
PT-36/Integrated Gas Control Cutting Data
Cut Data Manual (EN)
0558011611 Version 4.5 released on 13May13

BE SURE THIS INFORMATION REACHES THE OPERATOR.
YOU CAN GET EXTRA COPIES THROUGH YOUR SUPPLIER.
CAUTION
These INSTRUCTIONS are for experienced operators. If you are not fully familiar with the
principles of operation and safe practices for arc welding and cutting equipment, we urge
you to read our booklet, “Precautions and Safe Practices for Arc Welding, Cutting, and
Gouging,” Form 52-529. Do NOT permit untrained persons to install, operate, or maintain
this equipment. Do NOT attempt to install or operate this equipment until you have read
and fully understand these instructions. If you do not fully understand these instructions,
contact your supplier for further information. Be sure to read the Safety Precautions before installing or operating this equipment.
USER RESPONSIBILITY
This equipment will perform in conformity with the description thereof contained in this manual and accompanying labels and/or inserts when installed, operated, maintained and repaired in accordance with the instructions provided. This equipment must be checked periodically. Malfunctioning or poorly maintained equipment
should not be used. Parts that are broken, missing, worn, distorted or contaminated should be replaced immediately. Should such repair or replacement become necessary, the manufacturer recommends that a telephone
or written request for service advice be made to the Authorized Distributor from whom it was purchased.
This equipment or any of its parts should not be altered without the prior written approval of the manufacturer.
The user of this equipment shall have the sole responsibility for any malfunction which results from improper
use, faulty maintenance, damage, improper repair or alteration by anyone other than the manufacturer or a service facility designated by the manufacturer.
READ AND UNDERSTAND THE INSTRUCTION MANUAL BEFORE INSTALLING OR OPERATING.
PROTECT YOURSELF AND OTHERS!
2

TABLE OF CONTENTS
SUBSECTION TITLE ............................................................................PAGE
Safety Precautions..........................................................................................5
Carbon Steel Quality.......................................................................................13
Aluminum Quality .........................................................................................33
Stainless Steel Quality......................................................................................37
Carbon Steel Production ...................................................................................51
Aluminum Production .................................................................................... 69
Stainless Steel Production..................................................................................81
Water Injection Aluminum Production.................................................................... 103
Water Injection Stainless Steel Production .................................................................113
Carbon Steel Air ......................................................................................... 127
Aluminum Air ............................................................................................141
Stainless Steel Air ........................................................................................ 147
3

TABLE OF CONTENTS
4

SECTION 1 SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
Safety Precautions Safety - English
WARNING: These Safety Precautions are for your
protection. They summarize precautionary information from the references
listed in Additional Safety Information
section. Before performing any installation or operating procedures, be sure to read and
follow the safety precautions listed below as well
as all other manuals, material safety data sheets,
labels, etc. Failure to observe Safety Precautions
can result in injury or death.
PROTECT YOURSELF AND OTHERS -Some welding, cutting, and gouging
processes are noisy and require ear
protection. The arc, like the sun, e mits
ultraviolet (UV) and other radiation
and can injure skin and eyes. Hot metal can cause
burns. Training in the proper use of the processes
and equipment is essential to prevent accidents.
Therefore:
1. Always wear safety glasses with side shields in
any work area, even if welding helmets, face
shields, and goggles are also required.
2. Use a face shield tted with the correct lter and
cover plates to protect your eyes, face, neck, and
ears from sparks and rays of the arc when operating or observing operations. Warn bystanders
not to watch the arc and not to expose themselves
to the rays of the electric-arc or hot metal.
3. Wear ameproof gauntlet type gloves, heavy
long-sleeve shirt, cuess trousers, high -topped
shoes, and a welding helmet or cap for hair
protection, to protect against arc rays and hot
sparks or hot metal. A ameproo f apron may also
be desirable as protection against radiated heat
and sparks.
4. Hot spark s or metal can lodge in rolled up sleeves,
trouser cus, or pockets. Sleeves and collars
should be kept buttoned, and open pockets
eliminated from the front of clothing.
5. Protect other personnel from arc rays and hot
sparks with a suitable non-ammable partition
or curtains.
6. Use goggles over safety glasses when chipping
slag or grinding. Chipped slag may be hot and
can y far. Bystanders should also wear goggles
over safety glasses.
1. Remove all combustible materials well away from
the work area or cover the materials with a protective non-ammable covering. Combustible
materials include wood, cloth, sawdust, liquid
and gas fuels, solvents, paints and coatings,
paper, etc.
2. Hot sparks or hot metal can fall through cracks
or crevices in oors or wall openings and cause a
hidden smoldering re or res on the oor below.
Make certain that such openings are protected
from hot sparks and metal.“
3. Do not weld, cut or perform other hot work until
the work piece has been completely cleaned so
that there are no substances on the work piece
which might produce ammable or toxic vapors.
Do not do hot work on closed containers. They
may explode.
4. Have re extinguishing equipment handy for
instant use, such as a garden hose, water pail,
sand bucket, or portable re extinguisher. Be
sure you are trained in its use.
5. Do not use equipment beyond its ratings. For
example, overloaded welding cable can overheat
and create a re hazard.
6. After completing operations, inspect the work
area to make certain there are no hot sparks or
hot metal which could cause a later re. Use re
watchers when necessary.
7. For additional information, refer to NFPA Standard 51B, "Fire Prevention in Use of Cutting and
Welding Processes", available from the National
Fire Protection Association, Batter y march Park,
Quincy, MA 02269.
areas, if movement is conned, or if there is danger
of falling.
FIRES AND EXPLOSIONS -- Heat from
ames and arcs can start res. Hot
slag or sparks can also cause res and
explosions. Therefore:
ELECTRICAL SHOCK -- Contact with
live electrical parts and ground can
cause severe injury or death. DO
NOT use AC welding current in damp
5

SECTION 1 SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
1. Be sure the power source frame (chassis) is connected to the ground system of the input power.
2. Connect the work piece to a good electrical
ground.
3. Connect the work cable to the work piece. A poor
or missing connection can expose you or others
to a fatal shock.
4. Use well-maintained equipment. Replace worn or
damaged cables.
5. Keep everything dry, including clothing, work
area, cables, torch/electrode holder, and power
source.
6. Make sure that all parts of your body are insulated
from work and from ground.
7. Do not stand directly on metal or the earth while
working in tight quarters or a damp area; stand
on dry boards or an insulating platform and wear
rubber-soled shoes.
8. Put on dry, hole-free gloves before turning on the
power.
3. Welders should use the following procedures to
minimize exposure to EMF:
A. Route the electrode and work cables together.
Secure them with tape when possible.
B. Never coil the torch or work cable around your
body.
C. Do not place your body between the torch and
work cables. Route cables on the same side of
your body.
D. Connect the work cable to the work piece as close
as possible to the area being welded.
E. Keep welding power source and cables as far
away from your body as possible.
FUMES AND GASES -- Fumes and
gases, can cause discomfort or harm,
particularly in conned spaces. Do
not breathe fumes and gases. Shielding gases can cause asphyxiation.
Therefore:
9. Turn o the power before removing your gloves.
10. Refer to ANSI/ASC Standard Z49.1 (listed on
next page) for specic grounding recommendations. Do not mistake the work lead for a ground
cable.
ELECTRIC AND MAGNETIC FIELDS
— May be dangerous. Electric current owing through any conductor causes localized Electric and
Magnetic Fields (EMF). Welding and
cutting current creates EMF around welding cables
and welding machines. Therefore:
1. Welders having pacemakers should consult their
physician before welding. EMF may interfere with
some pacemakers.
2. Exposure to EMF may have other health eects which
are unknown.
1. Always provide adequate ventilation in the work area
by natural or mechanical means. Do not weld, cut, or
gouge on materials such as galvanized steel, stainless steel, copper, zinc, lead, beryllium, or cadmium
unless positive mechanical ventilation is provided.
Do not breathe fumes from these materials.
2. Do not operate near degreasing and spraying operations. The heat or arc rays can react with chlorinated
hydrocarbon vapors to form phosgene, a highly
toxic gas, and other irritant gases.
3. If you develop momentary eye, nose, or throat irritation while operating, this is an indication that
ventilation is not adequate. Stop work and take
necessary steps to improve ventilation in the work
area. Do not continue to operate if physical discomfort persists.
4. Refer to ANSI/ASC Standard Z49.1 (see listing below)
for specic ventilation recommendations.
6
SECTION 1 SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
5. WARNING: This product, when used for welding
or cutting, produces fumes or gases
which contain chemicals known to
the State of California to cause birth
defects and, in some cases, cancer.
(California Health & Safety Code
§25249.5 et seq.)
CYLINDER HANDLING -- Cylinders,
if mishandled, can rupture and violently release gas. Sudden rupture
of cylinder, valve, or relief device can
injure or kill. Therefore:
1. Use the proper gas for the process and use the
proper pressure reducing regulator designed to
operate from the compressed gas cylinder. Do not
use adaptors. Maintain hoses and ttings in good
condition. Follow manufacturer's operating instructions for mounting regulator to a compressed gas
cylinder.
1. Always have qualied personnel perform the installation, troubleshooting, and maintenance work.
Do not perform any electrical work unless you are
qualied to perform such work.
2. Before performing any maintenance work inside a
power source, disconnect the power source from
the incoming electrical power.
3. Maintain cables, grounding wire, connections, power
cord, and power supply in safe working order. Do
not operate any equipment in faulty condition.
4. Do not abuse any equipment or accessories. Keep
equipment away from heat sources such as furnaces,
wet conditions such as water puddles, oil or grease,
corrosive atmospheres and inclement weather.
5. Keep all safety devices and cabinet covers in position
and in good repair.
6. Use equipment only for its intended purpose. Do
not modify it in any manner.
2. Always secure cylinders in an upright position by
chain or strap to suitable hand trucks, undercarriages, benches, walls, post, or racks. Never secure
cylinders to work tables or xtures where they may
become part of an electrical circuit.
3. When not in use, keep cylinder valves closed. Have
valve protection cap in place if regulator is not connected. Secure and move cylinders by using suitable
hand trucks. Avoid rough handling of cylinders.
4. Locate cylinders away from heat, sparks, and ames.
Never strike an arc on a cylinder.
5. For additional information, refer to CGA Standard P-1,
"Precautions for Safe Handling of Compressed Gases
in Cylinders", which is available from Compressed
Gas Association, 1235 Jeerson Davis Highway,
Arlington, VA 22202.
EQUIPMENT MAINTENANCE -- Faulty or
improperly maintained equipment can
cause injury or death. Therefore:
ADDITIONAL SAFETY INFORMATION -- For
more information on safe practices for
electric arc welding and cutting equipment, ask your supplier for a copy of
"Precautions and Safe Practices for Arc
Welding, Cutting and Gouging", Form
52-529.
The following publications, which are available from
the American Welding Society, 550 N.W. LeJuene Road,
Miami, FL 33126, are recommended to you:
1. ANSI/ASC Z49.1 - "Safety in Welding and Cutting"
2. AWS C5.1 - "Recommended Practices for Plasma Arc
Welding"
3. AWS C5.2 - "Recommended Practices for Plasma Arc
Cutting"
4. AWS C5.3 - "Recommended Practices for Air Carbon
Arc Gouging and Cutting"
7
SECTION 1 SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
5. AWS C5.5 - "Recommended Practices for Gas Tungsten Arc Welding“
6. AWS C5.6 - "Recommended Practices for Gas Metal
Arc Welding"“
7. AWS SP - "Safe Practices" - Reprint, Welding Handbook.
8. ANSI/AWS F4.1, "Recommended Safe Practices for
Welding and Cutting of Containers That Have Held
Hazardous Substances."
MEANING OF SYMBOLS - As used
throughout this manual: Means Attention! Be Alert! Your safety is involved.
Means immediate hazards which,
if not avoided, will result in immediate, serious personal injury
or loss of life.
Means potential hazards which
could result in personal injury or
loss of life.
Means hazards which could result
in minor personal injury.
8

SECTION 1 SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
Hydrogen explosion hazard! Read the following before attempting
DANGER
A hazard exists whenever a water table is used with plasma arc cutting. Severe explosions have resulted from the accumulation of hydrogen beneath the plate being cut. Thousands of dollars in property damage have been caused by
these explosions. Personal injury or death could result from such an explosion.
The best available information indicates that three possible sources of hydrogen exists in water tables:
1. Molten Metal Reaction
Most of the hydrogen is liberated by a fast reaction of molten metal from the kerf in the water to form metallic ox-
ides. This reaction explains why reactive metals with greater anity for oxygen, such as aluminum and magnesium,
release greater volumes of hydrogen during the cut than does iron or steel. Most of this hydrogen will come to the
surface immediately, but some will cling to small metallic particles. These particles will settle to the bottom of the
water table and the hydrogen will gradually bubble to the surface.
2. Slow Chemical Reaction
Hydrogen may also result from the slower chemical reactions of cold metal particles with the water, dissimilar metals,
or chemicals in the water. The hydrogen gradually bubbles to the surface.
to cut when using a water table.
3. Plasma & Shield Gas
Hydrogen or other fuel gases, such as Methane (CH4), may come from the plasma or shield gas. H-35 is a commonly
used plasma gas. This gas is 35% hydrogen by volume. When using H-35 at high currents, as much as 125 cfh of
hydrogen will be released.
Regardless of the source, the hydrogen gas can collect in pockets formed by the plate being cut and slats on the
table, or pockets from warped plate. There can also be accumulation of hydrogen under the slag tray or even in the
air reservoir, if these are part of the table design. The hydrogen, in the presence of oxygen or air, can then be ignited
by the plasma arc or a spark from any source.
4. Follow these practices to reduce hydrogen generation and accumulation:
A. Clean the slag (especially ne particles) from the bottom of the table frequently. Rell the table with clean water.
B. Do not leave plates on the table overnight or a weekend.
C. If a water table has been unused for several hours, vibrate it in some way before the rst plate is laid in position.
This will allow accumulated hydrogen in the refuse to break loose and dissipate before it is conned by a plate
on the table. This might be accomplished by laying the rst plate onto the table with a slight jolt, then raising
the plate to permit hydrogen to escape before it is nally set down for cutting.
D. If cutting above water, install fans to circulate air between the plate and the water surface.
E. If cutting underwater, agitate the water under the plate to prevent accumulation of hydrogen. This can be done
by aerating the water using compressed air.
F. If possible, change the level of the water between cuts to dissipate accumulated hydrogen.
G. Maintain pH level of the water near 7 (neutral). This reduces the rate of chemical reaction between water and
metals.
9

