Extreme Networks RBTSAAA User Manual

®
RoamAbout
Wireless Networking
11a/b/g Wireless Ethernet Adapter User Guide
RBTSA-AA / RBTSA-AB
P/N 9034149


CONTENTS
ABOUT THIS GUIDE
Conventions 2
Related Documentation 4
Accessing Online Documentation 4
Product Registration and Support 5
1 INTRODUCTION
Product Features 7
Security 7
Wireless Network Standards 8
Network Configuration and Planning 9
Example Configurations 10
2 INSTALLING THE ETHERNET ADAPTER
Unpacking the Ethernet Adapter 11
Observing Safety Precautions 12
Deciding Where to Place the Ethernet Adapter 13
Wall-Mounting the Ethernet Adapter 13
Connecting the Ethernet Adapter 15
Connecting to a Serial Device 15
Connecting to an Ethernet Device 16
About the Client List 16
Connecting to a Hub 17
Connecting to a Network Printer 17
Connecting to a Computer 18
Checking the LED Indicators 18
Attaching An External Antenna 20
Determining if you Need to Configure the Ethernet Adapter 20
Using the Enterasys Networks Installation CD 23

3 CONFIGURING THE ETHERNET ADAPTER
Using Secure Web Server Connection 25
Using the Enterasys Networks Wireless Infrastructure Device Manager 26
Using the Configuration Management System 29
Clearing and Applying System Configuration Settings 30
Changing System Properties 31
Setting IP Network Properties 32
Setting Wireless Network Properties 33
Manually Selecting Radio Channels 35
Setting Up an Ad-Hoc Network 35
Changing Wireless Security Settings 36
Changing RADIUS Settings 39
Changing SNMP Settings 40
Using the Access Control List 40
Serial Port 42
Resetting the Ethernet Adapter 45
Restoring the Ethernet Adapter to Factory Defaults 45
Upgrading the System 46
Changing the Administration Login Name and Password 47
Backing up a Configuration 48
Restoring a Configuration 48
Logging Out 48
Clearing the Ethernet Client List 49
Viewing Connection Status 49
Viewing System Summary 50
4 TROUBLESHOOTING
Diagnosing Problems 51
Disconnecting the Ethernet Adapter 53
Uninstalling Software and Documentation 54
Upgrading Ethernet Adapter Firmware 54
A OBTAINING SUPPORT FOR YOUR ENTERASYS NETWORKS
P
RODUCT
Getting Help 55

END USER LICENSE AGREEMENT
REGULATORY INFORMATION


ABOUT THIS GUIDE
This guide provides all the information you need to install and use the
Enterasys Networks 11a/b/g Wireless Ethernet Adapter in its default state.
The guide is intended for use by IT managers and experienced network
installation and administration professionals who have a basic knowledge
of current networking concepts.
If the information in the release notes that are shipped with your product
differ from the information in this guide, follow the instructions in the
release notes.
Most user guides and release notes are available in Adobe Acrobat
Reader Portable Document Format (PDF) or HTML on the Enterasys
Networks World Wide Web site:
http://www.enterasys.com/products/wireless/

2 ABOUT THIS GUIDE
Conventions Table 1 and Table 2 list conventions that are used throughout this guide.
Tab le 1 Notice Icons
Icon Notice Type Description
Information note Information that describes important features or
instructions.
Caution Information that alerts you to potential loss of data or
potential damage to an application, system, or device.
Achtung: Verweist auf wichtige Informationen zum Schutz
gegen Beschadigungen.
Warning Information that alerts you to potential personal
injury.
Warnung Warnung vor samtlichen Handlungen, die zu Verletzung
von Personen oder Todesfallen - hervorgerufen durch
elektrische Spannung - fuhren konnen!
Tab le 2 Text Conventions
Convention Description
Screen displays This typeface represents information as it appears on the
screen.
Syntax The word “syntax” means that you must evaluate the syntax
provided and then supply the appropriate values for the
placeholders that appear in angle brackets. Example:
To change your password, use the following syntax:
system password <password>
In this example, you must supply a password for <password>.
The words “enter”
and “type”
Keyboard key names If you must press two or more keys simultaneously, the key
When you see the word “enter” in this guide, you must type
something, and then press Return or Enter. Do not press
Return or Enter when an instruction simply says “type.”
names are linked with a plus sign (+). Example:
Press Ctrl+Alt+Del

