
ESAB Fabricator® 141i
3-IN-1 Multi Process
Welding Systems
Operating
Manual
3163339
Révision : AA Issue Date: September 10, 2015 Manual No.: 0-5420
esab.com

WE APPRECIATE YOUR BUSINESS!
Congratulations on your new ESAB product. We are proud to have you as our customer and will strive to
provide you with the best service and reliability in the industry. This product is backed by our extensive
warranty and world-wide service network. To locate your nearest distributor or service agency, visit us on
the web at www.esab.com.
This Operating Manual has been designed to instruct you on the correct use and operation of your ESAB
product. Your satisfaction with this product and its safe operation is our ultimate concern. Therefore please
take the time to read the entire manual, especially the Safety Precautions. They will help you to avoid potential
hazards that may exist when working with this product.
YOU ARE IN GOOD COMPANY!
The Brand of Choice for Contractors and Fabricators Worldwide.
ESAB is a Global Brand of manual and automation Plasma Cutting Products.
We distinguish ourselves from our competition through market-leading, dependable products that have stood
the test of time. We pride ourselves on technical innovation, competitive prices, excellent delivery, superior
customer service and technical support, together with excellence in sales and marketing expertise.
Above all, we are committed to developing technologically advanced products to achieve a safer working
environment within the welding industry.

WARNING
!
Plasma Cutting Power Supply
ESAB Fabricator® 141i 3-in-1 Multi Process Welding Systems™
Operating Manual Number 0-5420
Published by:
ESAB
2800 Airport Rd.
Denton, TX 76208
www.esab.com
Copyright 2015 by ESAB
Read and understand this entire Manual and your employer’s safety practices before installing, operating, or servicing the equipment.
While the information contained in this Manual represents the Manufacturer's best judgement,
the Manufacturer assumes no liability for its use.
All rights reserved.
Reproduction of this work, in whole or in part, without written permission of the
publisher is prohibited.
The publisher does not assume and hereby disclaims any liability to any party for
any loss or damage caused by any error or omission in this Manual, whether such
error results from negligence, accident, or any other cause.
Original Publication Date: September 10, 2015
Revision Date:
Record the following information for Warranty purposes:
Where Purchased:_______________________________ __________
Purchase Date:__________________________________ __________
Power Supply Serial #:___________________________ __________
Torch Serial #:___________________________________ __________

Be sure this information reaches the operator.
You can get extra copies through your supplier.
CAUTION
These INSTRUCTIONS are for experienced operators. If you are not fully familiar
with the principles of operation and safe practices for arc welding and cutting equipment, we urge you to read our booklet, “Precautions and Safe Practices for Arc
Welding, Cutting, and Gouging,” Form 52-529. Do NOT permit untrained persons to
install, operate, or maintain this equipment. Do NOT attempt to install or operate this
equipment until you have read and fully understand these instructions. If you do not
fully understand these instructions, contact your supplier for further information. Be
sure to read the Safety Precautions before installing or operating this equipment.
USER RESPONSIBILITY
This equipment will perform in conformity with the description thereof contained in this manual and accompanying labels and/or inserts when installed, operated, maintained and repaired in accordance with the instructions
provided. This equipment must be checked periodically. Malfunctioning or poorly maintained equipment should not be
used. Parts that are broken, missing, worn, distorted or contaminated should be replaced immediately. Should such repair or replacement become necessary, the manufacturer recommends that a telephone or written request for service
advice be made to the Authorized Distributor from whom it was purchased.
This equipment or any of its parts should not be altered without the prior written approval of the manufacturer.
The user of this equipment shall have the sole responsibility for any malfunction which results from improper use,
faulty maintenance, damage, improper repair or alteration by anyone other than the manufacturer or a service facility
designated by the manufacturer.
!
READ AND UNDERSTAND THE INSTRUCTION MANUAL BEFORE INSTALLING OR
OPERATING.
PROTECT YOURSELF AND OTHERS!

TABLE OF CONTENTS
SECTION 1: SAFETY ........................................................................................ 1-1
1.0 Safety Precautions .......................................................................................... 1-1
SECTION 2 SYSTEM:
INTRODUCTION ..................................................................................... 2-1
2.01 How To Use This Manual ................................................................................ 2-1
2.02 Equipment Identification ................................................................................. 2-1
2.03 Receipt Of Equipment ..................................................................................... 2-1
2.04 Description ..................................................................................................... 2-1
2.05 Transportation Methods ........................................................................................ 2-2
2.06 User Responsibility ............................................................................................... 2-2
2.07 Fabricator 141i Portable System Package (Part No. W1003141) .......................... 2-2
2.08 Duty Cycle ............................................................................................................. 2-3
2.09 Specifications ....................................................................................................... 2-3
SECTION 3: INSTALLATION, OPERATION AND SETUP ................................................ 3-1
3.01 Environment ................................................................................................... 3-1
3.02 Location .......................................................................................................... 3-1
3.03 Ventilation ....................................................................................................... 3-1
3.04 Electricity Supply Voltage .............................................................................. 3-1
3.05 Electromagnetic Compatibility ........................................................................ 3-3
3.06 Victor Flowmeter/ Regulator ........................................................................... 3-4
3.07 Leak Testing the System ................................................................................. 3-5
3.08 When You Finish Using the Flowmeter/ Regulator ..........................................................3-5
3.09
3.10 Power Source Controls, Indicators and Features ............................................ 3-6
3.11 Attaching the Fusion 140A MIG Gun ............................................................. 3-11
3.12 Inserting Wire into the Wire Feed Mechanism .............................................. 3-11
3.13 Installing 4" (100mm) Diameter Spool ......................................................... 3-12
3.14 Installing 8" (200mm) Diameter Spool .......................................................... 3-13
3.15 Feed Roller Pressure Adjustment .................................................................. 3-14
3.16 Changing the Feed Roll ................................................................................. 3-14
3.17 Wire Reel Brake ............................................................................................ 3-14
Storage of the Flowmeter/ Regulator ..................................................................... 3-5
3.18 Flowmeter/ Regulator Operation ................................................................... 3-14
3.19 Setup for MIG (GMAW) Welding with Gas Shielded MIG Wire ..................... 3-15
3.20 Setup for MIG (FCAW) Welding with Flux Core (Gasless) Wire .................... 3-16

TABLE OF CONTENTS
3.21 Setup for SPOOL GUN MIG (GMAW) Welding with Gas Shielded MIG Wire . 3-17
3.22 Setup for LIFT TIG (GTAW) Welding ............................................................. 3-18
3.23 Setup for STICK (SMAW) Welding .............................................................. 3-19
3.24 Torch Adapter Thumb Screw Replacement ................................................... 3-20
SECTION 4: BASIC WELDING GUIDE .................................................................... 4-1
4.01 MIG (GMAW/FCAW) Basic Welding Technique ............................................... 4-1
4.02 MIG (GMAW/FCAW) Welding Troubleshooting ............................................... 4-5
4.03 Stick (SMAW) Basic Welding Technique ......................................................... 4-9
4.04 Effects of Stick Welding Various Materials ...................................................... 4-9
4.05 Stick (SMAW) Welding Troubleshooting ....................................................... 4-16
4.06 TIG (GTAW) Basic Welding Technique .......................................................... 4-18
4.07 TIG (GTAW) Welding Problems ..................................................................... 4-20
SECTION 5:
POWER SOURCE PROBLEMS AND ROUTINE SERVICE REQUIREMENTS .................... 5-1
5.01 Power Source Problems ................................................................................. 5-1
5.02 Routine Service............................................................................................... 5-2
5.03 Cleaning the Welding Power Source ............................................................... 5-3
5.04 Cleaning the Feed Rolls ................................................................................... 5-3
5.05 Volt-Ampere Curves ........................................................................................ 5-4
SECTION 6: KEY SPARE PARTS .......................................................................... 6-1
6.01 Tweco Fusion 140A MIG Gun Parts ................................................................ 6-1
6.02 Power Source ................................................................................................. 6-2
6.03 Hardware List ................................................................................................. 6-4
APPENDIX ................................................................................................... A-1
APPENDIX: FABRICATOR 141I CIRCUIT DIAGRAM .................................................... A-2
REVISION HISTORY ........................................................................................ A-4
INTERNATIONAL CONTACT INFORMATION ................................................. REAR COVER

ESAB FABRICATOR 141i
SECTION 1: SAFETY
1.0 Safety Precautions
Users of ESAB welding and plasma cutting equipment have the ultimate responsibility for ensuring that anyone who works
on or near the equipment observes all the relevant safety precautions. Safety precautions must meet the requirements
that apply to this type of welding or plasma cutting equipment. The following recommendations should be observed in
addition to the standard regulations that apply to the workplace.
All work must be carried out by trained personnel well acquainted with the operation of the welding or plasma cutting
equipment. Incorrect operation of the equipment may lead to hazardous situations which can result in injury to the
operator and damage to the equipment.
1. Anyone who uses welding or plasma cutting equipment must be familiar with:
- its operation
- location of emergency stops
- its function
- relevant safety precautions
- welding and / or plasma cutting
2. The operator must ensure that:
- no unauthorized person stationed within the working area of the equipment when it is started up.
- no one is unprotected when the arc is struck.
3. The workplace must:
- be suitable for the purpose
- be free from drafts
4. Personal safety equipment:
- Always wear recommended personal safety equipment, such as safety glasses, flame proof
clothing, safety gloves.
- Do not wear loose fitting items, such as scarves, bracelets, rings, etc., which could become
trapped or cause burns.
5. General precautions:
- Make sure the return cable is connected securely.
- Work on high voltage equipment may only be carried out by a qualified electrician.
- Appropriate fire extinguishing equipment must be clearly marked and close at hand.
- Lubrication and maintenance must not be carried out on the equipment during operation.
Dispose of electronic equipment at the recycling facility!
In observance of European Directive 2002/96/EC on Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment and its
implementation in accordance with national law, electrical and/or electronic equipment that has reached
the end of its life must be disposed of at a recycling facility.
As the person responsible for the equipment, it is your responsibility to obtain information on approved
collection stations.
For further information contact the nearest ESAB dealer.
ESAB can provide you with all necessary cutting protection and accessories.
Manual 0-5420 1-1 SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS AND WARNINGS

ESAB FABRICATOR 141i
WARNING
ELECTRIC SHOCK - Can kill.
- Install and earth (ground) the welding or plasma cutting unit in accordance with applicable standards.
- Do not touch live electrical parts or electrodes with bare skin, wet gloves or wet clothing.
- Insulate yourself from earth and the workpiece.
- Ensure your working stance is safe.
FUMES AND GASES - Can be dangerous to health.
- Keep your head out of the fumes.
- Use ventilation, extraction at the arc, or both, to take fumes and gases away from
your breathing zone and the general area.
ARC R AYS - Can injure eyes and burn skin.
- Protect your eyes and body. Use the correct welding / plasma cutting screen and
filter lens and wear protective clothing.
- Protect bystanders with suitable screens or curtains.
FIRE HAZARD
- Sparks (spatter) can cause fire. Make sure therefore that there are no inflammable
materials nearby.
Arc welding and cutting can be injurious to yourself and others.
Take precautions when welding and cutting. Ask for your employer's
safety practices which should be based on manufacturers' hazard
data.
NOISE - Excessive noise can damage hearing.
- Protect your ears. Use earmuffs or other hearing protection.
- Warn bystanders of the risk.
MALFUNCTION - Call for expert assistance in the event of malfunction.
READ AND UNDERSTAND THE INSTRUCTION MANUAL BEFORE INSTALLING OR OPERAT-
ING.
PROTECT YOURSELF AND OTHERS!
Do not use the power source for thawing frozen pipes.
WARNING
CAUTION
CAUTION
Class A equipment is not intended for use in residential locations
where the electrical power is provided by the public low-voltage
supply system. There may be potential difficulties in ensuring
electromagnetic compatibility of class A equipment in those locations, due to conducted as well as radiated disturbances.
This product is solely intended for metal removal. Any other use
may result in personal injury and / or equipment damage.
CAUTION
SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS AND WARNINGS 1-2 Manual 0-5420
Read and understand the instruction manual before
installing or operating.
!

ESAB FABRICATOR 141i
SECTION 2 SYSTEM:
INTRODUCTION
2.01 How To Use This Manual
This Owner’s Manual applies to just specification or part numbers listed on page i.
To ensure safe operation, read the entire manual, including the
chapter on safety instructions and warnings.
Throughout this manual, the words WARNING, CAUTION,
DANGER, and NOTE may appear. Pay particular attention to
the information provided under these headings. These special
annotations are easily recognized as follows:
NOTE!
An operation, procedure, or background
information which requires additional
emphasis or is helpful in efficient operation of the system.
CAUTION
!
A procedure which, if not properly followed, may cause damage to the equipment.
2.02 Equipment Identification
The unit’s identification number (specification or part number), model, and serial number usually appear on a data tag
attached to the rear panel. Equipment which does not have
a data tag such as torch and cable assemblies are identified only by the specification or part number printed on
loosely attached card or the shipping container. Record these
numbers on the bottom of page i for future reference.
2.03 Receipt Of Equipment
When you receive the equipment, check it against the invoice
to make sure it is complete and inspect the equipment for
possible damage due to shipping. If there is any damage,
notify the carrier immediately to file a claim. Furnish complete
information concerning damage claims or shipping errors to
the location in your area listed in the inside back cover of this
manual.
Include all equipment identification numbers as described
above along with a full description of the parts in error.
Move the equipment to the installation site before un-crating
the unit. Use care to avoid damaging the equipment when using bars, hammers, etc., to un-crate the unit.
2.04 Description
WARNING
!
!
Additional copies of this manual may be purchased by contacting ESAB at the address and phone number in your area listed
on back cover of this manual. Include the Owner’s Manual
number and equipment identification numbers.
Electronic copies of this manual can also be downloaded at no
charge in Acrobat PDF format by going to the ESAB web site
listed below
http://www.esab.com
A procedure which, if not properly followed, may cause injury to the operator or
others in the operating area.
WARNING
Gives information regarding possible
electrical shock injury. Warnings will be
enclosed in a box such as this.
DANGER
Means immediate hazards which, if not
avoided, will result in immediate, serious
personal injury or loss of life.
The ESAB Fabricator 141i is a self contained single phase multi
process welding system that is capable of performing MIG
(GMAW/FCAW), STICK (SMAW) and LIFT TIG (GTAW) welding
processes. The Power Source is equipped with an integrated
wire feed unit, digital voltage and amperage meters, and a
host of other features in order to fully satisfy the broad operating needs of the modern welding professional. The Power
Source is also fully compliant to Standard CSA E60974-1-00
and UL 60974.1.
The Fabricator 141i MIG provides excellent welding performance across a broad range of applications when used with
the correct welding consumables and procedures. The following instructions detail how to correctly and safely set up the
machine and give guidelines on gaining the best efficiency and
quality from the Power Source. Please read these instructions
thoroughly before using this equipment.
Manual 0-5420 2-1 INTRODUCTION