SECTION 1 SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
Possible explosion hazard from plasma cutting aluminum-lithium alloys!
Aluminum-Lithium (Al-Li) alloys are used in the aerospace industry because of 10% weight
savings over conventional aluminum alloys. It has been reported that molten Al-Li alloys
can cause explosions when they come into contact with water. Therefore, plasma cutting
of these alloys should not be attempted in the presence of water. These alloys should only
be dry cut on a dry table. Alcoa has determined that "dry" cutting on a dry table is safe
and gives good cutting results. DO NOT dry cut over water. DO NOT water injection cut.
WARNING
The following are some of the Al-Li alloys currently available:
Alithlite (Alcoa) X8192 (Alcoa)
Alithally (Alcoa) Navalite (U. S. Navy)
2090 Alloy (Alcoa) Lockalite (Lockhead)
X8090A (Alcoa) Kalite (Kaiser)
X8092 (Alcoa) 8091 (Alcan)
For additional details and information on the safe use from the hazards associated with
these alloys, contact your aluminum supplier.
WARNING
WARNING
WARNING
Oil And Grease Can Burn Violently!
• Never use oil or grease on this torch.
• Handle torch clean hands only on clean surface.
• Use silicone lubricant only where directed.
• Oil and grease are easily ignited and burn violently in the presence of
oxygen under pressure.
Hydrogen explosion hazard.
Do Not Cut Underwater With H-35! Dangerous buildup of hydrogen gas is possible in
the water table. Hydrogen gas is extremely explosive. Reduce the water level to 4 inches minimum below the workpiece. Vibrate plate, stir air and water frequently to prevent
hydrogen gas buildup.
Spark hazard.
Heat, spatter, and sparks cause re and burns.
• Do not cut near combustible material.
• Do not cut containers that have held combustibles.
• Do not have on your person any combustibles (e.g. butane lighter).
• Pilot arc can cause burns. Keep torch nozzle away from yourself and
others when activating plasma process.
• Wear correct eye and body protection.
• Wear gauntlet gloves, safety shoes and hat.
• Wear ame-retardant clothing that covers all exposed areas.
• Wear cuess trousers to prevent entry of sparks and slag.
10

SECTION 1 SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
Maximum Gas Flow Rates With PT-36 Torch
Gas &
Pressure
Air (85psi / 5.9bar)
Process
Air (85psi / 5.9bar)
Air Curtain
Argon
(125psi / 8.6bar)
CH-4
(75psi / 5.2bar)
H-35 / F5
(75psi / 5.2bar)
Nitrogen
(125psi / 8.6bar)
Oxygen
(125psi / 8.6bar)
Maximum Gas Flow Rates - CFH (CMH)
With PT-36 Torch
EPP-201 EPP-360 EPP-450 EPP-601
269
(7. 6)
1200
(34)
100
(2.8)
85
(2.4)
95
(2.7)
385
(10.9)
66
(1.9)
Note: No marking with the 600 ampere nozzle.
269
(7. 6)
1200
(34)
100
(2.8)
85
(2.4)
202
(5.7)
496
(14.0)
190
(5.4)
474
(13.4)
1200
(34)
100
(2.8)
85
(2.4)
202
(5.7)
496
(14.0)
295
(8.4)
474
(13.4)
1200
(34)
100
(2.8)
85
(2.4)
254
(7. 2)
496
(14.0)
295
(8.4)
Gas Purity
Clean, Dry, Oil Free
Filtered to 25 microns
Filtered to 25 microns
DIN Quality ISO 8573-1
Oil Quality mg/m3 = 0.1 Class 2
Particle Size 0.1µm Class 1
Temperature +3°C Class 4
99.995%, Filtered to 25 microns
93%, Filtered to 25 microns
99.995%, Filtered to 25 microns
99.99%, Filtered to 25 microns
99.5%, Filtered to 25 microns
11

12

Carbon Steel
Quality
13

14
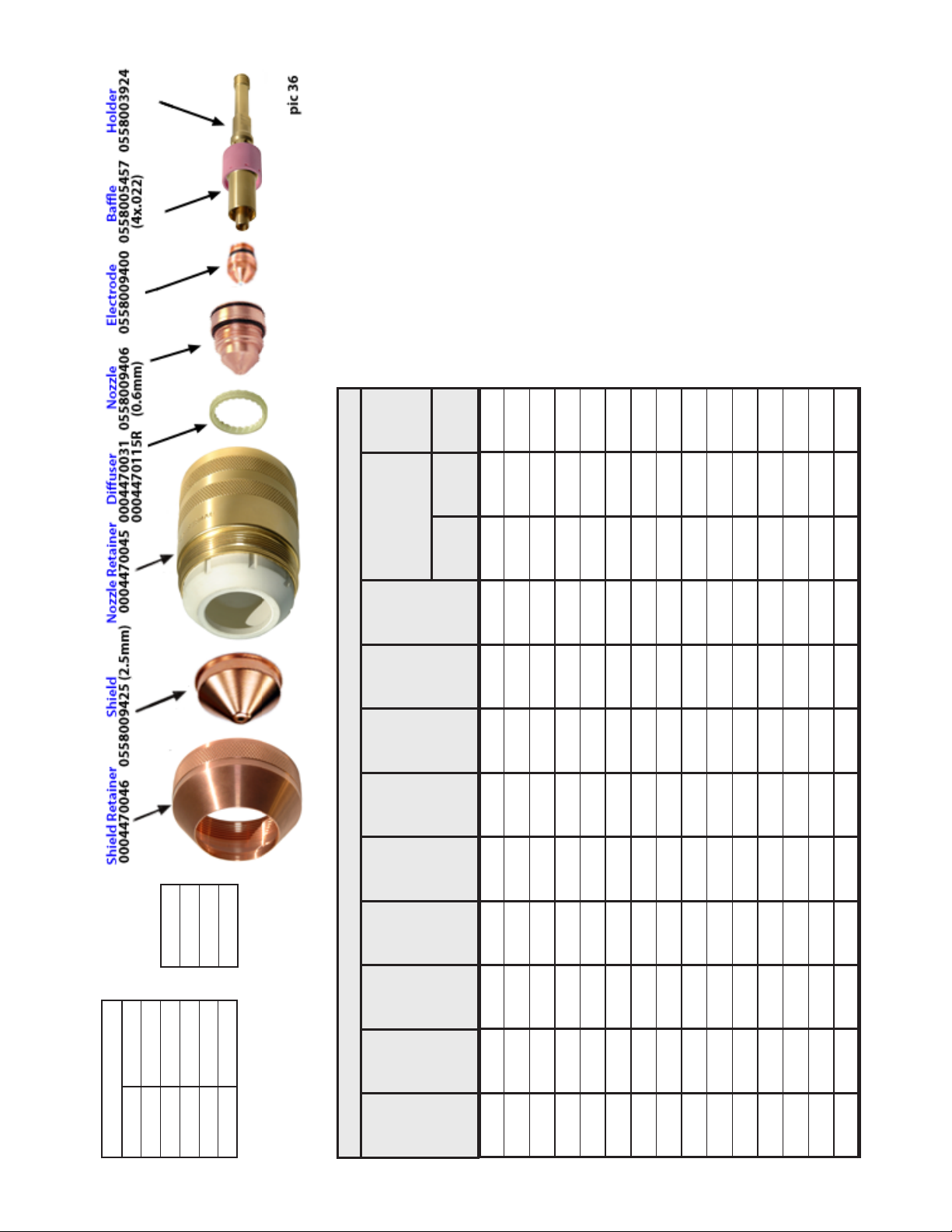
Gas
Shield
CFH
Start/Cut
psi
Cut
109
NCode
Plasma Gas
AHC
Pierce
ting
Cut-
Delay
Delay
psi
Start
sec
sec
in
Height
in
Pierce
Height
in
Initial
Height
N2
ARG
ARG
MARKING
or
Arc
age
Volt-
in
Kerf
MARKING
Amperes 30
Cut Gas ARG
Start Gas ARG
Shield Gas AIR
Material Carbon Steel
Gas Select 6
ESAB Welding and Cutting Products
in/m
Speed
in
ness
First Row Mark Amp: 12
Thick-
15
1.000 100 0.000 70 0.100 0.100 0.100 0.0 0.0 75 75 71
Version 4.5 released on 13May13
12 amp 12 amp 0.10 sec 0.10 sec 0.35 sec
StartCur EndCur CurUpTime CurDnTime GOffDelay
36
PicNo

Gas
Shield
CFH
Start/Cut
psi
Cut
109
NCode
Plasma Gas
AHC
Pierce
ting
Cut-
Delay
Delay
psi
Start
sec
sec
in
Height
in
Pierce
Height
in
Initial
Height
O2
AIR
AIR
PRODUCTION
or
Arc
age
Volt-
in
Kerf
QUALITY
Amperes 30
Start Gas N2
Cut Gas O2
Shield Gas N2
Material Carbon Steel
Gas Select 1
ESAB Welding and Cutting Products
Thick-
Speed
ness
in/m
in
16
0.040 150 0.065 11 0 0.130 0.130 0.080 0.4 0.3 70 65 18
0.080 55 0.065 110 0.130 0.130 0.080 0.5 0.5 70 65 18
0.125 45 0.065 112 0.150 0.150 0.120 0.5 0.3 70 65 35
30 amp 15 amp 0.10 sec 0.10 sec 0.10 sec
StartCur EndCur CurUpTime CurDnTime GOffDelay
36
PicNo
Version 4.5 released on 13May13

Gas
Shield
CFH
Start/Cut
psi
Cut
101
NCode
Plasma Gas
AHC
Pierce
ting
Cut-
Delay
Delay
psi
Start
sec
sec
in
Height
in
Pierce
Height
in
Initial
Height
N2
ARG
ARG
MARKING
or
Arc
age
Volt-
in
Kerf
MARKING
Material Carbon Steel
Gas Select 6
Cut Gas ARG
Start Gas ARG
Amperes 45
Shield Gas AIR
ESAB Welding and Cutting Products
in/m
Speed
in
ness
First Row Mark Amp: 14
Thick-
17
1.000 100 0.000 85 0.160 0.160 0.160 0.0 0.1 75 75 71
Version 4.5 released on 13May13
14 amp 14 amp 0.10 sec 0.10 sec 0.35 sec
StartCur EndCur CurUpTime CurDnTime GOffDelay
17
PicNo

Gas
Shield
CFH
Start/Cut
psi
Cut
101
NCode
Plasma Gas
AHC
Pierce
ting
Cut-
Delay
Delay
psi
Start
sec
sec
in
Height
in
Pierce
Height
in
Initial
Height
O2
AIR
AIR
PRODUCTION
or
Arc
age
Volt-
in
Kerf
QUALITY
Material Carbon Steel
Gas Select 1
Cut Gas O2
Start Gas N2
Amperes 45
Shield Gas N2
ESAB Welding and Cutting Products
Thick-
Speed
ness
in/m
in
18
50 amp 50 amp 0.60 sec 0.60 sec 0.35 sec
StartCur EndCur CurUpTime CurDnTime GOffDelay
0.125 55 0.110 140 0.160 0.200 0.200 0.3 0.3 50 65 0
0.080 75 0.080 132 0.160 0.200 0.180 0.3 0.3 50 58 0
0.040 150 0.090 123 0.160 0.160 0.120 0.2 0.1 50 65 0
17
PicNo
Version 4.5 released on 13May13

Gas
Shield
CFH
Start/Cut
psi
Cut
102
NCode
Plasma Gas
AHC
Pierce
ting
Cut-
Delay
Delay
psi
Start
sec
sec
in
Height
in
Pierce
Height
in
Initial
Height
N2
ARG
ARG
MARKING
or
Arc
age
Volt-
in
Kerf
MARKING
Material Carbon Steel
Gas Select 6
Cut Gas ARG
Start Gas ARG
Amperes 55
Shield Gas AIR
ESAB Welding and Cutting Products
in/m
Speed
in
ness
First Row Mark Amp: 14
Thick-
19
1.000 100 0.000 85 0.160 0.160 0.160 0.0 0.1 75 75 71
Version 4.5 released on 13May13
14 amp 14 amp 0.10 sec 0.10 sec 0.35 sec
StartCur EndCur CurUpTime CurDnTime GOffDelay
17
PicNo

Gas
Shield
CFH
Start/Cut
psi
Cut
102
NCode
Plasma Gas
AHC
Pierce
ting
Cut-
Delay
Delay
psi
Start
sec
sec
in
Height
in
Pierce
Height
in
Initial
Height
O2
AIR
AIR
PRODUCTION
or
Arc
age
Volt-
in
Kerf
QUALITY
Material Carbon Steel
Gas Select 1
Cut Gas O2
Start Gas N2
Amperes 55
Shield Gas N2
ESAB Welding and Cutting Products
Thick-
Speed
ness
in/m
in
20
50 amp 50 amp 0.60 sec 0.60 sec 0.35 sec
StartCur EndCur CurUpTime CurDnTime GOffDelay
0.250 40 0.120 137 0.160 0.200 0.200 0.3 0.1 50 60 0
0.200 55 0.100 132 0.160 0.200 0.200 0.3 0.1 50 60 0
0.160 85 0.100 127 0.160 0.200 0.200 0.3 0.3 50 60 0
17
PicNo
Version 4.5 released on 13May13

Gas
Shield
CFH
Start/Cut
psi
Cut
110
NCode
Plasma Gas
AHC
Pierce
ting
Cut-
Delay
Delay
psi
Start
sec
sec
in
Height
in
Pierce
Height
in
Initial
Height
N2
ARG
ARG
MARKING
or
Arc
age
Volt-
in
Kerf
MARKING
Amperes 60
Cut Gas ARG
Start Gas ARG
Shield Gas AIR
Material Carbon Steel
Gas Select 6
ESAB Welding and Cutting Products
in/m
Speed
in
ness
First Row Mark Amp: 12
Thick-
21
1.000 100 0.000 75 0.160 0.100 0.100 0.0 0.0 75 75 71
Version 4.5 released on 13May13
12 amp 12 amp 0.10 sec 0.10 sec 0.35 sec
StartCur EndCur CurUpTime CurDnTime GOffDelay
37
PicNo

Gas
Shield
CFH
Start/Cut
psi
Cut
110
NCode
Plasma Gas
AHC
Pierce
ting
Cut-
Delay
Delay
psi
Start
sec
sec
in
Height
in
Pierce
Height
in
Initial
Height
O2
AIR
AIR
PRODUCTION
or
Arc
age
Volt-
in
Kerf
QUALITY
Amperes 60
Start Gas N2
Cut Gas O2
Shield Gas N2
Material Carbon Steel
Gas Select 1
ESAB Welding and Cutting Products
Thick-
Speed
ness
in/m
in
22
0.125 150 0.060 105 0.160 0.120 0.120 0.6 0.3 60 65 70
0.160 120 0.060 105 0.160 0.160 0.110 0.6 0.3 60 65 70
0.200 80 0.060 105 0.160 0.160 0.110 0.6 0.3 60 65 70
0.250 75 0.065 108 0.160 0.160 0.140 1.0 0.1 60 65 70
45 amp 13 amp 0.30 sec 0.10 sec 0.10 sec
StartCur EndCur CurUpTime CurDnTime GOffDelay
37
PicNo
Version 4.5 released on 13May13

