Page 1

EUTECH INSTRUMENTS PTE LTD.
INSTRUCTION MANUAL
LEAD ION ELECTRODE
Page 2

TABLE OF CONTENTS
GENERAL INSTRUCTIONS ..........................................................................................................1
Introduction..............................................................................................................................................2
Required Equipment.................................................................................................................................2
Required Solutions...................................................................................................................................2
GENERAL PREPARATION............................................................................................................3
Electrode Preparation...............................................................................................................................3
Electrode Slope Check (with pH/mV meter) ...........................................................................................3
Electrode Slope Check (with ion meter) ..................................................................................................3
MEASUREMENT..............................................................................................................................4
Measuring Hints.......................................................................................................................................4
Sample Requirements...............................................................................................................................4
Units of Measurement..............................................................................................................................5
MEASUREMENT PROCEDURE ...................................................................................................5
Direct Measurement.................................................................................................................................5
Direct Measurement of Lead (using a pH/mV meter)..............................................................................5
Direct Measurement of Lead (using an ion meter)...................................................................................7
Low Level Lead Determination (using a pH/mV meter) .........................................................................8
Low Level Lead Determination (using an ion meter)..............................................................................9
Titration..................................................................................................................................................10
Titration of Lead ....................................................................................................................................10
Titration of Sulfate.................................................................................................................................11
ELECTRODE CHARACTERISTICS...........................................................................................13
Reproducibility.......................................................................................................................................13
Interferences...........................................................................................................................................13
Precipitation and Complexation............................................................................................................. 13
Temperature Influences..........................................................................................................................13
Electrode Response................................................................................................................................14
Limits of Detection.................................................................................................................................14
pH Effects...............................................................................................................................................15
Electrode Life.........................................................................................................................................15
Electrode Storage ...................................................................................................................................15
ELECTRODE THEORY................................................................................................................15
Electrode Operation ...............................................................................................................................15
TROUBLESHOOTING GUIDE....................................................................................................17
Meter......................................................................................................................................................17
Glass-ware/Plastic-ware.........................................................................................................................17
Electrodes...............................................................................................................................................17
Sample....................................................................................................................................................17
Technique...............................................................................................................................................18
TROUBLESHOOTING HINTS.....................................................................................................19
SPECIFICATIONS..........................................................................................................................21
ORDERING INFORMATION.......................................................................................................21
Page 3

Instruction Manual Lead Electrode
GENERAL INSTRUCTIONS ............................................................Error! Bookmark not defined.
Introduction............................................................................................................Error! Bookmark not defined.
Required Equipment...............................................................................................Error! Bookmark not defined.
Required Solutions.................................................................................................Error! Bookmark not defined.
GENERAL PREPARATION.........................................................ERROR! BOOKMARK NOT DEFINED.
Electrode Preparation...................................................................................... ERROR! BOOKMARK NOT DEFINED.
Electrode Slope Check (with pH/mV meter)................................................... E
Electrode Slope Check (with ion meter) ......................................................... E
RROR! BOOKMARK NOT DEFINED.
RROR! BOOKMARK NOT DEFINED.
MEASUREMENT..............................................................................................Error! Bookmark not defined.
Measuring Hints.............................................................................................. ERROR! BOOKMARK NOT DEFINED.
Sample Requirements...................................................................................... E
Units of Measurement..................................................................................... E
RROR! BOOKMARK NOT DEFINED.
RROR! BOOKMARK NOT DEFINED.
MEASUREMENT PROCEDURE ..................................................... Error! Bookmark not defined.
Direct Measurement........................................................................................ ERROR! BOOKMARK NOT DEFINED.
Direct Measurement of Silver (using a pH/mV meter) ................................... E
Direct Measurement of Silver (using an ion meter)........................................ E
Direct Measurement of Sulfide (using a pH/mV meter) ................................. E
Direct Measurement of Sulfide (using an ion meter)...................................... E
Low Level Silver Determinations (using a pH/mV meter) ............................. E
RROR! BOOKMARK NOT DEFINED.
RROR! BOOKMARK NOT DEFINED.
RROR! BOOKMARK NOT DEFINED.
RROR! BOOKMARK NOT DEFINED.
RROR! BOOKMARK NOT DEFINED.
TITRATION.........................................................................................Error! Bookmark not defined.
Titration of Sulfide.......................................................................................... ERROR! BOOKMARK NOT DEFINED.
Titration of Silver............................................................................................ E
Low Level Chloride Titration.......................................................................... E
Indicator Titration ........................................................................................... E
RROR! BOOKMARK NOT DEFINED.
RROR! BOOKMARK NOT DEFINED.
RROR! BOOKMARK NOT DEFINED.
ELECTRODE CHARACTERISTICS...............................................Error! Bookmark not defined.
Reproducibility ................................................................................................ ERROR! BOOKMARK NOT DEFINED.
Interference...................................................................................................... E
Complexation.................................................................................................. E
Temperature Influences................................................................................... E
Electrode Response ......................................................................................... E
Limits of Detection.......................................................................................... E
pH Effects........................................................................................................ E
Electrode Life.................................................................................................. E
Electrode Storage ............................................................................................ E
RROR! BOOKMARK NOT DEFINED.
RROR! BOOKMARK NOT DEFINED.
RROR! BOOKMARK NOT DEFINED.
RROR! BOOKMARK NOT DEFINED.
RROR! BOOKMARK NOT DEFINED.
RROR! BOOKMARK NOT DEFINED.
RROR! BOOKMARK NOT DEFINED.
RROR! BOOKMARK NOT DEFINED.
ELECTRODE THEORY....................................................................Error! Bookmark not defined.
Electrode Operation......................................................................................... ERROR! BOOKMARK NOT DEFINED.
TROUBLESHOOTING GUIDE........................................................ Error! Bookmark not defined.
Meter ............................................................................................................... ERROR! BOOKMARK NOT DEFINED.
Glassware........................................................................................................ E
Electrodes........................................................................................................ E
Standards and Reagents................................................................................... E
Sample............................................................................................................. E
Technique........................................................................................................ E
RROR! BOOKMARK NOT DEFINED.
RROR! BOOKMARK NOT DEFINED.
RROR! BOOKMARK NOT DEFINED.
RROR! BOOKMARK NOT DEFINED.
RROR! BOOKMARK NOT DEFINED.
TROUBLESHOOTING HINTS......................................ERROR! BOOKMARK NOT DEFINED.
SPECIFICATIONS.............................................................................. Error! Bookmark not defined.
ORDERING INFORMATION........................................ERROR! BOOKMARK NOT DEFINED.
1
Page 4

