
IP Service Manager User
Guide
Infrastructure Client for ISM Provision
Extreme Networks, Inc.
3585 Monr oe Street
Santa Clara, California 95051
(888) 257-3000
http://www.extremenetworks.com
Published: April, 2002
Part number: 100121-00 rev 01

©2002 Extreme Networks, Inc. All rights reserved. Extreme Networks and BlackDiamond are
registered trademarks of Extreme Networks, Inc. in the United States and certain other jurisdictions.
ExtremeWare, ExtremeWare Vista, ExtremeWorks, ExtremeAssist, ExtremeAssist1, ExtremeAssist2,
PartnerAssist, Extreme Standby Router Protocol, ESRP, SmartTraps, Alpine, Summit, Summit1,
Summit4, Summit4/FX, Summit7i, Summit24, Summit48, Summit Virtual Chassis, SummitLink,
SummitGbX, SummitRPS, and the Extreme Networks logo are trademarks of Extreme Networks, Inc.,
which may be registered or pending registration in certain jurisdictions. The Extreme Turbodrive logo
is a service mark of Extreme Networks, which may be registered or pending registration in certain
jurisdictions. Specifications are subject to change without notice.
All other registered trademarks and service marks are property of their respective owners.
ii

Contents
Preface
Introduction vii
Terminology viii
Conventions viii
Related Publications x
1 Infrastructure and Services Management Provision
Overview
Overview 1-1
Summary of Features 1-2
How ISM Provision works 1-3
Yo u r N e tw or k De v ic e s 1 - 4
ISM Provision Server 1-4
Device Communicators 1-4
Network Infrastructure Manager Client 1-5
IP Service Manager Client 1-5
2 Starting IP Service Manager
Overview 2-1
Starting IP Service Manager 2-1
Summary Steps 2-1
Detailed Steps 2-2
IP Service Manage r User Guid e iii

3 IP Service Manager Overview
IPSM Overview 3-1
Summary of Features 3-1
IPSM Views 3-2
Selecting IPSM Views 3-2
Service Activation View 3-4
Service Library View 3-5
Change Control View 3-6
IPSM Icons 3-6
Open Changes 3-7
Save Changes 3-7
Modify Object 3-7
Copy 3-7
Paste 3-7
Delete 3-7
Verify Configuration 3-8
Synchronize 3-8
Commit Changes 3-8
Revert Cha nges 3-8
Help 3-8
4 Service Library
Overview 4-1
Traffic Policies 4-2
Policy Based Services 4-2
Service Bundles 4-2
Service Categories 4-3
Key Information 4-3
Service Library Tasks 4-3
Add a Service Bundle 4-4
Add a Policy Based Service 4-7
Add an IP, TCP or UDP Traffic Policy 4-9
5 Service Activation
Overview 5-1
iv IP Service Manage r User Guid e

Subscriber 5-2
Customer 5-2
IP Aggregation Point 5-2
Service Activation Tasks 5-2
Add a Customer 5-3
Add an IP Subscriber 5-7
Add an IP Range Subscriber 5-9
Add an IP Aggregation Poin t 5-12
6 Change Control
Overview 6-1
Jobs 6-1
Change Control Tasks 6-2
View Current Job Changes 6-2
View Committed, Scheduled, or Saved Jobs 6-4
Delete Scheduled or Saved Jobs 6-6
Index
IP Service Manage r User Guid e v

vi IP Service Man ager User Gui de

Preface
This Preface provides an overview of this guide, describes guide conventions, and lists
other publications that may be useful.
Introduction
This guide provides the required information to m anage customers and subscribers
using Extreme Networks’ IP Service Manager (IPSM) client as the interface for Extreme
Networks’ Infrastructure and Services Mana gement Provision (ISM Provision).
This guide is intended for use by network administrators who are responsible for
configuring network equipmen t. It assumes a basic working kno wledge of:
• Local area networks (LANs).
• Ethern et conc epts.
• Ethernet switching and bridging concepts.
• Routing concepts .
• Internet Protocol (IP) co ncepts.
• Routing Information Protocol (RIP) and Open Shortest Path First (OSPF).
• Simple Network Managemen t Protocol (SNMP).
Additionally, th is guide assumes a familia rity with the features and function ality of
ExtremeWare Software and with Extreme Networks’ hardw a re. Se e t h e s ec t io n, “Related
Publications”, for documents covering Extreme Networks’ Softwa re and Hardware.
IP Service Manage r User Guid e vii