Gas
Shield
CFH
Start/Cut
psi
Cut
103
NCode
Plasma Gas
AHC
Pierce
ting
Cut-
Delay
Delay
psi
Start
sec
sec
in
Height
in
Pierce
Height
in
Initial
Height
N2
ARG
ARG
MARKING
or
Arc
age
Volt-
in
Kerf
MARKING
Material Carbon Steel
Gas Select 6
Cut Gas ARG
Start Gas ARG
Amperes 10 0
Shield Gas AIR
ESAB Welding and Cutting Products
in/m
Speed
in
ness
First Row Mark Amp: 12
Thick-
23
1.000 100 0.000 90 0.160 0.160 0.160 0.0 0.1 52 52 71
Version 4.5 released on 13May13
12 amp 12 amp 0.10 sec 0.10 sec 0.35 sec
StartCur EndCur CurUpTime CurDnTime GOffDelay
2
PicNo

CFH
Delay
Delay
Delay
Delay
Height
Height
Height
Height
CFH
Start/Cut
Start/Cut
psi
psi
Cut
Cut
psi
psi
Start
Start
sec
sec
sec
sec
in
in
Height
Height
in
in
in
in
Gas
Gas
Shield
Shield
Plasma Gas
Plasma Gas
AHC
AHC
Pierce
Pierce
ting
ting
Cut-
Cut-
Pierce
Pierce
Initial
Initial
103
NCode
O2
AIR
AIR
PRODUCTION
or
QUALITY
Material Carbon Steel
Gas Select 1
ESAB Welding and Cutting Products
Cut Gas O2
Start Gas N2
Amperes 10 0
Shield Gas N2
Arc
Arc
Thick-
Thick-
Volt-
Volt-
Kerf
Kerf
Speed
Speed
ness
ness
in
in
in/m
in/m
age
age
in
in
24
0.250 85 0.080 142 0.160 0.220 0.125 0.1 0.2 25 60 100
0.375 65 0.080 149 0.160 0.250 0.180 0.2 0.2 25 60 100
0.500 60 0.090 156 0.160 0.250 0.240 0.4 0.2 25 60 100
50 amp 50 amp 0.60 sec 0.60 sec 0.35 sec
StartCur EndCur CurUpTime CurDnTime GOffDelay
2
PicNo
Version 4.5 released on 13May13

CFH
Delay
Delay
Delay
Delay
Height
Height
Height
Height
CFH
Start/Cut
Start/Cut
psi
psi
Cut
Cut
psi
psi
Start
Start
sec
sec
sec
sec
in
in
Height
Height
in
in
in
in
Gas
Gas
Shield
Shield
Plasma Gas
Plasma Gas
AHC
AHC
Pierce
Pierce
ting
ting
Cut-
Cut-
Pierce
Pierce
Initial
Initial
104
NCode
N2
ARG
ARG
MARKING
or
MARKING
Material Carbon Steel
Gas Select 6
ESAB Welding and Cutting Products
Cut Gas ARG
Start Gas ARG
Amperes 130
Shield Gas AIR
Arc
Arc
age
age
Volt-
Volt-
in
in
Kerf
Kerf
in/m
in/m
Speed
Speed
in
in
ness
ness
Thick-
First Row Mark Amp: 12
Thick-
25
1.000 100 0.000 80 0.160 0.160 0.160 0.0 0.1 45 45 71
Version 4.5 released on 13May13
12 amp 12 amp 0.10 sec 0.10 sec 0.35 sec
StartCur EndCur CurUpTime CurDnTime GOffDelay
29
PicNo
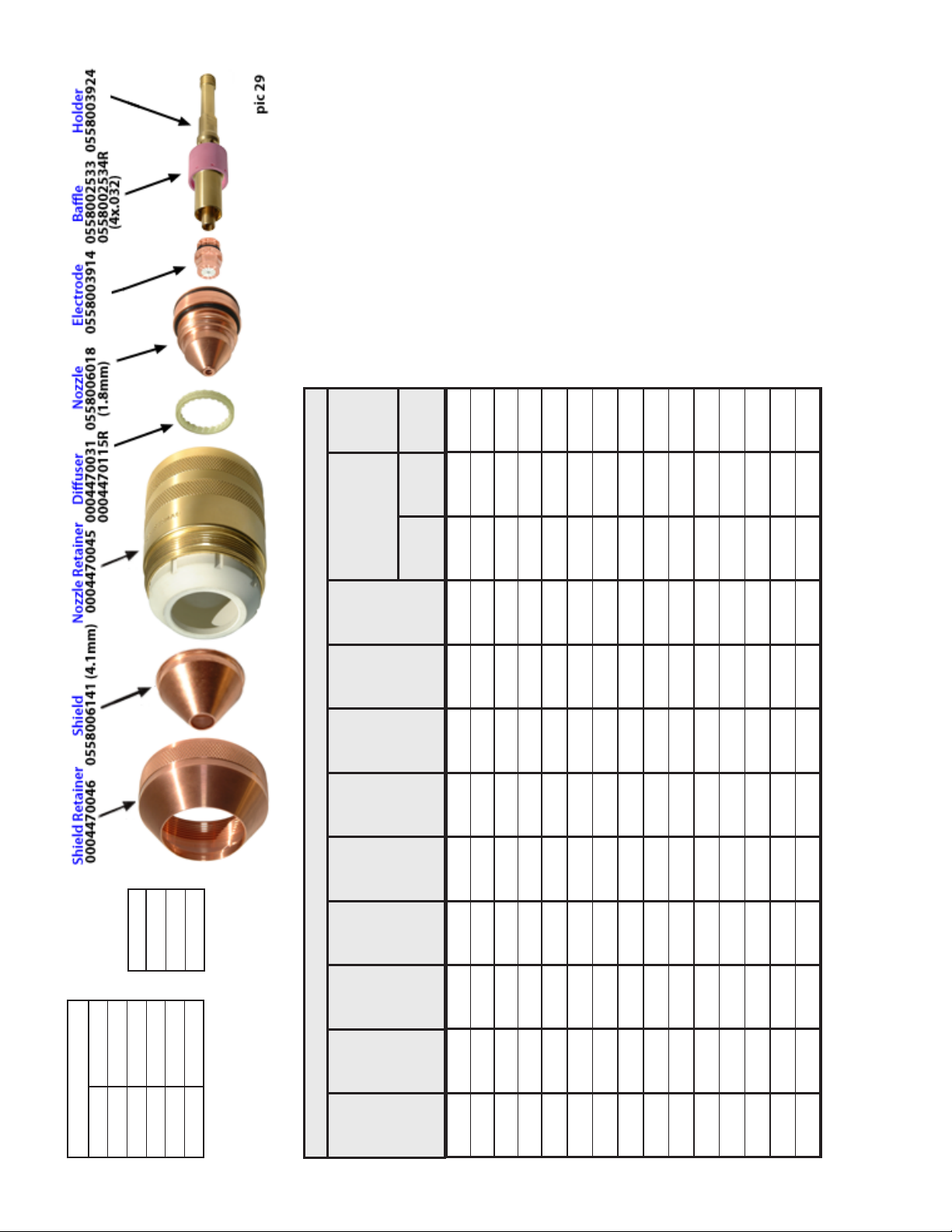
CFH
Delay
Delay
Delay
Delay
Height
Height
Height
Height
CFH
Start/Cut
Start/Cut
psi
psi
Cut
Cut
psi
psi
Start
Start
sec
sec
sec
sec
in
in
Height
Height
in
in
in
in
Gas
Gas
Shield
Shield
Plasma Gas
Plasma Gas
AHC
AHC
Pierce
Pierce
ting
ting
Cut-
Cut-
Pierce
Pierce
Initial
Initial
104
NCode
O2
AIR
AIR
PRODUCTION
or
QUALITY
Material Carbon Steel
Gas Select 1
ESAB Welding and Cutting Products
Cut Gas O2
Start Gas N2
Amperes 130
Shield Gas N2
Arc
Arc
Thick-
Thick-
Volt-
Volt-
Kerf
Kerf
Speed
Speed
ness
ness
in
in
in/m
in/m
age
age
in
in
26
0.250 100 0.095 125 0.160 0.250 0.100 0.5 0.2 25 50 120
0.375 85 0.095 133 0.160 0.250 0.130 0.5 0.2 25 50 120
0.500 75 0.095 142 0.160 0.250 0.200 0.5 0.2 25 50 160
0.625 53 0.100 152 0.160 0.500 0.275 0.5 0.2 25 50 160
60 amp 60 amp 0.60 sec 0.60 sec 0.35 sec
StartCur EndCur CurUpTime CurDnTime GOffDelay
29
PicNo
Version 4.5 released on 13May13

CFH
Delay
Delay
Delay
Delay
Height
Height
Height
Height
CFH
Start/Cut
Start/Cut
psi
psi
Cut
Cut
psi
psi
Start
Start
sec
sec
sec
sec
in
in
Height
Height
in
in
in
in
Gas
Gas
Shield
Shield
Plasma Gas
Plasma Gas
AHC
AHC
Pierce
Pierce
ting
ting
Cut-
Cut-
Pierce
Pierce
Initial
Initial
105
NCode
N2
ARG
ARG
MARKING
or
MARKING
Material Carbon Steel
Gas Select 6
ESAB Welding and Cutting Products
Cut Gas ARG
Start Gas ARG
Amperes 200
Shield Gas AIR
Arc
Arc
age
age
Volt-
Volt-
in
in
Kerf
Kerf
in/m
in/m
Speed
Speed
in
in
ness
ness
Thick-
First Row Mark Amp: 14
Thick-
27
1.000 100 0.000 70 0.160 0.160 0.160 0.0 0.1 40 40 71
Version 4.5 released on 13May13
12 amp 14 amp 0.10 sec 0.10 sec 0.35 sec
StartCur EndCur CurUpTime CurDnTime GOffDelay
3
PicNo
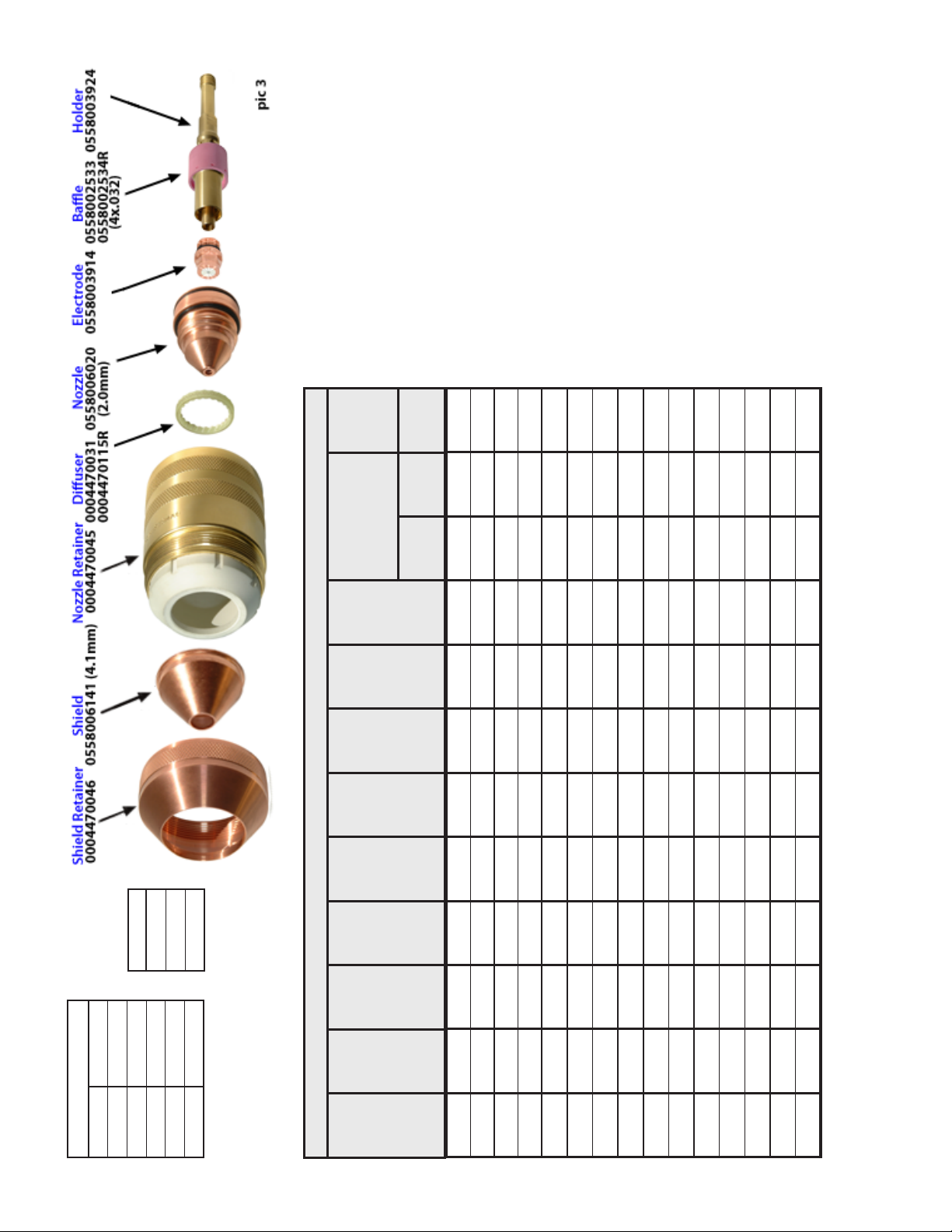
Gas
Shield
CFH
Start/Cut
psi
Cut
105
NCode
Plasma Gas
AHC
Pierce
ting
Cut-
Delay
Delay
psi
Start
sec
sec
in
Height
in
Pierce
Height
in
Initial
Height
O2
AIR
AIR
PRODUCTION
or
Arc
age
Volt-
in
Kerf
QUALITY
Material Carbon Steel
Gas Select 1
Cut Gas O2
Start Gas N2
Amperes 200
Shield Gas N2
ESAB Welding and Cutting Products
Thick-
Speed
ness
in/m
in
28
StartCur EndCur CurUpTime CurDnTime GOffDelay
100 amp 100 amp 0.60 sec 0.60 sec 0.35 sec
3
0.625 75 0.120 136 0.160 0.170 0.160 0.4 0.3 18 47 110
PicNo
1.250 30 0.150 155 0.160 0.260 0.260 1.0 0.5 18 47 110
1.000 45 0.120 148 0.160 0.360 0.240 1.0 0.4 18 47 110
0.750 65 0.120 140 0.160 0.180 0.180 0.5 0.4 18 47 110
Version 4.5 released on 13May13

