
PCC-14
Plumbing Box
Instruction Manual
This documentation is for ESAB equipment part number 0558005840
0558006574 03/2012

BE SURE THIS INFORMATION REACHES THE OPERATOR.
YOU CAN GET EXTRA COPIES THROUGH YOUR SUPPLIER.
CAUTION
These INSTRUCTIONS are for experienced operators. If you are not fully familiar with the
principles of operation and safe practices for arc welding and cutting equipment, we urge
you to read our booklet, “Precautions and Safe Practices for Arc Welding, Cutting, and
Gouging,” Form 52-529. Do NOT permit untrained persons to install, operate, or maintain
this equipment. Do NOT attempt to install or operate this equipment until you have read
and fully understand these instructions. If you do not fully understand these instructions,
contact your supplier for further information. Be sure to read the Safety Precautions before installing or operating this equipment.
USER RESPONSIBILITY
This equipment will perform in conformity with the description thereof contained in this manual and accompanying labels and/or inserts when installed, operated, maintained and repaired in accordance with the instructions provided. This equipment must be checked periodically. Malfunctioning or poorly maintained equipment
should not be used. Parts that are broken, missing, worn, distorted or contaminated should be replaced immediately. Should such repair or replacement become necessary, the manufacturer recommends that a telephone
or written request for service advice be made to the Authorized Distributor from whom it was purchased.
This equipment or any of its parts should not be altered without the prior written approval of the manufacturer.
The user of this equipment shall have the sole responsibility for any malfunction which results from improper
use, faulty maintenance, damage, improper repair or alteration by anyone other than the manufacturer or a service facility designated by the manufacturer.
READ AND UNDERSTAND THE INSTRUCTION MANUAL BEFORE INSTALLING OR OPERATING.
PROTECT YOURSELF AND OTHERS!
2

TABLE OF CONTENTS
Section / Title Page
1.0 Safety Precautions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .5
1.1 Safety - English . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .5
1.2 Safety - Spanish. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .9
1.3 Safety - French. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13
2.0 Plumbing Box Description. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .17
2.1 Specications. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .17
2.2 PCC-14 Plumbing Box Dimensions/ Mounting Hole Locations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .18
2.3 Plumbing Box Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .19
2.4 Spark Gap Adjustment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .21
2.5 Plumbing Box Connections. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
2.6 Adaptor for PCC-14 Plumbing Box use with ESP-150 or ESP-200 Power Supplies . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
2.7 PCC-14 Plumbing Box used with ESP-150 Power Supply . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .27
2.8 PCC-14 Plumbing Box use with ESP-200 Power Supply . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
2.9 PT-36R Torch Connections to Plumbing Box. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
2.10 ESP-150 Torch Connections. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .31
2.10.a ESP150 DUECE PACK Connections. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .33
2.11 ESP-200 Torch Connections. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .35
2.12 Voltage Divider Adjustment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
3.0 Maintenance. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
3.1 General. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
3.2 Cleaning. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
4.0 Replacement Parts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .41
4.1 General. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .41
4.2 Ordering . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .41
3

TABLE OF CONTENTS
4

SECTION 1 SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
1.0 Safety Precautions
WARNING: These Safety Precautions are
for your protection. They summarize precautionary information from the references
listed in Additional Safety Information section. Before performing any installation or operating
procedures, be sure to read and follow the safety precautions listed below as well as all other manuals, material
safety data sheets, labels, etc. Failure to observe Safety
Precautions can result in injury or death.
PROTECT YOURSELF AND OTHERS -Some welding, cutting, and gouging
processes are noisy and require ear
protection. The arc, like the sun, emits
ultraviolet (UV) and other radiation
and can injure skin and eyes. Hot metal can cause
burns. Training in the proper use of the processes
and equipment is essential to prevent accidents.
Therefore:
1. Always wear safety glasses with side shields in any
work area, even if welding helmets, face shields, and
goggles are also required.
2. Use a face shield tted with the correct lter and
cover plates to protect your eyes, face, neck, and
ears from sparks and rays of the arc when operating
or observing operations. Warn bystanders not to
watch the arc and not to expose themselves to the
rays of the electric-arc or hot metal.
3. Wear ameproof gauntlet type gloves, heavy long-
sleeve shirt, cuess trousers, high-topped shoes,
and a welding helmet or cap for hair protection, to
protect against arc rays and hot sparks or hot metal.
A ameproof apron may also be desirable as protection against radiated heat and sparks.
4. Hot sparks or metal can lodge in rolled up sleeves,
trouser cus, or pockets. Sleeves and collars should
be kept buttoned, and open pockets eliminated from
the front of clothing.
5. Protect other personnel from arc rays and hot
sparks with a suitable non-ammable partition or
curtains.
6. Use goggles over safety glasses when chipping slag
or grinding. Chipped slag may be hot and can y far.
Bystanders should also wear goggles over safety
glasses.
1.1 Safety - English
FIRES AND EXPLOSIONS -- Heat from
ames and arcs can start res. Hot
slag or sparks can also cause res and
explosions. Therefore:
1. Remove all combustible materials well away from
the work area or cover the materials with a protective non-ammable covering. Combustible materials
include wood, cloth, sawdust, liquid and gas fuels,
solvents, paints and coatings, paper, etc.
2. Hot sparks or hot metal can fall through cracks or
crevices in oors or wall openings and cause a hidden smoldering re or res on the oor below. Make
certain that such openings are protected from hot
sparks and metal.“
3. Do not weld, cut or perform other hot work until the
workpiece has been completely cleaned so that there
are no substances on the workpiece which might
produce ammable or toxic vapors. Do not do hot
work on closed containers. They may explode.
4. Have re extinguishing equipment handy for instant
use, such as a garden hose, water pail, sand bucket,
or portable re extinguisher. Be sure you are trained
in its use.
5. Do not use equipment beyond its ratings. For example, overloaded welding cable can overheat and
create a re hazard.
6. After completing operations, inspect the work area
to make certain there are no hot sparks or hot metal
which could cause a later re. Use re watchers when
necessary.
7. For additional information, refer to NFPA Standard
51B, "Fire Prevention in Use of Cutting and Welding
Processes", available from the National Fire Protection Association, Batterymarch Park, Quincy, MA
02269.
ELECTRICAL SHOCK -- Contact with
live electrical parts and ground can
cause severe injury or death. DO NOT
use AC welding current in damp areas,
if movement is conned, or if there is
danger of falling.
5

SECTION 1 SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
1. Be sure the power source frame (chassis) is connected to the ground system of the input power.
2. Connect the workpiece to a good electrical
ground.
3. Connect the work cable to the workpiece. A poor
or missing connection can expose you or others
to a fatal shock.
4. Use well-maintained equipment. Replace worn or
damaged cables.
5. Keep everything dry, including clothing, work
area, cables, torch/electrode holder, and power
source.
6. Make sure that all parts of your body are insulated
from work and from ground.
7. Do not stand directly on metal or the earth while
working in tight quarters or a damp area; stand
on dry boards or an insulating platform and wear
rubber-soled shoes.
8. Put on dry, hole-free gloves before turning on the
power.
3. Welders should use the following procedures to
minimize exposure to EMF:
A. Route the electrode and work cables together.
Secure them with tape when possible.
B. Never coil the torch or work cable around your
body.
C. Do not place your body between the torch and
work cables. Route cables on the same side of
your body.
D. Connect the work cable to the workpiece as close
as possible to the area being welded.
E. Keep welding power source and cables as far
away from your body as possible.
FUMES AND GASES -- Fumes and
gases, can cause discomfort or harm,
particularly in conned spaces. Do
not breathe fumes and gases. Shielding gases can cause asphyxiation.
Therefore:
9. Turn o the power before removing your gloves.
10. Refer to ANSI/ASC Standard Z49.1 (listed on
next page) for specic grounding recommendations. Do not mistake the work lead for a ground
cable.
ELECTRIC AND MAGNETIC FIELDS
— May be dangerous. Electric current owing through any conductor causes localized Electric and
Magnetic Fields (EMF). Welding and
cutting current creates EMF around welding cables
and welding machines. Therefore:
1. Welders having pacemakers should consult their
physician before welding. EMF may interfere with
some pacemakers.
2. Exposure to EMF may have other health eects which
are unknown.
1. Always provide adequate ventilation in the work area
by natural or mechanical means. Do not weld, cut, or
gouge on materials such as galvanized steel, stainless steel, copper, zinc, lead, beryllium, or cadmium
unless positive mechanical ventilation is provided.
Do not breathe fumes from these materials.
2. Do not operate near degreasing and spraying operations. The heat or arc rays can react with chlorinated
hydrocarbon vapors to form phosgene, a highly
toxic gas, and other irritant gases.
3. If you develop momentary eye, nose, or throat irritation while operating, this is an indication that
ventilation is not adequate. Stop work and take
necessary steps to improve ventilation in the work
area. Do not continue to operate if physical discomfort persists.
4. Refer to ANSI/ASC Standard Z49.1 (see listing below)
for specic ventilation recommendations.
6

