. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 82
7.2.1 Manually approving pending Altitude APs. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 84
7.3 Assigning names to Altitude APs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 85
7.4 Modifying Altitude APs’ properties . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 85
7.5 Configuring static IP address for Altitude APs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 86
7.6 Configuring VLAN tags for Altitude APs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 91
7.6.1 Resetting the Altitude AP to its factory default settings. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 92
7.7 Altitude AP’s LED states. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 93
8 WM-AD configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 95
8.1 WM-AD topology overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 95
8.2 Creating and configuring a Routed WM-AD . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 97
8.3 Creating and configuring a Bridge Traffic Locally At SWM WM-AD . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 100
8.4 Creating and configuring a Bridge Traffic Locally At WAP WM-AD . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 101
8.5 Configuring authentication mechanism for WM-AD . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 102
8.5.1 Authentication mechanism for SSID network assignment. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 103
8.5.1.1 Configuring internal Captive Portal authentication. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 104
8.5.1.2 Configuring external Captive Portal authentication . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 108
8.5.1.3 No Captive Portal support . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 109
8.5.1.4 Configuring MAC-based authentication . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 110
8.5.2 Authentication mechanism for AAA network assignment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 111
8.5.2.1 Configuring 802.1x authentication . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 111
8.5.2.2 Configuring MAC-based authentication . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 112
8.6 Configuring filtering rules . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 112
8.6.1 Configuring filtering rules for filters in SSID network assignment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 112
8.6.1.1 Configuring filtering rules for Exception filter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 112
8.6.1.2 Configuring filtering rules for a Non-authenticated filter. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 113
8.6.1.3 Configuring filtering rules for Default filter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 114

bkTOC.fm
120385-00 Rev 01, March 2007
Summit WM, Getting Started Guide 5
For internal use only Contents
8.6.2 Configuring filtering rules for filters in AAA network assignment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 115
8.7 Configuring privacy for WM-AD . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 115
8.7.1 Configuring privacy for SSID network assignment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 116
8.7.1.1 Configuring Static WEP. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 116
8.7.1.2 Configuring WPA-PSK. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 117
8.7.2 Configuring privacy for AAA network assignment. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 118
8.7.2.1 Configuring Static WEP. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 119
8.7.2.2 Configuring Dynamic WEP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 119
8.7.2.3 Configuring Wi-fi Protected Access (WPA v1 and WPA v2) privacy. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 119
9 Availability and Mobility configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 123
9.1 Availability overview. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 123
9.2 Configuring availability feature. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 123
9.2.1 Defining a WM-AD with the same SSID on both the Summit WM Switches. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 124
9.2.2 Assigning radios to WM-AD, and changing the poll timeout value on Altitude AP configuration screen .
125
9.2.3 Assigning the Altitude APs to their home Summit WM Switch . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 125
9.2.4 Enabling availability pair, defining primary Summit WM Switch, and selecting security mode. . . . . . 127
9.2.5 Viewing the Altitude AP availability display. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 128
9.2.6 Viewing the active Altitude APs report . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 129
9.3 Mobility overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 130
9.4 Configuring mobility . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 131
9.4.1 Configuring a Summit WM Switch as a mobility manager . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 131
9.4.2 Configuring Summit WM Switch as a mobility agent . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 134
9.4.2.1 Viewing the Mobility Manager display . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 135
9.4.2.2 Viewing Mobility Agent display . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 136
Index . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 137

Contents For internal use only
120385-00 Rev 01, March 2007
6 Summit WM, Getting Started Guide
bkTOC.fm

HWC_GSG_Preface.fm
120385-00 Rev 01, March 2007
Summit WM, Getting Started Guide 7
About this guide
Who should use this guide
1 About this guide
The purpose of the Getting Started Guide is to assist you in deploying Summit
WM-Series WLAN Solution by mapping preparation, installation, and
configuration tasks into a logical and efficient flow.
You can use this guide independently of other documents. However, if you are
looking for detailed information on any aspect of the system’s installation,
configuration, or management, use this guide in conjunction with the Summit
WM-Series WLAN Switch Software User Guide.
This guide is based on the following product families:
• Summit Switch WM2000
• Summit Switch WM200
• Summit SwitchWM1000
• Summit Switch WM100
1.1 Who should use this guide
The guide is written for Extreme Networks’ clients.
You must be familiar with computer networking concepts to use this guide.
1.2 What is in this guide
This contents in this guide are organized under the following ch ap ters:
• Chapter 1, “About this guide”– Describes the purpose, the target audience
and the architecture of this guide.
• Chapter 2, “Summit WM-Series WLAN Switch Sof tware Solution” – Captures
the essential concepts of the solution.
• Chapter 3, “Summit WM-Series WLAN Switch configuration”– Explains how
to configure the Summit WM Switch’s settings in order to make it operation al.
• Chapter 4, “Physical ports configuration”– Describes how to configure the
Summit WM Switch’s physical ports.
• Chapter 5, “Routing configuration”– Explains how to configur e the static and
OSPF routings on the Summit WM Switch’s physical ports.
• Chapter 6, “Configuring DHCP, DNS and IAS services”– Describes how to
configure DHCP , DNS and IAS services on Windows 2003 Server . In addition,
the chapter explains how to configure DHCP service on a Linux-based se rver .

About this guide
HWC_GSG_Preface.fm
Formatting conventions
120385-00 Rev 01, March 2007
8 Summit WM, Getting Started Guide
• Chapter 7, “Altitude AP’s configuration”– Explains how to configure and
manage the Altitude APs through the Summit WM Switch.
• Chapter 8, “WM-AD configuration”– Describes how to create and configure
WM-AD via the Summit WM Switch.
• Chapter 9, “Availability and Mobility configuration” – Explains how to
configure availability and mobility features via the Summit WM Switch.
1.3 Formatting conventions
The document uses the following formatting conventions to make it easier to find
information and follow procedures:
• Bold text is used to identify components of the management interface, such
as menu items and section of pages, as well as the na mes of buttons and text
boxes.
• For example: Click Logout.
• Monospace font is used in code examples and to indicate text that you type.
• For example: Type https://<SWM-address>[:mgmt-port>]
• The following symbols are used to draw your attention to additional
information:
Note: Notes identify useful information, including reminders, tips, or other
ways to perform a task.
Note: Cautionary notes identify essential information, which if ignored can
adversely affect the operation of your equipment or software.
Note: Warning notes iden tify essential information, which if ignored can lead
to personal injury.

HWC_GSG_Preface.fm
About this guide
Document feedback
120385-00 Rev 01, March 2007
Summit WM, Getting Started Guide 9
1.4 Document feedback
If you have any problems using this document, please contact the next level of
support:
• Customers should contact the Extreme Networks Technical Assistance
Center (TAC).
When you call, please have the following information ready. This will help us to
identify the document that you are referring to.
• Title: Summit WM-Series WLAN Switch Software Getting Started Guide
• Part Number: 120385-00 Rev 01

About this guide
HWC_GSG_Preface.fm
Document feedback
120385-00 Rev 01, March 2007
10 Summit WM, Getting Started Guide

HWC_GSG_Chapter 1_Overview.fm
120385-00 Rev 01, March 2007
Summit WM, Getting Started Guide 11
Summit WM-Series WLAN Switch Software Solution
Conceptual model
2 Summit WM-Series WLAN Switch Software Solution
This chapter describes the essential concepts of Summit WM-Series WLAN
Switch Software Solution.
The topics in this chapter are organized as follows:
• Conceptual model
• Collecting information for installation
2.1 Conceptual model
The Summit WM-Series WLAN Switch Software Solution is an enterprise WLAN
solution that consists of the following components:
• Summit WM-Series WLAN Switch (Summit WM Switch)
• Altitude AP
• Summit WM-Series WLAN Switch Software
2.1.1 Summit WM Switch
The Summit WM Switch is a high-performance server that provides several
functions, including centralized management and configuration of Altitude APs,
user authentication, and advanced radio freque ncy management.
The Summit WM Switch is driven by Summit WM-Series WLAN Switch Software.
The software resides on the Summit WM Switch and provides an intuitive webbased interface — Extreme Networks Summit WM-Series Console to enable you
to manage the entire wireless network from a wired laptop, o r a PC connected to
the network. A command line interface is also available to manage the wireless
network.
The Summit WM Switch is a full-functioning dynamic router that aggregates and
coordinates all Altitude APs and manages client devices.
Some key features of the Summit WM Switch provided in the following sections:

Summit WM-Series WLAN Switch Software Solution
HWC_GSG_Chapter 1_Overview.fm
Conceptual model
120385-00 Rev 01, March 2007
12 Summit WM, Getting Started Guide
2.1.1.1 Web-based centralized management of Altitude APs
The Summit WM Switch enables you to monitor and manage Altitude APs from a
centralized web-based interface called the Extreme Networks Summit WMSeries Console. You can separately configure, enable, or disable each Altitude
AP from the Summit WM Switch using the Extreme Networks Summit WM-Series
Console.
The Extreme Networks Summit WM-Series Console also allows you to group the
APs of similar attributes into one of ten upgrade profiles for the purpose of
deploying software upgrades.You can initiate the software updates on a profile
and the updates will be deployed to each AP in the profile. This saves you from
the cumbersome task of deploying the updates to each AP individually.
2.1.1.2 Virtualized user segmentation
The Summit WM Switch allows you to create and manage unique WM Access
Domain that enables you to group specific mobile users, devices and applications
on the basis of policy class in order to provide unique levels of service, access
permissions, encryption, and device authorization.
A WM-AD segment is a virtual network and each Altitude Access Points can
support multiple WM-AD segments.
WM-AD optimizes the dynamic nature of WLAN mobility as WM-AD groups can
follow users without depending on the physical configuration of the network.
The following is the list of Summit WM Switches and the number of WM-ADs they
can support.
• Summit Switch WM2000: 64 WM-ADs
• Summit Switch WM200: 32 WM-ADs
• Summit Switch WM1000: 50 WM-ADs
2.1.1.3 Summit Switch WM100: 32 WM-ADsAuthentication and
encryption
The Summit WM Switch and Altitude AP work together to support comprehensive
authentication, encryption, and intrusion detection capabilities. A range of robust
security features based upon the 802.11 and WPA2 standards ensure tha t your
network stays protected.
