Page 1

User’s Guide
FastFind Links
Unpacking and Installation
Computer Setup
Setting the initial IP address
EtherWAN Managed Switch – V2.01
EtherWAN Managed Switch Users Guide
1
Page 2

All Rights Reserved
Dissemination or reproduction of this document, or its contents, is not authorized except
where expressly permitted. Violators are liable for damages. All rights reserved, for the
purposes of patent application or trademark registration.
Disclaimer of Liability
The information contained in this document is subject to change without notice. EtherWAN is
not liable for any errors or omissions contained herein or for resulting damage in connection
with the information provided in this manual.
Registered Trademarks
The following words and phrases are registered Trademarks of EtherWAN Systems Inc.
EtherOS™
Ethernet to the World™
All other Trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
Warranty
For details on the EtherWAN warranty replacement policy, please visit our website at
https://kb.etherwan.com/index.php?CategoryID=13
Products Supported by this Manual:
V2.01 EtherWAN Managed Switch
Contact EtherWAN Systems
Corporate Headquarters
EtherWAN Systems Inc.
2301 E Winston Rd Anaheim
Anaheim, CA 92806
Tel: (714) 779 3800
Fax: (714) 779 3806
Email: support@etherwan.com
EtherWAN Managed Switch Users Guide
ii
Page 3

Preface
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Table of Contents ................................................................................................... iii
Table of Figures ...................................................................................................... xi
Preface .................................................................................................................... xv
Changes in this Revision ......................................................................................... xv
Document Conventions .......................................................................................... xvi
Safety and Warnings .............................................................................................. xvi
Typographic Conventions ....................................................................................... xvi
Unpacking and Installation ................................................................................... 17
Package Contents ................................................................................................... 17
Unpacking ............................................................................................................... 17
Required Equipment and Software .......................................................................... 18
Computer Setup ..................................................................................................... 19
Management Methods and Protocols ...................................................................... 19
Default IP ................................................................................................................. 20
Login Process and Default Credentials .................................................................... 20
Setting the initial IP address ................................................................................. 21
Simple IP Addressing .............................................................................................. 21
CLI Command Usage ............................................................................................. 22
Navigating the CLI Hierarchy ................................................................................... 22
CLI Keyboard Shortcuts ........................................................................................... 22
CLI Command modes .............................................................................................. 23
General Configuration Mode .............................................................................. 23
MSTP Configuration Mode ................................................................................. 23
Interface Configuration Mode ............................................................................. 24
VLAN Database Configuration Mode ................................................................. 24
Saving a Configuration from the CLI .................................................................. 24
System Menu ......................................................................................................... 25
System Information .................................................................................................. 25
System Name/Password.......................................................................................... 27
System Name/Password using the CLI .................................................................... 28
IP Address ............................................................................................................... 29
EtherWAN Managed Switch Users Guide
iii
Page 4

Preface
Static IP ............................................................................................................. 29
DHCP Client ...................................................................................................... 29
Default Gateway ................................................................................................ 29
DNS Server ........................................................................................................ 29
IP Address - Configuration using the CLI ................................................................. 31
IP Address ......................................................................................................... 31
Default Gateway ................................................................................................ 32
Domain Name Server (DNS) .............................................................................. 33
Enable/Disable DHCP Client on a VLAN ............................................................ 34
Enable/Disable Static IP on a VLAN................................................................... 34
Management Interface ................................................................ ............................. 36
HTTPS ............................................................................................................... 36
Telnet. ................................................................................................................ 36
SSH (Secure Shell) ............................................................................................ 37
Management Interface Configuration using the CLI ................................................. 38
Enabling/Disabling Telnet .................................................................................. 38
Enabling/Disabling SSH ..................................................................................... 39
Enabling/Disabling HTTP and/or HTTPS ........................................................... 40
Save Configuration Page ......................................................................................... 42
Save Configuration ............................................................................................ 42
Load Configuration ............................................................................................. 42
Backup Configuration ......................................................................................... 42
Restore Default .................................................................................................. 43
Auto Save .......................................................................................................... 43
Save Configuration Page using the CLI ................................................................... 44
Saving a Configuration ....................................................................................... 44
Restore Default Settings .................................................................................... 44
Load Configuration from a TFTP Server ............................................................ 45
Save Configuration to a TFTP Server ................................................................ 45
Auto Save Configuration .................................................................................... 46
Firmware Upgrade ................................................................................................... 47
Firmware Update using the CLI ............................................................................... 48
Reboot ................................................................................................ ..................... 49
Reboot using the CLI ............................................................................................... 49
Logout ..................................................................................................................... 49
Logout from the CLI ................................................................................................. 49
Diagnostics ............................................................................................................ 50
Utilization ................................................................................................................. 50
System Log.............................................................................................................. 51
System log using CLI command .............................................................................. 51
Remote Logging ...................................................................................................... 52
Remote Logging using CLI commands .................................................................... 54
EtherWAN Managed Switch Users Guide
iv
Page 5

Preface
ARP Table ............................................................................................................... 55
ARP Table using CLI Commands ............................................................................ 56
Route Table ............................................................................................................. 57
Route Table Using CLI Commands ......................................................................... 57
Alarm Setting ........................................................................................................... 58
Port ......................................................................................................................... 59
Configuration ........................................................................................................... 59
Port Status ............................................................................................................... 61
Rate Control ............................................................................................................ 62
RMON Statistics ...................................................................................................... 63
Per Port VLAN Activities .......................................................................................... 64
Setting the Port Description ............................................................................... 65
Enable or Disable a Port .................................................................................... 65
Setting the Port Speed ....................................................................................... 66
Setting Port Duplex ............................................................................................ 66
Enable or Disable Port FlowControl ................................................................... 67
Display Port Status ............................................................................................ 67
Setting a Ports Rate Control .............................................................................. 67
Display a Ports RMON Statistics ........................................................................ 68
Display a Ports VLAN Activities .......................................................................... 68
Switching ................................................................................................................ 69
Bridging ................................................................................................................... 69
Aging Time......................................................................................................... 70
Threshold Level ................................................................................................. 70
Storm Control Type ............................................................................................ 70
Block Multicast ................................................................................................... 71
Loopback Detect ...................................................................................................... 72
Loopback Detection (Global) .............................................................................. 72
Loopback Detect Action ..................................................................................... 72
Loopback Detect Recovery Time ....................................................................... 72
Polling Interval ................................................................................................... 73
Loopback Detection (Per Port) ........................................................................... 74
Storm Detect ............................................................................................................ 75
Enable/Disable Storm Detection ........................................................................ 75
Static MAC Entry ..................................................................................................... 77
Adding a Static MAC Address to a Port .............................................................. 77
Removing a Static MAC Address from a Port ..................................................... 78
Adding a MAC to the Static-MAC-Entry Discard Table ....................................... 78
Removing a MAC address from the Static-MAC-Entry Discard Table ................ 79
Port Mirroring ........................................................................................................... 80
Link State Tracking .................................................................................................. 82
EtherWAN Managed Switch Users Guide
v
Page 6

Preface
Enable/Disable Link State Tracking ................................................................... 82
Port Settings ...................................................................................................... 82
PoE - System and Port Settings ............................................................................... 84
PoE System Setting ........................................................................................... 84
PoE Port Setting ................................................................................................ 85
PoE Scheduling ....................................................................................................... 87
Switch Configuration Examples Using CLI Commands ............................................ 89
Setting the Aging Time Value ............................................................................. 89
Enabling Port Isolation ....................................................................................... 89
Enabling Block Multicast .................................................................................... 90
Setting Storm Control ......................................................................................... 90
Enabling Loopback Detect (Global) .................................................................... 91
Setting the Loopback Detect Action ................................................................... 91
Setting the Loopback Detect Recovery Time ..................................................... 91
Setting the Loopback Detect Polling Interval ...................................................... 92
Enabling Loopback Detect (Port) ....................................................................... 92
Configuring Storm-Detect ................................................................................... 93
Adding a MAC Address for Static-MAC-Entry Forwarding .................................. 97
Adding a MAC Address for Static-MAC-Entry Discarding ................................... 97
Configuring Port Mirroring .................................................................................. 98
Enabling a Link State Tracking Group ................................................................ 98
Assigning a Port to a Link State Tracking Group ................................................ 99
Setting PoE Power Budget ................................................................................. 99
PoE Port Settings............................................................................................. 100
PoE Scheduling ............................................................................................... 103
Trunking ............................................................................................................... 105
Overview ............................................................................................................... 105
Static Channel Trunking ................................................................................... 105
Link Aggregation Control Protocol .................................................................... 105
Port Trunking ......................................................................................................... 106
LACP Trunking ...................................................................................................... 107
Trunking Configuration Examples Using CLI Commands ....................................... 109
Adding an Interface to a Static Trunk ............................................................... 109
Adding an Interface to an LACP Trunk ............................................................. 109
Setting the LACP Port Priority .......................................................................... 110
Setting the LACP Timeout ................................................................................ 110
STP/Ring Page – Overview ................................................................................. 111
Choosing the Spanning Tree Protocols .................................................................. 111
Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) ......................................................................... 111
Rapid Spanning Tree protocol (RSTP) ............................................................. 111
Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol (MSTP) ................................ ......................... 111
EtherWAN Managed Switch Users Guide
vi
Page 7

Preface
STP/Ring Page - Configuring RSTP ................................................................... 112
Global Configuration Page ..................................................................................... 112
Enabling the RSTP Protocol ............................................................................ 112
Additional Global Configuration page settings .................................................. 112
The Root Bridge & Backup Root Bridge ........................................................... 114
Setting the MAX Age, Forward Delay, and Hello Timer .................................... 116
RSTP Port Setting Page ........................................................................................ 118
Spanning Tree Port Roles ................................................................................ 118
Path Cost & Port Priority .................................................................................. 119
Point to Point Link ............................................................................................ 121
Edge Port ......................................................................................................... 121
RSTP Configuration Examples Using CLI Commands ........................................... 122
Enabling the Spanning Tree Protocol ............................................................... 122
Bridge Priority, Max Age, Forward Delay, and Hello Time ................................ 122
Modifying the Port Priority and Path Cost ......................................................... 123
Manually Setting a Port to be a Shared or Point to Point Link .......................... 123
Enabling/Disabling a port to be an Edge Port ................................................... 124
STP/Ring Page - Configuring MSTP ................................................................ ... 125
Global Configuration Page ..................................................................................... 125
Enabling the MSTP Protocol ............................................................................ 125
The CIST Root Bridge & Backup CIST Root Bridge ......................................... 127
Setting Bridge Priority ...................................................................................... 127
Configuring the CST Network Diameter ........................................................... 129
MSTP Properties Page .......................................................................................... 130
Configuring an MSTP Region........................................................................... 130
Configuring the IST Network Diameter ............................................................. 132
MSTP Instance Setting Page ................................................................................. 133
Setting an MSTP Instance ............................................................................... 133
Modifying MSTP parameters for load balancing ............................................... 134
MSTP Port Setting page ........................................................................................ 136
Adjusting the blocking port in an MSTP network .............................................. 136
MSTI Instance Port Membership ...................................................................... 138
MSTP Configuration Examples Using CLI Commands .......................................... 139
Enabling Spanning Tree for MSTP ................................................................... 139
Bridge Priority, Max Age, Forward Delay, and Hello Time ................................ 140
IST MAX Hops ................................................................................................. 140
MSTP Regional Configuration Name and the Revision Level ........................... 141
Creating an MSTI Instance .............................................................................. 141
Setting MSTI Priority ........................................................................................ 142
Modifying CIST Port Priority and Port Path Cost .............................................. 142
Adding a Port to an MSTI Instance .................................................................. 143
EtherWAN Managed Switch Users Guide
vii
Page 8

Preface
STP/Ring Page - Alpha Ring ............................................................................... 144
Alpha Ring Setting Page ........................................................................................ 144
EtherWAN α-Ring Technology ......................................................................... 144
Implementing a Simple α-Ring ......................................................................... 144
Connecting two α-Ring Networks together ....................................................... 146
STP/Ring Page - Advanced Setting .................................................................... 147
Advanced Bridge Configuration ............................................................................. 147
Advanced Per Port Configuration ........................................................................... 148
Configuring Spanning Tree Advanced Settings using CLI commands.................... 149
Enabling BPDU Guard Globally ....................................................................... 149
Enabling BPDU Guard on a Port ...................................................................... 149
Enabling BPDU Guard Error Disable-timeout ................................................... 150
VLAN ..................................................................................................................... 151
802.1Q Tagged Based VLAN ................................................................................ 151
VLAN Configuration in 802.1Q Tag Based VLAN Mode ......................................... 152
General Overview ............................................................................................ 152
Configuring 802.1Q VLAN Database................................................................ 153
802.1Q Tag Based VLAN Configuration Examples Using CLI Commands ............ 154
Configuring a 802.1Q VLAN ............................................................................. 154
Configuring an IP Address for a Management VLAN ....................................... 154
Removing an IP Address from a Management VLAN ....................................... 155
Configuring an Access Port .............................................................................. 155
Configuring a Trunk Port .................................................................................. 156
Add an IP to the Management VLAN ..................................................................... 157
Configuring the Port Type and the PVID setting ..................................................... 158
Configuring the VLAN Egress (outgoing) Member Ports .................................. 159
QoS ....................................................................................................................... 161
Global Configuration Page ..................................................................................... 162
Web GUI Interface ........................................................................................... 162
QoS Global Configuration using the CLI Interface ................................................. 164
Enable/Disable QoS Trust ................................................................................ 165
Configuring the Egress Expedite Queue .......................................................... 165
802.1p Priority Page .............................................................................................. 167
Web GUI Interface ........................................................................................... 167
802.1p Priority Submenu – CLI Interface ............................................................... 168
DSCP Page – HTTP Interface ............................................................................... 169
DSCP Submenu – CLI Interface ............................................................................ 170
QoS Interface Commands – CLI Interface ............................................................. 171
viii
EtherWAN Managed Switch Users Guide
Page 9

