EXAR ST16C550 Service Manual
Y
-DSR
S
-
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
ST16C550
UART WITH 16-BYTE FIFO’s
April 2005
The ST16C550 (550) is a universal asynchronous receiver and transmitter with 16 byte transmit and receive
FIFO. It operates at 2.97 to 5.5 volts. A programmable
baud rate generator can select transmit and receive
clock rates from 50 bps to 1.5 Mbps.
The ST16C550 is an improved version of the NS16C550
UART with higher operating speed and lower access
time. The ST16C550 on board status registers provides
the error conditions, type and status of the transfer
operation being performed. Included is complete MODEM control capability, and a processor interrupt
system that may be software tailored to the user’s
requirements. The ST16C550 provides internal loopback capability for on board diagnostic testing.
The ST16C550 is available in 40 pin PDIP, 44 pin PLCC,
and 48 pin TQFP packages. It is fabricated in an
advanced CMOS process to achieve low drain power
and high speed requirements.
FEATURES
RCLK
N.C.
CS0
CS1
-CS2
-BAUDOUT
PLCC Package
D4D3D2D1D0
6
5
4
7
D5
8
D6
9
D7
10
11
RX
12
13
TX
14
15
16
17
1819202122232425262728
-IOW
XTAL1
XTAL2
N.C.VCC
3
2
1
4443424140
ST16C550CJ44
N.C.
-IOR
GND
IOW
-RI
IOR
-CD
-CT
39
RESET
38
-OP1
37
-DTR
36
-RTS
35
-OP2
34
N.C.
33
INT
32
-RXRD
31
A0
30
A1
29
A2
-AS
-DDIS
TXRDY
• Pin to pin and functionally compatible to the Industry
Standard 16C550
• 2.97 to 5.5 volt operation
• 24MHz clock operation at 5V
• Standard modem interface
• Compatible with ST16C450
• Low operating current ( 1.2mA typ.)
• 16MHz clock operation at 3.3V
• 16 byte transmit FIFO
• 16 byte receive FIFO with error flags
• Full duplex operation
• Transmit and receive control
• Four selectable receive FIFO interrupt trigger levels
ORDERING INFORMATION
Part number Package Operating temperature Device Status
ST16C550CP40 40-Lead PDIP 0° C to + 70° C Active. See the ST16C550CQ48 for new designs.
ST16C550CJ44 44-Lead PLCC 0° C to + 70° C Active
ST16C550CQ48 48-Lead TQFP 0° C to + 70° C Active
ST16C550IP40 40-Lead PDIP -40° C to + 85° C Active. See the ST16C550IQ48 for new designs.
ST16C550IJ44 44-Lead PLCC -40° C to + 85° C Active
ST16C550IQ48 48-Lead TQFP -40° C to + 85° C Active
Rev. 5.01
EXAR Corporation, 48720 Kato Road, Fremont, CA 94538 • (510) 668-7000 • FAX (510) 668-7017

ST16C550
-
Y
.
-
Y
Y
Figure 1, PACKAGE DESCRIPTION, ST16C550
48 Pin TQFP Package 40 Pin DIP Package
N.C.
RCLK
N.C.
CS0
CS1
-CS2
BAUDOUT
N.C.D4D3D2D1D0
4847464544434241403938
1
2
D5
3
D6
4
D7
5
6
7
RX
8
TX
9
10
11
12
1314151617181920212223
N.C.
XTAL1
XTAL2
ST16C550CQ48
-IOW
VCC
-RI
-CD
-DSR-CTSN.C
37
24
N.C.
IOR
-IOR
GND
IOW
-AS
-DDIS
-TXRDY
VCC
1
D0
2
D1
3
RCLK
RX
CS0
CS1
-CS2
BAUDOUT
XTAL1
XTAL2
-IOW
IOW
GND
D2
4
D3
5
D4
6
D5
7
D6
8
D7
9
10
11
TX
12
ST16C550CP40
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
N.C.
36
RESET
35
-OP1
34
-DTR
33
-RTS
32
-OP2
31
INT
30
-RXRD
29
A0
28
A1
27
A2
26
N.C.