Gas
Shield
CFH
Start/Cut
psi
Cut
106
NCode
Plasma Gas
AHC
Pierce
ting
Cut-
Delay
Delay
psi
Start
sec
sec
in
Height
in
Pierce
Height
in
Initial
Height
N2
ARG
ARG
MARKING
or
Arc
age
Volt-
in
Kerf
MARKING
Material Carbon Steel
Gas Select 6
Cut Gas ARG
Start Gas ARG
Amperes 280
Shield Gas AIR
ESAB Welding and Cutting Products
in/m
Speed
in
ness
First Row Mark Amp: 12
Thick-
29
1.000 100 0.000 70 0.160 0.160 0.160 0.0 0.1 30 30 71
Version 4.5 released on 13May13
12 amp 12 amp 0.10 sec 0.10 sec 0.35 sec
StartCur EndCur CurUpTime CurDnTime GOffDelay
4
PicNo

Gas
Shield
CFH
Start/Cut
psi
Cut
106
NCode
Plasma Gas
AHC
Pierce
ting
Cut-
Delay
Delay
psi
Start
sec
sec
in
Height
in
Pierce
Height
in
Initial
Height
O2
AIR
AIR
PRODUCTION
or
Arc
age
Volt-
in
Kerf
QUALITY
Material Carbon Steel
Gas Select 1
Cut Gas O2
Start Gas N2
Amperes 280
Shield Gas N2
ESAB Welding and Cutting Products
Thick-
Speed
ness
in/m
in
30
0.625 90 0.110 140 0.160 0.700 0.200 0.7 0.2 25 52 165
0.750 85 0.115 150 0.160 0.500 0.310 0.7 0.2 25 52 165
1.000 60 0.135 160 0.160 0.700 0.470 1.0 0.2 25 52 165
1.250 48 0.120 165 0.160 0.750 0.500 1.5 0.2 25 52 165
1.375 35 0.140 175 0.160 0.850 0.563 1.9 0.2 25 52 165
StartCur EndCur CurUpTime CurDnTime GOffDelay
150 amp 150 amp 0.60 sec 0.60 sec 0.35 sec
4
PicNo
Version 4.5 released on 13May13

Gas
Shield
CFH
Start/Cut
psi
Cut
107
NCode
Plasma Gas
AHC
Pierce
ting
Cut-
Delay
Delay
psi
Start
sec
sec
in
Height
in
Pierce
Height
in
Initial
Height
N2
ARG
ARG
MARKING
or
Arc
age
Volt-
in
Kerf
MARKING
Material Carbon Steel
Gas Select 6
Cut Gas ARG
Start Gas ARG
Amperes 360
Shield Gas AIR
ESAB Welding and Cutting Products
in/m
Speed
in
ness
First Row Mark Amp: 18
Thick-
31
1.000 100 0.000 62 0.160 0.160 0.160 0.0 0.1 30 30 71
Version 4.5 released on 13May13
18 amp 18 amp 0.10 sec 0.10 sec 0.35 sec
StartCur EndCur CurUpTime CurDnTime GOffDelay
31
PicNo

Gas
Shield
CFH
Start/Cut
psi
Cut
107
NCode
Plasma Gas
AHC
Pierce
ting
Cut-
Delay
Delay
psi
Start
sec
sec
in
Height
in
Pierce
Height
in
Initial
Height
O2
AIR
AIR
PRODUCTION
or
Arc
age
Volt-
in
Kerf
QUALITY
Material Carbon Steel
Gas Select 1
Cut Gas O2
Start Gas N2
Amperes 360
Shield Gas N2
ESAB Welding and Cutting Products
Thick-
Speed
ness
in/m
in
32
0.750 100 0.150 143 0.160 0.500 0.250 1.3 0.5 18 44 200
1.000 80 0.160 145 0.160 0.750 0.280 1.7 0.5 18 44 250
1.250 50 0.180 157 0.160 0.750 0.410 2.0 0.5 18 44 250
1.375 42 0.195 158 0.160 0.800 0.430 2.0 0.5 18 44 250
1.500 35 0.215 160 0.160 1.000 0.460 2.0 0.5 18 44 250
StartCur EndCur CurUpTime CurDnTime GOffDelay
150 amp 150 amp 0.60 sec 0.60 sec 0.35 sec
31
PicNo
Version 4.5 released on 13May13

Aluminum
Quality
33

34

Gas
Shield
CFH
Start/Cut
psi
Cut
166
NCode
Plasma Gas
AHC
Pierce
ting
Cut-
Delay
Delay
psi
Start
sec
sec
in
Height
in
Pierce
Height
in
Initial
Height
Arc
age
Volt-
in
Kerf
QUALIT Y
Material Aluminium
Gas Select 5
ESAB Welding and Cutting Products
Cut Gas H35
Start Gas N2
Amperes 360
Shield Gas N2
NOTE: Piercing not recommended on thicknesses greater than 1.5”
Pierce delay indicated for edge starts greater than 1.5”
Thick-
Speed
ness
in/m
in
35
0.625 100 0.190 177 0.160 0.700 0.540 0.2 0.2 5 55 300
0.750 90 0.175 180 0.160 0.700 0.390 0.2 0.2 5 55 300
1.000 60 0.190 190 0.160 0.700 0.410 0.2 0.2 5 55 300
1.250 45 0.210 205 0.160 1.000 0.560 0.3 0.2 5 55 300
1.500 33 0.270 215 0.160 1.250 0.700 0.4 0.3 5 55 300
1.750 25 0.280 220 0.167 1.250 0.680 0.5 0.2 5 55 300
Version 4.5 released on 13May13
StartCur EndCur CurUpTime CurDnTime GOffDelay
150 amp 150 amp 0.60 sec 0.60 sec 0.35 sec
28
PicNo

Gas
Shield
CFH
Start/Cut
psi
Cut
167
NCode
Plasma Gas
AHC
Pierce
ting
Cut-
Delay
Delay
psi
Start
sec
sec
in
Height
in
Pierce
Height
in
Initial
Height
Arc
age
Volt-
in
Kerf
QUALIT Y
Material Aluminium
Gas Select 5
ESAB Welding and Cutting Products
Cut Gas H35
Start Gas N2
Amperes 450
Shield Gas N2
NOTE: Piercing not recommended on thicknesses greater than 1.5”
Pierce delay indicated for edge starts greater than 1.5”
Thick-
Speed
ness
in/m
in
36
0.750 110 0.200 155 0.160 0.500 0.450 1.0 0.5 5 40 200
1.000 80 0.220 165 0.160 0.550 0.550 1.2 0.5 5 40 200
1.250 70 0.220 175 0.160 0.700 0.690 1.2 0.5 5 40 200
1.500 55 0.240 180 0.160 0.720 0.720 1.5 0.5 5 40 200
1.750 45 0.260 185 0.160 0.740 0.740 2.0 0.5 5 40 200
3.000 15 0.400 215 0.160 0.820 0.820 3.0 2.5 5 40 200
2.500 24 0.307 202 0.160 0.790 0.790 2.5 0.5 5 40 200
2.250 30 0.296 196 0.160 0.760 0.760 2.2 0.5 5 40 200
2.000 33 0.285 190 0.160 0.740 0.740 2.0 0.5 5 40 200
Version 4.5 released on 13May13
StartCur EndCur CurUpTime CurDnTime GOffDelay
200 amp 200 amp 0.60 sec 0.60 sec 0.35 sec
45
PicNo

Stainless Steel
Quality
37

38

Gas
Shield
CFH
Start/Cut
psi
Cut
136
NCode
Plasma Gas
AHC
Pierce
ting
Cut-
Delay
Delay
psi
Start
sec
sec
in
Height
in
Pierce
Height
in
Initial
Height
N2
ARG
ARG
MARKING
or
Arc
age
Volt-
in
Kerf
MARKING
Amperes 60
Cut Gas ARG
Start Gas ARG
Shield Gas AIR
Material Stainless Steel
Gas Select 6
ESAB Welding and Cutting Products
in/m
Speed
in
ness
First Row Mark Amp: 12
Thick-
39
1.000 100 0.000 75 0.160 0.100 0.100 0.0 0.0 75 75 71
Version 4.5 released on 13May13
12 amp 12 amp 0.10 sec 0.10 sec 0.35 sec
StartCur EndCur CurUpTime CurDnTime GOffDelay
50
PicNo

Gas
Shield
CFH
Start/Cut
psi
Cut
136
NCode
Plasma Gas
AHC
Pierce
ting
Cut-
Delay
Delay
psi
Start
sec
sec
in
Height
in
Pierce
Height
in
Initial
Height
Arc
age
Volt-
in
Kerf
QUALIT Y
Amperes 60
Start Gas N2
Cut Gas F5
Shield Gas N2
Material Stainless Steel
Gas Select 18
ESAB Welding and Cutting Products
Thick-
Speed
ness
in/m
in
40
0.080 210 0.045 145 0.160 0.160 0.135 0.5 0.1 70 75 106
0.100 165 0.045 145 0.160 0.160 0.135 0.5 0.1 70 75 106
0.125 140 0.045 145 0.160 0.160 0.135 0.5 0.1 70 75 143
0.188 55 0.045 148 0.160 0.160 0.135 0.5 0.1 70 75 90
0.250 45 0.045 150 0.160 0.160 0.140 0.5 0.1 70 75 71
45 amp 13 amp 0.30 sec 0.10 sec 0.10 sec
StartCur EndCur CurUpTime CurDnTime GOffDelay
50
PicNo
Version 4.5 released on 13May13

Gas
Shield
CFH
Start/Cut
psi
Cut
137
NCode
Plasma Gas
AHC
Pierce
ting
Cut-
Delay
Delay
psi
Start
sec
sec
in
Height
in
Pierce
Height
in
Initial
Height
N2
ARG
ARG
MARKING
or
Arc
age
Volt-
in
Kerf
MARKING
Material Stainless Steel
Gas Select 6
Cut Gas ARG
Start Gas ARG
Amperes 10 0
Shield Gas AIR
ESAB Welding and Cutting Products
in/m
Speed
in
ness
First Row Mark Amp: 12
Thick-
41
1.000 100 0.000 90 0.160 0.160 0.160 0.0 0.1 52 52 71
Version 4.5 released on 13May13
12 amp 12 amp 0.10 sec 0.10 sec 0.35 sec
StartCur EndCur CurUpTime CurDnTime GOffDelay
8
PicNo

NOTE: Thickness: 0.125” and 0.188” use N2 for cut gas.
Delay
Delay
CFH
Start/Cut
psi
Cut
psi
Start
sec
sec
in
Height
Gas
Shield
Plasma Gas
AHC
Pierce
ting
Cut-
137
NCode
in
Pierce
Height
in
Initial
Height
QUALIT Y
Material Stainless Steel
Gas Select 18
ESAB Welding and Cutting Products
Cut Gas F5
Start Gas N2
Amperes 10 0
Shield Gas N2
Arc
Thick-
Volt-
Kerf
Speed
ness
in
in/m
age
in
42
0.125 165 0.054 145 0.160 0.400 0.143 0.4 0.4 15 55 200
0.188 85 0.071 156 0.160 0.400 0.144 0.4 0.4 15 55 200
0.250 65 0.082 155 0.160 0.400 0.115 0.4 0.4 15 55 200
0.375 45 0.100 155 0.160 0.400 0.129 0.6 0.4 15 45 200
60 amp 60 amp 0.60 sec 0.60 sec 0.35 sec
StartCur EndCur CurUpTime CurDnTime GOffDelay
8
PicNo
Version 4.5 released on 13May13

Gas
Shield
CFH
Start/Cut
psi
Cut
131
NCode
Plasma Gas
AHC
Pierce
ting
Cut-
Delay
Delay
psi
Start
sec
sec
in
Height
in
Pierce
Height
in
Initial
Height
N2
ARG
ARG
MARKING
or
Arc
age
Volt-
in
Kerf
MARKING
Material Stainless Steel
Gas Select 6
Cut Gas ARG
Start Gas ARG
Amperes 130
Shield Gas AIR
ESAB Welding and Cutting Products
in/m
Speed
in
ness
First Row Mark Amp: 12
Thick-
43
1.000 100 0.000 80 0.160 0.062 0.062 0.0 0.1 45 45 141
Version 4.5 released on 13May13
12 amp 12 amp 0.10 sec 0.10 sec 0.35 sec
StartCur EndCur CurUpTime CurDnTime GOffDelay
9
PicNo

Gas
Shield
CFH
Start/Cut
psi
Cut
131
NCode
Plasma Gas
AHC
Pierce
ting
Cut-
Delay
Delay
psi
Start
sec
sec
in
Height
in
Pierce
Height
in
Initial
Height
Arc
age
Volt-
in
Kerf
QUALIT Y
Material Stainless Steel
Gas Select 5
ESAB Welding and Cutting Products
Cut Gas H35
Start Gas N2
Amperes 130
Shield Gas N2
Thick-
Speed
ness
in/m
in
44
0.375 40 0.135 158 0.160 0.400 0.300 0.6 0.4 15 45 200
0.500 35 0.140 163 0.160 0.400 0.310 0.6 0.4 15 45 200
0.750 20 0.160 183 0.160 0.500 0.460 0.8 0.4 15 45 200
1.000 12 0.180 189 0.160 0.600 0.470 1.2 0.4 15 45 200
60 amp 60 amp 0.60 sec 0.60 sec 0.35 sec
StartCur EndCur CurUpTime CurDnTime GOffDelay
9
PicNo
Version 4.5 released on 13May13

Gas
Shield
CFH
Start/Cut
psi
Cut
132
NCode
Plasma Gas
AHC
Pierce
ting
Cut-
Delay
Delay
psi
Start
sec
sec
in
Height
in
Pierce
Height
in
Initial
Height
N2
ARG
ARG
MARKING
or
Arc
age
Volt-
in
Kerf
MARKING
Material Stainless Steel
Gas Select 6
Cut Gas ARG
Start Gas ARG
Amperes 200
Shield Gas AIR
ESAB Welding and Cutting Products
in/m
Speed
in
ness
First Row Mark Amp: 14
Thick-
45
1.000 100 0.000 70 0.160 0.160 0.160 0.0 0.1 40 40 140
Version 4.5 released on 13May13
12 amp 16 amp 0.10 sec 0.10 sec 0.35 sec
StartCur EndCur CurUpTime CurDnTime GOffDelay
10
PicNo