Preface
ACL (Access Control List) .................................................................................. 172
General Overview .................................................................................................. 172
Configuring ACL .................................................................................................... 173
ACL Policy Map ..................................................................................................... 175
IP Access List .................................................................................................. 176
IP Access List (Extended) ................................................................................ 177
Mac Access List ............................................................................................... 179
Layer 4 ............................................................................................................. 181
Bandwidth Limiting ........................................................................................... 182
Applying a Policy Map to a Port ....................................................................... 184
Modifying/Adding an Existing Policy Map ......................................................... 185
Adding a New ACL Class to an Existing Policy Map ........................................ 185
Adding an Existing ACL Class to an Existing Policy Map ................................ . 186
Removing an ACL Class .................................................................................. 188
ACL Configuration Examples Using CLI Commands ............................................. 192
Enabling QoS ................................................................................................... 192
Creating a Standard IP Access List .................................................................. 193
Creating an Extended IP Access List ............................................................... 193
Creating a MAC Access List ............................................................................ 194
Creating an ACL Class Map with Layer 4 Access List ...................................... 195
Creating an ACL Class Map with an IP or MAC Access List ............................ 196
Creating an ACL Policy Map ............................................................................ 197
Appling an Existing ACL Policy to a Port .......................................................... 198
Deleting an ACL Class ..................................................................................... 198
Deleting an ACL Policy .................................................................................... 199
SNMP .................................................................................................................... 200
SNMP General Settings ......................................................................................... 200
Configuring SNMP v1 & v2 Community Groups ..................................................... 203
Configuring SNMP v3 Users .................................................................................. 204
Adding SNMP v3 Users to the switch ............................................................... 204
Deleting SNMP v3 Users from the switch ......................................................... 207
SNMP Configuration Examples Using CLI Commands .......................................... 208
Enabling SNMP and configuring general settings............................................. 208
Configuring SNMP Traps ................................................................................. 209
Configuring SNMP v1 & v2 Community Groups ............................................... 211
Adding SNMP v3 Users ................................................................................... 211
IEEE 802.1X .......................................................................................................... 212
Configuring 802.1X from the GUI system ............................................................... 212
Enabling Radius ............................................................................................... 212
Adding a Radius Server ................................................................................... 213
Enabling 802.1X on a Port ............................................................................... 215
EtherWAN Managed Switch Users Guide
ix
Page 10

Preface
LLDP ..................................................................................................................... 217
LLDP General Settings .......................................................................................... 218
Enable/Disable LLDP ................................ ....................................................... 218
Holdtime Multiplier ........................................................................................... 218
Global TLV Setting ........................................................................................... 219
LLDP Ports Settings .............................................................................................. 221
Enabling LLDP transmission for a specific Port ................................................ 221
Enabling LLDP Reception for a specific Port .................................................... 221
Enabling Notifications ...................................................................................... 221
LLDP Neighbors .................................................................................................... 223
LLDP Statistics ...................................................................................................... 224
LLDP Configuration Examples Using CLI Commands ........................................... 225
Enable/Disable LLDP ................................ ....................................................... 225
LLDP Holdtime Multiplier .................................................................................. 226
LLDP Transmit Interval .................................................................................... 226
Enable/Disable Global LLDP TLVs .................................................................. 227
Enabling LLDP Transmit on a Port ................................................................... 228
Enabling LLDP Receive on a Port .................................................................... 228
Enabling LLDP Notify ................................ ....................................................... 229
Enabling Transmission of the Management IP ................................................. 229
Enabling Specific TLV’s on a Port .................................................................... 230
Other Protocols.................................................................................................... 231
GVRP .................................................................................................................... 231
General Overview ............................................................................................ 232
Enabling the GVRP Protocol at the Global Level ............................................. 233
Enabling the GVRP Protocol at the Port Level ................................................. 234
GVRP Configuration Examples Using CLI Commands .................................... 235
IGMP Snooping ..................................................................................................... 238
General Overview ............................................................................................ 238
Enabling the IGMP Snooping Modes ............................................................... 239
Configuring IGMP Snooping General properties .............................................. 240
Configuring IGMP Passive Mode Specific properties ....................................... 241
Configuring IGMP Querier Mode Specific properties ........................................ 242
Configuring IGMP Unknown Multicast Forwarding ........................................... 243
Monitoring Registered Multicast Groups .......................................................... 247
IGMP Configuration Examples Using CLI Commands ..................................... 248
Network Time Protocol .......................................................................................... 256
Enabling NTP ................................................................................................... 256
Setting the NTP Server IP Address .................................................................. 256
Setting the Timezone ....................................................................................... 256
Manually Syncing Time .................................................................................... 256
Daylight Savings Time - Weekday Mode .......................................................... 257
EtherWAN Managed Switch Users Guide
x
Page 11

Preface
Daylight Savings Time – Date Mode ................................................................ 258
Network Time Protocol Configuration Examples Using CLI Commands ........... 260
GMRP .................................................................................................................... 263
General Overview ............................................................................................ 263
GMRP Normal mode ........................................................................................ 263
GMRP Fixed mode .......................................................................................... 263
GMRP Forbidden mode ................................................................................... 264
GMRP Forward All mode ................................................................................. 264
GMRP Disabled mode ..................................................................................... 264
Enabling the GMRP Feature Globally on the Switch ........................................ 264
Configuring the GMRP Feature Per Port .......................................................... 266
GMRP Configuration Examples Using CLI Commands .................................... 268
DHCP Server ......................................................................................................... 270
General Overview ............................................................................................ 270
Configuring the DHCP Server .......................................................................... 270
DHCP Configuration Examples Using CLI Commands .................................... 273
TABLE OF FIGURES
Figure 1: Login screen ......................................................................................................... 20
Figure 2: Assigning an IP address ....................................................................................... 21
Figure 3: System Information .............................................................................................. 26
Figure 4: System Name/Password ...................................................................................... 27
Figure 5: IP Address............................................................................................................ 30
Figure 6: Management Interface.......................................................................................... 37
Figure 7: Save Configuration Page ...................................................................................... 43
Figure 8: Firmware Upgrade Page ...................................................................................... 47
Figure 9: Utilization Page .................................................................................................... 50
Figure 10: System Log ................................................................................................ ........ 51
Figure 11: Remote Logging Page ........................................................................................ 53
Figure 12: ARP Table .......................................................................................................... 55
Figure 13: Route Table ........................................................................................................ 57
Figure 14: Alarm Trigger ..................................................................................................... 58
Figure 15: Trigger Enable .................................................................................................... 58
Figure 16: Port Configuration .............................................................................................. 60
Figure 17: Port Status ......................................................................................................... 61
Figure 18: Rate Control ....................................................................................................... 62
Figure 19: RMON Page ....................................................................................................... 63
Figure 20: Port VLAN Activities ........................................................................................... 64
EtherWAN Managed Switch Users Guide
xi
Page 12

Preface
Figure 21: Bridging .............................................................................................................. 71
Figure 22: Loopback Detection ............................................................................................ 73
Figure 23: Loopback Detection (port) .................................................................................. 74
Figure 24: Storm Detect – Global ........................................................................................ 75
Figure 25: Storm Detect – Per Port ..................................................................................... 76
Figure 26: MAC Static Entry ................................................................................................ 77
Figure 27: Removing a Static MAC ..................................................................................... 78
Figure 28: Adding a MAC – Static-MAC-Entry Table ................................ ........................... 78
Figure 29: Deleting a MAC – Static-MAC-Entry Table ......................................................... 79
Figure 30: Port Mirroring ..................................................................................................... 81
Figure 31: Disabling Port Mirroring ...................................................................................... 81
Figure 32: Link State Tracking ............................................................................................. 82
Figure 33: Link State Tracking – Port Settings..................................................................... 83
Figure 34: PoE System Setting ........................................................................................... 84
Figure 35: PoE Port Setting ................................................................................................. 86
Figure 36: Selecting a Port .................................................................................................. 87
Figure 37: PoE Power Scheduling ....................................................................................... 88
Figure 38: Port Trunking .................................................................................................... 106
Figure 39: LACP Trunking ................................................................................................. 108
Figure 40: STP/Ring Global Configuration ......................................................................... 113
Figure 41: Bridge ID .......................................................................................................... 114
Figure 42: Bridge ID Display .............................................................................................. 115
Figure 43: Max Age, Hello Timer & Forward Delay ............................................................ 117
Figure 44: Spanning Tree Port Roles ................................................................................ 118
Figure 45: Port ID ................................ ................................................................ .............. 119
Figure 46: Port Priority and Path Cost ............................................................................... 120
Figure 47: Enabling MSTP ................................................................................................ 126
Figure 48: Bridge ID .......................................................................................................... 127
Figure 49: Bridge ID Display .............................................................................................. 128
Figure 50: Max Age, Hello Timer & Forward Delay ............................................................ 130
Figure 51: MSTP Region and Revision Level ................................ .................................... 131
Figure 52: MSTP Properties – Max Hops .......................................................................... 132
Figure 53: VLAN Instance Configuration ........................................................................... 134
Figure 54: VLAN Instance ID ............................................................................................. 134
Figure 55: Setting the MSTI Regional Root Bridge ............................................................ 135
Figure 56: Port Cost & Priority ........................................................................................... 137
Figure 57: Port Instance Configuration .............................................................................. 138
Figure 58: Port Instance - Adding Ports ............................................................................. 139
Figure 59: α-Ring Settings ................................................................................................. 145
Figure 60: Ring Coupling ................................................................................................... 146
Figure 61: Advanced Bridge Configuration ........................................................................ 147
Figure 62: Advanced Per Port Configuration ..................................................................... 148
Figure 63: Add VLAN ........................................................................................................ 153
EtherWAN Managed Switch Users Guide
xii
Page 13

Preface
Figure 64: Add VLAN Page ............................................................................................... 153
Figure 65: Management VLAN IP Address ........................................................................ 157
Figure 66: VLAN Port Setting ............................................................................................ 158
Figure 67: VLAN Links ...................................................................................................... 159
Figure 68: VLAN Ports ...................................................................................................... 160
Figure 69: Tag or Untag ports ........................................................................................... 160
Figure 70: Global Configuration ......................................................................................... 162
Figure 71: 802.1p Priority .................................................................................................. 167
Figure 72: DSCP ............................................................................................................... 169
Figure 73: Enabling QoS ................................................................................................... 174
Figure 74: Policy Map ........................................................................................................ 175
Figure 75: IP Access List ................................................................................................... 176
Figure 76: Access List Extended ....................................................................................... 177
Figure 77: MAC Access list ............................................................................................... 179
Figure 78: Layer 4 ............................................................................................................. 181
Figure 79: IP Access List Name ........................................................................................ 182
Figure 80: Police Rate ....................................................................................................... 183
Figure 81: Policy Map Name ............................................................................................. 183
Figure 82: Applying a Policy Map to a Port ........................................................................ 184
Figure 83: Modifying a Policy Map ..................................................................................... 185
Figure 84: Adding a New ACL Class to an Existing Policy Map ......................................... 186
Figure 85: Policy Map Setting – Class Name..................................................................... 187
Figure 86: Policy Map Setting ............................................................................................ 187
Figure 87: Removing an ACL Class .................................................................................. 188
Figure 88: Verifying ACL Class Removal ........................................................................... 189
Figure 89: Removing a Policy Map .................................................................................... 190
Figure 90: Policy Map 2 ..................................................................................................... 191
Figure 91: Policy Map 3 ..................................................................................................... 192
Figure 92: SNMP General Settings ................................................................................... 202
Figure 93: Community Name V1/V2c ................................................................................ 203
Figure 94: Add User .......................................................................................................... 204
Figure 95: SNMP v3 Settings ............................................................................................ 205
Figure 96: User name & Access Mode .............................................................................. 205
Figure 97: Auth Password ................................................................................................. 206
Figure 98: Privacy PassPhrase ......................................................................................... 206
Figure 99: Delete User ................................................................ ...................................... 207
Figure 100: Select User ..................................................................................................... 207
Figure 101: Enable Radius ................................................................................................ 213
Figure 102: Radius Setup .................................................................................................. 214
Figure 103: Resulting Radius Server Setup ....................................................................... 215
Figure 104: Enabling 802.1X on a Port .............................................................................. 216
Figure 105: LLDP Global Settings ..................................................................................... 220
Figure 106: LLDP Ports Settings ....................................................................................... 222
EtherWAN Managed Switch Users Guide
xiii
Page 14

