Page 1

Instruction Manual
gyM
sy...
PC 510
Bench pH/Conductivity Meter
68X090816
Technol o
adeEa
Rev. 3 12/03
Page 2

Preface
Thank you for choosing the PC 510 pH and Conductivity bench meter series.
This manual serves to explain the use of the PC 510 bench meter. The manual functions as a step-by-
step operational guide to help you familiarise with the meter’s features and as a handy reference
guide.
This instruction manual is written to cover as many anticipated applications and uses of the PC 510
bench meter as possible. If there are doubts in the use of the meter, please do not hesitate to contact
the nearest Authorised Distributors.
Eutech Instruments/ Oakton Instruments cannot accept any responsibility for damage or malfunction
to the meter caused by improper use of the instrument.
The information presented in this manual is subject to change without notice as improvements are
made, and does not represent a commitment on the part of Eutech Instruments Pte Ltd/ Oakton
Instruments.
Note: Eutech Instruments Pte Ltd/ Oakton Instruments reserves the right to make
improvements in design, construction, and appearance of our products without notice.
Copyright © 2001 All rights reserved.
Eutech Instruments Pte Ltd
Oakton Instruments
Rev. 3 12/03
Page 3
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1
INTRODUCTION 1
2 METER INFORMATION 1
2.1 Meter parts 1
2.2 Customised LCD 1
2.3 Slide-out card 1
2.4 Rear instrument panel 1
2.5 AC/DC adapter 2
2.6 Electrodes 2
2.7 Electrode holder 2
3 KEYPAD FUNCTIONS 2
3.1 Keypad 2
3.2 Display 4
4 PREPARATION 5
4.1 Connecting the Sensor Electrode 5
4.1.1 To connect the pH electrode: 5
4.1.2 To connect the conductivity/temperature probe: 5
4.2 Connecting the A.C. Adapter 5
5 CALIBRATION 6
5.1 Important information on meter calibration 6
5.2 Preparing the meter for calibration 6
5.3 pH calibration 7
5.3.1 Preparing for pH calibration 7
5.3.2 Before starting 7
5.3.3 To calibrate pH 7
5.4 Conductivity/TDS calibration 9
5.4.1 Preparing for conductivity/TDS calibration 9
5.5 TDS Calibration 11
5.5.1 Calibrating for TDS directly 11
5.6 Calibration with Conductivity Standard and TDS factor 11
5.6 Calibration with Conductivity Standard and TDS factor 12
5.7 Temperature Calibration 13
6 MEASUREMENT 14
6.1 Taking pH Measurements 14
6.1.1 Automatic Temperature Compensation 14
6.1.2 Manual Temperature Compensation (pH) 14
6.1.3 Taking pH Measurements 15
6.2 Taking Conductivity or TDS Measurement 15
6.2.1 Automatic Temperature Compensation 15
6.2.2 Manual Temperature Compensation 16
6.2.3 Setting a manual temperature compensation value 17
6.2.4 Taking Measurements (Conductivity or TDS) 17
6.2.5 Using Auto and Manual Ranging Function (for conductivity & TDS) 18
7 HOLD FUNCTION 20
8 ADVANCED SETUP FUNCTIONS 20
8.1 Advanced SETUP mode Overview 22
8.2 P1.0: Viewing previous pH calibration data 25
8.3 P2.0: Viewing pH electrode data 26
8.4 P3.0: pH Measurement configuration 27
8.4.1 P3.1: READY Indicator and auto endpoint function 28
8.4.2 P3.2: Selecting number of pH calibration points 29
8.4.3 P3.3 Selecting USA or NIST buffer 29
8.4.4 P3.4 Selecting °C or °F 30
8.5 P4.0: Resetting to factory default settings (pH) 31
8.6 P5.0: Viewing previous conductivity calibration data 32
8.7 P6.0: Viewing conductivity probe data 33
8.8 P7.0: Conductivity or TDS measurement configuration 34
8.8.1 P7.1: READY indicator and auto endpoint function 34
8.8.2 P7.2: Selecting °C or °F 35
8.8.3 P7.3: Selecting Automatic or Manual Temperature Compensation 35
8.8.4 P7.4: Setting the TDS factor 36
8.9 P8.0: Temperature 37
8.9.1 P8.1: Selecting the temperature coefficient 37
8.9.2 P8.2: Adjusting the normalisation temperature 38
8.9.3 P9.0: Resetting to factory default settings (conductivity) 38
Page 4

9 PROBE CARE AND MAINTENANCE 39
9.1 pH Electrode care 39
9.2 Conductivity electrode 40
10 TROUBLE SHOOTING GUIDE 41
11 ERROR MESSAGES 42
12 SPECIFICATIONS 43
13 ACCESSORIES 44
14 ADDENDUM 2: CALCULATING TDS CONVERSION FACTORS 48
15 ADDENDUM 3: STANDARD pH BUFFERS 48
16 ADDENDUM 4: CALCULATING TEMPERATURE COEFFICIENTS 49
17 ADDENDUM 5: METER FACTORY DEFAULT SETTINGS 50
18 WARRANTY 51
19 RETURN OF ITEMS 51
Page 5