If the information i n the release notes sh ipped with your softw are differs from the
information in this guide, follow the release no tes.
Terminology
When features, functionality, or operation is specific to t he Summit, Alpine, or
BlackDiamond switch family, the family name is used. Explanations about features and
operations that are the same across all Extreme switch product families sim ply refer to
the product as the “Extreme device” or “Extreme switch.” Explanations about features
that are the same for all devices managed by Network In frastructure Manager (both
Extreme devices and others) simply refer to “devices.”
Conventions
Table 1 and Table 2 list conventions that are used throughout this guide.
Table 1: Notice Icons
Icon Notice Type Alerts you to...
Note Important features or instructions.
Caution Risk of personal injury, system damage, or loss of data.
Warning Risk of severe personal inju ry.
Table 2: Text Convent ions
Convention Description
Screen displays This typeface indicates command syntax, or represents information
as it appears on the screen.
Screen displays
bold
This typeface indicates how you would type a particular command.
viii IP Service Manage r User Guid e

Conventions
Table 2: Te xt Conventions (c ontinued)
Convention Description
The words “enter”
and “type”
[Key] names Key names are written with brackets, such as [Return] or [Esc].
Words in Bold type GUI elements are written in bold type. Example: the menu item
Words in italicized type Italics emphasize a point or denote new terms at the place where
When you see the word “enter” in this guide, you must type
something, and then press the Return or Enter key. Do not press the
Return or Ente r key when an inst ruction simpl y says “type.”
If you must press two or more keys simultaneously, the key names
are linked with a plus sign (+). Example:
Press [Ctrl]+[Alt]+[Del].
File>Open, the Browse button, the Password field name
they are defined in the text. Italics are also used to denote variables,
such as VLAN names, or user account names.
IP Service Manage r User Guid e ix

Related Publications
The publications related to this one are:
• ISM Provision Installation Guide
• Network Infrastructure Manager User Guide
• ExtremeWare Software User Guide
Documentation for Extreme Networks products is available on the World Wide Web at
the following location :
http://www.extremenetworks.com/
x IP Service Manager Us er Guide

1
Infrastructure and Services
Management Provision Overview
Overview
Extreme Networks’ Infrastructure and Services Managemen t Provision (ISM Provision)
is a tightly connected collection of componen ts for delivering services to customers and
for managing your network. ISM P rovision allows you to easily extend services to your
network users by defining and provisioning bundles of IP services. Services are
managed as simple objects that are easy to apply to customers, but the configuratio n
changes required to support the delivery of services is managed by ISM Provision. ISM
Provision also allows you to control all or a portion of you r network, by controlling the
configurations of the devices in the netw ork.
ISM Provision is designed to ma ke it much easier to roll out changes to th e network.
You can add devices and make configuratio n changes offline and apply th em to your
network later. Planned changes are verifie d against a comprehe nsive set of rules to
assure that the changes can be applied to your network and will n ot conflict with
existing configurations. Inco mplete sessions can be saved to be com pleted later.
Services provided across a group of customers can be easily modified. Once a service is
updated, the change is applied to all cus tomers using the service. ISM Provision
manages all the config uration changes to ma ke the modifications.
Network Infrastructure Manager (NIM) is the GUI client portio n of ISM Provision that
controls and manages the infrastruc ture of your network, the configurations o f your
network devices. NIM works closely wit h IP Service Manager (IPSM), the GUI client
portion of ISM Provision that a llows a provider to manage customers, service bund les,
and policy based services.
IP Service Manage r User Guid e 1-1

