ETIC RAS-E, RAS-EW, RAS-EC, RAS-ECW User Manual

RAS-E RAS-EW
RAS-EC RAS-ECW
_________________
_________________
USER GUIDE
Machine Access Box RAS DOC_DEV_RAS_User guide_A

CONTENT
The RAS router is manufactured by
ETIC TELECOM
13 Chemin du vieux chêne
38240 MEYLAN
FRANCE
TEL : + 33 4-76-04-20-05
FAX : + 33 4-76-04-20-01
E-mail : hotline@etictelecom.com
web : www.etictelecom.com
Page 2 DOC_DEV_RAS_User guide_A Machine Access Box RAS

CONTENT
CONTENT
PRODUCT OVERVIEW ................................................................................................................. 9
CERTIFICATE OF CONFORMITY ......................................................................................... 9
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION ............................................................................................. 10
DATA-SHEET ................................................................................................................... 14
PRODUCT OVERVIEW ...................................................................................................... 16
4.1 Main functions of the router RAS ........................................................................ 16
4.2 Router RAS organisation ................................................................................... 17
4.3 The M2Me_Connect connection .......................................................................... 18
4.4 Benefits of the M2Me_Connect service ............................................................... 19
USE CASES ..................................................................................................................... 20
5.1 Use case Nr 1 : The machine is connected to the factory network ........................ 22
5.2 Use case Nr 2 : The machine belongs to the factory network ............................... 24
5.3 Use case Nr3 : The machine is connected through a cellular network................... 25
5.4 Use case Nr4 : The machine is connected through a Wi-Fi network ...................... 26
5.5 Use case Nr 5 : Connecting the machine through the factory & a cellular ntwk ..... 27
5.6 Use case Nr 6 : Connecting the machine through the Wi-Fi & a cellular ntwk ........ 29
PRODUCT INSTALLATION ........................................................................................................ 31
PRODUCT DESCRIPTION ................................................................................................. 31
1.1 Dimensions ........................................................................................................ 31
1.2 Push-buttons ..................................................................................................... 32
1.3 Connectors ........................................................................................................ 32
1.4 RAS-E-100 router RAS ....................................................................................... 34
1.5 RAS-E or RAS-EW (Wi-Fi option) ......................................................................... 35
1.6 Cellular router RAS-EC ou RAS-ECW (Wi-Fi option) ............................................. 37
Machine Access Box RAS DOC_DEV_RAS_User guide_A Page 3

CONTENT
… PRODUCT INSTALLATION
MOUNTING THE PRODUCT ON A DIN RAIL ....................................................................... 39
COOLING ......................................................................................................................... 39
SUPPLY VOLTAGE ........................................................................................................... 39
RS232 ............................................................................................................................. 40
RS485 CONNECTION ....................................................................................................... 40
DIGITAL INPUT AND OUTPUT .......................................................................................... 40
CONNECTING THE ROUTER TO THE CELLULAR NETWORK ............................................... 41
8.1 Controls before installing the router .................................................................... 41
8.2 Cellular antenna ................................................................................................. 41
8.3 Déport de l’antenne ......................................................... Erreur ! Signet non défini.
8.4 Cellular service subscription ............................................................................... 42
8.5 Installing the SIM card........................................................................................ 42
8.6 Controlling the conformance of the connection ................................................... 43
PREPARING THE PRODUCT SET-UP ......................................................................................... 45
FIRST SET-UP ................................................................................................................. 45
PROTECTING THE ACCESS TO THE ADMINISTRATION WEB SERVER ............................... 46
SET-UP MODIFICATIONS WITH HTTPS OR THROUGH THE WAN INTERFACE .................... 46
RECOVERING THE FACTORY LAN IP ADDRESS ................................................................ 46
RETOUR À LA CONFIGURATION USINE ............................................................................ 46
SETTING-UP THE ROUTER WITH THE WIZARD.......................................................................... 47
USE CASE 1 SET-UP ........................................................................................................ 47
USE CASE NR 2 SET-UP .................................................................................................. 52
USE CASE 3 SET-UP ........................................................................................................ 54
USE CASE 4 SET-UP ........................................................................................................ 56
USE CASE 5 SET-UP ........................................................................................................ 58
USE CASE 6 SET-UP ........................................................................................................ 61
Page 4 DOC_DEV_RAS_User guide_A Machine Access Box RAS
CONTENT
ADVANCED SET-UP .................................................................................................................. 65
INTERNET ACCESS SET-UP ............................................................................................. 66
1.1 Overview ............................................................................................................ 66
1.2 Ethernet / WAN interface .................................................................................... 66
1.3 Cellular network interface ................................................................................... 68
1.3.1 SIM 1 or SIM 2 set-up ..................................................................................................... 68
1.3.2 Using the SIM cards 1 and 2 .......................................................................................... 69
1.3.3 Cellular connection control ............................................................................................ 70
1.4 Wi-Fi interface setup .......................................................................................... 71
LAN INTERFACE .............................................................................................................. 72
2.1 Overview ............................................................................................................ 72
2.2 Ethernet & IP menu ............................................................................................ 73
2.3 Wi-Fi access point set-up ................................................................................... 75
2.4 Device list set-up ............................................................................................... 76
2.5 DHCP server menu ............................................................................................. 77
M2ME_CONNECT CONNECTION SET-UP .......................................................................... 78
REMOTE ACCESS CONNECTION ...................................................................................... 79
4.1 Advantages of a remote access connection ........................................................ 79
4.2 Types of remote access connections .................................................................. 81
4.3 HTTPS connection and portal for smartphones, tablets or PCs ............................ 82
4.3.1 Overview .......................................................................................................................... 82
4.3.2 Set-up ............................................................................................................................... 83
4.3.3 Operation ......................................................................................................................... 83
4.4 OpenVPN remote user connection ...................................................................... 84
4.5 OpenVPN connection for smartphones ............................................................... 84
4.6 PPTP connection ................................................................................................ 85
4.7 L2TP / IPSec connection .................................................................................... 85
USER LIST ....................................................................................................................... 86
ASSIGNING RIGHTS TO REMOTE USERS ......................................................................... 88
IPSEC VPNS SET-UP ....................................................................................................... 89
7.1 Overview ............................................................................................................ 89
7.2 IPSec VPN connection set-up ............................................................................. 90
Machine Access Box RAS DOC_DEV_RAS_User guide_A Page 5

CONTENT
… ADVANCED SET-UP
OPENVPN TYPE VPN CONNECTION ................................................................................ 95
8.1 Overview ............................................................................................................ 95
8.1.1 Set-up principles ............................................................................................................. 97
8.2 OpenVPN server set-up ...................................................................................... 98
8.3 Setting up an outgoing connection ................................................................... 100
8.4 Setting up an ingoing VPN connection .............................................................. 102
IP ROUTING ................................................................................................................... 103
9.1 Basic routing function ...................................................................................... 103
9.2 Static routes .................................................................................................... 103
9.3 RIP protocol ..................................................................................................... 105
NETWORK ADDRESS TRANSLATION (NAT) .................................................................... 106
PORT FORWARDING ...................................................................................................... 106
11.1 Overview .......................................................................................................... 106
11.2 Set-up .............................................................................................................. 107
ADVANCED NAT ............................................................................................................ 108
12.1 Overview .......................................................................................................... 108
12.2 Set-up .............................................................................................................. 109
DYNDNS OR NOIP SET-UP ............................................................................................. 110
13.1 Overview .......................................................................................................... 110
13.2 Set-up .............................................................................................................. 110
FIREWALL SET-UP ........................................................................................................ 112
14.1 Overview .......................................................................................................... 112
14.2 Main filter ........................................................................................................ 113
14.2.1 Main filter prganisation .............................................................................................. 113
Page 6 DOC_DEV_RAS_User guide_A Machine Access Box RAS

CONTENT
… ADVANCED SET-UP
SERIAL TO IP GATEWAY CONFIGURATION ..................................................................... 115
15.1 Overview .......................................................................................................... 115
15.2 Modbus gateway .............................................................................................. 117
15.2.1 Glossary....................................................................................................................... 117
15.2.2 Selecting a Modbus client or a Modbus server gateway ........................................ 117
15.2.3 Modbus server gateway ............................................................................................. 118
15.2.4 Modbus client gateway .............................................................................................. 119
15.3 RAW TCP gateway ............................................................................................ 120
15.3.1 Raw client gateway .................................................................................................... 120
15.3.2 Raw server gateway ................................................................................................... 121
15.4 RAW UDP gateway ........................................................................................... 122
15.4.1 Overview ...................................................................................................................... 122
15.4.2 Set-up .......................................................................................................................... 122
USB GATEWAY .............................................................................................................. 123
16.1 Overview .......................................................................................................... 123
16.2 Set-up .............................................................................................................. 123
ALARM EMAIL OR A SMS .............................................................................................. 124
SNMP TRAPS ................................................................................................................ 125
ADDING A CERTIFICATE INTO THE ROUTER ................................................................... 125
MAINTENANCE ...................................................................................................................... 127
DIAGNOSTIC MENU ....................................................................................................... 127
1.1 Logs ................................................................................................................. 127
1.2 Network status ................................................................................................. 128
1.3 Serial gateways status ..................................................................................... 129
1.4 « Ping » tool ..................................................................................................... 129
1.5 « Wi-Fi » scanner tool ....................................................................................... 129
SAVING OR RESTORING A SET OF PARAMETERS .......................................................... 130
FIRMWARE UPDATE ...................................................................................................... 131
Machine Access Box RAS DOC_DEV_RAS_User guide_A Page 7

