ESD CAN-CBM-DP Software Manual

CAN-CBM-DP
y
PROFIBUS-DP / CAN-Gatewa
Software Manual
to Product: C.2844.xx
CAN-CBM-DP Software Manual Rev. 2.0
esd electronic system design gmbh
Vahrenwalder Str. 207 • 30165 Hannover • Germany
www.esd-electronics.com • Fax: 0511/37 29 8-68
Phone: 0511/37 29 80 • International: +49-5 11-37 29 80

N O T E
The information in this document has been carefully checked and is believed to be entirely reliable. esd
makes no warranty of any kind with regard to the material in this document, and assumes no
responsibility for any errors that may appear in this document. esd reserves the right to make changes
without notice to this, or any of it s product s, to improve reliability, performance or design.
esd assumes no responsibility for the use of any circuitry other than circuitry which is part of a product
of esd gmbh.
esd does not convey to the purchaser of the product described herein any license under the patent rights
of esd gmbh nor the rights of others.
esd electronic system design gmbh
Vahrenwalder Str. 207
30165 Hannover
Germany
Phone: +49-511-372 98-0
Fax: +49-511-372 98-68
E-mail: info@esd-electronics.com
Internet: www.esd-electronics.com
USA / Canada:
esd electronics Inc.
525 Bernardston Road
Suite 1
Greenfield, MA 01301
USA
Phone: +1-800-732-8006
Fax: +1-800-732-8093
E-mail: us-sales@esd-electronics.com
Internet: www.esd-electronics.us
CAN-CBM-DP Software Manual Rev. 2.0
Manual file:
I:\texte\Doku\MANUALS\CAN\CBM\DP\Englisch\DP_Software\DPCAN20S.en9
Date of print:
Manual order No.:
Software order No.:
Described software version:
15.12.2006
C.2844.21
CAN 2.0A: C.2844.02/03 CAN 2.0A/B: C.2844.05
Command-File: cbmdp18
DP/CANopen: V. 1.07
Command-File: cbmdpb01
DP/CANopen: V. 1.11
Changes in the chapters
The changes in the user’s manual listed below affect changes in the firmware as well as changes in the
description of the facts only.
Manual Rev. Chapter Changes versus previous version
5 Chapter restructured, notes inserted
1.9
7 Complete chapter restructured
7.1 Chapter: “Editing the GSD-File with a Text Editor” inserted
Technical details are subject to change without notice.
CAN-CBM-DP Software Manual Rev. 2.0

This page is intentionally left blank.
CAN-CBM-DP Software Manual Rev. 2.0

Contents
Page
1. Overview
1.1 About this Manual ....................................................5
1.2 Introduction into Functionality of the Firmware .............................. 5
1.3 Configuration via PROFIBUS-DP ........................................ 5
1.4 The Diagnose and Configuration Tool CICT ................................6
1.5 More addressable Identifiers via Page Mode................................. 6
2. Functionality of the Local Firmware
2.1 PROFIBUS-Slave Address.............................................. 7
2.2 User Data........................................................... 8
2.3 Watchdog (Reaction Control) ........................................... 8
2.4 Diagnose ........................................................... 8
2.5 Parameter Telegram (CAN Bit Rate) ...................................... 8
2.6 Global-Control Services (FREEZE, SYNC, UNSYNC) ........................8
2.7 PROFIBUS-DP Profiles................................................ 8
2.8 More Addressable CAN Identifiers in Page Mode.............................9
3. Implementing and Diagnose
3.1 Prerequisites for Implementation ........................................ 10
3.2 Implementation ..................................................... 10
3.3 Diagnose via LED Display ............................................. 12
3.4 Slave Diagnose...................................................... 13
................................................................. 5
................................................. 10
3.2.1 Strategy .................................................. 10
3.2.2 Start-Up .................................................. 11
3.2.3 Data Transfer .............................................. 11
3.4.1 Diagnose Bytes 0...5 ......................................... 13
3.4.1.1 Station Status 1....................................... 14
3.4.1.2 Station Status 2....................................... 15
3.4.1.3 Station Status 3....................................... 16
3.4.1.4 Diagnose Byte 3: Master-PROFIBUS Address ............... 16
3.4.1.5 Diagnose Bytes 4 and 5: Manufacturer Identification........... 16
3.4.2 External (Module-Specific) Diagnose Bytes........................ 17
........................................... 7
4. GSD File
5. Configuration via SIMATIC Manager
CAN-CBM-DP
................................................................. 18
5.1 Course of Configuration .............................................. 21
5.1.1 Set PROFIBUS address ...................................... 22
5.1.2 Parameter Telegram ......................................... 23
CAN-Bitrate ............................................... 24
Communication Window...................................... 24
RTR-Frames ............................................... 24
CANopen-Slave ............................................ 24
CANopen-Master ........................................... 24
Start-Frame................................................ 24
Page-Mode ................................................ 24
Module-ID:................................................ 25
Software Manual Rev. 2.0 1
......................................... 21

Contents
5.2 Description of Input Window ‘Properties - DP Slave’ ........................ 29
5.3 The Communication Window........................................... 31
Page
Wakeup Time .............................................. 25
SYNC Time:............................................... 26
5.1.3 Assigning the Slots of the DP Slave.............................. 27
5.1.4 Configuration of Slots ........................................ 28
5.1.5 Save Settings to Hard Disk .................................... 28
5.3.1 Introduction ............................................... 31
5.3.2 Configuring the Communication Window ......................... 32
5.3.3 Format of Communication Window.............................. 33
5.3.3.1 Write Bytes of the Communication Window ................. 33
5.3.3.2 Read Bytes of the Communication Window.................. 34
5.3.4 Examples on the Communication Window......................... 38
5.3.4.1 Transmitting data ..................................... 38
5.3.4.2 Receiving Data .......................................40
6. Page Mode
6.1 Properties.......................................................... 43
6.2 Activation ......................................................... 43
6.3 Communication Window in Page Mode ................................... 43
6.4 Mode of Operation................................................... 44
6.5 Using the Page Mode with FBs and DBs .................................. 54
6.6 Methodology .......................................................63
............................................................... 43
6.4.1 Overview ................................................. 44
6.4.2 Definition of PLC-Addresses................................... 45
6.4.3 Page Structure ............................................. 48
6.4.4 Setup via Page 0 and 1 ....................................... 49
6.4.5 Tx-Configuration via Pages 51...150 ............................. 50
6.4.6 Rx-Configuration via Pages 151...250 ............................51
6.4.7 Data Exchange via Pages 251...n ................................ 52
6.5.1 Function Block FB 2: Configuration and Data Exchange .............54
FREIGABE ...............................................55
WRITE_ADDRESS ......................................... 55
WRITE_CONFIG_DB .......................................55
READ_ADDRESS .......................................... 56
READ_CONFIG_DB ........................................ 57
WRITE_DB ...............................................59
READ_DB ................................................ 61
7. Configuration via Tools of other Manufacturers
7.1 Editing the GSD-File with a Text Editor................................... 64
7.2 Parameter Display and Configuration with the Tool CICT ..................... 67
7.2.1 Display and Configuration..................................... 67
7.2.2 Hardware Selection .......................................... 68
7.2.3 Online / Offline Configuration ..................................69
7.2.4 Configuration of the CAN-CBM-DP Module ...................... 70
7.2.4.1 Properties in the Data Mapping Dialog Box.................. 71
7.2.4.2 Display and Edit User Parameter Properties.................. 74
................................. 64
CAN-CBM-DP
Software Manual Rev. 2.02

Contents
Page
Meaning of User Parameters ............................. 74
Editing User Parameter Properties......................... 77
Deleting all User Parameter Properties...................... 78
Displaying Information about Wrong User Parameters.......... 78
7.2.4.3 Data-Mapping Dialog Box in Page Mode ................... 79
7.2.5 Configuration Example ....................................... 80
7.2.6 Managing the Configuration Files ............................... 81
7.2.7 Diagnose .................................................. 83
7.2.7.1 Search Modules....................................... 83
7.2.7.2 Look CANOPEN Modules .............................. 84
7.2.7.3 Config Modules.......................................85
7.2.8 Maintenance ............................................... 87
7.2.8.1 Memory ............................................ 87
8. Examples
8.1 Application Example with Page Mode .................................... 89
9. Important CANopen Messages
................................................................ 89
............................................. 101
CAN-CBM-DP
Software Manual Rev. 2.0 3