ESAB FABRICATOR 141i
Comes Complete With:
• Fabricator 141i Power Source
• 140 Amp MIG Gun
• Regulator/Flowmeter & Hose
• ESAB Electrode Holder & Ground Clamp
• Drive Rolls & Contact Tips
• Sample Electrodes & Shoulder Strap
• 20A to 15A Power Cord Adapter
• Operator Manual & CD
A-12917
2.05 Transportation Methods
WARNING
!
2.06 User Responsibility
This equipment will perform as per the information contained herein when installed, operated, maintained and repaired in accordance with the instructions provided. This equipment must be checked periodically. Defective equipment (including welding
leads) should not be used. Parts that are broken, missing, plainly worn, distorted or contaminated, should be replaced immediately.
Should such repairs or replacements become necessary, it is recommended that such repairs be carried out by appropriately qualified persons approved by ESAB. Advice in this regard can be obtained by contacting an Accredited ESAB Distributor.
This equipment or any of its parts should not be altered from standard specification without prior written approval of ESAB. The
user of this equipment shall have the sole responsibility for any malfunction which results from improper use or unauthorized
modification from standard specification, faulty maintenance, damage or improper repair by anyone other than appropriately qualified persons approved by ESAB.
2.07 Fabricator 141i Portable System Package (Part No. W1003141)
Disconnect input power conductors from de-energized supply line before moving the
welding Power Source.
Lift Power Source with handle on top of case. Use handcart or similar device of adequate
capacity. If using a fork lift vehicle, secure the Power Source on a proper skid before
transporting.
INTRODUCTION 2-2 Manual 0-5420
ESAB FABRICATOR 141i
Fabricator 141i
DESCRIPTION FABRICATOR 141i MULTI PROCESS 3 IN 1 WELDER
Power Source Part No. W1003140
Power Source Dimensions H16.14” x W8.27” x D17.72” (410mm x 210mm x 450mm)
Power Source Weight 32.2lb(14.6kg)
Cooling Fan Cooled
Welder Type Multi Process Welding System
Output Terminal Type DinseTM 25
Standards CSA E60974-1-00 / UL60974-1 / IEC 60974-1
Number of Phases Single Phase
Nominal Supply Voltage 115V AC
Supply Voltage Range 95-140V AC
Supply Frequency 50/60Hz
Welding Current Range (MIG Mode) 10- 90A
Welding Current Range (LIFT TIG Mode) 10- 140A
Welding Current Range (STICK Mode) 10- 90A
Wirefeed Speed Range 95-390 IPM
MIG Welding Voltage Range 10-19V DC
Nominal OCV 53V DC
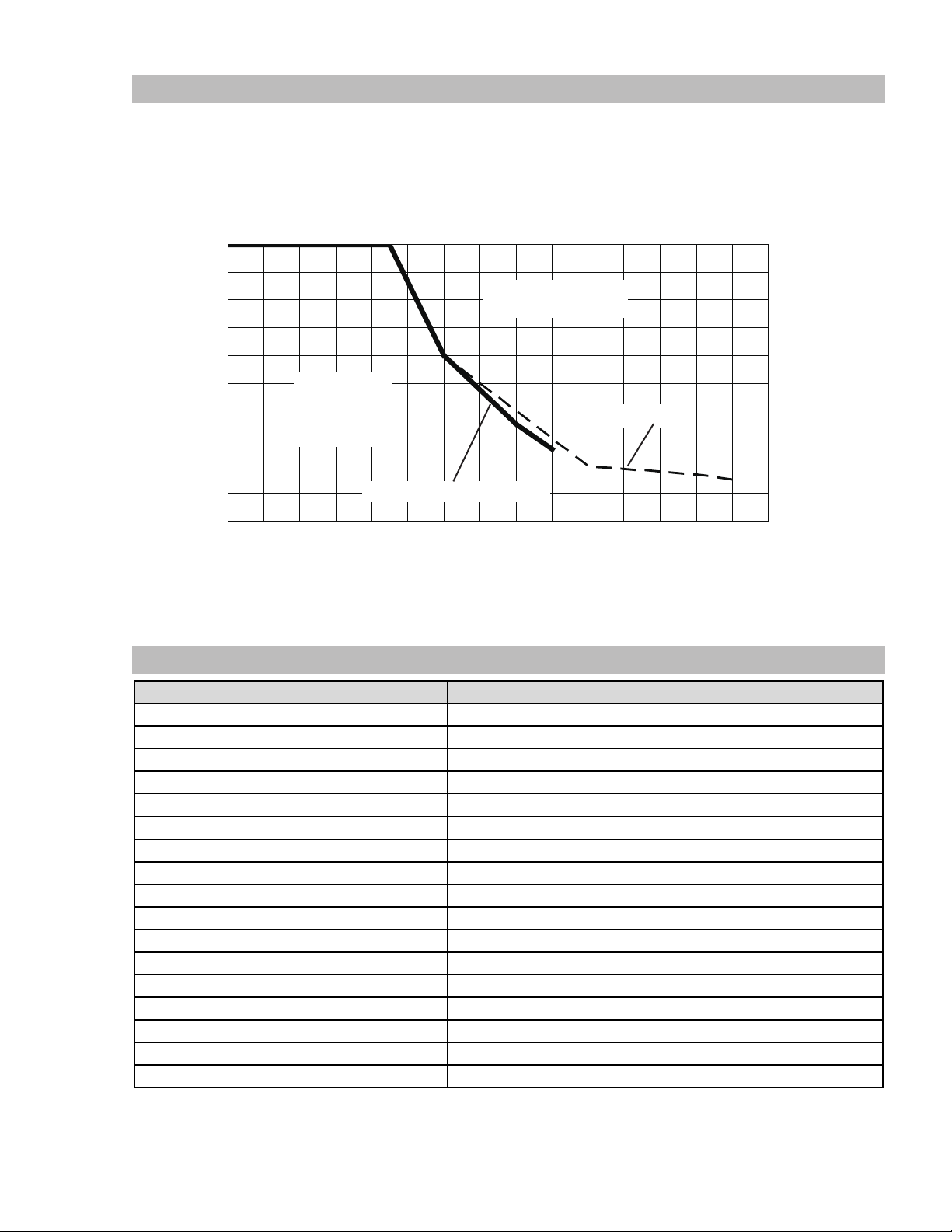
2.08 Duty Cycle
The rated duty cycle of a Welding Power Source, is a statement of the time it may be operated at its rated welding current output
without exceeding the temperature limits of the insulation of the component parts. To explain the 10 minute duty cycle period the
following example is used. Suppose a Welding Power Source is designed to operate at a 20% duty cycle, 100 amperes at 19 volts.
This means that it has been designed and built to provide the rated amperage (100 A) for 2 minutes, i.e. arc welding time, out of
every 10 minute period (20% of 10 minutes is 2 minutes). During the other 8 minutes of the 10 minute period the Welding Power
Source must idle and be allowed to cool.
100
90
80
70
60
50
40
30
Duty Cycle (percentage)
20
10
0
0102030405060708090100 110120 130140 150
2.09 Specifications
Safe
Operating
Region
STICK (SMAW)/ MIG (GMAW/ FCAW)
Welding Current (amps)
TIG (GTAW)
Art # A-11276_AB
Figure 2-1: Fabricator 141i Duty Cycle
Manual 0-5420 2-3 INTRODUCTION

ESAB FABRICATOR 141i
This Page Intentionally Blank
INTRODUCTION 2-4 Manual 0-5420

ESAB FABRICATOR 141i
SECTION 3: INSTALLATION,
OPERATION AND SETUP
3.01 Environment
This Power Source is designed for use in environments with
increased hazard of electric shock.
A. Examples of environments with increased hazard of
electric shock are:
1. In locations in which freedom of movement is restricted, so that the operator is forced to perform the
work in a cramped (kneeling, sitting or lying) position
with physical contact with conductive parts.
2. In locations which are fully or partially limited by
conductive elements, and in which there is a high risk
of unavoidable or accidental contact by the operator.
3. In wet or damp hot locations where humidity or
perspiration considerable reduces the skin resistance
of the human body and the insulation properties of
accessories.
B. Environments with increased hazard of electric shock
do not include places where electrically conductive parts
have been insulated.
3.02 Location
Be sure to locate the welder according to the following guidelines:
A. In areas, free from moisture and dust.
B. Ambient temperature between 32 to 104° F (0 to 40° C).
C. In areas, free from oil, steam and corrosive gases.
D. In areas, not subjected to abnormal vibration or shock.
E. In areas, not exposed to direct sunlight or rain.
F. Place at a distance of 12"(300mm) or more from walls
or similar that could restrict natural air flow for cooling.
G. The enclosure design of this Power Source meets the
requirements of IP23S as outlined in EN 60529. This provides adequate protection against solid objects (greater
than 1/2", 12mm), and direct protection from vertical
drops. Under no circumstances should the Power Source
be operated or connected in a micro environment that
will exceed the stated conditions. For further information
please refer to EN 60529.
H. Precautions must be taken against the power source
toppling over. The power source must be located on a
suitable horizontal surface in the upright position when
in use.
WARNING
This equipment should be electrically
connected by a qualified electrician.
3.03 Ventilation
!
WARNING
Since the inhalation of welding fumes can
be harmful, ensure that the welding area
is effectively ventilated.
3.04 Electricity Supply Voltage
CAUTION
!
SHUT DOWN welding Power Source, disconnect input power
employing lockout/tagging procedures. Lock-out/tagging procedures consist of padlocking line disconnect switch in open
position, removing fuses from fuse box, or shutting off and
red-tagging circuit breaker or other disconnecting device.
Electrical Input Requirements
Operate the welding Power Source from a single-phase 50/60
Hz, AC power supply. The input voltage must match one of the
electrical input voltages shown on the input data label on the
unit nameplate. Contact the local electric utility for information about the type of electrical service available, how proper
connections should be made, and inspection required. The line
disconnect switch provides a safe and convenient means to
completely remove all electrical power from the welding power
The Electricity Supply voltage should be
within 95-140V AC. Too low a voltage may
cause poor welding performance in STICK
mode. Too high a supply voltage will cause
components to overheat and possibly fail. The
Welding Power Source must be:
• Correctly installed, if necessary, by a qualified electrician.
• Correctly earthed (electrically) in accordance with local regulations.
• Connected to the correct size power point
and fuse as per the Specifications on page
2-4.
WARNING
The Fabricator 141i must be electrically connected by a qualified electrical trades-person. Damage to the PCA
(Power Control Assembly) could occur
if 140 VAC or higher is applied to the
Primary Power Cable.
WARNING
ELECTRIC SHOCK can kill; SIGNIFICANT
DC VOLTAGE is present after removal of
input power. DO NOT TOUCH live electrical parts.
Manual 0-5420 3-1 INSTALLATION, OPERATION AND SETUP

ESAB FABRICATOR 141i
source whenever necessary to inspect or service the unit.
Do not connect an input (WHITE or BLACK) conductor to the ground terminal.
Do not connect the ground (GREEN) conductor to an input line terminal.
• Correctly installed, if necessary, by a qualied electrician.
• Correctly earthed (electrically) in accordance with local regulations.
• Connected to the correct size power point, fuse and primary supply lead based on Table 3-1. Refer to Table 3-1.
WARNING
An electrical shock or fire hazard is probable if the following electrical service guide recommendations
Supply Voltage
Input Current at Maximum Output
Maximum Recommended Fuse* or Circuit Breaker Rating
*Time Delay Fuse, UL class RK5. Refer to UL248
Maximum Recommended Fuse^ or Circuit Breaker Rating
^Normal Operating , UL class K5. Refer to UL248
Single Phase Generator Requirement 5 KW
Minimum Recommended Input Cable Size 12AWG
Maximum Recommended Input Cable Length 10ft (3m)
Minimum Recommended Grounding Cable Size 12AWG
are not followed. These recommendations are for a dedicated branch circuit sized for the rated output
and duty cycle of the Welding Power Source.
50 / 60 Hz Single Phase Supply
115V AC
28.4 Amps
30 Amps
30 Amps
Table 3-1: Electrical Service Guide
NOTE!
Welding arc outs may be experienced if an extension cord is used when STICK welding when operating
the Power Source on 95 VAC due to the lack of DC voltage at the STICK electrode.
Input Power
Each unit incorporates an INRUSH circuit. When the MAIN CIRCUIT SWITCH is turned on, the inrush circuit provides pre-charging for
the input capacitors. A relay in the Power Control Assembly (PCA) will turn on after the input capacitors have charged to operating
voltage (after approximately 5 seconds)
NOTE!
Damage to the PCA could occur if 140V AC or higher is applied to the Primary Power Cord.
Model
Fabricator
Primary Supply
Cord Size
(Factory Fitted)
12AWG (3.3mm2) 115V/20A 90A@20% 80A@35% 100A@20%
Minimum Primary
Current Circuit Size
(Vin/Amps)
MIG (GMAW/
FCAW)
Current & Duty Cycle
STICK (SMAW)
LIFT TIG
(GTAW)
141i
10AWG (5mm2) 115V/30A 140A@15% 90A@15% 140A@15%
Table 3-2: Primary Circuit Sizes to Achieve Maximum Current
INSTALLATION, OPERATION AND SETUP 3-2 Manual 0-5420

ESAB FABRICATOR 141i
3.05 Electromagnetic Compatibility
WARNING
!
A. Installation and Use - Users Responsibility
The user is responsible for installing and using the weld-
ing equipment according to the manufacturer’s instructions. If electromagnetic disturbances are detected then
it shall be the responsibility of the user of the welding
equipment to resolve the situation with the technical assistance of the manufacturer. In some cases this remedial
action may be as simple as earthing the welding circuit,
see NOTE below. In other cases it could involve constructing an electromagnetic screen enclosing the Welding
Power Source and the work, complete with associated
input filters. In all cases, electromagnetic disturbances
shall be reduced to the point where they are no longer
troublesome.
B. Assessment of Area
Before installing welding equipment, the user shall make
an assessment of potential electromagnetic problems in
the surrounding area. The following shall be taken into
account
1. Other supply cables, control cables, signaling and
2. Radio and television transmitters and receivers.
3. Computer and other control equipment.
4. Safety critical equipment, e.g. guarding of industrial
5. The health of people around, e.g. the use of pacemak-
6. Equipment used for calibration and measurement.
7. The time of day that welding or other activities are to
Extra precautions for Electromagnetic
Compatibility may be required when
this Welding Power Source is used in a
domestic situation.
NOTE!
The welding circuit may or may not be
earthed for safety reasons. Changing the
earthing arrangements should only be
authorized by a person who is competent to assess whether the changes will
increase the risk of injury, e.g. by allowing parallel welding current return paths
which may damage the earth circuits
of other equipment. Further guidance
is given in EN 60974-13 Arc Welding
Equipment - Installation and use (under
preparation)..
telephone cables; above, below and adjacent to the
welding equipment.
equipment.
ers and hearing aids.
be carried out.
8. The compatibility of other equipment in the environment: the user shall ensure that other equipment
being used in the environment is compatible: this may
require additional protection measures.
The size of the surrounding area to be considered will
depend on the structure of the building and other activities
that are taking place. The surrounding area may extend
beyond the boundaries of the premises.
C. Methods of Reducing Electromagnetic Emissions
1. Electricity Supply
Welding equipment should be connected to the Elec-
tricity Supply according to the manufacturer’s recommendations. If interference occurs, it may be necessary to take additional precautions such as filtering of
the Electricity Supply. Consideration should be given
to shielding the supply cable of permanently installed
welding equipment in metallic conduit or equivalent.
Shielding should be electrically continuous throughout
it’s length. The shielding should be connected to the
Welding Power Source so that good electrical contact
is maintained between the conduit and the Welding
Power Source enclosure.
2. Maintenance of Welding Equipment
The welding equipment should be routinely main-
tained according to the manufacturer’s recommendations. All access and service doors and covers should
be closed and properly fastened when the welding
equipment is in operation. The welding equipment
should not be modified in any way except for those
changes and adjustments covered in the manufacturer’s instructions. In particular, the spark gaps of arc
striking and stabilizing devices should be adjusted
and maintained according to the manufacturer’s
recommendations.
3. Welding Cables
The welding cables should be kept as short as pos-
sible and should be positioned close together, running
at or close to the floor level.
4. Equipotential Bonding
Bonding of all metallic components in the welding
installation and adjacent to it should be considered.
However. Metallic components bonded to the work
piece will increase the risk that the operator could
receive a shock by touching the metallic components
and the electrode at the same time. The operator
should be insulated from all such bonded metallic
components.
5. Earthing of the Workpiece
Where the workpiece is not bonded to earth for
electrical safety, nor connected to earth because of
it’s size and position, e.g. ship’s hull or building steelwork, a connection bonding the workpiece to earth
may reduce emissions in some, but not all instances.
Care should be taken to prevent the earthing of the
workpiece increasing the risk of injury to users, or
damage to other electrical equipment. Where necessary, the connection of the workpiece to earth should
Manual 0-5420 3-3 INSTALLATION, OPERATION AND SETUP

ESAB FABRICATOR 141i
A-09414_AC
be made by direct connection to the workpiece, but
in some countries where direct connection is not
permitted, the bonding should be achieved by suitable
capacitance, selected according to national regulations.
6. Screening and Shielding
Selective screening and shielding of other cables
and equipment in the surrounding area may alleviate problems of interference. Screening the entire
welding installation may be considered for special
applications.
3.06 Victor Flowmeter/ Regulator
Flowmeter/ Regulator (Figure 3-1) attached to the cylinder
valve reduces high cylinder pressures to suitable low working
pressures for welding, cutting, and other applications.
conform with the requirements of UL 404,
“Indicating Pressure Gauges for Compressed Gas
Service.”
b) Low pressure gauges must be UL recognized for
the class of flowmeter/ regulator they are being
used on according to UL252A.
WARNING
!
DO NOT use a flowmeter/ regulator that
delivers pressure exceeding the pressure rating of the downstream equipment
unless pro visions are made to prevent
over-pressurization (i.e. system relief
valve). Make sure the pressure rating of
the down stream equipment is compatible
with the maximum delivery pressure of
the flowmeter/ regulator. .
4. Be sure that the flowmeter/ regulator has the correct
pressure rating and gas service for the cylinder used.
5. Carefully inspect the flowmeter/ regulator for damaged threads, dirt, dust, grease, oil, or other flammable substances. Remove dust and dirt with a clean
cloth. Be sure the inlet swivel filter is clean and in
place. Attach the flowmeter/ regulator (Figure 3-2) to
the cylinder valve. Tighten securely with a wrench.
Figure 3-1: Victor CS Flowmeter/ Regulator
WARNING
!
Use the flowmeter/ regulator for the gas
and pressure for which it is designed.
NEVER alter a flowmeter/ regulator for
use with any other gas.
NOTE!
Flowmeters/ Regulators supplied with
5/8" -18 standard inert gas connections.
Flowmeters/ Regulators purchased with
open 1/8”, 1/4”, 3/8”, or 1/2” NPT ports
must be assembled to their intended
system.
1. Note the maximum inlet pressure stamped on the
flowmeter/ regulator. DO NOT attach the flowmeter/
regulator to a system that has a higher pressure than
the maximum rated pressure stamped on the flowmeter/ regulator.
2. The flowmeter/ regulator body will be stamped “IN”
or “HP” at the inlet port. Attach the inlet port to the
system supply pressure connection.
3. If gauges are to be attached to the flowmeter/ regulator and the flowmeter/ regulator is stamped and listed
by a third party (i.e. “UL” or “ETL”). The following
requirements must be met:
a) Inlet gauges over 1000 PSIG (6.87 mPa) shall
WARNING
!
DO NOT attach or use the flowmeter/
regulator if oil, grease, flamma ble substances or damage is present! Have a
qualified repair technician clean the flowmeter/ regulator or repair any damage.
A-09845_AB
Figure 3-2: Flowmeter/ Regulator to Cylinder Valve
6. Before opening the cylinder valve, turn the flowmeter/
regulator adjusting screw counterclockwise until there
is no pressure on the adjusting spring and the screw
turns freely.
7. Relief Valve (where provided): The relief valve is
designed to protect the low pressure side of the flowmeter/ regulator from high pres sures. Relief valves
are not intended to protect down stream equipment
from high pressures.
INSTALLATION, OPERATION AND SETUP 3-4 Manual 0-5420