PRODUCT OVERVIEW
Standard
Title
EN301489-1
Electromagnetic compatibility and Radio spectrum Matters :
Part 1 : General requirements
EN301489-7
Electromagnetic compatibility and Radio spectrum Matters :
Part 7 : Specific conditions for mobile and portable radio and ancillary
equipment of digital cellular radio
EN61000-6-2
Ed. 2001
Immunity :
EN60100-4-2 Electrostatic Discharge
EN60100-4-3 Radiated Immunity
EN60100-4-4 EFT/Burst Immunity
EN60100-4-5 Surge Immunity
EN60100-4-6 Conducted Immunity
EN61000-6-4
Ed 2001
Emission :
EN55022 radiated and conducted emission
EN60950
Security
EN50385
Human exposure to radio frequency fields exposure
EN301511
Global System for mobile communication
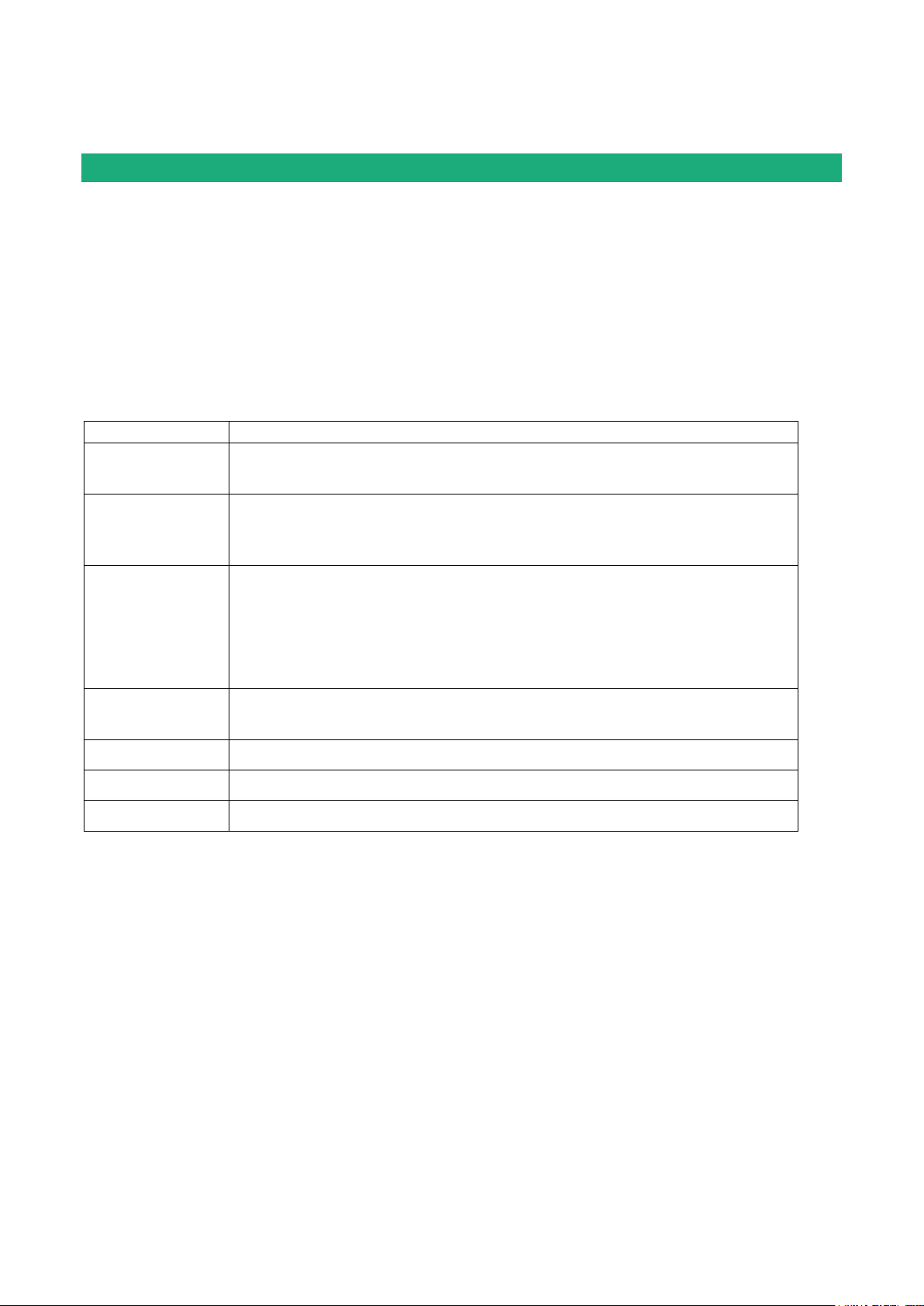
Certificate of conformity
The manufacturer, ETIC Telecom – 13 chemin du vieux chêne – 38240 Meylan – France, Hereby declares
that the listed products
Type of device: Router RAS family described in the next pages
Conform to the Council Directive 1999/5/EC related to radio and telecommunication terminal equipments.
The harmonized standards to which the equipment complies are :
Gilles Bénas
Quality manager
5th January 2015
Machine Access Box RAS DOC_DEV_RAS_User guide_A Page 9
PRODUCT OVERVIEW
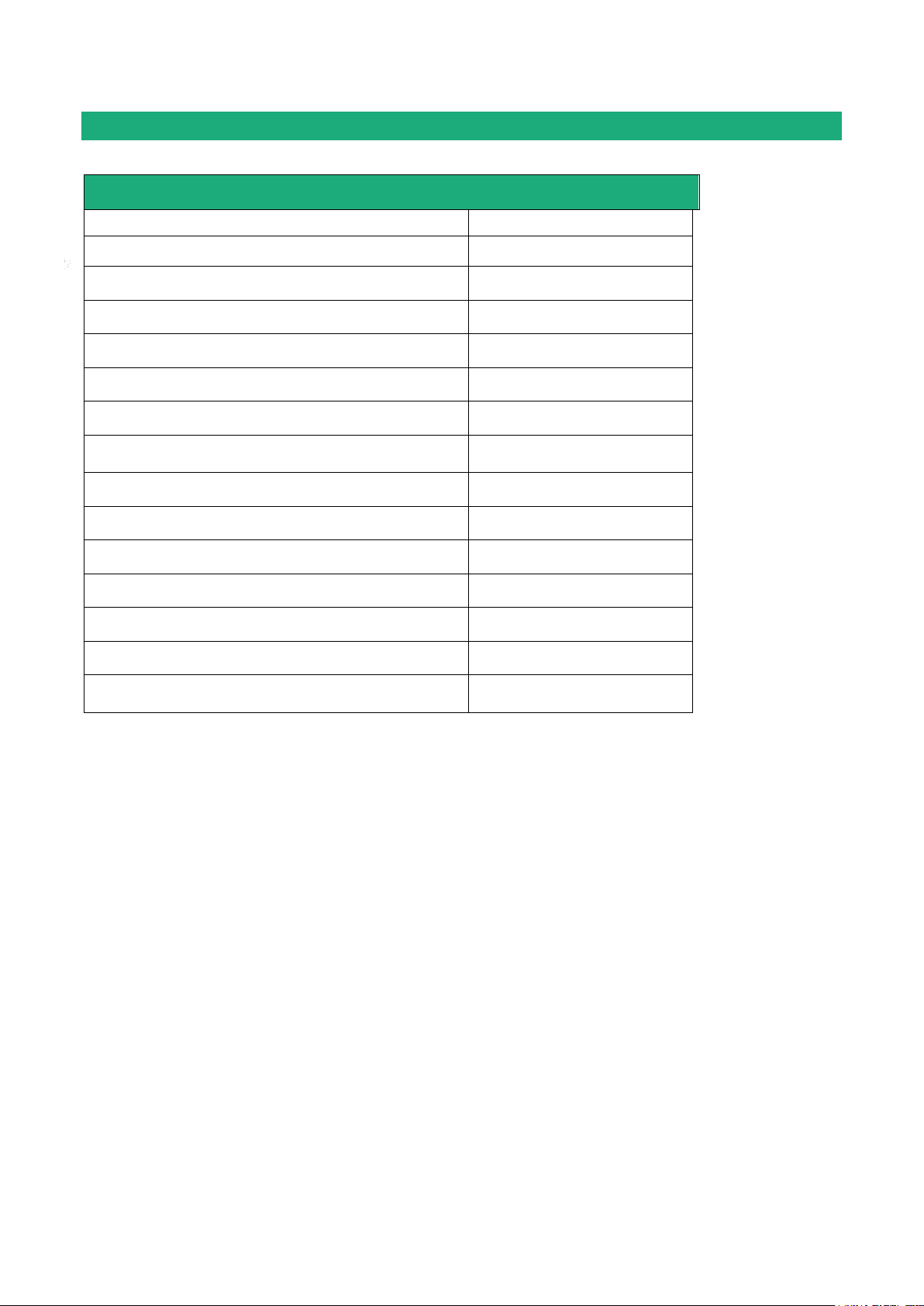
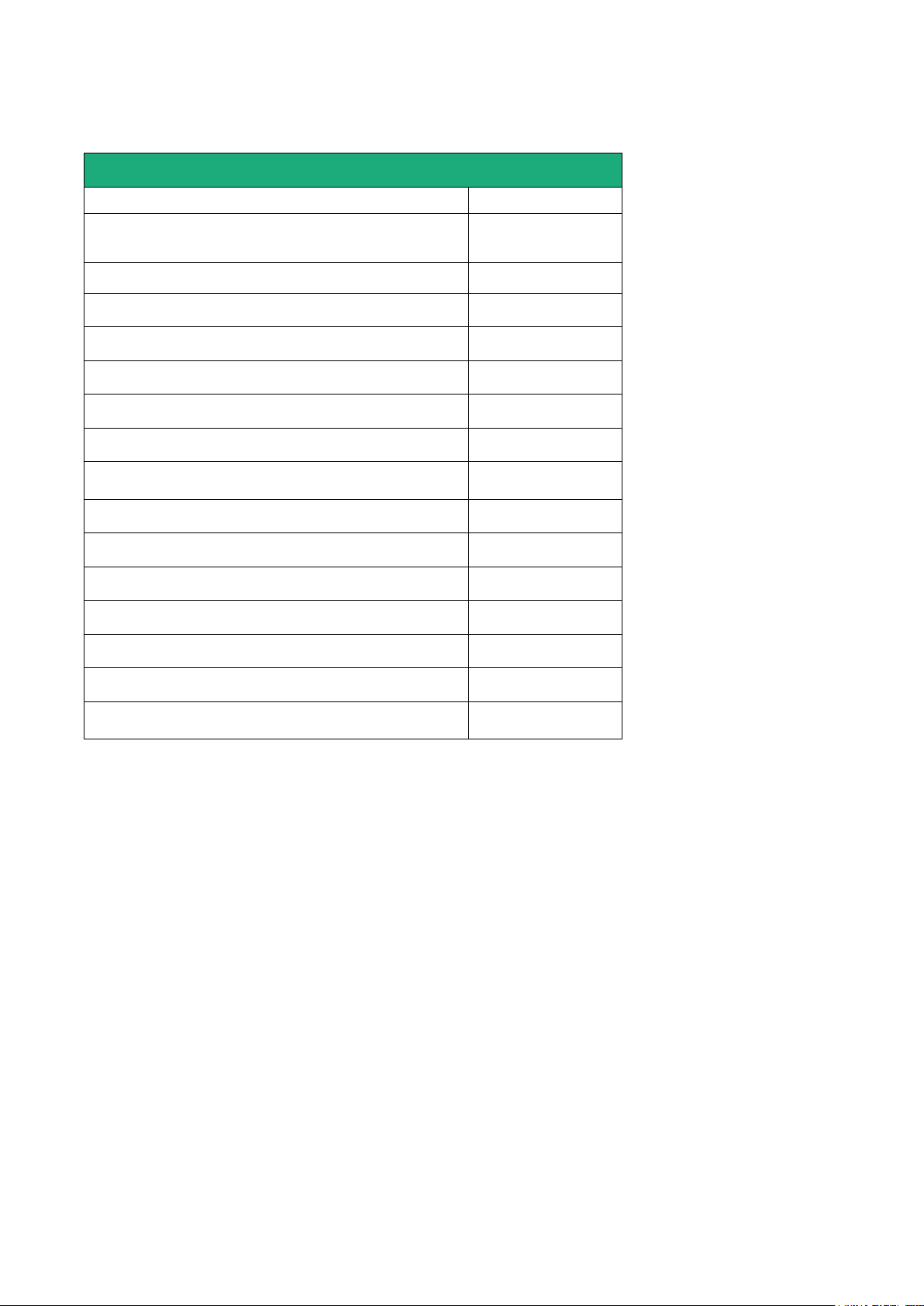
Router RAS with Ethernet interfaces
RAS-E-
100
400
220
Ethernet interfaces to Internet
1 1 1
M2Me ready
• • •
User list
• • •
Remote users firewall
• • •
Firewall SPI
• • •
VPN IPSEC & OpenVPN
• • •
Serial gateway
(Raw TCP et UDP, Telnet, Modbus, Unitelway)
- - •
Ethernet 10 / 100 BT (LAN)
1
4
2
RS232 - -
1
RS485 - -
1
USB 1 1
1
Digital input (emails – SMS)
1 1 1
HTTPS / HTML /SSH configuration
• • •
Advanced IP router functions
NAT, port forwarding, SNMP, DHCP
• • •
Product identification
Page 10 DOC_DEV_RAS_User guide_A Machine Access Box RAS
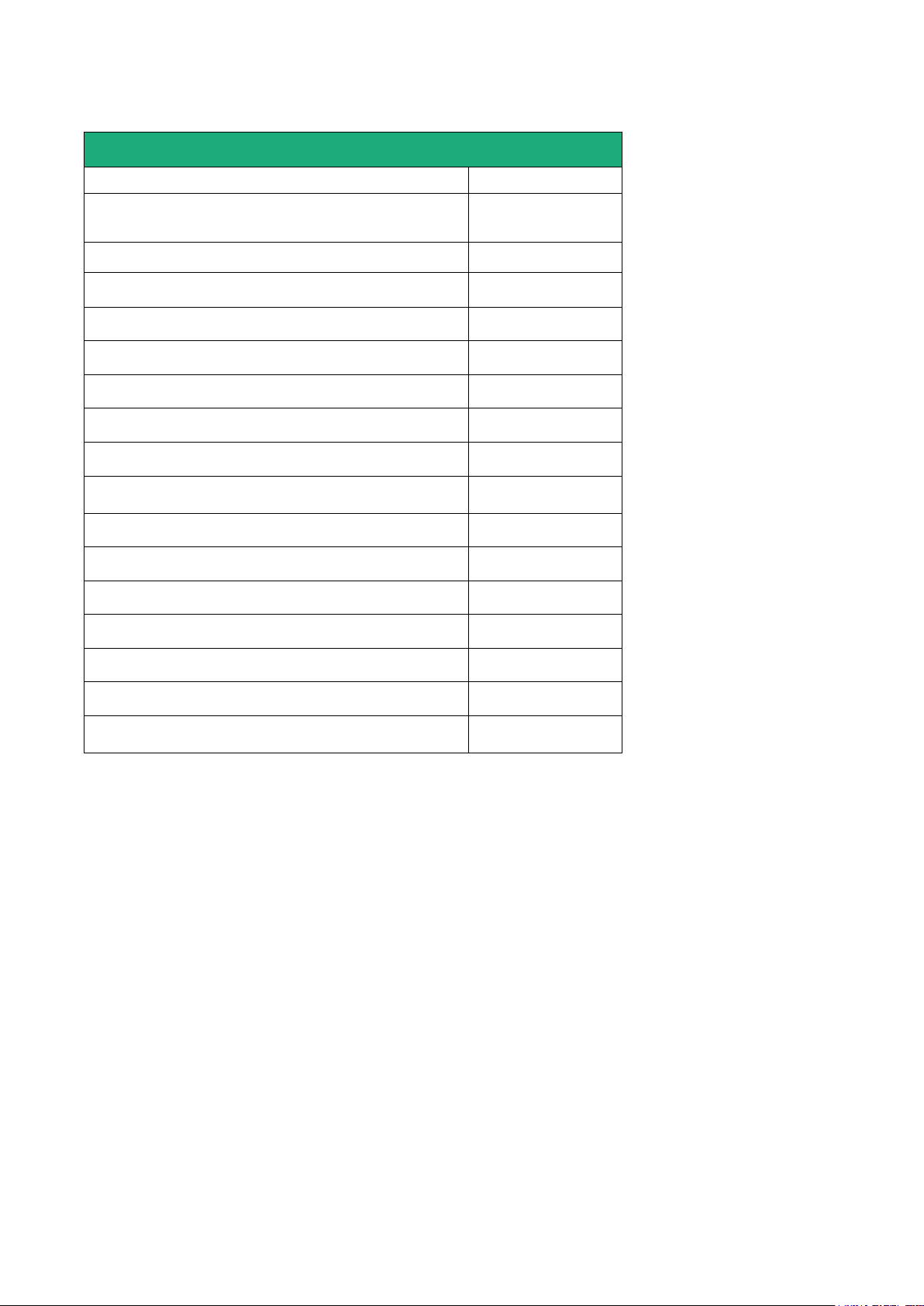
PRODUCT OVERVIEW
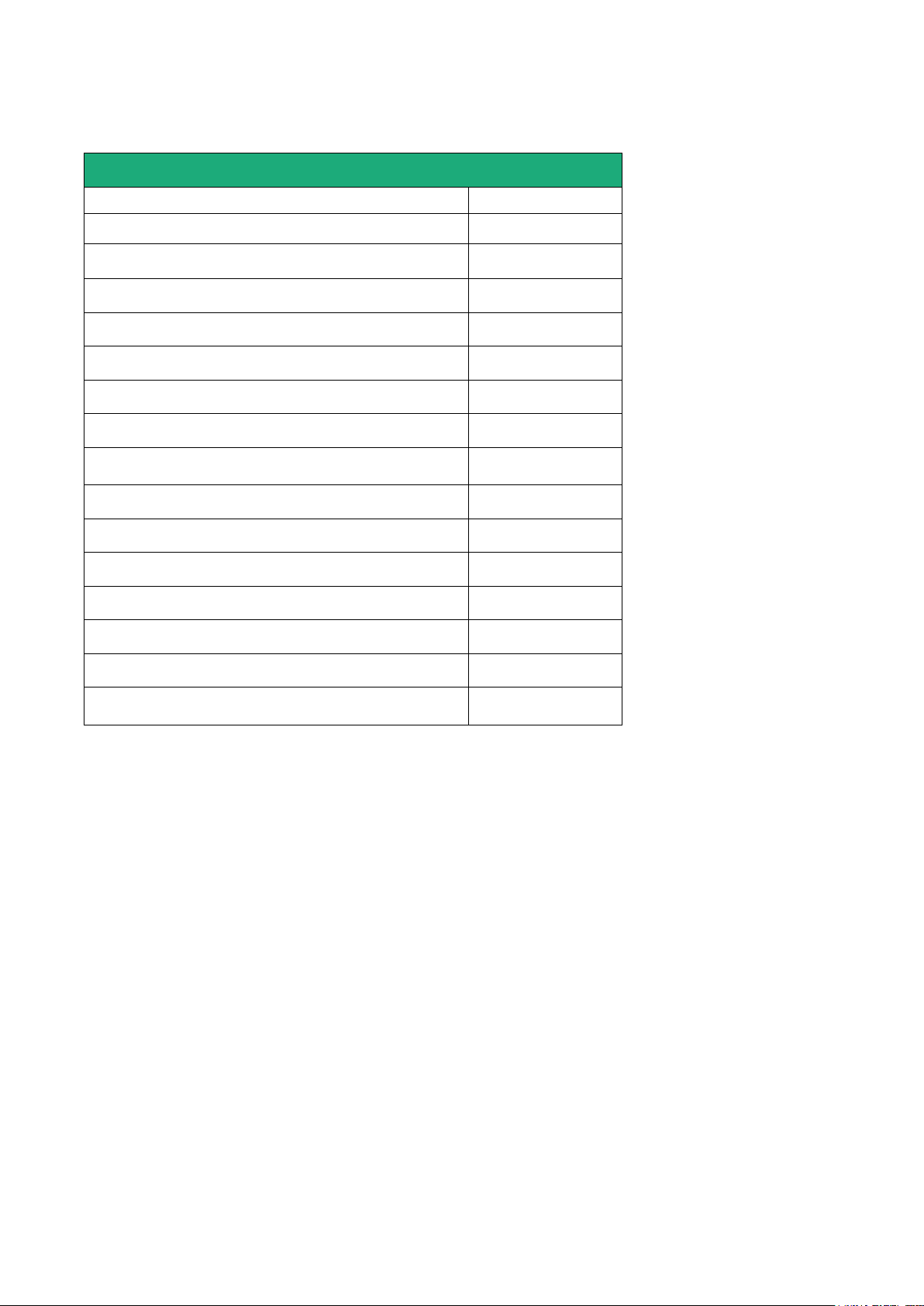
Router RAS with Ethernet & Wi-Fi interfaces
RAS-EW-
400
220
Ethernet interfaces to Internet
1
1
Wi-Fi interface (Access point & client)
•
•
M2Me ready
•
•
User list
•
•
Remote users firewall
•
•
Firewall SPI
•
•
VPN IPSEC & OpenVPN
•
•
Serial gateway
(Raw TCP et UDP, Telnet, Modbus, Unitelway)
-
•
Ethernet 10 / 100 BT (LAN)
4
2
RS232 - 1
RS485
-
1
USB
1
1
Digital input (emails – SMS)
1
1
HTTPS / HTML /SSH configuration
•
•
Advanced IP router functions
NAT, port forwarding, SNMP, DHCP
•
•
Machine Access Box RAS DOC_DEV_RAS_User guide_A Page 11
PRODUCT OVERVIEW
Router RAS with cellular & Ethernet interfaces
RAS-EC-
400
220
Cellular ntwk router LTE 4G - UMTS 3G -GPRS-EDGE
UMTS 3G -GPRS-EDGE : XY = HG
LTE 4G - UMTS 3G -GPRS-EDGE XY =LE
•
•
Ethernet interfaces to Internet
1
1
M2Me ready
•
•
User list
•
•
Remote users firewall
•
•
Firewall SPI
•
•
VPN IPSEC & OpenVPN
•
•
Serial gateway
(Raw TCP et UDP, Telnet, Modbus, Unitelway)
-
•
Ethernet 10 / 100 BT (LAN)
4
2
RS232 - 1
RS485
-
1
USB
1
1
Digital input (emails – SMS)
1
1
HTTPS / HTML /SSH configuration
•
•
Advanced IP router functions
NAT, port forwarding, SNMP, DHCP
•
•
Page 12 DOC_DEV_RAS_User guide_A Machine Access Box RAS
PRODUCT OVERVIEW
Router RAS with cellular, Wi-Fi & Ethernet interfaces
RAS-ECW-
400
220
Cellular ntwk router LTE 4G - UMTS 3G -GPRS-EDGE
UMTS 3G -GPRS-EDGE : XY = HG
LTE 4G - UMTS 3G -GPRS-EDGE XY =LE
•
•
Ethernet interfaces to Internet
1
1
Wi-Fi interface (Access point & client)
•
•
M2Me ready
•
•
User list
•
•
Remote users firewall
•
•
Firewall SPI
•
•
VPN IPSEC & OpenVPN
•
•
Serial gateway
(Raw TCP et UDP, Telnet, Modbus, Unitelway)
-
•
Ethernet 10 / 100 BT (LAN)
4
2
RS232 - 1
RS485
-
1
USB
1
1
Digital input (emails – SMS)
1
1
HTTPS / HTML /SSH configuration
•
•
Advanced IP router functions
NAT, port forwarding, SNMP, DHCP
•
•
Machine Access Box RAS DOC_DEV_RAS_User guide_A Page 13