SECTION 1 SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
5. WARNING: This product, when used for welding
or cutting, produces fumes or gases
which contain chemicals known to
the State of California to cause birth
defects and, in some cases, cancer.
(California Health & Safety Code
§25249.5 et seq.)
CYLINDER HANDLING -- Cylinders,
if mishandled, can rupture and violently release gas. Sudden rupture
of cylinder, valve, or relief device can
injure or kill. Therefore:
1. Use the proper gas for the process and use the
proper pressure reducing regulator designed to
operate from the compressed gas cylinder. Do not
use adaptors. Maintain hoses and ttings in good
condition. Follow manufacturer's operating instructions for mounting regulator to a compressed gas
cylinder.
1. Always have qualied personnel perform the installation, troubleshooting, and maintenance work.
Do not perform any electrical work unless you are
qualied to perform such work.
2. Before performing any maintenance work inside a
power source, disconnect the power source from
the incoming electrical power.
3. Maintain cables, grounding wire, connections, power
cord, and power supply in safe working order. Do
not operate any equipment in faulty condition.
4. Do not abuse any equipment or accessories. Keep
equipment away from heat sources such as furnaces,
wet conditions such as water puddles, oil or grease,
corrosive atmospheres and inclement weather.
5. Keep all safety devices and cabinet covers in position
and in good repair.
6. Use equipment only for its intended purpose. Do
not modify it in any manner.
2. Always secure cylinders in an upright position by
chain or strap to suitable hand trucks, undercarriages, benches, walls, post, or racks. Never secure
cylinders to work tables or xtures where they may
become part of an electrical circuit.
3. When not in use, keep cylinder valves closed. Have
valve protection cap in place if regulator is not connected. Secure and move cylinders by using suitable
hand trucks. Avoid rough handling of cylinders.
4. Locate cylinders away from heat, sparks, and ames.
Never strike an arc on a cylinder.
5. For additional information, refer to CGA Standard P-1,
"Precautions for Safe Handling of Compressed Gases
in Cylinders", which is available from Compressed
Gas Association, 1235 Jeerson Davis Highway,
Arlington, VA 22202.
EQUIPMENT MAINTENANCE -- Faulty or
improperly maintained equipment can
cause injury or death. Therefore:
ADDITIONAL SAFETY INFORMATION -- For
more information on safe practices for
electric arc welding and cutting equipment, ask your supplier for a copy of
"Precautions and Safe Practices for Arc
Welding, Cutting and Gouging", Form
52-529.
The following publications, which are available from
the American Welding Society, 550 N.W. LeJuene Road,
Miami, FL 33126, are recommended to you:
1. ANSI/ASC Z49.1 - "Safety in Welding and Cutting"
2. AWS C5.1 - "Recommended Practices for Plasma Arc
Welding"
3. AWS C5.2 - "Recommended Practices for Plasma Arc
Cutting"
4. AWS C5.3 - "Recommended Practices for Air Carbon
Arc Gouging and Cutting"
7

SECTION 1 SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
5. AWS C5.5 - "Recommended Practices for Gas Tungsten Arc Welding“
6. AWS C5.6 - "Recommended Practices for Gas Metal
Arc Welding"“
7. AWS SP - "Safe Practices" - Reprint, Welding Handbook.
8. ANSI/AWS F4.1, "Recommended Safe Practices for
Welding and Cutting of Containers That Have Held
Hazardous Substances."
MEANING OF SYMBOLS - As used
throughout this manual: Means Attention! Be Alert! Your safety is involved.
Means immediate hazards which,
if not avoided, will result in immediate, serious personal injury
or loss of life.
Means potential hazards which
could result in personal injury or
loss of life.
Means hazards which could result
in minor personal injury.
8

SECCION 1 SEGURIDAD
1.2 Safety - Spanish
ADVERTENCIA: Estas Precauciones de Se-
guridad son para su protección. Ellas hacen
resumen de información proveniente de las
referencias listadas en la sección "Información Adicional Sobre La Seguridad". Antes de hacer cualquier
instalación o procedimiento de operación , asegúrese
de leer y seguir las precauciones de seguridad listadas
a continuación así como también todo manual, hoja
de datos de seguridad del material, calcomanias, etc.
El no observar las Precauciones de Seguridad puede
resultar en daño a la persona o muerte.
PROTEJASE USTED Y A LOS DEMAS-Algunos procesos de soldadura, corte
y ranurado son ruidosos y requiren
protección para los oídos. El arco,
como el sol , emite rayos ultravioleta
(UV) y otras radiaciones que pueden dañar la piel
y los ojos. El metal caliente causa quemaduras. EL
entrenamiento en el uso propio de los equipos y
sus procesos es esencial para prevenir accidentes.
Por lo tanto:
1. Utilice gafas de seguridad con protección a los lados
siempre que esté en el área de trabajo, aún cuando
esté usando careta de soldar, protector para su cara
u otro tipo de protección.
2. Use una careta que tenga el ltro correcto y lente
para proteger sus ojos, cara, cuello, y oídos de las
chispas y rayos del arco cuando se esté operando y
observando las operaciones. Alerte a todas las personas cercanas de no mirar el arco y no exponerse
a los rayos del arco eléctrico o el metal fundido.
3. Use guantes de cuero a prueba de fuego, camisa
pesada de mangas largas, pantalón de ruedo liso,
zapato alto al tobillo, y careta de soldar con capucha
para el pelo, para proteger el cuerpo de los rayos y
chispas calientes provenientes del metal fundido.
En ocaciones un delantal a prueba de fuego es
necesario para protegerse del calor radiado y las
chispas.
4. Chispas y partículas de metal caliente puede alojarse
en las mangas enrolladas de la camisa , el ruedo del
pantalón o los bolsillos. Mangas y cuellos deberán
mantenerse abotonados, bolsillos al frente de la
camisa deberán ser cerrados o eliminados.
5. Proteja a otras personas de los rayos del arco y chis-
pas calientes con una cortina adecuada no-amable
como división.
6. Use careta protectora además de sus gafas de segu-
ridad cuando esté removiendo escoria o puliendo.
La escoria puede estar caliente y desprenderse con
velocidad. Personas cercanas deberán usar gafas
de seguridad y careta protectora.
FUEGO Y EXPLOSIONES -- El calor de
las amas y el arco pueden ocacionar
fuegos. Escoria caliente y las chispas
pueden causar fuegos y explosiones.
Por lo tanto:
1. Remueva todo material combustible lejos del área
de trabajo o cubra los materiales con una cobija a
prueba de fuego. Materiales combustibles incluyen
madera, ropa, líquidos y gases amables, solventes,
pinturas, papel, etc.
2. Chispas y partículas de metal pueden introducirse en
las grietas y agujeros de pisos y paredes causando
fuegos escondidos en otros niveles o espacios.
Asegúrese de que toda grieta y agujero esté cubierto
para proteger lugares adyacentes contra fuegos.
3. No corte, suelde o haga cualquier otro trabajo
relacionado hasta que la pieza de trabajo esté totalmente limpia y libre de substancias que puedan
producir gases inamables o vapores tóxicos. No
trabaje dentro o fuera de contenedores o tanques
cerrados. Estos pueden explotar si contienen vapores
inamables.
4. Tenga siempre a la mano equipo extintor de fuego para uso instantáneo, como por ejemplo una
manguera con agua, cubeta con agua, cubeta con
arena, o extintor portátil. Asegúrese que usted esta
entrenado para su uso.
5. No use el equipo fuera de su rango de operación. Por
ejemplo, el calor causado por cable sobrecarga en
los cables de soldar pueden ocasionar un fuego.
6. Después de termirar la operación del equipo, inspeccione el área de trabajo para cerciorarse de que las
chispas o metal caliente ocasionen un fuego más
tarde. Tenga personal asignado para vigilar si es
necesario.
7. Para información adicional , haga referencia a la
publicación NFPA Standard 51B, "Fire Prevention in
Use of Cutting and Welding Processes", disponible
a través de la National Fire Protection Association,
Batterymarch Park, Quincy, MA 02269.
CHOQUE ELECTRICO -- El contacto
con las partes eléctricas energizadas
y tierra puede causar daño severo o
muerte. NO use soldadura de corri-
ente alterna (AC) en áreas húmedas,
de movimiento connado en lugares estrechos o
si hay posibilidad de caer al suelo.
9