Instruction Manual PC 510
1 INTRODUCTION
Thank you for selecting the PC 510 pH and Conductivity bench meter. This step-by-step instruction
manual gives you a detailed description on the use and operation of features on the meter. This PC
510 pH and Conductivity bench meter is designed to be user-friendly while providing unprecedented
levels of accuracy, repeatability and reliability.
The PC 510 is an advanced microprocessor-based (ASIC - Application Specific Integrated Circuit)
ideal for routine measurement that best meets discerning user’s individual needs. This multi-parameter
meter reads pH, mV, Conductivity, Total Dissolved Solids (TDS) and temperature (°C or °F). It has
splash-proof keypad, simultaneous pH/mV/Conductivity/TDS and temperature display on a large
angled custom LCD. This instruction manual is illustrated with useful hints and diagrams that show
which specific key-presses to access for each function.
2 METER INFORMATION
The PC 510 meter is packaged in a corrugated box that is made of environment-friendly materials and
can be re-cycled.
2.1 Meter parts
The instrument is designed to give an aesthetic look as well as ergonomic functionality. A large
custom dual LCD is provided at an angle for optimum viewing. A splash-proof keypad with audible
tactile response gives you a good feel of the instrument. A slide-out instruction card offers a handy
reference. Listed below are the major components of the meter.
2.2 Customised LCD
The PC 510 bench meter is characterised by large dual custom LCD (Liquid Crystal Display). The
display has also mode annunciators for pH, temperature, mV, conductivity and TDS readings. The
secondary (lower) display shows the temperature readings simultaneously with the primary (upper)
display of measured mode. Special annunciators such as graphical symbols, error messages,
measurement units and modes of operation are arranged around the primary and secondary displays
to give a comprehensive display. The integration of graphics and error messages into the LCD
provides you a higher level of user-friendliness and easy readability.
2.3 Slide-out card
A plastic slide-out card is provided at the bottom of the PC 510 bench meter. The function of this card
is to provide a quick guide to the functions of the individual keys as well as to provide a useful
troubleshooting reference.
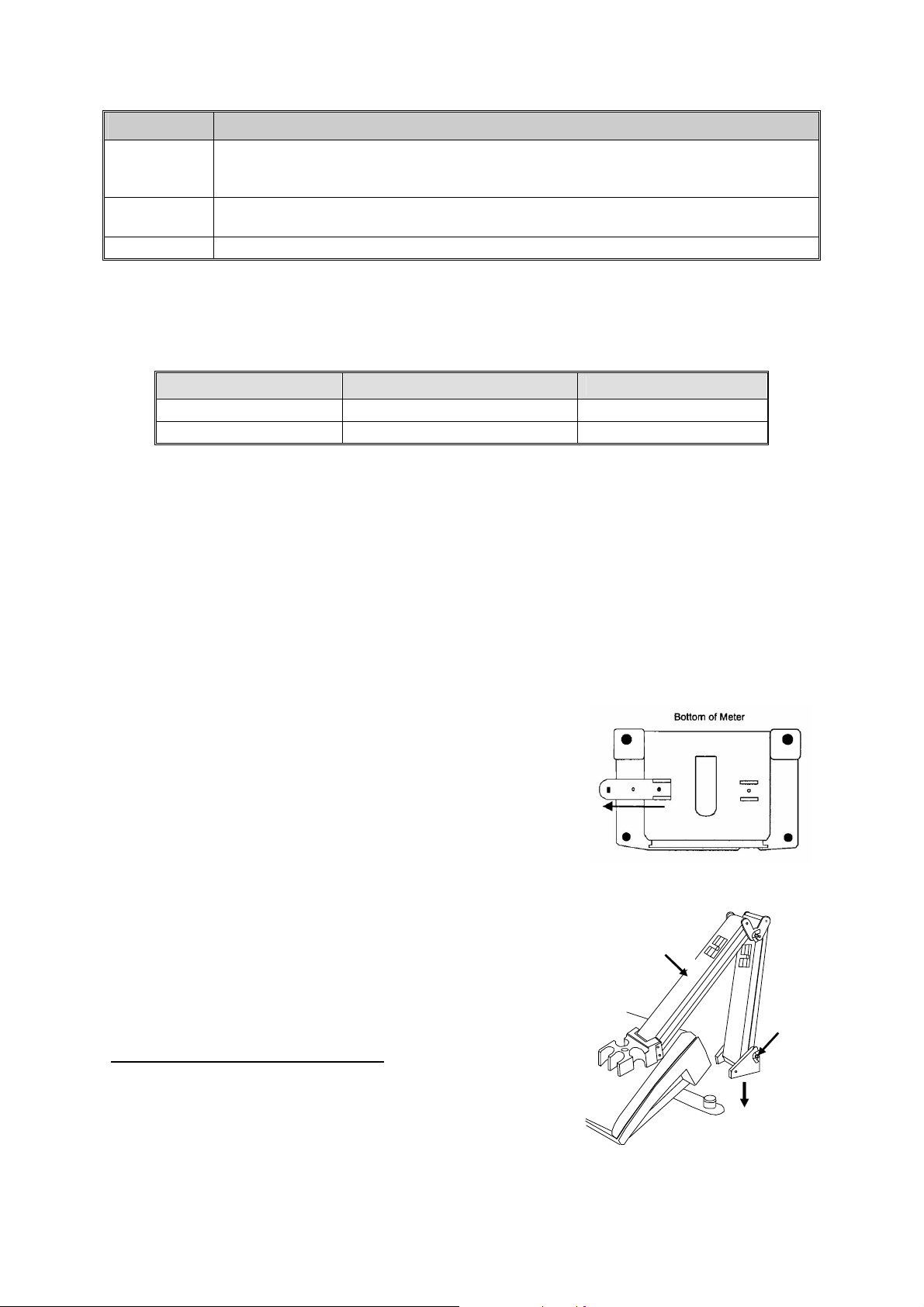
2.4 Rear instrument panel
The PC 510 bench meter provides three connectors at the rear of the meters. These connectors are
labeled CON/TEMP, pH and DC.
CON/TEMP pH
Figure 1 : View of meter rear panel
1
DC
Page 6
Instruction Manual PC 510
Connector Function
For connecting 6-pins conductivity/TDS sensor with built-in temperature sensor to the
CON/TEMP
meter or optional temperature probe for use with pH electrode (when applicable).
Always make sure that the connector is clean and dry.
pH
For connecting pH sensor with a BNC connector to the meter. Always make sure that
the connector is clean and dry.
DC For connection to the AC power source to the power jack (DC).
2.5 AC/DC adapter
The AC/DC adapter converts the power mains voltage 120/220 VAC to low DC voltage for the PC 510
bench meter operation. Two basic models of adapters are available depending upon power supply
specification of each country.
Description Order Code Voltage
AC Adapter 120 V EC-120-ADA / 35615-07 110-120 V, 50-60 Hz
AC Adapter 220 V EC-220-ADA / 35615-08 220-240 V, 50-60 Hz
2.6 Electrodes
Your meter includes two probes:
• pH electrode with BNC connector
• conductivity probe with built-in temperature sensor with a notched 6-pin connector
The temperature sensor built into the conductivity probe will also compensate for pH readings as long
as both probes are in your solution at the same time.
If you want to use a “3-in-1” pH probe with a built-in temperature sensor, or if you want to use a
separate temperature probe, you will need to disconnect the conductivity probe to allow for connection
of the separate temperature sensor.
2.7 Electrode holder
The integral electrode holder serves as a handy holder for mounting
the pH and conductivity/temperature probes during measurement or
when idle.
The bench meter’s base plate has a side metal bar to which you
can attach an integral swivel electrode holder. You can mount the
electrode holder on either right or left side of the meter.
To position the electrode arm:
Use a Philips screwdriver to remove the screw holding the
electrode holder. Slide the side metal bar until the second screw
holder.
slot lines up with the original screw hole. Use the screw removed
earlier to secure the electrode holder into position. Note the side
3 KEYPAD FUNCTIONS
metal bar is reversible. If desired, remove screw holding electrode
holder base and slide out of brackets. Slide base into brackets on
opposite side and tighten screws. See Figure 2.
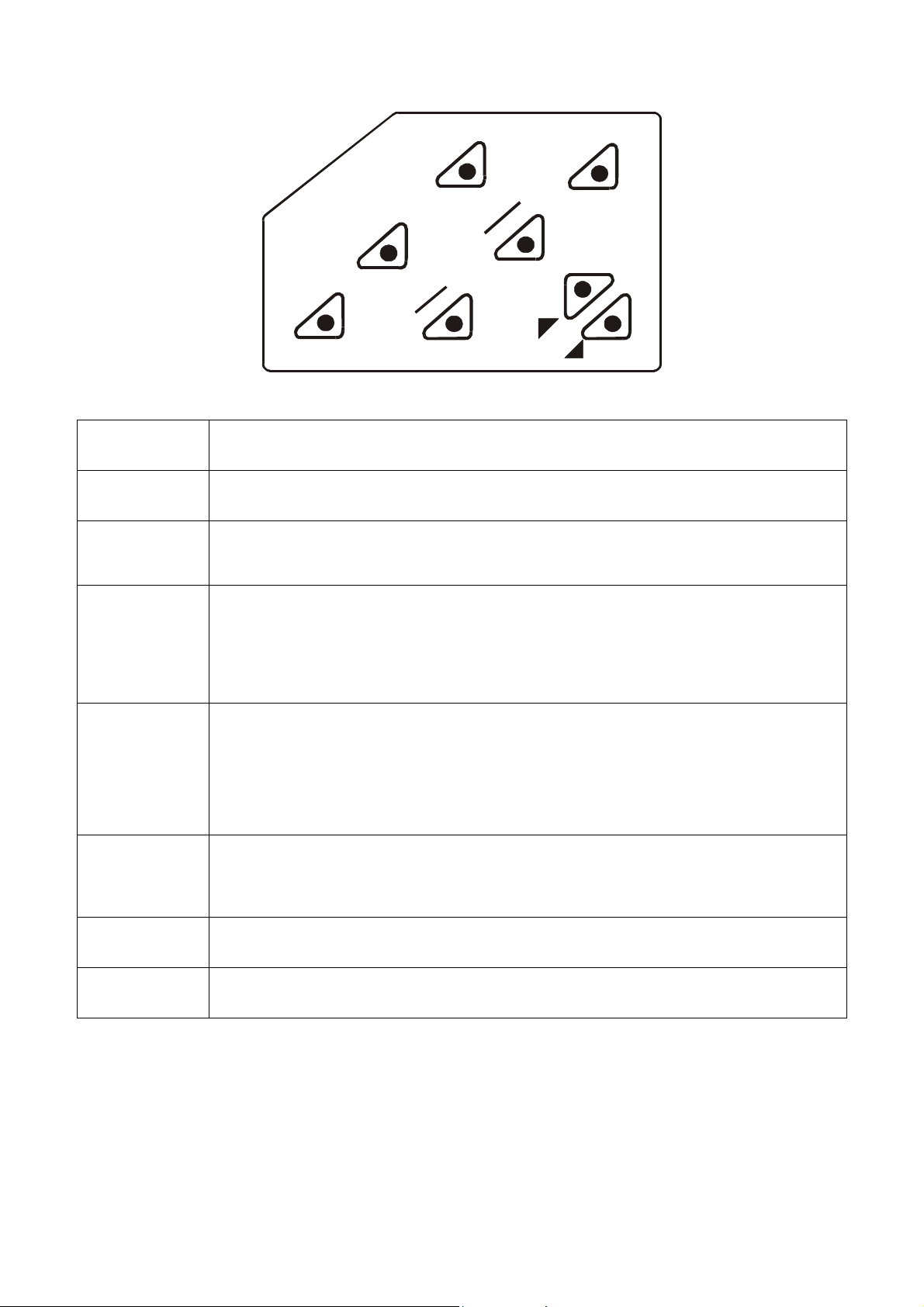
3.1 Keypad
To install electrode arm to the meter:
The PC 510 is equipped with large tactile response keypad for
To mount the electrode arm into the metal rod on the side bar,
ease of use. All keys have primary function with some keys having
align the slot with the metal rod and base of electrode arm. Push
secondary functions.
it downwards until it fully sits into position. Avoid using excessive
force when fixing or removing. The electrode arm is ready for use.
NOTE: Move the base of electrode holder if you wish to swing the
electrode holder about. To prevent the meter form toppling over
causing accidental spills, DO NOT swing the body of the
electrode holder.
Figure 2: To position electrode arm
Body of Electrode
Holder
Base of
Electrode
Holder
Side Metal Bar
Figure 3: Installing the
electrode arm
2
Page 7
Instruction Manual PC 510
ON/OFF
SET
MODE
D
L
O
H
R
E
E
T
G
E
D
O
M
L
T
E
S
A
C
A
E
M
Figure 4: Keypad
N
N
E
A
R
S
F
F
O
/
N
O
Powers the meter on or off. When meter is switched on, it starts in the mode the meter
was last in when powered off.
Enters advanced setup mode. SETUP mode lets you customise meter preferences and
defaults, and view calibration and probe data.
Measurement: Press MODE to toggle between pH, mV, conductivity and TDS.
Calibration: In calibration mode, press MODE to access temperature calibration.
HOLD
CAL/MEAS
ENTER/RANGE
Freezes the measured reading. To activate, press HOLD while in measurement mode. To
release, press HOLD again.
Note: When auto endpoint feature is switched on, meter automatically holds reading after
5 seconds of stability. The HOLD indicator appears on the display. Press HOLD to release
auto endpoint feature.
Toggles between Calibration and Measurement mode. Example: If you are in pH
measurement mode, press CAL/MEAS to enter pH calibration mode.
Note: Temperature calibration is available from pH, TDS or Conductivity calibration mode.
In Setup mode: Press CAL/MEAS to return to main menu from sub menus. Press
CAL/MEAS again to return to measurement mode from main menu.
ENTER: Press to confirm values in Calibration mode and to confirm selections in Setup
mode.
RANGE: Press to switch to manual ranging in Conductivity or TDS mode.
Press in Setup mode to scroll up through subgroups. Also lets you increase the values
in the conductivity, TDS and temperature calibration modes.
Press in Setup mode to scroll down through subgroups. Also lets you decrease the
values in the conductivity, TDS and temperature calibration modes.
3
Page 8
Instruction Manual PC 510
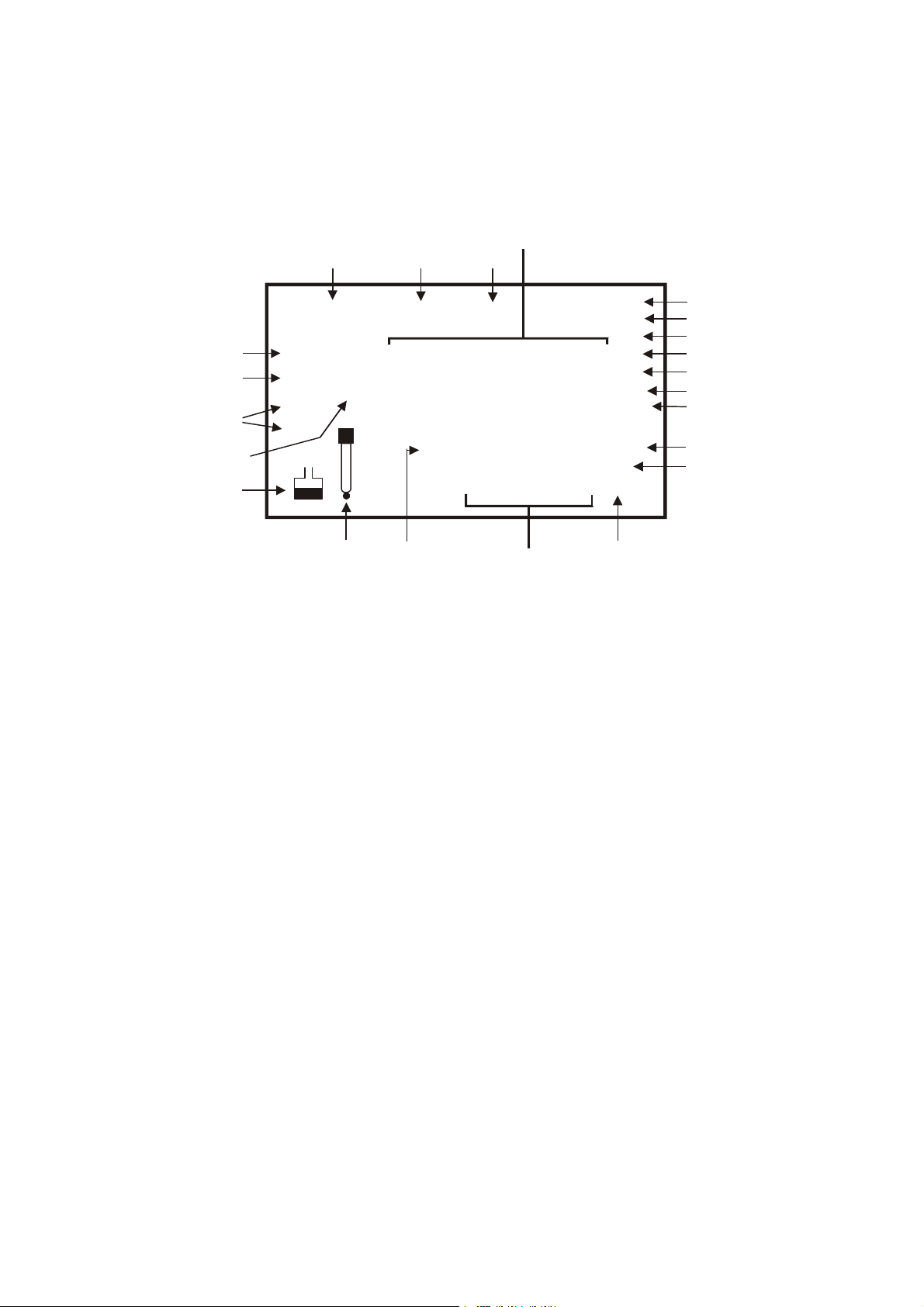
3.2 Display
The PC 510 features a large dual display that shows the measured parameter in the primary display,
plus temperature in °C or °F in the secondary display. It also features mode annunciators that describe
the meter’s functions.
Primary Display
123
SETUP MEAS CAL
20
19
18
17
16
1. SETUP mode indicator
2. MEASurement mode indicator
3. CALibration indicator
READY
HOLD
ON
OFF
K =
-8.8.8.8
ERR
-1.8.8.8
15
Figure 5: Full LCD Screen
8. micro-Siemens indicator
9. parts per thousand indicator
10. parts per million indicator
Secondary Display
mV
pH
mS
µ
S
ppt
ppm
°C °F
pH
%
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
ATC
1314
14. ERRor indicator
15. probe indicator
16. calibration solution indicator
4. mV indicator
5. % indicator
6. pH measurement indicator
7. milli-Siemens indicator
11. temperature indicator
12. pH indicator
13. Automatic Temperature
Compensation (ATC) indicator
17. cell constant indicator
18. ON/OFF indicator
19. HOLD indicator
20. READY indicator
4
Page 9
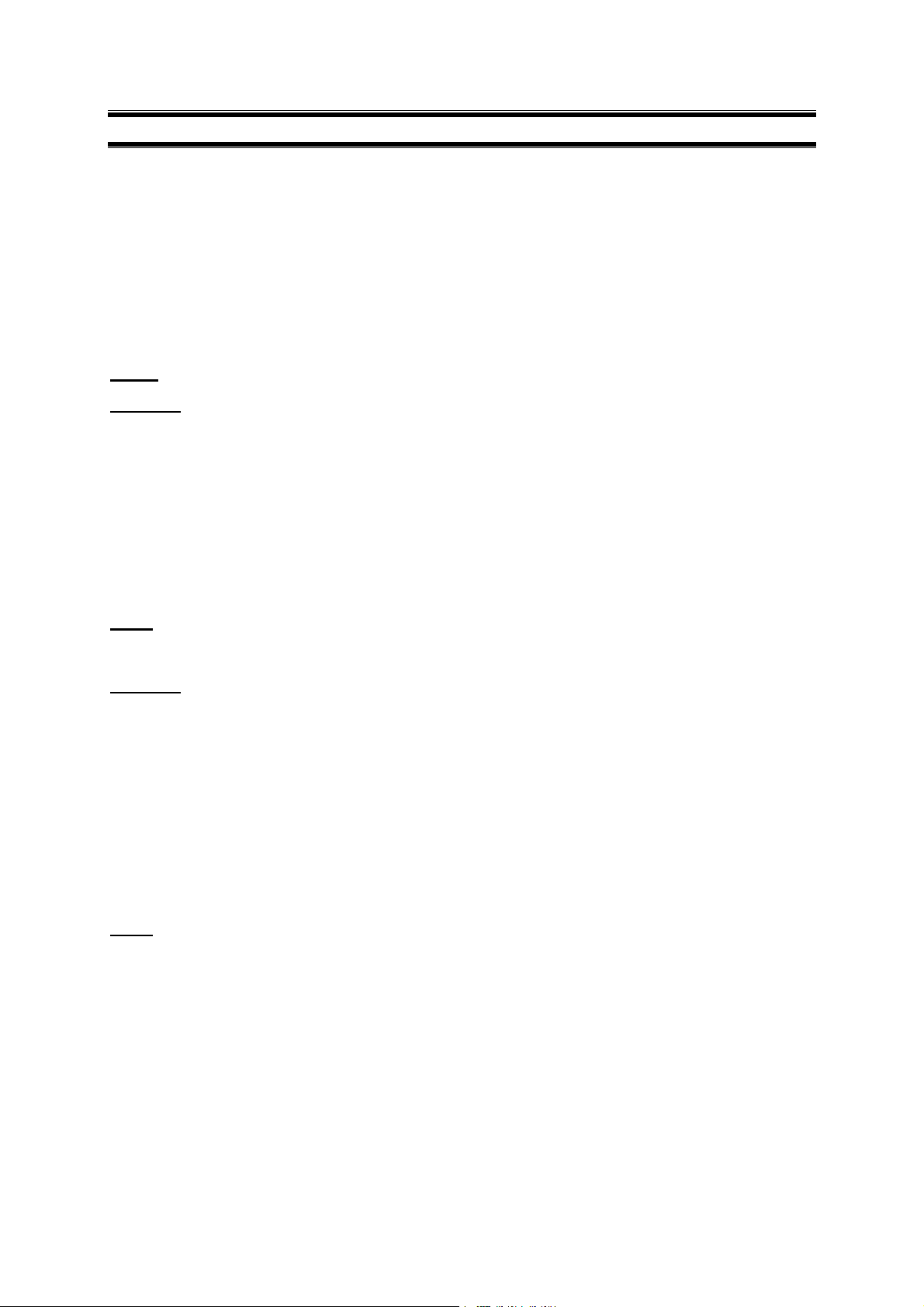
Instruction Manual PC 510
4 PREPARATION
4.1 Connecting the Sensor Electrode
4.1.1 To connect the pH electrode:
1. Slide the BNC connector of the probe over the BNC connector socket on the meter. Make sure the
slots of the connector are in line with the posts of the socket. Rotate and push the connector
clockwise until it locks.
2. To remove electrode, push and rotate the connector anti-clockwise. While holding onto the metal
part of connector, pull it away from the meter
NOTE:
CAUTION
Keep connector dry and clean. Do not touch connector with soiled hands.
: Do not pull the probe cord or the probe wires might disconnect.
4.1.2 To connect the conductivity/temperature probe:
1. Line up the notch and 6-pins on the probe connector with the holes in the connector located on the
top of the meter. Push down and screw the metal sleeve to lock the probe connector into place.
See Figure 1 on page 1 for the meter rear panel view.
2. To remove probe, unscrew the metal sleeve and slide up the probe connector. While holding onto
the metal sleeve, pull probe away from the meter.
NOTE
: Follow the same directions to connect an optional separate temperature element.
Keep connector dry and clean. Do not touch connector with soiled hand s.
CAUTION
: Do not pull on the probe cord or the probe wires might disconnect.
4.2 Connecting the A.C. Adapter
1. Before plugging in the A.C. adapter, switch off the meter and the power source of the A.C.
adapter. This is a safety precaution that should be adhered to safeguard your meter.
2. The A.C. adapter should have the following settings:
Output voltage: 9 V D.C.
Current: 500 mA
NOTE
: Ensure that the input mains voltage (110/220/240 V) matches your adapter requirements.
3. Insert the D.C. jack into the socket at rear panel of the meter as shown in Figure 1on page 1.
4. Switch on the power to the adapter, followed by the meter.
5
Page 10
Instruction Manual PC 510
5 CALIBRATION
5.1 Important information on meter calibration
When you calibrate your meter, old calibration points are replaced on a “point by point” basis in pH,
and on a “range by range” basis in conductivity or TDS.
For example:
• pH
: if you previously calibrated your meter at pH 4.01, 7.00 and 10.01, and you recalibrate at pH
7.00, the meter retains the old calibration data at pH 4.01 and pH 10.01.
• Conductivity
: if you previously calibrated your meter at 1413 µS in the 0 to 1999 µS range and
you recalibrate at 1500 µS (which is also in the 0 to 1999µS range), the meter will replace the old
calibration data (1413 µS) in that range. The meter will retain all calibration data in other ranges.
• TDS
: If you previously calibrated your conduc tivity meter at 300 ppm in the 0 to 999 ppm range
and you re-calibrate at 500 ppm (which is also in the 0 to 999 ppm), the meter will replace the old
calibration data (300 ppm) in that range. The meter will retain all calibration data in other ranges.
To view current calibration points:
• pH
• Conductivity & TDS
: Program P1.0 in the SETUP section 8.2 page 38.
: Program P5.0 in the SETUP section, page 32.
To completely recalibrate your meter, or when you use a replacement probe, it is best to clear old
calibration data by resetting the meter.
To reset the meter to its factory defaults:
• pH
• Conductivity & TDS
: Program P4.0 in the SETUP section, page 32.
: Program P9.0 in the SETUP section, page 38.
: Resetting the meter will set meter to factory defaults. Conductivity and pH must be reset
NOTE
separately.
For directions on how to calibrate your meter:
• See section 5.3 on page 7 for pH calibration
• See section 5.4 on pages 9 for conductivity calibration
• See section 5.5 on page 11 for TDS calibration
5.2 Preparing the meter for calibration
Before starting calibration, make sure you are in the correct measurement mode. When you switch on
the meter, the meter starts up in the measurement mode you shut it off in. For example, if you shut the
meter off in pH measurement mode, the meter will be in the pH measurement mode when you switch
the meter on.
Do not re-use calibration solutions after calibration. Contaminants in the solution can affect the
calibration, and eventually the accuracy of the measurements. See section 13 on “Accessories” on
page 44 for information on our high quality calibration solutions.
6
Page 11
Instruction Manual PC 510
5.3 pH calibration
NOTE: We recommend that you perform at least a 2-point calibration using standard buffers that
bracket (one above and one below) the expected sample range.
5.3.1 Preparing for pH calibration
This meter is capable of up to 5-point pH calibration to ensure accuracy across the entire pH range of
the meter. Select from the following buffer options:
• USA: pH 1.68, 4.01, 7.00, 10.01 and 12.45
• NIST: pH 1.68, 4.01, 6.86, 9.18 and 12.45
The meter automatically recognises and calibrates to these standard buffer values, which makes pH
calibration faster and easier.
NOTE:
Selection of USA or NIST buffer standards must be done prior to calibration. Refer to Section
8.4 on P3.3 on page 29.
5.3.2 Before starting
Be sure to remove the protective electrode storage bottle or rubber cap
of the probe before calibration or measurement. If the electrode has
been stored dry, hydrate the probe in tap water for 10 minutes before
calibrating or taking readings to saturate the pH electrode surface and
minimise drift.
Wash your probe in de-ionised water after use, and store in electrode
storage solution. If storage solution is not available, use pH 4.01 or
7.00 buffer for short term storage. DO NOT store electrode in distilled
or de-ionised water.
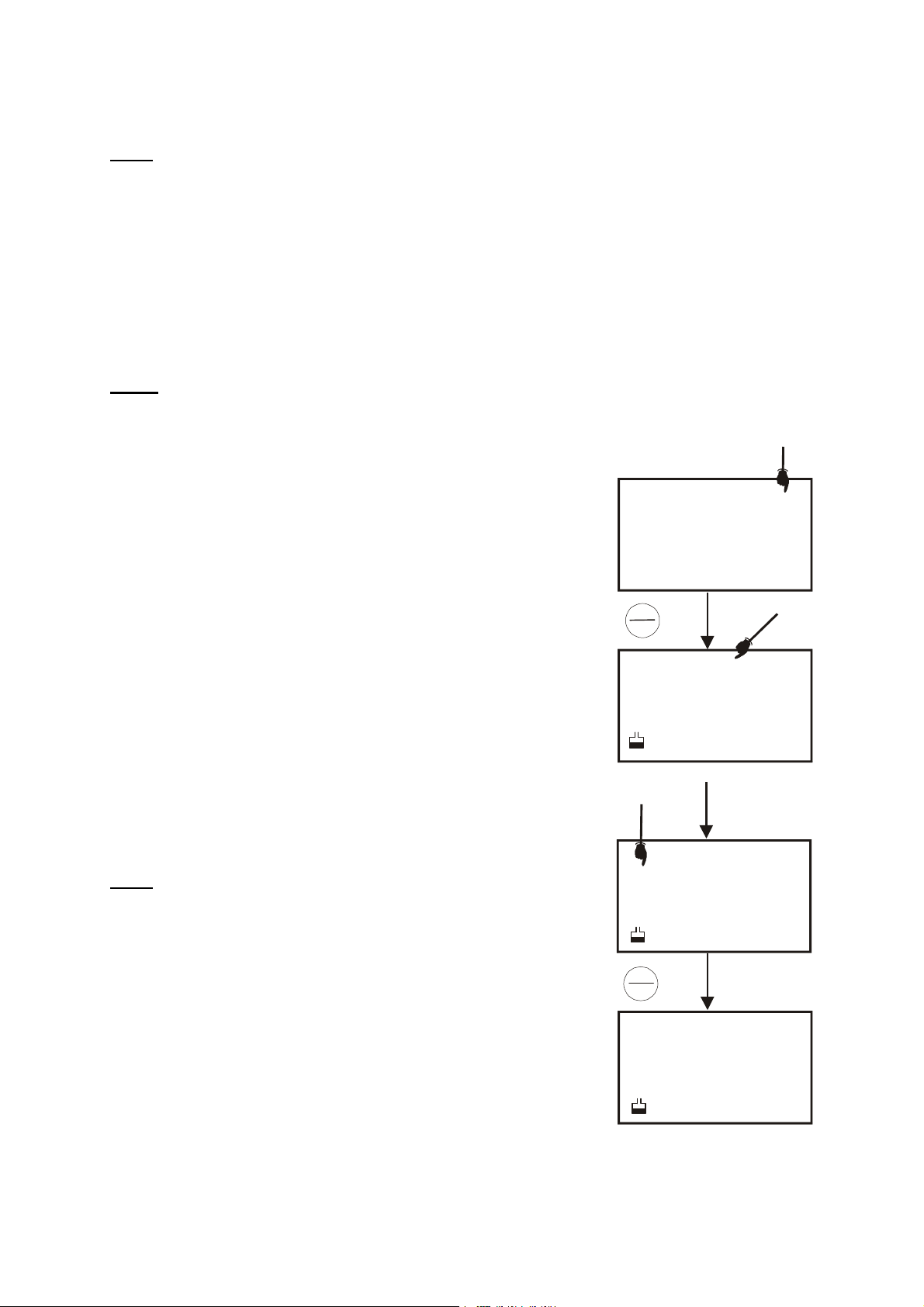
5.3.3 To calibrate pH
1. If necessary, press the MODE key to select pH mode. The pH
indicator appears in the upper right hand corner of the display.
2. Rinse the probe thoroughly with de-ionised water or rinse solution.
Do not wipe the probe as this causes a build-up of electrostatic
charge on the glass surface.
3. Dip the probe into the standard calibration buffer. The end of the
probe must be completely immersed into the sample. Stir the probe
gently to create a homogeneous sample.
NOTE
: The temperature element is in the conductivity cell. For
temperature compensated readings, dip the conductivity cell or ATC
probe into the calibration buffer as well.
4. Press CAL/MEAS to enter pH c alibration mode. The CAL indicator
will be shown. The primary display will show the measured reading
while the smaller secondary display will indicate the pH standard
buffer solution.
5. Wait for the measured pH value to stabilise. If the READY indicator
has been activated through the Setup, the READY appears when
the reading is stable.
A
C
E
M
READY
T
N
E
N
A
R
READY
MEAS
pH
7.16
°C
22.3
L
S
A
CAL
ATC
pH
7.16
7.00
CAL
pH
pH
7.16
7.00
R
E
E
G
CAL
pH
pH
7.00
6. Press ENTER to confirm calibration. The meter is now calibrated to
the current buffer. The lower display automatically scrolls through
the remaining buffer options.
• If you are performing multi-point calibration, go to step 7.
7
7.00
Figure 6: pH calibration
pH
Page 12
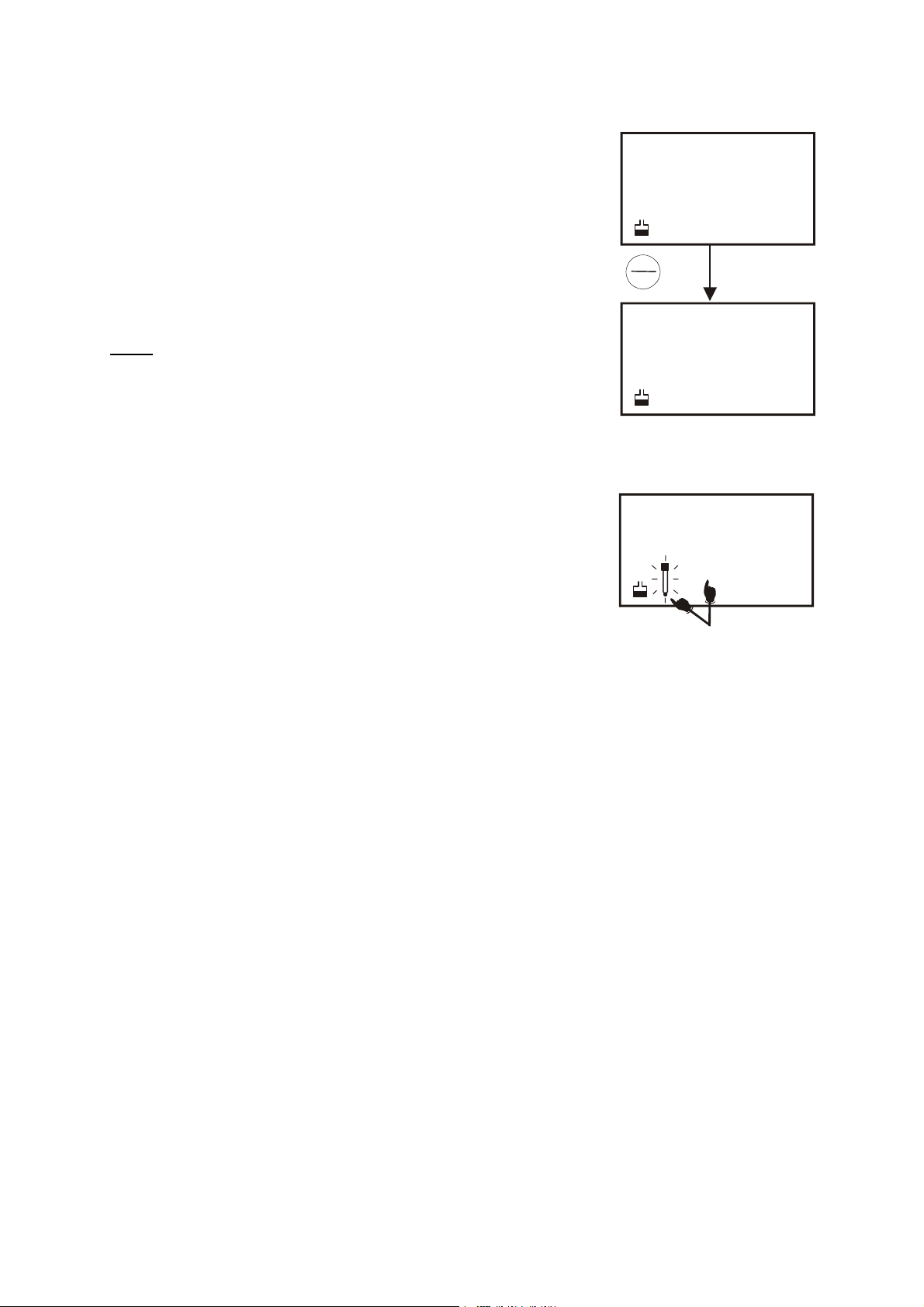
Instruction Manual PC 510
correct buffe
used
• If you are performing one-point calibration, go to step 9.
7. Rinse the electrode with de-ionised water or rinse solution, and
place it in the next pH buffer.
READY
CAL
pH
4.15
8. Follow steps 5 to 7 for additional calibration points.
pH
9. When calibration is complete, press CAL/MEAS to return to pH
measurement mode.
4.01
R
E
T
N
E
E
G
N
A
R
NOTE
: To exit from pH calibration mode without confirming calibration,
DO NOT press ENTER in step 6. Press CAL/MEAS instead.
If the selected buffer value is not within ±1.0 pH from the measured pH
value: the electrode and buffer icon blink and the ERR annunciator
appears in the lower left corner of the display.
To limit the number of pH buffer values available during calibration,
see section 8.4 Setup P3.2 on page 29.
CAL
READY
pH
4.01
4.01
Figure 7: Next point calibration
for pH 4.01
CAL
pH
pH
0.64
ERR
1.68
Figure 8: Err message and
electrode icon will appear if
in
r is
pH
8
Page 13
Instruction Manual PC 510
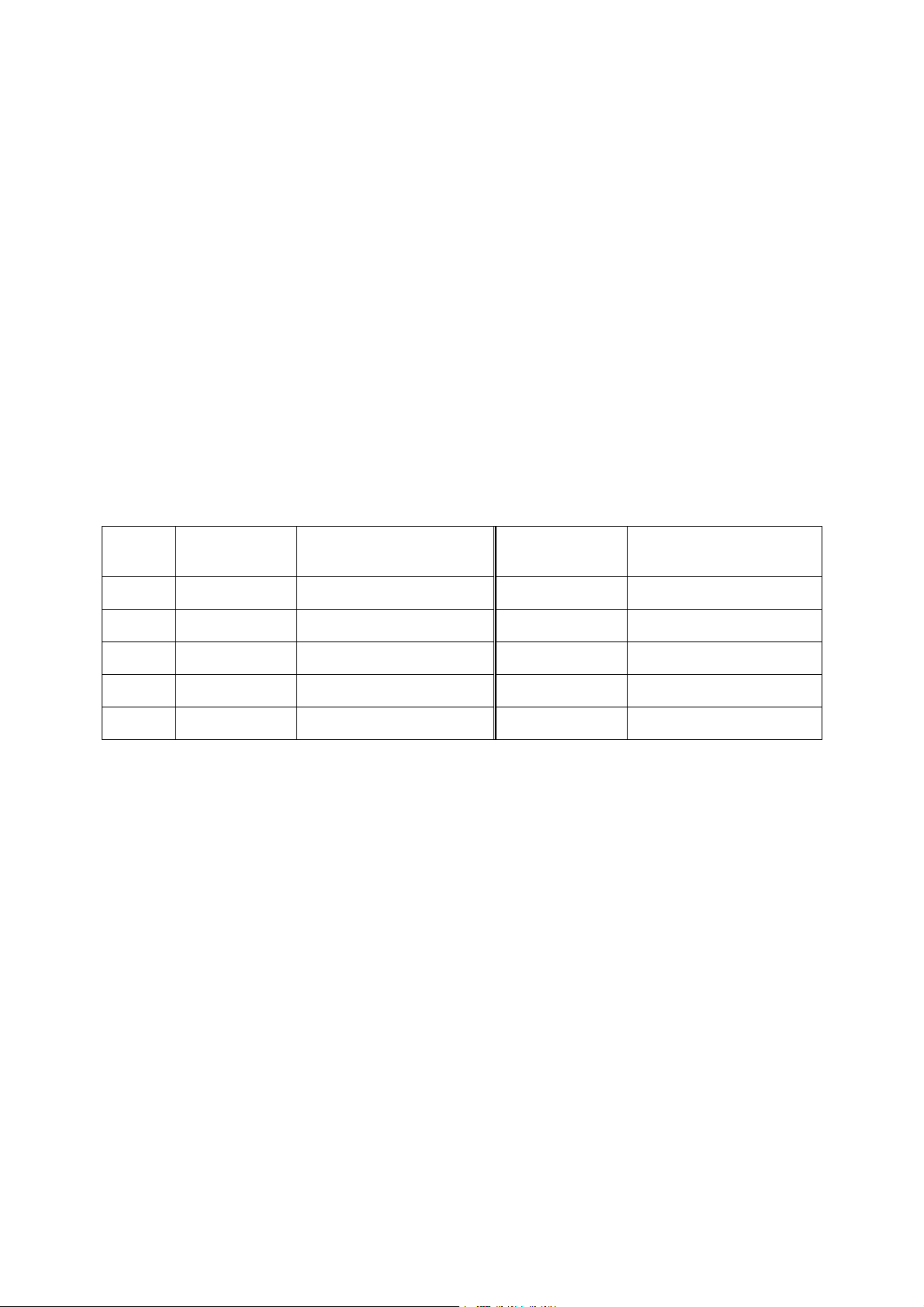
5.4 Conductivity/TDS calibration
The PC 510 has 5 measuring ranges. You can calibrate 1 point each of the measuring ranges (up to 5
points). If you are measuring values in more than 1 range, make sure to calibrate each of the ranges
you are measuring. All new calibration data will over-ride existing stored calibration data for each
measuring range you calibrate.
• If you are measuring in ranges near to or greater than 20 mS (10 ppt), or near to or lower than 100
µS (50 ppm), calibrate the meter at least once a week to get specified ±1% Full Scale accuracy.
• If you are measuring in the mid-ranges and you washed the probe in de-ionised water and stored
it dry, calibrate the meter at least once a month.
• If you take measurements at extreme temperatures, calibrate the meter at least once a week.
5.4.1 Preparing for conductivity/TDS calibration
For best results, select a standard value close to the sample value you are measuring. Alternatively,
use a calibration solution value that is approximately 2/3 the Full-Scale value of the measurement
range you plan to use. For example, in the 0 to 1999 µS conductivity range, a 1413 µS solution is a
good solution for calibration.
See the table below for recommended calibration solution ranges.
Range
Indicator
Conductivity
Range
Recommended Calibration
Solution Range
TDS Range
Recommended Calibration
Solution Range
r 1 0.00 to 19.99 µS 6.00 to 17.00 µS 0.00 to 9.99 ppm 3.00 to 8.50 ppm
r 2 0.0 to 199.9 µS 60.0 to 170.0 µS 10.0 99.9 ppm 30.0 to 85.0 ppm
r 3 0 to 1999 µS 600 to 1700 µS 100 to 999 ppm 300 to 850 ppm
r 4 0.00 to 19.99 mS 6.00 to 17.00 mS 1.00 to 9.99 ppt 3.00 to 8.50 ppt
r 5 0.0 to 199.9 mS 60.0 to 170.0 mS 10.0 to 200 ppt 30.0 to 170.0 ppt
Calibration Solution Ranges
Temperature Coefficient: These meters are factory set to a temperature coefficient of 2.1 % per °C.
For most applications this will provide good results. See Program P8.1 on page 37 to set the
temperature coefficient to different value. See Addendum 2, “Calculating Temperature Coefficients” to
determine the appropriate temperature coefficient for your solution.
Normalisation Temperature: The factory default value for normalisation temperature is 25 °C. If you
need to normalise to a value other than 25 °C, see Program P8.2 on page 38.
Do not reuse calibration solutions after calibration. Contaminants in the solution can affect the
calibration, and eventually the accuracy of the measurements. Use fresh calibration solution each time
you calibrate your meter.
All new calibration data will over-ride existing stored calibration data for each measuring range
calibrated.
9
Page 14
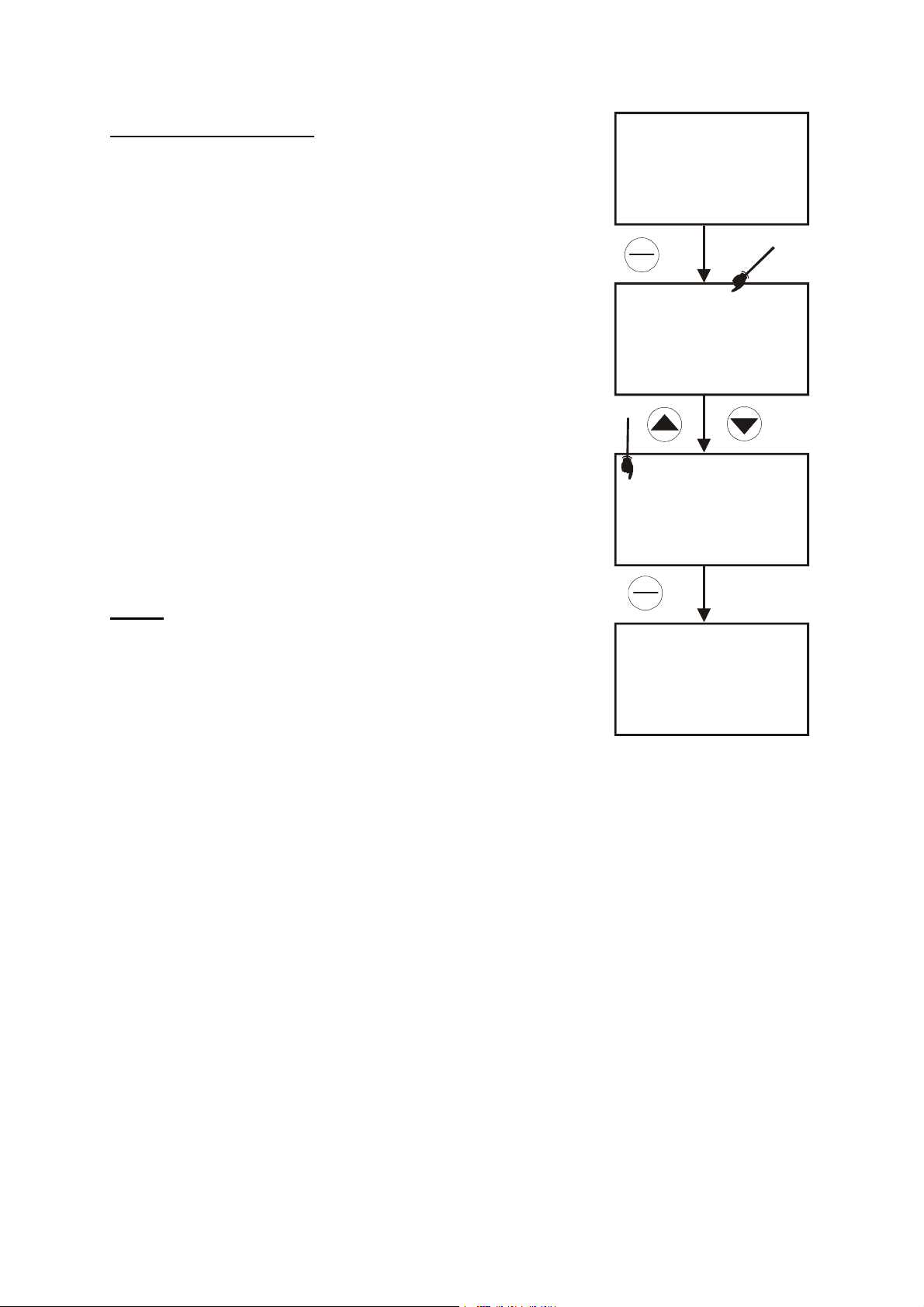
Instruction Manual PC 510
Calibrating for Conductivity:
1. If necessary, press the MODE key to select conductivity mode.
2. Rinse the probe thoroughly with de-ionised water or a rinse
solution, then rinse with a small amount of calibration standard.
3. If necessary, ensure that the probe’s yellow probe guard is
attached. Dip the probe into the calibration standard. Immerse the
probe tip beyond the upper steel band. Stir the probe gently to
create a homogeneous sample.
4. Wait for the measured conductivity value to stabilise. If the READY
indicator has been activated (SETUP program P7.1 – see page
31), the READY annunciator lights when the reading is stable.
5. Press CAL/MEAS to enter conductivity or TDS calibration mode.
The CAL indicator will appear in the upper right corner of the
display.
6. Press the or key to change the value on the primary display
to match the value of the calibration standard.
7. Press ENTER to confirm calibration value. The meter returns to the
MEAS (measurement) mode.
8. Repeat steps 1 to 7 for other measuring ranges.
NOTES
: When entering calibration mode, the meter will display the
factory default value. If the meter was previously calibrated, the display
may “jump” to the factory default / uncalibrated value when switching
from measurement to calibration mode.
To exit from Conductivity calibration mode confirming calibration,
DO NOT press the ENTER key in step 7. Press CAL/MEAS instead.
This will retain the meter’s old calibration data in the measuring range
of the calibration.
C
E
M
READY
E
R
READY
A
L
S
A
R
E
T
N
N
A
E
G
MEAS
1409
22.3
CAL
1409
22.3
CAL
1413
1409
MEAS
1413
22.3
°C
ATC
µ
°C
ATC
µ
°C
ATC
S
S
µ
S
µ
S
You can offset the conductivity reading up to ±40% from default
setting. If your measured value differs by more than ±40% clean or
Figure 9: Conductivity
calibration
replace probe as needed, or use a calibration standard with a higher
value as required.
A wide selection of high-quality calibration standards is available. See page 44 for more information.
10
Page 15
Instruction Manual PC 510
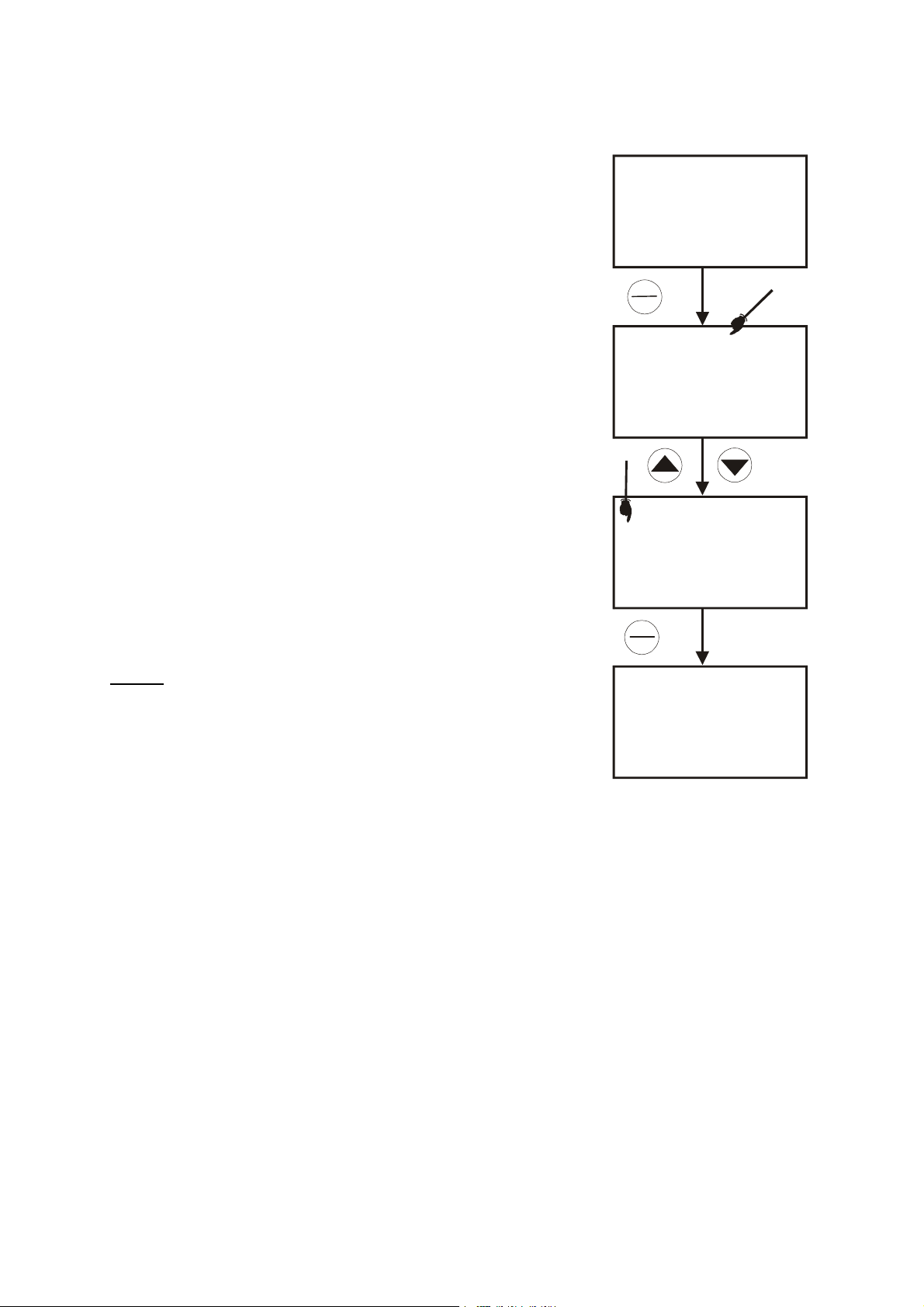
5.5 TDS Calibration
5.5.1 Calibrating for TDS directly
The factory default setting for TDS conversion factor is 0.5. If your
solution has a different TDS factor, you can improve calibration
accuracy by setting the TDS factor prior to calibration. See Program
P7.4 on page 36 for directions.
1. If necessary, press the MODE key to select TDS mode.
2. Rinse the probe thoroughly with de-ionised water or a rinse
solution, then rinse with a small amount of calibration standard.
3. If necessary, ensure that the probe’s yellow probe guard is
attached. Dip the probe into the calibration standard. Immerse the
probe tip beyond the upper steel band. Stir the probe gently to
create a homogeneous sample. Allow time for the reading to
stabilise.
4. Press the CAL/MEAS to enter TDS calibration mode. The CAL
indicator will appear in the upper right corner of the display.
5. Press the or key to change the value on the primary display
to match the value of the calibration standard.
6. Press ENTER to confirm the calibration value. The meter returns
to the MEAS (measurement) mode. See Figure 10.
M
READY
MEAS
265
25.8
L
A
C
S
A
E
CAL
265
25.8
CAL
300
ppm
°C
ATC
ppm
°C
ATC
ppm
265
7. Repeat steps 1 to 6 for other measuring ranges.
NOTES
:
To exit from TDS Calibration mode without confirming calibration, DO
NOT press ENTER key in step 6. Press CAL/MEAS instead. This will
retain the meter’s old calibration data in the measuring range of the
calibration. You can offset the TDS reading up to ±40% from the
default setting. If your measured value differs by more than ±40%,
clean or replace probe as needed, or use a calibration standard with a
higher value as required.
T
N
E
R
E
E
G
N
A
R
READY
MEAS
300
25.8
Figure 10: TDS calibration
ppm
°C
ATC
11
Page 16

