Page 1

Installation and Operating
®
®
SECTION 92.80 2008-07
Instructions
ABSOLYTE
For
®
GX Batteries
Page 2

TABLE OF CONTENTS
SECTION 1: GENERAL ...................................................................................................................................6
SECTION 2: SAFETY MESSAGES .................................................................................................................6
2.0 General Information.....................................................................................................................6
2.1 Sulfuric Acid Burns ......................................................................................................................6
2.2 Explosive Gases..........................................................................................................................6
2.3 Electrical Shock and Burns .........................................................................................................6
2.3.1 Static Discharge Precautions for Batteries..................................................................................6
2.4 Safety Alert ..................................................................................................................................6
2.5 Important Message......................................................................................................................6
SECTION 3: DELIVERY INFORMATION .........................................................................................................7
3.0 Receipt of Shipment ....................................................................................................................7
3.1 Concealed Damage.....................................................................................................................7
SECTION 4: STORAGE INFORMATION .........................................................................................................7
4.0 Storage Prior to Installation .........................................................................................................7
4.1 Storage Location .........................................................................................................................7
4.2 Storage Interval ...........................................................................................................................7
SECTION 5: INSTALLATION CONSIDERATIONS ..........................................................................................7
5.0 General........................................................................................................................................7
5.1 Space Considerations .................................................................................................................7
5.2 Battery Location & Ambient Temperature Requirements ............................................................7
5.3 Temperature Variations................................................................................................................9
5.4 Ventilation....................................................................................................................................9
5.5 Floor Loading...............................................................................................................................9
5.6 Floor Anchoring ...........................................................................................................................9
5.7 Connecting Cables: Battery System to Operating Equipment ....................................................9
5.7.1 Paralleling....................................................................................................................................9
5.8 Stacking Limitations...................................................................................................................10
5.9 Terminal Plates ..........................................................................................................................10
5.10 Grounding..................................................................................................................................10
SECTION 6: UNPACKING..............................................................................................................................10
6.0 General......................................................................................................................................10
6.1 Accessories ...............................................................................................................................10
6.2 Recommended Installation Equipment and Supplies................................................................10
6.3 Unpacking ..................................................................................................................................11
6.4 Handling of Modules ..................................................................................................................11
Page 3

SECTION 7: SYSTEM ARRANGEMENTS.....................................................................................................11
7.0 Module Arrangements................................................................................................................11
SECTION 8: SYSTEM ASSEMBLY ................................................................................................................11
8.0 Module Assembly Identification .................................................................................................11
8.1.1 Bottom Supports (I-beams) .......................................................................................................12
8.1.2 Handling of Modules..................................................................................................................12
8.1.3 Tip Over Procedure ...................................................................................................................12
8.2 Horizontal-Multiple Stacks .........................................................................................................14
8.2.1 Stacking Base Modules .............................................................................................................14
8.2.2 Stack Tie Plates.........................................................................................................................14
8.2.3 Horizontal Stacking....................................................................................................................14
SECTION 9: ELECTRICAL CONNECTIONS.................................................................................................14
9.0 Post Preparation........................................................................................................................14
9.1 Connections - System Terminals ...............................................................................................15
9.2 Connections - InterMODULE.....................................................................................................15
9.3 Connections - InterSTACK ........................................................................................................15
9.4 Torquing .....................................................................................................................................15
9.5 Connections - Check .................................................................................................................15
SECTION 10: IDENTIFICATION LABELS........................................................................................................15
10.0 Surfaces ....................................................................................................................................15
10.1 Cell Numerals ............................................................................................................................15
10.2 System Polarity Labels ..............................................................................................................17
10.3 Warning Label............................................................................................................................17
10.4 Battery Nameplate.....................................................................................................................17
SECTION 11: PROTECTIVE MODULE COVERS ...........................................................................................17
11.0 General......................................................................................................................................17
11.1 Transparent Cover Installation ..................................................................................................17
SECTION 12: BATTERY CHARGING..............................................................................................................17
12.0 Initial Charge .............................................................................................................................17
12.1 Constant Voltage Method ..........................................................................................................17
Page 4

SECTION 13: BATTERY OPERATION ............................................................................................................19
13.0 Cycle Method of Operation........................................................................................................19
13.1 Floating Charge Method ............................................................................................................19
13.2 Float Charge - Float Voltages ...................................................................................................19
13.3 Recharge ...................................................................................................................................19
13.4 Determining State-of-Charge.....................................................................................................19
13.5 Effects of Float Voltage .............................................................................................................20
13.6 Float Current and Thermal Management ..................................................................................20
13.7 AC Ripple ..................................................................................................................................20
13.8 Ohmic Measurements ...............................................................................................................20
SECTION 14: EQUALIZING CHARGE ............................................................................................................20
14.0 General......................................................................................................................................20
14.1 Equalizing Frequency ................................................................................................................21
14.2 Equalizing Charge Method ........................................................................................................21
SECTION 15: RECORDKEEPING ...................................................................................................................21
15.0 Pilot Cell ....................................................................................................................................21
15.1 Voltmeter Calibration .................................................................................................................21
15.2 Records .....................................................................................................................................21
SECTION 16: TAP CONNECTIONS ................................................................................................................22
16.0 Tap Connections........................................................................................................................22
SECTION 17: TEMPORARY NON-USE ..........................................................................................................22
17.0 Temporary Non-Use ..................................................................................................................22
SECTION 18: UNIT CLEANING.......................................................................................................................22
18.0 Unit Cleaning .............................................................................................................................22
SECTION 19 CONNECTIONS MAINTENANCE.............................................................................................22
19.0 Connections...............................................................................................................................22
SECTION 20 CAPACITY TESTING ................................................................................................................22
20.0 Capacity Testing ........................................................................................................................22
Page 5