EUTECH INSTRUMENTS PTE LTD.
LEAD ION ELECTRODE
INSTRUCTION MANUAL
GENERAL INSTRUCTIONS
Introduction
Eutech Instruments Lead Ion Electrode is used to measure lead or sulfate ions in aqueous solutions
quickly, simply, accurately, and economically.
Required Equipment
1. A pH/mV meter or an ion meter, either line operated or portable.
2. Semi-logarithmic 4-cycle graph paper for preparing calibration curves when using the
meter in the mV mode. Linear graph paper is recommended for low level measurements or
lead/sulfate titration.
3. A magnetic stirrer.
4. Eutech Lead Ion Combination Epoxy-body Electrode, Code no. EC-PB-03.
6. Lab-ware made of plastic, not glass, for all low level measurements.
7. Polishing Paper, Code no. EC-MIS-PP, to polish dirty or etched electrode membranes.
Required Solutions
1. Deionized or distilled water for solution and standard preparation.
2. Methanol-formaldehyde solution. To prepare this solution from your own laboratory stock,
add 3 drops of 37% formaldehyde to 1,000 ml of reagent-grade methanol. This solution is
used to decrease the solubility and retard oxidation of the membrane.
3. Eutech Ionic Strength Adjuster (ISA), 5M NaClO4, Code No. EC-ISA-PB1-BT. To
prepare this solution from your own laboratory stock, half fill a one liter volumetric flask
with distilled water and add 700 grams of reagent-grade NaClO4·H2O. Swirl the flask
gently to dissolve the solid. Fill the flask to the mark with distilled water, cap, and upend
several times to mix the solution. To each 100 ml of standard or sample, add 2 ml of ISA.
The background ionic strength of the resulting solution will be 0.1M.
4. Eutech Lead Perchlorate Standard, 0.1M Pb(ClO4)2, Code no. EC-SCS-PB1-BT. To
prepare this solution from your own laboratory stock, half fill a one liter volumetric flask
with distilled water and add 46.01 grams of reagent-grade lead perchlorate,
Page 5

Instruction Manual Lead Electrode
Pb(ClO4)2·3H2O. Swirl the flask gently to dissolve the solid. Fill the flask to the mark with
distilled water, cap, and upend several times to thoroughly mix the solution.
5. Eutech Lead Perchlorate Standard, 1,000 ppm Pb(ClO4)2, Code no. EC-SCS-PB2-BT. To
prepare this solution from your own laboratory stock, half fill a one liter volumetric flask
with distilled water and add 2.30 grams of reagent-grade lead perchlorate,
Pb(ClO4)2·3H2O. Swirl the flask to dissolve the solid. Fill the flask to the mark with
distilled water, cap, and upend several times to thoroughly mix the solution.
GENERAL PREPARATION
Electrode Preparation
Remove the rubber caps covering the electrode tips and the rubber insert covering the filling hole of
the lead combination ion electrode or the reference electrode. Fill the reference electrode or the
combination electrode with the filling solution shipped with the electrode to a level just below the
fill hole. No preparation is required with a sealed reference electrode. Connect the electrodes to the
proper terminals as recommended by the meter manufacturer.
Electrode Slope Check (with pH/mV meter)
(Check electrodes each day)
1. To a 150 ml beaker, add 50 ml of methanol-formaldehyde solution and 50 ml of distilled
water. Add 2 ml of ISA. Place the beaker on a magnetic stirrer and begin stirring at a
constant rate. After assuring that the meter is in the millivolt mode, lower the electrode tips
into the solution.
2. Using a pipet, add 1 ml of 0.1M or 1,000 ppm lead standard to the beaker. When the
reading has stabilized, record the mV reading.
3. Using a pipet, add 10 ml the same lead standard used above to the beaker. When the
reading has stabilized, record the mV reading.
4. Determine the difference between the two readings. The electrode is operating correctly if
o
the millivolt potential has changed by 25±2, assuming the temperature is between 20
o
25
C. See the TROUBLESHOOTING sections if the potential change is not within this range.
and
Slope is defined as the change in potential observed when the concentration changes by a factor of
10.
Electrode Slope Check (with ion meter)
(Check electrodes each day)
1. Prepare standard lead solutions whose concentrations vary by tenfold. Use either the 0.1M
or 1,000 ppm lead standard. Use the serial dilution method for this preparation.
2. To a 150 ml beaker, add 50 ml of methanol-formaldehyde solution and 50 ml of the lower
value standard. Add 2 ml of ISA. Place the beaker on a magnetic stirrer and begin stirring
at a constant rate. Lower the electrode tips into the solution. Assure that the meter is in the
concentration mode.
3
Page 6