SECCION 1 SEGURIDAD
1. Asegúrese de que el chasis de la fuente de poder
esté conectado a tierra através del sistema de
electricidad primario.
2. Conecte la pieza de trabajo a un buen sistema de
tierra física.
3. Conecte el cable de retorno a la pieza de trabajo.
Cables y conductores expuestos o con malas
conexiones pueden exponer al operador u otras
personas a un choque eléctrico fatal.
4. Use el equipo solamente si está en buenas condiciones. Reemplaze cables rotos, dañados o con
conductores expuestos.
5. Mantenga todo seco, incluyendo su ropa, el área de
trabajo, los cables, antorchas, pinza del electrodo,
y la fuente de poder.
6. Asegúrese que todas las partes de su cuerpo están
insuladas de ambos, la pieza de trabajo y tierra.
7. No se pare directamente sobre metal o tierra mientras trabaja en lugares estrechos o áreas húmedas;
trabaje sobre un pedazo de madera seco o una
plataforma insulada y use zapatos con suela de
goma.
8. Use guantes secos y sin agujeros antes de energizar
el equipo.
9. Apage el equipo antes de quitarse sus guantes.
10. Use como referencia la publicación ANSI/ASC
Standard Z49.1 (listado en la próxima página) para
recomendaciones especícas de como conectar el
equipo a tierra. No confunda el cable de soldar a
la pieza de trabajo con el cable a tierra.
CAMPOS ELECTRICOS Y MAGNETICOS - Son peligrosos. La corriente
eléctrica uye através de cualquier
conductor causando a nivel local
Campos Eléctricos y Magnéticos
(EMF). Las corrientes en el área de corte y soldadura,
crean EMF alrrededor de los cables de soldar y las
maquinas. Por lo tanto:
1. Soldadores u Operadores que use marca-pasos para
el corazón deberán consultar a su médico antes de
soldar. El Campo Electromagnético (EMF) puede
interferir con algunos marca-pasos.
2. Exponerse a campos electromagnéticos (EMF) puede
causar otros efectos de salud aún desconocidos.
3. Los soldadores deberán usar los siguientes procedimientos para minimizar exponerse al EMF:
A. Mantenga el electrodo y el cable a la pieza de
trabajo juntos, hasta llegar a la pieza que usted
quiere soldar. Asegúrelos uno junto al otro con
cinta adhesiva cuando sea posible.
B. Nunca envuelva los cables de soldar alrededor
de su cuerpo.
C. Nunca ubique su cuerpo entre la antorcha y el
cable, a la pieza de trabajo. Mantega los cables a
un sólo lado de su cuerpo.
D. Conecte el cable de trabajo a la pieza de trabajo
lo más cercano posible al área de la soldadura.
E. Mantenga la fuente de poder y los cables de soldar
lo más lejos posible de su cuerpo.
HUMO Y GASES -- El humo y los
gases, pueden causar malestar o
daño, particularmente en espacios
sin ventilación. No inhale el humo
o gases. El gas de protección puede
causar falta de oxígeno.
Por lo tanto:
1. Siempre provea ventilación adecuada en el área
de trabajo por medio natural o mecánico. No solde,
corte, o ranure materiales con hierro galvanizado,
acero inoxidable, cobre, zinc, plomo, berílio, o cadmio a menos que provea ventilación mecánica
positiva . No respire los gases producidos por
estos materiales.
2. No opere cerca de lugares donde se aplique sub-
stancias químicas en aerosol. El calor de los rayos
del arco pueden reaccionar con los vapores de
hidrocarburo clorinado para formar un fosfógeno,
o gas tóxico, y otros irritant es.
3. Si momentáneamente desarrolla inrritación de
ojos, nariz o garganta mientras est á operando, es
indicación de que la ventilación no es apropiada.
Pare de trabajar y tome las medidas necesarias
para mejorar la ventilación en el área de trabajo.
No continúe operando si el malestar físico persiste.
4. Haga referencia a la publicación ANSI/ASC Standard
Z49.1 (Vea la lista a continuación) para recomendaciones especícas en la ventilación.
10

SECCION 1 SEGURIDAD
5. ADVERTENCIA-- Este producto cuando se utiliza para soldaduras o cortes,
produce humos o gases, los
cuales contienen químicos
conocidos por el Estado de California de causar defectos en el
nacimiento, o en algunos casos,
Cancer. (California Health &
Safety Code §25249.5 et seq.)
MANEJO DE CILINDROS-- Los
cilindros, si no son manejados
correctamente, pueden romperse y liberar violentamente
gases. Rotura repentina del
cilindro, válvula, o válvula de
escape puede causar daño o
muerte. Por lo tanto:
1. Utilize el gas apropiado para el proceso y utilize
un regulador diseñado para operar y reducir la
presión del cilindro de gas . No utilice adaptadores. Mantenga las mangueras y las conexiones
en buenas condiciones. Observe las instrucciones
de operación del manufacturero para montar el
regulador en el cilindro de gas comprimido.
2. Asegure siempre los cilindros en posición vertical
y amárrelos con una correa o cadena adecuada
para asegurar el cilindro al carro, transportes, tablilleros, paredes, postes, o armazón. Nunca asegure
los cilindros a la mesa de trabajo o las piezas que
son parte del circuito de soldadura . Este puede ser
parte del circuito elélectrico.
3. Cuando el cilindro no está en uso, mantenga la
válvula del cilindro cerrada. Ponga el capote de
protección sobre la válvula si el regulador no
está conectado. Asegure y mueva los cilindros
utilizando un carro o transporte adecuado. Evite
el manejo brusco de los
1. Siempre tenga personal cualicado para efectuar l a instalación, diagnóstico, y mantenimiento
del equipo. No ejecute ningún trabajo eléctrico a
menos que usted esté cualicado para hacer el
trabajo.
2. Antes de dar mantenimiento en el interior de la
fuente de poder, desconecte la fuente de poder
del suministro de electricidad primaria.
3. Mantenga los cables, cable a tierra, conexciones,
cable primario, y cualquier otra fuente de poder
en buen estado operacional. No opere ningún
equipo en malas condiciones.
4. No abuse del equipo y sus accesorios. Mantenga
el equipo lejos de cosas que generen calor como
hornos, también lugares húmedos como charcos
de agua , aceite o grasa, atmósferas corrosivas y
las inclemencias del tiempo.
5. Mantenga todos los artículos de seguridad y
coverturas del equipo en su posición y en buenas
condiciones.
6. Use el equipo sólo para el propósito que fue
diseñado. No modique el equipo en ninguna
manera.
INFORMACION ADICIONAL DE SEGURIDAD -- Para más información sobre las
prácticas de seguridad de los equipos de
arco eléctrico para soldar y cortar, pregunte
a su suplidor por una copia de "Precautions
and Safe Practices for Arc Welding, Cutting
and Gouging-Form 52-529.
Las siguientes publicaciones, disponibles através de
la American Welding Society, 550 N.W. LeJuene Road,
Miami, FL 33126, son recomendadas para usted:
1. ANSI/ASC Z49.1 - "Safety in Welding and Cutting"
2. AWS C5.1 - "Recommended Practices for Plasma Arc
Welding"
MANTENIMIENTO DEL EQUIPO -- Equipo
defectuoso o mal mantenido puede
causar daño o muerte. Por lo tanto:
3. AWS C5.2 - "Recommended Practices for Plasma Arc
Cutting"
4. AWS C5.3 - "Recommended Practices for Air Carbon
Arc Gouging and Cutting"
11

SECCION 1 SEGURIDAD
SIGNIFICADO DE LOS SIMBOLOS
-- Según usted avanza en la lectura
de este folleto: Los Símbolos Signican ¡Atención! ¡Esté Alerta! Se
trata de su seguridad.
Signica riesgo inmediato que,
de no ser evadido, puede resultar
inmediatamente en serio daño
personal o la muerte.
Signica el riesgo de un peligro
potencial que puede resultar en
serio daño personal o la muerte.
Signica el posible riesgo que
puede resultar en menores daños
a la persona.
12

SECTION 1 SÉCURITÉ
1.3 Safety - French
AVERTISSEMENT : Ces règles de sécurité
ont pour but d'assurer votre protection. Ils
récapitulent les informations de précaution
provenant des références dans la section
des Informations de sécurité supplémentaires. Avant
de procéder à l'installation ou d'utiliser l'unité, assurezvous de lire et de suivre les précautions de sécurité cidessous, dans les manuels, les ches d'information sur la
sécurité du matériel et sur les étiquettes, etc. Tout défaut
d'observer ces précautions de sécurité peut entraîner
des blessures graves ou mortelles.
PROTÉGEZ-VOUS -- Les processus de
soudage, de coupage et de gougeage
produisent un niveau de bruit élevé et
exige l'emploi d'une protection auditive. L'arc, tout
comme le soleil, émet des rayons ultraviolets en plus
d'autre rayons qui peuvent causer des blessures à la
peau et les yeux. Le métal incandescent peut causer
des brûlures. Une formation reliée à l'usage des
processus et de l'équipement est essentielle pour
prévenir les accidents. Par conséquent:
1. Portez des lunettes protectrices munies d'écrans la-
téraux lorsque vous êtes dans l'aire de travail, même
si vous devez porter un casque de soudeur, un écran
facial ou des lunettes étanches.
2. Portez un écran facial muni de verres ltrants et de
plaques protectrices appropriées an de protéger
vos yeux, votre visage, votre cou et vos oreilles des
étincelles et des rayons de l'arc lors d'une opération
ou lorsque vous observez une opération. Avertissez
les personnes se trouvant à proximité de ne pas regarder l'arc et de ne pas s'exposer aux rayons de l'arc
électrique ou le métal incandescent.
3. Portez des gants ignifugiés à crispin, une chemise
épaisse à manches longues, des pantalons sans rebord
et des chaussures montantes an de vous protéger des
rayons de l'arc, des étincelles et du métal incandescent,
en plus d'un casque de soudeur ou casquette pour
protéger vos cheveux. Il est également recommandé
de porter un tablier ininammable an de vous protéger des étincelles et de la chaleur par rayonnement.
4. Les étincelles et les projections de métal incandescent
risquent de se loger dans les manches retroussées,
les rebords de pantalons ou les poches. Il est recommandé de garder boutonnés le col et les manches et
de porter des vêtements sans poches en avant.
5. Protégez toute personne se trouvant à proximité des
étincelles et des rayons de l'arc à l'aide d'un rideau ou
d'une cloison ininammable.
6. Portez des lunettes étanches par dessus vos lunettes
de sécurité lors des opérations d'écaillage ou de
meulage du laitier. Les écailles de laitier incandescent
peuvent être projetées à des distances considérables.
Les personnes se trouvant à proximité doivent également porter des lunettes étanches par dessus leur
lunettes de sécurité.
INCENDIES ET EXPLOSIONS -- La
chaleur provenant des ammes ou de
l'arc peut provoquer un incendie. Le
laitier incandescent ou les étincelles
peuvent également provoquer un
incendie ou une explosion. Par conséquent :
1. Éloignez susamment tous les matériaux combustibles de l'aire de travail et recouvrez les matériaux
avec un revêtement protecteur ininammable. Les
matériaux combustibles incluent le bois, les vêtements, la sciure, le gaz et les liquides combustibles,
les solvants, les peintures et les revêtements, le
papier, etc.
2. Les étincelles et les projections de métal incandescent peuvent tomber dans les ssures dans
les planchers ou dans les ouvertures des murs et
déclencher un incendie couvant à l'étage inférieur
Assurez-vous que ces ouvertures sont bien protégées
des étincelles et du métal incandescent.
3. N'exécutez pas de soudure, de coupe ou autre travail à chaud avant d'avoir complètement nettoyé la
surface de la pièce à traiter de façon à ce qu'il n'ait
aucune substance présente qui pourrait produire
des vapeurs inammables ou toxiques. N'exécutez
pas de travail à chaud sur des contenants fermés
car ces derniers pourraient exploser.
4. Assurez-vous qu'un équipement d'extinction
d'incendie est disponible et prêt à servir, tel qu'un
tuyau d'arrosage, un seau d'eau, un seau de sable
ou un extincteur portatif. Assurez-vous d'être bien
instruit par rapport à l'usage de cet équipement.
5. Assurez-vous de ne pas excéder la capacité de
l'équipement. Par exemple, un câble de soudage
surchargé peut surchauer et provoquer un incendie.
6. Une fois les opérations terminées, inspectez l'aire de
travail pour assurer qu'aucune étincelle ou projection de métal incandescent ne risque de provoquer
un incendie ultérieurement. Employez des guetteurs
d'incendie au besoin.
7. Pour obtenir des informations supplémentaires,
consultez le NFPA Standard 51B, "Fire Prevention in
Use of Cutting and Welding Processes", disponible au
National Fire Protection Association, Batterymarch
Park, Quincy, MA 02269.
CHOC ÉLECTRIQUE -- Le contact avec
des pièces électriques ou les pièces
de mise à la terre sous tension peut
causer des blessures graves ou mor-
telles. NE PAS utiliser un courant de
soudage c.a. dans un endroit humide, en espace
restreint ou si un danger de chute se pose.
13