ESAB FABRICATOR 141i
Art # A-09828
WARNING
!
!
8. Slowly and carefully open the cylinder valve (Figure
DO NOT tamper with the relief valve or
remove it from the flowmeter/ regulator.
WARNING
Stand to the side of the cylinder opposite
the flowmeter/ regulator when opening the cylinder valve. Keep the cylinder
valve between you and the flowmeter/
regulator. For your safety, NEVER STAND
IN FRONT OF OR BEHIND A FLOWMETER/
REGULATOR WHEN OPENING THE CYLINDER VALVE!
3-3) until the maximum pressure shows on the high
pressure gauge.
b) If the low-pressure gauge drops, there is a leak
in the down stream equipment, hose, hose fitting,
outlet fitting or low-pressure gauge. Check for
leaks using an approved leak detector solution.
c) If the high-pressure gauge drops and the low-
pressure gauge increases at the same time, there
is a leak in the flowmeter/ regulator seat.
d) If the flowmeter/ regulator requires service or
repair, take it to a qualified repair technician.
5. Once leak testing has been performed and there are
no leaks in the system, slowly open the cylinder valve
and proceed.
WARNING
!
If a leak has been detected anywhere in
the system, dis continue use and have
the system repaired. DO NOT use leaking
equipment. Do not attempt to repair a
leaking system while the system is under
pressure.
3.08 When You Finish Using the Flowmeter/ Regulator
Figure 3-3: Open Cylinder Valve
9. On all cylinders, open the valve completely to seal the
valve packing. On gaugeless flowmeters/ regulators,
the indicator will register the cylinder contents open.
CAUTION
!
10. Attach the desired downstream equipment.
Keep the cylinder valve wrench, if one is
required, on the cylinder valve to turn OFF
the cylinder quickly, if necessary.
3.07 Leak Testing the System
Leak test the system before putting into operation.
1. Be sure that there is a valve in the downstream equipment to turn off the gas flow.
2. With the cylinder valve open, adjust the Flowmeter/
regulator to deliver the maximum required delivery
pressure.
3. Close the cylinder valve.
4. Turn the adjusting screw/knob counterclockwise one
turn.
a) If the high-pressure gauge reading drops, there is
a leak in the cylinder valve, inlet fitting, or highpressure gauge.
1. Close the cylinder valve.
2. Open the valve on the downstream equipment. This
drains all pressure from the system.
3. Close the valve on the downstream equipment.
4. Turn the adjusting screw counterclockwise to release
the ten sion on the adjusting spring.
5. Check the gauges after a few minutes for verification
that the cylinder valve is closed completely.
3.09
When the regulator is not in use and has been removed from
the cylinder, it should be stored in an area where it will be protected from dust, oil, and grease. The inlet and outlet should be
capped to protect against internal contamination and prevent
insects from nesting.
Storage of the Flowmeter/ Regulator
Manual 0-5420 3-5 INSTALLATION, OPERATION AND SETUP
ESAB FABRICATOR 141i
3
4
5
8
7
10
11
12
13
14
2
1
16
15
A-13037
6
9
18
19
20
21
Art #
A-10355
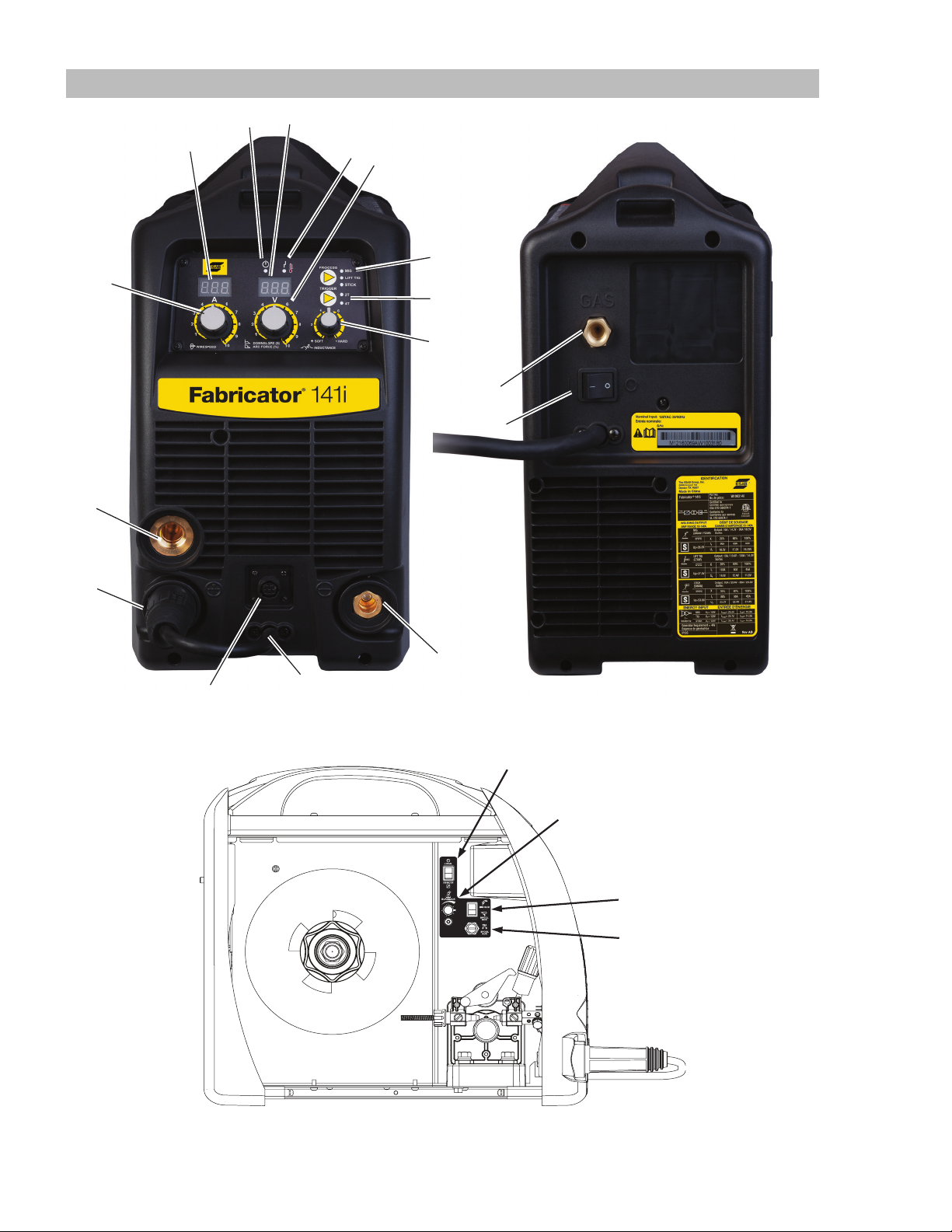
3.10 Power Source Controls, Indicators and Features
Figure 3-4: Front Panel
Figure 3-5: Rear Panel
INSTALLATION, OPERATION AND SETUP 3-6 Manual 0-5420
Figure 3-6: Wire Feed Compartment Control

ESAB FABRICATOR 141i
1. Power Indicator
The power indicator is illuminated when the Electricity
Supply is applied to the Power Source and when the ON/
OFF switch located on the rear panel is in the ON position.
2. Digital Wirespeed/Amperage Meter (Left Digital Display)
This digital meter displays preview Wirespeed in MIG mode
only then actual amperage (weld current) once an arc has
been established. It also displays preview amperage in both
the STICK and LIFT TIG modes only then actual amperage
(weld current) once an arc has been established.
At times of non-welding, the amperage meter will display
a preview value in both STICK and LIFT TIG modes. This
value can be adjusted by varying the Wire speed / Amperage potentiometer (Control No. 3). At times of non-welding,
the amperage meter will preview a wirefeed speed value
(Inches Per Minute) in MIG mode only. This can be identified
as preview wirefeed speed by a decimal point at the lower
right hand side of the display.
When welding, the amperage meter will display actual
amperage (weld current) in all modes.
At the completion of welding, the amperage meter will
hold the last recorded amperage value for a period of approximately 10 seconds in all modes. The amperage meter
will hold the value until; (1) any of the front panel controls
are adjusted in which case the Power Source will revert to
preview mode, (2) welding is recommenced, in which case
actual welding amperage will be displayed, or (3) a period
of 10 seconds elapses following the completion of welding
in which case the Power Source will return to preview mode.
NOTE!
The preview functionality provided on
this power source is intended to act as
a guide only. Some differences may be
observed between preview values and
actual welding values due to factors including the mode of welding, differences
in consumables/gas mixtures, individual
welding techniques and the transfer
mode of the welding arc (ie dip versus
spray transfer). Where exact settings are
required (in the case of procedural work),
it is recommended that alternate measurement methods be utilized to ensure
output values are accurate.
on the inside of the wire feed compartment door provides a
brief summary of the required settings for a basic range of
MIG (GMAW/FCAW) welding applications.
In STICK and LIFT TIG modes, the Wirespeed/Amperage
control knob adjusts the amount of amperage (weld current) delivered to the welding arc by the Power Source. It
directly adjusts the Power Source to deliver the desired level
of weld current.
4. MIG Gun Adapter (ESAB Style)
The MIG Gun adapter is standard ESAB connection with an
8 pin gun trigger for the Fusion MIG Gun. Connect the MIG
Gun by pushing the MIG Gun connector into the brass MIG
Gun Adapter firmly and screw the locking screw in the MIG
Gun Adapter within the Wire Feed Compartment to secure
the Fusion MIG Gun in position. Failure to properly lock the
Fusion MIG Gun into the MIG Gun Feedplate will result in the
MIG Gun being pushed out of the MIG Gun Feedplate by the
MIG welding wire or lack of shielding gas (porosity in the
weld) at the weld zone.
5. Positive Welding Output Terminal
The positive welding terminal is used to connect the welding output of the Power Source to the appropriate welding
accessory such as the MIG Gun (via the MIG Gun polarity
lead), electrode holder lead or work lead. Positive welding
current flows from the Power Source via 25mm Dinse style
connector. It is essential, however, that the Dinse adapter
and male plug are inserted and turned securely to achieve
a sound electrical connection.
!
CAUTION
Loose welding terminal connections can
cause overheating and result in the male
plug being fused in the Dinse connector.
6. MIG Gun Polarity Lead
The polarity lead is used to connect the MIG Gun to the
appropriate positive or negative output terminal (allowing
polarity reversal for different welding applications). In general, the polarity lead should be connected in to the positive
welding terminal (+) when using steel, stainless steel or
aluminum electrode wire. When using flux cored (gasless)
wire, the polarity lead is generally connected to the negative
welding terminal (-). If in doubt, consult the manufacturer
of the electrode wire for the correct polarity. It is essential,
however, that the Dinse adapter and male plug are inserted
and turned securely to achieve a sound electrical connection.
3. Wirespeed/Amperage Control
In MIG mode, the Wirespeed/Amperage control knob adjusts
the speed of the wire feed motor (which in turn adjusts the
output current by varying the amount of MIG wire delivered to
the welding arc). The optimum wire speed depends upon the
material type and the welding application. The setup chart
Manual 0-5420 3-7 INSTALLATION, OPERATION AND SETUP
!
CAUTION
Loose welding terminal connections can
cause overheating and result in the male
plug being fused in the Dinse connector..

ESAB FABRICATOR 141i
7. Negative Welding Output Terminal
The negative welding terminal is used to connect the welding output of the Power Source to the appropriate welding accessory
such as the MIG Gun (via the MIG Gun polarity lead), TIG Torch or work lead. Negative welding current flows to the Power Source
via 25mm Dinse style connector. It is essential, however, that the Dinse adapter and male plug are inserted and turned securely
to achieve a sound electrical connection.
CAUTION
!
8. Remote Control and Spool Gun Socket
The 8 pin socket is used to connect the Fusion MIG Gun, remote control device or spool gun plug to the welding Power Source.
To make connections, align keyway, insert plug, and rotate threaded collar fully clockwise.
Loose welding terminal connections can cause overheating and result in the male plug being fused in the Dinse connector..
2
1
5
4
8
7
Art # A-10421_AC
1
2
3
4
3
6
5
6
7
8
Remote Wirespeed in MIG (GMAW/FCAW) mode
Remote Amps in LIFT TIG (GTAW) mode
Trigger Switch
WV
Remote Volts in
MIG (GMAW/FCAW)
Negative
Spool Gun Motor
Positive
Figure 3-7: Remote Control Socket
Socket Pin
1 Spool gun motor (0V)
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
Trigger Switch Input
Trigger Switch Input
Spool gun motor (+24V DC)
5k ohm (maximum) connection to 5k ohm remote control potentiometer.
Zero ohm (minimum) connection to 5k ohm remote control potentiometer.
Wiper arm connection to 5k ohm potentiometer for the remote control of the Wirespeed in MIG mode.
Wiper arm connection to 5k ohm potentiometer for the remote control of the Amperage (Weld Current) in LIFT
TIG mode.
Wiper arm connection to 5k ohm remote control Volts MIG mode potentiometer.
Function
Table 3-3
Note that the Local/ Remote Switch (Control No. 18) located in the wirefeed compartment should be set to Remote for remote
amperage/voltage controls to operate.
9. Multifunction Control - Voltage, Down Slope & Arc Force
The multifunction control knob is used to adjust Voltage (MIG Mode), Down slope (LIFT TIG Mode) and Arc Force (STICK Mode)
depending on the welding mode selected.
NOTE!
The preview functionality provided on this power source is intended to act as a guide only. Some differences may be observed between preview values and actual welding values due to factors including
the mode of welding, differences in consumables/gas mixtures, individual welding techniques and the
transfer mode of the welding arc (ie dip versus spray transfer). Where exact settings are required (in the
case of procedural work), it is recommended that alternate measurement methods be utilized to ensure
output values are accurate.
INSTALLATION, OPERATION AND SETUP 3-8 Manual 0-5420

ESAB FABRICATOR 141i
When MIG Mode is Selected
In this mode the control knob is used to adjust the MIG
welding voltage of the Power Source. The welding voltage
is increased by turning the knob clockwise or decreased by
turning the knob counterclockwise. The optimum voltage
level required will depend on the type of welding application.
The setup chart on the inside of the wire feed compartment
door provides a brief summary of the required output settings
for a basic range of MIG welding applications.
When STICK Mode is Selected
In this mode the multifunction control knob is used to adjust
arc force. Arc force control provides an adjustable amount
of welding force (or “dig”) control. This feature can be
particularly beneficial in providing the operator the ability
to compensate for variability in joint fit-up in certain situations with particular electrodes. In general increasing the arc
force control toward ‘10’ (maximum arc force) allows greater
penetration control to be achieved. Arc force is increased by
turning the control knob clockwise or decreased by turning
the knob counterclockwise.
When LIFT TIG Mode is Selected
In this mode the multifunction control knob is used to adjust
down slope. Down slope allows the user to select the ramp
down time of the amperage at the completion of the weld.
The main function of down slope is to allow the welding
current to be gradually reduced over a pre-set time frame
such that the welding pool is given time to cool sufficiently.
Note that when in 2T normal mode (Control No. 11), the
Power Source will enter down slope mode as soon as the
trigger switch is released (ie if the multifunction control knob
is set to 5, the Power Source will ramp down from the present
welding current to zero over 5 seconds). If no down slope
time is set then the welding output will cease immediately.
If the Power Source is set to 4T latch mode, to enter down
slope mode the trigger must be held in for the selected time
period (ie press and release trigger to commence welding,
then press and hold trigger again to enter down slope mode).
Should the trigger be released during the down slope phase
(4T only), the output will cease immediately.
10. Arc Control (Inductance)
The arc control operates in MIG mode only and is used to
adjust the intensity of the welding arc. Lower arc control
settings make the arc softer with less weld spatter. Higher
arc control settings give a stronger driving arc which can
increase weld penetration. Soft means maximum inductance
while Hard means minimum inductance.
11. Trigger Mode Control (MIG and LIFT TIG Mode only)
The trigger mode control is used to switch the functionality
of the of the MIG or TIG Trigger Switch between 2T (normal)
and 4T (latch mode)
2T (Normal Mode)
In this mode, the MIG or TIG Trigger Switch must remain
depressed for the welding output to be active. Press and
hold the MIG or TIG Trigger Switch to activate the Power
Source (weld). Release the MIG or TIG Trigger Switch to
cease welding.
4T (Latch Mode)
This mode of welding is mainly used for long welding runs
to reduce operator fatigue. In this mode the operator can
press and release the MIG or TIG Trigger Switch and the
output will remain active. To deactivate the Power Source,
the trigger switch must again be depressed and released,
thus eliminating the need for the operator to hold the MIG
or TIG Trigger Switch
Note that when operating in LIFT TIG mode, the Power Source
will remain activated until the selected Downslope time has
elapsed (refer Control No. 9).
12. Process Selection Control
The process selection control is used to select the desired
welding mode. Three modes are available, MIG, LIFT TIG and
STICK modes. Refer to section 3.20 or 3.21 for MIG (GMAW/
FCAW) set up details, section 3.22 for LIFT TIG (GTAW) setup details or section 3.23 for STICK (SMAW) set-up details.
Note that when the Power Source is powered off the mode
selection control will automatically default to MIG mode. This
is necessary so as to prevent inadvertent arcing should an
electrode holder be connected to the Power Source and mistakenly be in contact with the work piece during power up.
13. Digital Voltage Meter (Right Digital Display)
The digital voltage meter is used to display the both the
preview voltage (MIG mode only) and actual output voltage
(all modes) of the Power Source.
At times of non-welding, the voltage meter will display a
preview value in MIG mode. This value can be adjusted by
varying the multifunction control knob (Control No. 9). Note
that in STICK and LIFT TIG modes, the voltage meter will not
preview welding voltage but will display Open Circuit Voltage
in STICK mode and 0V in LIFT TIG mode.
When welding, the voltage meter will display actual
welding voltage in all modes.
At the completion of welding, the digital voltage meter will
hold the last recorded voltage value for a period of approximately 10 seconds in all modes. The voltage meter will hold
the value until; (1) any of the front panel controls are adjusted
in which case the Power Source will revert to preview mode,
(2) welding is recommenced, in which case actual welding
amperage will be displayed, or (3) a period of 10 seconds
elapses following the completion of welding in which case
the Power Source will return to preview mode.
Manual 0-5420 3-9 INSTALLATION, OPERATION AND SETUP