Preface
Figure 107: LLDP Neighbors ............................................................................................. 223
Figure 108: LLDP Statistics ............................................................................................... 224
Figure 109: GVRP ............................................................................................................. 231
Figure 110: GVRP Configuration Distribution Switch ......................................................... 233
Figure 111: GVRP Configuration Access Switch ............................................................... 233
Figure 112: GVRP Per Port Settings ................................................................................. 234
Figure 113: IGMP Mode .................................................................................................... 239
Figure 114: IGMP General Properties ................................................................ ............... 240
Figure 115: IGMP Passive Mode ....................................................................................... 241
Figure 116: Querier Mode Properties ................................................................................ 242
Figure 117: Disabled Mode Forwarding Port ..................................................................... 243
Figure 118: PassiveForwardMode ..................................................................................... 244
Figure 119: ForceForwardMode ........................................................................................ 245
Figure 120: IGMP Querier Mode Forwarding ..................................................................... 246
Figure 121: Current Multicast Groups ................................................................................ 247
Figure 122: NTP Settings .................................................................................................. 257
Figure 123: Daylight Savings – Weekday Mode ................................................................ 258
Figure 124: Daylight Savings – Date Mode ....................................................................... 259
Figure 125: GMRP Global Setting ..................................................................................... 265
Figure 126: DHCP Server ................................................................................................. 271
Figure 127: DHCP Bindings .............................................................................................. 272
Figure 128: DHCP Binding Table ...................................................................................... 272
EtherWAN Managed Switch Users Guide
xiv
Page 15
Preface
Revision
Document Version
Date
Description
A
Version 1
10/26/2015
Initial release for Firmware version 2.01
PREFACE
Audience
This guide is designed for the person who installs, configures, deploys, and maintains the
Ethernet network. This document assumes the reader has moderate hardware, computer,
and Internet skills.
Document Revision Level
This section provides a history of the revision changes to this document.
Changes in this Revision
N/A
xv
EtherWAN Managed Switch Users Guide
Page 16
Preface
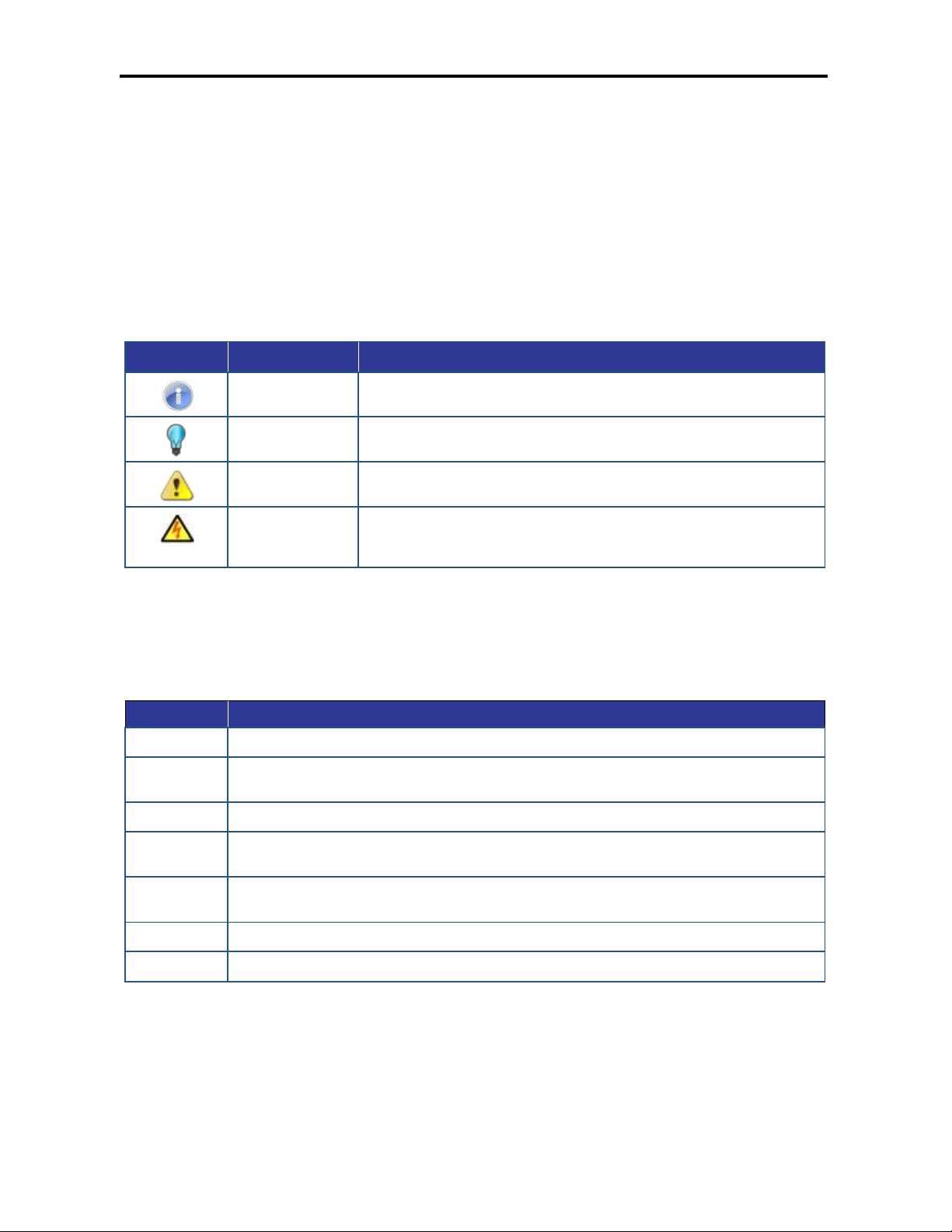
Symbol
Meaning
Description
Note
Notes emphasize or supplement important points of the main text.
Tip
Tips provide helpful information, guidelines, or suggestions for performing tasks more
effectively.
Warning
Warnings indicate that failure to take a specified action could result in damage to the
device, or could result in serious bodily injury.
Electric Shock Hazard
This symbol warns users of electric shock hazard. Failure to take appropriate
precautions such as not opening or touching hazardous areas of the equipment could
result in injury or death.
Convention
Description
Bold
Indicates text on a window, other than the window title, including menus, menu options, buttons, fields, and labels.
Italic
Indicates a variable, which is a placeholder for actual text provided by the user or system. Angled brackets (< >)
are also used to indicate variables.
screen/code
Indicates text that is displayed on the screen or entered by the user.
< > angled
brackets
Indicates a variable, which is a placeholder for actual text provided by the user or system. Italic font is also used to
indicate variables.
[ ] square
brackets
Indicates optional values.
{ } braces
Indicates required or expected values.
| vertical bar
Indicates that you have a choice between two or more options or arguments.
Document Conventions
This guide uses the following conventions to draw your attention to certain information.
Safety and Warnings
This guide uses the following symbols to draw your attention to certain information.
Typographic Conventions
This guide also uses the following typographic conventions.
EtherWAN Managed Switch Users Guide
xvi
Page 17

UNPACKING AND INSTALLATION
This chapter describes how to unpack and install the EtherWAN Managed Switch
The topics covered in this chapter are:
Package Contents (Page 17)
Unpacking (Page 17)
Required Equipment and Software (Page 18)
Computer Setup (Page 19)
Management Methods and Protocols (Page 19)
Default IP (Page 20)
Login Process and Default Credentials (Page 20)
Setting the initial IP address (Page 21)
Package Contents
When you unpack the product package, you will find the items listed below. Please inspect
the contents, and report any apparent damage or missing items immediately to your
authorized reseller.
This Managed Switch
Product CD
Quick Installation Guide
External power adapter/Cable (depending on model)
Unpacking
Follow these steps to unpack the EtherWAN Managed Switch and prepare it for operation:
1. Open the shipping container and carefully remove the contents.
2. Return all packing materials to the shipping container and save it.
3. Confirm that all items listed in the "Package Contents" section are included in the
shipment. Check each item for damage. If any item is damaged or missing, notify your
authorized EtherWAN representative.
EtherWAN Managed Switch Users Guide
17
Page 18

Required Equipment and Software
The following hardware and software are needed in order to manage the switch from the
web interface:
Computer with an Ethernet Interface (RJ-45)
Managing the switch requires a personal computer (PC) or notebook computer
equipped with a 10/100base-TX Ethernet interface and a physical RJ-45
connection. The preferred operating system for the computer is Microsoft Windows
XP/Vista/7. It is possible to use Apple OSX or Linux systems as well, but, for the
sake of brevity, all web configurations in this manual will be shown using Windows
7 as the underlying operating system.
Cat 5+ Ethernet Cables
An Ethernet cable of at least Category 5 rating is required to connect your
computer to the switch. The cable can be configured as “straight-through” or
crossover.
TFTP Server Software
Trivial file transfer protocol (TFTP) server software is needed to update the switch
firmware and to upload/download configuration files to the switch. Users not
performing these tasks do not need TFTP software installed. Several good TFTP
servers are available for free online. The server that will be used in this manual is
TFTPD32 by Philippe Jounin.
Web Browser Software
The end user can employ any of the following web browsers during switch
configuration: Internet Explorer, Firefox, or Chrome. Internet Explorer is the
preferred browser for EtherWAN switch configuration. If there is trouble with other
browsers while attempting to program the switch, Internet Explorer should be used.
18
EtherWAN Managed Switch Users Guide
Page 19

COMPUTER SETUP
The end user’s management computer may need to be reconfigured prior to connecting to
the switch in order to access the switch’s web interface through its default IP address (See
Default IP).
Management Methods and Protocols
There are several methods that can be used to manage the switch. This manual
will show the details of configuring the switch using a web browser. Each section
will be followed by the CLI (Command Line Interface) commands needed to
achieve the same results as described in that section.
The methods available to manage the EtherWAN Managed Switch include:
SSH - Secure Shell CLI that is accessible over TCP/IP networks which and
is generally regarded as the most secure method of remotely accessing a
device.
Telnet - is like SSH in that it allows a CLI to be established across a
TCP/IP network, but it does not encrypt the data stream.
HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol) is the most popular switch
management protocol involving the use of a web browser.
RS232 – The EtherWAN Managed Switch is equipped with an RS232 serial
port that can be used to access the switches CLI. The Serial port is DCE
DB9F. A straight through serial cable is used to connect to a typical
computer serial port.
EtherWAN Managed Switch Users Guide
19
Page 20
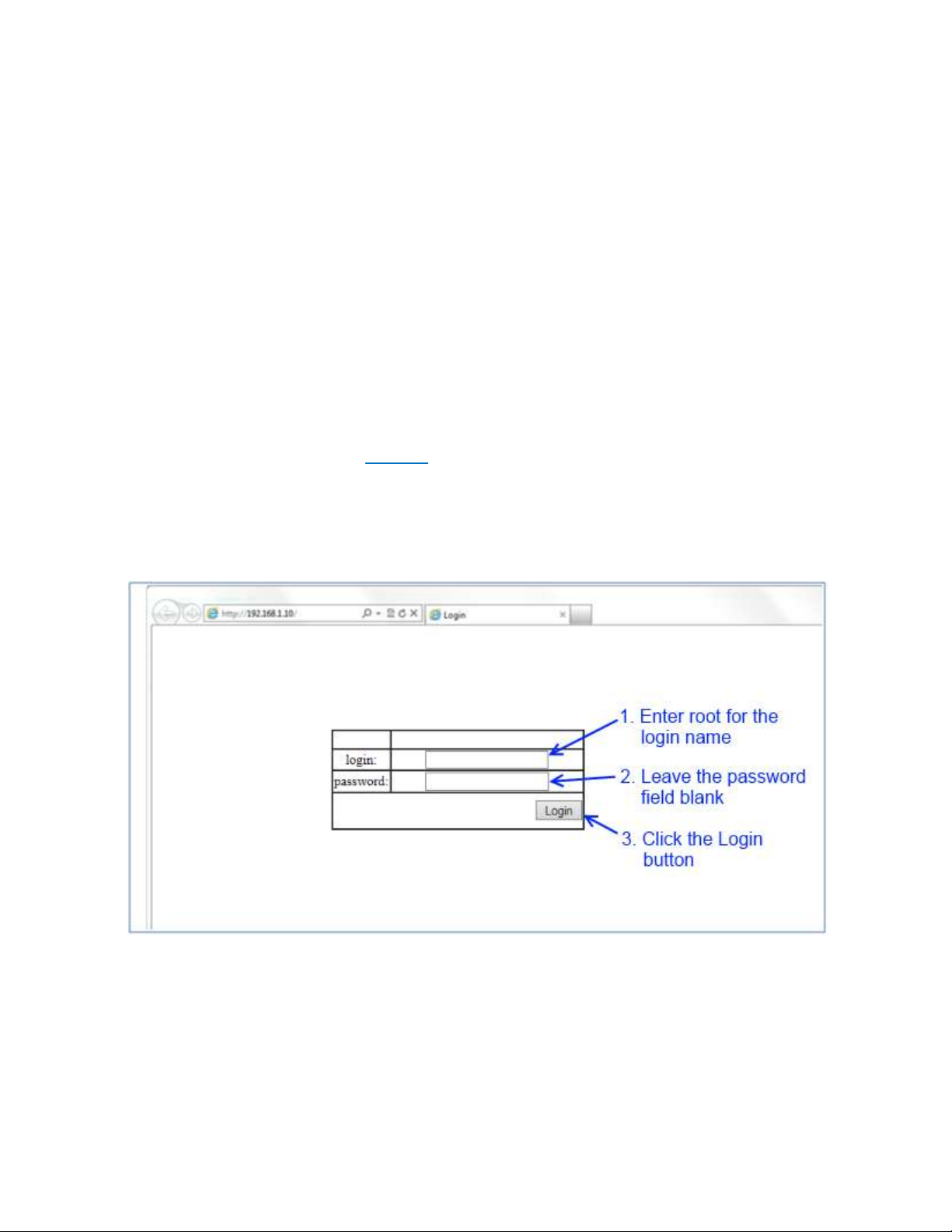
Default IP
The switch’s default IP address is 192.168.1.10. The user will need to modify the
management computer so that it is on the same network as the switch. For
example, the user could change the IP address of the management computer to
192.168.1.100 with a subnet mask of 255.255.255.0.
Login Process and Default Credentials
Once a compatible IP address has been assigned to the management computer,
the user is ready to log into the switch. To log in, type the URL http://192.168.1.10/
into the address field of the browser and hit return. The following will appear in the
browser window (See Figure 1)
The Default Login is root (case sensitive)
There is no password by default
Enter the login name and click the Login button
Figure 1: Login screen
20
EtherWAN Managed Switch Users Guide
Page 21
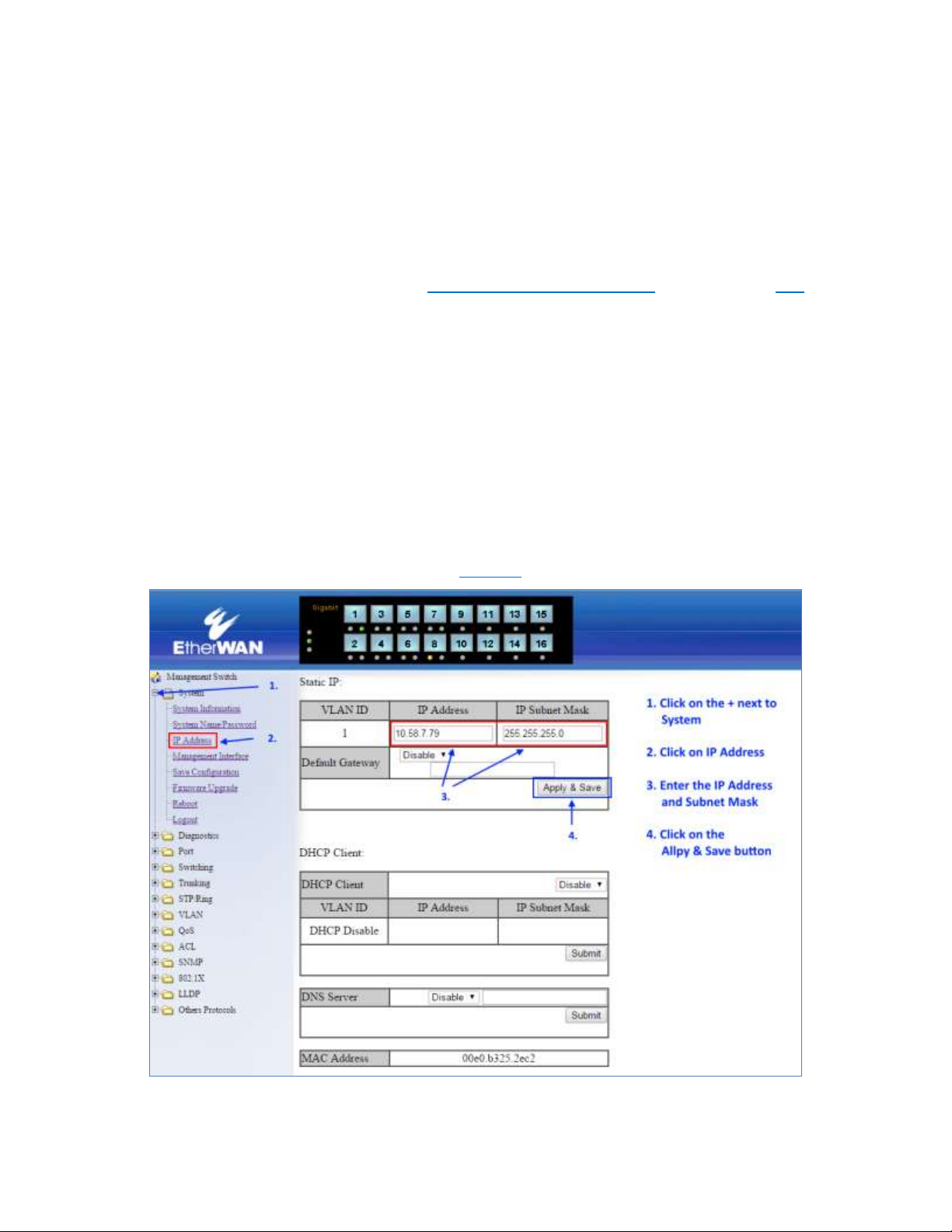
SETTING THE INITIAL IP ADDRESS
Once logged in the user can now configure the switch per the network requirements. The
two major addressing options are:
Simple IP addressing
Multiple VLAN addressing (See Add an IP to the Management VLAN on page 157).
Simple IP Addressing
A new IP address can now be assigned to the switch. From the System Information screen,
go to the left-hand navigation menu.
1. Click on the + next to System
2. Click on IP address
3. Enter the desired IP address and subnet mask in the IP Address/Subnet Mask
fields associated with VLAN 1
4. Click the Apply & Save button (See Figure 2)
Figure 2: Assigning an IP address
EtherWAN Managed Switch Users Guide
21
Page 22