Tab le 2 Text Conventions (continued)
Convention Description
Words in italics Italics are used to:
■ Emphasize a point.
■ Denote a new term at the place where it is defined in the
text.
■ Identify menu names, menu commands, and software
button names. Examples:
From the Help menu, select Contents.
Click OK.
Conventions 3

4 ABOUT THIS GUIDE
Related Documentation
Accessing Online Documentation
In addition to this guide, each Ethernet Adapter documentation set
includes the following:
■ Quick Start Guide—printed guide that describes basic installation.
■ Online Help—product help systems that describe how to use the
Configuration Management System and Enterasys Networks Wireless
Infrastructure Device Manager.
■ Release Note—printed note that describes important product
information.
■ README.TXT file—text file located on the Enterasys Networks
Installation CD that describes last-minute product information.
The CD supplied with your Ethernet Adapter contains the following
online documentation:
■ Enterasys Networks 11a/b/g Wireless Ethernet Adapter User Guide
■ Enterasys Networks Wireless Infrastructure Device Manager Online
Help
■ Enterasys Networks 11a/b/g Wireless Ethernet Adapter Configuration
Management System Online Help
To access the online documentation from the CD:
1 Insert the Enterasys Networks Installation CD supplied with your Ethernet
Adapter in the CD-ROM drive.
The setup menu appears. If it does not appear, you can start the setup
menu from the Windows Start menu. For example: Start > Run >
d:launch.exe.
2 In the menu, click View the Documentation to view the Ethernet Adapter
User Guide.
To view the online help, install and launch the Wireless Infrastructure
Device Manager or Configuration Management System. See Chapter 3
for instructions.

Product Registration and Support 5
Product Registration and Support
To register your product with Enterasys Networks, go to the following
Web page:
http://www.enterasys.com/support
For support information, see “Obtaining Support for Your Enterasys
Networks Product” on page 55 or log on to the Enterasys Networks Web
site at http://www.enterasys.com/products/wireless and
navigate to the product support page.

6 ABOUT THIS GUIDE

INTRODUCTION
1
Enterasys Networks wireless technology has all of the benefits of a local
area network (LAN) without the constraints and expense of network
wiring.
Enterasys Networks 11a/b/g Wireless LAN products provide easy,
affordable, flexible ways to extend wireless networks to more users. This
guide shows how you can use the Enterasys Networks 11a/b/g Wireless
Ethernet Adapter in your office or classroom to connect groups of wired
Ethernet client devices to your wireless LAN.
Product Features The Enterasys Networks 11a/b/g Wireless Ethernet Adapter includes a
robust suite of standards-based security features, and supports wireless
network standards including 802.11a and 802.11g.
Security To protect sensitive data broadcast over the radio, Enterasys Networks
supports Wireless Equivalent Privacy (WEP) RC4 64-bit, 128-bit and
152-bit shared-key encryption. Enterasys Networks strengthens this basic
security mechanism with additional security features, including:
■ MAC address access control lists
■ IEEE 802.1x per-port user authentication with RADIUS server
authentication support
■ Temporal Key Integrity Protocol (TKIP)
■ Advanced Encryption Standard (AES)
■ WiFi Protected Access (WPA)
■ Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP) support: EAP-TTLS and PEAP