This page is intentionally left blank.
CAN-CBM-DP Software Manual Rev. 2.04

Overview
1. Overview
1.1 About this Manual
This manual describes the local firmware of the CAN-CBM-DP module. The local firmware controls
the data exchange between PROFIBUS-DP (abbreviated to PROFIBUS below) and CAN.
Layer 2 Implementation
The manual describes the Layer 2 implementation and the implemented CANopen functions.
Furthermore, the Windows configuration tool CICT will be described. By means of CICT parameters
of the module can be displayed via the serial interface. A limited setting by means of CICT is possible,
as well.
Page Mode
Furthermore, the manual describes the Page Mode which was developed to allow more than 48 CAN
identifiers to be controlled by one gateway. For a general understanding fundamental functions of the
Page Mode will be described first, followed by descriptions of the function blocks (FBs) and data
blocks (DBs), which are used to realize the Page Mode.
11-Bit and 29-Bit Identifier
The module is available with two firmware versions. The version with the order-no. C.2844.03 supports
only 11-bit CAN identifier and the version with the order-no. C.2844.05 supports 11-bit and 29-bit
CAN identifier.
1.2 Introduction into Functionality of the Firmware
The gateway simulates a slave device with a defined number of input and output bytes to the
PROFIBUS. After the gateway has been configured CAN devices such as PROFIBUS slaves can be
operated.
The PROFIBUS output bytes are transmitted to the CAN-bus. One to eight output bytes are assigned
to an Tx-identifier. Rx-identifiers are assigned to the input bytes on CAN side. Received CAN data is
treated as input data by the PROFIBUS.
The PROFIBUS station address is set directly at the CAN-CBM-DP module by means of coding
switches.
1.3 Configuration via PROFIBUS-DP
The CAN-CBM-DP module is configured via the PROFIBUS. The Siemens SIMATIC Manager for
S7, for example, can be used as a configuration tool. Here, the gateway is assigned with logical modules
which are assigned with further parameters such as the PLC address, data direction, data length and
CAN identifier.
CAN-CBM-DP Software Manual Rev. 2.0 5

Overview
1.4 The Diagnose and Configuration Tool
The tool CICT offers an operating surface designed for the CAN-CBM-DP for the display of parameters
and configuration of the module. Since the module is mainly to be configured via the PROFIBUS, the
tool is mainly used for the display of transmitted parameters. Only a limited number of parameters can
be modified.
CICT
1.5 More addressable Identifiers via Page Mode
Page-Mode offers the possibility t o address more CAN-Identifiers than a PROFIBUS-Telegramm can
contain (thus more than 48). The number of t he identifiers possible is only limited by the available
memory capacity of the PLC and the CAN-Gateway.
Note: Page Mode can only be used, if the Siemens SIMATIC Manager for S7 is used as
configuration-tool!
CAN-CBM-DP Software Manual Rev. 2.06

2. Functionality of the Local Firmware
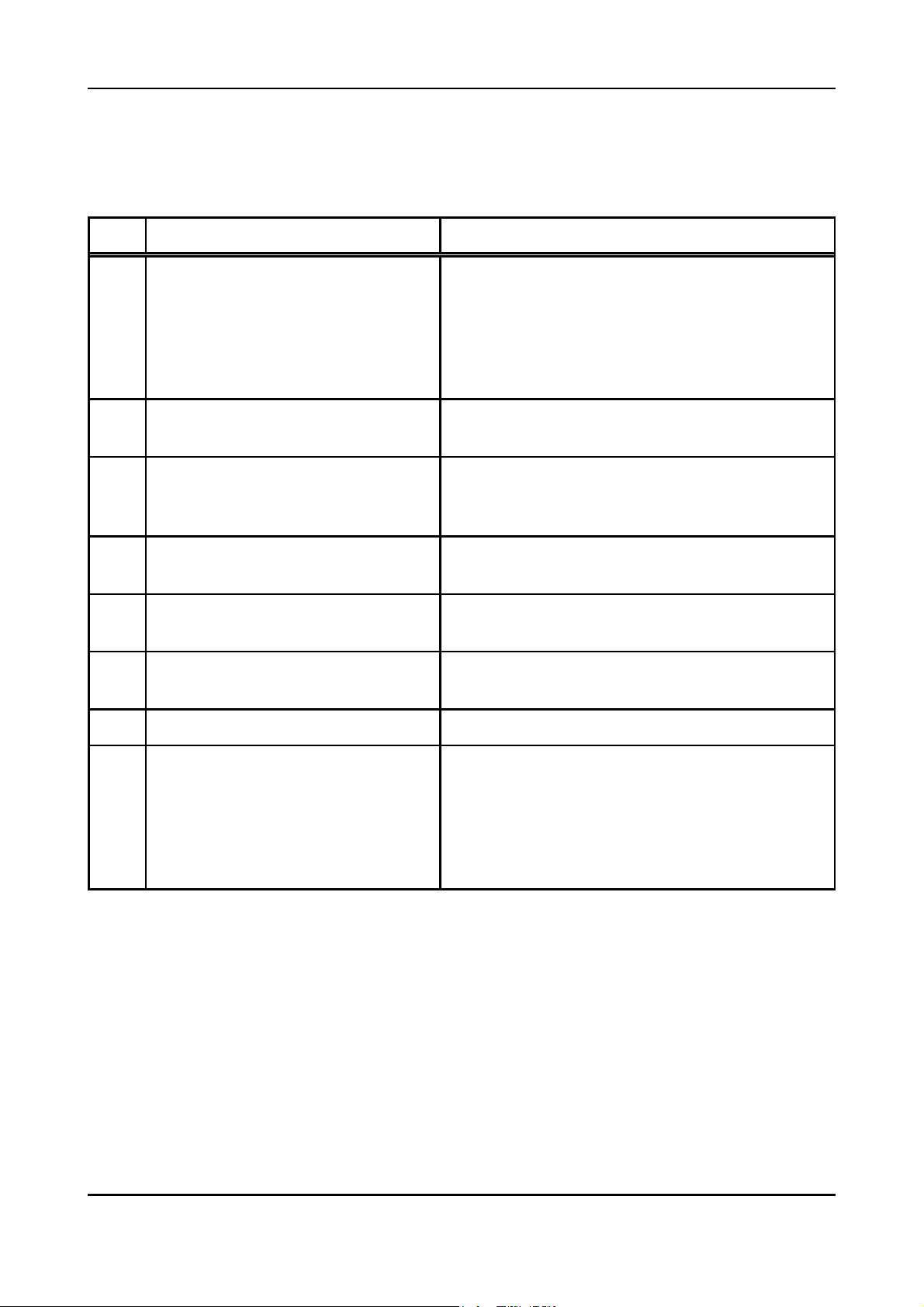
The following figure represents the functionality of the firmware.
CANProfibus
Slave
Address
output
xyz
Profibus CAN
(coding
switch)
input
Byte-no.Direction Identifier
0 Tx-Id_a
Tx-Id_a
1
2
Tx-Id_a
3
Tx-Id_a
Tx-Id_a
4
Tx-Id_a
5
n
Tx-Id_k
n+1
Tx-Id_k
0
Rx-Id_b
1
Rx-Id_b
2
Rx-Id_b
3
Rx-Id_b
Functionality of the Local Firmware
m
Rx-Id_l
m+1
Rx-Id_l
Fig. 2.1.1: Overview of functions of the CAN-CBM-DP module
2.1 PROFIBUS-Slave Address
The CAN-CBM-DP module simulates a slave module on the PROFIBUS side. The slave address is set
by means of coding switches at the module. When switching on the module the hexadecimal
PROFIBUS address set is requested. The settings have to be changed before switching on the module,
because changes are ineffective during operation.
The address range which can be set is hexadecimal 03 to 7C or decimal 3 to 124. If an address is set
which is smaller than 3 (decimal) or smaller than 03 (HEX), address 3 is valid. If an address is set
which is larger than 7C (HEX) or larger than 124 (decimal), address 124 is valid.
The upper coding switch (SW211, HIGH) is used to set the MSBs, while the LSBs are set by means of
the lower coding switch (SW210, LOW).
The PROFIBUS-slave address can only be set via coding switches. It cannot be programmed by means
of a class 2 master via the command ‘Set_Slave_Address’.
CAN-CBM-DP Software Manual Rev. 2.0 7