CLI COMMAND USAGE
This chapter describes accessing the EtherWAN Managed Switch by using Telnet, SSH, or
serial ports to configure the switch, navigating the Command Line Interface (CLI), typing
keyboard shortcuts, and moving between the levels. This chapter assumes the user has a
working understanding of Telnet, SSH, and Terminal emulation applications.
Note: For a serial port connection use a standard DB9F to DB9M Modem Cable. The
default Serial port parameters are 115200, 8 None 1, No Flow Control.
Navigating the CLI Hierarchy
The CLI is organized into a hierarchy of levels. Each level has a group of commands for a
specific purpose. For example, to configure a setting for the VLAN server, one would
navigate to the VLAN level, which is under the config level.
CLI Keyboard Shortcuts
Ctrl + a: place cursor at the beginning of a line
Ctrl + b: backspace one character
Ctrl + d: delete one character
Ctrl + e: place cursor at the end of the line
Ctrl + f: move cursor forward one character
Ctrl + k: delete from the current position to the end of the line
Ctrl + l: redraw the command line
Ctrl + n: display the next line in the history
Ctrl + p: display the previous line in the history
Ctrl + u: delete entire line and place cursor at start of prompt
Ctrl + w: delete one word back
EtherWAN Managed Switch Users Guide
22
Page 23

CLI Command modes
Throughout this manual, each section that has CLI commands relevant to that section
requires that the CLI be in a specific configuration mode. This section shows the main CLI
commands to needed to enter a specific mode.
General Configuration Mode
To set the EtherWAN Managed Switch to General configuration mode, run the
following commands from the CLI:
1. enable
2. configure terminal
Example:
switch_a>enable
switch_a#configure terminal
switch_a(config)#
MSTP Configuration Mode
To set the EtherWAN Managed Switch to General MSTP configuration mode, run the
following commands from the CLI:
1. enable
2. configure terminal
3. spanning-tree mst configuration
Example:
switch_a>enable
switch_a#configure terminal
switch_a(config)#spanning-tree mst configuration
switch_a(config-mst)#
23
EtherWAN Managed Switch Users Guide
Page 24

Interface Configuration Mode
Interface mode on the EtherWAN Managed Switch is used to configure the Ethernet ports
and VLAN information. Valid interfaces are:
fe<port #> - 100mb ports use fe followed by the port number. Example: fe1
ge<port #> - Gigabit ports use ge followed by the port number. Example: ge1
vlan1.<vlan#> - VLAN’s use vlan. Followed by the VLAN ID. Example: vlan1.10
Example 1 configures 100mb port 1
switch_a>enable
switch_a#configure terminal
switch_a(config)#interface fe1
switch_a(config-if)
Example 2 configures VLAN ID 9
switch_a>enable
switch_a#configure terminal
switch_a(config)#interface vlan1.9
switch_a(config-if)
VLAN Database Configuration Mode
VLAN Database Configuration Mode on the EtherWAN Managed Switch is used to
configure the VLAN settings.
Example:
switch_a>enable
switch_a#configure terminal
switch_a(config)#vlan database
switch_a(config-vlan)#
Saving a Configuration from the CLI
Example:
switch_a>enable
switch_a#write memory
Building configuration.....
[OK]
switch_a#>
EtherWAN Managed Switch Users Guide
24
Page 25

SYSTEM MENU
System Information
The System information link on the Left menu of the Web Configuration page takes you to a
page that shows the following (see Figure 3):
System Name
o The System name is typically used by network administrators. If SNMP is
enabled on the switch, the system name can be found using MIB II
(RFC1213) in the sysName property.
Firmware Version
o If SNMP is enabled on the switch, the Firmware version can be found using
MIB II in the sysDesc property
System Time
o System time can be change using NTP
MAC Address
o The hardware (MAC) address of the Management interface
Default Gateway
o The IP address of your networks Gateway (Typically a Router on your
network)
DNS Server
o The Dynamic Name Server (DNS) for your network
VLAN ID
o One or more listings depending on the number o VLANs defined on the
switch
o Lists VLAN ID, IP address, and subnet mask of the VLAN Interface(s)
25
EtherWAN Managed Switch Users Guide
Page 26
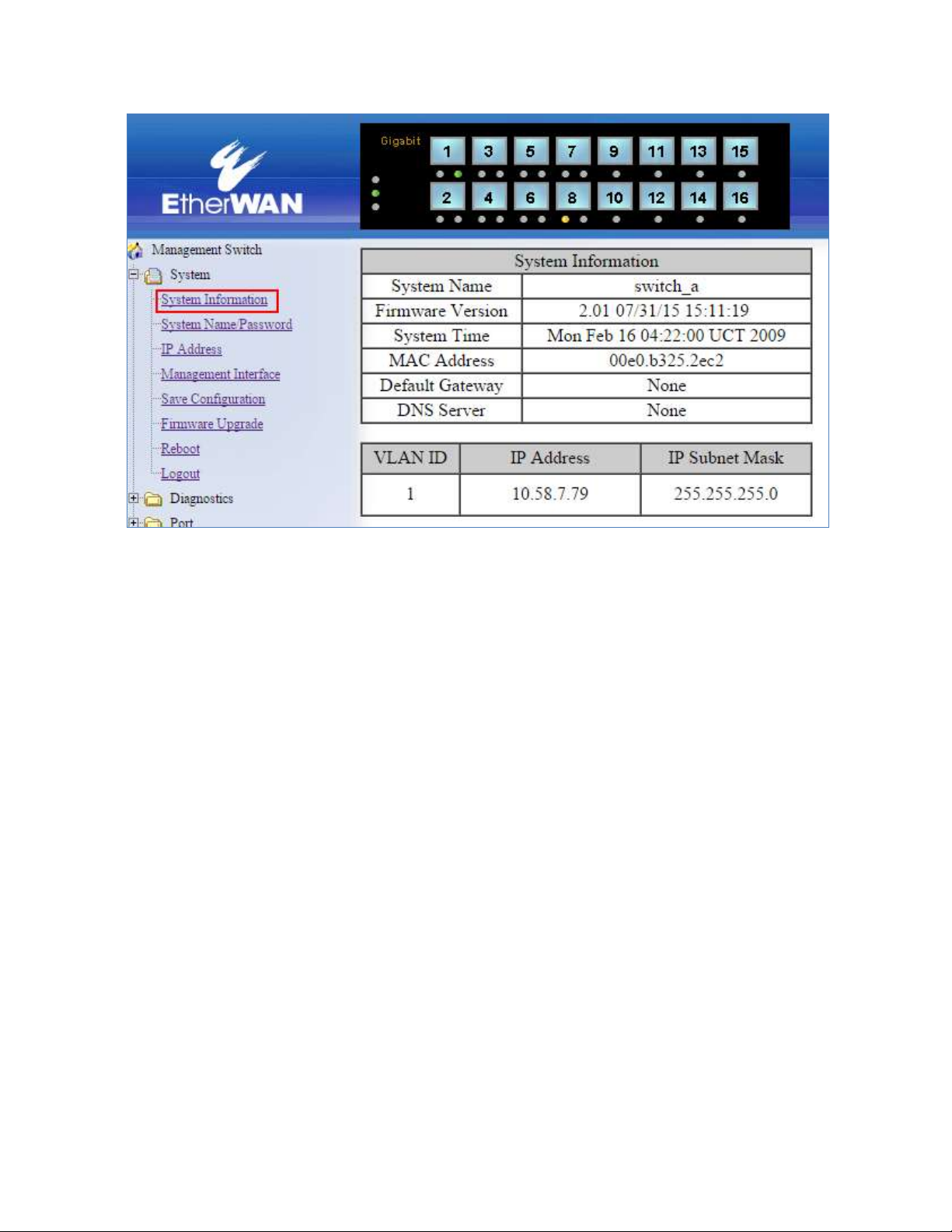
Figure 3: System Information
26
EtherWAN Managed Switch Users Guide
Page 27

System Name/Password
The System name is typically used by network administrators to make it easier to document
a networks infrastructure and locate equipment on large networks. If SNMP is enabled on
the switch, the system name can be found using MIB II (RFC1213) in the sysName property.
To change the system name:
1. Click on the + next to System.
2. Click on System Name/Password (see Figure 4).
3. Use your mouse to place the cursor in the System Name text box.
4. Replace the existing name with the name you want to assign to the switch.
5. Click on the Update Setting button.
By default, there is no password assigned to the switch. To add or change a password:
1. Click on the + next to System.
2. Click on System Name/Password (see Figure 4).
3. Use your mouse to place the cursor in the Password text box.
4. Enter the new password.
5. Retype the password in the Retype Password text box.
6. Click on the Update Setting button below the Retype Password text box.
Figure 4: System Name/Password
EtherWAN Managed Switch Users Guide
27
Page 28

System Name/Password using the CLI
For more information on CLI command usage see CLI Command Usage.
System Name
To set the system name on a switch, use the following CLI commands:
CLI Command Mode: General Configuration Mode
CLI Command Syntax:
hostname <name>
no hostname
Usage Example 1: Setting a Hostname
switch_a>enable
switch_a#configure terminal
switch_a(config)#hostname switch_a
switch_a(config)#q
switch_a#
Usage Example 2: Removing a Hostname
switch_a>enable
switch_a#configure terminal
switch_a(config)#no hostname
switch_a(config)#q
switch_a#
Password
To enable a password on a switch, use the following CLI commands:
CLI Command Mode: General Configuration Mode
CLI Command Syntax:
enable password <password>
Usage Example
switch_a>enable
switch_a#configure terminal
switch_a(config)#enable password mypassword
switch_a(config)#q
switch_a#
28
EtherWAN Managed Switch Users Guide
Page 29

IP Address
To navigate to the IP Address page:
1. Click on the + next to System
2. Click on IP Address (see Figure 5)
There are 4 settings on this page:
Static IP (see Simple IP Addressing)
DHCP Client
Use this to enable or disable DHCP on a VLAN.
To enable the DHCP Client:
1. Use the drop down box to enable the DHCP client on a particular VLAN
2. Click the Submit Button
Default Gateway
If DHCP is enabled, the gateway setting is controlled by the DHCP server. The
setting will be grayed out and the gateway supplied by the DHCP server will be
displayed. The default gateway setting can be used when using a Static IP address.
To enable the default gateway:
1. Use the drop-down box to enable the default gateway.
2. Type in the default gateway in the Default Gateway text box.
3. Click on the Apply & Save button.
DNS Server
If DHCP is enabled, the DNS Server setting is controlled by the DHCP server. The
setting will be grayed out and the DNS Server supplied by the DHCP server will be
displayed. The DNS Server setting can be used when using a Static IP address. To
enable the DNS Server:
1. Use the drop-down box to enable the DNS Server.
2. Type in the default gateway in the Default Gateway text box.
3. Click on the Submit button.
Note: After making changes to settings in the IP address section, the
configuration needs to be saved using the System/Save configuration page
(See Save Configuration)
29
EtherWAN Managed Switch Users Guide
Page 30
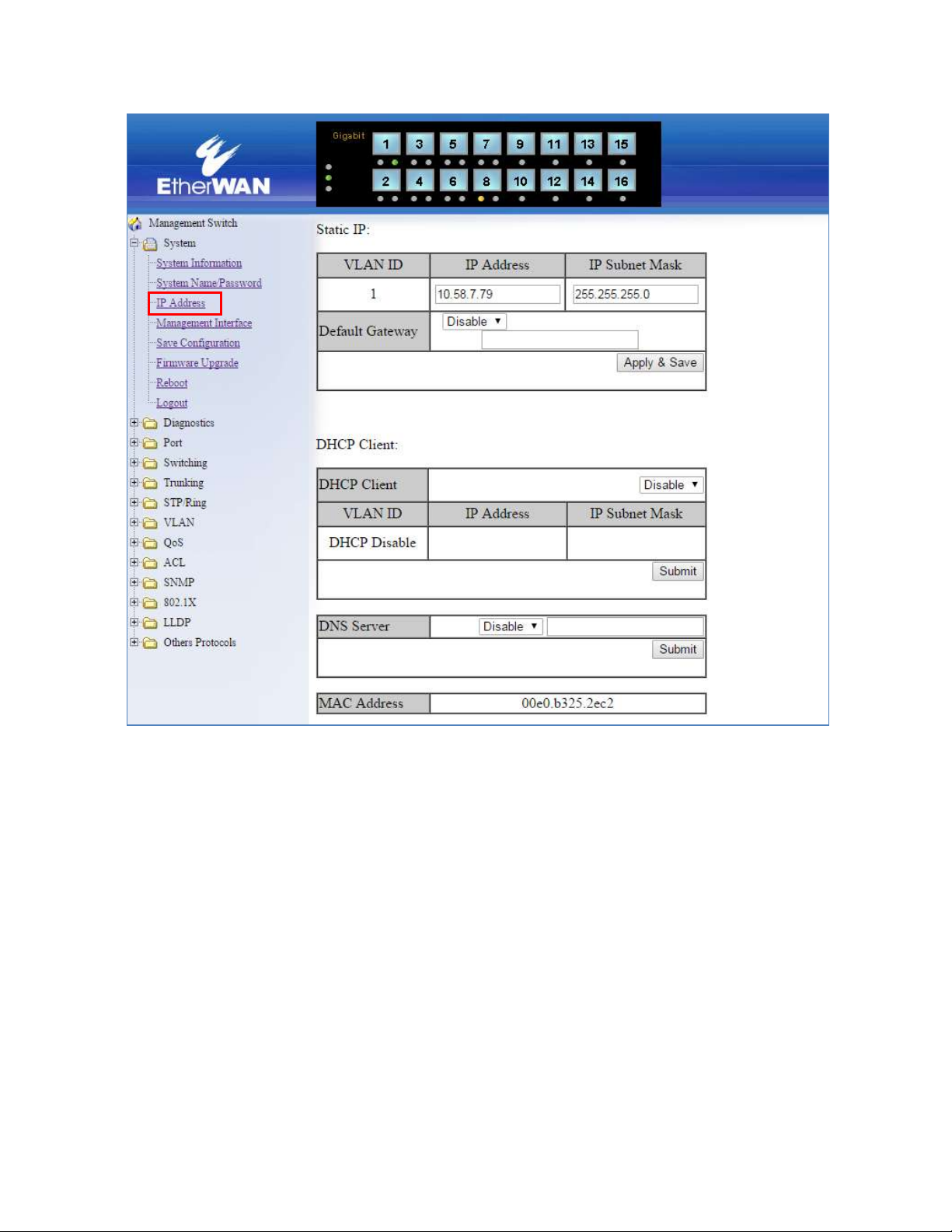
Figure 5: IP Address
30
EtherWAN Managed Switch Users Guide
Page 31