3. Adjust the meter to the concentration of the standard and fix the value in the memory
according to the meter manufacturer's instructions.
4. Rinse the electrodes with distilled water and blot dry.
5. To another 150 ml beaker, add 50 ml of methanol-formaldehyde solution and 50 ml of the
higher value standard. Add 2 ml of ISA. Place the beaker on a magnetic stirrer and begin
stirring at a constant rate. Lower the electrode tips into the solution.
6. Adjust the meter to the concentration of the standard and fix the value in the memory.
7. Read the electrode slope according to the meter manufacturer's instructions. Correct
electrode operation is indicated by a slope of 90-100%. See the TROUBLESHOOTING
sections if the slope is not within this range.
MEASUREMENT
Measuring Hints
All samples and standards should be at the same temperature for precise measurement. A difference
of 1oC in temperature will result in a 4% measurement error.
Constant, but not violent stirring is necessary for accurate measurement. Magnetic stirrers can
generate sufficient heat to change the solution temperature. To counteract this effect, place a piece
of insulation material, such as styrofoam sheet, between the stirrer and beaker.
Use plastic lab-ware for all low level measurements in order to minimize absorption on container
walls. Always rinse the electrodes with distilled water and blot dry between measurements. Use a
clean, dry tissue to prevent cross-contamination.
To prevent oxidation of the membrane, always use methanol-formaldehyde solution to mix with all
standards and samples.
For samples with high ionic strength, prepare standards whose composition is similar to the sample.
Dilute concentrated samples (>0.1M) before measurement.
Use fresh standards for calibration. Use 2 ml of ISA for each 100 ml of sample or standard.
Always check to see that the membrane is free from air bubbles after immersion into the standard or
sample.
Sample Requirements
All samples must be aqueous and not contain organics which can dissolve the epoxy electrode body
and/or the cement bonding the sensing crystal to the electrode body. Infrequent measurements in
solutions containing methanol, benzene, or acetonitrile are permitted. Highly polar solvents slowly
attack the electrode. Please check with Eutech Instruments Pte Ltd. before using these electrodes in
other organic solvents.
Page 7

Instruction Manual Lead Electrode
The temperature of the standard solutions and of the sample solutions should be the same and below
80oC. About a 4% error in the slope will occur for each 1oC difference in temperature.
Interferences should be absent. If they are present, use the procedure found in the Interferences
and Electrode Response sections to remove them.
Units of Measurement
Lead concentrations are measured in units of ppm as lead, moles per liter, or any other convenient
concentration unit. Table 1 indicates some concentration units and conversion factors.
TABLE 1: Concentration Unit Conversion Factors
ppm Pb+2 M ppm SO
-4
20.7 1.0X10
207.0 1.0X10
9.6
-3
96.0
-2
4
2070.0 1.0X10-2 960.0
MEASUREMENT PROCEDURE
Direct Measurement
Direct measurement is a simple procedure for measuring a large number of samples. A single meter
reading is all that is required for each sample. The ionic strength of samples and standards should
be made the same by adjustment with ISA. The temperature of both sample solution and standard
solution should be the same.
Direct Measurement of Lead (using a pH/mV meter)
1. By serial dilution, prepare 10-2M, 10-3M, and 10-4M or 100 ppm and 10 ppm standards,
from the 0.1M or 1,000 ppm standards. Prepare standards with a composition similar to
the samples if the samples have an ionic strength above 0.1M.
2. Place 50 ml of the 10-4M or 10 ppm standard in a 150 ml beaker and add 50 ml of
methanol-formaldehyde solution. Place the beaker on the magnetic stirrer and begin
stirring at a constant rate. Add 2 ml of ISA. After assuring that the meter is in the mV
mode, lower the electrode tips into the solution. When the reading has stabilized, record
the mV reading.
3. Place 50 ml of the 10-3M or 100 ppm standard in a 150 ml beaker and add 50 ml of
methanol-formaldehyde solution. Place the beaker on the magnetic stirrer and begin
stirring. Add 2 ml of ISA. After rinsing the electrodes with distilled water, blot dry, and
immerse the electrode tips in the solution. When the reading has stabilized, record the mV
reading.
4. Place 50 ml of the 10-2M or 1,000 ppm standard in a 150 ml beaker and add 50 ml of
methanol-formaldehyde solution. Place the beaker on the magnetic stirrer and begin
stirring. Add 2 ml of ISA. After rinsing the electrodes with distilled water, blot dry, and
immerse the electrode tips in the solution. When the reading has stabilized, record the mV
reading.
5
Page 8
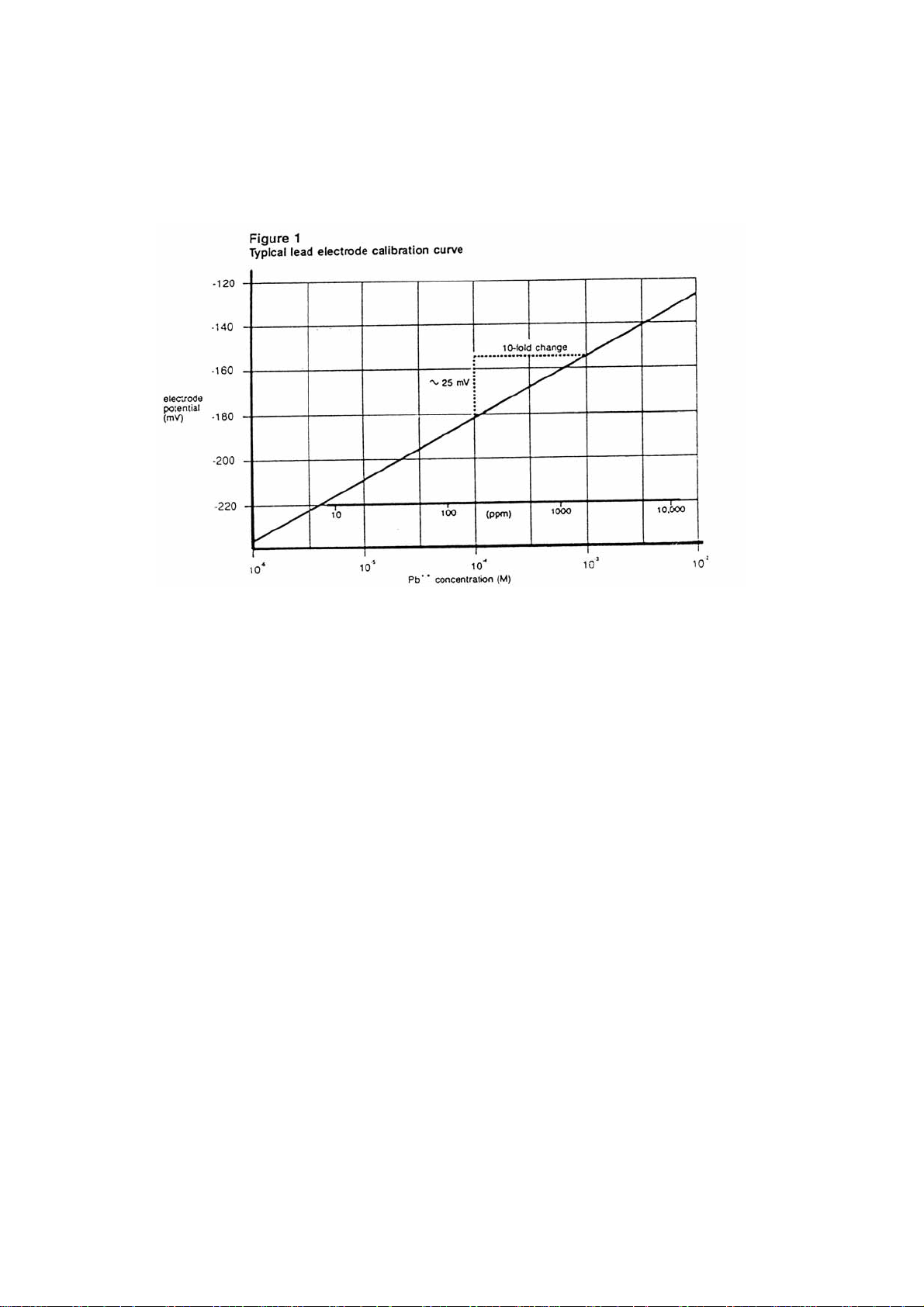
5. Using the semi-logarithmic graph paper, plot the mV reading (linear axis) against the
concentration (log axis). Extrapolate the calibration curve down to about 2.0X10-6M. A
typical calibration curve can be found in Figure 1.
A calibration curve is constructed on semi-logarithmic paper when using a
pH/mV meter in the millivolt mode. The measured electrode potential in mV
(linear axis) is plotted against the standard concentration (log axis). In the linear
region of the curve, only three standards are necessary to determine a calibration
curve. In the non-linear region, additional points must be measured. The direct
measurement procedures given are for the linear portion of the curve. The nonlinear portion of the curve requires the use of low level procedures.
6. To a clean, dry, 150 ml beaker, add 50 ml of the sample, 50 ml of methanol-formaldehyde
solution, and 2 ml of ISA. Place the beaker on the magnetic stirrer and begin stirring at a
constant rate. Rinse the electrodes with distilled water, blot dry, and lower the electrode
tips into the solution. When the reading has stabilized, record the mV reading. Using the
calibration curve determine the sample concentration.
7. The calibration should be checked every two hours. Assuming no change in ambient
temperature, immerse the electrode tips in the mid-range standard. After the reading has
stabilized, compare it to the original reading recorded in Step 3 above. A reading differing
by more than 0.5 mV or a change in the ambient temperature will necessitate the repetition
of Steps 2-5 above. A new calibration curve should be prepared daily.
Page 9