Functionality of the local Firmware
2.2 User Data
The CAN-CBM-DP-module simulates a total of up to 300 bytes for the input direction and the output
direction in the current software implementation. From these 300 bytes a maximum of 244 bytes can
be selected for one data direction, otherwise the division into input bytes and output bytes is entirely
up to the user. (Examples: 150 input bytes and 150 output bytes, or 244 input bytes and 56 output
bytes).
One to eight bytes (16 bytes when using the communication window, see page 31) each are assigned
to a Tx-or Rx-identifier. The same identifier cannot be used as Tx-and Rx-identifier. The automatic
response to remote requests (RTR) on the CAN bus cannot be used, therefore.
2.3 Watchdog (Reaction Control)
The firmware can be run with activated or deactivated reaction control. It is recommendable, though,
to run it with activated reaction control.
2.4 Diagnose
The status of the LED displays and the DP-slave diagnose can be used for diagnose. The module
supports five module-specific diagnose bytes. The diagnose will be described in more detail on page
12.
2.5 Parameter Telegram (CAN Bit Rate)
In addition to the seven standard bytes of the configuration, the CAN-CBM-DP module supports three
module-specific bytes. Here, the DP master can change the CAN bit rate. Setting the bit rate by means
of the parameter telegram is described on page 23.
2.6 Global-Control Services (FREEZE, SYNC, UNSYNC)
The Global-Control services have not yet been implemented.
2.7 PROFIBUS-DP Profiles
The PROFIBUS-DP profiles are not being supported yet.
CAN-CBM-DP Software Manual Rev. 2.08

Functionality of the Local Firmware
2.8 More Addressable CAN Identifiers in Page Mode
The Page Mode offers the chance to address more CAN identifiers than can be stored in one
PROFIBUS telegram (that means more than 48). Because of the additional protocol expenditure the
handling of the Page Mode is slightly more complicated than the standard operation of the gateway. The
data exchange between PROFIBUS and CAN requires two cycles instead of one PLC cycle.
CAN-CBM-DP Software Manual Rev. 2.0 9
Implementing and Diagnose
3. Implementing and Diagnose
3.1 Prerequisites for Implementation
This chapter describes the implementation of t he CAN-CBM module at a PROFIBUS which is
controlled by a Siemens SIMATIC-S7-300 or S7-400.
In order to be able to implement the module as will be described here, you need the configuratio n
program ‘SIMATIC-Manager’ with the tool ‘HW-configurator’.
Note for CANopen:
Configure the CAN-CBM-DP module absolutely first with the PLC via the SIMATICManager as described in chapter: “5. Configuration with the SIMATIC Manager”. Only
after carried out configuration the CAN-CBM-DP module can be identified as CANopen
slave!
3.2 Implementation
3.2.1 Strategy
Please make the following steps to implement the module:
1
2 Set the PROFIBUS address of the module by means of the coding switch.
3
4
5
Install and wire the CAN-CBM-DP module (power supply, CAN bus, see hardware
manual).
Connect the PROFIBUS connector to the PROFIBUS interface of the CAN-CBM-DP
module.
Configure the settings of the CAN-CBM-DP module in the PLC via the SIMATIC
manager
Switch on the power supply for the CAN-CBM-DP.
Now the module has to run.
The CAN-CBM-DP module is now automatically configured via the PLC.
Note: Take into account that in particular the CAN bit rate and the module ID (CANopen) must
be set via the PROFIBUS.
CAN-CBM-DP Software Manual Rev. 2.010