SECTION 1 SÉCURITÉ
1. Assurez-vous que le châssis de la source
d'alimentation est branché au système de mise à
la terre de l'alimentation d'entrée.
2. Branchez la pièce à traiter à une bonne mise de
terre électrique.
3. Branchez le câble de masse à la pièce à traiter et
assurez une bonne connexion an d'éviter le risque
de choc électrique mortel.
4. Utilisez toujours un équipement correctement
entretenu. Remplacez les câbles usés ou endommagés.
5. Veillez à garder votre environnement sec, incluant
les vêtements, l'aire de travail, les câbles, le porteélectrode/torche et la source d'alimentation.
6. Assurez-vous que tout votre corps est bien isolé
de la pièce à traiter et des pièces de la mise à la
terre.
7. Si vous devez eectuer votre travail dans un espace
restreint ou humide, ne tenez vous pas directement sur le métal ou sur la terre; tenez-vous sur
des planches sèches ou une plate-forme isolée et
portez des chaussures à semelles de caoutchouc.
8. Avant de mettre l'équipement sous tension, isolez
vos mains avec des gants secs et sans trous.
9. Mettez l'équipement hors tension avant d'enlever
vos gants.
10. Consultez ANSI/ASC Standard Z49.1 (listé à
la page suivante) pour des recommandations
spéciques concernant les procédures de mise à
la terre. Ne pas confondre le câble de masse avec
le câble de mise à la terre.
CHAMPS ÉLECTRIQUES ET MAGNÉTIQUES — comportent un risque de
danger. Le courant électrique qui
passe dans n'importe quel conduc-
teur produit des champs électriques
et magnétiques localisés. Le soudage et le courant de coupage créent des champs électriques
et magnétiques autour des câbles de soudage et
l'équipement. Par conséquent :
1. Un soudeur ayant un stimulateur cardiaque doit
consulter son médecin avant d'entreprendre une
opération de soudage. Les champs électriques et
magnétiques peuvent causer des ennuis pour certains stimulateurs cardiaques.
2. L'exposition à des champs électriques et magné-
tiques peut avoir des eets néfastes inconnus pour
la santé.
3. Les soudeurs doivent suivre les procédures suivantes
pour minimiser l'exposition aux champs électriques
et magnétiques :
A. Acheminez l'électrode et les câbles de masse
ensemble. Fixez-les à l'aide d'une bande adhésive
lorsque possible.
B. Ne jamais enrouler la torche ou le câble de masse
autour de votre corps.
C. Ne jamais vous placer entre la torche et les câbles
de masse. Acheminez tous les câbles sur le même
côté de votre corps.
D. Branchez le câble de masse à la pièce à traiter le
plus près possible de la section à souder.
E. Veillez à garder la source d'alimentation pour le
soudage et les câbles à une distance appropriée
de votre corps.
LES VAPEURS ET LES GAZ -- peuvent
causer un malaise ou des dommages
corporels, plus particulièrement
dans les espaces restreints. Ne respirez pas les vapeurs et les gaz. Le
gaz de protection risque de causer
l'asphyxie. Par conséquent :
1. Assurez en permanence une ventilation adéquate
dans l'aire de travail en maintenant une ventilation naturelle ou à l'aide de moyens mécanique.
N'effectuez jamais de travaux de soudage, de
coupage ou de gougeage sur des matériaux tels que
l'acier galvanisé, l'acier inoxydable, le cuivre, le zinc,
le plomb, le berylliym ou le cadmium en l'absence
de moyens mécaniques de ventilation ecaces. Ne
respirez pas les vapeurs de ces matériaux.
2. N'eectuez jamais de travaux à proximité d'une
opération de dégraissage ou de pulvérisation. Lorsque la chaleur
ou le rayonnement de l'arc entre en contact avec les
vapeurs d'hydrocarbure chloré, ceci peut déclencher
la formation de phosgène ou d'autres gaz irritants,
tous extrêmement toxiques.
3. Une irritation momentanée des yeux, du nez ou de la
gorge au cours d'une opération indique que la ventilation n'est pas adéquate. Cessez votre travail an
de prendre les mesures nécessaires pour améliorer
la ventilation dans l'aire de travail. Ne poursuivez
pas l'opération si le malaise persiste.
4. Consultez ANSI/ASC Standard Z49.1 (à la page
suivante) pour des recommandations spéciques
concernant la ventilation.
14
SECTION 1 SÉCURITÉ
5. AVERTISSEMENT : Ce produit, lorsqu'il est utilisé
dans une opération de soudage ou de
coupage, dégage des vapeurs ou des
gaz contenant des chimiques considéres par l'état de la Californie comme
étant une cause des malformations
congénitales et dans certains cas, du
cancer. (California Health & Safety
Code §25249.5 et seq.)
MANIPULATION DES CYLINDRES -La manipulation d'un cylindre, sans
observer les précautions nécessaires,
peut produire des fissures et un
échappement dangereux des gaz.
Une brisure soudaine du cylindre, de la soupape ou
du dispositif de surpression peut causer des blessures graves ou mortelles. Par conséquent :
1. Utilisez toujours le gaz prévu pour une opération
et le détendeur approprié conçu pour utilisation
sur les cylindres de gaz comprimé. N'utilisez jamais
d'adaptateur. Maintenez en bon état les tuyaux et
les raccords. Observez les instructions d'opération
du fabricant pour assembler le détendeur sur un
cylindre de gaz comprimé.
2. Fixez les cylindres dans une position verticale, à
l'aide d'une chaîne ou une sangle, sur un chariot
manuel, un châssis de roulement, un banc, un mur,
une colonne ou un support convenable. Ne xez
jamais un cylindre à un poste de travail ou toute autre
dispositif faisant partie d'un circuit électrique.
3. Lorsque les cylindres ne servent pas, gardez les
soupapes fermées. Si le détendeur n'est pas branché, assurez-vous que le bouchon de protection de
la soupape est bien en place. Fixez et déplacez les
cylindres à l'aide d'un chariot manuel approprié.
Toujours manipuler les cylindres avec soin.
4. Placez les cylindres à une distance appropriée
de toute source de chaleur, des étincelles et des
ammes. Ne jamais amorcer l'arc sur un cylindre.
5. Pour de l'information supplémentaire, consultez
CGA Standard P-1, "Precautions for Safe Handling
of Compressed Gases in Cylinders", mis à votre disposition par le Compressed Gas Association, 1235
Jeerson Davis Highway, Arlington, VA 22202.
ENTRETIEN DE L'ÉQUIPEMENT -- Un équipement entretenu de façon défectueuse ou
inadéquate peut causer des blessures
graves ou mortelles. Par conséquent :
1. Efforcez-vous de toujours confier les tâches
d'installation, de dépannage et d'entretien à un
personnel qualié. N'eectuez aucune réparation
électrique à moins d'être qualié à cet eet.
2. Avant de procéder à une tâche d'entretien à
l'intérieur de la source d'alimentation, débranchez
l'alimentation électrique.
3. Maintenez les câbles, les ls de mise à la terre,
les branchements, le cordon d'alimentation et la
source d'alimentation en bon état. N'utilisez jamais un équipement s'il présente une défectuosité
quelconque.
4. N'utilisez pas l'équipement de façon abusive. Gardez
l'équipement à l'écart de toute source de chaleur,
notamment des fours, de l'humidité, des aques
d'eau, de l'huile ou de la graisse, des atmosphères
corrosives et des intempéries.
5. Laissez en place tous les dispositifs de sécurité et
tous les panneaux de la console et maintenez-les
en bon état.
6. Utilisez l'équipement conformément à son usage
prévu et n'eectuez aucune modication.
INFORMATIONS SUPPLÉMENTAIRES RELATIVES À LA SÉCURITÉ -- Pour obtenir de
l'information supplémentaire sur les règles
de sécurité à observer pour l'équipement
de soudage à l'arc électrique et le coupage,
demandez un exemplaire du livret "Precautions and Safe Practices for Arc Welding,
Cutting and Gouging", Form 52-529.
Les publications suivantes sont également recommandées et mises à votre disposition par l'American Welding
Society, 550 N.W. LeJuene Road, Miami, FL 33126 :
1. ANSI/ASC Z49.1 - "Safety in Welding and Cutting"
2. AWS C5.1 - "Recommended Practices for Plasma Arc
Welding"
3. AWS C5.2 - "Recommended Practices for Plasma Arc
Cutting"
4. AWS C5.3 - "Recommended Practices for Air Carbon
Arc Gouging and Cutting"
15