IP Address - Configuration using the CLI
For more information on CLI command usage see CLI Command Usage.
IP Address
To set the IP address, use the following CLI commands:
CLI Command Mode: General Configuration Mode
CLI Command Syntax:
ip address <A.B.C.D/M> (IP Address/Mask e.g. 10.0.0.1/8)
no ip address
Note: The Subnet Mask is defined as a Network Prefix instead of the common dotted
decimal (ex. 255.255.255.0).
The most commonly used Network Prefixes are:
/8 – Known as Class A. Also known in dotted decimal as 255.0.0.0
/16– Known as Class B. Also known in dotted decimal as 255.255.0.0
/24– Known as Class C. Also known in dotted decimal as 255.255.255.0
Usage Example 1: Assigning an IP address
switch_a>enable
switch_a#configure terminal
switch_a(config)#ip address 192.168.1.1/24
switch_a(config)#q
switch_a#write memory
Building configuration.....
[OK]
switch_a#q
switch_a#
Usage Example 2: Removing an IP address
switch_a>enable
switch_a#configure terminal
switch_a(config)#no ip address
switch_a(config)#q
switch_a#write memory
Building configuration.....
[OK]
switch_a#q
switch_a#
EtherWAN Managed Switch Users Guide
31
Page 32

Default Gateway
To set the Default Gateway, use the following CLI commands:
CLI Command Mode: General Configuration Mode
CLI Command Syntax:
ip default-gateway <A.B.C.D>
no ip default gateway
Usage Example 1: Setting the Gateway
switch_a>enable
switch_a#configure terminal
switch_a(config)#ip default-gateway 192.168.1.254
switch_a(config)#q
switch_a#write memory
Building configuration.....
[OK]
switch_a#q
switch_a#
Usage Example 2: Removing the Gateway
switch_a>enable
switch_a#configure terminal
switch_a(config)#no ip default-gateway
switch_a(config)#q
switch_a#write memory
Building configuration.....
[OK]
switch_a#q
switch_a#
32
EtherWAN Managed Switch Users Guide
Page 33

Domain Name Server (DNS)
To set the DNS, use the following CLI commands:
CLI Command Mode: General Configuration Mode
CLI Command Syntax:
ip dns <A.B.C.D>
no ip dns
Usage Example:
switch_a>enable
switch_a#configure terminal
switch_a(config)#ip dns 192.168.1.253
switch_a(config)#q
switch_a#write memory
Building configuration.....
[OK]
switch_a#q
switch_a#
Usage Example 2: Remove a DNS IP Address
switch_a>enable
switch_a#configure terminal
switch_a(config)#no ip dns
switch_a(config)#q
switch_a#write memory
Building configuration.....
[OK]
switch_a#q
switch_a#
EtherWAN Managed Switch Users Guide
33
Page 34

Enable/Disable DHCP Client on a VLAN
To enable the DHCP client on a VLAN, use the following CLI commands:
CLI Command Mode: Interface Configuration Mode
CLI Command Syntax:
get ip dhcp enable
no get ip dhcp enable
Usage Example – Enable DHCP Client on VLAN2:
switch_a>enable
switch_a#configure terminal
switch_a(config)#interface vlan1.2
switch_a(config-if)#get ip dhcp enable
switch_a(config-if)#q
switch_a(config)#q
switch_a#write memory
Building configuration.....
[OK]
switch_a#q
switch_a#
Enable/Disable Static IP on a VLAN
To set the IP address, use the following CLI commands:
CLI Command Mode: Interface Configuration Mode
CLI Command Syntax:
ip address <A.B.C.D>
no ip address <A.B.C.D>
Usage Example 1 – Enable Static IP on VLAN2:
switch_a>enable
switch_a#configure terminal
switch_a(config)#interface vlan1.2
switch_a(config-if)#ip address 192.168.1.11
switch_a(config-if)#q
switch_a(config)#q
switch_a#write memory
Building configuration.....
[OK]
switch_a#q
switch_a#
34
EtherWAN Managed Switch Users Guide
Page 35

Usage Example 2 – Enable DHCP Client on VLAN2:
switch_a>enable
switch_a#configure terminal
switch_a(config)#interface vlan1.2
switch_a(config-if)#no ip address 192.168.1.11
switch_a(config-if)#q
switch_a(config)#q
switch_a#write memory
Building configuration.....
[OK]
switch_a#q
switch_a#
EtherWAN Managed Switch Users Guide
35
Page 36

Management Interface
To navigate to the Management Interface page:
1. Click on the + next to System
2. Click on Management Interface
The Management Interface configuration page has three settings that allow the user to
configure the methods available to manage the EtherWAN Managed Switch.
HTTPS
HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure) allows the user to determine what
method, if any, is used to configure the EtherWAN Managed Switch. The default is
unencrypted HTTP (see Figure 6).
To disable the Web interface:
1. Uncheck Http and Https.
2. Click on the Update setting button.
Warning! Once the Submit button is pressed, the Web console will no longer
function. As a safety precaution, the configuration is not saved by default. Rebooting
the EtherWAN Managed Switch will restore the Web Console. To save the
configuration, connect using the new IP address.
To enable the Web Interface:
1. Check HTTP, HTTPS or both
2. Click on the Update Setting button.
3. Save the Configuration (see Save Configuration)
Telnet.
Telnet is a network protocol that allows a remote computer to log into the EtherWAN
Managed Switch to access its CLI (Command Line Interface). The CLI can be
accessed using Telnet, SSH and the serial port on the EtherWAN Managed Switch.
The secure method of accessing the CLI over a network is SSH.
To enable or disable Telnet:
1. Click the Enable or Disable radio button in the Telnet section on the
Management Interface page (see Figure 6 below)
2. Click on the Update Setting button
3. Save the Configuration (see Save Configuration)
EtherWAN Managed Switch Users Guide
36
Page 37

SSH (Secure Shell)
Secure Shell or SSH is a network protocol that allows data to be exchanged using a
secure channel between two networked devices such as a computer and the
EtherWAN Managed Switch. SSH is disabled by default on the V2.01 EtherWAN
Managed Switch.
To enable or disable SSH:
1. Click the Enable or Disable radio button in the SSH section on the
Management Interface page (see Figure 6)
2. Click on the Update Setting button
3. Save the Configuration (see Save Configuration)
Figure 6: Management Interface
37
EtherWAN Managed Switch Users Guide
Page 38

Management Interface Configuration using the CLI
For more information on CLI command usage see CLI Command Usage.
Enabling/Disabling Telnet
To enable or disable telnet, use the following CLI commands:
CLI Command Mode: General Configuration Mode
CLI Command Syntax:
ip telnet
no ip telnet
Usage Example 1: Enabling Telnet:
switch_a>enable
switch_a#configure terminal
switch_a(config)#ip telnet
switch_a(config)#q
switch_a#write memory
Building configuration.....
[OK]
switch_a#q
switch_a#
Usage Example 2: Disabling Telnet:
switch_a>enable
switch_a#configure terminal
switch_a(config)#no ip telnet
switch_a(config)#q
switch_a#write memory
Building configuration.....
[OK]
switch_a#q
Note: If using Telnet to run the CLI Commands that disable telnet you will lose your
connection. To Disable Telnet using the CLI, use SSH or the RS232 Console port on
the switch.
EtherWAN Managed Switch Users Guide
38
Page 39

Enabling/Disabling SSH
To enable or disable SSH, use the following CLI commands:
CLI Command Mode: General Configuration Mode
CLI Command Syntax:
ip ssh
no ip ssh
Usage Example 1: Enabling SSH:
switch_a>enable
switch_a#configure terminal
switch_a(config)#ip ssh
switch_a(config)#q
switch_a#write memory
Building configuration.....
[OK]
switch_a#q
switch_a#
Usage Example 2: Disabling SSH:
switch_a>enable
switch_a#configure terminal
switch_a(config)#no ip ssh
switch_a(config)#q
switch_a#write memory
Building configuration.....
[OK]
switch_a#q
Note: If using SSH to run the CLI Commands that disable SSH you will lose your
connection. To Disable SSH using the CLI, use Telnet or the RS232 Console port on
the switch.
EtherWAN Managed Switch Users Guide
39
Page 40

Enabling/Disabling HTTP and/or HTTPS
To enable or disable telnet, use the following CLI commands:
CLI Command Mode: General Configuration Mode
CLI Command Syntax:
ip http server
ip http secure-server
no ip http server
no ip http secure-server
Usage Example 1: Enabling HTTP:
switch_a>enable
switch_a#configure terminal
switch_a(config)#ip http server
switch_a(config)#q
switch_a#write memory
Building configuration.....
[OK]
switch_a#q
switch_a#
Usage Example 2: Disabling HTTP:
switch_a>enable
switch_a#configure terminal
switch_a(config)#no ip http server
switch_a(config)#q
switch_a#write memory
Building configuration.....
[OK]
switch_a#q
40
EtherWAN Managed Switch Users Guide
Page 41

Usage Example 3: Enabling HTTPS:
switch_a>enable
switch_a#configure terminal
switch_a(config)#ip http secure-server
switch_a(config)#q
switch_a#write memory
Building configuration.....
[OK]
switch_a#q
switch_a#
Usage Example 4: Disabling HTTPS:
switch_a>enable
switch_a#configure terminal
switch_a(config)#no ip http secure-server
switch_a(config)#q
switch_a#write memory
Building configuration.....
[OK]
switch_a#q
EtherWAN Managed Switch Users Guide
41
Page 42

Save Configuration Page
To navigate to the Save Configuration page:
1. Click on the + next to System
2. Click on Save Configuration
The Save Configuration page contains the following configuration functions (see Figure 7):
Save Configuration
To save the currently running configuration to the flash memory on the EtherWAN
Managed Switch:
1. Click the Save Configuration button
2. If the save is successful you will see the message:
Building configuration….. [OK]
Load Configuration
This function is used to load a previously saved configuration. Backing up and
loading a configuration is achieved using a TFTP server.
To load a configuration:
1. Enter the IP address of your TFTP server in the TFTP Server text box
2. Enter the name of the configuration file in the FILE text box
3. Click on the Backup button
4. If the file is successfully loaded the following message will be shown:
Success! System reboot is required!
Backup Configuration
This function is used to backup the current configuration of the EtherWAN Managed
Switch. Backing up the configuration is achieved using a TFTP server such as
TFTPD32.
To backup a configuration:
1. Enter the IP address of your TFTP server in the TFTP Server text box
2. Enter the name of the configuration file in the FILE text box
3. Click on the Backup button
4. If the backup is successful the following message will be shown:
tftp <filename> to ip <ip address> success!!
EtherWAN Managed Switch Users Guide
42
Page 43

Restore Default
To restore the V2.01 EtherWAN Managed Switch to factory defaults:
1. Click on the Restore Default button.
Auto Save
The Auto Save function is used to set the switch to automatically save the
configuration to flash. If the saved configuration is the same as the running
configuration then a save is not made. The Auto Save interval is used to determine
how often the running configuration is checked for changes.
To set the Auto Save function:
1. Click the drop-down box next to Auto Save.
2. Set the Auto Save interval (5~65535 sec)
Note: If a Firewall is running on the PC that is running the TFTP server it may need
to be temporarily disabled.
Figure 7: Save Configuration Page
EtherWAN Managed Switch Users Guide
43
Page 44

Save Configuration Page using the CLI
For more information on CLI command usage see CLI Command Usage.
Saving a Configuration
To save a running configuration, use the following CLI commands:
CLI Command Mode: General Configuration Mode
CLI Command Syntax:
write memory
Usage Example 1: Saving a Configuration
switch_a>enable
switch_a#write memory
Building configuration.....
[OK]
switch_a#q
switch_a#
Restore Default Settings
To restore the switch to its default settings, use the following CLI commands:
CLI Command Mode: General Configuration Mode
CLI Command Syntax:
restore default
Usage Example 1: Restoring Defaults
switch_a>enable
switch_a#restore default
switch_a#q
switch_a#
44
EtherWAN Managed Switch Users Guide
Page 45

Load Configuration from a TFTP Server
To Load a Configuration from a TFTP server, use the following CLI commands:
CLI Command Mode: Privileged Exec Mode
CLI Command Syntax:
install config-file <tftpserver_ipaddress> <filename>
Usage Example: Loading a Configuration
switch_a>enable
switch_a#install config-file 192.168.1.100 file_name.txt
switch_a#q
switch_a#
Save Configuration to a TFTP Server
To Save a Configuration to a TFTP server, use the following CLI commands:
CLI Command Mode: Privileged Exec Mode
CLI Command Syntax:
write config-file <tftpserver_ipaddress> <filename>
Usage Example: Saving a Configuration
switch_a>enable
switch_a#write config-file 192.168.1.100 flash.tgz
switch_a#q
switch_a>
45
EtherWAN Managed Switch Users Guide
Page 46