PRODUCT OVERVIEW
General characteristics
Dimensions
137 x 48 x 116 mm (h, l, p)
Electrical safety
EN 60950- UL 1950
EMC
ESD : EN61000-4-2 : Discharge 6 KV
RF field : EN61000-4-3 : 10V/m < 2 GHz
Fast transient : EN61000-4-4
Surge voltage : EN61000-4-5 : 4KV line / earth
RoHS
2002/95/CE (RoHS)
Supply voltage
RAS-3G-1220 : 10 to 30 VDC - 125 mA / 24 VDC
RAS-3G-1201 : 10 to 60 VDC - 125 mA / 24 VDC
RAS-3G-1230 : 10 to 60 VDC - 125 mA / 24 VDC
RAS-3G-1400 : 10 to 60 VDC - 210mA / 24 VDC
Operating T°
-20°C / + 60°C Humidity 5 – 95 %
Cellular network
Type
4G / 3G+ / GPRS-EDGE
RF connector
SMA female
Models
LE
LS
LA
HG
LTE 4G
Europe
USA
Asia
-
UMTS 3G+
Yes (*1)
Yes (*1)
Yes (*1)
Yes (*2)
GPRS-EDGE
Yes (*3)
Yes (*3)
Yes (*3)
Yes (*3)
Wi-Fi
Type
2.4 et 5 GHz
RF connector
R-SMA female
Wi-Fi transmission
802.11 a/b/g/n
Data-sheet
(*1) 850 / 900 / 1900 / 2100 MHz
(*2) 850 / 900 / 1700 / 1900 / 2100 MHz
(*3) 850 / 900 / 1800 / 1900 MHz
Page 14 DOC_DEV_RAS_User guide_A Machine Access Box RAS