SECTION 1 SÉCURITÉ
SIGNIFICATION DES SYMBOLES
Ce symbole, utilisé partout dans ce manuel,
signie "Attention" ! Soyez vigilant ! Votre
sécurité est en jeu.
DANGER
Signie un danger immédiat. La situation peut
entraîner des blessures graves ou mortelles.
AVERTISSEMENT
Signie un danger potentiel qui peut entraîner des
blessures graves ou mortelles.
ATTENTION
Signie un danger qui peut entraîner des blessures
corporelles mineures.
16

SECTION 2 DESCRIPTION / INSTALLATION
2.0 Plumbing Box Description
The PCC-14 Plumbing Box is a Plasmarc Cutting Control used to connect PT-36R, PT-26,
PT-19XL, PT-19XLS, PT-600 or PT-251 torches to a remotely located ESP-150, ESP-200, or
Deucepack system. The PCC-14 includes high frequency starting circuits to eliminate
starting problems with long torches and to minimize high frequency interference with
other customer systems.
2.1 Specications
Weight: 41lbs. (18.6 kg)
Plasma and Start Gases:
The PCC-14 may be used with O2, N2, Air, or H-35 (35% H2/65% Ar) with a maximum input pressure of 110 psig (7.6 bar).
It is recommended, but not required, that N2 be used as the start gas when using H-35. The ow rate of gas will depend on
the pressure set, the torch connected to the plumbing box, and the parts installed in the torch. Without a torch attached,
the maximum ow rate for these gases at 100 psig (6.9 bar) is about 1000 scfh (28.3 cu-m/h). The minimum acceptable
pressure for the start gas is 19 psig (1.3 bar); for the plasma gas it is 24 psig (1.7 bar). Below these pressures the pressure
switches may not be satised.
Shield Gases:
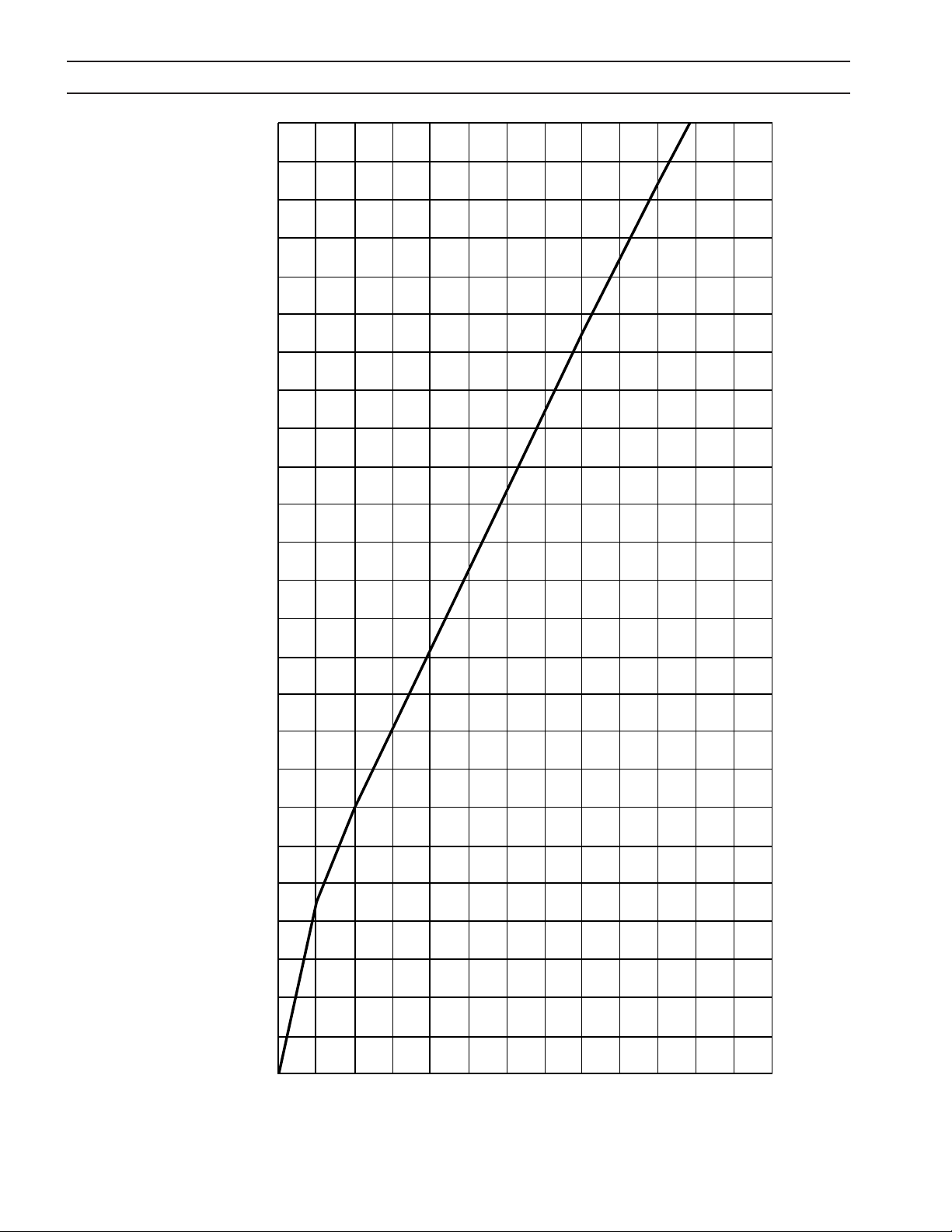
The PCC-14 may be used with Air, N2, Ar, or CO2. The maximum pressure is 110 psig (7.6 bar). This will result in a ow of
250scfh (7.1 cu-m/h) N2. See Graph 2-1. There is no pressure interlock on the shield gas.
Coolant:
The PCC-14 is designed for use with water based coolants using either ethylene glycol or propylene glycol antifreeze (ESAB
P/N’s 156F05 or 0558004297). Maximum design pressure is 200 psig (13.8 bar). Flow rates depend on the torch but typically
vary from .9 to 2 gpm (4.1 to 9.1 l/min).
17

SECTION 2 DESCRIPTION / INSTALLATION
2.2 PCC-14 Plumbing Box Dimensions/ Mounting Hole Locations
Install the PCC-14 Plumbing Box in an appropriate location so as to maintain adequate and unrestricted airow
into and out of the cabinetry. For permanent mounting refer to the gure below for mounting hole dimensions
in the base of this unit.
13.0"
(330.2 mm)
(477.5 mm)
16.625"
(422.28 mm)
12.500"
(317.5 mm)
18.8"
2.125"
(53.98 mm)
15.4"
(391.2 mm)
1.060"
(26.92 mm)
18
4.500"
(114.3 mm)
6.875"
(174.63 mm)

SECTION 2 DESCRIPTION / INSTALLATION
2.3 Plumbing Box Installation
ELECTRICITY CAN KILL!
HIGH VOLTAGE CAN BE PRESENT BEHIND COVER PLATE. DO NOT OP
WARNING
CAUTION
See appropriate equipment literature for operating conditions and necessary gas purities.
ERATE WITHOUT COVER PLATE IN PLACE. BEFORE REMOVING COVER
PLATE OR PERFORMING ANY MAINTENANCE OR ASSEMBLY OF THIS
EQUIPMENT, ENSURE THE POWER SOURCE IS TURNED OFF AND DIS
CONNECTED.
Only qualied maintenance personnel should repair and maintain
this equipment.
Unit is NOT designed for use in rain or snow. Damage to equipment
may result.
Unit is to be lifted only by the handle provided . Failure to do so may
result in damage to the equipment.
Note:
Flashback arrestors are required to prevent re from propagating back
to the gas supply through lines carrying oxygen or fuel gases.
Use AWG 1/0 power cable to carry electrode current from the power
source to the PCC-14. See Table 2-2 for additional cables.
CAUTION
Gas Purging:
When switching between H-35 and an oxidizing gas (air or oxygen) it is recommended that the following procedure be
followed:
1. Turn o the gas.
2. Put the system into plasma gas test until line pressure is exhausted. If the start gas is being switched to or from
H-35, switch to start gas test until that line is exhausted as well.
3. Disconnect the old gas and connect a relatively inert gas such as nitrogen, argon, carbon dioxide, C-25, etc. Set the
pressure to 50 psig (3.5 bar) and purge each aected line for 60 seconds.
4. Then shut o the gas and exhaust each line per Step 2.
5. Connect the gas to be used. Set the pressure to recommended values for the cutting condition to be used, and
purge each aected line for 15 seconds per 25 ft. (7.6 m) of line.
Avoid using the same supply lines for both oxygen and air if oil may
be mixed with the air. Oil in the presence of 100% oxygen can be
highly ammable.
Failure to observe above cautions may result in personal injury and /
or damage to the equipment.
Note:
The expected life of the internal exible hoses is 10 years.
Replace them earlier if cracking or brittleness is noted.
19
SECTION 2 DESCRIPTION / INSTALLATION
250 (7.1)
240 (6.8)
230 (6.5)
220 (6.2)
210 (5.9)
200 (5.7)
190 (5.4)
180 (5.1)
170 (4.8)
2
160 (4.5)
150 (4.2)
Graph 2-1 - Gas Pressure / Flow
140 (4.0)
130 (3.7)
120 (3.4)
110 (3.1)
100 (2.8)
Shield Gas Flow SCFH (CU-M/H) N
90 (2.5)
80 (2.3)
70 (2.0)
60 (1.7)
50 (1.4)
40 (1.1)
30 (0.8)
20 (0.6)
10 (0.3)
0
0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 110 120 130
(0.7) (1.4) (2.1) (2.8) (3.5) (4.1) (4.8) (5.5) (6.2) (6.9) (7.6) (8.3) (9.0)
PSIG (BAR) Pressure Setting to 0.052 in. (1.32 mm) Diameter Orice
20