Auto Save Configuration
To set the Auto Save Configuration, use the following CLI commands:
CLI Command Mode: Privileged Exec Mode
CLI Command Syntax:
service auto-config enable
no service auto-config enable
service auto-config interval <number>
Usage Example 1: Enabling Auto Save and setting the interval
switch_a>enable
switch_a#service auto-config enable
switch_a#service auto-config interval 10
switch_a#q
switch_a>
Usage Example 2: Disabling Auto Save
switch_a>enable
switch_a#no service auto-config enable
switch_a#q
switch_a>
EtherWAN Managed Switch Users Guide
46
Page 47

Firmware Upgrade
To navigate to the Firmware Upgrade page:
1. Click on the + next to System
2. Click on Firmware Upgrade
To upgrade the firmware on the EtherWAN Managed Switch, a TFTP server is required. The
firmware file for the V2.01 EtherWAN Managed Switch is in a .TGZ or .IMG format. This is a
compressed file; however, it should not be decompressed before updating the V2.01
EtherWAN Managed Switch.
To update the firmware on the EtherWAN Managed Switch (see Figure 8):
1. Copy the firmware file to the correct directory for your TFTP server. The correct
directory depends on your TFTP server settings
2. Enter the filename of the firmware in the Filename text box.
3. Enter the IP Address of your TFTP server in the TFTP Server IP text box.
4. Click on the Upgrade button.
5. During the firmware upgrade, you will see the following messages. Do not reboot or
unplug the switch until the final message is received.
a. Downloading now, please wait...
b. tftp <filename>.img from ip <ip address> success!!
Install now. This may take several minutes, please
wait...
c. Firmware upgrade success!
Note: If a Firewall is running on the PC that is running the TFTP server it may need to
be temporarily disabled.
Figure 8: Firmware Upgrade Page
EtherWAN Managed Switch Users Guide
47
Page 48

Firmware Update using the CLI
For more information on CLI command usage see CLI Command Usage.
CLI Command Mode: Privileged Exec Mode
CLI Command Syntax:
install image <tftpserver_ipaddress> <filename>
Usage Example:
switch_a>enable
switch_a#install image 192.168.1.100 flash.img
switch_a#q
switch_a#
Note: Depending on the firmware being loaded, the extension may not be .img. The
Switch does not use the extension to validate firmware.
EtherWAN Managed Switch Users Guide
48
Page 49

Reboot
To navigate to the Reboot page:
1. Click on the + next to System
2. Click on Reboot
To reboot the EtherWAN Managed Switch:
1. Click on the Reboot button.
2. Click OK on the popup message.
Reboot using the CLI
For more information on CLI command usage see CLI Command Usage.
CLI Command Mode: Privileged Exec Mode
CLI Command Syntax:
reload
Usage Example:
switch_a>enable
switch_a#reload
switch_a#q
switch_a#
Logout
To log out of the Web Configuration Console:
1. Click on the + next to System
2. Click on Logout
Logout from the CLI
CLI Command Mode: Exec mode or Privileged Exec Mode
CLI Command Syntax:
logout
49
EtherWAN Managed Switch Users Guide
Page 50

DIAGNOSTICS
Utilization
To navigate to the Utilization page:
1. Click on the + next to Diagnostics.
2. Click on Utilization.
The Utilization page shows (see Figure 9):
CPU Utilization – Current and Max Utilization
Memory Utilization – Total, Used and Free Memory
Figure 9: Utilization Page
50
EtherWAN Managed Switch Users Guide
Page 51

System Log
To navigate to the System Log page:
1. Click on the + next to Diagnostics.
2. Click on System Log.
The System Log shows switch and port specific information as seen in Figure 10.
Figure 10: System Log
System log using CLI command
For more information on CLI command usage see CLI Command Usage.
CLI Command Mode: Exec Mode or Privileged Exec Mode
CLI Command Syntax:
show system-log
Usage Example:
switch_a#show system-log
switch_a#q
switch_a#
EtherWAN Managed Switch Users Guide
51
Page 52

Remote Logging
To navigate to the Remote Logging page:
1. Click on the + next to Diagnostics.
2. Click on Remote Logging.
Remote Logging to a Syslog server allows administrators to log important system and
debugging information. The Remote Logging configuration page allows reporting to a Syslog
server to be enabled or disabled as well as management of a list of Syslog servers to report
to (see Figure 11).
To configure the Remote Logging on the EtherWAN Managed Switch:
1. Click on the Enable or Disable radio button under Remote Logging.
2. Click on the Update Setting button.
To add a Syslog server:
1. Enter the IP Address of the Syslog Server in the Syslog Server IP text box.
2. Click on the Add Syslog Server button.
To delete a Syslog server from the list of servers currently on the switch:
1. Select the Syslog server from the Drop down box
2. Click on the Delete Syslog Server button
EtherWAN Managed Switch Users Guide
52
Page 53

Figure 11: Remote Logging Page
EtherWAN Managed Switch Users Guide
53
Page 54

Remote Logging using CLI commands
For more information on CLI command usage see CLI Command Usage.
Enable/Disable Remote Logging
CLI Command Mode: General Configuration Mode
CLI Command Syntax:
remote-log enable
no remote-log enable
Usage Example 1: Enable Remote Logging
switch_a>enable
switch_a#remote-log enable
switch_a#q
switch_a#
Usage Example 2: Disable Remote Logging
switch_a>enable
switch_a#no remote-log enable
switch_a#q
switch_a#
Add/Delete a Remote Logging Host
CLI Command Mode: General Configuration Mode
CLI Command Syntax:
remote-log add <ip_address>
remote-log del <ip_address>
remote-log del all
Usage Example 1: Add a Remote Logging Host
switch_a>enable
switch_a#remote-log add 192.168.1.100
switch_a#q
switch_a#
Usage Example 2: Delete a Remote Logging Host
switch_a>enable
switch_a#remote-log del 192.168.1.100
switch_a#q
switch_a#
EtherWAN Managed Switch Users Guide
54
Page 55

ARP Table
To navigate to the ARP Table page:
1. Click on the + next to Diagnostics.
2. Click on ARP Table.
The ARP Table page shows ARP (Address Resolution Protocol) entries that are stored in
the Switches ARP Table. This is useful for System Administrators for troubleshooting
purposes. The information shown is:
IP Address of the listed device
Hardware Address – For Ethernet devices this will always be 1.
Flags
o 2 = Device responded to ARP Request
o 0 = No response to ARP Request
Hardware Address – MAC Address of the listed device
VLAN – The VLAN that the listed device is on
Figure 12: ARP Table
55
EtherWAN Managed Switch Users Guide
Page 56

ARP Table using CLI Commands
For more information on CLI command usage see CLI Command Usage.
CLI Command Mode: General Configuration Mode
CLI Command Syntax:
show arp-table
Usage Example:
switch_a>enable
switch_a#show arp-table
IP address HW type Flags HW address Mask VLAN
10.58.7.130 1 2 00:50:B6:65:2A:22 * 1
switch_a#q
switch_a#
EtherWAN Managed Switch Users Guide
56
Page 57

Route Table
To navigate to the Route Table page:
1. Click on the + next to Diagnostics.
2. Click on Route Table.
The Route Table lists the routes to network destinations and metrics (distances) that are
associated with those routes. The Route Table contains information about the topology of
the network around it.
Figure 13: Route Table
Route Table Using CLI Commands
For more information on CLI command usage see CLI Command Usage.
CLI Command Mode: General Configuration Mode
CLI Command Syntax:
show route-table
Usage Example:
switch_a>enable
switch_a#show route-table
Destination Gateway Genmask Flags Metric Ref Use VLAN
10.58.7.0 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.0 U 0 0 0 1
switch_a#q
switch_a#
EtherWAN Managed Switch Users Guide
57
Page 58

Alarm Setting
This setting applies only to Switch models that have a hardware relay.
To navigate to the Alarm Setting page:
1. Click on the + next to Diagnostics.
2. Click on Alarm Setting.
The Alarm Setting page allows users to define Ethernet port Link-down and Power failure
alarms for triggering an alarm using the relay on the switch.
To configure an Ethernet port or Power input:
1. Select an Ethernet port or Power input from the drop-down box (see Figure 14).
Figure 14: Alarm Trigger
3. Select YES or NO from the drop-down box next to Trigger Enabled (see Figure 15).
4. Click Update Setting to save any changes made.
Figure 15: Trigger Enable
EtherWAN Managed Switch Users Guide
58
Page 59

PORT
Configuration
To navigate to the Configuration page:
1. Click on the + next to Port.
2. Click on Configuration.
Port configuration contains such useful features as flow control, port speed, and duplex
settings. Some users will find these settings very valuable such as when the switch is
connected to a latency-critical device such as a VOIP phone or IP camera or video
multiplexor. In these cases and others, the ability to alter the port settings can make the
difference between a poorly responding device and one that functions without loss of data or
clarity.
.The Configuration page shows (see Figure 16):
Port Number – fe(n) for 100mb ports and ge(n) for Gigabit ports
Link Status – Operational State of the Port’s Link (Read-Only)
Port Description – User-supplied Port Description
Admin Setting – Administratively Enable or Disable the Port.
Speed – Speed and Duplex Settings for Port.
Flow Control – State of Flow Control for the Port.
To provide a description to a port on the EtherWAN Managed Switch:
1. Click in the Description text box for the appropriate port.
2. Type in the description of the port.
3. Click on the Submit button.
To enable or disable a port on the EtherWAN Managed Switch:
1. Click on the drop-down box under Admin Setting and select either Link Up or Link
Down.
2. Click on the Submit button.
59
EtherWAN Managed Switch Users Guide
Page 60

To set the Port Speed and/or Port Duplex Settings on the EtherWAN Managed Switch:
1. Click on the drop-down box under Speed and select the desired port speed / duplex
settings for that port. Please note, not all port types will have the same options. For
example, 100Mb fiber ports will typically be limited to a single option of 100M/FD
(100Mbps and Full Duplex) while running 1Gb UTP ports will have six options for
speed/duplex.
2. Click on the Submit button.
To enable or disable a port’s Flow Control settings on the EtherWAN Managed Switch:
1. Click on the drop-down box under Flow Control and select either Enable or Disable.
2. Click on the Submit button.
Figure 16: Port Configuration
60
EtherWAN Managed Switch Users Guide
Page 61

Port Status
To navigate to the Port Status page:
1. Click on the + next to Port.
2. Click on Port Status.
This page is a read-only page that lists the settings described in the previous section. It is
useful if all the user intends to do is read the values of the port settings, not modify the port
settings. .The Port Status page shows (see Figure 17):
Port Number – fe(n) for 100mb ports and ge(n) for Gigabit ports
Link Status – Operational State of the Port’s Link.
Port Description – User-supplied Port Description
Admin Setting – Administratively State of the Port.
Speed – Speed and Duplex Settings for Port.
Flow Control – State of Flow Control for the Port.
Figure 17: Port Status
EtherWAN Managed Switch Users Guide
61
Page 62

Rate Control
To navigate to the Rate Control page:
1. Click on the + next to Port.
2. Click on Rate Control.
The Rate Control page allows the user to set the maximum throughput on a port or ports on
both packets entering the port (from the connected device) or packets leaving the port.
The Ingress text box controls the rate of data traveling into the port while the Egress text
box controls the rate of data leaving the port.
Note: Entries will be rounded down to the nearest acceptable rate value. If the value
entered is below the lowest acceptable value then the lowest acceptable value will be
used.
The Rate Control page is shown below (see Figure 18):
To provide either an ingress or egress rate control for a port on the EtherWAN Managed
Switch:
1. Click in the Ingress or Egress TextBox for the appropriate port.
2. Type in the ingress/egress rate for the port according to the values listed above.
3. Click on the Update Setting button.
Figure 18: Rate Control
EtherWAN Managed Switch Users Guide
62
Page 63

RMON Statistics
To navigate to the RMON Statistics page:
1. Click on the + next to Port.
2. Click on RMON Statistics.
RMON Statistics gives a detailed listing of the types and quantity of packets that a particular
port has seen since the last reboot of the switch (see Figure 19).
To view the RMON statistics for a particular port on the EtherWAN Managed Switch:
1. Click on the link to the port at the top of the RMON Statistics page.
To clear the RMON statistics for a particular port on the EtherWAN Managed Switch:
1. Click on the link to the port at the top of the RMON Statistics page.
2. Click on the Clear button at the bottom of the page.
3. The statistics for the port will update every ten seconds.
Pay particular attention to the values for CRC/Alignment errors and collisions. Nonzero
values for these fields can indicate that a port speed or duplex mismatch exists on the port.
Figure 19: RMON Page
EtherWAN Managed Switch Users Guide
63
Page 64

Per Port VLAN Activities
To navigate to the Per Port VLAN Activities page:
1. Click on the + next to Port.
2. Click on Per Port VLAN Activities.
This is a read-only page that will allow the user to see what devices are connected to a
particular port and the vlan associated with that device and port.
To clear the MAC addresses for a particular port on the EtherWAN Managed Switch (see
Figure 20):
1. Click on the link to the port at the top of the Per Port VLAN Activities page.
2. Click on the Clear MAC button at the bottom of the page.
3. The statistics for the port will update every ten seconds.
Figure 20: Port VLAN Activities
EtherWAN Managed Switch Users Guide
64
Page 65

Port Configuration Examples Using CLI Commands
For more information on CLI command usage see CLI Command Usage.
Setting the Port Description
To provide a description of a port use the CLI commands below:
CLI Command Mode: Interface Configuration Mode
CLI Command Syntax: description <description text>
Usage Example:
switch_a>enable
switch_a#configure terminal
switch_a(config)#int fe1
switch_a(config-if)#description A_Port_Description
switch_a(config)#q
switch_a(config)#q
switch_a#
Enable or Disable a Port
To administratively enable or disable a port use the CLI commands below:
CLI Command Mode: Interface Configuration Mode
CLI Command Syntax:
shutdown
no shutdown
Usage Example 1: Disabling a port:
switch_a>enable
switch_a#configure terminal
switch_a(config)#int fe1
switch_a(config-if)#shutdown
switch_a(config)#q
switch_a(config)#q
switch_a#
Usage Example 2: Enabling a port:
EtherWAN Managed Switch Users Guide
65
Page 66

switch_a>enable
switch_a#configure terminal
switch_a(config)#int fe1
switch_a(config-if)#no shutdown
switch_a(config)#q
switch_a(config)#q
switch_a#
Setting the Port Speed
To set the port speed for a port use the CLI commands below:
CLI Command Mode: Interface Configuration Mode
CLI Command Syntax: bandwidth <1-10000000000 bits> (usable units : k, m, g)
Usage Example:
switch_a>enable
switch_a#configure terminal
switch_a(config)#int fe1
switch_a(config-if)#bandwidth 100m
switch_a(config)#q
switch_a(config)#q
switch_a#
Setting Port Duplex
To set the duplex for a port use the CLI commands below:
CLI Command Mode: Interface Configuration Mode
CLI Command Syntax: duplex <full | half | auto>
Usage Example:
switch_a>enable
switch_a#configure terminal
switch_a(config)#int fe1
switch_a(config-if)#duplex full
switch_a(config)#q
switch_a(config)#q
switch_a#
EtherWAN Managed Switch Users Guide
66
Page 67