Instruction Manual PC 510
5.6 Calibration with Conductivity Standard and TDS factor
The concentration of salts dissolved in solution increases the conductivity of that solution. This
relationship varies from salt to salt and is roughly linear over a given range for a given salt.
The TDS conversion factor is the number used by the meter to convert from conductivity to TDS.
Instead of calibrating for TDS directly (described above), you can calibrate the PC 510 bench meter
by:
1. Calibrating to conductivity standards (as described above) and then
2. Entering the appropriate TDS conversion factor into the meter.
To determine the conductivity to TDS conversion factor for your solution:
• Addendum 1 on page 47 lists some commonly used conversion factors.
• Addendum 2 on page 48 describes how to calculate the TDS conversion factor for other
solutions.
Enter the TDS conversion factor into your meter as described under Section 8.8, in Program P7.4,
Setting the TDS Factor on page 36.
12
Page 17
Instruction Manual PC 510
A
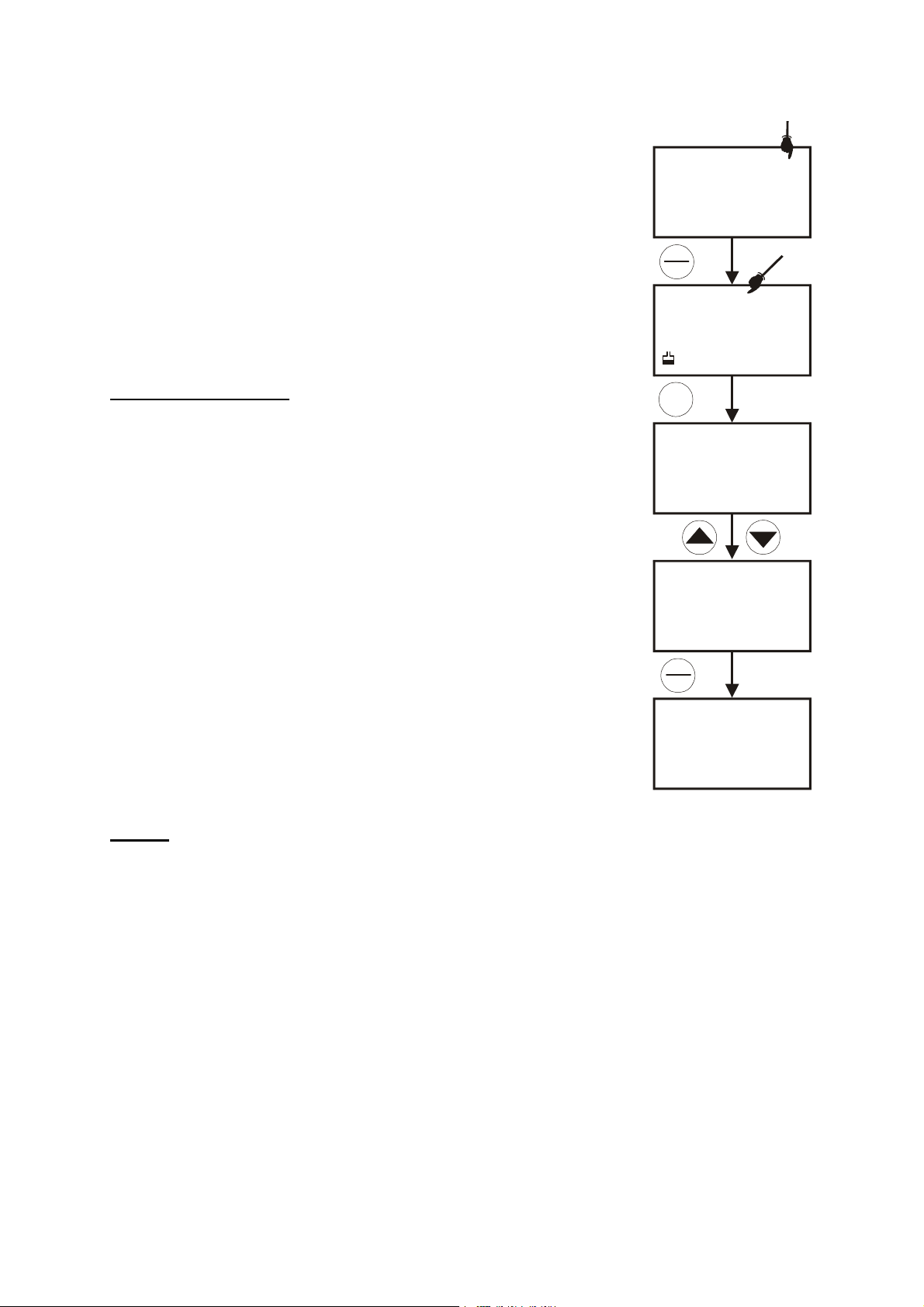
5.7 Temperature Calibration
The conductivity electrode (EC-CONSEN91W / 35608-50) supplied has a
built-in temperature sensor. Alternatively, a separate temperature sensing
element can be used (such as temperature probe EC-WPPHTEM-01W /
35618-05), or a “3-in-1” pH/Temperature combination electrode with ATC
connection.
The conductivity probe is factory calibrated. Temperature calibration is
recommended only if you suspect temperature errors may have occurred
over a long period of time, or if you have a replacement probe.
Temperature calibration is accessible during pH, conductivity or TDS
calibration.
Temperature Calibration
1. Make sure the conductivity electrode, or temperature probe, or “3-in-1”
electrode is attached to the 6-pin connector.
2. Switch the meter on.
3. Press the CAL/MEAS key to enter calibration mode (either from pH or
conductivity mode). The CAL indicator will appear above the primary
display.
4. While in pH (or conductivity or TDS) calibration mode, press the MODE
key to enter temperature calibration mode. The primary display shows
the last set temperature value and the secondary display shows the
temperature reading with zero offset.
5. Dip the ATC probe into a solution of known temperature (i.e. a
temperature bath). Allow time for the temperature probe to stabilise.
MEAS
pH
7.16
22.3
A
C
L
S
A
E
M
CAL
°C
ATC
pH
7.16
7.00
M
O
D
E
pH
CAL
22.3
°C
22.3
CAL
TC
22.0
22.3
R
E
T
N
E
E
G
N
A
R
°C
ATC
READY
MEAS
7.16
22.0
pH
°C
ATC
6. Scroll with the or key to set the correct temperature value (i.e. the
temperature of the temperature bath). You can adjust the reading by 0.1
°C or °F increments.
7. Once you have selected the correct temperature press the ENTER key.
The meter automatically returns to measurement mode.
NOTES:
Figure 12: Temperature calibration
in pH mode
• You can offset the temperature reading up to ±5° from default reading.
• To exit this program without confirming the temperature calibration value, DO NOT press ENTER,
press CAL/MEAS in step 7 instead.
13
Page 18