LIST OF ILLUSTRATIONS
PAGE FIGURE DESCRIPTION
8 Fig. 1 Typical System Spacing
10 Fig. 2 Packaged Modules
11 Fig. 3 Unpacking Modules
11 Fig. 4 Handling - Lifting Strap Placement
11 Fig. 5 Handling - Module
11 Fig. 6 Typical System Arrangements
12 Fig. 7 I-Beam Hardware Installation
12 Fig. 8 I-Beam Support Installed
12 Fig. 9 Tip-Over Procedure - Shackle-Strap Usage
13 Fig. 10 Tip-Over Procedure - Photo
13 Fig. 11 Module with Base Assembly After Tip-Over
13 Fig. 12 Horizontal Stacking - Shackle-Strap Usage
13 Fig. 13 Handling and Stacking Horizontal Modules
13 Fig. 14 Hardware Installation Sequence
14 Fig. 15 Installing Hardware
14 Fig. 16 Completed Horizontal Stack
14 Fig. 17 Positioning Horizontal Base Modules
14 Fig. 18 Tie Plate Assemblies
15 Fig. 19 Stack Connections
16 Fig. 20 Terminal Plate Kit Materials & Assembly
18 Fig. 21 Protective Cover Materials & Assembly
23 Fig. 22 Sample Record Form
LIST OF TABLES
PAGE TABLE DESCRIPTION
9A Temperature Effects on Life
10 B Absolyte GX Stacking Limitations
17 C Initial Charge Voltages
20 D Float Voltage Effects on Life
21 E Equalize Charge Voltages
APPENDICES
PAGE APPENDIX DESCRIPTION
25 A Temperature Corrected Float Voltages
26 B Maximum Storage Interval Between Freshening Charges
Versus Average Storage Temperature
27 C Bonding and Grounding of Battery Rack
Page 6
SECTION 1: GENERAL
1.0 General Information
Multi-cell systems attain high voltages, therefore, extreme
caution must be exercised during installation of a battery
system to prevent serious electrical burns or shock.
CAUTION!
Before proceeding with the unpacking, handling, installation and operation of this sealed lead-acid storage
battery, the following information should be reviewed
thoroughly. The safety procedures should be strictly
adhered to when working with Absolyte GX batteries.
SECTION 2: SAFETY MESSAGES
2.1 Sulfuric Acid Burns
DANGER!
SULFURIC ACID BURNS
Batteries contain sulfuric acid which can cause burns and
other serious injury. In the event of contact with sulfu-
ric acid, flush immediately and thoroughly with water.
Secure medical attention immediately.
When working with batteries, wear rubber apron and rubber gloves. Wear safety goggles or other eye
protection. These will help prevent injury if contact is
made with the acid.
Interrupt the AC and DC circuits before working on
batteries or charging equipment.
Ensure that personnel understand the risk of working with
batteries, and are prepared and equipped to take the necessary safety precautions. These installation
and operating instructions should be understood and
followed. Assure that you have the necessary equipment
for the work, including insulated tools, rubber gloves, rubber aprons, safety goggles and face protection.
CAUTION!
If the foregoing precautions are not fully
understood, clarification should be obtained
from your nearest GNB representative.
Local conditions may introduce situations
not covered by GNB Safety Precautions. If
so, contact the nearest GNB representative
for guidance with your particular safety
problem; also refer to applicable federal,
state and local regulations as well as industry standards.
2.3.1 Static Discharge Precautions for Batteries
2.2 Explosive Gases
DANGER!
EXPLOSIVE GASES
Hydrogen gas formation is an inherent feature of all lead
acid batteries.
Absolyte GX VRLA batteries, however, significantly
reduce hydrogen formation. Tests have shown that 99%
or more of generated gases are recombined within the
cell under normal operating conditions. Under abnormal
operating conditions (e.g. charger malfunction), the safety valve may open and release these gases through the
vent. The gases can explode and cause blindness and
other serious injury.
Keep sparks, flames, and smoking materials away from
the battery area and the explosive gases.
All installation tools should be adequately insulated to
minimize the possibility of shorting across connections.
Never lay tools or other metallic objects on modules as
shorting, explosions and personal injury may result.
2.3 Electrical Shock and Burns
DANGER!
ELECTRICAL SHOCK AND BURNS
HIGH VOLTAGE…
RISK OF SHOCK.
DO NOT TOUCH
UNINSULATED
TERMINALS OR
CONNECTORS.
When maintaining a connected battery string, care must
be taken to prevent build-up of static charge. This
danger is particularly significant when the worker is
electrically isolated, i.e. working on a rubber mat or an
epoxy painted floor or wearing rubber shoes.
Prior to making contact with the cell, discharge static electricity by touching a grounded surface.
Wearing a ground strap while working on a connected
battery string is not recommended.
2.4 Safety Alert
The safety alert symbol on the left appears
througout this manual. Where the symbol
appears, obey the safety message to avoid
personal injury.
2.5 Important Message
The symbol on the left indicates an important message. If not followed, damage to
and/or impaired performance of the battery
may result.
6
Page 7
SECTION 3: DELIVERY INFORMATION
3.0 Receipt of Shipment
Immediately upon delivery, examine packaging for possible
damage caused in transit. Damaged packing material or
staining from leaking electrolyte could indicate rough handling. Make a descriptive notation on the delivery receipt
before signing. If cell or unit damage is found, request an
inspection by the carrier and file a damage claim.
NOTE: Storage in temperatures above 25°C (77°F)
will result in loss of operating life.
Initial and freshening charge data should be saved and
included with the battery historical records (see Section 15).
SECTION 5: INSTALLATION
CONSIDERATIONS
5.0 General
3.1 Concealed Damage
Within 10 days of receipt, examine all cells for concealed
damage. If damage is noted, immediately request an
inspection by the carrier and file a concealed damage
claim. Pay particular attention to packing material exhibiting
damage or electrolyte staining. Delay in notifying carrier
may result in loss of right to reimbursement for damages.
SECTION 4: STORAGE INFORMATION
4.0 Storage Prior to Installation
Do not remove shipping materials if a storage period is
planned, unless charging is required per Section 4.2.
4.1 Storage Location
If the battery is not to be installed at the time of receipt, it
is recommended that it be stored indoors in a cool (25°C,
77°F), clean, dry location.
4.2 Storage Interval
The storage interval from the date of battery shipment to
the date of installation and initial charge should not
exceed six (6) months. If extended storage is necessary,
the battery should be charged at regular intervals until
installation can be completed and float charging can be
initiated. When in extended storage, it is advised to mark
the battery pallets with the date of shipment and the date
of every charge. If the battery is stored at 77°F (25°C) or
below, the battery should be given its initial charge (refer
to Section 10) within 6 months of the date of shipment and
receive a freshening charge (perform per Section 10 Initial
Charge) at 6 month intervals thereafter. Storage at ele
vated temperatures will result in accelerated rates of self
discharge. For every 18°F (10°C) temperature increase
above 77°F (25°C), the time interval for the initial charge
and subsequent freshening charges should be halved.
Thus, if a battery is stored at 95°F (35°C), the maximum
storage interval between charges would be 3 months (reference Appendix B). Storage beyond these periods without proper charge can result in excessive sulphation of
plates and positive grid corrosion which is detrimental to
battery performance and life. Failure to charge accord-
ingly may void the batteryʼs warranty.
Prior to starting installation of the Absolyte GX
Battery System, a review of this section is
strongly recommended.
Any modifications, alterations or additions to an
Absolyte GX system, without the expressed written
consent of GNB Engineering, may void any warranties
and/or seismic qualifications. Contact your GNB
representative for additional information.
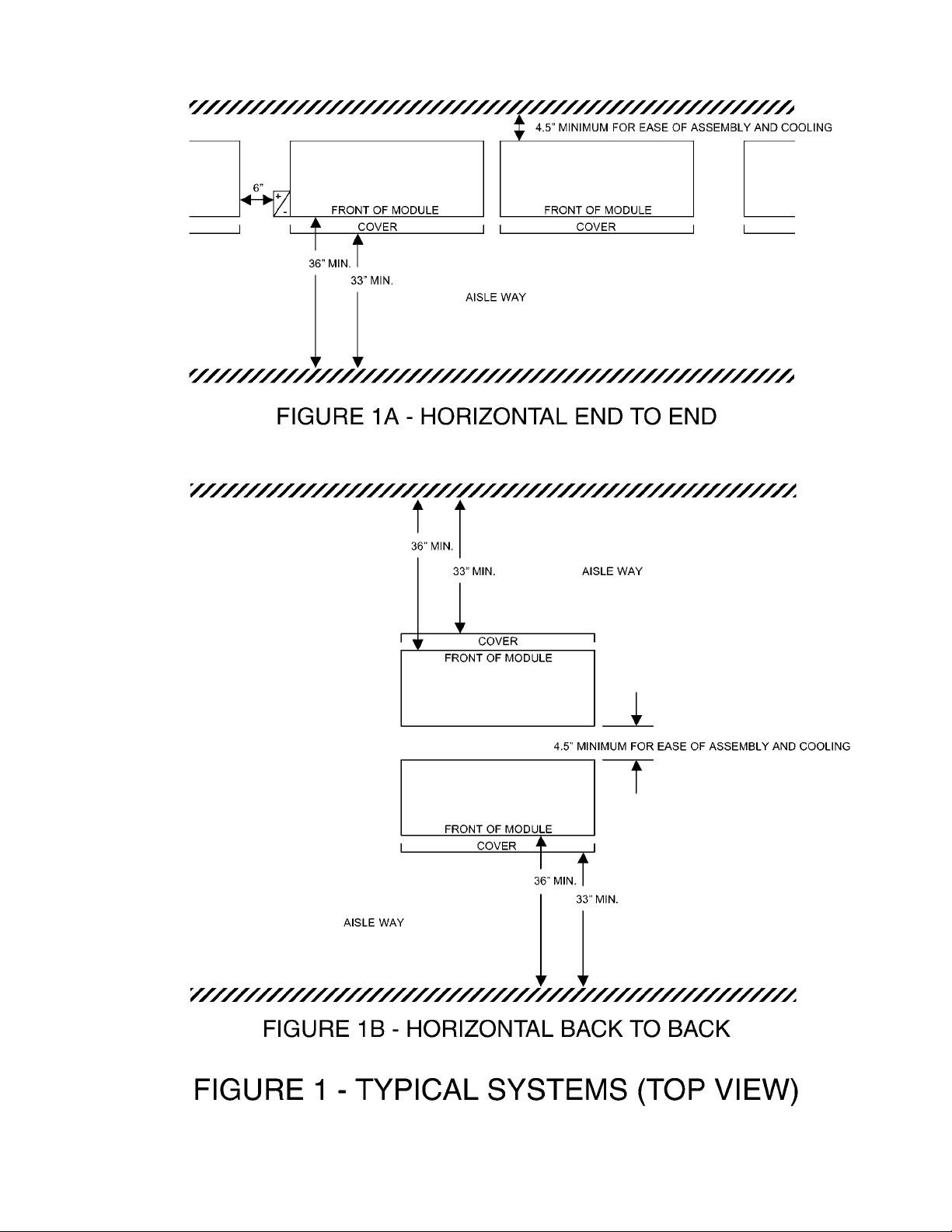
5.1 Space Considerations
It is important to know certain restrictions for the area
where the battery is to be located. First, a designated
aisle space should be provided to permit initial installation
as well as for service or surveillance. After installation,
any additional equipment installed after the battery should
not compromise access to the battery system.
A minimum aisle space of 36 inches from modules / 33
inches from clear covers should be available adjacent to
the battery system. See Figure 1 for typical space allocations required. Following the spacing requirements will
aid in maintenance of the battery and help maintain air
flow to battery surfaces to enhance heat dissipation.
NOTE: When planning system space requirements, allow
at least 6 inches past system total length wherever a terminal plate assembly is to be located (Figure 1A). Allow
4.5” minimum between back to back stacks (Figure 1B).
See Figure 1 for typical space allocations required. For
total length, width and height dimensions of connected
systems, consult layout/wiring diagram for the
particular system.
-
5.2 Battery Location & Ambient
Temperature Requirements
It is recommended that the battery unit be installed in a
clean, cool, dry location. Floors should be level.
A location having an ambient temperature of 24°C (75°F)
to 25°C (77°F) will result in optimum battery life and
performance. Temperatures below 25°C (77°F) reduce
battery charge efficiency and discharge performance.
Temperatures above 25°C (77°F) will result in a
7
Page 8
8
Page 9
TABLE A
TEMPERATURE EFFECTS ON LIFE
Maximum Annual Maximum Percent
Average Battery Battery Reduction
Temperature Temperature In Battery Life
25°C (77°F) 50°C (122°F) 0%
30°C (86°F) 50°C (122°F) 30%
35°C (95°F) 50°C (122°F) 50%
40°C (104°F) 50°C (122°F) 66%
45°C (113°F) 50°C (122°F) 75%
50°C (122°F) 50°C (122°F) 83%
The total battery weight will depend on the cell size, number of cells, as well as module configuration involved.
Consult layout/wiring diagram for the battery system
weight Prior to installation, a determination should be
made that the floor integrity is adequate to accommodate
the battery system.
5.6 Floor Anchoring
Where seismic conditions are anticipated, floor anchoring
should be provided. Such anchoring is the responsibility
of the user.
For example: If a battery has a design life of 20 years at
77°F (25°C), but the actual annual average battery
temperature is 95°F (35°C), the projected life of the
battery is calculated to be only 10 years.
The battery temperature shall not be allowed to exceed
50°C (122°F). Minimum battery temperature is -40°C
(-40°F). Temperature records shall be maintained by the
user in accordance with the maintenance schedule published in this manual.
5.3 Temperature Variations
Sources of heat or cooling directed on portions of the battery can cause temperature variations within the strings
resulting in cell voltage differences and eventual compromise of battery performance.
Heat sources such as heaters, sunlight or associated
equipment can cause such temperature variations.
Similarly, air conditioning or outside air vents may cause
cell string temperature variations. Every effort should be
made to keep temperature variations within 3°C (5°F).
Where non-seismic conditions are anticipated, anchoring
is recommended for maximum stability.
Four 9/16” (14.3 mm) holes are provided in the I-Beam for
anchoring.
5.7 Connecting Cables:
Battery System to Operating Equipment
The Absolyte cell is a UL recognized component.
Battery performance is based on the output at the battery
terminals. Therefore, the shortest electrical connections
between the battery system and the operating equipment
results in maximum total system performance.
DO NOT SELECT CABLE SIZE BASED ON CURRENT
CARRYING CAPACITY ONLY. Cable size selection
should provide no greater voltage drop between the battery system and operating equipment than necessary.
Excess voltage drop will reduce the desired support time
of the battery system.
5.7.1 Paralleling
5.4 Ventilation
The Absolyte battery is a Valve Regulated Lead Acid
(VRLA) low maintenance design. Tests have confirmed
that under recommended operating conditions in stationary applications, 99% or more of gases generated are
recombined within the cell. In most cases, no special
ventilation and or battery room is required. Consult your
local building and fire codes for requirements that may
apply to your specific location.
Hydrogen and oxygen gases can be vented to the atmosphere under certain conditions. Therefore, the battery should
never be installed in an air-tight enclosure. Sufficient precautions must be taken to prevent excessive overcharge.
5.5 Floor Loading
The floor of the area where the battery system is to be
installed should have the capability of supporting the
weight of the battery as well as any auxiliary equipment.
Where it is necessary to connect battery strings in parallel in order to obtain sufficient load backup time, it is
important to minimize the differences in voltage drop
between the battery strings in parallel in order to promote
equal load sharing upon discharge. Therefore, equal
resistance of cable connections for each parallel string is
important. When paralleling multiple strings to a load or
common bus, please follow these guidelines:
• Each parallel string must have the same number of cells
(same string voltage).
• The cables connecting the positive and negative termi-
nals of each string to the load (or bus) should be of the
same size (i.e. same capacity/cross-sectional area).
• The cables connecting the positive and negative termi-
nals of each string to the load (or bus) should be of the
same length. Choose the shortest cable length that will
connect the battery string that is furthest from the load,
and cut all cables used to connect each string to the load
to this same length.
9
Page 10