8 CHAPTER 1: INTRODUCTION
Wireless Network
Standards
Understanding the characteristics of the 802.11a and 802.11g standards
can help you
make the best choice for your wireless implementation plans.
802.11a
Ratified in 2002, 802.11a is IEEE’s more recent wireless standard. It
operates at the 5 GHz band and supports data rates at up to 54 Mbps.
Because there are fewer devices in the 5 GHz band, there’s less potential for
RF interference. However, because it is at an entirely different radio spectrum,
it is not compatible with 802.11g.
The higher spectrum provides about 50 m (164 ft) of coverage—about
what 802.11g offers.
half
Consider 802.11a when you need high throughput in a confined space
and you are:
■ Running high-bandwidth applications like voice, video, or multimedia
over a wireless network that can benefit from a five-fold increase in
data throughput.
■ Transferring large files like computer-aided design files, preprint
publishing documents or graphics files, such as MRI scans for medical
applications, that demand additional bandwidth.
■ Supporting a dense user base confined to a small coverage area.
Because 802.11a has a greater number of non-overlapping channels,
you can pack more wireless devices in a tighter space.
802.11g
802.11g operates in the 2.4 GHz band at up to 54 Mbps. Ratified in
2003, it supports
the widest coverage—up to 100 m (328 ft). However, is
subject to a greater risk of radio interference because it operates in the more
popular 2.4 GHz band.
802.11b operates at up to 11 Mbps and supports coverage up to 100 m
(328 ft).

Network Configuration and Planning 9
Consider 802.11g when you need wider coverage and vendor
compatibility and you are:
■ Maintaining support for existing 802.11b users and the existing
wireless investment while providing for expansion into 802.11g.
■ Implementing a complete wireless LAN solution, including Ethernet
Adapters, gateways, access points and clients; Wi-Fi certification
guarantees compatibility among vendors.
■ Providing access to hot spots in public spaces such as coffee shops or
university cafeterias.
Network Configuration and Planning
The Ethernet Adapter can operate in either infrastructure or ad-hoc
mode, and can support a stand-alone wireless network configuration or
an integrated configuration with 10/100 Mbps Ethernet LANs.
Operating in infrastructure mode and connected to an Ethernet hub, a
single Ethernet Adapter can combine up to 16 client devices—such as
computers with network adapters and printers—into a multiclient
workgroup. The workgroup associates with the wired network through a
wireless LAN access point such as the Enterasys Networks 11a/b/g
Wireless LAN Access Point. Infrastructure configurations extend your
wireless LAN to devices that would otherwise have to be connected to
the wired network.
Operating in ad-hoc mode, two or more Ethernet Adapters can associate
among themselves and communicate with one another at close range
without an access point. You may wish to set up an ad-hoc network, for
example, if a group is working away from the office, or if a group in the
office needs to share files apart from the wired LAN.

10 CHAPTER 1: INTRODUCTION
PO
WER
ETHERNET
WIRELESS
POWER
ETHERNET
WIRELES
S
Example Configurations
The following examples illustrate ways you can use the Ethernet Adapter to
configure Ethernet client devices into workgroups. (Details for setting up
specific configurations are in “Installing the Ethernet Adapter” on page 11.)
Wireless Infrastructure Network
You can connect several computers, including those with non-Windows
operating systems, and network printers, as shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1 Wireless Infrastructure Network
Hub
T
T
E
E
N
N
R
R
E
S
E
S
R
S
H
R
S
H
E
T
E
E
T
E
L
E
L
E
W
W
E
E
O
O
R
R
I
P
I
P
W
W
Access
Point
11a/b/g Wireless
Ethernet Adapter
Workgroup Ad-Hoc Network
You can provide flexible wireless network association for small groups in
areas that cannot be wired, as shown in Figure 2.
Figure 2 Workgroup Ad-Hoc Network
Hub
11a/b/g Wireless
Ethernet Adapter
Hub
11a/b/g Wireless
Ethernet Adapter