802.1X mechanism in conjunction with RADIUS and pre-shared key
authentication ensure that only authorized users can access the network.
Other features include Captive Portal for redirected web-based authentication.

HWC_GSG_Chapter 1_Overview.fm
Summit WM-Series WLAN Switch Software Solution
Conceptual model
120385-00 Rev 01, March 2007
Summit WM, Getting Started Guide 13
2.1.1.4 Intrusion detection
The Summit WM Switch allows you to configure Altitude APs to detect rogue
access points on the network by scanning the radio frequency (RF) space at
specific intervals. Scan results are then forwarded to the Summit WM Switch; the
Summit WM Switch processes and presents the data centrally. Rogue detection
data can be viewed via the Extreme Networks Summit WM-Series Console.
2.1.1.5 Automatic assignment of IP addresses to the client
devices
The Summit WM Switch has built-in DHCP server that assigns IP addresses to
the client devices. The Summit WM Switch is also capable of working with an
external DHCP server.
2.1.1.6 Web authentication
The Summit WM Switch has a built-in Captive Portal capability that allows Web
authentication (Web redirection) to take place. The Summit WM Switch is also
capable of working with external Captive Portal.
2.1.2 Altitude AP
Altitude APs are wireless LAN access points that bridge the network traffic
between wireless devices and the Ethernet LAN .
2.1.3 Summit WM-Series WLAN Solution topology
and network elements
The following figure illustrates a typical configuration with a single Summit WM
Switch and two Altitude APs, each supporting a wireless device. A RADIUS
server on the network provides user authentication, and a DHCP server assigns
IP addresses to the Altitude APs. Network inter-connectivity is provided by the
infrastructure routing and switching devices.
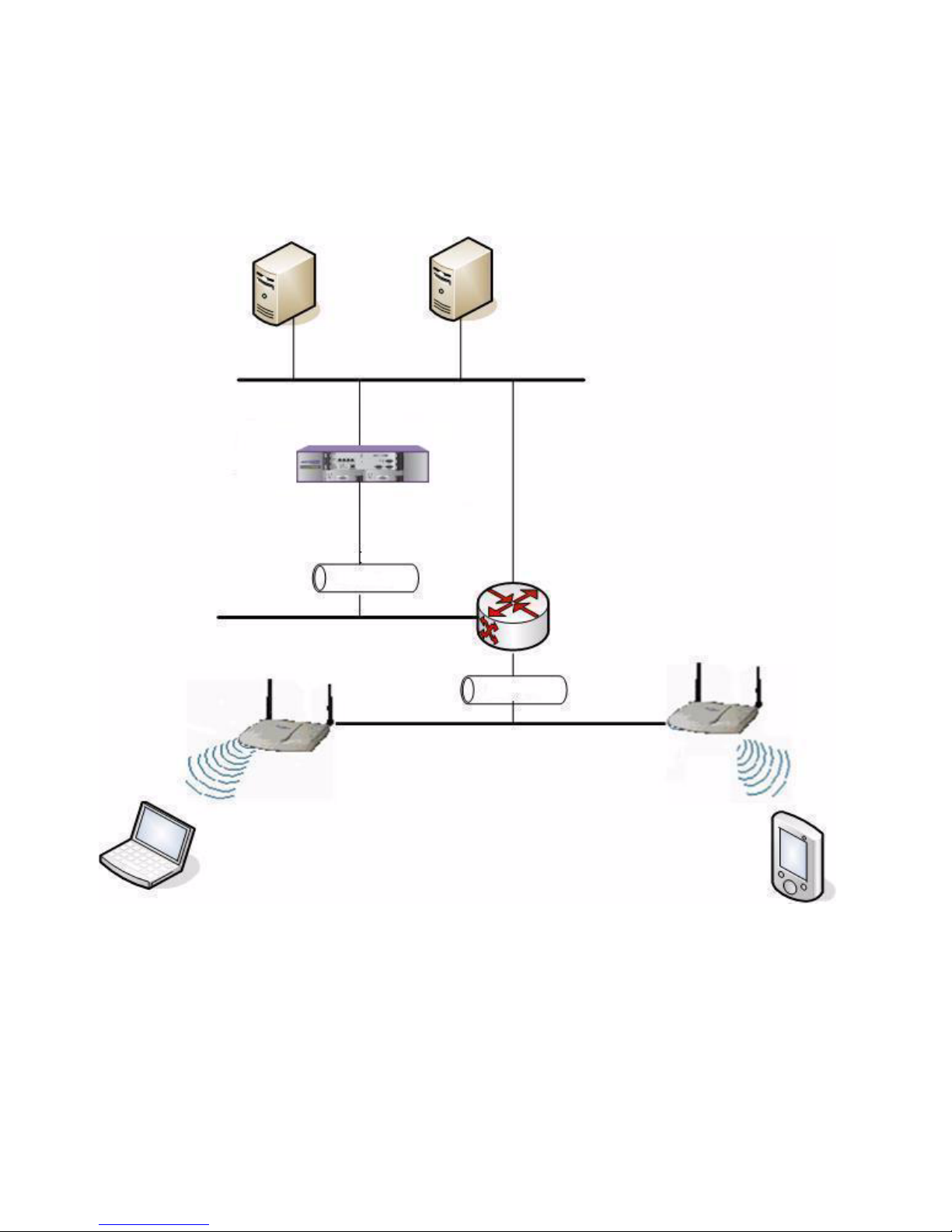
Summit WM-Series WLAN Switch Software Solution
HWC_GSG_Chapter 1_Overview.fm
Conceptual model
120385-00 Rev 01, March 2007
14 Summit WM, Getting Started Guide
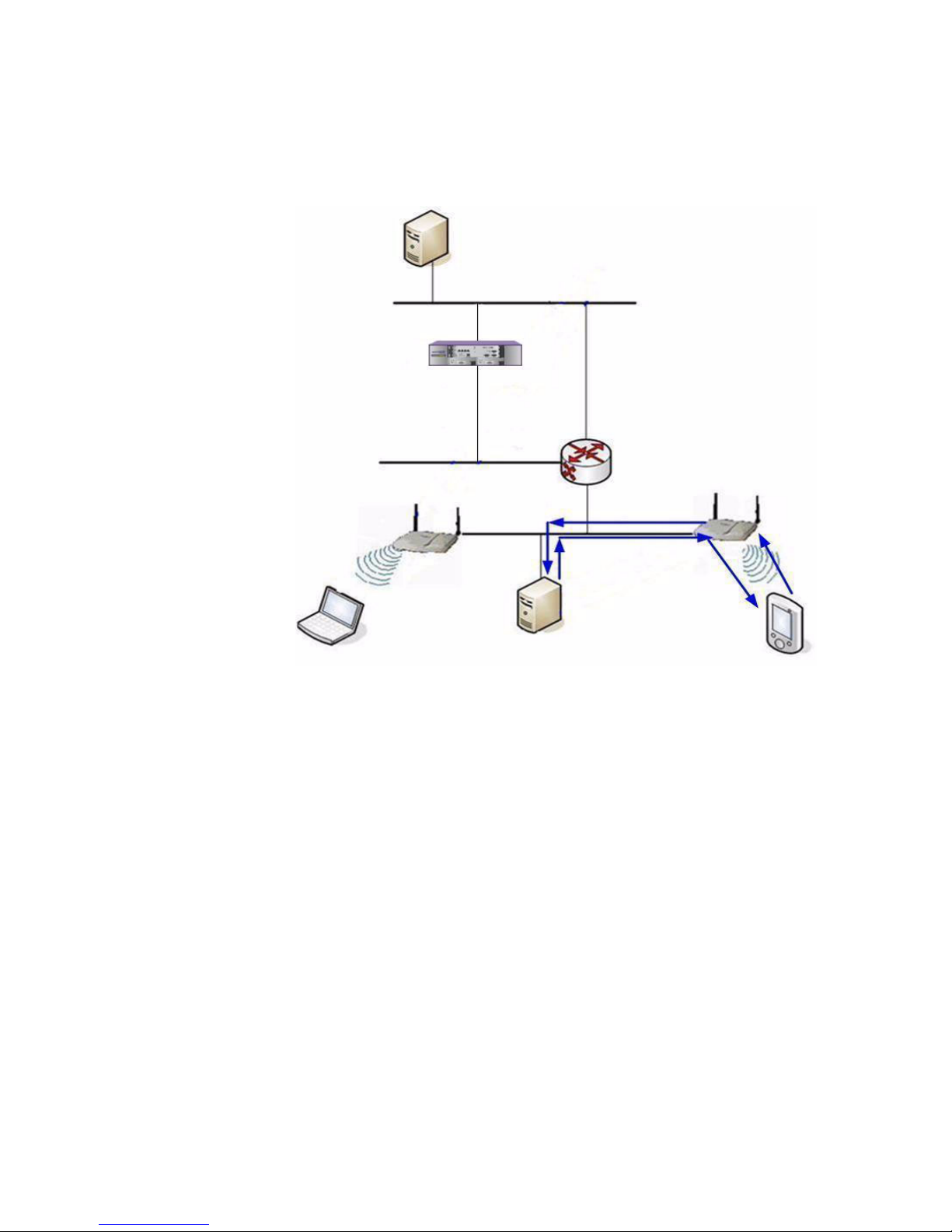
Figure 1 Summit WM-Series WLAN topology
The Summit WM Switch supports the following network elements.
• RADIUS Server (Remote Access Dial-in User Service) – An authentication
server that assigns and manages ID and Password protection throughout the
network. The RADIUS server system can be set-up for certain standard
attributes such as filter ID, and for the vendor specific attributes (VSAs). The
Summit WM Switch supports external RADIUS server.
Summit WM-Series WLAN Topology
DHCP
Server
Wireless Device
Router
Altitude AP
Altitude AP
Control & Routing
• The Summit WM Switch
authenticates wireless user
• The Summit WM Switch
forwards the IP packet to the
wired network
Tunnelling
• Altitude AP sends data traffic to
the Summit WM Switch through
the UDP tunnel called CTP
• The Summit WM Switch
controls the Altitude APs
through the CTP tunnel
Wireless Device
Ethernet
RADIUS
Server
Ethernet
Summit WM Switch

HWC_GSG_Chapter 1_Overview.fm
Summit WM-Series WLAN Switch Software Solution
Conceptual model
120385-00 Rev 01, March 2007
Summit WM, Getting Started Guide 15
• DHCP Server (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) – A server that
assigns the IP addresses, gateways, and subnet masks dynamically. The
external DHCP server depicted in Figure 2-1 is primarily utilized to provide
addresses to infrastructure equipment such as APs. T he IP addresses to the
mobile devices are provided by the built-in DHCP server of Summit WM
Switch. You can also configure the Summit WM Switch to relay DHCP
requests to the external DHCP server.
