Page 1
FCC COMPLIANCE STATEMENTS
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a
Class B digital device, pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These
limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful
interference in a residential installation. This equipment generates, uses
and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in
accordance with the instructions, may cause harmful interference to
radio communications. However, there is no guarantee that interference
will not occur in a particular installation. If this equipment does cause
harmful interference to radio or television reception, which can be
determined by turning the equipment off and on, the user is encouraged
to try to correct the interference by one or more of the following
measures:
Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
Increase the Distance between the equipment and receiver.
Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to
which the receiver is connected.
Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
CAUTION
CHANGE OR MODIFICATIONS NOT EXPRESSLY APPROVED BY
PARTY RESPONSIBLE FOR COMPLIANCE COULD VOID THE
USER’S AUTHORITY TO OPERATE THE EQUIPMENT.
Page 2

TRADEMARKS
SystemSoft is a registered trademark of SystemSoft Corporation.
CardSoft is a trademark of SystemSoft Corporation.
Phoenix is a registered trademark of Phoenix Technologies, Ltd.
Databook is a registered trademark of Databook Inc.
Cardtalk is a trademark of Databook Inc.
PCMCIA is a trademark of Personal Computer Memory Card
International Association.
MS-DOS, Windows and MSCDEX are trademarks of Microsoft
Corporation.
Photo CD is a trademark of Kodak.
Page 3

CONTENTS
INTRODUCTION............................................................................... 1
SYSTEM REQUIREMENTS ..................................................... 1
FEATURES.............................................................................. 1
SPECIFICATIONS............................................................................. 2
PART NAMES AND FUNCTIONS ..................................................... 3
HARDWARE INSTALLATION ........................................................... 4
SOFTWARE INSTALLATION FOR Windows 95/98........................... 5
SOFTWARE INSTALLATION FOR DOS/Windows 3.11.................... 9
AUTOMATIC INSTALLATION .................................................. 9
MANUAL INSTALLATION........................................................ 11
TROUBLE SHOOTING...................................................................... 12
PCMCIA SOFTWARE....................................................................... 14
Page 4

INTRODUCTION
The PCMCIA Sound Module provides a mobile sound solution for
portable multimedia. With its real 16 bits stereo CD sound quality, the
Sound Module can play high-fidelity CD-quality audio which meets the
need of most users under any environment. The PCMCIA Sound Module
consists of a PCMCIA Type I card connected to a small Audio Module
with a build-in microphone and speaker and volume control. For your
convenience, there are also external jacks for a microphone and
speaker and a line-in jack for recording from an audio CD or cassette
player. This is the simplest way to economically and completely upgrade
your traditional notebook computer to become a multimedia version.
SYSTEM REQUIREMENTS
1. Notebook or desktop computer with a PCMCIA 2.1 Type I, II or III slot
2. MS-DOS Version 6.0 or later
3. Microsoft Windows 3.1
Features
§ Complies with PCMCIA 2.1
Standard
§ Easy-to-install device driver
software
§ No external power supply required
§ Real 16 bit stereo sound
§ Build-in speaker (Mono), no
additional external speaker
required
§ Build-in microphone (Mono), no
additional external microphone
required
§ Stereo line-in jack (3.5mm stereo
plug)
§ Stereo output external speaker
jack (3.5 mm stereo plug)
§ Microphone input jack (3.5mm
stereo plug)
§ 20-voice stereo FM synthesis
§ Compatible with Windows 3.1
§ ADPCM and ESPCM
decompression
§ Adjustable volume control by S/W
or manually
§ Ultra slim PCMCIA Card
Size: 85.6 x 54.0 x 3.3 mm (Type I)
§ Pocket-sized sound module
Size: 75x 45x 16mm
Weight ≤ 100g
- 1 -
Page 5