Enable or Disable Port FlowControl
To enable or disable flowcontrol for a port use the CLI commands below:
CLI Command Mode: Interface Configuration Mode
CLI Command Syntax: flowcontrol on
Usage Example:
switch_a>enable
switch_a#configure terminal
switch_a(config)#int fe1
switch_a(config-if)#flowcontrol on
switch_a(config)#q
switch_a(config)#q
switch_a#
Display Port Status
To display the port status for a port use the CLI commands below:
CLI Command Mode: Privileged Exec Mode
CLI Command Syntax: show interface <ifname>
Usage Example:
switch_a>enable
switch_a#show interface fe1
Setting a Ports Rate Control
To set a ports rate control use the CLI commands below:
CLI Command Mode: Interface Configuration Mode
CLI Command Syntax: rate-control <ingress | egress> value <value in kbps>
Usage Example:
switch_a>enable
switch_a#configure terminal
switch_a(config)#int fe1
switch_a(config-if)#rate-control ingress value 100000
switch_a(config)#q
switch_a(config)#q
switch_a#
67
EtherWAN Managed Switch Users Guide
Page 68

Display a Ports RMON Statistics
To display a ports RMON statistics use the CLI commands below:
CLI Command Mode: Privileged Exec Mode
CLI Command Syntax: show interface statistics <interface name>
Usage Example:
switch_a>enable
switch_a#show interface statistics fe1
switch_a#
Display a Ports VLAN Activities
To display a port’s VLAN activities use the CLI commands below:
CLI Command Mode: Privileged Exec Mode
CLI Command Syntax: show bridge interface <interface name>
Usage Example:
switch_a>enable
switch_a#show bridge interface fe1
switch_a#
EtherWAN Managed Switch Users Guide
68
Page 69

SWITCHING
Bridging
To learn MAC addresses, a switch reads all packets that it detects on the LAN or on the
local VLAN, looking for MAC addresses of sending nodes. It places these addresses into its
Ethernet Switching table, along with the interface on which the traffic was received and the
time when the address was learned. When the switch receives traffic on an interface, it
searches the Ethernet switching table for the MAC address of the destination. If the MAC
address is not found, the traffic is flooded out all of the other interfaces associated with the
VLAN. If traffic is received on an interface that is associated with VLAN 1 and there is no
entry in the Ethernet switching table for VLAN 1, then the traffic is flooded to all access and
trunk interfaces that are members of VLAN 1.
Flooding allows the switch to learn about destinations that are not yet in its Ethernet
switching table. If a certain destination MAC address is not in the Ethernet switching table,
the switch floods the traffic to all interfaces except the interface on which it was received.
When the destination node receives the flooded traffic, it sends an acknowledgment packet
back to the switch, allowing the switch to learn the MAC address of the node and to add the
address to its Ethernet switching table.
The switch uses a process called aging to keep the Ethernet switching table current. For
each MAC address in the Ethernet switching table, the switch records a timestamp of when
the information about the network node was learned. Each time the switch detects traffic
from a MAC address that is in its Ethernet switching table, it updates the timestamp of that
MAC address. A timer on the switch periodically checks the timestamp, and if it is older than
the value set for mac-table-aging-time, the switch removes the node's MAC address from
the Ethernet switching table. This aging process ensures that the switch tracks only active
MAC addresses on the network and that it is able to flush out from the Ethernet switching
table MAC addresses that are no longer available.
The user can configure:
How long MAC addresses remain in the Ethernet switching table
Add a MAC address permanently to the switching table
Prevent a MAC address from ever being registered in the switching table.
To navigate to the Bridging page:
1. Click on the + next to Switching.
2. Click on Bridging.
EtherWAN Managed Switch Users Guide
69
Page 70

Aging Time
The Aging Time value is a global value and represents the time that a networked device’s
MAC address will live in the switch’s memory before being removed. The default value is
300s (5 minutes) (see Figure 21).
To update the Aging Time value on the EtherWAN Managed Switch:
1. Click in the Error Disable Recovery text box at the top of the Port Security DynamicMAC page.
2. Type in the desired value. Values can be from 0 to 65535 seconds. A value of 0
indicates that the port is not to return to normal operating condition until an
administrator resets the port or the switch is restarted.
3. Click on the Update Setting button.
Threshold Level
The Threshold Level setting is a per port value. A traffic storm occurs when packets flood
the LAN, creating excessive traffic and degrading network performance. The traffic storm
control feature prevents LAN ports from being disrupted by a broadcast or multicast traffic
storm on physical interfaces. A Threshold is set to determine when the switch will react to
Broadcasts and/or Multicasts.
To set the Threshold level per port:
1. Type in the desired value. Values can be from 0.1 to 100. This value is a percentage
of allowable broadcast traffic for this port. Once this percentage of traffic is
exceeded, all broadcast traffic beyond this percentage is dropped.
2. Click on the Update Setting button.
Storm Control Type
The Storm Control Enabled Type setting is a per port value. The Storm Control Enabled
Type allows users to determine the type of storm control to be used by the switch.
To set the Storm Control Enabled Type:
1. Select the check box next to Broadcast and/or DFL-Multicast for the port that
needs to be changed
2. Click on the Update Setting button.
EtherWAN Managed Switch Users Guide
70
Page 71

Block Multicast
The Block Multicast setting is a per port value. Block Multicast is a straight-forward
description of a feature that is used to block multicast traffic from accessing a port (see
Figure 21).
To update the Block Multicast value for a port on the EtherWAN Managed Switch:
1. Click on the Block Multicast drop-down box for the port to be isolated.
2. Select the value enable on the Block Multicast drop-down box.
3. Click on the Update Setting button.
4. Repeat as necessary for all ports that are to have multicast traffic blocked.
Figure 21: Bridging
71
EtherWAN Managed Switch Users Guide
Page 72

Loopback Detect
Loopback detection is quite simply the ability of the switch to detect when a port on the
switch has been connected directly (or “looped back”) to another port on the switch. This
configuration would likely lead to a broadcast storm on the switch which would cause
network performance to suffer. Loopback detection offers the ability of the switch to detect
this condition and shut down the loop-backed port before any disruption of network traffic
occurs.
To navigate to the Loopback Detect page:
1. Click on the + next to Switching.
2. Click on Loopback Detect.
Loopback Detection (Global)
To globally enable the Loopback Detect feature of the EtherWAN Managed Switch (see
Figure 22):
1. Click on the Loopback Detect drop-down box.
2. Select Enable from the drop-down list.
3. Click on the Update Setting button.
Loopback Detect Action
To change the action that the switch takes when a loopback condition is detected (see
Figure 22):
1. Choose an action from the Loopback Detect Action drop-down list. The available
options are None and Error Disable.
2. Click on the Update Setting button.
Loopback Detect Recovery Time
To change the length of time that the Loopback Detect Action will stay in effect (see Figure
22):
1. Enter a value in the text box next to Error Disable Recovery. Valid values range
from 0 to 65535 seconds.
2. Click on the Update Setting button.
EtherWAN Managed Switch Users Guide
72
Page 73

Polling Interval
To change the polling interval of the Loopback Detect function (see Figure 22):
1. Enter a value in the text box next to Interval. Valid values range from 1 to 65535
seconds.
2. Click on the Update Setting button.
Figure 22: Loopback Detection
EtherWAN Managed Switch Users Guide
73
Page 74

Loopback Detection (Per Port)
To enable Loopback Detection for a particular port or ports on the EtherWAN Managed
Switch (see Figure 23):
1. Select the value Enable from the Mode drop-down list for a port on the Loopback
Detect page.
2. Click on the Update Setting button.
Figure 23: Loopback Detection (port)
74
EtherWAN Managed Switch Users Guide
Page 75

Storm Detect
The Storm Detect feature allows the switch to be configured to disable a port that is
receiving a large number of Broadcast and/or Multicast packets. The switch can monitor for
packets and take action based on percentage of bandwidth utilization or number of packets
per second.
To navigate to the Storm Detect page:
1. Click on the + next to Switching.
2. Click on Storm Detect.
Enable/Disable Storm Detection
1. Enable or Disable Storm Detection by Clicking on the drop down box in the StormDetect Configuration box (see Figure 24).
2. Set the Storm Detect interval to a number between 2 and 65535 seconds. The
Default value is 10 seconds.
3. Set the Storm-Detect errdisable-recovery time to value between 0 and 65535
seconds. The Default is 0 (disabled). This value determines if the switch should reenable the port after the specified value or leave the port disabled.
Figure 24: Storm Detect – Global
4. Set the By Utilization(%) for each port in the Storm-Detect Per Port Configuration
box (see Figure 25). The default is 0 (not limited). Setting this to a value between 1
and 100 will cause the port to be disabled when the defined percentage of bandwidth
is reached.
5. Set the type of packet to be monitored in the Drop-down box under By Broadcast /
Multicast+Broadcast Packets Per Second. Set the value to BC to monitor
Broadcast packets and BC-MC to monitor both Broadcast and Multicast packets.
EtherWAN Managed Switch Users Guide
75
Page 76

6. Set the number of packets per second to a value between 0 and 1000000 packets.
The default is 0 (not limited).
Figure 25: Storm Detect – Per Port
76
EtherWAN Managed Switch Users Guide
Page 77

Static MAC Entry
Occasionally, it may be useful to specify a MAC address on a particular port and VLAN
rather than adjusting the aging time for the entire switch. Alternatively, it is also possible and
even desirable to prevent a MAC address from ever being registered with a switch. These
features are offered under the Static MAC Entry menu.
To navigate to the Static MAC Entry menu:
1. Click on the + next to Switching.
2. Click on Static MAC Entry.
Adding a Static MAC Address to a Port
To add a static MAC entry for a particular port (see Figure 26):
1. Enter the MAC address for end the corresponding port’s text box. The format of the
MAC address should be in the form aaaa:bbbb:cccc).
2. Select the VLAN that this MAC address is associated with from the VLAN ID dropdown list for the port.
3. Click on the Submit button.
Figure 26: MAC Static Entry
EtherWAN Managed Switch Users Guide
77
Page 78

Removing a Static MAC Address from a Port
To remove a static MAC entry for a particular port (see Figure 27):
1. For a particular port, select the MAC address to be deleted from the Delete MAC
Address drop down box.
2. Click on the Submit button.
Figure 27: Removing a Static MAC
Adding a MAC to the Static-MAC-Entry Discard Table
To add a MAC address to the Static-MAC-Entry Discard table (see Figure 28):
1. Enter a MAC address in the form “0000.1234.abdc” in the Add MAC Address text
box of the Static-MAC-Entry-Discard section.
2. Select the VLAN associated with the MAC address.
3. It should be noted that while static MAC address for forwarding is associated with the
switch on a per-port basis. Static MAC discards are associated with the switch for all
ports.
4. Click on the Submit button.
Figure 28: Adding a MAC – Static-MAC-Entry Table
EtherWAN Managed Switch Users Guide
78
Page 79

Removing a MAC address from the Static-MAC-Entry Discard Table
To remove a MAC address from the Static-MAC-Entry Discard table (see Figure 29):
1. From the drop-down box underneath Delete MAC Address, select the MAC address
to be deleted.
2. Click on the Submit button.
Figure 29: Deleting a MAC – Static-MAC-Entry Table
EtherWAN Managed Switch Users Guide
79
Page 80

Port Mirroring
Port mirroring allows network traffic from one port to be copied or mirrored to another port.
This is a very useful troubleshooting feature in that all data from one port is sent to another
port which is attached to a computer or other network device that is configured to capture
packets. This enables a network administrator or technician to see the traffic that is entering
or leaving a particular port without disrupting normal network operations on the port that is
being mirrored.
To navigate to the Port Mirroring menu:
1. Click on the + next to Switching.
2. Click on Port Mirroring.
To configure port mirroring for a port or ports on the EtherWAN Managed Switch (see Figure
30):
1. Select the port or ports that traffic is to be mirrored from under the Mirror From
column.
2. Select the destination port under the Mirror To drop down box.
3. Select the type of traffic that should be mirrored from the Mirror Mode drop down
box. The available options are:
a. TX – transmit only
b. RX – Receive Only
c. TX/RX – Transmit and Receive.
4. Click on the Submit button.
EtherWAN Managed Switch Users Guide
80
Page 81

Figure 30: Port Mirroring
To disable port mirroring for a port or ports on the EtherWAN Managed Switch (see Figure
31):
1. Under the Current Settings section, the current port mirroring configuration should
be displayed.
2. Click on the Delete button.
.
Figure 31: Disabling Port Mirroring
EtherWAN Managed Switch Users Guide
81
Page 82

Link State Tracking
Link-state tracking binds the link state of multiple interfaces. Link-state tracking provides
redundancy in the network when used with server network interface card (NIC) adapter
teaming or bonding. When the server network adapters are configured in a primary or
secondary relationship known as teaming and the link is lost on the primary interface,
connectivity transparently changes to the secondary interface.
To navigate to the Link State Tracking menu:
1. Click on the + next to Switching.
2. Click on Link State Tracking.
Enable/Disable Link State Tracking
To enable Link State Tracking for a particular group on the EtherWAN Managed Switch (see
Figure 32):
1. Under Group Setting, click the check box of the Link State groups that are to be
enabled (or disabled).
2. Click on Update Setting.
Figure 32: Link State Tracking
Port Settings
To configure individual ports for a Link State group on the EtherWAN Managed Switch (see
Figure 33):
1. Under Port Setting, select the Link State Group that the port will belong to from the
Group drop-down box
EtherWAN Managed Switch Users Guide
82
Page 83

2. Select if the port is upstream or downstream from the Up/Down Stream)drop down
box.
3. Click on Update Setting.
Figure 33: Link State Tracking – Port Settings
EtherWAN Managed Switch Users Guide
83
Page 84