Implementing and Diagnose
3.2.2 Start-Up
After switching on the power supply, the CAN-CBM module starts automatically. It does not have its
own mains switch.
During start-up LEDs 2 (PROFIBUS LED) and 3 (data exchange LED) flash. The PROFIBUS address
set via the coding switches is read in.
The module receives projection data from the DP master and evaluates the specifications in them. If
the projection complies with the structure, the CAN-CBM-DP module starts the data transfer.
3.2.3 Data Transfer
If the module is configured, the data transfer starts automatically after start-up: If the PLC master
changes transmission data of an identifier, the data is transmitted from the CAN-CBM-DP module to
the CAN bus. When the CAN-CBM-DP module receives data, it provides these to the PLC master.
The configuration is described in chapter 5 ‘Configuration via the SIMATIC-Manager’ from page 21.
CAN-CBM-DP Software Manual Rev. 2.0 11
Implementing and Diagnose
g
y
3.3 Diagnose via LED Displa
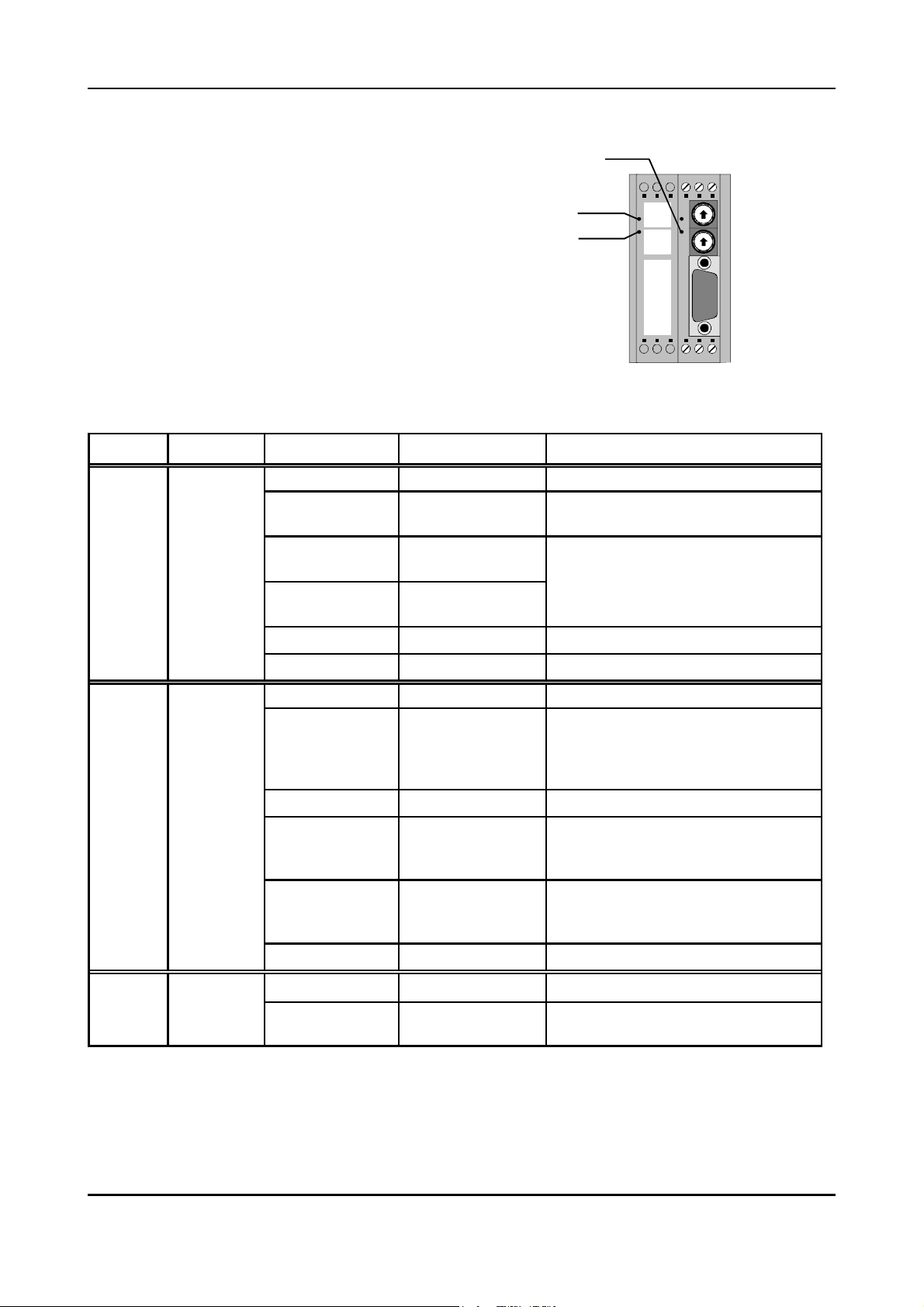
LED3
The function of LEDs has been defined by the firmware.
In normal operation the LEDs are never switched off, i.e.
they either flash or shine permanently.
LED 2
LED 1
The flash sequences which are listed in the following
table are repeated about every six seconds.
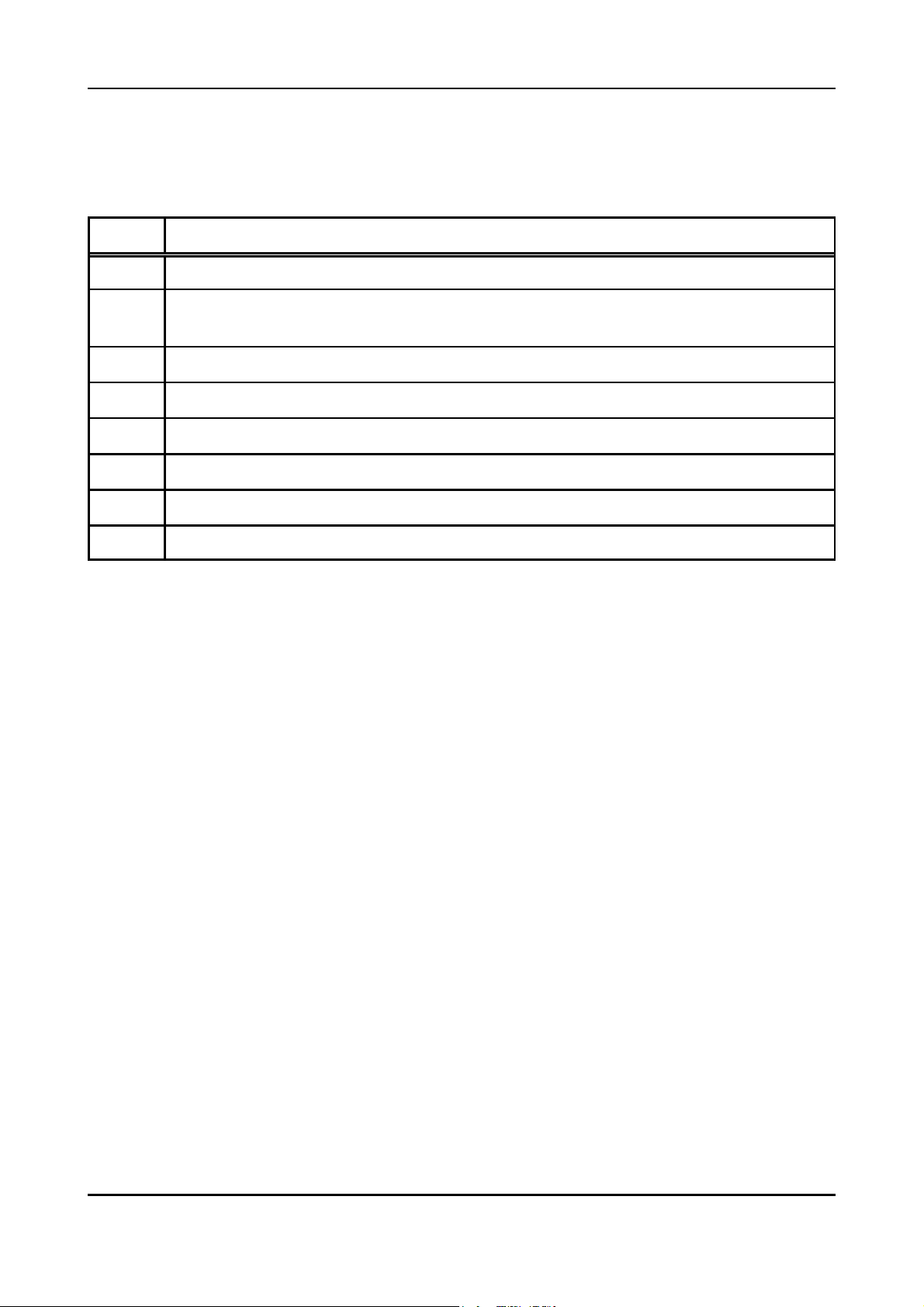
Fig. 3.3.1: Position of LEDs
LED Function Status Meaning Error handling
off no power supply check the 24 V power supply
PROFI
ADR.
HIGH
PROFI
ADR.
LOW
SERIAL
8
Coding Switch
SW211
0
8
Codin
Switch
SW210
0
LED 1
(red)
LED 2
(red)
CAN bus
status
modulePROFIBUS
status
1x short flash
only 29-bit version:
3x long flash
CAN error
(morse signal ‘E’)
CAN off
(morse signal ‘O’)
-
-
only 11-bit version:
5x long flash
CAN off
short-long-long CAN warning (‘W’) -
on CAN bus OK -
off no power supply check the 24 V power supply
the connection to the DP master has failed,
1x short flash looking for bit rate
check the PROFIBUS connection (fault in
wiring in PROFIBUS cable, short circuit,
terminating impedance in wrong position)?
2x short flashes bit rate is monitored check the PROFIBUS address specified
parameter telegram is faulty. Diagnose via
SIMATIC-Manager or system function
SFC13 (DPNRM_DG) (see chap. 3.4)
configuration telegram is faulty. Diagnose
via SIMATIC-Manager or system function
SFC13 (DPNRM_DG) (see chap. 3.4)
3x short flashes
4x short flashes
waiting for parameter
telegram
waiting for
configuration
telegram
on PROFIBUS OK -
LED 3
(red)
PROFIBUSdata
exchange
off no data exchange -
on
data exchange via
PROFIBUS
-
Table 3.3.1: LED status
CAN-CBM-DP Software Manual Rev. 2.012
Implementing and Diagnose
3.4 Slave Diagnose
In addition to the six diagnose bytes predefined in norm DIN EN 19245, part 3, the module supports
three further module-specific diagnose bytes.