SPECIFICATION
1. 16 Bit Sampling and Playback:
* 8, 16 Bit PCM 2KHz-44kHz in Stereo.
* ADPCM compression (2:1) and decompression (2:1, 3:1, 4:1)
2. Synthesizer:
* YAMAHA YMF262, 20 Voice Stereo Synthesizer
* 4 Operator FM sound.
3. Audio Playing Mixing:
* Internal Synthesizer (Stereo)
* Digital Audio (Stereo)
* CD Audio (Stereo)
* Speaker (Built-in or external, Mono)
4. Audio Recording Mixing:
* CD-Audio (Stereo)
* External Line-in (Stereo)
* Microphone (Built-in, Mono)
5. Volume Control: hardware or one on-screen software control
* Master Volume: 9 to 62 dB (1 dB/step)
* Input Mixer: +1 to 60 dB (2dB/step)
6. Signal Quality: (1V p-p Reference)
* Synthesized and Mixed Audio: 85 dB
* Sampled Audio PCM: 85 dB
* Total Harmonic Distortion:0.05%
7. Frequency Response:
* 30Hz to 20kHz(+/- 3dB)
8. Audio Output:
* Output Level: 11.5V Max (p-p)
* Output Connection: Stereo mini Jack
9. Controller Interface:
PCMCIA TYPE I
10. Compatible with:
* Sound Blaster 2.0
* Sound Blaster Pro
* AdLib
- 2 -
Page 6
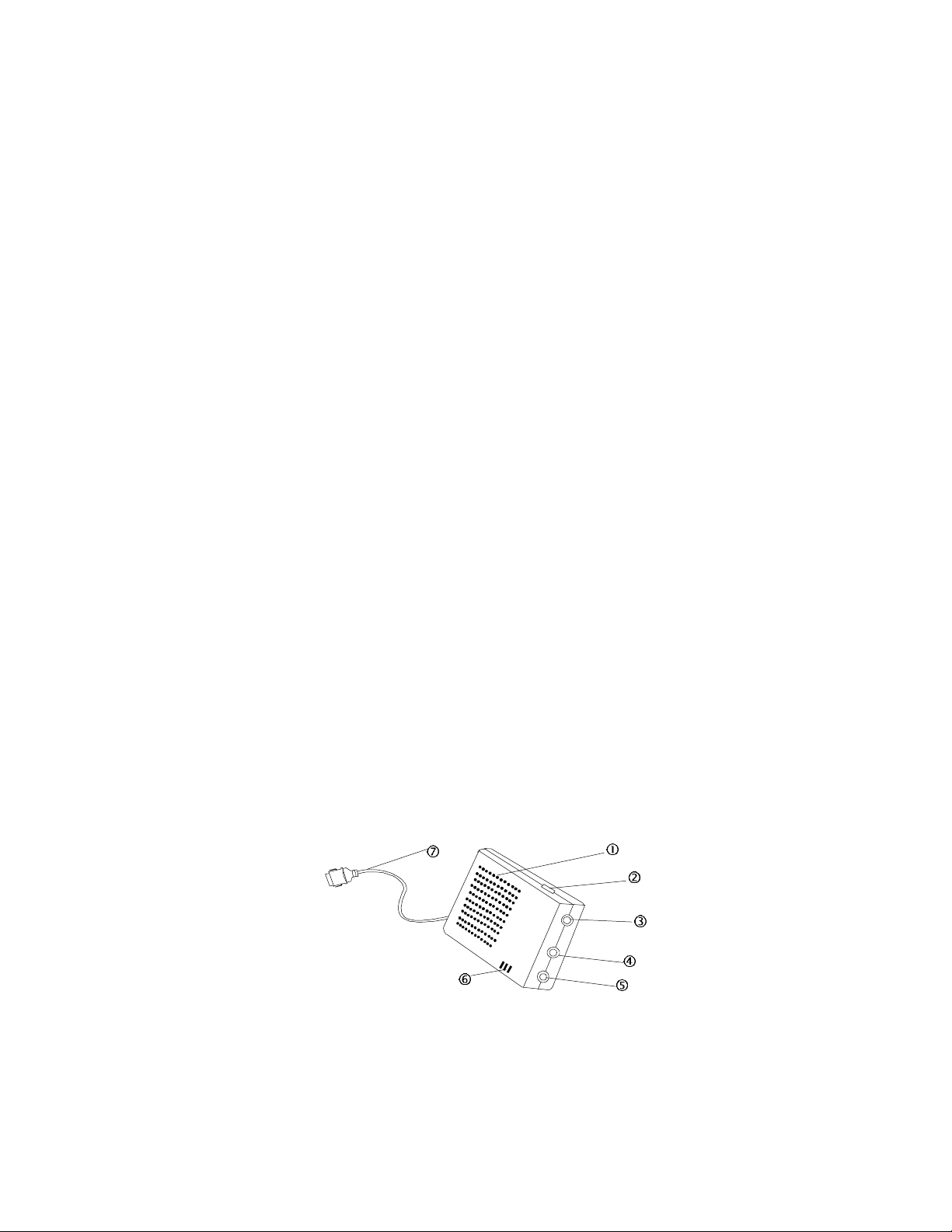
PART NAMES AND FUNCTIONS
•• Build-in Speaker:
This build-in 28 mm speaker is a MONO sound speaker.
‚‚ Volume Control Knob:
This knob is used to adjust the volume of the build-in speaker and
the external headphone jack.
ƒƒ External Headphone Jack:
This is used to connect to a headphone or a self-powered external
speaker with the standard 3.5mm stereo plug. When using with
the external headphone or speaker, the build-in speaker will be
disabled.
„„ External Microphone Jack:
This jack is used to connect to an external microphone with a
standard 3.5mm plug. When using with an external microphone,
the build-in speaker will be disabled.
(Note: This jack is designed for condenser type microphone only.
Do not use a magnetic type microphone..)
…… Stereo Line-in Jack:
Use the cable that came with your Sound Module to connect with
another audio source. (CD player, Cassette tape player)
†† Build-in Microphone
‡‡ Sound Module Cable:
This 15-pin cable connects to the PCMCIA interface card.
- 3 -
Page 7