Instruction Manual PC 510
6 MEASUREMENT
6.1 Taking pH Measurements
6.1.1 Automatic Temperature Compensation
Automatic Temperature Compensation only occurs when a temperature sensing element is plug ged
into the meter.
Temperature sensing element refers to the following probes made specifically for this meter. See
accessories for ordering information
• The conductivity electrode with a built-in temperature
sensor
• Temperature probe; or
• The 3-in-1 pH/Temperature combination electrode.
If there is no temperature sensor plugged into the meter, the default
manual temperature setting is automatically 25 °C. You can manually
MEAS
READY
pH
7.05
°C
24.5
Figure 13: ATC annunciator will
light up when connected to
ATC
set the temperature to match your working conditions using a separate
thermometer.
For automatic temperature compensation (ATC) simply plug the temperature probe into the meter (see
page 5 for directions). The ATC indicator will light up on the LCD. See Figure 13.
: The temperature sensing element must be submersed in the liquid you are measuring.
NOTE
6.1.2 Manual Temperature Compensation (pH)
IMPORTANT: For manual compensation, you must disconnect the
temperature probe (see page 5 for instructions).
1. Switch the meter on. Press MODE key to select pH mode.
2. Press the CAL/MEAS key to enter pH calibration mode. The CAL
indicator will appear above the primary display.
CAL
25.0
°C
25.0
3. While in pH calibration mode, press the MODE key to enter
temperature calibration mode. The primary and secondary displays
show the last set temperature value.
4. Check the temperature of your sample using an accurate
thermometer.
5. Press the or key to set the temperature to the measured
value from step 4.
6. Press ENTER to confirm the selected temperature and to return to
the pH measurement mode.
See Figure 14.
The meter will now compensate pH readings for the manually set
temperature.
NOTES
: To exit this program without confirming the manual
temperature compensation value, DO NOT press ENTER in step 6.
Press CAL/MEAS instead.
14
CAL
30.0
°C
pH
T
N
E
N
A
R
READY
25.0
R
E
E
G
MEAS
7.05
°C
30.0
Figure 14: Manual temperature
compensation
Page 19