The slave diagnose can be requested by the following function components:
Automation device family Number Name
SIMATIC with IM 308-C
SIMATIC S7/M7
Table 3.4.1: Function component for requesting the slave diagnose
3.4.1 Diagnose Bytes 0...5
The assignment of these diagnose bytes has been predefined in norm DIN EN 19425, part 3. Below, the
status messages will be described in consideration of the CAN-CBM-DP module.
The following designations will be used for this:
Byte number Status-byte designation
0
1
2
3
4
5
station status 1
station status 2
station status 3
master-PROFIBUS address
manufacturer-identification high byte
manufacturer-identification low byte
FB 192
SFC 13
FB IM308C
SFC DPNRM_DG
Table 3.4.2: Diagnose bytes 0...5
CAN-CBM-DP Software Manual Rev. 2.0 13
Implementing and Diagnose
3.4.1.1 Station Status 1
Station status 1 contains error messages of the DP slave. If a bit is ‘0’, no error applies. A bit set to ‘1’
signalizes an error.
Bit Error message if bit = ‘1’ Error handling
- correct PROFIBUS address set at the CANCBM-DP?
DP slave cannot be addressed by the
0
master
- bus connector correctly wired?
- power supply available at CAN-CBM-DP?
- power off/power on executed at CAN-CBM-DP
in order to read in DP address?
DP slave is not yet ready for data
1
exchange
The configuration data transmitted
2
from DP master to DP slave do not
correspond to the DP slave structure.
The slave has got external diagnose
3
data.
The requested function is not being
4
supported by the DP slave.
DP master cannot interpret the
5
response of the DP slave.
6 Wrong setting. - evaluate diagnose bytes 9 and 10
DP slave has already been set by
7
another master.
- wait until the CAN-CBM-DP has completed
start up
- check whether the station type and the CANCBM-DP structure have been correctly entered
via the configuration tool
- request and evaluate external diagnose data
- check projecting
- check bus structure
- this bit is always ‘1’, if you, e.g., just access the
CAN-CBM-DP by means of a PG or another
DP master.
The PROFIBUS address of the setting master is
in the diagnose byte ‘Master-PROFIBUS
address’.
Table 3.4.3: Bits of station status 1
CAN-CBM-DP Software Manual Rev. 2.014
Implementing and Diagnose
3.4.1.2 Station Status 2
Station status 2 contains status messages to the DP slave. If a bit is ‘1’, the according message is active.
A bit set to ‘0’ signalizes an inactive message.
Bit Error message if bit = ‘1’
0 DP slave has to be set again.
1
2 This bit is always ‘1’.
3 The response monitoring for the CAN-CBM-DP is activated.
4 DP slave has received freeze command.
5 DP slave has received SYNC command.
6 This bit is always ‘0’.
7 DP slave is deactivated.
A diagnose message applies. The DP slave cannot operate until the error has been
removed (static diagnose message).
Table 3.4.4: Bits of station status 2
CAN-CBM-DP Software Manual Rev. 2.0 15