PRODUCT OVERVIEW
Security
VPN
Client or server IPSEC or TLS/SSL
Encryption AES256 3DES
Certificate X509 or preshared key
25 VPNs maximum of the same type (TLS or IPSec)
Firewall
Stateful packet inspection (50 rules)
Source & destination IP address & port number filter
Logs
Date and time stamped logs
Remote access server (RAS)
User list
25 users
Connection
VPN PPTP / L2TP-IPSec / TLS Open VPN
Login & password
Certificate X509
M2Me (*)
VPN Compliant with the M2Me_Secure VPN client
Compliant with the M2Me_Connect mediation service
Alarms
3 inputs : emails
Asynchronous serial interface
Data rate
1200 to 115200 kb/s parity N / E / O
Gateway
Raw client & server - Modbus master & slave
Multicast - Telnet - Unitelway
USB
1 USB host port
PPP client over the usb interface
IP router
Ethernet
10/100 BT – 2 or 4 switched ports
IP router
Remote connections - static routes – RIP V2
IP address
translation
Source IP @ translation (NAT)
Destination IP @ translation (DNAT)
Port translation (Port forwarding)
DNS
Domain name
IP address
assignment
Fixed IP @ or DHCP client or DHCP server
Machine Access Box RAS DOC_DEV_RAS_User guide_A Page 15
PRODUCT OVERVIEW
Product overview
4.1 Main functions of the router RAS
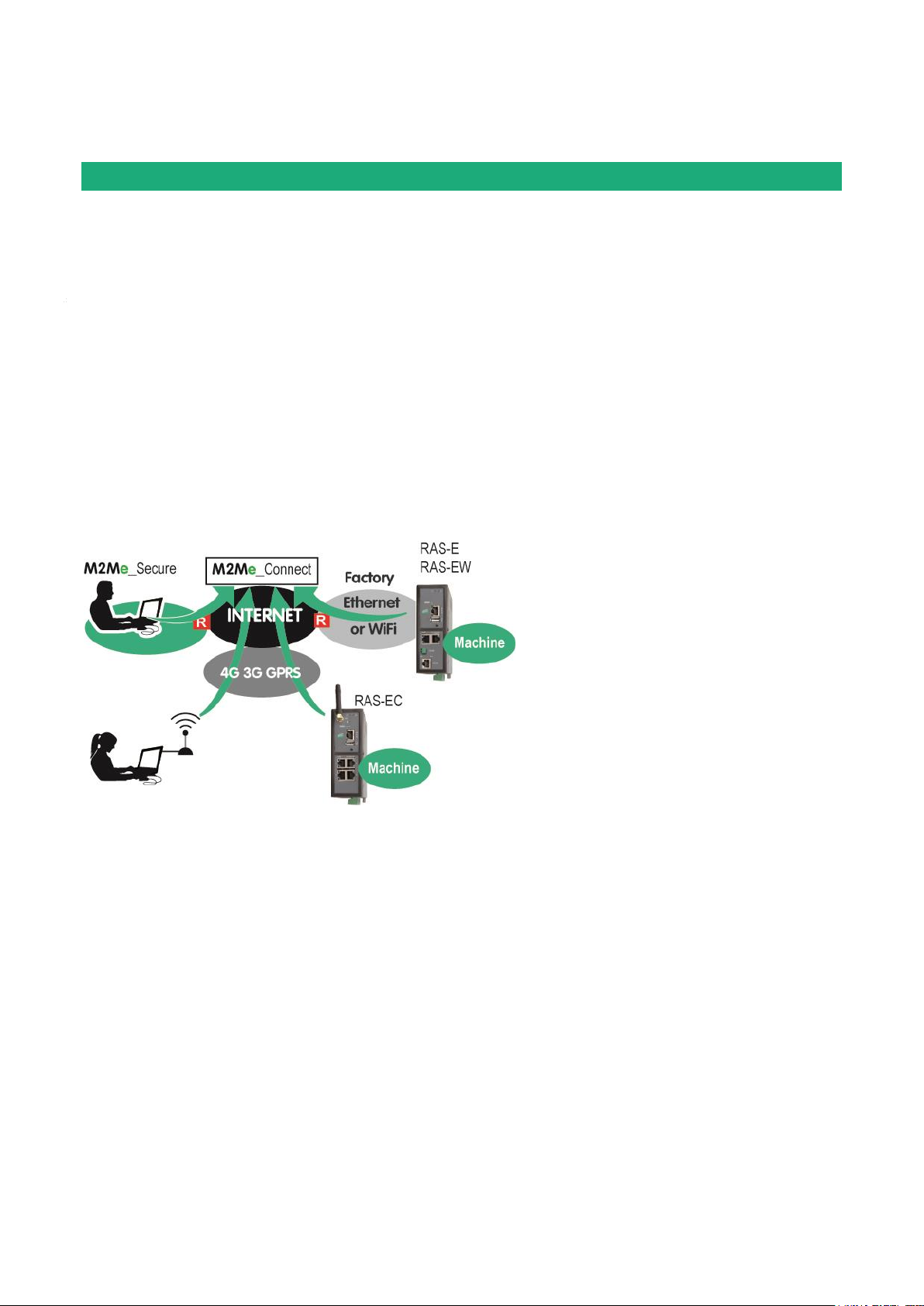
Remote maintenance of machines using the M2Me_Connect service
The RAS family allows to connect easily and safely a machine to a remote PC, through the M2Me_Connect
Internet cloud service, for operation like remote maintenance.
When the remote PC is connected, the remote user can exchange any kind of data with each device of the
machine network as if his PC was directly connected to the machine network.
Ethernet or serial devices
The machine can consist of one or several devices connected through an Ethernet machine network or
connected through a serial RS232-RS485 interface.
The router RAS can be connected to the Internet through a cellular network, a Wi-Fi network or a factory
network
An Up-to-date IP router for particular situations
When using the Expert mode set-up, the router RAS becomes a powerful IP router-RAS-firewall for industrial
IP networks applications.
Page 16 DOC_DEV_RAS_User guide_A Machine Access Box RAS
PRODUCT OVERVIEW
WAN interfaces
RAS-E
RAS-EW
RAS-EC
RAS-ECW
Ethernet
Wi-Fi
Cellular
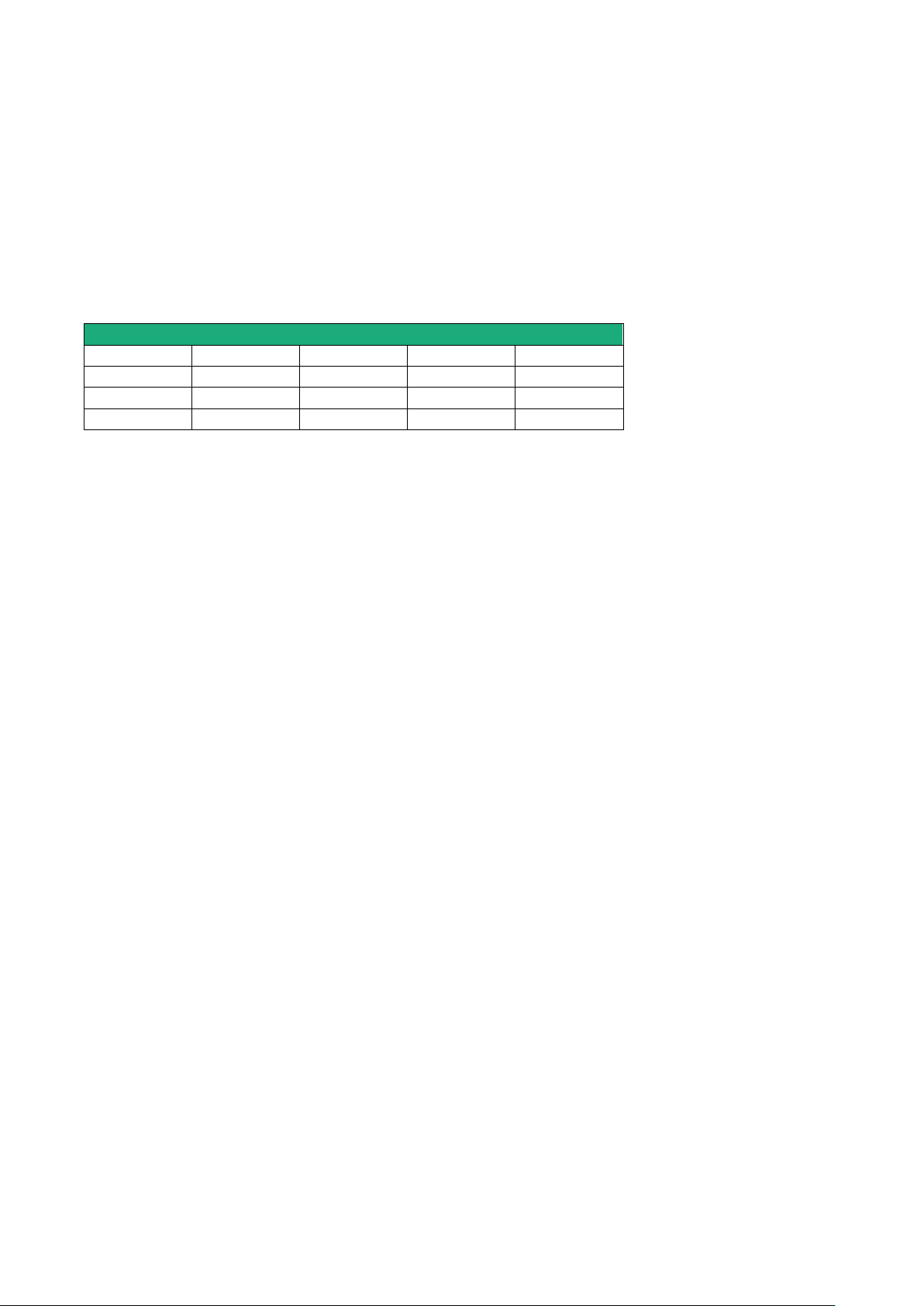
4.2 Router RAS organisation
The router RAS connects to the devices network (called machine) and on the other hand to the Internet
The router RAS provides two IP interfaces : The WAN interface to reach the Internet and the LAN interface to
connect the machine.
WAN interface :
Depending on the model, the router RAS provides the following interfaces to reach the Internet :
The network connected to the WAN interface is called the WAN network or factory network.
LAN interface :
Depending on the model, the router RAS provides 1 to 4 switched Ethernet ports to connect the devices of
the machine.
That network is called the machine network.
1 serial RS232 and 1 serial RS485 interfaces are provided optionally.
Firewall
The firewall filters data between the WAN interface or any VPN interface on one hand, and the LAN interface
on the other hand.
The firewall filters source and destination IP addresses, but also remote users according to their identity.
Machine Access Box RAS DOC_DEV_RAS_User guide_A Page 17