5.8 Stacking Limitations
6.1 Accessories
There are recommended limits on stacked (horizontal
only) battery configurations, see Table B and consult your
layout/wiring diagram.
TABLE B
Absolyte GX Stacking Limitations for the 2-Cell Tray
GX System Non-Seismic Seismic
GX2000 6 High 6 High
GX3000 6 High 6 High
GX4000 6 High 6 High
GX5000 6 High 6 High
GX6000 6 High 6 High
3-Cell GX2000 trays provide UBC Zone 4 compliance
when stacked 4 modules high and UBC Zone 1 compliance at 8 modules high.
5.9 Terminal Plates
Each system is supplied with a terminal plate assembly
for the positive and negative terminations. These should
always be used to provide proper connection to the operating equipment and cell terminals.
Any attempt to connect load cables directly to cell terminal may compromise battery system performance as well
as the integrity of cell post seals.
5.10 Grounding
It is recommended that the modules or racks be grounded in accordance with NEC and/or local codes. See
Appendix C for recommended procedure.
SECTION 6: UNPACKING
NOTE: Check accessory package against packing list to
assure completeness. Do not proceed with installation until all accessory parts are available.
Accessories are packed separately and will include the
following:
• Layout/wiring diagram
• Installation and operating instructions
• Lifting straps and lifting shackles
• Bottom Supports - I beams
• Hardware bag for I beam installation
• Hardware bag for module to module connections
• Standard clear covers
• Top clear covers
• Clear cover mounting brackets and assembly hardware
• Terminal plates
• Terminal plate mounting bracket
• Terminal plate hardware kit
• Terminal Plate Cover and assembly hardware
• Module tie plates and hardware (where required)
• Lead-Tin Plated copper connectors
• Hardware bag for connectors
®
• NO-OX-ID
“A” * grease
• Battery warning label
• Battery nameplate
• Cell numerals with polarity indicators
• Shims (leveling)
• Seismic Shims (where required)
• Alignment (drift) pins
*Registered Trademark of Sanchem Inc.
6.2 Recommended Installation Equipment
and Supplies
PACKAGED MODULES
Figure 2
6.0 General
Do not remove shipping materials if a storage period is
planned, unless charging is required per Section 4.2.
The battery modules are generally packed in groups.
Lag bolts retain the modules to the shipping pallet
together with a protective hood bolted in place. Modules
are also bolted together at the top adjacent channels.
See Figure 2.
• Fork lift, portable boom crane or A-Frame hoist
— GX2000 Module Weight: 315 kg (695 lb)
— GX3000 Module Weight: 447 kg (985 lb)
GX2000 3-Cell Module Weight: 478 kg (1050 lb)
—
— Bottom Support (I-beams) Height: 10 mm (4 in)
• Chalk line
• Line Cord
• Torpedo level (Plastic)
• Plywood straight edge 1/2” x 4” x 48”
• Torque wrenches (100 in-lbs, 35 ft-lbs)
• Ratchet wrench with 10, 13, 17, 19 mm and
1/2 in. sockets
• Box wrenches 10, 13, 17, 19 mm sizes
• Vinyl electrical tape
• Paper wipers
• 3M Scotch Brite® scour-pads™*
• Hammer drill (Floor anchoring)
* Registered trademark of 3M
10
Page 11