2
INSTALLING THE ETHERNET ADAPTER
This chapter contains the information you need to install and set up the
Ethernet Adapter. It covers the following topics:
■ Unpacking the Ethernet Adapter
■ Observing Safety Precautions
■ Deciding Where to Place the Ethernet Adapter
■ Connecting the Ethernet Adapter
■ Checking the LED Indicators
■ Attaching An External Antenna
■ Determining if you Need to Configure the Ethernet Adapter
■ Using the Enterasys Networks Installation CD
Unpacking the Ethernet Adapter
Make sure that you have the following items, which are included with the
Ethernet Adapter:
■ Power adapter and power cord.
■ Standard Category 5 unshielded twisted pair (UTP) Ethernet cable.
■ Rubber feet (four; used for a flat-surface installation).
■ Enterasys Networks Installation CD.
For wall-mounting installations, you need the following items, which
are not included with the Ethernet Adapter:
■ Mounting screws.
■ Plastic anchors (for drywall mounting).
12 CHAPTER 2: INSTALLING THE ETHERNET ADAPTER
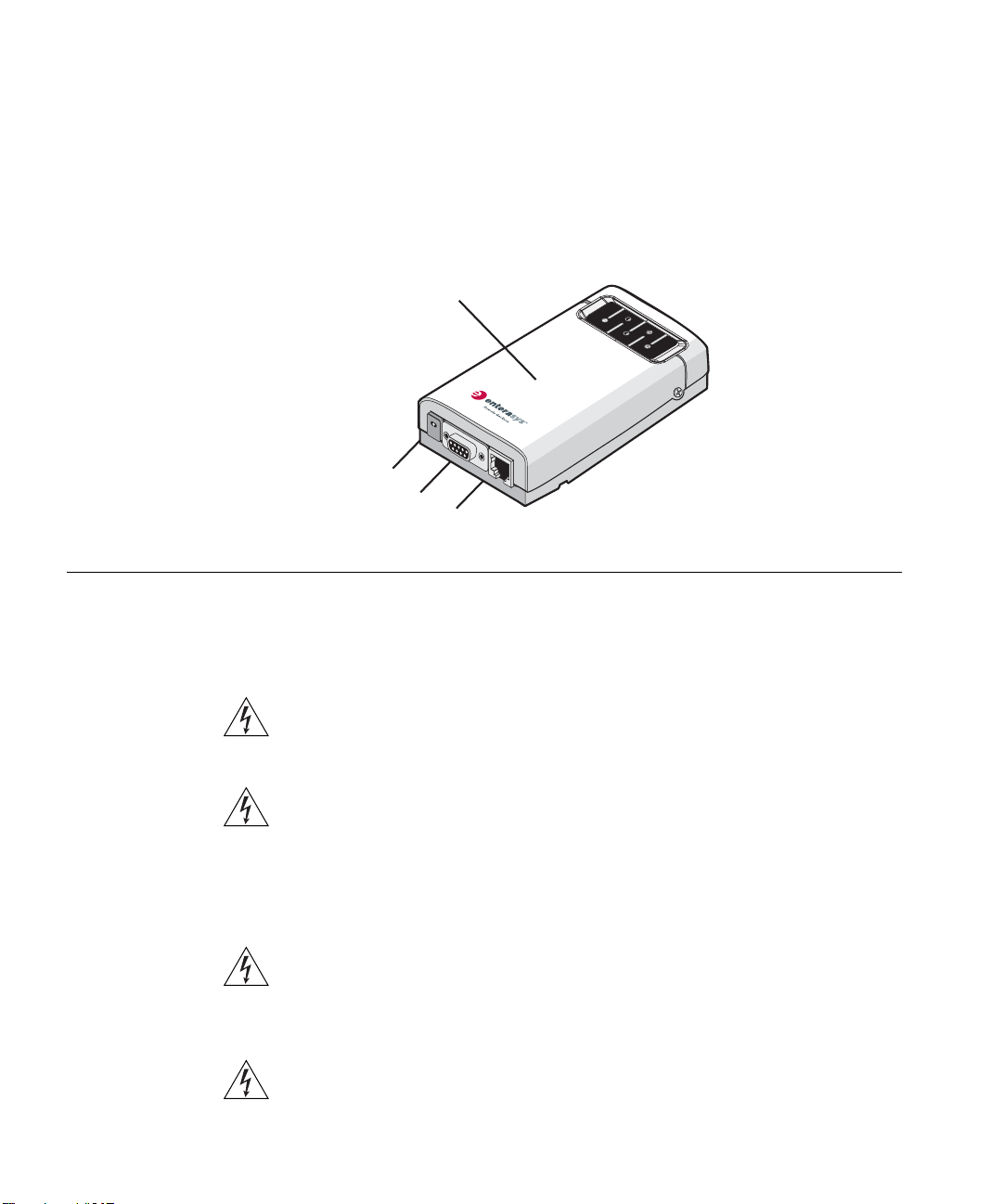
Figure 3 shows the front view of the Ethernet Adapter, including the LEDs and
connecting ports. It also shows the cradle, which is used to mount the
Ethernet Adapter to a wall or to install the Ethernet Adapter on a flat surface.
Figure 3 Ethernet Adapter
11a/b/g Wireless
Ethernet Adapter
Power Port
Serial Port
Ethernet Port