PRODUCT OVERVIEW
4.3 The M2Me_Connect connection
Connecting a remote PC to a machine in any situation
M2Me Connect service is an ideal solution when a « machine », made of a set of devices connected to the
same LAN, is located in a private network (such as a Factory network).
Let’s take the example of a « machine » made of a set of connected devices and connected to the Factory
Network via a RAS-E.
Assuming that an expert is willing to remotely have access to the machine for breakdown diagnosis,
technical data acquisition, Web page display, file or program refreshment, M2Me Connect service enables
the remote operator to have access to the machine even if the machine does not have any public IP address.
Operation
When it is powered on or if the digital input is enabled, the router RAS settles a secured VPN connection
onto the M2Me Connect cloud service.
The remote PC is authenticated by the M2Me Cloud service.
Assuming that the router RAS provides two WAN connections (Cellular and Ethernet as an example), it
settles the best connection (Through the Ethernet network if possible) to the M2Me cloud service.
On the other hand, the remote user launches its M2Me secure software and settles a secured VPN
connection to the M2Me Cloud.
The directory offered by M2Me_Secure is helping the user to point the remote machine onto which he wants
to be connected.
The router RAS verifies thenafter that the remote user is allowed to be connected by checking its login &
password and as an option the certificate of the remote PC.
The router RAS grants to the remote user access rights according to its identity.
In order to warrant the level of security requested by industrial application, connection from PC to RAS is
fully encrypted and cannot be recovered even in case of intrusion onto the M2Me Connect cloud service.
Page 18 DOC_DEV_RAS_User guide_A Machine Access Box RAS

PRODUCT OVERVIEW
4.4 Benefits of the M2Me_Connect service
Outgoing connection
M2Me connection onto the Internet is powered from the RAS. This non intrusive solution is better admitted
than an ingoing connection from the Internet onto the Machine.
Private & dynamic IP address
The machine connected into a factory network or connected to the Internet via a cellular network does not
have a public IP address. M2Me solution does not require a public IP address to settle a connection onto the
machine.
Access to each device of the machine
M2Me teleport your PC onto the machine network enabling you to have access to each device of the
machine as if you were in front of the machine.
Machine with Ethernet or serial connection
The family of RAS enables you to set up a connection to any type of PLC offering an Ethernet or a serial
connectivity.
Simple configuration of router RAS
Html configuration Server is delivered with a Wizard which gives an intuitive way of configuring the device.
Simple Operation
M2Me Secure software offers e set of directories for the remote machines. One click is enough to be
connected.
Security of customer network (Factory or WAN network)
Router RAS enables the remote operator to have access only to the machine network protecting the factory
network from any intrusion.
Machine & Device Access protection
A remote user can access to the machine if and only if its identification (login & password) has been
preregistered in the RAS router
An extra security option is offered. RAS can also demand the certificate installed in the PC of the remote
user.
The RAS can also give restricted access to the machine network giving access only to certain devices of the
machine and not to all.
Internet & Security
The flow of information passing through the M2Me connection is fully encrypted and requires authentication
to the M2Me server of both the PC of the remote user and the RAS router. A third party cannot consequently
have access to the machine preserving the integrity of the industrial process to be remote maintained.
Machine Access Box RAS DOC_DEV_RAS_User guide_A Page 19

PRODUCT OVERVIEW
Use cases
There are different ways to connect the router RAS to the Internet and to the machine depending on the
situation which is encountered and also on the router RAS model.
We describe hereafter six typical situations.
Page 20 DOC_DEV_RAS_User guide_A Machine Access Box RAS
PRODUCT OVERVIEW
Use case
Internet
access
Internet
1
RAS-E
RAS-EW
RAS-EC
RAS-ECW
Factory
network
The machine is
connected to the
factory network
through the router RAS.
2
RAS-E
RAS-EW
RAS-EC
RAS-ECW
Factory
network
The machine belongs to
the factory network.
3
RAS-EC
RAS-ECW
Cellular
network
The machine is
connected to the
Internet through a
cellular network.
4
RAS-EW
RAS-ECW
Wi-Fi
The machine is
connected to the
Internet through a Wi-Fi
network.
5
RAS-EC
RAS-ECW
Factory
network
+ cellular
network
The machine is
connected to the
Internet through the
factory network and, if
it is not available,
through a cellular
network.
6
RAS-ECW
Wi-Fi
+ cellular
network
The machine is
connected to the
Internet through the WiFi network and, if it is
not available, through a
cellular network.
Machine Access Box RAS DOC_DEV_RAS_User guide_A Page 21
PRODUCT OVERVIEW
Models
Way to the Internet
Router RAS interface to
the Internet
Machine interface
All models
Factory network
Ethernet WAN
Ethernet LAN 1 to 4
Serial interface
Examples :
Remote PC
network
Factory
network
Machine
network
OK
192.168.10.0
192.168.1.0
192.168.12.0
OK
192.168.10.0
192.168.10.0
192.168.12.0
The IP domain of the machine ntwk and of the
factory ntwk are the same.
The machine IP domain must be modified or the
RAS must be used according to the use case 2
192.168.10.0
192.168.1.0
192.168.1.0
The IP domain of the machine ntwk and of the
remote PC ntwk are the same.
The machine IP domain must be modified or the
address translation option must be selected (see
the wizard menu).
192.168.10.0
192.168.1.0
192.168.10.0
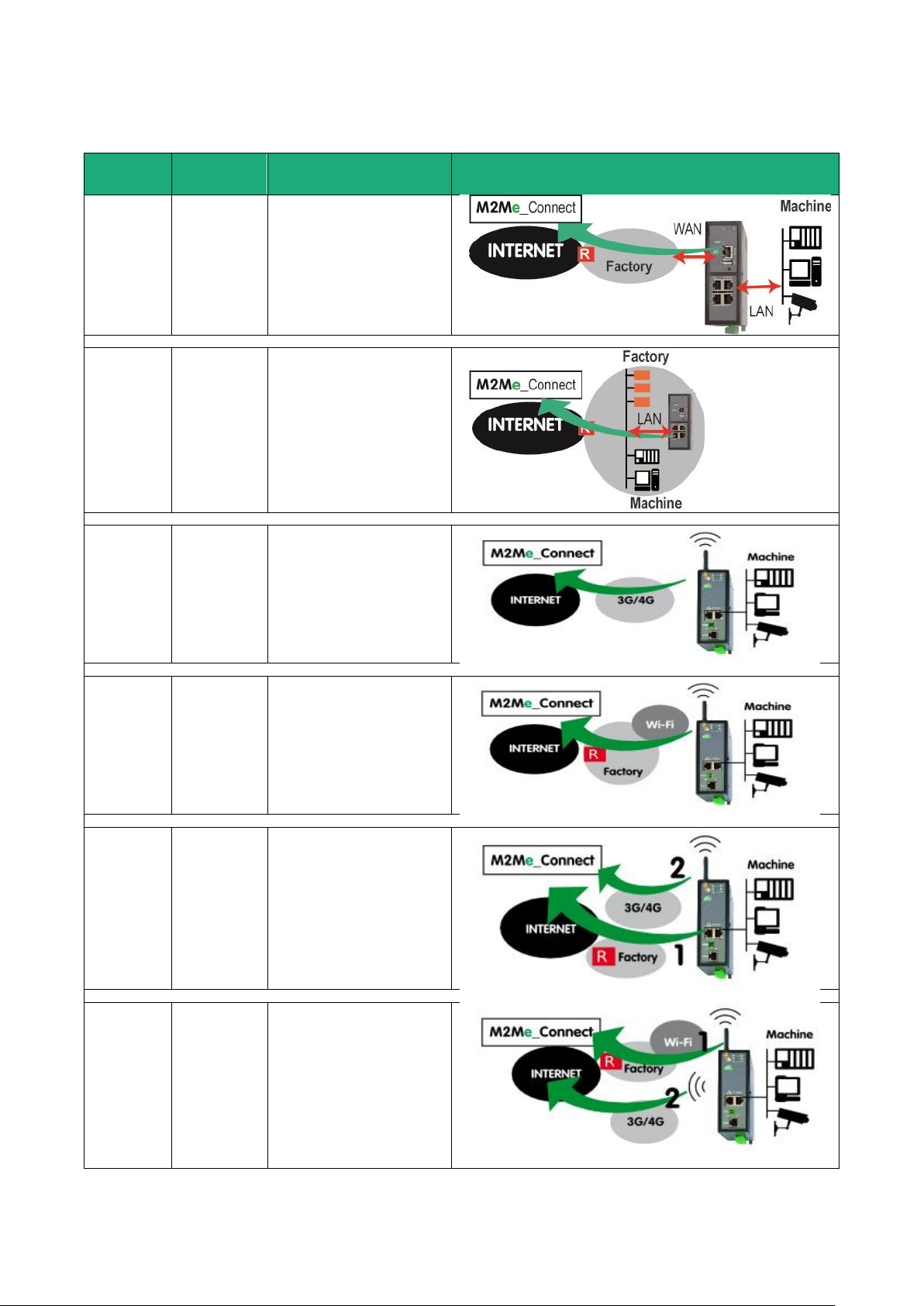
5.1 Use case 1 : The machine is connected to the factory network
Description
The machine is separated from the factory network by the router RAS. The Internet is reached through the
factory network.
Machine IP address
Rule 1 : The IP domain of the machine network and the IP domain of the factory network must be different.
If both domains are identical, the IP domain of the machine must be modified or he RAS must be used
according to the Use case Nr 2 described below.
Rule 2 : The IP domain of the machine network and the IP domain of the remote PC must be different.
If both IP domains are identical, the IP domain of the machine must be modified or the machine network
translation option must be selected.
Page 22 DOC_DEV_RAS_User guide_A Machine Access Box RAS