6.3 Unpacking
Carefully remove bolts and protective shipping hood. See
Figure 3. Remove the bolts holding modules to shipping
pallet. Also remove hardware bolting upper channels of
modules together. Do not remove modules at this time.
Base supports for horizontally stacked modules are more
easily attached before removing modules from pallet (see
Section 8 System Assembly).
Note: Placement of modules on shipping pallet has
no relationship to final installation and should be
disregarded.
4) Never lift more than one module with straps and
hooks.
HANDLING MODULE
Figure 5
SECTION 7: SYSTEM ARRANGEMENTS
7.0 Module Arrangements
Absolyte GX batteries may only be arranged horizontally.
Figure 6 shows some typical arrangements.
UNPACKING MODULES
Figure 3
6.4 Handling of Modules
The design of the modular tray permits handling by a fork
lift, portable crane or by a hoist sling . Whichever method
is used, make sure equipment can safely handle the module weight. See Section 6.2 for module weights.
Always use the two lifting straps and four lifting shackles
for lifting and placement of modules. See Figure 4.
Absolyte GX
3 Stacks
4 High
End to End
Absolyte GX
2 Stacks
6 High
Back to Back
TYPICAL SYSTEM ARRANGEMENTS
Figure 6
Modules are shipped without connectors installed. The
wiring diagram enclosed with shipment will show proper
battery hook-up. Module stack height limitation depends on
cell size and the seismic requirements of the application.
SECTION 8: SYSTEM ASSEMBLY
HANDLING - LIFTING STRAP PLACEMENT
Figure 4
NOTE (for Figure 4):
1) Straps must be criss-crossed.
2) Observe lifting shackle orientation
and proper channel hole use.
3) See Figure 13 for handling modules in horizontal
orientation.
8.0 Module Assembly Identification
Consult layout/wiring diagram for total number and type
of module assemblies in system. Compare required
module assemblies called for on layout/wiring diagram
with modules in shipment for completeness before
continuing further.
The Absolyte GX has a standard module configuration of
two cells per module. Where application voltage requires,
11
Page 12

a module may have only one cell in a two-cell tray. For
example, a 46 volt system will consist of eleven full modules and one single-cell module. Assemblies can be rotated 180° for proper polarity location.
8.1.1 Bottom Supports (I-beams)
8.1.2 Handling
The module/I-beam assembly may now be removed from
the pallet using methods outlined in Section 6.5. See
Figures 4 and 5. Remaining modules may be removed in
a similar manner.
Locate bottom I-beam supports and M10 serrated flange
bolts and nuts. I-beam supports and seismic shims should
be attached to the appropriate module assembly shown
on the layout/wiring diagram prior to removal from shipping pallet. Consult layout/wiring diagram for proper location of positive/negative terminals relative to I-beam.
NOTE: Failure to use seismic shims (on systems where
seismic shims are indicated) will result in the
assembly not meeting seismic certification criteria.
Secure I-beam support to a module channel as shown in
Figures 7 & 8, with access slots outward.
Torque hardware to 47 Newton-meters (35 Ft-Lbs) using
insulated tools. The side of the I-beam will be approximately 3.2mm (.125”) away from the end of the channels.
8.1.3 Tip Over Procedure
In order to stack modules in the horizontal position, refer
to Figures 9 through 11 to perform the tip-over procedure.
The module/I-Beam assembly tip-over should be performed first. This procedure can be performed using a
portable boom crane or fork lift in conjunction with the lifting straps and lifting shackles supplied.
A. Install lifting strap using lifting shackles in channel base
holes at each end of module upper front channel as
shown in Figure 9.
B. Center the lifting hook onto strap and lift until strap is
under tension and raises bottom of module from floor
surface.
C. While exerting manual force on the upper front of
module, lower hoist until module is in horizontal position. See Figures 10 and 11.
D. After tip over procedure when module is horizontal,
install the four lifting shackles and two lifting straps as
shown in Figure 12 to position and handle battery in
horizontal position.
I-BEAM
HARDWARE INSTALLATION
Figure 7
I-BEAM SUPPORT INSTALLED
Figure 8
Similarly, install the remaining I-beam on the other side of
the module.
TIP-OVER PROCEDURE - SHACKLE-STRAP USAGE
Figure 9
NOTE (for Figure 9):
1) One strap with shackles used for
tip-over procedure.
2) Observe channel hole used as well as
direction of shackle insertion.
3) Tip over procedure for single modules only.
12
Page 13

bolts and nuts in open holes, finger tight. Use leveling
shims to fill gaps between trays. See Figures 13, 14
and 15.
B. At this time, check to see that the first two modules are
plumb front to back and side to side using wooden or
plastic level together with plywood straight edge. This
is to insure proper alignment for module interconnection later on. Torque hardware to 47 Newton-meters
(35 Ft-Lbs).
TIP-OVER PROCEDURE MODULE AFTER TIP-OVER
Figure 10 Figure 11
HORIZONTAL STACKING SHACKLE-STRAP USAGE
Figure 12
Where floor anchoring is required, position module/I-Beam
assembly in desired location. Mark floor through I-beam
holes and remove module/base assembly. Install floor
anchoring and reposition module/base assembly over
anchoring. Prior to installing nuts and washers, check that
assembly is level in both axes. Level using shims provided. When level, fasten assembly and torque nuts to 47
Newton-meters (35 Ft-Lbs).
C. Proceed with stacking of remaining modules, checking
that stack is plumb in both axes as stacking progresses before torquing hardware. Be certain to check the
layout/wiring diagram for correct horizontal orientation
to provide proper polarity interconnection as stacking
progresses. See Figure 16 for completed assembly.
HANDLING AND STACKING HORIZONTAL MODULES
Figure 13
In order to complete stacking of a horizontal single stack
refer to Figures 12 to 15 and steps A through C listed
below.
NOTE: The use of leveling shims is required when
assembling any Absolyte GX system in order to
meet seismic requirements. Failure to use the
shims to level each module and to fill spaces
between tray channels during module assembly
will result in the assembly not meeting seismic
certification criteria. In extreme cases, stack to
stack connectors cannot be installed.
A. Using Section 6.5 and 8.1.3 and the layout/wiring
diagram, position the next module on top of first so that
channels of each mate with one another. Use drift pins
to align channel holes. Make sure channel ends and
sides of the upper and lower modules are flush.
Remove lifting straps and install M10 serrated flange
HARDWARE INSTALLATION SEQUENCE
Figure 14
13
Page 14

INSTALLING COMPLETED
HARDWARE HORIZONTAL STACK
Figure 15 Figure 16
8.2 Horizontal-Multiple Stacks
8.2.1 Stacking Base Modules
To achieve maximum stack stability, especially where
seismic conditions may exist, as well as proper interfacing
of inter-stack connections, metal tie plates are provided.
The plates used on stacks end to end are 3” x 1” x 1/8”
with two 9/16” holes. Use one tie plate at each interface to
connect the module channels of adjacent stacks. See
Figure 18.
It is recommended that all of the first modules with bottom
supports attached (see Section 8.1.1) be placed in position
first. A chalk line floor mark should be used to assure all
stacks will be in a straight line. This applies for stacks endto-end or end-to-end and back-to-back. Refer to Sections
6.5 and 8.1.3 for handling and tip over procedures.
For stacks end-to-end, module ends should be butted
together so that module side channel ends meet (see
Figure 17).
TOP MODULE
BASE MODULE
TIE PLATE ASSEMBLIES - HORIZONTAL STACKS
Figure 18
Position plates on the module channels and secure with
hardware as shown. Where stacks have different heights
(for example a 3 high stack adjacent to 4 high stack), install
plates on shorter stack top module and adjacent module.
Torque hardware to 47 Newton-meters (35 Ft-Lbs).
8.2.3 Horizontal Stacking
When all base modules are set in place, continue with
stacking of subsequent modules. Procedures for assembly of multiple horizontal stacks are the same as outlined
in section 8.1.3. Also consult layout/wiring diagram. Each
stack should be built up in sequence to the same level
until the top modules in all stacks are the last to be
installed. The use of a line chord attached to upper module corners of opposite end modules as stacking progresses aids in alignment.
POSITIONING HORIZONTAL BASE MODULES
Figure 17
For stacks back-to-back, the two base modules are positioned to provide a minimum 4.5” spacing between the
bottoms of the modules (not I-beam edges). Refer back to
Figure 1.
Refer to layout/wiring diagram for seismic shim requirements.
8.2.2 Stack Tie Plates
At this time stack tie plates should be installed. It will be
necessary to temporarily remove the hardware fastening
the base modules to the I-beams.
This completes the mechanical assembly of the battery
system.
For installation of intermodular connections and terminal
plate assembly, see Section 9.
For installation of protective module cover, see Section 11.
SECTION 9: ELECTRICAL CONNECTIONS
9.0 Post Preparation
All cell posts were greased at the factory. Using either a
brass bristle suede shoe brush or 3M Scotch Brite scouring pad, brighten the flat copper terminal surfaces to
ensure lowest resistance connections.
14
Page 15