Instruction Manual Lead Electrode
Direct Measurement of Lead (using an ion meter)
1. By serial dilution of the 0.1M or l,000 ppm lead standard, prepare two lead standards
whose concentration is near the expected sample concentration. Measure out 50 ml of each
standard into individual 150 ml beakers. Add 50 ml of methanol-formaldehyde solution
and 2 ml of ISA to each beaker.
2. Place the more dilute solution on the magnetic stirrer and begin stirring at a constant rate.
Assure that the meter is in the concentration mode.
3. Lower the electrode tips into the solution.
4. Adjust the meter to the concentration of the lead standard and fix the value in the memory
according to the meter manufacturer's instructions after stabilization of the reading.
5. Rinse the electrodes with distilled water and blot dry.
6. Place the more concentrated solution on the magnetic stirrer and begin stirring at a
constant rate.
7. Lower the electrode tips into the solution.
8. Adjust the meter to the concentration of the lead standard and fix the value in the memory
according to the manufacturer's instructions after stabilization of the reading.
9. Place 50 ml of the sample, 50 ml of methanol-formaldehyde solution, and 2 ml of ISA into
a 150 ml beaker. Place the beaker on the magnetic stirrer and begin stirring at a constant
rate.
10. After rinsing the electrodes, blot dry, and lower the electrode tips into the solution. After
stabilization, read the concentration directly from the meter display.
11. The calibration should be checked every two hours. Assuming no change in ambient
temperature, immerse the electrode tips in the more dilute standard. After the reading has
stabilized, compare it to the original reading recorded in Step 4 above. A reading differing
by more than 0.5 units or a change in ambient temperature will necessitate repetition of
Steps 2-8 (2-9) above. The meter should be re-calibrated daily.
7
Page 10
Low Level Lead Determination (using a pH/mV meter)
This procedure is recommended for solutions with lead concentrations of less than 1.0X10
-6
M. If
the solution is high in ionic strength, but low in lead ion concentration, use the same procedure, but
prepare a calibration solution with a composition similar to the sample.
1. Using 20 ml of standard ISA, dilute to 100 ml with distilled water. This low level ISA
(1.0M NaClO4) is added at the rate of 1 ml low level ISA to each 100 ml of solution. The
background ionic strength will be 1.0X10-2M.
2. Dilute 1ml of 0.1M standard to one liter to prepare a 1.0X10-4M solution for measurements
in moles per liter. Prepare a 10 ppm standard solution by diluting 1 ml of the 1,000 ppm
standard to 100 ml for measurements in ppm. Standards should be prepared fresh daily.
Plastic lab-ware is recommended to avoid absorption of lead on the beaker walls.
3. Add 50 ml of distilled water, 50 ml of methanol-formaldehyde solution, and 1 ml of low
level ISA to a 150 ml plastic beaker. Place the beaker on the magnetic stirrer and begin
stirring at a constant rate.
4. Place the electrode tips in the solution. Assure that the meter is in the mV mode.
5. Add increments of the 1.0X10-4M or 10 ppm standard as given in Table 2 below.
6. After the reading has stabilized, record the mV reading.
TABLE 2: Step-wise Calibration For Low Level Lead Measurements
Added Concentration
Step Pipet Volume (ml) ppm M
1 A 0.1 1.0X10-2 1.0X10-7
2 A 0.1 2.0X10-2 2.0X10-7
3 A 0.2 4.0X10-2 4.0X10-7
4 A 0.2 6.0X10
-2
6.0X10
-7
5 A 0.4 1.0X10-1 9.9X10-7
6 B 2.0 2.9X10-1 2.9X10
7 B 2.0 4.8X10
-1
4.8X10-6
-6
Pipet A = 1 ml graduated pipet
Pipet B = 2 ml pipet
-4
Solutions: additions of 10 ppm or 1.0X10
M standard to 100 ml of solution prepared in
Step 3 above
7. On a semi-logarithmic graph paper, plot the mV reading (linear axis) against the
concentration (log axis) as in Figure 1.
8. Rinse the electrodes and blot dry.
9. Measure out 50 ml of the sample into a 150 ml plastic beaker. Add 50 ml of methanolformaldehyde solution and 1 ml of low level ISA. Place the beaker on the magnetic stirrer
and begin stirring at a constant rate. Lower the electrode tips into the solution. After the
Page 11