ESAB FABRICATOR 141i
NOTE!
The preview functionality provided on
this power source is intended to act as
a guide only. Some differences may be
observed between preview values and
actual welding values due to factors including the mode of welding, differences
in consumables/gas mixtures, individual
welding techniques and the transfer
mode of the welding arc (ie dip versus
spray transfer). Where exact settings are
required (in the case of procedural work),
it is recommended that alternate measurement methods be utilized to ensure
output values are accurate.
14. Fault Indicator
This welding Power Source is protected by a self resetting
thermostat. The indicator will illuminate if the duty cycle
of the Power Source has been exceeded or if a fault is detected in the Inverter. Should the Fault Indicator illuminate
the output of the Power Source will be disabled. Once the
Power Source cools down this light will go OFF and the over
temperature condition will automatically reset. Note that the
power switch should remain in the on position such that the
fan continues to operate thus allowing the Power Source to
cool sufficiently. Do not switch the Power Source off should
a thermal overload condition be present. If the fault condition
does not extinguish, then the Power Supply will need to be
taken to an authorized repair center for analysis.
15. Gas Inlet (MIG mode only for MIG Gun or Spool Gun
operation)
The Gas Inlet connection is used to supply the appropriate
MIG welding gas to the Power Source. Refer to section 3.19
to 3.20 for MIG (FCAW/GMAW) set up details.
WARNING
!
Only Welding Shielding Gases specifically
designed for arc welding applications
should be used.
16. On / Off Switch
This switch is used to turn the Power Source on/off.
WARNING
!
When the front digital displays
are lit, the machine is connected to the Mains supply
voltage and the internal electrical components are at Mains
voltage potential.
17. Intelligent Fan Control
When Power Supply is first turned on it will default in MIG
Mode. The Fan will operate for approximately 10 seconds,
then shut down.
When triggered in MIG mode, fan will not turn on until Power
Supply reaches temperatures in which cooling is required.
When in Lift TIG mode, as soon as output is enabled, the
fan will come on immediately and will not shut down until
welding has ceased and Power Supply is at proper operating temperature. When set to Stick mode, fan will turn on
immediately and will not turn off until welding has ceased
and Power Supply is at proper operating temperature.
Note in STICK mode the fan operates continuously.
18. Local / Remote Switch (located in wirefeed compartment)
The local/ remote switch is used only when a remote control
device (such as a TIG Torch with remote current control) is
fitted to the Power Source via the remote control socket
(8 Pin Remote Socket). When the local/remote switch is in
the remote position, the Power Source will detect a remote
device and work accordingly. When in the local mode, the
Power Source will not detect the remote device and will
operate from the Power Source controls only. Note that the
trigger will operate at all times on the remote control socket
irrespective of the position of the local remote switch (ie in
both local and remote modes).
Should a remote device be connected and the local/ remote
switch set to remote, the maximum setting of the Power
Source will be determined by the respective front panel
control, irrespective of the remote control device setting.
As an example, if the output current on the Power Source
front panel is set to 50% and the remote control device is set
to 100%, the maximum achievable output from the Power
Source will be 50%. Should 100% output be required, the
respective front panel control must be set to 100%, in which
case the remote device will then be able to control between
0-100% output.
19. Burnback Control (located in wirefeed compartment)
The Burnback control is used to adjust the amount of MIG
wire that protrudes from the MIG Gun after the completion of
MIG welding (commonly referred to as stick-out). To decrease
the Burnback time (or lengthen the amount of wire protruding
from the MIG Gun at the completing of welding), turn the
Burnback control knob counterclockwise. To increase the
Burnback time (or shorten the amount of wire protruding
from the MIG Gun at the completing of welding), turn the
Burnback Control knob clockwise.
20. MIG Gun & Spool Gun Switch
The MIG Gun / Spool Gun switch is used to switch welding
mode between MIG Gun function and Spool Gun function.
21. 10A Fuse
The 10A fuse is used to protect both the spool gun motor
and internal motor.
INSTALLATION, OPERATION AND SETUP 3-10 Manual 0-5420

ESAB FABRICATOR 141i
Art #
A-10356_AB
MIG Gun Adaptor
MIG Gun Connector
MIG Gun Connector
Thumb Screw
8 pin socket
8 pin plug
3.11 Attaching the Fusion 140A MIG Gun
Fit the MIG Gun to the Power Source by pushing the MIG Gun connector into the MIG Gun Adapter and tightening the Locking
Screw to secure the MIG Gun in the MIG Gun Adapter.
Connect the 8 pin plug by aligning the keyway then inserting the 8 pin plug into the 8 pin socket and rotate threaded collar fully
clockwise to lock the plug into position.
Figure 3-8: Attaching MIG Gun
3.12 Inserting Wire into the Wire Feed Mechanism
Release the tension from the Pressure Roller Arm by turning the adjustable Wire Drive Tension Screw in a counterclockwise. Then
to release the pressure roller arm push the tension screw toward the front of the machine which releases the pressure roller arm.
With the MIG welding wire feeding from the bottom of the spool (Figure 3-10) pass the electrode wire through the inlet guide,
between the rollers, through the outlet guide and into the MIG Gun. Re-secure the pressure roller arm and wire drive tension screw
and adjust the pressure accordingly (Figure 3-9). Remove the nozzle and contact tip from the MIG Gun. With the MIG Gun lead
reasonably straight, feed the wire through the MIG Gun by depressing the trigger switch. Fit the appropriate contact tip.
Manual 0-5420 3-11 INSTALLATION, OPERATION AND SETUP

ESAB FABRICATOR 141i
WARNING
Before connecting the work clamp to the work piece, make sure you have ceased feeding wire so premature arcing will not occur.
The electrode wire will be at welding voltage potential while it is being fed through the system.
Keep MIG Gun away from eyes and face.
Wire Drive Tension Screw
Pressure Roller Arm
Outlet Guide
Art #
A-10359_AB
Figure 3-9: Wire Drive Assembly Components
Inlet Guide
Art #
MIG Welding Wire
Figure 3-10: MIG Welding Wire - Installation
A-10360
3.13 Installing 4" (100mm) Diameter Spool
As delivered from the factory, the Power Source is fitted with a Wire Spool Hub which accepts a 8" (200mm) diameter spools. In
order to fit a 4" (100mm) diameter spool assemble parts in the sequence shown below in Figure 3-11.
Adjustment of the nut with nylon insert will control the MIG Wire Spool Brake. Clockwise rotation of this nut with nylon insert
tightens the brake. The brake is correctly adjusted when the spool stops within 4" (100mm) to 8" (200mm) (measured at the outer
edge of the spool) after MIG Gun trigger is released. Wire should be slack without becoming dislodged from the spool.
CAUTION
!
Overtension of brake will cause rapid wear of mechanical WIRE FEED parts, overheating of
electrical components and possibly an increased incidence of electrode wire Burnback into
contact tip.
INSTALLATION, OPERATION AND SETUP 3-12 Manual 0-5420

ESAB FABRICATOR 141i
Art #
A-10357
Friction Washer
4”(100mm)
Diameter spool
Nut with
Nylon Insert
Spring
Plastic Spacer
Brass Flat
Washer
Flat Washer
Art #
A-10358
Spring
Nut with
Nylon Insert
8” (200mm)
diameter spool
Spool Hub Nut
Alignment pin
Brass Flat
Washer
Wire Spool Hub
Friction
Washer
Plastic Spacer
Flat Washer
Alternate
Alignment Pin
Position
Figure 3-11: 4" (100mm)Diameter Spool Installation
3.14 Installing 8" (200mm) Diameter Spool
As delivered from the factory, the Power Source is set for a 8" (200mm) diameter spool.
In order to re-fit a 8" (200mm) spool assemble parts in the sequence shown below in Figure 3-12.
Adjustment of the nut with nylon insert will control the MIG Wire Spool Brake. Clockwise rotation of this nut with nylon insert tightens the brake. The Brake is correctly adjusted when the spool stops within 3/8" (10mm) to 3/4" (20mm) (measured at the outer
edge of the spool) after MIG Gun trigger is released. Wire should be slack without becoming dislodged from the spool.
Manual 0-5420 3-13 INSTALLATION, OPERATION AND SETUP
!
CAUTION
Overtension of brake will cause rapid wear of mechanical WIRE FEED parts, overheating of electrical
components and possibly an increased incidence of electrode wire Burnback into contact tip.
Ensure that the alignment pin on the wire spool hub aligns with the hole allocated in 8" (200mm) diameter spool..
NOTE!
This alignment pin can be removed by unscrewing in an counterclockwise direction and locating in the
appropriate position..
Figure 3-12: 8" (200mm) Diameter Spool Installation

ESAB FABRICATOR 141i
GROOVE “B”GROOVE “A”
GROOVE “A” SIZE
GROOVE “B” SIZE
A-09583
Feed Roll
Retaining Screw
Feed Roll
Art #
A-09584_AC
Wire Reel Brake Adjustment Nut
Art #
A-10361
3.15 Feed Roller Pressure Adjustment
The pressure (top) roller applies pressure to the grooved
feed roller via an adjustable pressure screw. These devices
should be adjusted to a minimum pressure that will provide
satisfactory wire feed without slippage. If slipping occurs, and
inspection of the wire contact tip reveals no wear, distortion or
burn back jam, the conduit liner should be checked for kinks
and clogging by metal flakes and debris. If it is not the cause of
slipping, the feed roll pressure can be increased by rotating the
pressure screw clockwise.
WARNING
Before changing the feed roller ensure
that the Electricity Supply to the Power
Source is switched off.
CAUTION
!
The use of excessive pressure may cause
rapid wear of the feed rollers, shafts and
bearing.
3.16 Changing the Feed Roll
To change feed roll remove the feed roll retaining screw by
turning in an counterclockwise direction. Once the feed roll is
removed then to replace feed roll simply reverse these directions.
A dual groove feed roller is supplied as standard. It can accommodate 023"(0.6mm) -.030" (0.8mm) diameter hard wires.
Select the roller required with the chosen wire size marking
facing outward.
3.17 Wire Reel Brake
The wire reel hub incorporates a friction brake which is
adjusted during manufacture for optimum breaking. If it is
considered necessary, adjustment can be made by turning the
large nut inside the open end of the hub clockwise to tighten
the brake. Correct adjustment will result in the wire reel
circumference continuing no further than 3/8" (10mm) - 3/4"
(20mm) after release of the trigger. The electrode wire should
be slack without becoming dislodged from wire spool.
CAUTION
!
Overtension of brake will cause rapid
wear of mechanical WIREFEED parts,
overheating of electrical components
and possibly an increased incidence of
electrode wire Burnback into contact tip..
Figure 3-13: Dual Groove Feed Roller
Figure 3-14: Changing the Feed Roll
Figure 3-15: Wire Reel Brake
3.18 Flowmeter/ Regulator Operation
With the flowmeter/ regulator connected to cylinder or pipeline,
and the adjustment screw/knob fully disengaged, pressurize as
follows:
1. Stand to one side of flowmeter/ regulator and slowly
open the cylinder valve. If opened quickly, a sudden
pressure surge may damage internal parts.
2. With valves on downstream equipment closed, adjust
flowmeter/ regulator to approximate working pressure. It is recommended that testing for leaks at the
flowmeter/ regulator connection points be carried
out using a suitable leak detection solution or soapy
water.
3. Purge air or other unwanted welding grade shielding gas from equipment connected to the flowmeter/
regulator by individually opening then closing the
equipment control valves. Complete purging may take
up to ten seconds or more, depending upon the length
and size of the hose being purged.
INSTALLATION, OPERATION AND SETUP 3-14 Manual 0-5420

ESAB FABRICATOR 141i
Adjusting Flow Rate
With the flowmeter/ regulator ready for operation, adjust working flow rate as follows:
1. Adjust the gas flow rate. The recommended rate for
MIG welding is 15-25 CFH. The recommended rate for
LIFT TIG welding is 10-25 CFH.
NOTE!
It may be necessary to re-check the
shielding gas flowmeter/ regulator flow
rate following the first weld sequence
due to back pressure present within
shielding gas hose assembly.
Shutdown
Close cylinder valve whenever the flowmeter/ regulator is
not in use. To shut down for extended periods (more than 30
minutes).
1. Close cylinder or upstream valve tightly.
2. Open downstream equipment valves to drain the
lines. Bleed gas into a well ventilated area and away
from any ignition source.
3. After gas is drained completely, disengage adjusting
screw and close downstream equipment valves.
4. Before transporting cylinders that are not secured on
a cart designed for such purposes, remove flowmeters/ regulators. Put caps on all cylinders that do not
have flowmeters/ regulators on them.
G. Switch the LOCAL/REMOTE switch
inside the wire feed compartment
to LOCAL to use the Power Sources
Wirespeed and Voltage controls.
H. Switch the MIG GUN/SPOOL GUN switch
inside the wire feed compartment to MIG
GUN.
WARNING
!
Before connecting the work
clamp to the work piece,
make sure you have ceased
feeding wire so premature
arcing will not occur.
Secure the shielding gas
cylinder in an upright position
by chaining it to a suitable
stationary support to prevent
falling or tipping.
CAUTION
!
Loose welding terminal connections can
cause overheating and result in the male
plug being fused in the terminal.
3.19 Setup for MIG (GMAW) Welding with Gas Shielded MIG Wire
A. Select MIG mode with the process selection control.
(Refer to Section 3.10 for further information)
B. Connect the MIG Gun Polarity Lead to the positive welding
terminal (+). If in doubt, consult the electrode wire manufacturer. Welding current flows from the Power Source
via Dinse style connectors. It is essential, however, that
the male plug is inserted and turned securely to achieve
a sound electrical connection.
C. Fit the MIG Gun to the Power Source. (Refer to Section
3.11 Attaching the Fusion 140A MIG Gun).
D. Connect the work lead to the negative welding terminal
(-). If in doubt, consult the electrode wire manufacturer.
Welding current flows from the Power Source via Dinse
style connectors. It is essential, however, that the male
plug is inserted and turned securely to achieve a sound
electrical connection.
E. Fit the flowmeter/ regulator to the shielding gas cylinder
(Refer to Section 3.06) then connect the shielding gas
hose from the rear of the Power Source to the flowmeter/
regulator outlet.
F. Refer to the Weld Guide located on the inside of the
wirefeed compartment door for further information.
Manual 0-5420 3-15 INSTALLATION, OPERATION AND SETUP

ESAB FABRICATOR 141i
MIG Gun
Art #
A-10362
Secure the gas cylinder
in an upright position
by chaining it to a
stationary support to
prevent falling or tipping.
Positive Welding
Terminal (+)
8 pin Plug
Work Lead
MIG Gun
Polarity Lead
Negative Welding
Terminal (-)
Shielding Gas Hose Fitted
with 5/8"-18 UNF
connection
Primary Cord
Figure 3-16: Setup for MIG Welding with Gas Shielded MIG Wire
3.20 Setup for MIG (FCAW) Welding with Flux Core (Gasless) Wire
A. Select MIG mode with the process selection control (refer to Section 3.10.12 for further information).
B. Connect the MIG Gun Polarity Lead to the negative welding terminal (-). If in doubt, consult the electrode wire manufacturer.
Welding current flows from the Power Source via Dinse style connectors. It is essential, however, that the male plug is
inserted and turned securely to achieve a sound electrical connection.
C. Connect the work lead to the positive welding terminal (+). If in doubt, consult the electrode wire manufacturer. Welding
current flows from the Power Source via Dinse style connectors. It is essential, however, that the male plug is inserted
and turned securely to achieve a sound electrical connection.
D. Refer to the Weld Guide located on the inside of the wirefeed compartment door for further information.
E. Switch the LOCAL/REMOTE switch inside the
wire feed compartment to LOCAL to use the
Power Sources Wirespeed and Voltage controls.
F. Switch the MIG GUN/SPOOL GUN switch inside
the wire feed compartment to MIG GUN.
!
WARNING
Before connecting the work clamp to the work piece, make sure you have ceased feeding
wire so premature arcing will not occur.
CAUTION
!
Loose welding terminal connections can cause overheating and result in the male plug being
fused in the terminal.
Remove any packaging material prior to use. Do not block the air vents at the front or rear of
the Welding Power Source.
INSTALLATION, OPERATION AND SETUP 3-16 Manual 0-5420

ESAB FABRICATOR 141i
A-09587_AD
MIG Gun
Polarity Lead.
Negative Welding
Terminal (-)
Positive Welding
Terminal
(+)
MIG Gun
8 pin Plug
Work Lead
Art #
A-10363
Figure 3-17: Setup for MIG (FCAW) Welding with Flux Cored (Gasless) Wire
3.21 Setup for SPOOL GUN MIG (GMAW) Welding with Gas Shielded MIG Wire
Set the Process Selection Control to MIG for Spool Gun welding.
For setup and operation of the spool gun, please refer to the spool gun operations manual.
Switch the MIG GUN/SPOOL GUN switch inside the wire feed compartment to SPOOL GUN.
Connect the Argon shielding gas to the Shielding Gas Inlet on the rear panel of the Power Source.
1. Make sure the welding power source is turned
OFF before connecting the welding gun.
2. Open side panel and loosen thumb screw.
3. Insert the back end of the Spool gun into the
gun receiving bushing.
4. Tighten thumb screw and replace side panel.
Manual 0-5420 3-17 INSTALLATION, OPERATION AND SETUP
5. Connect gas supply fitting and tighten with a
wrench.
6. Connect the 8 pin plug by aligning the keyway
then inserting the 8 pin plug into the 8 pin
socket and rotate threaded collar fully
clockwise to lock the plug into position.