Apply a thin film of NO-OX-ID “A” grease (supplied) to all
terminal surfaces, bolts, and washers. This will
preclude oxidation after connections are completed.
9.1 Connections - System Terminals
Each system is supplied with a terminal plate
assembly for the positive and negative terminations. These should always be used to provide proper
connection to the operating equipment and cell terminals.
Any attempt to connect load cables directly to cell terminal may compromise battery system performance as well
as the integrity of cell post seals.
Refer to layout/wiring diagram for location of terminal plate
assembly in your battery configuration. Assemble Terminal
Support Bracket to module channel using hardware indicated, items 3, 4, 5, 6. Hardware will be located in a bag
labeled K17-417240P for top termination or K17417256 for
side termination. Assemble Terminal Plate to Support
Bracket and battery posts. Hardware to attach to Support
bracket is also located in the terminal plate kit. It is recommended that all connections be torqued to 11 Newtonmeters (100 in-Lbs). After making cable connections,
assemble Terminal Plate Covers, Items 7 & 8, to the Terminal
Support Bracket using hardware indicated. Hardware to
assemble Terminal Plate Covers will be located in the terminal plate kit. Refer to Sections 9.0 and 9.2 for electrical
contact surface preparation of terminal plate components.
Refer to layout/wiring diagram for connector placement
and materials list. Figure 19 shows typical module
connections, intrastack connections and interstack
connections.
9.3 Connections - Inter-STACK
Multiple stacks end to end are interconnected as shown in
layout/wiring diagram. Follow the procedures in Sections
9.1 and 9.3.
9.4 Torquing
When all inter-module and inter-stack connections have
been installed, tighten all connections to 11.3 Newtonmeters (100 in-Lbs) Use insulated tools. Recheck connections after the initial charge due to heating during charge.
Terminal plate assembly varies with termination location.
Refer to layout/wiring diagram termination location on
your battery. Figure 20 shows top termination assembly
with instructions. Do not make connections to operat-
ing system at this time.
9.2 Connections - Inter-MODULE
Consult layout/wiring diagram for correct quantity of leadtin plated copper connectors required for each
connection. Follow procedure in Section 9.0 and brighten
lead-tin plated surfaces coming in contact with copper
posts. Apply a thin film of NO-OX-ID “A” grease to these
areas.
NOTE: Apply a minimum amount of grease to cover the
surface. As a rule: "If you can see it, it's too much".
Where multiple connectors are required across any single
connection, brighten both sides of connectors along the
entire length. Grease these areas as well. It is recommended when installing connectors on horizontal
arrangements that the upper bolts be installed first to
reduce risk of accidental shorting.
WASHERS SHOULD BE INSTALLED WITH THE CURVED
EDGE TOWARD THE CONNECTORS.
STACK CONNECTIONS
Figure 19
9.5 Connection - Check
Again, visually check to see that all module terminals are
connected positive (+) to negative (-) throughout the
battery. Positive terminals have red cap. Negative
terminals have black cap.
Also measure the total open circuit voltage from terminal
plate to terminal plate. This should be approximately
equal to 2.14 volts times the number of cells in the
system, e.g., a 24 cell system would read:
24 x 2.14v = 51.4 volts. An incorrect voltage reading may
mean connectors were installed incorrectly.
SECTION 10: IDENTIFICATION LABELS
10.0 Surfaces
Make sure surfaces are free of dirt and grease by wiping
with clean, dry wipers (isopropyl alcohol may be used) to
ensure proper label adhesion.
10.1 Cell Numerals
BOLT WASHER CONNECTOR POST
A set of pressure sensitive cell numerals and system
polarity labels are supplied and should be applied at this time.
Cell numerals should be applied to the cell being identified.
Designate the positive terminal cell as #1 with succeeding
cells in series in ascending order.
15
Page 16

BILL OF MATERIALS — TOP TERMINAL PLATE ASSEMBLY
ITEM DESCRIPTION QTY PER SYSTEM
1 PLATE, TOP TERMINAL 2
2 BRACKET, TERMINAL SUPPORT 2
3 LOCK WASHER, M10 8
4 FLAT WASHER, M10 16
5 NUT, M10 X .8D 8
6 BOLT, M10 X 40 8
7 COVER, FRONT 2
8 COVER, BACK 2
9 NUT, M6 X .8D 4
10 BOLT, M6 X 25 VARIES
11 WASHER, M6 VARIES
Terminal Plate Kit Materials & Assembly
Figure 20
16
Page 17

10.2 System Polarity Labels
The system polarity labels should be applied next to the
positive and negative system terminals.
10.3 Warning Label
Apply pressure sensitive warning label provided on a
prominently visible module side or end.
Determine the maximum voltage that may be applied to
the system equipment. This voltage, divided by the number of cells connected in series, will establish the maximum volts per cell (VPC) that is available. Table C lists
recommended voltages and charge times for the initial
charge. Select the highest voltage the system allows to
perform the initial charge in the shortest time period.
10.4 Battery Nameplate
For future reference and warranty protection, apply
pressure sensitive nameplate on a prominently visible
module. Fill in date of installation and the specified capacity and rate.
SECTION 11: PROTECTIVE MODULE COVERS
11.0 General
Each module is provided with a transparent protective cover
to help prevent accidental contact with live electrical connections, and to provide easy visual access to the system.
When all system assembly has been completed, as well
as initial testing, including initial charge and cell float voltage readings, all covers should be installed. Covers
should remain in place at all times during normal operation of the battery system.
11.1 Module Clear Cover Installation
Temperature Correction of Charger Voltage
V corrected = V25°C - ((T actual -25°C) x (.0055 V/°C))
or
V corrected = V77°F - ((T actual - 77°F) x .003V/°F))
Please refer to Appendix A for standard values.
STEP 1
1. Set constant voltage charger to maximum setting without exceeding 2.35 VPC.
Example: For a target charge of 2.35 VPC on a 24-cell
system, you would set the charger voltage to 56.4 volts.
Depending on the batteryʼs state of charge, the charger
may go into current limit at the beginning and decline
slowly once the target charge voltage is reached.
2. Record time and current at regular intervals – every
hour as a minimum.
3. Continue charging the battery until there is no further
drop in charge current over 3 consecutive hours. This could
take days if the battery has been in storage for a long time.
Refer to Figure 21 for Module Clear Cover installation.
Install standoff legs and standoff keys first, as shown.
The cover is then installed by grasping it so that the GNB
logo is upright. Locate slots at bottom of cover to the bottom standoff legs and slide in place. Locate holes at top of
cover and install to top standoff legs. Refer to Figure 21.
SECTION 12: INITIAL CHARGE
12.0 General
Batteries lose some charge during shipment as well as
during the period prior to installation. A battery should be
installed and given its initial charge as soon after receipt
as possible. Battery positive (+) terminal should be
connected to charger positive (+) terminal and battery
negative (-) terminal to charger negative (-) terminal.
Failure to perform the initial charge within the time
limits stated in section 4.2 will affect the performance
and life of the battery and may void the warranty.
12.1 Constant Voltage Method
Constant voltage is the only charging method
allowed. Most modern chargers are of the
constant voltage type.
4. When the current has stabilized, proceed to step 2.
STEP 2
1. Continue the charge for the time listed in Table C
depending on the charger voltage setting. The time is IN
ADDITION to the time spent charging in Step 1.
Example: charge for 12 hours if the charger voltage is set
to 2.35 VPC.
TABLE C
EQUALIZE CHARGE (77°F)
CELL VOLTS TIME (HOURS)
2.30 24
2.33 18
2.35 12
2. Record cell voltages hourly during the last 3 hours of
the charge time. If, after the charge time has completed,
but the lowest cell voltage has continued to rise, you may
extend the charge, monitoring cell voltages hourly, until
the lowest cell voltage ceases to rise.
3. Proceed to Step 3.
17
Page 18

BILL OF MATERIALS — MODULE CLEAR COVER MATERIALS
ITEM DESCRIPTION QTY PER SYSTEM
1 Cover 1
2 Standoff Leg 4
3 Standoff Key 4
Assembly Instructions:
Install standoff legs and standoff keys to module channel as shown. The cover is then installed by grasping it so that the GNB logo is upright. Locate slots at bottom of cover to bottom standoff legs and slide in
place. Locate holes at top of cover and install to top standoff legs.
Standoff legs need not be removed to access cells, simply remove protective cover.
Module Clear Cover Materials and Assembly
Figure 21
18
Page 19