Infrastructure an d Services M anagement Pro vision Overview
Summary of Features
• Version Control of Network Co nfiguration
• Staging of Network Co nfiguration Change s
• Configuration rules checking
• Helps Manage the VLAN s, Access Lists, and QoS Profile s Required to Support
Subscribers
• Provides Service-Level Abstractions to Manage Subscribers
• Client/Server Java architecture - platform independent and scala ble
• Offline and on-line tool - used in both green field a nd existing network
environments
• Co-exists with other mana gement tools using CLI or SN MP
• Version control for config urations and deployment modu le for system rollouts
• Provides an abstraction model that simplifies and autom ates both infrastructure and
subscriber provisioning life-cycles
• Distributed device communicat ion infrastructure for redundancy and scalin g
1-2 IP Service Manager U ser Guide
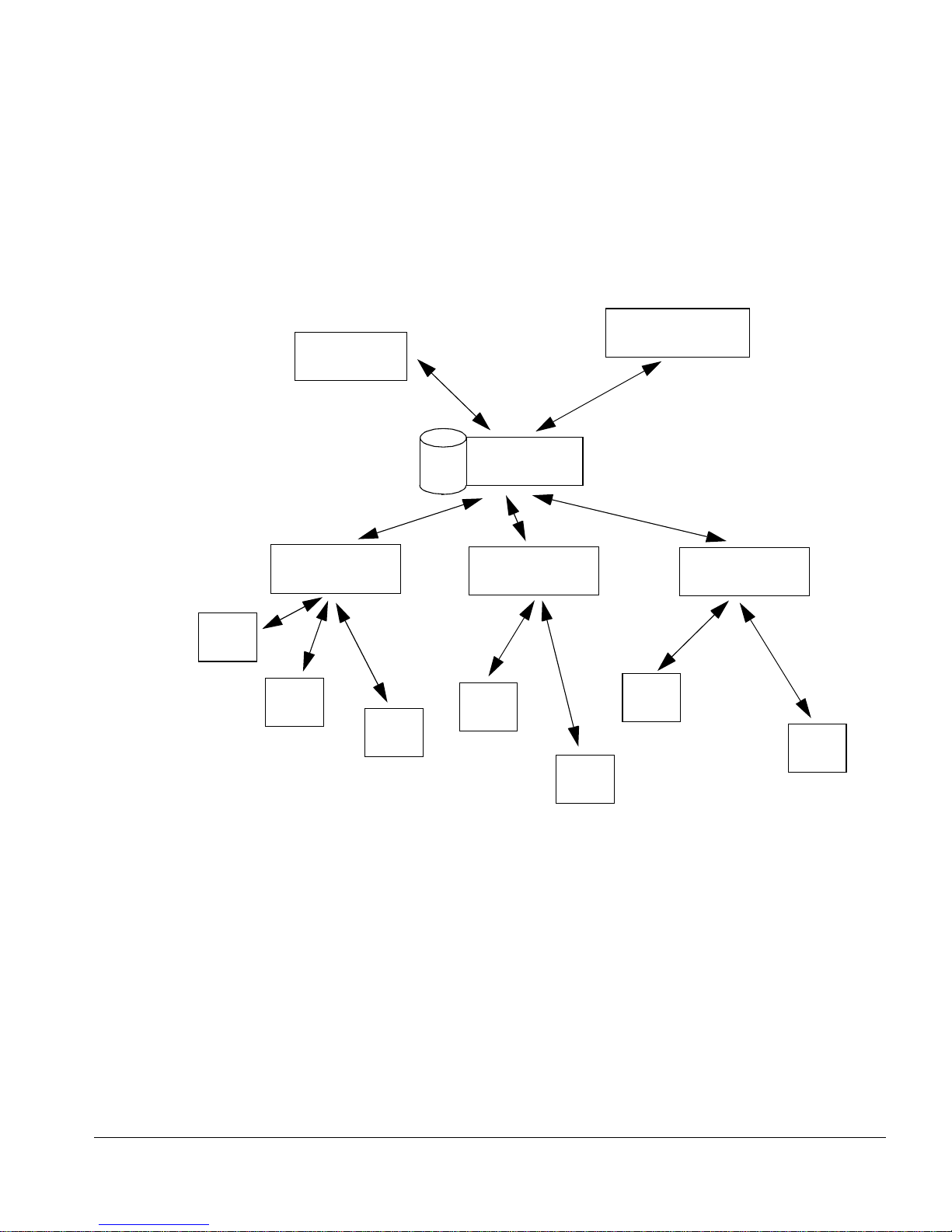
How ISM Provision works
NIM Client
ISM Provision
Server
How ISM Provision works
IP Service
Manager Client
Device
Communicator
Device
Communicator
Device
#1
Device
#2
Device
Device
#4
#3
Device
#5
Figure 1-1: ISM Provision Componen ts
ISM Provision consists of severa l different components:
• ISM Provision Server
• Device Communicators
• Network Infrastructure Manager Client
• IP Service Manager Client
Device
Communicator
Device
#6
Device
#7
These components work toget her to manage another important com ponent:
IP Service Manage r User Guid e 1-3