ESAB FABRICATOR 141i
3.22 Setup for LIFT TIG (GTAW) Welding
A. Select LIFT TIG mode with the process selection control (refer to Section 3.10.12 for further information).
B. Using the supplied 50mm to 25mm DINSE adapter, connect the TIG torch to the negative welding terminal (-). Welding
current flows from the Power Source via Dinse style connectors. It is essential, however, that the male plug is inserted
and turned securely to achieve a sound electrical connection.
C. Connect the work lead to the positive welding terminal (+). Welding current flows from the Power Source via Dinse style
terminals. It is essential, however, that the male plug is inserted and turned securely to achieve a sound electrical connection.
D. Connect the TIG torch trigger switch via the 8 pin socket located on the front of the Power Source. The TIG torch will
require a trigger switch to weld in LIFT TIG Mode.
NOTE!
A ESAB 17V TIG torch with an 8 pin plug must be used to turn the weld current on/off via the TIG torch
trigger switch to TIG weld OR a ESAB Foot Control with an 8 pin plug must be used to turn the weld
current on/off as well as providing remote control of the weld current. Please refer to "2.10 Options and
Accessories".
E. Fit the flowmeter/ regulator to the shielding gas cylinder (refer to Section 3.06) then connect the shielding gas hose from
the TIG torch to the flowmeter/ regulator outlet. Note that the TIG torch shielding gas hose is connected directly to the
flowmeter/ regulator. The Power Source is not fitted with a shielding gas solenoid to control the gas flow in LIFT TIG mode
therefore the TIG torch will require a gas valve.
WARNING
!
!
F. Switch the LOCAL/REMOTE switch inside the
wire feed compartment to LOCAL to use the
Power Sources Amperage control or REMOTE
for remote amperage using a Foot Control.
Before connecting the work clamp to the work piece, make sure you have ceased feeding
wire so premature arcing will not occur.
Secure the shielding gas cylinder in an upright position by chaining it to a stationary support to prevent falling or tipping.
CAUTION
Remove any packaging material prior to use. Do not block the air vents at the front or rear
of the Welding Power Source.
Loose welding terminal connections can cause overheating and result in the male plug being fused in the terminal.
INSTALLATION, OPERATION AND SETUP 3-18 Manual 0-5420

Art # A-11576_AB
Positive Welding
Terminal (+)
ESAB FABRICATOR 141i
Connect to shielding gas
regulator/flow gauge.
Secure the gas cylinder
in an upright position by
chaining it to a stationary
support to prevent falling
or tipping.
MIG Torch
polarity lead
not connected
Work Lead
50mm- 25mm Adaptor
Note: A Tweco 17V TIG torch with
an 8 pin plug must be used to turn the
weld current on/off via the TIG torch trigger
switch to TIG weld OR a Tweco Foot Control
with an 8 pin plug must be used to turn the
TIG Torch
weld current on/off as well as providing
remote control of the weld current.
Negative welding terminal (-)
Figure 3-18: Setup for TIG Welding
3.23 Setup for STICK (SMAW) Welding
A. Connect the Electrode Holder lead to the positive welding terminal (+). If in doubt, consult the electrode manufacturer.
Welding current flows from the Power Source via Dinse style connectors. It is essential, however, that the male plug is
inserted and turned securely to achieve a sound electrical connection.
B. Connect the work lead to the negative welding terminal (-). If in doubt, consult the electrode manufacturer. Welding cur-
rent flows from the Power Source via Dinse style connectors. It is essential, however, that the male plug is inserted and
turned securely to achieve a sound electrical connection.
WARNING
Before connecting the work clamp to the work and inserting the electrode in the electrode
holder make sure the Electricity Supply is switched off..
CAUTION
!
C. Switch the LOCAL/REMOTE switch inside the wire
feed compartment to LOCAL to use the Power Sources
Amperage control or REMOTE for remote amperage
control using a Hand Pendant Control.
Manual 0-5420 3-19 INSTALLATION, OPERATION AND SETUP
Remove any packaging material prior to use. Do not block the air vents at the front or rear of
the Welding Power Source.

ESAB FABRICATOR 141i
Art #
A-10365
Negative Welding
Terminal (-)
Positive Welding
Terminal
(+)
Work Lead
Electrode
Holder
MIG Gun
polarity lead
not connected.
Figure 3-19: Setup for Stick Welding(SMAW)
3.24 Torch Adapter Thumb Screw Replacement
WARNING
1. Place unit on its back.
2. Remove 2 screws in bottom of the front panel. A securing block will become detached and fall free from the front panel
All power to unit should be removed.
as you turn each screw out. Set these aside for reassembly. Leave screws sitting in the pockets of the panel.
A-12958
INSTALLATION, OPERATION AND SETUP 3-20 Manual 0-5420

ESAB FABRICATOR 141i
Screws
Art # A-11483
Securing Block
3. Open the wire compartment door and release the tension knob so the pressure arm and tension knob hang downwardly.
Tension Knob
Pressure Arm
Art # A-11484
4. Gently push the bottom of the front panel upward until the thumb screw is fully exposed.
Manual 0-5420 3-21 INSTALLATION, OPERATION AND SETUP

ESAB FABRICATOR 141i
Thumb Screw
Fully Exposed
Art # A-11485_AB
5. Remove damaged thumb screw and replace with new one.
Art # A-11486
6. To reassemble, reverse steps 1 through 4.
Push Upward
INSTALLATION, OPERATION AND SETUP 3-22 Manual 0-5420

ESAB FABRICATOR 141i
Shielding Gas
SECTION 4: BASIC WELDING
GUIDE
4.01 MIG (GMAW/FCAW) Basic Welding Technique
Two different welding processes are covered in this section
(GMAW and FCAW), with the intention of providing the very
basic concepts in using the MIG mode of welding, where a
welding MIG Gun is hand held, and the electrode (welding wire)
is fed into a weld puddle, and the arc is shielded by an inert
welding grade shielding gas or inert welding grade shielding
gas mixture.
GAS METAL ARC WELDING (GMAW): This process, also known
as MIG welding, CO2 welding, Micro Wire Welding, short arc
welding, dip transfer welding, wire welding etc., is an electric
arc welding process which fuses together the parts to be
welded by heating them with an arc between a solid continuous, consumable electrode and the work. Shielding is obtained
from an externally supplied welding grade shielding gas or
welding grade shielding gas mixture. The process is normally
applied semi automatically; however the process may be operated automatically and can be machine operated. The process
can be used to weld thin and fairly thick steels, and some nonferrous metals in all positions.
Shielding Gas
Molten Weld Metal
Solidified
Weld Metal
GMAW Process
Figure 4-1
FLUX CORED ARC WELDING (FCAW): This is an electric arc
welding process which fuses together the parts to be welded
by heating them with an arc between a continuous flux filled
electrode wire and the work. Shielding is obtained through
decomposition of the flux within the tubular wire. Additional
shielding may or may not be obtained from an externally supplied gas or gas mixture. The process is normally applied semi
automatically; however the process may be applied automatically or by machine. It is commonly used to weld large diameter electrodes in the flat and horizontal position and small
electrode diameters in all positions. The process is used to a
lesser degree for welding stainless steel and for overlay work.
Nozzle
Electrode
Arc
Base Metal
Art # A-8991_AB
Nozzle
(Optional)
Flux Cored
Electrode
Arc
Base Metal
Art # A-08992_AB
Slag
(Optional)
Molten Metal
Molten
Slag
Solidified
Weld Metal
FCAW Process
Figure 4-2
Position of MIG Gun
The angle of MIG Gun to the weld has an effect on the width of
the weld.
Push
Vertical
Drag/Pull
Art # A-07185_AB
Figure 4-3
The welding Gun should be held at an angle to the weld joint.
(see Secondary Adjustment Variables below)
Hold the MIG Gun so that the welding seam is viewed at all
times. Always wear the welding helmet with proper filter
lenses and use the proper safety equipment.
CAUTION
!
Do NOT pull the welding MIG Gun back
when the arc is established. This will create excessive wire extension (stick-out)
and make a very poor weld.
The electrode wire is not energized until the MIG Gun trigger
switch is depressed. The wire may therefore be placed on the
seam or joint prior to lowering the helmet.
5° to 15°
Longitudinal
Angle
Direction of
90°
Transverse
Angle
Travel
Art # A-08993
Butt & Horizontal Welds
Figure 4-4
Manual 0-5420 4-1 BASIC WELDING GUIDE

ESAB FABRICATOR 141i
10° to 20° Longitudinal
Direction of Travel
5° to 15°
Longitudinal Angle
Direction of
Travel
Horizontal Fillet Weld
Figure 4-5
10°
Longitudinal Angle
30° to 60°
Transverse
Angle
Direction of Travel
Vertical Fillet Welds
Figure 4-6
30° to 60°
Transverse Angle
30° to 60°
Transverse Angle
Art # A-08994
Angle
Art # A-08995
5° to 15°
Longitudinal
Angle
30° to 60°
Transverse
Angle
Preselected Variables
Preselected variables depend upon the type of material being
welded, the thickness of the material, the welding position, the
deposition rate and the mechanical properties. These variables
are:
• Type of electrode wire
• Size of electrode wire
• Type of gas (not applicable to self shielding wires FCAW)
• Gas flow rate (not applicable to self shielding wires
FCAW)
Primary Adjustable Variables
These control the process after preselected variables have
been found. They control the penetration, bead width, bead
height, arc stability, deposition rate and weld soundness. They
are:
• Arc Voltage
• Welding current (wire feed speed)
• Travel speed
Secondary Adjustable Variables
These variables cause changes in primary adjustable variables
which in turn cause the desired change in the bead formation.
They are:
1. Stick-out (distance between the end of the contact
tube (tip) and the end of the electrode wire). Maintain
at about 3/8" (10mm) stick-out
2. Wire Feed Speed. Increase in wire feed speed
increases weld current, Decrease in wire feed speed
decreases weld current.
Gas Nozzle
Tip to
Work Distance
Contact Tip (Tube)
Electrode Wire
Actual Stick-out
Art # A-08996
Figure 4-7
Electrode Stick-Out
Distance from the MIG Gun Nozzle to the Work Piece
Average Arc Length
Art # A-08997_AD
Figure 4-8
The electrode wire stick-out from the MIG Gun nozzle should
be between 3/8" (10mm) to 3/4" (20.0mm). This distance may
vary depending on the type of joint that is being welded.
Travel Speed
The speed at which the molten pool travels influences the
width of the weld and penetration of the welding run.
MIG Welding Variables
Most of the welding done by all processes is on carbon steel.
The items below describe the welding variables in short-arc
welding of 24 ga. (0.6mm) to ¼” (6.4mm) mild sheet or plate.
The applied techniques and end results in the MIG process are
3. Nozzle Angle. This refers to the position of the welding
MIG Gun in relation to the joint. The transverse angle
is usually one half the included angle between plates
forming the joint. The longitudinal angle is the angle
between the centre line of the welding MIG Gun and a
line perpendicular to the axis of the weld. The longitudinal angle is generally called the Nozzle Angle and
can be either trailing (pulling) or leading (pushing).
Whether the operator is left handed or right handed
has to be considered to realize the effects of each
angle in relation to the direction of travel.
controlled by these variables.
BASIC WELDING GUIDE 4-2 Manual 0-5420

Longitudinal
Transverse
Direction of Gun Travel
Angle
Axis of Weld
Transverse and Longitudinal
Nozzle Axes
Figure 4-9
Leading or “Pushing”
Angle
(Forward Pointing)
90°
Trailing or “Pulling”
(Backward Pointing)
Nozzle Angle, Right Handed Operator
Figure 4-10
Angle
Art # A-08998_AB
Angle
Art # A-08999_AC
ESAB FABRICATOR 141i
When changing to a different electrode wire diameter, different
control settings are required. A thinner electrode wire needs
more Wirespeed to achieve the same current level.
A satisfactory weld cannot be obtained if the Wirespeed and
Voltage settings are not adjusted to suit the electrode wire
diameter and the dimensions of the work piece.
If the Wirespeed is too high for the welding voltage, “stubbing”
will occur as the wire dips into the molten pool and does not
melt. Welding in these conditions normally produces a poor
weld due to lack of fusion. If, however, the welding voltage is
too high, large drops will form on the end of the wire, causing
spatter. The correct setting of voltage and Wirespeed can be
seen in the shape of the weld deposit and heard by a smooth
regular arc sound. Refer to the Weld Guide located on the
inside of the wirefeed compartment door for setup information.
Electrode Wire Size Selection
The choice of Electrode wire size and shielding gas used
depends on the following
• Thickness of the metal to be welded
• Type of joint
• Capacity of the wire feed unit and Power Source
• The amount of penetration required
• The deposition rate required
• The bead prole desired
• The position of welding
• Cost of the wire
Establishing the Arc and Making Weld Beads
Before attempting to weld on a finished piece of work, it is
recommended that practice welds be made on a sample metal
of the same material as that of the finished piece.
The easiest welding procedure for the beginner to experiment
with MIG welding is the flat position. The equipment is capable
of flat, vertical and overhead positions.
For practicing MIG welding, secure some pieces of 16 ga.
(1.6mm) or 1/8" (3.2mm) mild steel plate 6” (150mm) x 6”
(150mm). Use 0.035” (0.9mm) gas shielded steel or gasless
flux cored wire.
Setting of the Power Source
Power source and Wirefeeder setting requires some practice
by the operator, as the welding plant has two control settings
that have to balance. These are the Wirespeed control (refer
to section 3.10.3) and the welding Voltage Control (refer to
section 3.10.9). The welding current is determined by the
Wirespeed control, the current will increase with increased
Wirespeed, resulting in a shorter arc. Less wire speed will reduce the current and lengthen the arc. Increasing the welding
voltage hardly alters the current level, but lengthens the arc.
By decreasing the voltage, a shorter arc is obtained with a little
change in current level.
Manual 0-5420 4-3 BASIC WELDING GUIDE

ESAB FABRICATOR 141i
A-12918
ESAB MIG, Lift TIG, Stick Wire Selection Chart
Table 4-1: MIG, Lift TIG, Stick Welding Set up Chart
BASIC WELDING GUIDE 4-4 Manual 0-5420

ESAB FABRICATOR 141i
4.02 MIG (GMAW/FCAW) Welding Troubleshooting
Solving Problems Beyond the Welding Terminals
The general approach to fix Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW) problems is to start at the wire spool then work through to the MIG
Gun. There are two main areas where problems occur with MIG, Porosity and Inconsistent wire feed
Solving Problems Beyond the Welding Terminals - Porosity
When there is a gas problem the result is usually porosity within the weld metal. Porosity always stems from some contaminant
within the molten weld pool which is in the process of escaping during solidification of the molten metal. Contaminants range from
no gas around the welding arc to dirt on the work piece surface. Porosity can be reduced by checking the following points.
FAULT CAUSE
1
Limited or no shielding gas flows
out of the MIG Gun nozzle.
2
No shielding gas flow. Ensure that the shielding gas cylinder is not empty and the flow
3
Gas leaks. Check for gas leaks between the regulator/cylinder connection and
Check that the MIG Gun connection is fully engaged into the MIG
Gun Adapter. The o-rings in the MIG Gun connection must seal
the shielding gas within the MIG Gun Adapter so the shielding gas
flows into the MIG Gun and out thru the MIG Gun nozzle.
meter is correctly adjusted to workshop welding: 15-25 CFH or
outdoors welding: 35-46 CFH.
in the gas hose to the Power Source.
4
Welding in a windy environment. Shield the weld area from the wind or increase the gas flow.
5
Welding dirty, oily, painted,
Clean contaminates off the work piece.
oxidized or greasy plate.
6
Distance between the MIG Gun
nozzle and the work piece.
7
Maintain the MIG Gun in good
working order.
Keep the distance between the MIG Gun nozzle and the work piece
to a minimum. Refer to section 4.01
A
Ensure that the gas holes are not blocked and gas is exiting out of
the MIG Gun nozzle.
B
Do not restrict gas flow by allowing spatter to build up inside the
MIG Gun nozzle.
C
Check that the MIG Gun O-rings are not damaged.
Table 4-2: Solving Problems beyond the Welding Terminals-Porosity
WARNING
!
Disengage the feed roll when testing for gas flow by ear.
Manual 0-5420 4-5 BASIC WELDING GUIDE

ESAB FABRICATOR 141i
Solving Problems Beyond the Welding Terminals - Inconsistent Wire Feed
Wire feeding problems can be reduced by checking the following points.
FAULT CAUSE
1
Feed roller driven by motor in the
cabinet slipped
2
Wire spool unwinds and tangles Wire spool brake is too loose.
Wire spool brake is too tight or drive roll tension not
tight enough.
3
Wire slipping
4
Wire rubbed against the mis-aligned
guides and reduced wire feedability.
5
Liner blocked with debris
6
Incorrect or worn contact tip
A
Worn or incorrect feed roller size. Use a feed roller
matched to the size you are welding.
B
Replace feed roller if worn.
Mis-alignment of inlet/outlet guides
A
Increased amounts of debris are produced by the
wire passing through the feed roller when excessive
pressure is applied to the pressure roller adjuster.
B
Debris can also be produced by the wire passing
through an incorrect feed roller groove shape or size.
C
Debris is fed into the conduit liner where it
accumulates thus reducing wire feedability.
A
The contact tip transfers the weld current to the
electrode wire. If the hole in the contact tip is too
large then arcing may occur inside the contact tip
resulting in the wire jamming in the contact tip.
B
When using soft wire such as aluminum it may
become jammed in the contact tip due to expansion of
the wire when heated. A Velocity contact tip designed
for soft wires should be used.
7
Poor work lead contact to work piece If the work lead has a poor electrical contact to the
work piece then the connection point will heat up and
result in a reduction of power at the arc.
8
Bent liner This will cause friction between the wire and the liner
thus reducing wire feedability
Table 4-3: Wire Feeding Problems
BASIC WELDING GUIDE 4-6 Manual 0-5420

ESAB FABRICATOR 141i
Basic MIG Welding Troubleshooting
FAULT CAUSE REMEDY
1 Undercut A Welding arc voltage too high. A Decrease voltage or increase the wire feed
speed.
B Incorrect MIG Gun angle B Adjust angle.
C Excessive heat input C Increase the MIG Gun travel speed and/or
decrease welding current by decreasing the
voltage or decreasing the wire feed speed.
2 Lack of penetration A Welding current too low A Increase welding current by increasing wire
feed speed and increasing voltage.
B Joint preparation too narrow or
gap too tight
C Shielding gas incorrect C Change to a gas which gives higher penetration.
3 Lack of fusion Welding current too low Increase welding current.
4 Excessive spatter A Voltage too high A Decrease voltage or increase the wirespeed
B Voltage too low B Increase the voltage or decrease wirespeed.
5 Irregular weld shape A Incorrect voltage and travel
speed settings. Convex, voltage
too low. Concave, voltage too
high.
B Wire is wandering. B Check to see if it is near the end of the roll
C Incorrect shielding gas C Check shielding gas.
D Insufficient or excessive heat
input
B Increase joint angle or gap.
control.
A Adjust voltage and travel speed by adjusting the
voltage control and the wirespeed control.
of wire and replace when necessary. If the
problem continues, tighten the nozzle to see
if this corrects the problem. Then replace
contact tip.
D Adjust the wirespeed control or the voltage
control.
E Incorrect gun manipulation or
angle
Manual 0-5420 4-7 BASIC WELDING GUIDE
E Manipulate the gun correctly or place it in
correct angle.