• SLP (Service Location Protocol) – A service discovery protocol that allows
computers and other devices to find services in a local area network without
prior configuration. The client applications are user agents and services that
are advertised by a service agent. In larger installations, a directory agent
collects information from service agents and creates a central repository. SLP
is one of the several modes that the Summit WM Switch uses to discover the
Altitude APs.
• Domain Name Server – A server that translates the domain names into IP
addresses. The DNS is used as an alternative mechanism for the a utoma tic
discovery process. The Summit WM Switch, its software, and the APs rely on
the DNS for Layer 3 deployments. In addition, DNS is utilized for the static
configuration of APs. The Summit WM Switch can be registered in DNS to
provide DNS assisted AP discovery.
2.1.4 Discovery mechanism in Summit WM-Series
WLAN Solution
The Summit WM-Series WLAN Solution provides auto-discovery capabilities
between the following components:
• Altitude APs and Summit WM Switch
• Mobility manager and mobility agents (For more information, see Chapter 9,
“Availability and Mobility configuration”.)
2.1.4.1 Discovery mechanism between Altitude AP and
Summit WM Switch
The Altitude APs discover the Summit WM Switch by one of the following modes:
• SLP (Multicast and Unicast) – For more information, see SLP’s description in
Section 2.1.4, “Discovery mechanism in Summit WM-Series WLAN Solution”,
on page 15.
• DNS – For more information, see Domain Name Server’s description in
Section 2.1.4, “Discovery mechanism in Summit WM-Series WLAN Solution”,
on page 15.

Summit WM-Series WLAN Switch Software Solution
HWC_GSG_Chapter 1_Overview.fm
Conceptual model
120385-00 Rev 01, March 2007
16 Summit WM, Getting Started Guide
• St atic IP address config uration – Summit WM Switch’s IP address is defined
in Altitude AP configuration. For more information, see Section 7.5,
“Configuring static IP address for Altitude APs”, on page 86.
2.1.4.2 Discovery mechanism between mobility manager and
mobility agents
The mobility agents discover the mobility manager by one of the following modes:
• SLP with DHCP Option 78 – The mobility agent on each Summit WM Switch
discovers the address of the mobility manager using DHCP Option 78.
• Direct IP address option – Defined while configuring the mob ility ag en t. By
explicitly defining the manager’s IP address while configuring the agents,
enables the manager and agents to find each other directly witho ut using the
SLP discovery mechanism.
2.1.5 DHCP usage scenarios in Summit WM-Series
WLAN Solution
DHCP usage has four scenarios in Summit WM-Series WLAN Solution:
• DHCP for Altitude APs
• DHCP for WM-AD
• DHCP relay for WM-AD
• DHCP for traffic bridged locally at Altitude AP
The following sections explain the four scenarios with the help of graphical
illustrations.
HWC_GSG_Chapter 1_Overview.fm
Summit WM-Series WLAN Switch Software Solution
Conceptual model
120385-00 Rev 01, March 2007
Summit WM, Getting Started Guide 17
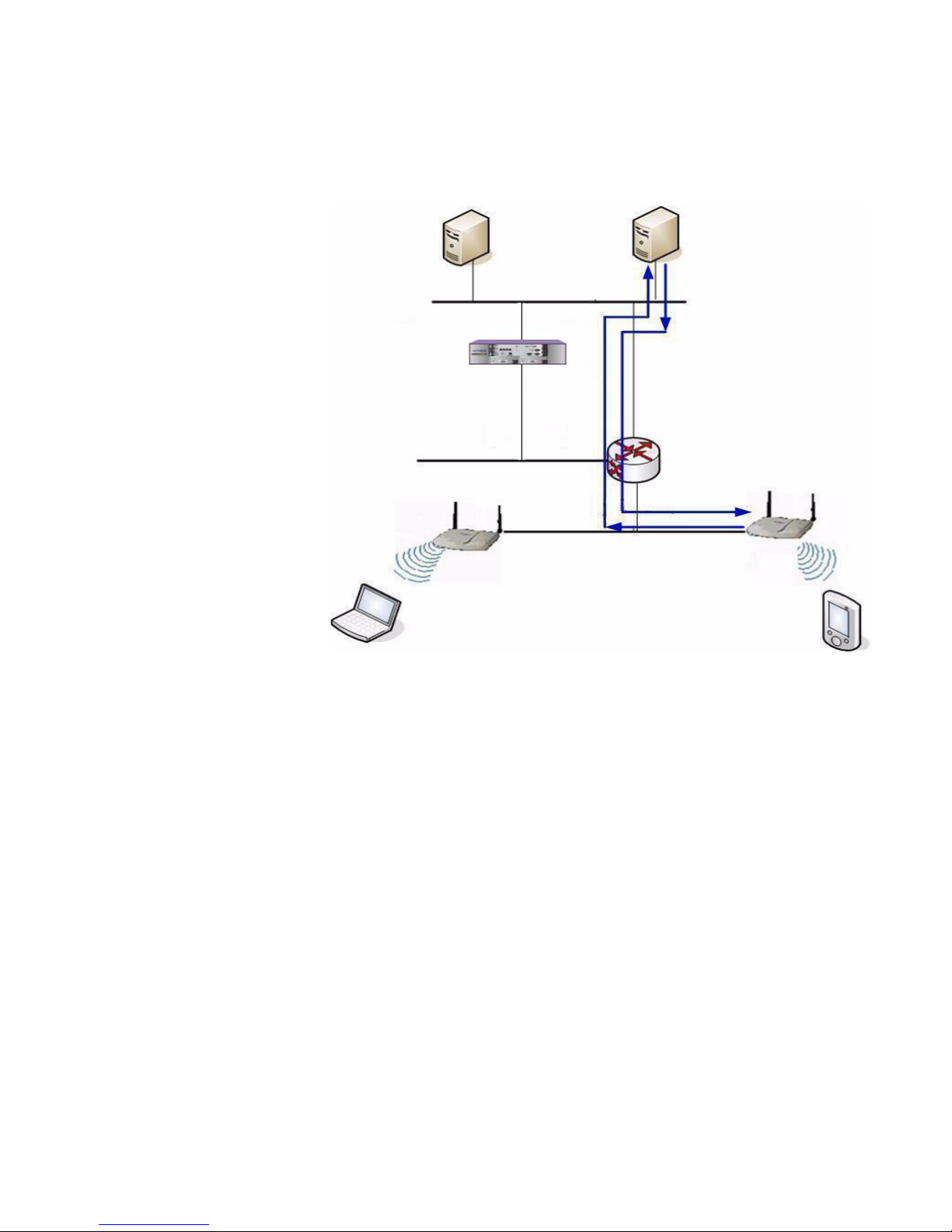
2.1.5.1 DHCP for Altitude APs
Figure 2 DHCP for Altitude APs
Y ou can use Windows 2003 server , amongst others, for deploying DHCP service
for Altitude APs. For more information, see Section 6.1, “DHCP service
configuration”, on page 61.
* The Altitude AP
requests an IP
address from the
external DHCP
server
* The DHCP server
responds by
sending the IP
address to the
Altitude AP
Altitude AP
Altitude AP
Wireless
Device
Wireless
Device
DNS Server
DHCP Server
Summit WM Switch
Summit WM-Series WLAN Switch Software Solution
HWC_GSG_Chapter 1_Overview.fm
Conceptual model
120385-00 Rev 01, March 2007
18 Summit WM, Getting Started Guide
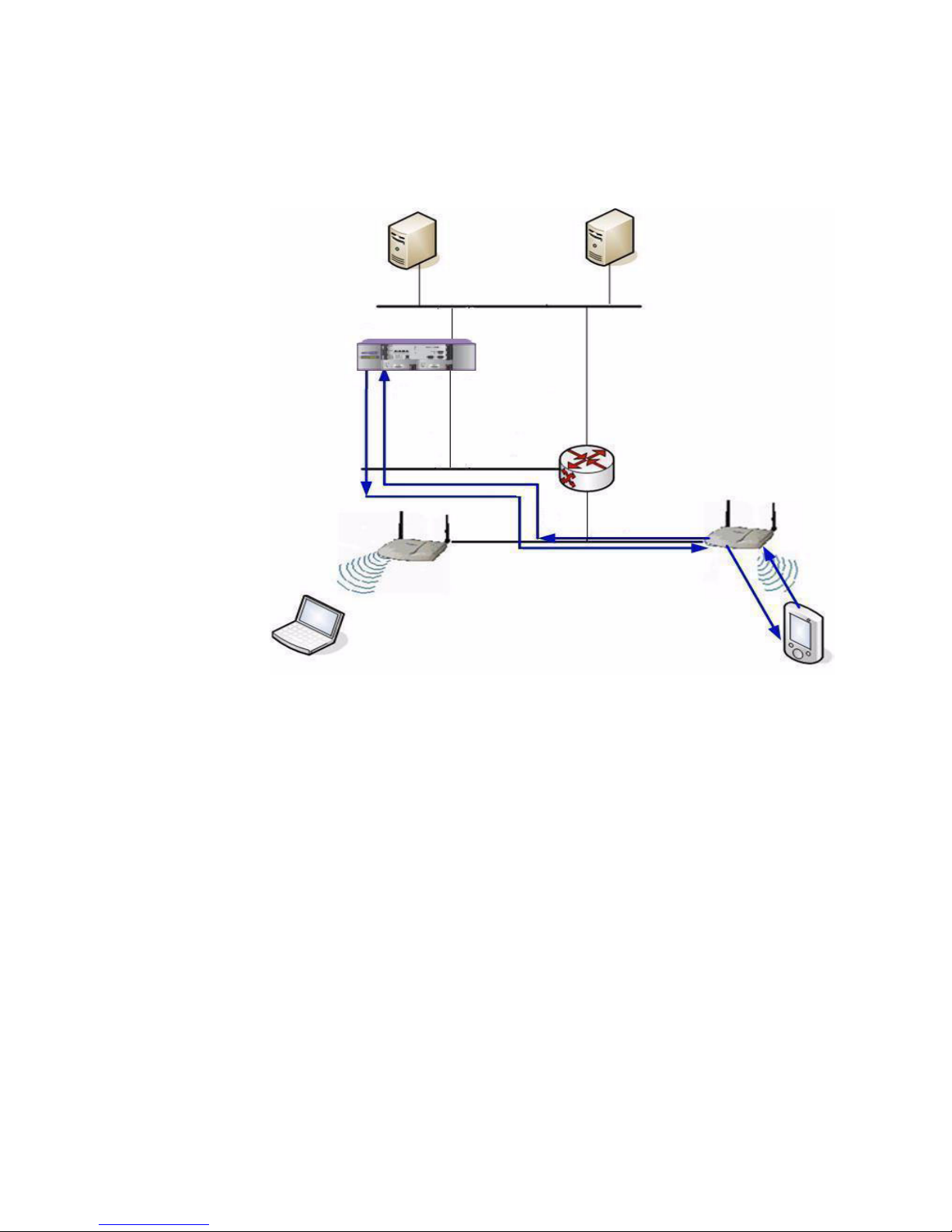
2.1.5.2 DHCP for WM-AD
Figure 3 DHCP for WM-AD
The DHCP configuration for WM-AD is done via Summit WM Switch. For more
information, see Section 8.2, “Creating and configuring a Routed WM-AD”, on
page 97.