25
40
-RI
39
-CD
38
-DSR
37
-CTS
36
RESET
35
-OP1
34
-DTR
33
-RTS
32
-OP2
31
INT
30
-RXRD
29
A0
28
A1
27
A2
26
-AS
25
-TXRD
24
-DDIS
23
IOR
22
-IOR
21
Rev. 5.01
2
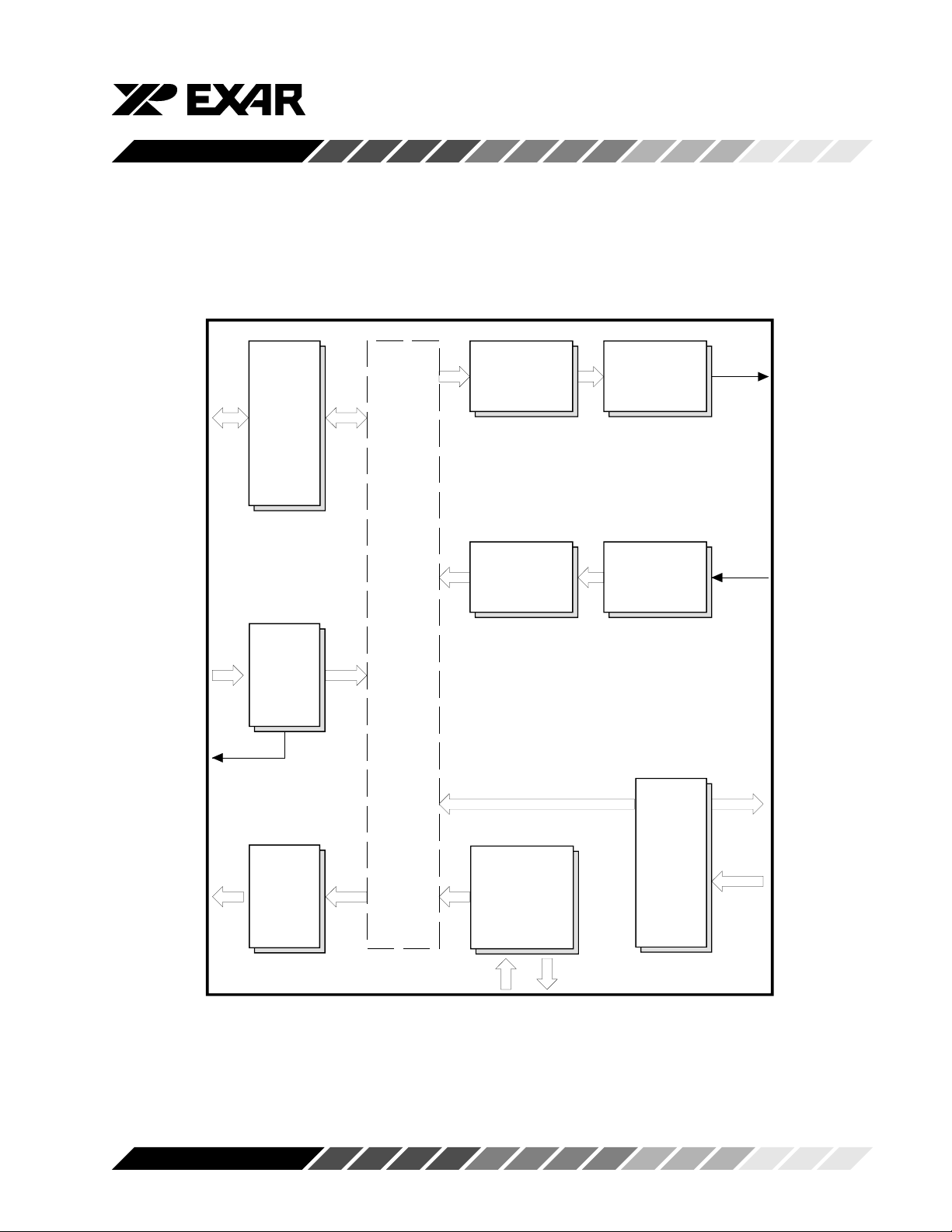
Figure 2, BLOCK DIAGRAM
-
-DTR,-RTS
2
-
ST16C550
Transmit
D0-D7
-IOR,IOR
IOW,IOW
RESET
A0-A2
-AS
CS0,CS1
-CS2
-DDIS
&
Data bus
Control Logic
&
Logic
Select
Register
Control signals
Inter Connec t Bus Li nes
FIFO
Registers
Receive
FIFO
Registers
Transmit
Shift
Register
Receive
Shift
Register
TX
RX
INT
-RXRDY
-TXRDY
Rev. 5.01
-OP1,-OP
Modem
Clock
&
Logic
Control
Interrupt
Baud Rate
Generator
3
RCLK
XTAL1
XTAL2
BAUDOUT
Control
Logic
-CTS
-RI
-CD
-DSR
ST16C550