Gas
Shield
CFH
Start/Cut
psi
Cut
132
NCode
Plasma Gas
AHC
Pierce
ting
Cut-
Delay
Delay
psi
Start
sec
sec
in
Height
in
Pierce
Height
in
Initial
Height
Arc
age
Volt-
in
Kerf
QUALIT Y
Material Stainless Steel
Gas Select 5
ESAB Welding and Cutting Products
Cut Gas H35
Start Gas N2
Amperes 200
Shield Gas N2
Thick-
Speed
ness
in/m
in
46
0.375 50 0.150 169 0.160 0.350 0.270 0.6 0.7 15 55 200
0.500 45 0.155 160 0.160 0.350 0.240 0.6 0.7 15 55 200
0.750 30 0.160 180 0.160 0.400 0.340 0.6 0.7 15 55 200
1.000 20 0.185 192 0.160 0.500 0.430 1.0 0.7 15 55 200
1.250 14 0.210 200 0.160 0.700 0.490 1.5 0.5 15 55 200
1.500 12 0.220 210 0.160 0.750 0.550 1.8 0.5 15 55 200
Version 4.5 released on 13May13
StartCur EndCur CurUpTime CurDnTime GOffDelay
100 amp 100 amp 0.60 sec 0.60 sec 0.35 sec
10
PicNo

Gas
Shield
CFH
Start/Cut
psi
Cut
133
NCode
Plasma Gas
AHC
Pierce
ting
Cut-
Delay
Delay
psi
Start
sec
sec
in
Height
in
Pierce
Height
in
Initial
Height
N2
ARG
ARG
MARKING
or
Arc
age
Volt-
in
Kerf
MARKING
Material Stainless Steel
Gas Select 6
Cut Gas ARG
Start Gas ARG
Amperes 260
Shield Gas AIR
ESAB Welding and Cutting Products
in/m
Speed
in
ness
First Row Mark Amp: 25
Thick-
47
1.000 100 0.000 65 0.160 0.180 0.180 0.0 0.1 30 30 141
Version 4.5 released on 13May13
12 amp 25 amp 0.10 sec 0.10 sec 0.35 sec
StartCur EndCur CurUpTime CurDnTime GOffDelay
33
PicNo

Gas
Shield
CFH
Start/Cut
psi
Cut
133
NCode
Plasma Gas
AHC
Pierce
ting
Cut-
Delay
Delay
psi
Start
sec
sec
in
Height
in
Pierce
Height
in
Initial
Height
Arc
age
Volt-
in
Kerf
QUALIT Y
Material Stainless Steel
Gas Select 5
ESAB Welding and Cutting Products
Cut Gas H35
Start Gas N2
Amperes 260
Shield Gas N2
Thick-
Speed
ness
in/m
in
48
0.375 70 0.165 156 0.160 0.375 0.220 0.3 0.2 15 55 250
0.500 55 0.165 160 0.160 0.375 0.250 0.3 0.2 15 55 250
0.750 37 0.185 185 0.160 0.600 0.395 0.6 0.2 15 55 250
1.000 25 0.210 190 0.160 0.750 0.530 1.0 0.2 15 55 250
1.250 20 0.215 195 0.160 0.750 0.550 1.3 0.2 15 55 250
1.500 15 0.240 200 0.160 0.750 0.540 1.9 0.2 15 55 250
Version 4.5 released on 13May13
StartCur EndCur CurUpTime CurDnTime GOffDelay
150 amp 150 amp 0.60 sec 0.60 sec 0.35 sec
33
PicNo

Gas
Shield
CFH
Start/Cut
psi
Cut
134
NCode
Plasma Gas
AHC
Pierce
ting
Cut-
Delay
Delay
psi
Start
sec
sec
in
Height
in
Pierce
Height
in
Initial
Height
N2
ARG
ARG
MARKING
or
Arc
age
Volt-
in
Kerf
MARKING
Material Stainless Steel
Gas Select 6
Cut Gas ARG
Start Gas ARG
Amperes 360
Shield Gas AIR
ESAB Welding and Cutting Products
in/m
Speed
in
ness
First Row Mark Amp: 18
Thick-
49
1.000 100 0.000 62 0.160 0.183 0.183 0.0 0.1 30 30 141
Version 4.5 released on 13May13
18 amp 18 amp 0.10 sec 0.10 sec 0.35 sec
StartCur EndCur CurUpTime CurDnTime GOffDelay
28
PicNo

Gas
Shield
CFH
Start/Cut
psi
Cut
134
NCode
Plasma Gas
AHC
Pierce
ting
Cut-
Delay
Delay
psi
Start
sec
sec
in
Height
in
Pierce
Height
in
Initial
Height
Arc
age
Volt-
in
Kerf
QUALIT Y
Material Stainless Steel
Gas Select 5
ESAB Welding and Cutting Products
Cut Gas H35
Start Gas N2
Amperes 360
Shield Gas N2
Thick-
Speed
ness
in/m
in
50
0.750 45 0.225 180 0.160 0.700 0.500 0.6 0.5 5 52 300
1.000 35 0.240 185 0.160 1.000 0.550 1.0 0.5 5 52 300
1.250 30 0.255 195 0.160 1.000 0.690 1.3 0.5 5 52 250
1.375 25 0.270 205 0.160 1.000 0.705 1.6 0.5 5 52 250
1.500 20 0.270 205 0.160 1.000 0.730 1.6 0.5 5 52 250
StartCur EndCur CurUpTime CurDnTime GOffDelay
150 amp 150 amp 0.60 sec 0.60 sec 0.35 sec
28
PicNo
Version 4.5 released on 13May13

Carbon Steel
Production
51

52

Gas
Shield
CFH
Start/Cut
psi
Cut
112
NCode
Plasma Gas
AHC
Pierce
ting
Cut-
Delay
Delay
psi
Start
sec
sec
in
Height
in
Pierce
Height
in
Initial
Height
N2
ARG
ARG
MARKING
or
Arc
age
Volt-
in
Kerf
MARKING
Material Carbon Steel
Gas Select 6
Cut Gas ARG
Start Gas ARG
Amperes 10 0
Shield Gas AIR
ESAB Welding and Cutting Products
in/m
Speed
in
First Row Mark Amp: 12
ness
Thick-
53
1.000 100 0.000 90 0.160 0.160 0.160 0.0 0.1 52 52 71
Version 4.5 released on 13May13
12 amp 12 amp 0.10 sec 0.10 sec 0.35 sec
StartCur EndCur CurUpTime CurDnTime GOffDelay
2
PicNo

Gas
Shield
CFH
Start/Cut
psi
Cut
112
NCode
PRODUCTION
PRODUCTION
O2
AIR
or
N2O2N2
or
Plasma Gas
AHC
Pierce
ting
Cut-
Delay
Delay
psi
Start
sec
sec
in
Height
in
Pierce
Height
AIR
in
Initial
Height
Arc
age
Volt-
in
Kerf
PRODUCTION
Material Carbon Steel
Gas Select 9
Cut Gas O2
Start Gas N2
Amperes 10 0
Shield Gas AIR
ESAB Welding and Cutting Products
Thick-
Speed
ness
in/m
in
54
0.125 225 0.065 142 0.160 0.250 0.125 0.1 0.1 25 60 100
0.250 140 0.080 149 0.160 0.250 0.125 0.1 0.1 25 60 100
0.375 75 0.100 153 0.160 0.250 0.125 0.2 0.1 25 60 100
0.500 60 0.100 155 0.160 0.250 0.125 0.4 0.1 25 60 100
50 amp 50 amp 0.60 sec 0.60 sec 0.35 sec
StartCur EndCur CurUpTime CurDnTime GOffDelay
2
PicNo
Version 4.5 released on 13May13

Gas
Shield
CFH
Start/Cut
psi
Cut
113
NCode
Plasma Gas
AHC
Pierce
ting
Cut-
Delay
Delay
psi
Start
sec
sec
in
Height
in
Pierce
Height
in
Initial
Height
N2
ARG
ARG
MARKING
or
Arc
age
Volt-
in
Kerf
MARKING
Material Carbon Steel
Gas Select 6
Cut Gas ARG
Start Gas ARG
Amperes 130
Shield Gas AIR
ESAB Welding and Cutting Products
in/m
Speed
in
First Row Mark Amp: 12
ness
Thick-
55
1.000 100 0.000 80 0.160 0.160 0.160 0.0 0.1 45 45 71
Version 4.5 released on 13May13
12 amp 12 amp 0.10 sec 0.10 sec 0.35 sec
StartCur EndCur CurUpTime CurDnTime GOffDelay
29
PicNo

Gas
Shield
CFH
Start/Cut
psi
Cut
113
NCode
PRODUCTION
N2O2N2
or
Plasma Gas
AHC
Pierce
ting
Cut-
Delay
Delay
psi
Start
sec
sec
in
Height
in
Pierce
Height
in
Initial
Height
Arc
age
Volt-
in
Kerf
PRODUCTION
Material Carbon Steel
Gas Select 2
ESAB Welding and Cutting Products
Cut Gas O2
Start Gas AIR
Amperes 130
Shield Gas AIR
NOTE: Piercing not recommended on thicknesses greater than 1.00” Pierce delay indicated for edge starts greater than 1.00”
Thick-
Speed
ness
in/m
in
56
60 amp 60 amp 0.60 sec 0.60 sec 0.35 sec
StartCur EndCur CurUpTime CurDnTime GOffDelay
1.500 10 0.180 180 0.160 0.380 0.380 1.5 1.0 25 50 110
1.375 12 0.180 177 0.160 0.380 0.380 1.5 1.0 25 50 110
1.250 15 0.180 175 0.160 0.380 0.340 1.5 1.0 25 50 110
1.000 20 0.160 172 0.160 0.380 0.380 1.5 1.0 25 50 110
0.750 55 0.110 144 0.160 0.260 0.214 1.0 0.2 25 50 110
0.625 60 0.080 146 0.160 0.260 0.255 0.6 0.2 25 50 110
0.500 80 0.080 145 0.160 0.260 0.240 0.6 0.2 25 50 110
0.375 110 0.080 135 0.160 0.170 0.170 0.6 0.2 25 50 110
0.250 150 0.080 127 0.160 0.130 0.100 0.3 0.2 25 50 110
0.125 240 0.080 127 0.160 0.130 0.080 0.3 0.2 25 50 110
Version 4.5 released on 13May13
29
PicNo

Gas
Shield
CFH
Start/Cut
psi
Cut
114
NCode
Plasma Gas
AHC
Pierce
ting
Cut-
Delay
Delay
psi
Start
sec
sec
in
Height
in
Pierce
Height
in
Initial
Height
N2
ARG
ARG
MARKING
or
Arc
age
Volt-
in
Kerf
MARKING
Material Carbon Steel
Gas Select 6
Cut Gas ARG
Start Gas ARG
Amperes 200
Shield Gas AIR
ESAB Welding and Cutting Products
in/m
Speed
in
First Row Mark Amp: 14
ness
Thick-
57
1.000 100 0.000 70 0.160 0.160 0.160 0.0 0.1 40 40 71
Version 4.5 released on 13May13
12 amp 14 amp 0.10 sec 0.10 sec 0.35 sec
StartCur EndCur CurUpTime CurDnTime GOffDelay
56
PicNo

Gas
Shield
CFH
Start/Cut
psi
Cut
114
NCode
PRODUCTION
PRODUCTION
O2
AIR
or
N2O2N2
or
Plasma Gas
AHC
Pierce
ting
Cut-
Delay
Delay
psi
Start
sec
sec
in
Height
in
Pierce
Height
AIR
in
Initial
Height
Arc
age
Volt-
in
Kerf
PRODUCTION
Material Carbon Steel
Gas Select 2
Cut Gas O2
Start Gas N2
Amperes 200
Shield Gas AIR
ESAB Welding and Cutting Products
NOTE: Piercing not recommended on thicknesses greater than 1.25” Pierce delay indicated for edge starts greater than 1.25”
Thick-
Speed
ness
in/m
in
58
0.188 275 0.081 130 0.230 0.500 0.064 0.3 0.5 25 60 185
0.250 210 0.089 140 0.230 0.500 0.090 0.3 0.5 25 60 185
0.375 140 0.109 138 0.230 0.500 0.090 0.3 0.5 25 60 185
0.500 120 0.109 143 0.230 0.500 0.104 0.3 0.5 25 60 200
0.750 80 0.125 145 0.230 0.750 0.165 0.7 0.1 25 60 200
2.000 11 0.225 187 0.230 0.750 0.449 1.5 0.1 25 60 200
1.750 17 0.209 173 0.230 0.500 0.291 1.3 0.1 25 60 200
1.500 25 0.180 170 0.230 0.500 0.319 1.3 0.1 25 60 200
1.250 38 0.147 160 0.230 0.500 0.282 1.3 0.1 25 60 200
1.000 50 0.128 158 0.230 0.750 0.250 1.0 0.1 25 60 200
0.875 65 0.126 152 0.230 0.750 0.208 0.8 0.1 25 60 200
Version 4.5 released on 13May13
75 amp 75 amp 0.60 sec 0.60 sec 0.01 sec
StartCur EndCur CurUpTime CurDnTime GOffDelay
56
PicNo

Gas
Shield
CFH
Start/Cut
psi
Cut
127
NCode
Plasma Gas
AHC
Pierce
ting
Cut-
Delay
Delay
psi
Start
sec
sec
in
Height
in
Pierce
Height
in
Initial
Height
N2
ARG
ARG
MARKING
or
Arc
age
Volt-
in
Kerf
MARKING
Material Carbon Steel
Gas Select 6
Cut Gas ARG
Start Gas ARG
Amperes 260
Shield Gas AIR
ESAB Welding and Cutting Products
First Row Mark Amp: 12
Thick-
Speed
ness
in/m
in
59
1.000 100 0.000 70 0.160 0.160 0.160 0.0 0.1 30 30 71
12 amp 12 amp 0.10 sec 0.10 sec 0.35 sec
StartCur EndCur CurUpTime CurDnTime GOffDelay
53
PicNo
Version 4.5 released on 13May13