ESAB FABRICATOR 141i
FAULT CAUSE REMEDY
6 Weld cracking A Weld high carbon steel without
pre/post heat treatment
B Incompatible filler metal used
to the base metal
C Weld beads too small C Decrease travel speed.
D Weld penetration narrow and
deep
E Excessive weld stresses E Increase weld metal strength or revise design
F Excessive voltage F Decrease voltage.
G Cooling rate too fast G Slow the cooling rate by preheating part to be
7 Cold weld puddle A Welding voltage too high A Decrease voltage or increase the wirespeed
B Loose welding cable
connection
C Low primary voltage C Contact supply authority.
D Fault in power source D Have an Accredited ESAB Service Provider to
A Have sufficient pre/post heat treatment before
welding high carbon steel.
B Use correct filler metal.
D Reduce current and voltage and increase MIG
Gun travel speed or select a lower penetration
shielding gas.
welded or cool slowly.
control.
B Check all welding cable connections.
test then replace the faulty component.
8 Arc does not have a
crisp sound that short
arc exhibits when the
wirefeed speed and
voltage are adjusted
correctly.
9 Poor weld result from
setup chart parameters
The MIG Gun has been
connected to the wrong voltage
polarity on the front panel
A Incorrect welder setup, polarity,
shielding gas, wire type and
size
B Contact tip has arc marks in the
bore causing excessive drag on
the wire
Table 4-4: MIG Welding Problems
Connect the MIG Gun to the positive (+)
welding terminal for solid wires and gas
shielded flux cored wires. Refer to the
electrode wire manufacturer for the correct
polarity.
A Check to make sure that the welder is set up
correctly; also check polarity, shielding gas,
wire type and size.
B Replace the contact tip with only a Genuine
Velocity contact tip.
BASIC WELDING GUIDE 4-8 Manual 0-5420

ESAB FABRICATOR 141i
Art # A-07688
Art # A-07689
Art # A-07690
4.03 Stick (SMAW) Basic Welding Technique
Size of Electrode
The electrode size is determined by the thickness of metals
being joined and can also be governed by the type of welding
machine available. Small welding machines will only provide
sufficient current (amperage) to run the smaller size electrodes.
For thin sections, it is necessary to use smaller electrodes
otherwise the arc may burn holes through the job. A little
practice will soon establish the most suitable electrode for a
given application.
Storage of Electrodes
Always store electrodes in a dry place and in their original
containers.
Electrode Polarity
Electrodes are generally connected to the ELECTRODE HOLDER
with the Electrode Holder connected positive polarity. The
WORK LEAD is connected negative polarity and is connected to
the work piece. If in doubt consult the electrode data sheet or
your nearest Accredited ESAB Distributor.
Types of Electrodes
Arc Welding electrodes are classified into a number of groups
depending on their applications. There are a great number
of electrodes used for specialized industrial purposes which
are not of particular interest for everyday general work.
These include some low hydrogen types for high tensile steel,
cellulose types for welding large diameter pipes, etc The range
of electrodes dealt with in this publication will cover the vast
majority of applications likely to be encountered; are all easy
to use.
Arc Welding Practice
The techniques used for arc welding are almost identical
regardless of what types of metals are being joined. Naturally
enough, different types of electrodes would be used for different metals as described in the preceding section.
Welding Position
The electrodes dealt with in this publication can be used in
most positions, i.e. they are suitable for welding in flat, horizontal, vertical and overhead positions. Numerous applications
call for welds to be made in positions intermediate between
these. Some of the common types of welds are shown in
Figures 4-11 through 4-18.
4.04 Effects of Stick Welding Various Materials
High Tensile and Alloy Steels
The two most prominent effects of welding these steels are
the formation of a hardened zone in the weld area, and, if
suitable precautions are not taken, the occurrence in this zone
of under-bead cracks. Hardened zone and under-bead cracks
in the weld area may be reduced by using the correct electrodes, preheating, using higher current settings, using larger
electrodes sizes, short runs for larger electrode deposits or
tempering in a furnace.
Manganese Steels
The effect on manganese steel of slow cooling from high
temperatures is to embrittle it. For this reason it is absolutely
essential to keep manganese steel cool during welding by
quenching after each weld or skip welding to distribute the
heat.
Cast Iron
Most types of cast iron, except white iron, are weldable. White
iron, because of its extreme brittleness, generally cracks when
attempts are made to weld it. Trouble may also be experienced
when welding white-heart
malleable, due to the porosity caused by gas held in this type
of iron.
Art # A-07687
Figure 4-11: Flat Position, Down Hand Butt Weld
Figure 4-12: Flat Position, Gravity Fillet Weld
Figure 4-13: Horizontal Position, Butt Weld
Copper and Alloys
The most important factor is the high rate of heat conductivity
of copper, making pre-heating of heavy sections necessary to
give proper fusion of weld and base metal.
Figure 4-14: Horizontal-Vertical (HV) Position
Manual 0-5420 4-9 BASIC WELDING GUIDE

ESAB FABRICATOR 141i
Art A-07691
Figure 4-15: Vertical Position, Butt Weld
Art # A-07692
Figure 4-16: Vertical Position, Fillet Weld
Art# A-07693
Figure 4-17: Overhead Position, Butt Weld
Art # A-07694
Figure 4-18: Overhead Position, Fillet Weld
Joint Preparations
In many cases, it will be possible to weld steel sections without any special preparation. For heavier sections and for repair work
on castings, etc., it will be necessary to cut or grind an angle between the pieces being joined to ensure proper penetration of the
weld metal and to produce sound joints.
In general, surfaces being welded should be clean and free of rust, scale, dirt, grease, etc. Slag should be removed from oxy-cut
surfaces. Typical joint designs are shown in Figure 4-19.
BASIC WELDING GUIDE 4-10 Manual 0-5420

ESAB FABRICATOR 141i
Open Square Butt
Single Vee Butt Joint
Not less than
Joint
Gap varies from
1/16" (1.6mm) to 3/16" (4.8mm)
depending on plate thickness
Single Vee Butt Joint
Lap Joint
Fillet Joint
Corner Weld
Not less than
45°
Double Vee Butt Joint
Tee Joints
(Fillet both sides of the
joint)
Edge Joint
1.6mm (1/16”)
1/16" (1.6mm)
70°
Not less than
70°
1/16" (1.6mm) max
1/16" (1.6mm) max
Plug Weld Plug Weld
Art # A-10367
Figure 4-19: Typical Joint Designs for Arc Welding
Arc Welding Technique - A Word to Beginners
For those who have not yet done any welding, the simplest way to commence is to run beads on a piece of scrap plate. Use mild
steel plate about 1/4" (6.4mm) thick and a 1/8"(3.2mm) electrode. Clean any paint, loose scale or grease off the plate and set it
firmly on the work bench so that welding can be carried out in the downhand position. Make sure that the work clamp is making
good electrical contact with the work, either directly or through the work table. For light gauge material, always clamp the work
lead directly to the job, otherwise a poor circuit will probably result.
Striking the Arc
Practice this on a piece of scrap plate before going on to more exacting work. You may at first experience difficulty due to the tip of
the electrode "sticking" to the work piece. This is caused by making too heavy a contact with the work and failing to withdraw the
electrode quickly enough. A low amperage will accentuate it. This freezing-on of the tip may be overcome by scratching the electrode along the plate surface in the same way as a match is struck. As soon as the arc is established, maintain a 1/16"(1.6mm) to
1/8"(3.2mm) gap between the burning electrode end and the parent metal. Draw the electrode slowly along as it melts down.
Another difficulty you may meet is the tendency, after the arc is struck, to withdraw the electrode so far that the arc is broken
again. A little practice will soon remedy both of these faults.
Manual 0-5420 4-11 BASIC WELDING GUIDE

ESAB FABRICATOR 141i
20°-30°
Art # A-10368
1/16" (1.6mm)
Figure 4-20: Striking an Arc
Arc Length
The securing of an arc length necessary to produce a neat
weld soon becomes almost automatic. You will find that a long
arc produces more heat. A very long arc produces a crackling or spluttering noise and the weld metal comes across in
large, irregular blobs. The weld bead is flattened and spatter
increases. A short arc is essential if a high quality weld is to be
obtained although if it is too short there is the danger of it being blanketed by slag and the electrode tip being solidified in. If
this should happen, give the electrode a quick twist back over
the weld to detach it. Contact or "touch-weld" electrodes such
as E7014 Stick electrodes do not stick in this way, and make
welding much easier.
Rate of Travel
After the arc is struck, your next concern is to maintain it, and
this requires moving the electrode tip towards the molten pool
at the same rate as it is melting away. At the same time, the
electrode has to move along the plate to form a bead. The
electrode is directed at the weld pool at about 20º from the
vertical. The rate of travel has to be adjusted so that a wellformed bead is produced.
If the travel is too fast, the bead will be narrow and strung
out and may even be broken up into individual globules. If the
travel is too slow, the weld metal piles up and the bead will be
too large.
Making Welded Joints
Having attained some skill in the handling of an electrode, you
will be ready to go on to make up welded joints.
A. Butt Welds
Set up two plates with their edges parallel, as shown in
Figure 4-21, allowing 1/16"(1.6mm) to 3/32"(2.4mm)
gap between them and tack weld at both ends. This is to
prevent contraction stresses from the cooling weld metal
pulling the plates out of alignment. Plates thicker than 1/4"
(6.4mm) should have their mating edges beveled to form a
70º to 90º included angle. This allows full penetration of the
weld metal to the root. Using a 1/8"(3.2mm) E7014 Stick
electrode at 100 amps, deposit a run of weld metal on the
bottom of the joint.
Do not weave the electrode, but maintain a steady rate of
travel along the joint sufficient to produce a well-formed
bead. At first you may notice a tendency for undercut to form,
but keeping the arc length short, the angle of the electrode at
about 20º from vertical, and the rate of travel not too fast, will
help eliminate this. The electrode needs to be moved along
fast enough to prevent the slag pool from getting ahead of
the arc. To complete the joint in thin plate, turn the job over,
clean the slag out of the back and deposit a similar weld.
Tack Weld
Heavy plate will require several runs to complete the joint.
After completing the first run, chip the slag out and clean the
weld with a wire brush. It is important to do this to prevent
slag being trapped by the second run. Subsequent runs are
then deposited using either a weave technique or single
beads laid down in the sequence shown in Figure 4-22. The
width of weave should not be more than three times the core
wire diameter of the electrode. When the joint is completely
filled, the back is either machined, ground or gouged out
to remove slag which may be trapped in the root, and to
prepare a suitable joint for depositing the backing run. If a
backing bar is used, it is not usually necessary to remove
this, since it serves a similar purpose to the backing run in
securing proper fusion at the root of the weld.
B. Fillet Welds
These are welds of approximately triangular cross-section
made by depositing metal in the corner of two faces meeting
at right angles. Refer to Figure 4-14.
A piece of angle iron is a suitable specimen with which to
begin, or two lengths of strip steel may be tacked together
at right angles. Using a 1/8"(3.2mm) E7014 Stick electrode
at 100 amps, position angle iron with one leg horizontal and
the other vertical. This is known as a horizontal-vertical (HV)
fillet. Strike the arc and immediately bring the electrode to
a position perpendicular to the line of the fillet and about
Electrode
Figure 4-21: Butt Weld
Art # A-07698
Figure 4-22: Weld Build up Sequence
Tack Weld
Art # A-07697_AB
BASIC WELDING GUIDE 4-12 Manual 0-5420

ESAB FABRICATOR 141i
Art # A-07699_AB
45º from the vertical. Some electrodes require to be sloped
about 20º away from the perpendicular position to prevent
slag from running ahead of the weld. Refer to Figure 4-23.
Do not attempt to build up much larger than 1/4"(6.4mm)
width with a 1/8"(3.2mm) electrode, otherwise the weld
metal tends to sag towards the base, and undercut forms on
the vertical leg. Multi-runs can be made as shown in Figure
4-24. Weaving in HV fillet welds is undesirable.
45° from
vertical
60° - 70° from line
of weld
Figure 4-23: Electrode Position for HV Fillet Weld
Art # A-07700_AB
Art # A-07701
Figure 4-25: Single Run Vertical Fillet Weld
Art # A-07702
6
3
1
5
2
4
Figure 4-24: Multi-runs in HV Fillet Weld
C. Vertical Welds
1. Vertical Up
Tack weld a three feet length of angle iron to your
work bench in an upright position. Use a 1/8"(3.2mm)
E7014 Stick electrode and set the current at 100
amps. Make yourself comfortable on a seat in front
of the job and strike the arc in the corner of the
fillet. The electrode needs to be about 10º from the
horizontal to enable a good bead to be deposited.
Refer Figure 4-25. Use a short arc, and do not attempt
to weave on the first run. When the first run has been
completed de-slag the weld deposit and begin the
second run at the bottom. This time a slight weaving
motion is necessary to cover the first run and obtain
good fusion at the edges. At the completion of each
side motion, pause for a moment to allow weld metal
to build up at the edges, otherwise undercut will form
and too much metal will accumulate in the centre of
the weld. Figure 4-26 illustrates multi-run technique
and Figure 4-27 shows the effects of pausing at the
edge of weave and of weaving too rapidly.
Figure 4-26: Multi Run Vertical Fillet Weld
Art # A-07703
Figure 4-27: Examples of Vertical Fillet Welds
2. Vertical Down
The E7014 Stick electrode makes welding in this po-
sition particularly easy. Use a 1/8"(3.2mm) electrode
at 100 amps. The tip of the electrode is held in light
contact with the work and the speed of downward
travel is regulated so that the tip of the electrode just
keeps ahead of the slag. The electrode should point
upwards at an angle of about 45º.
3. Overhead Welds
Apart from the rather awkward position necessary,
overhead welding is not much more difficult that
downhand welding. Set up a specimen for overhead
welding by first tacking a length of angle iron at right
angles to another piece of angle iron or a length of
waste pipe. Then tack this to the work bench or hold
in a vice so that the specimen is positioned in the
Manual 0-5420 4-13 BASIC WELDING GUIDE

ESAB FABRICATOR 141i
Upsetting
Art # A-07706_AC
Weld
Permanent Upset
Contraction
with tension
Distortion
Distortion in some degree is present in all forms of welding. In many cases it is so small that it is barely perceptible,
but in other cases allowance has to be made before welding
commences for the distortion that will subsequently occur. The
study of distortion is so complex that only a brief outline can
be attempted hear.
The Cause of Distortion
Distortion is caused by:
BASIC WELDING GUIDE 4-14 Manual 0-5420
overhead position as shown in the sketch. The electrode is held at 45º to the horizontal and tilted 10º in
the line of travel (Figure 4-28). The tip of the electrode
may be touched lightly on the metal, which helps to
give a steady run. A weave technique is not advisable
for overhead fillet welds. Use a 1/8"(3.2mm) E6013
Stick electrode at 100 amps, and deposit the first run
by simply drawing the electrode along at a steady
rate. You will notice that the weld deposit is rather
convex, due to the effect of gravity before the metal
freezes.
Art # A-07704
Figure 4-28: Overhead Fillet Weld
A. Contraction of Weld Metal:
Molten steel shrinks approximately 11 per cent in volume on
cooling to room temperature. This means that a cube of molten metal would contract approximately 2.2 per cent in each
of its three dimensions. In a welded joint, the metal becomes
attached to the side of the joint and cannot contract freely.
Therefore, cooling causes the weld metal to flow plastically,
that is, the weld itself has to stretch if it is to overcome the
effect of shrinking volume and still be attached to the edge
of the joint. If the restraint is very great, as, for example, in
a heavy section of plate, the weld metal may crack. Even in
cases where the weld metal does not crack, there will still
remain stresses "Locked-up" in the structure. If the joint
material is relatively weak, for example, a butt joint in 5/64"
(2.0mm) sheet, the contracting weld metal may cause the
sheet to become distorted.
B. Expansion and Contraction of Parent Metal in the
Fusion Zone:
While welding is proceeding, a relatively small volume of the
adjacent plate material is heated to a very high temperature
and attempts to expand in all directions. It is able to do this
freely at right angles to the surface of the plate (i.e., "through
the weld", but when it attempts to expand "across the weld"
or "along the weld", it meets considerable resistance, and
to fulfill the desire for continued expansion, it has to deform
plastically, that is, the metal adjacent to the weld is at a
high temperature and hence rather soft, and, by expanding,
pushes against the cooler, harder metal further away, and
tends to bulge (or is "upset". When the weld area begins
to cool, the "upset" metal attempts to contract as much as
it expanded, but, because it has been "upset" it does not
resume its former shape, and the contraction of the new
shape exerts a strong pull on adjacent metal. Several things
can then happen.
The metal in the weld area is stretched (plastic deformation), the job may be pulled out of shape by the powerful
contraction stresses (distortion), or the weld may crack, in
any case, there will remain "locked-up" stresses in the job.
Figures 4-29 and 4- 30 illustrate how distortion is created.
Hot
Weld
Hot
Expansion with
compression
Cool
Art # A-07705_AB
Figure 4-29: Parent Metal Expansion
Figure 4-30: Parent Metal Contraction
Overcoming Distortion Effects
There are several methods of minimizing distortion effects.
A. Peening
This is done by hammering the weld while it is still hot.
The weld metal is flattened slightly and because of this the
tensile stresses are reduced a little. The effect of peening
is relatively shallow, and is not advisable on the last layer.
B. Distribution of Stresses
Distortion may be reduced by selecting a welding sequence
which will distribute the stresses suitably so that they tend
to cancel each other out. See Figures 4-31 through 4-33 for
various weld sequences. Choice of a suitable weld sequence
is probably the most effective method of overcoming distortion, although an unsuitable sequence may exaggerate it.
Simultaneous welding of both sides of a joint by two welders
is often successful in eliminating distortion.
C. Restraint of Parts
Forcible restraint of the components being welded is often
used to prevent distortion. Jigs, positions, and tack welds
are methods employed with this in view.