SECTION 2 DESCRIPTION / INSTALLATION
Table 2-2 - Hoses / Cables / Regulators
2.4 Spark Gap Adjustment
Spark Gap
Spark Gap
Access Cover
1. Disconnect input power to power source.
2. Remove access cover from spark gap opening.
3. Check / set to recommended spark gap of 0.040” (1 mm).
4. Replace cover.
21
SECTION 2 DESCRIPTION / INSTALLATION
2.5 Plumbing Box Connections
THIS EQUIPMENT CAN BE HAZARDOUS IF NOT PROPERLY
OPERATED AND MAINTAINED.
READ AND UNDERSTAND ALL EQUIPMENT LITERATURE AND
WARNING LABELS BEFORE OPERATING THIS EQUIPMENT.
WARNING
WARNING
FOLLOW THESE INSTRUCTIONS TO PREVENT INJURY OR
PROPERTY DAMAGE.
YOU MUST COMPLY WITH LOCAL, STATE AND NATIONAL
ELECTRICAL AND SAFETY CODES.
ON LY TRA INE D PE R SO N NE L SH OUL D P ERF ORM
MAINTENANCE OR REPAIRS ON THIS EQUIPMENT.
ELECTRIC SHOCK CAN KILL!
TUR N OFF PR IM ARY INP UT P OWER AT T HE WAL L
DISCONNECT BOX BEFORE MAKING ANY CONNECTIONS TO
THE POWER SUPPLY.
DISCONNECT CURRENT SUPPLY AT WALL DISCONNECT
BEFORE SERVICING PLUMBING BOX.
• DO NOT OPERATE PLUMBING BOX WITH ANY COVERS
REMOVED / OPEN.
• DO NOT TOUCH ANY TORCH FRONTEND PARTS WITH
POWER ON.
• DO NOT ATTEMPT TO SERVICE UNLESS POWER HAS BEEN
DISCONNECTED AT THE WALL.
22

SECTION 2 DESCRIPTION / INSTALLATION
Connection Locations Inside Plumbing Box
23

SECTION 2 DESCRIPTION / INSTALLATION
Pilot Arc Cable
From Power Supply
Shield Gas Hose From Torch
Plasma Gas Hose From Torch
Typical For All Torch Congurations
Pilot Arc Cable From Torch
Power / Coolant Supply
Hose From Torch
Power / Coolant Return
Hose From Torch
Coolant Supply Hose
Power Cables
Coolant Return Hose
Plumbing Box Style Torches - PT-36R, PT-600 All, PT-19XLS 4.5 ft. (1.4 m) to 25 ft. (7.6 m)
24
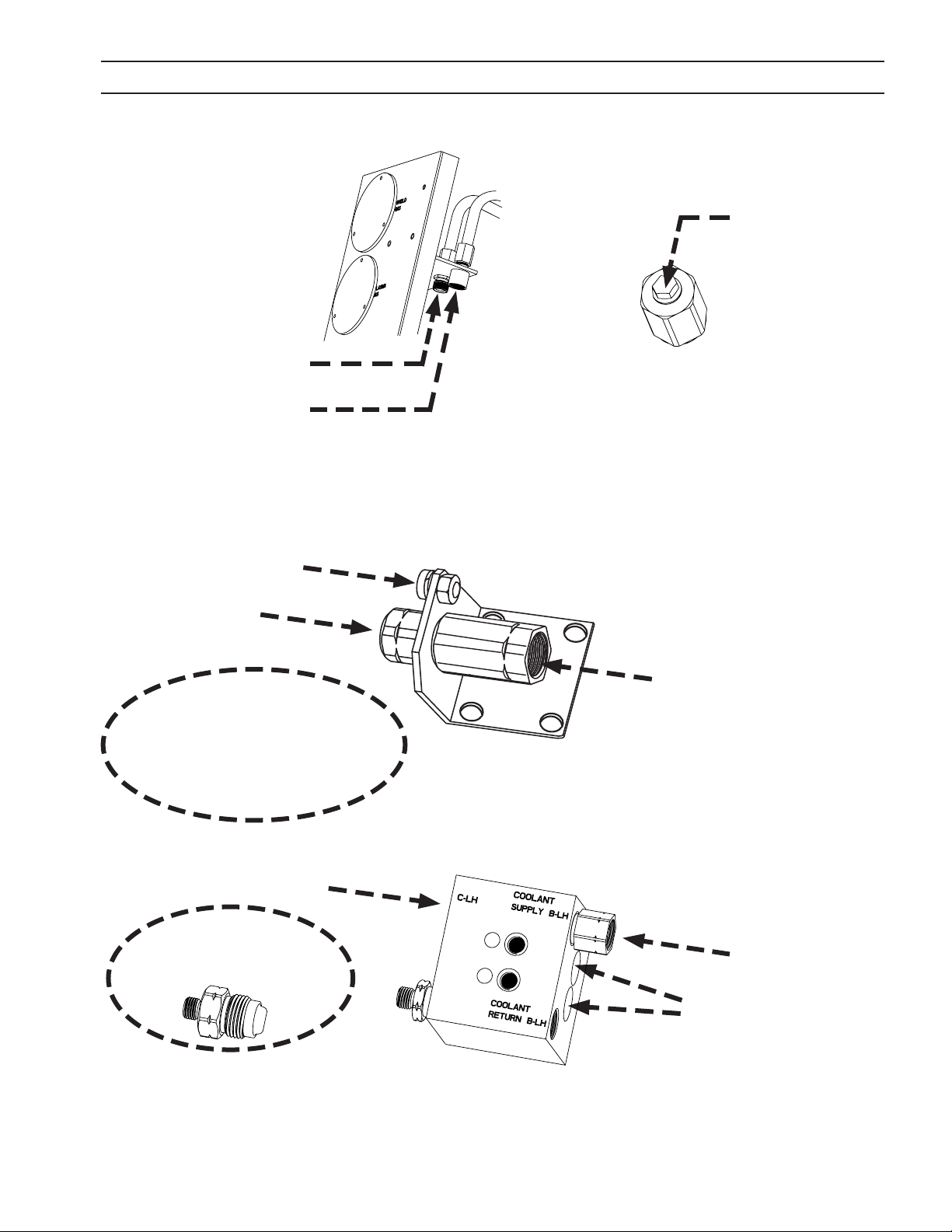
SECTION 2 DESCRIPTION / INSTALLATION
Pilot Arc Cable
From Power Supply
Shield Gas Hose From Torch
Plasma Gas Hose From Torch
Typical For All Torch Congurations
Pilot Arc Cable From Torch
Coolant Return
Hose From Torch
NOTE
On all PT-26 Torches the Pilot Arc
Cable is included inside the Cool-
ant Return Hose Assembly and the
separate pilot arc cable connection
shown above is NOT used.
Power / Coolant Supply
Hose From Torch
NOTE
This Fitting Must Be Removed To
Make Connection From Torch
Coolant Return Hose
Coolant Supply Hose
Power Cables
Direct Connect Style Torches - PT-26 All, PT-19XLS 25 ft. (7.6 m) and 50 ft. (15.2 m)
25
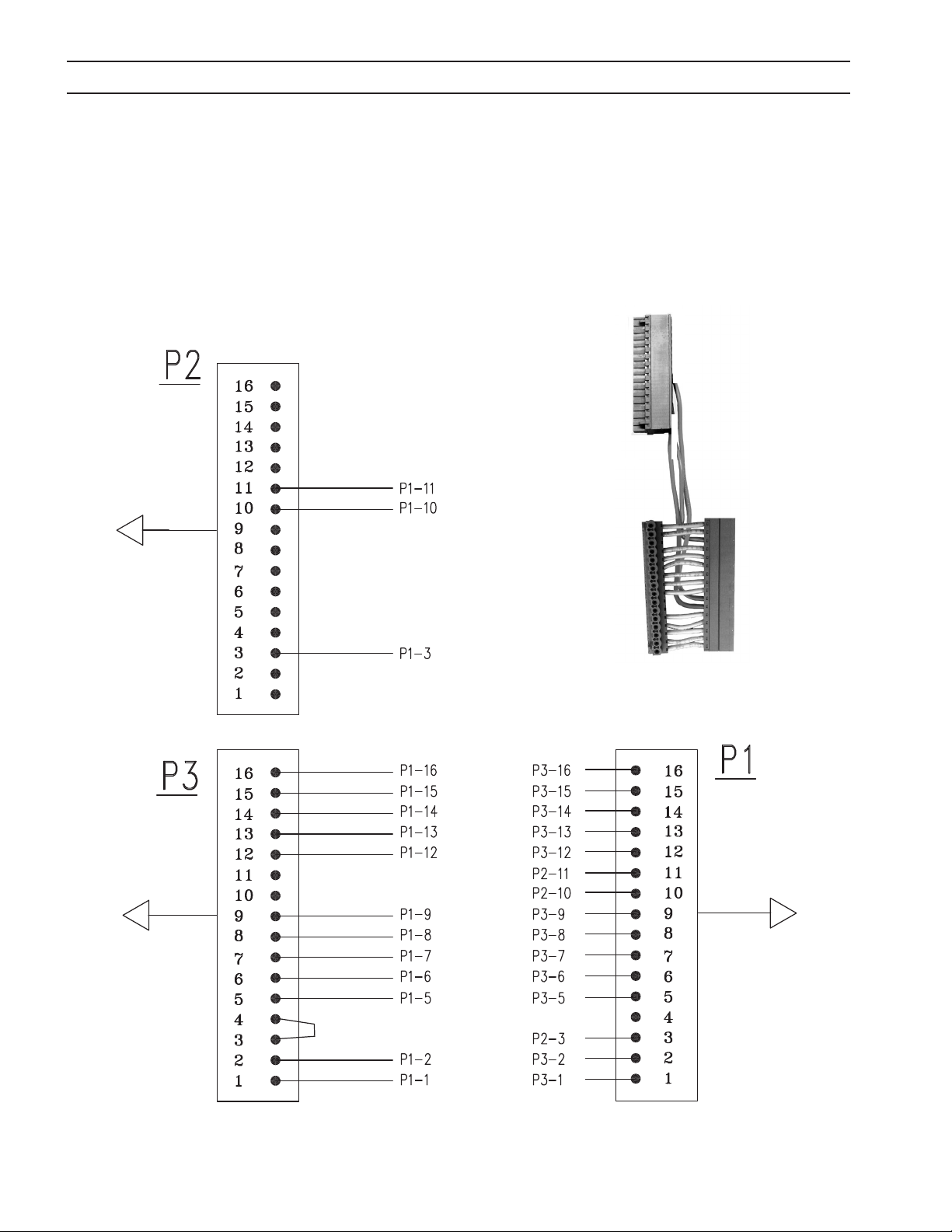
SECTION 2 DESCRIPTION / INSTALLATION
2.6 Adaptor for PCC-14 Plumbing Box use with ESP-150 or ESP-200 Power Supplies
Note:
The ESP-150 and the ESP-200 are supplied from the factory connected for manual use. If the unit
is to be used with a PCC-14 Plumbing Box, Adaptor (0558006530) must be installed.
P2
Adaptor
0558006530
P1P3
26