PoE - System and Port Settings
This section only applies to Managed EtherWAN Switches with support for PoE.
To navigate to the PoE page:
1. Click on the + next to Switching.
2. Click on PoE.
PoE System Setting
The PoE Page provides access to PoE System Setting information and configuration. The
information provided is (See Figure 34):
1. Main Supply Voltage
2. System Temperature
3. Power Allocation – Actual wattage supplied to attached PoE device(s)
4. System Power Budget – Configurable. The default value depends on the model of
switch.
Figure 34: PoE System Setting
EtherWAN Managed Switch Users Guide
84
Page 85

PoE Port Setting
The PoE Port Setting section provides the following configurable settings and information:
1. Enable Mode – Set the PoE Enable Mode by selecting one of the following settings
in the drop-down box under PoE Mode (see Figure 35)
o Enable – Enable PoE on a specific port
o Disable – Disable PoE on a specific port
o Scheduling – Schedule time of day that PoE will be enabled per port (see
PoE Scheduling)
2. Fixed Power Limit – Provides a ceiling to the maximum Wattage that can be
allocated to an attached PoE (PD) device on a port.
3. Power Priority – Use the Drop-Down box in the Power Priority column to set the
priority to High, Medium or Low. Once the PoE power requirements on the switch
has exceeded the PoE power budget. Power will be supplied to the port(s) with the
highest priority. In the case where multiple ports have the same priority, ports will be
prioritized by port number with the lower numbered port receiving priority.
4. Power Down Alarm – This setting only applies to EtherWAN Switches that have a
relay. If this box is check, losing PoE power on a port triggers the relay on the switch.
5. Status – Informational only. Provides the status of the PoE port
6. PD Class - Informational only. Provides the PoE Classification of the PoE (PD)
device attached to the PoE port
7. Current (mA) – Informational only. Shows the current draw from the attached PoE
(PD) device.
8. Consumption (W) - Informational only. Shows the power consumption of the
attached PoE (PD) device.
EtherWAN Managed Switch Users Guide
85
Page 86

Figure 35: PoE Port Setting
EtherWAN Managed Switch Users Guide
86
Page 87

PoE Scheduling
PoE Scheduling allows PoE ports to have their power up time scheduled by hour of the day
and day of the week. In order for a port to follow a schedule defined here, the port must be
set to Scheduling on the PoE settings page (see PoE Port Setting)
To navigate to the PoE Scheduling page:
1. Click on the + next to Switching.
2. Click on PoE Scheduling.
Each PoE port on the switch can be schedule to power up and down automatically. To
configure a port:
1. Select the port from the drop-down list (See Figure 36)
Figure 36: Selecting a Port
2. Select the hour(s) of day for each day of the week (see Figure 37).
3. Click on the Submit button.
EtherWAN Managed Switch Users Guide
87
Page 88

Figure 37: PoE Power Scheduling
EtherWAN Managed Switch Users Guide
88
Page 89

Switch Configuration Examples Using CLI Commands
For more information on CLI command usage see CLI Command Usage.
Setting the Aging Time Value
To update the Aging Time value on the EtherWAN Managed Switch, use the CLI
commands below:
CLI Command Mode: General Configuration Mode
CLI Command Syntax: bridge 1 ageing-time (time in ms)
Usage Example:
switch_a>enable
switch_a#configure terminal
switch_a(config)#bridge 1 ageing time 300
switch_a(config)#q
switch_a#
Enabling Port Isolation
To enable Port Isolation for a port on the EtherWAN Managed Switch, use the CLI
commands below:
CLI Command Mode: Interface Configuration Mode
CLI Command Syntax: port-isolation enable
Usage Example:
switch_a>enable
switch_a#configure terminal
switch_a#configure interface fe1
switch_a(config)#port-isolation enable
switch_a(config)#q
switch_a(config)#q
switch_a#
89
EtherWAN Managed Switch Users Guide
Page 90

Enabling Block Multicast
To enable Block Multicast for a port on the EtherWAN Managed Switch, use the CLI
commands below:
CLI Command Mode: Interface Configuration Mode
CLI Command Syntax: switchport block multicast
Usage Example:
switch_a>enable
switch_a#configure terminal
switch_a#configure interface fe1
switch_a(config)#switchport block multicast
switch_a(config)#q
switch_a(config)#q
switch_a#
Setting Storm Control
To set the value for the Broadcast and or DLF-Multicast Storm Control value of a port on
the EtherWAN Managed Switch, use the CLI commands below:
CLI Command Mode: Interface Configuration Mode
CLI Command Syntax: stormcontrol <broadcast | dlf-multicast> <level>
Usage Example:
switch_a>enable
switch_a#configure terminal
switch_a#configure interface fe1
switch_a(config)#storm-control broadcast 20
switch_a(config)#q
switch_a(config)#q
switch_a#
90
EtherWAN Managed Switch Users Guide
Page 91

Enabling Loopback Detect (Global)
To enable Loopback Detect on the EtherWAN Managed Switch, use the CLI commands
below:
CLI Command Mode: General Configuration Mode
CLI Command Syntax: bridge 1 loopback-detect <enable | disable>
Usage Example:
switch_a>enable
switch_a#configure terminal
switch_a(config)#bridge 1 loopback-detect enable
switch_a(config)#q
switch_a#
Setting the Loopback Detect Action
To set the action for Loopback Detect on the EtherWAN Managed Switch, use the CLI
commands below:
CLI Command Mode: General Configuration Mode
CLI Command Syntax: bridge 1 loopback-detect action <err-disable | none>
Usage Example:
switch_a>enable
switch_a#configure terminal
switch_a(config)#bridge 1 loopback-detect action err-disable
switch_a(config)#q
switch_a#
Setting the Loopback Detect Recovery Time
To set the recovery time for Loopback Detect on the EtherWAN Managed Switch, use the
CLI commands below:
CLI Command Mode: General Configuration Mode
CLI Command Syntax: bridge 1 loopback-detect errdisable-recovery <0-65535>
Usage Example:
switch_a>enable
switch_a#configure terminal
switch_a(config)#bridge 1 loopback-detect errdisable-recovery 30
switch_a(config)#q
switch_a#
91
EtherWAN Managed Switch Users Guide
Page 92

Setting the Loopback Detect Polling Interval
To set the polling interval for Loopback Detect on the EtherWAN Managed Switch, use the
CLI commands below:
CLI Command Mode: General Configuration Mode
CLI Command Syntax: bridge 1 loopback-detect interval <1-65535>
Usage Example:
switch_a>enable
switch_a#configure terminal
switch_a(config)#bridge 1 loopback-detect interval 5
switch_a(config)#q
switch_a#
Enabling Loopback Detect (Port)
To enable Loopback Detection on a port on the EtherWAN Managed Switch, use the CLI
commands below:
CLI Command Mode: Interface Configuration Mode
CLI Command Syntax: loopback-detect enable
Usage Example:
switch_a>enable
switch_a#configure terminal
switch_a#interface fe1
switch_a(config)# loopback-detect enable
switch_a(config)#q
switch_a(config)#q
switch_a#
92
EtherWAN Managed Switch Users Guide
Page 93

Configuring Storm-Detect
To Enable or Disable Storm-Detect use the CLI command Below:
CLI Command Mode: General Configuration Mode
CLI Command Syntax:
bridge 1 storm-detect errdisable
no bridge 1 storm-detect errdisable
Default: Disabled
Usage Example – Enabling storm detect:
switch_a>enable
switch_a#configure terminal
switch_a(config)# bridge 1 storm-detect errdisable
switch_a(config)#q
switch_a#
Usage Example – Disabling storm detect:
switch_a>enable
switch_a#configure terminal
switch_a(config)# no bridge 1 storm-detect errdisable
switch_a(config)#q
switch_a#
To set the storm-detect interval use the following CLI commands:
CLI Command Mode: General Configuration Mode
CLI Command Syntax: bridge 1 storm-detect interval <2-65535>
Default: 10
Usage Example:
switch_a>enable
switch_a#configure terminal
switch_a(config)# bridge 1 storm-detect interval 10
switch_a(config)#q
switch_a#
93
EtherWAN Managed Switch Users Guide
Page 94

To set the storm-detect recovery time use the following CLI commands:
CLI Command Mode: General Configuration Mode
CLI Command Syntax: bridge 1 storm-detect errdisable-recovery <0-65535>
Default: 0 No errdisable recovery.
Usage Example:
switch_a>enable
switch_a#configure terminal
switch_a(config)# bridge 1 storm-detect errdisable-recovery 60
switch_a(config)#q
switch_a#
Storm Detect Packet Type
Enable this port’s storm detect by detect number of broadcast or broadcast plus
multicast packets per second. Unit is packets per second. Set to 0 to disable this feature.
To set the storm-detect packet type use the following CLI commands:
CLI Command Mode: Interface Mode
CLI Command Syntax: storm-detect (bc | mc-bc) pps <0-100000>
bc = broadcast only
mc-bc = count broadcast & multicast packets together.
Default: 0 (Disabled)
Usage Example 1 – Enabling Multicast + Broadcast:
switch_a>enable
switch_a#configure terminal
switch_a(config)# interface fe1
switch_a(config-if)#storm-detect mc-bc pps 50000
switch_a(config-if)#q
switch_a(config)#q
switch_a#
94
EtherWAN Managed Switch Users Guide
Page 95

Usage Example 2 – Enabling Multicast + Broadcast:
switch_a>enable
switch_a#configure terminal
switch_a(config)# interface fe1
switch_a(config-if)#storm-detect bc pps 50000
switch_a(config-if)#q
switch_a(config)#q
switch_a#
To set the storm-detect utilization use the following CLI commands:
CLI Command Mode: Interface Mode
CLI Command Syntax: storm-detect utilization <0-100>
Default: 0 (Disabled)
Usage Example:
switch_a>enable
switch_a#configure terminal
switch_a(config)# interface fe1
switch_a(config-if)#storm-detect utilization 80
switch_a(config-if)#q
switch_a(config)#q
switch_a#
To disable storm-detect on a port use the following CLI commands:
CLI Command Mode: Interface Mode
CLI Command Syntax: no storm-detect port enable
Usage Example:
switch_a>enable
switch_a#configure terminal
switch_a(config)# interface fe1
switch_a(config-if)#no storm-detect port enable
switch_a(config-if)#q
switch_a(config)#q
switch_a#
95
EtherWAN Managed Switch Users Guide
Page 96

To disable storm-detect on a port use the following CLI commands:
CLI Command Mode: Interface Mode
CLI Command Syntax: no storm-detect port enable
Usage Example:
switch_a>enable
switch_a#configure terminal
switch_a(config)# interface fe1
switch_a(config-if)#no storm-detect port enable
switch_a(config-if)#q
switch_a(config)#q
switch_a#
EtherWAN Managed Switch Users Guide
96
Page 97

Adding a MAC Address for Static-MAC-Entry Forwarding
To add a MAC address for Static-MAC-Entry Forwarding for a port on the EtherWAN
Managed Switch, use the CLI commands below:
CLI Command Mode: General Configuration Mode
CLI Command Syntax:
bridge 1 address <mac address> forward <interface> vlan <vlan id>
Usage Example:
switch_a>enable
switch_a#configure terminal
switch_a(config)# bridge 1 address 00e0.abcd.1245 forward fe1 vlan 1
switch_a(config)#q
switch_a#
Adding a MAC Address for Static-MAC-Entry Discarding
To add a MAC address for Static-MAC-Entry Discarding for a port on the EtherWAN
Managed Switch, use the CLI commands below:
CLI Command Mode: General Configuration Mode
CLI Command Syntax: bridge 1 address <mac address> discard vlan <vlan id>
Usage Example:
switch_a>enable
switch_a#configure terminal
switch_a(config)# bridge 1 address 00e0.abcd.1245 discard vlan 1
switch_a(config)#q
switch_a#
97
EtherWAN Managed Switch Users Guide
Page 98

Configuring Port Mirroring
To configure a port for Port Mirroring on the EtherWAN Managed Switch, use the CLI
commands below:
CLI Command Mode: Interface Configuration Mode
CLI Command Syntax: mirror interface <interface> direction <both | tx | rx>
Usage Example:
switch_a>enable
switch_a#configure terminal
switch_a#interface ge1
switch_a(config)# mirror interface fe1 direction both
switch_a(config)#q
switch_a(config)#q
switch_a#
Enabling a Link State Tracking Group
To enable a Link State Tracking Group on the EtherWAN Managed Switch, use the CLI
commands below:
CLI Command Mode: General Configuration Mode
CLI Command Syntax: link state track <group #>
Usage Example:
switch_a>enable
switch_a#configure terminal
switch_a(config)# link state track 4
switch_a(config)#q
switch_a#
98
EtherWAN Managed Switch Users Guide
Page 99

Assigning a Port to a Link State Tracking Group
To assign a port to a Link State Tracking group on the EtherWAN Managed Switch, use the
following CLI commands:
CLI Command Mode: Interface Configuration Mode
CLI Command Syntax: link state group <group #> <upstream | downstream>
Usage Example:
switch_a>enable
switch_a#configure terminal
switch_a(config)#interface fe1
switch_a(config-if)# link state group 4 downstream
switch_a(config-if)#q
switch_a(config)#q
switch_a#
Setting PoE Power Budget
To set the PoE Power Budget use the following CLI commands
CLI Command Mode: General Configuration Mode
CLI Command Syntax: poe system-power-budget <value>
Usage Example:
switch_a>enable
switch_a#configure terminal
switch_a(config)# poe system-power-budget 144.14
switch_a(config)#q
switch_a#
EtherWAN Managed Switch Users Guide
99
Page 100

CLI Command (click link for syntax)
Function
enable
Enables PoE on a port
fixed-power-limit
Sets a fixed wattage for a PoE port
power-down-alarm
Turns on alarm by relay on PoE power down
power-priority
Sets priority of power distribution to ports
scheduling
Enable Scheduling
schedule-time
Sets schedule time to power PoE ports
schedule-time-hour
Schedule time (hour)
PoE Port Settings
The following commands are used to set PoE functions related directly to individual PoE
ports:
enable
To enable or disable PoE on a port use the following CLI commands
CLI Command Mode: Interface Configuration Mode
CLI Command Syntax:
poe enable
no poe enable
Usage Example 1 – Enabling PoE on a port:
switch_a>enable
switch_a#configure terminal
switch_a(config)# interface fe1
switch_a(config-if)# poe enable
switch_a(config-if)#q
switch_a(config)#q
switch_a#
Usage Example 2 – Disabling PoE on a port:
switch_a>enable
switch_a#configure terminal
switch_a(config)# interface fe1
switch_a(config-if)# no poe enable
switch_a(config-if)#q
switch_a(config)#q
switch_a#
100
EtherWAN Managed Switch Users Guide
 Loading...
Loading...