Instruction Manual PC 510
6.1.3 Taking pH Measurements
Be sure to remove the electrode storage bottle or protective rubber cap
on the electrode before measurement.
To take readings:
1. Rinse the pH electrode with de-ionised or distilled water before use
MEAS
8.23
21.3
pH
°C
ATC
to remove any impurities adhering to the probe body. If the pH
electrode has dehydrated, soak it for 30 minutes in electrode
storage solution or 2M – 4 M KCL solution (sold separately).
Figure 15: Measurement mode
2. Press ON to switch meter on.
3. Press the MODE key to select pH measurement mode. The MEAS annunciator appears on the
top center of the LCD. The ATC indicator appears in the lower right-hand corner to indicate
Automatic Temperature Compensation.
NOTE
: For pH manual temperature compensation, you must disconnect the conductivity cell from the
6-pin connector. The ATC indicator will disappear form the display. You also need to set a manual
temperature compensation value. See Section 6.2.2: Manual Temperature Compen sation on page 16.
4. Dip the probe into the sample. Since the conductivity cell contains the temperature sensor, make
sure it is also immersed in your solution.
When dipping the probe into the sample, the sensor or the glass bulb of the electrode must be
completely immersed into the sample. Stir the probe gently in the sample to create a homogeneous
sample.
5. Allow time for the reading to stabilise. Note the reading on the display. If the READY indicator is
selected on, it will appear when the reading is stable. See below for more information.
Taking measurements with READY indicator selected on
If the READY indicator has been activated, the READY annunciator lights when the reading is stable *.
Switch the READY indicator on or off in SETUP program P3.1. See page 28 for directions.
* The READY indicator appears and the reading holds until the measured value exceeds the tolerance
(±0.02 pH; +0.8 mV < 400; ±1.2 mV > 400). Then READY annunciator turns off.
Taking measurements with the auto endpoint feature selected on
When a reading is stable for more than 5 seconds, the auto endpoint feature will automatically “HOLD”
the reading. The “HOLD” indicator appears on the left side of the display. Press the HOLD key to
release the reading. Switch the Auto endpoint feature on or off in SETUP program P3.1, see page 28
for instructions.
6.2 Taking Conductivity or TDS Measurement
6.2.1 Automatic Temperature Compensation
For automatic temperature compensation (ATC), simply plug the
conductivity probe into the meter (see page 5 for directions). The ATC
indicator will light on the LCD.
NOTE
: If the ATC indicator does not light, manual temperature
compensation may be selected in the meter’s SETUP mode. See
Program P7.3 on page 35 for directions on selecting Automatic
Temperature Compensation.
Figure 16: ATC annunciator will
MEAS
READY
1402
°C
24.5
light up when connected to
temperature probe
ATC
µ
S
15
Page 20

Instruction Manual PC 510
6.2.2 Manual Temperature Compensation
IMPORTANT: For manual compensation, you must deactivate the
temperature probe.
Selecting Manual Temperature Compensation for conductivity
Selecting between Automatic Temperature Compensation (ATC) and
Manual Temperature Compensation in the SETUP program P7.3 on
page 35. Meter default is ATC on.
From Conductivity or TDS measurement mode
1. Press SETUP key to enter Setup mode.
2. Press the or key to scroll through subgroups until you view
parameter P7.0. See Figure 17.
3. Press ENTER key three times to select parameter 7.3. The upper
display shows “ATC” and the lower display shows “P7.3”.
4. Press ENTER key again. The upper display shows “ATC” and the
lower display shows “YES” or “NO”.
5. Press the or key to select the Automatic Temperature
Compensation feature on (ATC) or off (ATC off). See Figure 14.
6. Press ENTER key to confirm selection and to return to the
subgroup menu. Press the CAL/MEAS key to return to
measurement mode.
SETUP
mS
µ
COF
ppt
ppm
P 7.0
Figure 17: P7.0 configuration
setup for conductivity & TDS
R
E
T
N
E
E
G
N
A
R
SETUP
°C
ATC
T
N
E
N
A
R
SETUP
p 7.3
R
E
E
G
S
Note that the ATC indicator no longer appears on the display.
Proceed to the next section to select a manual temperature
compensation value.
YES
SETUP
Figure 18: Turning ATC
feature ON or OFF
°C
ATC
°C
16
Page 21

Instruction Manual PC 510
6.2.3 Setting a manual temperature compensation value
To use manual temperature compensation, you need to enter the temperature value of your process
into the meter. This is the value at which reading will manually temperature compensate. You can
select any temperature between 0 and 100 °C (32 to 212 °F). Default value is 25 °C (77 °F).
To select a manual temperature compensation value
1. Switch the meter on. Press the MODE key to select conductivity or
TDS measurement mode.
2. If necessary, select ATC off as described in P7.3 on page 35. The
ATC indicator will not appear on the display.
3. Press the CAL/MEAS key to enter conductivity or TDS calibration
mode. The CAL indicator will appear above the primary display.
4. While in conductivity (or TDS) calibration mode, press the MODE
key to enter temperature calibration mode. The primary and
secondary displays show the last set temperature value.
5. Check the temperature of your sample using an accurate
thermometer.
6. Press the or key to offset the temperature to the measured
value from step 5.
7. Press ENTER to confirm the selected temperature and to return to
the conductivity measurement mode. See Figure 18.
The meter will now compensate conductivity or TDS readings for
manually set temperature.
NOTES
: To exit this program without confirming the manual
temperature compensation value, DO NOT press ENTER in step 7.
Press CAL/MEAS instead.
Setting the manual temperature compensation value for conductivity
will change the manual temperature compensation value for pH to the
same value, and vice versa.
CAL
25.0
25.0
CAL
°C
30.0
°C
E
T
N
E
N
A
R
READY
G
25.0
R
E
MEAS
256
°C
30.0
Figure 19: Manual Temperature
Compensation
6.2.4 Taking Measurements (Conductivity or TDS)
To take readings:
1. Rinse the probe with de-ionised or distilled water before use to
remove any impurities adhering to the probe body. Shake or air
dry. To avoid contamination or dilution of your sample, rinse probe
with a small volume of your sample liquid.
2. Press ON to switch meter on.
3. Press the MODE key to select conductivity or TDS measurement
mode. The MEAS annunciator appears on the top center of the
MEAS
READY
µ
S
345
°C
21.3
Figure 20: During measurement
ATC
LCD. The ATC indicator appears in the lower right hand corner to
indicate Automatic Temperature Compensation.
NOTE
: For conductivity manual temperature compensation, you must de-activate the temperature
sensor built into the conductivity probe and set a manual temperature compensation. See page 14 for
more information. The ATC indicator will disappear from the display.
17
Page 22

Instruction Manual PC 510
4. If necessary, ensure that the probe’s yellow probe guard is attached. Dip the probe into the
sample. When dipping the probe into the sample, take care to ensure that the liquid level is above
its upper steel band. Stir the probe gently in the sample to create a homogeneous sample.
5. Allow time for the reading to stabilise. Note the reading on the display. If the READY indicator is
selected on, it will appear when the reading is stable. See Program P7.1 on page 34 for more
information.
6. Press the MODE key to toggle between conductivity, TDS and pH readings.
NOTE
: You can use the Conductivity Manual Ranging function to manually select a specific range in
which your readings will appear. See page 19 for directions.
Taking measurements with READY indicator on
If the READY indicator has been activated, the READY annunciator lights when the reading is stable *.
Switch the READY indicator on or off in SETUP program P7.1. See page 34 for directions.
Taking measurements with the auto endpoint feature selected on
When a reading is stable for more than 5 seconds, the auto endpoint feature will automatically “HOLD”
the reading. The “HOLD” indicator appears on the left side of the display. Press the HOLD key to
release the reading. Switch the Auto endpoint features on or off in SETUP program P7.1, see page 34
for instructions.
6.2.5 Using Auto and Manual Ranging Function (for conductivity
& TDS)
MEAS
µ
S
199.9
Auto-ranging
Your meter automatically selects the range in which your readings
appear. For example:
°C
ATC
1. Dip the conductivity probe into a standard solution, say, 12.88 mS.
2. It will automatically select the most appropriate range, r 4, which is
0.00 to 19.99 mS.
3. The secondary display on the LCD will momentarily display r 4
before it switches to measured temperature value.
4. The primary display will show the actual conductivity value. See
Figure 20.
MEAS
1999
MEAS
19.99
MEAS
12.88
25.5
°C
ATC
mS
°C
ATC
mS
°C
ATC
µ
S
18
Figure 21: Auto-ranging feature
Page 23

Instruction Manual PC 510
Manual-ranging
The manual ranging function lets you select the specific range you want to work in. Refer to page 9 for
the table of range.
1. To select the desired measuring range manually, press the RANGE
key while in measurement mode. The meter will lock on to the
appropriate range and the “MEAS” indicator blinks.
2. Press RANGE key again (if needed) until desired range is selected.
3. To re-select the Auto-ranging function, repeatedly press the RANGE
key until the “MEAS” indicator appears without blinking.
MEAS
READY
R
E
T
N
E
G
N
A
R
E
1413
22.3
MEAS
µ
°C
ATC
µ
1999
°C
ATC
MEAS
READY
µ
1413
°C
22.3
Figure 22: Manual ranging
ATC
S
S
S
NOTES
:
The meter will not let you manually select a range in which the reading will be over-range.
The meter resets to the Auto-ranging function once it is turned off. You will have to reset the manual
ranging function each time you turn the meter off.
19
Page 24

Instruction Manual PC 510
µ
7 HOLD FUNCTION
This feature lets you freeze the display for a delayed observation. HOLD can be used any time in
MEAS mode.
1. To hold a measurement, press the HOLD key while in measurement mode. “HOLD” will appear on
the display.
2. To release the held value, press the HOLD key again. Continue to take measurements
MEAS
READY
HOLD
678
20.7
Figure 23: HOLD function
S
°C
ATC
:
NOTE
• If the meter is shut off manually, the HOLD value will be lost.
• Your meter has an auto endpoint feature. When this feature is switched on, and when a
reading is stable for more than 5 seconds, the display will automatically “HOLD” the
reading. The “HOLD” indicator appears. Press the HOLD key to release the reading. To
switch on or off the auto endpoint feature, see SETUP Program P3.1 on page 28 for pH
and SETUP Program P7.1 on page 34 for conductivity/TDS.
8 ADVANCED SETUP FUNCTIONS
The advanced setup mode lets you customise your meter’s preferences and defaults. The PC 510
bench meter features different sub-groups that organise setup parameters.
The sub-groups are:
For pH For Conductivity & TDS
P1.0 View calibration data (CAL) P5.0 View calibration data (CAL)
P2.0 View electrode data (ELE) P6.0 View ele ctro d e data (ELE)
P3.0 Unit Configuration (COF) P7.0 Unit Configuration (COF)
P4.0 Reset to factory default
settings (rSt)
P8.0 Temperature (tPr)
P9.0 Reset to factory default settings
(rSt)
20
Page 25

Instruction Manual PC 510
SETUP
SETUP
SETUP
SETUP
CAL
P 1.0
ELE
P 2.0
COF
P 3.0
SETUP
pH
SETUP
CAL
mS
µ
ppt
ppm
S
P 5.0
pH
SETUP
ELE
mS
µ
ppt
ppm
S
P 6.0
pH
SETUP
COF
mS
µ
ppt
ppm
S
P 7.0
SETUP MEAS
pH
P 4.0
SETUP
P 8.0
SETUP MEAS
P 9.0
Figure 24: Overall view of SETUP programs for pH (on left) & conductivity/TDS (on right)
mS
µ
ppt
ppm
°C °F
mS
µ
ppt
ppm
S
S
21
Page 26