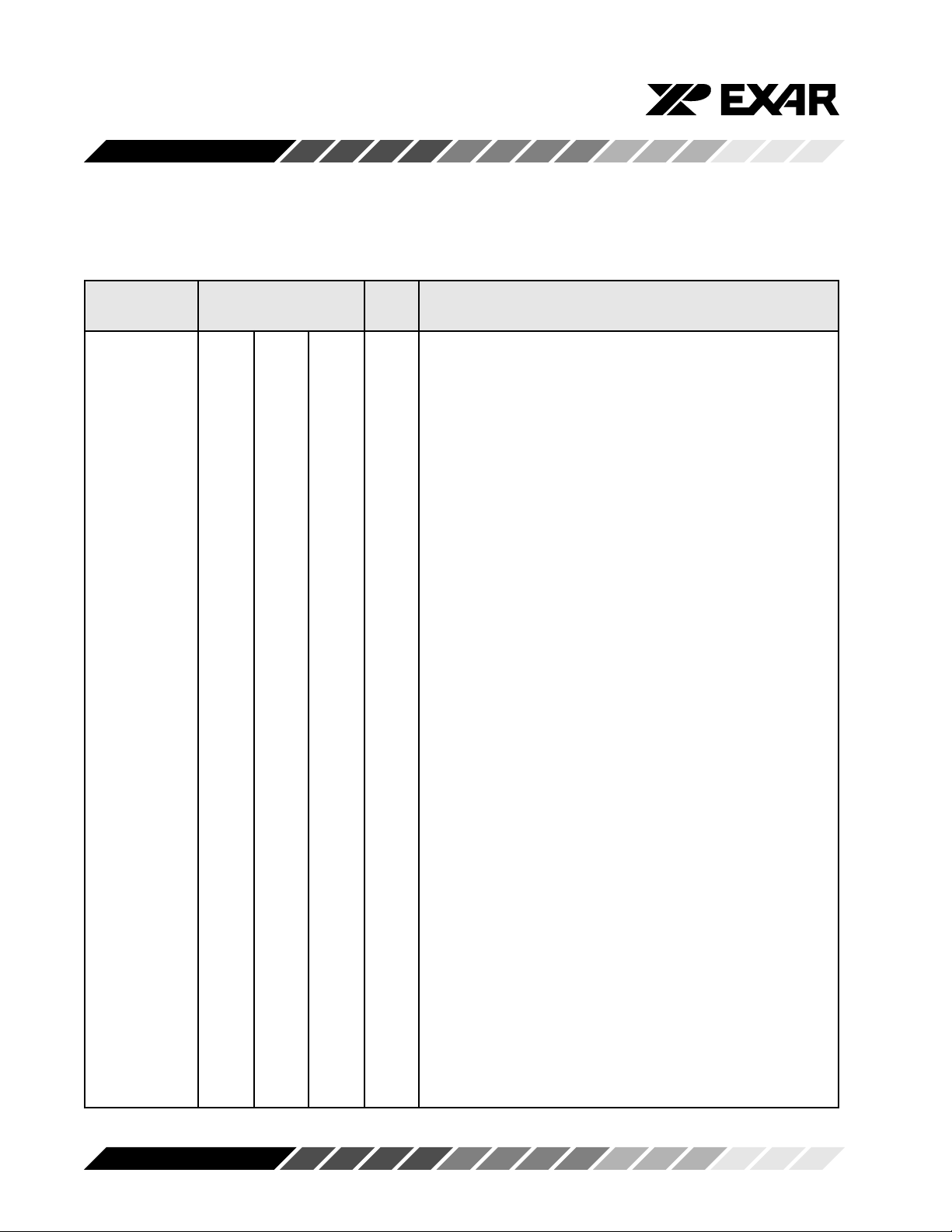
SYMBOL DESCRIPTION
Symbol Pin Signal Pin Description
40 44 48 type
A0 28 31 28 I Address-0 Select Bit Internal registers address selection.
A1 27 30 27 I Address-1 Select Bit Internal registers address selection.
A2 26 29 26 I Address-2 Select Bit Internal registers address selection.
IOR 22 25 20 I Read data strobe. Its function is the same as -IOR (see -
IOR), except it is active high. Either an active -IOR or IOR
is required to transfer data from 16C550 to CPU during a
read operation. Connect to logic 0 when using -IOR.
CS0 12 14 9 I Chip Select-0. Logical 1 on this pin provides the chip select-
0 function. Connect CS0 to logic 1 if using CS1 or -CS2.