* The wireless device
requests an IP address from
Altitude AP
* The Altitude AP forwards
the request to Summit WM
Switch via WM-AD tunnel
* The built-in DHCP server
in Summit WM Switch
responds by sending the IP
address to Altitude AP
* The Altitude AP sends the
IP address to the wireless
device
.
Wireless
Device
Wireless
Device
Altitude AP
Summit WM Switch
DHCP Server
DNS Server
HWC_GSG_Chapter 1_Overview.fm
Summit WM-Series WLAN Switch Software Solution
Conceptual model
120385-00 Rev 01, March 2007
Summit WM, Getting Started Guide 19
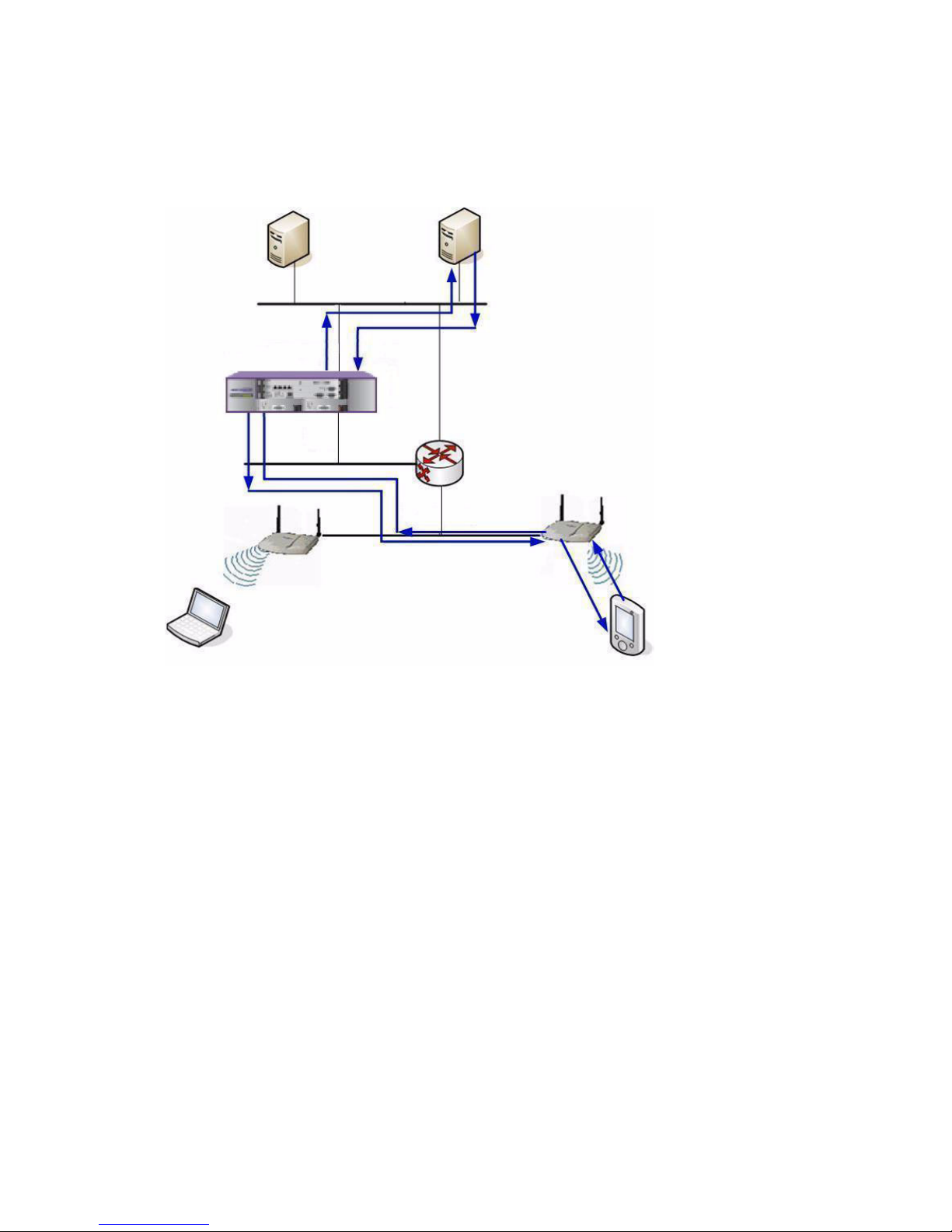
2.1.5.3 DHCP relay for WM-AD
Figure 4 DHCP relay for WM-AD
The DHCP relay configuration is done via Summit WM Switch. For more
information, see Section 8.2, “Creating and configuring a Routed WM-AD”, on
page 97.
* A wireless device sends a
request for IP address to
Altitude AP
* The Altitude AP forwards
the request to Summit WM
Switch via WM-AD tunnel
* The Summit WM Switch
relays the request to the
DHCP server
* The DHCP server responds
by sending the IP address to
the Summit WM Switch
* The Summit WM Switch
relays the IP address to the
Altitude AP
* The Altitude AP sends the
IP address to the wireless
device
DNS Server
DHCP Server
Wireless
Device
Altitude AP
Altitude AP
Wireless
Device
Summit WM Switch
Summit WM-Series WLAN Switch Software Solution
HWC_GSG_Chapter 1_Overview.fm
Summit WM Switch’s physical description
120385-00 Rev 01, March 2007
20 Summit WM, Getting Started Guide
2.1.5.4 DHCP for traffic bridged locally at Altitude AP
Figure 5 DHCP for traffic bridged locally at Altitude AP
The DHCP relay configuration is done via Summit WM Switch. For more
information, see Section 8.4, “Creating and configuring a Bridge T raffic Locally At
WAP WM-AD”, on page 101.
2.2 Summit WM Switch’s physical description
This section provides a physical description of the Summit WM Switch.
2.2.1 Summit Switch WM2000 front panel
The Summit Switch WM2000is composed of the following three cards:
• Media Flash 1000 (MF 1000)
• Network Processor 4000 (NP 4000)
• Supervisor 1100 (SC 1100)
* A wireless device sends a
request for IP address to
Altitude AP
* The Altitude AP forwards
the request to the DHCP
server
* The DHCP server responds
by sending the IP address to