Instruction Manual PC 510
8.1 Advanced SETUP mode Overview
1. In either pH or Conductivity measurement mode, press the SETUP key to enter Setup mode.
2. Press the or key to scroll through sub-groups.
3. Press ENTER key to enter a particular parameter.
See Addendum 4 on page 49 for a table of meter factory default settings.
SETUP in pH measurement mode
SETUP
SETUP
SETUP
CAL
P 1.0
ELE
P 2.0
COF
P 3.0
P1.0: View previous calibration data
pH
pH
pH
P1.1 First calibration point (pH 1.68)
P1.2 Second calibration point (pH 4.01)
P1.3 Third calibration point (pH 7.00 or 6.86)
P1.4 Fourth calibration point (pH 10.01 or 9.18)
P1.5 Fifth calibration point (pH 12.45)
P2.0: View electrode data
P2.1: pH electrode offset
P2.2: pH electrode slope
P3.0: Unit Configuration
P3.1 READY indicator and auto endpoint function – select on or off
P3.2 Number of pH calibration points: 2, 3, 4 or 5
P3.3 Select USA or NIST buffer set
P3.4 Select °C or °F
SETUP MEAS
P 4.0
pH
P4.0: Reset to factory defaults
P4.0 Reset meter to factory defaults
22
Page 27

Instruction Manual PC 510
SETUP in Conductivity Measurement Mode
SETUP
CAL
mS
µ
ppt
ppm
P5.0: View previous calibration data
P5.1 First range calibration point (0.00 – 19.99 µS)
S
P5.2 Second range calibration point (0.0 – 199.9 µS)
P5.3 Third range calibration (0 – 1999 µS)
P 5.0
P5.4 Fourth range calibration point (0.00 – 19.99 mS)
P5.5 Fifth range calibration point (0.0 – 199.9 mS)
SETUP
ELE
P 6.0
mS
µ
ppt
ppm
P6.0: View electrode data
P6.1 Effective cell constant for first range (0.00 – 19.99 µS)
S
P6.2 Effective cell constant for second range (0.0 – 199.9 µS)
P6.3 Effective cell constant for third range (0 – 1999 µS)
P6.4 Effective cell constant for fourth range (0 – 19.99 mS)
P6.5 Effective cell constant for fifth range (0.0 – 199.9 mS)
SETUP
COF
mS
µ
ppt
ppm
P7.0: Unit configuration
S
P7.1 READY indicator and auto endpoint function – select on or off
P7.2 Select °C or °F
P7.3 Select Automatic or Manual Temperature Compensation
P 7.0
P7.4 Setting TDS conversion factor
SETUP
P 8.0
mS
µ
ppt
ppm
°C °F
S
P8.0: Temperature
P8.1 Adjusting temperature coefficient
P8.2 Adjusting normalisation temperature
SETUP MEAS
P 9.0
mS
µ
ppt
ppm
P9.0: Reset to factory defaults
S
P9.1 Reset meter to factory defaults
23
Page 28

Instruction Manual PC 510
SETUP in TDS Measurement Mode
SETUP
CAL
P 5.0
mS
µ
ppt
ppm
P5.0: View previous calibration data
P5.1 First range calibration point (0.00 – 9.99 ppm)
S
P5.2 Second range calibration point (0.0 – 99.9 ppm)
P5.3 Third range calibration point (0 – 999 ppm)
P5.4 Fourth range calibration point (0.00 – 9.99 ppt)
P5.5 Fifth range calibration point (0.0 – 200 ppt)
SETUP
ELE
P 6.0
mS
µ
ppt
ppm
P6.0: View electrode data
P6.1 Effective cell constant for first range (0.00 – 9.99 ppm)
S
P6.2 Effective cell constant for second range (0.0 – 99.9 ppm)
P6.3 Effective cell constant for third range (0 – 999 ppm)
P6.4 Effective cell constant for fourth range (0.00 – 9.99 ppt)
P6.5 Effective cell constant for fifth range (0.0 – 200 ppt)
SETUP
COF
mS
µ
ppt
ppm
P7.0: Unit configuration
S
P7.1 READY indicator and auto endpoint function – select on or off
P7.2 Select °C or °F
P7.3 Select Automatic or Manual Temperature Compensation
P 7.0
P7.4 Setting TDS conversion factor.
SETUP
P 8.0
mS
µ
ppt
ppm
°C °F
S
P8.0: Temperature
P8.1 Adjusting temperature coefficient
P8.2 Adjusting normalisation temperature
SETUP MEAS
P 9.0
mS
µ
ppt
ppm
S
P9.0: Reset to factory defaults
P9.0 Reset meter to factory defaults.
24
Page 29

Instruction Manual PC 510
8.2 P1.0: Viewing previous pH calibration data
This mode lets you recall previous pH calib ration data, which helps you
know when to re-calibrate your meter. This is a “view-only” mode.
From measurement mode:
1. Press the MODE key to select pH measurement mode if necessary.
2. Press the SETUP key to enter Setup mode.
3. Press the or key to scroll through sub-groups until you view
parameter P1.0.
4. Press the ENTER key repeatedly to view previous calibration data.
See Figure 24.
USA
NIST
• P1.1 = pH 1.68 1.68
• P1.2 = pH 4.01 4.01
• P1.3 = pH 7.00 6.86
• P1.4 = pH 10.01 9.18
• P1.5 = pH 12.45 12.45
5. When you have scrolled through all calibration data, you will
automatically return to the sub-group menu. Press CAL/MEAS key
to return to measurement mode.
SETUP
E
T
N
E
G
N
A
R
SETUP
E
T
N
E
G
N
A
R
SETUP
E
T
N
E
G
N
A
R
SETUP
R
E
R
E
R
E
cal
p 1.0
---
p 1.1
CAL
7.00
p 1.3
CAL
pH
pH
pH
NOTES
: If there is no previous calibration data at a particular point, the
primary display will show “----“.
10.01
p 1.4
Figure 25: P1.0 - View
calibration data for pH
25
Page 30

Instruction Manual PC 510
8.3 P2.0: Viewing pH electrode data
Program 2 has two “view-only” options that let you check the electrode
parameters for diagnostic purposes. It lets you view:
• P2.1 = Electrode offset
SETUP
pH
ele
p 2.0
• P2.2 = Electrode slope
R
E
T
N
E
E
G
N
A
From pH measurement mode
R
1. Press the MODE key to select pH measurement mode.
2. Press the SETUP key to enter Setup mode.
3. Press the or key to scroll through sub-groups until you view
parameter P2.0.
4. Press the ENTER key to select parameter 2.1.
5. The display shows the electrode offset value. It is the mV offset at
pH 7.00. If you have not calibrated at any buffer, the primary display
shows 0.00 mV.
6. Press the ENTER key to proceed to P2.2.
7. The display shows electrode slope in percentage. Slope displayed
is the average slope based on the pH calibrations. Default setting is
100.0.
8. At any point, you can press the CAL/MEAS key to return to
measurement mode.
SETUP
mV
5.3
p2.1
R
E
T
N
E
E
G
N
A
R
SETUP
%
98.7
p 2.2
Figure 26: Viewing electrode's
offset and slope status from
pH measurement mode
26
Page 31

Instruction Manual PC 510
8.4 P3.0: pH Measurement configuration
This sub-group program allows customis ing the meter to your specific needs. You can program the
meter to:
1. Select READY indicator ON or OFF.
2. Select the number of pH calibration points.
3. Select between USA and NIST buffers.
4. Select between °C and °F units for temperature readings.
Figure 26 on the right shows the setup sequence for this program subgroup.
SETUP
E
T
N
E
G
N
A
R
SETUP
READY
ON
cof
p 3.0
R
E
pH
p 3.1
R
E
T
N
E
E
G
N
A
R
SETUP
READY
ON
3 p
p 3.2
R
E
T
N
E
E
G
N
A
R
SETUP
usa
p 3.3
R
E
T
N
E
E
G
N
A
R
SETUP
p 3.4
Figure 27: P3.0 - Unit
configuration program
C
°C
27
Page 32

Instruction Manual PC 510
8.4.1 P3.1: READY Indicator and auto endpoint function
This program lets you select:
• “READY indicator on
• “READY indicator off
• Auto endpoint function on
” to indicate when the reading is stable
” for faster meter response.
. Select auto endpoint on to “hold” the
reading when it is stable for more than 5 seconds. The display
automatically freezes, and the HOLD indicator appears on the left
side of the display. Press the HOLD key to release the display and
access other functions.
From measurement mode
1. Press the MODE key to select pH measurement mode.
2. Press SETUP key to enter Setup mode.
3. Press the or key to scroll through sub-groups until you view
parameter P3.0.
4. Press the ENTER key to select parameter 3.1.
5. Press the or key to select the configuration you require.
• OFF switches the READY indicator off.
• ON switches the READY indicator on.
• ON and HOLD together switches the auto endpoint feature on.
SETUP
R
E
T
N
E
E
G
N
A
R
SETUP
READY
ON
SETUP
READY
OFF
SETUP
READY
HOLD
ON
cof
p 3.0
p 3.1
p 3.1
6. Press the ENTER key to confirm selection and to proceed to step 4
p 3.1
of P 3.2. Press the CAL/MEAS key to return to measurement mode.
Figure 28: P3.1 - Selecting
READY function
NOTES
: Meter default is set for READY indicator on and auto endpoint function off.
You can also change the READY indicator and auto endpoint function in Program P7.1 (available from
conductivity or TDS mode). Any changes you make to the READY indicator/auto endpoint function in
pH mode will also change in conductivity mode.
28
Page 33

Instruction Manual PC 510
8.4.2 P3.2: Selecting number of pH calibration points
SETUP
Program P3.2 lets you select the number of calibration points that
appear in pH calibration mode: 2, 3, 4 or 5. The meter will automatically
exit calibration mode after you have calibrated to your selected number
of points.
From measurement mode
1. Press the MODE key to select pH measurement mode.
2. Press SETUP key to enter Setup mode.
3. Press the or key to scroll through sub-groups until you view
parameter P3.0.
4. Press the ENTER key twice to select parameter P3.2.
5. Press the or key to select 2, 3, 4 or 5 point pH calibration.
READY
ON
SETUP
READY
ON
2 p
p 3.2
3 p
p 3.2
6. Press the ENTER key to confirm selection and proceed to step 4 of
P3.3. Press CAL/MEAS key to return to measurement mode.
See Figure 28.
8.4.3 P3.3 Selecting USA or NIST buffer
Program P3.3 lets you select between the following calibration buffer
sets:
USA: pH 1.68, 4.01, 7.00, 10.01, 12.45
NIST: pH 1.68, 4.01, 6.86, 9.18, 12.45
Factory default is USA buffer set.
From measurement mode
1. Press the MODE key to select pH measurement mode.
2. Press SET key to enter Setup mode.
SETUP
READY
ON
4 p
p 3.2
SETUP
READY
ON
5 p
p 3.2
Figure 29: P3.2 - Select number of
pH calibration points
SETUP
usa
p 3.3
3. Press the or key to scroll through subgroups until you view
parameter P3.0.
4. Press ENTER three times to select parameter P3.3.
5. Press the or key to toggle between USA and NIST buffer
sets.
6. Press ENTER key to confirm selection and proceed to step 4 of
P3.4. Press CAL/MEAS key to return to measurement mode.
29
SETUP
p 3.3
Figure 30: P3.3 - Select
buffer set
Page 34

Instruction Manual PC 510
8.4.4 P3.4 Selecting °C or °F
This meter lets you select between °C and °F units for temperature readings.
From measurement mode
R
E
T
N
E
E
G
N
A
1. Press the MODE key to select pH measurement mode.
R
2. Press SETUP key to enter Setup MODE.
3. Press the or key to scroll through sub-groups until you view
parameter P3.0.
4. Press the ENTER key four times to select parameter P3.4.
5. Press the or key to toggle between °C and °F.
6. Press the ENTER key to confirm selection and to return to the subgroup menu. Press the CAL/MEAS key to return to measurement
mode.
NOTE
: You can switch between °C and °F in Program P7.2 (available
°
from conductivity or TDS mode). If you switch between
C and °F in pH
mode, the meter will also switch in conductivity or TDS mode.
SETUP
C
°C
p 3.4
SETUP
F
°F
p 3.4
Figure 31: P3.4- Select
temperature units
30
Page 35

Instruction Manual PC 510
8.5 P4.0: Resetting to factory default settings (pH)
This program lets you reset all pH parameters to factory default settings. This clears all calibration
data and any other pH setup functions you might have changed.
The following settings will remain as you have set them:
SETUP MEAS
• Temperature unit of measure (°C or °F)
pH
• The temperature offset calibration value
• All conductivity calibration data and parameters
From measurement mode
1. Press the MODE key to select pH measurement mode.
2. Press SETUP key to enter Setup mode.
SETUP MEAS
pH
3. Press the or key to scroll through sub-groups until you view
parameter P4.0.
yes
4. Press the ENTER key to enter parameter P4.0. See Figure 32.
Figure 32: P4.0 - Reset to
5. Press the or to toggle between NO and YES.
factory default values
• NO retains current settings
• YES resets to factory default settings
6. Press the ENTER key to confirm selection and to return to the measurement mode. Otherwise
press CAL/MEAS key to return to measurement mode without resetting to factory default.
:
NOTE
• To clear all conductivity & TDS data, see page 38.
• See Addendum 4 on page 49 for a table of factory default settings.
31
Page 36

Instruction Manual PC 510
8.6 P5.0: Viewing previous conductivity calibration data
This mode lets you recall previous calibration data, which helps you know when to re-calibrate your
meter. This is a “view-only” mode.
This function applies for conductivity & TDS mode.
From conductivity or TDS mode
1. Press the MODE key to select conductivity or TDS measurement
mode.
2. Press the SETUP key to enter Setup mode.
3. Press the or key to scroll through sub-groups until you view
parameter P5.0.
4. Press ENTER key repeatedly to view previous calibration data.
5. Each calibration data corresponds to each measurement range.
• P5.1 = Range 1 (0.00 – 19.99 µS or 0.0 – 9.99 ppm)
• P5.2 = Range 2 (0.0 – 199.9 µS or 0.0 – 99.9 ppm)
• P5.3 = Range 3 (0 – 1999 µS or 0 – 999 ppm)
• P5.4 = Range 4 (0.00 – 19.99 mS or 0.00 – 9.99 ppt)
• P5.5 = Range 5 (0.0 – 199.9 mS or 0.0 – 99.9 ppt)
6. When you have scrolled through all calibration data, you will
automatically return to the sub-group menu. Press CAL/MEAS key
to return to measurement mode.
: If there is no previous calibration data at a particular point, the
NOTE
primary display will show “----“.
SETUP
E
T
N
E
G
N
A
R
SETUP
R
E
T
N
E
E
G
N
A
R
SETUP
R
E
T
N
E
G
N
A
R
SETUP
R
E
E
cal
p 5.0
---
p 5.1
CAL
1413
p 5.3
CAL
12.88
mS
S
µ
ppt
ppm
µ
mS
S
32
p 5.4
Figure 33: View calibration
data in conductivity probe
Page 37

Instruction Manual PC 510
8.7 P6.0: Viewing conductivity probe data
Program 6 has five “view-only” options that let you check the probe’s parameters for diagnostic
purposes. These options show you the effective cell constant for each range. The cell constant adjusts
according to your calibration.
This function applies for conductivity & TDS mode.
From conductivity or TDS measurement mode
1. Press the MODE key to select conductivity or TDS measurement
mode.
2. Press the SETUP key to enter Setup mode.
3. Press the or key to scroll through sub-groups until you view
parameter P6.0.
4. Press the ENTER key repeatedly to view the effective cell
constant for each range.
• P6.1 = Range 1 (0.00 – 19.99 µS or 0.00 – 9.99 ppm)
• P6.2 = Range 2 (0.0 – 199.9 µS or 0.0 – 99.9 ppm)
• P6.3 = Range 3 (0 – 1999 µS or 0 – 999 ppm)
• P6.4 = Range 4 (0.00 – 19.99 mS or 0.00 – 9.99 ppt)
• P6.5 = Range 5 (0.0 –199.9 mS or 0.0 – 99.9 ppt)
5. When you have scrolled through all probe data, you will
automatically return to the sub-group menu. Press the CAL/MEAS
key to return to measurement mode.
NOTE:
Cell constants will degrade with time and usage. You can use
this feature to alert you to the need for a new probe prior to total
failure.
SETUP
E
T
N
E
G
N
A
R
SETUP
E
T
N
E
R
G
N
A
SETUP
R
E
T
N
E
E
G
N
A
R
SETUP
R
E
k =
1.000
R
E
k =
1.000
k =
ele
p 6.0
p 6.1
p 6.2
.985
mS
µ
S
ppt
ppm
33
p 6.3
Figure 34: View probe data for
each measurement range
Page 38