Implementing and Diagnose
3.4.1.3 Station Status 3
Station status 3 is reserved and without significance for the CAN-CBM-DP.
3.4.1.4 Diagnose Byte 3: Master-PROFIBUS Address
The PROFIBUS address of the master which was the last to set the DP slave and has got reading and
writing access to the DP slave is stored in this byte.
3.4.1.5 Diagnose Bytes 4 and 5: Manufacturer Identification
The manufacturer identification has been coded into two bytes. For the CAN-CBM-DP module the
designation 04A4 hex is returned.
CAN-CBM-DP Software Manual Rev. 2.016
Implementing and Diagnose
3.4.2 External (Module-Specific) Diagnose Bytes
The CAN-CBM module supports diagnose bytes 6 to 10 for module-specific diagnose messages.
Diagnose
bytes
0...5 defined in the PROFIBUS specification (see previous chapter)
6
7
8 DP service (SAP) which led to error
9
length specification for module-specific diagnose information
(here always 5)
header byte: bits 0...5 contain the block length including header
(here always 4)
depending on status of byte 8:
byte 8 = 3D hex setting (SAP61) faulty, byte 9 contains the number of the faulty
setting byte
byte 8 = 3E hex configuration (SAP62) faulty, byte 9 contains the number of the
faulty PROFIBUS module (= address of the simulated PLC
module)
depending on status of byte 8:
byte 8 = 3D hex setting (SAP61) faulty, byte 10 shows the PROFIBUS master
with the correct values
Meaning
10
byte 8 = 3E hex configuration (SAP62) faulty
1 wrong I/O type: "out- input" or "blank")
correct: "input" or "output"
2 wrong unit, such as "words"
correct: unit = "byte"
3 wrong length
correct: length = 1-8 or 16
4 only one byte has been specified for identifier
5 format specification is missing
6 wrong identifier
Table 3.4.5: Module-specific status messages
CAN-CBM-DP Software Manual Rev. 2.0 17
GSD File
4. GSD File
Below, the GSD file (Device Master Data) of the CAN-CBM-DP module has been printed. The
specification printed here are for orientation. Decisive is the data contained in the GSD file
CDPS04A4.GSD, included in the product package.
;======================================================================================================
; (c) esd electronic system design GmbH Hannover
;
; PROFIBUS-DP Geraetestammdatei
; Version: 1.06
;
; Autor: Olaf Kruse
; Erstellungsdatum: V1.0 30.04.1999 ok
; Aenderungen: V1.01 03.08.1999 ok baudrate 6 MBaud, MaxTsdr-times
; ...
; V1.06 10.04.2000 uh menu structure for parameter
;======================================================================================================
; Art des Parameters
; (M) Mandatory (zwingend notwendig)
; (O) Optional (zusõtzlich m÷glich)
; (D) Optional mit Default=0 falls nicht vorhanden
; (G) mindestens einer aus der Gruppe passend zur entsprechenden Baudrate
#PROFIBUS_DP
;--- Kapitel 2.3.2 Allgemeine DP-Schluesselwoerter --GSD_Revision = 1 ; (M ab GSD_Revision 1) (Unsigned8)
Vendor_Name = "esd" ; (M) Herstellername (Visible-String 32)
Model_Name = "CAN-CBM/DP" ; (M) Herstellerbezeichnung des DP-Geraetes (Visible-String 32)
Revision = "V1.0" ; (M) Ausgabestand des DP-Geraetes (Visible-String 32)
Revision_Number = 1 ; (M ab GSD_Revision 1) (Unsigned8 (1 bis 63)) (1234)
Ident_Number = 1188 ; (M) Gerõtetyp des DP-Gerõtes (Unsigned16)
Protocol_Ident = 0 ; (M) Protokollkennung des DP-Geraetes 0: Profibus-DP (Unsigned8)
Station_Type = 0 ; (M) DP-Geraetetyp 0: DP-Slave (Unsigned8)
FMS_supp = 0 ; (D) kein FMS/DP-Mischgeraet (Boolean)
Hardware_Release = "V1.0" ; (M) Hardware Ausgabestand des DP-Geraetes (Visible-String 32)
Software_Release = "V1.0" ; (M) Software Ausgabestand des DP-Geraetes (Visible-String 32)
9.6_supp = 1 ; (G) 9,6 kBaud wird unterstuetzt
19.2_supp = 1 ; (G) 19,2 kBaud wird unterstuetzt
;31.25_supp = 1 ; fuer Gateway CAN-CBM-DP nicht moeglich (1234)
45.45_supp = 1 ; (G ab GSD_Revision 2) 45,45 kBaud wird unterstuetzt
93.75_supp = 1 ; (G) 93,75 kBaud wird unterstuetzt
187.5_supp = 1 ; (G) 187,5 kBaud wird unterstuetzt
500_supp = 1 ; (G) 500 kBaud wird unterstuetzt
1.5M_supp = 1 ; (G) 1,5 MBaud wird unterstuetzt
3M_supp = 1 ; (G ab GSD_Revision 1) 3 MBaud wird unterstuetzt
6M_supp = 1 ; (G ab GSD_Revision 1) 6 MBaud wird unterstuetzt
12M_supp = 1 ; (G ab GSD_Revision 1) 12 MBaud wird unterstuetzt
MaxTsdr_9.6 = 60 ; (G)
MaxTsdr_19.2 = 60 ; (G)
;MaxTsdr_31.25 = 15 ; fuer Gateway CAN-CBM-DP nicht moeglich (1234)
MaxTsdr_45.45 = 60 ; (G ab GSD_Revision 2)
MaxTsdr_93.75 = 60 ; (G)
MaxTsdr_187.5 = 60 ; (G)
MaxTsdr_500 = 100 ; (G)
MaxTsdr_1.5M = 150 ; (G)
MaxTsdr_3M = 250 ; (G ab GSD_Revision 1)
MaxTsdr_6M = 450 ; (G ab GSD_Revision 1)
MaxTsdr_12M = 800 ; (G ab GSD_Revision 1)
Redundancy = 0 ; (D) keine redundante Uebertragungstechnik
Repeater_Ctrl_Sig = 0 ; (D) RTS-Signalpegel (CNTR-P) Pin 4 des 9pol. SUB-D
24V_Pins = 0 ; (D) Bedeutung der 24V Pins des 9pol. SUB-D (Pin 7 24V; Pin 2 GND)
; Implementation_Type = "Visible-String" ; (1234)
Bitmap_Device = "CDPS00_N" ; (O ab GSD_Revision 1)
Bitmap_Diag = "CDPS00_D" ; (O ab GSD_Revision 1)
Bitmap_SF = "CDPS00_S" ; (O ab GSD_Revision 1)
;--- Kapitel 2.3.4 DP-Slave-bezogene Schluesselwoerter --Freeze_Mode_supp = 0 ; (D) Der Freeze-Mode wird nicht unterstuetzt
Sync_Mode_supp = 0 ; (D) Der Sync-Mode wird nicht unterstuetzt
Auto_Baud_supp = 1 ; (D) Die Automatische Baudratenerkennung wird unterstuetzt
Set_Slave_Add_supp = 0 ; (D) Die Slave-Adresse kann vom Master nicht gesetzt werden
;User_Prm_Data_Len = 9 ; (D) Hoechstlaenge von User-Parameter-Daten
;User_Prm_Data=0x00,0x06,0x00,0x00,0x00,0x00,0xff,0xff,0xff ; (O) User-Parameter-Daten ( byte 7 - 15 )
Min_Slave_Intervall = 20 ; (M) Minimaler Abstand zwischen 2 DDLM_Data_Exchange-Aufrufen (xx * 100us)
Modular_Station = 1 ; (D) 0: Kompaktstation 1: Modulare Station
Max_Module = 244 ; (M falls modulare Station) Hoechstanzahl der Module einer Modularen
Max_Input_Len = 240 ; M falls modulare Station) Hoechstlaenge der Eingangsdaten einer
; 0: nicht vorhanden 1: RS 485 2: TTL
; 0: nicht angeschlossen 1: Input 2: Output
Station
Modularen Station
CAN-CBM-DP Software Manual Rev. 2.018
GSD File
Max_Output_Len = 240 ; (M falls modulare Station) Hoechstlaenge der Ausgangsdaten einer
Max_Data_Len = 465 ; (O nur falls modulare Station) Groesste Summe der Ein- und
; --- (1234) --->
;PrmText = 1
;Text(0) = "STOPP"
;Text(1) = "START"
;PrmText = 2
;Text(0) = "Drehzahl 1"
;Text(1) = "Drehzahl 2"
;Text(2) = "Drehzahl 3"
;Text(3) = "Drehzahl 4"
;EndPrmText
; <--- (1234) --Unit_Diag_Bit(0000) = "Wert 0" ; (1234)
Unit_Diag_Bit(0001) = "Wert 1" ; (1234)
Unit_Diag_Bit(0002) = "Wert 2" ; (1234)
Unit_Diag_Bit(0003) = "Wert 3" ; (1234)
Unit_Diag_Bit(0004) = "Wert 4" ; (1234)
Unit_Diag_Bit(0005) = "Wert 5" ; (1234)
Unit_Diag_Bit(0006) = "Wert 6" ; (1234)
Unit_Diag_Bit(0007) = "Wert 7" ; (1234)
Unit_Diag_Bit(0008) = "Wert 8" ; (1234)
Unit_Diag_Bit(0009) = "Wert 9" ; (1234)
Unit_Diag_Bit(0010) = "Wert 10" ; (1234)
Unit_Diag_Bit(0011) = "Wert 11" ; (1234)
Unit_Diag_Bit(0012) = "Wert 12" ; (1234)
Unit_Diag_Bit(0013) = "Wert 13" ; (1234)
Unit_Diag_Bit(0014) = "Wert 14" ; (1234)
Unit_Diag_Bit(0015) = "Wert 15" ; (1234)
;Unit_Diag_Area = 0 - 5 ; (1234)
;Value(0) = "Fehlerfrei" ; (1234)
;Value(1) = "Fehler auf Eingang 0 - 23" ; (1234)
;Value(2) = "Fehler auf Ausgang 0 - 15" ; (1234)
;Value(3) = "24V ausgefallen" ; (1234)
;Unit_Diag_Area_End ; (1234)
Max_Diag_Data_Len = 16 ; max. 16 Byte Diagnosedaten
Modul_Offset = 0 ; (D ab GSD_Revision 1) erste Steckplatznummer
Max_User_Prm_Data_Len = 9
PrmText=1
Text(0)="1000 kbit/s"
Text(1)=" 666.6 kbit/s"
Text(2)=" 500 kbit/s"
Text(3)=" 333.3 kbit/s"
Text(4)=" 250 kbit/s"
Text(5)=" 166 kbit/s"
Text(6)=" 125 kbit/s"
Text(7)=" 100 kbit/s"
Text(8)=" 66.6 kbit/s"
Text(9)=" 50 kbit/s"
Text(10)=" 33.3 kbit/s"
Text(11)=" 20 kbit/s"
Text(12)=" 12.5 kbit/s"
Text(13)=" 10 kbit/s"
EndPrmText
PrmText=2
Text(0)="No"
Text(1)="Yes"
EndPrmText
PrmText=3
Text(0)="Yes"
Text(1)="No"
EndPrmText
ExtUserPrmData=1 "CAN-Bitrate"
Unsigned8 6 0-13
Prm_Text_Ref=1
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData=2 "Communication Window"
Bit(7) 0 0-1
Prm_Text_Ref=2
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData=3 "RTR-Frames"
Bit(4) 0 0-1
Prm_Text_Ref=3
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData=4 "CANopen-Slave"
Bit(3) 0 0-1
Prm_Text_Ref=2
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData=5 "CANopen-Master"
Bit(2) 0 0-1
Prm_Text_Ref=2
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData=6 "Start-Frame"
Bit(1) 0 0-1
Prm_Text_Ref=2
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData=7 "Page-Mode"
Bit(0) 0 0-1
Prm_Text_Ref=2
EndExtUserPrmData
Modularen Station
Ausgangsdaten einer Modularen Station in Bytes
CAN-CBM-DP Software Manual Rev. 2.0 19