the Altitude AP
* The Altitude AP sends the
IP address to the wireless
device
Wireless
Device
Wireless
Device
Altitude AP
Altitude AP
DHCP Server
DNS Server
Summit WM Switch
HWC_GSG_Chapter 1_Overview.fm
Summit WM-Series WLAN Switch Software Solution
Summit WM Switch’s physical description
120385-00 Rev 01, March 2007
Summit WM, Getting Started Guide 21
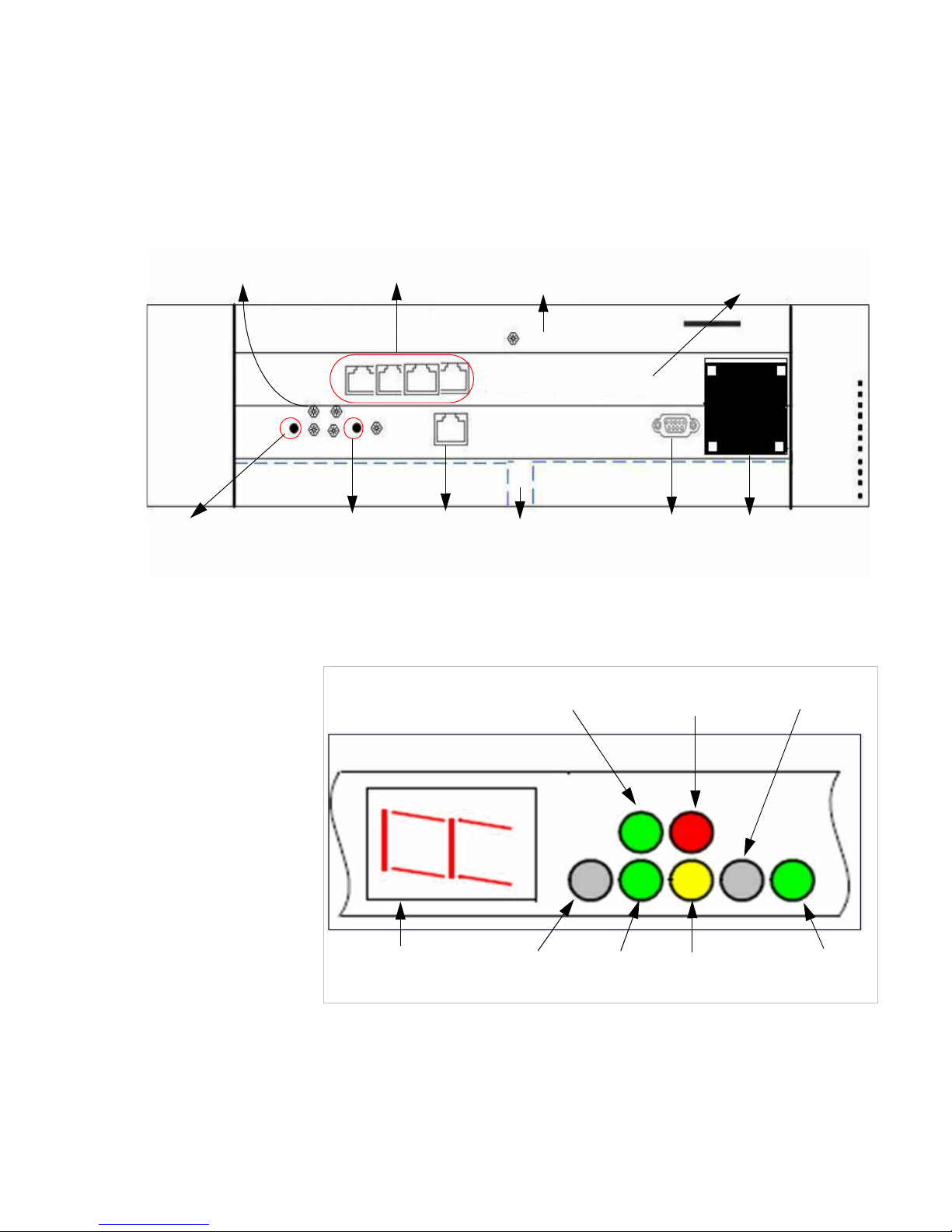
The following figure identifies the main component s on the fr ont pane l of Summit
Switch WM2000
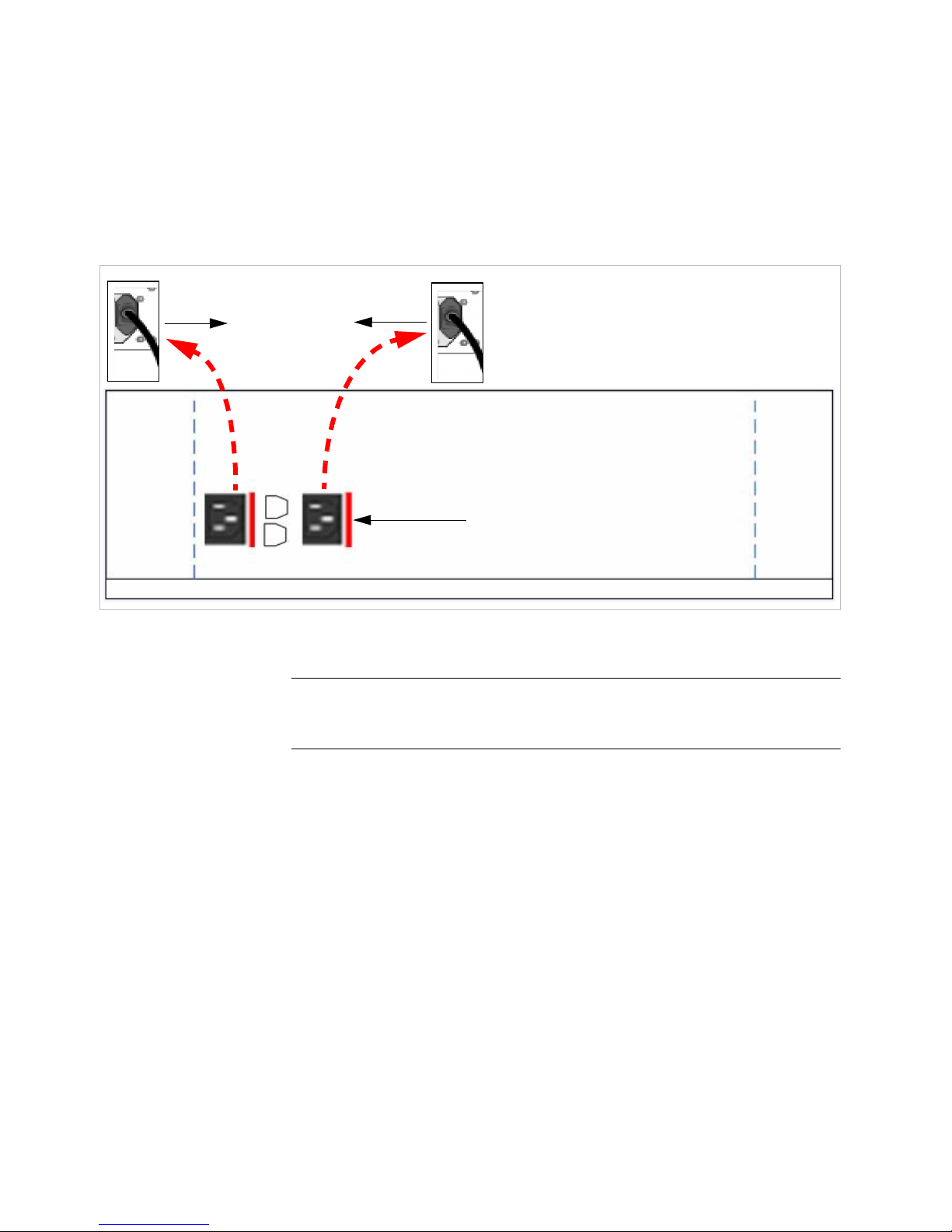
Figure 6 Summit Switch WM2000 front panel
The Summit Switch WM2000 has five LED lights and two switches on its front
panel.
Figure 7 Summit Switch WM2000’s LED lights and switches
The description of the LED states and switches is provided below:
• Reset Switch – Reboots the system.
Reset
Switch
Diagnostic
Switch
RJ45 Port
Console
Port
Data Ports
LED Lights
Supervisor
1100 Card
Media Flash 1000 Card Network Processor 4000
Card
Console Adapter
Reset
Switch
WARNING
LED
ERROR
LED
INT
LED
Diagnostic
Switch
RUN
LED
ACT
LED
Seven-Segment
Display
Summit WM-Series WLAN Switch Software Solution
HWC_GSG_Chapter 1_Overview.fm
Summit WM Switch’s physical description
120385-00 Rev 01, March 2007
22 Summit WM, Getting Started Guide
• RUN LED – Indicates the CPU’s initialization has completed and the system
is ready to provide application level services.
• ACT LED – Indicates the system’s software is in active running state.
• WARNING/ERROR LEDs – Indicate a problem in the running state of the
system.
• Whenever either of the alarm LEDs is lit, the seven-segm ent display
provides the corresponding code point for th e e rror ind ica tion. Whe n the
system is fully active and running, the console displays the letter A as
seen in Figure 7.
• Diagnostic Switch – Pressing the Reset and Diagnostic switch
simultaneously reboots the system in diagnostic mode.
Note: The diagnostic switch should be used only upon the request of a service
technician.
• INT LED – Not used in the current release.
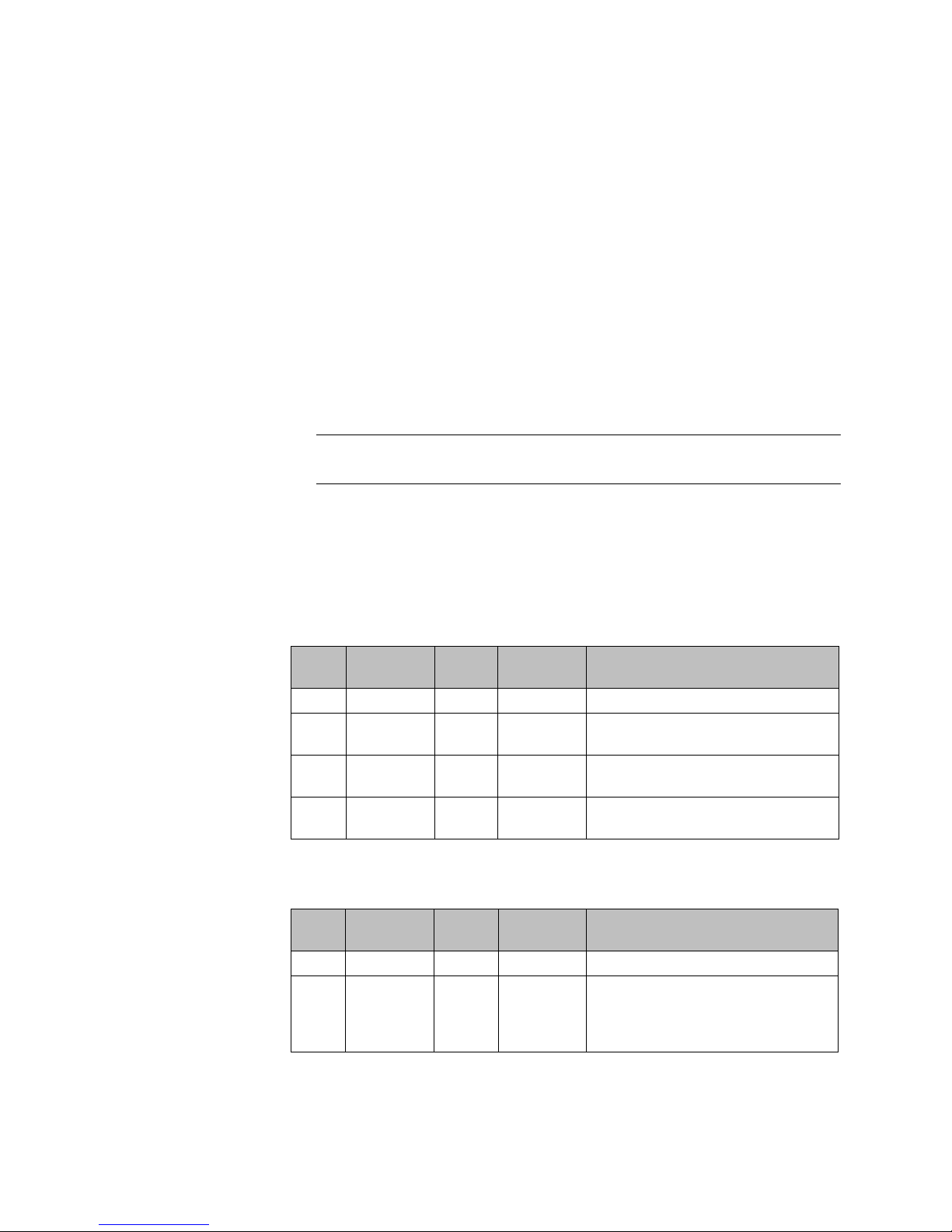
2.2.1.1 LED states and Seven Segment Display (SSD) codes
Application initialization
Warning conditions
Active
LED
Warning
LED
Error
LED
SSD Code Condition
Green 0 Application initialization started.