PRODUCT OVERVIEW
Available functions
Connecting the remote PC to each device of the machine network through M2Me
Individual rights for each the remote user
Communication initiated by devices belonging to the machine network towards
devices belonging to the factory network
Communication initiated by devices belonging to the factory network towards
devices belonging to the machine network
Enabled by creating
a firewall rule
Setting an additional VPN towards a server
Sending an email (all models) or a SMS (RAS-EC or RAS-ECW)
Security
The factory network and the machine network are separated by the router RAS. This is why the firewall can
operate to filter exchanges between these two networks; the machine is protected from unexpected
exchanges initiated by any device connected to the factory network. The firewall can be configured to
authorise particular exchanges.
Machine Access Box RAS DOC_DEV_RAS_User guide_A Page 23
PRODUCT OVERVIEW
Models
Way to the Internet
Router RAS interface to
the Internet
Machine interface
All models
Factory network
Ethernet LAN ports
Ethernet LAN 1 to 4
Serial interface
Available functions
Connecting the remote PC to each device of the machine network through M2Me
Individual rights for each the remote user
Not filtered communication between the devices of the machine and devices of
the factory network
Setting an additional VPN towards a server
Sending an email (all models) or a SMS (RAS-EC or RAS-ECW)
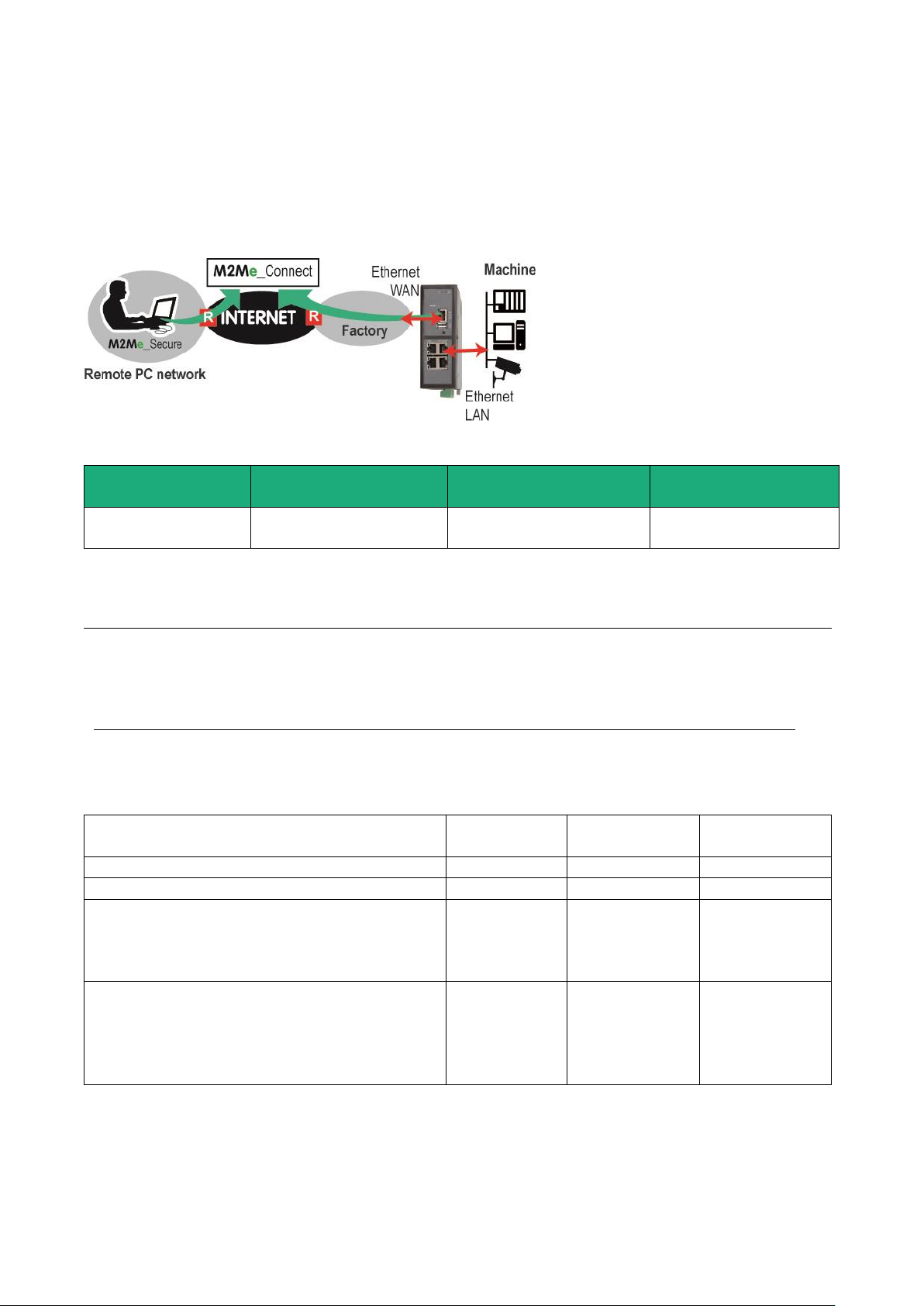
5.2 Use case 2 : The machine belongs to the factory network
Description
The devices of the machine belong to the factory network.
The Internet is reached through the existing access.
In that case, the router RAS has to be connected to the factory network with its LAN Ethernet port.
Machine IP addresses
Rule : The IP domain of the machine network and the IP domain of the remote PC network must be
different.
If both IP domains are identical, it is possible to select the machine network translation option (see the
wizard configuration menu for detailed information); the IP domain of the devices of the machine is virtually
modified for the remote PC.
Security
The remote users can access only to the authorized devices of the unique machine and factory network.
But, because all the devices are connected to the same network, exchanges cannot be filtered on the local
network.
Page 24 DOC_DEV_RAS_User guide_A Machine Access Box RAS
PRODUCT OVERVIEW
Models
Way to the Internet
Machine interface
RAS-EC
RAS-ECW
Cellular network
Ethernet LAN 1 to 4
Serial interface
Available functions
Connecting the remote PC to each device of the machine network through M2Me
Individual rights for each the remote user
Setting an additional VPN towards a server
Sending an email (all models) or a SMS (RAS-EC or RAS-ECW)
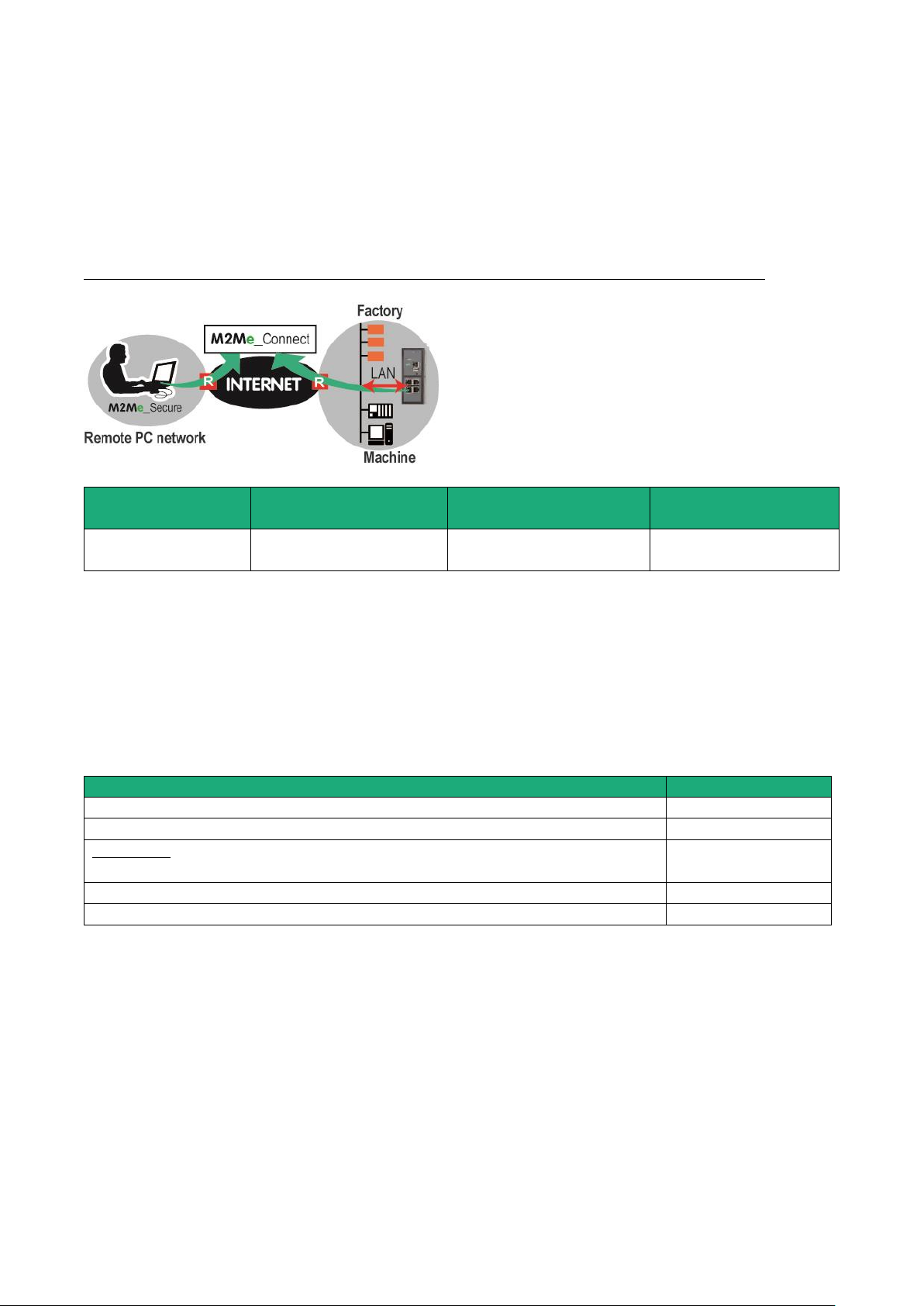
5.3 Use case 3 : The machine is connected through a cellular network
Description
The Internet is reached through a cellular network.
Machine IP address
Rule : The IP domain of the machine network and the IP domain of the remote PC must be different.
If both IP domains are identical, the IP domain of the machine must be modified or the machine network
translation option must be selected (see the wizard configuration menu for detailed information).
Security
The remote user can only communicate with the authorised devices.