GSD File
Unsigned8 1 1-127
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData=9 "WakeUp Time (0=Off, 255=Default)"
Unsigned8 255 0-255
EndExtUserPrmData
ExtUserPrmData=10 "Sync Time (0=Off, 65535=Default)"
Unsigned16 65535 0-65535
EndExtUserPrmData
Ext_User_Prm_Data_Const(0)=0x00,0x06,0x00,0x00,0x00,0x00,0xff,0xff,0xff
Ext_User_Prm_Data_Ref(1)=1
Ext_User_Prm_Data_Ref(2)=2
Ext_User_Prm_Data_Ref(2)=3
Ext_User_Prm_Data_Ref(2)=4
Ext_User_Prm_Data_Ref(2)=5
Ext_User_Prm_Data_Ref(2)=6
Ext_User_Prm_Data_Ref(2)=7
Ext_User_Prm_Data_Ref(3)=8
Ext_User_Prm_Data_Ref(6)=9
Ext_User_Prm_Data_Ref(7)=10
Slave_Family = 9@CAN@V01
Periphery = "ET 200"
OrderNumber = "C.2844.03"
CAN-CBM-DP Software Manual Rev. 2.020

Configuration via SIMATIC Manager
5. Configuration via SIMATIC Manager
5.1 Course of Configuration
The CAN-CBM-DP module is configured via the PROFIBUS or the serial interface by means of tool
CICT (limited configuration). The configuration via the PROFIBUS is of higher priority, i.e. the
PROFIBUS configuration overwrites the configuration made via the serial interface. It is not possible
to change parameters which have been set via the PROFIBUS by means of the serial interface.
Note: Without correct configuration via the SIMATIC manager the CAN-CBM-DP module and
the CAN participants connected do not operate together and operation of the CAN
participants connected can be disturbed.
In particular the CAN-Bitrate configured in the CAN-CBM-DP-module and the moduleID (at CANopen) must match the settings of the CAN participants connected!
If problems should occur, further information can be obtained with the diagnose as
described in the chapters “4.3 Diagnose via LED Display” and “4.4 Slave Diagnose”.
Please follow the steps below to configure the CAN-CBM-DP module:
1. Select CAN-CBM-DP
Select menu Hardware Catalogue and there Additional Field Devices and Other. There select GSD
CAN-CBM-DP.
2. Set PROFIBUS Address
Set the PROFIBUS address as described in chapter 5.1.1 on page 22.
3. Parameter Telegramm (set CAN bit rate, general configuration and CANopen module ID)
Configure the configuration settings by means of the parameter telegram as described in chapter
5.1.2 on page 23.
4. Assignment of the Slots of the DP-slaves
Assign the slots as described in chapter 5.1.3 on page 27.
5. Configuration of the Slots (SPS-Adresse)
Configure the slots as described in chapter 5.1.4 on page 28.
6. Save settings on hard disk
Save the settings as described in chapter 5.1.5 on page 28.
CAN-CBM-DP Software Manual Rev. 2.0 21
Configuration via SIMATIC Manager
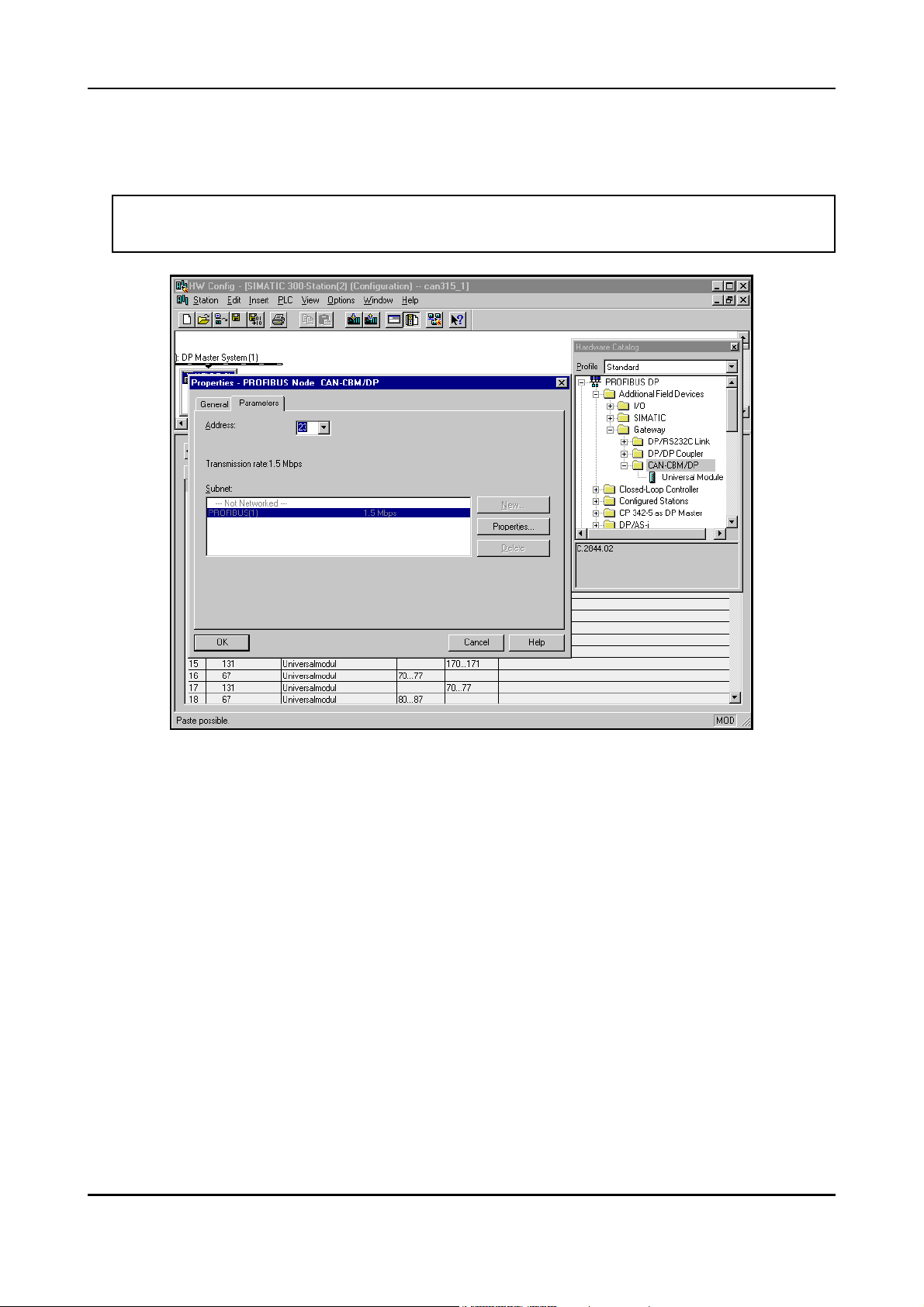
5.1.1 Set PROFIBUS address
A window opens in which you have to specify the PROFIBUS station address.
Attention!! The hexadecimal address set at the coding switches has to be converted into a
decimal value and entered here!
Fig. 5.1.1: Setting the PROFIBUS address of the CAN-CBM-DP
CAN-CBM-DP Software Manual Rev. 2.022
Configuration via SIMATIC Manager
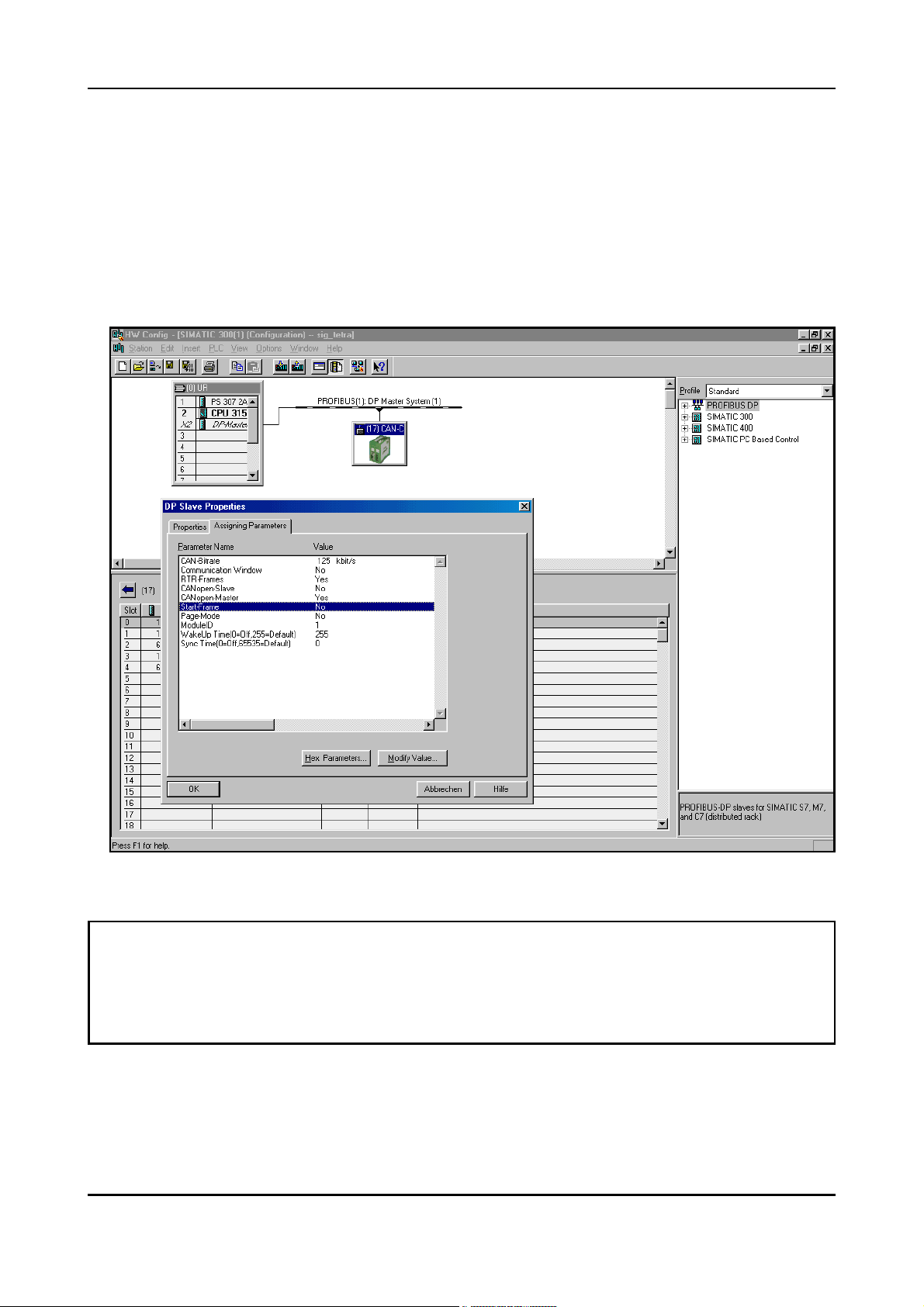
5.1.2 Parameter Telegram
In the configuration window the module ‘DP slave’ is now automatically added. If you desire
another CAN bit rate than the standard setting of 125 kbit/s, you can change it by means of the
parameter telegram.
The module-specific bytes of the parameter telegram can be changed in the Properties window
which opens, if the header of the DP-slave window is double clicked (here line ‘(23) DP-
Slave’).
Fig. 5.1.2: Setting the parameters in the DP-slave properties window
Note: By means of selection point Hex-Parameter the parameters can be specified by means of
entering hexadecimal values, as in older software versions. More comfortable, however,
is of course the specification in the format shown above. Here, the parameters can be
configured ‘directly’. Therefore, in the following descriptions the configuration by means
of hexadecimal values will not be considered.
CAN-CBM-DP Software Manual Rev. 2.0 23