Green 1 Forwarding Engine initialization
complete. Application initialization.
Green A Application initialization complete.
System active.
Green H System halted. Administrator requested
halting of system.
Table 1 LED states and SSD codes during application initialization
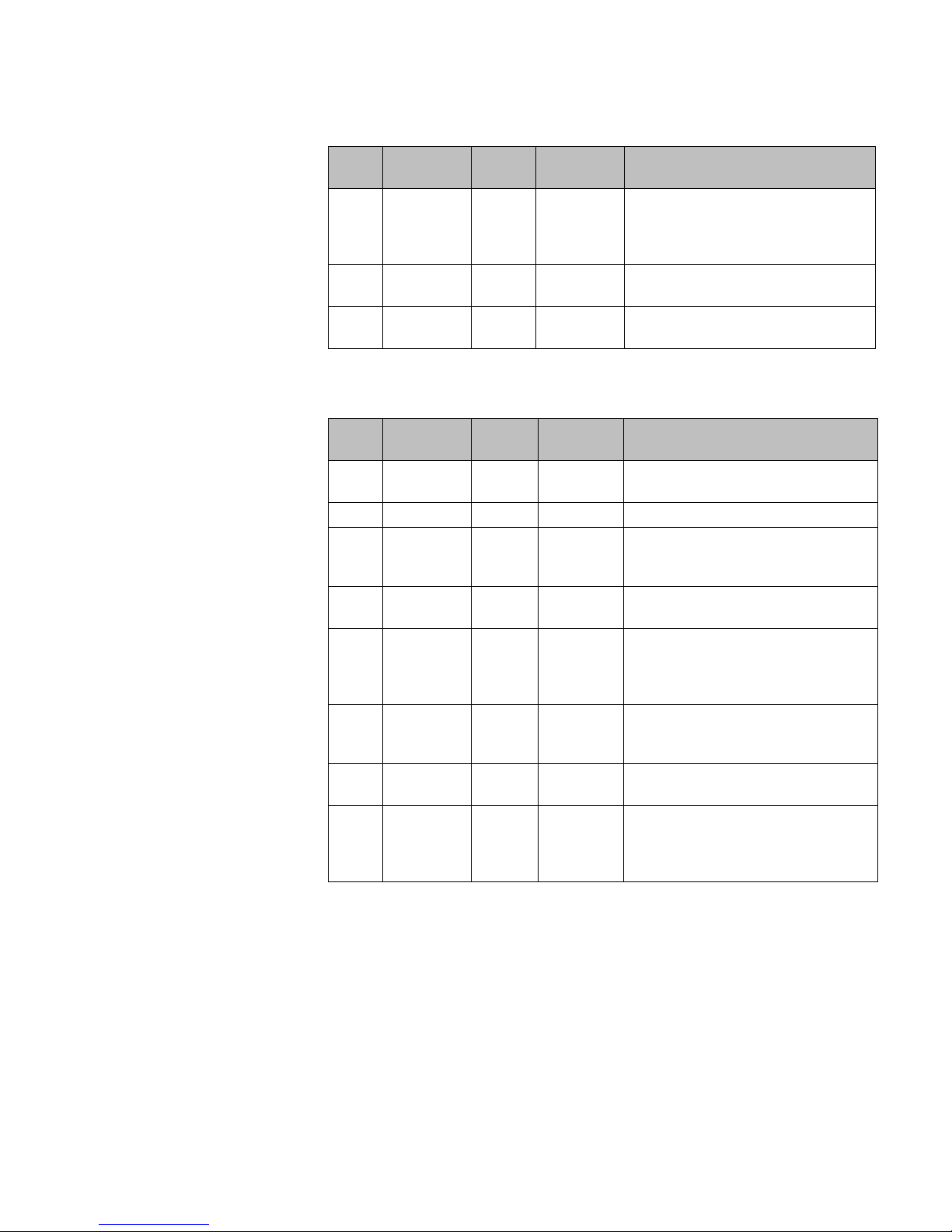
Active
LED
Warning
LED
Error
LED
SSD Code Condition
Green Yellow 1 High temperature reached.
Green Yellow 2 Fan unit failure. Rotation counter
indicates zero speed for one of the
lateral trays. May be the result of fan
tray removal.
Table 2 LED states and SSD codes during warning conditions
HWC_GSG_Chapter 1_Overview.fm
Summit WM-Series WLAN Switch Software Solution
Summit WM Switch’s physical description
120385-00 Rev 01, March 2007
Summit WM, Getting Started Guide 23
Error conditions:
Green Yellow 3 Power supply failure. Failed to detect
one of the power supplies. May be the
result of the fan tray removal of one of
the power supplies.
Green Yel low 4 FDD low sector count (40 backup
sectors remaining).
Green Yel low 5 FDD extremely low sector count (20
backup sectors remaining)
Active
LED
Warning
LED
Error
LED
SSD Code Condition
Green Red 1 Failed to identify FDD. Possibly due to
removal of FDD card.
Green Red 2 Failed to initialize NPE card.
Green Red 3 Critical threshold reached (95C for
NPE).
The system will reboot.
Green Red 4 Full fan assembly failure (both trays).
The system will reboot.
Green Red 5 Application initialization failure. Startup
manager failed to initialize all the
components of the system.
The system will reboot.
Green Red 6 Lost connectivity with ethernet interface.
Possible failure of NPE card.
The system will reboot.
Green Red 7 MF 1000 card failure. Backup sectors
exhausted.
Green Red 8 NP 4000 card initialization failure.
Firmware self test (BIST) has detected
failure in one or more components
(memory, bus, interconnects)
Table 3 LED states and SSD codes during error conditions
Active
LED
Warning
LED
Error
LED
SSD Code Condition
Table 2 LED states and SSD codes during warning conditions
Summit WM-Series WLAN Switch Software Solution
HWC_GSG_Chapter 1_Overview.fm
Summit WM Switch’s physical description
120385-00 Rev 01, March 2007
24 Summit WM, Getting Started Guide
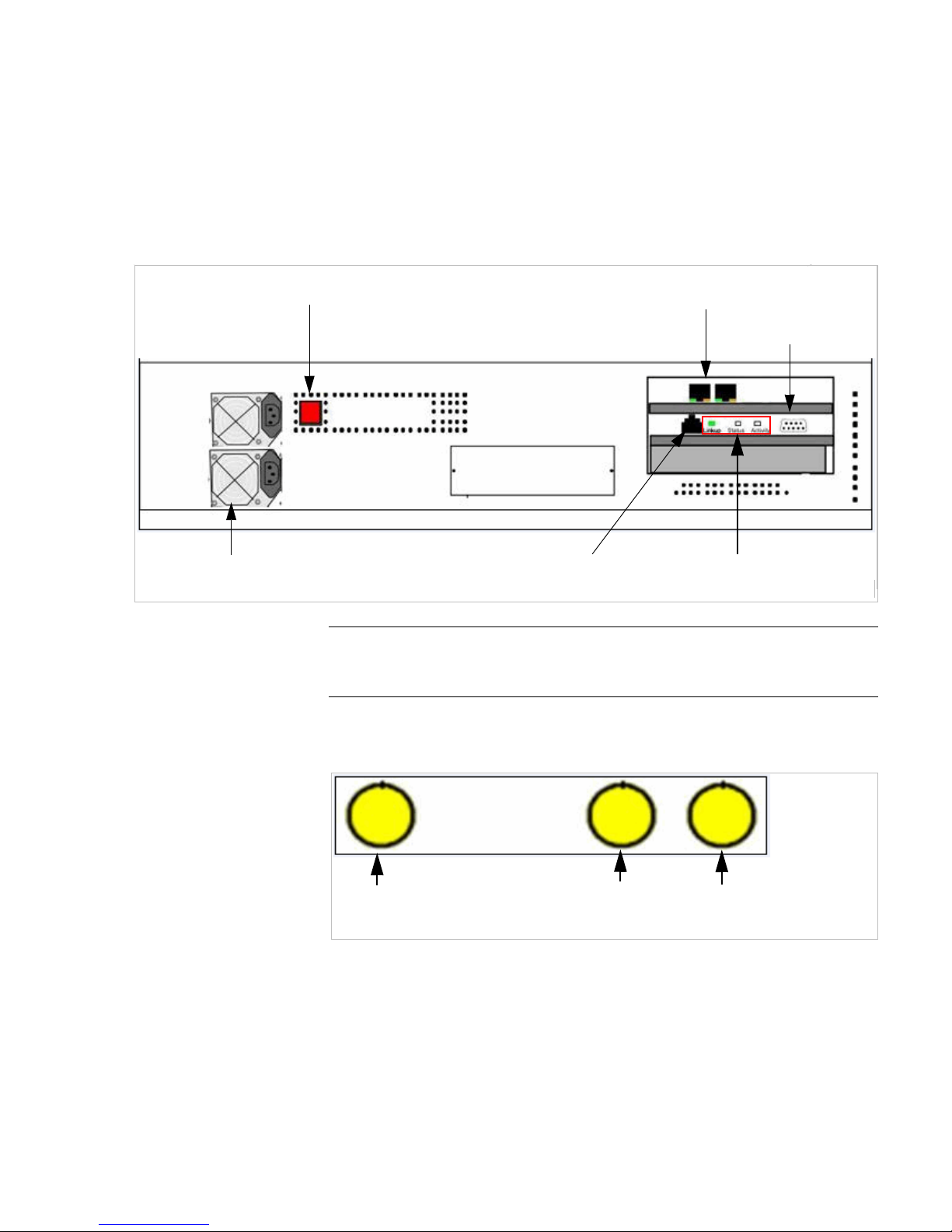
2.2.2 Summit Switch WM2000 back panel
The following figure identifies the main components on th e back panel of Summit
WM Switch WM2000.
Figure 8 Summit Switch WM2000 back panel
Figure 9
Note: The hardware for the Summit Switch WM200 and the Summit Switch WM2000 are
identical. For more information, see Section 2.2.1, “Summit Switch WM2000 front panel”,
on page 20 and Section 2.2.2, “Summit Switch WM2000 back panel”, on page 24.