Gas
Shield
CFH
Start/Cut
psi
Cut
127
NCode
PRODUCTION
N2O2N2
or
Plasma Gas
AHC
Pierce
ting
Cut-
Delay
Delay
psi
Start
sec
sec
in
Height
in
Pierce
Height
in
Initial
Height
Arc
age
Volt-
in
Kerf
PRODUCTION
Material Carbon Steel
Gas Select 2
ESAB Welding and Cutting Products
Cut Gas O2
Start Gas AIR
Amperes 260
Shield Gas AIR
NOTE: Piercing not recommended on thicknesses greater than 1.50” Pierce delay indicated for edge starts greater than 1.50”
Thick-
Speed
ness
in/m
in
60
0.375 170 0.125 135 0.200 0.150 0.150 0.6 0.1 25 60 250
0.500 145 0.150 137 0.230 0.500 0.200 0.6 0.1 25 60 250
0.625 126 0.150 142 0.230 0.500 0.200 0.6 0.1 25 60 250
0.750 90 0.160 145 0.230 0.500 0.200 0.6 0.1 25 60 250
0.875 78 0.170 146 0.230 0.500 0.200 0.5 0.1 25 60 250
2.500 10 0.250 188 0.160 0.600 0.460 1.5 0.1 25 60 250
2.000 16 0.200 175 0.160 0.600 0.400 1.5 0.1 25 60 250
1.500 38 0.200 158 0.160 0.600 0.275 1.5 0.1 25 60 250
1.375 42 0.200 155 0.160 0.600 0.275 1.5 0.1 25 60 250
1.250 45 0.175 154 0.160 0.500 0.200 1.5 0.1 25 60 250
1.000 65 0.175 148 0.230 0.500 0.200 1.0 0.1 25 60 250
Version 4.5 released on 13May13
75 amp 75 amp 0.60 sec 0.60 sec 0.01 sec
StartCur EndCur CurUpTime CurDnTime GOffDelay
53
PicNo

Gas
Shield
CFH
Start/Cut
psi
Cut
115
NCode
Plasma Gas
AHC
Pierce
ting
Cut-
Delay
Delay
psi
Start
sec
sec
in
Height
in
Pierce
Height
in
Initial
Height
N2
ARG
ARG
MARKING
or
Arc
age
Volt-
in
Kerf
MARKING
Material Carbon Steel
Gas Select 6
Cut Gas ARG
Start Gas ARG
Amperes 300
Shield Gas AIR
ESAB Welding and Cutting Products
in/m
Speed
in
ness
First Row Mark Amp: 20
Thick-
61
1.000 100 0.000 70 0.160 0.160 0.160 0.0 0.1 30 30 71
Version 4.5 released on 13May13
20 amp 20 amp 0.10 sec 0.10 sec 0.35 sec
StartCur EndCur CurUpTime CurDnTime GOffDelay
5
PicNo

Gas
Shield
CFH
Start/Cut
psi
Cut
115
NCode
PRODUCTION
PRODUCTION
O2
AIR
or
N2O2N2
or
Plasma Gas
AHC
Pierce
ting
Cut-
Delay
Delay
psi
Start
sec
sec
in
Height
in
Pierce
Height
AIR
in
Initial
Height
Arc
age
Volt-
in
Kerf
PRODUCTION
Material Carbon Steel
Gas Select 9
Cut Gas O2
Start Gas N2
Amperes 300
Shield Gas AIR
ESAB Welding and Cutting Products
NOTE: Piercing not recommended on thicknesses greater than 1.75” Pierce delay indicated for edge starts greater than 1.75”
Thick-
Speed
ness
in/m
in
62
0.250 190 0.120 135 0.160 0.250 0.250 0.0 0.3 25 43 200
0.375 180 0.126 145 0.160 0.320 0.320 0.5 0.3 25 43 200
0.500 140 0.130 145 0.160 0.345 0.345 0.5 0.3 25 43 200
0.625 125 0.115 151 0.160 0.400 0.400 0.5 0.5 25 43 200
0.750 95 0.140 153 0.160 0.418 0.418 0.7 0.6 25 43 200
1.750 24 0.190 182 0.160 0.710 0.710 2.0 0.8 25 46 180
1.625 30 0.190 180 0.160 0.670 0.670 1.8 0.8 25 46 180
1.500 35 0.190 175 0.160 0.615 0.615 1.7 0.7 25 43 180
1.375 40 0.160 173 0.160 0.620 0.620 1.5 0.7 25 46 200
1.250 45 0.170 170 0.160 0.600 0.600 1.3 0.7 25 46 200
1.000 70 0.160 160 0.160 0.532 0.532 0.6 0.7 25 43 200
Version 4.5 released on 13May13
StartCur EndCur CurUpTime CurDnTime GOffDelay
150 amp 150 amp 0.60 sec 0.60 sec 0.35 sec
5
PicNo

Gas
Shield
CFH
Start/Cut
psi
Cut
120
NCode
Plasma Gas
AHC
Pierce
ting
Cut-
Delay
Delay
psi
Start
sec
sec
in
Height
in
Pierce
Height
in
Initial
Height
N2
ARG
ARG
MARKING
or
Arc
age
Volt-
in
Kerf
MARKING
Material Carbon Steel
Gas Select 6
Cut Gas ARG
Start Gas ARG
Amperes 300
Shield Gas AIR
ESAB Welding and Cutting Products
in/m
Speed
in
ness
First Row Mark Amp: 20
Thick-
63
1.000 100 0.000 70 0.160 0.160 0.160 0.0 0.1 30 30 71
Version 4.5 released on 13May13
20 amp 20 amp 0.10 sec 0.10 sec 0.35 sec
StartCur EndCur CurUpTime CurDnTime GOffDelay
5
PicNo

Gas
Shield
CFH
Start/Cut
psi
Cut
120
NCode
SEVER
SEVER
O2
AIR
or
N2O2N2
or
Plasma Gas
AHC
Pierce
ting
Cut-
Delay
Delay
psi
Start
sec
sec
in
Height
in
Pierce
Height
AIR
in
Initial
Height
Arc
age
Volt-
in
Kerf
SEVER
Material Carbon Steel
Gas Select 9
Cut Gas O2
Start Gas N2
Amperes 300
Shield Gas AIR
ESAB Welding and Cutting Products
NOTE: Piercing not recommended on thicknesses greater than 1.75” Pierce delay indicated for edge starts greater than 1.75”
Thick-
Speed
ness
in/m
in
64
0.188 300 0.110 134 0.160 0.250 0.230 0.4 0.1 25 45 200
0.250 240 0.110 135 0.160 0.250 0.200 0.4 0.1 25 45 200
0.312 230 0.120 140 0.160 0.250 0.250 0.5 0.1 25 45 200
0.375 200 0.126 145 0.160 0.320 0.320 0.5 0.1 25 43 200
0.500 170 0.080 150 0.160 0.480 0.480 0.5 0.2 25 43 160
1.750 40 0.290 185 0.160 1.000 0.670 1.8 0.6 25 43 160
1.625 52 0.290 181 0.160 1.000 0.660 1.6 0.6 25 43 160
1.500 60 0.280 177 0.160 1.200 0.650 1.3 0.6 25 43 160
1.375 67 0.240 170 0.160 1.200 0.620 1.2 0.6 25 43 160
1.250 75 0.200 165 0.160 0.600 0.600 1.0 0.6 25 43 160
1.000 120 0.140 160 0.160 1.000 0.570 0.7 0.6 25 43 160
0.750 120 0.140 160 0.160 1.000 0.542 0.5 0.6 25 43 160
0.625 150 0.140 155 0.160 0.750 0.430 0.5 0.6 25 43 160
Version 4.5 released on 13May13
StartCur EndCur CurUpTime CurDnTime GOffDelay
150 amp 150 amp 0.60 sec 0.60 sec 0.35 sec
5
PicNo

Gas
Shield
CFH
Start/Cut
psi
Cut
116
NCode
Plasma Gas
AHC
Pierce
ting
Cut-
Delay
Delay
psi
Start
sec
sec
in
Height
in
Pierce
Height
in
Initial
Height
N2
ARG
ARG
MARKING
or
Arc
age
Volt-
in
Kerf
MARKING
Material Carbon Steel
Gas Select 6
Cut Gas ARG
Start Gas ARG
Amperes 360
Shield Gas AIR
ESAB Welding and Cutting Products
in/m
Speed
in
ness
First Row Mark Amp: 18
Thick-
65
1.000 100 0.000 62 0.160 0.160 0.160 0.0 0.1 30 30 71
Version 4.5 released on 13May13
18 amp 18 amp 0.10 sec 0.10 sec 0.35 sec
StartCur EndCur CurUpTime CurDnTime GOffDelay
55
PicNo

Gas
Shield
CFH
Start/Cut
psi
Cut
116
NCode
N2O2N2
PRODUCTION
or
Plasma Gas
AHC
Pierce
ting
Cut-
Delay
Delay
psi
Start
sec
sec
in
Height
in
Pierce
Height
in
Initial
Height
Arc
age
Volt-
in
Kerf
PRODUCTION
Material Carbon Steel
Gas Select 2
ESAB Welding and Cutting Products
Cut Gas O2
Start Gas AIR
Amperes 360
Shield Gas AIR
NOTE: Piercing not recommended on thicknesses greater than 2.00” Pierce delay indicated for edge starts greater than 2.00”
Thick-
Speed
ness
in/m
in
66
0.500 170 0.135 150 0.160 0.200 0.160 0.5 0.2 15 60 200
0.625 150 0.135 150 0.160 0.200 0.219 0.5 0.2 15 60 200
0.750 115 0.150 145 0.160 0.500 0.180 0.7 0.2 15 60 200
1.000 85 0.165 150 0.160 0.500 0.180 0.7 0.2 15 60 200
1.250 65 0.189 155 0.160 0.500 0.200 1.5 0.2 15 60 200
3.000 8 0.265 200 0.375 0.400 0.400 3.0 0.2 15 50 200
2.500 18 0.250 180 0.375 0.400 0.400 3.0 0.2 15 50 200
2.250 25 0.225 175 0.375 0.400 0.400 3.0 0.2 15 50 250
2.000 30 0.189 162 0.160 1.000 1.000 3.0 0.2 15 50 250
1.500 48 0.189 158 0.160 0.625 0.200 1.5 0.2 15 60 250
1.375 55 0.189 158 0.160 0.500 0.200 1.5 0.2 15 60 200
Version 4.5 released on 13May13
75 amp 125 amp 0.30 sec 0.40 sec 0.01 sec
StartCur EndCur CurUpTime CurDnTime GOffDelay
55
PicNo

Gas
Shield
CFH
Start/Cut
psi
Cut
129
NCode
Plasma Gas
AHC
Pierce
ting
Cut-
Delay
Delay
psi
Start
sec
sec
in
Height
in
Pierce
Height
in
Initial
Height
N2
ARG
ARG
MARKING
or
Arc
age
Volt-
in
Kerf
MARKING
Material Carbon Steel
Gas Select 6
Cut Gas ARG
Start Gas ARG
Amperes 450
Shield Gas AIR
ESAB Welding and Cutting Products
in/m
Speed
in
ness
First Row Mark Amp: 25
Thick-
67
1.000 100 0.000 65 0.160 0.160 0.160 0.0 0.1 30 30 71
Version 4.5 released on 13May13
18 amp 25 amp 0.10 sec 0.10 sec 0.35 sec
StartCur EndCur CurUpTime CurDnTime GOffDelay
39
PicNo

Gas
Shield
CFH
Start/Cut
psi
Cut
129
NCode
PRODUCTION
PRODUCTION
O2
AIR
or
N2O2N2
or
Plasma Gas
AHC
Pierce
ting
Cut-
Delay
Delay
psi
Start
sec
sec
in
Height
in
Pierce
Height
AIR
in
Initial
Height
Arc
age
Volt-
in
Kerf
PRODUCTION
Material Carbon Steel
Gas Select 9
Cut Gas O2
Start Gas N2
Amperes 450
Shield Gas AIR
ESAB Welding and Cutting Products
NOTE: Piercing not recommended on thicknesses greater than 2.00” Pierce delay indicated for edge starts greater than 2.00”
Thick-
Speed
ness
in/m
in
68
1.000 93 0.120 145 0.160 0.750 0.275 0.8 0.2 15 45 150
1.250 70 0.140 150 0.160 0.750 0.270 1.5 0.2 15 45 150
1.500 55 0.160 155 0.160 0.750 0.300 2.0 0.2 15 45 250
1.750 45 0.165 160 0.160 0.750 0.340 2.5 0.2 15 45 250
2.000 33 0.200 165 0.160 0.750 0.400 3.5 0.2 15 45 250
3.000 10 0.315 185 0.160 0.750 0.540 3.5 0.2 15 50 200
2.500 22 0.250 180 0.160 0.750 0.491 3.5 0.2 15 50 200
2.250 27 0.224 172 0.160 0.750 0.445 3.5 0.2 15 45 250
Version 4.5 released on 13May13
StartCur EndCur CurUpTime CurDnTime GOffDelay
200 amp 200 amp 0.60 sec 0.60 sec 0.45 sec
39
PicNo

Aluminum
Production
69

70

Gas
Shield
CFH
Start/Cut
psi
Cut
171
NCode
Plasma Gas
AHC
Pierce
ting
Cut-
Delay
Delay
psi
Start
sec
sec
in
Height
in
Pierce
Height
in
Initial
Height
Arc
age
Volt-
in
Kerf
PRODUCTION
Material Aluminium
Gas Select 3
ESAB Welding and Cutting Products
Cut Gas N2
Start Gas N2
Amperes 35
Shield Gas N2
Thick-
Speed
ness
in/m
in
71
0.040 240 0.071 160 0.160 0.120 0.120 0.1 0.4 30 85 80
0.080 200 0.060 160 0.160 0.120 0.120 0.1 0.4 30 85 80
0.125 140 0.060 165 0.160 0.120 0.120 0.1 0.4 30 85 70
35 amp 35 amp 0.60 sec 0.60 sec 0.35 sec
StartCur EndCur CurUpTime CurDnTime GOffDelay
18
PicNo
Version 4.5 released on 13May13

Gas
Shield
CFH
Start/Cut
psi
Cut
172
NCode
Plasma Gas
AHC
Pierce
ting
Cut-
Delay
Delay
psi
Start
sec
sec
in
Height
in
Pierce
Height
in
Initial
Height
Arc
age
Volt-
in
Kerf
PRODUCTION
Amperes 50
Start Gas N2
Cut Gas N2
Shield Gas N2
Material Aluminium
Gas Select 3
ESAB Welding and Cutting Products
Thick-
Speed
ness
in/m
in
72
0.125 160 0.050 172 0.160 0.160 0.156 0.2 0.8 25 80 150
0.160 120 0.050 176 0.160 0.160 0.160 0.2 0.8 25 80 150
0.200 85 0.050 180 0.160 0.166 0.166 0.2 0.8 25 80 150
0.250 75 0.060 188 0.160 0.250 0.250 0.2 0.8 25 80 150
50 amp 50 amp 0.60 sec 0.60 sec 0.35 sec
StartCur EndCur CurUpTime CurDnTime GOffDelay
7
PicNo
Version 4.5 released on 13May13