Observing Safety Precautions
This equipment must be installed in compliance with local and national
building codes, regulatory restrictions, and FCC rules. For the safety of
people and equipment, only professional network personnel should
install the Ethernet Adapter.
WARNING: To comply with FCC radio frequency (RF) exposure limits, a
minimum body-to-antenna distance of 20 cm (8 in.) must be maintained
when the Ethernet Adapter is operational.
WARNING: To avoid possible injury or damage to equipment, you must
use either the provided power supply or power supply equipment that is
safety certified according to UL, CSA, IEC, or other applicable national or
international safety requirements for the country of use. All references to
power supply in this document refer to equipment meeting these
requirements.
WARNUNG: In Übereinstimmung mit den von der FCC (Federal
Communications Commission) festgelegten Grenzwerten für die
Einwirkung von Radiowellen muss bei Betrieb des Ethernet-Adapters der
Abstand zwischen Körper und Antenne 20 cm betragen.
WARNUNG: Zur Vermeidung möglicher Verletzungen oder Schäden am
Gerät muss entweder das mitgelieferte Netzteil oder ein Netzteil
verwendet werden, das von der UL (Underwriters Laboratories Inc.), CSA
Deciding Where to Place the Ethernet Adapter 13
(Canadian Standards Organisation), IEC (International Electrotechnical