ESAB FABRICATOR 141i
D. Presetting
It is possible in some cases to tell from past experience or
to find by trial and error (or less frequently, to calculate) how
much distortion will take place in a given welded structure.
By correct pre-setting of the components to be welded,
constructional stresses can be made to pull the parts into
correct alignment. A simple example is shown in Figure 4-31.
E. Preheating
Suitable preheating of parts of the structure other than the
area to be welded can be sometimes used to reduce distortion. Figure 4-32 shows a simple application. By removing
the heating source from b and c as soon as welding is
completed, the sections b and c will contract at a similar
rate, thus reducing distortion.
Art # A-07707
Figure 4-31: Principle of Presetting
Art # A-07710_AB
4
Art # A-07711_AB
1
2
Block Sequence.
The spaces between the welds are
filled in when the welds are cool.
3
Figure 4-34: Welding Sequence
2
3
Figure 4-35: Step back Sequence
1
Art # A-07708
B
Dotted lines show effect if no preheat is used
Weld
C
PreheatPreheat
Figure 4-32: Reduction of Distortion by Preheating
Art # A-07709
Figure 4-33: Examples of Distortion
Art # A-07428_AB
Figure 4-36: Chain Intermittent Welding
Art # A-07713_AB
Figure 4-37: Staggered Intermittent Welding
Manual 0-5420 4-15 BASIC WELDING GUIDE

ESAB FABRICATOR 141i
Insufficient Gap
Incorrect Sequence
Art # A-05866_AC
4.05 Stick (SMAW) Welding Troubleshooting
FAULT CAUSE REMEDY
1 Welding current
varying
2 A gap is left by
failure of the weld
metal to fill the
root of the weld.
3 Non-metallic
particles are
trapped in the
weld metal.
ARC FORCE control knob
is set at a value that causes
the welding current to vary
excessively with the arc
Reduce the ARC FORCE control knob until welding
current is reasonably constant while prohibiting the
electrode from sticking to the work piece when you
“dig” the electrode into the workpiece.
length.
A Welding current too low A Increase welding current.
B Electrode too large for joint. B Use smaller diameter electrode.
C Insufficient gap. C Allow wider gap.
A Non-metallic particles may
be trapped in undercut from
A If a bad undercut is present clean slag bout and
cover with a run from a smaller gauge electrode.
previous run.
B Joint preparation too
restricted.
C Irregular deposits allow slag
B Allow for adequate penetration and room for
cleaning out the slag.
C If very bad, chip or grind out irregularities.
to be trapped.
D Lack of penetration with slag
trapped beneath weld bead.
D Use smaller electrode with sufficient current to give
adequate penetration. Use suitable tools to remove
all slag from comers.
E Rust or mill scale is
E Clean joint before welding.
preventing full fusion.
F Wrong electrode for position
in which welding is done.
F Use electrodes designed for position in which
welding is done, otherwise proper control of slag is
difficult.
Figure 1- Example of insufficient gap or incorrect sequence
BASIC WELDING GUIDE 4-16 Manual 0-5420

ESAB FABRICATOR 141i
Lack of fusion caused by dirt,
FAULT CAUSE REMEDY
4 A groove has been
formed in the base
metal adjacent to
the toe of a weld
and has not been
filled by the weld
metal (undercut).
5 Portions of the
weld run do not
fuse to the surface
of the metal or
edge of the joint.
A Welding current is too high. A Reduce welding current.
B Welding arc is too long. B Reduce the length of the welding arc.
C Angle of the electrode is
incorrect.
D Joint preparation does not
allow correct electrode angle.
C Electrode should not be inclined less than 45° to
the vertical face.
D Allow more room in joint for manipulation of the
electrode.
E Electrode too large for joint. E Use smaller gauge electrode.
F Insufficient deposit time at
edge of weave.
G Power Source is set for MIG
F Pause for a moment at edge of weave to allow weld
metal buildup.
G Set Power Source to STICK (SMAW) mode.
(GMAW) welding.
A Small electrodes used on
A Use larger electrodes and preheat the plate.
heavy cold plate.
B Welding current is too low. B Increase welding current.
C Wrong electrode angle. C Adjust angle so the welding arc is directed more
into the base metal.
D Travel speed of electrode is
D Reduce travel speed of electrode.
too high.
electrode angle incorrect,
rate of travel too high
Art # A-05867_AC
Lack of side fusion,
scale dirt, small electrode,
amperage too low
6 Gas pockets or
voids in weld
metal (porosity)
E Scale or dirt on joint surface. E Clean surface before welding.
Lack of
inter-run fusion
Lack of root fusion
Figure 2: Example of Lack of Fusion
A High levels of sulfur in steel. A Use an electrode that is designed for high sulfur
steels.
B Electrodes are damp. B Dry electrodes before use.
C Welding current is too high. C Reduce welding current.
D Surface impurities such as
D Clean joint before welding.
oil, grease, paint, etc.
E Welding in a windy
E Shield the weld area from the wind.
environment.
F Electrode damaged ie flux
coating incomplete.
F Discard damaged electrodes and only use
electrodes with a complete flux coating.
Manual 0-5420 4-17 BASIC WELDING GUIDE

ESAB FABRICATOR 141i
Not cleaned,
or incorrect
electrode
Slag
trapped in
undercut
Slag trapped in root
Art # A-05868_AC
FAULT CAUSE REMEDY
7 Crack occurring in
weld metal soon
after solidification
commences
8 The Stick
electrode is
difficult to run
with multiple arcouts when welding
A Rigidity of joint. A Redesign to relieve weld joint of severe stresses or
use crack resistance electrodes.
B Insufficient throat thickness. B Travel slightly slower to allow greater build up in
throat.
C Weld current is too high. C Decrease welding current.
Figure 3: Example of Slag Inclusion
The Stick electrode being
used is not suitable for use
with this machine.
Use E6013 or E7018 Stick electrodes for steel or
300 series stainless steel Stick electrodes for 300
series stainless steel.
Table 4-5: Welding Problems - Stick (SMAW)
4.06 TIG (GTAW) Basic Welding Technique
Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (GTAW) or TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas) as it is commonly referred to, is a welding process in which fusion is
produced by an electric arc that is established between a single tungsten (non-consumable) electrode and the work piece. Shielding is obtained from a welding grade shielding gas or welding grade shielding gas mixture which is generally Argon based. A filler
metal may also be added manually in some circumstances depending on the welding application.
Art # A-10369_AB
Gas Cup
Either Ceramic,
Work Piece
Can Be Any Commercial
Metal
Welds Made With or Without
Addition of Filler Metal
Figure 4-38: TIG Welding Application Shot
High Impact or
Water Cooled
Metal
Tungsten Electrode
Non-Consumable
Inert Gas
Shields Electrode
and Weld Puddle
BASIC WELDING GUIDE 4-18 Manual 0-5420

Tungsten Electrode Current Ranges
Electrode Diameter DC Current (Amps)
0.040” (1.0mm) 30-60
Table 4-6: Current Ranges for Various Tungsten Electrode Sizes
Guide for Selecting Filler Wire Diameter
Filler Wire Diameter DC Current Range (Amps)
ESAB FABRICATOR 141i
1/16” (1.6mm) 60-115
3/32” (2.4mm) 100-165
1/8” (3.2mm) 135-200
5/32” (4.0mm) 190-280
3/16” (4.8mm) 250-340
1/16” (1.6mm) 20-90
3/32” (2.4mm) 65-115
1/8” (3.2mm) 100-165
3/16” (4.8mm) 200-350
Table 4-7: Filler Wire Selection Guide
Tungsten Electrode Types
Electrode Type
(Ground Finish)
Thoriated 2%
Zirconated 1%
Ceriated 2%
NOTE!
The Fabricator 141i is not suited for AC TIG welding.
Welding Application Features Color Code
DC welding of mild
steel, stainless steel
and copper
High quality AC
welding of aluminum,
magnesium and their
alloys.
AC & DC welding
of mild steel,
stainless steel,
copper, aluminum,
magnesium and their
alloys
Excellent arc starting,
Long life, High current
carrying capacity
Self cleaning, Long
life, Maintains balled
end, High current
carrying capacity.
Longer life, More
stable arc, Easier
starting, Wider current
range, Narrower more
concentrated arc.
Table 4-8
Red
Brown
Grey
Manual 0-5420 4-19 BASIC WELDING GUIDE

ESAB FABRICATOR 141i
Base Metal
Thickness
0.040”
1.0mm
0.045”
1.2mm
1/16”
1.6mm
1/8”
3.2mm
3/16”
4.8mm
1/4”
6.4mm
TIG Welding is generally regarded as a specialized process that requires operator competency. While many of the principles outlined in the previous Arc Welding section are applicable a comprehensive outline of the TIG Welding process is outside the scope of
this Operating Manual. For further information please refer to www.victortechnologies.com or contact ESAB.
DC Current
for Mild
Steel
35-45
40-50
45-55
50-60
60-70
70-90
80-100
90-115
115-135
140-165
160-175
170-200
DC Current
for Stainless
Steel
20-30
25-35
30-45
35-50
40-60
50-70
65-85
90-110
100-125
125-150
135-160
160-180
Tungsten
Electrode
Diameter
0.040”
1.0mm
0.040”
1.0mm
1/16”
1.6mm
1/16”
1.6mm
3/32”
2.4mm
1/8”
3.2mm
Table 4-9
Filler Rod
Diameter (if
required)
1/16”
1.6mm
1/16”
1.6mm
1/16”
1.6mm
3/32”
2.4mm
1/8”
3.2mm
5/32”
4.0mm
Argon Gas
Flow Rate
CFH
10-15 Butt/Corner
10-15 Butt/Corner
15 Butt/Corner
15 Butt/Corner
20 Butt/Corner
20 Butt/Corner
Joint Type
Lap/Fillet
Lap/Fillet
Lap/Fillet
Lap/Fillet
Lap/Fillet
Lap/Fillet
4.07 TIG (GTAW) Welding Problems
FAULT CAUSE REMEDY
1 Excessive bead build up or
poor penetration or poor
fusion at edges of weld.
2 Weld bead too wide and
flat or undercut at edges
of weld or excessive burn
through.
3 Weld bead too small or
insufficient penetration or
ripples in bead are widely
spaced apart.
4 Weld bead too wide or
excessive bead build up or
excessive penetration in
butt joint.
5 Uneven leg length in fillet
joint
Welding current is too
low
Welding current is too
high
Travel speed too fast Reduce travel speed.
Travel speed too slow Increase travel speed.
Wrong placement of
filler rod
Increase weld current and/or faulty joint
preparation.
Decrease weld current.
Re-position filler rod.
BASIC WELDING GUIDE 4-20 Manual 0-5420

ESAB FABRICATOR 141i
FAULT CAUSE REMEDY
6 Electrode melts or oxidizes
when an arc is struck.
A TIG Torch lead
connected to positive
welding terminal.
B No gas flowing to
welding region.
C TIG Torch is clogged
with dust or dirt.
D Gas hose is cut. D Replace gas hose.
E Gas passage contains
impurities.
F Gas regulator turned off
or cylinder shut off.
G TIG Torch valve is
turned off.
H The electrode is too
small for the welding
current.
A Connect TIG Torch lead to negative welding
terminal.
B Turn TIG Torch gas valve ON. Check the gas
lines for kinks or breaks and gas cylinder
contents.
C Clean TIG Torch.
E Disconnect gas hose from the rear of Power
Source then raise gas pressure and blow out
impurities.
F Turn on.
G Turn on.
H Increase electrode diameter or reduce the
welding current.
I Power Source is set for
MIG welding.
7 Dirty weld pool A Electrode contaminated
by contact with work
piece or filler rod
material.
B Work piece surface has
foreign material on it.
C Gas contaminated with
air.
8 Poor weld finish Inadequate shielding
gas.
I Set Power Source to LIFT TIG mode.
A Clean the electrode by grinding off the
contaminates.
B Clean surface.
C Check gas lines for cuts and loose fitting or
change gas cylinder.
Increase gas flow or check gas line for gas
flow problems.
Manual 0-5420 4-21 BASIC WELDING GUIDE

ESAB FABRICATOR 141i
FAULT CAUSE REMEDY
9 Arc start is not smooth. A Tungsten electrode
is too large for the
welding current.
B The wrong electrode
is being used for the
welding job.
C Gas flow rate is too
high.
D Incorrect shielding gas
is being used.
E Poor work clamp
connection to work
piece.
F Tungsten not properly
sharpened.
10 Arc flutters during TIG
welding.
Tungsten electrode
is too large for the
welding current.
A Select the right size electrode. Refer to Table
4-7 Current Ranges for Various Tungsten
Electrode Size.
B Select the right electrode type. Refer to Table
4-9 Tungsten Electrode Types.
C Select the right rate for the welding job. Refer
to Table 4-10.
D Select the right shielding gas.
E Improve connection to work piece.
F Grind tungsten to proper shape.
Select the right size electrode. Refer to Table
4-7 Current Ranges for Various Electrode
Size.
11 Tungsten blackens due to
lack of shielding gas or
wrong shield gas.
A Gas valve on the TIG
Torch has not be turned
on.
B Gas cylinder valve off
or TIG Torch hose not
connected to regulator
C Incorrect shielding gas
is being used.
Table 4-10: TIG (GTAW) Welding Problems
A Turn on TIG Torch gas valve before you
B Turn on gas cylinder valve or connect TIG
C Select the right shielding gas.
commence welding.
Torch hose to regulator.
BASIC WELDING GUIDE 4-22 Manual 0-5420

POWER SOURCE PROBLEMS AND ROUTINE SERVICE
5.01 Power Source Problems
FAULT CAUSE REMEDY
1 Primary Power Supply
is ON, power indicator is
illuminated however the
Power Source will not
commence welding when
the torch trigger switch is
depressed.
A Power Source is not in the
correct mode of operation.
B Welding leads, or polarity cable
not connected.
C Faulty torch trigger. C Repair or replace torch trigger
ESAB FABRICATOR 141i
SECTION 5:
REQUIREMENTS
A Set the Power Source to the
correct mode of operation with the
process selection switch.
B Connect welding leads or polarity
cable.
switch/lead.
2 Fault Indicator is
illuminated and the
Power Source will not
commence welding when
the torch trigger switch is
depressed.
3 The Power Source will not
feed wire in MIG mode.
4 Welding wire continues to
feed when torch trigger is
released.
Duty cycle of Power Source has
been exceeded.
A Electrode wire stuck in conduit
liner or contact tip (burn-back
jam).
B 8 pin gun connector not
connected.
C MIG GUN/SPOOL GUN switch is
switched to SPOOL GUN.
D Faulty torch trigger. D Repair or replace torch trigger.
E Wire tension too loose. E Tighten wire tension.
F Brake tension too tight. F Loosen brake tension.
A Trigger mode selection switch is
in 4T latch mode.
Leave the Power Source
switched ON and allow it to
cool. Note that fault indicator
must be extinguished prior to
commencement of welding.
A Check for clogged / kinked MIG
Gun conduit liner, loose nozzle or
worn contact tip. Replace faulty
components.
B Connect 8 pin gun connector.
C Switch the MIG GUN/SPOOL GUN
switch to MIG GUN.
A Change the trigger mode selection
switch from 4T latch mode to 2T
normal mode.
B Torch trigger leads shorted. B Repair or replace torch trigger
switch/lead.
5 Welding arc cannot be
established in MIG mode.
Manual 0-5420 5-1 TROUBLESHOOTING AND SERVICE
A MIG Gun polarity lead is not
connected into a welding output
terminal.
B Poor or no work lead contact. B Clean work clamp area and ensure
A Connect the MIG Gun polarity
lead to either the positive welding
output terminal or the negative
welding output terminal as
required.
good electrical contact.