CS1 13 15 10 I Chip Select-1. Logical 1 on this pin provides the chip select-
1 function. Connect CS1 to logic 1 if using CS0 or -CS2.
-CS2 14 16 11 I Chip Select -2. Logical 0 on this pin provides the chip select2 function. Connect to logic 0 if using CS0 or CS1.
IO W 19 21 17 I Write data strobe. Its function is the same as -IOW (see -
IOW), but it acts as an active high input signal. Either -IOW
or IOW is required to transfer data from the CPU to
ST16C550 during a write operation. Connect to logic 0 when
using -IOW.
-AS 2 5 2 8 2 4 I Address Strobe. A logic 1 transition on -AS latches the state
of the chip selects and the register select bits, A0-A2. This
input is used when address and chip selects are not stable
for the duration of a read or write operation, i.e., a microprocessor that needs to de-multiplex the address and data bits.
If not required, the -AS input can be permanently tied to a
logic 0.
D0-D7 1-8 2-9 43-47
2-4 I/O Data Bus (Bi-directional) - These pins are the eight bit, tri-
state data bus for transferring information to or from the
controlling CPU. D0 is the least significant bit and the first
data bit in a transmit or receive serial data stream.
GN D 2 0 22 18 Pw r Signal and Power Ground.
Rev. 5.01
4
ST16C550
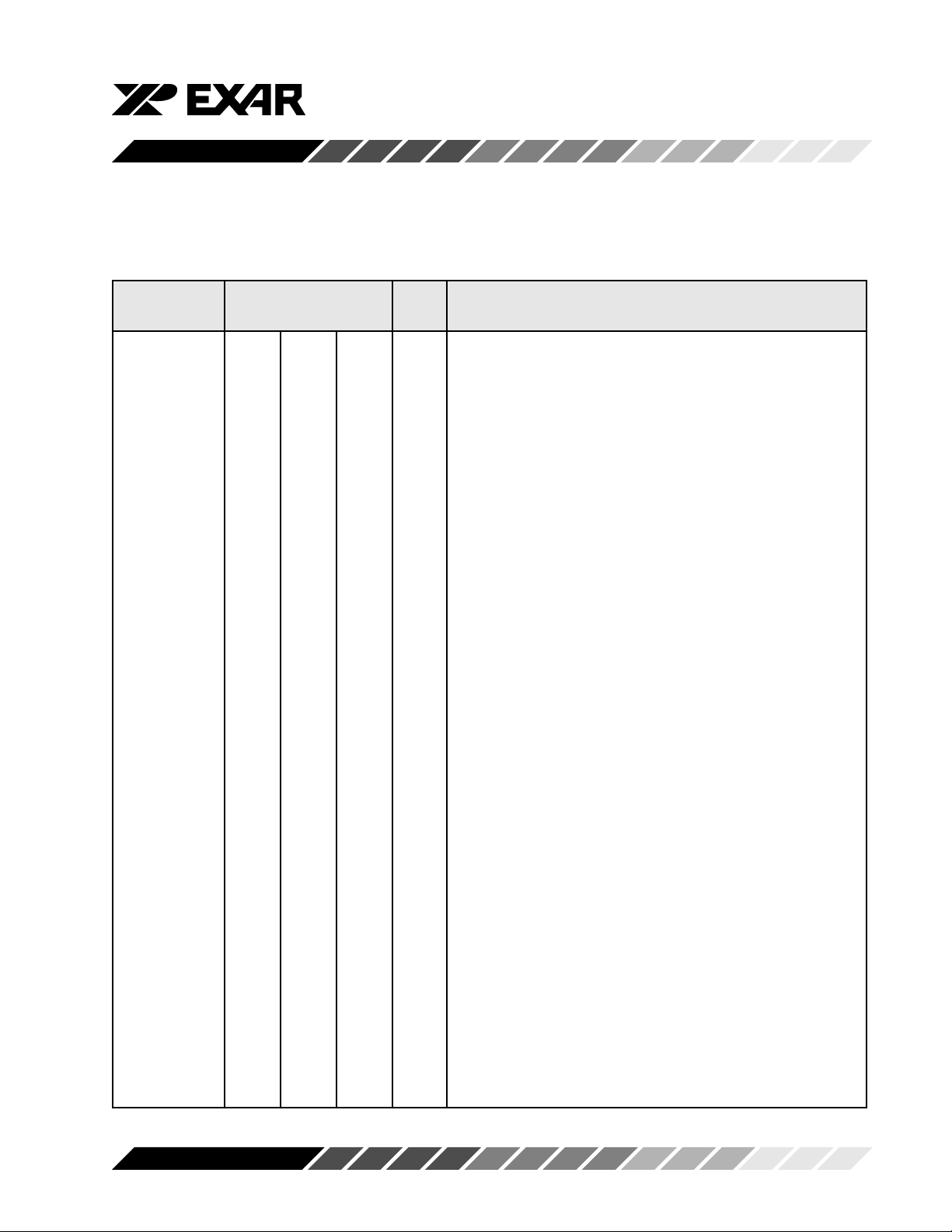
SYMBOL DESCRIPTION
Symbol Pin Signal Pin Description
40 44 48 type
-IOR 21 24 19 I Read data strobe (active low strobe). A logic 0 on this pin
transfers the contents of the ST16C550 data bus to the CPU.