HARDWARE INSTALLATION
Before you begin, make sure you turn your system OFF before connecting
the PCMCIA Sound Module.
1. Connect the cable of the Sound module with the PCMCIA interface card.
(Note: The 15-pin keyed connector can be easily attached to the card if
you are plugging it with the right side up.)
2. Locate the PCMCIA slot of your computer, or consult your computer’s
owner manual for the location of the PCMCIA slot.
3. Align the PCMCIA interface card with
the arrow sign pointing to the computer’s
slot. (Please note that the card is keyed
to guide the proper insertion.)
4. Slowly insert the PCMCIA interface card
into the slot and press firmly until the
connector is seated.
5. You are now ready to install the PCMCIA Sound device driver. Please
follow the Software Installation procedures.
CAUTION
You should connect the PCMCIA interface card to Sound Module
first before inserting the PCMCIA interface card into your
computer. DO NOT connect/disconnect the PCMCIA interface
card to/from the Sound Module when the system is in the poweron state.
- 4 -
Page 8

Software installation Guide for Windows 95/98
PCMCIA Sound Card can be also used under Windows 95/98 that you may
enjoy the true plug and play convenience. Before you start using PCMCIA
Sound Card under Windows 95, make sure your computer is Windows 95
installed and follow the below instruction to install PCMCIA Sound Card.
USING PCMCIA SOUND CARD UNDER WINDOWS 95
The following dialog box will appear when you are using the PCMCIA Sound
Card under Windows 95/98 for the very first time.
If the dialog box does not appear and the PCMCIA Sound Card folder can
not be found in My Computer, please refer to next section titled “Enabling
32-Bit Card Support”.
- 5 -
Page 9

Select “Driver from disk provided by hardware manufacturer” and click on
OK button, Windows 95/98 will then prompt you to insert the manufacturer’s
installation disk. Insert the PCMCIA Sound Card device driver disk into your
floppy drive. Specify the directory as A:\WIN95 (or B:\WIN95 whichever
containing the diskette) and select OK.
When the following dialog box appear, select PCMCIA Sound Card and click
on the OK button. Follow the on-screen instruction to continue.
Note that it is not necessary to connect the PCMCIA Sound Card every time
you reboot your computer; plug it just when you need to use it.
- 6 -
Page 10

ENABLING 32-BIT CARD SUPPORT OF WINDOWS 95
(For Windows 98 the 32-bit card support is enbled by default.)
Your system should be ready for PCMCIA socket support prior to operating the PCMCIA Sound
Card. To check whether your computer is PCMCIA Socket supported, first, double-click on the
“System” icon from “Control Panel” folder (you can select the “Control Panel”
under “Settings” from the “Start” menu to open the “Control Panel” folder).
Click on the Device Manager Tab. If “PCMCIA Socket” is found with a cross
(x) sign next to the PCMCIA Controller as the following figure shown, it
means the PCMCIA device driver is not using 32-Bit Card Support.
In this case, double click on the PCMCIA Controller, and a dialog box will be
displayed as below. Please place a check mark next to the current
configuration of Device usage box, then select OK.
- 7 -
Page 11

After the PCMCIA 32-Bit Card support is installed, Windows will ask you to
reboot your computer. Then you should refer to the previous section titled
“Using Sound Card Under Windows 95” to configure the PCMCIA Sound
Card.
If the PCMCIA Socket is not found, then you must add a PCMCIA socket to
your system. Please click on the “Add New Hardware” icon in the Control
Panel folder and select “PCMCIA socket”. Select the appropriate type of
PCMCIA Controller that matches with yours and follow the on-screen
instructions.
- 8 -
Page 12