Infrastructure an d Services M anagement Pro vision Overview
• Yo u r N e tw ork Dev ice s
The following sections describe these components and how they interact in more detail.
Your Network Devices
The network managed by IS M Provision consists of your current existing network of
Extreme Network devices, or a subset of your devices. Many devices can be managed
by ISM Provision simultaneous ly. The devices are managed by querying th em for their
configurations, and by sending new configuration commands to them. Once ISM
Provision manages a device, it will periodically check that the device conf iguration for
changes.
ISM Provision Server
The ISM Provision server is the heart of ISM Provision . You may have m ore than one
instance of the othe r components, but on ly one server. The server contains the
information about the co nfigurations of the mana ged devices, configurations th at are
scheduled to be applied to the network a t a later time, and previous configurations. An
ISM Provision server can cont ain the configurations of a la rge number of devices, but
does not communicate with the devices directly. Instead, it uses device communicators
to handle this task.
The ISM Provision serve r also contains th e saved configura tion changes that have not
yet been applied to the network. These changes may be saved to edit later, or may be
applied at a f uture time to t he network.
Device Communicators
The device communicators control the communication between the network devices
and the ISM Provision server. All queries to devices from the ISM Provision server and
all commands from the ISM Provision server to the devices are handled by the device
communicators. To spread the processing load across hosts, there can be more than one
device communicator in an ISM Provision installation, but only one per ho st.
For example, in a network of 100 d evices all managed with the sa me ISM Provision
server, you m ight have five different device communicators, each talking with twen ty
devices. Any one managed device can only be managed by one device communicator,
otherwise conflicts will occur.
1-4 IP Service Manager U ser Guide

How ISM Provision works
Typically, you will install one devi ce communicator on the same host a s the ISM
Provision server, and then add other device comm unicators on oth er hosts as need ed to
manage the processing load of com municating with your devi ces.
Network Infrastructure Manager Client
The Network Infrastructure Manager (NIM) client is us ed to manage changes to the
network infrastructure. With NIM you can prepare and commit changes to the current
network configuration, and add new devices to be provisioned. Before changes are
rolled out to your network, NIM tests your proposed cha nges against a set of rules
designed to spot and help you correct errors (for example, duplicate IP addresses
assigned to different VLANs).
The NIM client also manages the providers, provider accounts, and provider access to
network resources. With NIM you can define a provider and restrict that provider’s
control to a specific set of ports o n a specific set of devices. You can also restrict the
allowable VLAN IDs and IP addresses that the provider can assign.
The NIM client also manages the ISM Provision server and device communicators. You
can see the status of the server and communicators and examine their logs. You can also
see who is currently connected to the ISM Provision server and send a broa dcast
message to them. You can shutdown the ISM Provision server from within NIM.
Finally, you can review the current changes in y our session, review committed, saved
and scheduled jobs, and perform configuration versioning.
IP Service Manager Client
The IP Service Manager client allows p roviders to manage subscribers (subscribers
consist of a VLAN and a single port in your netwo rk). IP Service Manager als o allows
you to configure service bundles (these correspond to Qo S profiles) and policy based
services (these correspond to access control lists) for these subscribers.
IP Service Manage r User Guid e 1-5

Infrastructure an d Services M anagement Pro vision Overview
1-6 IP Service Manager U ser Guide