Connect to logic 1 when using IOR.
-IOW 18 20 16 I Write data strobe (active low strobe). A logic 0 on this pin
transfers the contents of the CPU data bus to the addressed
internal register. Connect to logic 1 when using IOW.
INT 30 33 30 O Interrupt Request (active high). Interrupts are enabled in the
interrupt enable register (IER), and when an interrupt condition exists. Interrupt conditions include: receiver errors,
available receiver buffer data, transmit buffer empty, or
when a modem status flag is detected.
-RXRDY 29 32 29 O Receive Ready. When operating in the FIFO mode, one of
two types of DMA signaling can be selected using the FIFO
control register bit-3. When operating in the ST16C450
mode, only DMA mode “0” is allowed. Mode “0” supports
single transfer DMA in which a transfer is made between
CPU bus cycles. Mode “1” supports multi-transfer DMA in
which multiple transfers are made continuously until the
receiver FIFO has been emptied. In DMA mode “0” -RXRDY
is low, when there is at least one character in the receiver
FIFO or receive holding register. In DMA mode “1”, -RXRDY
is low, when the trigger level or the time-out has been
reached.
-TXRDY 24 27 23 O Transmit Ready. When operating in the FIFO mode, one of
two types of DMA signaling can be selected using the FIFO
control register bit-3. When operating in the ST16C450
mode, only DMA mode “0” is allowed. Mode “0” supports
single transfer DMA in which a transfer is made between
CPU bus cycles. Mode “1” supports multi-transfer DMA in
which multiple transfers are made continuously until the
transmit FIFO has been filled.
-BAUDOUT 15 17 12 O Baud Rate Generator Output. This pin provides the 16X
clock of the selected data rate from the baud rate generator.
The RCLK pin must be connected externally to -BAUDOUT
when the receiver is operating at the same data rate.
Rev. 5.01
5
ST16C550
SYMBOL DESCRIPTION
Symbol Pin Signal Pin Description
40 44 48 type
-DDIS 23 26 22 O Drive Disable. This pin goes to a logic 0 when the external
CPU is reading data from the ST16C550. This signal can be
used to disable external transceivers or other logic functions.
-OP1 34 38 34 O Output-1 (User Defined) - See bit-2 of modem control
register (MCR bit-2).
RESET 35 39 35 I Reset. (active high) - A logic 1 on this pin will reset the
internal registers and all the outputs. The UART transmitter
output and the receiver input will be disabled during reset
time. (See ST16C550 External Reset Conditions for initialization details.)
RCLK 9 10 5 I Receive Clock Input. This pin is used as external 16X clock
input to the receiver section. External connection to Baudout pin is required in order to utilize the internal baud
rate generator.
-OP2 31 35 31 O Output-2 (User Defined). This pin provides the user a
general purpose output. See bit-3 modem control register
(MCR bit-3).
VCC 40 44 42 Pwr Power Supply Input.
XTAL1 16 18 14 I Crystal or External Clock Input - Functions as a crystal input
or as an external clock input. A crystal can be connected
between this pin and XTAL2 to form an internal oscillator
circuit. An external 1 MΩ resistor is required between the
XTAL1 and XTAL2 pins (see figure 3). Alternatively, an
external clock can be connected to this pin to provide
custom data rates (Programming Baud Rate Generator
section).
XTAL2 17 19 15 O Output of the Crystal Oscillator or Buffered Clock - (See also
XTAL1). Crystal oscillator output or buffered clock output.
-CD 38 42 40 I Carrier Detect (active low) - A logic 0 on this pin indicates
that a carrier has been detected by the modem.