Instruction Manual Lead Electrode
reading has stabilized, record the mV reading and determine the concentration from the
low level calibration curve. Prepare a new low level calibration curve daily. Check the
calibration curve every two hours by repeating Steps 3- 7 above.
Low Level Lead Determination (using an ion meter)
1. Using 20 ml of standard ISA, dilute to 100 ml with distilled water. This low level (1.0M
NaClO4) is added at a the rate of 1 ml low level ISA to each 100 ml of solution. The
background ionic strength will be 1.0X10-2M.
2. Follow the steps given in Direct Measurement of Lead (using an ion meter) to the end
of Step 8. Use plastic lab-ware to avoid adsorption of lead on the beaker walls.
3. Add 50 ml of distilled water, 50 ml of methanol-formaldehyde, and 1 ml of low level ISA
to a 150 ml plastic beaker. Place the beaker on the magnetic stirrer and begin stirring at a
constant rate. Lower the electrode tips into the solution. When the reading has stabilized,
fix the blank value in the meter according to the meter manufacturer's instructions.
4. Place 50 ml of the sample, 50 ml of methanol- formaldehyde solution, and 1 ml of low
level ISA in a 150 ml plastic beaker. Place the beaker on the magnetic stirrer and begin
stirring at a constant rate. Lower the electrode tips into the solution. When the reading has
stabilized, read the sample concentration directly from the meter display.
5. The calibration should be checked every two hours. Assuming no change in ambient
temperature, immerse the electrode tips in the more dilute standard. After the reading has
stabilized, compare it to the original reading recorded in Step 3 above. If the reading
differs by more than ±0.5 units, or the temperature has changed from ambient, recalibrate
the electrode.
9
Page 12

Titration
Titration is a very accurate determination of total lead or sulfate ion concentration. This method
makes use of the electrode as an endpoint detector. The endpoint break is enhanced by the use of
methanol-formaldehyde solution added to samples to reduce the solubility of the product formed
during titration.
Titration of Lead
The method outlined in this section makes use of the lead ion electrode as a highly sensitive
endpoint detector for lead-containing sample. The titrant used is EDTA. The sample concentrations
should be above 1.0X10-3M lead ion. If the samples contain lower lead concentrations, the titration
will not be as accurate and the EDTA titrant must be diluted correspondingly.
EDTA complexes lead as well as other cations. The sample pH can be adjusted to eliminate
unwanted ion complexes. Masking agents may be added in some cases.
1. Prepare a 0.01M EDTA titrant by adding 3.772 grams of reagent-grade Na2EDTA·2H2O to
a 1 liter volumetric flask containing 500 ml of methanol-formaldehyde solution. Swirl the
flask gently to dissolve the solid. Fill the flask to the mark with distilled water, cap, and
upend the flask several times to mix the solution.
2. Fill a 50 ml buret with the EDTA solution. Pipet 50 ml of the sample into a 150 ml beaker
and add 50 ml of methanol-formaldehyde solution. Place the beaker on a magnetic stirrer,
and begin stirring at a constant rate.
3. Position the electrode tips in the solution about halfway between the center of the beaker
and the beaker wall.
4. Begin adding the EDTA in 0.5 ml to 1.0 ml increments, followed by smaller increments
down to about 0.1 ml to 0.2 ml increments as the potential change increases. Record the
mV potential after each addition. Continue the additions several milliliters past the
endpoint until little change is noted in the mV reading even when adding 0.5-1.0
increments.
5. Plot the milliliters of EDTA added against the mV potential on standard coordinate graph
paper. The point of greatest potential change is the endpoint. The lead ion concentration
from the unknown is calculated as follows:
Vt Mt
M
V
+2
= ⎯⎯⎯⎯
Pb
Pb
+2
where:
M
+2
= concentration of lead ion in the sample (moles/liter)
Pb
Vt = volume of EDTA added at endpoint
Mt = EDTA concentration (moles/liter)
V
+2
= volume of unknown sample (50 ml)
Pb
Page 13