Gas
Shield
CFH
Start/Cut
psi
Cut
173
NCode
Plasma Gas
AHC
Pierce
ting
Cut-
Delay
Delay
psi
Start
sec
sec
in
Height
in
Pierce
Height
in
Initial
Height
Arc
age
Volt-
in
Kerf
PRODUCTION
Material Aluminium
Gas Select 3
ESAB Welding and Cutting Products
Cut Gas N2
Start Gas N2
Amperes 10 0
Shield Gas N2
Thick-
Speed
ness
in/m
in
73
0.250 80 0.065 153 0.160 0.160 0.160 0.7 0.5 20 40 170
0.375 75 0.065 155 0.160 0.180 0.180 0.6 0.8 20 40 105
0.500 50 0.045 160 0.160 0.250 0.190 0.6 0.8 20 40 105
60 amp 60 amp 0.60 sec 0.60 sec 0.35 sec
StartCur EndCur CurUpTime CurDnTime GOffDelay
8
PicNo
Version 4.5 released on 13May13

Gas
Shield
CFH
Start/Cut
psi
Cut
174
NCode
Plasma Gas
AHC
Pierce
ting
Cut-
Delay
Delay
psi
Start
sec
sec
in
Height
in
Pierce
Height
in
Initial
Height
Arc
age
Volt-
in
Kerf
PRODUCTION
Material Aluminium
Gas Select 3
ESAB Welding and Cutting Products
Cut Gas N2
Start Gas N2
Amperes 200
Shield Gas N2
Thick-
Speed
ness
in/m
in
74
0.250 125 0.100 140 0.160 0.250 0.115 0.5 0.6 10 46 145
0.375 105 0.100 145 0.160 0.250 0.120 0.5 0.6 10 46 145
0.500 85 0.095 162 0.160 0.250 0.218 0.5 0.6 10 46 145
0.625 62 0.102 170 0.160 0.500 0.274 0.5 0.6 10 46 145
0.750 40 0.110 180 0.160 0.500 0.330 0.5 0.6 10 46 145
1.500 15 0.180 195 0.160 0.380 0.380 0.5 0.6 10 40 100
1.375 17 0.180 193 0.160 0.380 0.380 1.1 1.1 10 40 100
1.250 20 0.157 192 0.160 0.500 0.375 1.1 1.1 10 46 145
1.000 27 0.120 192 0.160 0.500 0.271 0.7 0.9 10 46 160
Version 4.5 released on 13May13
StartCur EndCur CurUpTime CurDnTime GOffDelay
100 amp 100 amp 0.60 sec 0.60 sec 0.35 sec
9
PicNo

Gas
Shield
CFH
Start/Cut
psi
Cut
175
NCode
Plasma Gas
AHC
Pierce
ting
Cut-
Delay
Delay
psi
Start
sec
sec
in
Height
in
Pierce
Height
in
Initial
Height
Arc
age
Volt-
in
Kerf
PRODUCTION
Material Aluminium
Gas Select 3
ESAB Welding and Cutting Products
Cut Gas N2
Start Gas N2
Amperes 260
Shield Gas N2
Thick-
Speed
ness
in/m
in
75
0.250 300 0.110 160 0.160 0.250 0.230 0.5 0.6 7 50 145
0.375 200 0.110 165 0.160 0.270 0.270 0.5 0.6 7 50 145
0.500 150 0.110 168 0.160 0.300 0.300 0.5 0.6 7 50 145
0.625 120 0.110 174 0.160 0.380 0.340 0.5 0.2 7 50 145
0.750 90 0.110 180 0.160 0.380 0.380 0.5 0.6 7 50 145
1.250 25 0.140 194 0.160 1.000 0.370 1.5 0.2 7 50 145
1.000 45 0.110 192 0.160 0.500 0.380 0.5 0.6 7 50 145
Version 4.5 released on 13May13
StartCur EndCur CurUpTime CurDnTime GOffDelay
150 amp 150 amp 0.60 sec 0.60 sec 0.35 sec
10
PicNo

Gas
Shield
CFH
Start/Cut
psi
Cut
176
NCode
Plasma Gas
AHC
Pierce
ting
Cut-
Delay
Delay
psi
Start
sec
sec
in
Height
in
Pierce
Height
in
Initial
Height
Arc
age
Volt-
in
Kerf
PRODUCTION
Material Aluminium
Gas Select 3
ESAB Welding and Cutting Products
Cut Gas N2
Start Gas N2
Amperes 360
Shield Gas N2
Thick-
Speed
ness
in/m
in
76
0.250 230 0.120 147 0.160 0.250 0.110 0.0 0.2 10 40 300
0.375 180 0.130 155 0.160 0.500 0.195 0.2 0.2 10 40 300
0.500 160 0.130 160 0.160 0.625 0.250 0.2 0.2 10 40 300
0.625 125 0.135 164 0.160 0.700 0.295 0.2 0.2 10 40 300
0.750 90 0.140 168 0.160 0.700 0.340 0.2 0.2 10 40 300
1.250 35 0.200 190 0.160 1.000 0.420 0.5 0.2 10 40 200
1.000 55 0.150 180 0.160 0.800 0.440 0.5 0.2 10 40 200
Version 4.5 released on 13May13
StartCur EndCur CurUpTime CurDnTime GOffDelay
150 amp 150 amp 0.60 sec 0.60 sec 0.35 sec
11
PicNo

Gas
Shield
CFH
Start/Cut
psi
Cut
179
NCode
N2N2N2
PRODUCTION
or
Plasma Gas
AHC
Pierce
ting
Cut-
Delay
Delay
psi
Start
sec
sec
in
Height
in
Pierce
Height
in
Initial
Height
Arc
age
Volt-
in
Kerf
PRODUCTION
Material Aluminium
Gas Select 10
ESAB Welding and Cutting Products
Cut Gas N2
Start Gas N2
Amperes 450
Shield Gas AIR
in/m
Speed
in
ness
NOTE: Piercing not recommended on thicknesses greater than 1.5”
Pierce delay indicated for edge starts greater than 1.5”
Thick-
0.500 190 0.145 160 0.160 0.500 0.310 1.0 0.2 5 40 200
0.625 155 0.150 163 0.160 0.500 0.330 1.0 0.2 5 40 200
0.750 125 0.170 170 0.160 0.500 0.350 1.0 0.2 5 40 200
1.000 80 0.175 175 0.160 0.500 0.350 1.0 0.2 5 40 200
1.250 55 0.185 180 0.160 0.700 0.370 1.3 0.2 5 40 200
1.500 40 0.220 185 0.160 0.700 0.390 1.5 0.2 5 40 200
77
2.000 20 0.285 200 0.160 0.700 0.400 1.5 0.5 5 40 200
1.750 30 0.250 190 0.160 0.700 0.390 1.5 0.2 5 40 200
Version 4.5 released on 13May13
StartCur EndCur CurUpTime CurDnTime GOffDelay
200 amp 200 amp 0.60 sec 0.60 sec 0.35 sec
14
PicNo

Gas
Shield
CFH
Start/Cut
psi
Cut
177
NCode
Plasma Gas
AHC
Pierce
ting
Cut-
Delay
Delay
psi
Start
sec
sec
in
Height
in
Pierce
Height
in
Initial
Height
Arc
age
Volt-
in
Kerf
PRODUCTION
Material Aluminium
Gas Select 5
ESAB Welding and Cutting Products
Cut Gas H35
Start Gas N2
Amperes 600
Shield Gas N2
NOTE: Piercing not recommended on thicknesses greater than 2.0”
Pierce delay indicated for edge starts greater than 2.0”
Thick-
Speed
ness
in/m
in
78
1.000 90 0.300 172 0.160 0.800 0.500 0.5 0.3 10 45 350
1.500 75 0.290 175 0.160 0.800 0.580 0.8 0.3 10 45 350
2.000 45 0.350 195 0.160 1.000 0.750 1.0 0.3 10 45 350
3.000 25 0.415 215 0.160 1.000 0.930 1.5 0.3 10 45 350
StartCur EndCur CurUpTime CurDnTime GOffDelay
200 amp 200 amp 0.60 sec 0.60 sec 0.45 sec
12
PicNo
Version 4.5 released on 13May13

Gas
Shield
CFH
Start/Cut
psi
Cut
178
NCode
Plasma Gas
AHC
Pierce
ting
Cut-
Delay
Delay
psi
Start
sec
sec
in
Height
in
Pierce
Height
in
Initial
Height
N2
N2
H35
PRODUCTION
or
Arc
age
Volt-
in
Kerf
PRODUCTION
Material Aluminium
Gas Select 4
Cut Gas H35
Start Gas N2
Amperes 600
Shield Gas AIR
NOTE: Piercing not recommended on thicknesses greater than 3.0”
ESAB Welding and Cutting Products
in/m
Speed
in
ness
Pierce delay indicated for edge starts greater than 3.0”
Creep speed 1/2 cut speed rst 1/2”
Thick-
3.000 25 0.445 170 0.500 0.750 0.540 1.7 0.3 6 25 250
79
4.000 15 0.810 200 0.500 1.250 1.150 3.0 1.5 6 25 180
5.000 12 0.620 215 0.500 1.250 1.390 5.0 1.5 6 25 230
6.000 8 0.760 230 0.500 1.250 1.400 5.0 1.5 6 25 230
StartCur EndCur CurUpTime CurDnTime GOffDelay
200 amp 200 amp 0.60 sec 0.60 sec 0.45 sec
15
PicNo
Version 4.5 released on 13May13

80

Stainless Steel
Production
81

82

Gas
Shield
CFH
Start/Cut
psi
Cut
141
NCode
Plasma Gas
AHC
Pierce
ting
Cut-
Delay
Delay
psi
Start
sec
sec
in
Height
in
Pierce
Height
in
Initial
Height
N2
ARG
ARG
MARKING
or
Arc
age
Volt-
in
Kerf
MARKING
Material Stainless Steel
Gas Select 6
Cut Gas ARG
Start Gas ARG
Amperes 70
Shield Gas AIR
ESAB Welding and Cutting Products
in/m
Speed
in
ness
First Row Mark Amp: 14
Thick-
83
1.000 100 0.000 85 0.130 0.063 0.063 0.0 0.1 75 75 141
Version 4.5 released on 13May13
14 amp 14 amp 0.10 sec 0.10 sec 0.35 sec
StartCur EndCur CurUpTime CurDnTime GOffDelay
16
PicNo

Gas
Shield
CFH
Start/Cut
psi
Cut
141
NCode
Plasma Gas
AHC
Pierce
ting
Cut-
Delay
Delay
psi
Start
sec
sec
in
Height
in
Pierce
Height
in
Initial
Height
Arc
age
Volt-
in
Kerf
PRODUCTION
Material Stainless Steel
Gas Select 3
ESAB Welding and Cutting Products
Cut Gas N2
Start Gas N2
Amperes 70
Shield Gas N2
Thick-
Speed
ness
in/m
in
84
0.040 275 0.040 140 0.160 0.160 0.080 0.0 0.1 25 50 350
0.080 190 0.050 140 0.160 0.160 0.080 0.0 0.1 25 50 350
0.125 130 0.050 146 0.160 0.160 0.110 0.0 0.4 25 50 350
0.160 100 0.050 148 0.160 0.160 0.119 0.0 0.4 25 50 350
0.200 70 0.050 150 0.160 0.160 0.120 0.0 0.4 25 50 350
50 amp 50 amp 0.60 sec 0.60 sec 0.35 sec
StartCur EndCur CurUpTime CurDnTime GOffDelay
16
PicNo
Version 4.5 released on 13May13

Gas
Shield
CFH
Start/Cut
psi
Cut
142
NCode
Plasma Gas
AHC
Pierce
ting
Cut-
Delay
Delay
psi
Start
sec
sec
in
Height
in
Pierce
Height
in
Initial
Height
N2
ARG
ARG
MARKING
or
Arc
age
Volt-
in
Kerf
MARKING
Material Stainless Steel
Gas Select 6
Cut Gas ARG
Start Gas ARG
Amperes 130
Shield Gas AIR
ESAB Welding and Cutting Products
First Row Mark Amp: 18
Thick-
Speed
ness
in/m
in
85
1.000 100 0.000 80 0.160 0.160 0.160 0.0 0.1 45 45 141
18 amp 18 amp 0.10 sec 0.10 sec 0.35 sec
StartCur EndCur CurUpTime CurDnTime GOffDelay
8
PicNo
Version 4.5 released on 13May13

Gas
Shield
CFH
Start/Cut
psi
Cut
142
NCode
Plasma Gas
AHC
Pierce
ting
Cut-
Delay
Delay
psi
Start
sec
sec
in
Height
in
Pierce
Height
in
Initial
Height
Arc
age
Volt-
in
Kerf
PRODUCTION
Material Stainless Steel
Gas Select 3
ESAB Welding and Cutting Products
Cut Gas N2
Start Gas N2
Amperes 130
Shield Gas N2
Thick-
Speed
ness
in/m
in
86
0.250 85 0.090 150 0.160 0.190 0.090 0.3 0.3 15 55 260
0.375 45 0.105 155 0.160 0.190 0.120 0.5 0.3 15 55 200
0.500 30 0.105 165 0.160 0.190 0.125 0.6 0.3 15 55 150
0.625 27 0.105 170 0.160 0.500 0.200 0.7 0.3 15 55 140
0.750 25 0.110 180 0.160 0.500 0.300 0.9 0.3 15 55 140
60 amp 60 amp 0.60 sec 0.60 sec 0.35 sec
StartCur EndCur CurUpTime CurDnTime GOffDelay
8
PicNo
Version 4.5 released on 13May13

Gas
Shield
CFH
Start/Cut
psi
Cut
143
NCode
Plasma Gas
AHC
Pierce
ting
Cut-
Delay
Delay
psi
Start
sec
sec
in
Height
in
Pierce
Height
in
Initial
Height
N2
ARG
ARG
MARKING
or
Arc
age
Volt-
in
Kerf
MARKING
Material Stainless Steel
Gas Select 6
Cut Gas ARG
Start Gas ARG
Amperes 200
Shield Gas AIR
ESAB Welding and Cutting Products
First Row Mark Amp: 16
Thick-
Speed
ness
in/m
in
87
1.000 100 0.000 70 0.160 0.160 0.160 0.0 0.1 40 40 140
12 amp 16 amp 0.10 sec 0.10 sec 0.35 sec
StartCur EndCur CurUpTime CurDnTime GOffDelay
10
PicNo
Version 4.5 released on 13May13