STEP 3
1. The initial charge is complete. Charger voltage can
now be reduced to float voltage setting per Section 13.2.
For a target float charge of 2.25 VPC on a 24-cell system,
you would set the charger voltage to 54 volts.
TEMPERATURE CORRECTION
V corrected = V25°C - (( T actual-25°C) x ( .0055V/°C)) or
V corrected = V77°F - ((T actual-77°F) x (.003V/°F))
See Appendix A for standard values.
SECTION 13: BATTERY OPERATION
13.0 Cycle Method of Operation
In cycle operation, the degree of discharge will vary for different applications. Therefore, the frequency of recharging and the amount of charge necessary will vary.
Generally, Absolyte GX cells require approximately 105110% of the ampere-hours removed to be returned to a
full state of charge.
The upper voltage settings recommended, given that the
maxium charge current is 5% of the nominal C100
Amp-hour rating and the ambient temperature is 25°C
(77°F), are as follows:
2.28 ± 0.02 VPC @ 0-2% DOD
2.33 ± 0.02 VPC @ 3-5% DOD
2.38 ± 0.02 VPC @ >5% DOD
Due to the variety of applications and charging
equipment (particularly in photovoltaic systems) it is
recommended that you contact a GNB representative
when determining proper recharge profiles.
13.1 Floating Charge Method
In this type of operation, the battery is connected in
parallel with a constant voltage charger and the critical
load circuits. The charger should be capable of
maintaining the required constant voltage at battery
terminals and also supply a normal connected load where
applicable. This sustains the battery in a fully charged
condition and also makes it available to assume the emergency power requirements in the event of an AC power
interruption or charger failure.
13.2 Float Charge - Float Voltages
Following are the float voltage ranges recommended for the
Absolyte Battery System. Select any “volts per cell” (VPC)
value within the range listed that will result in the series
string having an average volts per cell equal to that value.
RECOMMENDED FLOAT RANGE (@77°F)
2.23 to 2.25 VPC
NOTE: Recommended float voltages are for 77°F. For
other temperatures a compensation factor of .003 V/°F
(.0055 V/°C) per cell is recommended. The minimum voltage is 2.20 VPC, temperature correction does not apply
below this voltage. The maximum voltage is 2.35 VPC,
temperature correction does not apply above this voltage.
Modern constant voltage output charging equipment is
recommended for the floating charger method of operation of GNB Absolyte batteries. This type of charger, properly adjusted to the recommended float voltages and following recommended surveillance procedures, will assist
in obtaining consistent serviceability and optimum life.
After the battery has been given its initial charge (refer to
Section 12), the charger should be adjusted to provide the
recommended float voltages at the battery terminals
.
Do not use float voltages higher or lower than those recommended. Reduced capacity or battery life will result.
Check and record battery terminal voltage on a regular
basis. Monthly checks are recommended. See Section
15.0, Records. If battery float voltage is above or below
the correct value, adjust charger to provide proper voltage
as measured at the battery terminals
.
13.3 Recharge
All batteries should be recharged as soon as possible following a discharge with constant voltage chargers. To
recharge in the shortest period of time, raise the charger
output voltage to the highest value which the connected
system will permit. Do not exceed the voltages and times
listed in Table E in Section 14.2.
13.4 Determining State-of-Charge
If the normal connected load is constant (no emergency
load connected), the following method can be used to
determine the approximate state-of-charge of the battery.
The state-of-charge can be identified to some degree by
the amount of charging current going to the battery. When
initially placed on charge or recharge following a discharge, the charging current, read at the charger ammeter, will be a combination of the load current plus the current necessary to charge the battery. The current to the
battery will start to decrease and will finally stabilize when
the battery becomes fully charged. If the current level
remains constant for three consecutive hours, then this
reflects a state-of-charge of approximately 95 to 98%. For
most requirements, the battery is ready for use.
If the normal connected load is variable (i.e. telecommunications), the following method may be used to check the
state-of-charge of the battery. Measure the voltage across
a pilot cell (See Section 15 for definition of pilot cell). If the
voltage is stable for 24 consecutive hours, the battery
reflects a state of charge of approximately 95%.
19
Page 20

13.5 Effects of Float Voltage
13.8 Ohmic Measurements
Float voltage has a direct effect on the service
life of your battery and can be the cause of
thermal instability.
A float voltage above the recommended values reduces
service life. Table D shows the effects of float voltage
(temperature corrected) on battery life.
TABLE D
FLOAT VOLTAGE EFFECTS ON LIFE
Temperature corrected 25°C (77°F) Percent
Float voltage per cell Reduction
Minimum Maximum in Battery Life
2.23 2.25 0%
2.28 2.30 50%
2.33 2.35 75%
Voltage records must be maintained by the user in accordance with the maintenance schedule published in this
manual. To obtain the optimum service life from the battery, it is important to make sure the batteryʼs float voltage
is within the recommended range.
13.6 Float Current and Thermal Management
Increased float current can portend a condition known as
thermal runaway, where the battery produces more heat
than it can dissipate. VRLA batteries are more prone to
thermal runaway because the recombination reaction that
occurs at the negative plate, and reduces water loss, also
produces heat. High room temperature, improper applications, improper voltage settings, and incorrect installation
practices can increase the chances of thermal runaway.
Impedance, resistance and conductance testing is collectively
known in the industry as ohmic measurements. Each measurement is derived using a manufacturer-specific and proprietary algorithm and / or frequency. This means that one type of
measurement cannot be converted or related easily to another.
“Reference” ohmic values are of dubious value because
so many factors can affect the way the readings are made
and displayed by the devices. Connector configuration
and AC ripple as well as differences between readings of
temperature and probe placement will prevent the ohmic
devices from generating consistent and meaningful data.
The meters work better with monoblocs and small capacity VRLA products and less well with large (>800-Ah)
VRLA and flooded battery designs. Users should be particularly skeptical of data taken on series-parallel VRLA
battery configurations as the feedback signal to the device
may follow unforeseen paths that can overwhelm it.
It is best for users to establish their own baseline values
for their battery as specifically configured. Do not rely on
reference values.
If users wish to enhance normal maintenance and recordkeeping with ohmic measurements, GNB recommends
the trending of this data over time. Use a first set of readings taken 6 months after initial charge and installation as
the baseline data. Because cell positioning within the
string (connector configuration to a particular cell) can
affect the reading, always compare each cell at baseline
to itself in the new data. Standalone ohmic data is not sufficient to justify warranty cell replacement.
As with good record-keeping practices, monitoring float
current can prevent a minor excursion from becoming a
major issue.
13.7 AC Ripple
AC ripple is noise or leftover AC waveform riding on the
DC charge current to the battery that the rectifier did not
remove. It is usually more pronounced in UPS than telecom systems. Proper maintenance of the UPS capacitors
will reduce the amount of ripple going into the battery.
Establishment of absolute limits for AC ripple has always
been problematic because the degree of damage it causes depends on the wave shape, peak-to-peak magnitude
and frequency. Accurate characterization of AC ripple
requires an oscilloscope and even then, only represents a
picture of the ripple at that moment in time.
Whatever its exact characteristics, AC ripple is always harmful to batteries. Depending on its particular properties, ripple
can result in overcharge, undercharge and micro-cycling
that can prematurely age the battery. The most common and
damaging result of AC ripple is battery heating which can
lead to thermal runaway. AC ripple will decrease battery life
and should be reduced as much as possible.
Responsible ohmic device manufacturers acknowledge
that there is no direct relationship between percent ohmic
change from baseline and battery capacity. A change from
baseline of 25% or less is in the normal noise or variability
range. Changes between 25% and 50% may call for additional scrutiny of the system. An IEEE compliant discharge
test is usually warranted on systems exhibiting more than
a 50% change from baseline. Consult a GNB representative for specific questions about ohmic data.
SECTION 14: EQUALIZING CHARGE
14.0 General
Under normal operating conditions an equalizing charge
is not required. An equalizing charge is a special charge
given a battery when non-uniformity in voltage has developed between cells. It is given to restore all cells to a fully
charged condition. Use a charging voltage higher than the
normal float voltage and for a specified number of hours,
as determined by the voltage used.
Non-uniformity of cells may result from low float voltage due
to improper adjustment of the charger or a panel voltmeter
which reads an incorrect (higher) output voltage. Also, vari-
20
Page 21