SECTION 2 DESCRIPTION / INSTALLATION
2.7 PCC-14 Plumbing Box used with ESP-150 Power Supply
Remove Plug P45 from J4 Receptacle
Note:
The ESP-150 is supplied from the factory with Plug P45 connected to the J4 Receptacle. If the unit is to be used with
a PCC-14 Plumbing Box, install Adaptor (0558006530) as
shown.
ESP-150 Power Supply
Adaptor
0558006530
P2
Connect Plug P2 into J4 Receptacle
Connect Plug P3 into J5 Receptacle
Reconnect Plug P45
into P1 Receptacle
P1P3
27

SECTION 2 DESCRIPTION / INSTALLATION
2.8 PCC-14 Plumbing Box use with ESP-200 Power Supply
Remove Plug P5 from J5 Receptacle
J5
J6
Note:
The ESP-200 is supplied from the factory with
Plug P5 connected to the J5 Receptacle. If the
unit is to be used with a PCC-14 Plumbing Box,
install Adaptor (0558006530) as shown.
J5 J6
ESP-200 Power Supply
Adaptor
0558006530
P2
Connect Plug P2 into J5 Receptacle
Connect Plug P3 into J6 Receptacle
Reconnect Plug P5
into P1 Receptacle
ESP-200 Power Supply
P1P3
28

SECTION 2 DESCRIPTION / INSTALLATION
ELECTRIC SHOCK CAN KILL!
WARNING
2.9 PT-36R Torch Connections to Plumbing Box
1. Torch connections are rst made in the PCC-14 plumbing box. Remove the cover of the plumbing box to access input
and output connections . For both manual and mechanized torch applications, pass the torch lines through the
openings in the front of plumbing box and make connections as shown.
TURN OFF PRIMARY INPUT POWER AT THE WALL DISCONNECT BOX
BEFORE MAKING ANY CONNECTIONS TO THE PCC14.
4
Pilot Arc Cable
3
2B
2A
1
Power Cable
4
2a
Power Cable
1
Shield Gas Hose
3
Plasma Gas Hose
2b
29

SECTION 2 DESCRIPTION / INSTALLATION
2. Connect lines from plumbing box to the power source. Open top front cover to gain access to the torch connections.
chassis ground
Pilot arc adapter
(P/N 0558009992)
2
2
Power/Coolant adapter
(P/N 36743)
4
4
3. Thread the ve service lines of the PT-26 torch through bushing at upper left corner of the front panel and connect them
to the matching ttings on output terminal. Hose connections should be wrench-tight. Make sure plug of the switch
lead is rmly locked in place. Then close hinged cover.
Water IN (+)
2
(Pilot Arc)
Water OUT (-)
4
(Electrode)
Interconnection Diagram - Front of ESP-150
30

SECTION 2 DESCRIPTION / INSTALLATION
ELECTRIC SHOCK CAN KILL!
WARNING
2.10 ESP-150 Torch Connections
1. Torch connections are rst made in the PCC-14 plumbing box. Remove the cover of the plumbing box to access input
and output connections . For both manual and mechanized torch applications, pass the torch lines through the
openings in the front of plumbing box and make connections as shown.
TURN OFF PRIMARY INPUT POWER AT THE WALL DISCONNECT BOX
BEFORE MAKING ANY CONNECTIONS TO THE ESP150.
1
2
3
4
lines from torch
1 Shield Gas Hose
2 Coolant Return Hose
3 Plasma Cut Gas Hose
4 Electrode Cable/Coolant Supply Hose
5 Switch Lead (PT-26 manual torch only)
The PT-26M requires an auxiliary pilot ON switch box. Switch Lead, Item Number 5, is not in-
1
Shield Gas
Water IN (+)
2
(Pilot Arc)
Plasma/Start Gas
3
4
Water OUT (-)
(Electrode)
5
Note:
cluded in the PT-26M torch bundle.
1
2
3
4
31

SECTION 2 DESCRIPTION / INSTALLATION
OFF
ON
Note:
If a PT-26 In-line torch is being used in a mechanized installation where only an
5
arc start signal is required, connect the optional Remote Hand Switch, ESAB part
number 2075600, to the Torch Switch Receptacle on the hook-up panel in the
front of the ESP-150 console.
Connect cable , in place of item 5 from the torch bundle, to adapt the mechanized version of the PT-26 plasma torch.
2. Connect lines from plumbing box to the power source. Open top front cover to gain access to the
torch connections.
2
2
4
5
Pilot arc adapter
(P/N 0558009992)
Power/Coolant adapter
(P/N 36743)
4
5
(Manual torch only)
chassis ground
3. Thread the ve service lines of the PT-26 torch through bushing at upper left corner of the front panel and connect them
to the matching ttings on output terminal. Hose connections should be wrench-tight. Make sure plug of the switch
lead is rmly locked in place. Then close hinged cover.
Water IN (+)
2
(Pilot Arc)
Water OUT (-)
4
(Electrode)
Torch Switch
5
Receptacle
Interconnection Diagram - Front of ESP-150
32

SECTION 2 DESCRIPTION / INSTALLATION
2.10.a ESP150 DUECE PACK Connections
primary ESP-150 unit
secondary ESP-150 unit
plumbing box
slave control cable
power output cable
power output cable
slave control cable
Power/Coolant adapter
(P/N 36743)
Coolany supply hose/
Electrode cable adapter
supplied w/
secondary unit
33

SECTION 2 DESCRIPTION / INSTALLATION
Connections to the Master Power Supply
1. A power output cable attaches to a large adapter which is installed in the Water OUT ( - ) tting.
2. The Pilot Arc cable connects to a small adapter installed in the Water IN ( + ) tting.
3. Coolant out hose connects to the large adapter installed in the Water OUT ( - ) tting.
4. Coolant in hose connects to the small adapter installed in the Water IN ( + ) tting.
5. Torch Switch Extension cable plugs into the Torch Switch Receptacle
6. The Plumbing Box Control cable connects to the Amphenol receptacle on the rear of the power supply labeled "REMOTE PLUMBING BOX".
The other ends of all six of the above hoses/cables will connect to the Plumbing Box.
7. A work cable connects to the "Work" terminal on the front-lower-left of the console. The other end is attached to the
cutting table or work piece.
Connections to the Slave Power Supply
1. A slave control cable has been wired into the master supply. This cable plugs into the slave's Torch Switch Receptacle
(5 pin plug).
2. A power output cable attaches to a large adapter which is installed in the Water OUT ( - ) tting.
3. A work cable connects to the "Work" terminal on the front-lower-left of the console. The other end is attached to the
cutting table or work piece.
No gas hoses connect to either power supply when a plumbing box is being used.
Connections to the rear of the Plumbing Box
1. The Start, Cut & Shield gas hoses from the regulator panel attach to the rear of the plumbing box.
2. The Plumbing Box Control cable connects to the Amphenol receptacle labeled "CONTROL CABLE FROM POWER
SOURCE".
The Torch Switch Extension cable, both power cables, the pilot arc cable and both coolant hoses enter the plumbing box
from the rear and are connected internally.
34