2.2.3 Summit Switch WM1000 front panel
The Summit Switch WM1000 doesn’t have any component on the front panel
except two LED lights. These two LED lights are:
• STATUS LED – For more information, see the STATUS LED description in
Section 2.2.4, “Summit Switch WM1000 back panel”, on page 25.
• ACTIVITY LED – For more information, see the ACTIVITY LED description in
Section 2.2.4, “Summit Switch WM1000 back panel”, on page 25.
These two LED lights are also located on the back panel of the Summit Switch
WM1000.
Redundant
Power Supply
Power Switches
HWC_GSG_Chapter 1_Overview.fm
Summit WM-Series WLAN Switch Software Solution
Summit WM Switch’s physical description
120385-00 Rev 01, March 2007
Summit WM, Getting Started Guide 25
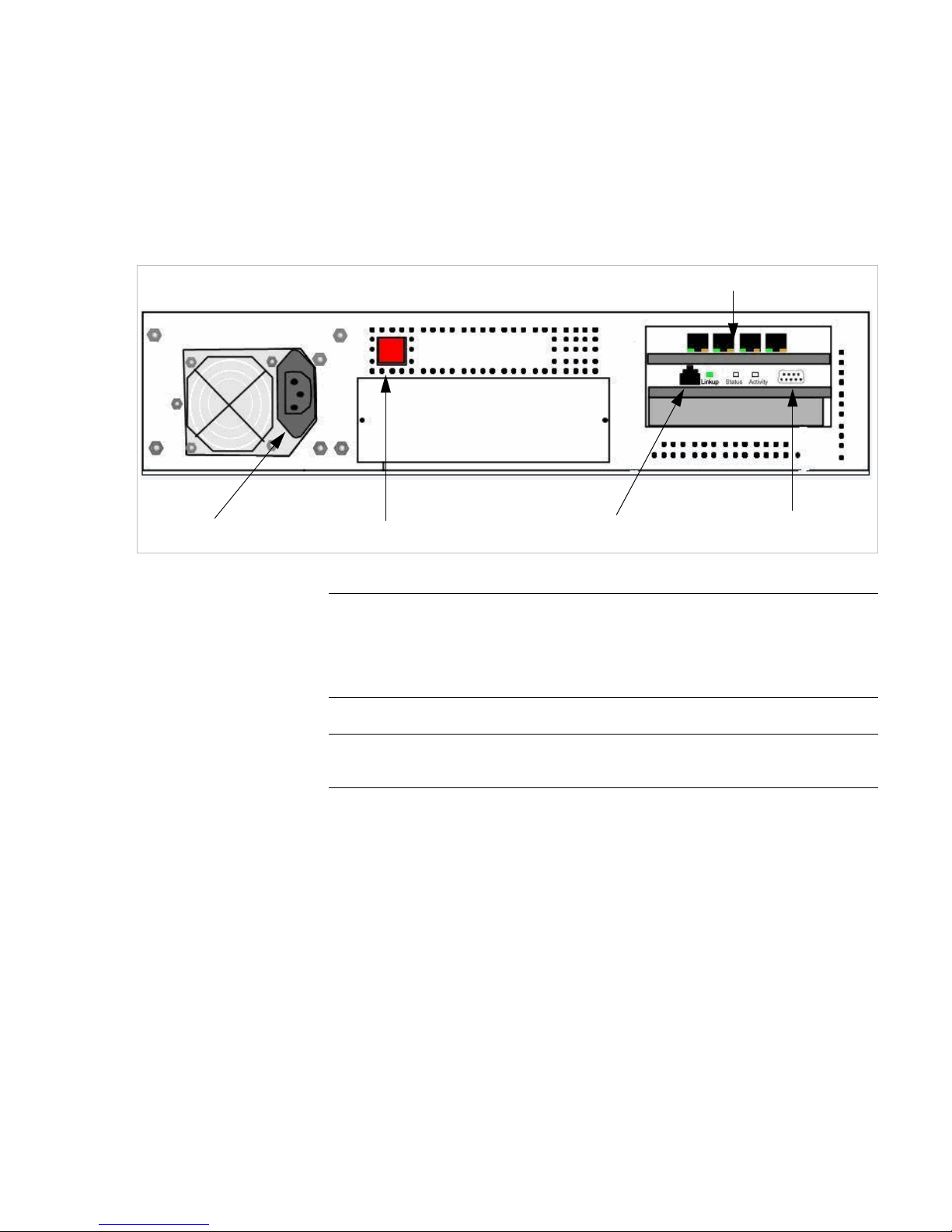
2.2.4 Summit Switch WM1000 back panel
The following figure identifies the main components on the back pa nel of Summit
Switch WM1000.
Note: Summit Switch WM1000 back panel The Summit Switch WM1000may have a
standard power supply (one power supply) or a redundant power supply (two power
supplies).
The Summit Switch WM1000has three LED lights on its back panel.
Figure 10 Summit Switch WM1000 LED lights
The description of the LED states is provided below:
• LINK-UP LED – Displays the link status of managemen t port Ethernet link as
seen by the system’s software. This LED is located only on the back p anel of
the Summit Switch WM1000.
Redundant Power Supply
Power Switch
Data Ports
Management Port
Console Port
LED Lights
LINK-UP
LED
STATUS
LED
ACTIVITY
LED

Summit WM-Series WLAN Switch Software Solution
HWC_GSG_Chapter 1_Overview.fm
Summit WM Switch’s physical description
120385-00 Rev 01, March 2007
26 Summit WM, Getting Started Guide
• ST A TUS LED – Indicates the normal st ate of the Summit WM Switch as seen
by the system’s software. This LED covers all stages of the Summit WM
Switch, ranging from restarting, to shutting-down. As long as the Summ it WM
Switch is running normally, this LED will remain lit. The STATUS LED is
located on the back panel as well as the front panel.
• ACTIVITY LED – Indicates the amount of traffic carried to and from the
Altitude APs. The ACTIVITY LED is located on the back panel as well as the
front panel.
2.2.5 Summit Switch WM100 front panel
The Summit Switch WM100does not have any component on the front panel
except two LED lights.
The description of the LED states is provided below:
• STATUS LED– For more information, see the STATUS LED de sc rip tio n in
Section 2.2.4, “Summit Switch WM1000 back panel”, on page 25.
• ACTIVITY LED – For more information, see the ACTIVITY LED description in
Section 2.2.4, “Summit Switch WM1000 back panel”, on page 25.
The STATUS LED is located on the back panel as well as the front panel of the
Summit Switch WM100.
HWC_GSG_Chapter 1_Overview.fm
Summit WM-Series WLAN Switch Software Solution
Summit WM Switch’s physical description
120385-00 Rev 01, March 2007
Summit WM, Getting Started Guide 27
2.2.6 Summit Switch WM100 back panel
The following figure identifies the main components on the back pa nel of Summit
Switch WM100.
Figure 11 Summit Switch WM100 back panel
Note: The Summit Switch WM100 has the same number of LED lights on the back panel
as the Summit Switch WM1000. The LED description of their state is also identical to
WM1000. For information on Summit Switch WM100’s LEDs’ states, see the descriptions
of STATUS LED and ACTIVITY LED in Section 2.2.4, “Summit Switch WM1000 back
panel”, on page 25.
Note: The Summit Switch WM100 may have a standard power supply (one power supply)
or a redundant power supply (two power supplies).