ations in cell temperatures greater than 5°F (2.78°C) in the
series string at a given time, due to environmental conditions or module arrangement, can cause low cells.
14.1 Equalizing Frequency
STEP 2
A. Continue the charge for the time listed in Table E depending on the charger voltage setting. The time is IN ADDITION
to the time spent charging in Step 1.
An equalizing charge should be given when any of the following conditions exist:
A. The float voltage of any cell is less than 2.18 VPC.
B. A recharge of the battery is required in a minimum time
period following an emergency discharge.
C. Individual cell(s) float is more than +/- 0.05 volts from
average.
D. Accurate periodic records (See Section 15) of individ-
ual cell voltages show an increase in spread since the
previous semi-annual readings.
An annual equalize charge is recommended to help
ensure uniform cell performance.
14.2 Equalizing Charge Method
Constant voltage charging is the method for giving an
equalizing charge. Determine the maximum voltage that
may be applied to the system equipment. This voltage,
divided by the number of cells connected in series, will
establish the maxi-mum volts per cell that may be used to
perform the equalizing charge in the shortest period of time
(not to exceed 2.35 VPC applicable at 77°F, 25°C). Refer
to Table E for voltages and recommended time periods.
NOTE: Charge volts listed in Table E are for 77°F. For other
temperatures a compensation factor of .003 V/°F (.0055 V/°C)
per cell is recommended. The minimum voltage is 2.20 VPC.
The maximum voltage is 2.35 VPC. Temperature correction
does not apply outside of this range.
Example, charge for 12 hours if the charger voltage is set to
2.35 VPC.
TABLE E
EQUALIZE CHARGE (77°F)
CELL VOLTS TIME (HOURS)
2.30 24
2.33 18
2.35 12
B. Record cell voltages hourly during the last 3 hours of the
charge time. If, after the charge time has completed, but the
lowest cell voltage has continued to rise, you may extend the
charge, monitoring cell voltages hourly, until the lowest cell
voltage ceases to rise.
C. Proceed to Step 3.
STEP 3
The Equalize charge is now complete. Charger voltage can
now be reduced to float voltage setting per Section 13.2. For
a target float charge of 2.25 VPC on a 24-cell system, you
would set the charger voltage to 54 volts.
SECTION 15: RECORDKEEPING
15.0 Pilot Cell
A pilot cell is selected in the series string to reflect the
general condition of cells in the battery. The cell selected
should be the lowest cell voltage in the series string following the initial charge. See Section 12.0 - Initial Charge.
Reading and recording pilot cell voltage monthly serves
as an indicator of battery condition between scheduled
overall individual cell readings.
V corrected = V25°C - ((T actual-25°C) x (.0055 V/°C)) or V
corrected = V77°F - ((T actual-77°F) x (.003 V/°F))
See Appendix A for standard values.
STEP 1
A. Set constant voltage charger to maximum setting without
exceeding 2.35 VPC.
Example: For a target charge of 2.35 VPC on a 24-cell system, you would set the charger voltage to 56.4 volts.
B. Record time and current at regular intervals – every hour
as a minimum.
C. Continue charging the battery until there is no further drop
in charge current over 3 consecutive hours.
D. When the current has stabilized, proceed to step 2.
15.1 Voltmeter Calibration
Panel and portable voltmeters used to indicate battery float
voltages should be accurate at the operating voltage value.
The same holds true for portable meters used to read individual cell voltages. These meters should be checked against a
standard every six months and calibrated when necessary.
15.2 Records
The following information must be recorded at installation,
and annually for every year of operation after installation.
These records must be maintained throughout the life of
the battery and made available for review by GNB representatives for capacity or life related warranty claims.
Failure to collect and store these maintenance data will
void the warranty. Please review the warranty statement
specific to the application for any additional requirements.
21
Page 22

• Individual cell voltages
• Overall string voltage
• Ambient temperature immediately surrounding battery
• Battery temperature at several places throughout the
string. Recommend 1 reading per battery stack. More
data points are recommended for larger batteries and to
check for temperature gradients. Readings on the tray,
cell cover or negative terminal are good places to measure battery temperature. Take readings away from
HVAC sources.
• Float current measured at stack to stack connections
(optional)
• Ohmic measurements (optional). Baseline ohmic readings of individual cells should be taken 6 months from
the date of initial charge.
• Retorque connectors as part of annual maintenance.
damp with electrolyte or show signs of corrosion, contact
your local GNB representative.
CAUTION!
Do not clean plastic parts with solvents,
detergents, oils, mineral spirit or spray
type cleaners as these may cause crazing
or cracking of the plastic materials.
SECTION 19: MAINTENANCE
19.0 Connections
ONCE PER YEAR READINGS ARE THE ABSOLUTE
MINIMUM REQUIRED TO PROTECT WARRANTY. More
frequent readings are recommended, especially for critical
sites. Good record-keeping will prevent minor issues from
escalating into more serious problems over time. See
Figure 22 for a sample record-keeping form.
SECTION 16: TAP CONNECTIONS
16.0 Tap Connections
Tap connections are not to be used on a battery. This can
cause overcharging of the unused cells and undercharging
of those cells supplying the load, thus reducing battery life.
SECTION 17: TEMPORARY NON-USE
17.0 Temporary Non-Use
An installed battery that is expected to stand idle longer
than the maximum storage interval (see Section 4.2),
should be treated as stated below. The maximum storage
interval is 6 months if stored at 25°C, 77°F.
Give the battery an equalizing charge as per Section 14.
Following the equalizing charge, open connections at the battery terminals to remove charger and load from the battery.
Repeat the above after every 6 months (25°C, 77°F) or at
the required storage interval. See Section 4.2 for adjustments to storage intervals when the storage temperature
exceeds 25°C, 77°F.
To return the battery to normal service, re-connect the battery to the charger and the load, give an equalizing charge
and return the battery to float operation.
SECTION 18: UNIT CLEANING
18.0 Unit Cleaning
Periodically clean cell covers with a dry 2” paintbrush to
remove accumulated dust. If any cell parts appear to be
Battery terminals and intercell connections should be corrosion free and tight for trouble-free operation. Periodically
these connections should be inspected.
CAUTION: DO NOT WORK ON CONNECTIONS WITH BATTERY CONNECTED TO
CHARGER OR LOAD.
If corrosion is present, disconnect the connector from the
terminal.
Gently clean the affected area using a suede brush or
Scotch Brite scouring pad. Apply a thin coating of NO-OXID “A” grease to the cleaned contact surfaces, reinstall
connectors and retorque connections to 11.3 Newtonmeters (100 inch pounds).
All terminal and intercell connections
should be retorqued at least once every year
to 11.3 Newton-meters (100 inch pounds).
NOTE: Design and/or specifications subject to change
without notice. If questions arise, contact your
local sales representative for clarification.
SECTION 20: CAPACITY TESTING
20.0 Capacity Testing
When a capacity discharge test is desired, it is recommended that it be performed in accordance with IEEE1188*, latest revision.
An equalizing charge, as described in Section 14.2, must
be performed within 7 days prior to the capacity test. The
batteries must be returned to float charging immediately
after the equalize charge completes.
After the capacity discharge has completed, the batteries
can be recharged in the shortest amount of time by following the equalize charge procedure described in
Section 14.2.
*IEEE-1188: Recommended Practice for Maintenance,
Testing, and Replacement of Valve-Regulated Lead-Acid
(VRLA) Batteries for Stationary Applications.
22
Page 23

ABSOLYTE BATTERY MAINTENANCE REPORT
PAGE 1 OF
No. of CELLS:
CHARGER VOLTAGE: CHARGER CURRENT:
Temp Temp Temp Temp
ADDITIONAL COMMENTS:
Ohmic
C / R / I
Ohmic
C / R / I
Cell Conn.
No. Volts Resist.
Ohmic
C / R / I
Ohmic
C / R / I
Cell Conn.
No. Volts Resist.
Cell Conn.
No. Volts Resist.
29
30 12060 90
1198959
11858 88
1178757
11656 86
1158555
11454 84
1138353
11252 82
1118151
11050 80
1097949
10848 78
1077747
10646 76
1057545
10444 74
1037343
10242 72
1017141
10040 70
996939
9838 68
976737
9636 66
956535
9434 64
9333 63
32 9262
9161
Conn.
Resist.
2324252627
28
192021
22
151617
18
111213
14
789
10
31
5
6
Cell
DATE:
INSTALL DATE:
BATTERY LOCATION / NUMBER:
SYSTEM VOLTAGE: TEMPERATURE:
ADDRESS:
COMPANY:
TYPE: MANUF. DATE:
SERIAL NUMBER:
No. Volts
4
123
®
Figure 22.1
23
Page 24

ABSOLYTE BATTERY MAINTENANCE REPORT
PAGE 1 OF
No. of CELLS:
CHARGER VOLTAGE: CHARGER CURRENT:
Temp Temp Temp Temp
ADDITIONAL COMMENTS:
Ohmic
C / R / I
Ohmic
C / R / I
Ohmic
C / R / I
Ohmic
C / R / I
240210150 180
239149 179 209
238208148 178
237147 177 207
236206146 176
235145 175 205
234204144 174
233143 173 203
232202142 172
231141 171 201
230200140 170
229139 169 199
228198138 168
227137 167 197
226196136 166
225135 165 195
224194134 164
223133 163 193
COMPANY: SERIAL NUMBER:
ADDRESS: BATTERY LOCATION / NUMBER:
DATE:
TYPE: MANUF. DATE: INSTALL DATE:
SYSTEM VOLTAGE: TEMPERATURE:
Cell Conn. Cell Conn. Cell Conn. Cell Conn.
No. Volts Resist. No. Volts Resist. No. Volts Resist. No. Volts Resist.
121 151 181 211
122 152 182 212
123 153 213
124 154 184 214
125 155 185 215
126 156 186 216
127 157 187 217
128 158 188 218
129 159 189 219
130 160 190 220
131 191
183
221
132 162
161
222192
®
Figure 22.2
24
Page 25