Instruction Manual Lead Electrode
Titration of Sulfate
Titration of sulfate ion with lead perchlorate make use of the lead ion electrode as a sensitive
endpoint detector. Sulfate determinations by the gravimetric or turbidimetric methods are more
complicated and more time consuming than titration. Titration offers the same or greater precision
in solutions as dilute as 10-4M or 10 ppm sulfate ion. If present in amounts in excess of the
following,
NO
-
∼ 50 X SO
3
-2
4
Cl
-
∼ 50 X SO
-2
4
HCO
-
∼ 100 X SO
3
-2
at pH 4,
4
the above ions will interfere with the titration. Phosphate and calcium must be absent.
The titrant is Eutech Lead Standard, 0.1M, Code no. EC-SCS-PB1-BT, and should be diluted to the
proper range for the expected concentration of the unknown. The methanol-formaldehyde solution
is used to dilute the unknown 1:1 before performing the titration.
The concentration of lead perchlorate titrant should be about 10 times greater than the expected
sulfate ion concentration of the unknown. Unknowns containing about 10-3M sulfate ion are ideal
for this titration method. If the sulfate samples are more dilute, the lead perchlorate titrant should
be correspondingly more dilute.
1. Prepare 0.01M lead perchlorate titrant by pipeting 100 ml of the 0.1M lead standard into a
one liter volumetric flask. Fill to the mark with distilled water, cap, and upend several
times to thoroughly mix the contents.
2. Into a 150 ml beaker, pipet 50 ml of sample and 50 ml of methanol-formaldehyde solution.
Place the beaker on the magnetic stirrer and begin stirring at a constant rate.
3. Fill a 50 ml burette with the lead perchlorate titrant. Position the electrode tips in the
solution about halfway between the center of the beaker and the beaker wall.
4. Begin adding the titrant in 0.5 ml to 1.0 ml increments, followed by smaller increments
down to about 0.1 ml to 0.2 ml increments as the potential change increases. Record the
mV potential after each addition. Continue the additions several milliliters past the
endpoint until little change is noted in the mV reading even when adding 0.5-1.0 ml
increments.
5. Plot the milliliters of lead perchlorate added against the mV potential on standard
coordinate graph paper. The point of greatest potential change is the endpoint. (See Figure
4.)
11
Page 14

6. The sulfate ion concentration from the unknown is calculated as follows:
Vt Mt
M
V
-2
= ⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯
4
SO
SO
-2
4
where:
M
-2
= concentration of sulfate ion in the unknown (moles/liter)
4
SO
Vt = volume of lead added at endpoint
Mt = lead concentration (moles/liter)
V
-2
= volume of unknown sample (50 ml)
4
SO
Page 15

Instruction Manual Lead Electrode
ELECTRODE CHARACTERISTICS
Reproducibility
Electrode measurements reproducible to ±2% can be obtained if the electrode is calibrated
frequently. Factors such as temperature fluctuations, drift, and noise limit reproducibility.
Reproducibility is independent of concentration within the electrode's operating range.
Interferences
A surface layer of silver metal may be formed by strongly reducing solutions. A layer of silver salt
may be deposited on the membrane if high levels of ions forming very insoluble salts are present in
the sample. Proper performance can be restored by polishing. See the section entitled Electrode
Response
for proper polishing procedure.
The lead ion electrodes do not respond to anions or to most cations. The electrode membrane is
poisoned by solutions containing copper, mercury, and silver. These ions must be absent from the
solution.
If the level of ferric or cadmium ion is less than the level of lead ion, no interference occurs. If the
level of ferric or cadmium ion is more than the level of lead ion, interferences will be present,
resulting in false readings. The ferric ion interference is eliminated by pH adjustment to above pH 4
by the addition of NaOH.
Precipitation and Complexation
Sulfide, phosphate, hydroxide, and other ions precipitate insoluble lead salts. The level of lead ion,
the level of the precipitated ion, and the pH of the sample determine formation of a precipitate.
A wide variety of species, including acetate, ammonia, amino acids, citrate, cyanide, and EDTA,
form complexes with lead ion. The total lead concentration, the concentration of the complexing
species, the solution pH, and the ionic strength all determine the extent of complexation.
Complexation reduces the free lead ion concentration and, since the electrode responds only to free
lead ions, a false reading results.
Temperature Influences
Samples and standards should be within ±1oC of each other, since electrode potentials are
influenced by changes in temperature. A 1oC difference in temperature results in a 4% error at
1.0X10-3M lead ion concentration. Because of the solubility equilibrium on which the electrode
depends, the absolute potential of the reference electrode changes slowly with temperature. The
slope of the electrode, as indicated by the factor "S" in the Nernst equation, also varies with
temperature. Table 3 gives values for the "S" factor in the Nernst equation for the lead ion.
TABLE 3
: Temperature vs. Values for the Electrode Slope
Temp(
o
C) S
0 27.10
10 28.09
20 29.08
25 29.58
13
Page 16