SOFTWARE INSTALLATION FOR DOS/WINDOW 3.11
Take note that this section describes the installation of the PCMCIA Sound
device driver only. To install the Windows Sound Application you have to
refer to the Audio Applications USER’S GUIDE that comes with this unit after
completing the installation of the PCMCIA Sound device driver.
AUTOMATIC INSTALLATION
The device driver installation programs provide an INSTALL program to help
you to install the device driver into the computer easily. Please follow the
instructions below to proceed with the automatic installation.
1. Insert the device driver diskette into a floppy disk drive on your
computer.
2. Change the working directory to the floppy drive containing the device
driver diskette by typing “A:” or “B:” then press ENTER.
3. At the DOS prompt (A:\> or B:\>), type “INSTALL” followed by the
ENTER key.
4. Press ENTER or click on the OK button to continue when the opening
screen appears. A dialog box will be displayed for you to specify 1) the
directory to place the device driver; 2) the I/O port and 3) the IRQ
desired for the PCMCIA Sound Module. Enter the directory you select
to install the driver and press the TAB key to set the I/O port and then
the IRQ. The default setting of the I/O ports are 220-22F, and the
default IRQ is 10. After completing the selection, click on Install button
to continue.
- 9 -
Page 13

5. The rest of the installation should proceed automatically, and the
CONFIG.SYS file on your computer will be updated automatically.
6. Now you should reboot your computer to activate the PCMCIA Sound.
Please refer to the previous section of “Hardware Installation” to make
sure the PCMCIA Sound has been connected to your system properly.
7. After the system is rebooted, you also will have to install the Windows
device driver for Sound. Go to Windows and insert the Audio
Application Software Disk #1 into a floppy drive. Run the File Manager
and select the drive containing Audio Application Software Disk#1.
Find and double-click file setup.exe. Once you see the Audio
Applications Setup window, select the Driver Installation, then select
the Custom Board Configuration button to set the proper Sound I/O
address, Interrupt (IRQ number) and DMA channel. The I/O address
and Interrupt number are the same as you selected in the INSTALL
program. The DMA should be set at 0.
Note: Due to the lack of DMA channel support in the PCMCIA structure,
some of the DOS GAME will not play Sound properly.
- 10 -
Page 14

MANUAL INSTALLATION
You may also manually install the PCMCIA Sound Module device driver if
the default setting conflicts with your system. Perform the following
procedure to complete the manual installation.
1. Copy the files PCMSND.EXE from the PCMCIA Sound Module device
driver disk to your hard disk.
2. Add the following lines near the BOTTOM of your CONFIG.SYS file:
DEVICE=drive:\path\PCMSND.EXE /P220 /I10
where drive:\path specifies the directory containing file PCMSND.EXE.
If your CONFIG.SYS file is already loaded with PCMCIA software, such as
Cardsoft of SystemSoft or Cardtalk of Databook, it is necessary to add the
above line AFTER the PCMCIA software. Otherwise, the PCMCIA interface
card will not be initialized properly. To make sure if any PCMCIA software
has been loaded in your system and to know more about PCMCIA, please
refer to the section of “PCMCIA Software Information”.
PCMSND.EXE is the device driver for the PCMCIA Sound Module. The
parameters of PCMSND.EXE are described as below:
/P is used to set the I/O ports, and the valid I/O ports are 220-22F, 230-
23F, and 240-24F. The default setting is /P220.
/I is used to set the IRQ number, the valid IRQs are 5, 7, 9, 10, and the
default setting is /I10.
3. After the system is rebooted, you also will have to install the Windows
device driver for Sound. Go to Windows and insert the Audio
Application Software Disk #1 into a floppy drive. Run the File Manager
and select the drive containing Audio Application Software Disk#1.
Find and double-click file setup.exe. Once you see the Audio
Applications Setup window, select the Driver Installation, then select
the Custom Board Configuration button to set the proper Sound I/O
address, Interrupt (IRQ number) and DMA channel. The I/O address
and Interrupt number are the same as you selected in INSTALL
program. The DMA should be set at 0.
Note: Due to the lack of DMA channel support in the PCMCIA structure,
some of the DOS GAME will not play Sound properly.
- 11 -
Page 15