Rev. 5.01
6
ST16C550
SYMBOL DESCRIPTION
Symbol Pin Signal Pin Description
40 44 48 type
-CTS 36 40 38 I Clear to Send (active low) - A logic 0 on the -CTS pin
indicates the modem or data set is ready to accept transmit
data from the ST16C550. Status can be tested by reading
MSR bit-4. This pin has no effect on the UART’s transmit or
receive operation.
-DSR 37 41 39 I Data Set Ready (active low) - A logic 0 on this pin indicates
the modem or data set is powered-on and is ready for data
exchange with the UART. This pin has no effect on the
UART’s transmit or receive operation.
-DTR 33 37 33 O Data Terminal Ready (active low) - A logic 0 on this pin
indicates that the ST16C550 is powered-on and ready. This
pin can be controlled via the modem control register.
Writing a logic 1 to MCR bit-0 will set the -DTR output to
logic 0, enabling the modem. This pin will be a logic 1 after
writing a logic 0 to MCR bit-0, or after a reset. This pin has
no effect on the UART’s transmit or receive operation.
-RI 39 43 41 I Ring Indicator (active low) - A logic 0 on this pin indicates the
modem has received a ringing signal from the telephone
line. A logic 1 transition on this input pin will generate an
interrupt.
-RTS 32 36 32 O Request to Send (active low) - A logic 0 on the -RTS pin
indicates the transmitter has data ready and waiting to send.
Writing a logic 1 in the modem control register (MCR bit-1)
will set this pin to a logic 0 indicating data is available. After
a reset this pin will be set to a logic 1. This pin has no effect
on the UART’s transmit or receive operation.
RX 10 11 7 I Receive Data - This pin provides the serial receive data
input to the ST16C550. A logic 1 indicates no data or an idle
channel. During the local loop-back mode, the RX input pin is
disabled and TX data is internally connected to the UART RX
Input, internally, see figure 12.
TX 11 13 8 O Transmit Data - This pin provides the serial transmit data
from the ST16C550, the TX signal will be a logic 1 during
reset, idle (no data). During the local loop-back mode, the
TX pin is set to a logic 1 and TX data is internally connected
to the UART RX Input, see figure 12.
Rev. 5.01
7

ST16C550
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The ST16C550 provides serial asynchronous receive
data synchronization, parallel-to-serial and serial-toparallel data conversions for both the transmitter and
receiver sections. These functions are necessary for
converting the serial data stream into parallel data that
is required with digital data systems. Synchronization
for the serial data stream is accomplished by adding
start and stops bits to the transmit data to form a data
character (character orientated protocol). Data integrity is insured by attaching a parity bit to the data
character. The parity bit is checked by the receiver for
any transmission bit errors. The electronic circuitry to
provide all these functions is fairly complex especially
when manufactured on a single integrated silicon
chip. The ST16C550 represents such an integration
with greatly enhanced features. The ST16C550 is
fabricated with an advanced CMOS process.
The ST16C550 is an upward solution that provides 16
bytes of transmit and receive FIFO memory, instead
of 1 byte provided in the 16C450. The ST16C550 is
designed to work with high speed modems and shared
network environments, that require fast data processing time. Increased performance is realized in the
ST16C550 by the larger transmit and receive FIFO’s.
This allows the external processor to handle more
networking tasks within a given time. The 4 selectable
levels of FIFO trigger provided for maximum data
throughput performance especially when operating in
a multi-channel environment. The combination of the
above greatly reduces the bandwidth requirement of
the external controlling CPU, increases performance,
and reduces power consumption.
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTIONS
Internal Registers
The ST16C550 provides 12 internal registers for
monitoring and control. These registers are shown in
Table 3 below. These registers function as data holding registers (THR/RHR), interrupt status and control
registers (IER/ISR), a FIFO control register (FCR),
line status and control registers, (LCR/LSR), modem
status and control registers (MCR/MSR), programmable data rate (clock) control registers (DLL/DLM),
and a user assessable scratchpad register (SPR).
The ST16C550 is capable of operation to 1.5Mbps
with a 24 MHz crystal or external clock input.
With a crystal of 14.7464 MHz and through a software
option, the user can select data rates up to 460.8Kbps
or 921.6Kbps.
Rev. 5.01
8

ST16C550
9
ST16C550
ample: T = [(programmed word length = 7) + (stop bit
= 1) + (start bit = 1) = 9]. 40 (bit times divided by 9) =
4.4 characters.