SECTION 2 DESCRIPTION / INSTALLATION
ELECTRIC SHOCK CAN KILL!
WARNING
2.11 ESP-200 Torch Connections
1. Torch connections are rst made in the PCC-14 plumbing box. Remove the cover of the plumbing box to access input
and output connections . For both manual and mechanized torch applications, pass the torch lines through the
openings in the front of plumbing box and make connections as shown.
TURN OFF PRIMARY INPUT POWER AT THE WALL DISCONNECT BOX
BEFORE MAKING ANY CONNECTIONS TO THE ESP200.
1
2
3
4
lines from torch
1 Shield Gas Hose
2 Coolant Return Hose
3 Plasma Cut Gas Hose
4 Electrode Cable/Coolant Supply Hose
5 Switch Lead (PT-26 manual torch only)
The PT-26M requires an auxiliary pilot ON switch box. Switch Lead, Item Number 5, is not in-
1
Shield Gas
Water IN (+)
2
(Pilot Arc)
Plasma/Start Gas
3
Water OUT (-)
4
(Electrode)
5
Note:
cluded in the PT-26M torch bundle.
1
2
3
4
35

OFF
ON
SECTION 2 DESCRIPTION / INSTALLATION
Note:
If a mechanized torch is being used in an installation where only
5
an arc start signal is required, connect the optional Remote Hand
Switch, ESAB part number 2075600, to the Torch Switch Recep-
tacle on the hook-up panel in the front of the ESP-200 console.
chassis ground
Connect cable , in place of item 5 from the torch bundle, to control the
5
mechanized plasma torch.
Pilot arc adapter
(P/N 0558009992)
2
2
Power/Coolant adapter
(P/N 36743)
4
4
5
Water IN (+)
2
(Manual torch only)
(Pilot Arc)
4
Water OUT (-)
(Electrode)
Torch Switch Receptacle
5
(optional/only used with manual PT-26 torch)
36

SECTION 2 DESCRIPTION / INSTALLATION
2. Remove the side panel of the ESP-200 and thread torch lines from the
plumbing box through the bushing at middle right side of front panel
and proceed as follows:
a. Insert pilot arc adapter into left hand threaded pilot arc tting.
b. Connect coolant return hose (male left-hand thread) to the adapter.
Pilot arc adapter
(P/N 0558009992)
Thread torch lines through
bushing.
Pilot arc tting
c. Connect pilot arc cable to one of 3 threaded holes on the outside
of adapter with supplied screw.
Pilot Arc Cable
d. Connect coolant supply/power cable to tting labeled “TORCH”.
Coolant Supply/electrode
cable connection
37

SECTION 2 DESCRIPTION / INSTALLATION
2.12 Voltage Divider Adjustment
The PCC-14 contains a voltage divider board used for lift assemblies that make use of voltage height
control. The voltage divider can be adjusted to accurately reect the arc voltage during cutting operations for voltage height control.
You can set the ratio by adjusting the resistance of R1. To set R1 to a specic value, measure the resistance between points W2 and W3 on the voltage divider board. See the illustration of the voltage
divider board below. The chart below outlines some common ratios and resistance values.
Ratio Resistance
17:1 900 Ohms
21:1 780 Ohms
25:1 625 Ohms
Voltage Divider Board
38

SECTION 3 MAINTENANCE
3.0 Maintenance
3.1 General
WARNING
ELECTRIC SHOCK CAN KILL! ENSURE THE LINE WALL DISCONNECT SWITCH OR CIRCUIT
BREAKER IS OPEN BEFORE ATTEMPTING ANY INSPECTION OR WORK ON THE INSIDE OF
THE PLUMBING BOX. ALWAYS WEAR SAFETY GOGGLES WITH SIDE SHIELDS WHEN BLOW
ING OUT THE PLUMBING BOX WITH LOW PRESSURE AIR.
Maintenance work must be performed by an experienced person. Do not permit untrained persons to inspect, clean, or
lubricate this equipment.
On a regular basis, check cylinder valves, regulators, hoses, and gas connections for leaks using a soap solution or a leak
test solution.
Keep the plumbing box dry, free of oil and grease, and protected at all times from damage by hot metal and sparks.
3.2 Cleaning
Periodically, remove the cover from the plumbing box and, wearing proper eye protection, blow accumulated dust and dirt
from the air passages and the interior components using clean low-pressure air. It is imperative that the air passages to the
interior of the unit be kept free of dirt accumulation to ensure adequate circulation of cooling air.
The length of time between cleaning will depend on the location of the unit and the amount of dust in the atmosphere.
After cleaning with low-pressure air, check for and tighten any loose hardware, including all electrical connections. Check
for frayed and/or cracked insulation on all power cables and replace if necessary.
WARNING
ELECTRIC SHOCK CAN KILL! FAILURE TO REPLACE WORN OR DAMAGED CABLES MAY RE
SULT IN A BARE CABLE TOUCHING A GROUNDED SURFACE. THE RESULTING ELECTRICAL
ARC MAY DAMAGE THE UNPROTECTED EYES AND WILL PRESENT A SERIOUS FIRE HAZ
ARD. BODILY CONTACT WITH A BARE CABLE, CONNECTOR, OR CONDUCTOR MAY RESULT
IN SEVERE ELECTRICAL SHOCK, CAUSING SERIOUS BURNS OR DEATH.
39

SECTION 3 MAINTENANCE
40

SECTION 4 REPLACEMENT PARTS
4.0 Replacement Parts
4.1 General
Always provide the serial number of the unit on which the parts will be used. The serial number is stamped on
the unit nameplate.
4.2 Ordering
To ensure proper operation, it is recommended that only genuine ESAB parts and products be used with this
equipment. The use of non-ESAB parts may void your warranty.
Replacement parts may be ordered from your ESAB Distributor.
Be sure to indicate any special shipping instructions when ordering replacement parts.
Refer to the Communications Guide located on the back page of this manual for a list of customer service phone
numbers.
Note
Bill of material items that have blank part numbers are provided for reference only.
These items should be available through local sources.
Note
Replacement Parts, Schematics and Wiring Diagrams are printed on 279.4mm x
431.8mm (11” x 17”) paper and are included inside the back cover of this manual.
41

SECTION 4 REPLACEMENT PARTS
42

SECTION 4 REPLACEMENT PARTS
43
SECTION 4 REPLACEMENT PARTS
46
107
108
105
44

SECTION 4 REPLACEMENT PARTS
45
see also 11 x 17 fold-out
for BOM part numbers of
this assembly

SECTION 4 REPLACEMENT PARTS
46

SECTION 4 REPLACEMENT PARTS
VOLTAGE
DIVIDER
47

SECTION 4 REPLACEMENT PARTS
TB3
XFMR HIGH VOLTAGE951179
GROMMET RUB 1.51 ID 1.75 GD x .06 W
5
48

SECTION 4 REPLACEMENT PARTS
49

SECTION 4 REPLACEMENT PARTS
PCB2
50

SECTION 4 REPLACEMENT PARTS
51

NOTES
52

NOTES
53

NOTES
54

REVISION HISTORY
1. Original release - 08/2006
2. Revision of 03/2007 - Chgd page 18, line 3 from: purge each aected line for 10 seconds per 25 ft. (7.6
m) of line to: purge each aected line for 60 seconds per WSS 2/28/07.
3. Revision of 07/2007 - Chgd page 25 to show jumper per CN# 0734136.
4. Revision of 11/2008 - Added ESP-150/200 power supply torch connection details.
5. Revision of 08/2009 - Updated Adaptor wiring on Page 25 and Replacement Parts per ECN #093149.
6. Revision of 11/2009 - Added voltage divider board adjustment information per Tor Murray.
7. Revision of 06/2010 - changed pics to black, aded vdr to illustrations.
8. Revision 08/2010 - updated to show box dimensions.
9. Revision 12/2010 - added 0558001952, assy dwg to BOM 11x17 format.
10. Revision 09/2011 - various updates to connection instructions per K. Li.
11. Revision 03/2012 - replacement parts updates per D. Grin.
55

ESAB Welding & Cutting Products, Florence, SC
COMMUNICATION GUIDE - CUSTOMER SERVICES
A. CUSTOMER SERVICE QUESTIONS:
Telephone: (800)362-7080 / Fax: (800) 634-7548 Hours: 8:00 AM to 7:00 PM EST
Order Entry Product Availability Pricing Order Information Returns
B. ENGINEERING SERVICE:
Telephone: (843) 664-4416 / Fax : (800) 446-5693 Hours: 7:30 AM to 5:00 PM EST
Warranty Returns Authorized Repair Stations Welding Equipment Troubleshooting
C. TECHNICAL SERVICE:
Telephone: (800) ESAB-123/ Fax: (843) 664-4452 Hours: 8:00 AM to 5:00 PM EST
Part Numbers Technical Applications Specications Equipment Recommendations
D. LITERATURE REQUESTS:
Telephone: (843) 664-5562 / Fax: (843) 664-5548 Hours: 7:30 AM to 4:00 PM EST
E. WELDING EQUIPMENT REPAIRS:
Telephone: (843) 664-4487 / Fax: (843) 664-5557 Hours: 7:30 AM to 3:30 PM EST
Repair Estimates Repair Status
F. WELDING EQUIPMENT TRAINING
Telephone: (843)664-4428 / Fax: (843) 679-5864 Hours: 7:30 AM to 4:00 PM EST
Training School Information and Registrations
G. WELDING PROCESS ASSISTANCE:
Telephone: (800) ESAB-123 Hours: 7:30 AM to 4:00 PM EST
H. TECHNICAL ASST. CONSUMABLES:
Telephone : (800) 933-7070 Hours: 7:30 AM to 5:00 PM EST
IF YOU DO NOT KNOW WHOM TO CALL
Telephone: (800) ESAB-123
Fax: (843) 664-4462
Hours: 7:30 AM to 5:00 PM EST
or
visit us on the web at http://www.esabna.com
The ESAB web site oers
Comprehensive Product Information
Material Safety Data Sheets
Warranty Registration
Instruction Literature Download Library
Distributor Locator
Global Company Information
Press Releases
Customer Feedback & Support
 Loading...
Loading...