TROUBLE SHOOTING
This section explains the most common error messages and their solutions.
After rebooting your computer, the following messages will be displayed on
your screen, which is generated by PCMSND.EXE
Configure card to:
I/O Port: 220-22F, 388-38B
IRQ number: 10
Power: connected
PCMCIA Sound card is present in socket 1
If any error occurs or the PCMCIA Sound Module does not work, you should
reboot your computer again. When the system displays 'Starting MS-DOS...',
press the F8 key to make the system execute CONFIG.SYS and
AUTOEXEC.BAT step by step. You can see each the command by pressing
the “Y” key.
ERROR MESSAGES GENERATED BY PCMSND.EXE:
vv Error: PCMCIA Sound card is not present!
If the above message appears, it means PCMSND can't find any PCMCIA
Sound interface card in your PCMCIA slots. Make sure the card is inserted
firmly.
vv Error: Illegal arguments!
For help, type “PCMSND /?”.
The above error message means there are invalid arguments in PCMSND
line of CONFIG.SYS. Please refer to the previous section of “MANUAL
INSTALLATION” for the usage of PCMSND.EXE.
vv Error: I/O port must be specified!
The above message means you have not specified the I/O port argument in
PCMSND line of CONFIG.SYS.
vv Error: IRQ must be specified!
The above message means you have not specified the IRQ number in
PCMSND line of CONFIG.SYS.
vv Error: Illegal I/O port!
The above message means an invalid I/O ports in PCMSND line of
CONFIG.SYS has been selected. The legal I/O ports are : 220, 230 and 240.
vv Error: Illegal IRQ number!
- 12 -
Page 16

The above message means an invalid IRQ number in PCMSND line of
CONFIG.SYS has been selected. The legal IRQ number are 5, 7, 9, and 10.
vv Error: There is no available 4K memory for mapping!
The above message means PCMSND can't find available 4K memory
between C000:0 to EFFF:0. This error can be corrected by changing the
EMM386 line of CONFIG.SYS to exclude at least 4K memory. For example,
DEVICE=C:\DOS\EMM386.EXE ... X=D000-D3FF
vv Error: The INTEL 82365SL PCMCIA controller is not
detected in your system. You should contact your
dealer to get a PCMCIA support software.
The above message means the PCMCIA controller of your system is not
INTEL 82365SL compatible. In this case, you should install PCMCIA support
software which should have been supplied by the notebook manufacture.
If the error message displayed if none of the above, please contact your
dealer for customer support.
- 13 -
Page 17

PCMCIA SOFTWARE INFORMATION
If you have installed the PCMCIA software, such as SystemSoft’s CardSoft
or Databook’s Cardtalk, then PCMSND.EXE will call these PCMCIA software
to enable the card. If you don’t have one, the PCMSND still can directly
access your hardware to enable the card. In this case, your computer should
have an Intel 82365SL Personal Computer Interface Controller (PCIC) or
another compatible controller.
PCMCIA software contains several components: Socket services, Card
services, Resource Initialization Utility and Card Installation Utility. The
remainder of this section will explain the four components and list the device
driver names for the major PCMCIA software.
Socket Services provide the interface between a system’s BIOS and the host
controller chips (such as the Intel 82365SL PCIC, Vadem 468, etc ) Socket
Services includes functions such as configuring a socket for an I/O or
memory interface and controlling socket power voltages. The Socket
Services driver you have varies with the host computer chip of your
computer.
Card Services provides the interface between the PC Card and the PCMCIA
sockets. Card Services must be aware of the I/O, IRQ, and memory
resources already used by the system so it can accurately assign unused
resources to the PC Cards.
To ensure Card Services will operate reliably regardless of the system it is
installed on, some PCMCIA software provides its own resource initialization
utility, which will check I/O ports, IRQs, and memory addresses and then
report that information to Card Services.
The Card Installation Utility detects the insertion and removal of PC cards,
and automatically determines the card type upon insertion so the card and
socket will be configured properly.
- 14 -
Page 18