Example -B: If the user programs the word length = 7,
with parity and one stop bit, the time out will be:
T = 4 X 7(programmed word length) + 12 = 40 bit times.
Character time = 40 / 10 [ (programmed word length
= 7) + (parity = 1) + (stop bit = 1) + (start bit = 1) = 4
characters.
Programmable Baud Rate Generator
The ST16C550 supports high speed modem technologies that have increased input data rates by
employing data compression schemes. For example
a 33.6Kbps modem that employs data compression
may require a 115.2Kbps input data rate. A 128.0Kbps
ISDN modem that supports data compression may
need an input data rate of 460.8Kbps. The ST16C550
can support a standard data rate of 921.6Kbps.
The programmable Baud Rate Generator is capable
of accepting an input clock up to 24 MHz, as required
for supporting a 1.5Mbps data rate. The ST16C550 can
be configured for internal or external clock operation.
For internal clock oscillator operation, an industry
standard microprocessor crystal (parallel resonant/
22 pF load) is connected externally between the
XTAL1 and XTAL2 pins, with an external 1 MΩ resistor
across it. Alternatively, an external clock can be
connected to the XTAL1 pin to clock the internal baud
rate generator for standard or custom rates. See
figure 3 for crystal oscillator connection.
The generator divides the input 16X clock by any
divisor from 1 to 216 -1. The ST16C550 divides the
basic crystal or external clock by 16. The frequency of
the -BAUDOUT output pin is exactly 16X (16 times) of
the selected baud rate (-BAUDOUT =16 x Baud Rate).
Customized Baud Rates can be achieved by selecting
the proper divisor values for the MSB and LSB sections of baud rate generator.
Programming the Baud Rate Generator Registers
DLM (MSB) and DLL (LSB) provides a user capability
for selecting the desired final baud rate. The example
in Table 3 below shows selectable baud rates when
using a 1.8432 MHz crystal.
For custom baud rates, the divisor value can be calculated using the following equation:
Divisor (in decimal) = (XTAL1 clock frequency) / (serial data rate x 16)
Table 3, BAUD RATE GENERATOR PROGRAMMING TABLE (1.8432 MHz CLOCK):
Output User User DLM DLL
Baud Rate 16 x Clock 16 x Clock Program Program
Divisor Divisor Value Value
(Decimal) (HEX) (HEX) (HEX)
50 2304 900 09 00
75 1536 600 06 00
150 768 300 03 00
300 384 180 01 80
600 192 C0 00 C0
1200 96 60 00 60
2400 48 30 00 30
4800 24 18 00 18
7200 16 10 00 10
9600 12 0C 00 0C
19.2k 6 0 6 00 06
38.4k 3 0 3 00 03
57.6k 2 0 2 00 02
115.2k 1 01 0 0 01
Rev. 5.01
10
ST16C550
DMA Operation
The ST16C550 FIFO trigger level provides additional
flexibility to the user for block mode operation. The user
can optionally operate the transmit and receive FIFO’s
in the DMA mode (FCR bit-3). The DMA mode affects
the state of the -RXRDY and -TXRDY output pins. The
following tables show this:
-RXRDY pin:
Non-DMA mode DMA mode
1 = FIFO empty 0 to 1 transition when FIFO
empties
0 = at least 1 byte 1 to 0 transition when FIFO
in FIFO reaches trigger level, or
timeout occurs
-TXRDY pin:
Non-DMA mode DMA mode
1 = at least 1 byte 1 = FIFO is full
in FIFO
0 = FIFO empty 0 = FIFO has at least 1
empty location
Loop-back Mode
D0-D7. The user optionally compares the received
data to the initial transmitted data for verifying error
free operation of the UART TX/RX circuits.
In this mode , the receiver and transmitter interrupts are
fully operational. The Modem Control Interrupts are also
operational. The interrupts are still controlled by the
IER.