Commission) oder von anderen, nationalen oder internationalen
Sicherheitsvorschriften für das entsprechende Land zugelassen wurde.
Alle Verweise auf Netzteile in diesem Dokument beziehen sich auf
Netzgeräte, die diesen Anforderungen entsprechen.
CAUTION: The Enterasys Networks power supply (part number
61-0107-000) input relies on a 16A rated building fuse or circuit
protector for short circuit protection of the line to neutral conductors.
VORSICHT: Der Eingang des Enterasys Networks-Netzteils (Teilenummer
61-0107-000) benötigt zum Schutz vor Kurzschlüssen in den Nullleitern
eine 16-A-Sicherung oder eine Überstromsicherung.
Deciding Where to Place the Ethernet Adapter
Wall-Mounting the
Ethernet Adapter
Place the Ethernet Adapter in a dry, clean location near the hub,
computer, or printer that will be connected to the Ethernet Adapter. The
location must have a power source and be within the following distance
of a Wi-Fi compliant wireless LAN access point or ad-hoc wireless station:
■ For 802.11a compatibility, place the Ethernet Adapter within 50 m
(164 ft) of a Wi-Fi compliant wireless LAN access point.
■ For 802.11b/g compatibility, place the Ethernet Adapter within 100 m
(328 ft) of a Wi-Fi compliant wireless LAN access point.
The location should be away from transformers, heavy-duty motors,
fluorescent lights, microwave ovens, refrigerators, or other equipment