Instruction Manual PC 510
8.8 P7.0: Conductivity or TDS measurement configuration
8.8.1 P7.1: READY indicator and auto endpoint function
This program lets you select:
• “READY indicator on
• “READY indicator off
• Auto endpoint function on
” to indicate when the reading is stable.
” for faster meter response.
. Select auto endpoint on to “hold” the
reading when it is stable for more than 5 seconds. The display
automatically freezes, and the HOLD indicator appears on the left
side of the display. Press the HOLD key to release the display and
access other functions.
From measurement mode
1. Press the MODE key to select conductivity or TDS measurement
mode.
2. Press the SETUP key to enter Setup mode.
3. Press the or key to scroll through sub-groups until you view
parameter P7.0.
4. Press ENTER key to select parameter P7.1.
5. Press the or key to select the configuration you require.
SETUP
R
E
T
N
E
E
G
N
A
R
SETUP
READY
ON
SETUP
READY
OFF
cof
p 7.0
p 7.1
p 7.1
mS
µ
S
ppt
ppm
• OFF switches the READY indicator off.
• ON switches the READY indicator on.
• ON and HOLD together switches the auto endpoint feature on.
6. Press ENTER key to confirm selection and to proceed to step 4 of
P7.2. You can also press the CAL/MEAS key to return back to
measurement mode.
NOTE
: Meter default is set for Ready indicator on, and auto endpoint function off.
SETUP
READY
HOLD
ON
p 7.1
Figure 35: P3.1 - Selecting
READY function
34
Page 39

Instruction Manual PC 510
°
8.8.2 P7.2: Selecting
C or °F
You can select between °C and °F units for temperature readings. Meter default is °C.
R
E
T
N
From measurement mode
E
E
G
N
A
R
1. Press the MODE key to select conductivity measurement mode.
SETUP
2. Press the SETUP key to enter Setup mode.
3. Press the or key to scroll through sub-groups until you view
parameter P7.0.
C
°C
p 7.2
4. Press the ENTER key two times to select parameter P7.2.
5. Press the or key to toggle between °C and °F.
6. Press the ENTER key to confirm selection and to proceed to step 4
of P7.3. Press the CAL/MEAS key to return to measurement mode.
NOTE
: You can switch between °C and °F in Program P3.4 (available
°
from pH mode). If you switch between
C and °F in conductivity mode,
SETUP
F
°F
p 7.2
the meter will also switch in pH mode.
Figure 36: Change temperature
measurement unit
8.8.3 P7.3: Selecting Automatic or Manual Temperature
Compensation
This feature lets you select between Automatic Temperature
Compensation (ATC) and Manual Temperature Compensation. Meter
default is ATC.
From measurement mode
1. Press the MODE key to select conductivity measurement mode.
2. Press SETUP key to enter Setup mode.
3. Press the or key to scroll through the sub-groups until you
view parameter P7.0.
4. Press the ENTER key three times to select parameter P7.3. The
upper display shows “ATC” and the lower display shows “P7.3”.
5. Press the ENTER key again. The upper display shows “ATC” and
the lower display shows “YES” or “NO”.
6. Press the or key to select the Automatic Temperature
Compensation on or off.
• YES = ATC on; NO = ATC off
7. Press the ENTER key to confirm selection and proceed to step 3 of
P7.4. Press the CAL/MEAS key to return to measurement mode.
T
N
E
N
A
R
SETUP
T
N
E
N
A
R
SETUP
SETUP
R
E
E
G
p 7.3
R
E
E
G
YES
°C
ATC
°C
ATC
°C
35
Figure 37: Selecting ATC
ON or OFF
Page 40

Instruction Manual PC 510
8.8.4 P7.4: Setting the TDS factor
The concentration of salts dissolved in solution increases the conductivity of that solution. This
relationship varies from salt to salt and is roughly linear over a given range for a given salt. The TDS
conversion factor is the number used by the meter to convert from conductivity to TDS.
To determine the conductivity to TDS conversion factor for your
solution:
Addendum 1 and 2 on this sheet describes the conversion factors and
how to calculate the TDS conversion factor for other solutions.
You can set the TDS conversion factor between 0.4 and 1.0; meter
default is 0.5. When the factor is set to 1.0, conductivity = TDS.
From measurement mode
1. Press SETUP key to enter Setup mode.
2. Press the or key to scroll through sub-groups until you view
parameter P7.0.
3. Press the ENTER key four times to select parameter P7.4. The
upper display shows “tdS” and the lower display shows “P7.4”.
4. Press the ENTER key again. The upper display shows a value and
the lower display shows “tdS”.
5. Calculate the TDS factor of your solution. See Addendum 2 on this
sheet for information on how to calculate the TDS factor.
6. Press the or key to select your calculated TDS conversion
factor.
E
T
N
E
G
N
A
R
SETUP
E
T
N
E
G
N
A
R
SETUP
SETUP
R
E
R
E
p 7.4
0.50
0.75
ppt
ppm
ppt
ppm
ppt
ppm
7. Press the ENTER key to confirm selection and to return to the subgroup menu. Press the CAL/MEAS key to return to the
measurement mode.
Figure 38: Change of TDS factor
36
Page 41

Instruction Manual PC 510
8.9 P8.0: Temperature
8.9.1 P8.1: Selecting the temperature coefficient
The temperature coefficient is the amount of change in conductivity per degree of temperature; it is
expressed in percent per °C. Entering the exact temperature coefficient of your solution lets you
accurately compensate temperature for almost any solution*.
You can adjust 0.0 to 10.0% per °C. The meter default is 2.1% per °C. A temperature coefficient
setting of 0.0% does not apply a correction factor to the reading for
temperature.
From measurement mode
1. Press the MODE key to select conductivity measurement mode.
SETUP
p 8.0
°C °F
mS
µ
S
ppt
ppm
2. Press SETUP key to enter Setup mode.
3. Press the or key to scroll through sub-groups until you view
parameter P8.0.
4. Press the ENTER key to select parameter P8.1. The display shows
“t.CO” on the upper display.
5. Press the ENTER key again. The upper display shows the
temperature coefficient and the lower display shows “t.CO”.
6. Press the or key to select the temperature coefficient of your
solution.
7. Press the ENTER key to confirm selection and to proceed to step 3
of P8.2. Press the CAL/MEAS key twice to return to measurement
mode.
NOTE
: *If you do not know the temperature coefficient of your solution
you can determine the correct value using the formula in Addendum 3
“Calculating Temperature Coefficients” on page 48.
R
E
T
N
E
G
N
A
R
SETUP
R
E
T
N
E
N
A
R
G
SETUP
SETUP
E
°C °F
p 8.1
E
2.1
3.5
37
Figure 39: Changing the
temperature coefficient
Page 42

Instruction Manual PC 510
SETUP
8.9.2 P8.2: Adjusting the normalisation temperature
3.5
Your meter will normalise its conductivity measurement to a standard
temperature that you can select. This feature is useful if your samples
are consistently at a temperature other than 25°C (77 °F). You can
adjust the normalisation temperature from 15 to 30 °C (59 to 86 °F).
Meter default is 25 °C (77 F). When using non-standard normalisation
temperatures, it is important to calibrate to the value of your calibration
standard at your normalisation temperature setting. From measurement
mode
R
E
T
N
E
G
N
A
R
SETUP
E
1. Press the MODE key to select conductivity measurement mode
p 8.2
2. Press SETUP key to enter Setup mode.
R
E
T
N
3. Press the or key to scroll through sub-groups until you view
parameter P8.0.
4. Press the ENTER key two times to select parameter P8.2. The
display shows “t.nr” on the upper display.
5. Press the ENTER key again. The upper display shows the
normalisation temperature and the lower display shows “t.nr”.
6. Press the or key to select the normalisation temperature.
7. Press the ENTER key to confirm selection and to return to the subgroup menu. Press CAL/MEAS key to return to measurement mode.
8.9.3 P9.0: Resetting to factory default settings (conductivity)
Program P9.0 lets you reset all parameters to factory default settings.
This clears all calibration data and any other conductivity setup functions you might have changed.
E
E
G
N
A
R
SETUP
25.0
SETUP
20.0
Figure 40: Adjusting the
normalisation temperature
°C °F
°C
°C
From measurement mode
1. Press the MODE key to select conductivity measurement mode.
2. Press SETUP key to enter Setup mode.
3. Press the or key to scroll through sub-groups until you view
parameter P9.0.
4. Press the ENTER key to enter parameter P9.0.
5. Press the or to toggle between NO and YES
• NO retains current settings; YES resets to factory default
settings.
6. Press the ENTER key to confirm selection and to return to the
measurement mode. Otherwise press CAL/MEAS key to return to
measurement mode without resetting to factory default.
NOTE
: To clear all pH data, see page 38. See Addendum 4 on page 49
for a table of factory default settings.
SETUP MEAS
SETUP MEAS
yes
Figure 41: P9.0 - Reset to
factory default values
mS
µ
ppt
ppm
S
38
Page 43

Instruction Manual PC 510
9 PROBE CARE AND MAINTENANCE
9.1 pH Electrode care
Since your pH electrode is susceptible to dirt and cont amination, clean as necessary depending on the
extent and condition of use.
: For specialty electrode care, consult your electrode instruction manual .
NOTE
pH electrode storage
For best results, keep the pH bulb hydrated. Use the protective electrode storage bottle or rubber cap
filled with electrode storage solution to store your electrode. Alternatively, you can store in a pH 4
buffer with 1/100 part of saturated KCl. Other pH buffers are OK for short term storage, but NEVER
use distilled water for storage.
After measuring
1. Rinse the pH electrode and reference junction in de-ionised water.
2. Store the electrode as recommended above in “pH electrode storage solution”, or as
recommended by the manufacturer.
3. Prior to next use, rinse the liquid junction with de-ionised water and tap dry – never wipe
electrode.
NOTE
: If this does not restore electrode to normal response, see “Reactivating the pH electrode”
section below.
pH electrode cleaning
• Salt deposits: Dissolved the deposits by immersing the electrode in tap water for ten to fifteen
minutes. Then thoroughly rinse with distilled water.
• Oil/Grease film: Wash electrode pH bulb gently in some detergent and water. Rinse electrode tip
with distilled water or use a general purpose electrode cleaner (see ordering informatio n).
• Clogged reference junction: Heat a diluted KCl solution to 60 to 80 °C. Place the sensing part of
the electrode into the heated solution for about 10 minutes. Allow the electrode to cool in some
unheated KCl solution.
• Protein deposits: Prepare a 1% pepsin solution in 0.1 M of HCl. Set the electrode in the solution
for five to ten minutes. Rinse the electrode with distilled water.
Reactivating the pH electrode
If stored and cleaned properly, your pH electrode should be ready for immediate use. However, a
dehydrated bulb may cause sluggish response. To rehydrate the bulb, immerse the electrode in a pH
4 buffer solution for 10 to 30 minutes. If this fails, the electrode requires activation. Never touch or rub
glass bulb. Contact builds up an electro-static charge.
39
Page 44

Instruction Manual PC 510
pH electrode activation (for glass body electrodes only)
WARNING
: Only qualified persons with proficient with the safe handling of dangerous chemicals
should perform the procedure below. Provide proper containers, fume hoods, ventilation and waste
disposal. Safety goggles and protective clothing must be worn while performing this procedure. If
possible, replace with another electrode instead of performing this re-activation procedure.
1. Dip or stir the pH electrode in alcohol for 5 minutes.
2. Leave the electrode in tap water for 15 minutes.
3. Dip and stir the electrode in concentrate acid (such as HCl or H2SO4) for 5 minutes.
4. Repeat Step 2.
5. Dip and stir in strong base (NaOH) for 5 minutes.
6. Leave for 15 minutes in tap water.
7. Now test with standard calibration buffer solutions to see if the electrode yields acceptable results.
You may repeat step 3 through 6 up to three times for better response. If the response does not
improve, then your electrode is no longer functioning. Replace with a new electrode – call your
distributor for information.
9.2 Conductivity electrode
Keep the conductivity probe clean. Rinse the probe twice and gently
swirl it while you take readings. For best accuracy, soak a dry probe for
at least 5 to 10 minutes or longer before calibration. Rinse the probe
with de-ionised or tap water before storing. Never scratch the bands
with a hard substance. Do not strike the probe against any hard surface.
Do not immerse the probe in oily solutions. Clean the electrode
thoroughly by stirring it in a mild detergent bath or isopropyl alcohol.
Wipe the probe with a soft tissue paper. Rinse thoroughly in tap water
and then in de-ionised water. Re-calibrate the meter after cleaning the
probe.
The conductivity probe included with your meter features a removable
probe guard for easy cleaning.
To remove probe guard:
1. Grip yellow probe guard and twist clockwise. The locking notch will
release.
2. Slide probe guard off end of probe.
Figure 42: Conductivity probe
40
Page 45

Instruction Manual PC 510
10 TROUBLE SHOOTING GUIDE
Problem Cause Solution
Press ‘ON’ key but no display. a) AC outlet power not is
switched on.
b) DC adapter socket is not
properly inserted.
Not responding to key press. a) HOLD mode in operation.
b) Damaged keypad.
c) Internal program error.
Unstable readings. a) Air bubbles in probe.
b) Dirty probe.
c) Probe not deep enough in
sample.
d) External noise pickup or
induction caused by nearby
electric motor.
a) Switch on the power supply.
b) Re-insert DC adapter
socket.
a) Cancel HOLD mode by
pressing Hold key.
b) Return to dealer.
c) Reset all internal programs
by re-inserting the power
socket.
a) Tap probe to remove
bubbles.
b) Clean the probe and
recalibrate.
c) Make sure sample entirely
covers the probe sensors.
d) Move or switch off
interfering motor.
e) Broken probe.
“OR” on upper display. a) Probe is shorted.
b) Probe is in an out-of-range
solution.
c) Broken probe.
Temperature reading erratic or
lower display reads “OR”
a) Temperature of solution is
out of range.
e) Replace probe.
a) Test probe. Make sure
probe is fully connected to
meter.
b) Use different solution.
c) Replace probe.
a) Heat or cool solution.
Slow response a) Dirty/Oily probe. a) Clean probe. See “ Probe
Care and Maintenance”,
page 39.
41
Page 46

Instruction Manual PC 510
11 ERROR MESSAGES
LCD Display Indicates Cause Solution
Err annunciator. Unrecognised input
from keypad.
Wrong input in selected
mode.
Release key. Select
valid operations
depending on mode.
CAL & Err
annunciators on /
Calibration error. Wrong value input at
calibration.
Check your input
value, clean probe.
Buffer and electrode
indicators blink.
Dirty probe.
See Calibration
section or Probe
Maintenance section.
If an error persists, or the meter shows incorrect values, return the meter. See “Warranty” and “Return
of Items” on page 51.
For a complete diagram of the display, see page 4.
42
Page 47

Instruction Manual PC 510
12 SPECIFICATIONS
Mode pH Temperature Conductivity TDS mV
0 to 9.99 ppm
0 to 19.99 µS
Range -2.00 to 16.00 pH
Resolution 0.01 pH
Accuracy ±0.01 pH
Calibration
pH Buffer Option
pH Slope & Offset
Display
Conductivity Cell
constant (k)
Conductivity
Temperature
Coefficient
Normalisation
Temperature
TDS Conversion
Factor
Auto-ranging Yes Yes
Inputs BNC
Temperature
Compensation
Operating
Temperature
HOLD function Yes
Averaging / Stability
(READY) / Auto-hold
Display Custom Dual LCD
Power 9 V DC adapter (110 V AC / 230 V AC)
Dimensions / Weight
Up to 5 points,
with automatic
buffer recognition
USA (pH 1.68,
4.01, 7.00,
10.01,12.45)
NIST (pH 1.68,
4.01, 6.86, 9.18,
12.45)
Yes
1.0 1.0
0.4 to 1.0
-10.0 to 110.0 °C
(14 to 230 °F)
0.1 °C
(0.1 °F)
+0.5 °C
(±0.9 °F)
Offset in 0.1 °C
increments
6-pin round
connector
Automatic / Manual from 0 to 100 °C
Meter (with electrode arm): 18 x 23 x 6 cm; 950 g
0 to 199.9 µS
0 to 1999 µS
0 to 19.99 mS
0 to 199.9 mS
0.01 µS
0.1 µS
1 µS
0.01 mS
0.1 mS
±1% Full Scale + 1
digit
Up to 5 points (one
point per range)
0.0 to 10.0% per
°C
15.0 to 30.0 °C
(adjustable)
6-pin round
connector
0 to 50 °C
Yes
Boxed: 40 x 26 x 9 cm; 1650 g
0 to 99.9 ppm
0 to 999 ppm
0 to 9.99 ppt
0 to 99.9 ppt
Max. of 199.9 ppt
based on factor
setting
0.01 ppm
0.1 ppm
1 ppm
0.01 ppt
0.1 ppt
±1% Full Scale + 1
digit
Up to 5 points (one
point per range)
0.0 to 10.0% per
°C
15.0 to 30.0 °C
(adjustable)
6-pin round
connector
-600 to +600 mV
0.1 mV
(-199.99 to +199.9
mV)
1 mV
(beyond ± 199.9
mV)
±0.2 mV
(-199.9 to +199.9
mV)
±2 mV
(beyond ±199.9
mV)
BNC
43
Page 48