The availability and the quality of a cellular network is sometimes lower than a company network internet
access. It is important to check this situation will not provoke any kind of danger for people on the machine
site or of any other kind.
Machine Access Box RAS DOC_DEV_RAS_User guide_A Page 25
PRODUCT OVERVIEW
Models
Way to the Internet
Machine interface
RAS-EC
RAS-ECW
Cellular network
Ethernet LAN 1 to 4
Serial interface
Available functions
Connecting the remote PC to each device of the machine network through M2Me
Individual rights for each the remote user
Setting an additional VPN towards a server
Sending an email (RAS-EW) or a SMS (RAS-ECW)
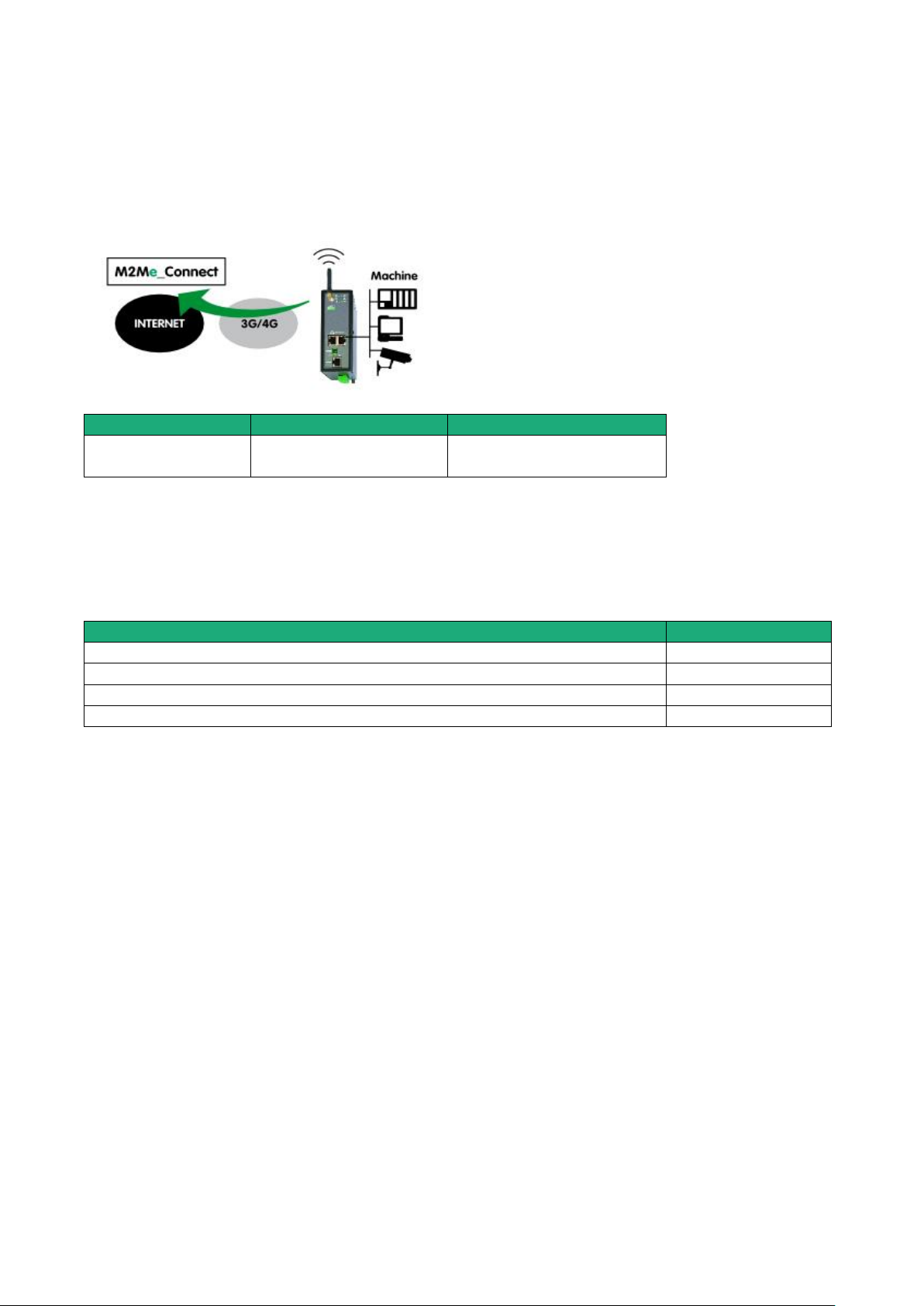
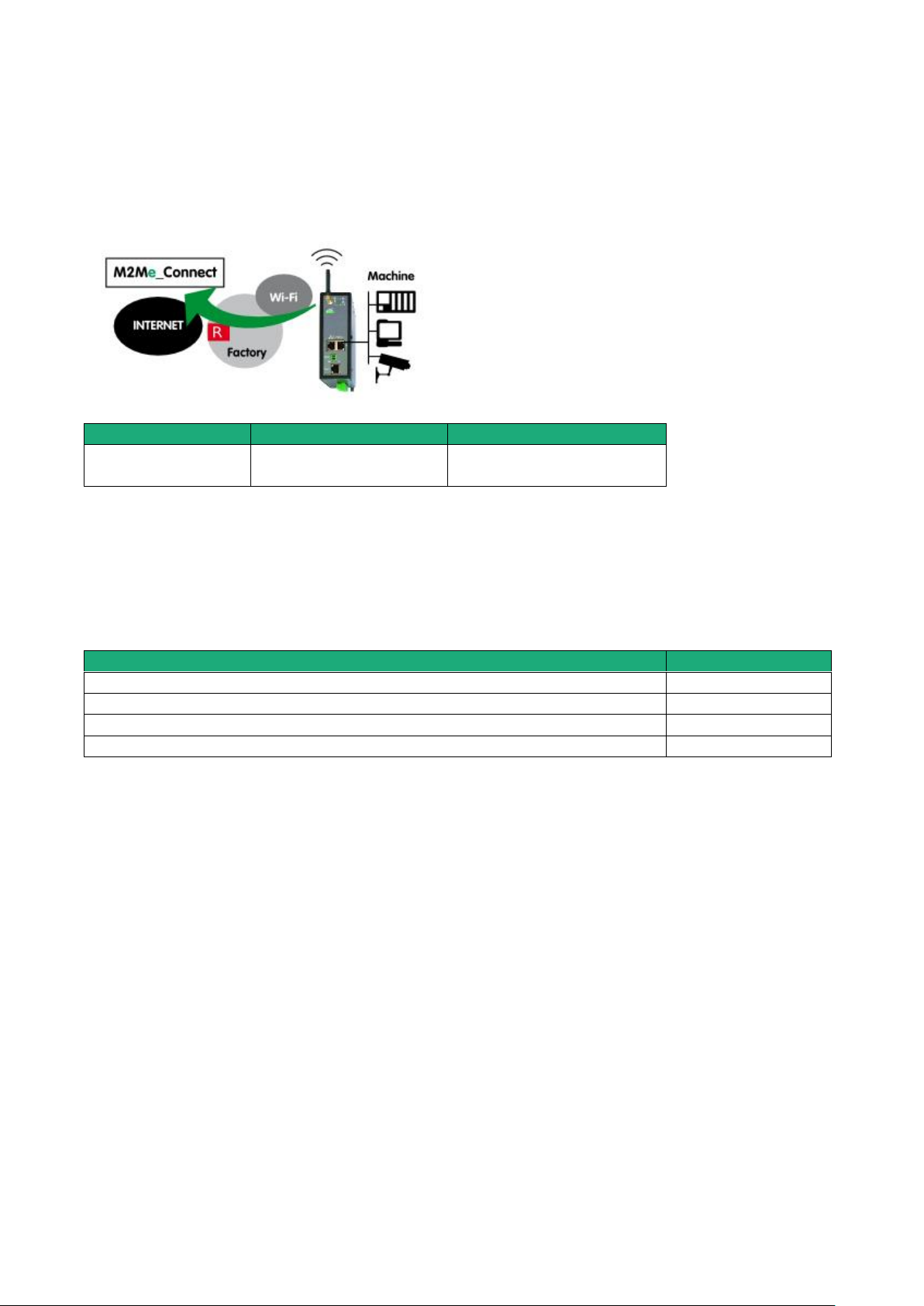
5.4 Use case 4 : The machine is connected through a Wi-Fi network
Description
The Internet is reached through a Wi-Fi network.
Machine IP address
Rule : The IP domain of the machine network and the IP domain of the remote PC must be different.
If both IP domains are identical, the IP domain of the machine must be modified or the machine network
translation option must be selected (see the wizard configuration menu for detailed information).
Security
The remote user can only communicate with the authorized devices.
The availability and the quality of a Wi-Fi network is sometimes lower than a company network. It is
important to check this situation will not provoke any kind of danger.
Page 26 DOC_DEV_RAS_User guide_A Machine Access Box RAS
PRODUCT OVERVIEW
Models
Way to the Internet
Internet interface
Machine interface
RAS-EC
RAS-ECW
Factory network
Ethernet WAN
Ethernet LAN 1 to 4
Serial interface
Cellular network
Cellular antenna
Examples :
Remote PC
network
Factory
network
Machine
network
OK
192.168.10.0
192.168.1.0
192.168.12.0
OK
192.168.10.0
192.168.10.0
192.168.12.0
The IP domain of the machine ntwk and of the
factory ntwk are the same.
The machine IP domain must be modified or the
RAS must be used according to the use case 2
192.168.10.0
192.168.1.0
192.168.1.0
The IP domain of the machine ntwk and of the
remote PC ntwk are the same.
The machine IP domain must be modified or the
address translation option must be selected (see
the wizard menu).
192.168.10.0
192.168.1.0
192.168.10.0
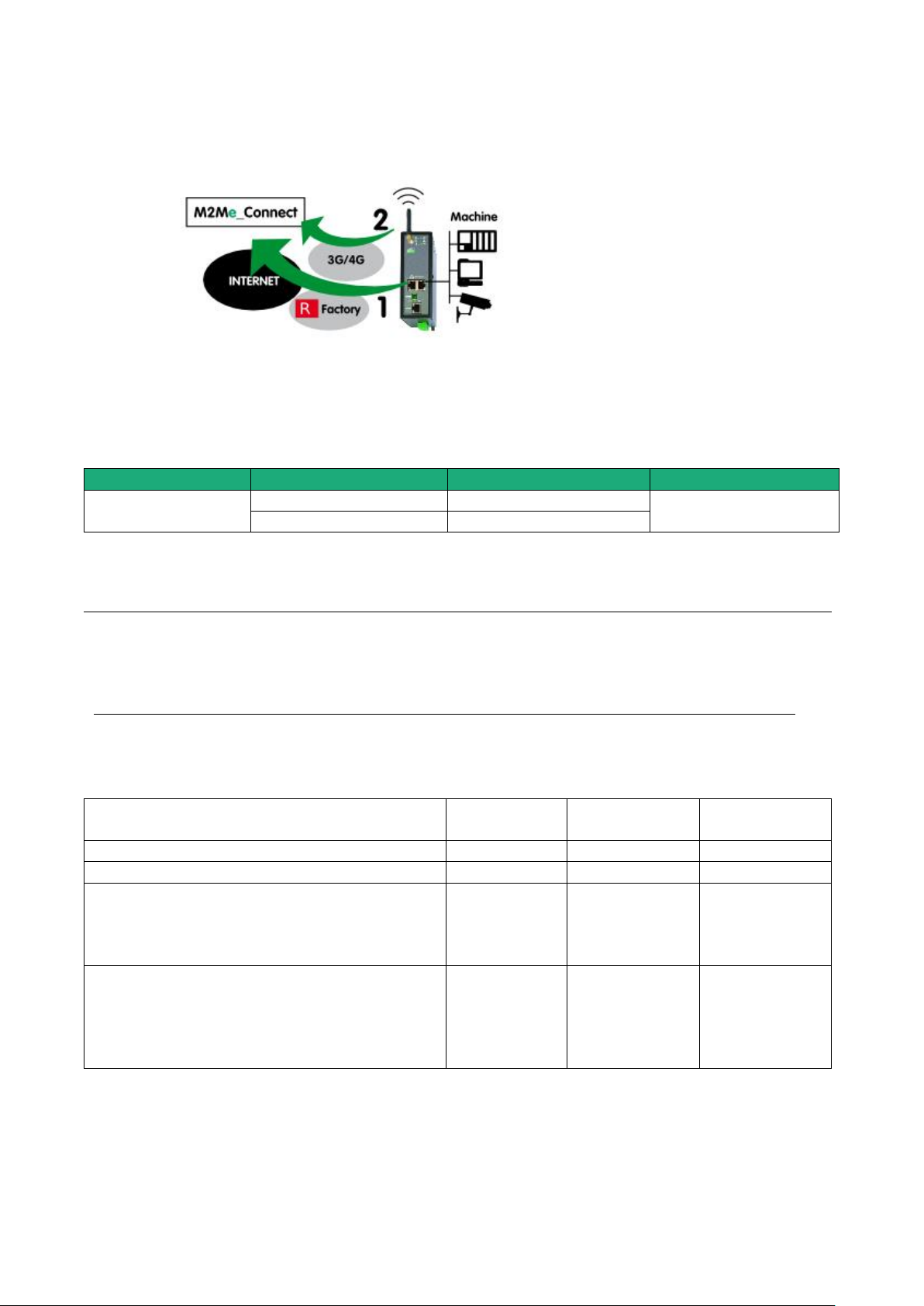
5.5 Use case 5 : The machine is connected through the factory & a cellular ntwk
Description
Reaching the Internet through the factory network may not be immediately authorized or available at the
moment of the machine installation; it is the reason why, the router RAS (RAS-EC or RAS-ECW) is able to
select the available way to the Internet; the factory network access to the Internet is selected as a priority
and the cellular network is used as a backup solution. The router RAS switches automatically between that
both ways.
Machine IP address
Rule 1 : The IP domain of the machine network and the IP domain of the factory network must be different.
If both domains are identical, the IP domain of the machine must be modified or he RAS must be used
according to the use case Nr 2 described above.
Rule 2 : The IP domain of the machine network and the IP domain of the remote PC must be different.
If both IP domains are identical, the IP domain of the machine must be modified or the machine network
translation option must be selected.
Machine Access Box RAS DOC_DEV_RAS_User guide_A Page 27