Configuration via SIMATIC Manager
Description of Parameters:
CAN-Bitrate: For the bit rate the following selections can be made:
Bitrate [kbit/s]
1000
666.6
500
333.3
250
166
125
100
66.6
50
33.3
Communication Window:
(CW)
RTR-Frames:
(NR)
CANopen-Slave:
(CS)
CANopen-Master:
(CM)
20
12.5
10
Table 5.1.1: Setting the bit rate in 14 levels
This parameter activates the Communication Window. It is
described in detail at page 31.
Transmit RTR-frames for the Rx-identifiers configured via
PROFIBUS.
Configure gateway as CANopen slave.
Configure gateway as CANopen master.
Start-Frame:
(AS)
Page-Mode:
(PM)
After wake-up time has expired, a start frame is transmitted, if the
gateway is a master (autostart).
Activate Page-Mode.
CAN-CBM-DP Software Manual Rev. 2.024
Configuration via SIMATIC Manager
p
p
p
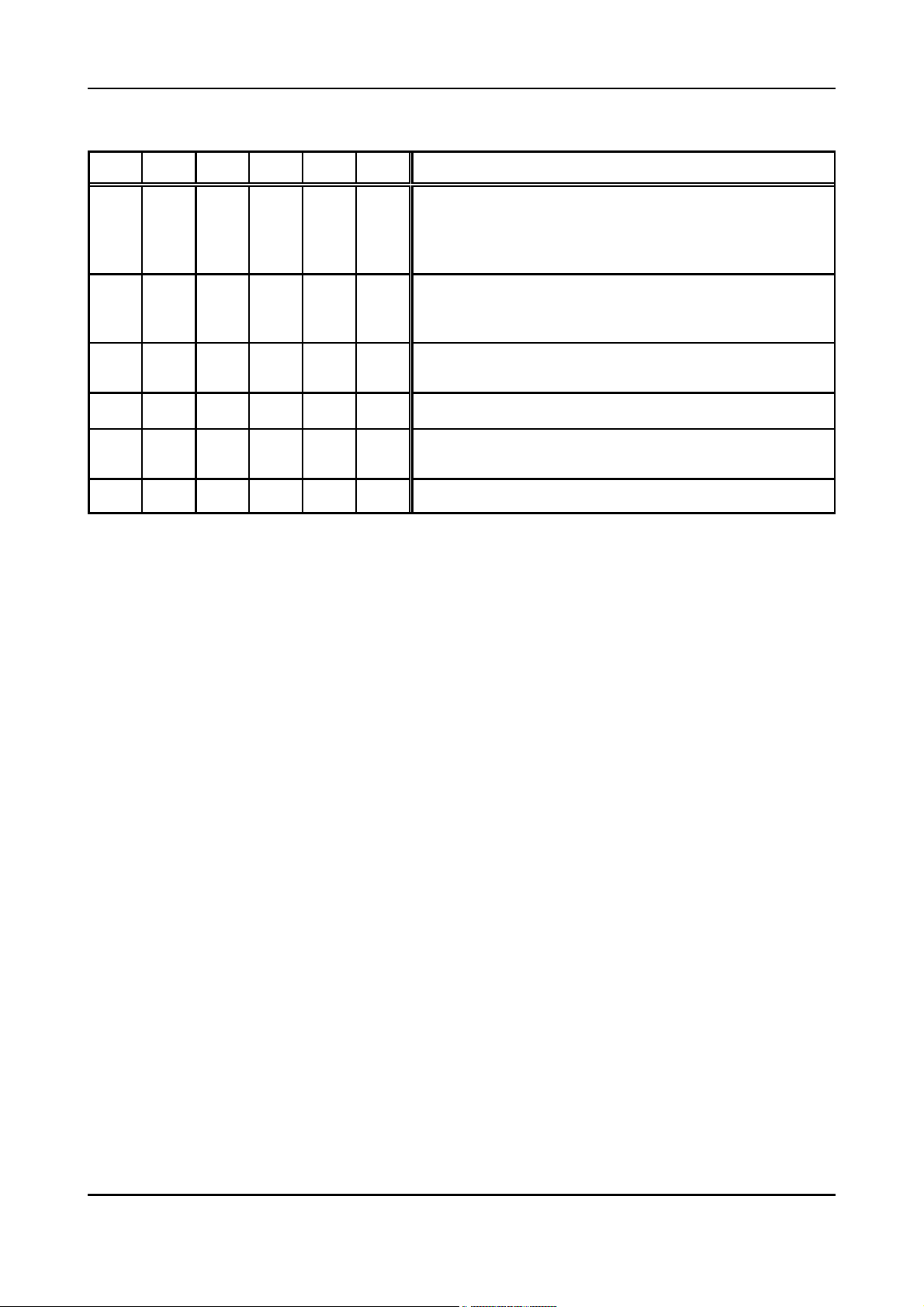
Permissible combinations:
CW NR CS CM AS PM Meaning
xnoyesnoxno
xyesyesno x no
x no no yes no no
xyesnoyesnono
xnonoyesyesno
x yes no yes yes no
Table 5.1.2: Example for permissible settings
Module-ID: The
Module-ID
under which the gateway is addressed is set via this byte, if the
gateway has been configured as CANopen slave.
- after wake-up time the module automatically transmits
+ Module-No.
- after a start frame has been received: put out TxId, transmit
RTR-frames on RxId
- after wake-up time the module automatically transmits
+ Module-No.
- after a start frame has been received: put out TxId
- after wake-up time, put out TxId
- transmit RTR-frames on RxId
- after wake-up time, put out TxId
- after wake-up time start frame, put out TxId, transmit RTRframes on RxId
- after wake-up time start frame, put out TxId
and is in ‘Pre-Operational’ status
and is in ‘Pre-Operational’ status
128 dec
128 dec
Value range: 1 ... 127 (decimal)
Wakeup Time Via parameter
time a module has to wait after a RESET or power-on, before it starts to transmit
data to the CAN.
The
Wakeu
Time
previously in the CAN-CBM-DP gateway, if another value than ‘255’ was
specified. If ‘255’ is specified, the value stored in the gateway will be used.
If parameter
Wakeu
transmission of data as soon as they are available.
The Wakeup Time is specified as a decimal value, here.
Wakeu
Time
a delay in seconds is specified. It determines the
specified here, overwrites the value of
Time
is set to ‘0’, the module does not wait, but start the
Wakeup Time
stored
CAN-CBM-DP Software Manual Rev. 2.0 25
Configuration via SIMATIC Manager
Parameter
Wakeup Time
Value range
[dec] in [s]
0 Wakeup-Time function off
1...254 Wakeup Time in seconds
255 Use current value from gateway (default)
Explanations
Table 5.1.3: Function of parameter Wakeup Time
Attention:
Wakeup Time can be set in two different ways:
1. As described above.
2. Via the configuration tool CICT (refer to page 72)
Both entries are equal. That means that the last specification is
valid!
Note:
If the software is updated to a version t 1.03, when using an
existing application program (older than 12/1999), the missing entry
of the configuration data would be interpreted as ‘0’, and the
Wakeup-Time function would be deactivated, therefore.
SYNC Time:
The CAN-CBM-DP module can cyclically transmit the commands
SYNC and START for simple CANopen applications. The SYNC Time
for the transmission can be specified in the properties window as
described above, via the Communication Window or via the tool CICT.
The specified cycle is used for the SYNC command as well as the
START command. It is specified in milliseconds.
SYNC Time
Parameter
SYNC Time
is specified as a decimal value, here.
Value range
[dec] in [ms]
0 No SYNC and Start transmissions possible
1...65534
65535 Use current value from gateway (default)
SYNC Time and Start Time in milliseconds
(1...65534 ms)
Explanations
Table 5.1.4: Function of parameter SYNC Time
CAN-CBM-DP Software Manual Rev. 2.026
 Loading...
Loading...