2
Starting IP Service Manager
Overview
Since the IP Service Manager (IPSM) client is part of ISM Provision, IPSM relies on a
running ISM Provision server and device communicat or. This chapter assumes that you
already have a functioning ISM Provisio n server and device communicato r.
Starting IP Service Manager
The following is a short summary of the steps to start I P Service Manager
Summary Steps
To start IP Service M anager you must:
1 Launch the IPSM Client
2 Specify the ISM Provision S erver
3 Enter your Provider Name
4 Enter a User Account Name
5 Enter the Password for the Account
IP Service Manage r User Guid e 2-1
Starting IP Serv ice Manager
Detailed Steps
1 Launch the IPSM Client
Launch the IPSM client as you would launch other applications on your host. For
example, Windows users can select Network Infrastructure Manager from the
Start>Programs>Extreme Networks>ISM Provision>Applications menu. Solaris users
can launch the ipsm executable file from the /opt/extreme/ismprov/bin directory by
using a graphical file mana ger application to double-click o n its icon, or by typing:
/opt/extreme/ismprov/bin/ipsm
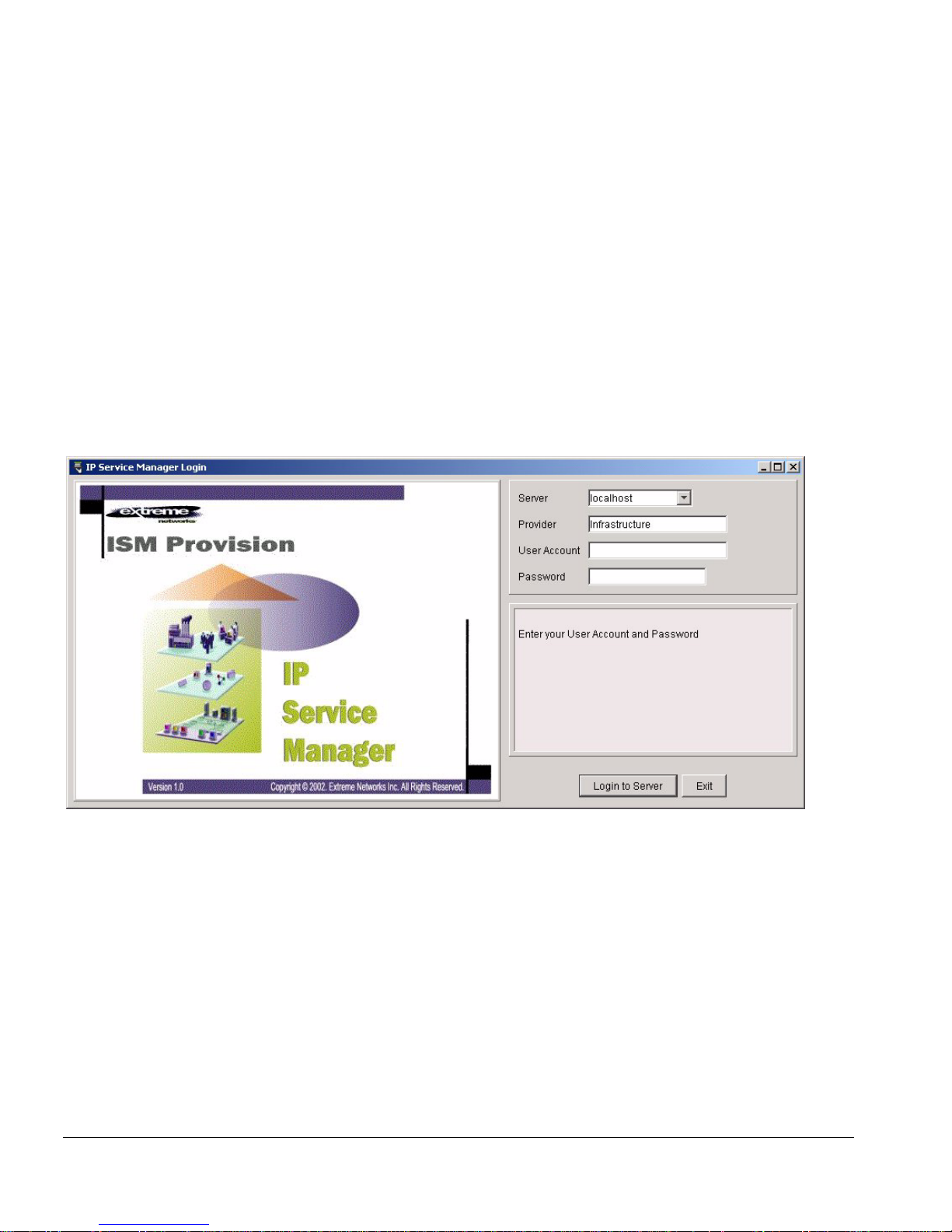
Once the application starts, you wil l see the login screen similar to the one sho wn in
Figure 2-1.
Figure 2-1: IP Service Manag er Login Screen
2 Specify the ISM Provision S erver
Once the login screen appears, you will specify th e ISM Provision server. Specify the IP
address of the server or the hostname by typing it into the server field. Figure 2-2 shows
the login screen and server field in more detail.
IPSM will store the IP addresses and names tha t you have specified in previous
sessions, so you may find your server already specified, or you may be abl e to select it
from the drop-down list in the server field. Click on the down-a rrow on the right side
of the field and select the server.
2-2 IP Service Manager U ser Guide
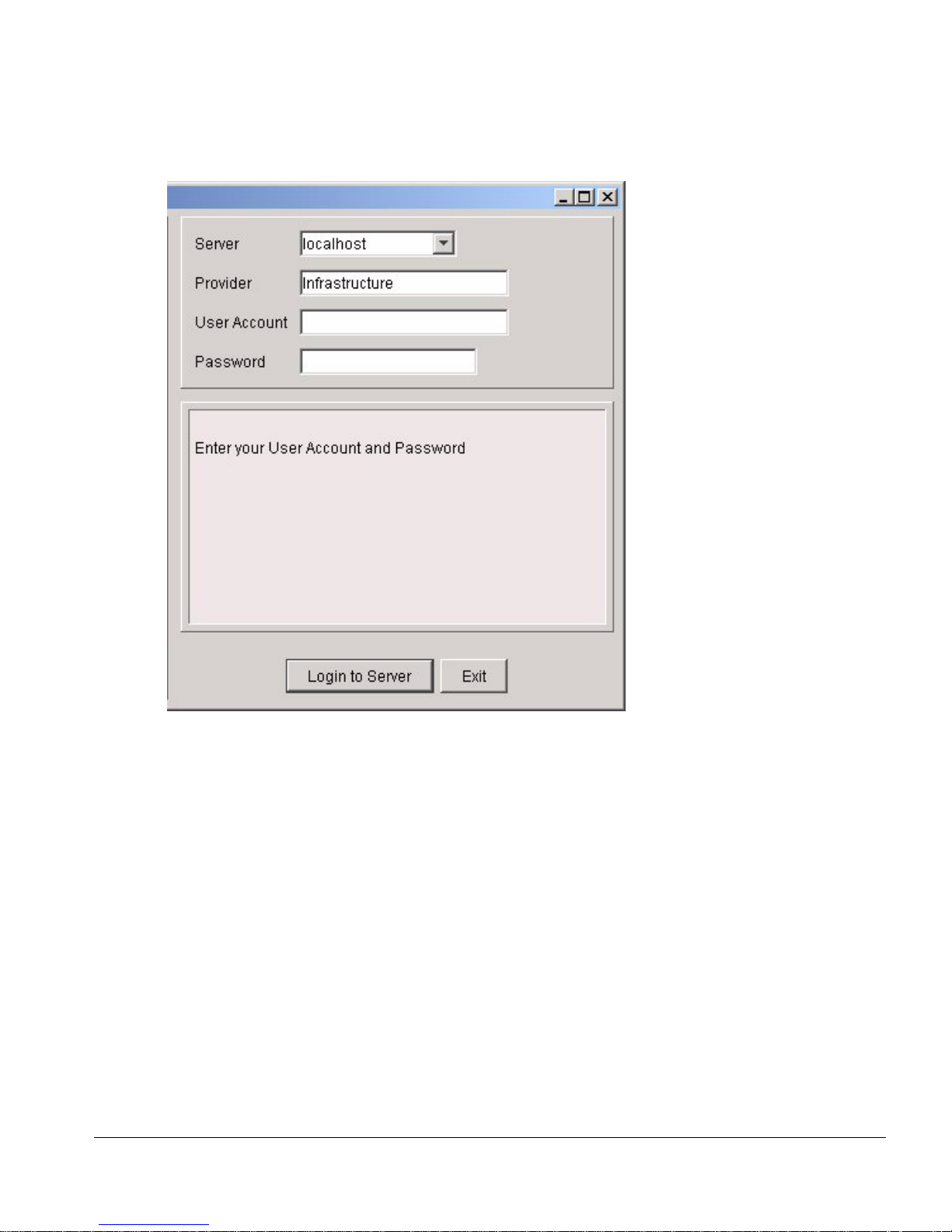
Overview