PRODUCT OVERVIEW
Available functions
Connecting the remote PC to each device of the machine network through M2Me
Individual rights for each the remote user
Communication initiated by devices belonging to the machine network towards
devices belonging to the factory network
Communication initiated by devices belonging to the factory network towards
devices belonging to the machine network
Enabled by creating
a firewall rule
Setting an additional VPN towards a server
Sending an email or a SMS
Security
The remote user can only communicate with the authorized devices.
The availability and the quality of a cellular network is sometimes lower than a company network. It is
important to check this situation will not provoke any kind of danger.
Page 28 DOC_DEV_RAS_User guide_A Machine Access Box RAS
PRODUCT OVERVIEW
Models
Way to the Internet
Internet interface
Machine interface
RAS-EC
RAS-ECW
Wi-Fi network
Ethernet WAN
Ethernet LAN 1 to 4
Serial interface
Cellular network
Cellular antenna
Examples :
Remote PC
network
Factory
network
Machine
network
OK
192.168.10.0
192.168.1.0
192.168.12.0
OK
192.168.10.0
192.168.10.0
192.168.12.0
The IP domain of the machine ntwk and of the
factory ntwk are the same.
The machine IP domain must be modified or the
RAS must be used according to the use case 2
192.168.10.0
192.168.1.0
192.168.1.0
The IP domain of the machine ntwk and of the
remote PC ntwk are the same.
The machine IP domain must be modified or the
address translation option must be selected (see
the wizard menu).
192.168.10.0
192.168.1.0
192.168.10.0
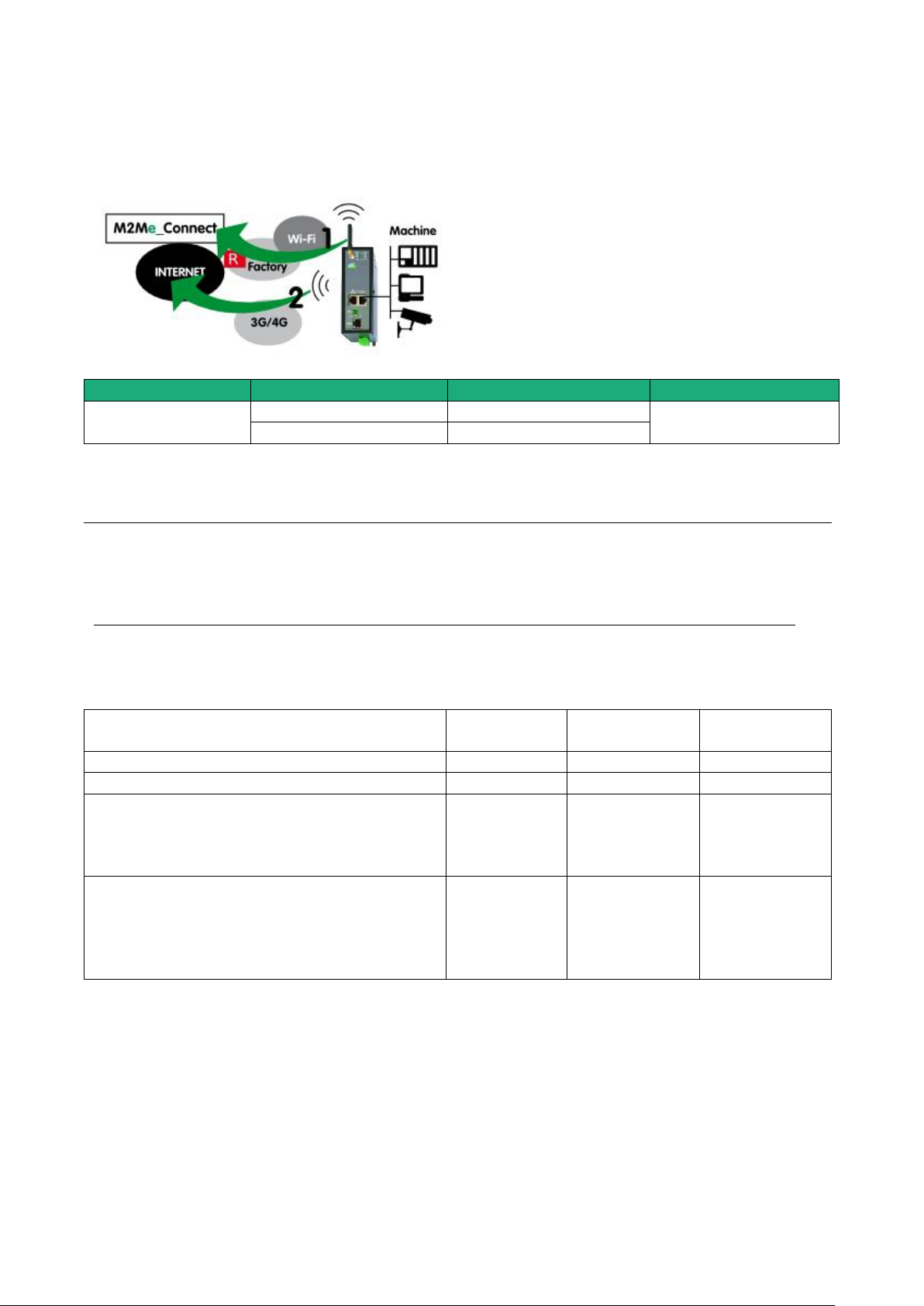
5.6 Use case 6 : The machine is connected through a Wi-Fi & a cellular ntwk
Description
Machine IP address
Rule 1 : The IP domain of the machine network and the IP domain of the factory network must be different.
If both domains are identical, the IP domain of the machine must be modified or he RAS must be used
according to the use case Nr 2 described below.
Rule 2 : The IP domain of the machine network and the IP domain of the remote PC must be different.
If both IP domains are identical, the IP domain of the machine must be modified or the machine network
translation option must be selected.
Machine Access Box RAS DOC_DEV_RAS_User guide_A Page 29

PRODUCT OVERVIEW
Available functions
Connecting the remote PC to each device of the machine network through M2Me
Individual rights for each the remote user
Communication initiated by devices belonging to the machine network towards
devices belonging to the factory network
Communication initiated by devices belonging to the factory network towards
devices belonging to the machine network
Enabled by creating
a firewall rule
Setting an additional VPN towards a server
Sending an email or a SMS
Security
The remote user can only communicate with the authorized devices.
The availability and the quality of a cellular network is sometimes lower than a company network. It is
important to check this situation will not provoke any kind of danger.
Page 30 DOC_DEV_RAS_User guide_A Machine Access Box RAS
 Loading...
Loading...