Power Switch
Data Ports
Management Port
Power Supply
Console Port

Summit WM-Series WLAN Switch Software Solution
HWC_GSG_Chapter 1_Overview.fm
Collecting information for installation
120385-00 Rev 01, March 2007
28 Summit WM, Getting Started Guide
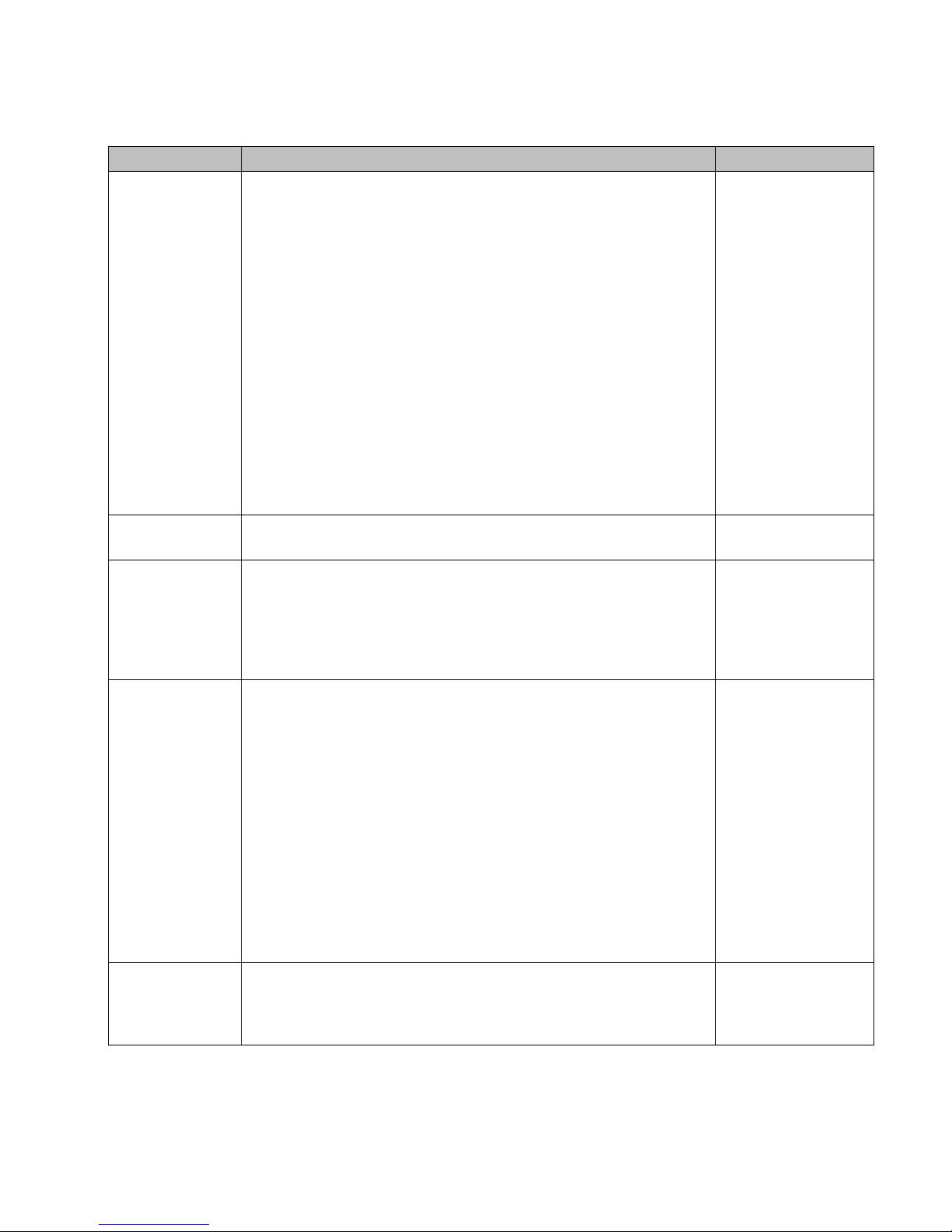
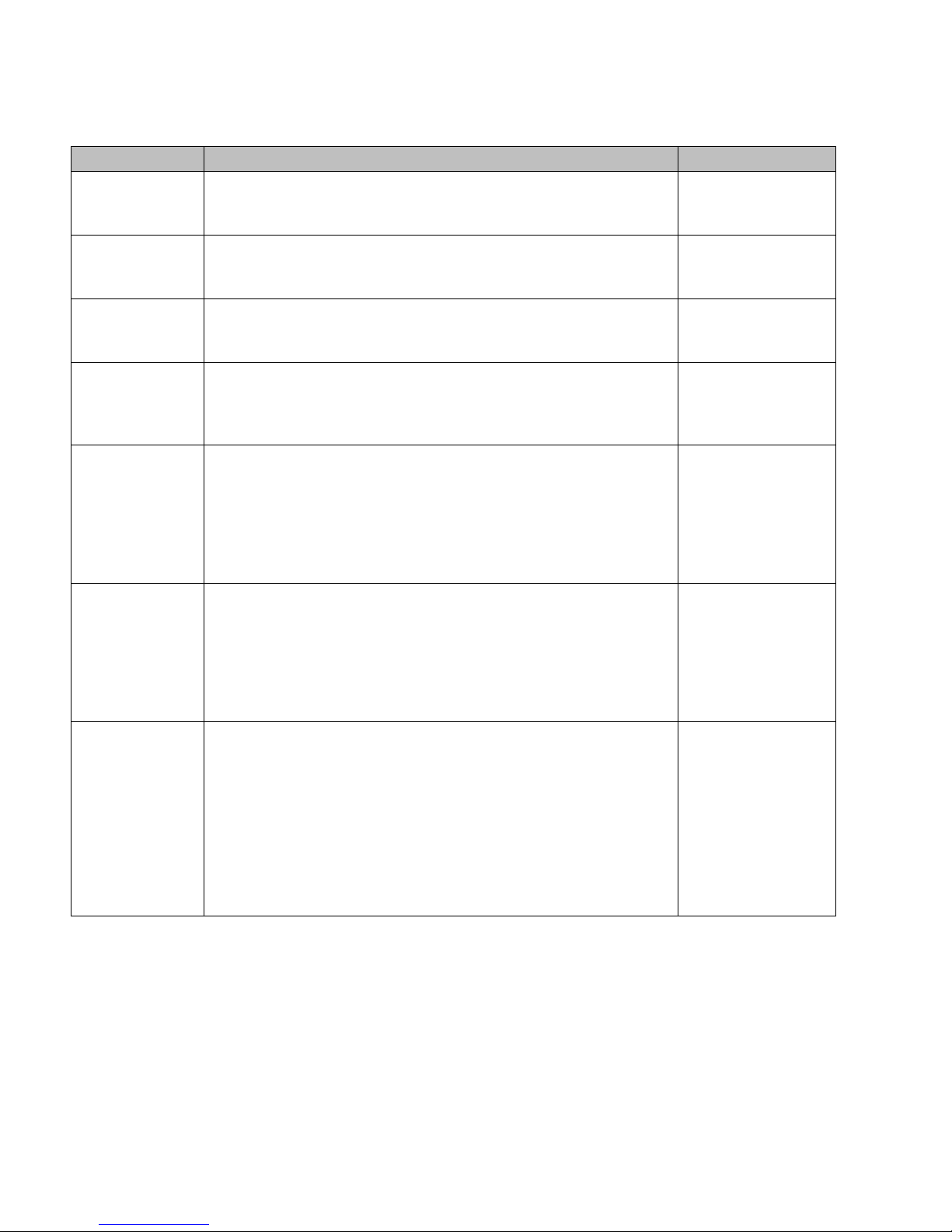
2.3 Collecting information for installation
You must use the following table to document all the pertinent information about
the Summit WM Switch before starting the installation process.
Some of the information listed in the table may not be relevant to your network
configuration. You must only record the information that is pertinent to your
network configuration.
Configuration data Description Yo ur entry
Accessing the
Summit WM
Switch for the first
time
• Unused IP address in the 192.168.10.0/24 subnet – This IP
address must be assigned to the Ethernet port of your laptop
computer. You can use any IP address between 192.168.10.2 a nd
192.168.10.255.
• Factory default IP address of Summit WM Switch – The fa ctory
default IP address is https//192.168.10.1:5825. You must
type this IP address in the address bar of your Web browser when
you access the Summit WM Switch for the first time.
• Login Information – The login information is as follows:
• User Name: admin
• Password: abc123
Management Port
information
•Hostname – Specifies the name of the Summit WM Switch.
•Domain – Specifies the IP domain name of the enterprise
network.
• Management IP Address – The new IP address for the Summit
WM Switch’s management port. Change the value in this text bo x
to the IP address assigned t o the S ummit WM Switch’s
management port by your network administrator.
• Subnet Mask – The subnet mask for the IP address to separate
the network portion from the host portion of the address (typically
255.255.255.0)
• Management Gateway – The default gateway of the network.
• Primary DNS – The primary DNS server used by the network.
• Secondary DNS – The secondary DNS server used by the
network.
Hardware
information
•MAC Address – MAC address of the Summit WM Switch’s
management port
•Serial # – The Summit WM Switch’s serial #.
License Key (File) An .xml file that is provided along with the product. This file must be
applied to the product to enable all the functionalities.
Table 4 Information gathering table
HWC_GSG_Chapter 1_Overview.fm
Summit WM-Series WLAN Switch Software Solution
Collecting information for installation
120385-00 Rev 01, March 2007
Summit WM, Getting Started Guide 29
Data Ports
information
• IP address – IP address of the physical ethernet port.
• Subnet mask – Subnet mask for the IP address, which sep arates
the network portion from the host portion of the address (typically
255.255.255.0).
•MTU – The maximum transmission unit or maximum packet size
for this port. The default setting is 1500. If you change this settin g,
and are using OSPF, you must m ake sur e th at the M TU of eac h
port in the OSPF link matches.
• Function – The port’s function.
•Host Port – A port for connecting Altitude APs with no
dynamic routing.
• Third-party AP Port – A port to which the third-party AP is
connected.
• Router Port – A port that connects to an upstream, next-hop
router in the network.
•VLAN ID – The ID of the VLAN to which the AP is connected.
Static Routing Static IP address – The static IP address that is assigned to the
Summit WM Switch when it is configured for static routing.
OSPF Routing •Router ID – The router ID is its own IP address. You must record
the Summit WM Switch’s IP address here.
• Area ID of OSPF – Id of OSPF’s area. 0.0.0.0. is the main area in
OSPF.
• OSPF Authentication Password – If you select Authentication
type as Password, then you will need a password.
DHCP Service • IP address range – This is the range from which the IP address
will be distributed across the network.
• Start IP address – This is the start IP address of the range.
• End IP address – This is the end IP address of the range.
• Lease duration – The DHCP server assigns a client an IP address for a
given amount of time. The amount of time for which the IP address can
be given is called lease duration.
•Days – The number of days for which the lease can be given.
•Hours – The number of hours for which the lease can be
given.
• Minutes – The number of minutes for which the lease can be
given.
IP Address for
installing DHCP
service
IP Address – If you are using WM-AD, you will need the WM-AD’s
IP address.
If you are not using WM-AD, you will need the Summit WM Switch IP
address.
Configuration data Description Yo ur entry
Tab le 4 Information gathering table
Summit WM-Series WLAN Switch Software Solution
HWC_GSG_Chapter 1_Overview.fm
Collecting information for installation
120385-00 Rev 01, March 2007
30 Summit WM, Getting Started Guide
WM-AD gateway
for installing
DHCP service
WM-AD gateway – If you are using WM-AD, you will need the WMAD gateway.
Domain name for
installing DHCP
service
Domain name – Your organization’s domain name.
Windows 2003
Server’s IP
address
IP address – The IP address of Windows 2003 Server.
SLP DA’s IP
address
Hexa values of SLP DA’s IP address – The Altitude APs use the
SLP DA to discover the Summit WM Switch .
The mobility agents use the SLP DA to discover the mobility
manager. The hexa values of the SLP DA’s IP address.
Internet Protocol
configuration for
DNS Service in
Windows 2003
server
• Static IP address – Windows 2003 server’s static IP addr ess.
• Subnet Mask – Subnet mask of Windows 2003 server’s static IP
address.
• Gateway – Windows 2003 server’s gateway.
• ISP’s IP address – Your ISP’s (Internet Service Provider) IP
address.
• IP address– Summit WM Switch’s IP address.
Port information
for installing IAS
in Windows 2003
server
• Authentication Port – Summit WM Switch’s used to access the
IAS service.
• Accounting Port – Type the Summit WM Switch’s port # that is
used to access the accounting service.
The values you record here should match what you define in the Port
text box of Auth section in the Acc & Acct tab of Summit WM
Switch’s WM-AD screen.
Altitude AP’s
properties
• Summit WM Switch’s Port # – Summit WM Switch’s ethernet
port to which the Altitude AP is connected.
• Country – The country where the Altitude AP operate s.
•Serial # – A unique identifier that is assigned during the
manufacturing process of the Altitude APs.
• Hardware version – The current version of the Altitude AP
hardware.
• Application version – The current version of the Altitude AP
software.
• VLAN ID – The ID of the VLAN on which the Altitude AP operates.
Configuration data Description Yo ur entry
Table 4 Information gathering table
 Loading...
Loading...