30 30.07
40 31.07
50 32.06
If changes in temperature occur, the electrodes should be re-calibrated. The temperature range for
the Eutech Lead Ion Electrode is 0o-80oC, provided that temperature equilibrium has occurred. If
the temperature varies substantially from room temperature, equilibrium times up to one hour are
recommended.
Electrode Response
Plotting the electrode mV potential against the lead concentration on semi-logarithmic paper results
in a straight line with a slope of about 25 mV per decade. (Refer to Figure 1.)
The time needed to reach 99% of the stable electrode potential reading, the electrode response time,
varies from several seconds in highly concentrated solutions to several minutes near the detection
limit.
A drifting potential reading or a decrease in electrode slope may mean that the electrode membrane
needs polishing.
To polish the membrane:
1. If using polishing paper, cut off a 1-2" piece and place it face up on the lab bench.
2. Put a few drops of distilled or deionized water in the center of the paper.
3. Holding the paper (cotton) steady with one hand, bring the membrane of the electrode
down perpendicular to the paper and, with a slight swirling motion, gently polish the tip of
the electrode against the surface of the polishing paper (cotton) for a few seconds.
4. Rinse the electrode surface with distilled or deionized water and soak the electrode tip in
standard solution for about five minutes before use.
5. If using jeweller's rouge, place a cotton ball on the table top and flatten it using the bottom
of a beaker.
6. Put 1-2 drops of distilled or deionized water in the center of the cotton pad.
7. Add a small amount of jeweller's rouge to the damp cotton.
8. Continue with Steps 3 and 4 above.
Limits of Detection
The upper limit of detection in pure lead perchlorate solutions is 0.1M. In the presence of other
ions, the upper limit of detection is above 1.0x10-2M lead, but two factors influence this upper limit.
Both the possibility of a liquid junction potential developing at the reference electrode and the salt
extraction effect influence this upper limit. Some salts may extract into the electrode membrane at
high salt concentrations, causing deviation from the theoretical response. Either dilute samples
between 0.1M and 1.0x10-2M or calibrate the electrode at 4 or 5 intermediate points.
Page 17

Instruction Manual Lead Electrode
The lower limit of detection is influenced by the slight water solubility of the electrode pellet. Refer
to Figure 1 for a comparison of the theoretical response to the actual response at low levels of lead
ion. Neutral solutions containing free lead ions can be measured down to 1.0X10-6M (0.2 ppm).
Extreme care must be taken with measurements below 1.0X10-5M (2.0 ppm) to avoid adsorption of
lead ions in the sample onto container walls.
pH Effects
Figure 2 shows the electrode response to lead ion in solution at various pH levels. Hydrogen ion
interferes with low lead ion measurements. The minimum pH at which lead ion concentrations can
be measured without interference is given by the shaded area to the left in Figure 2.
At a high pH, free lead ion precipitates with hydroxide ion, thereby reducing the lead ion
concentration. The maximum pH at which the lead concentrations can be measured without
interference from hydroxide is given by the shaded area to the right in Figure 2. Within this shaded
area, lead combines with hydroxide to form Pb(OH)2. Since only free lead concentration can be
measured with the lead ion electrodes, a false reading results.
Electrode Life
A lead electrode will last six months in normal laboratory use. On-line measurements might shorten
operational lifetime to several months. In time, the response time will increase and the calibration
slope will decrease to the point calibration is difficult and electrode replacement is required.
Electrode Storage
The lead electrode may be stored for short periods of time in 1.0x10-2M lead solution. For longer
storage (longer than two weeks), rinse and dry the sensing pellet and cover the membrane tip with
any protective cap shipped with the electrode. The reference portion of the combination electrode
(or the outer chamber of the reference electrode) should be drained of filling solution, if refillable,
and the rubber insert placed over the filling hole.
ELECTRODE THEORY
Electrode Operation
The lead ion electrodes are composed of sulfides of lead and silver bonded into an epoxy or glass
body. When an electrode potential develops across the membrane, the membrane is in contact with
a solution containing lead ions. This electrode potential is measured against a constant reference
potential, using a pH/mV meter or an ion meter. The level of lead ion, corresponding to the
measured potential, is described by the Nernst equation:
E = Eo + S log X
where:
E = measured electrode potential
Eo = reference potential (a constant)
S = electrode slope (∼25 mV/decade)
X = level of lead ions in solution
15
Page 18

The activity, X, represents the effective concentration of free lead ion in the solution. Both bound,
Cb, and free, Cf, lead ions are included in the total lead ion concentration, Ct. The lead ion
electrode will only respond to free lead ions, the concentration of which is:
Cf = Ct - Cb
The activity is related to the free lead ion concentration, Cf, by the activity coefficient, γ, by:
X = γ Cf
Activity coefficients vary, depending on total ionic strength, I, defined as:
I = ½ Σ CxZ
2
x
where:
Cx = concentration of ion X
Zx = charge of ion X
Σ = sum of all of the types of ions in the solution
In the case of high and constant ionic strength relative to the sensed ion concentration, the activity
coefficient, γ , is constant and the activity, X, is directly proportional to the concentration. The lead
ion activity coefficients depend, to some extent, on the anions present. Pure lead nitrate and lead
perchlorate solutions do not display the same activity coefficient, even though both solutions have
the same total ionic strength.
To adjust the background ionic strength to a high and constant value, ionic strength adjuster (ISA)
is added to samples and standards. The recommended ISA solution for the lead electrodes is sodium
perchlorate, NaClO4. Solutions other than this may be used as ionic strength adjusters as long as
ions that they contain do not interfere with the electrode's response to lead ions.
The reference electrode must also be considered. When two solutions of different composition are
brought into contact with one another, liquid junction potentials arise. Millivolt potentials occur
from the inter-diffusion of ions in the two solutions. Electrode charge will be carried unequally
across the solution boundary resulting in a potential difference between the two solutions, since
ions diffuse at different rates. When making measurements, it is important to remember that this
potential be the same when the reference is in the standardizing solution as well as in the sample
solution or the change in liquid junction potential will appear as an error in the measured electrode
potential.
The composition of the liquid junction filling solution in the reference electrode is most important.
The speed with which the positive and negative ions in the filling solution diffuse into the sample
should be equitransferent. No junction potential can result if the rate at which positive and negative
charge carried into the sample is equal.
Strongly acidic (pH = 0-2) and strongly basic (pH = 12-14) solutions are particularly troublesome
to measure. The high mobility of hydrogen and hydroxide ions in samples make it impossible to
mask their effect on the junction potential with any concentration of an equitransferent salt. One
must either calibrate the electrodes in the same pH range as the sample or use a known increment
method for ion measurement.
Page 19