Instruction Manual PC 510
13 ACCESSORIES
Replacement Meter and Meter accessories
Eutech Instruments
Item Description
Eutech Instruments
Order Code No.
PC 510 meter, pH electrode (EC-FC72522-01B), conductivity/temp probe (ECCONSEN91W) and integral electrode stand.
PC 510 meter, pH electrode (EC-FC72522-01B), conductivity/temp probe (ECCONSEN91W), integral electrode stand and 110 VAC power adapter.
PC 510 meter, pH electrode (EC-FC72522-01B), conductivity/temp probe (ECCONSEN91W), integral electrode stand and 220 VAC power adapter.
Plastic-body double-junction pH combination electrode (1 meter cable) EC-FC72522-01B
Epoxy-body single-junction pH electrode (3 ft cable) EC-FC72521-01B
Ultem-body, conductivity/temperature electrode, k=1.0, 1 m cable EC-CONSEN91W
Temperature probe, stainless steel, 6 pin connector EC-PHWPTEM01W
“3-in-1” pH/Temperature, combination epoxy-body, sealed, single-junction,
electrode, 120 mm x 12 mm diameter, 1 m cable
AC/DC power adapter (120 V AC, 50/60 Hz) EC-120-ADA
AC/DC power adapter (220 V AC, 50/60 Hz) EC-220-ADA
EC-PC510/03S
EC-PC510/13S
EC-PC510/23S
EC-FE73528-01W
44
Page 49

Instruction Manual PC 510
Oakton Instruments
Item Description Oakton Instruments
Order Code No.
PC 510 meter, pH electrode (35641-51), ,conductivity/temp probe ( 35608-50),
integral electrode stand, (110 & 220 VAC Adapters)
PC 510 meter, “3-in-1” pH electrode (35808-71), ,conductivity/temp probe
(35608-50), integral electrode stand, (110 & 220 VAC adapters)
PC 510 meter, integral electrode stand, 110 & 220 VAC adapters. 35610-12
Plastic-body double-junction pH combination electrode (1 meter cable) 35641-51
Epoxy-body single-junction pH electrode (3 ft cable) 35801-00
Ultem-body, conductivity/temperature electrode, k=1.0, 1 m cable 35608-50
Temperature probe, stainless steel, 6 pin connector 35618-05
“3-in-1” pH/Temperature, combination epoxy-body, sealed, single-junction,
electrode, 120 mm x 12 mm diameter, 1 m cable
“3-in-1” pH/Temperature combination epoxy-body, sealed, doub le-junction,
electrode, 120 mm x 12 mm diameter, 1 m cable
AC/DC power adapter (120 V AC, 50/60 Hz) 35615-07
AC/DC power adapter (220 V AC, 50/60 Hz) 35615-08
35610-10
35610-11
35808-71
35808-72
45
Page 50

Instruction Manual PC 510
Calibration Solutions
Item Eutech Instruments
Ordering Code
pH 4.01 buffer solution, 480 mL bottle (1 pint) EC-BU-4BT 00654-00
pH 7.00 buffer solution, 480 mLmL bottle (1 pint) EC-BU-7BT 00654-04
pH 10.01 buffer solution, 480 mLmL bottle (1 pint) EC-BU-10BT 00654-08
pH 4.01 buffer sachets, 20 mL x 20 pcs. EC-BU-4BS 35653-01
pH 7.00 buffer sachets, 20 mL x 20 pcs. EC-BU-7BS 35653-02
pH 10.01 buffer sachets, 20 mL x 20 pcs. EC-BU-10BS 35653-03
12.88 mS Calibration Solution in 480-mLL bottle (1 pint) EC-CON-1288BT 00606-10
2,764 µS Calibration Solution in 480-mL bottle (1 pint) EC-CON-2764BT 00653-20
10 µS conductivity standard pouch (20 units x 20 mL per
box)mL
447 µS Conductivity pouch (20 units x 20 mL per box) EC-CON-447BS 35653-10
1,413 µS Conductivity pouch (20 units x 20 mL per box) EC-CON-1413 BS 35653-11
2,764 µS Conductivity pouch (20 units x 20 mL per box) EC-CON-2764 BS 35653-12
EC-CON-10BS 35653-09
Oakton Instruments
Ordering Code
15,000 µS Conductivity pouch (20 units x 20 mL per box) EC-CON-15000BS 35653-13
Note:
°
pH buffer solutions have ±0.01 pH accuracy at 25
accuracy at 25
°
C. Pouches contain 20-mL calibration solution in individually sealed, single-use
C. Conductivity standard solutions have ±1%
packets
46
Page 51

Instruction Manual PC 510
14 ADDENDUM 1: CONDUCTIVITY TO TDS CONVERSION FACTORS
1. Factor – the conductivity to ppm TDS conversion factor. Multiply conductivity by this factor to get
ppm TDS for the type of TDS reading needed.
2. 442 – a formulation that most closely represents the conductivity to ppm relationship, on average,
for naturally occurring fresh water. (4
3. TDS Your Material – These columns are for you to write in your application-specific conductivityto-ppm values and conversion factors for future reference.
Factor = Actual TDS ÷ Actual Conductivity @ 25 °C
0% NaSO4, 40% NaHCO3, 20% NaCl)
Conductivity at 25
°C
84 µS
447 µS
1413 µS
1500 µS
8974 µS
12,880 µS
15,000 µS
ppm Value Factor ppm Value Factor
40.38 0.5048 38.04 0.4755
225.6 0.5047 215.5 0.4822
744.7 0.5270 702.1 0.4969
757.1 0.5047 737.1 0.4914
5101 0.5685 4487 0.500
7447 0.5782 7230 0.5613
8759 0.5839 8532 0.5688
TDS KCl TDS NaCl
80 mS 52,168 0.6521 48,384 0.6048
Conductivity at 25
°C
84 µS
ppm Value Factor ppm Value Factor
50.50 0.6563
TDS 442 TDS Your Material
447 µS
1413 µS
1500 µS
8974 µS
12,880 µS
15,000 µS
300.0 0.6712
1000 0.7078
1050 0.7000
7608 0.8478
11,367 0.8825
13,455 0.8970
80 mS 79,688 0.9961
47
Page 52

Instruction Manual PC 510
15 ADDENDUM 2: CALCULATING TDS CONVERSION FACTORS
You can calibrate your meter using TDS calibration standard solutions. The calibration standard only
needs to give the TDS value at a standard temperature such as 25 °C. To determine the conductivityto-TDS conversion factor use the following formula:
Factor = Actual TDS ÷ Actual Conductivity @ 25 °C
Definitions
:
• Actual TDS: Value from the solution bottle label or as a standard you make using high
purity water and precisely weighed salts.
• Actual Conductivity: Value measured using a properly calibrated
Conductivity/Temperature meter.
Both the Actual TDS and the Actual Conductivity values must be in the same magnitude of units. For
example, if the TDS value is in ppm the conductivity value must be in µS; if the TDS value is in ppt the
conductivity value must me in mS.
Check your factor by multiplying the conductivity reading by the factor in the above formula. The result
should be in TDS value.
16 ADDENDUM 3: STANDARD pH BUFFERS
The following table shows the various pH values at different temperature of the solution during
calibration. The table also illustrates why a calibration value may be different from the buffer value at
25 °C.
Temperature USA Buffer NIST Buffer
(oC) pH 1.68 pH 4.01 pH 7.00 pH 10.01 pH 12.45 pH1.68 pH 4.01 pH 6.86 pH 9.18 pH 12.45
0 1.67 4.01 7.12 10.32 13.43 1.67 4.01 6.98 9.47 13.43
5 1.67 4.01 7.09 10.25 13.21 1.67 4.01 6.95 9.38 13.21
10 1.67 4.00 7.06 10.18 13.00 1.67 4.00 6.92 9.32 13.00
15 1.67 4.00 7.04 10.12 12.81 1.67 4.00 6.90 9.27 12.81
20 1.68 4.00 7.02 10.06 12.63 1.68 4.00 6.88 9.22 12.63
25 1.68 4.01 7.00 10.01 12.45 1.68 4.01 6.86 9.18 12.45
30 1.69 4.01 6.99 9.97 12.29 1.69 4.01 6.85 9.14 12.29
35 1.69 4.02 6.98 9.93 12.13 1.69 4.02 6.84 9.10 12.13
40 1.70 4.03 6.97 9.89 11.99 1.70 4.03 6.84 9.07 11.99
45 1.70 4.04 6.97 9.86 11.84 1.70 4.04 6.83 9.04 11.84
50 1.71 4.06 6.97 9.83 11.70 1.71 4.06 6.83 9.01 11.70
55 - 4.08 6.97 9.81 - - 4.08 6.83 8.99 60 - 4.10 6.98 9.79 - - 4.10 6.84 8.96 70 - 4.12 6.99 9.76 - - 4.12 6.85 8.92 80 - 4.16 7.00 9.74 - - 4.16 6.86 8.89 90 - 4.20 7.02 9.73 - - 4.20 6.88 8.85 -
48
Page 53

Instruction Manual PC 510
17 ADDENDUM 4: CALCULATING TEMPERATURE COEFFICIENTS
To determine the temperature coefficient of your sample solution use this formula:
C
– CT1
T2
tc = 100 x
CT1(T2 – 25) – CT2(T1 - 25)
Where:
tc = Temperature coefficient 25 = 25 °C
C
T
= Conductivity at Temp 1 CT2 = Conductivity at Temp 2
T1
= Temp 1 T
1
= Temp 2
2
NOTE: A controlled temperature water bath is ideal for this procedure.
1. Immerse the probe into a sample of your solution and adjust the temperature coefficient to 0%
(that is, no compensation) by performing the following:
A. From measurement mode, press the SETUP key to enter Setup mode.
B. Press the or key until the lower display reads P8.0.
C. Press the ENTER key twice. The lower display reads tCO and the upper display shows the
temperature coefficient value.
D. Press the key until the upper display shows 0.0.
E. Press ENTER key to confirm the value.
F. Press CAL/MEAS key twice to return to measurement mode
2. Wait for 5 minutes. Note T
3. Condition the sample solution and probe to a temperature (T
from T
, and note the conductivity reading CT2.
1
NOTE: Record your results for future reference. Ideally T
and CT1 (conductivity at T1).
1
) that is about 5 °C to 10 °C different
2
and T2 should bracket your
1
measurement temperature, and should not be different by more than 5 °C.
4. Calculate the temperature coefficient of your solution according to the formula shown above.
5. Enter the temperature coefficient you calculated into the meter.
A. From measurement mode, press the SETUP key to enter Setup mode.
B. Press the key until the lower display reads P8.0.
C. Press the ENTER key twice. The lower display reads tCO and the upper display shows the
temperature coefficient value (should be 0, as per step 1 above).
D. Press the key until the upper display shows your calculated temperature coefficient.
E. Press ENTER key to confirm the value.
F. Press CAL/MEAS key twice to return to measurement mode.
The calculated temperature coefficient will not be applied to all the meter readings.
49
Page 54

Instruction Manual PC 510
18 ADDENDUM 5: METER FACTORY DEFAULT SETTINGS
Resetting the meter to factory default settings clears all calibration data and most other setup
functions you might have changed. The following settings will remain as you have set them:
• Temperature unit of measure (°C or °F)
• The temperature offset calibration value.
NOTE: Conductivity and pH data are cleared separately from each other.
• To clear pH data, see Sub group P4.0.
• To clear conductivity/TDS data, see Sub group P9.0.
Type Parameter Default Remarks
pH parameters
P1.1
P1.2
P1.3
P1.4
P1.5
View pH calibration data ----
----
----
----
----
No calibration data for 1
No calibration data for 2
No calibration data for 3
No calibration data for 4
No calibration data for 5
st
buffer, pH 1.68
nd
buffer, pH 4.01
rd
buffer, pH 7.00 or 6.86
th
buffer, pH 10.01 or 9.18
th
buffer, pH 12.45
P2.1
P2.2
P3.1
P3.2
P3.3
P3.4
P4.0 pH factory default No Retains your current settings
Conductivity and TDS parameters
P5.1
P5.2
P5.3
P5.4
P5.5
P6.1
P6.2
P6.3
P6.4
P6.5
P7.1
P7.2
P7.3
P7.4
P8.1
P8.2
View electrode offset
View electrode slope
Ready indicator
# pH calibration points
Buffer set option
°C or °F
Viewing conductivity or TDS
calibration data
Viewing conductivity or TDS
calibration data
Ready indicator
°C or °F
ATC on or off
TDS factor
Temperature coefficient
Normalisation temperature
0.00 mV
100.0%
Ready on
3
USA
No default
----
----
----
----
----
1.0
1.0
1.0
1.0
1.0
Ready on
No default
ATC on
0.5
2.1% per °C
25 °C
No offset adjustment
No slope adjustment
Ready indicator on; auto endpoint off
3 pH calibration points available (1 – 5 pt range)
USA or NIST buffer set
°C or °F remains as selected
No calibration data for range 1
No calibration data for range 2
No calibration data for range 3
No calibration data for range 4
No calibration data for range 5
No offset for effective cell constant for range 1
No offset for effective cell constant for range 2
No offset for effective cell constant for range 3
No offset for effective cell constant for range 4
No offset for effective cell constant for range 5
Ready indicator on; auto endpoint off
°C or °F remains as selected
---Adjustable from 0.4 to 1.0
Adjustable from 0 to 10%
Adjustable from 15 to 30 °C
P9.0 Conductivity factory default No Retains your current settings
50
Page 55

Instruction Manual PC 510
19 WARRANTY
The PC510 bench meter is supplied with a 3-year warranty from manufacturing defects and
electrodes for 6 months from the date of purchase.
If repair or adjustment is necessary and has not been the result of abuse or misuse within the
designated period, please return – freight pre-paid – and correction will be made without charge.
Eutech Instruments/ Oakton Instruments will determine if the product problem is due to deviations or
customer misuse.
Out of warranty products will be repaired on a charged basis.
Exclusions
The warranty on your instrument shall not apply to defects resulting from:
• Improper or inadequate maintenance by customer
• Unauthorised modification or misuse
• Operation outside of the environment specifications of the products
20 RETURN OF ITEMS
Authorisation must be obtained from our Customer Service Department or authorised distributor
before returning items for any reason. A “Return Goods Authorisation” (RGA) form is available through
our Authorised Distributor. Please include data regarding the reason the items are to be returned. For
your protection, items must be carefully packed to prevent damage in shipment and insured against
possible damage or loss. Eutech Instruments/ Oakton Instruments will not be responsible for damage
resulting from careless or insufficient packing. A restocking charge will be made on all unauthorised
returns.
NOTE: Eutech Instruments Pte Ltd/ Oakton Instruments reserves the right to make improvements in
design, construction, and appearance of products without notice.
51
Page 56

For more information on Eutech Instruments/ Oakton Instruments’ products, contact your nearest
distributor or visit our website listed below:
Oakton Instruments
P.O Box 5136,
Vernon Hills, IL 60061, USA
Tel: (1) 888-462-5866
Fax: (1) 847-327-2984
E-mail: info@4oakton.com
www.4oakton.com
Web:
Eutech Instruments Pte Ltd
Blk 55, Ayer Rajah Crescent,
#04-16/24 Singapore 139949
Tel: (65) 6778 6876
Fax: (65) 6773 0836
E-mail:
Web: www.eutechinst.com
marketing@eutechinst.com
Distributed by:
 Loading...
Loading...