Gas
Shield
CFH
Start/Cut
psi
Cut
143
NCode
Plasma Gas
AHC
Pierce
ting
Cut-
Delay
Delay
psi
Start
sec
sec
in
Height
in
Pierce
Height
in
Initial
Height
Arc
age
Volt-
in
Kerf
PRODUCTION
Material Stainless Steel
Gas Select 3
ESAB Welding and Cutting Products
Cut Gas N2
Start Gas N2
Amperes 200
Shield Gas N2
Thick-
Speed
ness
in/m
in
88
0.250 165 0.085 135 0.160 0.250 0.150 0.5 0.3 15 30 200
0.375 80 0.093 145 0.160 0.250 0.245 0.5 0.3 15 30 150
0.500 70 0.093 148 0.160 0.340 0.340 0.5 0.3 15 30 150
0.625 47 0.115 158 0.160 0.700 0.400 0.7 0.3 15 30 150
0.750 35 0.115 164 0.160 0.700 0.460 1.4 0.3 15 30 150
1.000 30 0.120 175 0.160 0.750 0.580 1.6 0.3 15 30 150
Version 4.5 released on 13May13
StartCur EndCur CurUpTime CurDnTime GOffDelay
100 amp 100 amp 0.60 sec 0.60 sec 0.35 sec
10
PicNo

Gas
Shield
CFH
Start/Cut
psi
Cut
144
NCode
Plasma Gas
AHC
Pierce
ting
Cut-
Delay
Delay
psi
Start
sec
sec
in
Height
in
Pierce
Height
in
Initial
Height
N2
ARG
ARG
MARKING
or
Arc
age
Volt-
in
Kerf
MARKING
Material Stainless Steel
Gas Select 6
Cut Gas ARG
Start Gas ARG
Amperes 260
Shield Gas AIR
ESAB Welding and Cutting Products
First Row Mark Amp: 25
Thick-
Speed
ness
in/m
in
89
1.000 100 0.000 65 0.160 0.180 0.180 0.0 0.1 30 30 141
12 amp 25 amp 0.10 sec 0.10 sec 0.35 sec
StartCur EndCur CurUpTime CurDnTime GOffDelay
33
PicNo
Version 4.5 released on 13May13

Gas
Shield
CFH
Start/Cut
psi
Cut
144
NCode
Plasma Gas
AHC
Pierce
ting
Cut-
Delay
Delay
psi
Start
sec
sec
in
Height
in
Pierce
Height
in
Initial
Height
Arc
age
Volt-
in
Kerf
PRODUCTION
Material Stainless Steel
Gas Select 3
ESAB Welding and Cutting Products
Cut Gas N2
Start Gas N2
Amperes 260
Shield Gas N2
Thick-
Speed
ness
in/m
in
90
0.250 170 0.105 140 0.160 0.250 0.170 0.5 0.3 15 40 150
0.375 135 0.105 150 0.160 0.250 0.245 0.5 0.3 15 40 150
0.500 100 0.105 160 0.160 0.320 0.320 0.6 0.3 15 40 150
0.625 85 0.115 168 0.160 0.750 0.385 0.8 0.3 15 45 200
0.750 68 0.115 175 0.160 0.750 0.450 1.0 0.3 15 40 200
1.000 40 0.150 190 0.167 0.750 0.590 1.2 0.3 15 45 200
Version 4.5 released on 13May13
StartCur EndCur CurUpTime CurDnTime GOffDelay
150 amp 150 amp 0.60 sec 0.60 sec 0.35 sec
33
PicNo

Gas
Shield
CFH
Start/Cut
psi
Cut
145
NCode
Plasma Gas
AHC
Pierce
ting
Cut-
Delay
Delay
psi
Start
sec
sec
in
Height
in
Pierce
Height
in
Initial
Height
N2
ARG
ARG
MARKING
or
Arc
age
Volt-
in
Kerf
MARKING
Material Stainless Steel
Gas Select 6
Cut Gas ARG
Start Gas ARG
Amperes 360
Shield Gas AIR
ESAB Welding and Cutting Products
First Row Mark Amp: 18
Thick-
Speed
ness
in/m
in
91
1.000 100 0.000 62 0.160 0.183 0.183 0.0 0.1 30 30 141
18 amp 18 amp 0.10 sec 0.10 sec 0.35 sec
StartCur EndCur CurUpTime CurDnTime GOffDelay
34
PicNo
Version 4.5 released on 13May13

Gas
Shield
CFH
Start/Cut
psi
Cut
145
NCode
Plasma Gas
AHC
Pierce
ting
Cut-
Delay
Delay
psi
Start
sec
sec
in
Height
in
Pierce
Height
in
Initial
Height
Arc
age
Volt-
in
Kerf
PRODUCTION
Material Stainless Steel
Gas Select 3
ESAB Welding and Cutting Products
Cut Gas N2
Start Gas N2
Amperes 360
Shield Gas N2
Thick-
Speed
ness
in/m
in
92
0.250 220 0.115 135 0.160 0.250 0.110 0.2 0.1 5 40 100
0.375 140 0.130 135 0.160 0.250 0.160 0.2 0.1 5 40 100
0.500 115 0.135 150 0.160 0.300 0.260 0.2 0.1 5 40 100
0.625 90 0.140 157 0.160 0.400 0.310 0.5 0.3 5 40 200
0.750 70 0.150 163 0.160 0.500 0.360 0.6 0.2 5 40 200
1.000 38 0.175 175 0.160 0.750 0.490 1.0 0.3 5 40 200
Version 4.5 released on 13May13
StartCur EndCur CurUpTime CurDnTime GOffDelay
150 amp 150 amp 0.60 sec 0.60 sec 0.35 sec
34
PicNo

Gas
Shield
CFH
Start/Cut
psi
Cut
146
NCode
Plasma Gas
AHC
Pierce
ting
Cut-
Delay
Delay
psi
Start
sec
sec
in
Height
in
Pierce
Height
in
Initial
Height
N2
ARG
ARG
MARKING
or
Arc
age
Volt-
in
Kerf
MARKING
Material Stainless Steel
Gas Select 6
Cut Gas ARG
Start Gas ARG
Amperes 450
Shield Gas AIR
ESAB Welding and Cutting Products
in/m
Speed
in
ness
First Row Mark Amp: 35
Thick-
93
1.000 100 0.000 54 0.160 0.130 0.130 0.0 0.1 30 30 140
Version 4.5 released on 13May13
18 amp 35 amp 0.10 sec 0.10 sec 0.35 sec
StartCur EndCur CurUpTime CurDnTime GOffDelay
14
PicNo

Gas
Shield
CFH
Start/Cut
psi
Cut
146
NCode
Plasma Gas
AHC
Pierce
ting
Cut-
Delay
Delay
psi
Start
sec
sec
in
Height
in
Pierce
Height
in
Initial
Height
Arc
age
Volt-
in
Kerf
PRODUCTION
Material Stainless Steel
Gas Select 3
ESAB Welding and Cutting Products
Cut Gas N2
Start Gas N2
Amperes 450
Shield Gas N2
Thick-
Speed
ness
in/m
in
94
0.750 85 0.160 160 0.160 0.750 0.410 0.8 0.3 5 30 250
1.000 55 0.180 175 0.160 0.750 0.540 1.0 0.3 5 30 250
1.250 40 0.215 195 0.160 0.800 0.610 1.3 0.3 5 40 300
1.500 30 0.240 198 0.160 1.000 0.710 2.2 0.5 5 40 300
StartCur EndCur CurUpTime CurDnTime GOffDelay
200 amp 200 amp 0.60 sec 0.60 sec 0.45 sec
14
PicNo
Version 4.5 released on 13May13

Gas
Shield
CFH
Start/Cut
psi
Cut
160
NCode
Plasma Gas
AHC
Pierce
ting
Cut-
Delay
Delay
psi
Start
sec
sec
in
Height
in
Pierce
Height
in
Initial
Height
N2
ARG
ARG
MARKING
or
Arc
age
Volt-
in
Kerf
MARKING
Material Stainless Steel
Gas Select 6
Cut Gas ARG
Start Gas ARG
Amperes 450
Shield Gas AIR
ESAB Welding and Cutting Products
in/m
Speed
in
ness
First Row Mark Amp: 35
Thick-
95
1.000 100 0.000 54 0.160 0.130 0.130 0.0 0.1 30 30 140
Version 4.5 released on 13May13
18 amp 35 amp 0.10 sec 0.10 sec 0.35 sec
StartCur EndCur CurUpTime CurDnTime GOffDelay
45
PicNo

Gas
Shield
CFH
Start/Cut
psi
Cut
160
NCode
Plasma Gas
AHC
Pierce
ting
Cut-
Delay
Delay
psi
Start
sec
sec
in
Height
in
Pierce
Height
in
Initial
Height
Arc
age
Volt-
in
Kerf
PRODUCTION
Material Stainless Steel
Gas Select 5
ESAB Welding and Cutting Products
Cut Gas H35
Start Gas N2
Amperes 450
Shield Gas N2
NOTE: Piercing not recommended on thicknesses greater than 1.5”
Pierce delay indicated for edge starts greater than 1.5”
Thick-
Speed
ness
in/m
in
96
0.750 45 0.235 170 0.160 0.700 0.610 1.0 0.5 5 45 250
1.000 42 0.225 175 0.160 0.750 0.660 1.0 0.5 5 45 250
1.250 38 0.250 185 0.160 1.000 0.800 1.4 0.6 5 45 250
1.500 33 0.260 187 0.160 1.000 0.780 1.6 0.8 5 45 250
1.750 28 0.285 190 0.160 1.000 0.800 1.6 0.8 5 45 250
3.000 10 0.340 205 0.160 1.000 0.770 2.5 2.0 5 45 250
2.500 18 0.340 195 0.160 1.000 0.750 1.5 2.0 5 45 250
2.000 22 0.295 190 0.160 1.000 0.830 1.5 2.0 5 45 250
Version 4.5 released on 13May13
StartCur EndCur CurUpTime CurDnTime GOffDelay
200 amp 200 amp 0.60 sec 0.60 sec 0.45 sec
45
PicNo

Gas
Shield
CFH
Start/Cut
psi
Cut
150
NCode
Plasma Gas
AHC
Pierce
ting
Cut-
Delay
Delay
psi
Start
sec
sec
in
Height
in
Pierce
Height
in
Initial
Height
N2
ARG
ARG
MARKING
or
Arc
age
Volt-
in
Kerf
MARKING
Material Stainless Steel
Gas Select 6
Cut Gas ARG
Start Gas ARG
Amperes 450
Shield Gas AIR
ESAB Welding and Cutting Products
in/m
Speed
in
ness
First Row Mark Amp: 35
Thick-
97
1.000 100 0.000 54 0.160 0.130 0.130 0.0 0.1 30 30 140
Version 4.5 released on 13May13
18 amp 35 amp 0.10 sec 0.10 sec 0.35 sec
StartCur EndCur CurUpTime CurDnTime GOffDelay
14
PicNo

Gas
Shield
CFH
Start/Cut
psi
Cut
150
NCode
PRODUCTION
N2N2N2
or
Plasma Gas
AHC
Pierce
ting
Cut-
Delay
Delay
psi
Start
sec
sec
in
Height
in
Pierce
Height
in
Initial
Height
Arc
age
Volt-
in
Kerf
PRODUCTION
Material Stainless Steel
Gas Select 10
ESAB Welding and Cutting Products
Cut Gas N2
Start Gas N2
Amperes 450
Shield Gas AIR
in/m
Speed
in
ness
NOTE: Piercing not recommended on thicknesses greater than 1.5”
Pierce delay indicated for edge starts greater than 1.5”
Thick-
0.750 85 0.160 160 0.160 0.750 0.310 0.3 0.5 5 30 350
1.000 55 0.180 175 0.160 0.750 0.250 0.5 0.6 5 30 350
1.250 40 0.215 195 0.160 0.800 0.400 0.5 0.7 5 40 350
98
1.500 30 0.220 198 0.160 0.800 0.480 0.7 0.8 5 40 350
1.750 20 0.210 185 0.160 0.800 0.560 1.0 0.8 5 40 350
Version 4.5 released on 13May13
StartCur EndCur CurUpTime CurDnTime GOffDelay
200 amp 200 amp 0.60 sec 0.60 sec 0.45 sec
14
PicNo

Gas
Shield
CFH
Start/Cut
psi
Cut
148
NCode
Plasma Gas
AHC
Pierce
ting
Cut-
Delay
Delay
psi
Start
sec
sec
in
Height
in
Pierce
Height
in
Initial
Height
Arc
age
Volt-
in
Kerf
PRODUCTION
Material Stainless Steel
Gas Select 3
ESAB Welding and Cutting Products
Cut Gas N2
Start Gas N2
Amperes 600
Shield Gas N2
Thick-
Speed
ness
in/m
in
99
1.000 60 0.215 155 0.160 0.750 0.240 0.7 0.3 5 30 250
1.250 45 0.240 180 0.160 0.800 0.680 1.3 0.3 5 30 350
1.500 32 0.255 200 0.160 1.000 0.830 1.8 0.5 5 30 350
2.000 22 0.280 210 0.160 1.000 0.900 1.8 0.5 5 40 250
StartCur EndCur CurUpTime CurDnTime GOffDelay
200 amp 200 amp 0.60 sec 0.60 sec 0.35 sec
12
PicNo
Version 4.5 released on 13May13

Gas
Shield
CFH
Start/Cut
psi
Cut
147
NCode
Plasma Gas
AHC
Pierce
ting
Cut-
Delay
Delay
psi
Start
sec
sec
in
Height
in
Pierce
Height
in
Initial
Height
Arc
age
Volt-
in
Kerf
PRODUCTION
Material Stainless Steel
Gas Select 5
ESAB Welding and Cutting Products
Cut Gas H35
Start Gas N2
Amperes 600
Shield Gas N2
in/m
Speed
in
ness
NOTE: Piercing not recommended on thicknesses greater than 2.0”
Pierce delay indicated for edge starts greater than 2.0”
Thick-
1.000 40 0.310 178 0.160 0.750 0.510 0.5 0.2 5 50 350
1.250 35 0.330 185 0.160 1.000 0.620 0.8 0.2 5 50 350
1.500 30 0.345 190 0.160 1.000 0.660 0.9 0.3 5 50 350
1.750 20 0.355 204 0.160 1.000 0.948 0.9 0.3 5 50 350
100
2.000 20 0.410 205 0.160 1.000 0.850 1.5 0.3 5 50 350
3.000 10 0.450 205 0.160 1.000 0.680 1.5 0.5 5 50 300
Version 4.5 released on 13May13
StartCur EndCur CurUpTime CurDnTime GOffDelay
200 amp 200 amp 0.60 sec 0.60 sec 0.45 sec
12
PicNo
 Loading...
Loading...