The device driver names of the major PCMCIA software are listed below:
Software/Device
Driver
Socket Services SS365SL.EXE,
Card Services CS.EXE PCMCS.EXE PCCS.EXE IBMDOSCS.SYS
Resource
Initialization Utility
IDE/ATA Driver ATADRV.EXE PCMATA.SYS
SRAM Card Driver MTSRAM.EXE
Flash Card Support MTAA.EXE,
Memory Card
Driver
Card Installation
Utility
Card Services Power
Management
SystemSoft
CardSoft
SS365LP.EXE,
SSCIRRUS.EXE,
SSDBOOK.EXE,
SVADEM.EXE,
SSVLSI.EXE
CSALLOC.EXE PCMRMAN.SYS PCRM.EXE DICRMU02.SYS
MTAB.EXE,
MTI1,EXE
MTI2P.EXE
MEMDRV.EXE
CARDID.EXE PCMSCD.EXE PCENABLE.EXE AUTODRV.SYS
CS_APM.EXE $ICPMDOS.SYS
Phoenix Award
Cardware
PCMSS.EXE SSPCIC.EXE IBMDSS02.SYS
IBM
ThinkPad
If you are not sure which PCMCIA software you are using, you may check it
by typing TYPE CONFIG.SYS at the DOS prompt followed by the ENTER key.
The file should come up and look like one of the following examples.
SYSTEMSOFT PCMCIA SOFTWARE SAMPLE CONFIG.SYS FILE
LASTDRIVE=Z
DEVICE=C:\DOS\HIMEM.SYS
DEVICE=C:\DOS\EMM386.EXE NOEMS X=D000-D3FF
FILES=40
BUFFERS=20
STACKS=9,256
DEVICEHIGH=C:\CARSOFT\SS36SSL.EXE
- 15 -
Page 19

DEVICEHIGH=C:\CARDSOFT\CS.EXE
DEVICEHIGH=C:\CARDSOFT\CSALLOC.EXE
REM** The REM’s should be removed from the follwing
REM** lines to enable memory and hard drive card support
REM** DEVICEHIGH=C:\CARDSOFT\ATADRV.EXE
REM** DEVICEHIGH=C:\CARDSOFT\MTSRAM.EXE
REM** DEVICEHIGH=C:\CARDSOFT\MTDDRV.EXE
DEVICEHIGH=C:\CARDSOFT\CARDID.EXE
DEVICE=C:\PCMSND\PCMSND.EXE /P220 /I10
PHOENIX PCMCIA SOFTWARE SAMPLE CONFIG.SYS FILE
LASTDRIVE=Z
DEVICE=C:\DOS\HIMEN.SYS
DEVICE=C:\DOS\EMM386.EXE NOEMS X=D000-D3FF
DOS=HIGH, UMB
STACKS=9,256
DEVICE=c:\PCMPLUS3\CNFIGNAME.EXE/DEFAULT
DEVICE=C:\PCMPLUS3\PCMSS.EXE
DEVICE=C:\PCMPLUS3\PCMCS.EXE
DEVICE=C:\PCMPLUS3\PCMRMAN.EXE
DEVICE=C:\PCMPLUS3\PCMSCD.EXE
DEVICE=C: \PCMSND\PCMSND.EXE /P220 /I10
AWARD PCMCIA SOFTWARE SAMPLE CONFIG.SYS FILE
LASTDRIVE=Z
DEVICE=C:\DOS\HIMEN.SYS
DEVICE=C:\DOS\EMM386.EXE NOEMS X=D000-D3FF
FILES=40
BUFFERS:20
STACKS=9,256
DEVICE=C:\CARDWARE\SSPCIC.EXE
DEVICE=C:\CARDWARE\PCCS.EXE
DEVICE=C:\CARDWARE\PCRM.EXE/AUTODETECT
DEVICE=C:\CARDWARE\PCENABLE.EXE
DEVICE=C:\PCMSND\PCMSND.EXE /P220 /I10
IBM PCMCIA SOFTWARE SAMPLE CONFIG.SYS FILE
LASTDRIVE=Z
DEVICEHIGH=C:\DOS\HIMEN.SYS/TESTMEM:OFF /MACHINE:2
DEVICEHIGH=C:\DOS\EMM386.EXE NOEMS X=D000-DFFF
BUFFERS=40
FILES=40
STACKS=9,256
DOS=HIGH
DEVICEHIGH=C:\THINKPAD\IBMDSS02.SYS /S0=2
- 16 -
Page 20

DEVICEHIGH=C:\THINKPAD\IBMDOSCS.SYS
DEVICEHIGH=C:THINKPAD\DICRMU02.SYS /MA=D000-DFFF
DEVICEHIGH=C:\THINKPAD\$ICPMDOS.SYS
DEVICE=C:\THINKPAD\AUTODRV.SYS C:\THINKPAD\AUTODRV.INI
DEVICE=C:\PCMSND\PCMSND.EXE /P220 /I10
- 17 -
 Loading...
Loading...