2.23 2.24 2.25 2.26 2.27 2.23 2.24 2.25 2.26 2.27
3 2.35 55 2.30 2.31 2.32 2.33 2.34
4 2.35 2.35 56 2.29 2.30 2.31 2.32 2.33
5 2.34 2.35 57 2.29 2.30 2.31 2.32 2.33
6 2.34 2.35 58 2.29 2.30 2.31 2.32 2.33
7 2.33 2.34 2.35 59 2.28 2.29 2.30 2.31 2.32
8 2.33 2.34 2.35 60 2.28 2.29 2.30 2.31 2.32
9 2.32 2.33 2.34 2.35 61 2.28 2.29 2.30 2.31 2.32
10 2.32 2.33 2.34 2.35 62 2.28 2.29 2.30 2.31 2.32
11 2.31 2.32 2.33 2.34 2.35 63 2.27 2.28 2.29 2.30 2.31
12 2.31 2.32 2.33 2.34 2.35 64 2.27 2.28 2.29 2.30 2.31
13 2.30 2.31 2.32 2.33 2.34 65 2.27 2.28 2.29 2.30 2.31
14 2.30 2.31 2.32 2.33 2.34 66 2.26 2.27 2.28 2.29 2.30
15 2.29 2.30 2.31 2.32 2.33 67 2.26 2.27 2.28 2.29 2.30
16 2.28 2.29 2.30 2.31 2.32 68 2.26 2.27 2.28 2.29 2.30
17 2.28 2.29 2.30 2.31 2.32 69 2.25 2.26 2.27 2.28 2.29
18 2.27 2.28 2.29 2.30 2.31 70 2.25 2.26 2.27 2.28 2.29
19 2.27 2.28 2.29 2.30 2.31 71 2.25 2.26 2.27 2.28 2.29
20 2.26 2.27 2.28 2.29 2.30 72 2.25 2.26 2.27 2.28 2.29
21 2.26 2.27 2.28 2.29 2.30 73 2.24 2.25 2.26 2.27 2.28
22 2.25 2.26 2.27 2.28 2.29 74 2.24 2.25 2.26 2.27 2.28
23 2.25 2.26 2.27 2.28 2.29 75 2.24 2.25 2.26 2.27 2.28
24 2.24 2.25 2.26 2.27 2.28 76 2.23 2.24 2.25 2.26 2.27
25 2.23 2.24 2.25 2.26 2.27 77 2.23 2.24 2.25 2.26 2.27
26 2.23 2.24 2.25 2.26 2.27 78 2.23 2.24 2.25 2.26 2.27
27 2.22 2.23 2.24 2.25 2.26 79 2.22 2.23 2.24 2.25 2.26
28 2.22 2.23 2.24 2.25 2.26 80 2.22 2.23 2.24 2.25 2.26
29 2.21 2.22 2.23 2.24 2.25 81 2.22 2.23 2.24 2.25 2.26
30 2.21 2.22 2.23 2.24 2.25 82 2.22 2.23 2.24 2.25 2.26
31 2.20 2.21 2.22 2.23 2.24 83 2.21 2.22 2.23 2.24 2.25
32 2.20 2.21 2.22 2.23 2.24 84 2.21 2.22 2.23 2.24 2.25
33 2.20 2.21 2.22 2.23 85 2.21 2.22 2.23 2.24 2.25
34 2.20 2.21 2.22 2.23 86 2.20 2.21 2.22 2.23 2.24
35 2.20 2.21 2.22 87 2.20 2.21 2.22 2.23 2.24
36 2.20 2.20 2.21 88 2.21 2.22 2.23 2.24
37 2.20 2.21 89 2.20 2.21 2.22 2.23
38 2.20 90 2.20 2.21 2.22 2.23
39 2.20 91 2.21 2.22 2.23
92 2.21 2.22 2.23
93 2.20 2.21 2.22
94 2.20 2.21 2.22
95 2.21 2.22
Expressed in Volts per Cell
Temperature Corrected Float Voltages
APPENDIX A
Battery Temperature (°F)
Float Voltage at 25°C
Battery Temperature (°C)
Float Voltage at 77°F
25
Page 26

Months Days Months Days
25 6 0 77 6 0
26 5 18 78 5 23
27 5 7 79 5 17
28 4 26 80 5 10
29 4 16 81 5 4
30 4 7 82 4 29
31 3 29 83 4 23
32 3 21 84 4 18
33 3 13 85 4 12
34 3 7 86 4 7
35 3 0 87 4 3
36 2 24 88 3 28
37 2 18 89 3 23
38 2 13 90 3 19
39 2 8 91 3 15
40 2 4 92 3 11
41 1 29 93 3 7
42 1 25 94 3 4
43 1 22 95 3 0
44 1 18 96 2 27
45 1 15 97 2 23
98 2 20
99 2 17
100 2 14
101 2 11
102 2 9
103 2 6
104 2 4
105 2 1
106 1 29
107 1 27
108 1 25
109 1 23
110 1 21
111 1 19
112 1 17
113 1 15
APPENDIX B
MAXIMUM STORAGE INTERVAL BETWEEN FRESHENING CHARGES
VERSUS AVERAGE STORAGE TEMPERATURE
Average Ambient Storage Temperature (°F)
Average Ambient Storage Temperature (°C)
Maximum Storage IntervalMaximum Storage Interval
26
Page 27

APPENDIX C
BONDING & GROUNDING OF BATTERY RACK
INTRODUCTION
1. To insure personnel safety, and equipment protection, operation, and reliability, the battery rack should be connected to the
Common Bonding Network (CBN).
2. Electrical continuity between modules is provided through the use of serrated hardware. Testing has shown that standard sys-
tems are compliant with the GR-1089-CORE, Issue 4, Section 9 requirements of the Bonding and Grounding tests.
GROUNDING KIT INSTALLATION (OPTIONAL)
1. Each kit consists of the following components:
(2) #6 AWG, 12 in. 90°C cables
(4) “C” shaped beam clamps
(4) 1/4-20 x 0.75 in. bolts
(4) 1/4-20 x 1.00 in. bolts
2. Using (1) 1/4-20 x 1.00 in. bolt per beam clamp, connect (1) beam clamp to the I-beam flange and (1) beam clamp to the back
flange of the module (see Figure 1). Be sure to securely tighten the bolts such that the paint is penetrated (see Figure 2).
3. Attach each end of cable assembly to a beam clamp using (1) 1/4-20 x 0.75 in. bolt per end (see Figure 3). Tighten hardware securely.
4. Repeat Steps 2 and 3 for the second horizontal support (I-beam).
Figure 1: Beam Clamp Installation Figure 2: Adequate Paint Penetration Figure 3: Cable Assembly Installation
CONNECTING TO THE CBN
1. The recommended location for attaching the frame ground is the back “C” channel on the
upper module of the stack (see Figure 4).
Figure 4: Recommended Frame
Ground Location
2. Once the location is determined, it will be necessary to drill (2) holes for the frame ground conductor/lug (installer supplied).
Note, hole size and spacing will be dependent on the lug.
3. Using a grinder, etc., remove the paint from around the holes drilled in Step 2.
Apply a thin film of NO-OXID grease to the bare metal and attach the frame ground conductor/lug.
27
Page 28

28
Page 29

Exide Technologies –
®
®
The Industry Leader.
GNB Industrial Power, a division of Exide Technologies, is a
global leader in stored electrical energy solutions for all major
critical reserve power applications and needs. Network power
applications include communication/data networks, UPS
systems for computers and control systems, electrical power
generation and distribution systems, as well as a wide range of
other industrial standby power applications. With a strong
manufacturing base in both North America and Europe and a
truly global reach (operations in more than 80 countries) in
sales and service, GNB Industrial Power is best positioned
to satisfy your back up power needs locally as well as all over
the world.
GNB Industrial Power
A Division of Exide Technologies
USA – Tel: 888.898.4GNB (4462)
Canada – Tel: 800.268.2698
www.exide.com
SECTION 92.80 2008-07
Based on over 100years oftechnological innovationthe Network
Power Division leads the industry with the most recognized
global brands such as ABSOLYTE
MARATHON
CLASSIC
performance and excellence in all the markets served.
Exide Technologies takes pride in its commitment to a better
environment. Its Total Battery Management program, an
integrated approach to manufacturing, distributing and
recycling of lead acid batteries, has been developed to ensure
a safe and responsible life cycle for all of its products.
®
, SPRINTER®, RELAY GEL®and GNB FLOODED
™
. They have come to symbolize quality, reliability,
®
, SONNENSCHEIN®,
 Loading...
Loading...