that could cause radio signal interference.
The Ethernet Adapter comes with two plastic anchors and two flat head
mounting screws for mounting on a wall.
14 CHAPTER 2: INSTALLING THE ETHERNET ADAPTER
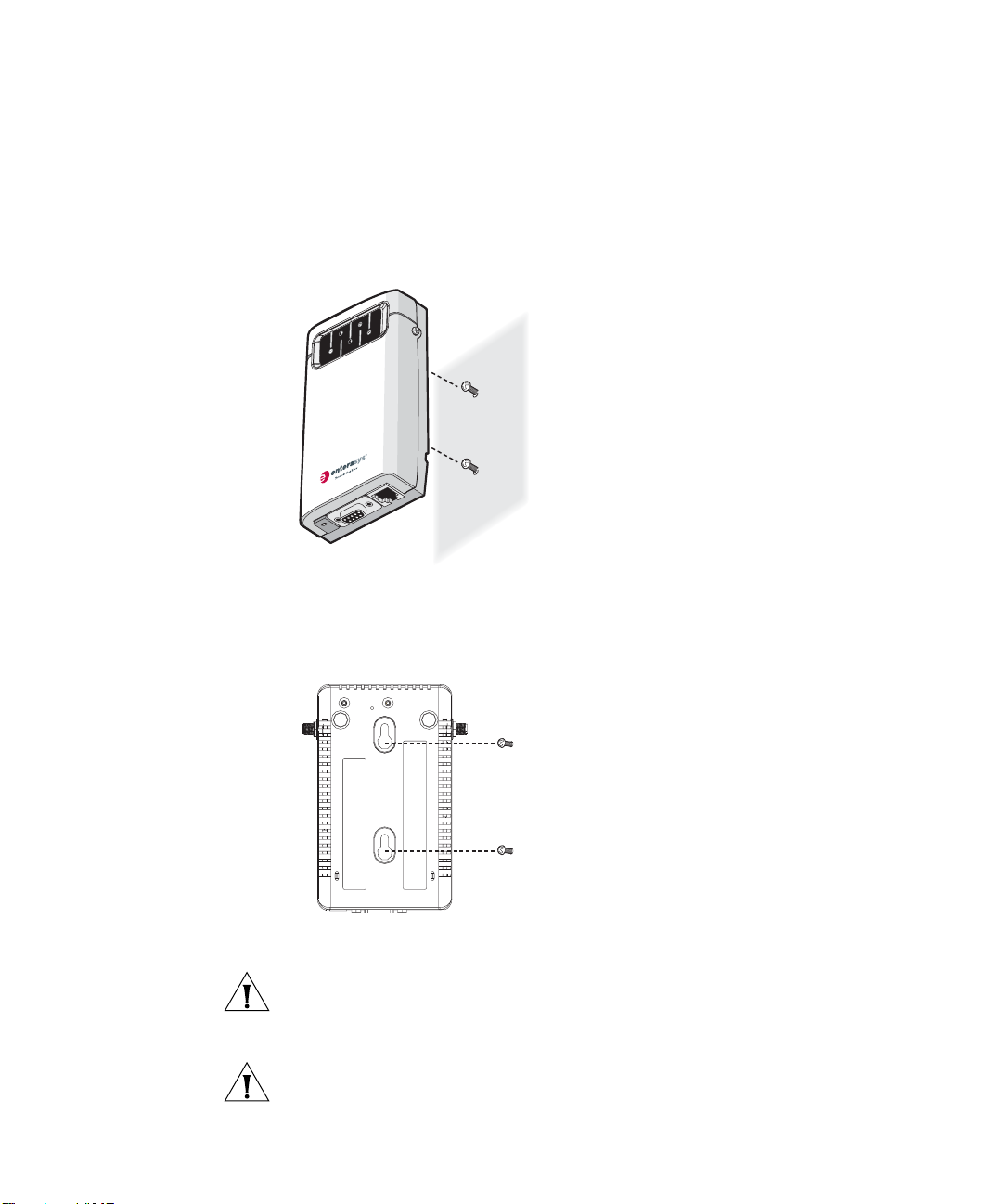
To wall-mount the Ethernet Adapter:
1 1 Place the two plastic anchors into a wall, then place two flat head
mounting screws inside the plastic anchors, as shown in Figure 4
Figure 4 Place the screw on the wall
2 Place the Ethernet Adapter onto the wall, as shown in Figure 5.
.
Figure 5 Place the unit onto the wall
CAUTION: Do not place the Ethernet Adapter on any type of metal
surface. Select a location that is clear of obstructions and provides good
reception.
VORSICHT: Legen Sie den Ethernet-Adapter nicht auf Metallflächen ab.
Wählen Sie einen Ort ohne Störungen und mit gutem Empfang aus.
Connecting the Ethernet Adapter 15
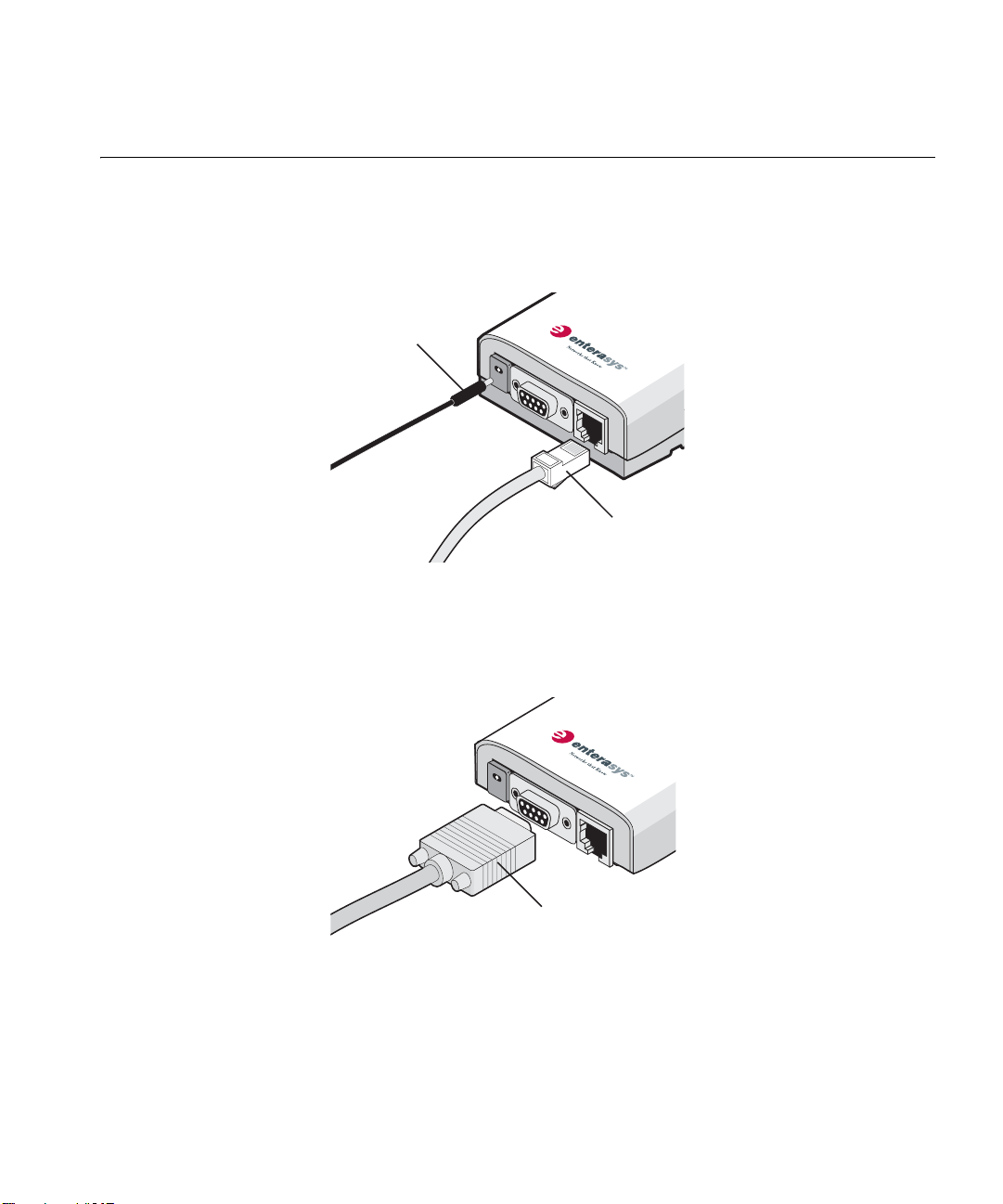
Connecting the Ethernet Adapter
Connecting to a
Serial Device
The Ethernet Adapter has power, Ethernet, and serial ports, as shown in
Figure 6. Before connecting the Ethernet Adapter to an Ethernet device,
connect the power.
Figure 6 Connecting the Power
Power
Cable
Ethernet
Cable
The Ethernet Adapter can also be connected to a serial device, as shown
in Figure 7. Serial cables come with a variety of connector sizes.
Figure 7 Connecting a Serial Cable
Serial Cable
 Loading...
Loading...