Figure 2-2: IPSM Login Scree n Detail
3 Enter your Provider Name
In the Provider field, enter the name of the provider that you belong to. If you have
previously used IPSM, you will find the previous provider nam e already entered.
4 Enter a User Account Name
In the User Account field, enter your user account name.
5 Enter the Password for the Account
In the Password field, enter the account password. The account passwords are not
saved and will need to be entered every session.
IP Service Manage r User Guid e 2-3
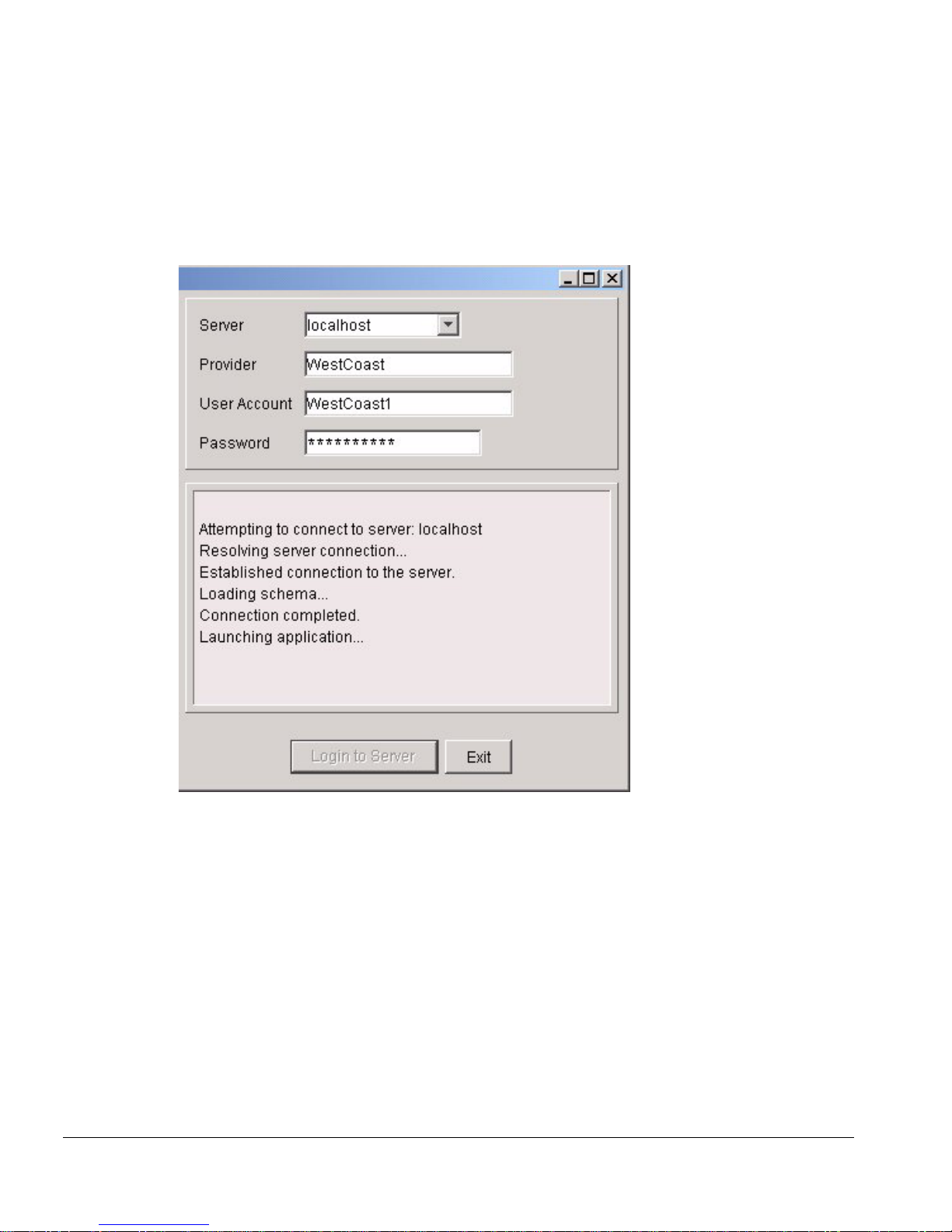
Starting IP Serv ice Manager
Once the information has been en tered, the IPSM client will attempt to connect with the
ISM Provision server. While it is connecting you will see messages s imilar to those in
Figure 2-3.
Figure 2-3: The IPSM Client Conn ecting to the ISM Provis ion Server
Once the IPSM client is launched, you w ill see the Service Activati on view.
2-4 IP Service Manager U ser Guide
 Loading...
Loading...