Instruction Manual Lead Electrode
TROUBLESHOOTING GUIDE
The goal of troubleshooting is the isolation of a problem through checking each of the system
components in turn: the meter, the glass-ware, the electrodes, the standards and reagents, the
sample, and the technique.
Meter
The meter may be checked by following the check-out procedure in the instrument instruction
manual.
Glass-ware/Plastic-ware
Clean glass-ware is essential for good measurement. Be sure to wash the glass-ware/plastic-ware
well with a mild detergent and rinse very well with distilled or deionized water. Clean glass-ware
will drain without leaving water droplets behind.
Electrodes
The electrodes may be checked by using the procedure found in the sections entitled Electrode
Slope Check.
1. Be sure to use distilled or deionized water when following the procedures given in
Electrode Slope Check.
2. If the electrode fails to respond as expected, see the sections Measuring Hints and
Electrode Response. Repeat the slope check.
3. If the electrodes still fail to respond as expected, substitute another lead ion electrode that
is known to be in good working order for the questionable electrode. If the problem
persists and you are using an electrode pair, try the same routine with a working reference
electrode.
4. If the problem persists, the reagent may be of poor quality, interferences in the sample may
be present or the technique may be faulty. (See Standards and Reagents, Sample, and
Technique sections below.)
5. If another electrode is not available for test purposes, or if the electrode in use is suspect,
review the instruction manual and be sure to:
- Clean and rinse the electrodes thoroughly.
- Prepare the electrodes properly.
- Use the proper filling solution.
- Adjust the pH and the ionic strength of the solution by the use of the proper ISA.
- Measure correctly and accurately.
- Review TROUBLESHOOTING HINTS.
Sample
Look for possible interferences, complexing agents, or substances which could affect the response
or physically damage the sensing electrode (or the reference electrode) if the electrodes work
perfectly in the standard, but not in the sample. Try to determine the composition of the samples
prior to testing to eliminate a problem before it starts. (See sections on Measuring Hints, Sample
Requirements
, and Interferences.)
17
Page 20

Technique
Be sure that the electrode's limit of detection has not been exceeded. Be sure that the analysis
method is clearly understood and is compatible with the sample. Refer to the instruction manual
again. Reread sections on
GENERAL PREPARATION and ELECTRODE CHARACTERISTICS.
If trouble still persists, call Eutech Instruments Pte Ltd. at (65) 6778-6876 ask for the Customer
Services Department.
Page 21

Instruction Manual Lead Electrode
TROUBLESHOOTING HINTS
Symptom Possible Causes Next Step
Out of Range defective meter check meter with shorting strap
Reading (see meter instruction manual)
defective electrode check electrode operation
electrodes not unplug electrodes and reset
plugged in properly
reference electrode be sure reference electrode
not filled is filled
air bubble on membrane remove bubble by re-dipping electrode
electrodes not put electrodes in solution
in solution
Noisy or defective meter check meter with shorting strap
Unstable Readings
(readings air bubble on membrane remove bubble by re-dipping electrode
continuously
or rapidly changing) electrode exposed soak electrode in lead standard
to interferences
defective electrode replace electrode
ISA not used use recommended ISA
meter or stirrer ground meter or stirrer
not grounded
Drift (reading samples and standards allow solutions to come to room
slowly at different temperatures temperature before measurement
changing in one
direction) complexing agents check section entitled
in sample Precipitation and Complexation
incorrect reference use recommended
filling solution filling solution
membrane dirty polish membrane; use
or oxidized methanol-formal dehyde solution
19
Page 22

Low Slope or standards contaminated prepare fresh standards
No Slope or incorrectly made
standard used as ISA use ISA
ISA not used use recommended ISA
membrane dirty polish membrane; use
or oxidized methanol-formaldehyde solution
air bubble on remove bubble by
membrane re-dipping probe
"Incorrect Answer" incorrect scaling plot millivolts on the linear axis. On
(but calibration of semi-log paper the log axis, be sure concentration
curve is good) numbers within each decade are
increasing with increasing
concentration
incorrect sign be sure to note sign
of millivolt reading correctly
incorrect standards prepare fresh standards
wrong units used apply correct conversion factor:
10-3M = 207 ppm Pb+2
= 96 ppm SO
-2
4
complexing agents check section entitled
in sample Precipitation and Complexation;
use titration method
Page 23

Instruction Manual Lead Electrode
SPECIFICATIONS
Concentration Range: 10-1M to 10-6M Pb+2
(20,700 to 0.2 ppm Pb+2)
pH Range: 3 to 8
Temperature Range: 0o - 80oC
Resistance: < 1 Mohm
Reproducibility: +/- 2%
Samples: Aqueous solutions only; no organic solvents
Size: 110 mm length; 12 mm diameter; 1 m cable length
Storage: Store in lead solution
ORDERING INFORMATION
CODE NO. DESCRIPTION
EC-PB-03 Lead Ion Electrode, epoxy body combination,
EC-SCS-PB1-BT Lead Standard, 0.1M Pb(ClO4)2
EC-SCS-PB2-BT Lead Standard, 1,000 ppm Pb(ClO4)2
EC-ISA-PB1-BT Ionic Strength Adjuster (ISA), 5M NaClO
4
EC-MIS-PP Polishing Paper for the Lead Ion Electrodes
21
 Loading...
Loading...