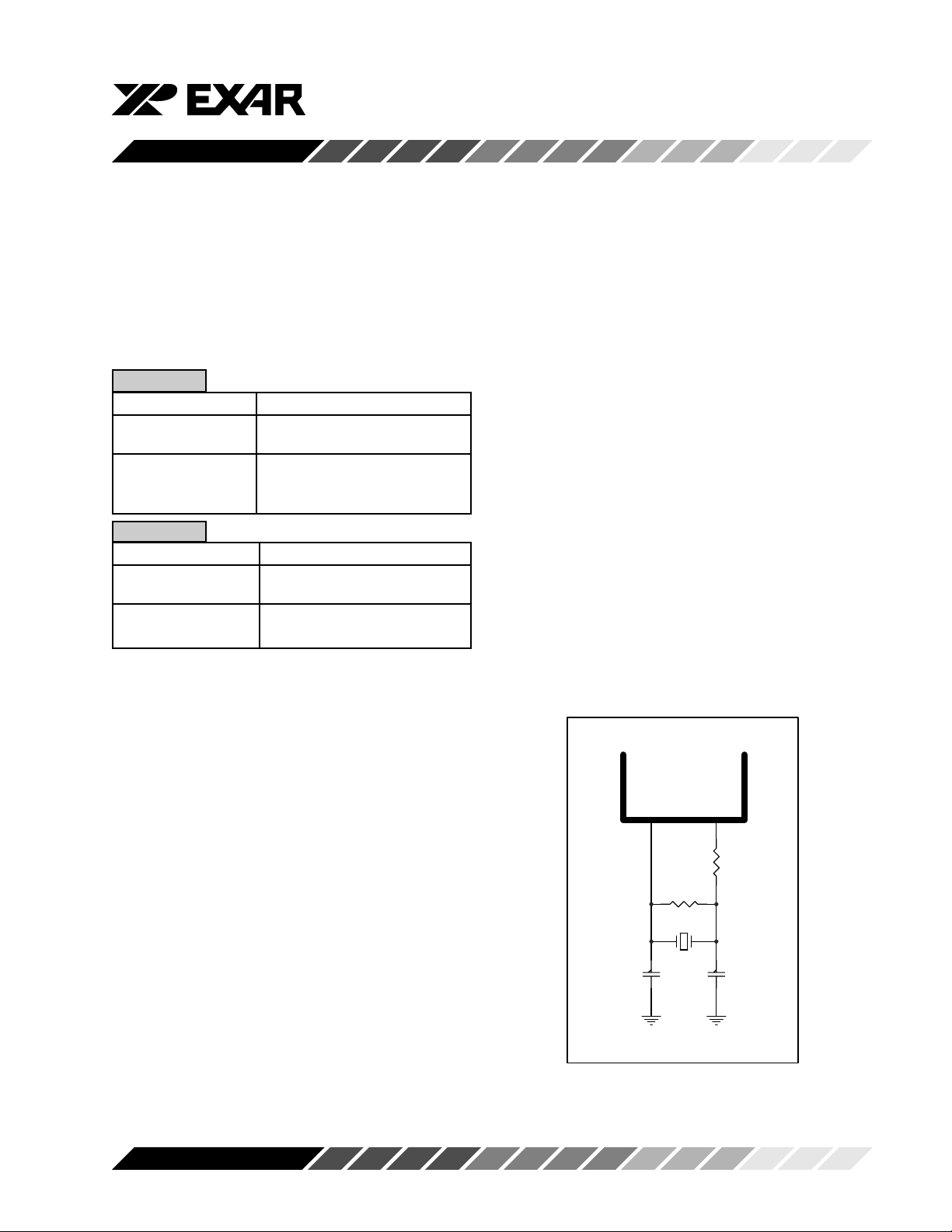
Figure 3, TYPICAL EXTERNAL CRYSTAL OSCILLATOR CONNECTION
The internal loop-back capability allows onboard diagnostics. In the loop-back mode the normal modem
interface pins are disconnected and reconfigured for
loop-back internally. In this mode MSR bits 4-7 are
also disconnected. However, MCR register bits 0-3
can be used for controlling loop-back diagnostic testing. In the loop-back mode -OP1 and -OP2 in the MCR
register (bits 0-1) control the modem -RI and -CD
inputs respectively. MCR signals -DTR and -RTS (bits
0-1) are used to control the modem -CTS and -DSR
inputs respectively. The transmitter output (TX) and the
receiver input (RX) are disconnected from their associated interface pins, and instead are connected together
internally (See Figure 4). The -CTS, -DSR, -CD, and -RI
are disconnected from their normal modem control
inputs pins, and instead are connected internally to DTR, -RTS, -OP1 and -OP2. Loop-back test data is
entered into the transmit holding register via the user
data bus interface, D0-D7. The transmit UART serializes the data and passes the serial data to the receive
UART via the internal loop-back connection. The receive
UART converts the serial data back into parallel data
that is then made available at the user data interface,
Rev. 5.01
XTAL1 XTAL2
R2
1M
Y1
C1
22-47pF
R1
0-120
(Optional)
1.8432 - 24 MHz
C2
22-47pF
11
 Loading...
Loading...