ESAB FABRICATOR 141i
FAULT CAUSE REMEDY
6 Inconsistent wire feed. A Fouled contact tip. A Replace Velocity contact tip if
necessary.
B Drive roll tension not tight
B Tighten drive roll tension.
enough.
C Worn feed roll. C Replace.
D Excessive brake tension on wire
reel hub.
E Worn, kinked or dirty conduit
D Reduce brake tension on spool
hub
E Clean or replace conduit liner
liner.
7 No gas flow in MIG mode. A Gas hose is damaged. A Replace or repair.
B Gas passage contains debris. B Disconnect gas hose from the rear
of Power Source and blow out
debris.
C Shielding gas cylinder valve shut
C Turn on the cylinder.
off.
D Flowmeter/ Regulator turned off. D Turn on flowmeter/ regulator.
E Empty gas cylinder. E Replace gas cylinder.
8 Gas flow continues after
the torch trigger switch
has been released (MIG
Gas valve has jammed open due
to debris in the gas or the gas
line.
Have an accredited ESAB service
provider repair or replace gas
valve.
mode).
9 Power indicator will not
illuminate and welding arc
The Electricity supply is
inadequate.
Ensure that the Electricity Supply
voltage is within 95-140 VAC.
cannot be established.
10 TIG electrode melts when
arc is struck.
11 Arc flutters during TIG
welding.
TIG Torch is connected to the (+)
polarity terminal.
Tungsten electrode is too large
for the welding current.
Table 5-1
Connect the TIG Torch to the (-)
polarity terminal.
Select the correct size of tungsten
electrode. Refer to Table 4-7.
5.02 Routine Service
WARNING
There are extremely dangerous voltage and power levels present inside this Power Source. Do
Routine Inspection, Testing & Maintenance
The inspection and testing of the Power Source and associated accessories shall be carried out in accordance with Section 5 of EN
60974-1: Safety in Welding and Allied Processes-Part 2 Electrical. This includes an insulation resistance test and an earthing test to
ensure the integrity of the Power Source is compliant with ESAB's original specifications.
If equipment is to be used in a hazardous location or environments with a high risk of electrocution as outlined in EN 60974-1,
then the above tests should be carried out prior to entering this location.
A. Testing Schedule
1. For transportable equipment, at least once every 3 months; and
2. For fixed equipment, at least once every 12 months.
The owners of the equipment shall keep a suitable record of the periodic tests and a system of tagging, including the date of
the most recent inspection.
TROUBLESHOOTING AND SERVICE 5-2 Manual 0-5420
not attempt to open or repair unless you are an accredited ESAB Service Provider. Disconnect
the Welding Power Source from the Electricity Supply Voltage before disassembling.

ESAB FABRICATOR 141i
A transportable Power Source is deemed to be any equipment that is not permanently connected and fixed in the position in
which it is operated.
NOTE!
Please refer to local guidelines for further information.
B. General Maintenance Checks
Welding equipment should be regularly checked by an accredited ESAB Service Provider to ensure that:
1. Flexible cord is of the multi-core tough rubber or plastic sheathed type of adequate rating, correctly connected and in
good condition.
2. Welding terminals are in suitable condition and are shrouded to prevent inadvertent contact or short circuit.
3. The Welding System is clean internally, especially from metal filing, slag, and loose material.
C. Accessories
Accessory equipment, including output leads, electrode holders, torches, wire feeders and the like shall be inspected at least
monthly by a competent person to ensure that the equipment is in a safe and serviceable condition. All unsafe accessories shall
not be used.
D. Repairs
If any parts are damaged for any reason, it is recommended that replacement be performed by an accredited ESAB Service Provider.
5.03 Cleaning the Welding Power Source
WARNING
There are dangerous voltage and power levels present inside this product. Do not attempt to open or
repair unless you are a qualified electrical tradesperson. Disconnect the Welding Power Source from the
Electricity Supply Voltage before disassembling.
5.04 Cleaning the Feed Rolls
Clean the grooves in the drive rolls frequently. This can be done by using a small wire brush. Also wipe off, or clean the grooves on
the upper feed roll. After cleaning, tighten the feed roll retaining knobs.
CAUTION
!
Do not use compressed air to clean the Welding Power Source. Compressed air can force metal particles to lodge between live electrical parts and earthed metal parts within the Welding Power Source.
This may result in arcing between this parts and their eventual failure.
Manual 0-5420 5-3 TROUBLESHOOTING AND SERVICE

ESAB FABRICATOR 141i
5.05 Volt-Ampere Curves
Voltage-Amperage Curves shows maximum voltage and amperage output capabilities of welding power source. Curves of other
settings fall between curves shown.
60
50
40
30
20
Output Voltage (Volts)
10
0
0102030405060708090 100 110 120 130 140 150
MIG (GMAW/ FCAW)
Fabricator 141i
TIG (GTAW)
STICK (SMAW)
Welding Current (Amps)
Figure 5-1: Fabricator 141i Volt-Ampere Curves
Art # A-11807
TROUBLESHOOTING AND SERVICE 5-4 Manual 0-5420

SECTION 6: KEY SPARE PARTS
6.01 Tweco Fusion 140A MIG Gun Parts
ESAB FABRICATOR 141i
Torch Part No: 1017-1321
Art# A-11672_AB
Item
No.
1 Velocity Nozzle**
2
3
4 Conduit Assembly* WS42-3035-15 1420-1140
5
Description Part No.
VNS-50 1220-1201
VNS-50F 1220-1200
VNS-62 1220-1203
VNS-62F 1220-1202
VNS-37 1220-1206
VNS-37F 1220-1204
VNS-75FAS 1220-1205
VTS-23 1110-1308
VTS-30 1110-1309
VTS-35 1110-1310
VTS-40 1110-1311
Velocity Contact
Tip**
Handle / Trigger
Repair Kit
ESAB Rear
5A
Connector
5B ESAB Control Wire 35K-350-1 2000-2352
ESAB Control Wire &
5C
Plug
VTS-45 1110-1312
VTS-52 1110-1314
VTS-116 1110-1315
VTSA-116 1110-1317
VTSA-364 1110-1313
VTS-564 1110-1316
F8 2020-2025
350-174H 2035-2110
WS-354-TA-LC 2060-2141
Table 6-1: Tweco Fusion 140A MIG Gun Parts
Figure 6-1
** Patent Pending
* Refer to ESAB Catalog No. 64-2103 for additional
options.
Manual 0-5420 6-1 KEY SPARE PARTS

ESAB FABRICATOR 141i
6.02 Power Source
A-11811_AB
Art #
31
KEY SPARE PARTS 6-2 Manual 0-5420
Figure 6-2

ESAB FABRICATOR 141i
FABRICATOR 141i POWER SOURCE SPARE PARTS
ITEM PART NUMBER DESCRIPTION
1 W7006216 PCB,Power,141i
2 W7006227 PCB,Control,141i
3 W7003033 Solenoid,Valve,24VDC
4 W7006226 PCB, Remote Interface Integrated with Display, 141i
5 W7006209 Wiredrive Assy,w/ Motor,141i
6 W7004906 Feedroll retaining thumb screw
7 7977036 Feed Roll .024(0.6mm)-.030"(0.8mm) V groove Installed
8 W7004947 Fan,24VDC,4.75"x4.75"x1",141i
9 W7003010 Rectifier Bridge,1000V,50A
10 W7003215 Connector,Gas Inlet,5/8"-18UNF
11 W7006210 Dinse,Socket,141i
12 W7004983 Shoulder strap, 141i (not shown)
13 W7006224 Input Power Cable (not shown)
14 W7004942 Socket,8 Pin,w/ Harness
15 W7003053 Switch,On/Off,250V
16 W7004911 CT Sensor,Output,141i
17 W7004912 Wire Hub Assy,141i
18 W7006220 Panel, Front
19 W7006223 Panel, Rear
20 W7004922 Handle,141i
21 W7006222 Side and Top Panels (not shown)
22 W7004966 Adapter,ESAB 4,141i
23 W7004925 Guide,Inlet,.023-.045,141i
24 W7004967 Guide,Outlet,.023-.045,141i
25 W7006221 Panel,Door (not shown)
26 W7006208 Panel,Base,141i
27 870734 Knob,1/4" IDx.72" ODx.9" H
28 W7004972 Knob,1/4" IDx1" ODx0.9" H
29 W7006211 Panel,Front Control,141i
30 W7004953 Push Button Actuator
31 OTWAK/1S Screw,Locking,MIG Gun
32 W7004961 Thermistor,NTC,K45 47K,141i
33 W7004940 PCB Burnback Potentiometer
34 W7006214 PCB,Spool Gun,141i
35 W7004979 Fuse Holder,141i
36 W7006217 Fuse,10 Amp
37 W7006218 Label,Setup Chart,141i,English (not shown)
38 W7006219 Label,Setup Chart,141i,French (not shown)
39 W7006212 Inductor,141i (not shown)
40 W7004951 Spool Hub,141i
41 W7004943 Remote/Local and MIG/ Spool Gun Switch
42 W4017500 Dinse Adapter, 50mm- 25mm (not shown)
Table 6-2
Manual 0-5420 6-3 KEY SPARE PARTS

ESAB FABRICATOR 141i
6.03 Hardware List
ITEM DESCRIPTION WHERE USED Qty
1 Nut Lock, M20 25mm Dinse 2
2 Screw Hexagon, M10 × 1.5-20 ST ZP 25mm Dinse 2
3 Washer, M4, ET Lock Handle 2
4 SC PHCR M4 × 0.7-10 ST ZP Handle 2
5 SC PHCR M4 × 0.7-16 ST BK Front Panel 2
6 SC PHCR ST 6G × 3/8 STBK 8 Pin Remote Socket 2
Side Panel 3
Rear Panel 2
Front Panel 3
Side Panel 3
Door Assy 2
Rear Moulding 2
Front PCB 4
7 Nut Hexagon M4 × 0.7 ST ZP Fan 4
8 SC PHSL M4 × 0.7-30 ST ZP Fan 4
9 Nut Hexagon M12 × 1.75 ST ZP Gas Adaptor Inlet 1
10 Washer Flat, 7.91 D (M8) Wirefeeder Plate 2
11 Washer Spring, 7.91 D Wirefeeder Plate 2
12 Screw Hexagon M8 × 1.25-30 ST ZP Wirefeeder Plate 2
13 Nut Hexagon M8 × 1.25 ST ZP Wirefeeder Plate 2
14 Screw Hexagon HD 9/32 × 16 ×19 Wirefeeder Plate 2
15 Screw Skt Set M4 × 0.7 ESAB No. 4 Torch Adaptor 1
16 Screw Hexagon M6 × 1.0-10 ST ZP ESAB No. 4 Torch Adaptor 1
17 Nut Hexagon M10 × 1. 5 ST ZP ESAB No. 4 Torch Adaptor 1
Table 6-3
NOTE!
All the hardware can be purchased from local store.
KEY SPARE PARTS 6-4 Manual 0-5420

ESAB FABRICATOR 141i
4
1
4
1
4
1
SCREW ITEM 4, OFF
USED TO SECURE
MOULDING TO INTERNAL
PANEL
SCREW ITEM 5, OFF USED
5
TO SECURE MOULDING TO
2
BASE PANEL
4
1
3
4
1
1
3
4
1
1
6
4
8
4
7
4
6
2
2
1
2
2
9
1
3
4
1
1
3
4
1
1
4
1
3
4
1
1
5
2
SCREW ITEM 5, 2 OFF USED
TO SECURE REAR MOULDING
TO BASE PANEL
SCREW ITEM 4, 2 OFF USED
TO SECURE DOOR ASSY TO
BASE PANEL
17
1
12
1111101
13
2
4
1
4
1
14
2
16
1
Art # A-11932_AB
15
1
Figure 6-3
Manual 0-5420 6-5 KEY SPARE PARTS

ESAB FABRICATOR 141i
This Page Intentionally Blank
KEY SPARE PARTS 6-6 Manual 0-5420

APPENDIX
ESAB FABRICATOR 141i
This Page Intentionally Blank.
Manual 0-5420 A-1 APPENDIX

ESAB FABRICATOR 141i
YOUT
DIAGRAM
J1
J3
J16
J18
DRIV
E
PWM
IFB
SOURCE
SCR
APPENDIX: FABRICATOR 141i CIRCUIT DIAGRAM
123
ON
WVIN
J15
QF
/DY
J13
GUN
J24J10
T
O
4
CONNECTOR
NTCS
FUN
J7
J8
LA
J19
MB
J5
PPENDIX A-2 Manual 0-5420
A

DIAGRAM
J16
PWM
ESAB FABRICATOR 141i
J18
IFB
SOURCE
J3
DRIV
E
J1
Art # A-11792 _AC
Manual 0-5420 A-3 APPENDIX

ESAB FABRICATOR 141i
Date Rev Description
09/10/2015 AA Manual release
Revision History
PPENDIX A-4 Manual 0-5420
A


ESAB subsidiaries and representative offices
Europe
AUSTRIA
ESAB Ges.m.b.H
Vienna-Liesing
Tel: +43 1 888 25 11
Fax: +43 1 888 25 11 85
BELGIUM
S.A. ESAB N.V.
Heist-op-den-Berg
Tel: +32 70 233 075
Fax: +32 15 257 944
BULGARIA
ESAB Kft Representative Office
Sofia
Tel/Fax: +359 2 974 42 88
THE CZECH REPUBLIC
ESAB VAMBERK s.r.o.
Vamberk
Tel: +420 2 819 40 885
Fax: +420 2 819 40 120
DENMARK
Aktieselskabet ESAB
Herlev
Tel: +45 36 30 01 11
Fax: +45 36 30 40 03
FINLAND
ESAB Oy
Helsinki
Tel: +358 9 547 761
Fax: +358 9 547 77 71
FRANCE
ESAB France S.A.
Cergy Pontoise
Tel: +33 1 30 75 55 00
Fax: +33 1 30 75 55 24
GERMANY
ESAB GmbH
Solingen
Tel: +49 212 298 0
Fax: +49 212 298 218
GREAT BRITAIN
ESAB Group (UK) Ltd
Waltham Cross
Tel: +44 1992 76 85 15
Fax: +44 1992 71 58 03
ESAB Automation Ltd
Andover
Tel: +44 1264 33 22 33
Fax: +44 1264 33 20 74
HUNGARY
ESAB Kft
Budapest
Tel: +36 1 20 44 182
Fax: +36 1 20 44 186
ITALY
ESAB Saldatura S.p.A.
Bareggio (Mi)
Tel: +39 02 97 96 8.1
Fax: +39 02 97 96 87 01
THE NETHERLANDS
ESAB Nederland B.V.
Amersfoort
Tel: +31 33 422 35 55
Fax: +31 33 422 35 44
NORWAY
AS ESAB
Larvik
Tel: +47 33 12 10 00
Fax: +47 33 11 52 03
POLAND
ESAB Sp.zo.o.
Katowice
Tel: +48 32 351 11 00
Fax: +48 32 351 11 20
PORTUGAL
ESAB Lda
Lisbon
Tel: +351 8 310 960
Fax: +351 1 859 1277
ROMANIA
ESAB Romania Trading SRL
Bucharest
Tel: +40 316 900 600
Fax: +40 316 900 601
RUSSIA
LLC ESAB
Moscow
Tel: +7 (495) 663 20 08
Fax: +7 (495) 663 20 09
SLOVAKIA
ESAB Slovakia s.r.o.
Bratislava
Tel: +421 7 44 88 24 26
Fax: +421 7 44 88 87 41
SPAIN
ESAB Ibérica S.A.
Alcalá de Henares (MADRID)
Tel: +34 91 878 3600
Fax: +34 91 802 3461
SWEDEN
ESAB Sverige AB
Gothenburg
Tel: +46 31 50 95 00
Fax: +46 31 50 92 22
ESAB international AB
Gothenburg
Tel: +46 31 50 90 00
Fax: +46 31 50 93 60
SWITZERLAND
ESAB AG
Dietikon
Tel: +41 1 741 25 25
Fax: +41 1 740 30 55
UKRAINE
ESAB Ukraine LLC
Kiev
Tel: +38 (044) 501 23 24
Fax: +38 (044) 575 21 88
North and South America
ARGENTINA
CONARCO
Buenos Aires
Tel: +54 11 4 753 4039
Fax: +54 11 4 753 6313
BRAZIL
ESAB S.A.
Contagem-MG
Tel: +55 31 2191 4333
Fax: +55 31 2191 4440
CANADA
ESAB Group Canada Inc.
Missisauga, Ontario
Tel: +1 905 670 02 20
Fax: +1 905 670 48 79
MEXICO
ESAB Mexico S.A.
Monterrey
Tel: +52 8 350 5959
Fax: +52 8 350 7554
USA
ESAB Welding & Cutting Products
Florence, SC
Tel: +1 843 669 44 11
Fax: +1 843 664 57 48
Asia/Pacific
AUSTRALIA
ESAB South Pacific
Archerfield BC QLD 4108
Tel: +61 1300 372 228
Fax: +61 7 3711 2328
CHINA
Shanghai ESAB A/P
Shanghai
Tel: +86 21 2326 3000
Fax: +86 21 6566 6622
INDIA
ESAB India Ltd
Calcutta
Tel: +91 33 478 45 17
Fax: +91 33 468 18 80
INDONESIA
P.T. ESABindo Pratama
Jakarta
Tel: +62 21 460 0188
Fax: +62 21 461 2929
JAPAN
ESAB Japan
Tokyo
Tel: +81 45 670 7073
Fax: +81 45 670 7001
MALAYSIA
ESAB (Malaysia) Snd Bhd
USJ
Tel: +603 8023 7835
Fax: +603 8023 0225
SINGAPORE
ESAB Asia/Pacific Pte Ltd
Singapore
Tel: +65 6861 43 22
Fax: +65 6861 31 95
SOUTH KOREA
ESAB SeAH Corporation
Kyungnam
Tel: +82 55 269 8170
Fax: +82 55 289 8864
UNITED ARAB EMIRATES
ESAB Middle East FZE
Dubai
Tel: +971 4 887 21 11
Fax: +971 4 887 22 63
Africa
EGYPT
ESAB Egypt
Dokki-Cairo
Tel: +20 2 390 96 69
Fax: +20 2 393 32 13
SOUTH AFRICA
ESAB Africa Welding & Cutting
Ltd
Durbanvill 7570 - Cape Town
Tel: +27 (0)21 975 8924
Distributors
For addresses and phone numbers to our distributors in other
countries, please visit our home
page
www.esab.eu
www.esab.eu
©2015 ESAB Welding and Cutting Products
Printed in China
 Loading...
Loading...